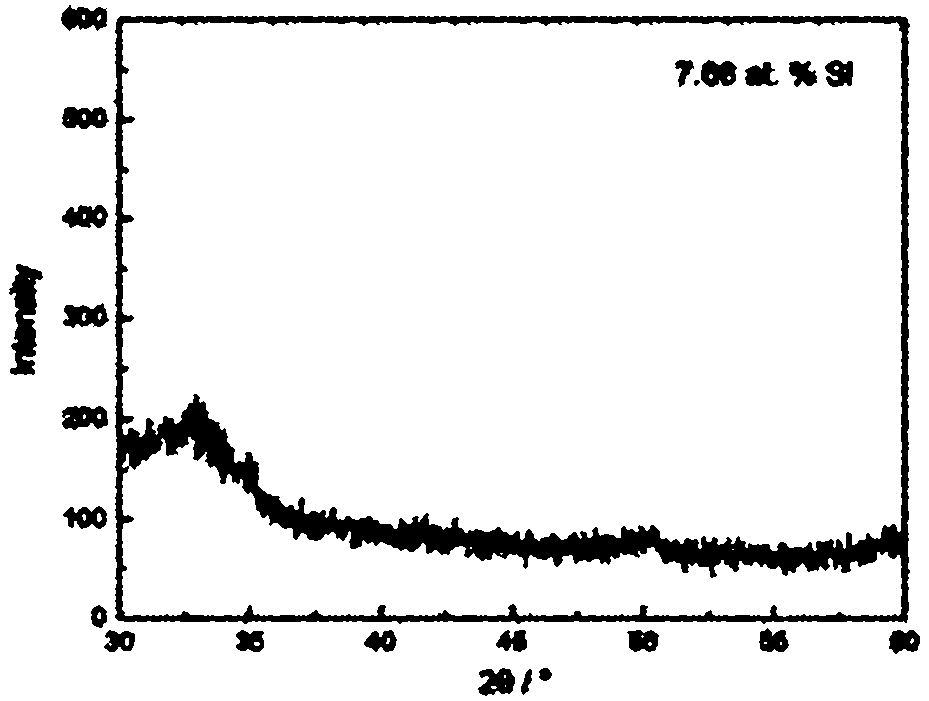
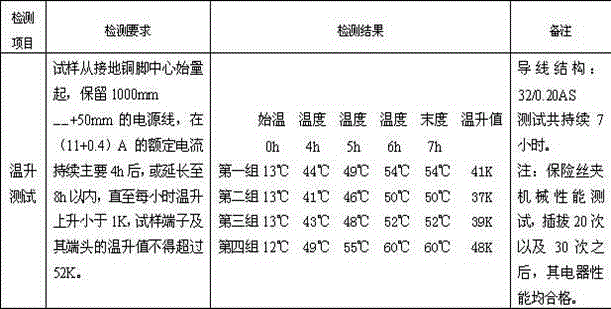
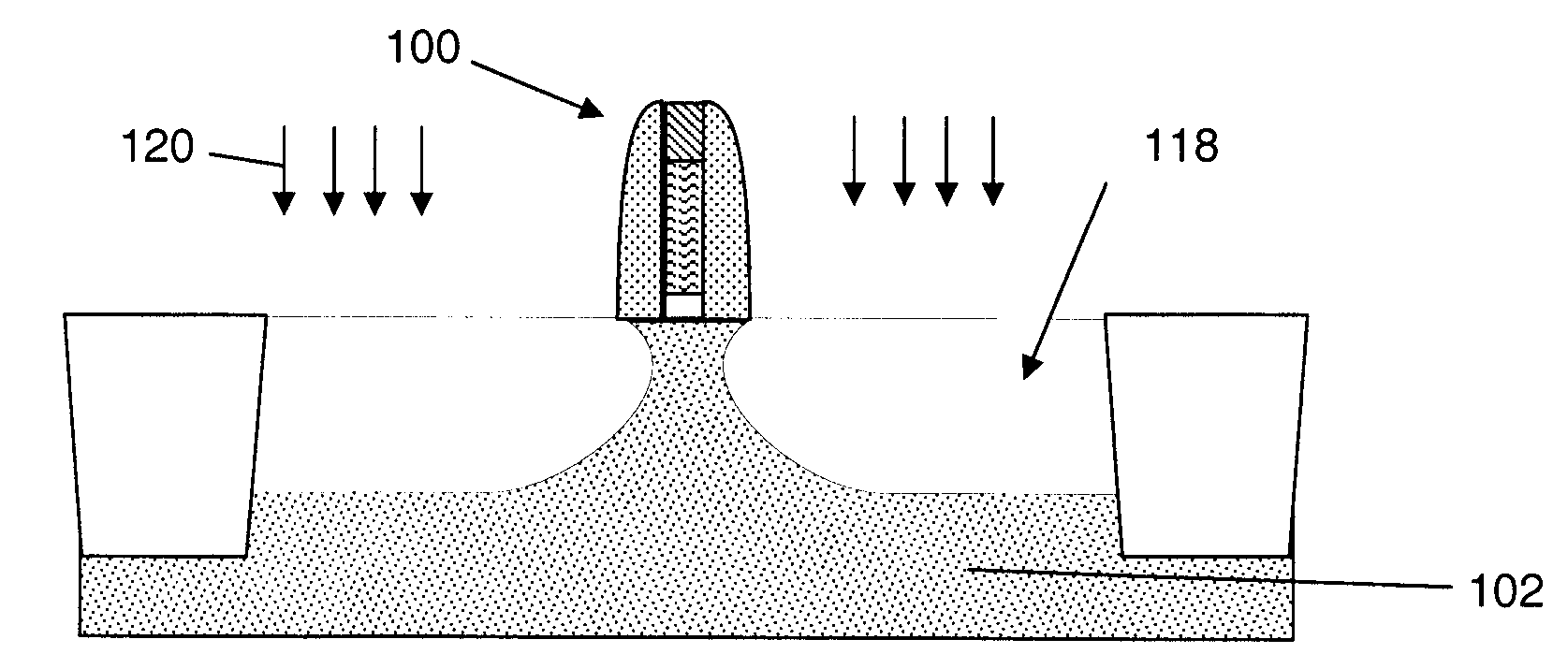
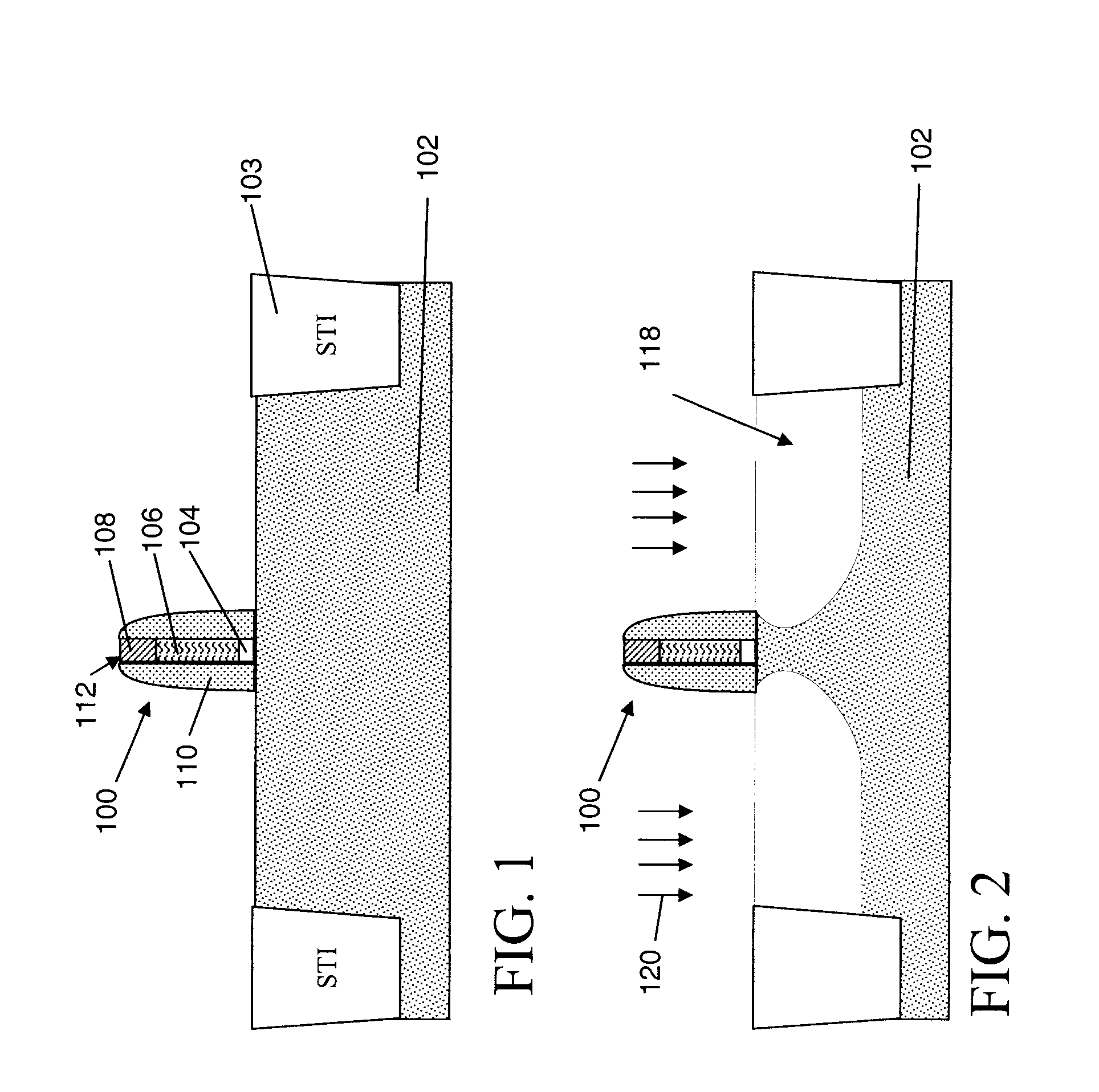
Patents
Literature
339 results about "Solid solubility" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Solubility is the property of a solid, liquid or gaseouschemical substance called solute to dissolve in a solid, liquid or gaseous solvent. The solubility of a substance fundamentally depends on the physical and chemical properties of the solute and solvent as well as on temperature, pressure and presence of other chemicals (including changes to the pH) of the solution.
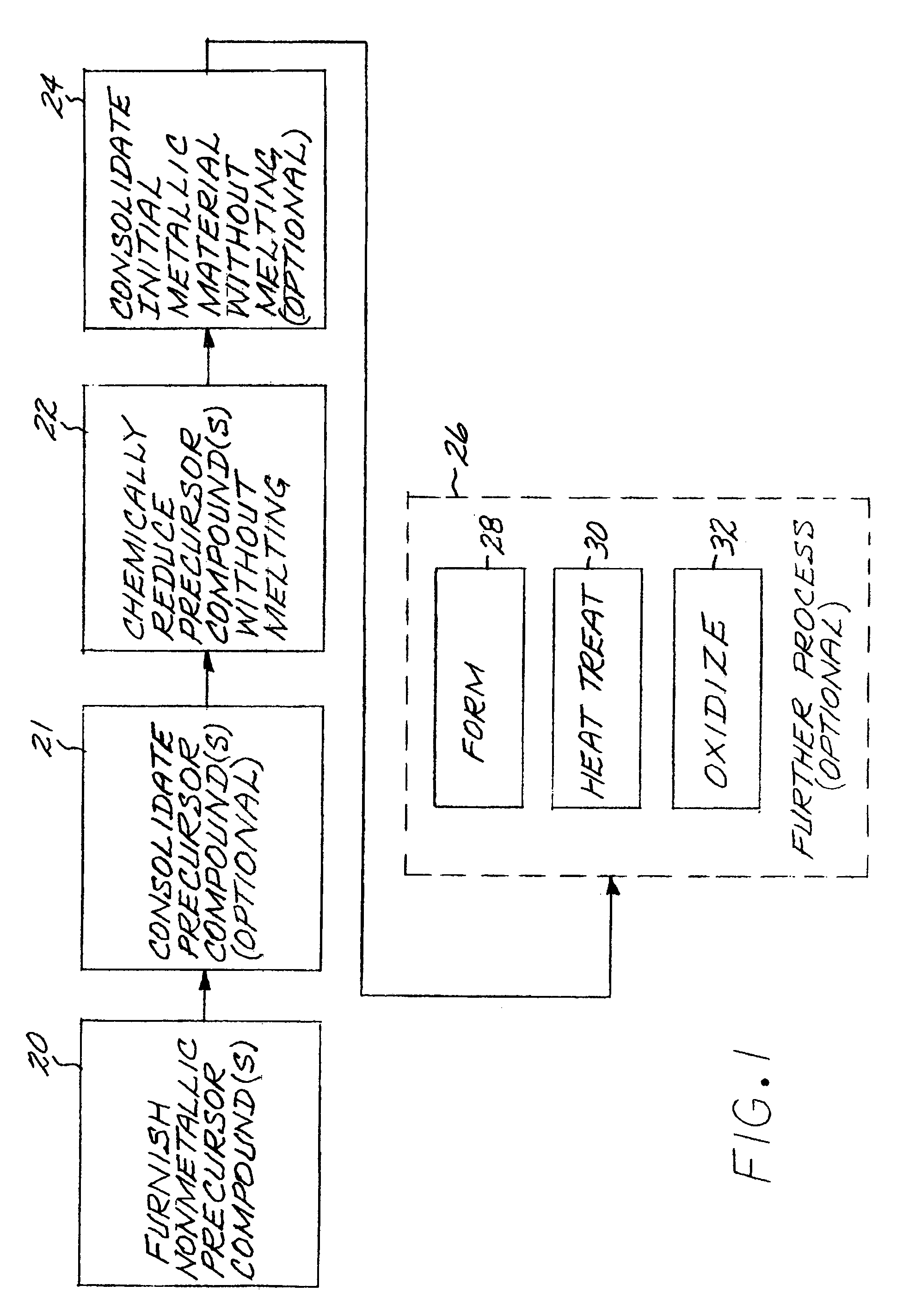
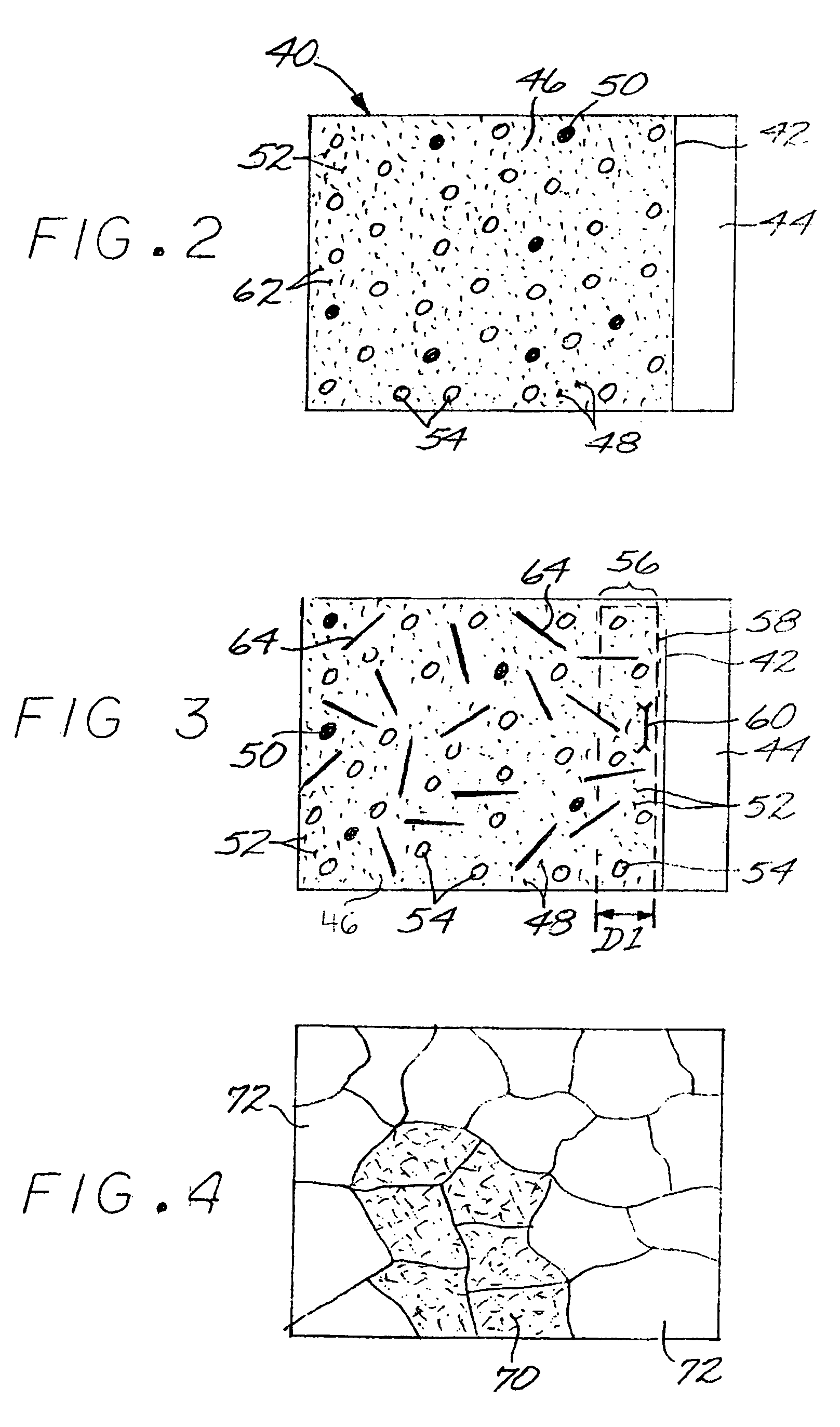
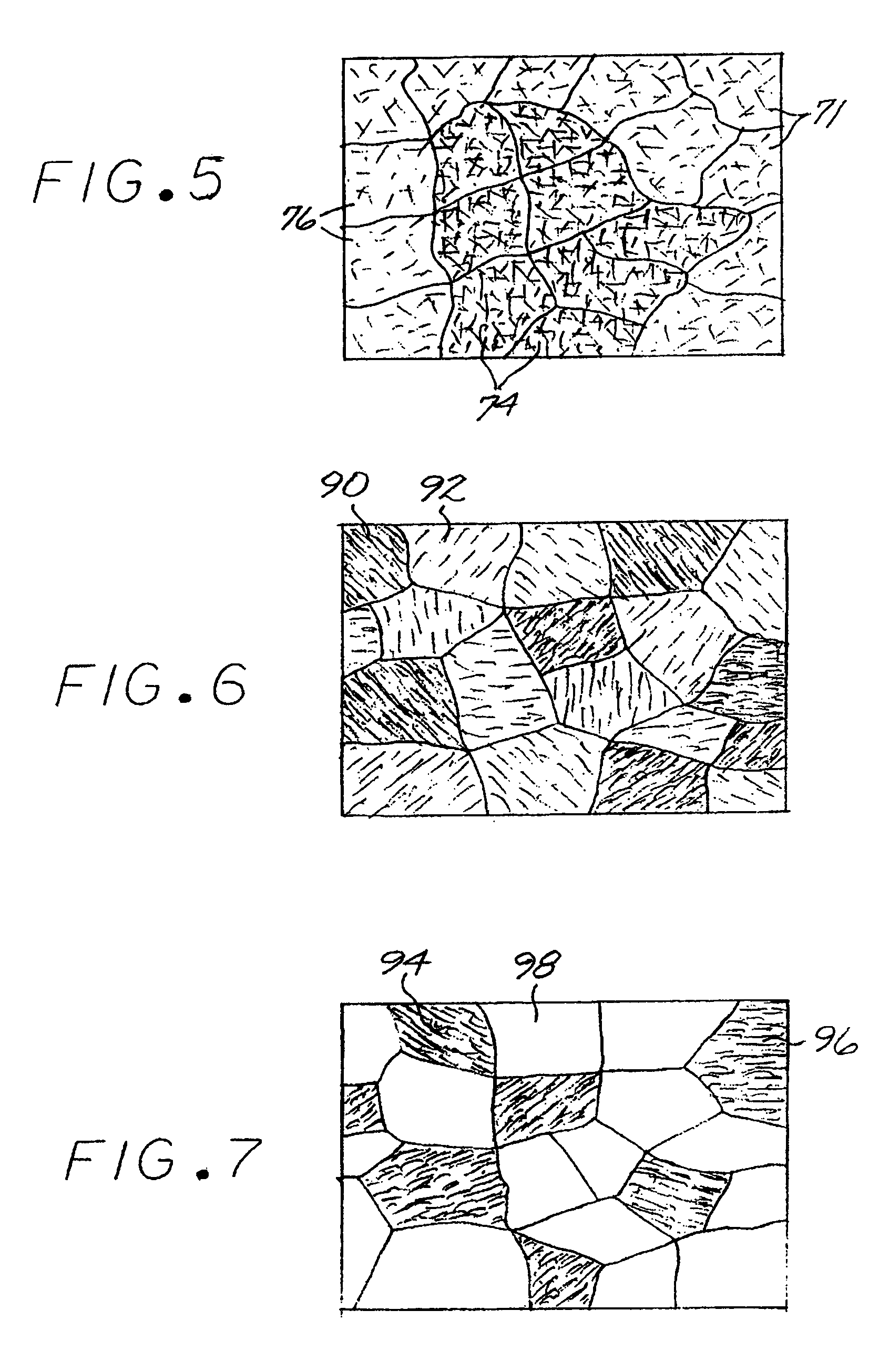
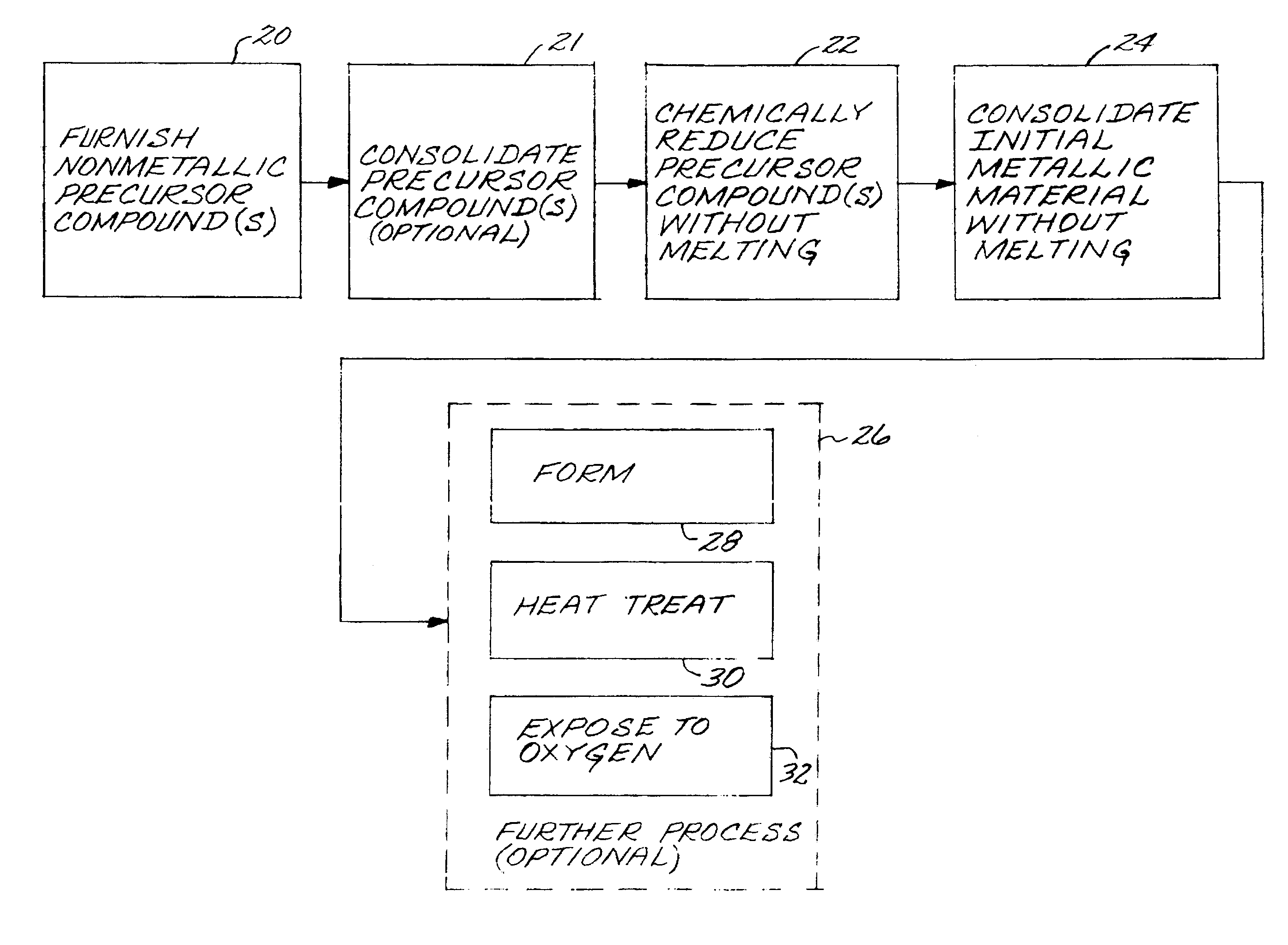
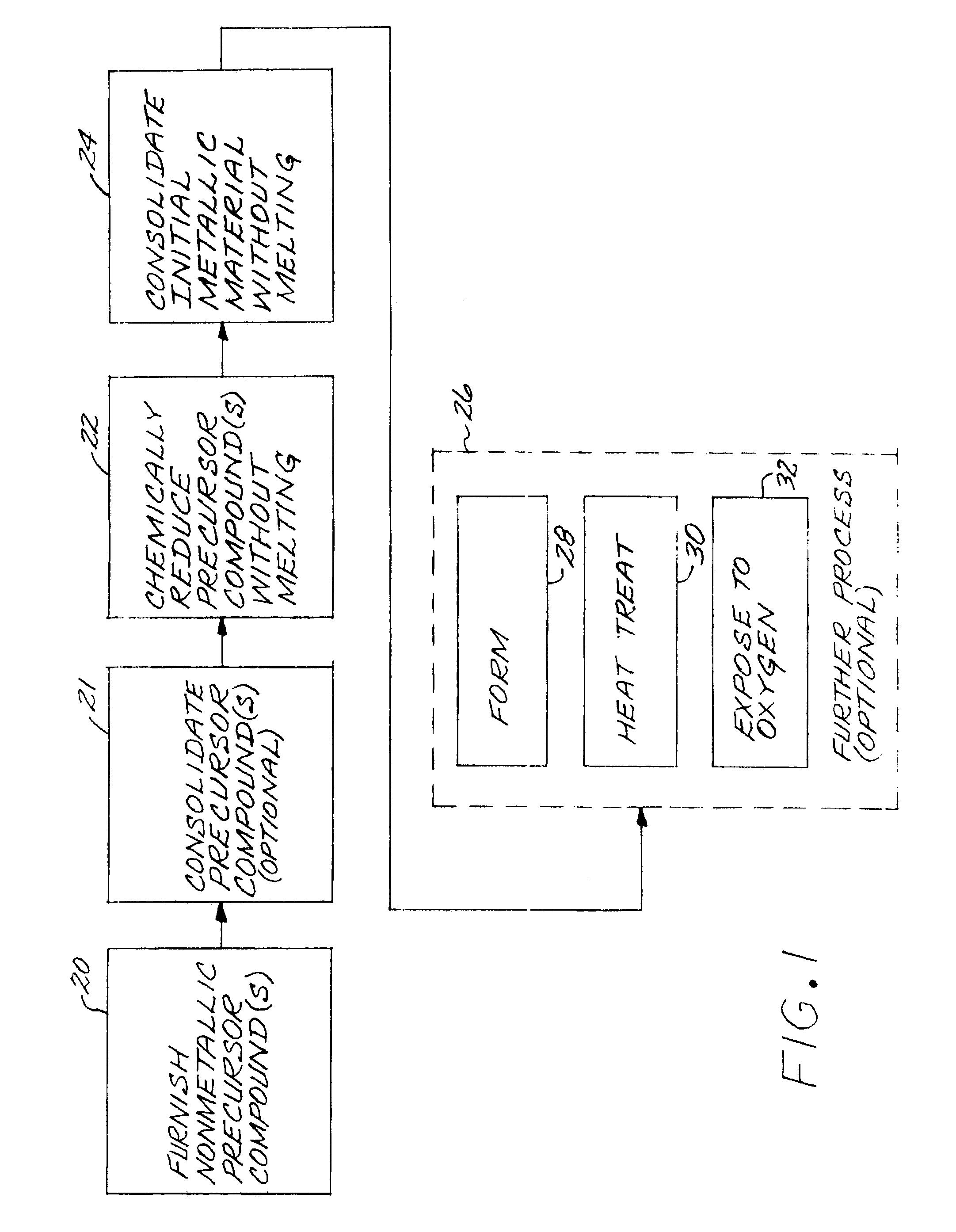
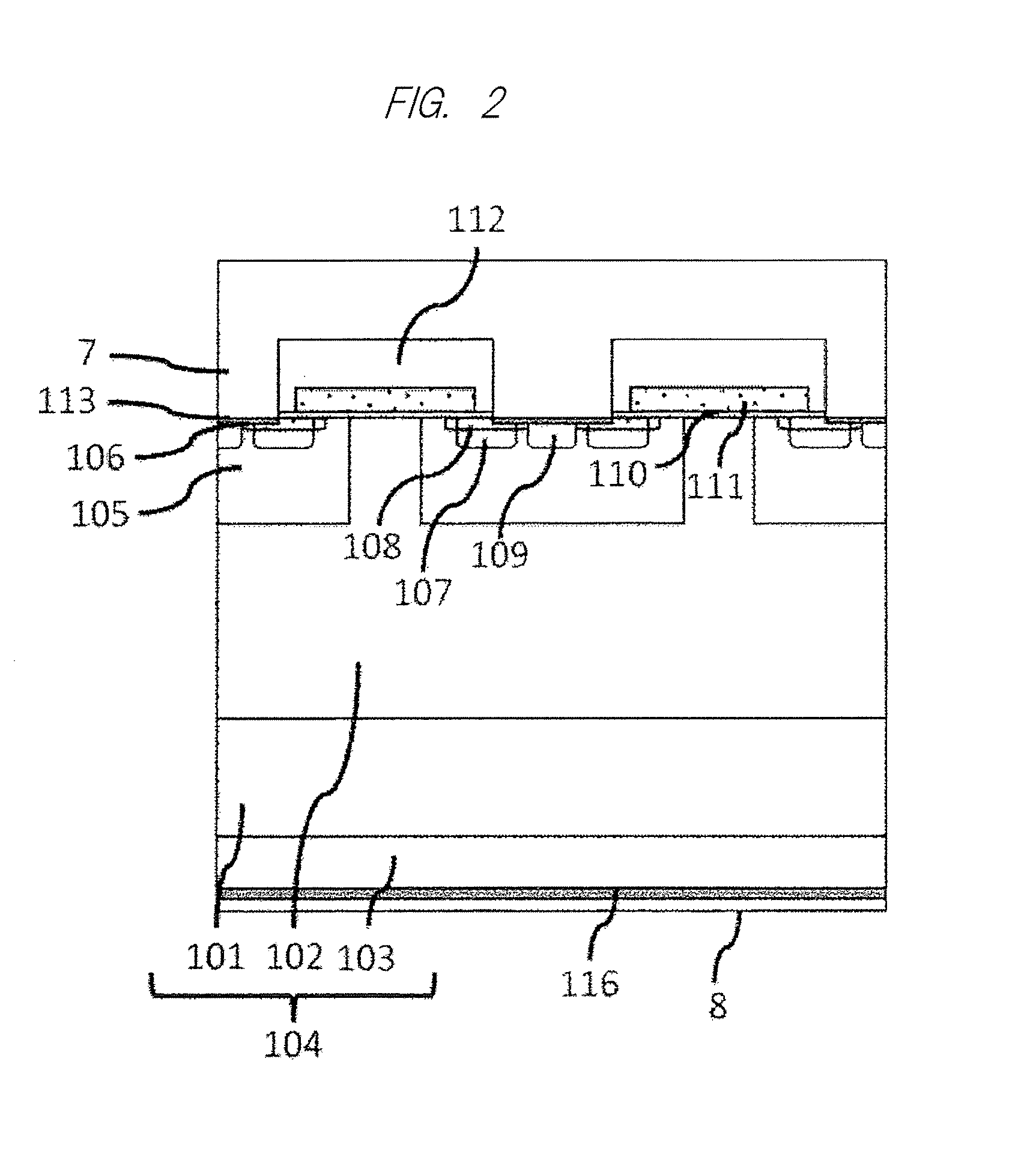
Method for producing a titanium metallic composition having titanium boride particles dispersed therein
InactiveUS7410610B2Reduce incidenceMaintain good propertiesPump componentsBlade accessoriesElemental compositionRoom temperature
An article made of constituent elements is prepared by furnishing at least one nonmetallic precursor compound, wherein all of the nonmetallic precursor compounds collectively contain the constituent elements. The constituent elements include a titanium-base metallic composition, boron present at a level greater than its room-temperature solid solubility limit, and, optionally, a stable-oxide-forming additive element present at a level greater than its room-temperature solid solubility limit. The precursor compounds are chemically reduced to produce a material comprising a titanium-base metallic composition having titanium boride particles therein, without melting the titanium-base metallic composition. The titanium-base metallic composition having the titanium boride particles therein is consolidated without melting.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
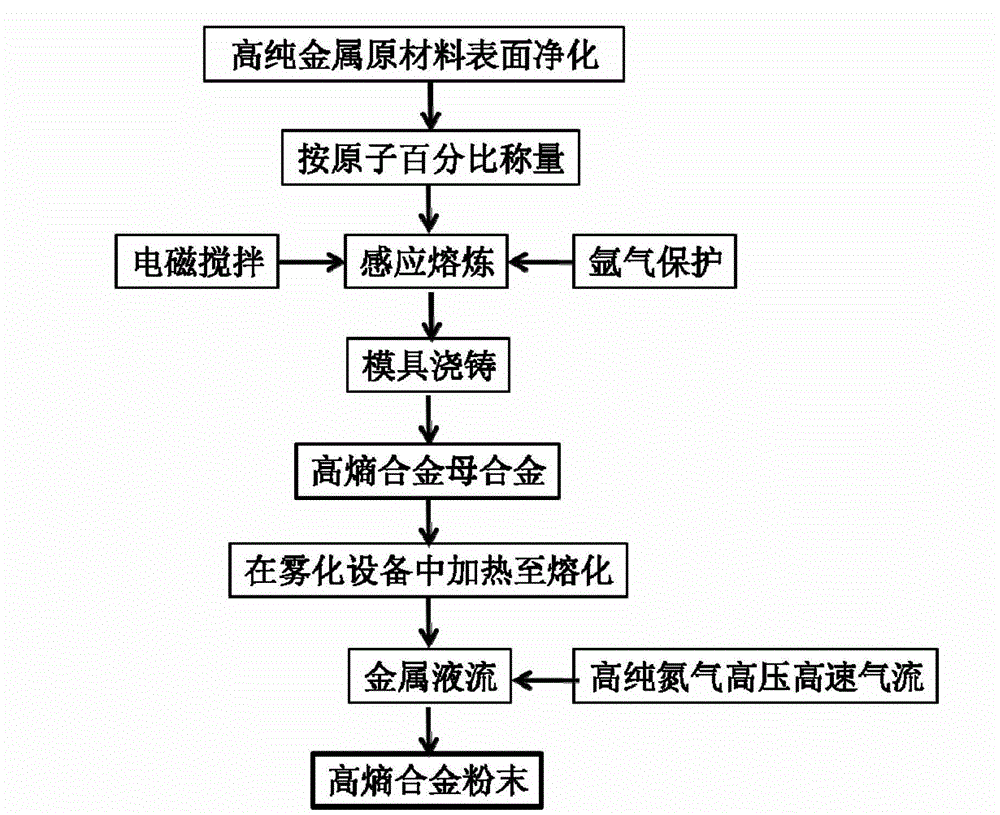
High-entropy alloy powder material for supersonic spraying and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103056352AImprove organizationImprove performanceMolten spray coatingHigh entropy alloysOxygen content
The invention relates to a high-entropy alloy powder material for supersonic spraying and a manufacturing method thereof. The high-entropy alloy powder material for the supersonic spraying can be obtained and is characterized in that the high-entropy alloy powder material comprises, by atomic percent, 10-20% of Al, 15-20% of Fe, 15-20% of Co, 15-20% of Ni, 15-20% of Cr and 15-20% of Cr, and total percent is 100%. The high-entropy alloy powder material is made by a gas atomization rapid solidification process. Particles of high-entropy alloy powder are spherical or ellipsoidal, a phase structure is composed of a solid solution phase with a simple face-centered cubic or body-centered cubic structure, ingredients and tissues are even, alloy solid solubility is high, and segregation is small. The manufacturing method of the high-entropy alloy powder material is controllable in powder size, good in mobility, low in oxygen content, small in environment pollution, high-entropy alloy coating with excellent combination property or a block high-entropy alloy material with more excellent performance can be obtained through a supersonic spraying process.
Owner:ACADEMY OF ARMORED FORCES ENG PLA
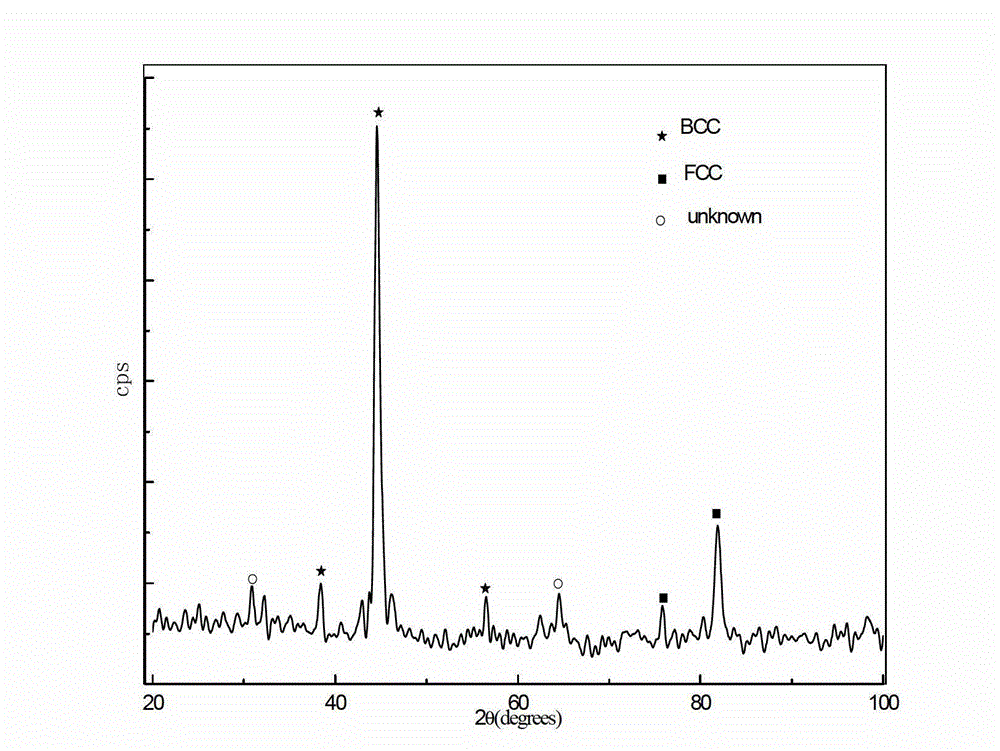
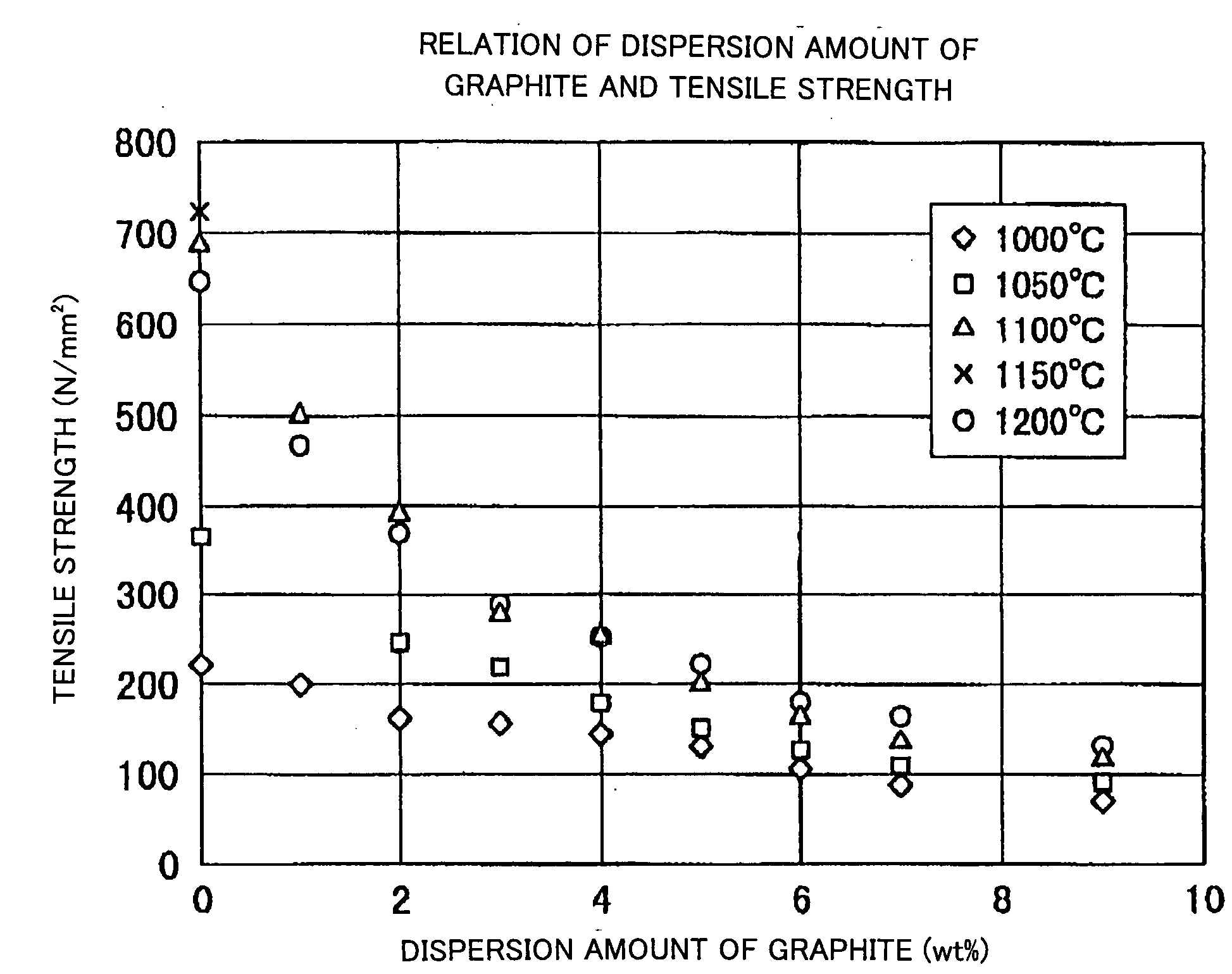
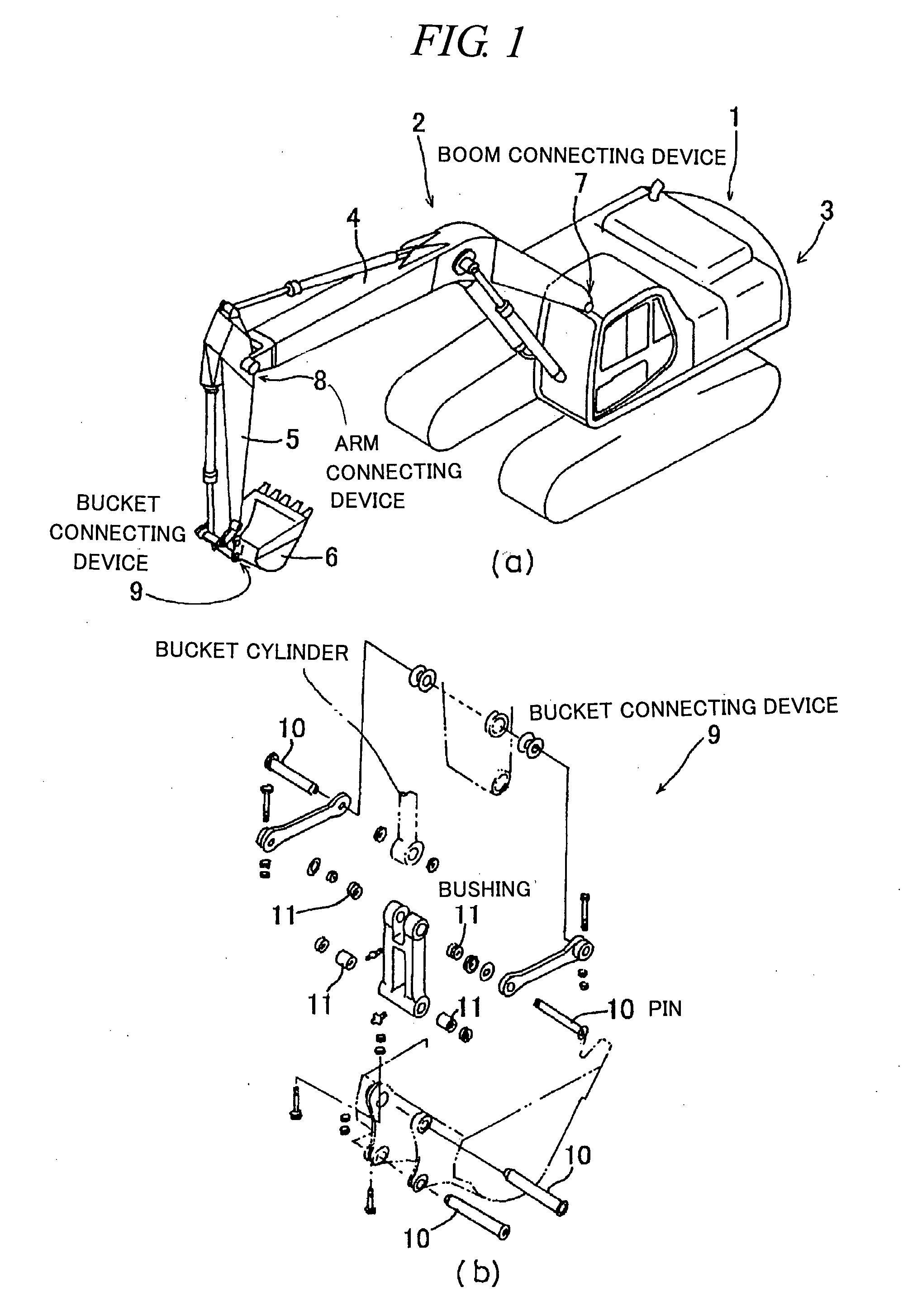
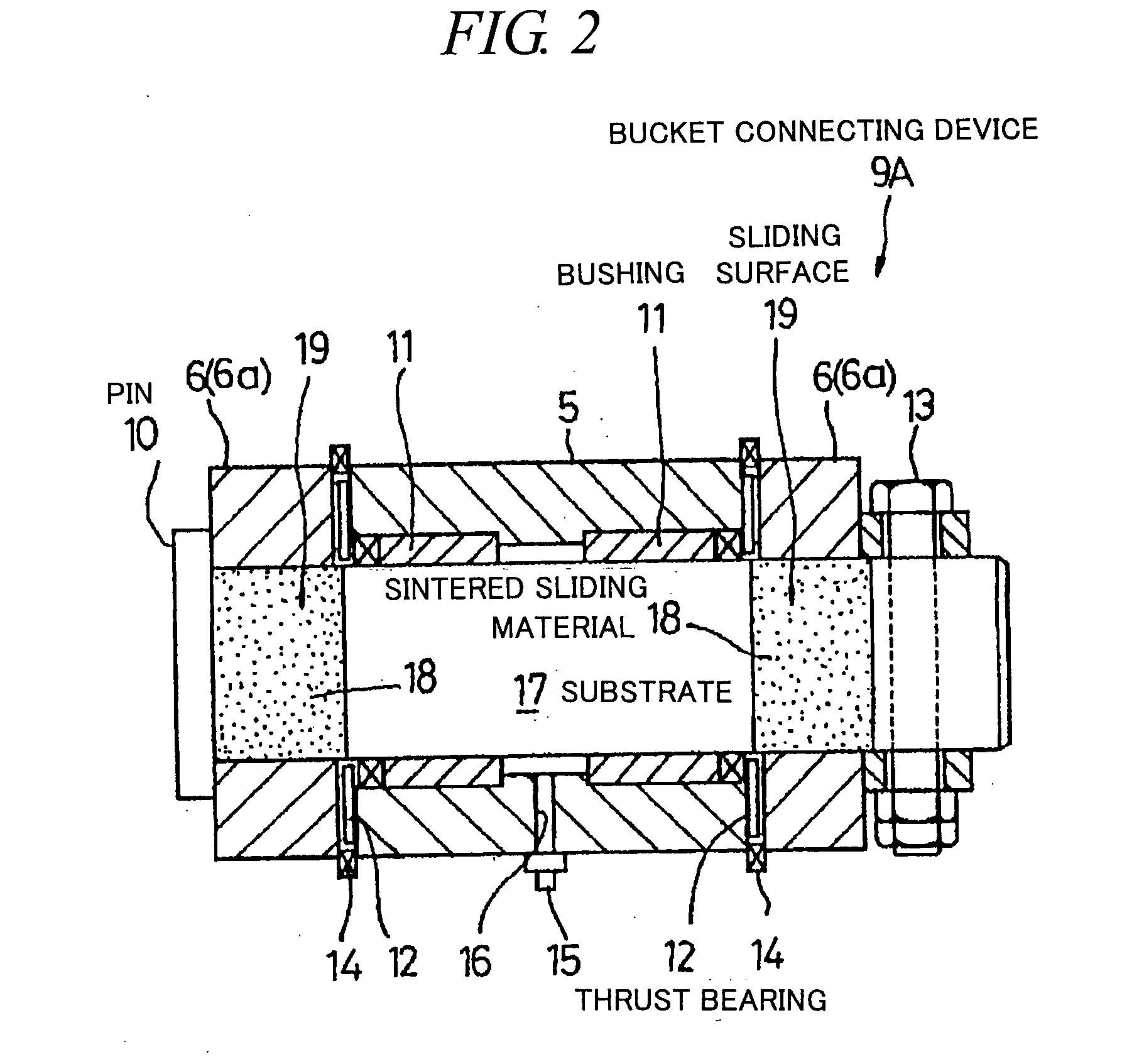
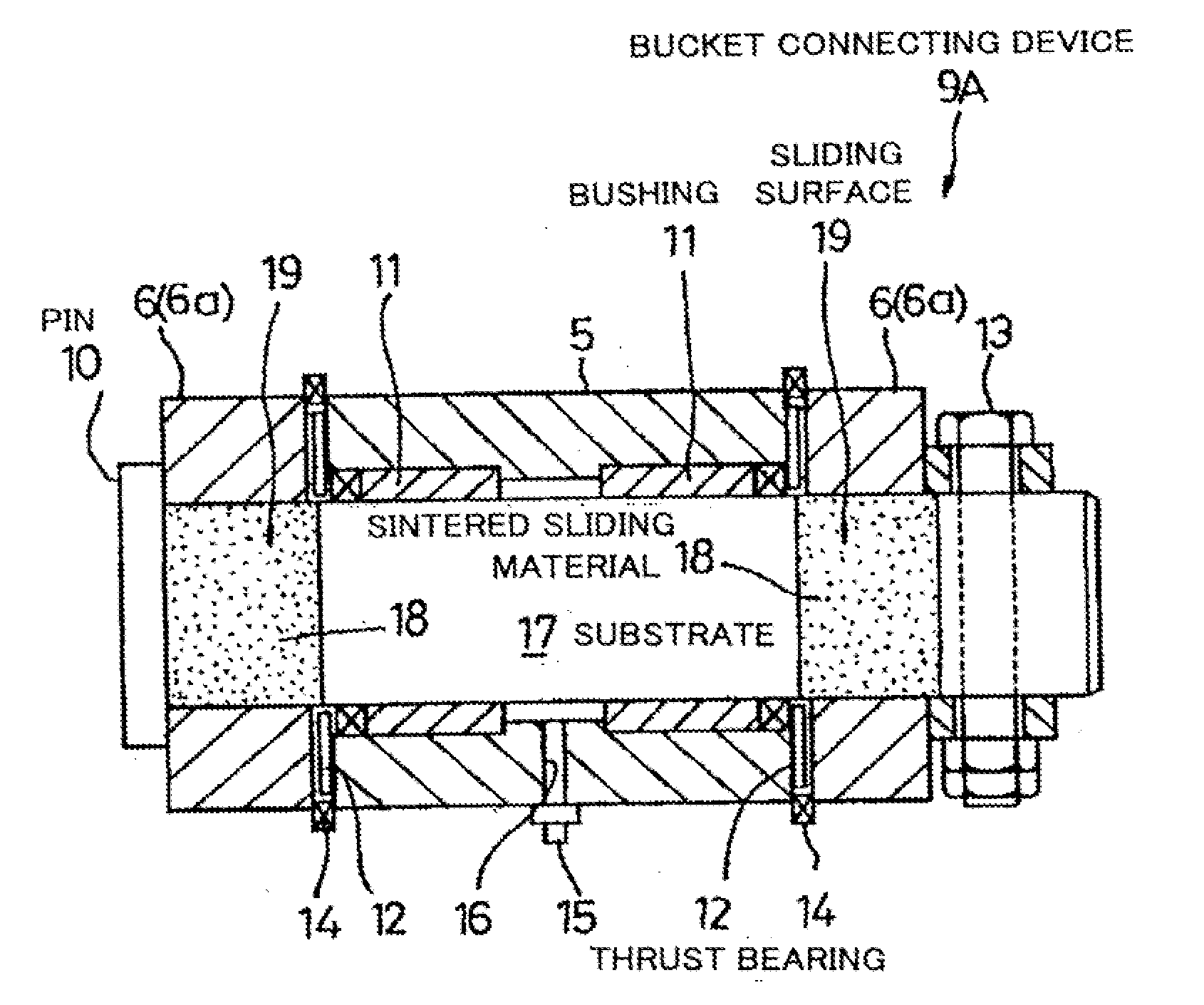
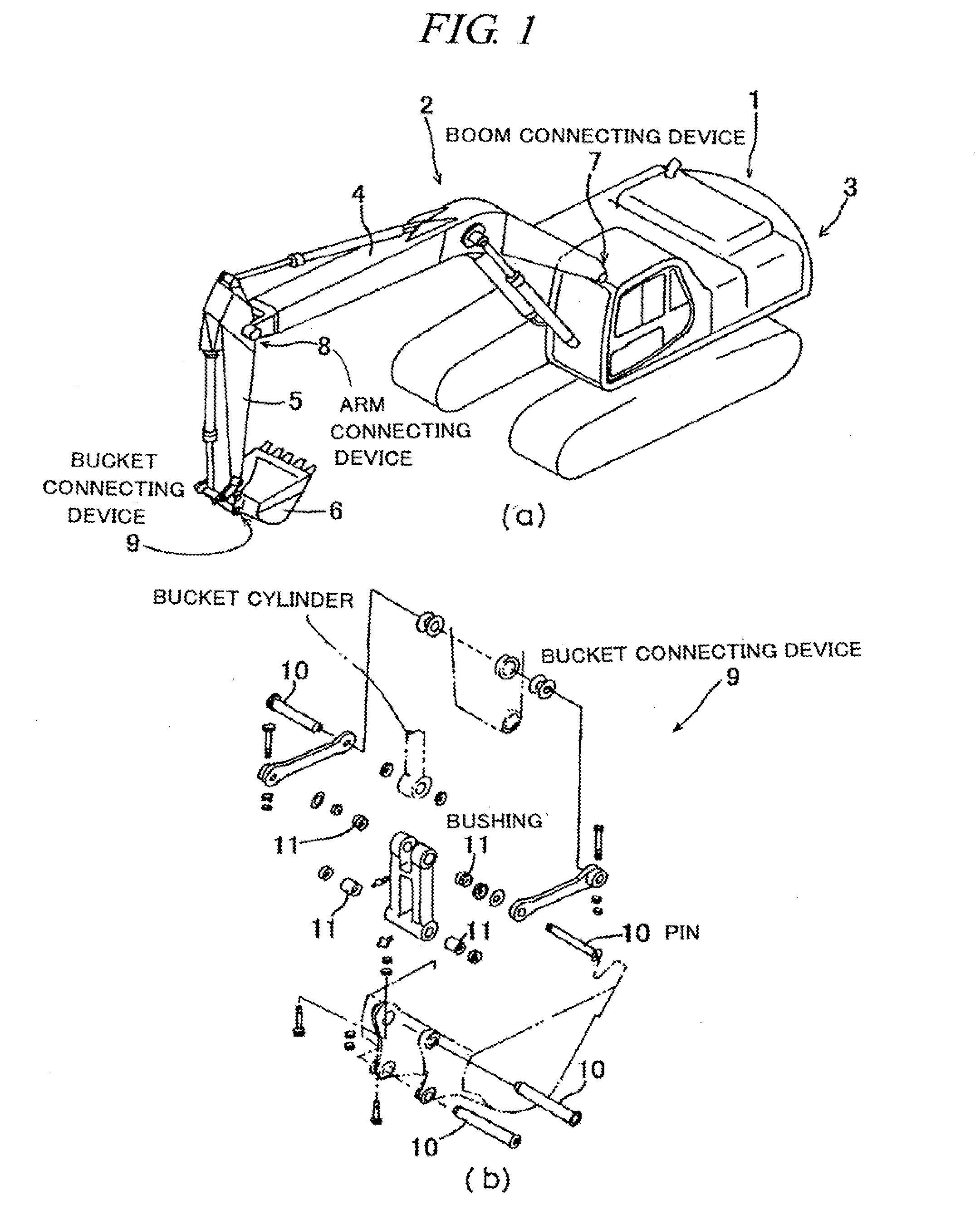
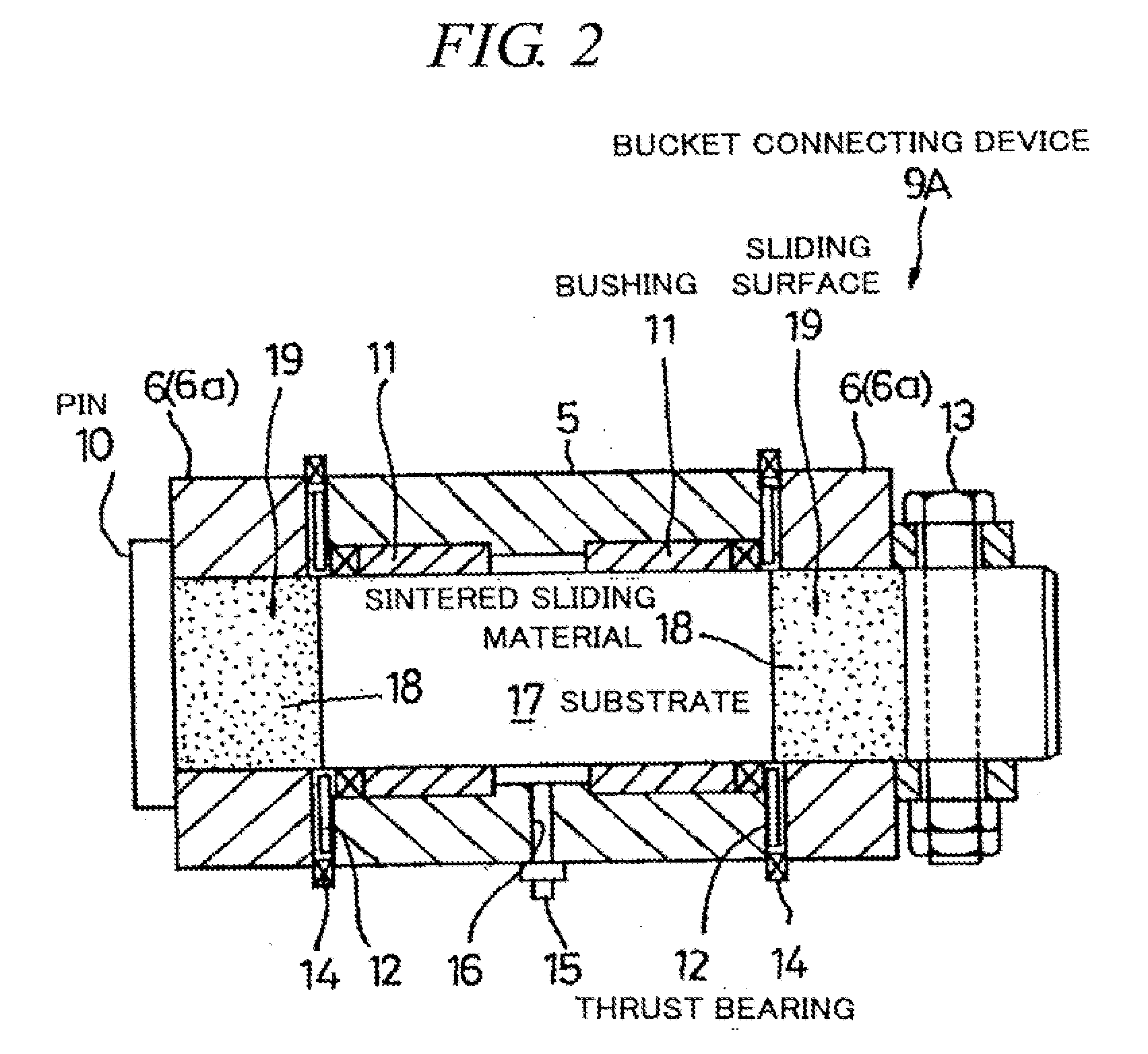
Sintered Material, Ferrous Sintered Sliding Material, Producing Method of the Same, Sliding Member, Producing Method of the Same and Coupling Device
InactiveUS20080146467A1Excellent abrasion resistanceReduce necessityBearing componentsPowder mixtureGraphite particle
The iron-based sintered sliding material comprises: a sintered structure which contains 10-50 wt. % copper and 1-15 wt. % carbon and has been formed by sintering a powder mixture obtained by mixing at least one of an Fe—Cu alloy powder containing copper in an amount which is the solid solubility or larger and is 5-50 wt. %, excluding 50 wt. %, and an Fe—Cu—C alloy powder containing copper in an amount which is the solid solubility or larger and is 5-50 wt. %, excluding 50 wt. %, and containing carbon in an amount of 0-5 wt. %, excluding 0 wt. %, with a graphite powder and at least one of a copper powder and a copper alloy powder; and graphite particles dispersed in the sintered sliding material in an amount of 1-14 wt. % or 3-50 vol. %.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
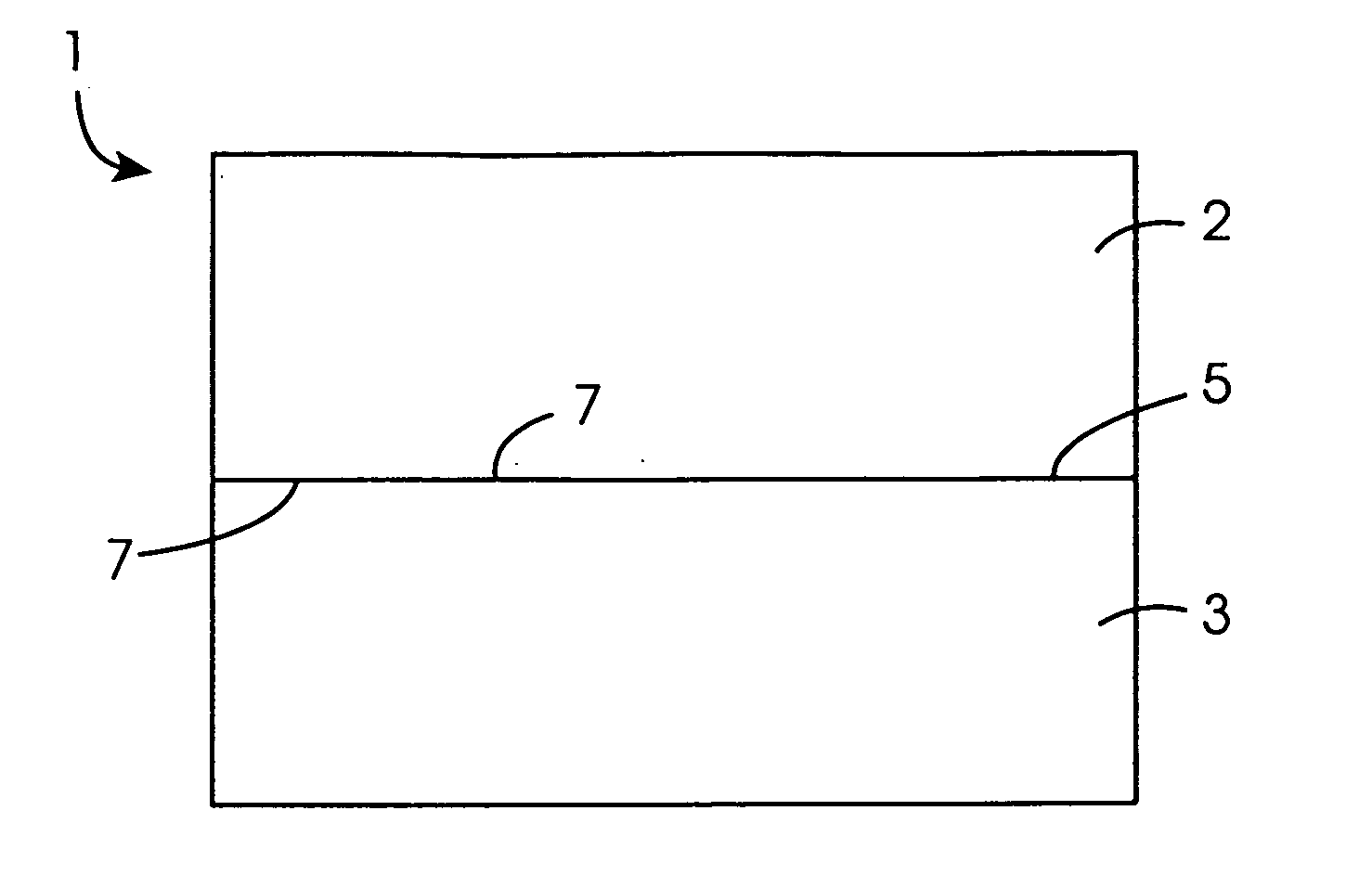
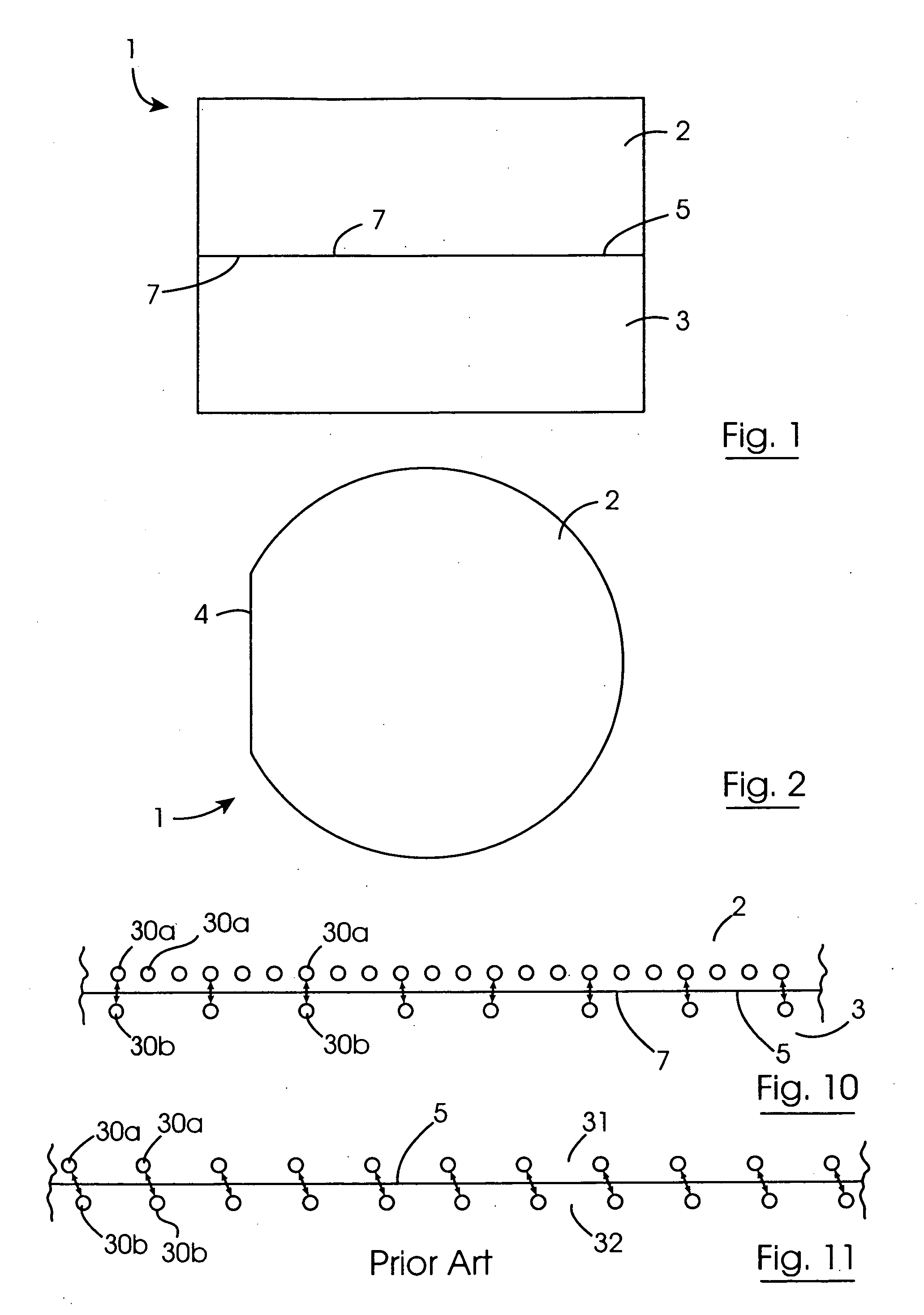
Method for direct bonding two silicon wafers for minimising interfacial oxide and stresses at the bond interface, and an SOI structure
InactiveUS20040087109A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingInterfacial oxideBond interface
A semiconductor substrate (1) comprises first and second silicon wafers (2,3) directly bonded together with interfacial oxide and interfacial stresses minimised along a bond interface (5), which is defined by bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3). Interfacial oxide is minimised by selecting the first and second wafers (2,3) to be of relatively low oxygen content, well below the limit of solid solubility of oxygen in the wafers. In order to minimise interfacial stresses, the first and second wafers are selected to have respective different crystal plane orientations. The bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are polished and cleaned, and are subsequently dried in a nitrogen atmosphere. Immediately upon being dried, the bond faces (7) of the first and second wafers (2,3) are abutted together and the wafers (2,3) are subjected to a preliminary anneal at a temperature of at least 400° C. for a time period of a few hours. As soon as possible after the preliminary anneal, and preferably, within forty-eight hours of the preliminary anneal, the first and second wafers (2,3) are fusion bonded at a bond anneal temperature of approximately 1,150° C. for a time period of approximately three hours. The preliminary anneal may be omitted if fusion bonding at the bond anneal temperature is carried out within approximately six hours of the wafers (2,3) being abutted together. An SOI structure (50) may subsequently be prepared from the semiconductor structure (1) which forms a substrate layer (52) supported on a handle layer (55) with a buried insulating layer (57) between the substrate layer (52) and the handle layer (55).
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
Sintered material, ferrous sintered sliding material, producing method of the same, sliding member, producing method of the same and coupling device
InactiveUS20120177528A1Excellent abrasion resistanceImprove the lubrication effectShaftsSoil-shifting machines/dredgersPowder mixtureGraphite particle
An iron-based sintered sliding material includes: a sintered structure which contains 10-50 wt. % copper and 1-15 wt. % carbon and has been formed by sintering a powder mixture obtained by mixing at least one of an Fe—Cu alloy powder containing copper in an amount which is the solid solubility or larger and is 5-50 wt. %, excluding 50 wt. %, and an Fe—Cu—C alloy powder containing copper in an amount which is the solid solubility or larger and is 5-50 wt. %, excluding 50 wt. %, and containing carbon in an amount of 0-5 wt. %, excluding 0 wt. %, with a graphite powder and at least one of a copper powder and a copper alloy powder; and graphite particles dispersed in the sintered sliding material in an amount of 1-14 wt. % or 3-50 vol. %.
Owner:KOMATSU LTD
Sputtering target of multi-component single body and method for preparation thereof, and method for producing multi-component alloy-based nanostructured thin films using same
InactiveUS20120247948A1Prevent such non-uniformityEvenly distributedCellsVacuum evaporation coatingNitrogenAlloy
The present invention relates to a sputtering target of a multi-component single body, a preparation method thereof, and a method for fabricating a multi-component alloy-based nanostructured thin film using the same. The sputtering target according to the present invention comprises an amorphous or partially crystallized glass-forming alloy system composed of a nitride forming metal element, which is capable of reacting with nitrogen to form a nitride, and a non-nitride forming element which has no or low solid solubility in the nitride forming metal element and does not react with nitrogen or has low reactivity with nitrogen, wherein the nitrogen forming metal element comprises at least one element selected from Ti, Zr, Hf, V, Nb, Ta, Cr, Y, Mo, W, Al, and Si, and the non-nitride forming element comprises at least one element selected from Mg, Ca, Sc, Ni, Cu, Ag, In, Sn, La, Au, and Pb.
Owner:KOREA INST OF IND TECH
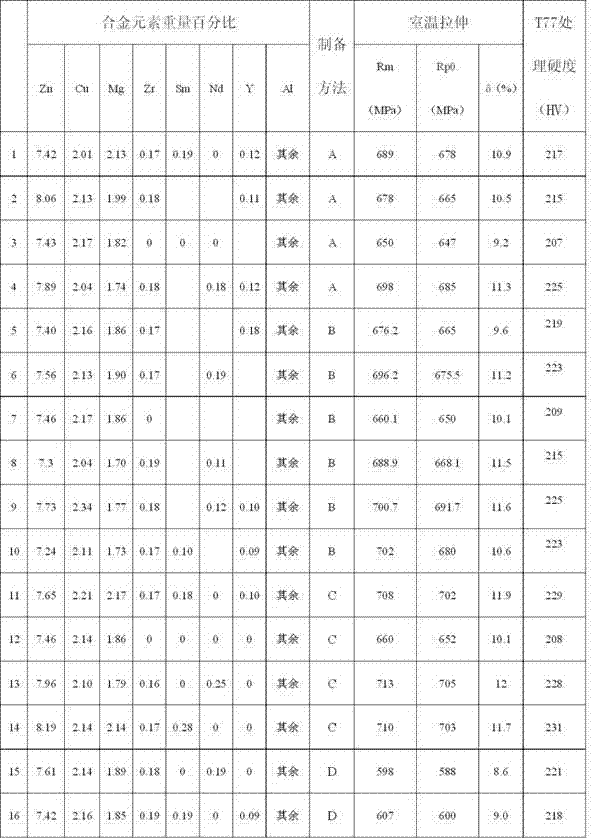
Ultra-strong strength, high-toughness and anticorrosive aluminum alloy and preparation method for same
ActiveCN103667825AImprove corrosion resistanceImprove solid solubilityRare-earth elementElectromagnetic casting
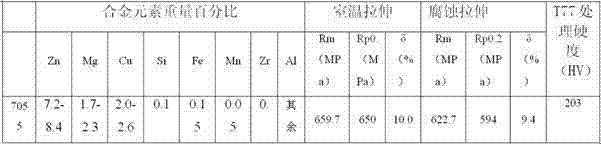
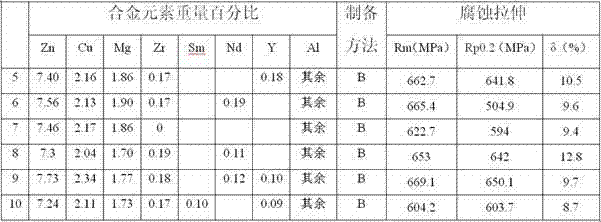
The invention relates to an ultra-strong strength, high-toughness and anticorrosive aluminum alloy and a preparation method for the same. A trace amount of specially-reinforced rare earth elements Sm, Nd and Y are added on the basis of an Al-Zn-Mg-Cu-Zr alloy, an electromagnetic casting mode is adopted for improving the solid solubility of the alloy, homogenizing the structure and reducing segregation, and the proportion of main alloy elements is optimized to make a breakthrough in the strength of the alloy. The aluminum alloy has ultra-strong strength, higher plasticity and high anticorrosive performance; in addition, the high-abundance rare earth element such as Sm and Y serving as one of raw materials is excessively overstocked in the market, and is low in cost, so that not only can be the cost of the alloy remarkably lowered, but also the problem of application unbalance of the rare earth elements can be relieved; the strength of a material prepared from the alloy is stronger than 700MPa after the material is subjected to T77 treatment, and is remarkably stronger than that of a material prepared from a 7055 alloy, and the comprehensive performance of the material is remarkably higher than that of a material prepared from an Al-Zn-Cu-Mg aluminum alloy currently with the highest comprehensive performance.
Owner:华峰铝业有限公司
Method for preparing nano-structured nitrogen silicon zirconium coating on surface of hard alloy substrate
InactiveCN101921982AHigh hardnessGrowth inhibitionVacuum evaporation coatingSputtering coatingNano structuringAlloy substrate
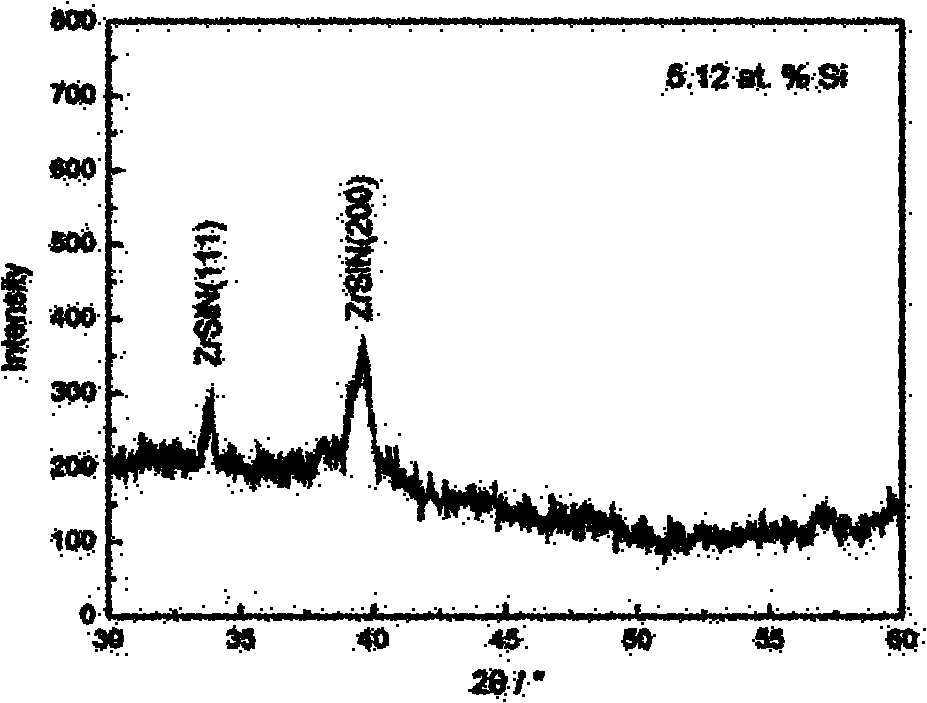
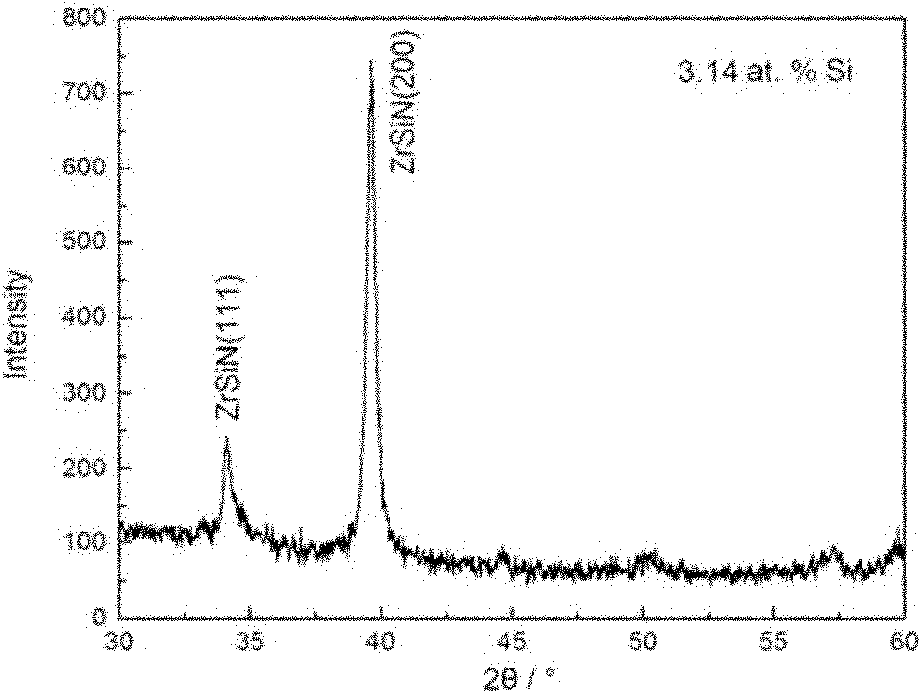
The invention provides a method for preparing a nano-structured nitrogen silicon zirconium coating on the surface of a hard alloy substrate, relating to a hard alloy. A direct-current and radio frequency reaction co-sputtering method is used to prepare the nano-structured nitrogen silicon zirconium coating through controlling the power of a Si target. When the content of Si in a ZrSiN coating is reduced, the Si atoms in the coating exist in the mode of replacing Zr atoms, the ZrSiN coating with low content of Si is solid solution, and the cross section of the ZrSiN coating is in a column structure. The solid solubility and the hardness of the ZrSiN coating are increased with the increment of the content of Si. When the content of Si in the coating reaches a definite amount, excessive element of Si can form amorphous Si3N4 at crystal boundary with element of N. When the content of Si in the coating is further increased, a great amount of amorphous Si3N4 is generated, thus seriously inhabiting the growth of ZrN crystal particles and influencing the degree of crystallization of the coating, in addition, the coating is changed to be in an amorphous state and is in a non-column equiaxial structure.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Elastic brass alloy and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an elastic brass alloy material. The material comprises the following components in percentage by weight: 70 to 71 percent of copper, 24 to 25 percent of zinc, 2 to 3 percent of aluminum, 1 to 3 percent of nickel and 0.5 to 1 percent of chromium. A preparation method comprises the following steps of: smelting; performing hot rolling; performing solid solution treatment; annealing, and performing cold rolling; and performing ageing treatment. The chromium element of which the solid solubility is reduced with the reduction of temperature is added into a metal matrix, a supersaturated solid solution is formed through high temperature sold solution quenching treatment, and is decomposed through ageing treatment to form a large number of fine dispersed Cr particles, and the particles are dispersedly distributed in the matrix to form a precipitated phase, so that the strength, electrical conductivity and elasticity of an alloy are improved. An elastic brass alloy strip prepared by the method meets the technical requirements on temperature rise, electrical performance and the like after being made into a fuse clip, can replace scarce tin phosphorus bronze and is applied to related fields.
Owner:JINTIAN COPPER GROUP CORP NINGBO
BORON DOPED SiGe HALO FOR NFET TO CONTROL SHORT CHANNEL EFFECT
InactiveUS20080023752A1Improve solid solubilityReduce the probability of spreadingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesField-effect transistorBoron
An n-type field effect transistor (NFET) and methods of forming a halo for an NFET to control the short channel effect are disclosed. One method includes forming a gate over a silicon substrate; recessing the silicon adjacent to the gate; forming a halo by epitaxially growing boron in-situ doped silicon germanium (SiGe) in the recess; and epitaxially growing silicon over the silicon germanium. Alternatively, the halo can be formed by ion implanting boron into an embedded SiGe region within the silicon substrate. The resulting NFET includes a boron doped SiGe halo embedded within the silicon substrate. The embedded SiGe layer may be a relaxed layer without inserting strain in the channel. The high solid solubility of boron in SiGe and low diffusion rate allows formation of a halo that will maintain the sharp profile, which provides better control of the short channel effect and increasing control over NFET threshold voltage roll-off.
Owner:IBM CORP +1
Method for preparing nanocrystalline metal material containing nano-sized precipitates within crystal
The invention provides a method for preparing a nanocrystalline metal material containing nano-sized precipitates within a crystal. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, performing high-temperature solution treatment on a coarse crystalline metal material, thereby obtaining single phase solid solution with supersaturated and dissolved alloy element, wherein the coarse crystalline metal material contains alloy element in a matrix, and the solid solubility is reduced as the temperature is reduced; then, performing severe plastic deformation and high-pressure reverse processing at or below the room temperature, thereby obtaining single phase solid solution nanocrystalline material composed of nanocrystalline grains with supersaturated and dissolved alloy element; and finally, ageing the obtained nanocrystalline material at a pressure of 3-25 GPa and at a temperature of 100-800 DEG C, and holding the temperature for 5-8 h, thereby obtaining a nanocrystalline metal material containing nano-sized precipitates within a crystal. The method provided by the invention is wide in suitable material component range, and can be used for effectively avoiding severe plastic deformation to produce microcrack in a material, and the prepared nano-sized precipitates in the nanocrystalline material are distributed uniformly.
Owner:YANSHAN UNIV
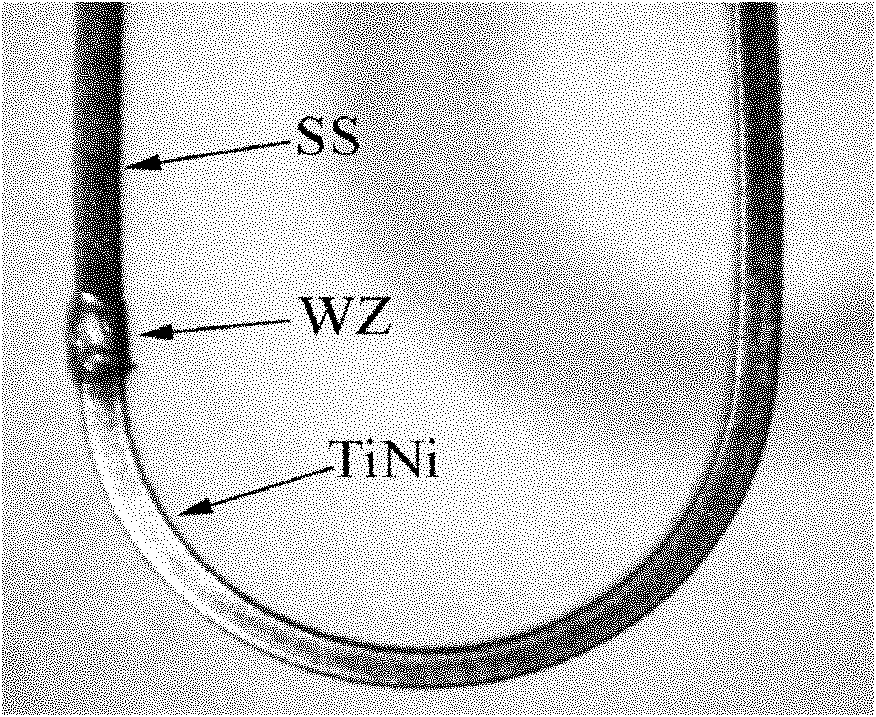
Method for connecting TiNi shape memory alloy and austenitic stainless steel heterogenetic material
InactiveCN102152017AHigh strengthHigh tensile strengthWelding/soldering/cutting articlesWelding apparatusShape-memory alloyAustenite
The invention relates to a method for connecting a TiNi shape memory alloy and an austenitic stainless steel heterogenetic material, and belongs to a heterogenetic material connection technology. In the method, aiming at the welding problem of the TiNi shape memory alloy and the austenitic stainless steel heterogenetic material, on the basis of the characteristics of limitless mutual solubility of copper and nickel, finite solid solubility of copper and titanium, iron and chromium, higher strength and plasticity of copper solid solution, lower brittleness of a copper-titanium intermetallic compound and the like, the copper solid solution can be extracted from a welding line region and the brittle intermetallic compounds can be reduced by adopting a pure copper packing material (a copper middle layer or a copper welding wire) and reducing the penetration ratio of a TiNi alloy base material, so the strength and flexibility of a welding joint between the TiNi shape memory alloy and the stainless steel heterogenetic material. The method comprises the following processes of: adding the pure copper middle layer (pure copper welding wire), adjusting the position of a heat source, protecting a welding region, and melting and welding.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Cariaceous high-damping deformation magnesium alloy and its prepn process
The process relates to excellent magnesium base material, and is coriaceous high-damping deformation magnesium alloy and its preparation process. For obtaining both high damping performance and high mechanical performance, the present invention adds Cu, Si and other alloy element with small solid solubility into Mg material to reduce dislocation pinning points and to raise damping performance, while adding Zr, Mn and other crystal grain fining alloy element to raise the mechanical performance. Through conventional extrusion on ingot and intense plastic deformation, the alloy has regulated grain orientation, superfine crystal structure and raised toughness and damping performance. The present invention has wide application value.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
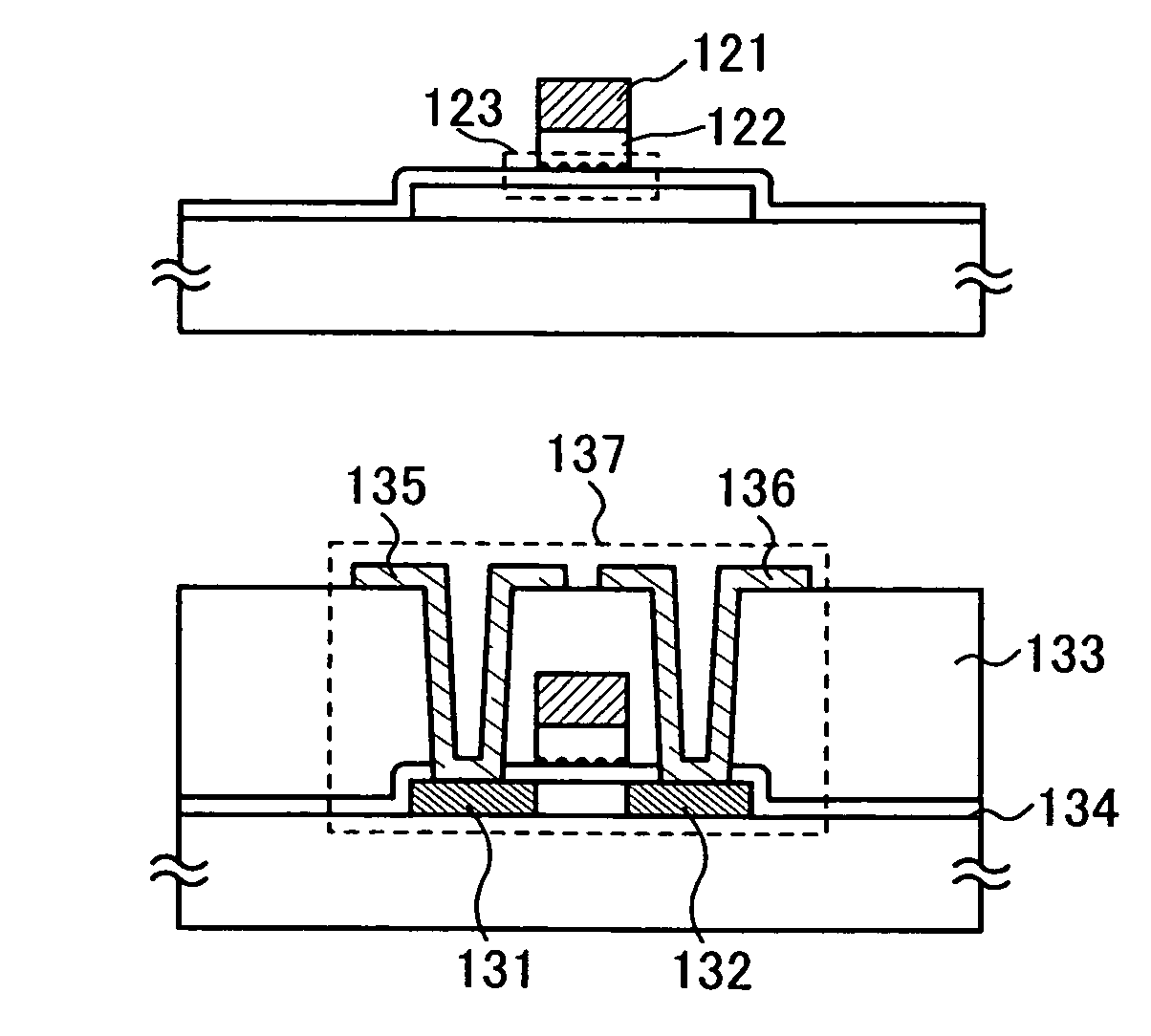
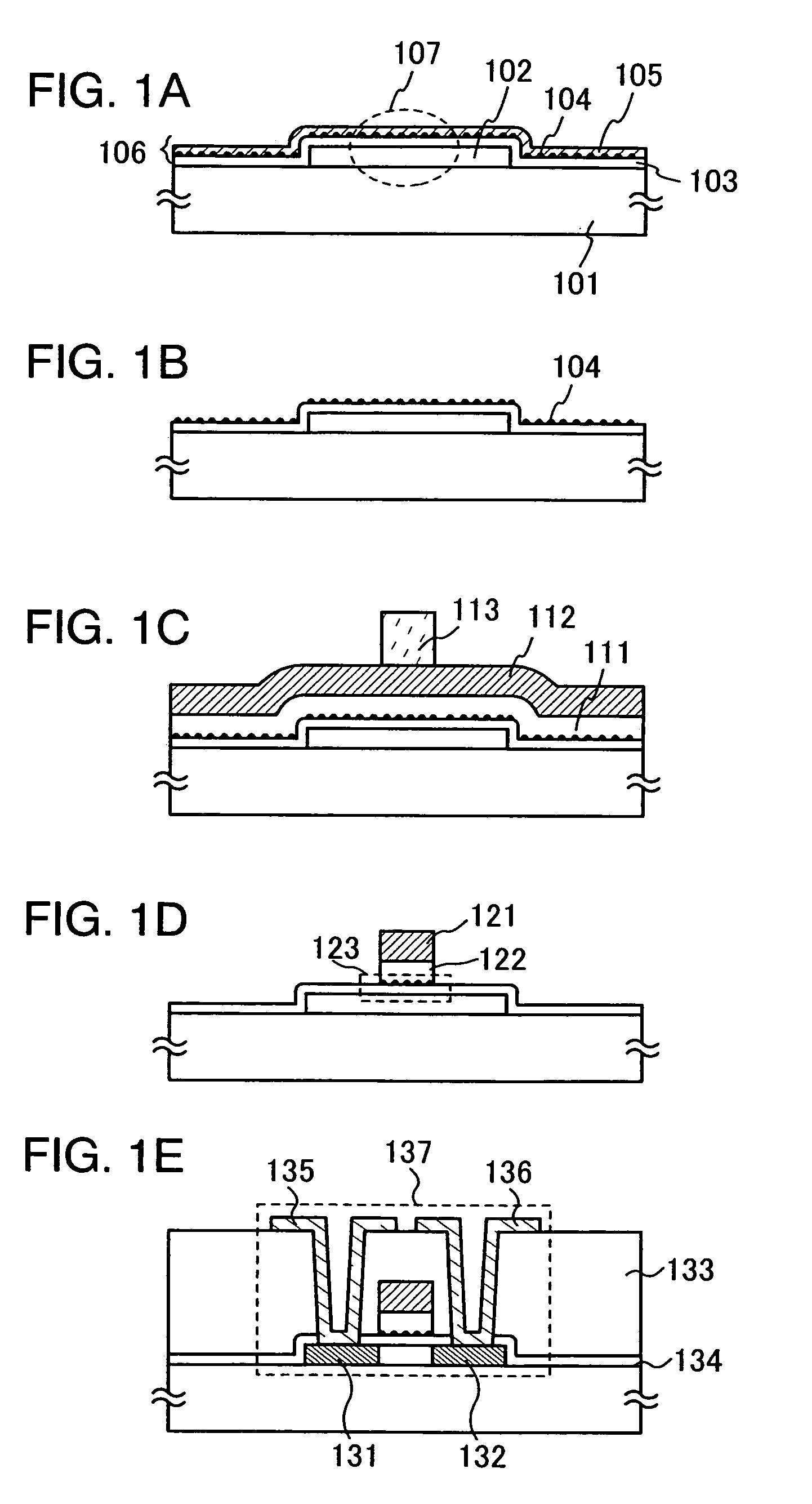
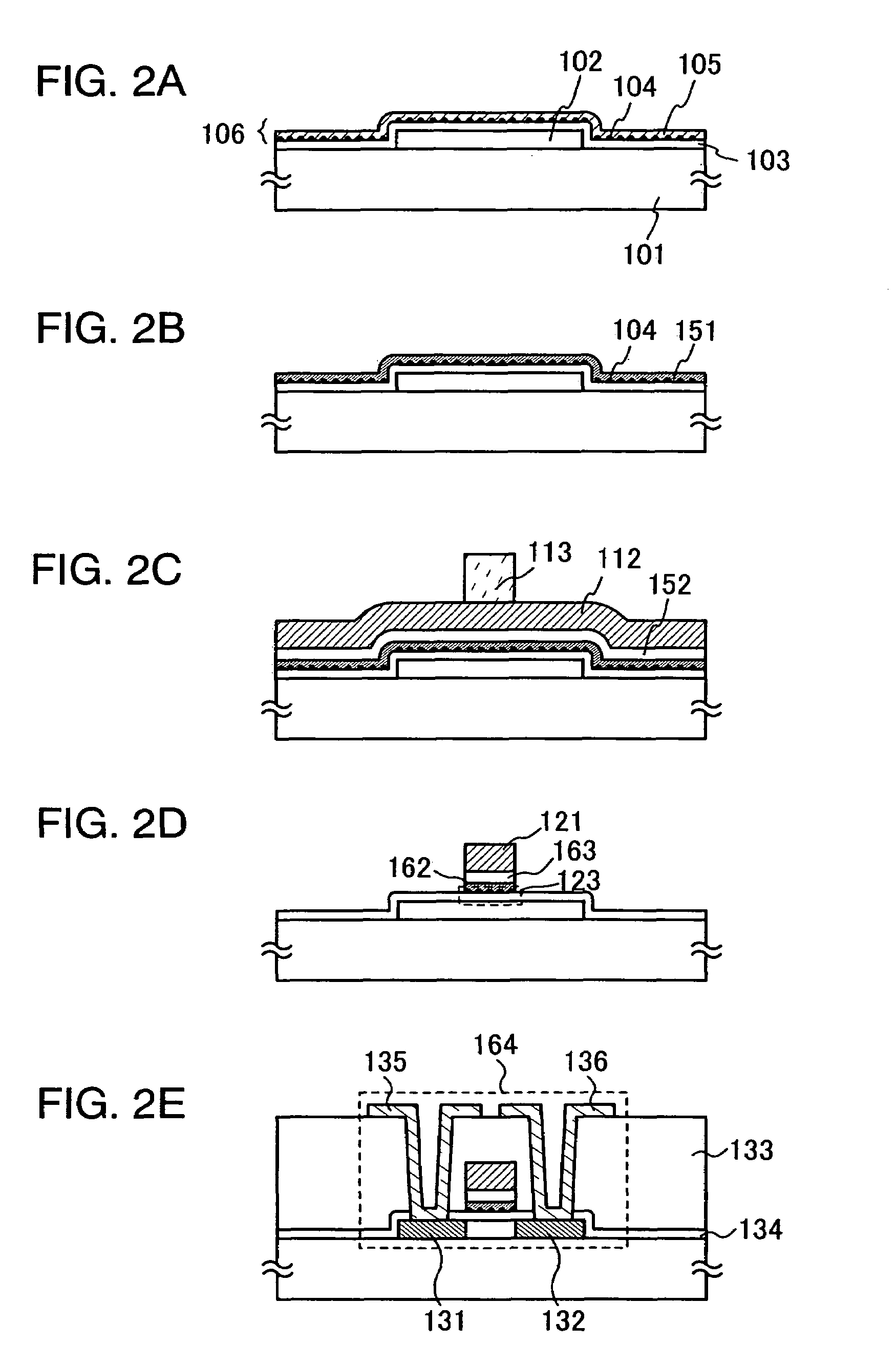
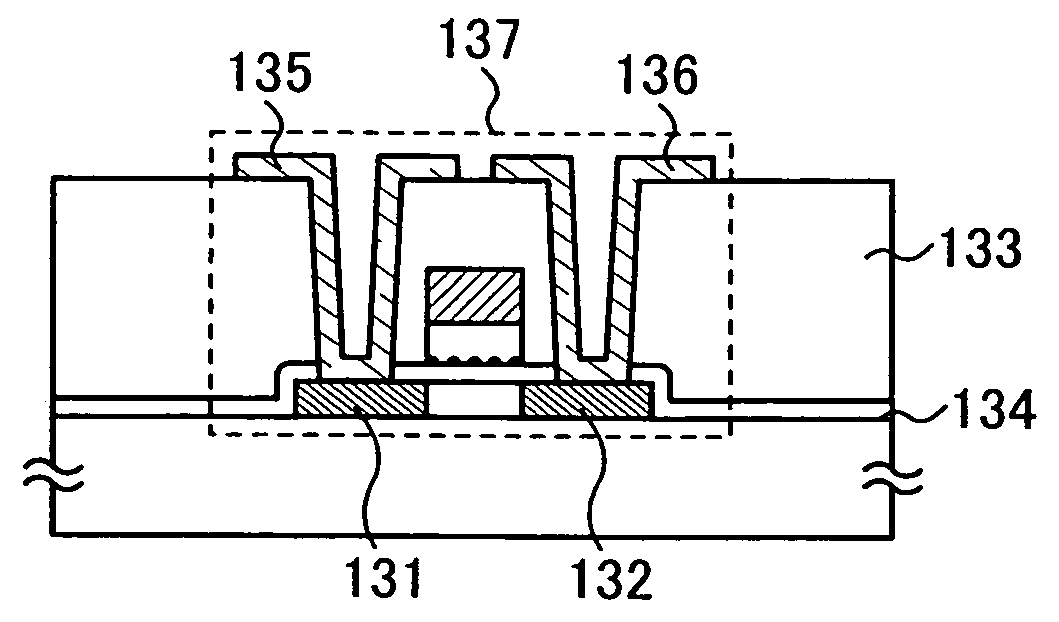
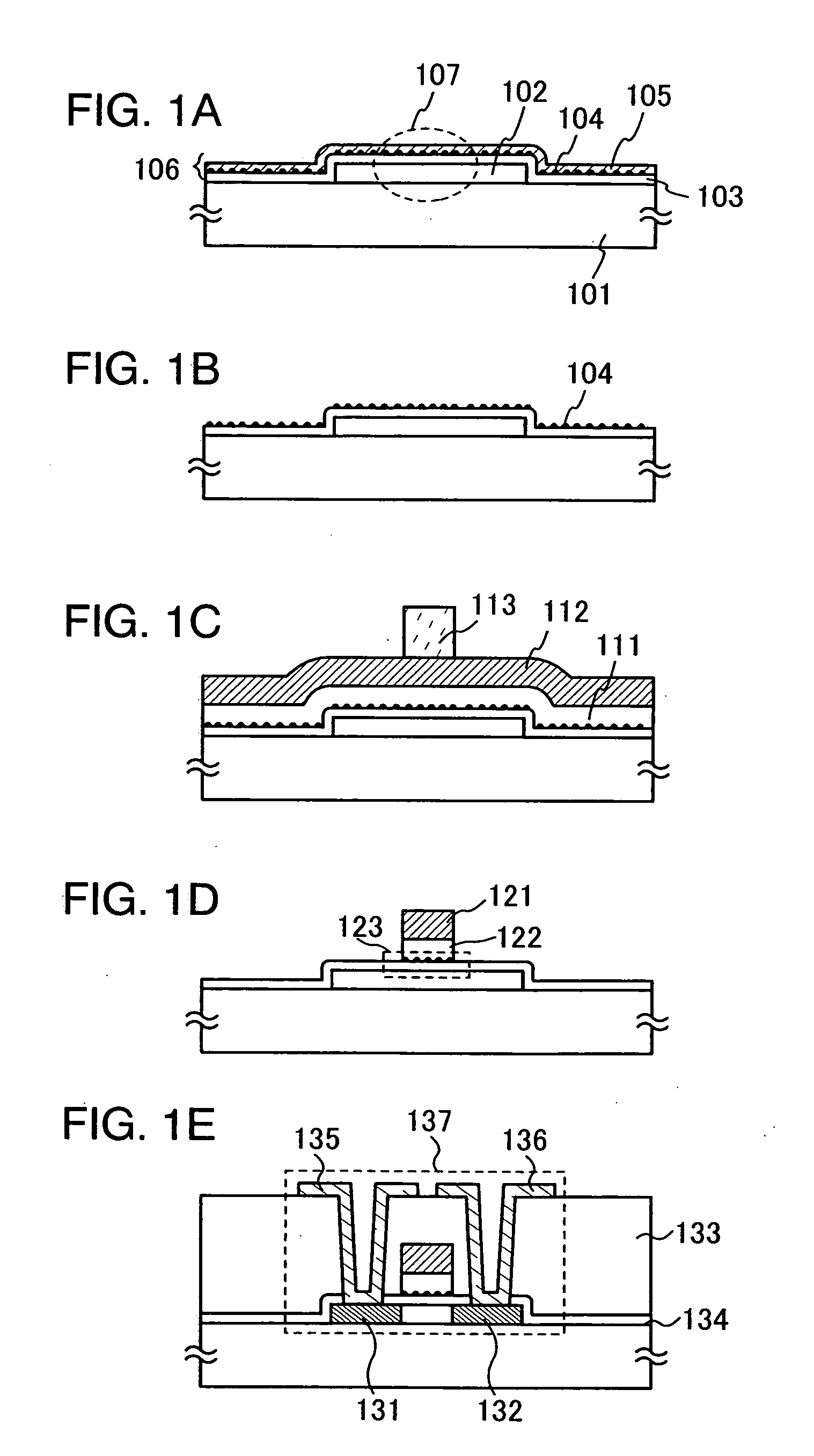
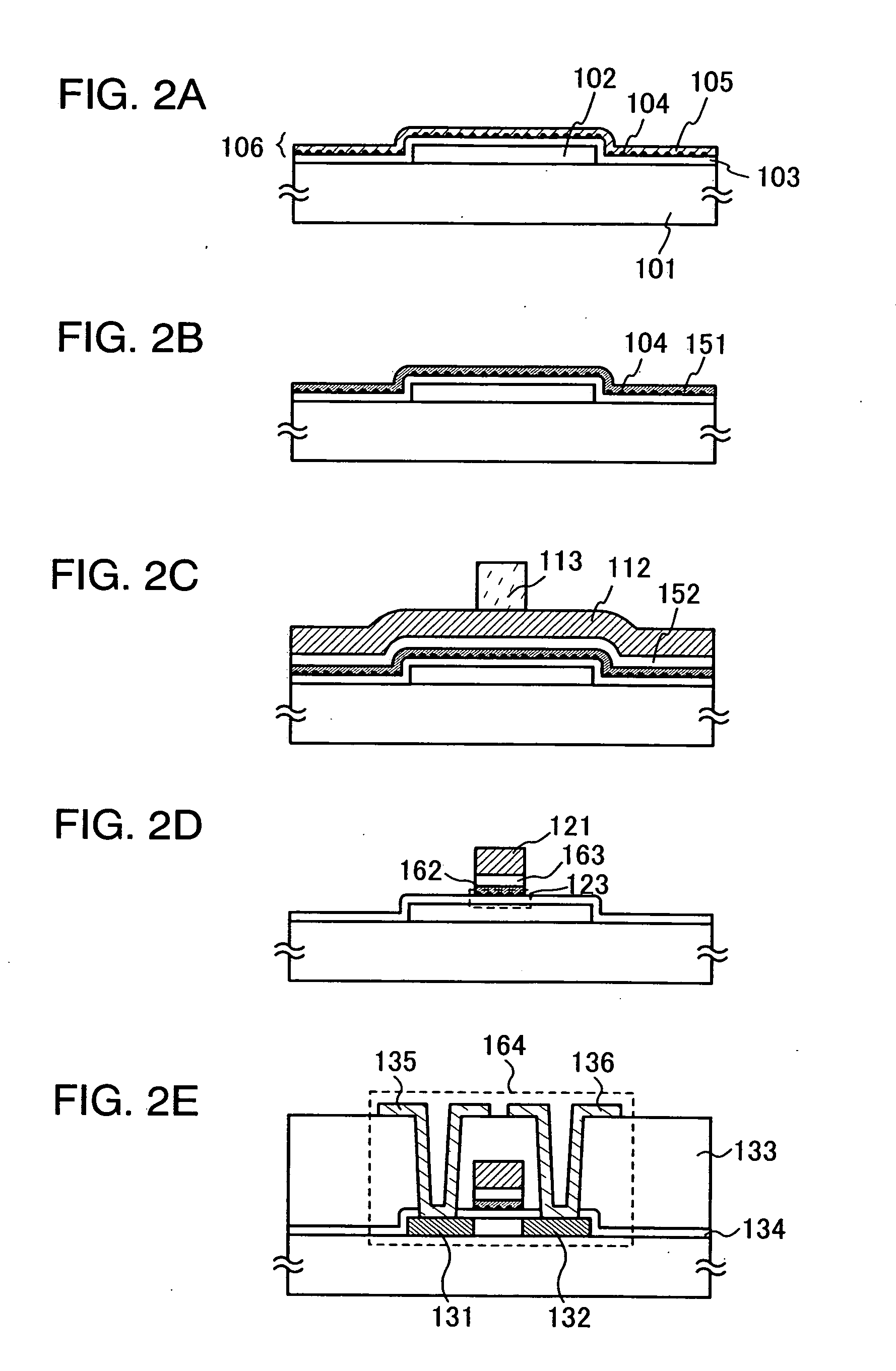
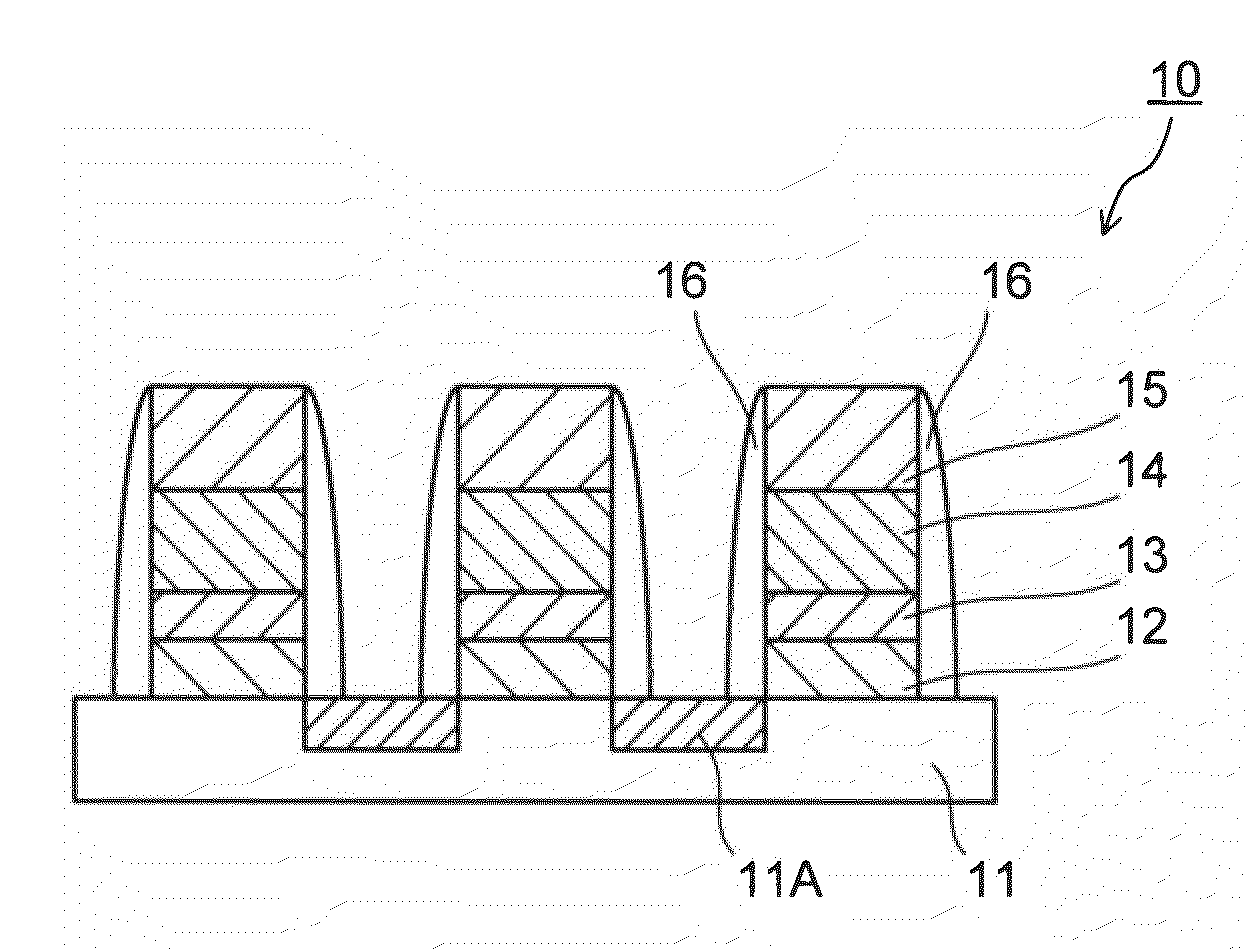
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
InactiveUS7335556B2Increase the number ofSmall variationTransistorNanoinformaticsSputteringEngineering
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device having a semiconductor nonvolatile memory element that is highly reliable and that can increase a variation of a threshold voltage. Further, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having a highly reliable semiconductor nonvolatile memory element using a large substrate. According to the present invention, sputtering using, as a target, a solid solution containing silicon that exceeds a solid solubility limit is conducted, so that a conductive film including a conductive layer of a metal element that is a main component of the solid solution and silicon particles is formed, and then, the conductive layer of the metal element is removed to expose silicon particles. Furthermore, a semiconductor device having a semiconductor nonvolatile memory element using the silicon particles as a floating gate electrode is manufactured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Lead-free piezoceramics-polymer piezoelectric composite material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101591461ASimple processMaterials are readily availablePiezoelectric/electrostrictive device manufacture/assemblySilicone oil bathPiezoelectric composite
The invention relates to a lead-free piezoceramics-polymer piezoelectric composite material and a preparation method thereof. The method comprises the following steps: preparing materials according to compositions in a chemical general formula (1-x)(LiaNabK1-a-b)(Nb1-cSbc)O3-xABO3-yM, taking analytically pure anhydrous carbonates or oxides as raw materials, and preparing ceramic powder by the conventional ceramic preparing process; performing mixing and ball-milling on the ceramic powder and polyvinylidene fluoride in a volume ratio of between 10:90 and 95:5; and drying, performing ultrasonic oscillation for 10 to 100 minutes, performing cold press molding on the mixed powder material by a tablet press, processing by heating through a muffle furnace, finally sputtering gold electrodes on the surface of the powder material, and performing polarization in a silicone oil bath at a temperature of between 80 and 130 DEG C for 10 to 120 minutes to prepare the potassium-sodium niobate-based lead-free piezoceramics-polymer piezoelectric composite material. The piezoelectric composite material has pure perovskite crystalline phase and no impurity phase to prove that the two have good solid solubility, and has good piezoelectric and dielectric properties.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
High-quality 6-series aluminum alloy extrusion casting blank and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN110735073AReduce hardnessImprove extrusion deformationFurnace typesHeat treatment furnacesIngotUltimate tensile strength
The invention discloses a high-quality 6-series aluminum alloy extrusion casting blank and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of performing primary cooling treatment, bath treatment and subsequent cooling treatment on a 6-series aluminum alloy ingot subjected to homogenization heat treatment in sequence. Compared with a traditional uniform casting blank in actual production, the prepared casting blank has the advantages that a large number of dispersed micron-sized precipitated phases are distributed in a matrix, the structure can not only effectively reduce the extrusion deformation resistance of a cast ingot, improve the surface quality of an extruded product, but also improve the online quenching solid solubility of the extruded product, so that a good tissue basis is provided for later aging treatment. Finally, the high-quality extrusion casting blank capable of improving the extrusion performance and improving the final aging strength is finally obtained.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV +1
Deforming magnesium alloy and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102828094AImprove high temperature stabilityImprove mechanical propertiesRare-earth elementYttrium
The invention provides a deforming magnesium alloy and a preparation method thereof. The deforming magnesium alloy comprises the following components in percentage by mass: 0.1-10% of neodymium, 10-12% of gadolinium, 3-5% of yttrium, 0.5-2% of zinc, 0.3-0.8% of zirconium, and the balance of magnesium and inevitable impurities. Compared with WE54 in the prior art, the invention is characterized in that rare-earth elements neodymium, gadolinium and yttrium are added into the Mg-Zn-Zr magnesium alloy. Firstly, after adding zinc, abundant strip Mg12YZn precipitated phases are formed at the alloy grain boundary to prevent grain boundary migration at high temperature and enhance the high-temperature stability of the alloy, and the precipitated phases are uniformly arranged in the extrusion direction to prevent basal dislocation migration and enhance the mechanical properties of the alloy; and secondly, the three rare-earth elements gadolinium, yttrium and neodymium are added, so the interactions among the rare-earth elements can be utilized to lower the solid solubility of the gadolinium, yttrium and neodymium in the magnesium base, thereby promoting the formation of the precipitated phases and enhancing the mechanical properties of the alloy.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-plasticity five-element refractory high-entropy alloy and preparation method thereof
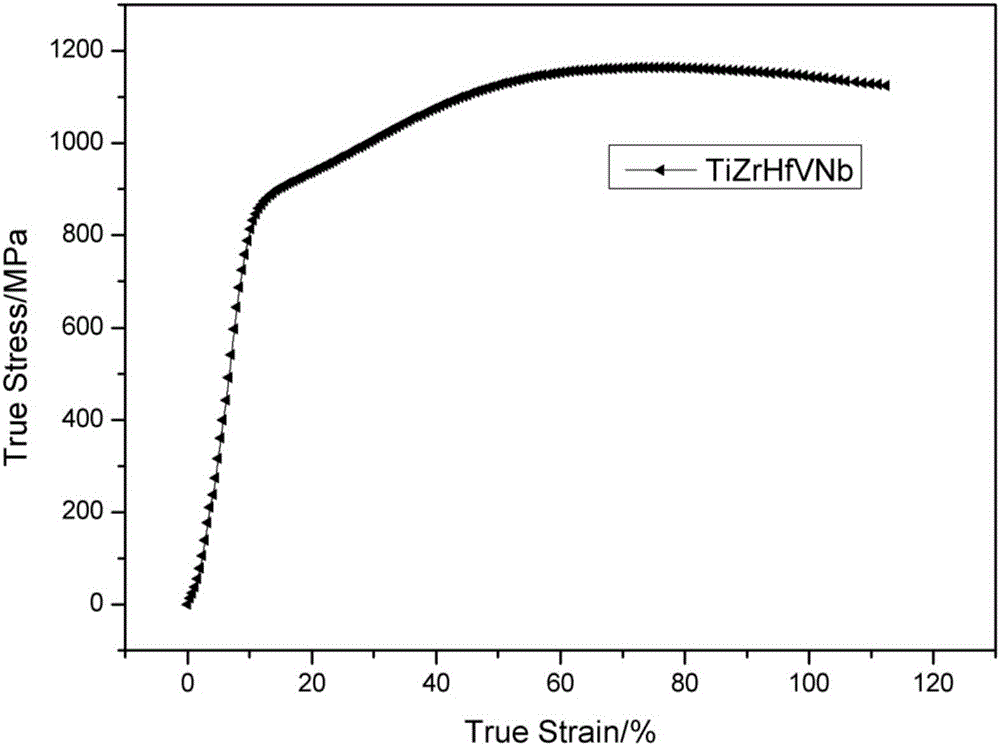
The invention relates to high-plasticity five-element refractory high-entropy alloy and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the field of metal materials. The high-entropy alloy is prepared from zirconium, titanium, hafnium, vanadium and niobium, wherein the molar weights of the zirconium, the titanium, the hafnium, the vanadium and the niobium are equal. The preparation method of the high-plasticity five-element refractory high-entropy alloy comprises the steps that the zirconium, the titanium, the hafnium, the vanadium and the niobium are placed in a water-cooling metal crucible in a melting point progressively-decreasing sequence, the element with the lowest melting point is placed at the bottom, and the element with the highest melting point is placed at the top; and arc striking smelting is conducted in an oxygen-free environment till the five elements are fully mixed, and the high-entropy alloy is obtained. The high-entropy alloy is of a single body-centered cubic structure, the yield strength of the high-entropy alloy is higher than 800 MPa, the tensile strength is over 1100 MPa, and the plastic strain is larger than 55%; and the large solid solubility between the elements is obtained, and a simple solid-solution phase is formed. The preparation method has the advantages that the power is high, the performance is table, operation is convenient, the melting point is high, the vacuum degree is high, and the quantity of impurities is small.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Method for preparing aluminum powder and aluminum alloy powder through water atomization
The invention discloses a method for preparing aluminum powder and aluminum alloy powder through water atomization. The method comprises the following steps of melting aluminum ingots or aluminum alloy by using a guide crucible, and ensuring that the temperature of a melt is kept between 700DEG C and 1,100DEG C for 30 to 60 minutes; meanwhile, heating the guide crucible; pouring molten aluminum alloy into the guide crucible, and allowing the molten aluminum alloy to continuously flow out along a guide tube at the bottom of the guide crucible; starting a high pressure water pump, controlling the pressure of high pressure current to be 2-16MPa and the water temperature to be 10-40DEG C, enabling the high pressure current into which an inhibitor is added and of which the pH is 4.0-5.0 to be sprayed by nozzles on the top of an atomizing chamber, and atomizing the molten aluminum to obtain the aluminum and aluminum alloy powder. According to the method, the aluminum powder can be safely produced through the water atomization; compared with aluminum powder prepared through gas atomization, the aluminum powder prepared through the water atomization is finer in particle size, large in specific surface area and high in activity; moreover, the water atomization is higher in cooling speed, the extended solid solubility of alloy elements is greatly improved, and aluminum alloy which is hardly prepared by a casting process is produced. In addition, the cost of preparing the aluminum powder through the water atomization is lower than the cost of preparing the aluminum powder through the gas atomization, and the method is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Manufacturing method of semiconductor device
The present invention provides a manufacturing method of a semiconductor device having a semiconductor nonvolatile memory element that is highly reliable and that can increase a variation of a threshold voltage. Further, the present invention provides a method for manufacturing a semiconductor device having a highly reliable semiconductor nonvolatile memory element using a large substrate. According to the present invention, sputtering using, as a target, a solid solution containing silicon that exceeds a solid solubility limit is conducted, so that a conductive film including a conductive layer of a metal element that is a main component of the solid solution and silicon particles is formed, and then, the conductive layer of the metal element is removed to expose silicon particles. Furthermore, a semiconductor device having a semiconductor nonvolatile memory element using the silicon particles as a floating gate electrode is manufactured.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Method for producing a titanium-base alloy having an oxide dispersion therein
A metallic article is prepared by first furnishing at least one nonmetallic precursor compound, wherein all of the nonmetallic precursor compounds collectively containing the constituent elements of the metallic article in their respective constituent-element proportions. The constituent elements together form a titanium-base alloy having a stable-oxide-forming additive element therein, such as magnesium, calcium, scandium, yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, promethium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium, and lutetium, and mixtures thereof. The stable-oxide-forming additive element forms a stable oxide in a titanium-based alloy. At least one additive element is present at a level greater than its room-temperature solid solubility limit in the titanium-base alloy. The precursor compounds are chemically reduced to produce an alloy material, without melting the alloy material. The alloy material may be consolidated. The alloy material, or consolidated metallic article, is thereafter desirably exposed to an oxygen-containing environment at a temperature greater than room temperature.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Erbium-doped barium-yttrium-fluoride-nanocrystalline containing transparent oxyfluoride glass ceramic and preparation thereof
The invention relates to erbium-doped transparent glass ceramic containing nanocrystalline barium yttrium fluoride and the preparation method thereof, which relates to the field of luminescent material. The components of glass ceramic are (mole ratio): 40SiO2-25Al2O3-xBaCO3-10YF3-yBaF2-zErF3 (x=5-20, z=0.1-3.0, y=25-x-z). The invention is prepared by melt-spinning technique and adopts SiO2, Al2O3, BaCO3, YF3, BaF2 and ErF3 powder as raw materials, and the raw materials are well mixed, heated to 1300-1600 DEG C and the temperature is preserved for 1-4 hours, and then melting fluid is prepared into vitreous body; the vitreous body is annealed to relieve internal stress, continues to be heated to 650-800 DEG C, the temperature is preserved for 1-10 hours, and the obtained nanocrystalline has extremely high solid solubility of erbium ion. With the infrared excitation, the up-conversion emission intensity of the glass ceramic is greatly improved by adjusting heat treatment temperature.
Owner:FUJIAN INST OF RES ON THE STRUCTURE OF MATTER CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
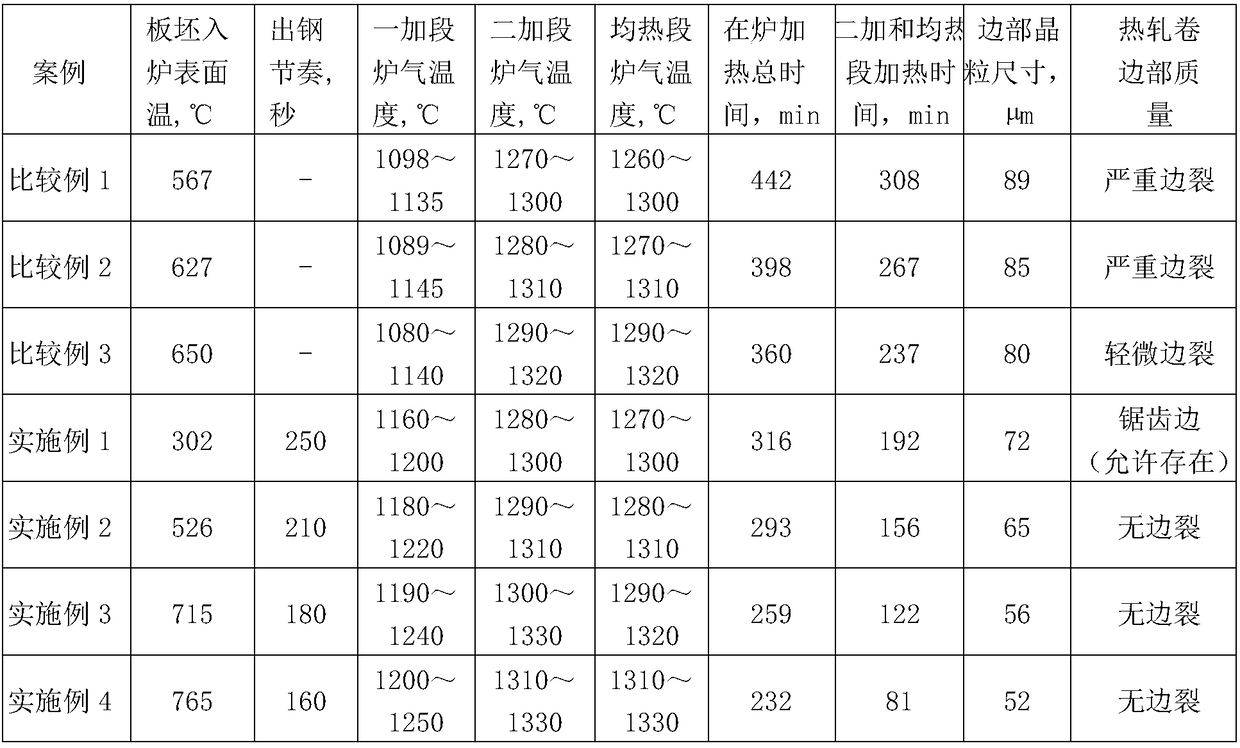
Process for preventing hot-rolling edge cracking of oriented silicon steel
ActiveCN108193037AFully solid solutionTemperature control deviceHeat treatment process controlHeating timeHeating furnace
The invention discloses a process for preventing hot-rolling edge cracking of oriented silicon steel. The process comprises the steps that the surface temperature of a plate blank is no smaller than 300 DEG C before the plate blank enters a heating furnace; the furnace gas temperature of a first heating section is 1160-1250 DEG C; the furnace gas temperatures of a second heating section and a soaking section are each 1270-1330 DEG C, the heating time is 80-200 minutes, and the standing time is no longer than 30 minutes; the average grain size of the edge of a hot-rolled finished product is nolarger than 72 [mu]m; the final rolling temperature of finish rolling is 880-960 DEG C; the coiling temperature is 500-620 DEG C; and tension of a seven-rack finish rolling unit is reasonably controlled. On the premises that sufficient solid solubility of an oriented silicon steel inhibitor is ensured and electromagnetic performance of the finished product meets the target requirement, the problems that the edge of the plate blank is decarburized or the plate blank is locally decarburized when the heating time of the second heating section and the soaking section is too long or when the standing time is too long, grains grow excessively, and edge cracking occurs in the hot-rolling process are avoided.
Owner:新余钢铁股份有限公司
High-strength high-toughness high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel welding wire and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN108526750AIncrease contentImprove solid solubilityArc welding apparatusWelding/cutting media/materialsManganeseAustenite
The invention relates to a high-strength high-toughness high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel welding wire and a preparation method thereof. The welding wire is prepared from the alloy components in percentage by weight: less than 0.1 percent of C, less than 0.02 percent of S, less than 0.03 percent of P, 0.1 to 0.9 percent of Si, 5 to 21 percent of Mn, 15 to 23 percent of Cr, 0 to 8 percent ofNi, 0 to 5 percent of Mo, 0.2 to 0.95 percent of N, the balance Fe, and less than 0.1 percent of other impurities. The preparation process comprises the steps of smelting through an induction furnace, electro slags remelting, hot forging, hot rolling, heat treating, and drawing of the welding wire. According to the welding wire provided by the invention, the component proportion is scientific andreasonable, the content of nitrogen elements is increased, the content of manganese elements is adjusted, and the solid solubility of the nitrogen is increased, so that the prepared welding wire is stable in welding process, less in escape amount of hydrogen elements, less in blowhole defects, good in welding processability, high in deposited metal strength, excellent in impact toughness at the temperature of minus 40 DEG C, suitable for welding high-nitrogen austenitic stainless steel, particularly suitable for welding the austenitic stainless steel with the requirement on low-temperature impact toughness, and capable of being surfacing-welded so as to be used as anti-corrosion layers for other steel and iron materials.
Owner:CHINA WEAPON SCI ACADEMY NINGBO BRANCH
Boron-aluminum common gettering method for silicon slice
ActiveCN101944554AGetterGood repeatabilityFinal product manufactureSemiconductor devicesScreen printingSurface layer
The invention discloses an aluminum-boron common gettering method for a silicon slice, which comprises the following steps of: preparing a boron-doped aluminum source, cleaning the silicon slice, forming a boron aluminum layer on the surface of the silicon slice by using screen printing or spin coating technology, performing annealing with one or more steps, and removing the surface layer of the silicon slice. The boron is doped into the aluminum by using the characteristic that the boron has high solid solubility in silicon compared with the aluminum, and the boron is doped into a heavy doped layer on the back of the silicon by using an alloying process of the aluminum and the silicon to obtain an aluminum-boron common gettering layer with high doping concentration. The aluminum-boron common gettering method can form a deeper and uniform gettering layer with higher doping concentration at the same annealing temperature, achieve the gettering effect of other processes at a low temperature, and reduce the influence of high temperature on the performance of the silicon slice. The aluminum-boron common gettering method has the characteristics of low cost, easy operation and good gettering effect, and has great application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
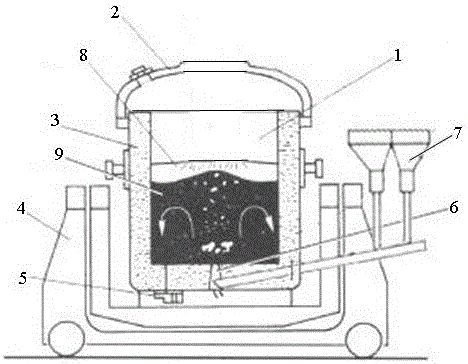
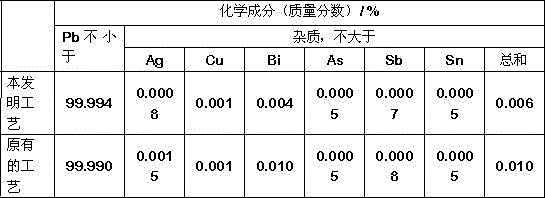
Regenerated lead fire method basic refining bottom-blowing process
The invention discloses a regenerated lead fire method basic refining bottom-blowing process. The process comprises the following steps: discharging lead of crude lead liquid from a melting furnace, casting the lead in a refining furnace, introducing argon from the bottom of the furnace, when the temperature of the lead liquid is reduced to about 330 DEG C, removing the slag, reducing the lead-containing copper to about 0.1% through liquation decoppering, injecting sulfur powder at the bottom of the refining furnace for removing copper after slag removal, heating the material to 450-480 DEG C, reacting the material for 30-60 min, taking the sulfuration slag out to complete a copper-removal process; when the lead liquid temperature is about 45 DEG C, blowing powdery sodium nitrate and sodium hydroxide into the bottom of the refining furnace, reacting the materials for 30 min, and blowing NaCl powder at the bottom of the refining furnace by following with argon to complete arsenic, antimony and tin removal. According to the bottom-blowing process, a refining agent and / or alloy loss are greatly reduced; the lead liquid contains inert gas with little solid solubility, the lead liquid and a lead ingot are difficulty oxidized, no lead slag is generated in the lead liquid and the lead ingot, lead slag is little when the regenerated lead is used, the slag yield is low; the lead liquid surface is protected by argon during a refining process, high temperature Ag removal can be carried out, the content of Ag in the regenerated lead is low; argon at the bottom and the minimal bismuth compound particles are floated, and the bismuth content in the lead ingot is low.
Owner:安徽省陶庄湖废弃物处置有限公司
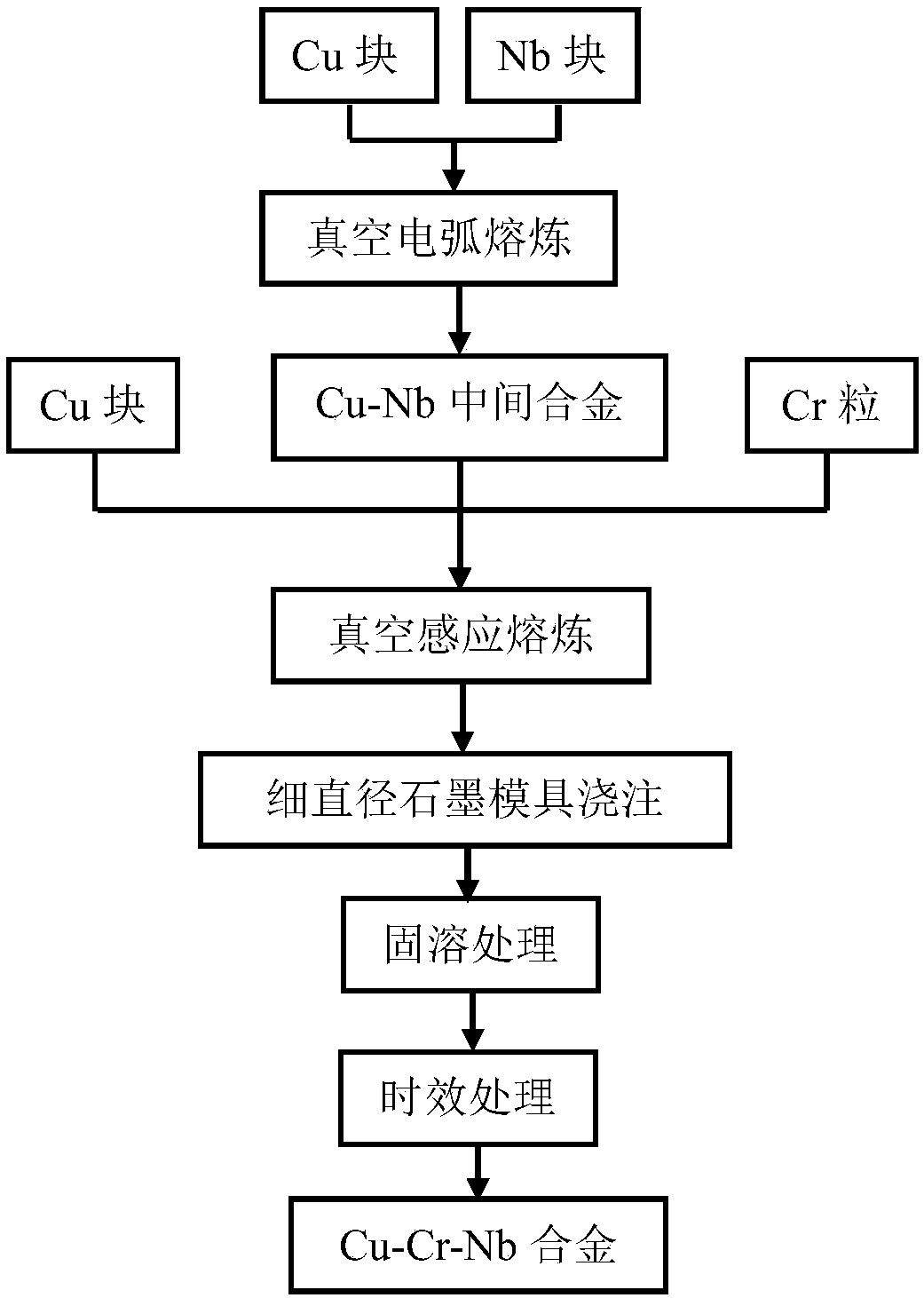
Preparation method for high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy bar
The invention discloses a preparation method for a high-strength high-conductivity copper alloy bar. The preparation method comprises the following concrete steps: placing Cu-Nb intermediate alloy, Crparticles and Cu blocks in a crucible, and carrying out melting in an induction melting furnace protected by argon so as to obtain Cu-Cr-Nb alloy liquid; subjecting the Cu-Cr-Nb alloy liquid to casting and cooling in a fine-diameter graphite mold so as to obtain a Cu-Cr-Nb alloy bar; and putting the bar into a heat treatment furnace for solutionizing and aging heat treatment, and carrying out mechanical processing so as to obtain the finished Cu-Cr-Nb alloy bar. According to the invention, the Cu-Cr-Nb alloy is prepared by using a fine-diameter graphite mold casting and cooling method, so thecooling rate of the alloy is improved, the structure of the alloy is refined, and the solid solubility of elemental Cr and Nb in a Cu substrate is greatly improved; and through the aging treatment, dispersed fine second-phase particles are precipitated from the copper substrate, so the performance of the alloy is improved.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF TECH
Silicon carbide semiconductor device and manufacturing method of the same
ActiveUS20160141371A1Easy to spreadHigh-performance and reliableTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNitrogenOptoelectronics
In order to provide a high-performance and reliable silicon carbide semiconductor device, in a silicon carbide semiconductor device including an n-type SiC epitaxial substrate, a p-type body layer, a p-type body layer potential fixing region and a nitrogen-introduced n-type first source region formed in the p-type body layer, an n-type second source region to which phosphorus which has a solid-solubility limit higher than that of nitrogen and is easily diffused is introduced is formed inside the nitrogen-introduced n-type first source region so as to be separated from both of the p-type body layer and the p-type body layer potential fixing region.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Aluminum copper dissimilar metal rotation friction welding method added with middle layer
InactiveCN106346128AHigh strengthLow soldering temperatureWelding/soldering/cutting articlesNon-electric welding apparatusFriction weldingAluminum metal
The invention discloses an aluminum copper dissimilar metal rotation friction welding method added with a middle layer. The method is used for solving the technical problem of low joint intensity of the existing aluminum copper dissimilar metal rotation friction welding method, and has the technical scheme that firstly, aluminum metal and middle layer metal are subjected to rotation friction welding; then, the aluminum metal with the middle layer metal is subjected to rotation friction welding with copper metal; the middle layer metal uses metal with high solid solubility with the aluminum and copper; in the welding process, the middle layer metal is respectively diffused to the two sides of the aluminum and copper to form sosoloids. The aluminum and copper also diffuse to the middle layer, but the rotation friction welding time is short; the welding temperature is low; the diffusion substance concentration of the aluminum and copper towards the middle layer is low; a great number of intermetallic compounds cannot be sufficiently formed. A small number of intermetallic compounds formed by the diffusion of the aluminum and copper towards the middle layer can be extruded out in a flash mode; finally, no aluminum and copper intermetallic compounds are generated in the obtained aluminum copper dissimilar metal rotation friction welding joint; the joint intensity is improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
Semiconductor device and method for manufacturing a semiconductor device
InactiveUS20090242963A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricComposite oxide
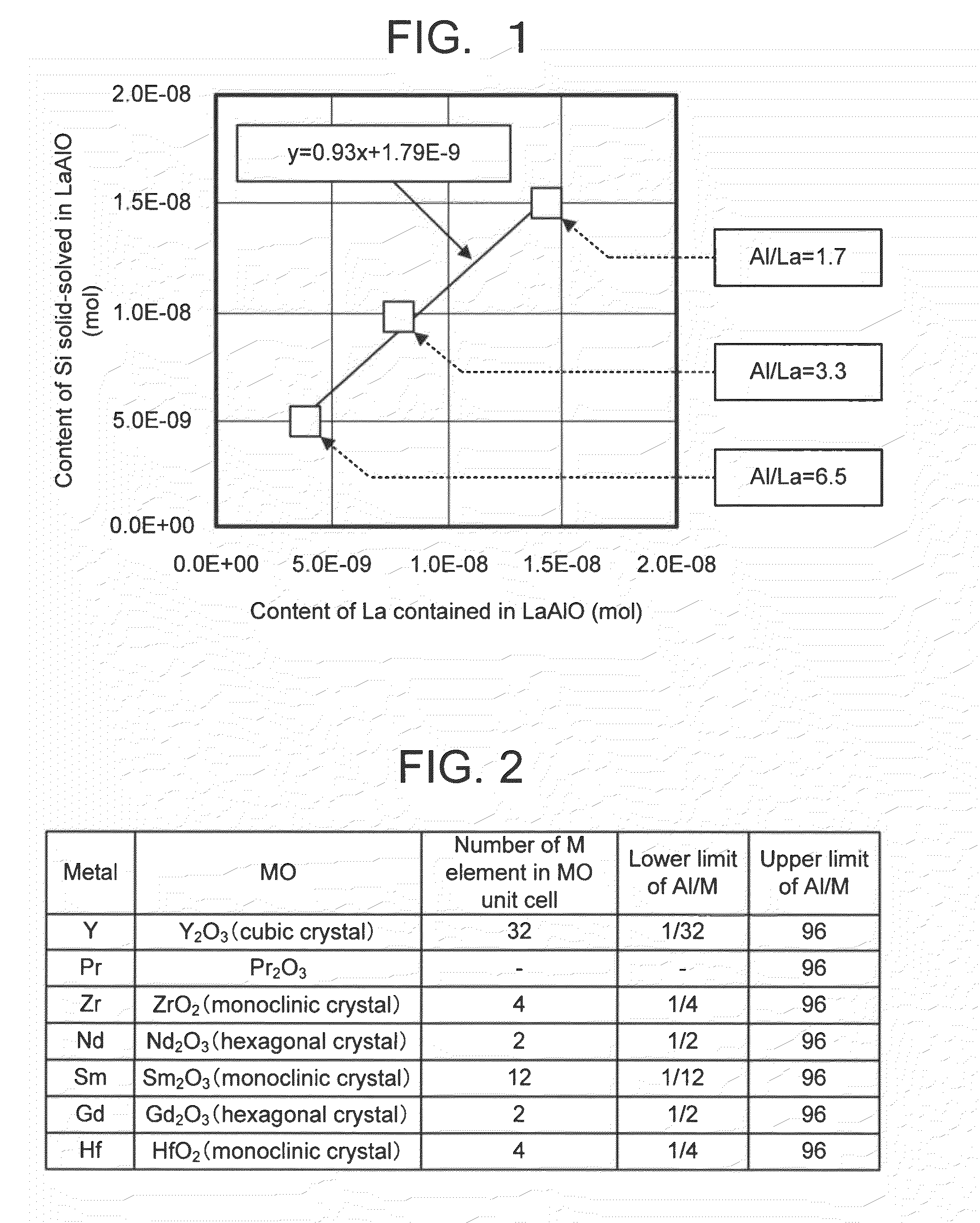
In a semiconductor device, the side walls are made of SiO2, SiN or SiON, and the top insulating film or gate insulating film is made of an oxide including Al, Si, and metal element M so that the number ratio Si / M is set to no less than a number ratio Si / M at a solid solubility limit of SiO2 composition in a composite oxide including metal element M and Al and set to no more than a number ratio Si / M at the condition that the dielectric constant is equal to the dielectric constant of Al2O3 and so that the number ratio Al / M is set to no less than a number ratio Al / M where the crystallization of an oxide of said metal element M is suppressed due to the Al element and set to no more than a number ratio Al / M where the crystallization of the Al2O3 is suppressed due to the metal element M.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com