Set of methods suitable for evaluating toxicity changes of pesticide residues in soil
A pesticide residue and soil technology, which is applied in the field of evaluating changes in the toxicity of pesticide residues in soil, can solve the problems of incomplete and inaccurate determination of the residual toxicity, and the degradation products cannot be extracted or detected, so as to facilitate genotoxicity and ecotoxicity Measurement, wide applicability, and reproducible effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Embodiment 1 determines residual toxicity extraction method process
[0030] Organic solvent extraction method
[0031] Preliminary experiment scheme: Take 20g of test soil sample and use petroleum ether: acetone (volume ratio is 1: 1) mixed solution 120mL, first soak in Soxhlet extractor for 12h and then extract for 6h. The extract was concentrated to about 1mL on a rotary evaporator to obtain a soil extract; Note: when the amount is small, add DMSO 2-3 times, 1ml each time, and continue to blow.), use DMSO (dimethyl sulfoxide) solvent to make the volume to 5mL, and use it to prepare for the test.
[0032] According to this experimental plan, if all the earthworms used in the experiment die, the experimental method should be modified. The revision mainly solves the following three questions: (1) whether dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) is toxic to earthworms, and whether DMSO can be used to fix the volume; (2) the mixture of petroleum ether and acetone (volume ratio 1:1 ) ...
Embodiment 2
[0084] Comparison of different property pesticide residue toxicity determination methods in the soil of embodiment 2
[0085] 1. Test soil
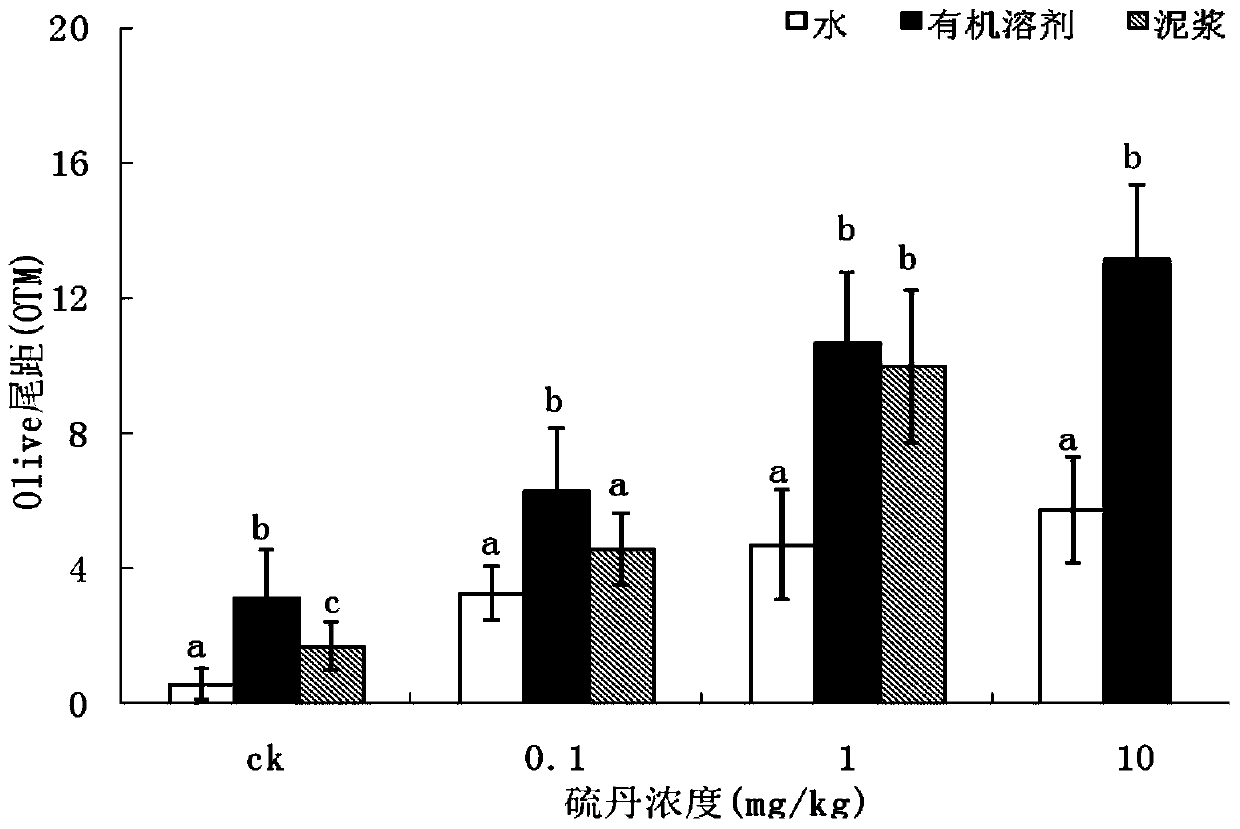
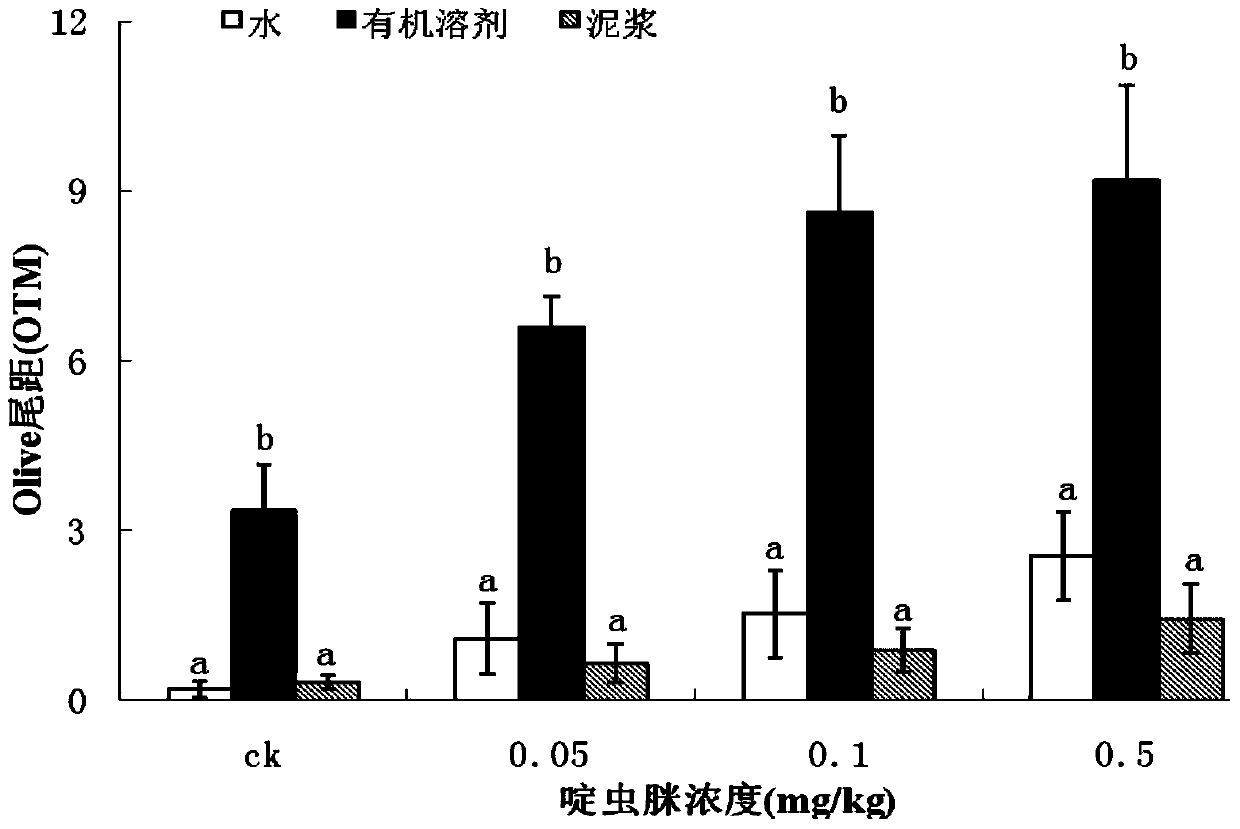
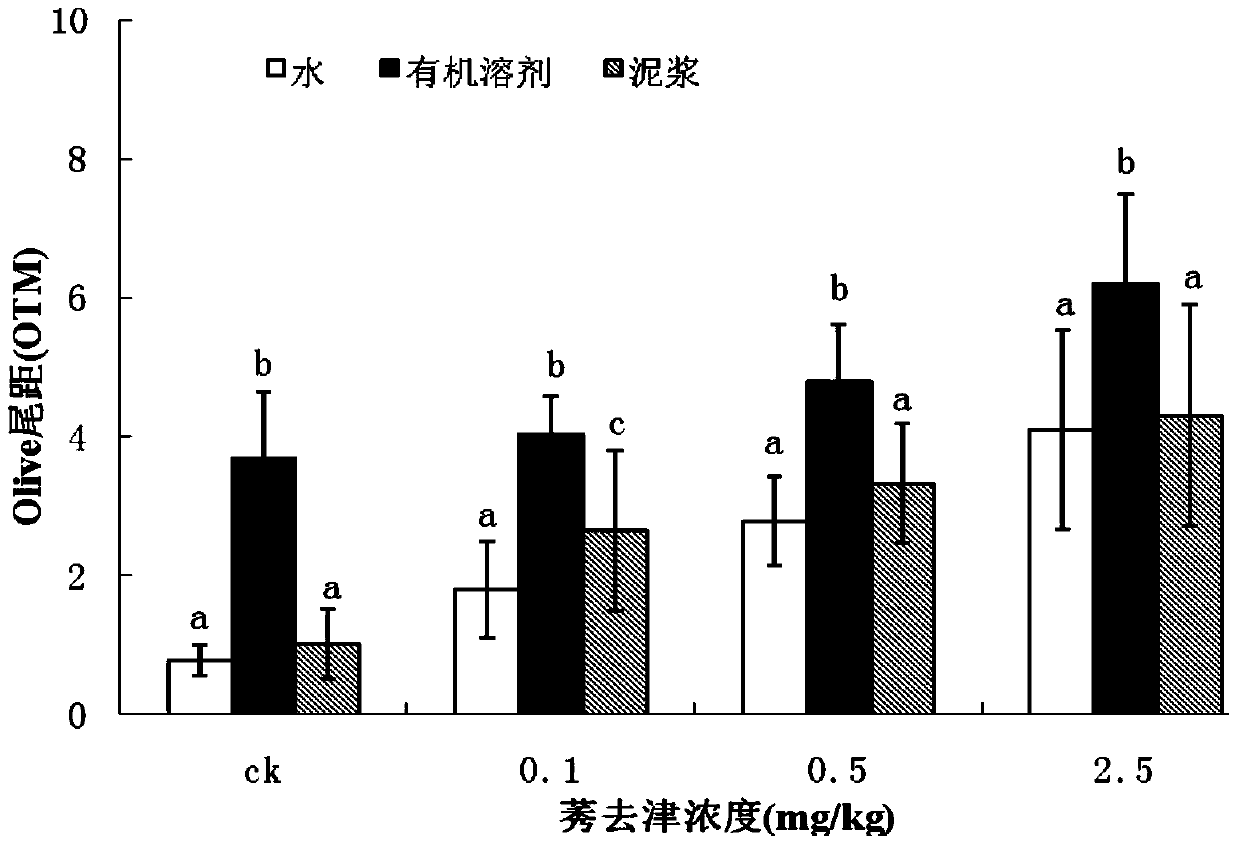
[0086]After the soil was ground, it passed through a 2mm sieve, and four pesticides with different properties were selected as representatives and added to the soil at a certain concentration. These four kinds of pesticides are respectively endosulfan, acetamiprid, imidacloprid and atrazine, and the concentration of each pesticide in the soil is set as follows: the concentration of endosulfan in the soil is set as: control group (0), 0.1 , 1.0, 10.0mg / kg four treatments; adding acetamiprid to the soil set the concentration as: control group (0), 0.05, 0.1, 0.5mg / kg four treatments; adding imidacloprid to the soil set the concentration as: control Group (0), 0.1, 0.5, 1mg / kg four treatments; adding atrazine to the soil set the concentration as: control group (0), 0.1, 0.5, 2.5mg / kg four treatments. After the pollutants are added to the s...
Embodiment 3
[0143] Embodiment 3 Application of the present invention in endosulfan degradation dynamic process
[0144] Centrifuge the cultured strains in a low-temperature refrigerated centrifuge at 8000rpm for 8min at 15°C. After the centrifugation, pour off the supernatant and collect the sediment at the bottom of the centrifuge tube, that is, the wet bacteria. Dissolve the wet bacteria in 20mL (pH 7.0 ) of 0.05mol / L phosphate buffer (Na 2 HPO 4 -NaH 2 PO 4 ) to wash the components 3 times, centrifuge again under the above conditions for 8min, and then use 0.05mol·L -1 Phosphate buffer solution and wet bacteria were prepared by vortexing and mixing at a mass ratio of 3:1 to prepare endosulfan-degrading bacteria suspension. Get 40 brown bottles of 125ml, be divided into 2 test groups: one group adds endosulfan to soil, another group adds endosulfan and endosulfan degrading bacteria to soil, each group respectively establishes 20 brown bottles, two test groups Add 20g of soil to the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com