Device for measuring Seebeck coefficient and resistivity of semi-conductor film material
A technology of Seebeck coefficient and thin film materials, applied in the direction of material resistance, etc., can solve the problems of increasing test costs, singleness, and complicated test process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0013] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing and example the present invention is described in further detail.
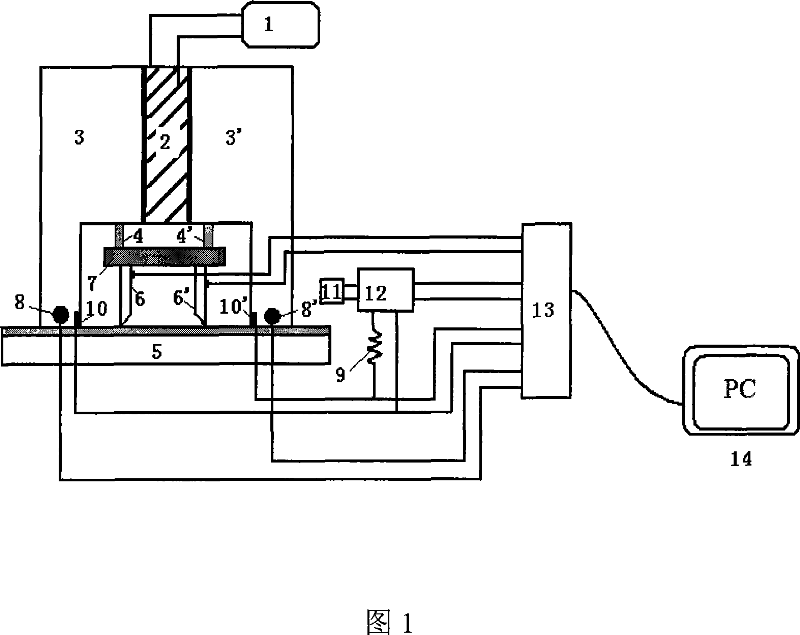
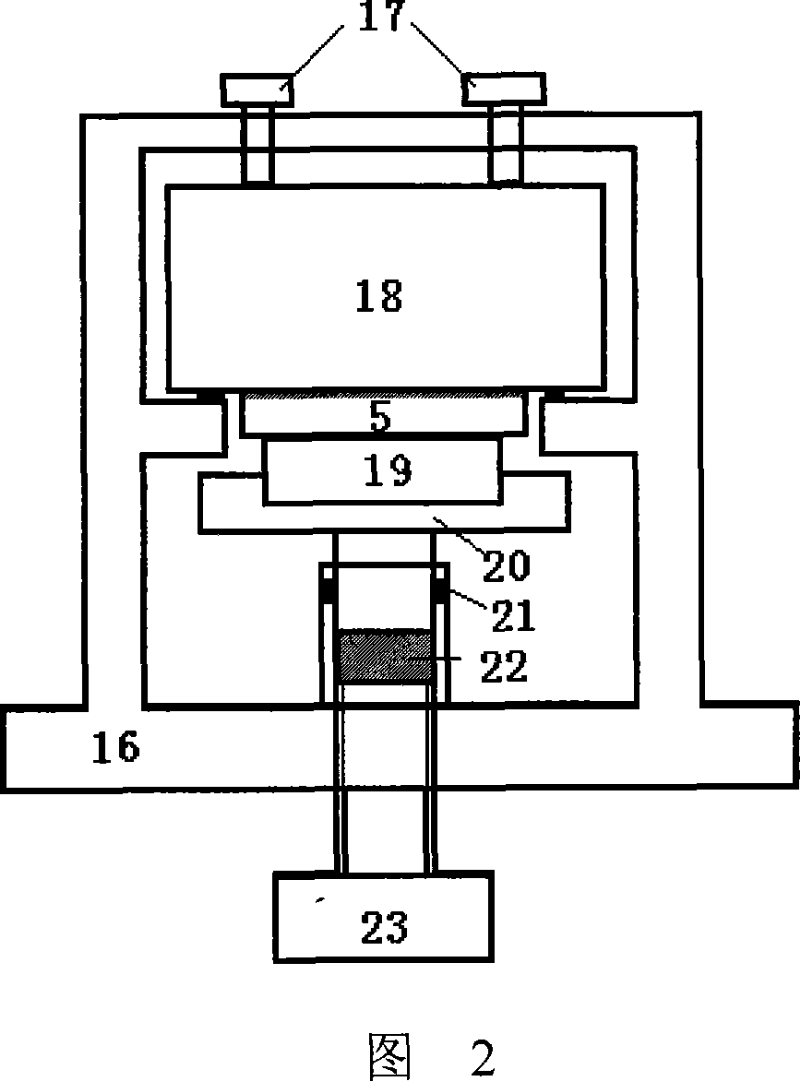
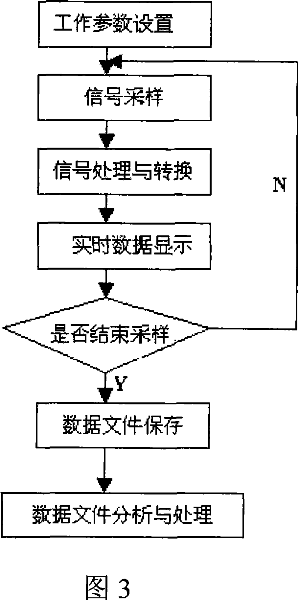
[0014] The structure of the device of the present invention includes three parts: a test component, a test platform, and a data transmission and acquisition device.
[0015] As shown in Figure 1, the structure of the test assembly is as follows: the thermopile 2 is connected to the DC power supply 1; the cold-end heat-conducting copper block 3 and the hot-end heat-conducting copper block 3' are respectively located at the cold end and the hot end of the thermopile 2, and the three are fixed In order to realize good heat conduction between the two ends of the thermopile and the copper block, and then realize the temperature difference between the two ends of the thin film sample 5 . The heat-conducting copper block 3 at the cold end and the heat-conducting copper block 3' at the hot end are preferably symmetrical structures, which form a cavity under the the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com