Patents
Literature
76results about How to "Degradation safety" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Biological and adsorbable bone internal fixation implantation instrument
InactiveCN101283922APromote healingUniform corrosion degradationInternal osteosythesisProsthesisInternal bone fixationReconstructive surgery
The invention relates to a bone implanting and internal fixation appliance with bioactivity and absorbability, which belongs to the field of bio-medical appliances, particularly to the field of medical appliances used for bone wound surgery, reparative and reconstructive surgery and plastic and cosmetic surgery. The appliance includes bone nails and a bone plate made of magnesium and the alloy thereof with bioactivity and absorbability. The bone implanting and internal fixation appliance is a bone internal fixation device, which comprises a blade plate and matched screws, intramedullary nails, a fracture and dislocation fixing device of vertebral column, bone nails or screws having individual fixation effect, wherein the bone internal fixation device is made of magnesium and the alloy thereof with bioactivity and absorbability. The bone internal fixation device can solve the problem in bioactivity of prior bone internal fixation device and promote healing the tissue where the device in implanted. The device also includes a protection layer prepared on the surface of the internal fixation device for controlling the degradation rate of magnesium alloy and the dissolution rate of magnesium ions, thus controlling the bioactivity and the absorption speed of the magnesium alloy device in an organism.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Mycobacterium 16F for efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and benzene organic matters and application thereof
ActiveCN102899271AEfficient degradationDegradation safetyBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementKanamycinM-Xylene
The invention provides a strain of Mycobacterium sp.16F for efficiently degrading polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon and benzene organic matters, which has a preservation number of CGMCC No.6367. The mycobacterium 16F can efficiently, safely and rapidly degrade polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and benzene organic matters, can grow and degrade by using fluorene, naphthalene, anthracene, acenaphthene, phenanthrene, pyrene and benzopyrene as the sole carbon source and energy in aerobic condition, and can utilize benzene, m-xylene, toluene, salicylic acid, catechol and other multiple aromatic organic matters. The mycobacterium 16F is sensitive to streptomycin, rifampin, tetracycline, kanamycins and other antibiotics, has good degradation effects to mixed polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in aging soils and monocyclic benzene organic matters in water bodies, can be used for restoring and purifying the water-soil environment combinedly polluted by aromatic hydrocarbon organic matters, is important for promoting sustainable development, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION RES INST OF LIGHT IND
Zn-Ag series zinc alloy as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN107456610AAdjustable degradation rateGood biocompatibilitySuture equipmentsTissue regenerationCorrosionBlood compatibility
The invention discloses a Zn-Ag series zinc alloy as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The Zn-Ag series zinc alloy consists of Zn and Ag; and in percentage by weight, the Ag accounts for 0-30%, not including 0, in the Zn-Ag series zinc alloy by mass. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) mixing the Zn and the Ag, so that a mixture is obtained; and (2) processing the mixture in accordance with a step a) or a step b), and cooling the processed mixture, so that the Zn-Ag series zinc alloy is obtained: a) in a CO2 and SF6 atmosphere, melting or sintering the mixture; and b) in a vacuum atmosphere, dissolving hydrogen in the mixture and implementing the melting. The Zn-Ag series zinc alloy prepared by the invention is appropriate in mechanical performance, adjustable in corrosion rate and excellent in cell compatibility and blood compatibility, and the Zn-Ag series zinc alloy is also excellent in antibacterial performance; and the Zn-Ag series zinc alloy is applicable to preparation of bio-medical implantation apparatuses.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Bacillus aryabhattai, microbial inoculums thereof, preparation method and application
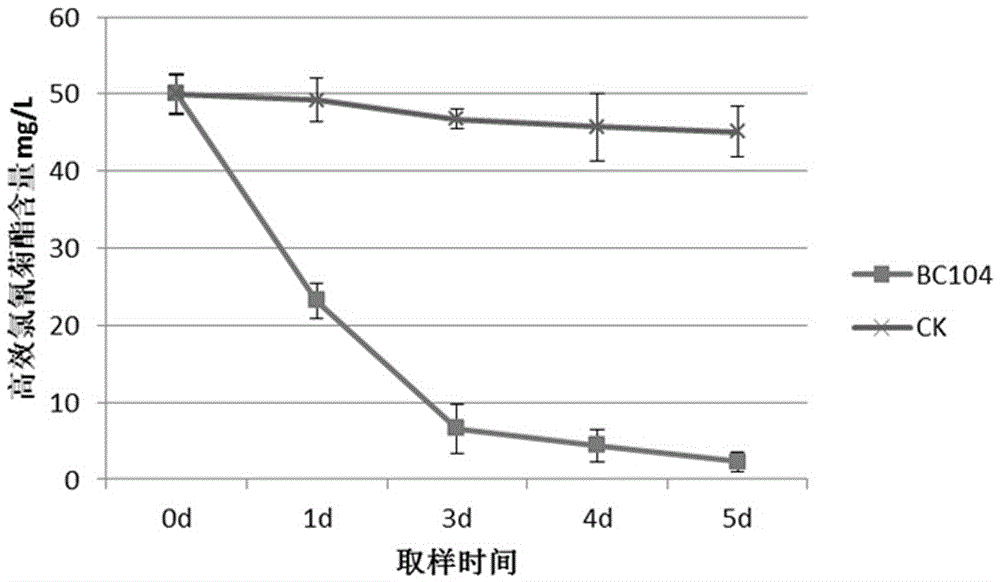
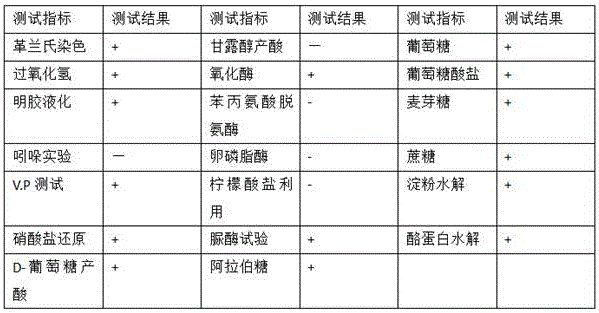
The invention discloses bacillus aryabhattai, microbial inoculum thereof, a preparation method and application. The bacillus aryabhattai BC104 is beta-cypermethrin degrading bacteria, and the preservation unit is the China General Microbiological Culture Collection center (CGMCC), the preservation date is 15th, Dec, 2015, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.11664; the bacillus aryabhattai belongs to mycomonera, phylum firmicutes, bacillus class, bacilli bacteria, bacillaceae and bacillus. The microbial inoculum with the bacillus aryabhattai as an active ingredient is the microbial inoculum obtained by preforming activation culture and fermentation culture on the bacillus aryabhattai BC104. The preparation method comprises the steps of activation culture and fermentation culture; the application of the microbial inoculum is to prepare a medicine for degrading beta-cypermethrin. The strain disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process of the microbial inoculum, low cost, convenience in use and good application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof for degrading decabromodiphenyl oxide
InactiveCN101921716APromote degradationLow costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFuranDecabromobiphenyl ether
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis DB-2 and application thereof for degrading decabromodiphenyl oxide. The bacillus subtilis is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on 27th November 2009 with the preservation number of CCTCC No:M 209286. The bacillus subtilis has stronger degrading ability and is capable of debrominating decabromodiphenyl oxide to generate free bromonium ions. The bacillus subtilis does not generate high-toxicity secondary pollutants of polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxins, polybrominated dibenzo-furans, low-brominated diphenyl ether, and the like after being biodegraded, and can be used for treating the pollution of the decabromodiphenyl oxide in the environment, thereby providing a decabromodiphenyl oxide degrading bacterium with low cost and high efficiency and without secondary pollution for treating the decabromodiphenyl oxide in chemical sludge or wastewater.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Acinetobacter calcoaceticus and application thereof in degrading decabromodiphenyl ether
The invention discloses acinetobacter calcoaceticus DB-3 and application thereof in degrading decabromodiphenyl ether. The acinetobacter calcoaceticus is preserved in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on November 27th, 2009, and the collection number is CCTCC No:M 209287. The acinetobacter calcoaceticus has relatively strong degradation capability for the decabromodiphenyl ether and can debrominate the decabromodiphenyl ether to produce dissociative bromonium ions. After the biological degradation of the acinetobacter calcoaceticus, the decabromodiphenyl ether does not produce highly-toxic secondary pollutants such as polybrominated dibenzo-p-dioxin, polybrominated dibenzofuran, low-brominated diphenyl ether and the like. The acinetobacter calcoaceticus strain can be used for controlling the decabromodiphenyl ether pollution in the environment so as to provide low-cost and high-efficiency decabromodiphenyl ether degrading bacteria without secondary pollution for treating the decabromodiphenyl ether in chemical industrial sludge or wastewater.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Device for degrading aflatoxin by using plasma and application of device
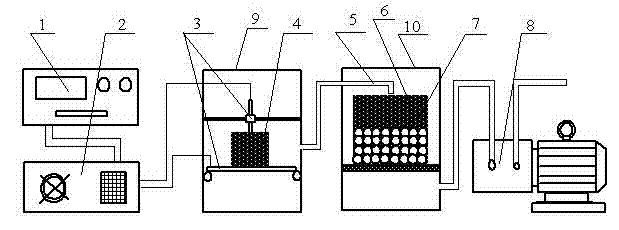
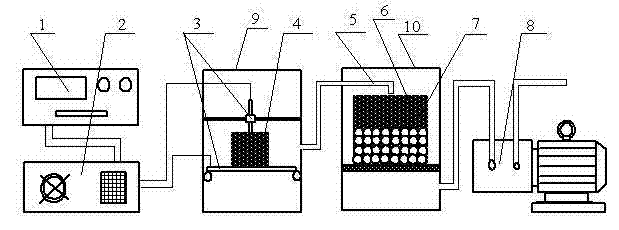
The invention provides a device for degrading aflatoxin by using plasma. The device comprises a plasma emitter, a water cooler, a plasma generator and a processor, wherein the plasma emitter is connected with the water cooler; the water cooler is connected with the plasma generator; a plasma generating storehouse and a plasma electrode capable of adjusting pitch are arranged in the plasma generator; the plasma generator is connected with the processor through a connecting pipe; and the processor is externally connected with a vacuum pump for adjusting density of gas in the device. Based on physical treatment, the device can degrade the aflatoxin in agricultural products efficiently, quickly and safely. According to experimental verification, the device has the obvious effect of degrading the aflatoxin; the degrading rate can reach over 50 percent; and the problems of pollution to chemical agents, damage to nutrients, sense and functional characteristics of products, overhigh cost and the like in the prior art are solved.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
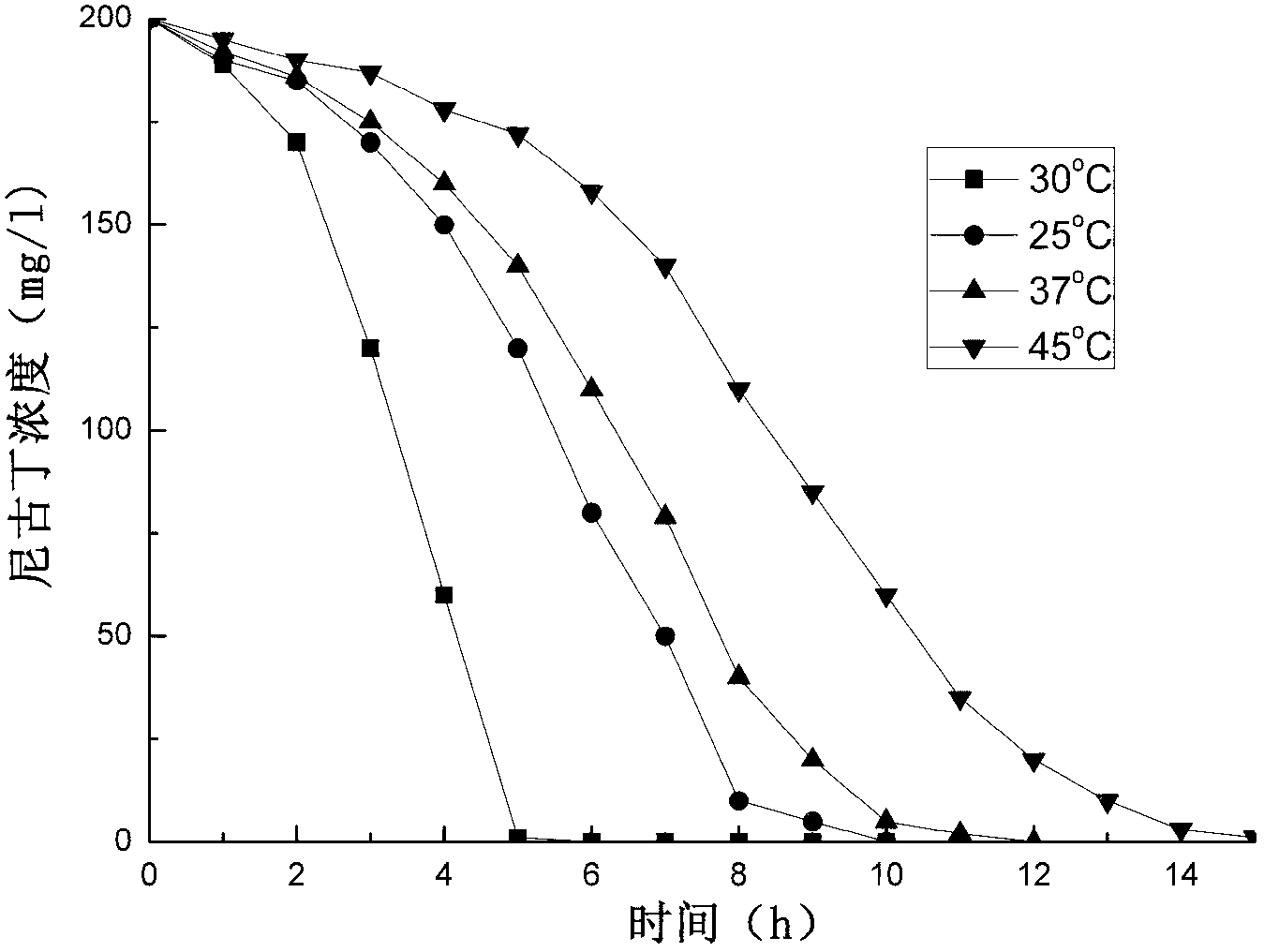
Shinella sp. HZN1 capable of effectively degrading nicotine and application thereof
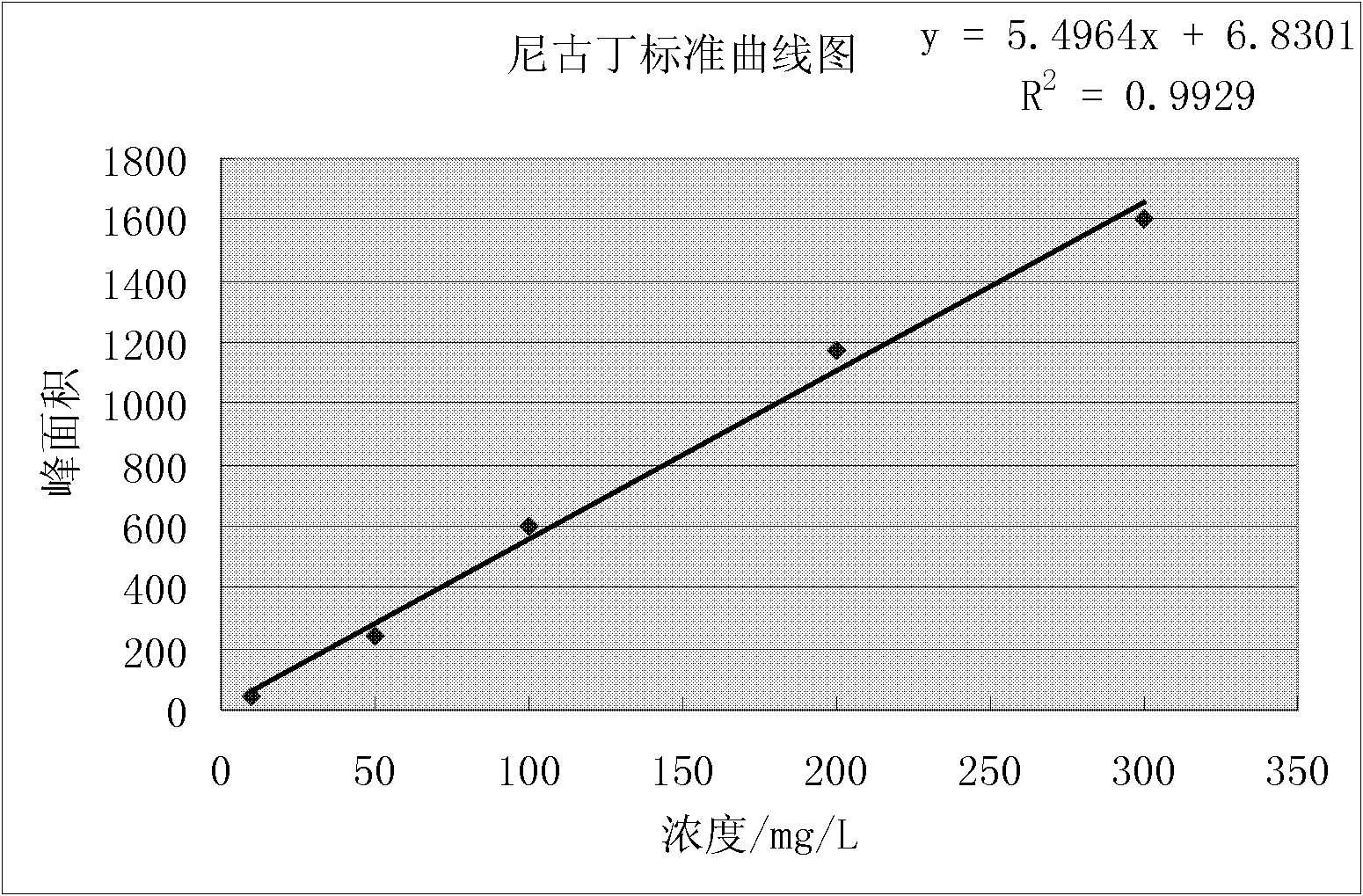
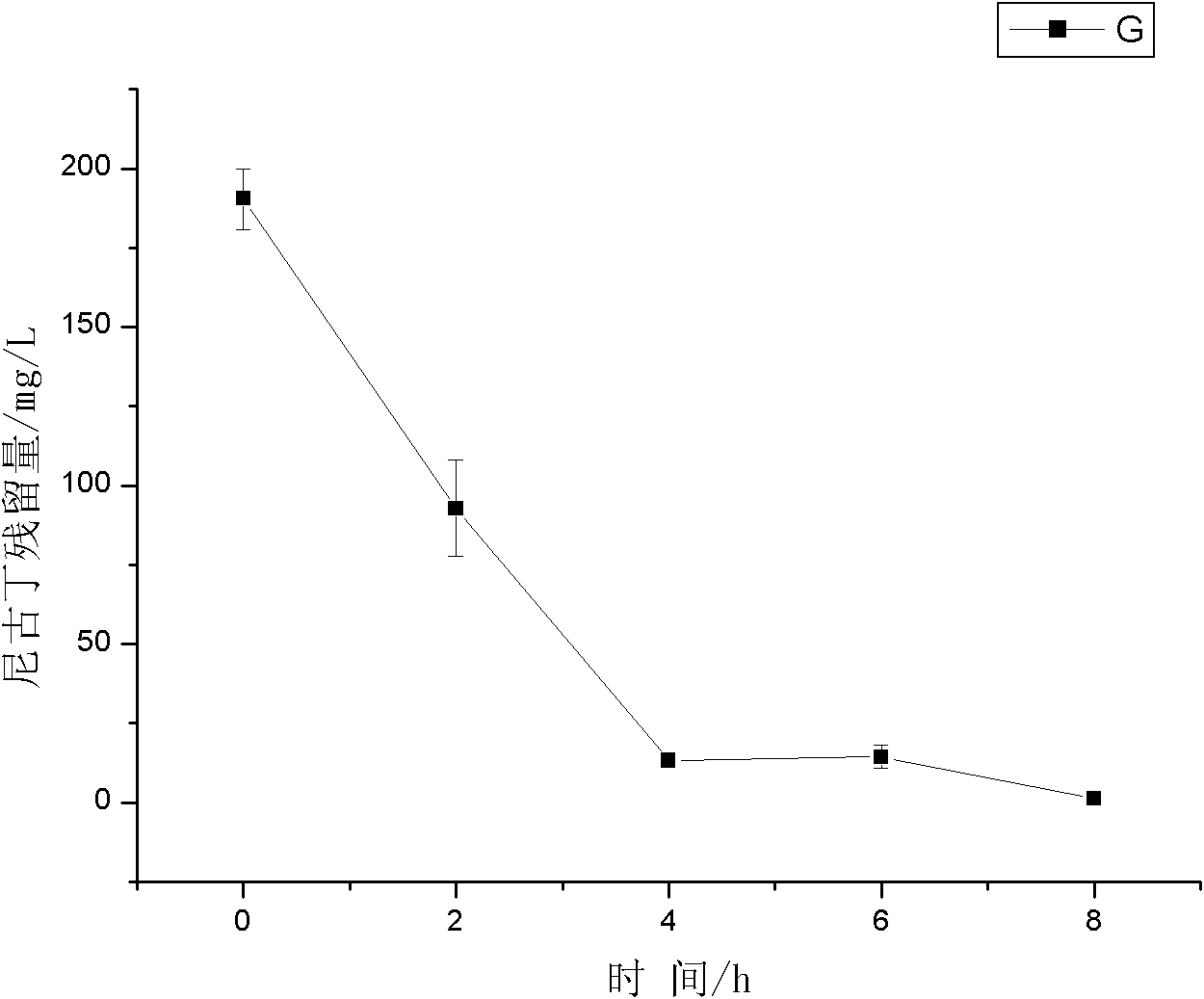
InactiveCN101928690ADegradation safetyEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsShinella sp.Microbiology
The invention provides a novel Shinella sp. HZN1 capable of effectively degrading nicotine and application thereof. The Shinella sp. HZN1 is preserved in China Center for Type Culture Collection; the address is 430072, Wuhan University, Wuhan, China; the preservation number is CCTCC No:M 2010154; and the preservation date is June 23rd, 2010. The nicotine-degrading bacterium can be directly thrown in a water body to degrade nicotine, and can safely, efficiently and quickly degrade the residual nicotine in the water body, soil and the like. Besides, the microbial inoculum containing the strain has the advantages of simple preparation process, low cost and convenient use, thereby having favorable application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
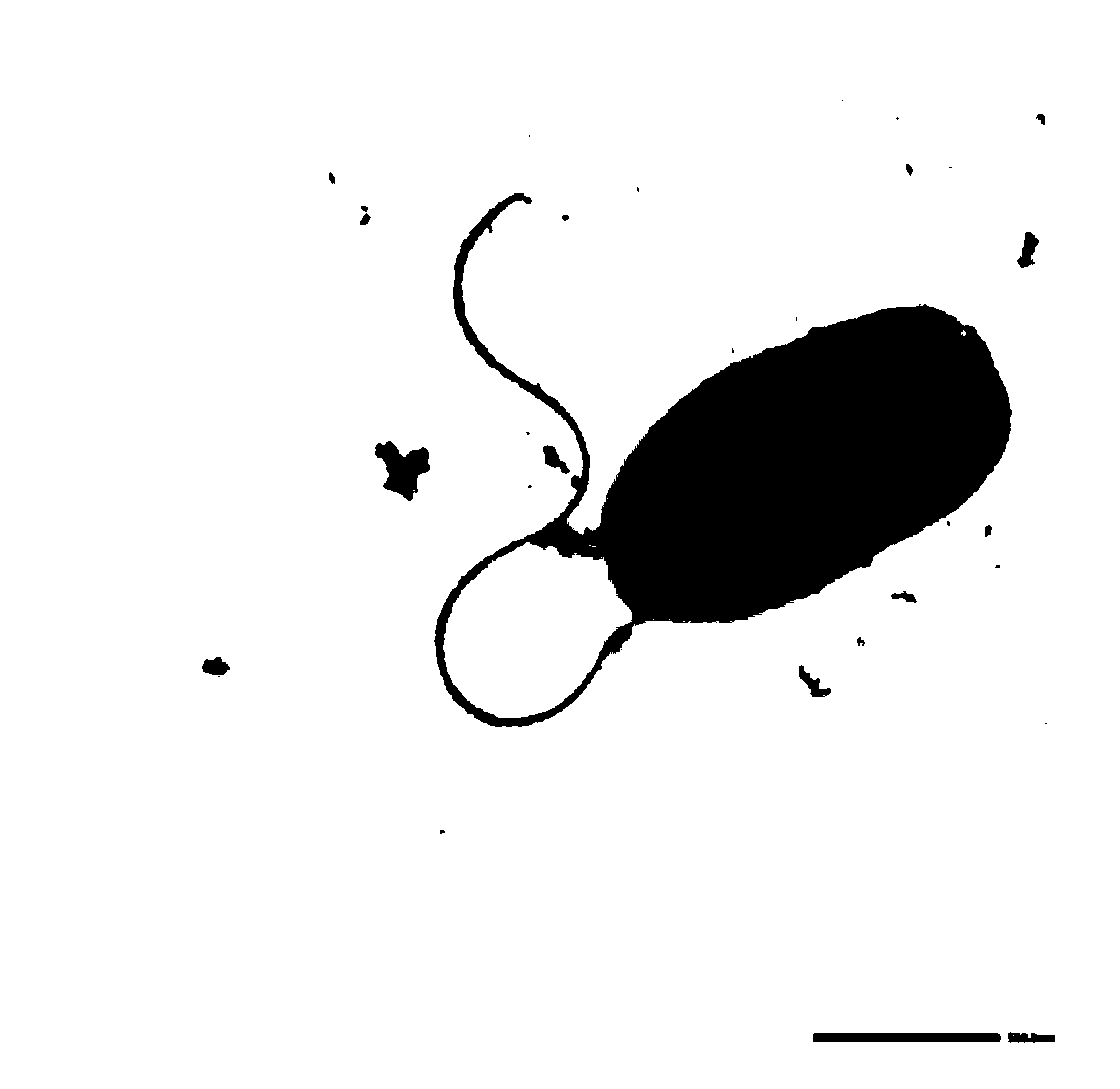
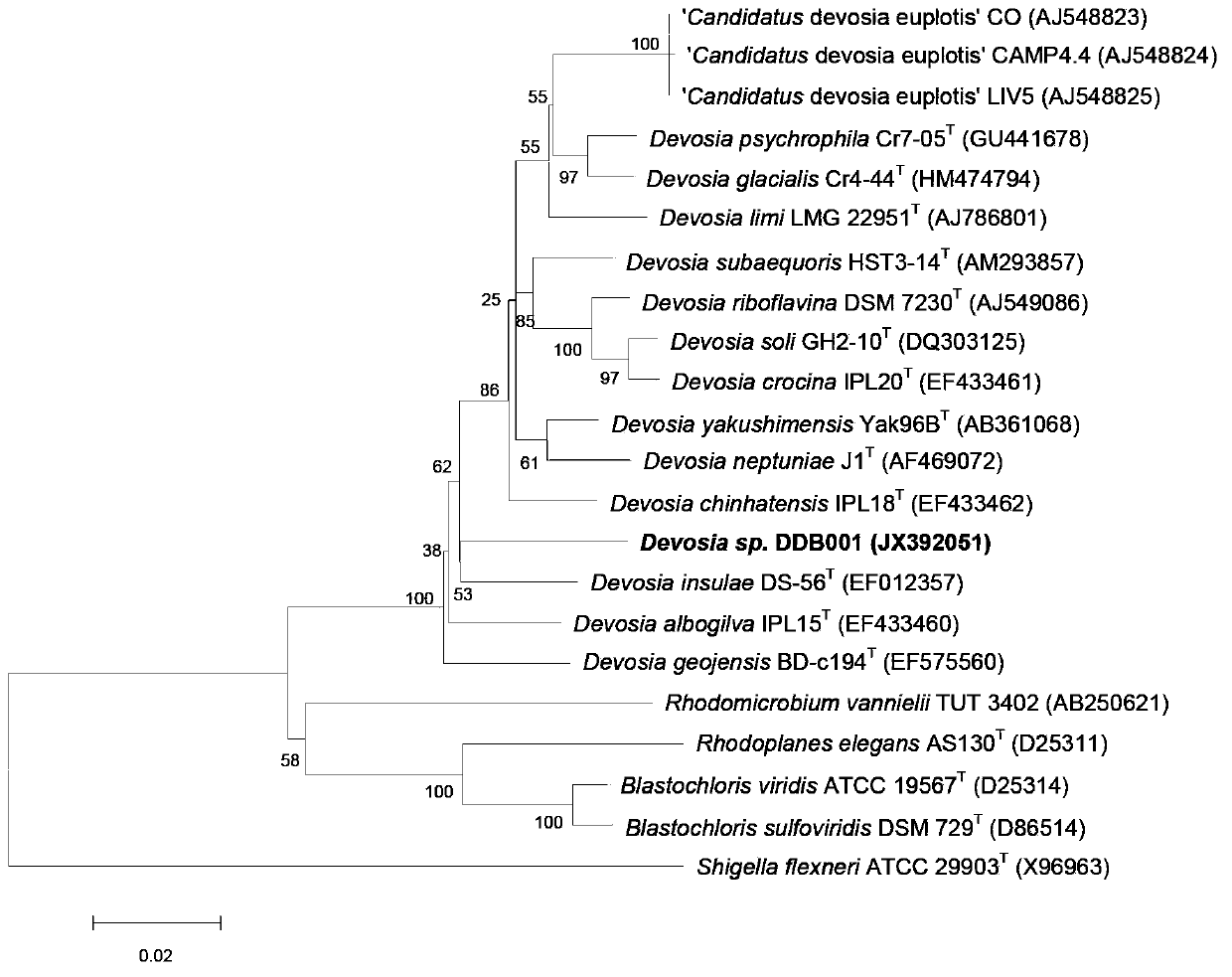
Devosia sp and application thereof in degrading vomitoxin
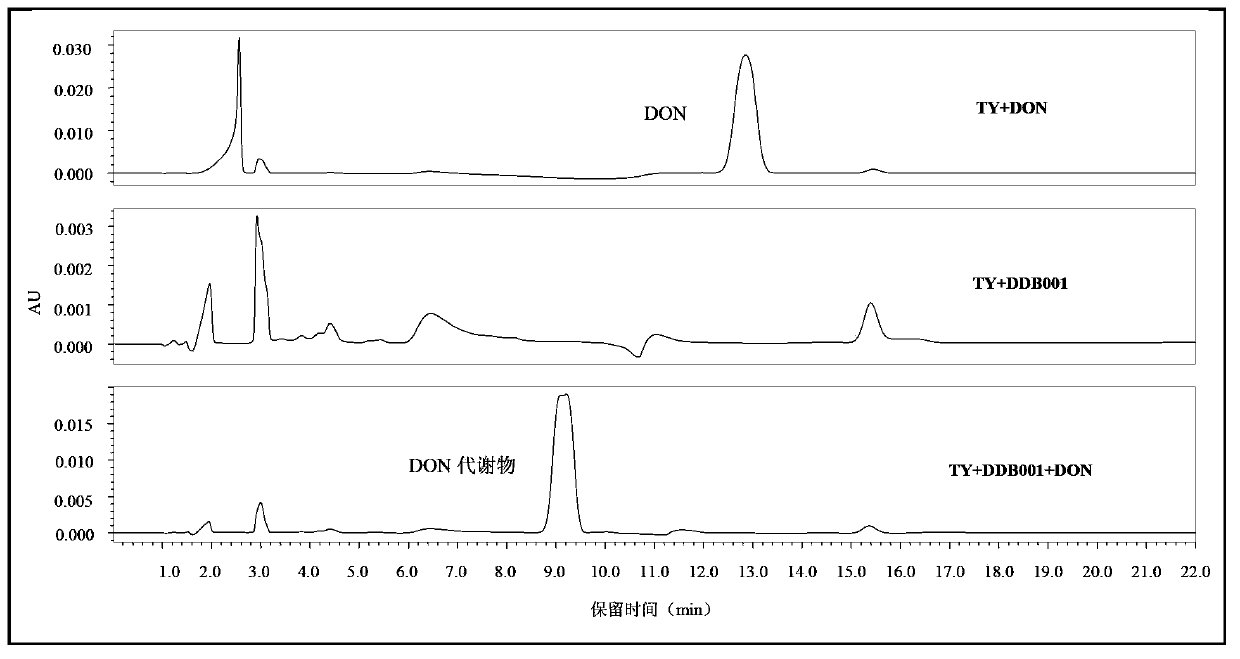
ActiveCN103387950APromote degradationDegradation safetyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFungicideDevosia sp.
The invention discloses devosia sp. and application thereof in degrading vomitoxin. The strain provided by the invention belongs to a new strain in the Devosia Nakagawa et al, and the preservation number of Devosia sp. DDB001 is CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) No.7185. The invention also provides a fungicide containing the preserved strain and a preparation method thereof. Furthermore, the invention also provides an application of the strain or fungicide in degrading vomitoxin.
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
Method for treating heavy metal in soil
InactiveCN105798059ADegradation safetyEnvironmental degradationFungiBacteriaEnvironmental resistanceBiology
The invention discloses a method for treating heavy metal in soil. An effective microbial community and a substrate for providing nutrition to the microbial community are uniformly mixed according to a mass ratio of 1: 5-10 to form a microorganism agent; the microorganism agent is uniformly spread on a land needing to be treated; 2-3 kg microorganism agent is applied to each Mu land; soil is loosened and the land is overturned to fully contact the microorganism agent with the soil; the land is irrigated after overturning; the soil is tested at the seventh day to observe the heavy metal degrading condition; and the application quantity and the application times of the microorganism agent are adjusted according to the heavy metal pollution degree and the degrading demands. The method for treating the heavy metal in the soil can safely, environment-friendly and efficiently degrade the heavy metal in the soil to satisfy the social and economic development demands.
Owner:XIAMEN RENTIANJING AGRI TECH CO LTD
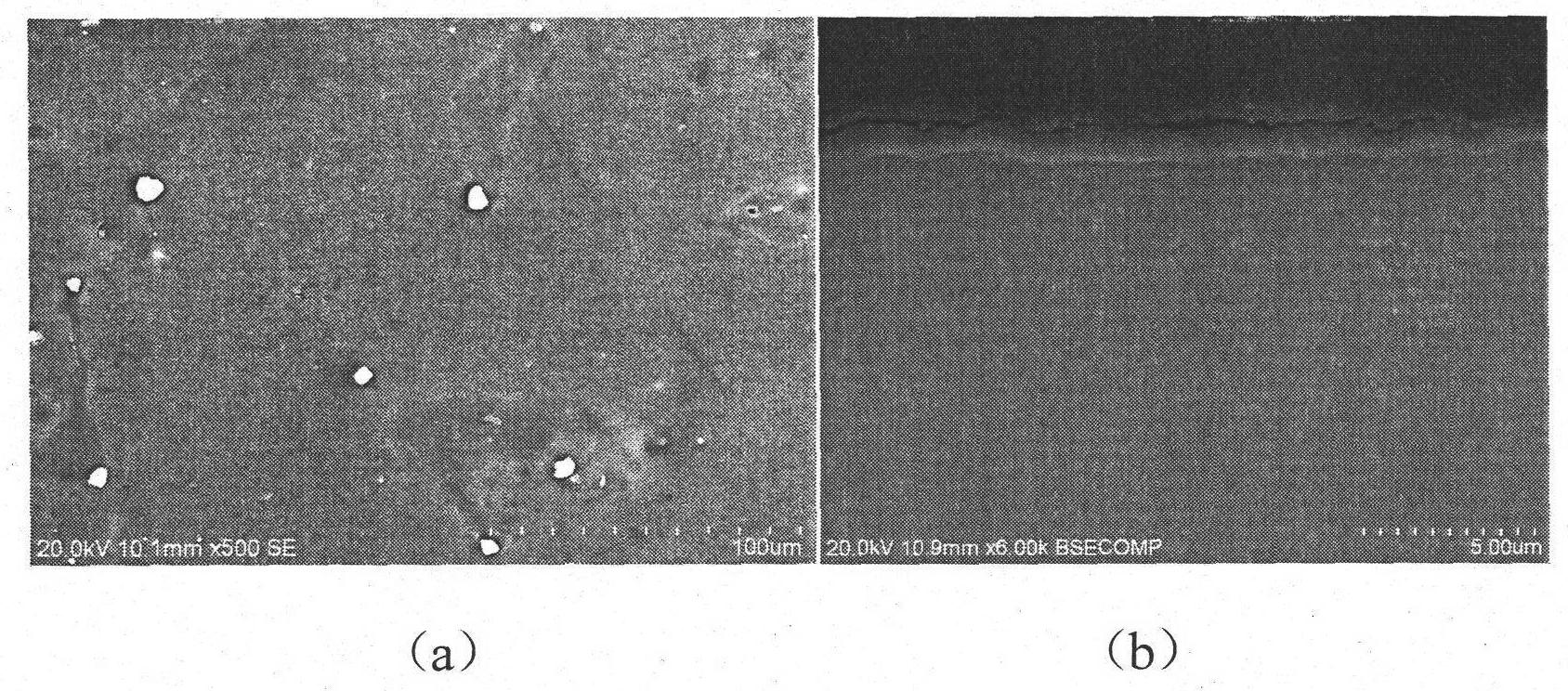
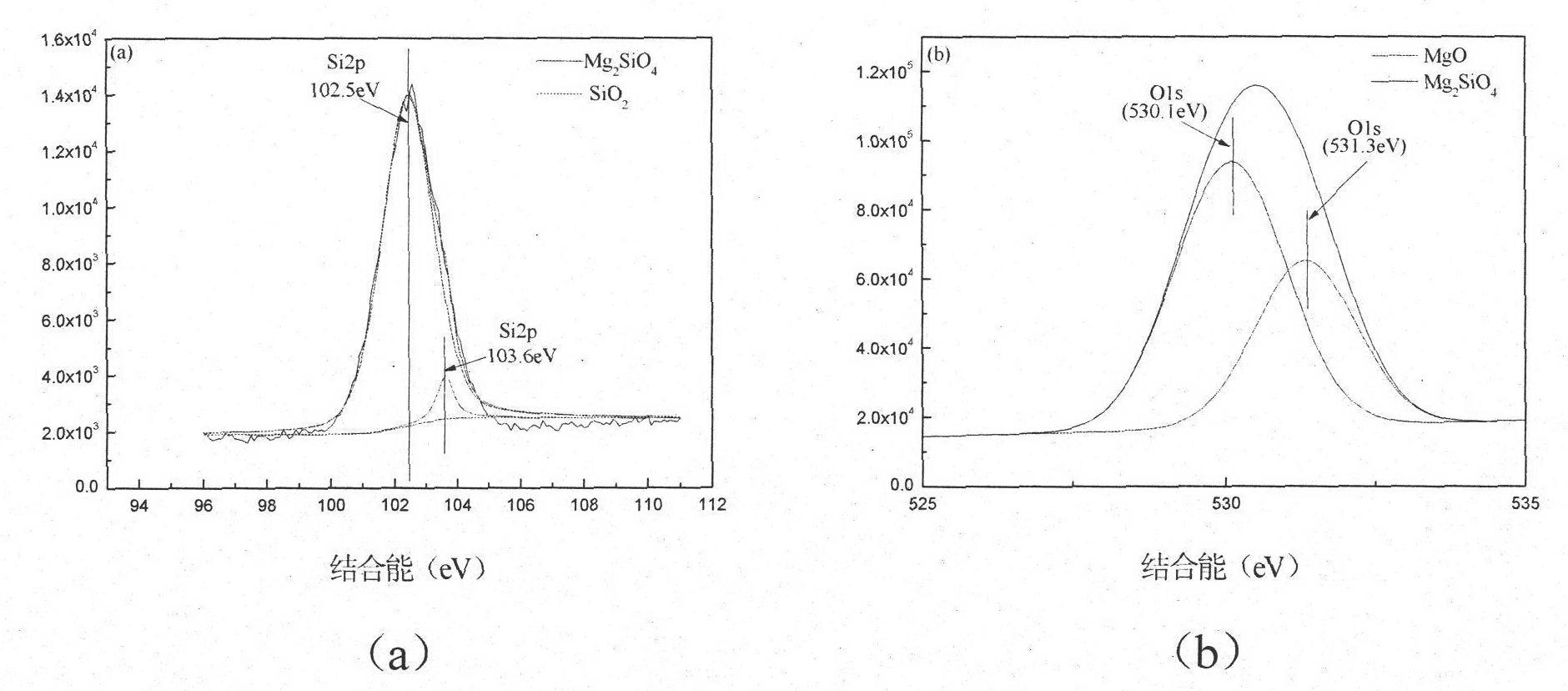
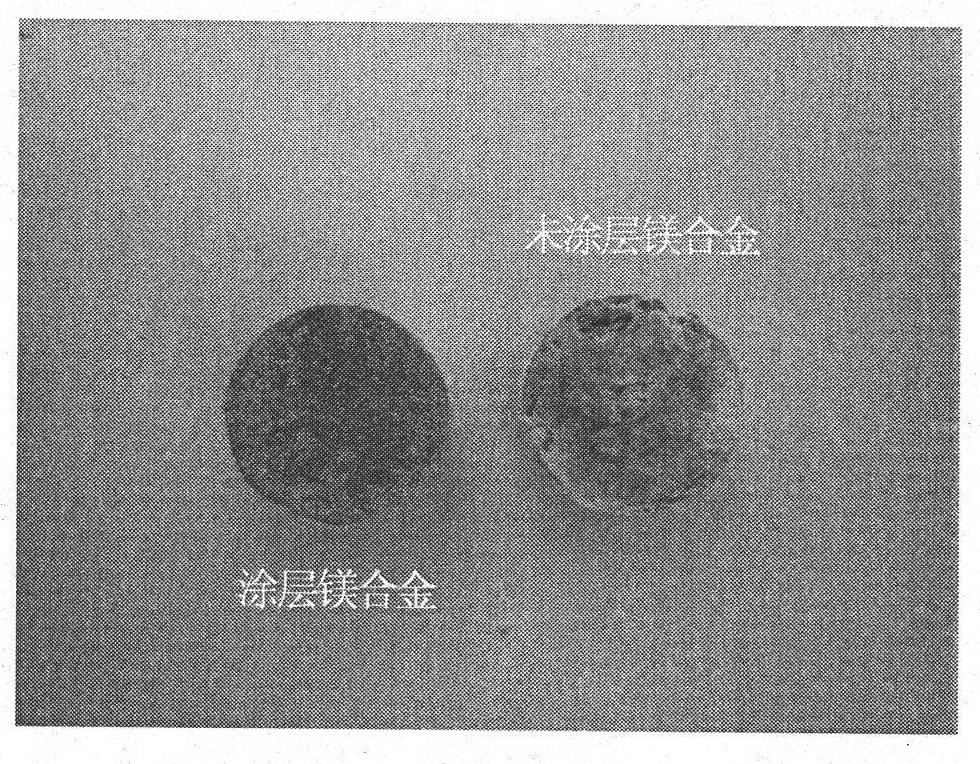
Silicate coating-containing absorbable medical magnesium-based metal and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102146562APromote healingSlow degradationMetallic material coating processesProsthesisCorrosionMagnesium silicate
The invention relates to a silicate coating-containing absorbable medical magnesium-based metal, a preparation method and application thereof. The magnesium-based metal belongs to the field of biomedical appliances and is particularly suitable for the field of medical appliances used for bone trauma surgery, reparative and reconstructive surgery, and coining and cosmetology. The magnesium-based metal consists of a magnesium-based metal substrate and a silicate coating formed on the surface of the substrate, wherein the silicate coating consists of magnesium silicate and magnesium oxide. In an alkaline environment, a protective coating is prepared on the surface of the magnesium-based metal by a low temperature chemical deposition method. The method is simple and feasible and has low requirement on equipment; and the thickness of the coating can be controlled to be between several hundred nanometers and 5 mu m. The protective coating is uniform and dense, has high corrosion resistance, simultaneously has high biological activity and metal appearance, and can control the degradation rate of the magnesium-based metal and the dissolution rate of magnesium ions so as to control the biological activity and the absorption rate of magnesium-based metal implanted devices in organisms. The magnesium-based metal can be used for preparing intra-osteal fixing devices.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Environment-friendly clean water-based automobile cleaning agent and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102533460ANot harmful to healthReduce pollutionNon-ionic surface-active compoundsOrganic detergent compounding agentsLimoneneCleansing Agents
The invention discloses an environment-friendly clean water-based automobile cleaning agent, which comprises the following components: disodium fatty acid amido sulphosuccinate, fatty alcohol-polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulfate, limonene and deionized water. The invention further discloses a preparation method of the cleaning agent. The environment-friendly clean water-based automotive cleaning agent disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simple preparation process, low production cost, good deterging effect, natural and non-toxic components and good biodegradability, and meets the requirements for high efficiency and environmental friendliness.
Owner:任航
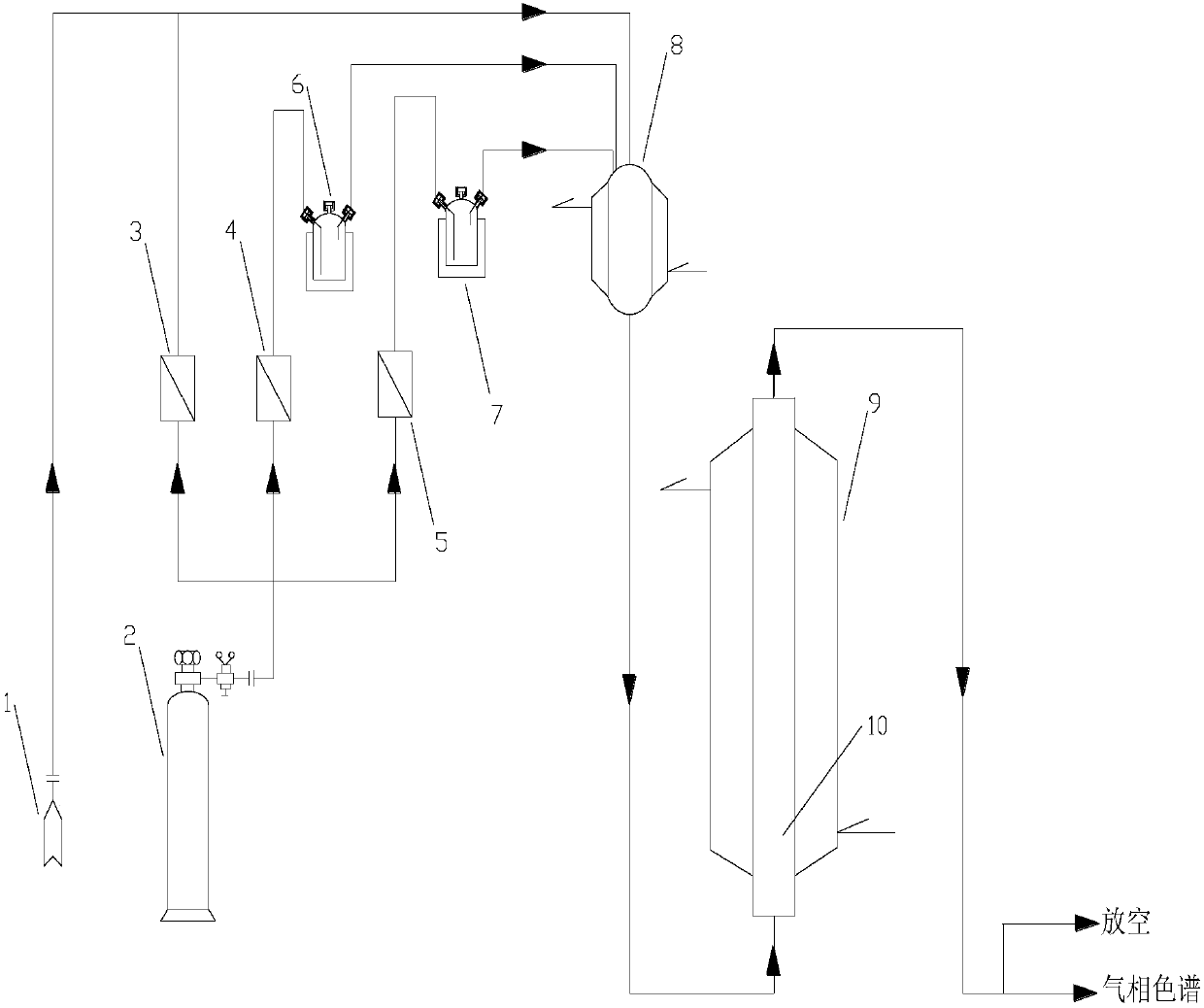
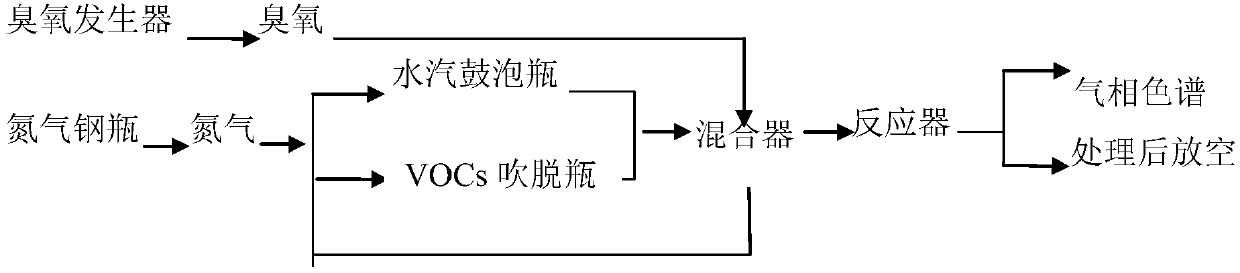
Method for degrading VOCs via normal temperature catalytic oxidation
InactiveCN107930380AEfficient degradationPromote degradationGas treatmentDispersed particle separationOzone generatorWater vapor
The invention discloses a method for normal temperature catalytic oxidation of VOCs. The method comprises a gas distribution stage, a catalytic reaction stage, and a detection stage. A nitrogen steelcylinder provides three steams of nitrogen, wherein one stream passes through a VOCs-stripping bottle, one stream is taken as a cushion gas, and one stream passes through a steam bubbling bottle, andan ozone generator provides ozone. Ozone is mixed with a nitrogen cushion gas, the mixed gas together with VOCs-containing nitrogen and steam-containing nitrogen enters a mixer for mixing, after the mixing is complete, the obtained mixture enters a reactor, and after the reaction is complete, one part of the produced gas passes through gas chromatography for on-line concentration detection, and the other part of the produced gas is treated and discharged. The method allows VOCs to be effectively removed.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Fusarium oxysporum and application of same in degrading autotoxins resulting in successive cropping obstacles
InactiveCN103834573APromote degradationEfficient degradationFungiContaminated soil reclamationBenzoic acidFusarium oxysporum
The invention discloses Fusarium oxysporum and application of the same in degrading autotoxins resulting in successive cropping obstacles. The Fusarium oxysporum has an accession number of CCTCC No. M2013432. The Fusarium oxysporum can use autotoxins as sole carbon source and energy for growth, which belongs to mineralization, and the Fusarium oxysporum has positive meaning to removal of autotoxins in a cultivation water body or soil and overcoming of successive cropping obstacles. As the Fusarium oxysporum has grown for 72 h with autotoxins as sole carbon source and energy, a highest degradation rate of cinnamic acid reaches 99.53%, a highest degradation rate of benzoic acid reaches 97.9%, a highest degradation rate of vanillin reaches 92.5%, a highest degradation rate of p-hydroxybenzoic acid reaches 95.6%, and no side effects are exerted on crops in degradation of autotoxins. Application of the Fusarium oxysporum is simple and convenient and has low cost and wide application prospects.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing aluminum oxide with large specific surface area
InactiveCN103112878APromote degradationDegradation safetyAluminium oxide/hydroxide preparationAluminium chlorideLauroyl glutamate
The invention relates to a method for preparing aluminum oxide. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: dissolving aluminum oxide solid in 0.1-0.5mol / L lauroyl sodium glutamate aqueous liquor to obtain 1-5mol / L aluminum chloride liquor; adding ammonia water or mixed liquor of ammonia water and organic amine into the aluminum chloride liquor, and adjusting pH value to 7-8 so as to obtain Al<3+>:OH<-> in the liquid; standing the liquor for 3-5hours at 20-50 DEG C by lauroyl glutamate ions, wherein the molar ratio is 1: (0.05-3): (1.5-7.5); crystallizing the liquor after standing in a reaction kettle at 100-140 DEG C for 24-96hours; and filtering and washing the crystallizing liquid and roasting in a muffle furnace at 500-700 DEG C for 4-6 hours to obtain solid aluminum oxide. The specific surface area of gamma-aluminum oxide can reach 240-400<m2> / g.
Owner:CHINA SHENHUA ENERGY CO LTD
Beta-cypermethrin degrading bacteria and application thereof
InactiveCN101880641AEfficient degradationDegradation safetyBacteriaWater contaminantsHigh concentrationCypermethrin
The invention provides a beta-cypermethrin degrading bacteria-nitrogen-fixing vibrio (Azoarcus Indigens) HZ5, which is collected at the China center for type culture collection, wherein the address is Wuhan University of Luojia hill, Wuhan, Hubei, 430072, the collection data is March 17, 2010, and the collection number CCTCC No is M 2010060. The bacteria of the invention has certain degradation capacity to high-concentration beta-cypermethrin, the degradation rate for the 50mg / L of beta-cypermethrin under pure culture conditions reaches 65.2%, and the enantioselectivit does not exist in the degradation process. The degrading bacteria can be applied to the degradation of the beta-cypermethrin in a water body by direct adding, and can safely, efficiently and fast degrade the residual beta-cypermethrin on the water body, soil and other objects; and the bactericide containing the bacterial strain has simple preparation process, low cost, convenient use, and good application prospect.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
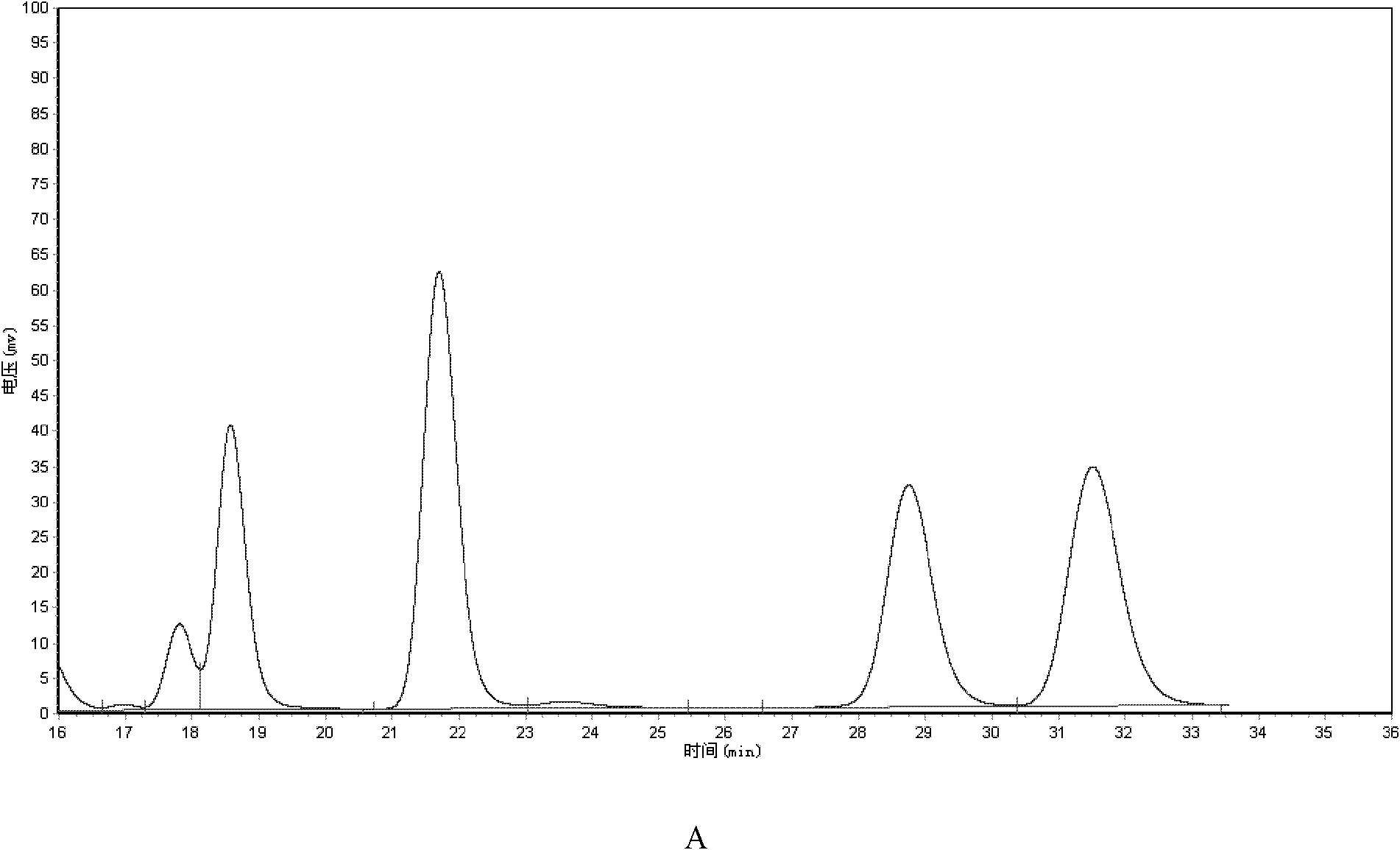
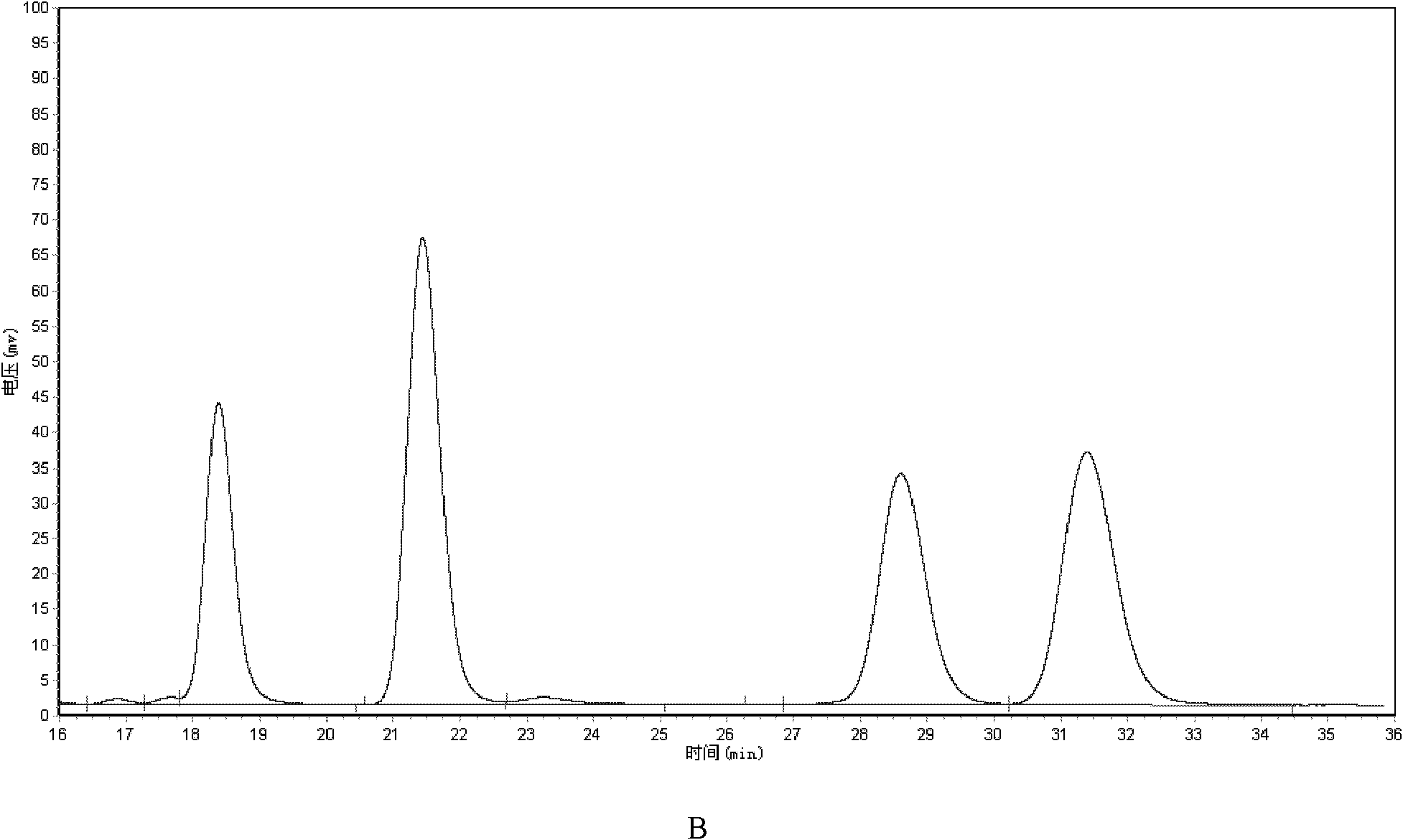
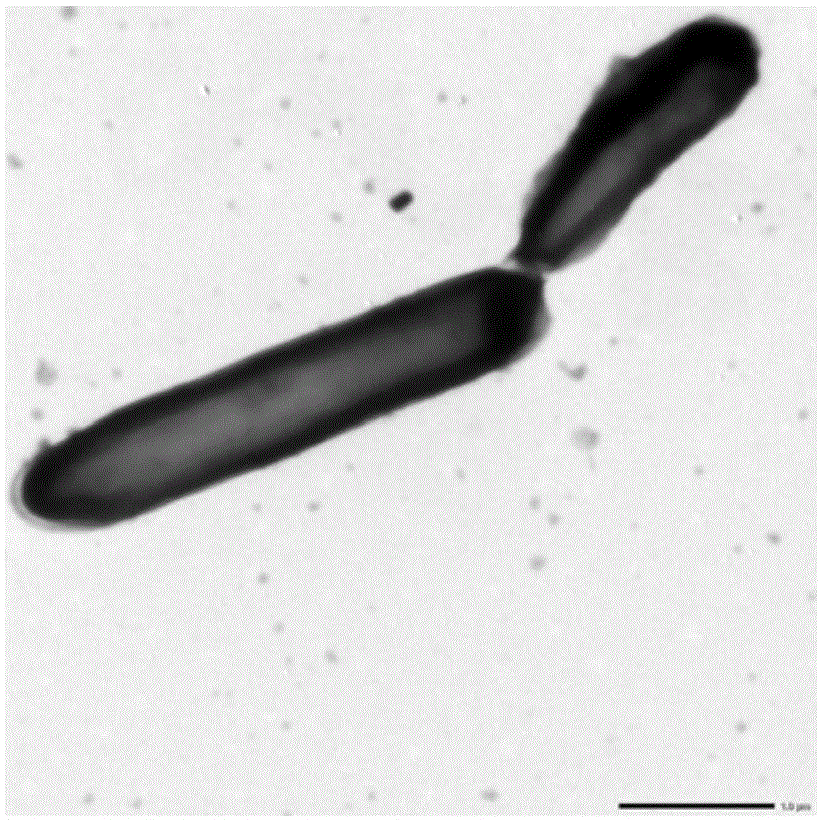
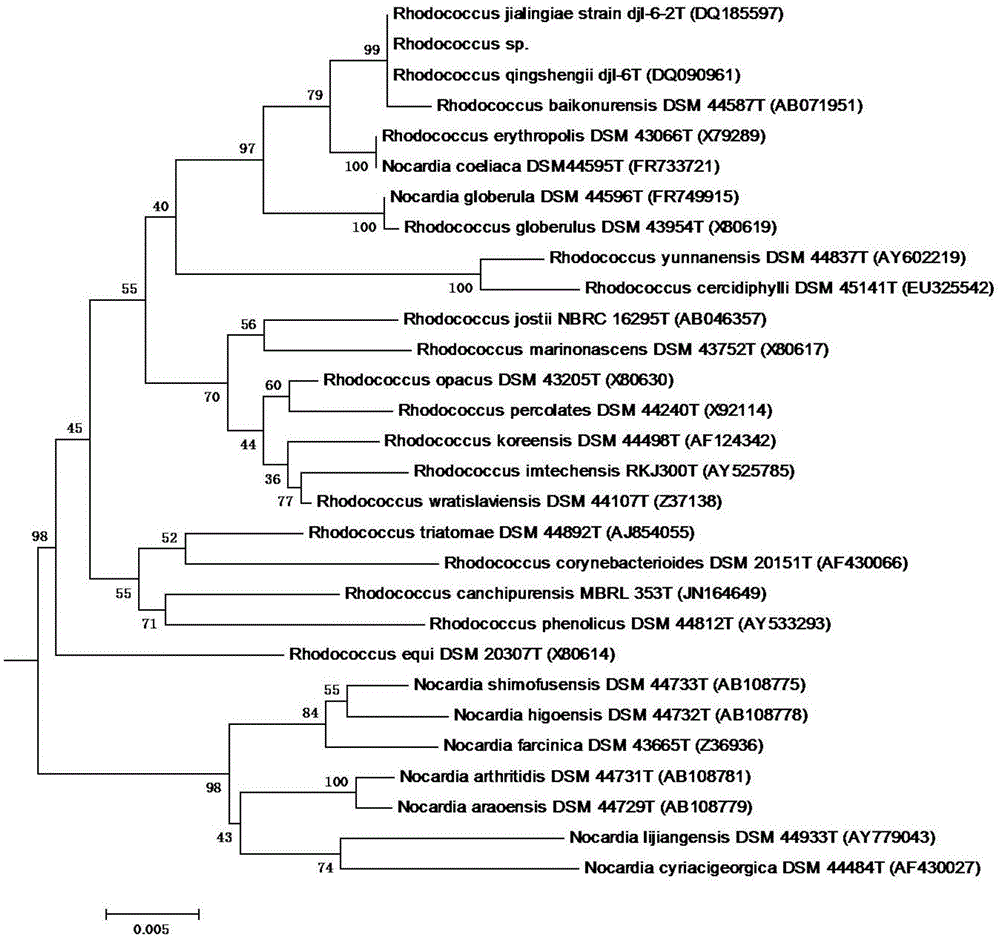
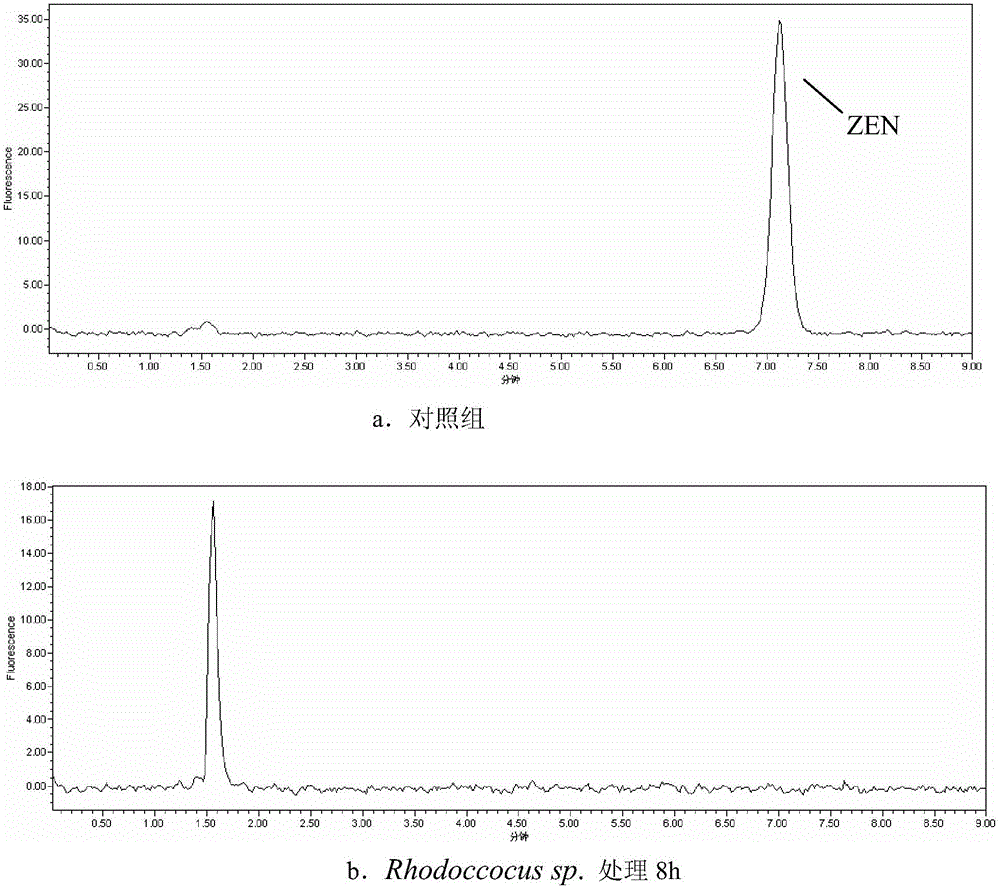
Rhodococcus sp. and application of rhodococcus sp. to zearalenone degradation
ActiveCN105154351ASolve pollutionIncrease profitBacteriaMicroorganism based processesRhodococcus sp. WB1Microbiology
The invention discloses rhodococcus sp. and application of the rhodococcus sp. to zearalenone degradation. The preservation number of the rhodococcus sp. is CGMCC No.7186. The invention also provides a biological detoxication agent containing the preserved bacterial strain of the rhodococcus sp. and a preparing method of the biological detoxication agent. In addition, the invention also provides application of the bacterial strain or the biological detoxication agent to the zearalenone degradation.
Owner:ACAD OF NAT FOOD & STRATEGIC RESERVES ADMINISTRATION
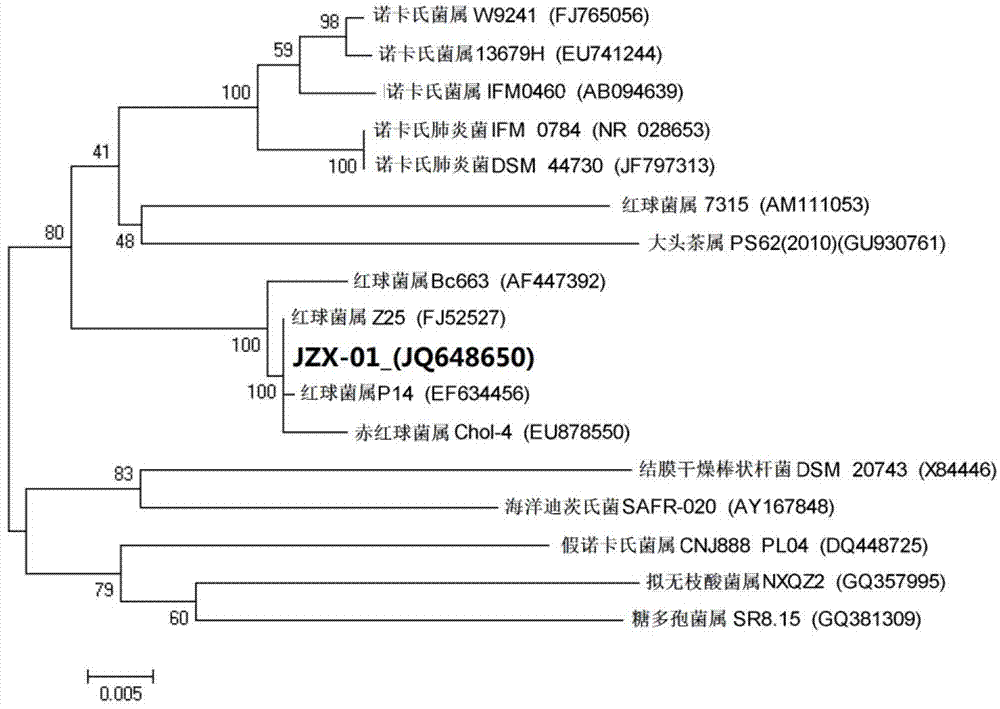
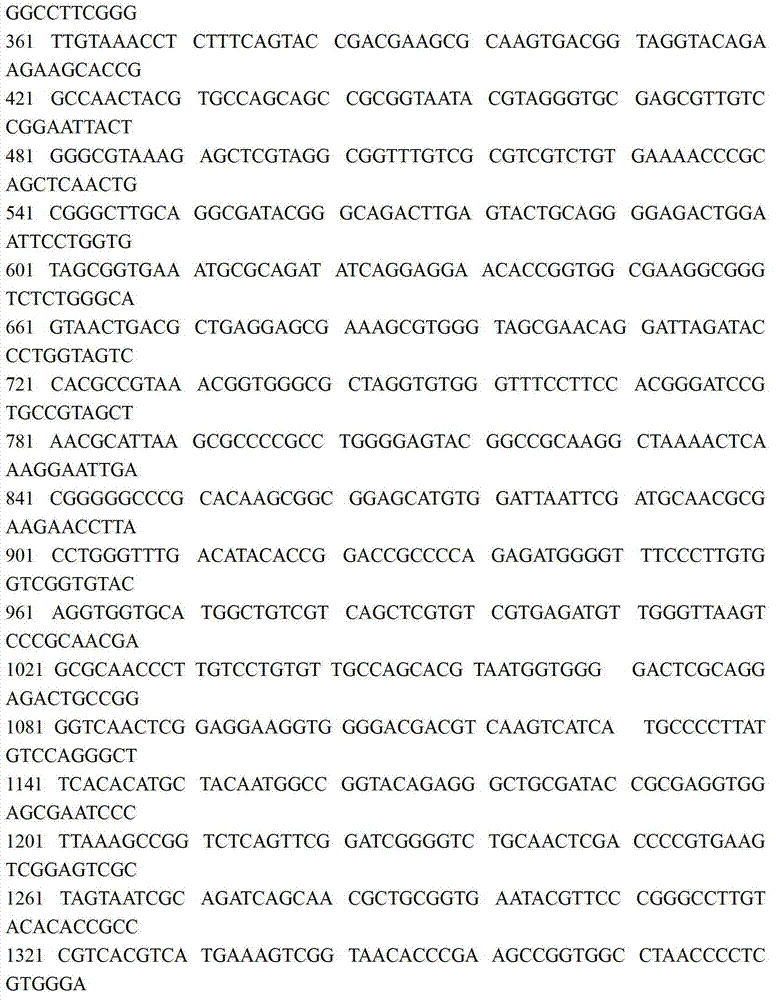
Rhodococcus JZX-01 used for degrading petroleum pollutants, and culturing method thereof
InactiveCN102851234APromote degradationImprove degradation rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRhodococcus strain
The invention relates to a rhodococcus JZX-01 used for degrading petroleum pollutants, and a culturing method thereof. The identification of the rhodococcus is achieved through 16S rDNA sequencing and comparison on NCBI. An adopted 16S rDNA upstream primer is a universal primer 27F with a specific sequence of 5'-AGA GTT TGA TCC TGGCTCAG-3'. A downstream universal primer is 1492R with a specific sequence of 5'-GGT TAC CTT GTT ACG ACTT-3'. According to the invention, an inducing agent is added into a culture medium or culture solution, and soil is added into the culture solution or culture medium; culturing is carried out in a shaking table under a culturing temperature of 10-40 DED C and a culturing rotation speed of 100-300rpm; when culturing is carried out for 1-4days, a product is transferred into a fresh culture medium or culture solution, and screening is carried out. The rhodococcus strain is collected by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and has a collection register number of CGMCC No. 5958. The collection date is April 9th, 2012. With a surfactant-producing capacity of rhodococcus JZX-01, petroleum degradation efficiency is further enhanced. The rhodococcus JZX-01 can be used in biological treatments of petroleum pollutants.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
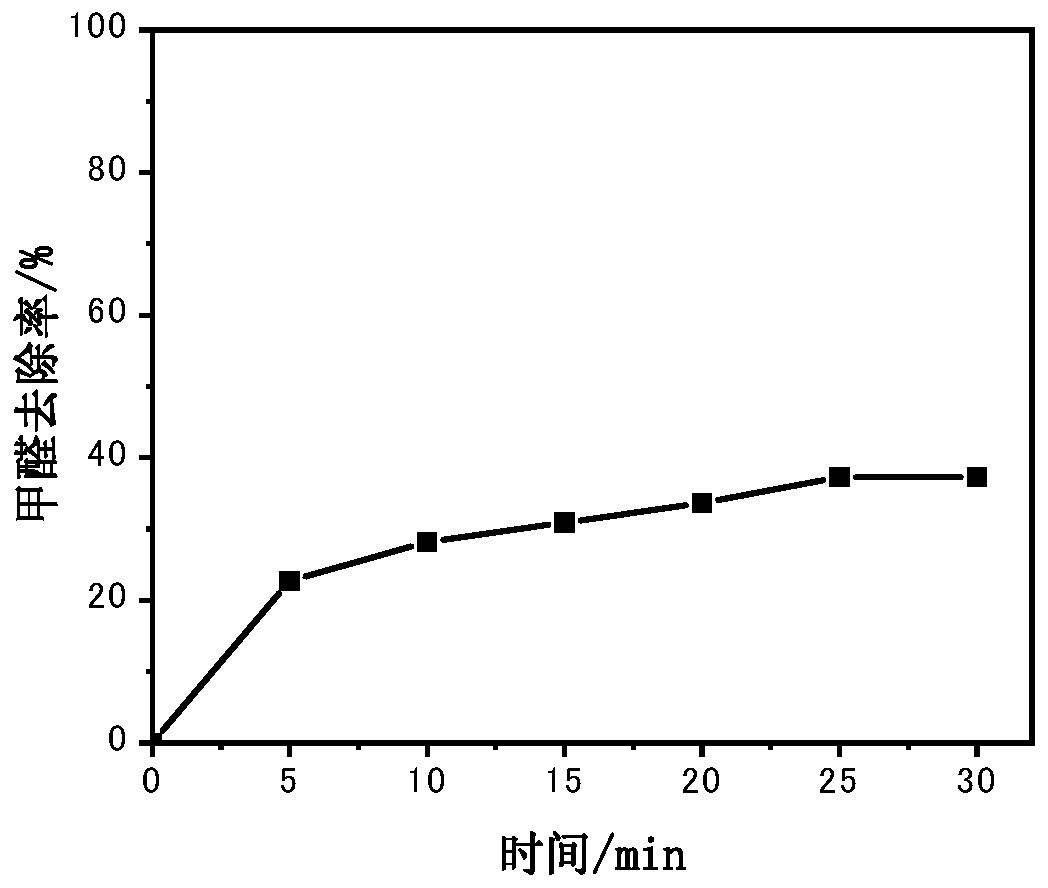
Antibacterial formaldehyde-removing catalytic material, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110639550AImprove transfer efficiencyRapid catalytic degradationGas treatmentAntifouling/underwater paintsPermanganate saltIron salts
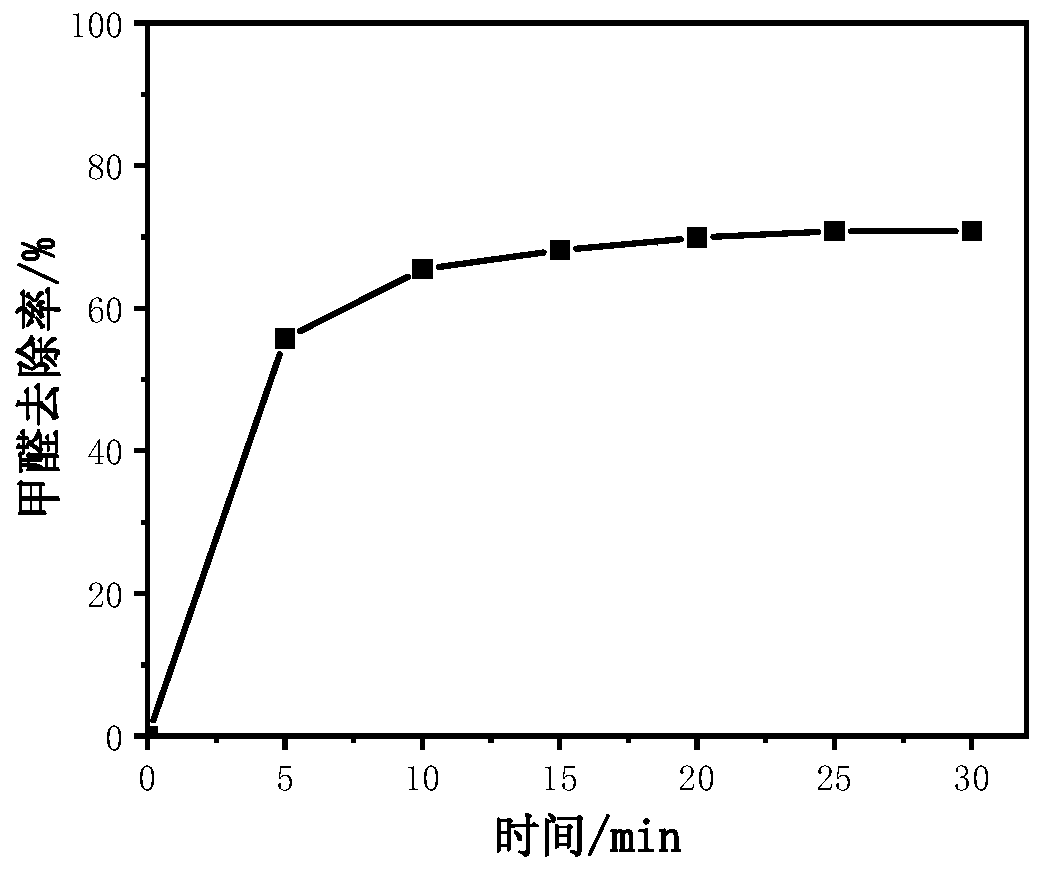
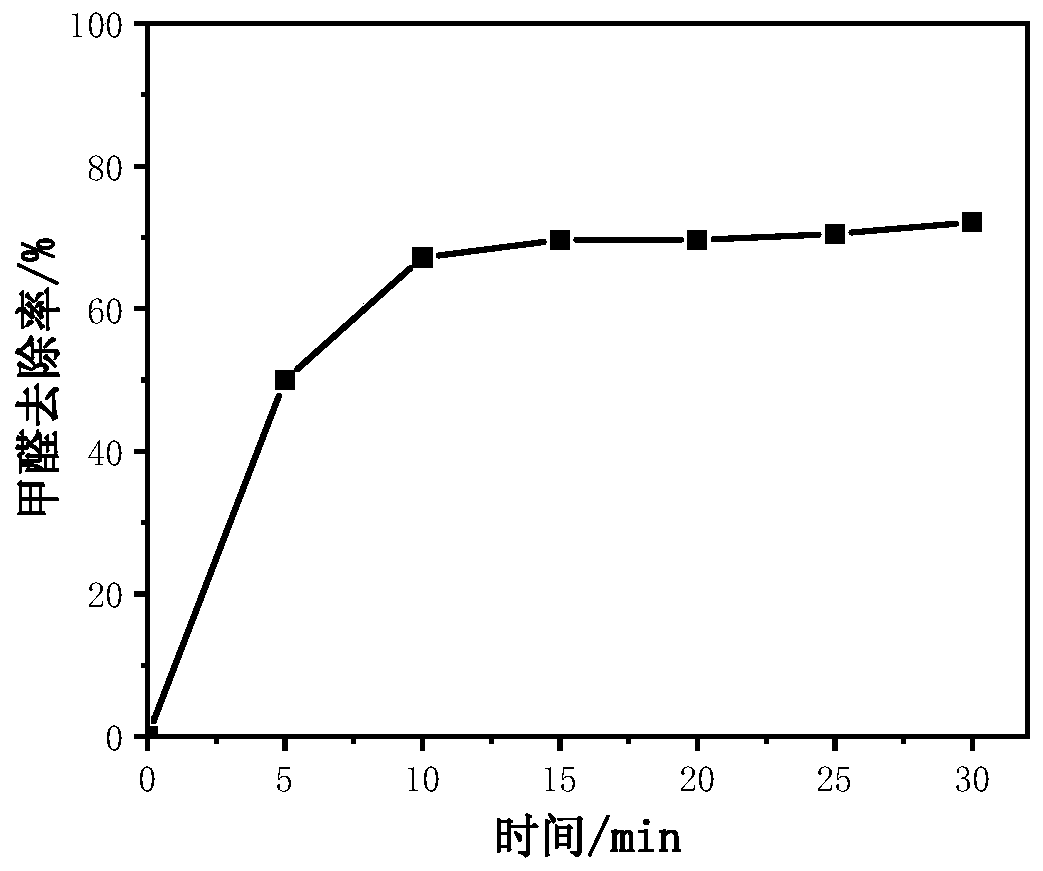
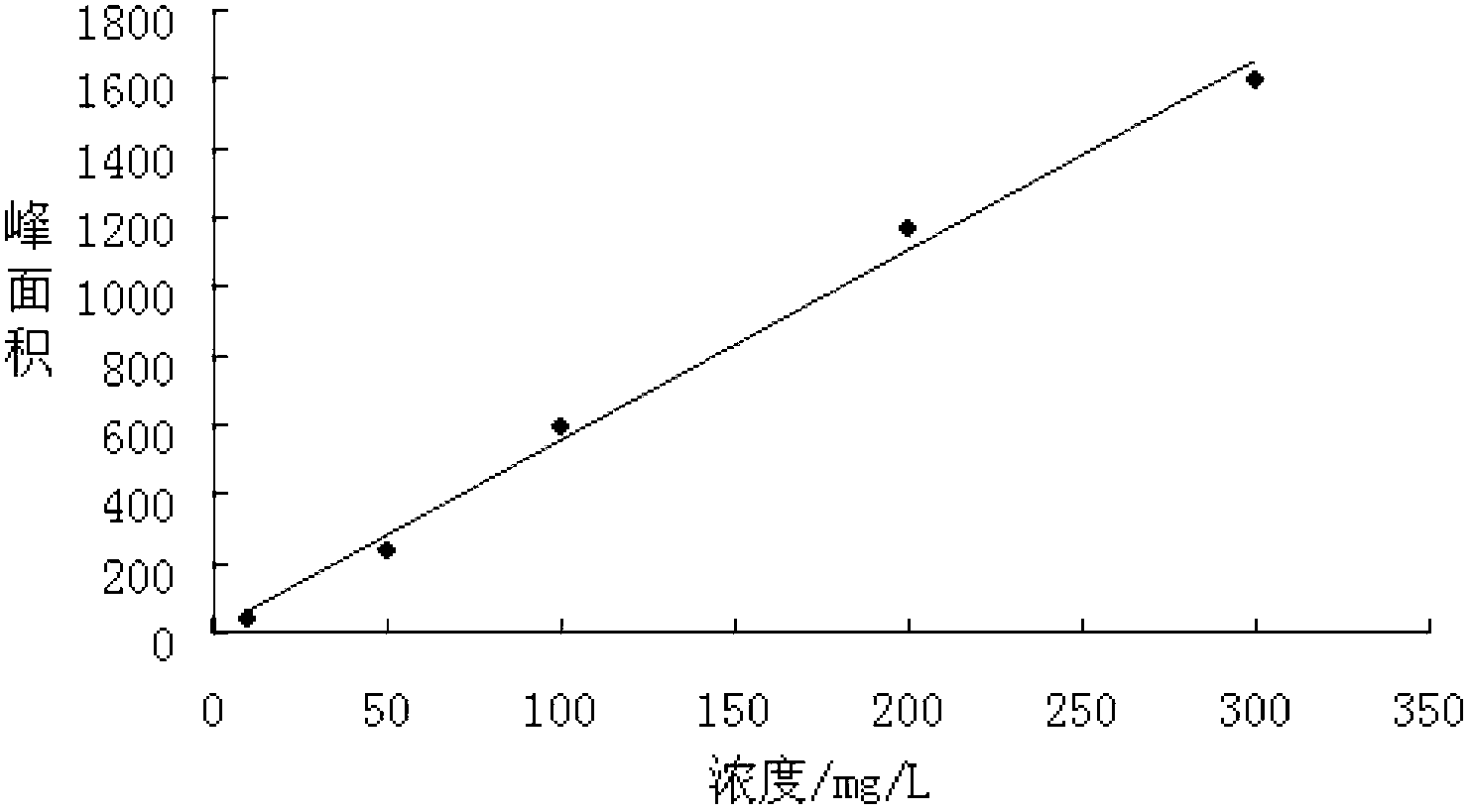
The invention belongs to the technical field of catalytic materials and coatings, and discloses an antibacterial formaldehyde-removing catalytic material, and a preparation method and an application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: adding a permanganate, an iron salt, an oxalate and silver nitrate into water, performing stirring for uniform mixing, carrying out a hydrothermal reaction at 70-120 DEG C, naturally cooling the obtained solution to room temperature after the reaction is finished, and separating, washing and drying the obtained solid product to obtain the powdery antibacterial formaldehyde-removing catalytic material. The antibacterial formaldehyde-removing catalytic material, titanium dioxide, a styrene-acrylic emulsion and water are stirred and mixed, assistants are added, and stirring is performed for uniform mixing to obtain an antibacterial formaldehyde-removing coating. The obtained catalytic material can be used for carrying out efficientcatalytic oxidation on formaldehyde under the condition of no light at room temperature, so that formaldehyde is degraded into harmless carbon dioxide and water. The obtained antibacterial formaldehyde-removing coating can be well smeared on artificial boards, plastic wallpaper and walls, and is safe, nontoxic and odorless. The catalytic material can quickly and safely degrade formaldehyde for along time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
Pseudomonas sp.HZN6 and application thereof to nicotine degradation
ActiveCN102796681ADegradation safetyEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsInorganic saltsNutrient solution
The invention discloses Pseudomonas sp.HZN6 and application thereof to nicotine degradation. In application, with nicotine as a substrate, an inorganic salt nutrient solution as a reaction medium and Pseudomonas sp.HZN6 as an enzyme, the reaction is carried out for 8-15h under the conditions that temperature is 25-45 DEG C and a Ph value is 5.5-9.0 to ensure that the content of nicotine in the reaction solution is less than 0.1 percent by mass, thus the purpose of degrading nicotine is reached. The Pseudomonas sp.HZN6 can be directly added to a water body and soil to degrade nicotine in the water body and soil, and can be used for safely, efficiently and rapidly degrading residual nicotine on objects such as water and soil. A bactericide containing the Pseudomonas sp.HZN6 is prepared by a simple process with low cost, is convenient to use, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:菏泽建数智能科技有限公司
Catalyst for degrading hydrogen peroxide as well as preparation method and application of catalyst
ActiveCN104785254AHigh catalytic activity and stabilityMild reaction conditionsMetal/metal-oxides/metal-hydroxide catalystsSolventActivated carbon
The invention discloses a catalyst for degrading hydrogen peroxide. The catalyst comprises an activated carbon carrier, Pd, metal M1 and metal M2, wherein the Pd, the metal M1 and the metal M2 are loaded on the carbon carrier; the mass percentage content of the Pd in the catalyst is 0.3-1.5 percent, the mass percentage content of the metal M1 is 0.1-1 percent, and the mass percentage content of the metal M2 is 0.05-2 percent; the metal M1 is Pt, Ru or Sn; the metal M2 is K, Ag or Ce. In addition, the invention further discloses a preparation method of the catalyst and a method for catalyzing, hydrogenating and degrading the hydrogen peroxide by applying the catalyst. The catalyst disclosed by the invention has very high catalytic activity and stability and can safely and efficiently catalyze and degrade the hydrogen peroxide in a solvent, so that the hydrogen peroxide is converted into water and does not generate oxygen; the degradation rate of the hydrogen peroxide is larger than 99.5 percent. The catalyst disclosed by the invention has an important safety guarantee effect on chemical industrial solvent recycling and is very wide in market application prospect.
Owner:XIAN CATALYST NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
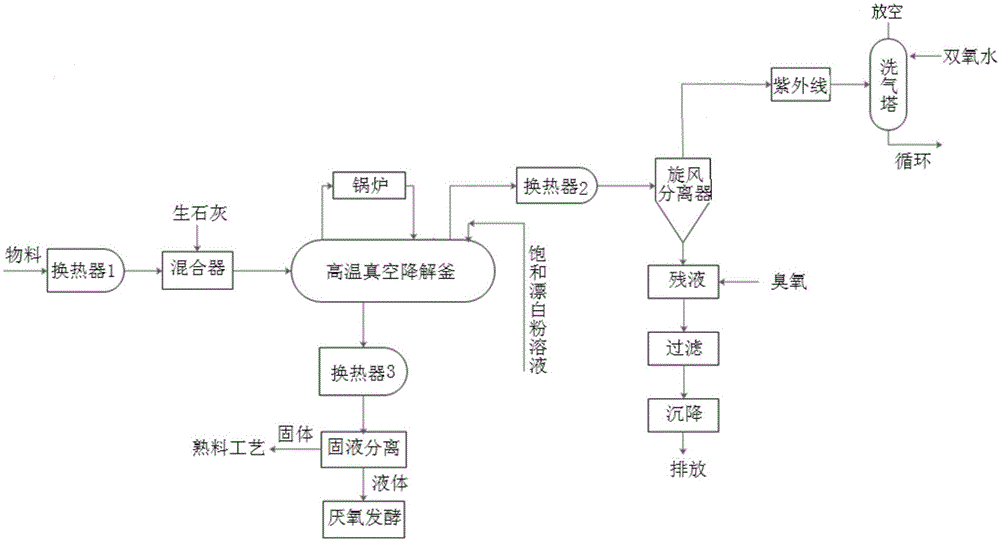
Degradation and harmless treatment method for residual antibiotics in livestock excrement
ActiveCN105084685APromote degradationEasy to handleSludge treatment by thermal conditioningSolid waste disposalHuman wasteDecomposition
The invention discloses a degradation and harmless treatment method for residual antibiotics in livestock excrement. The method comprises the following processing steps that 1, the livestock excrement enters a mixer after being preheated; 2, quicklime is put in the mixer and stirred; 3, the mixture is input into a degradation kettle, stirred and heated; 4, gas is sucked through a vacuum system when the mixture is heated; 5, gas-liquid separation is performed after the sucked gas is cooled, gas is exhausted after being irradiated through ultraviolet light and washed through a washing tower, and liquid is drained after being treated through ozone, filtered and precipitated; 6, bleaching powder saturated solutions accounting for 3%-5% of the total mass of the materials are sprayed into the degradation kettle and stirred; 7, the materials are discharged, solid-liquid separation is performed after the materials are cooled, solids are stacked for decomposition, and liquid is treated through anaerobic fermentation. The degradation and harmless treatment method for the residual antibiotics in the livestock excrement is convenient to operate, high in mechanization degree, large in treatment capacity, efficient, rapid, capable of effectively degrading and harmlessly treating the residual antibiotics in the livestock excrement and suitable for industrialization production, and meanwhile sterilization and disinfection for the livestock excrement also can be completed; after the livestock excrement is treated through the technologies, and the effects of achieving complete degradation of the residual antibiotics and being free of residues harmful to various organisms in a natural environment can be achieved.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
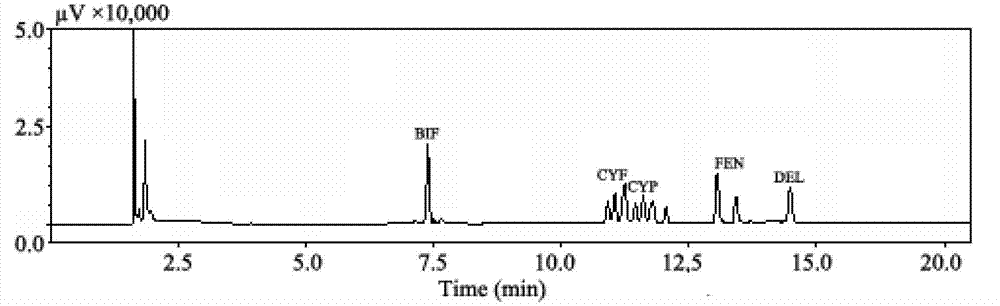
Pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria, separation and purification method thereof and application thereof
ActiveCN102899270AEfficient degradationHigh-efficiency pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria can degrade safelyBacteriaWater contaminantsPurification methodsBifenthrin
The invention discloses a pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria, wherein the bacteria is an HS-24 strain, with a classification naming as Methylophagasp., and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 24, 2012, an accession number being CGMCCNo. 6046; and a Genbank accession number of the 16SrRNA of the strain is JX087925. The invention simultaneously discloses a separation and purification method and an application of the pyrethroid pesticide degrading bacteria. The invention is advantageous in that the bacteria can safely, highly-efficiently and rapidly degrade 5 kinds of pyrethroid pesticide: cypermethrin, deltamethrin, fenvalerate, cyfluthrin and bifenthrin in a marine environment, and has a good application prospect in the aspects of offshore environmental protection, pollution treatment of pesticide residues in an aquaculture environment and food safety guarantee.
Owner:路亚科消防车辆制造有限公司
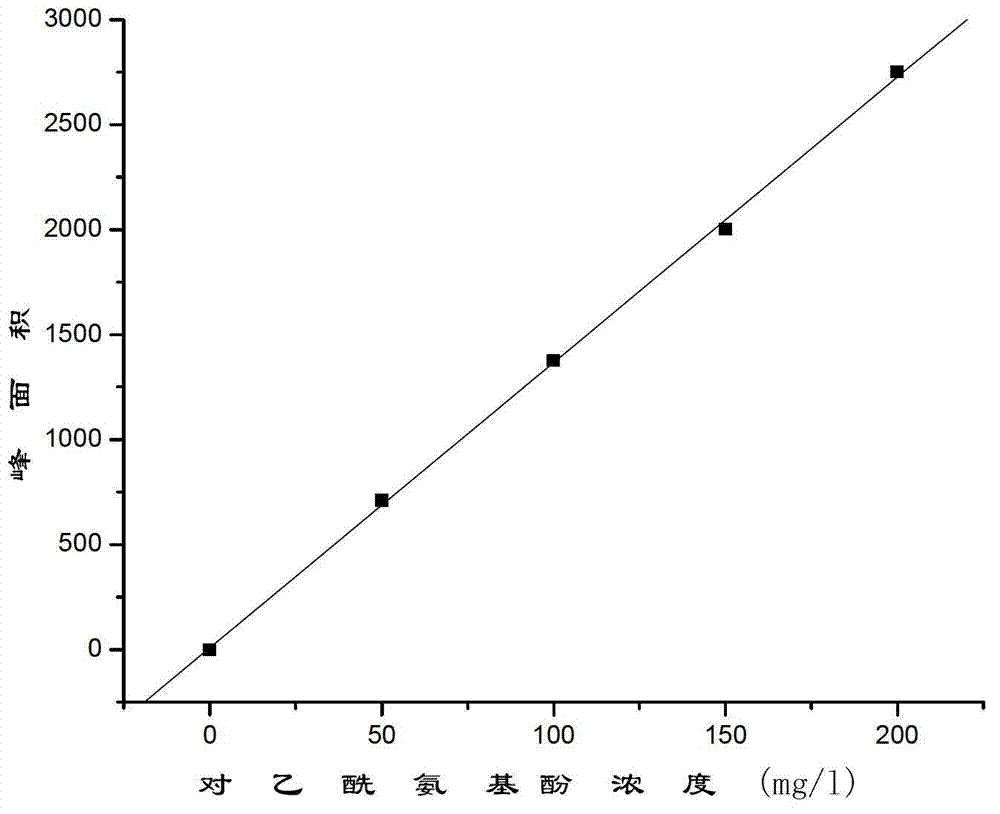
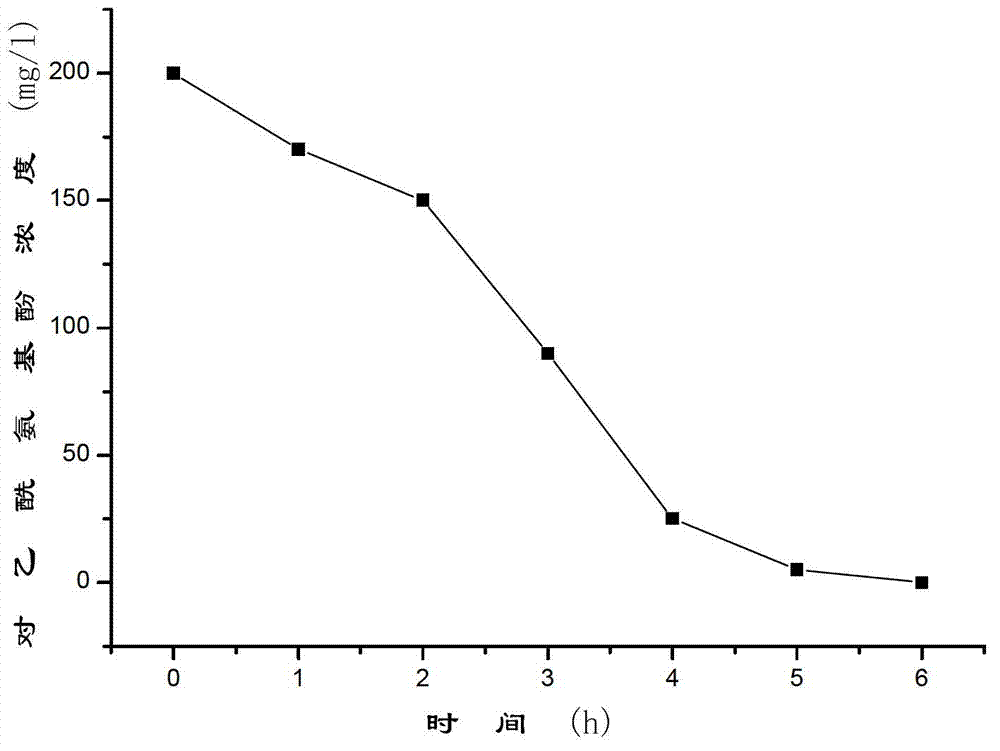
Shinella sp. and application thereof to micro-biologically degrading acetaminophen
ActiveCN102965310ADegradation safetyEfficient degradationBacteriaWater contaminantsFungicideMicroorganism
The invention provides a novel efficient acetaminophen degrading bacterium-Shinella sp. HZA2 and an application thereof to micro-biologically degrading acetaminophen. The strain was collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC), with the collection date being October 15, 2012 and collection number being CCTCC No: M2012405. The address of the CCTCC is Wuhan University, Wuhan, China and the postcode is 430072. The Shinella sp. HZA2 can be applied to degrading acetaminophen in water and soil by way of direct addition and can safely, efficiently and quickly degrade residual acetaminophen on such objects as water and soil. The fungicides containing the strain are simple in preparation processes, low in costs and convenient to use and have good application prospects.
Owner:沛县度创科技发展有限公司
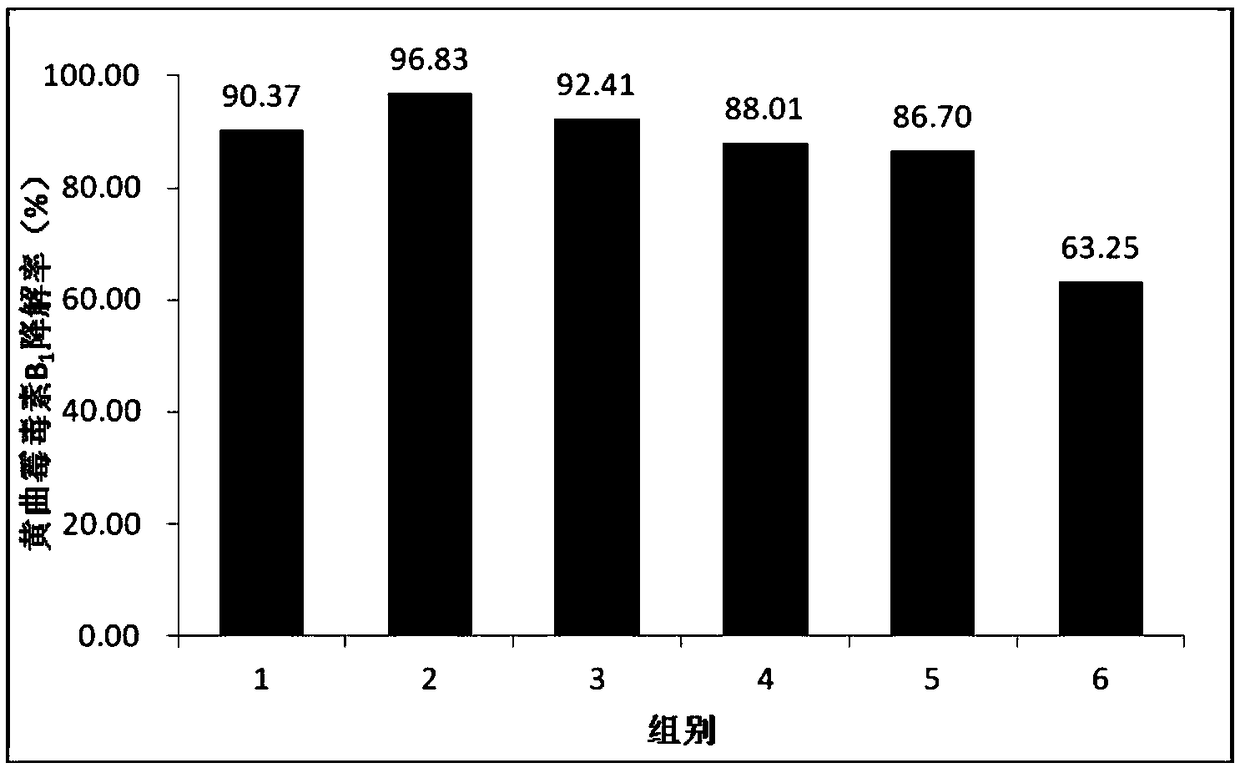
Fermentation agent for degrading aflatoxin, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108913627ADegradation product safetyImprove bioavailabilityFungiBacteriaMicrobial agentStreptococcus thermophilus
The invention discloses a fermentation agent for degrading aflatoxin, and a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of toxin degradation. The fermentation agentfor degrading the aflatoxin is formed by a compound microbial agent and a synergist according to the weight-to-volume ratio of 4:1, and the compound microbial agent is formed by Streptococcus thermophilus, bifidobacterium, candida utilis and bacillus licheniformis which are mixed according to the weight ratio of (1-5):(1-5):(3-8):(3-8). The fermentation agent can effectively degrade the aflatoxinB1 in crops or agricultural products, and a degraded product is safe and does not generate the toxic effect on animal bodies.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
Production method of barley leaf and wheat germ compound beverage
The invention discloses a production method of barley leaf and wheat germ compound beverage. The production method is characterized by comprising the steps of taking barley leaves as raw materials, performing impurity removal, high pressure cleaning, purifying rinsing, artificial cleaning, cutting, leachating, withering, oxidative fermentation, evaporation and sizing, primary drying, secondary drying, magnetic sieving, excessive metal detection, cutting and crushing, water-cooling crushing and low-temperature wall breaking to prepare barley seedling powder, and then adding small-molecular wheat germ powder and mixing to prepare the solid beverage. According to the solution, by scientific combination of raw material components of barley leaves and wheat germs, the barley leaf and wheat germ resources are fully used, and the type of the barley leaf and wheat germ compound solid beverage is enriched; meanwhile, by the application of a modern food processing technology and a biological technology, the shortcomings in the prior art are overcome, and the beverage with the characteristics of nature, nutrition, convenience, safety, good taste and the like is prepared; people can eat the beverage frequently to fulfill the aims of nourishing the life and protecting the health.
Owner:WEIHAI XINYI BIOLOGICAL TECH
Bacillus subtilis and application thereof in degrading zearalenone
ActiveCN112410269AReduce concentrationProlong degradation timeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses Bacillus subtilis and application thereof in degrading zearalenone. The Bacillus subtilis is specifically Bacillus subtilis 816, and the preservation number of the Bacillus subtilis 816 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center is CGMCC No. 14854. Experiments prove that the Bacillus subtilis 816 CGMCC No. 14854 can degrade the zearalenone into zearalenone phosphate which is greatly reduced in biotoxicity and exists stably. The Bacillus subtilis has important application value.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
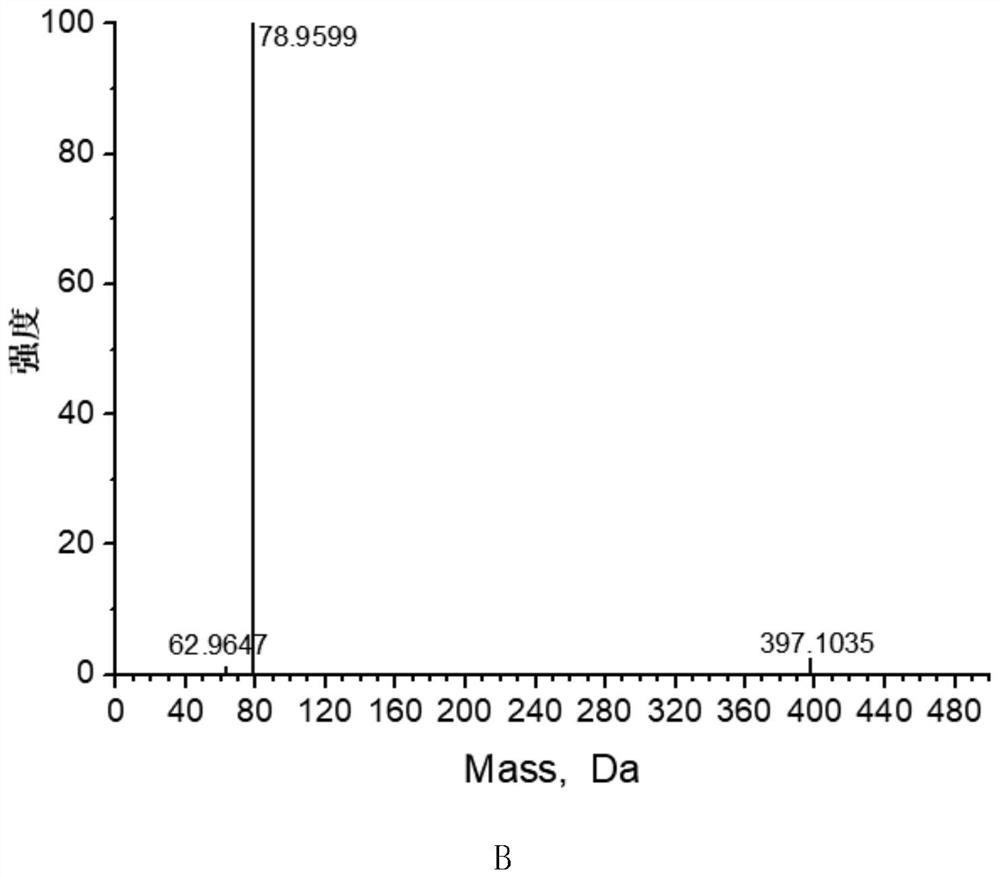
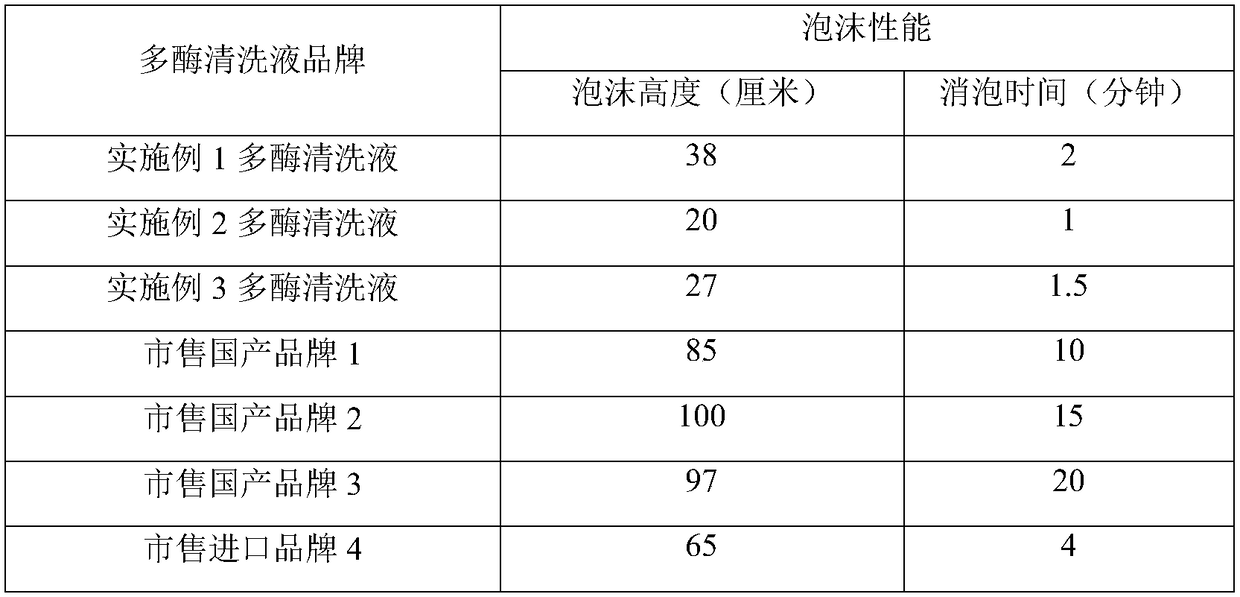
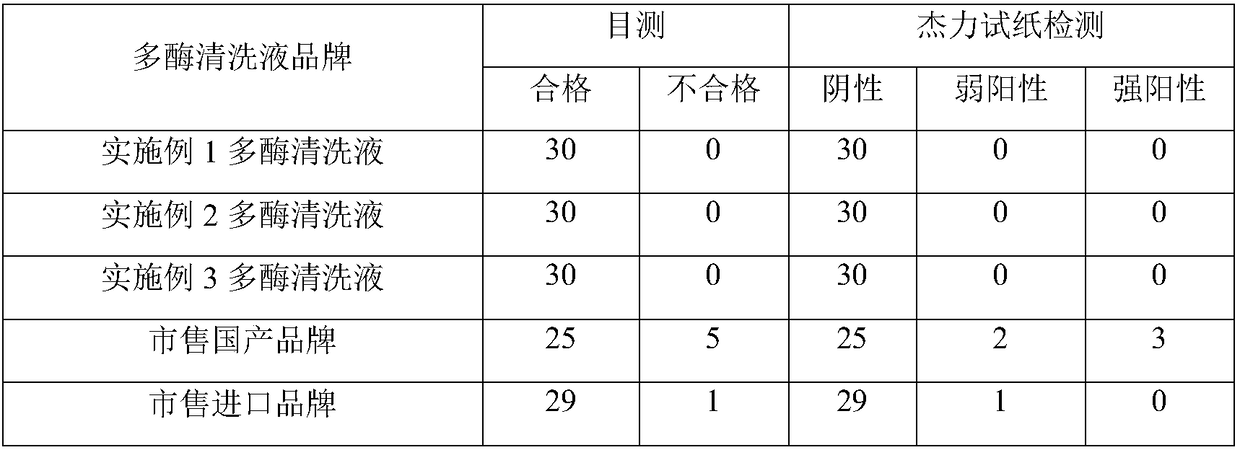
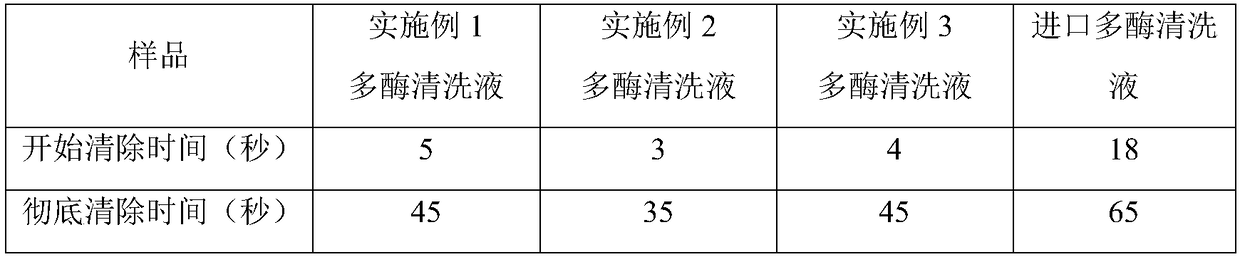
Medical multienzyme cleaning liquid and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN109234045AReduce usageReduce air bubblesOrganic detergent compounding agentsPolymeric surface-active compoundsChemistryProtease
The invention discloses a medical multienzyme cleaning liquid and a preparation method thereof and belongs to the technical field of medical detergents. According to the medical multienzyme cleaning liquid, protease and other enzymes such as lipase, catalase, ligninase and glucose oxidase coexist by matching the components, and meanwhile, the use level of total enzymes is reduced, so that the costis lowered. The cleaning liquid still has a relatively good cleaning efficiency and cleaning effect. Meanwhile, a safer and easily degraded antibacterial preservative theta-polylysine is added, so that the more stable, environment-friendly and efficient cleaning liquid can be formed.
Owner:重庆奥舍生物化工有限公司
Cleaning liquid and its application in cleaning household electrical appliance
InactiveCN1827758AGood compatibilitySecurity compatibilityInorganic/elemental detergent compounding agentsSurface-active detergent compositionsSodium metasilicateAlkyl polyglycoside
A cleaning fluid consists of 35-63 % of isopropanol, 5-32 % of alcohol, 28-55 % of deionized water, 0.1-0.3 % of alkyl polyglycoside, 0.4-1.2 % of alkyl sodium benzene sulfonate, 0.1-0.2 % of nipagin, 0.3-0.5 % of sodium metasilicate and 0.1-0.2 % of lemon essence. The process includes the following steps: heating the deionized water to 65-70 DEG C, then separately adding alkyl sodium benzene sulfonate, nipagin, alkyl polyglycoside, lemon essence and sodium metasilicate, stirring evenly, cooling to a room temperature, then adding dimethyl carbinol and alcohol and mixing them evenly. The cleaning fluid can be used in cleaning domestic appliances, which not only has good washing effect and simple operation but also has safety compatibility with the plastics and the painted surface of the domestic appliances, and can not pollute the environment.
Owner:史秀宁
Preparation for degrading pesticide residue in plants and preparation method for same
ActiveCN102550553BEfficient degradationDegradation safetyBiocideAnimal repellantsPesticide residueFerrous sulfate iron
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com