Paracoccus GN-9 and application thereof
A technology of GN-9 and Paracoccus, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve the problems of changing soil nitrogen cycle, not being able to meet the demand of crop high yield to the maximum extent, and limited nitrogen, so as to promote plant growth, rich in carbon sources, and eco-friendly toxic effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0019] Isolation and Identification of Bacteria
[0020] 1. Medium:
[0021] Ashby nitrogen-fixing culture medium (Ashby 1L): potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.2g, magnesium sulfate 0.2g, sodium chloride 0.2g, calcium carbonate 5.0g, mannitol 10g, calcium sulfate 0.1g, with ddH 2 O to constant volume, adjust the pH to 7.0-7.5.
[0022] Nitrogen fixation medium (1L): mannitol 20g, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.2g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.8g, magnesium sulfate 0.2g, calcium sulfate 0.1g, yeast extract 0.5g, iron chloride trace, sodium molybdate trace, with ddH 2 O to constant volume, adjust the pH to 7.2.
[0023] 2. Source of the strain:
[0024] Azotobacter isolated from coral sand. Take 5g of the sample and put it into a 100ml centrifuge tube, add 50ml of sterile water to shake evenly, place it at room temperature, and let it stand until it becomes clear. The prepared soil suspension was gradiently diluted in an ultra-clean workbench, and 100 μL of the suspen...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Physiological and biochemical analysis of bacterial strains
[0032] The physiological and biochemical indicators of the strain GN-9 were tested using the Mérieux API 20NE non-fermenting G-bacteria identification kit.
[0033] GN-9 can utilize glucose, maltose, arabinose and mannose as the sole carbon source, but cannot utilize galactose.
[0034] Potassium nitrate reduction test was positive, indicating that GN-9 can reduce nitrate.
[0035] Oxidase and urea tests were all positive, indicating that the bacteria can decompose hydrogen peroxide and urea.
[0036] The detailed results are as follows:
[0037] Table 1 Physiological and biochemical properties analysis
[0038] Table 1 Analysis of Physiological and Biochemical Properties
[0039]
[0040] Note: +: Positive reaction; -: Negative reaction
Embodiment 3
[0042] Phosphate-solubilizing ability test results of strains
[0043] Phosphorus-dissolving medium (1L): glucose 10g, ammonium sulfate 0.5g, sodium chloride 0.3g, magnesium sulfate 0.3g, manganese sulfate 0.03g, potassium sulfate 0.3g, ferrous sulfate 0.03g, tricalcium phosphate 5.0g, agar 15g.
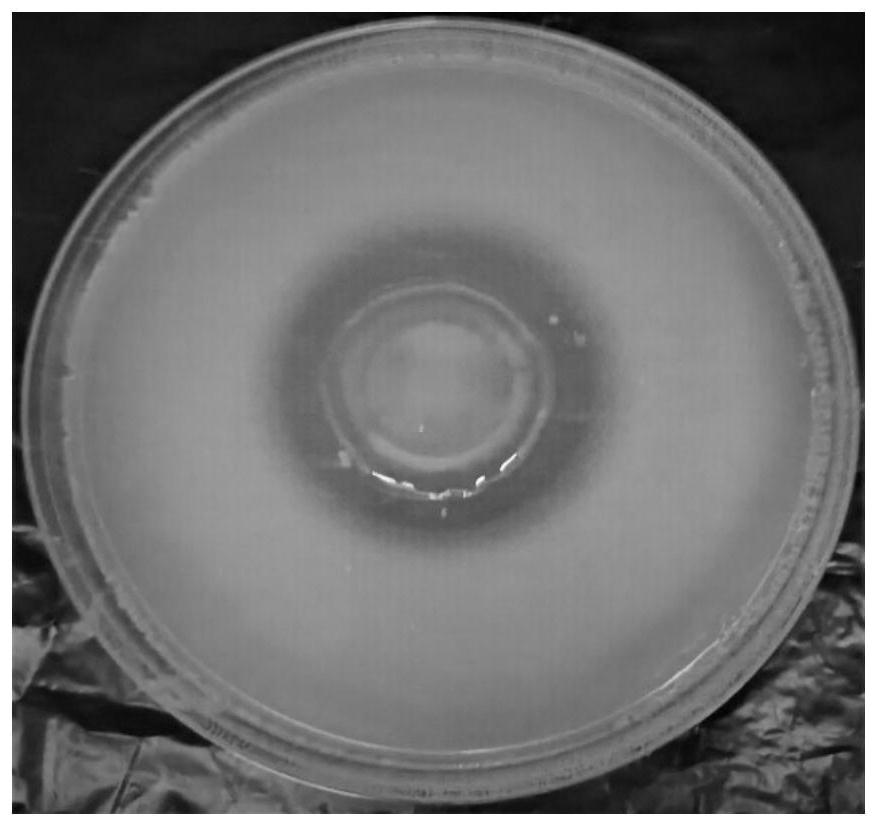
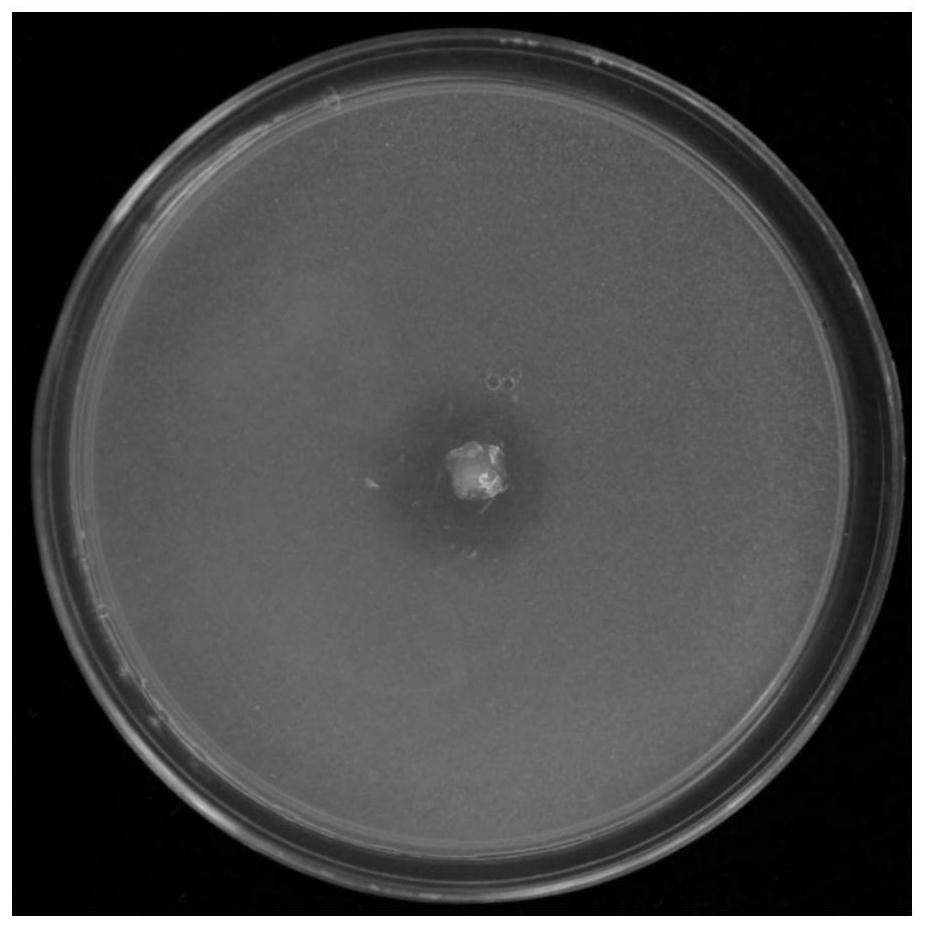
[0044] Drop 6 μL of strain GN-9 on the phosphorus-dissolving medium, and after 5 days of growth, the size of the phosphorus-dissolving circle tends to be stable (such as figure 2 As shown), the colony is raised, light yellow, translucent, sticky, and the size of the phosphorus-dissolving circle is 37.08mm. It is proved that the strain has strong phosphorus-dissolving ability, that is, it can convert ineffective phosphorus that plants cannot absorb into available phosphorus that plants can absorb.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com