Patents
Literature
411 results about "Seebeck coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
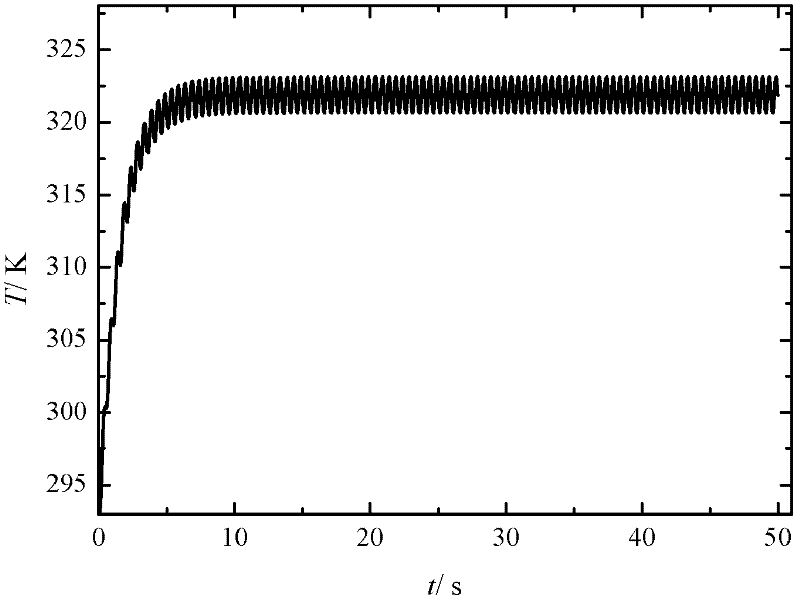
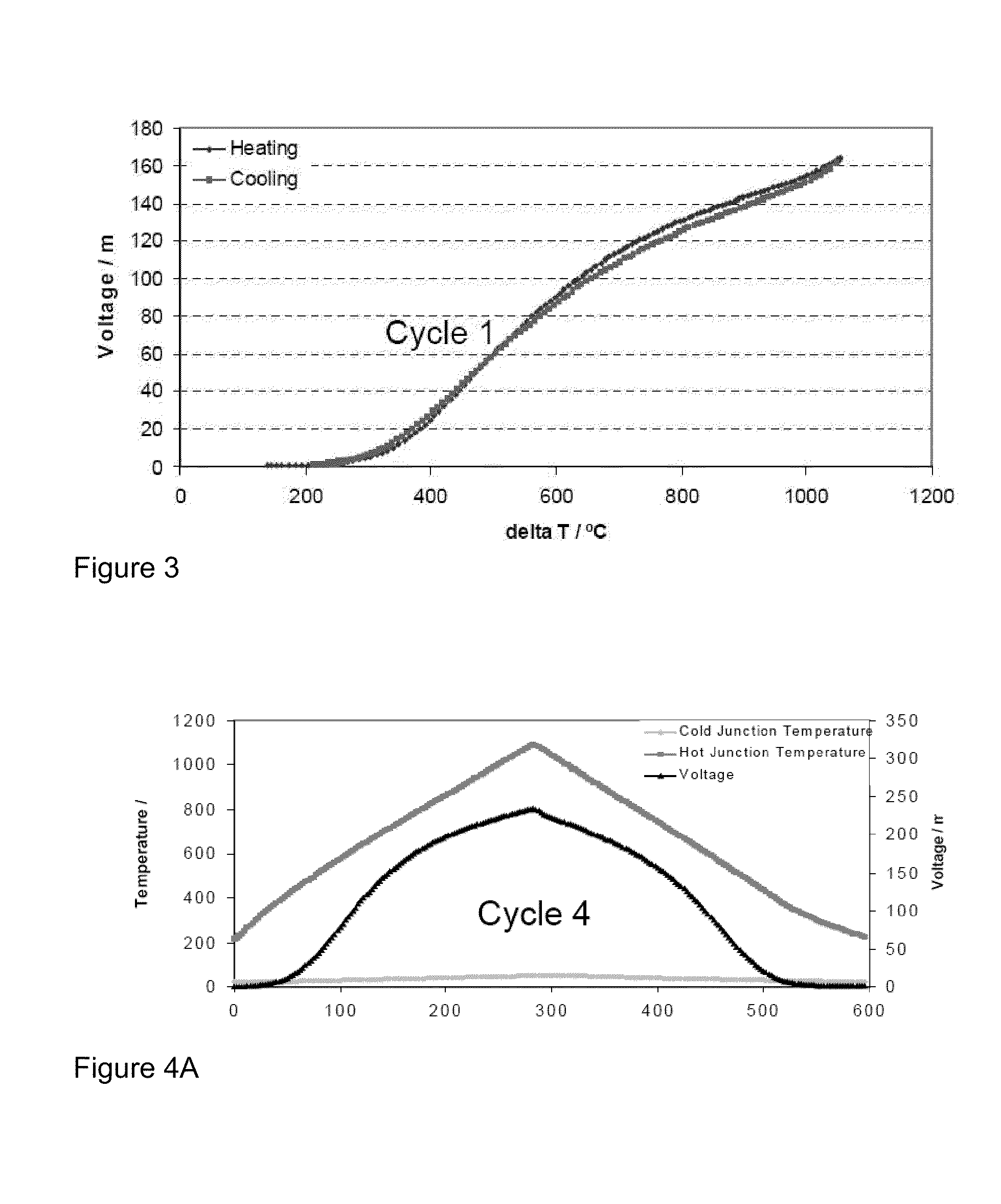
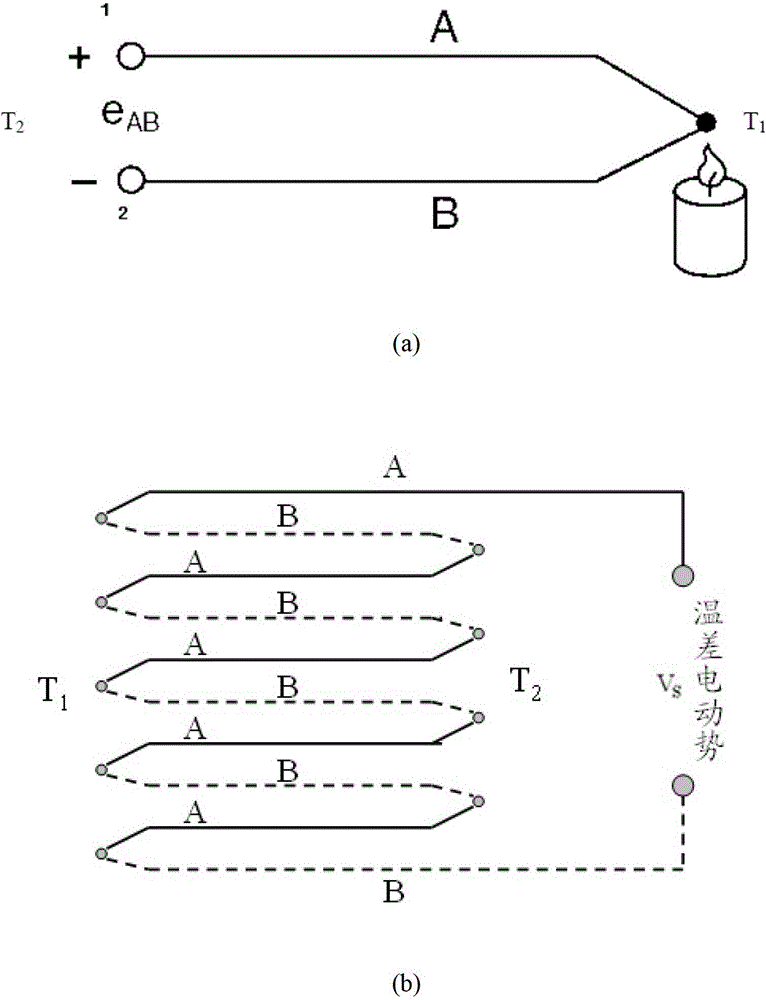
The Seebeck coefficient (also known as thermopower, thermoelectric power, and thermoelectric sensitivity) of a material is a measure of the magnitude of an induced thermoelectric voltage in response to a temperature difference across that material, as induced by the Seebeck effect. The SI unit of the Seebeck coefficient is volts per kelvin (V/K), although it is more often given in microvolts per kelvin (μV/K).
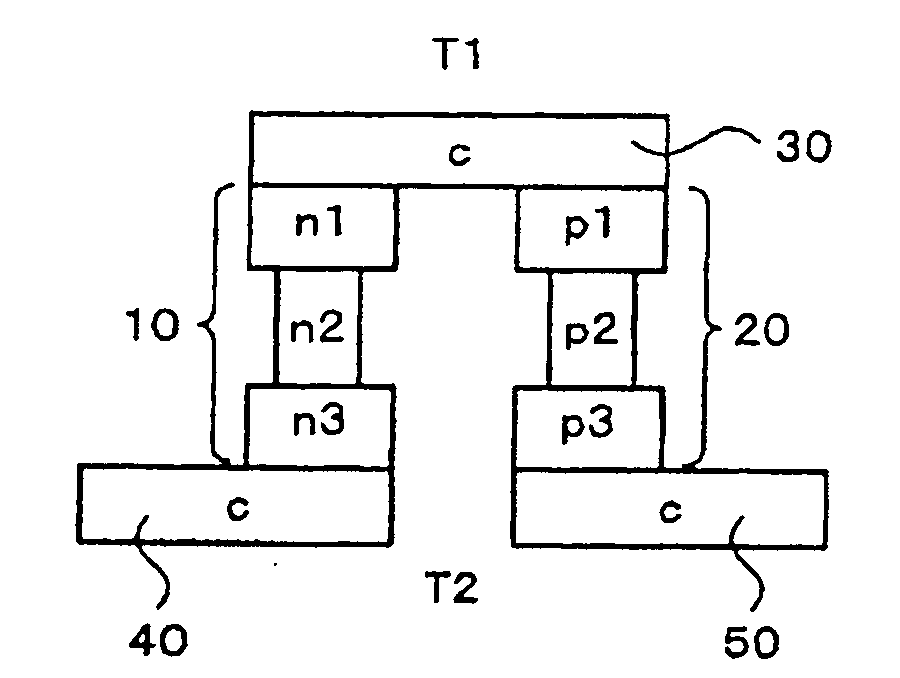
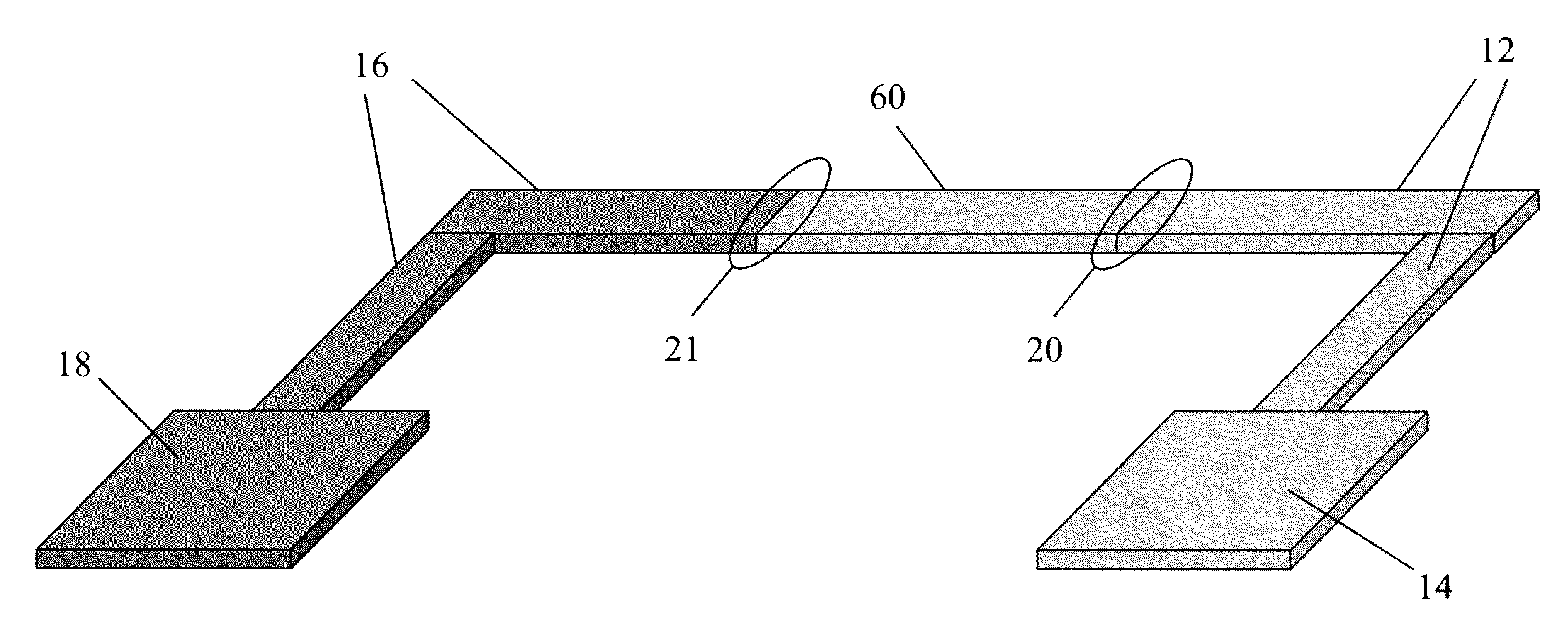
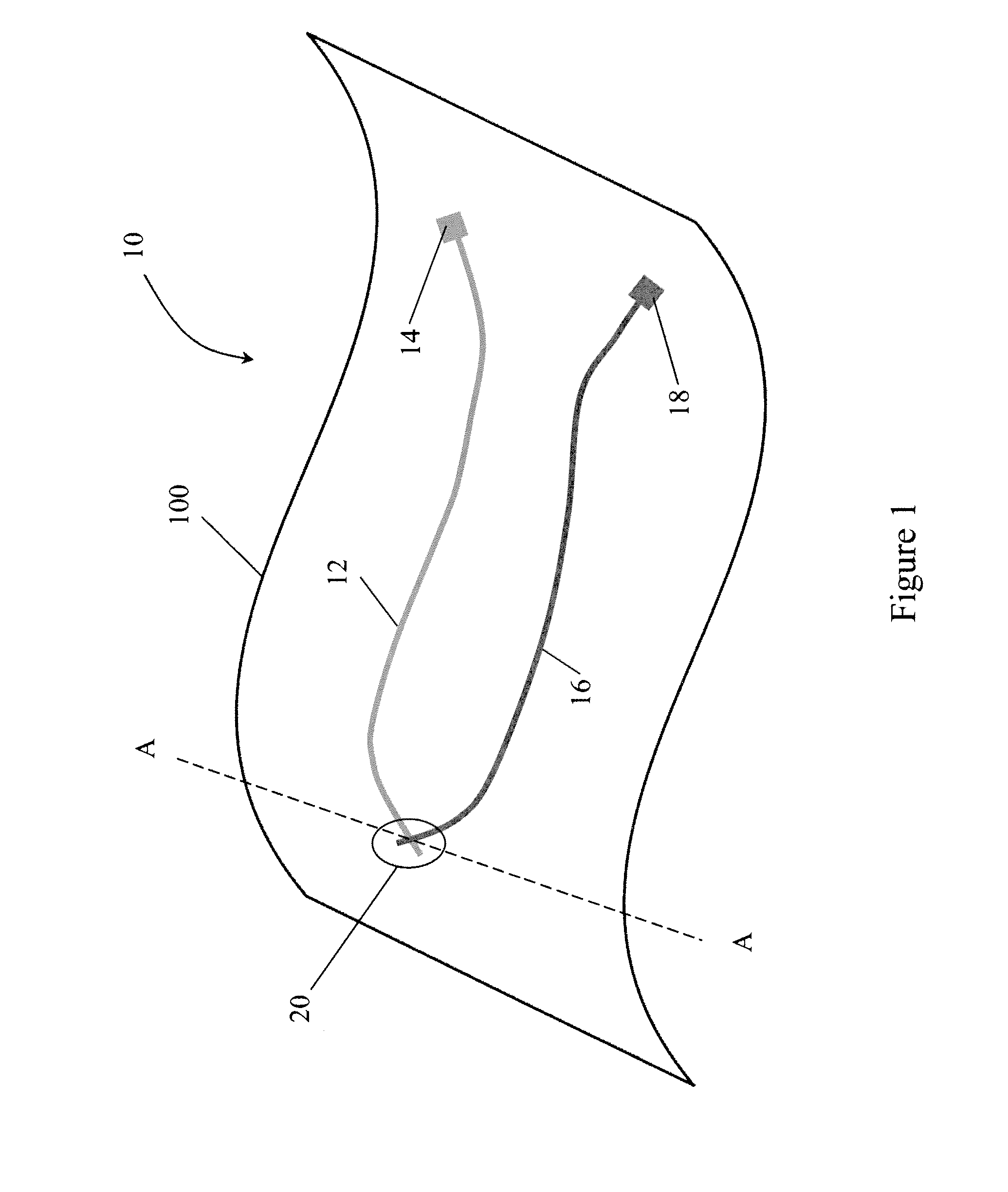
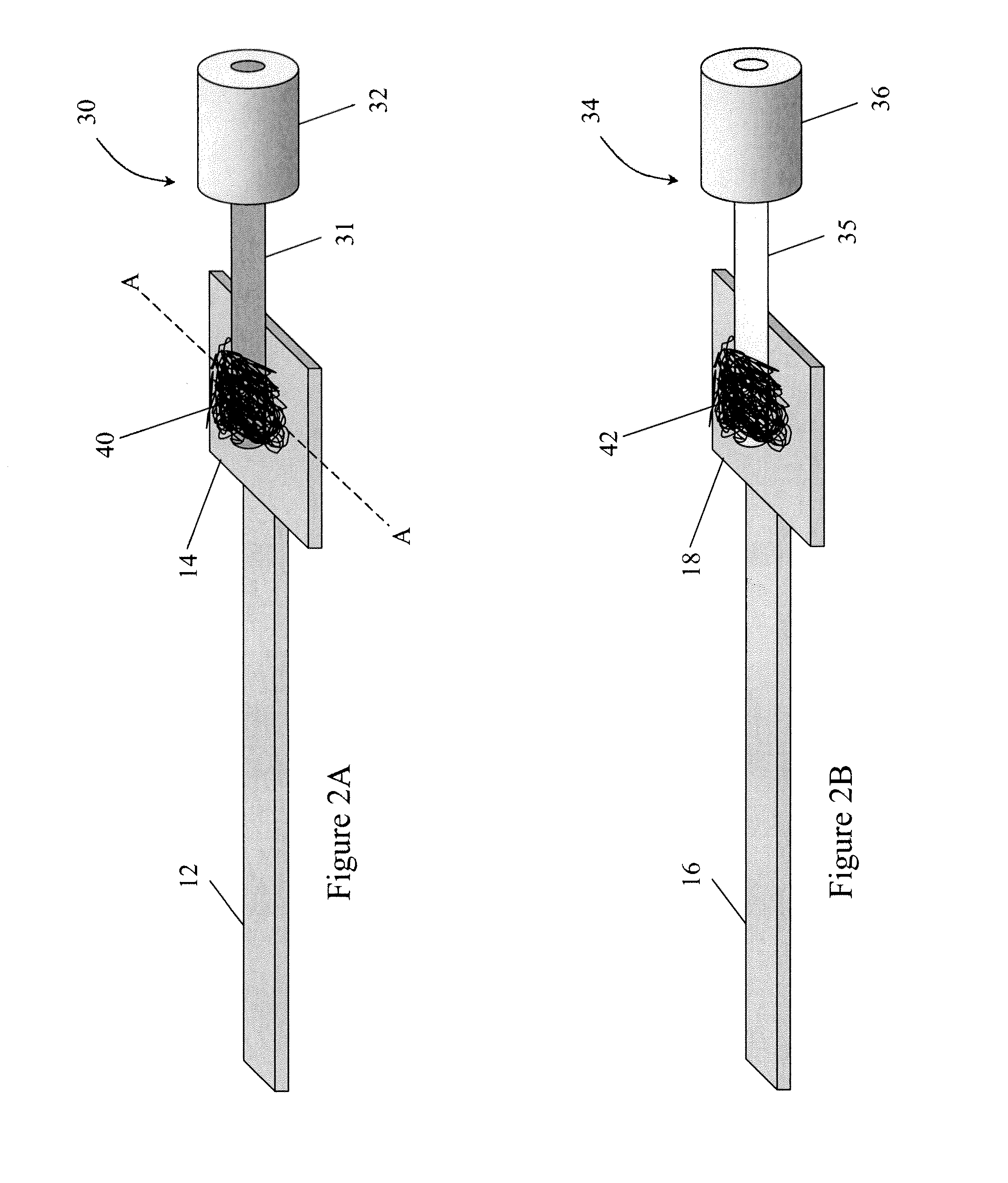
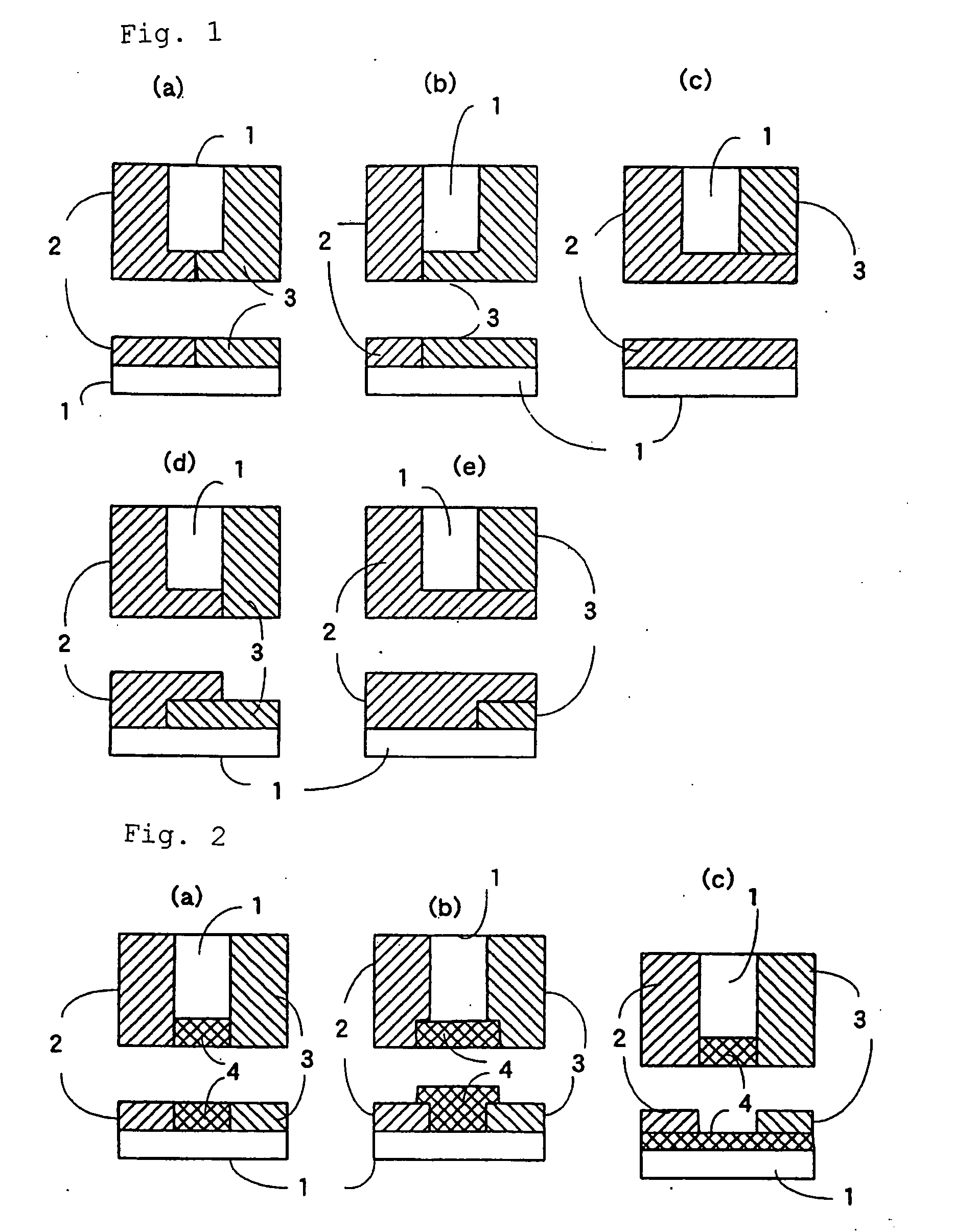
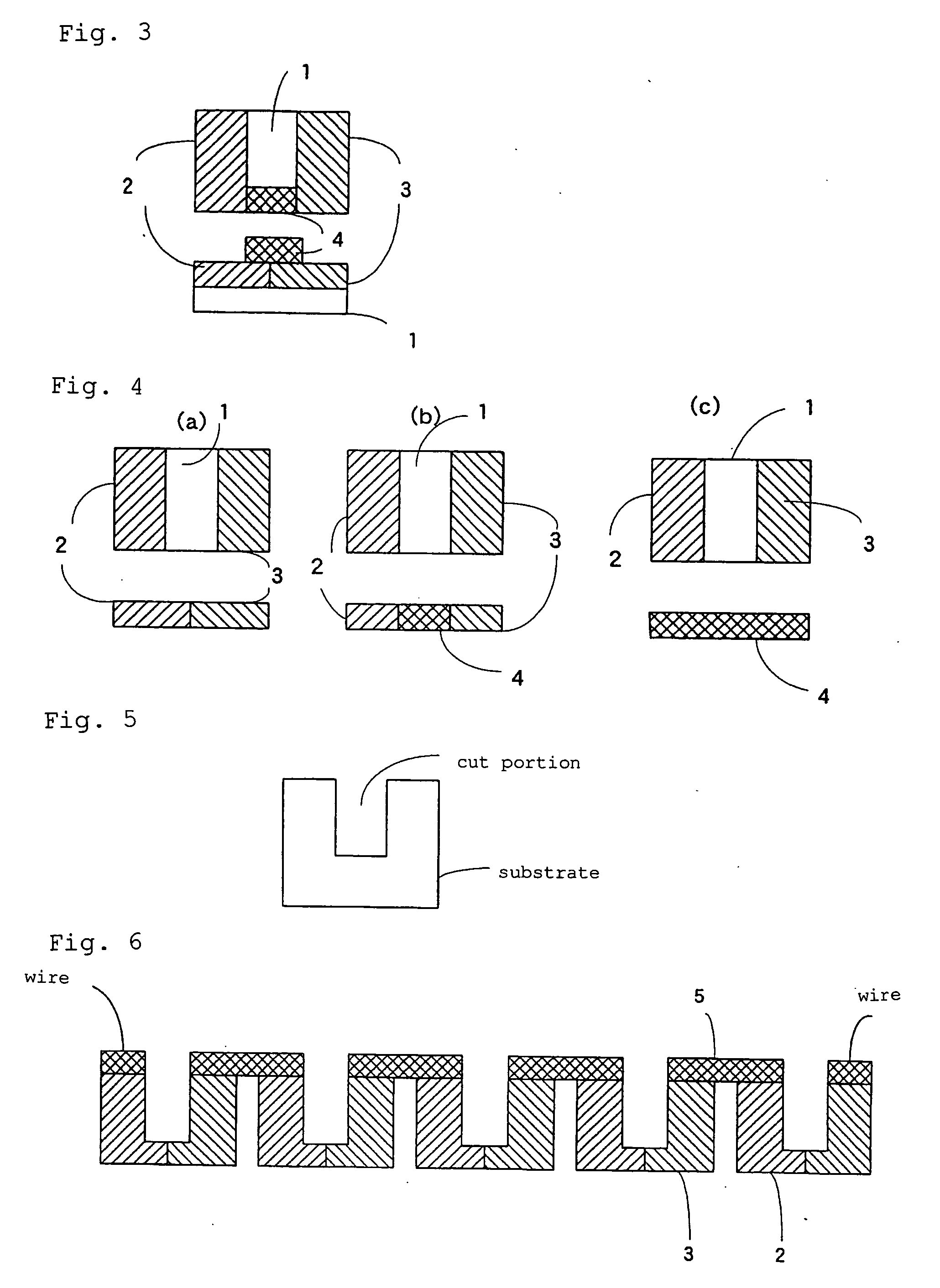
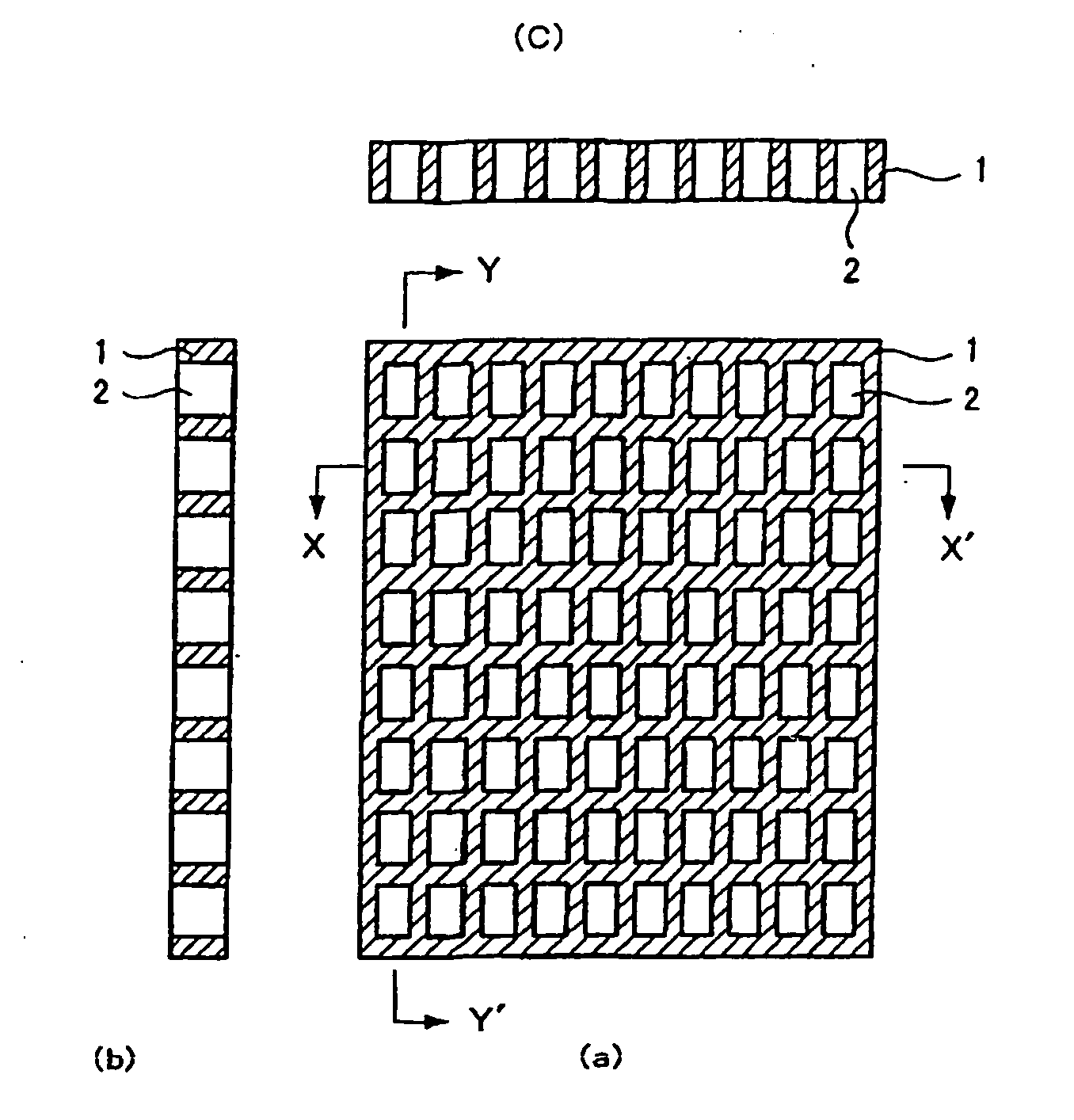
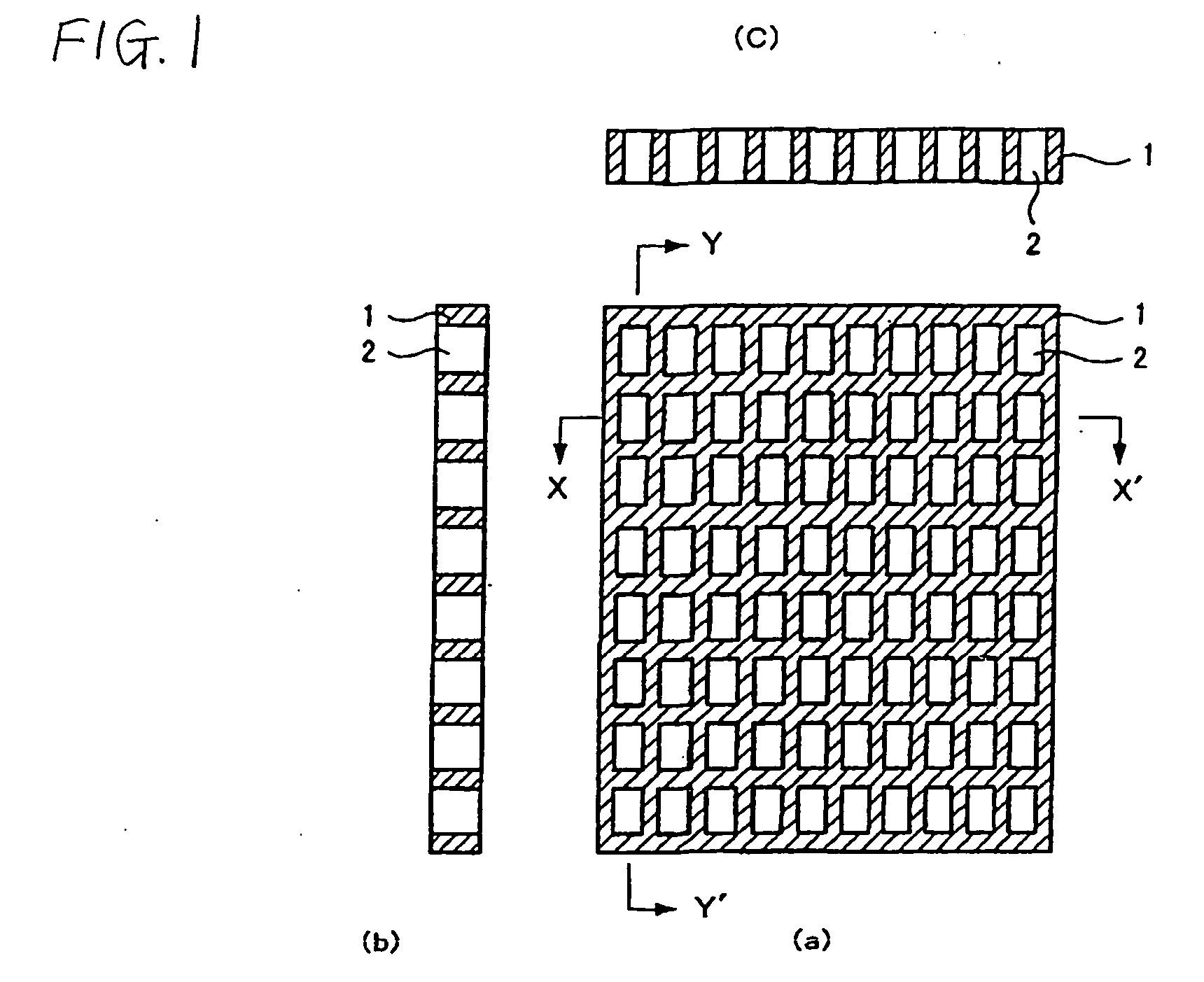
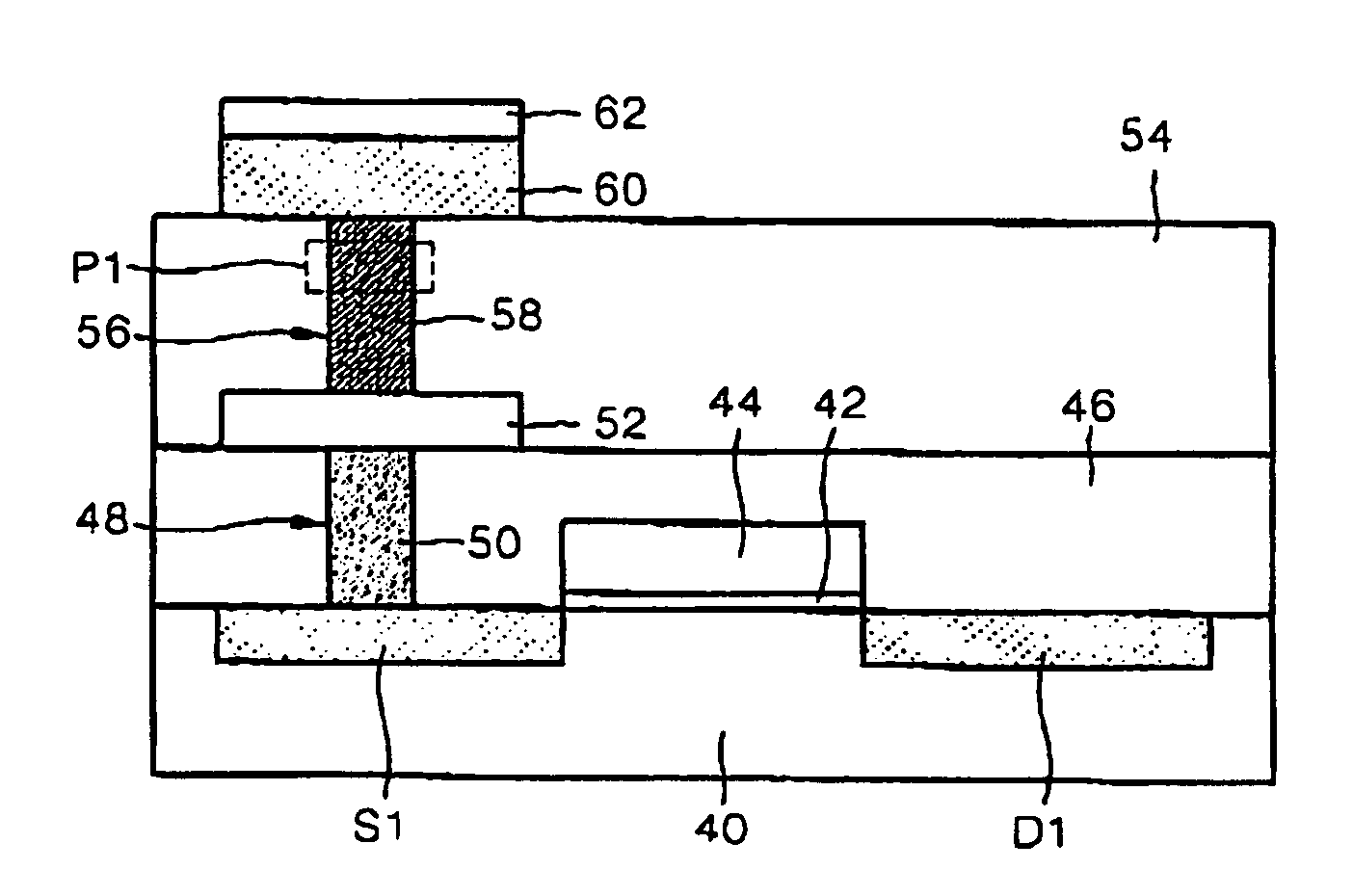
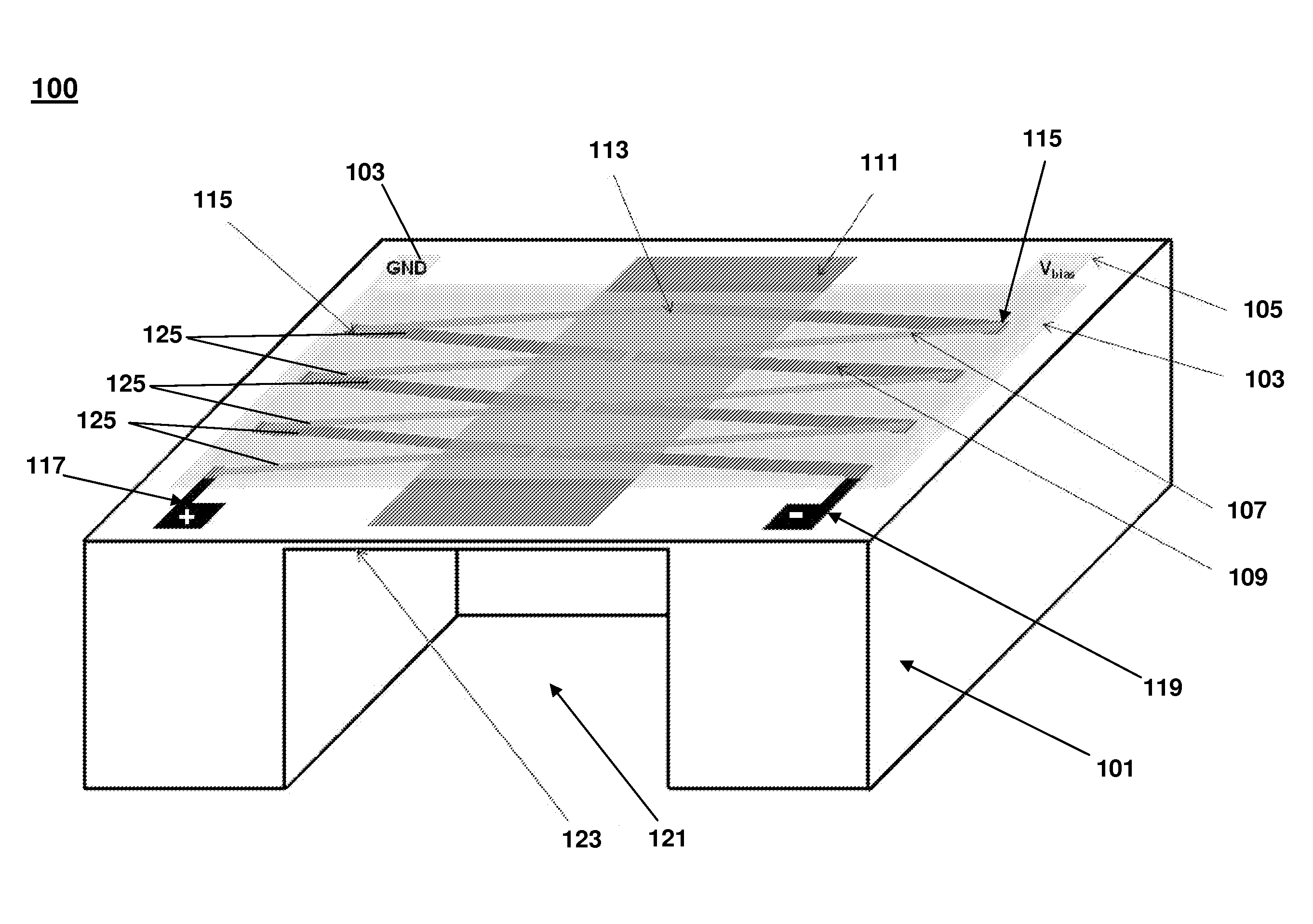
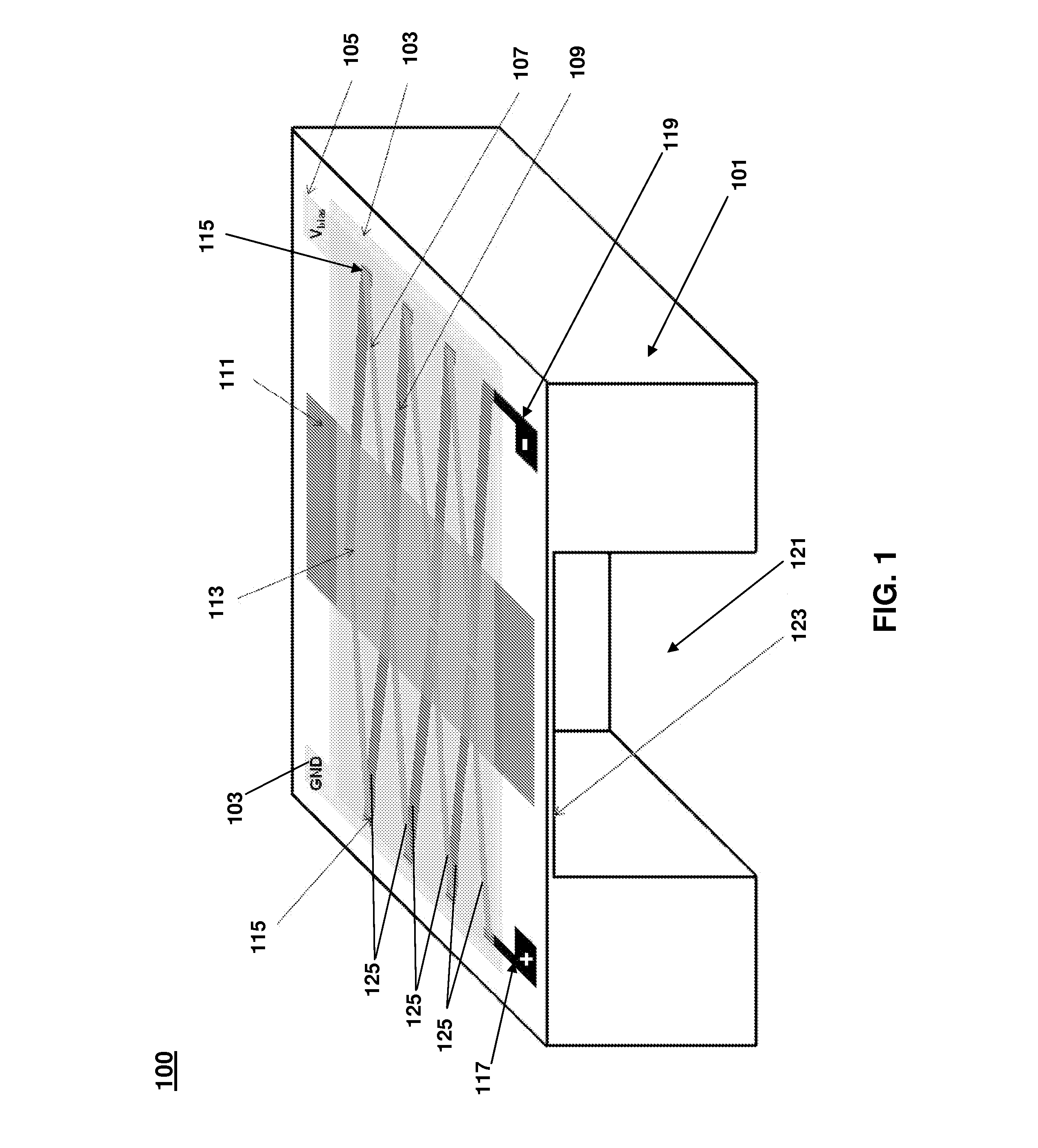
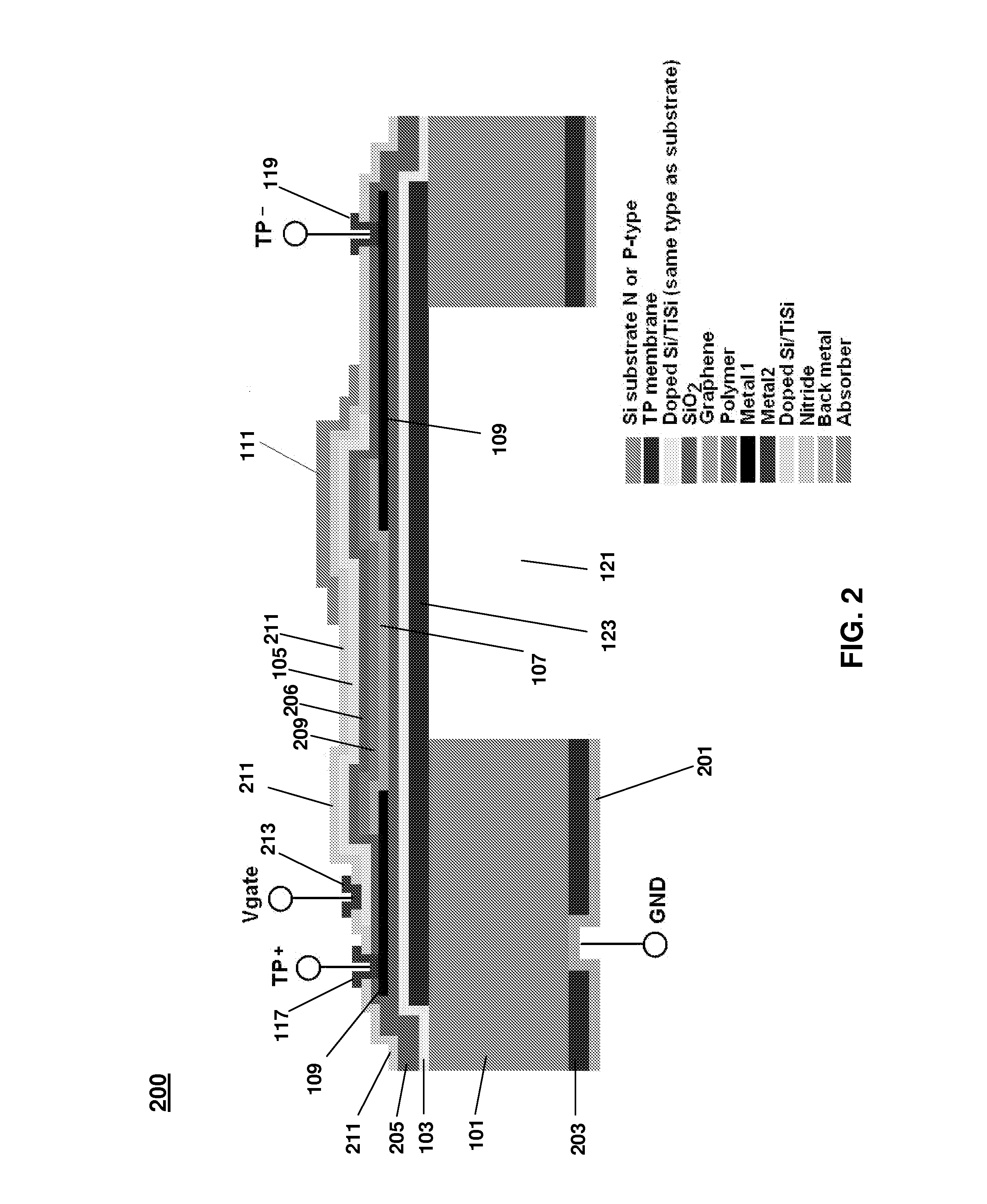
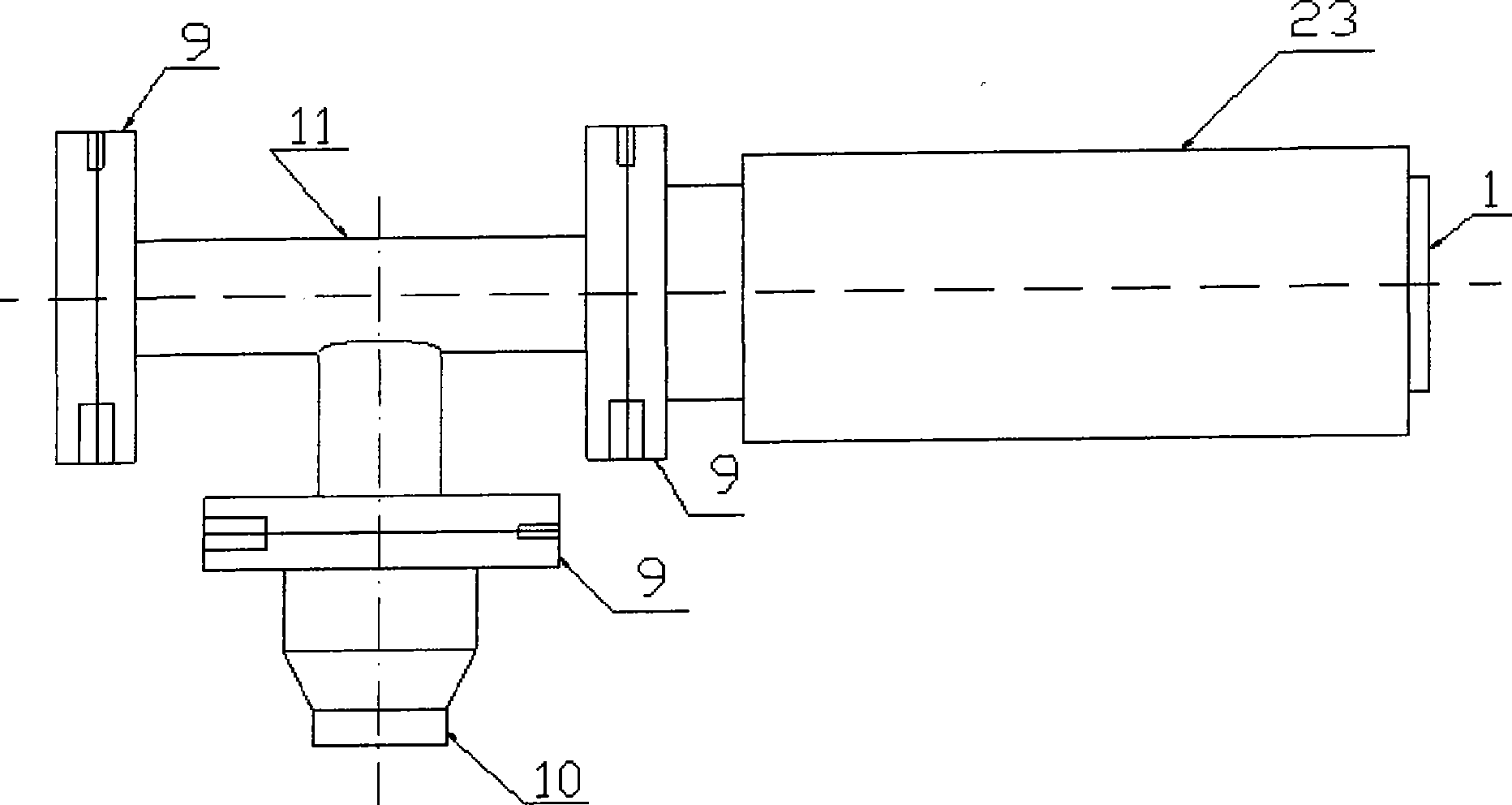
Structure of Peltier Element or Seebeck Element and Its Manufacturing Method
InactiveUS20090007952A1Heat movement weakenedImprove efficiencyThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAmorphous siliconTemperature difference
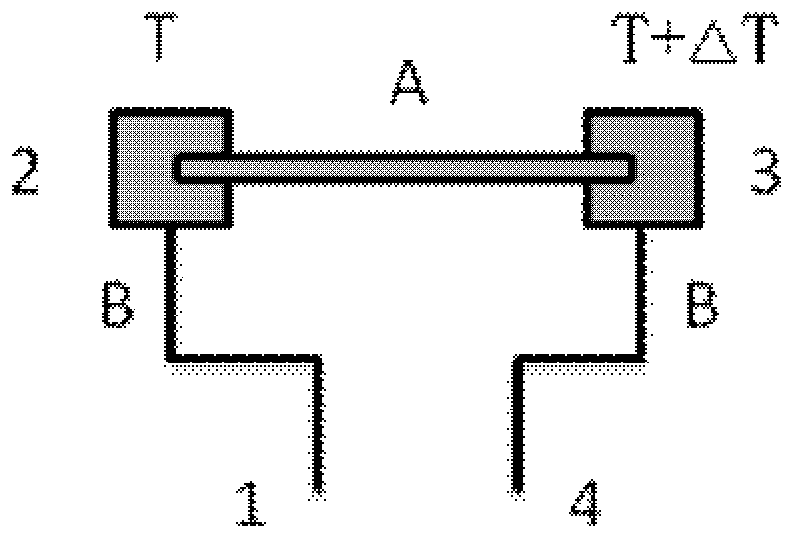
A Peltier or Seebeck element has first and second conductive members having different Seebeck coefficients. To decrease the heat conduction from one to the other end of each of the conductive members, the cross-section area at the intermediate part in the length direction is smaller than those at both ends parts. In place of the decrease of the cross-section, the shape of the cross-section of the intermediate part of each of the conductive members may be changed by dividing the intermediate part into pieces, or amorphous silicon or the like having a heat conductivity lower than those of the materials of both end parts may be used for the material of the intermediate part. In such a way, a high-performance Peltier / Seebeck element such that the difference between the temperature of the heated portion of the Peltier / Seebeck element and the opposite portion can be kept to a predetermined temperature difference for a long time and its manufacturing method are provided.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD +2
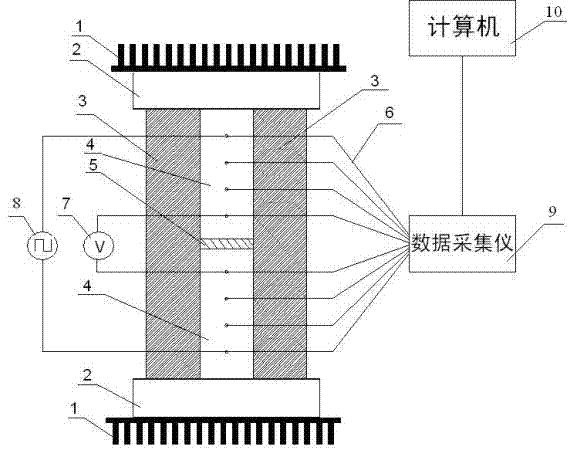
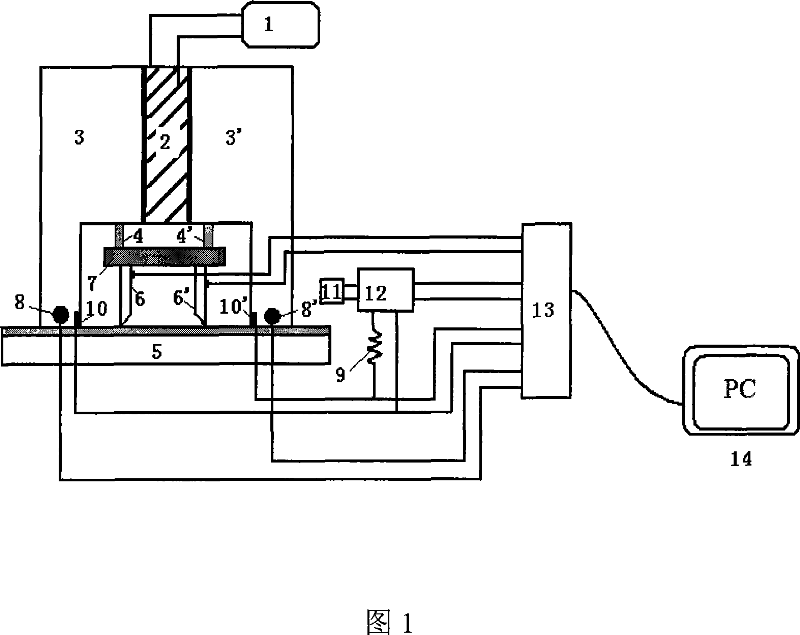
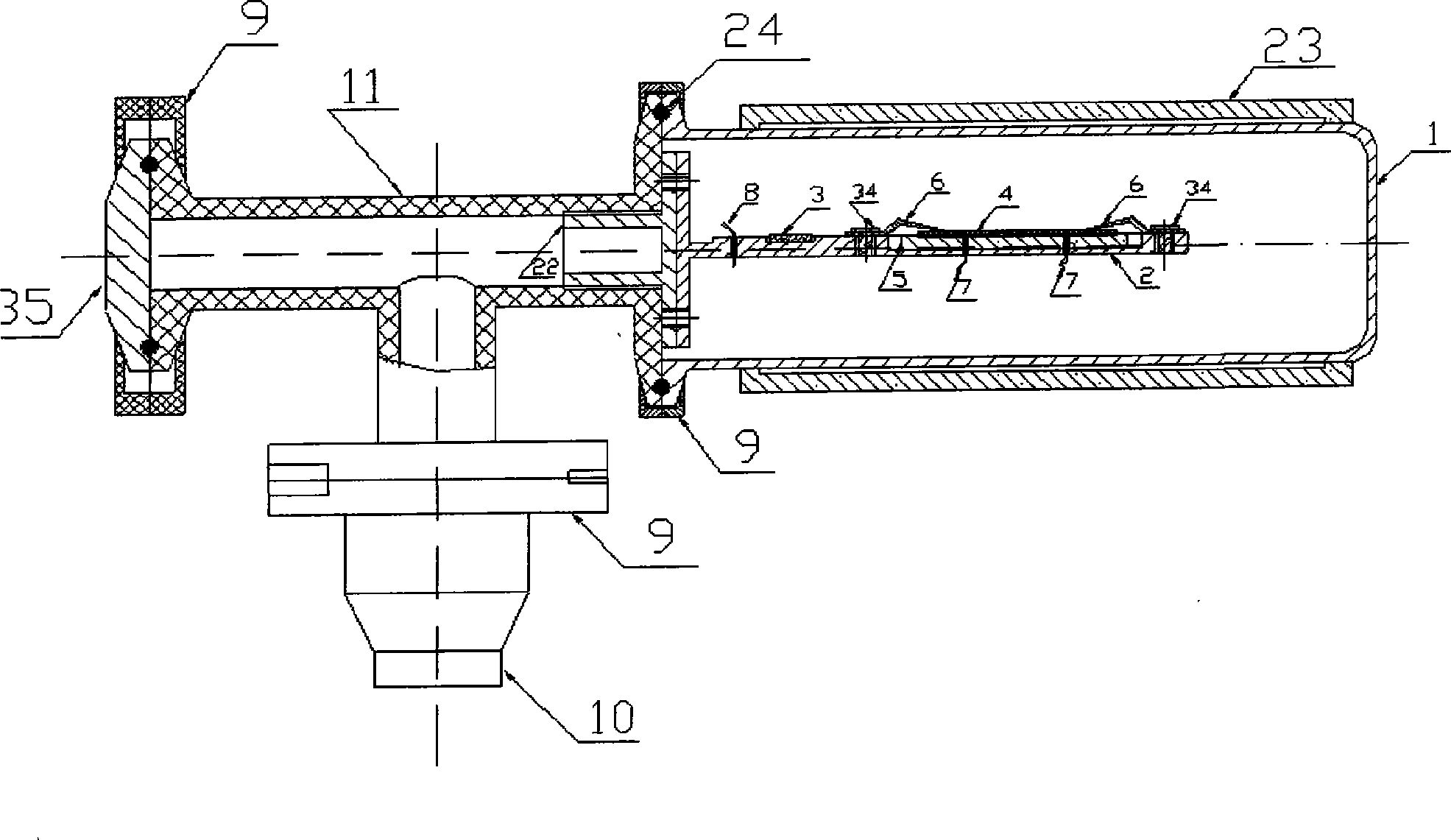
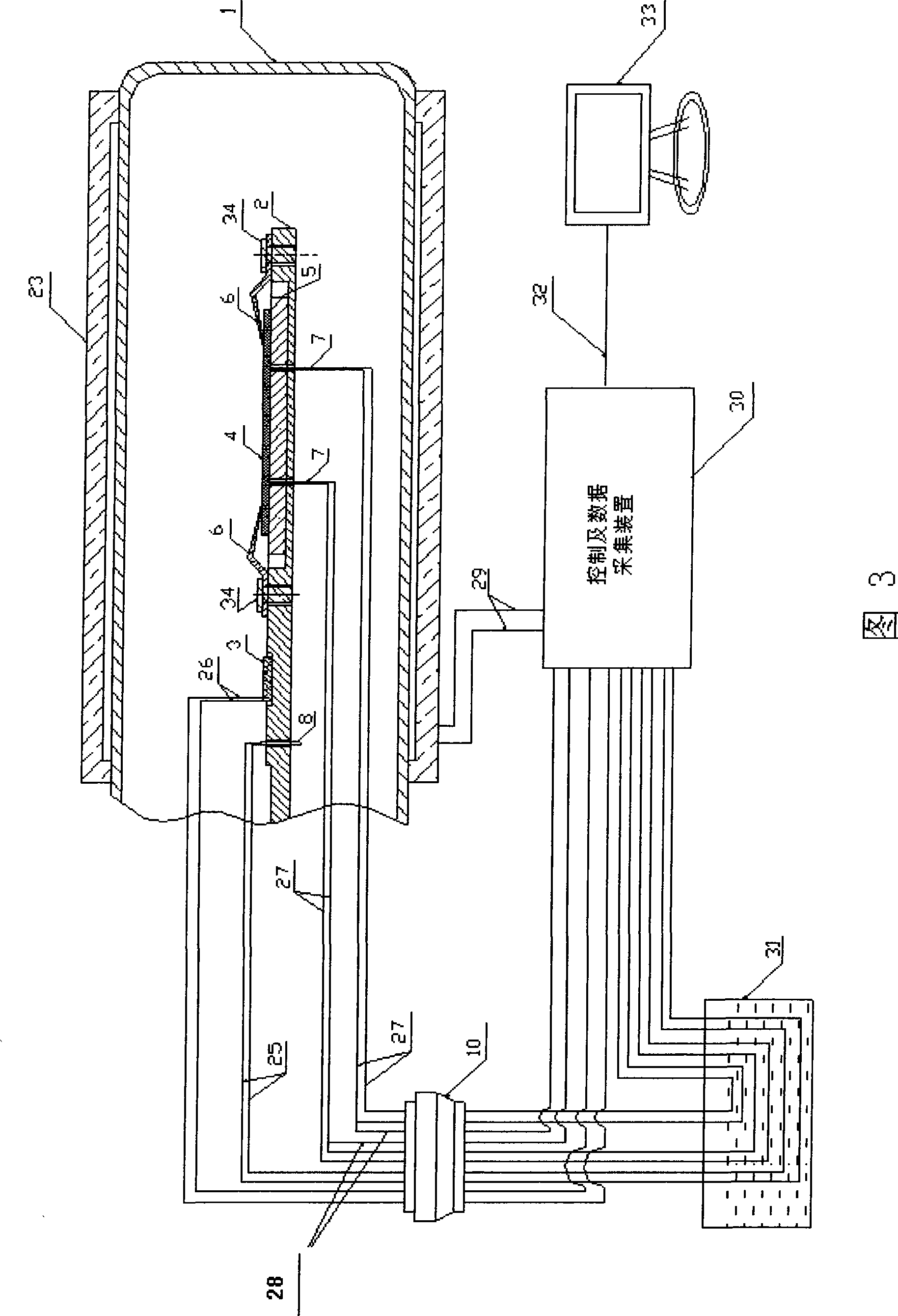
A kind of measuring device and method of thin film thermoelectric performance parameters
InactiveCN102297877AHigh temperature control accuracySave resourcesResistance/reactance/impedenceMaterial heat developmentThermoelectric materialsMeasurement device
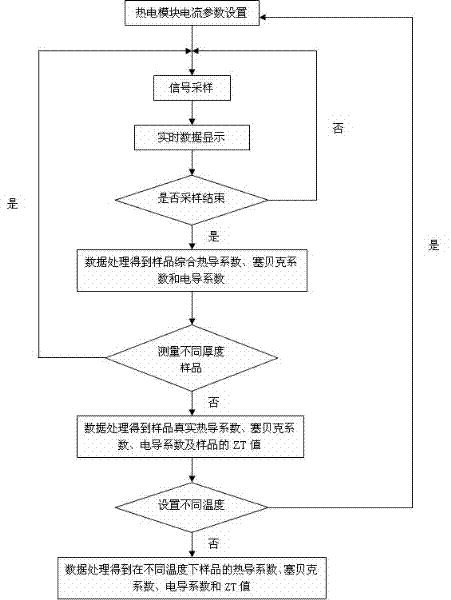
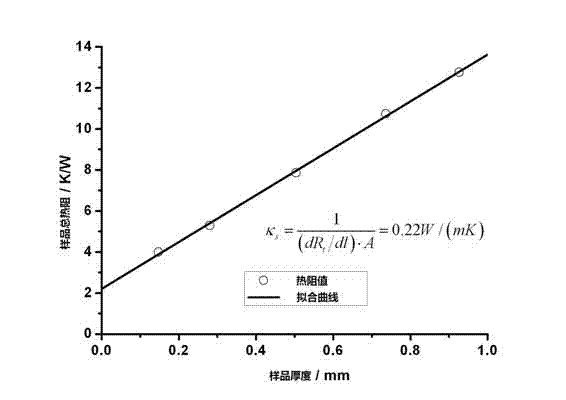
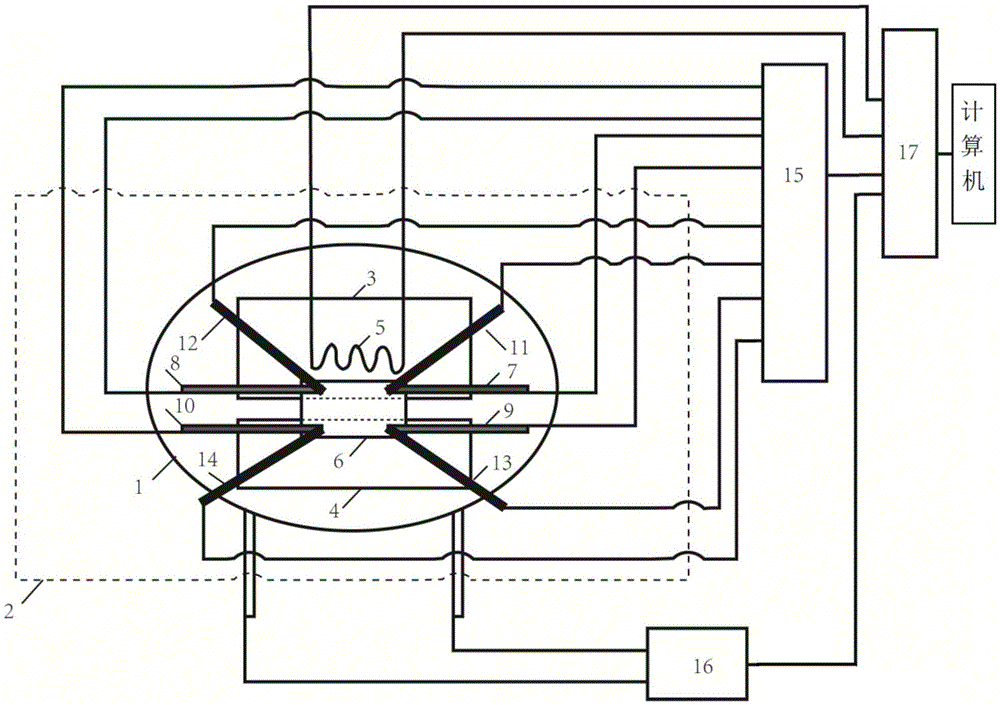
The invention provides a device and a method for measuring thermoelectric parameters of a film. The measuring device, which has a symmetric structure, comprises a radiating fin, a thermoelectric module, a heat insulation material, metal round rods, a thermocouple wire, a voltmeter, a power supply, a data acquisition instrument and a computer. The measuring method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: clamping a film to be measured between two upper and lower metal round rods which are completely same while the area of the film sample is the same as the cross-sectional area of the metal round rods, controlling the ambient temperature of the measuring device and the heat flow of the film sample by the use of the thermoelectric module, detecting and recording each performance parameter of the film thermoelectric material at real time by the use of the data acquisition instrument. The invention has the following advantages: the performance of the film thermoelectric material at different temperatures can be measured, that is to say, the same device can be utilized to simultaneously measure the thermal conductivity coefficient, Seebeck coefficient and conductance coefficient of the film thermoelectric material so as to calculate ZT values of the film thermoelectric material at different temperatures. According to the invention, the measuring device has a simple principle, is convenient to operate, is small in size, has many test functions and has high measuring precision.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Thermoelectric conversion material and method of producing the same
InactiveUS7002071B1Low thermal conductivitySacrificing high Seebeck coefficient and electrical conductivityThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric conversionGrain boundary
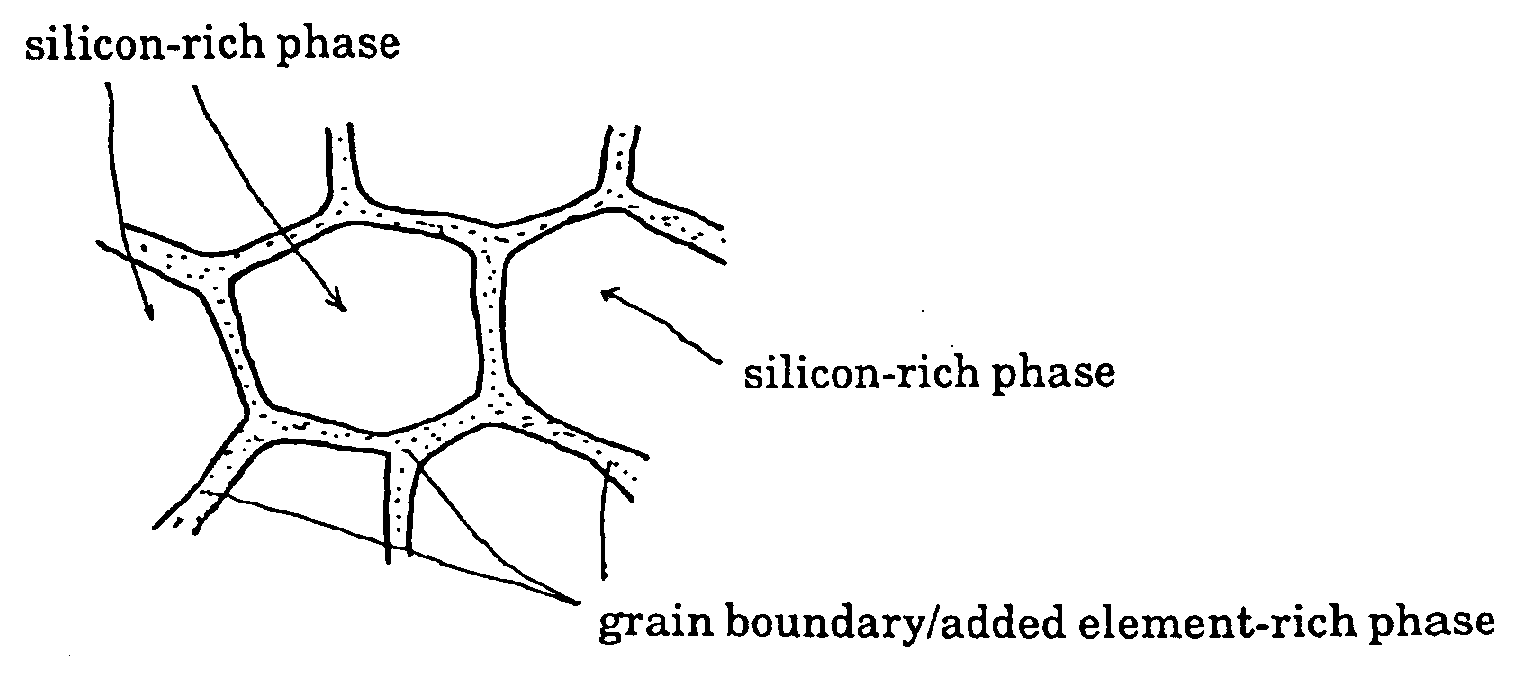
A thermoelectric conversion material is formed of a polycrystal structure of crystal grains composed of a silicon-rich phase, and an added element-rich phase in which at least one type of added element is deposited at the grain boundary thereof, the result of which is an extremely large Seebeck coefficient and low thermal conductivity, allowing the thermoelectric conversion rate to be raised dramatically, and affording a silicon-based thermoelectric conversion material composed chiefly of silicon, which is an abundant resource, and which causes extremely low environmental pollution.
Owner:SUMITOMO SPECIAL METAL CO LTD
Thermoelectric semiconductor compound and method of making the same
InactiveUS6225548B1Thermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsMean free pathSingle crystal
A thermoelectric semiconductor compound is provided whose performance index Z is remarkably improved without sacrificing Seebeck coefficient, electrical conductivity or thermal conductivity. The thermoelectric semiconductor compound includes a first thermoelectric semiconductor which is in the form of matrix and a second thermoelectric semiconductor which is in the form of particles dispersed in the matrix. The first thermoelectric semiconductor and the second thermoelectric semiconductor have a common element. The average diameter D of the dispersed particles complies with a formula of A<D<B, where A is the mean free path of a carrier in a single crystal of the second thermoelectric semiconductor and B is the mean free path of a long wave length phonon in the single crystal of the second thermoelectric semiconductor. A method for making the a thermoelectric semiconductor compound is provided.
Owner:AISIN SEIKI KK
Thermocouple device
ActiveUS20110277803A1Shorten the counting processDensely packedThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentPlanar substrateEngineering
In one aspect, the present invention relates to a thermocouple device comprising a flexible non-planar substrate, a first printed thermocouple element comprising a first metal containing ink composition applied to the flexible non-planar substrate, and a second printed thermocouple element in electrical contact with the first printed thermocouple element making a thermocouple junction. The second printed thermocouple element comprises a second metal containing ink composition with a Seebeck coefficient sufficiently different from the first metal containing ink composition for the first and second printed thermocouple elements to together produce a thermocouple effect. The present application further relates to medical devices comprising the thermocouple and methods of making such devices.
Owner:MICROPEN TECH CORP
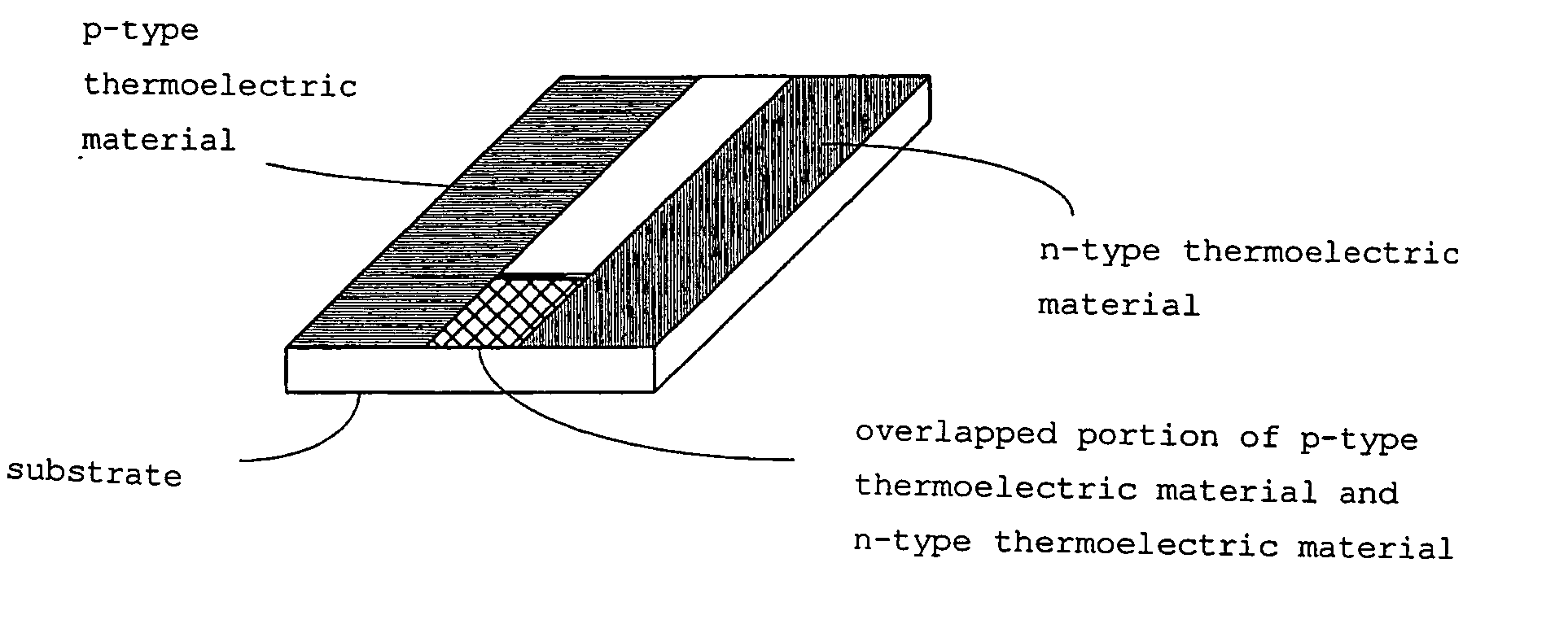
Thermoelectric conversion element and thermoelectric conversion module
InactiveUS20070144573A1Improve thermoelectric conversion efficiencyImprove conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentElectricityThermoelectric materials
The present invention provides a thermoelectric element in which a thin film of p-type thermoelectric material and a thin film of n-type thermoelectric material, which are formed on an electrically insulating substrate, are electrically connected, in which the p-type thermoelectric material and the n-type thermoelectric material are selected from specific complex oxides with a positive Seebeck coefficient and specific complex oxides with a negative Seebeck coefficient, respectively. The present invention also provides a thermoelectric module using the thermoelectric element(s) and a thermoelectric conversion method. In the thermoelectric element of the present invention, since a p-type thermoelectric material and an n-type thermoelectric material are formed into a thin film on an electrically insulating substrate, the thermoelectric element of the invention can be formed on substrates having various shapes, thereby providing thermoelectric elements having various shapes.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
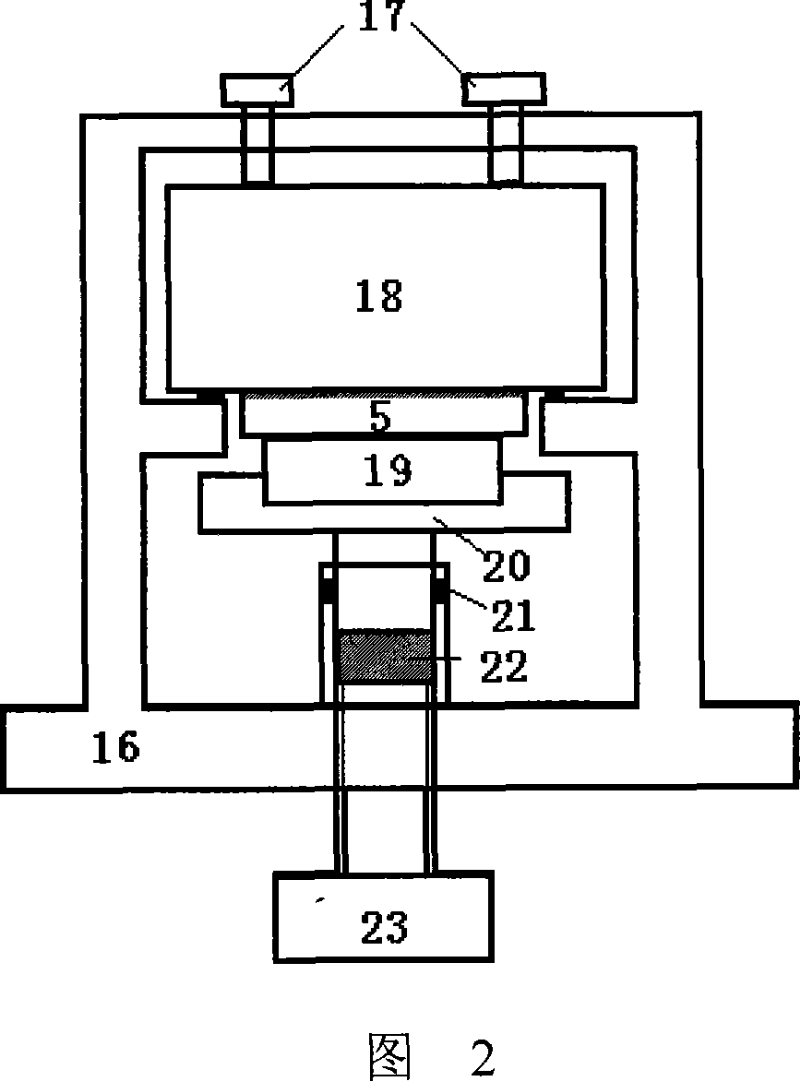
Pyroelectric material measuring apparatus
InactiveCN101285788AAvoid the hassle of disassembly and reassemblyLow costMaterial resistanceTemperature controlThermoelectric materials
The invention relates to a thermoelectric material measurement instrument, comprising a sample stage and a testing device thereof. The sample stage comprises a base as well as a first sample clip and a second sample clip which are arranged on the base, wherein, the inside of the first sample clip and the inside of the second sample clip are both provided with heating elements and refrigerating elements; one end of the first sample clip and one end of the second sample clip near samples are both provided with temperature sensors and voltage probes; and the testing device comprises a temperature controller connected with the heating elements and the refrigerating elements, a data collector connected with the heating elements and the refrigerating elements, and a central controller connected with the temperature controller and the data collector. The instrument can measure the Seebeck coefficient of thermoelectric materials in any direction and need not confirm the polarity of the sample to be tested, which ensures that the test is simpler, more convenient and quicker.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
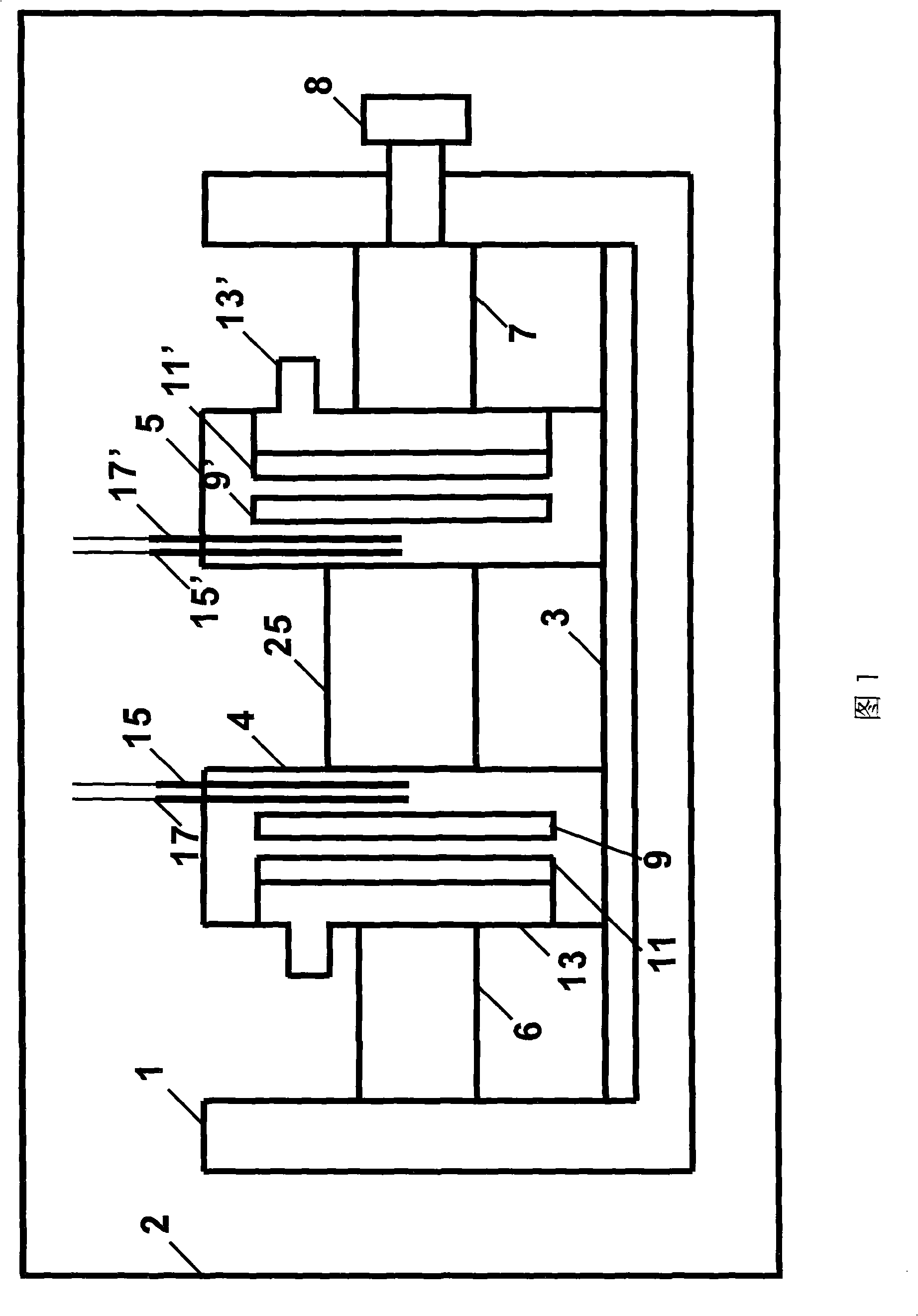
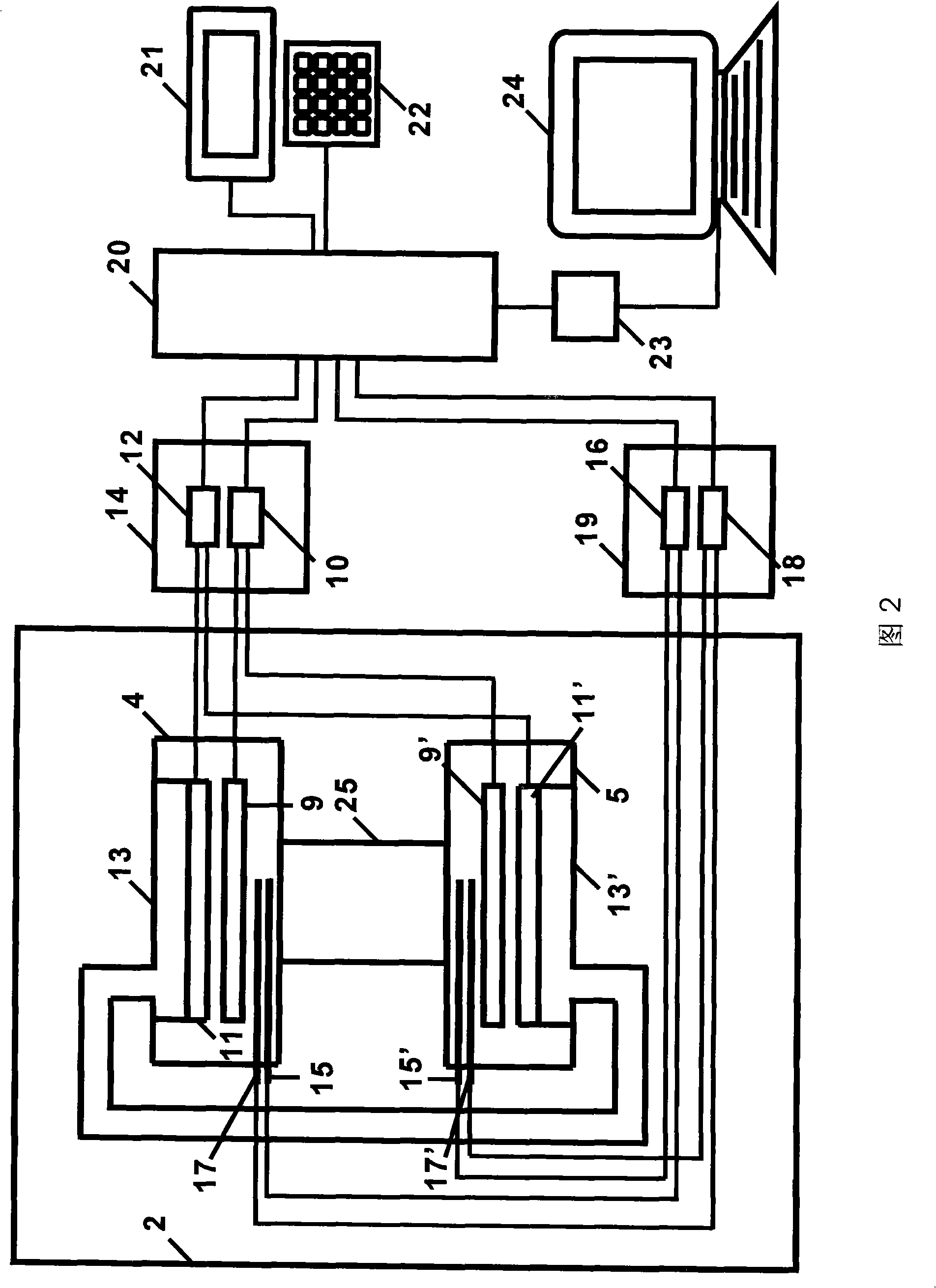
Integrated Parallel Peltier/Seebeck Element Chip and Production Method Therefor, Connection Method
ActiveUS20070256722A1Rapid temperature measurementImprove thermal conductivityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentElectricityThermal energy
First and second conductive members having different Seebeck coefficients are formed on an insulating substrate. The first and second conductive members are connected by ohmic contact, and the surfaces connected by ohmic contact are covered with a material sheet having a superior heat conductivity and an electric insulating property in the junction surface, such as an aluminum sheet formed with surfaces provided with electric insulating property by alumite treatment or the like. On the opposite side, bonding wires are connected with the first and second conductive members by ohmic contact. The bonding wires are insulated from one another, and used as output terminals of an integrated parallel Peltier Seebeck element chip. The thus produced integrated parallel Peltier Seebeck element chips are connected by one or more serial or parallel cables, to form energy conversion apparatus from electricity to heat and thermal energy transfer apparatus.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD +1
Method and system for measuring quasi one-dimensional nano-material Seebeck coefficient
InactiveCN101354388AGet real attributesGood repeatabilityMaterial thermal analysisPotential differenceMicrometer scale
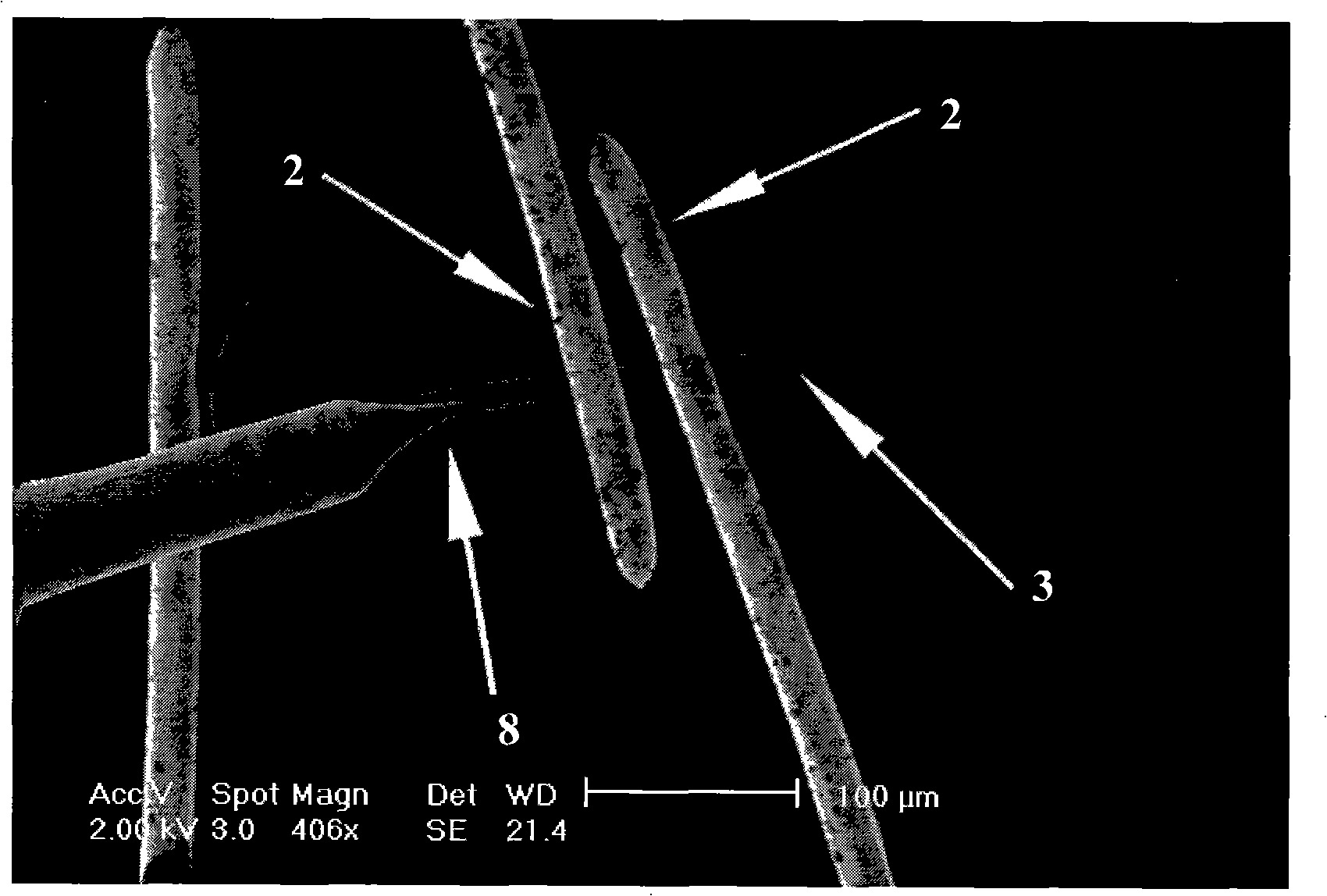
The invention discloses a method and a system that are used for measuring the Seebeck coefficient of a quasi-one-dimensional nano material; two line transition electrodes with micrometer-scaled cross sections are respectively contacted with two centimeter-scaled block metal electrodes, a nano probe system is utilized for leading a single rod of the quasi-one-dimensional nano material to be detected to be connected with the two transition electrodes, temperature difference between the two block metal electrodes is altered, and the temperature difference and corresponding potential difference between the two electrodes are simultaneously measured, thus obtaining the Seebeck coefficient of the quasi-one-dimensional nano material. The corresponding testing system comprises three parts of an experimental platform, a temperature altering device and a data collecting and processing device. The method and the system solve the problem of the contact transition between the centimeter-scaled electrodes and the nano sample to be detected through the micrometer-scaled transition electrodes, utilize the nano probe system for installing the nano material, and lead the nano material not to be randomly dispersed at two sides of the electrodes, thus improving experimental success rate, controllability and reliability; and the provided measuring system has the advantages of simple structure, low cost and easy popularization and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Method for measuring Seebeck coefficient of micro/nano thermoelectric materials or devices
ActiveCN102305807AHigh measurement accuracyThe experimental setup is simpleMaterial heat developmentElectrical testingThermoelectric materialsTemperature difference
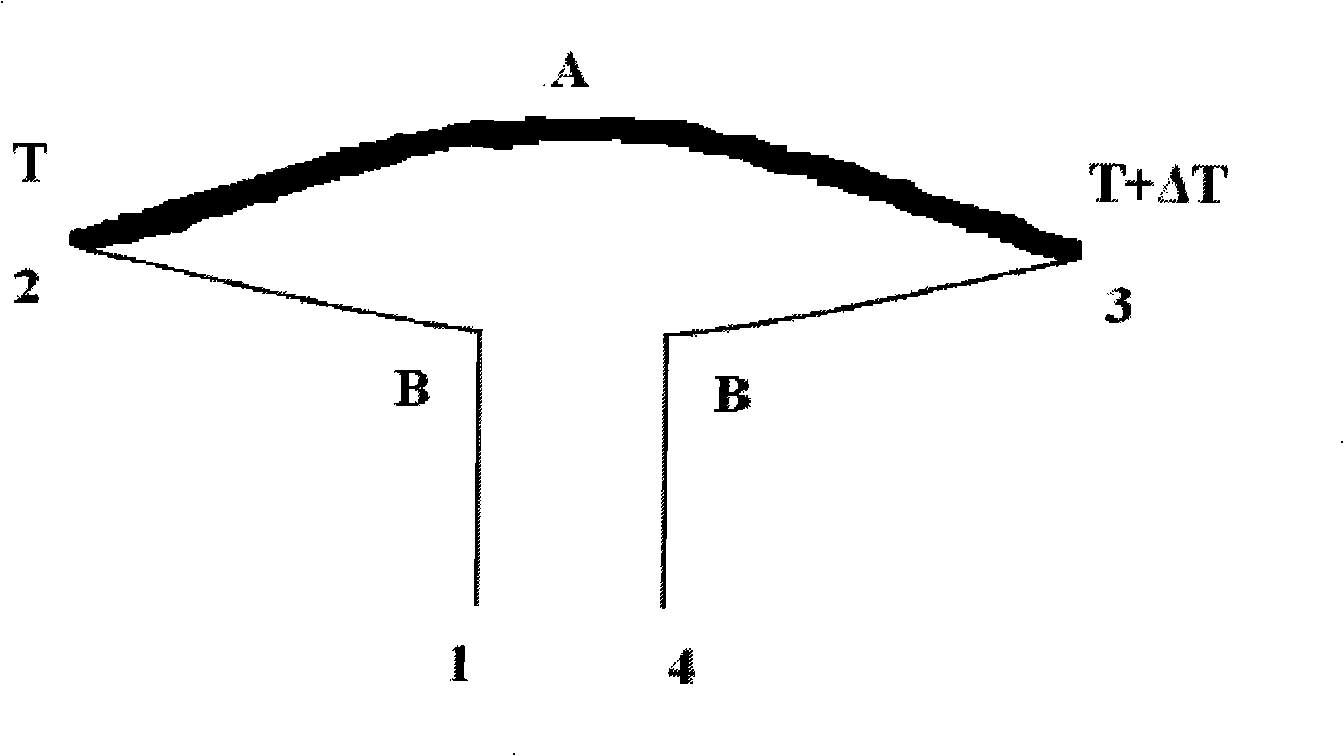
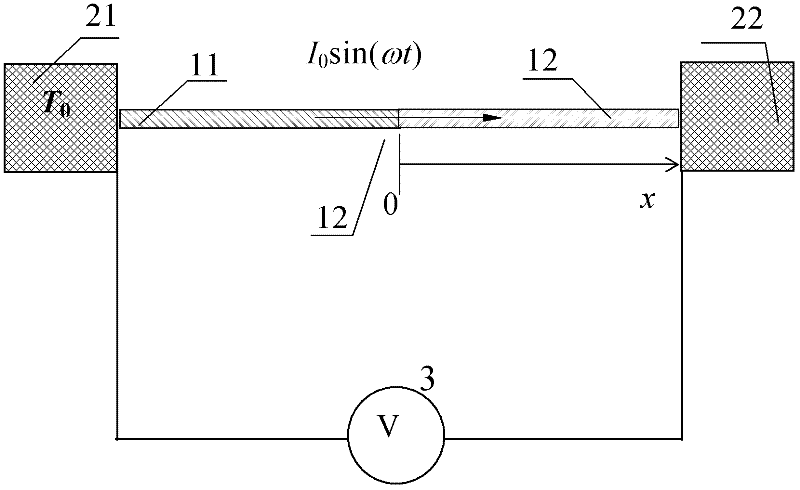
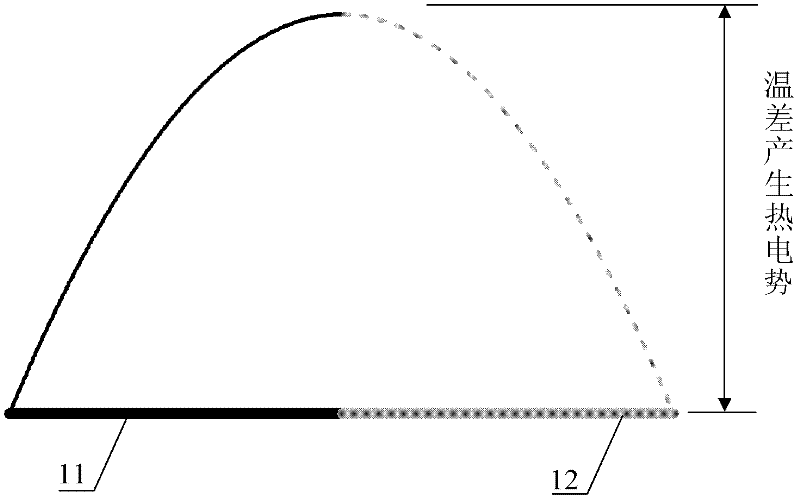
The invention discloses a method for measuring the Seebeck coefficient of micro / nano thermoelectric materials or devices, which comprises the following steps of: connecting the two ends of a sample formed by connecting two thermoelectric materials with heat sinks, putting into a vacuum environment, introducing alternating current I0 sin(omega t) with frequency omega and amplitude I0, generating parabolic temperature distribution on the sample to be measured through a Joule heating effect, and adding one steady component and two harmonic components to obtain the temperature at a junction of the materials to be measured, wherein for the thermoelectric materials, the steady temperature component at the junction and a temperature difference formed at the heat sink ends can generate direct-current Seebeck thermal electromotive force due to a Seebeck effect; and acquiring a direct-current voltage signal and theoretically solving a steady temperature difference simultaneously, so that the Seebeck coefficient of the thermoelectric materials to be measured can be obtained. The method has the advantages of high measuring accuracy, simple experiment device, low test cost and the like, and iseasy to implement, and a new idea is provided for evaluating and representing a micro / nano scale thermoelectric conversion system.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Phase change random access memory devices and methods of operating the same
ActiveUS7705343B2Total current dropHighly integratedSolid-state devicesBulk negative resistance effect devicesRandom access memoryPhase change
Provided are phase change random access memory (PRAM) devices and methods of operating the same. The PRAM device may include a switching device, a lower electrode, a lower electrode contact layer, a phase change layer and / or an upper electrode. The lower electrode may be connected to a switching device. The lower electrode contact layer may be formed on the lower electrode. The phase change layer, which may include a bottom surface that contacts an upper surface of the lower electrode contact layer, may be formed on the lower electrode contact layer. The upper electrode may be formed on the phase change layer. The lower electrode contact layer may be formed of a material layer having an absolute value of a Seebeck coefficient higher than TiAlN. The Seebeck coefficient of the lower electrode contact layer may be negative. The material layer may have lower heat conductivity and / or approximately equivalent electrical resistance as TiAlN.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
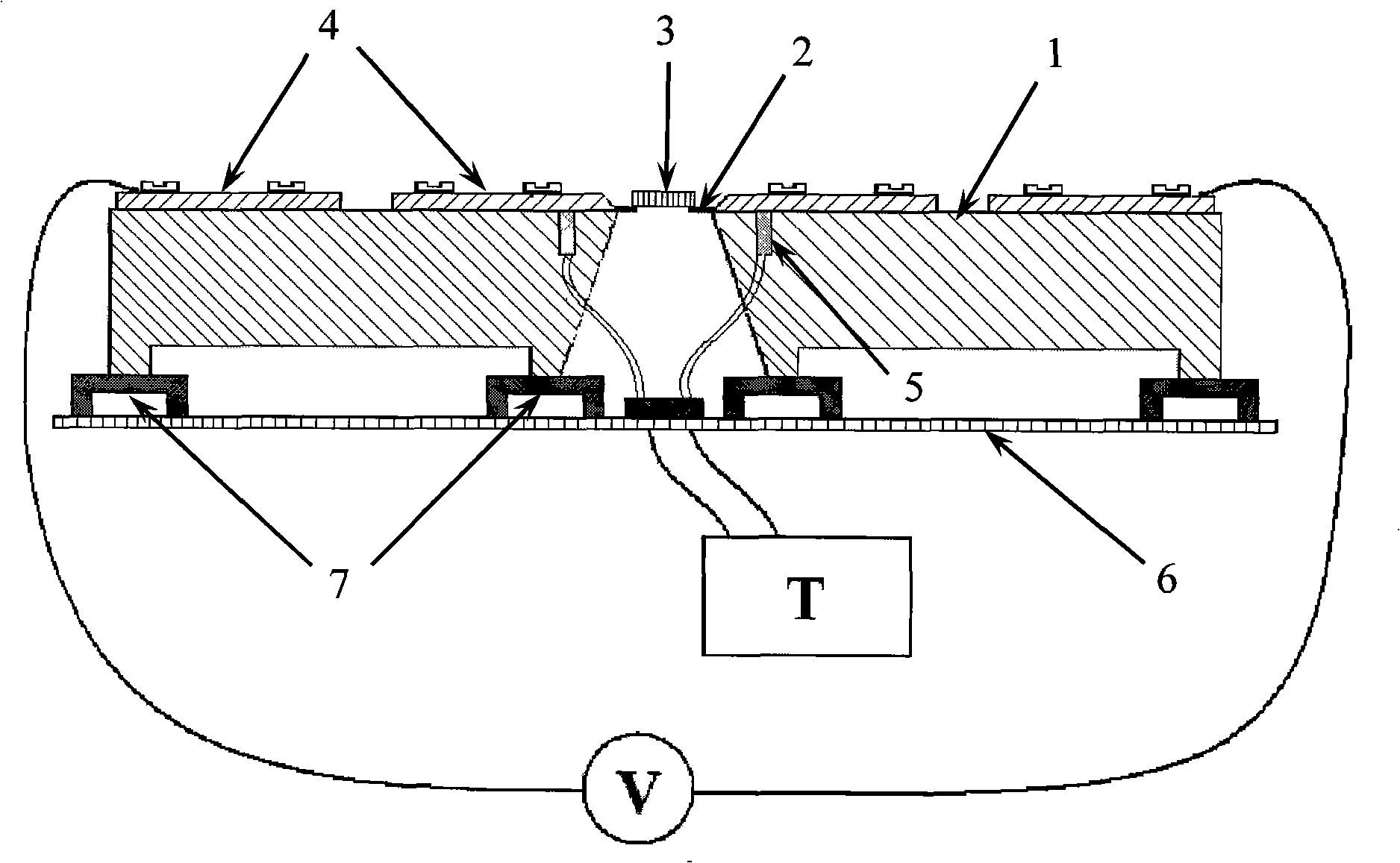
Device for measuring Seebeck coefficient and resistivity of semi-conductor film material
InactiveCN101038265AGuaranteed electrical contactSimple structureMaterial resistanceThermopileEngineering
The present invention discloses a device used for measuring seebeck coefficient and electrical resistivity of semiconductor film materials at room temperature, wherein a thermopile and a heat conduction copper block having cold and heat terminals are integrated into a whole block, a cavum is formed at the lower part of the block, and an electric potential probe is deposited in the cavum. The seebeck electric potential detection points and the cold / heat ends thermocouple are deposited at the lower end of the heat conduction copper block; the electric potential probe, the detection points and the thermocouple are connected respectively to a gathering module; a reference resistor is connected in serial to a conversion switch and is also connected to the detection points; a constant current source is connected to the conversion switch; the conversion switch is connected to a data gathering module; the data gathering module is connected to a computer wherein gathered data is processed through a virtual instrument software to obtain the detection results. A detection platform is divided into two parts, wherein the upper part is used for fixing detection modules, and the lower part is used for supporting samples and has a screw used for lifting samples upwards to achieve a contact of samples and detection points. Said device is capable of perform a measurement of seebeck coefficient and electrical resistivity at the same time without destroying the thin film; furthermore, the measuring course is simple, and both the device lost and the testing cost are lower.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nano-composites for thermal barrier coatings and thermo-electric energy generators
InactiveUS20090290614A1High voltage outputLow thermal conductivityNanotechLiquid surface applicatorsTurbine bladeHigh temperature electronics
A nano-composite material having a high electrical conductivity and a high Seebeck coefficient and low thermal conductivity. The nano-composite material is capable of withstanding high temperatures and harsh conditions. These properties make it suitable for use as both a thermal barrier coating for turbine blades and vanes and a thermoelectric generator to power high temperature electronics, high temperature wireless transmitters, and high temperature sensors. Unique to these applications is that the thermal barrier coatings can act as a temperature sensor and / or a source of power for other sensors or high temperature electronics and wireless transmitters.
Owner:BOARD OF GOVERNORS FOR HIGHER EDUCATION STATE OF RHODE ISLAND & PROVIDENCE PLANTATIONS +1
Thermoelectric conversion element and thermoelectric conversion module
InactiveUS7649139B2Improve efficiencyIncreased durabilityThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentElectricityThermoelectric materials
The present invention provides a thermoelectric element in which a thin film of p-type thermoelectric material and a thin film of n-type thermoelectric material, which are formed on an electrically insulating substrate, are electrically connected, in which the p-type thermoelectric material and the n-type thermoelectric material are selected from specific complex oxides with a positive Seebeck coefficient and specific complex oxides with a negative Seebeck coefficient, respectively. The present invention also provides a thermoelectric module using the thermoelectric element(s) and a thermoelectric conversion method. In the thermoelectric element of the present invention, since a p-type thermoelectric material and an n-type thermoelectric material are formed into a thin film on an electrically insulating substrate, the thermoelectric element of the invention can be formed on substrates having various shapes, thereby providing thermoelectric elements having various shapes.
Owner:NAT INST OF ADVANCED IND SCI & TECH
Preparation method of composite nanomaterial of nano ZnO and graphene nanosheet
InactiveCN103252228AGood chemical stabilitySimple manufacturing methodMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsElectronic band structureChemical stability
The invention discloses a preparation method of a composite nanomaterial of a nano ZnO substrate and a graphene nanosheet. Nano ZnO and the graphene nanosheet are composited to form the composite nanomaterial in a sol-gel method and mechanical alloying combined mode, so that the preparation method is simple and easy to realize and short in reaction time; the finished composite nanomaterial is good in chemical stability; graphene has higher conductivity and can adjust an energy band structure of nano ZnO; nano ZnO has a higher seebeck coefficient, and the nano ZnO substrate and the graphene nanosheet are synthesized, so that interface scattering of phonons can be increased significantly; a recombination rate of an electron-hole pair can be reduced; the appearance of nano ZnO can be adjusted; the heat conductivity of nano ZnO can be reduced; and the photocatalytic efficiency of nano ZnO can be improved. Nitrate of to-be-doped ions comprises any one of aluminum nitrate, ferric nitrate, cobalt nitrate, nickel nitrate, silver nitrate and gold nitrate.
Owner:JIANGSU YUEDA NEW MATERIAL TECH +1
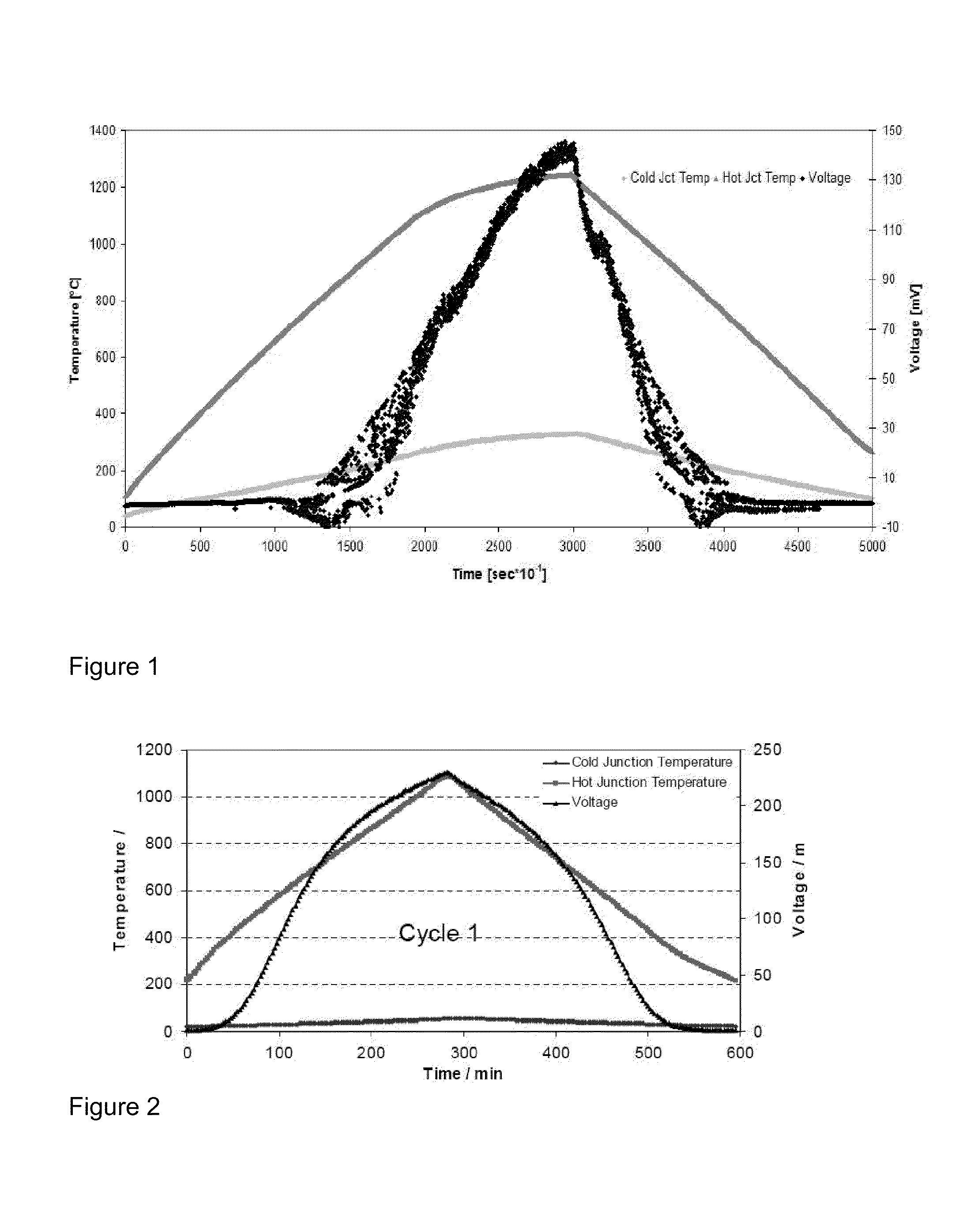
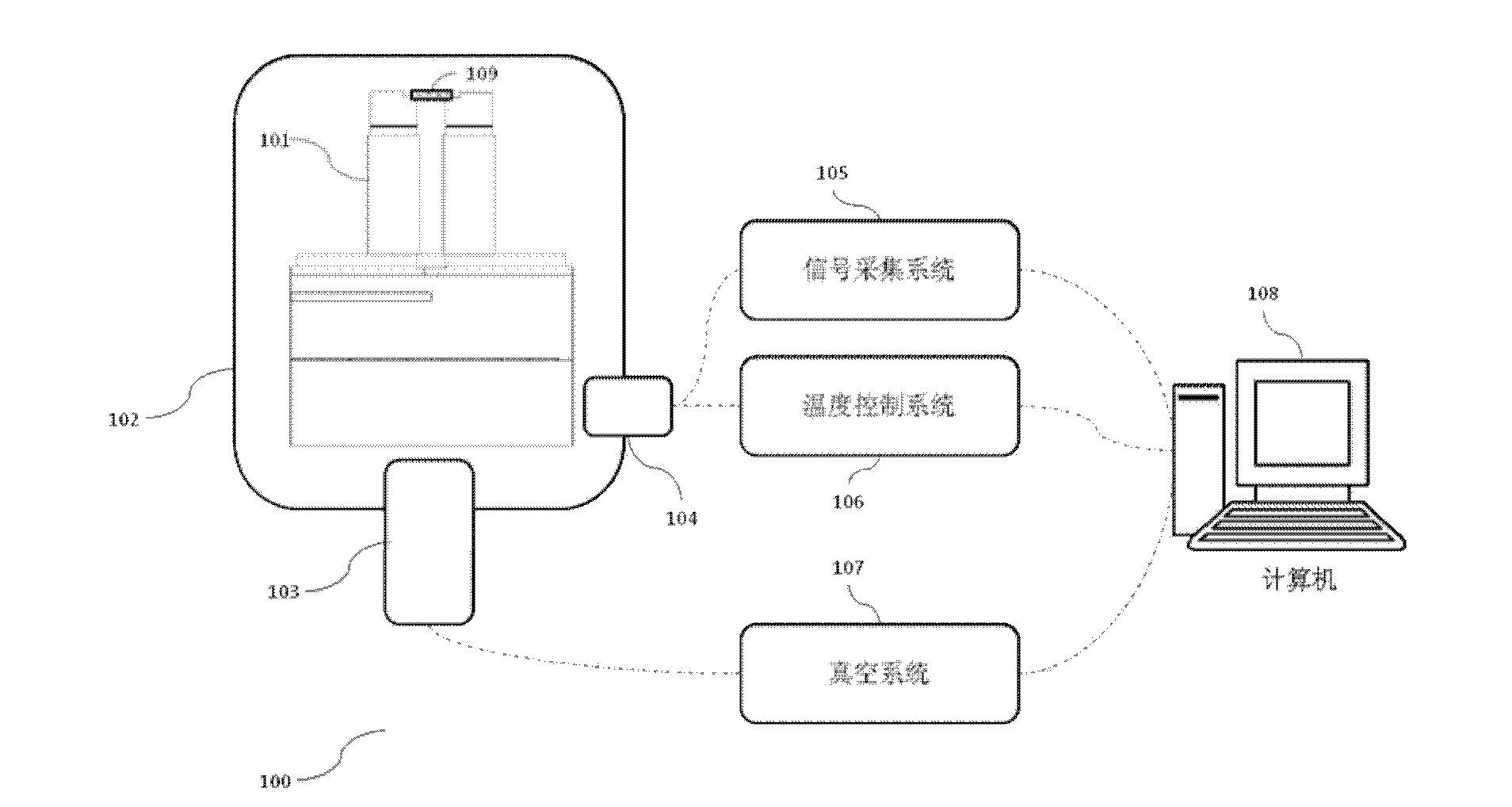
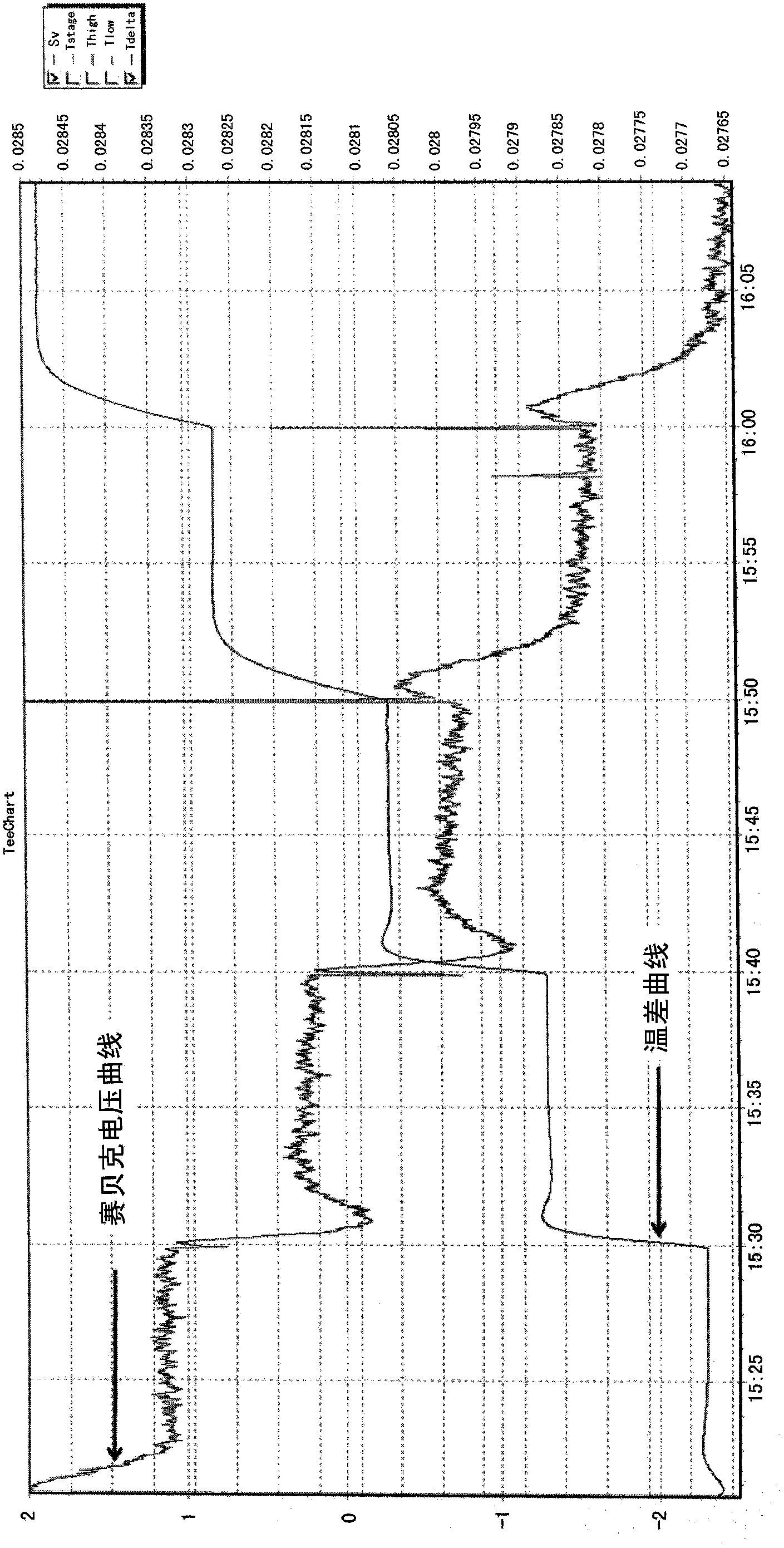
Seebeck coefficient measuring system
ActiveCN103512914ARealize determinationRealize measurementMaterial heat developmentTemperature controlNegative temperature
The invention provides a seebeck coefficient measuring system, comprising a test sample platform, a temperature difference heating platform, a hot end sample placing platform, a cold end sample placing platform, a signal acquiring and processing system and a temperature control system, wherein the test sample platform is used for placing a to-be-tested sample and forming a predetermined temperature difference between two ends of the to-be-tested sample; the temperature difference heating platform comprises a temperature difference heating platform body, a hot end heating pillar and a cold end heating pillar, wherein the hot end heating pillar and the cold end heating pillar are arranged on the temperature difference heating platform body, the hot end heating pillar and the cold end heating pillar insulate heat from each other, and have respective heating systems, respectively; the hot end sample placing platform and the cold end sample placing platform are arranged on the hot end heating pillar and the cold end heating pillar, respectively, and are used for placing the hot end and the cold end of the to-be-tested sample; the signal acquiring and processing system is used for calculating the seebeck coefficient; and the temperature control system is used for controlling the temperature difference between two ends of the to-be-tested sample. The seebeck coefficient measuring system provided by the invention can realize the positive and negative temperature difference measurements of the sample.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter in-situ quantitative characterization device based on atomic force microscope
ActiveCN102692427AExpand the evaluation functionHigh resolutionMaterial heat developmentMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansThermoelectric materialsAtomic force microscopy
The invention relates to a nano-thermoelectric energy material multi-parameter in-situ quantitative characterization device based on an atomic force microscope, which is used for detecting a micro-area heat conduction coefficient, a Seebeck coefficient and other thermoelectric property parameters of a detected nano-thermoelectric material sample. The device comprises a nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter atomic force microscope in-situ excitation platform and a nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter in-situ detection platform, wherein the nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter atomic force microscope in-situ excitation platform is used for providing a basic hardware platform required in nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter excitation and realizing in-situ simultaneous excitation of a micro-area frequency-tripled heat conduction signal and a micro-area stable-state Seebeck direct current voltage signal of a nano-thermoelectric material; and the nano-thermoelectric multi-parameter in-situ detection platform is used for realizing in-situ real-time detection and data processing of micro-area heat conduction and Seebeck voltage of the nano-thermoelectric material and realizing real-time display of the quantitative characterization results of the micro-area heat conduction coefficient and the Seebeck coefficient. According to the device disclosed by the invention, the nano-detection function of the atomic force microscope, the frequency tripling detection principle of macro-heat conductivity and the test principle of the macro-Seebeck coefficient are combined for establishing a nano in-situ evaluation device which is based on the commercial atomic force microscope and combines the properties of nano-scale heat excitation and thermoelectric multi-parameter detection.
Owner:江苏先进无机材料研究院
Automatic measuring instrument for parameter of thermoelectric material
InactiveCN102053100AGood research toolsMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentThermoelectric materialsTemperature control
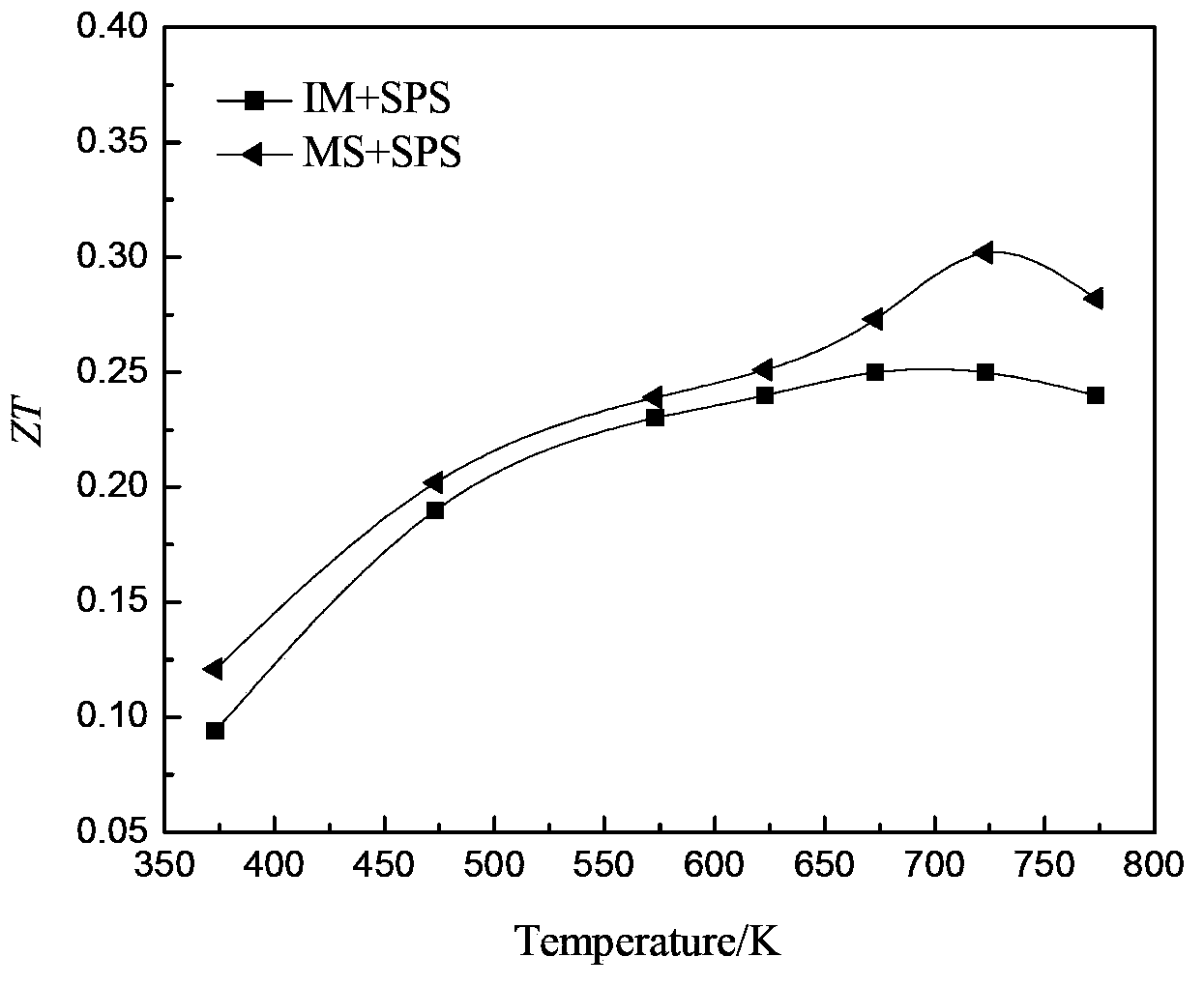
The invention provides an automatic measuring instrument for the parameters of a thermoelectric material, which comprises a vacuum testing system and a computer control system, wherein the vacuum testing system comprises a mechanical pump, a vacuum cover, a low-temperature constant-temperature tank, a furnace body, a thermal coupler, a temperature controller, a sample supporter, an alternating-current power supply and a direct-current power supply, and the computer control system comprises a control circuit, an analog-to-digital multifunctional card and a computer system. The automatic measuring instrument can be used for automatically measuring the electrical conductivity s, the Seebeck coefficient S and the thermal conductivity k of the thermoelectric material at each temperature point within the temperature range of -30 to 800 DEG C according to selected temperature intervals so as to obtain the value of a quality factor ZT (wherein Z= S2s / k) of the thermoelectric material at absolute temperature T.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Device and method for carrying out in-situ testing on transport properties of conductor materials at high temperature and high pressure
InactiveCN103399044AEasily brokenGuaranteed insulation performanceMaterial resistanceElectrical conductorCopper wire
The invention discloses a device and a method for carrying out in-situ testing on the transport properties of conductor materials at high temperature and high pressure, and belongs to the field of high-pressure science and technologies and material science technologies. In the device, four copper wires (4) are introduced to a side face of a high-temperature and high-pressure synthetic assembling block and used as electrodes for measuring the resistivity, two pairs of thermocouples (10) are introduced for measuring seebeck coefficients, and welding points of a sample (5) and the electrodes as well as the sample (5) and the thermocouples (10) are fixed by using a pressure generated by a high-temperature and high-pressure device. The resistivity of the sample is calculated through measuring relative resistance values RA and RB and the thickness d of the sample subjected to pressurization; the seebeck coefficient of the sample is calculated through measuring a potential difference Vef between positive poles of the two pairs of thermocouples and a potential difference Vhg between negative poles of the two pairs of thermocouples. The method disclosed by the invention is simple, easy to implement, high in success rate, and good in experimental repetition rate; a problem that wires and the thermocouples are easy to fracture at the high pressure is solved; a situation that measured electrical signals are interfered by heating current is prevented, thereby ensuring the accuracy of results.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Graphene-based thermopile
ActiveUS20130069194A1PhotovoltaicsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingThermopileOptoelectronics
Graphene-based thermopiles are provided. The graphene-based thermopiles may include thermocouples having one or more graphene strips that may be polarized to adjust their Seebeck coefficients. The polarized graphene strips may have larger Seebeck coefficients than the materials conventionally used in thermopile devices. As a result, the graphene-based thermopiles may generate large output voltages using fewer thermocouples than conventional thermopile devices.
Owner:EXCELITAS TECH SINGAPORE PTE
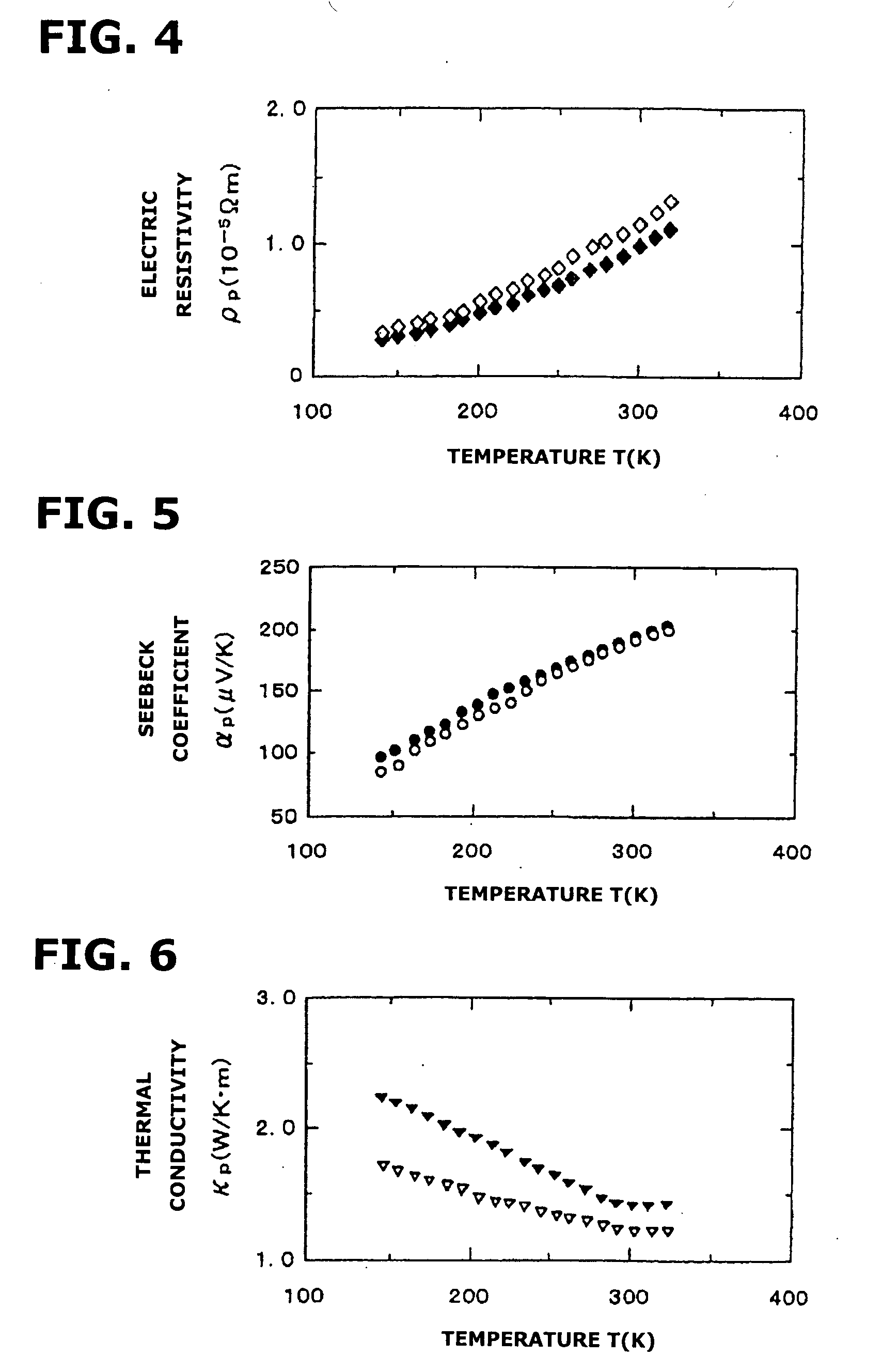
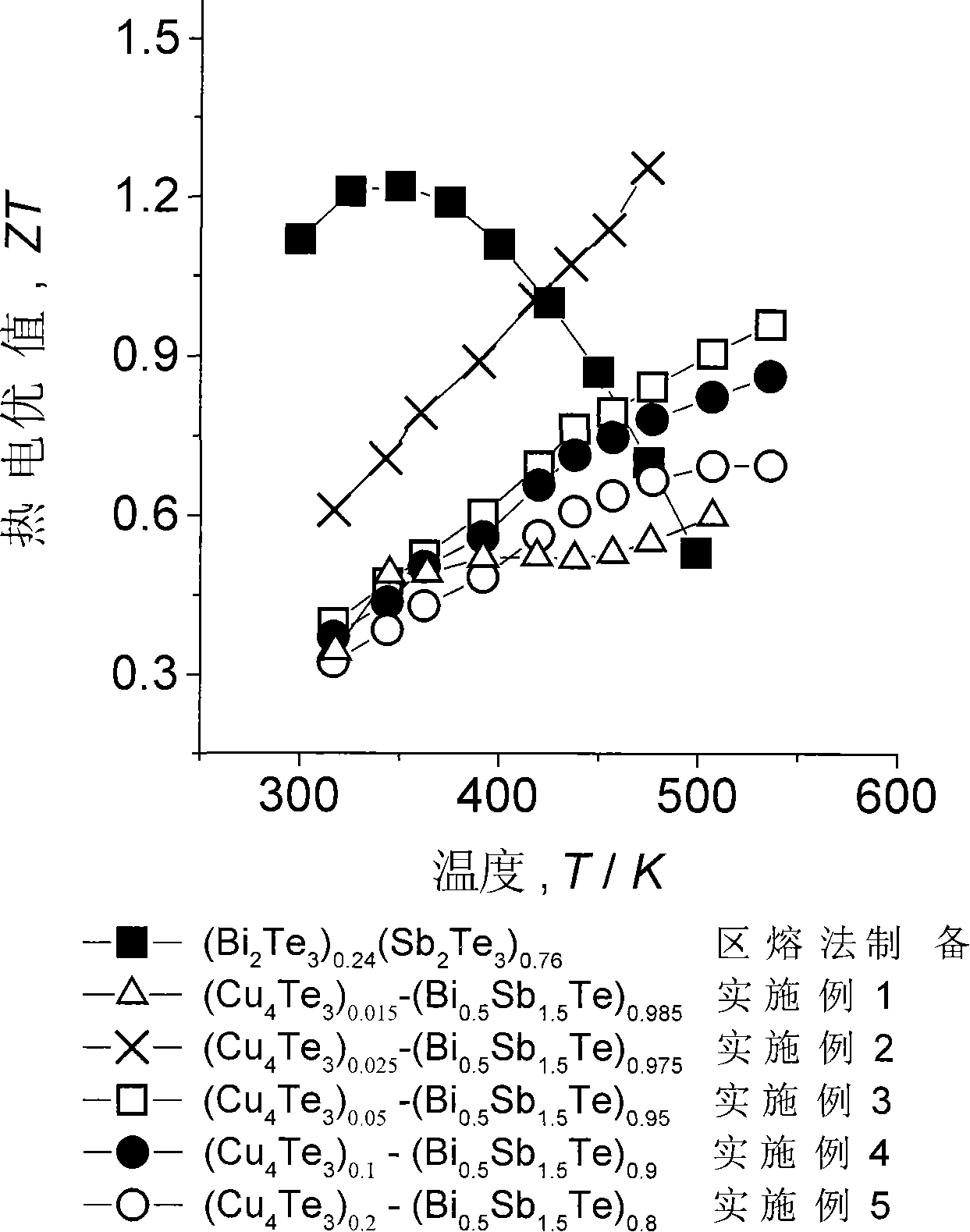
Middle-low temperature pseudo-binary electrothermal alloy and preparation process
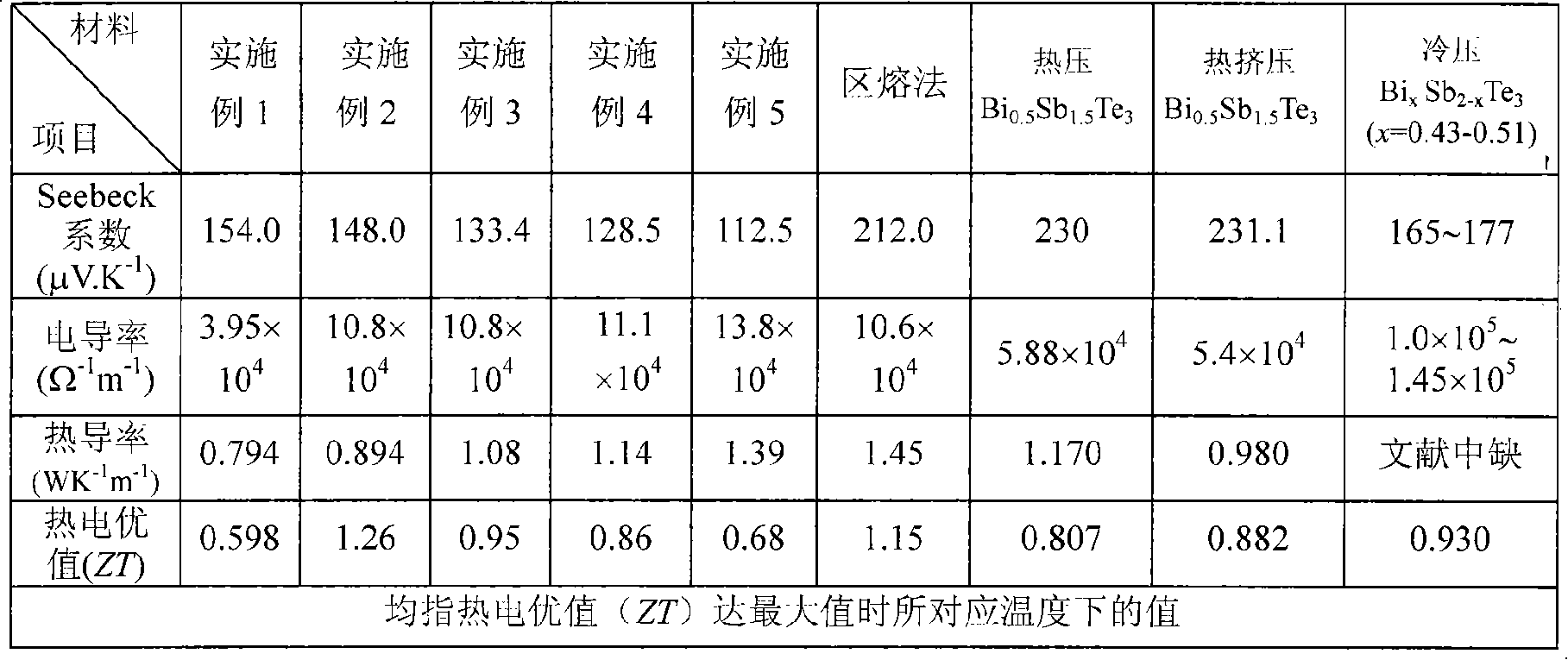
The present invention relates to new material, and is especially one kind of low and medium temp pseudo binary thermoelectric alloy with high thermoelectric Q value and its production process. The pseudo binary thermoelectric alloy with the composition of (Cu4Te3)0.025(Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3)0.975 is produced through the following steps: vacuum smelting Cu4Te3 at 1000-1100 deg.c and Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 at 700-800 deg.c; smelting alloy (Cu4Te3)0.025(Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3)0.975 with Cu4Te3 and Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 at 1000-1100 deg.c for 10 hr; ball milling into powder and plasma discharging sintering at 400 deg.c and 50 MPa for 10 min. The pseudo binary thermoelectric alloy has Seebeck coefficient of 148.0 MV / K, electrical conductivity of 10.8x10<4> / omega .m, thermal conductivity of 0.89 W / K.m, and maximum thermoelectric Q value ZT of 1.26. It is applied in making low and medium temp power generating devices.
Owner:NINGBO UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
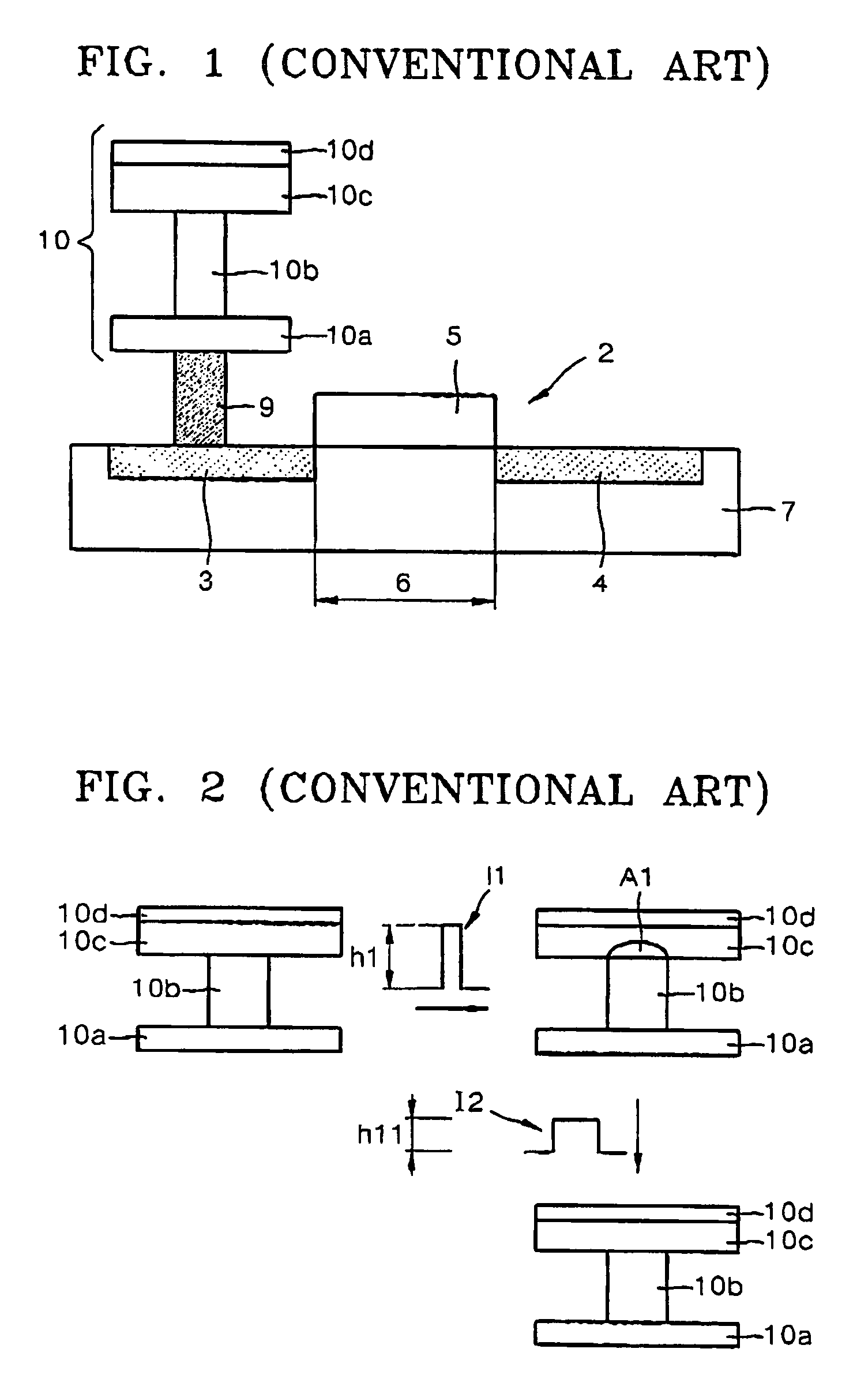
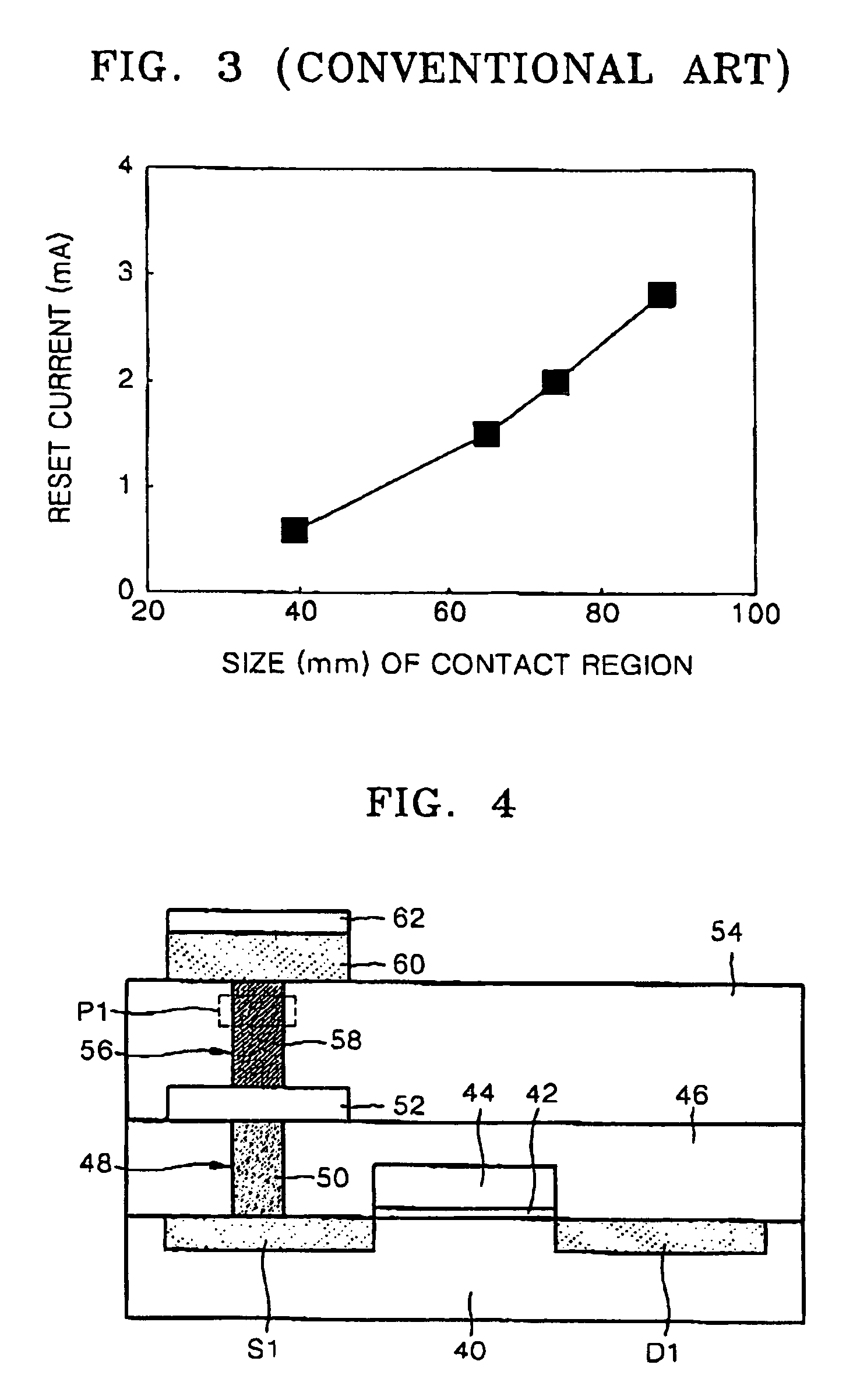
Structure of peltier element or seebeck element and its manufacturing method
ActiveCN101044638AReduce manufacturing costReduce movementThermoelectric device with peltier/seeback effectThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentAmorphous siliconEngineering
A Peltier or Seebeck element has first and second conductive members having different Seebeck coefficients. To decrease the heat conduction from one to the other end of each of the conductive members, the cross-section area at the intermediate part in the length direction is smaller than those at both end parts, and consequently, the heat conductivity of the intermediate part is lower than those at both ends parts. In place of the decrease of the cross-section, the shape of the cross-section of the intermediate part of each of the conductive members may be changed by dividing the intermediate part into pieces, or amorphous silicon or the like having a heat conductivity lower than those of the materials of both end parts may be used for the material of the intermediate part. In such a way, a high-performance Peltier / Seebeck element such that the difference between the temperature of the heated portion of the Peltier / Seebeck element and the opposite portion can be kept to a predetermined temperature difference for a long time and its manufacturing method are provided.
Owner:MEIDENSHA ELECTRIC MFG CO LTD +2
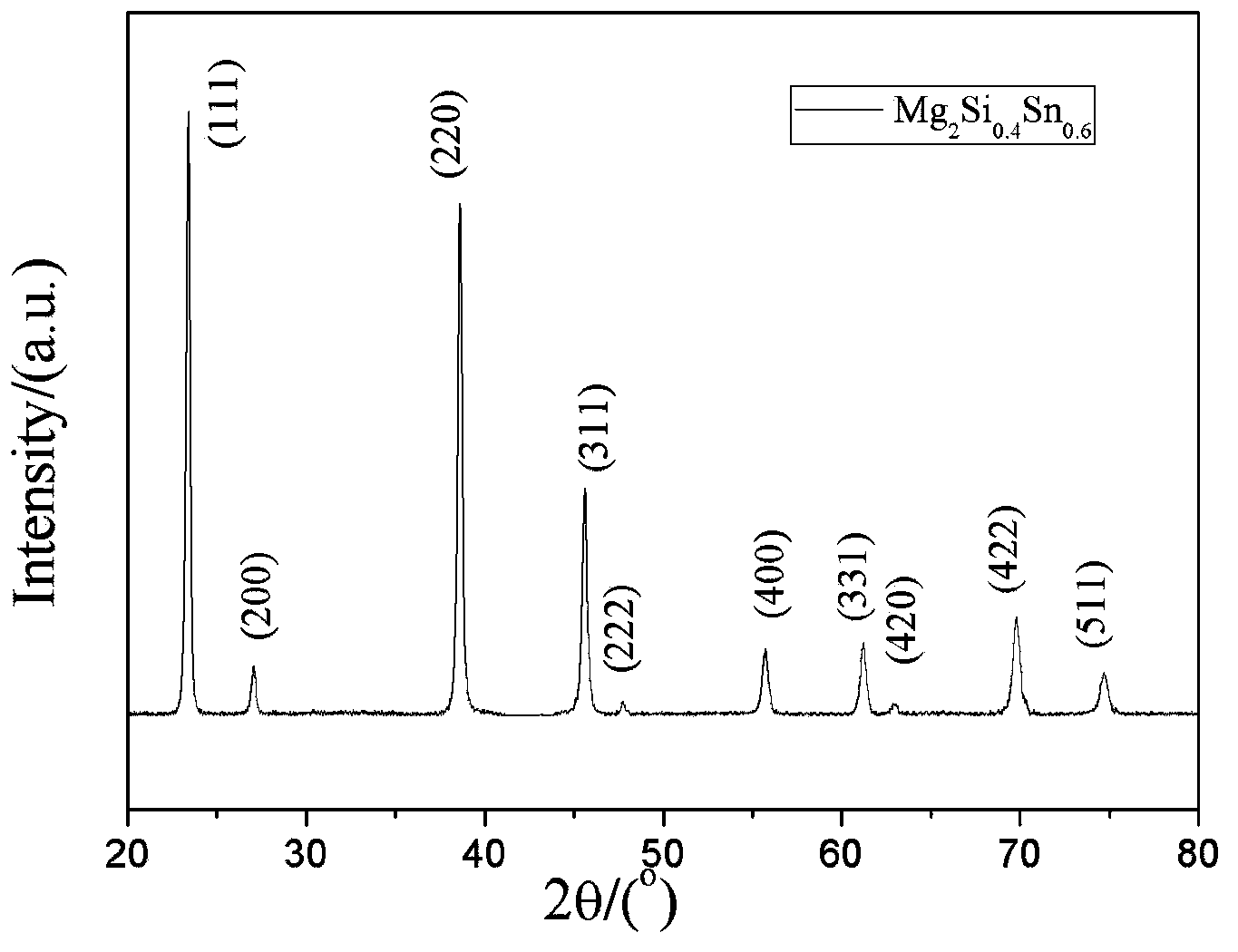
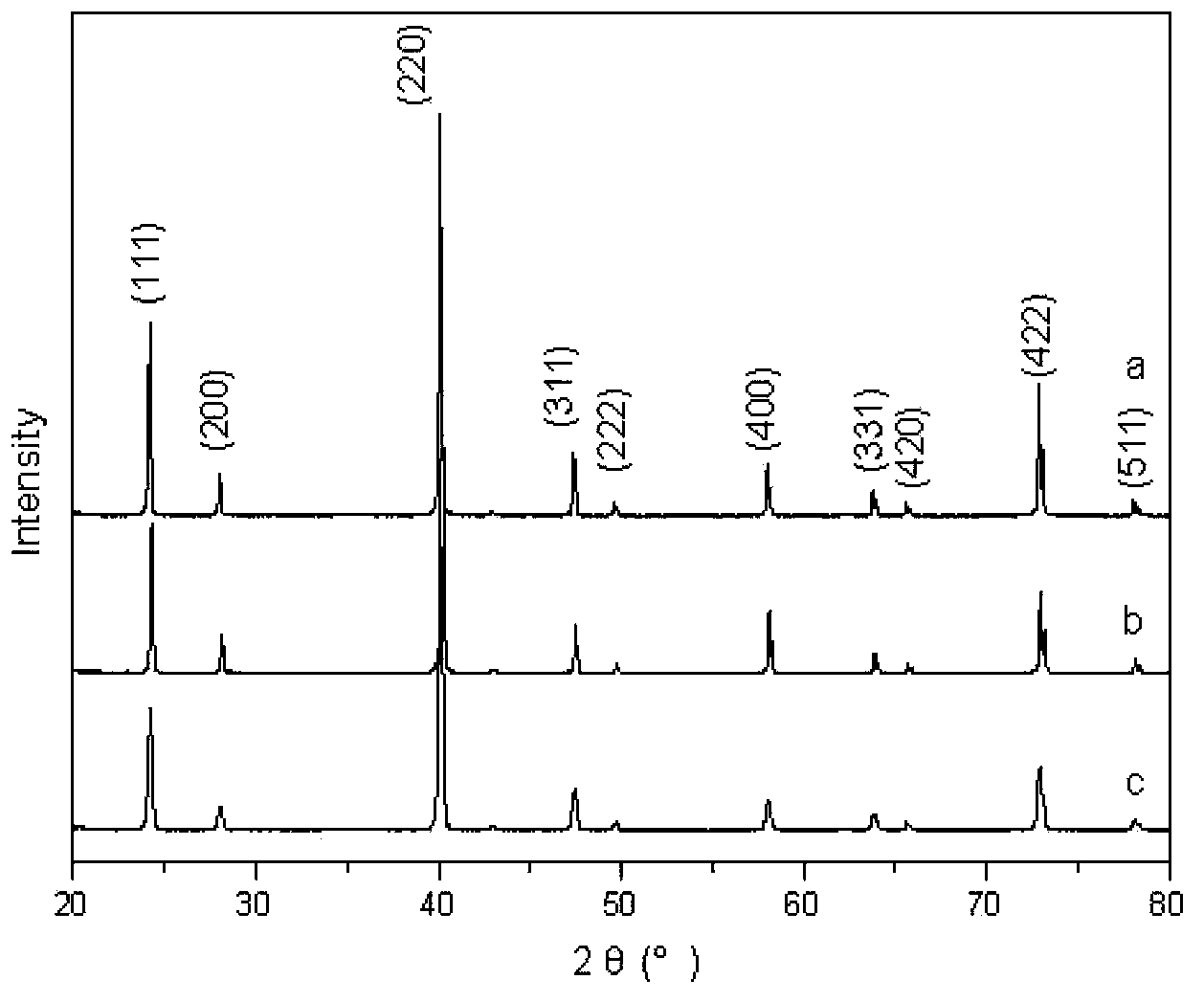
Nanocomposite structure Mg2Si-based thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103700759APrevent oxidationPrevent volatilizationThermoelectric device manufacture/treatmentThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsMolten state
The invention relates to a nanocomposite structure Mg2Si-based thermoelectric material and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of semiconductor thermoelectric materials. The preparation method comprises the following steps: taking Mg, Si and Sn elementary substance materials according to a stoichiometric ratio and performing high-frequency induction smelting to form cast ingot; crushing the smelted cast ingots, filling into a quartz glass tube with a lower open end, vertically placing into an induction smelting coil, vacuumizing a cavity of a rapid quenching furnace, filling protective gas, performing induction smelting to enable the block to reach a molten state, spraying the melt to a copper rod, throwing out to form belt materials, and collecting the belt materials; placing the belt materials into a glove box under the argon protective atmosphere, grinding into powder, and performing spark plasma sintering into blocks. The preparation method is simple and feasible; the process flow is short; oxidation of Mg can be effectively inhibited; process parameters are easy to control. An amorphous / nanocrystalline composite structure exists in a sample, the grain size is obviously refined, the grain size distribution is controllable, scattering of electrons and phonons is increased, the Seebeck coefficient is greatly increased, and the thermoelectric property of the material is improved.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
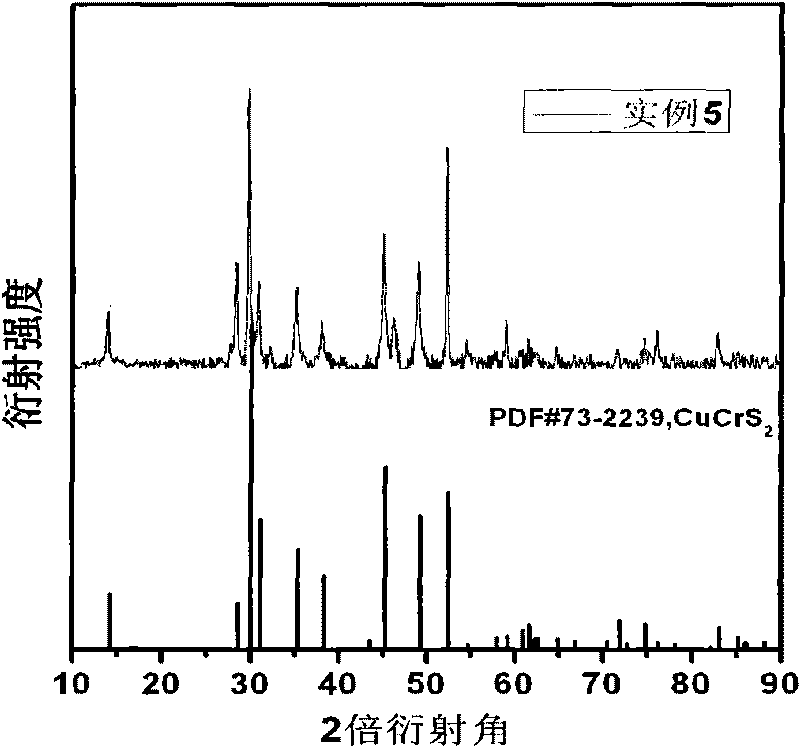
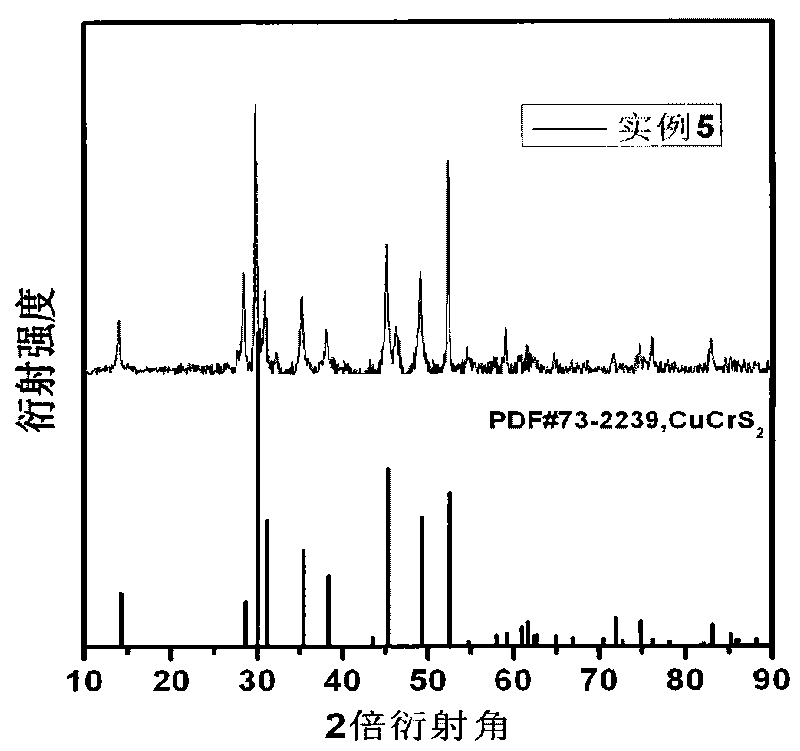
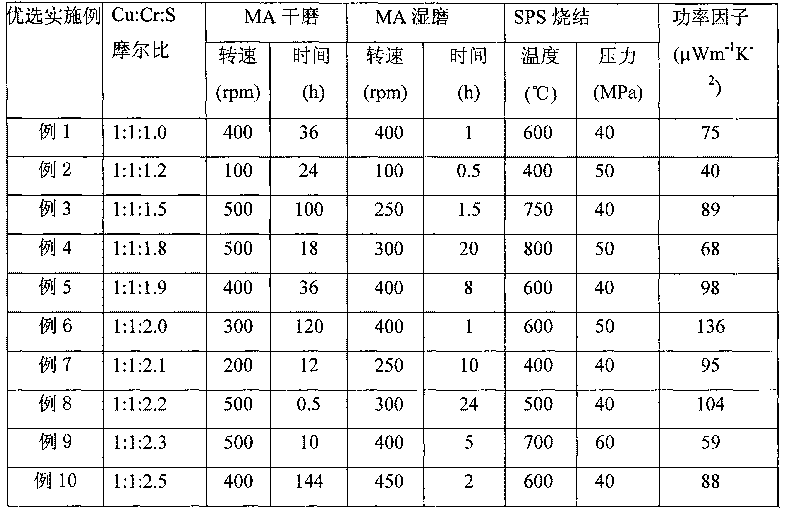
Cu-Cr-S ternary thermoelectric material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101704672AOptimizing Carrier ConcentrationImprove conductivityThermoelectric device junction materialsThermoelectric materialsMetallurgy
The invention discloses a Cu-Cr-S ternary thermoelectric material and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of energy material. Cu, Cr and S are collocated according to the stoichiometric ratio Cu Cr Sx, wherein the numeric area of x is more than or equal to 1.0 and less than or equal to 2.5. The Cu powder (mass percent more than or equal to 99.9%), Cr powder (mass percent more than or equal to 99.9%) and S powder (mass percent more than or equal to 99.5%) are taken as raw materials, compound powder can be synthesized by mechanical alloying, and then a block body can be sintered by discharge plasma. The invention has the technical characteristics that by adjusting the concentration of sulphur vacancy and optimizing the concentration of a current carrier, the conductivity and the Seebeck coefficient can be improved; and the nano-structure block body material prepared by combining the mechanical alloying and discharge plasma sintering is beneficial to reducing the thermal conductivity and obtaining a higher thermoelectricity optimum value. The preparation method has low price of raw materials, simple and convenient preparation process, easy operation, low requirement for equipment and preparation environment and short period, and is suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Thermocouple and forming method of thermocouple
ActiveCN102865938AHigh Seebeck coefficientIncreased sensitivityThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsUsing electrical meansGate voltageContact resistance
The invention discloses a thermocouple and a forming method of the thermocouple. The method comprises the following steps: providing a substrate; forming a dielectric layer on the substrate; forming a metal layer on the dielectric layer; carrying out photoetching and etching on the metal layer to form a first pressure welding block, a second pressure welding block and a thermocouple metal strip, wherein the second pressure welding block is connected with the thermocouple metal strip; forming a carbon-based film on the dielectric layer, wherein one end of the carbon-based film is contacted with the pressure welding block and the other end of the carbon-based film is contacted with the thermocouple metal strip; forming a first metal contact on the first pressure welding block; and forming a second metal contact on the second pressure welding block. According to the thermocouple and the forming method of the thermocouple, by adopting graphene, the thermocouple has a high seebeck coefficient and can be modulated by gate voltage, so that the produced thermocouple has high sensitivity; the carbon-based film formed by using air pressure is flat, compact and good in quality; the working procedures after forming the carbon-based film are few, the carbon-based film is less stained or damaged; and the finally formed electrode with two-side clamp structure is high in intensity and low in contact resistance.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
System and method for testing thin film thermoelectricity material Seebeck coefficient
ActiveCN101413908ASolve the unmeasurableAccurate measurementMaterial resistanceThermoelectric materialsElectricity
The invention relates to a system used for testing Seebeck coefficient of film thermoelectric material and a method thereof. The system comprises a testing device and a control and test circuit system; the sample to be tested is arranged on an insulative sheet on a sample supporting frame and closely contacts with two thermocouples used for measuring the temperature of the sample by a sample fixed clamp; temperature difference is established in the sample to be tested by an electric heating block which is arranged at one side of the sample to be tested; furthermore, the temperature of the film thermoelectric material at the position where the thermocouple is arranged is measured by the two thermocouples which are used for measuring the temperature of the sample and intermittently distributed along the temperature difference direction; the Seebeck electromotive force generated by the sample inside the film thermoelectric material at the position where the thermocouple is arranged is measured by the Seebeck electromotive force measuring line educed by one of two leads which are respectively arranged in the two thermocouples used for measuring the temperature of the sample. The structure used for testing Seebeck coefficient of the film thermoelectric material and the method thereof can quickly and exactly measure the Seebeck coefficient of the film thermoelectric material and solve the problem that the Seebeck coefficient of the film thermoelectric material can not be measured at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
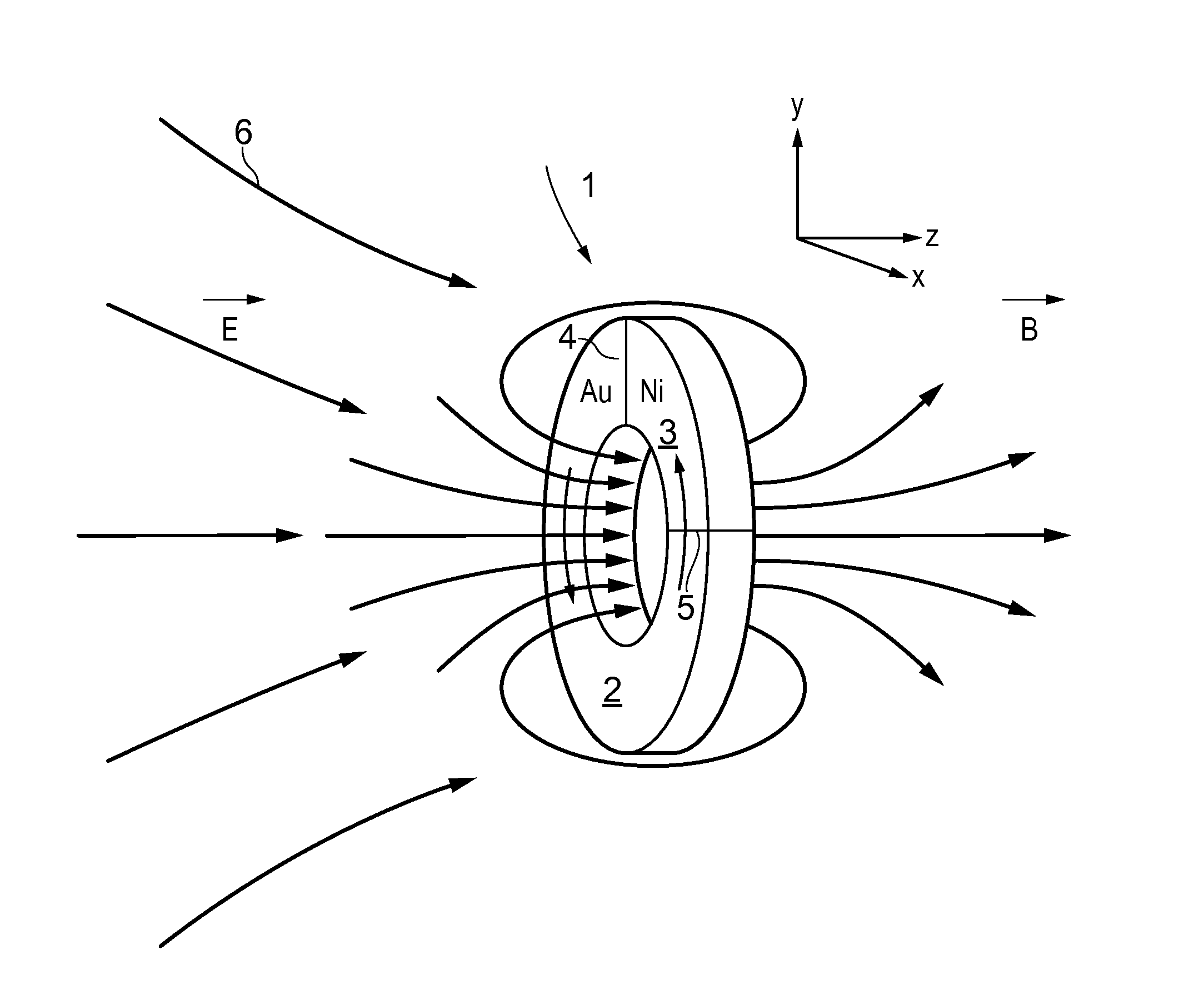
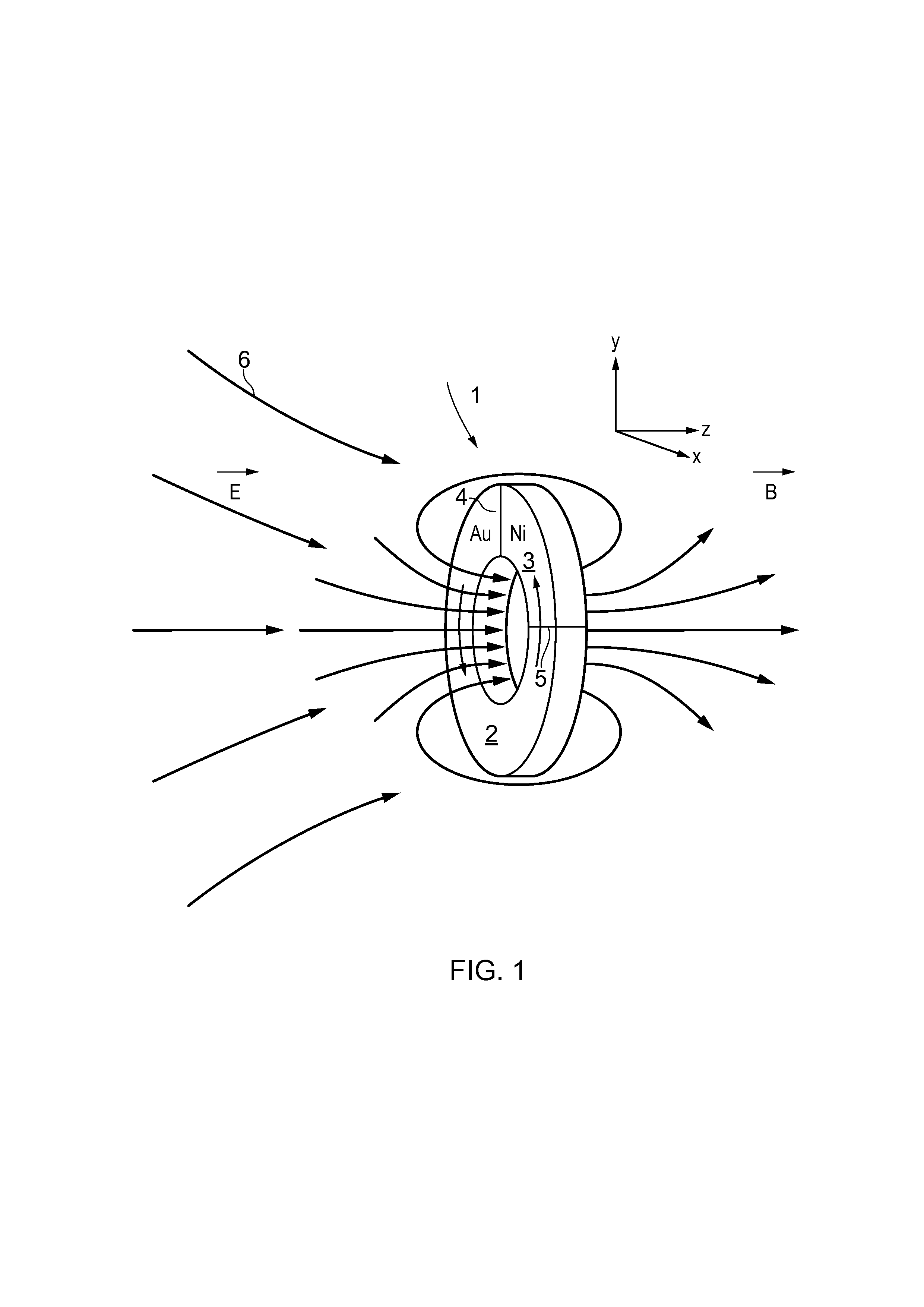
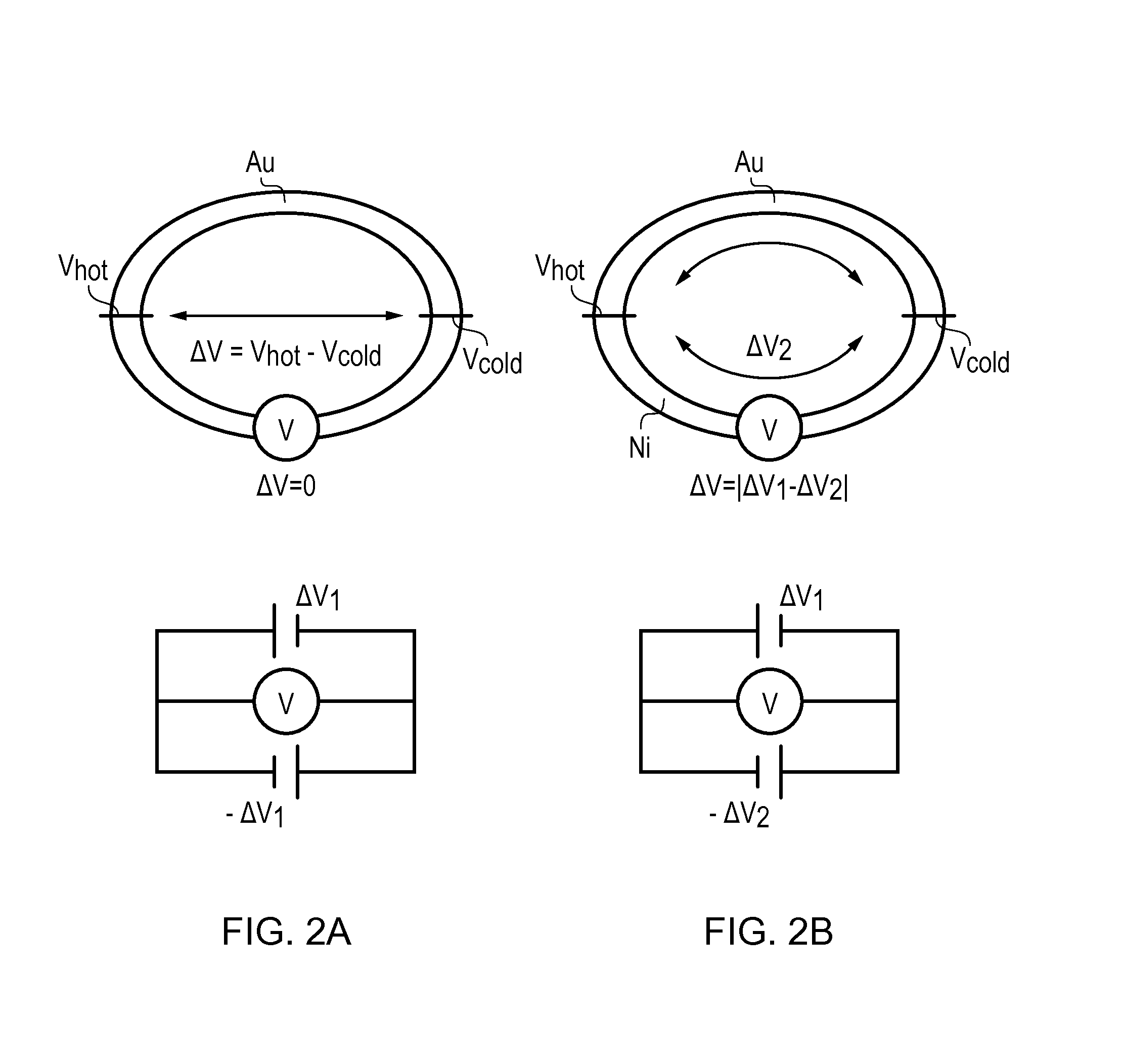
Magnetic field generator
InactiveUS20130176836A1Increase data storage densityIncrease the magnetic field strengthRecord information storageRecording/reproducing/erasing methodsThermoelectric materialsTerahertz radiation
A metallic ring is made of two metals, wherein one metal forms a major arcuate portion and the other a minor arcuate portion of the ring, thereby forming a thermocouple-type structure as a result of the two inter-metallic junctions. The metallic ring supports a surface plasmon whose energy is matched to the energy, i.e. wavelength, of an incident light beam so that the oscillating electromagnetic field of the light resonates with the plasmon. The resonating plasmon causes a temperature difference to arise between the two inter-metallic junctions in the ring. The different Seebeck coefficients of the two metals results in the temperature difference causing a net current to flow around the ring, which in turn generates a magnetic field. Such a thermoelectric metamaterial ring transforms high frequency optical energy into long duration magnetic radiation pulses in the terahertz range. Applications of these devices include high density magnetic recording, magnetic field spectroscopy, and efficient terahertz radiation sources.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
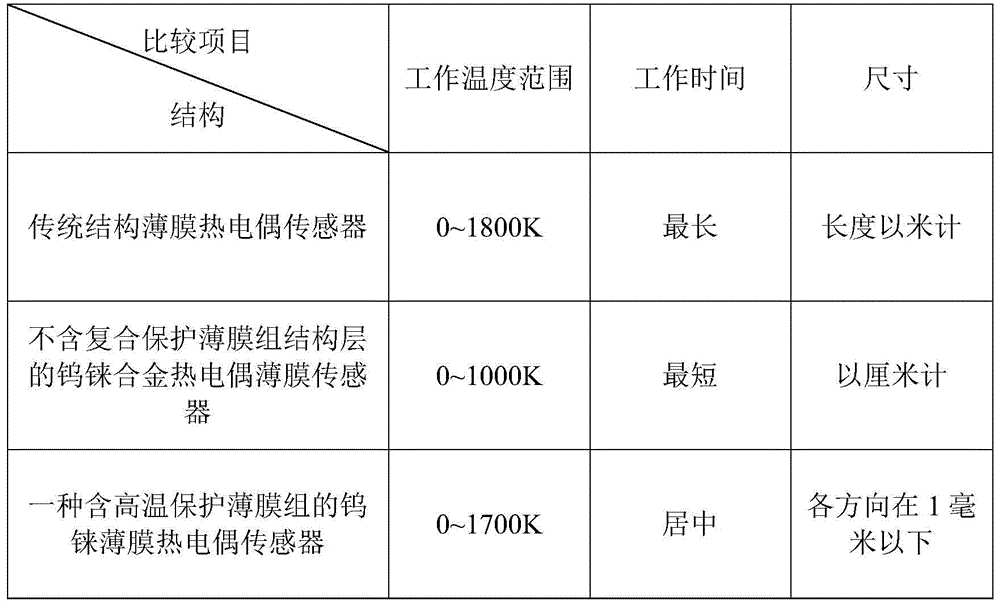
Tungsten-rhenium film thermocouple sensor containing high temperature protection film group and preparation method
ActiveCN105675160ASolve transpirationSolve sheddingThermometer detailsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsThin film thermocouplesRhenium
The invention discloses a tungsten-rhenium film thermocouple sensor containing a high temperature protection film group and a preparation method. The high temperature protection film group and parallel tungsten-rhenium film thermocouple jointly form a sensor chip. A tungsten-rhenium film group, a high-temperature electrode and an aluminium oxide film protective layer are connected on a silicon carbide-based substrate, and cover an amorphous silicon carbide film protective layer. The tungsten-rhenium film thermocouple sensor can measure temperature signals for a long time under high temperature (1000 to 1700K), has the characteristics of high temperature resistance, oxidation prevention and high Seebeck coefficient, and solves the problems in existing technologies, such as the problems of thermal mismatch and oxidation under high temperature and failure around 1400K.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Graphene quantum dot/carbon nanotube/PEDOT:PSS composite film and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a graphene quantum dot / carbon nanotube / PEDOT:PSS composite film and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method includes blending graphene quantum dots and carbon nanotubes in water sufficiently to form a graphene quantum dot / carbon nanotube hybrid, and dispersing the hybrid to an electroconductive polymer PEDOT:PSS to form the graphene quantum dot / carbon nanotube / PEDOT:PSS composite film. The graphene quantum dot / carbon nanotube / PEDOT:PSS composite film and the preparation method thereof have the advantages that both the graphene quantum dots and the carbon nanotubes structurally comprise large delocalized pi-bonds, a graphene quantum dot layer is modified on the wall of each of the carbon nanotubes through pi-pi conjugation, and accordingly excellent water solubility is achieved; the graphene quantum dot / carbon nanotube hybrid is evenly dispersed into a PEDOT:PSS water solution through uniform dispersity of the graphene quantum dots and the PEDOT:PSS in water, and the graphene quantum dots, the carbon nanotubes and PEDOT:PSS are combined together uniformly and effectively with the aid of pi-pi interaction between the graphene quantum dots and PEDOT, so that the graphene quantum dot / carbon nanotube / PEDOT:PSS composite film is formed. The graphene quantum dot / carbon nanotube / PEDOT:PSS composite film is excellent in electroconductivity, high in Seebeck coefficient and low in heat conduction coefficient.
Owner:TIANJIN RES INST FOR ADVANCED EQUIP TSINGHUA UNIV
Device for measuring Seebeck coefficient and method of device
InactiveCN105628732AEasy to installOvercoming shape limitationsMaterial heat developmentThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsEngineeringThermocouple
The invention discloses a device for measuring a Seebeck coefficient and a method of the device. The device comprises a main heater, an assistant heater, a first insulated thermal conductor, a second insulated thermal conductor, a first main probe, a first assistant probe, a second main probe, a second assistant probe, a first main thermocouple, a first assistant thermocouple, a second main thermocouple and a second assistant thermocouple; the first insulated thermal conductor and the second insulated thermal conductor are both used for carrying a sample to be measured; the first main probe, the first assistant probe, the second main probe and the second assistant probe are used for measuring the electric potential of the sample to be measured; the first main thermocouple, the first assistant thermocouple, the second main thermocouple and the second assistant thermocouple are used for measuring the temperature of the sample to be measured. The morphology of the measured sample can be flexible and diverse, the device can measure the material Seebeck coefficients under the different temperature conditions and is simple in structure, and due to the fact that the measurement method that an average value is resolved through multiple sets of the Seebeck coefficients which are resolved on the basis of the four probes is adopted, the measured Seebeck coefficient is high in measurement accuracy.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com