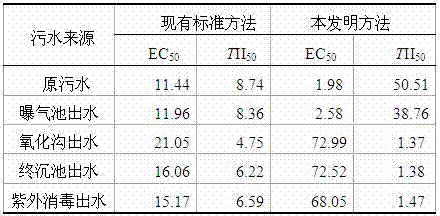
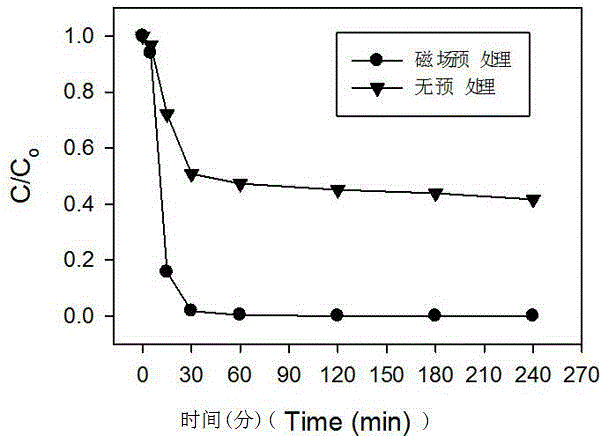
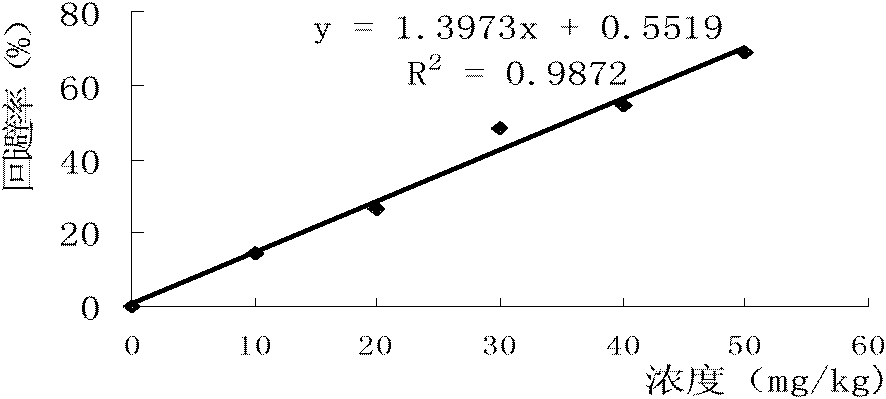
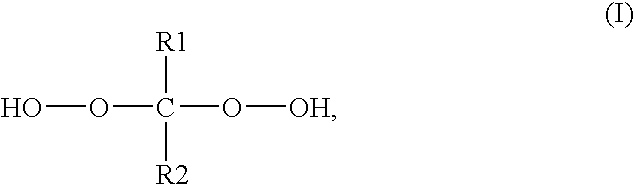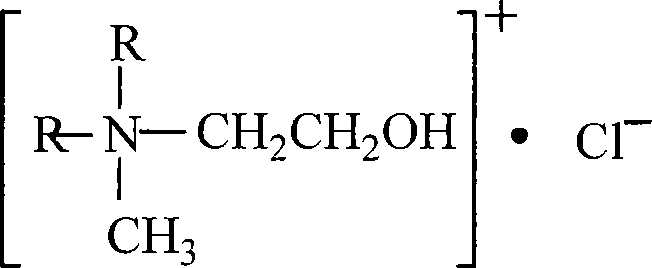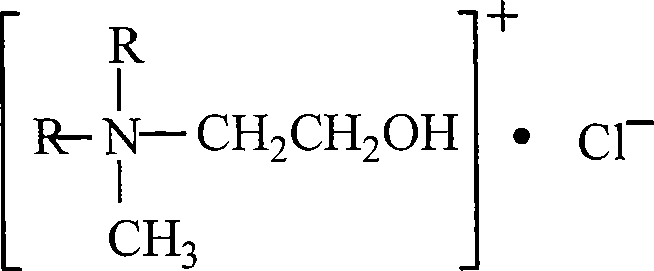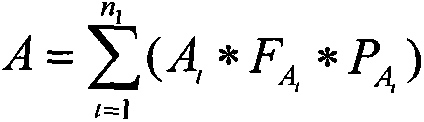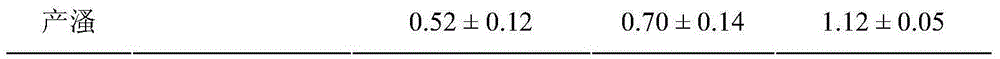Patents
Literature
115 results about "Ecotoxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Ecotoxicity, the subject of study of the field of ecotoxicology (a portmanteau of ecology and toxicology), refers to the potential for biological, chemical or physical stressors to affect ecosystems. Such stressors might occur in the natural environment at densities, concentrations or levels high enough to disrupt the natural biochemistry, physiology, behavior and interactions of the living organisms that comprise the ecosystem.
Method for studying influence of biological carbon on cadmium contaminated soil properties and cadmium form
InactiveCN107716532AImprove adsorption capacityReduce the effective Cd contentContaminated soil reclamationSoil propertiesBinding state
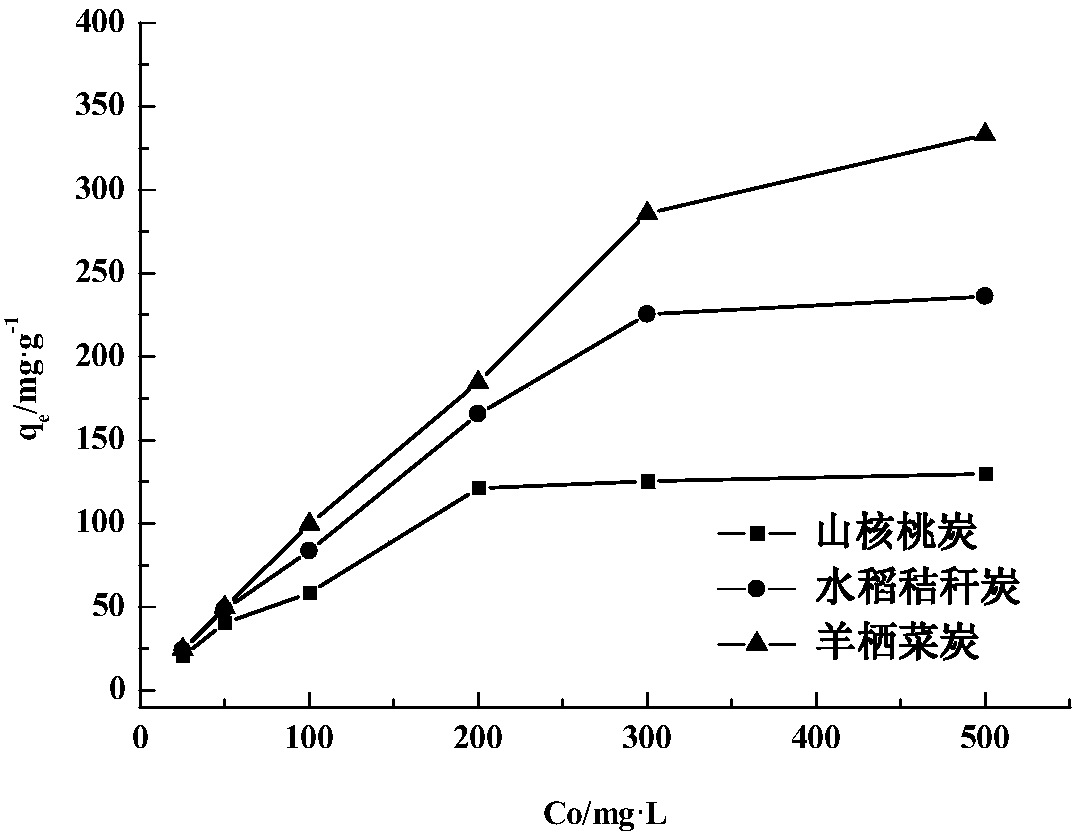
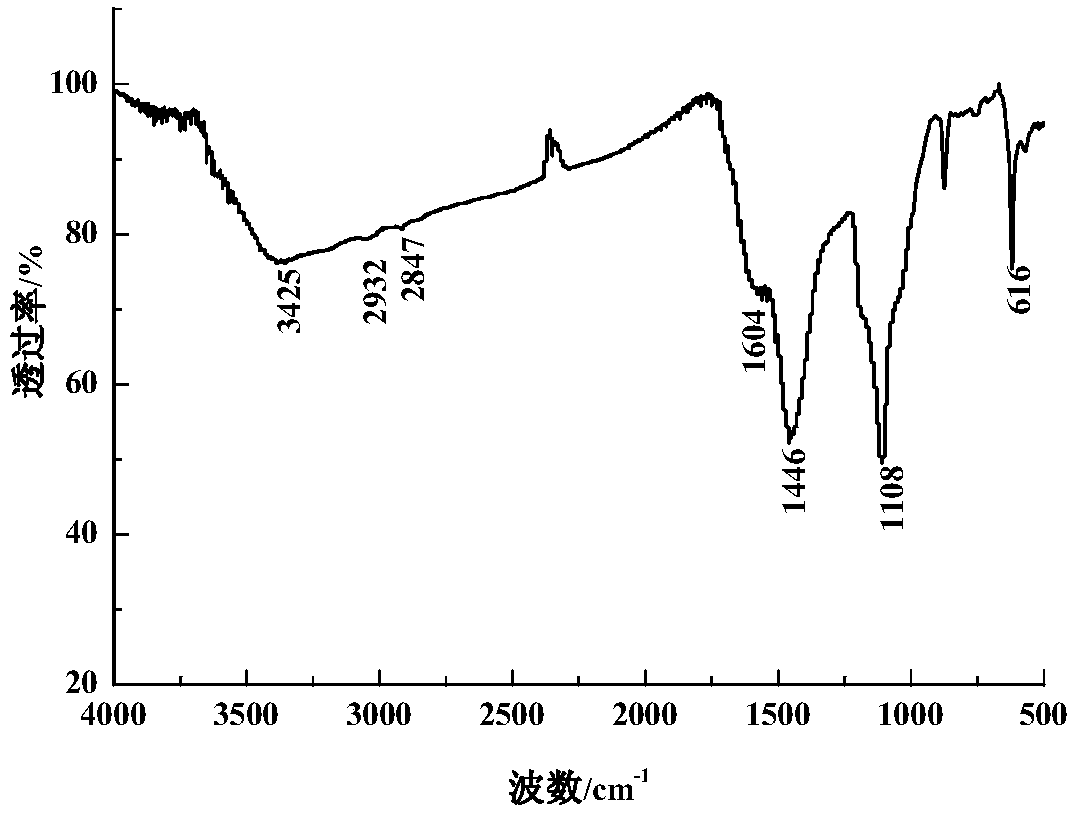
The invention discloses a method for studying influence of biological carbon on cadmium contaminated soil properties and a cadmium form. According to the studying method, three biochar is prepared byusing hizikia fusifarme, rice straw and hickory shells as raw materials, adsorbing effects of the three biochar on cadmium in an aqueous solution are compared, and thus the best biochar which absorbscadmium is optimized. The optimized biochar of different dosages is applied into cadmium contaminated soil, changes of basic physical and chemical properties of the cadmium contaminated soil and the chemical form of the cadmium are measured, and passivation effects of the biochar on the physical and chemical properties of the actual cadmium contaminated soil and soil cadmium pollution are preliminarily discussed. The influence of the biochar on the physical and chemical properties of the actual cadmium-contaminated soil and the chemical form of the cadmium is studied. The effective-state Cd content of the soil is reduced, an exchanging state of the soil heavy metal Cd is promoted to be converted into a carbonate binding state, an iron and manganese oxide binding state, an organic binding state and a residue state, the bioavailability and ecological toxicity of the heavy metal Cd are reduced, and thus the harm of the heavy metal cadmium is greatly reduced.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Biological control agent for fusarium wilt and preparation and use method of biological control agent
ActiveCN102726454APromote growthImprove the effect of disease preventionBiocideAgriculture tools and machinesDiseaseSolanaceae
Owner:ENZYME ENG INST SHAANXI PROVINCE ACAD OF SCI
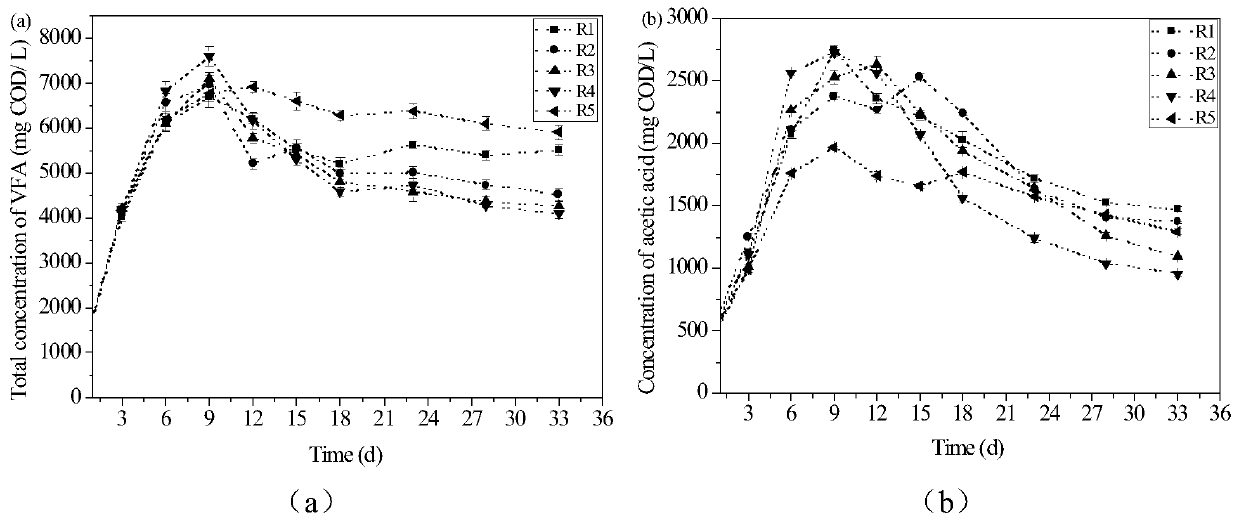
Method for simultaneously improving sludge anaerobic digestion efficiency and reducing ecotoxicity of heavy metals
ActiveCN110127972ALower pHIncrease productionWater contaminantsBiological sludge treatmentChemical reactionMicrowave
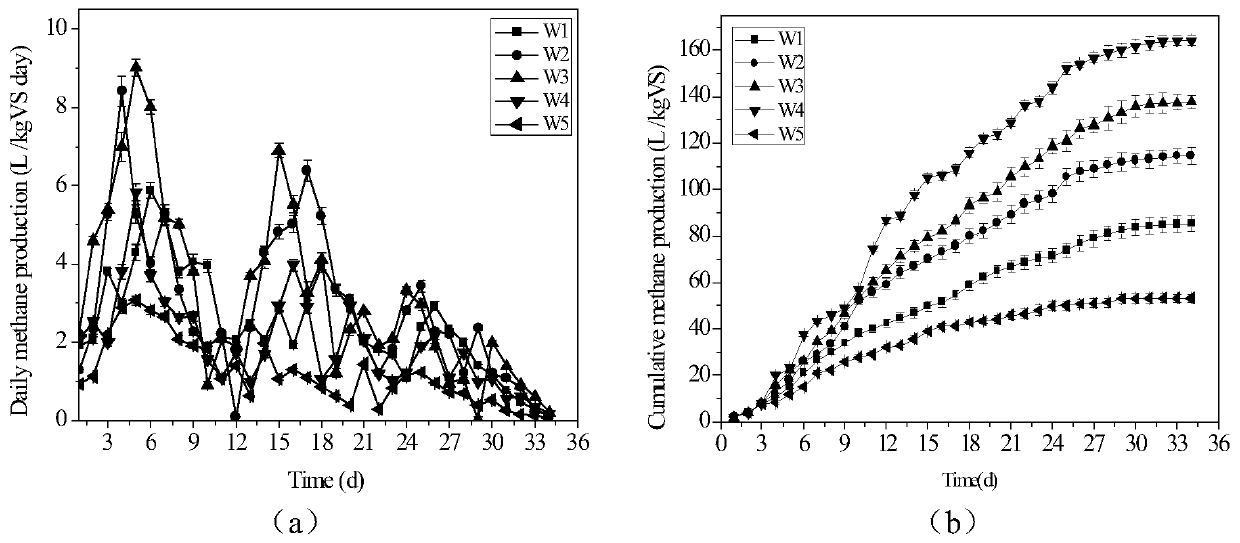
The invention relates to a method for simultaneously improving sludge anaerobic digestion efficiency and reducing the ecotoxicity of heavy metals. According to the method, after straws are activated with a ZnCl2 solution, straw biochar is prepared under a 550 DEG C high-temperature anaerobic condition, and further modification is performed by using an HCl solution and microwave; and by using modified biochar as carrier, a zero-valent nano-iron loaded modified biochar composite material HCl-FBC is prepared through a chemical reaction. According to the present invention, by adding the modified biochar composite HCl-FBC to the anaerobic digestion reactor at the initial stage of sludge anaerobic digestion, the organic matter conversion rate of sludge can be significantly increased, and the cumulative gas production of methane can be increased; HCl-FBC can easily increase the microbial diversity and the activity of the digested sludge and change the microbial community structure; and with the method, the sludge anaerobic digestion efficiency can be significant increased, the biogas production can be increased, the biological toxicity of the heavy metal in the digested sludge is effectively reduced, and the great significance is provided in the resource utilization of sludge and the reduction of the risk of sludge land use.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
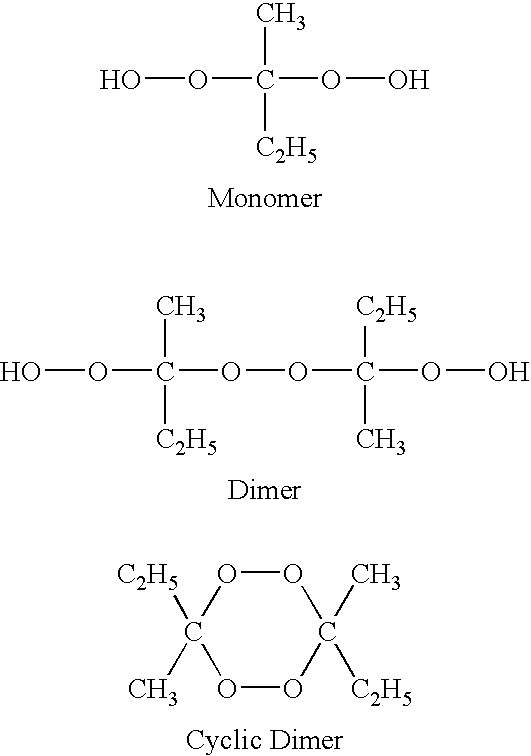
Use of dialkylketone peroxide as biocidal, sterilizing, antiseptic, disinfecting and anti-parasitic agent
The invention presented here establishes the use of a dialkyl ketone peroxide as a sterilizing, antiseptic, disinfecting and anti-parasitic agent, with no apparent toxicity nor ecotoxicity, and a very wide spectrum of activity in terms of the type of organisms on which it acts (bacteria, virus, fungi, spores, mycobacteria, protozoa, algae, prions, arachnids, mites, insects, etc.), and in terms of the type of applications in which it can be employed (human and animal therapy, hygiene, packing, medical and industrial instruments, sanitary surfaces and healthcare environments, premises, surfaces in general, industrial installations, refrigeration towers, sanitary hot water systems, purification of drinking water for human or animal consumption, etc.). Likewise, the current invention illustrates the use of a composition comprising such dialkyl ketone peroxides. Finally, the invention presented here provides a method of sterilisation, disinfection, asepsia or deparasitisation that involves the application of said composition.
Owner:NEOCHEMICAL DESARROLLOS AVANZADOS SA
Method for detecting acute biological toxicity of sewage
InactiveCN102175606AReduce distractionsGuaranteed stabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by optical meansSample waterSewage
The invention specifically relates to a method for detecting acute biological toxicity of sewage, belonging to the field of environmental water detection. A method for accurately detecting the acute biological toxicity of a sewage sample can be established by the following steps of: extracting and concentrating organic matter in a sewage sample, removing the interference of inorganic matter, and finally detecting by using fresh water luminous bacteria Qinghai vibrio Q67. The method can provide accurate final results, is stable and has good reproducibility. The method is the effective improvement of the traditional method.
Owner:XI'AN UNIVERSITY OF ARCHITECTURE AND TECHNOLOGY
Sewage flocculant
InactiveCN104843841APromote degradationLow ecotoxicityWater/sewage treatment by flocculation/precipitationSludgeMolybdenum chloride
The invention relates to the technical field of sewage treatment, in particular to a sewage flocculant. The flocculant consists of the following components in parts by weight: 12-25 parts of poly-aluminum calcium chloride, 5-15 parts of ferric chloride, 2-10 parts of aluminum potassium sulfate, 2-8 parts of sodium carboxymethylcellulose, 1-6 parts of sodium hypochlorite, 10-30 parts of poly-molybdenum chloride, 10-20 parts of diatomite, 10-20 parts of zeolite and 0.01-0.05 part of additives. The sewage flocculant has the beneficial effects that the obtained flocculant is good in degradability, low in ecotoxicity, free of stimulation on human bodies, obvious in flocculation effect on the treatment of various complex sewage and high in cost performance for dehydration of sludge; the sewage flocculant has the characteristics of no toxicity and residue for human bodies, good flocculation effect and wide application range.
Owner:ZHANGJIAGANG SHANMU NEW MATERIAL TECH DEV
Bacillus subtilis bacterial strain Xi-55 and its preparing method
InactiveCN1580238AGood control effectNo pollution in the processBacteriaMicrobiologyBacterial strain
The invention publishes a kind of dull grass Bacillu subtilis atrain, Xi-55(CGMCCNo.1070), and its preparation method. The strain can well restrain murrain germ in paddy. used to prevent and cure paddy murrain, it has no pollution and no residual and better security. Its preparation is easier, the fermentation cycle is shorter, cost is lower and it is easier to be stored. Thus, it is more convenient for agriculture.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION SICHUAN ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Water and waste water purification method for improving reactivity of zero-valent iron through magnetic field pretreatment
InactiveCN103332766AIncrease corrosion rateHigh reactivityWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsPurification methodsPollution
The invention belongs to the technical field of water and waste water treatment, and relates to a water and waste water purification method for improving reactivity of zero-valent iron through magnetic field pretreatment. The method is characterized by pretreating the zero-valent iron by utilizing the magnetic field, and adding the pretreated zero-valent iron into a relevant reactor for purifying the water or waste water. The method aims at the application of the zero-valent iron in environment pollution improvement. The zero-valent iron is pretreated in the magnetic field, and a passive film on the surface of the zero-valent iron is destroyed, so that the corrosion rate of the zero-valent iron can be accelerated, and the removal rate of the contaminant can be improved. The method can be used not only for improving the reactivity of unused zero-valent iron but also for improving the reactivity of used zero-valent iron with the passive film on the surface. Compared with the prior art, the method is simple to use, does not consume any chemical substance, and is environment-friendly and energy-saving, after the reaction, no toxic metal ions are left, and the method has no ecotoxicity.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
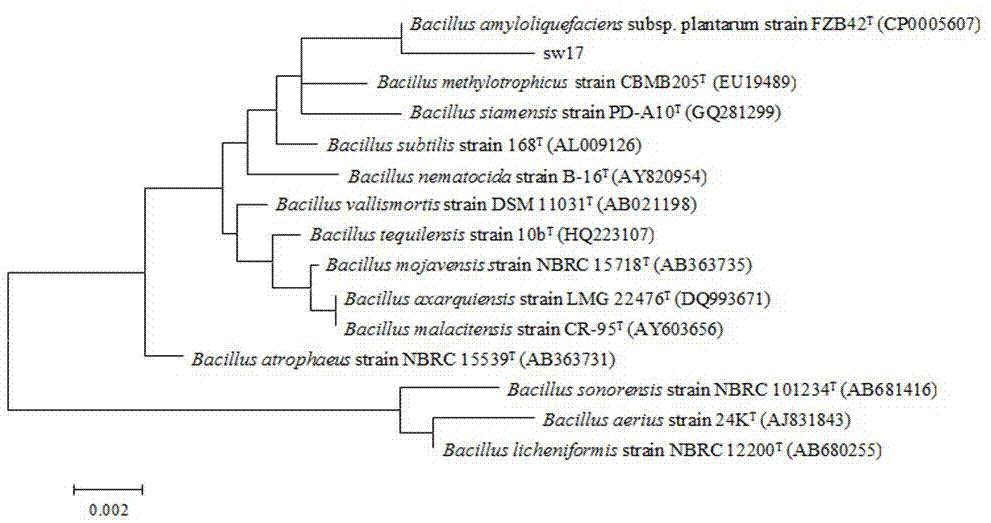
Bacillus amyloliquefaciens for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea in plants and application of bacillus amyloliquefaciens
InactiveCN107338207APromote colonizationGood biological control effectBiocideBacteriaKnema cinereaPlant disease
The invention relates to bacill us amyloliquefaciens sw17 for preventing and treating botrytis cinerea in plants and an application of the bacillus amyloliquefaciens. The bacterium (the bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17) is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with preservation number of CGMCC No.14365; and the bacterium can take an inhibitory effect on gray mold of strawberry, gray mold of tomato and gray mold of cucumber caused by botrytis cinerea Pers., with a bacteriostasis rate ranging from 62% to 74%. The bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17, which is provided by the invention is separated from rhizosphere soil of healthy fruit trees in a demonstration orchard, is free from ecological toxicity, high in safety and good in antibacterial effect, and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17 is simple in culture and short in cycle; and the bacillus amyloliquefaciens sw17 has a quite broad application prospect in biological control of plant diseases.
Owner:MICROBIOLOGY INST OF SHAANXI
Paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof
The invention discloses a paenibacillus polymyxa strain and application thereof. The strain belongs to paenibacillus polymyxa strains YT9, and the preservation number of the strain is CGMCC NO.15958.The separated strain not only has a strong inhibition effect on phytophthora sojae but also has a great antagonism effect on plant pathogenic oomycetes and phytopathogenic fungi, wherein the plant pathogenic oomycetes include phytophthora capsici, phytophthora nicotianae and the like, and phytopathogenic fungi include wheat sheath blight bacteria, wheat root rot bacteria, cercospora personata, cercospora arachidicola and the like; the bacteriostatic effect on phytophthora sojae is the strongest, wherein the bacteriostatic rate reaches 86.27%+ / -1.62%. In addition, the paenibacillus polymyxa strain YT9 is separated from healthy soybean rhizosphere soil and is free of ecological toxicity, high in safety, wide in bacteriostatic spectrum, stable and lasting in bacteriostatic activity and easy to culture. The strain has a broad application prospect in biological control over plant diseases.
Owner:LUDONG UNIVERSITY
Method for detecting ecotoxicity effect quantification of low-dose polluted soil
InactiveCN101907619ASensitive concentration decreasedOvercome limitationsEarth material testingBiologyLow dose
The invention discloses a method for detecting the ecotoxicity effect quantification of low-dose polluted soil, comprising the following steps of: averagely dividing a detection device into six avoiding grooves by using waterproof partition boards; preparing contaminated soil and adding the contaminated soil in the detection device; equivalently adding 10-20 soil test animals in each avoiding groove and cultivating at constant temperature; calculating the avoiding percentage of earthworms in the soil; establishing the dose-reaction relationship between different concentrations of contaminants and the earthworm avoiding percentage by using a linear model fitting method and preparing a standard curve; and placing the field adopted contaminated soil in one of the avoiding grooves, calculating the avoiding reaction of the soil test animals and calculating the concentration of the contaminant. The invention has the advantages of simple operation, low cost, easy observation, short test period, high reaction sensitivity, relevance of a test ending point with the ecology and the like, is not only suitable for repairing and detecting the contaminated soil, but also can be used for carrying out quick risk screening and detection on the contaminated soil in emergency or sudden events.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Method for predicating embryotoxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants on early-phase life stage of zebra fish
ActiveCN105044317AAddressing non-reflective typical NSAID sewage biotoxicityBiological testingLife stageFish embryo
The invention discloses a method for predicating the embryotoxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants on an early-phase life stage of zebra fish. The method comprises the following steps: exposing zebra fish embryos in the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants which have equal logarithm space concentrations; recording the death rate and the aberration rate of the zebra fish embryos 7 days after exposing; and calculating by using SPSS software to obtain corresponding LC50 and teratogenetic EC50, which are used for evaluating the toxicity of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants. With the adoption of the method, the toxicity feature and the toxicity level of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants are subjected to an analytical test and quantitative description; and meanwhile, the method also can be used as an index for monitoring and evaluating the wastewater biological toxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and reference is provided for risk predication and evaluation of the potential biological toxicity of the pollutants in a water body.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Hand cleansing formulation
InactiveUS7410937B2Inorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsCosmetic preparationsNatural sourceFatty alcohol
This invention provides heavy-duty cleansers (HDHC), with a high level of biodegradability and little or no ecotoxicity, with a high level of efficiency and a maximum skin tolerance and no systemic toxicity. In the broadest aspect of the invention there is provided a cleansing formulation comprising 5 to 10% of one or more methylesters of vegetable saturated and / or unsaturated fatty acids which may be from several natural sources including sunflower seed oil, soybean oil, rape seed oil, or coconut oil. The formulation includes between about 10% to 30% of one or more surfactants and a preferred combination of surfactants includes at least one ethoxylated fatty alcohol, one alkyl polyoxyethylene glycol, one alkanolamide and one polymeric quaternary ammonium salt.
Owner:DEB IP
Bialkyl methyl ethoxyl quaternary ammonium salt and synthesis method thereof
ActiveCN101165045AShort reaction timeReduce the temperatureOrganic compound preparationAmino-hyroxy compound preparationSynthesis methodsToxicity
The present invention is one kind of bisalkyl methyl ethoxyl quaternary ammonium salt in the structure as shown and its synthesis process. The process has short reaction period, low temperature and low pressure; and the bisalkyl methyl ethoxyl quaternary ammonium salt has high biodegradability, low ecological toxicity and environmental compatability.
Owner:CHINA RES INST OF DAILY CHEM IND
Acyl-homoserine lactone compound and application thereof in environmental protection
ActiveCN106146378AEasy to makeNo secondary pollutionBiocideOrganic chemistryThiobacillus ferrooxidansHigh concentration
As existence of acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans on surface of metal sulfide ore in the form of a bio-membrane, dissolution-out of the metal is greatly improved, thereby forming acidic pit water in high concentration of heavy metal ions and further causing serious environment pollution. The invention discloses a compound which can inhibit formation of bio-membrane of the acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans. The compound, without influence on normal growth of the acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans, can inhibit the formation of the bio-membrane of the acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans, thus reducing the erosion speed of the acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans on the metal sulfide ore and significantly reducing generation of acidic heavy metal pit water in a sulfide mining area. Compared with a bactericide or an antibacterial agent for treating acidic heavy metal pit water pollution, the ecologic toxicity on environment of the compound is reduced to minimum during the treatment on the acidic heavy metal pit water pollution. The acidophilic thiobacillus ferrooxidans is free of drug resistance caused by the bactericide or the antibacterial agent.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
Method for measuring pollutant ecological toxic effect threshold concentration through microcosm periodical biomass
ActiveCN106501474AImprove reliabilityImprove accuracyTesting waterEcological environmentWater quality
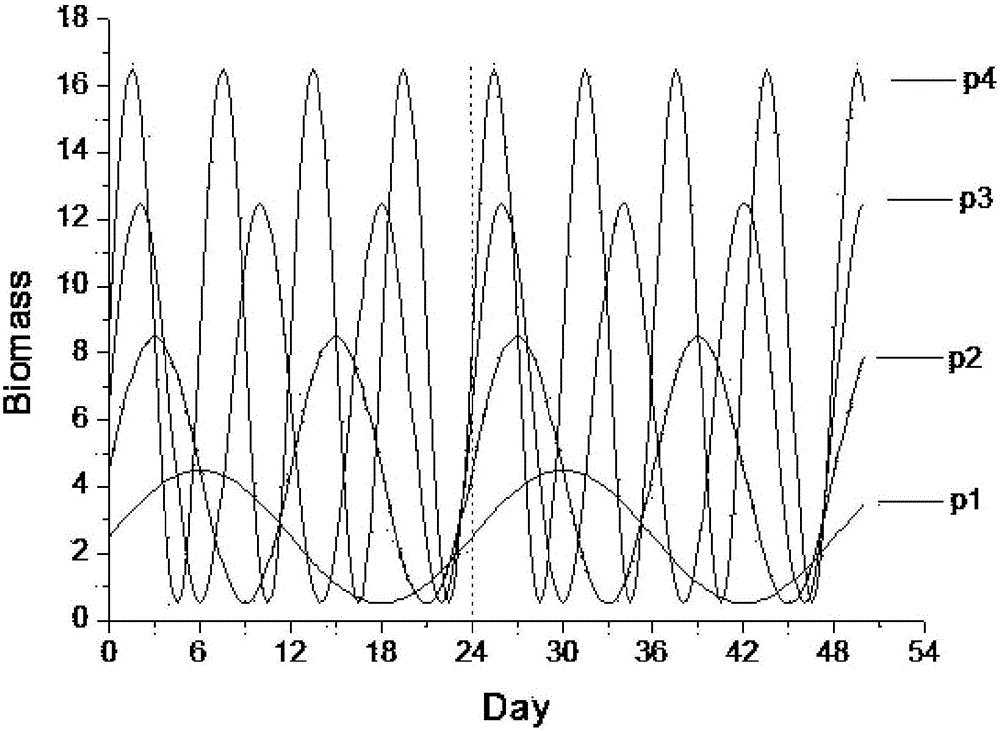
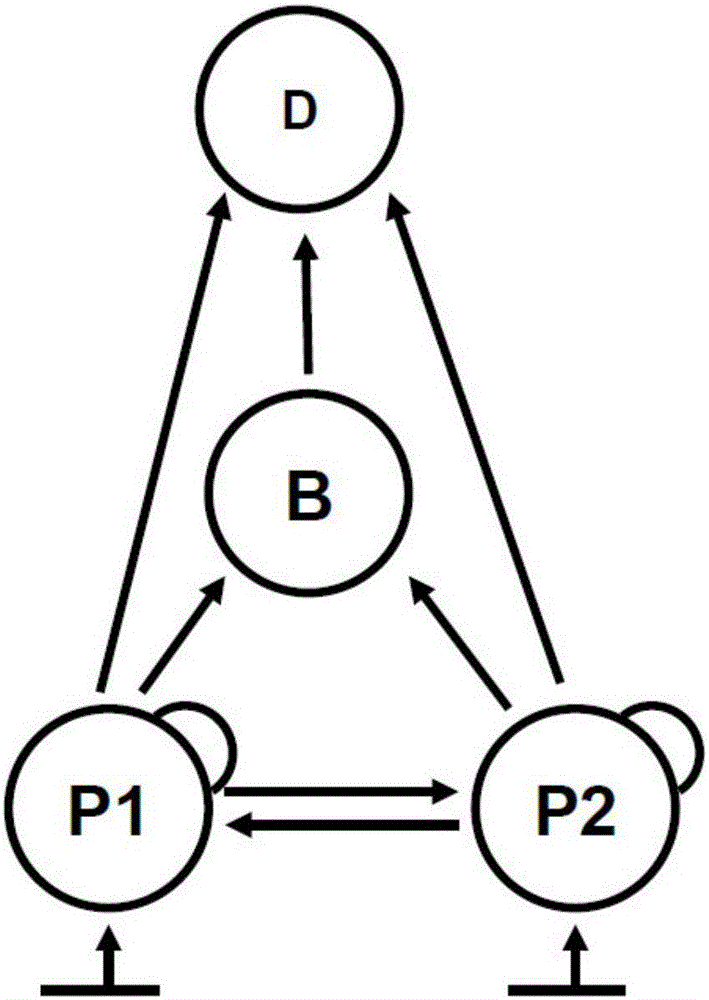
The invention discloses a method for measuring a pollutant ecological toxic effect threshold concentration through microcosm periodical biomass. According to the method, based on a population-level toxic effect testing result, a microcosm model is structured through inter-population ecological relation to correlate a population-level reaction endpoint with a community-level reaction endpoint; through the quantitative relation between population-level pollutant concentration and toxic effects, a quantitative relation between community-level pollutant concentration and the toxic effects can be structured; taking whether microcosm community periodical biomass at a certain pollutant concentration deviates from control microcosm community periodical biomass as threshold concentration criteria, the pollutant ecological toxic effect threshold concentration can be calculated. The method for measuring the pollutant ecological toxic effect threshold concentration through microcosm periodical biomass can help perfect pollutant water quality criteria deduction methods, lay a solid scientific foundation of water quality criteria setting, avoid environmental underprotection or overprotection caused by water quality criteria setting and ensure harmonic economic and ecological environment development.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
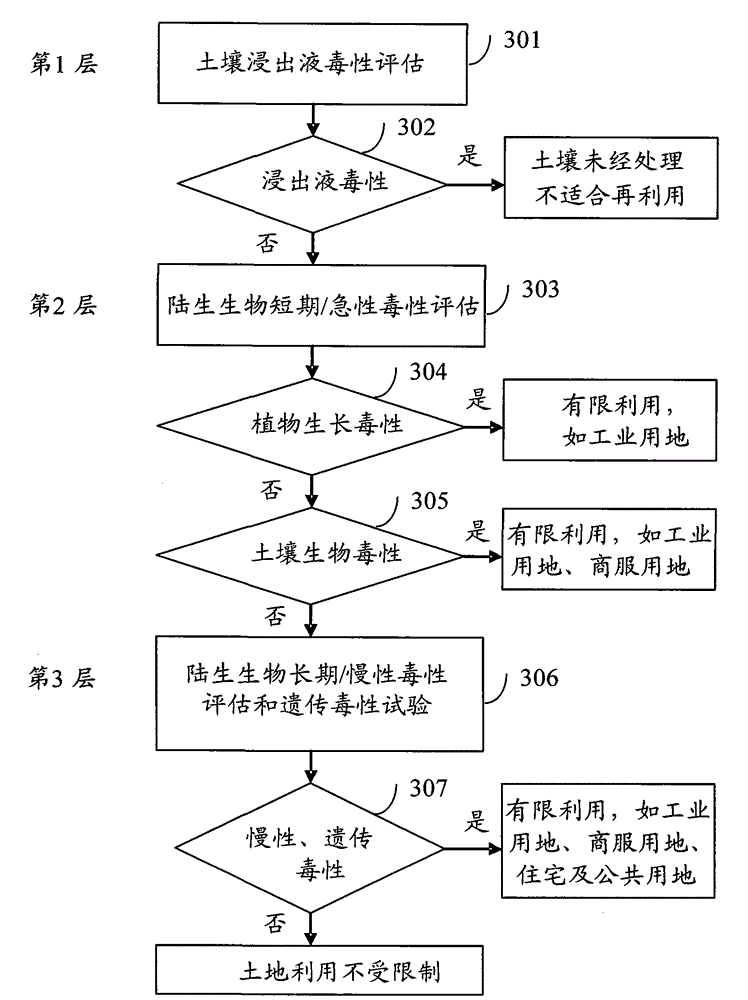
Method for diagnosing ecotoxicity of soil in polluted place, and apparatus thereof
InactiveCN105223334AReduce the number of trialsShort test timeEarth material testingContent distributionComputer science
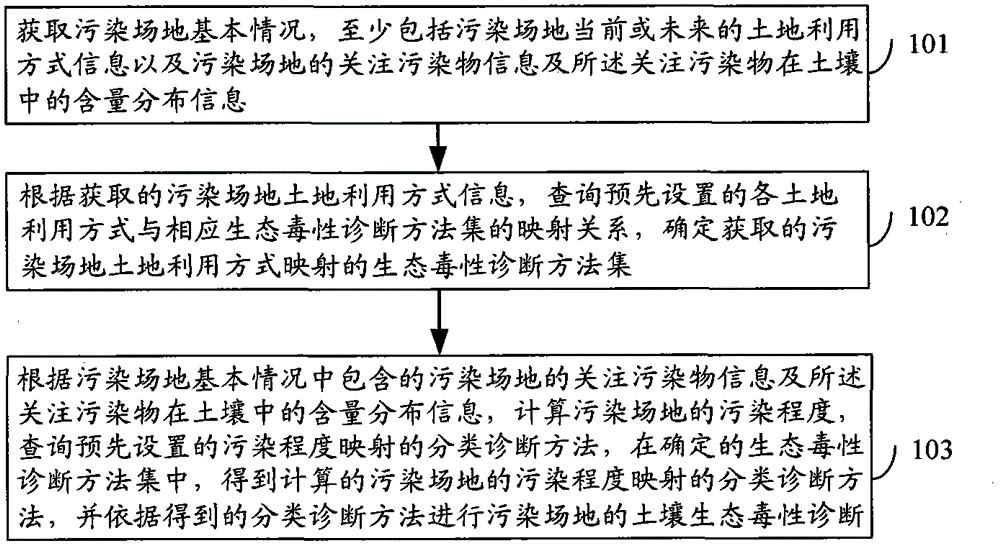
The invention discloses a method for diagnosing the ecotoxicity of soil in a polluted place, and an apparatus thereof. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring the basic condition of the polluted place; querying a mapping relationship between all preset land utilization modes and corresponding ecotoxicity diagnosis method sets according to the acquired polluted land utilization mode information to determine the ecotoxicity diagnosis method set mapping with the acquired land utilization mode of the polluted place; and calculating the pollution degree of the polluted land according to polluted land concerned pollutant information included in the basic condition of the polluted land and content distribution information of the concerned pollutants in soil, querying preset pollution degree mapped classification diagnosis methods, obtaining the classification diagnosis method mapping with the calculated pollution degree of the polluted land in the determined ecotoxicity diagnosis method set, and carrying out soil ecotoxicity diagnosis on the polluted land according to the obtained classification diagnosis method. The method and the apparatus are used to effectively improve the ecotoxicity diagnosis efficiency of soil.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
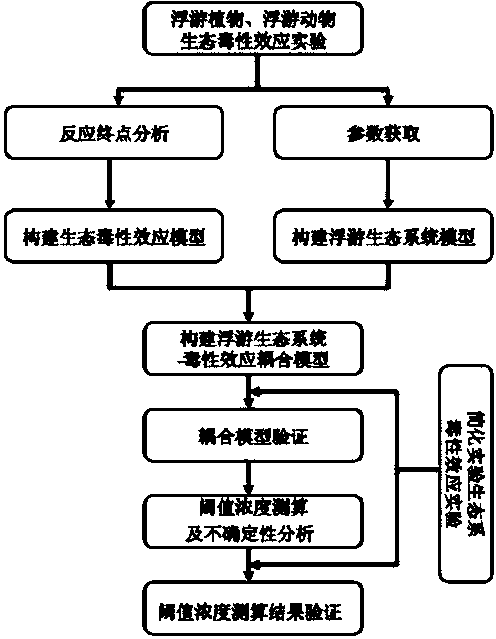
Method for measuring and calculating threshold concentration of ecological toxic effect of environmental pollutants
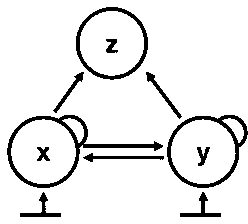
The invention discloses a method for measuring and calculating the threshold concentration of an ecological toxic effect of environmental pollutants. According to the method, on the basis of the experimental result of the toxic effect of biological single species, the sensitivity, reliability and stability of reaction endpoints are analyzed, the ecological relationship between populations is utilized for constructing an ecological system model, the multiple reaction end points which are in the different trophic levels and population levels are combined, then, an ecological system-toxic effect coupling model is constructed, and the threshold concentration of the ecological toxic effect of the pollutants is calculated by using the phenomenon whether ecological system asymptotic positive balance points (x*, y* and z*) in the certain pollutant concentration deviate from original balance points or not (namely whether the significant difference exists or not) as the criterion of the threshold concentration. According to the method for measuring and calculating the threshold concentration of the ecological toxic effect of the environmental pollutants, the ecological correlation between the ecological system populations is considered, the toxic effect measurement and calculation are carried out on the population level, and the result is more real and reliable.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF INFORMATION SCI & TECH
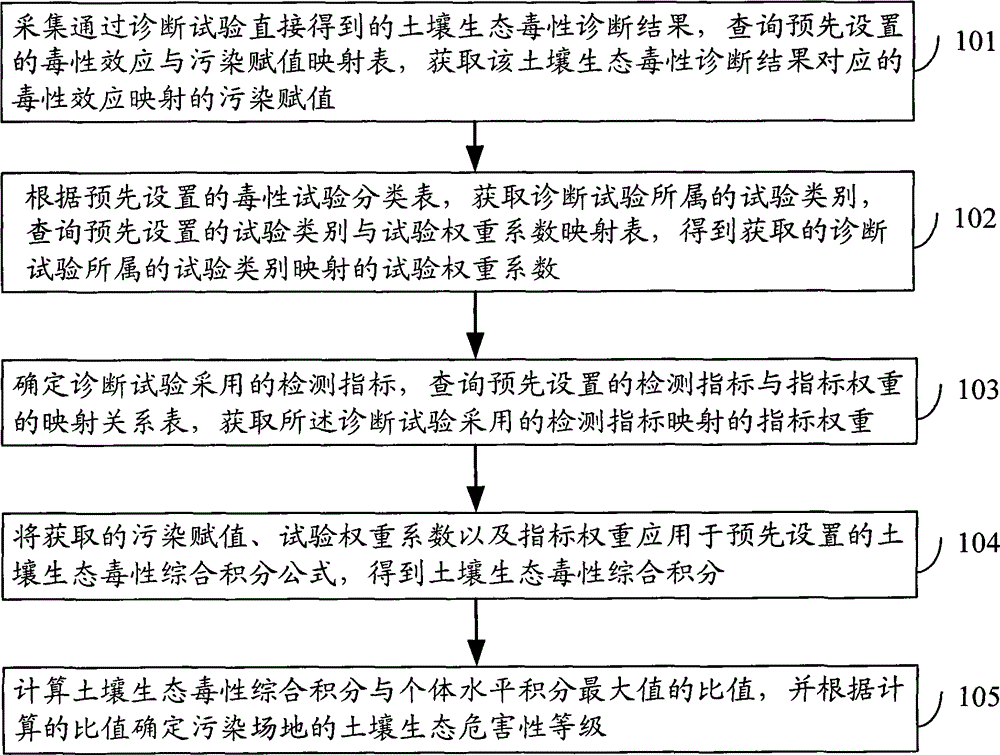
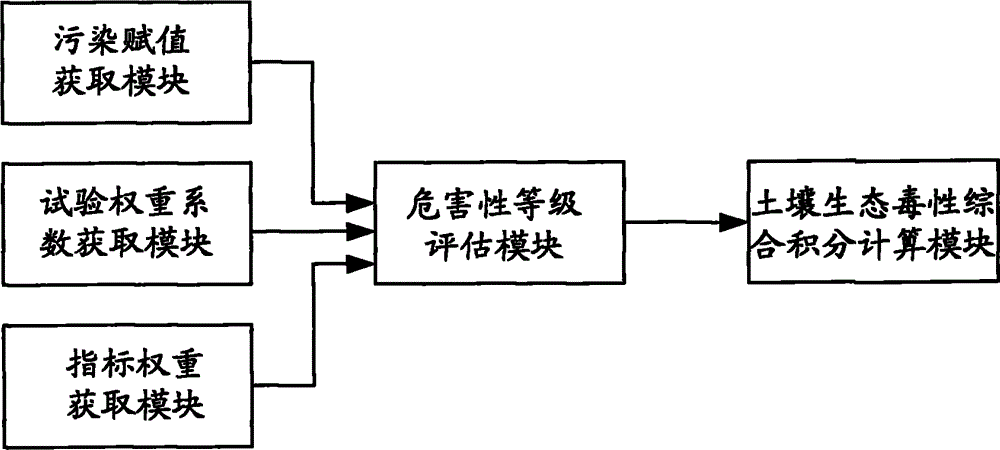
Method and apparatus for optimizing soil ecotoxicity diagnosis result of contaminated site
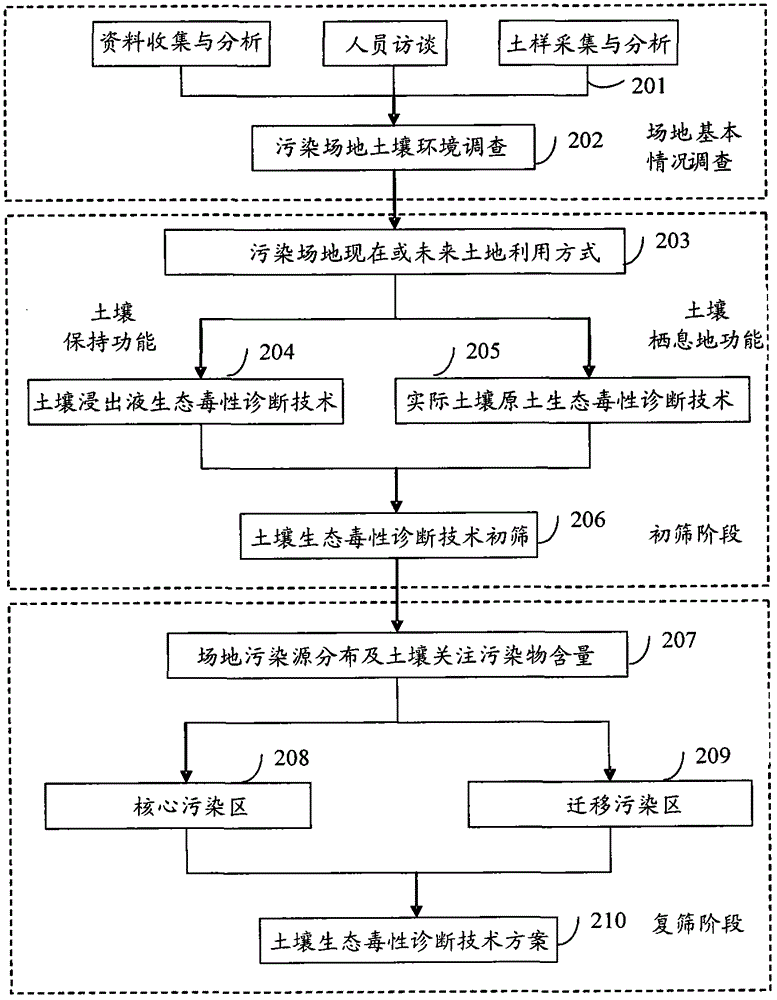
InactiveCN105303015AImprove accuracyReflect the actual pollution situationSpecial data processing applicationsWeight coefficientComputer science
The present invention discloses a method and an apparatus for optimizing a soil ecotoxicity diagnosis result of a contaminated site. The method comprises: acquiring a soil ecotoxicity diagnosis result, and searching a mapping table of toxic effects versus contamination values to obtain a contamination value mapping a toxic effect corresponding to the soil ecotoxicity diagnosis result; acquiring an experiment classification of a diagnostic experiment according to a toxicity experiment classification table, and searching for a mapping table of experiment classifications versus experiment weight coefficients to obtain an experiment weight coefficient mapping the experiment classification; determining a detection indicator used by the diagnostic experiment, and searching a mapping relationship table of detection indicators versus indicator weights to obtain an indicator weight mapping the used detection indicator; and according to the obtained contamination value, the experiment weight coefficient and the indicator weight, acquiring a soil ecotoxicity comprehensive score, calculating a ratio of the soil ecotoxicity comprehensive score to an individual level score maximum, and determining a soil ecological harmfulness level of the contaminated site according to the ratio. The application of the method and apparatus provided by the present invention can effectively improve accuracy of assessment of a contaminated site.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
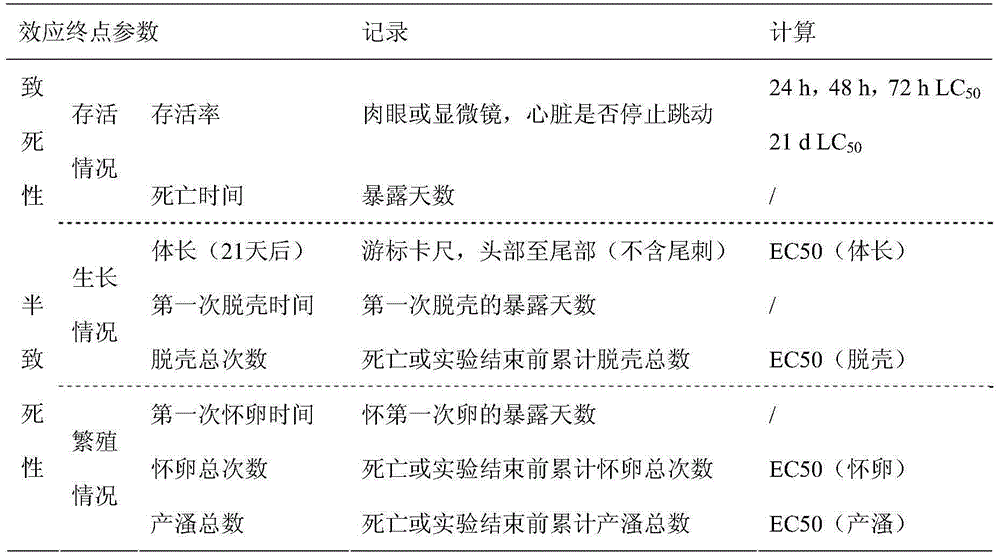
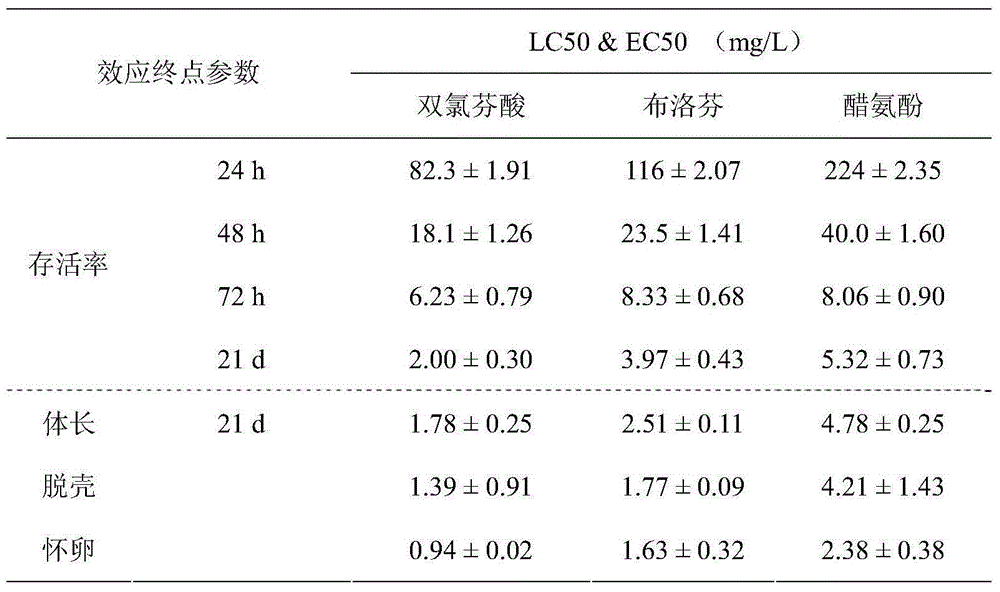
Method for predicting and evaluating toxicity of novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant based on daphnia magna toxicity
The invention discloses a method for predicting and evaluating toxicity of a novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant based on daphnia magna. According to the method, daphnia magna is exposed to the novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant with equal logarithm spacing concentration, the survival rates of daphnia magna generated when the daphnia magna is exposed for 24 h, 48 h and 72 h, and the survival rate, the body length, the total number of shelling and egg carrying times and the total daphnia magna producing amount of the daphnia magna exposed for 21 d are recorded respectively; corresponding 24 h LC50, 48 h LC50 and 72 h LC50 are obtained through calculation of SPSS software and used for evaluating acute toxicity, and corresponding 21 d LC50, body length EC50, shelling EC50, egg carrying EC 50 and daphnia magna producing EC50 are obtained and used for evaluating chronic toxicity; thus, the toxicity characteristic and the toxicity level of the novel non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent pollutant are analyzed, tested and quantitatively described, meanwhile can serve as indexes for monitoring and evaluating biotoxicity of non-steroid anti-inflammatory agent sewage, and can provide reference for predicting and evaluating potential ecotoxicity risks of the pollutant in water.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
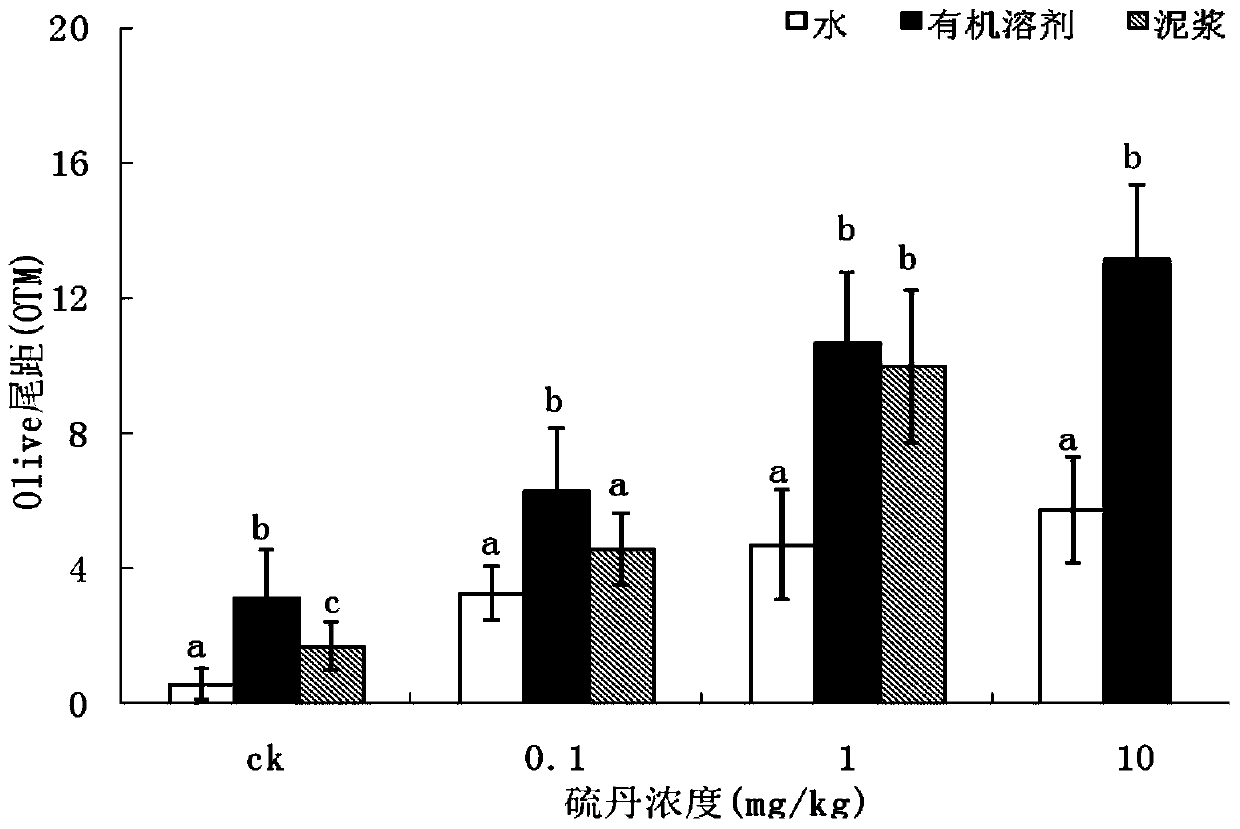
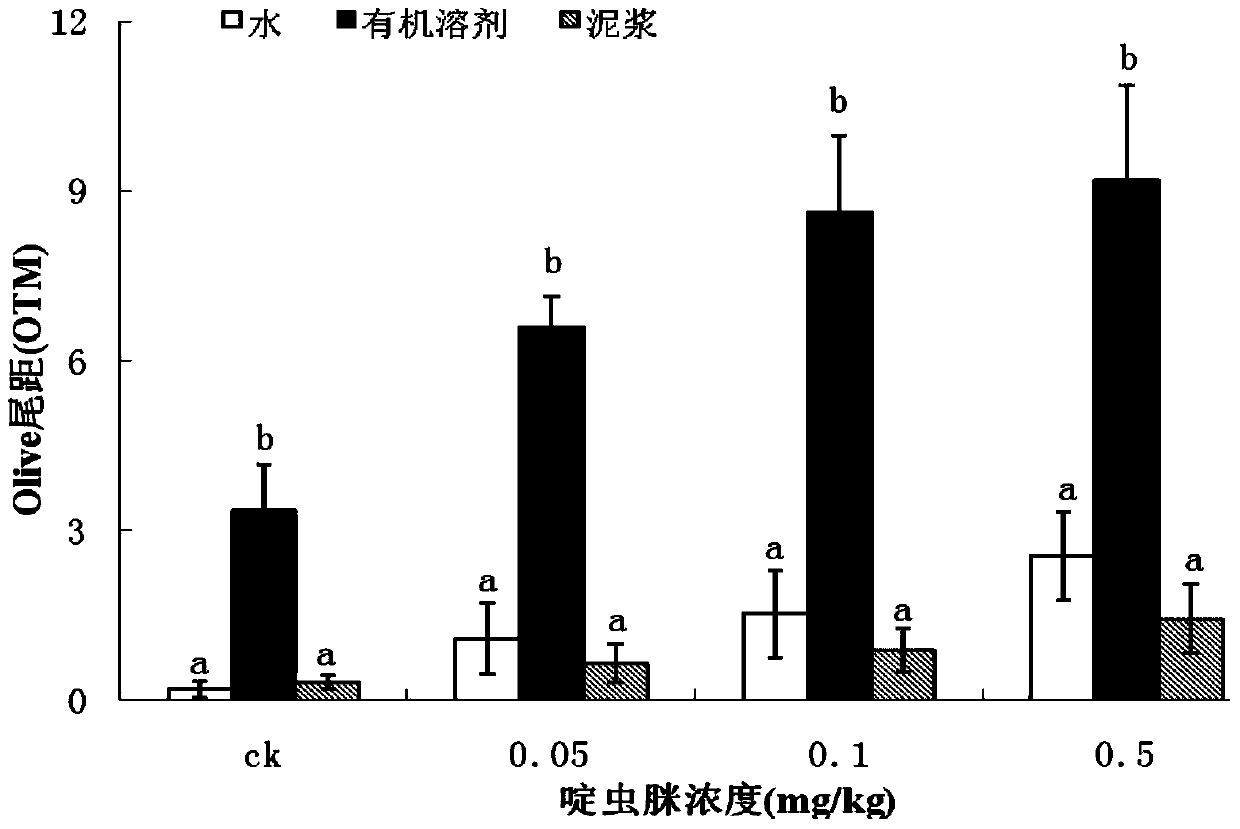
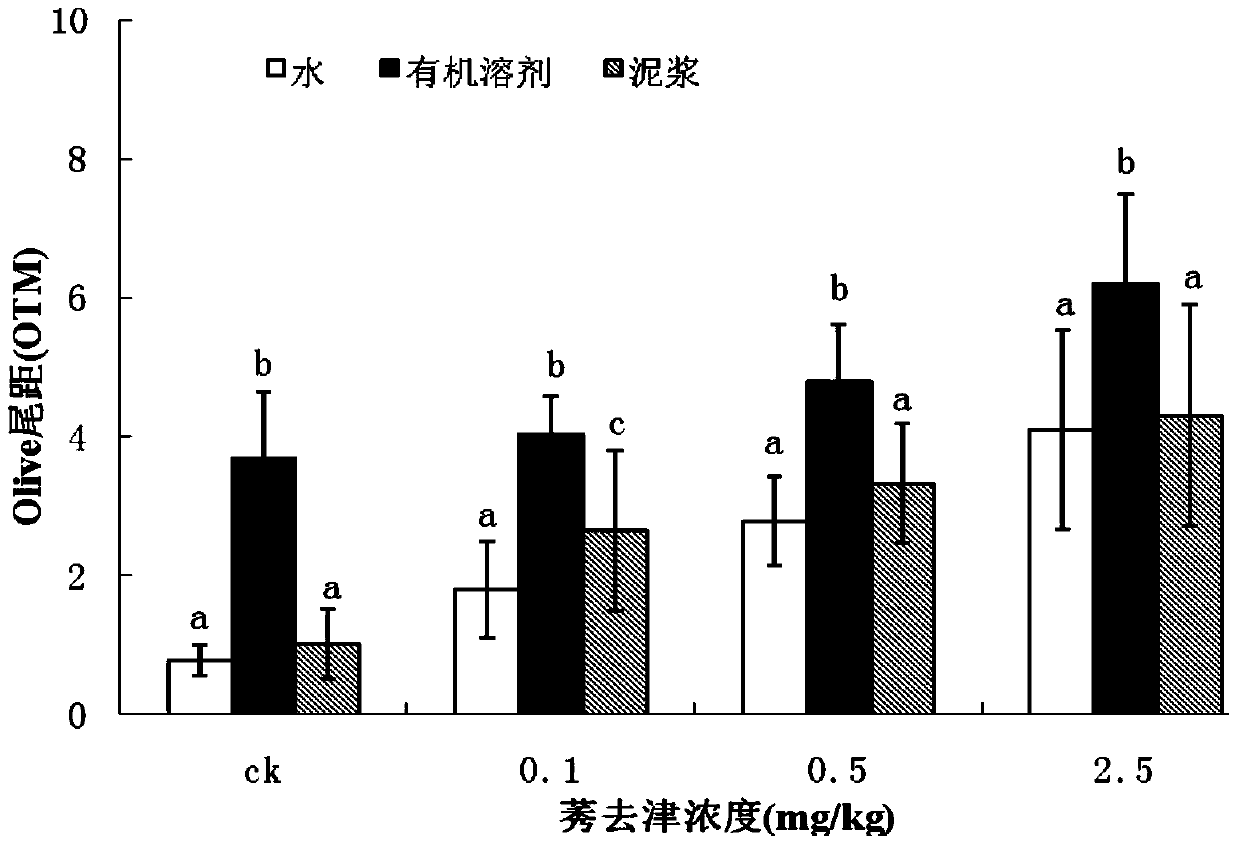
Set of methods suitable for evaluating toxicity changes of pesticide residues in soil
The invention relates to a set of methods suitable for evaluating toxicity changes of pesticide residues in soil. According to different properties of the pesticide residues in the soil, the set of methods comprises an organic solvent extraction method, a deionized water extraction method and a slurry direct exposure infection method respectively; through an earthworm comet assay and a broad bean micronucleus test, soil ecotoxicity is detected on the basis of double indexes; the set of methods suitable for evaluating the toxicity changes of the pesticide residues in the soil is established, thereby providing a technical support for evaluating influence of toxicities of the pesticide residues on the environment and human health. The set of methods is simple and feasible, high in repeatability and wide in applicability and can be applied to pesticides with different polar properties; by the set of methods, the subsequent determination of the ecotoxicity is facilitated; the set of methods has a relatively great practical application value.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Endosulfan degradation bacterium JBW4
ActiveCN102827789ADegradation safetyPromote degradationBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentMicrobiology
The invention provides an endosulfan degradation bacterium JBW4 (Alcaligenes faecalis.JBW4), which was preserved in the China center for type culture collection (CCTCC) on May 24th, 2012 with the preservation serial number being CCTCC No:M2012181. The endosulfan degradation bacterium JBW4 is prepared to be bacteria suspending liquid, and the bacteria suspending liquid is applied to the degradation of endosulfan in the soil in a mode that the bacteria suspending liquid is directly added into the soil, so that endosulfan remained on objects of water bodies, soils and the like can be safely, effectively and quickly degraded, genetic toxicity and ecotoxicity of the endosulfan to the environment are reduced and the actions of restoring the soil polluted by the endosulfan and protecting the ecological environment are exerted. The bactericide of the strain is simple in preparation process, low in cost and high in efficiency, and has good application prospect; and moreover, the secondary pollution is avoided.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for determination of ecotoxicity of soil contaminated by residues of organophosphorus and pyrethroid insecticides
InactiveCN109580913AImprove diagnostic efficiencyShorten detection timeBiological material analysisEarth material testingPesticide residueOrganism
The invention belongs to the field of environmental protection, and particularly relates to a method for determination of the ecotoxicity of soil contaminated by residues of organophosphorus and pyrethroid insecticides. The method is characterized in that eisenia foetida is selected, and after being domesticated, the eisenia foetida is subjected to an exposure test in the soil to be tested; through the steps of protein extraction, SDS-PAGE protein isolation and Western Blotting detection purity analysis, if a test group and a control group are significantly different and p is less than 0.05, it is indicated that pesticide residues in the soil to be tested are toxic to soil biological growth; and if no significant difference exists, the soil to be tested is not toxic to growth. The method is suitable for early diagnosis and early warning of contaminated soil, greatly shortens the determination time of ecotoxicity, and effectively improves the diagnostic efficiency of soil ecotoxicity.
Owner:SOUTHWEST FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
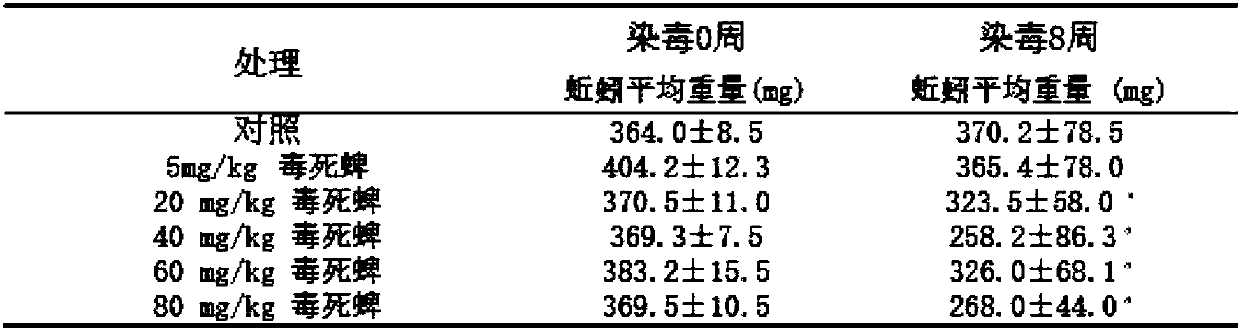
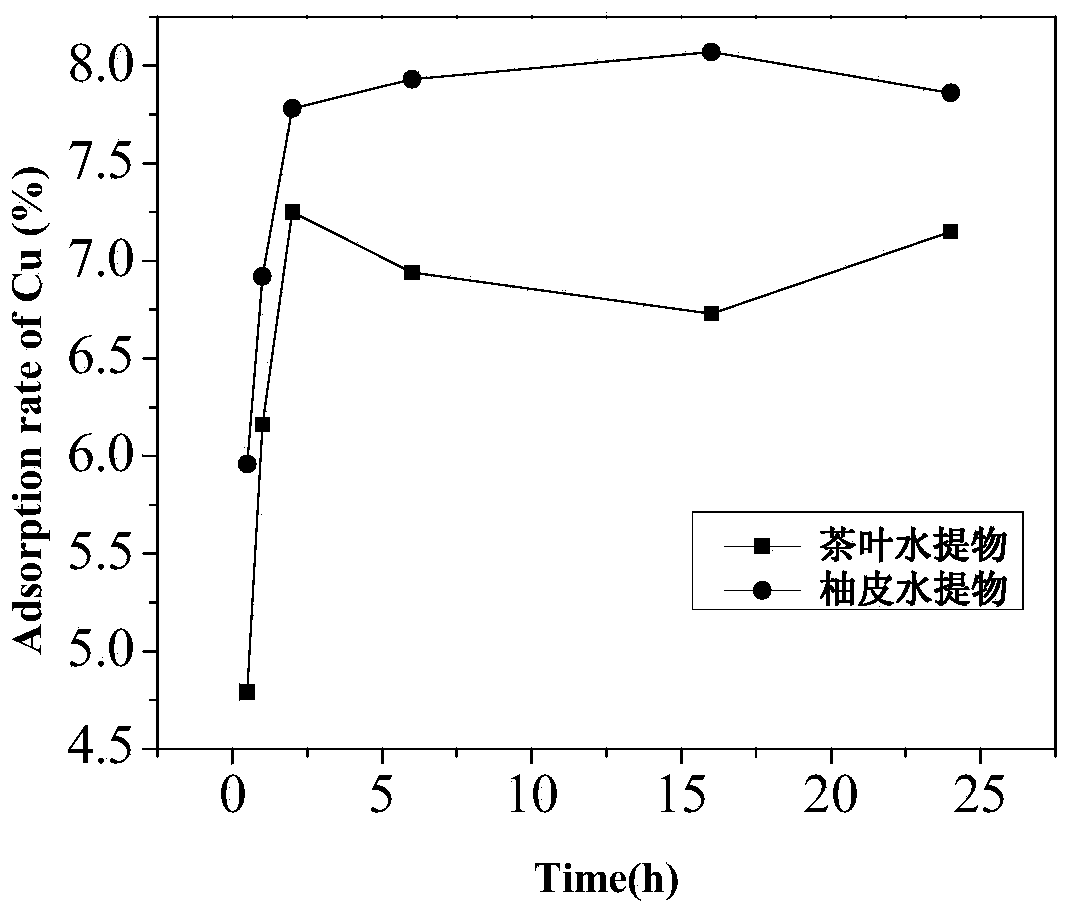
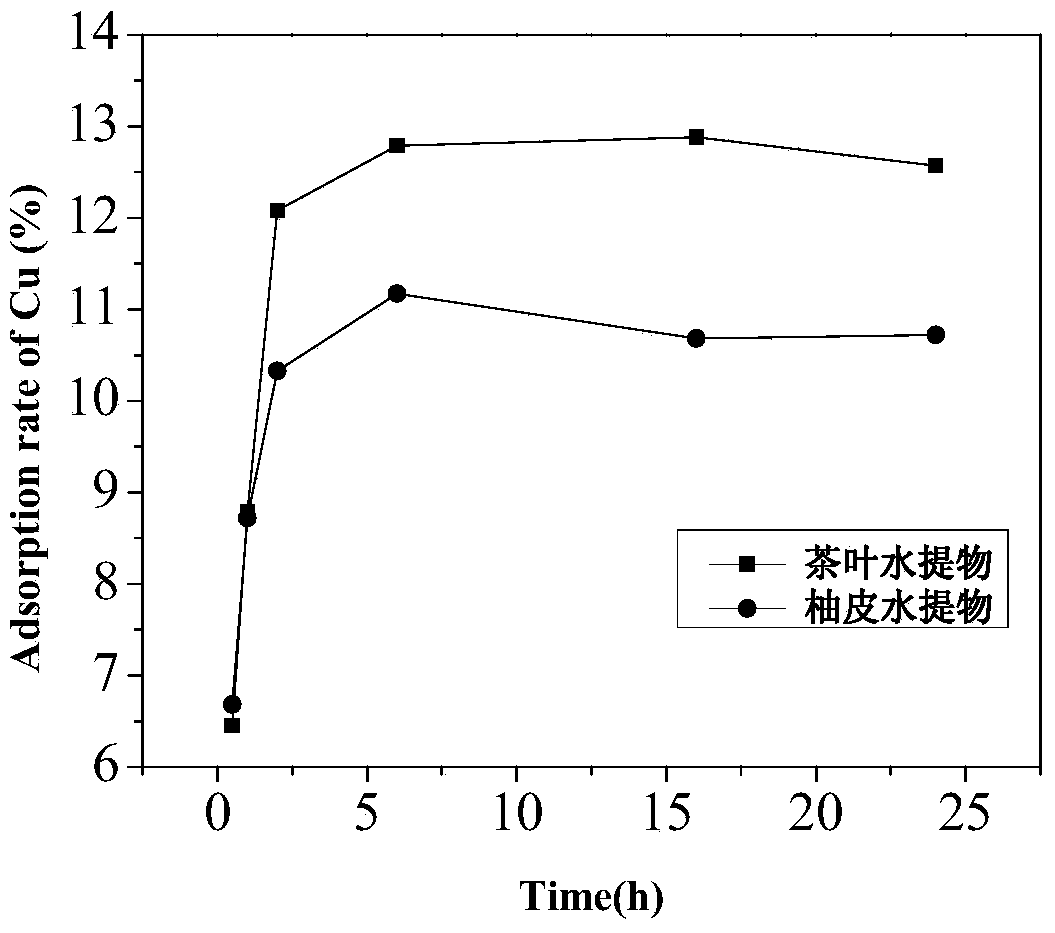
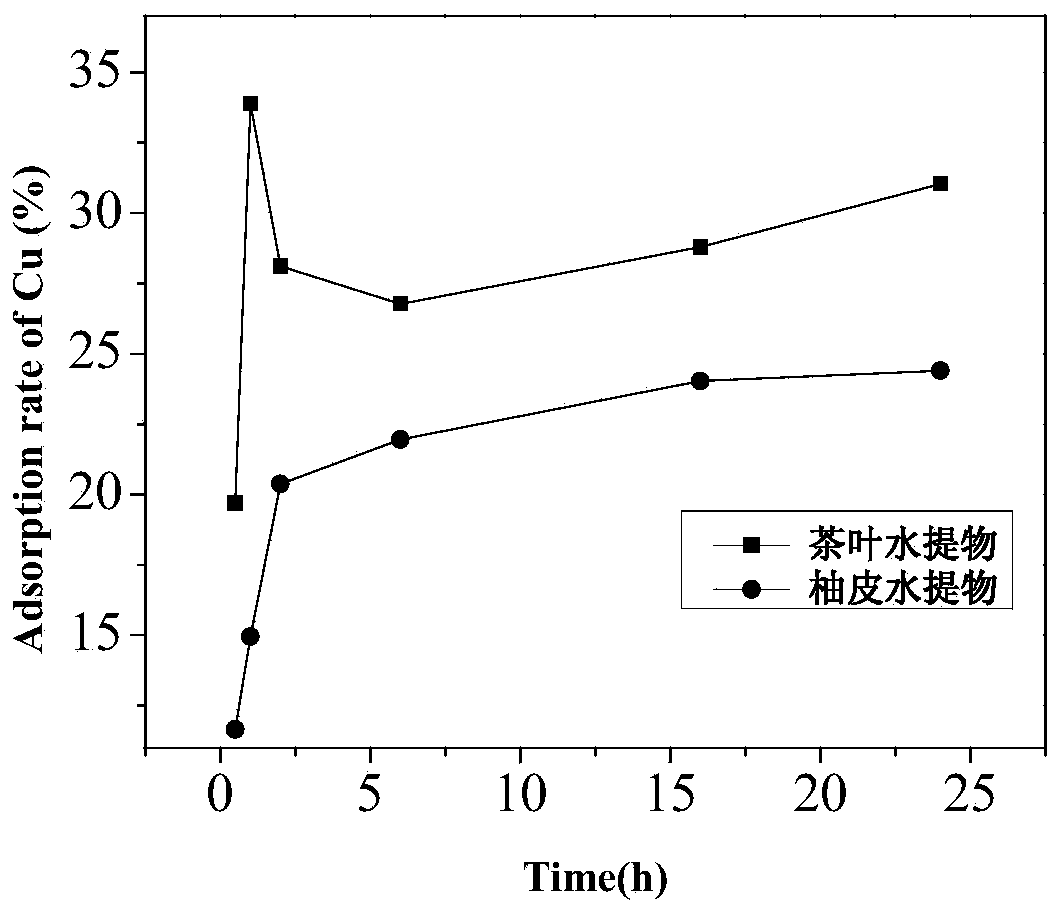
Application and adsorption method of tea water extract or shaddock peel water extract for adsorbing heavy metal ions
InactiveCN103922435AImprove adsorption capacityLow costWater/sewage treatment by sorptionPlastics industryWastewater
Owner:安徽省应用技术研究院
Perspiration and odor control compositions
The present disclosure is directed to a cosmetic composition for controlling perspiration and odor. Despite being free of volatile silicones—which have garnered a bad reputation due to their ecotoxicity and bioaccumulability in aquatic species—the composition of the instant disclosure replicates the textural and sensorial benefits provided by the use of volatile silicones like cyclotetrasiloxane, cyclopentasiloxane and cyclohexasiloxane.
Owner:LOREAL SA
Marine fish water ecology toxicity test method
The invention discloses a marine fish water ecology toxicity test method. The method comprises the following steps of selecting gobies as tested fish species and domesticating in standard water which has a same water quality condition as a tested water sample; preparing a stock solution of the water sample to be tested; selecting a concentration gradient range through acute toxicity and chronic toxicity trial tests of the gobies, setting a concentration gradient with a small difference, taking sea water as a contrast group, and taking the water sample to be tested as a test group; simultaneously, carrying out acute toxicity and chronic toxicity tests of the gobies, recording changes in the gobies and the environment, carrying out variance analysis on data, and drawing a mortality curve of the gobies; and determining water quality toxicity through combining a physical condition of the gobies and water body index changes. Problems that current domestic research on a fish toxicity test is relatively simple, and there is aquatic ecotoxicity test method suitable for a salt-containing condition are solved.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Method for quickly evaluating ecological toxicity of petroleum-contaminated soil
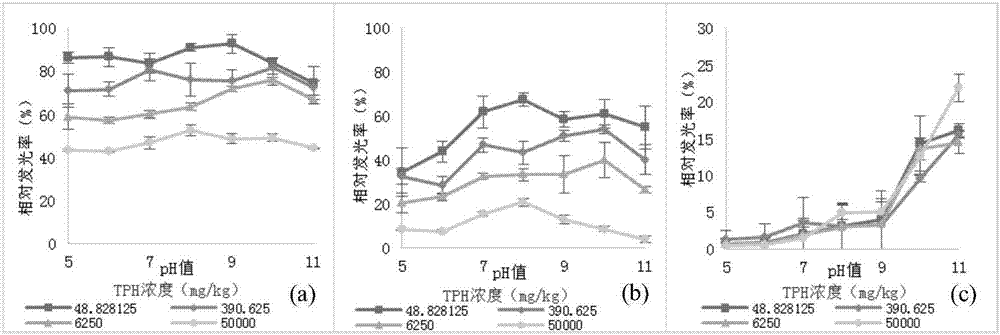
InactiveCN107091833AStable responseResponsiveChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceEcotoxicityContaminated soils
The invention provides a method for quickly evaluating ecological toxicity of petroleum-contaminated soil. The method comprises the following steps: 1) with rhamnolipid solution as an extracting agent, extracting petroleum pollutants in to-be-detected petroleum-contaminated soil, thereby acquiring a to-be-detected petroleum pollutant extracting solution; 2) mixing the to-be-detected petroleum pollutant extracting solution with luminous bacteria and reacting, and meanwhile, with a NaCl solution as contrast, mixing the NaCl solution with luminous bacteria and reacting for the same time, respectively recording the real-time luminescence volume of the test sample and the contrast and calculating the relative luminous emissivity (%) of the sample; 3) evaluating the ecological toxicity level of the soil sample according to the relative luminous emissivity of the sample. According to the invention, the luminous bacteria are selected as induction bacteria for soil petroleum contamination and a quick detection technology and an evaluation standard for the ecological toxicity of petroleum-contaminated soil are established in the manner of selecting bacteria capable of stably, sensitively and quickly reflecting the change in petroleum contamination concentration in the environment, regarding the light intensity thereof as a detection index and constructing the relation models of light intensity-petroleum contamination concentration and petroleum contamination concentration-toxicity.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Uniform lighting device for alga culture based on aquatic organism ecotoxicity evaluation
ActiveCN105861302ADisadvantages that changing the intensity cannot meet the experimental requirementsPrevent excessive growth on one side, that is, uneven growthBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsEcotoxicityAlgae
The invention discloses a uniform lighting device for alga culture based on aquatic organism ecotoxicity evaluation. The uniform lighting device comprises an incubator body, wherein an automatic temperature control system is arranged inside the incubator body; a plurality of net plate layers parallel to one another are arranged inside the incubator body through a height adjusting device; the net plate layers are structural net layers with an inner cavity consisting of a lower net plate layer and an upper net plate layer; a plurality of alloy transverse rods perpendicular to the incubator body are uniformly arranged on the upper surface of the upper net plate layer of the net plate layers; a plurality of stripy light sources which are arranged uniformly are arranged on the lower net plate layer inside the net plate layer; the positions and the number of the stripy light source correspond to those of the alloy transverse rods. By adopting the uniform lighting device for alga culture based on aquatic organism ecotoxicity evaluation, the lighting condition for acute toxicity of algae can be controlled, and thus culture in an incubator can be subjected to effective light sources of same intensity.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Bacillus thuringiensis strain YN-2-2 and application thereof
The invention discloses a bacillus thuringiensis strain YN-2-2 CGMCC No.19316, which is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on Jan.17,2020, wherein the accession number is CGMCC No.19316, the preservation date is Jan.17,2020, and the address of the preservation unit is No.3, Yard 1, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. The bacillus thuringiensis strain YN-2-2 provided by the invention has the advantages of simple culture, short period, no ecological toxicity, abundant available carbon sources, high salt tolerance, wide tolerable PH range and capability of effectively inhibiting growth of pathogenic bacteria of potato deep scab.
Owner:NINGXIA UNIVERSITY +1
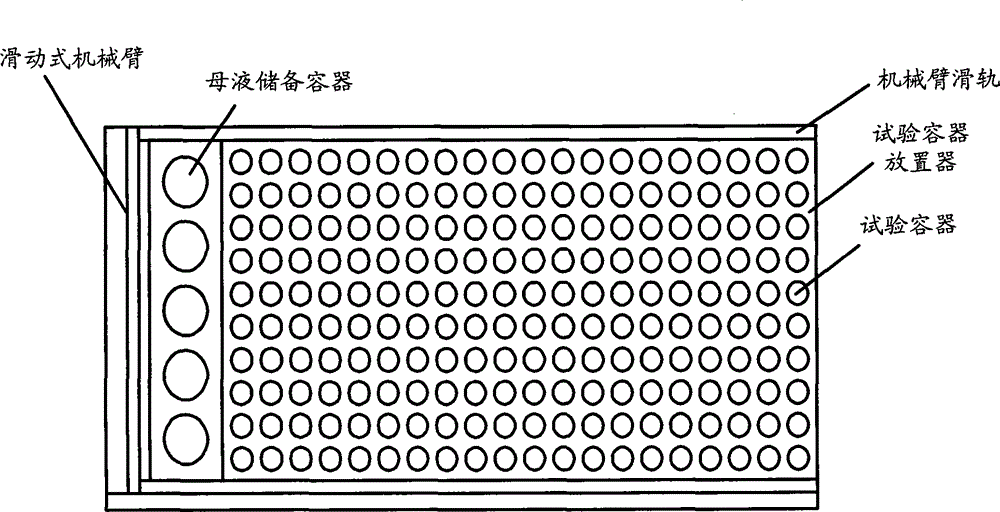
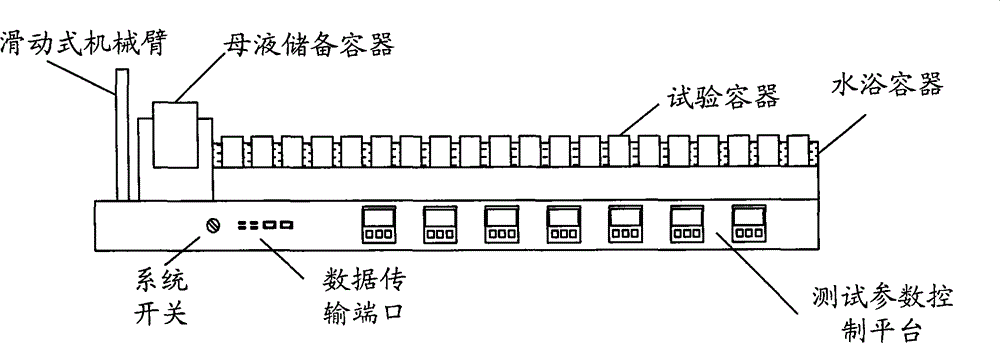
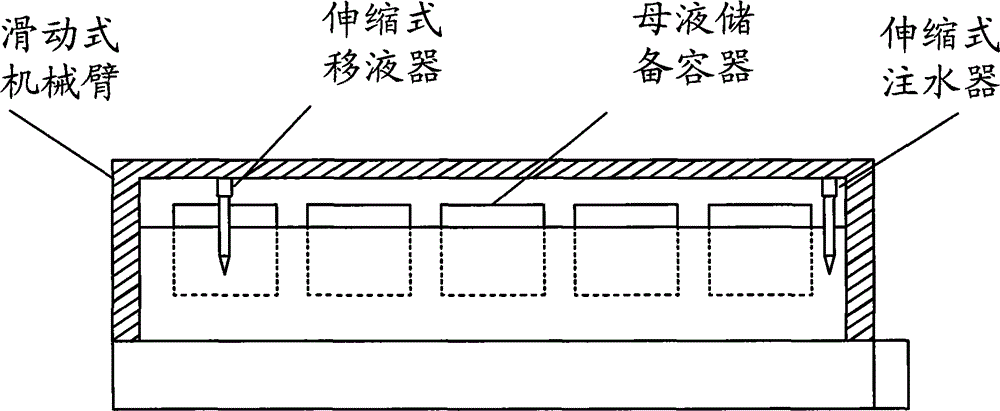
High-throughput fish ecotoxicity test system
InactiveCN105301212AImprove accuracyRealize automatic observationTesting waterBiological testingPipetteData transmission
The invention discloses a high-throughput fish ecotoxicity test system. The system comprises experiment vessels, an experiment vessel placing device, mother liquid storage vessels, a sliding mechanical arm, a telescopic injector, a telescopic pipette, a data transmission port and a test parameter control platform, wherein the experiment vessel placing device is connected with the telescopic injector and the data transmission port separately; the mother liquid storage vessels are connected with the telescopic pipette; the sliding mechanical arm is connected with the telescopic injector, the telescopic pipette and the data transmission port separately; the data transmission port is also connected with the test parameter control platform. Through the adoption of the system, the output efficiency of ecotoxicological toxicity data can be improved.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com