Method for producing astaxanthin by inducing Haematococcus pluvialis
A technology of Haematococcus pluvialis and astaxanthin, which is applied in the field of microorganism application, can solve problems such as inability to meet high-efficiency utilization, and achieve the effects of increasing yield, simple and easy method, and accelerating accumulation process.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
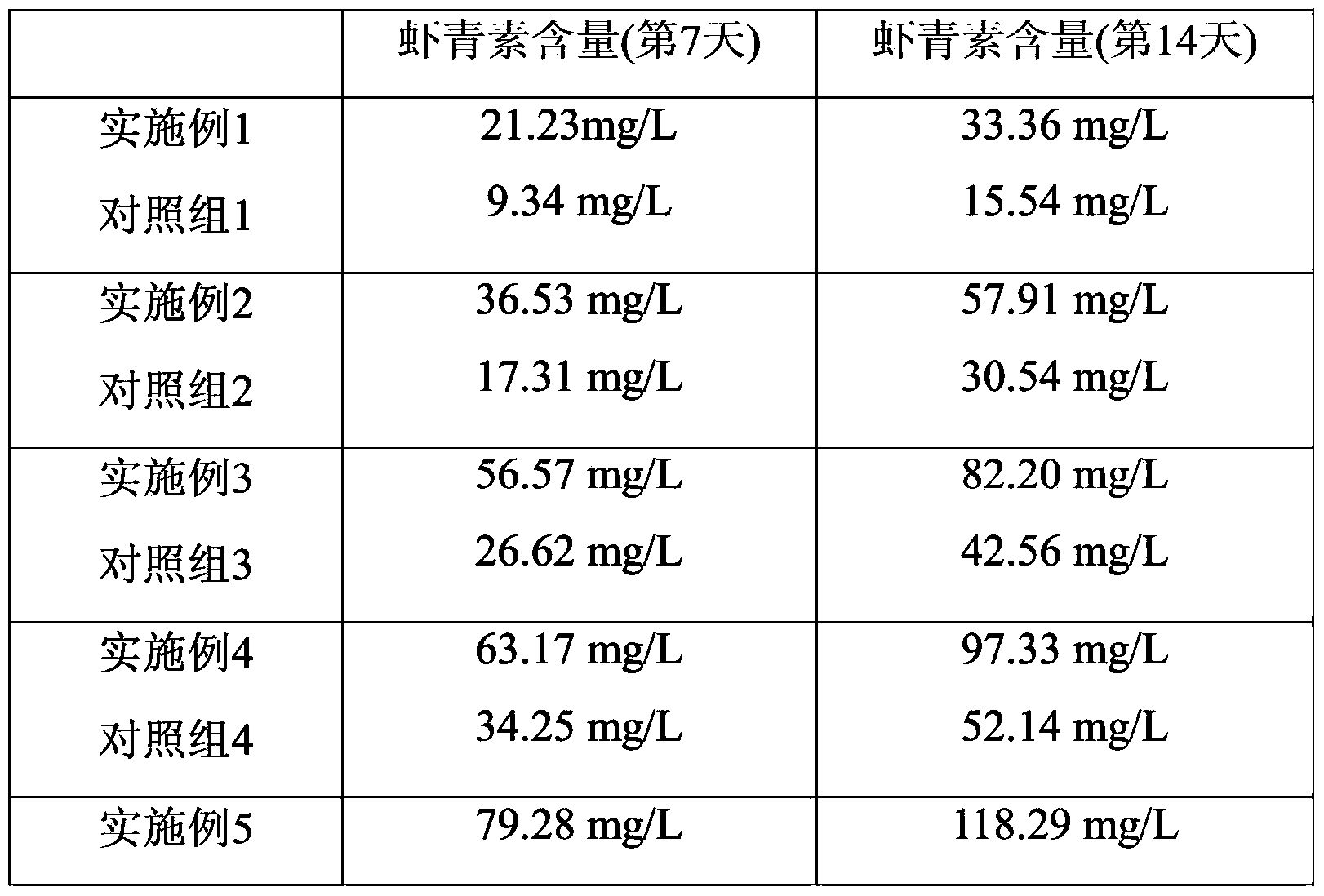
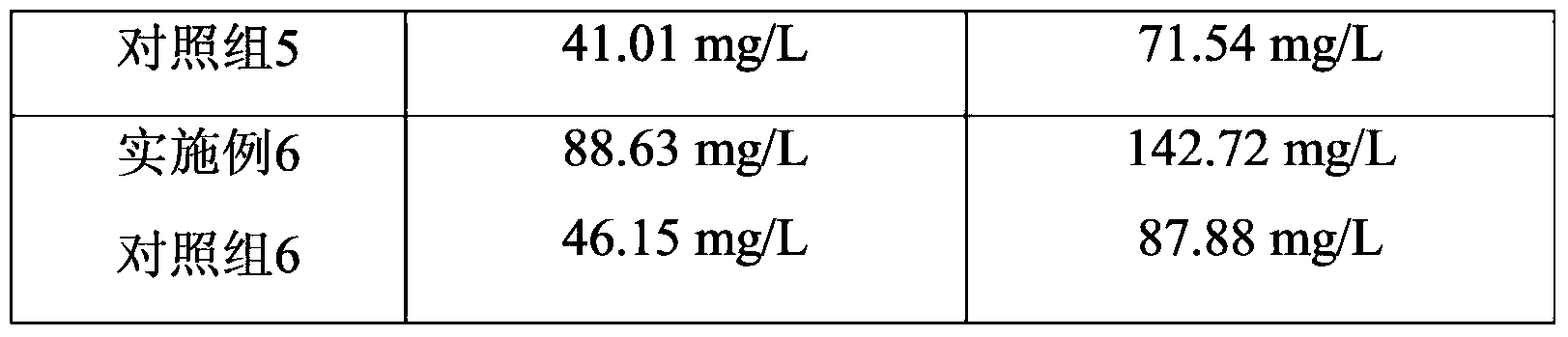
Embodiment 1
[0029] Step 1. Massive propagation of algae species: inoculate Haematococcus pluvialis into the propagation medium, at a temperature of 22°C and a continuous light intensity of 20 μmol·m -2 ·s -1 And at the same time continue to pass into the breeding medium through filtering and mixed with the air condition of 1% carbon dioxide to propagate, and its feed rate is to feed 0.2L / min in every 1L of breeding medium, until Reach the end of the logarithmic growth phase of Haematococcus pluvialis, and obtain a large number of algae species;
[0030] Step 2. Production of astaxanthin: Inoculate Haematococcus pluvialls into the production medium, and produce astaxanthin at a temperature of 22°C, wherein the light on Haematococcus pluvialls is continuously maintained during the cultivation process, and Ensure that the light intensity reaching the cell surface of Haematococcus pluvialis is 20 μmol m -2 ·s -1 Adding ethanol to the nutrient medium at the same time, wherein the ethanol ad...
Embodiment 2
[0033] Step 1. Massive propagation of algae species: inoculate Haematococcus pluvialis into the propagation medium, at a temperature of 24°C and a continuous light intensity of 60 μmol·m -2 ·s -1 And at the same time continue to pass into the breeding medium through filtering and mixed with the air condition of 1% carbon dioxide to propagate, and its feed rate is to feed 0.2L / min in every 1L of breeding medium, until Reach the end of the logarithmic growth phase of Haematococcus pluvialis, and obtain a large number of algae species;
[0034] Step 2, producing astaxanthin: Inoculate Haematococcus pluvialls into the production medium, and produce astaxanthin at a temperature of 24°C, wherein the light on Haematococcus pluvialls is continuously maintained during the cultivation process, and Ensure that the light intensity reaching the cell surface of Haematococcus pluvialis is 60 μmol m -2 ·s -1 Adding ethanol and sea crystals simultaneously in the production medium, wherein t...
Embodiment 3
[0037] Step 1. Massive propagation of algae species: inoculate Haematococcus pluvialis into the propagation medium, at a temperature of 26°C and a continuous light intensity of 100 μmol·m -2 ·s -1And at the same time continue to pass into the breeding medium through filtering and mixed with the air condition of 2% carbon dioxide to propagate, and its feed rate is to feed 0.3L / min in every 1L of breeding medium, until Reach the end of the logarithmic growth phase of Haematococcus pluvialis, and obtain a large number of algae species;
[0038] Step 2. Production of astaxanthin: inoculate Haematococcus pluvialls into the production medium, and produce astaxanthin at a temperature of 26°C, wherein the light on Haematococcus pluvialls is continuously maintained during the cultivation process, and Ensure that the light intensity reaching the cell surface of Haematococcus pluvialis is 100 μmol m -2 ·s -1 Add ethanol and sea crystal simultaneously in the production medium, wherein ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com