Method for predicating embryotoxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants on early-phase life stage of zebra fish
A technique for NSAIDs, zebrafish embryos, applied in the field of environmental toxicology
Active Publication Date: 2015-11-11
GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
View PDF4 Cites 11 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
[0003] The purpose of the present invention is to provide a method for predicting the effect of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug new pollutants on the conventional physical and chemical indicators in the prior art that cannot reflect the toxicity of low-dose non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug new pollutants in the actual environment. A method for embryotoxicity in the early life stages of zebrafish, enabling the analytical testing and quantitative description of the toxicity profile and toxicity levels of novel pollutants from non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
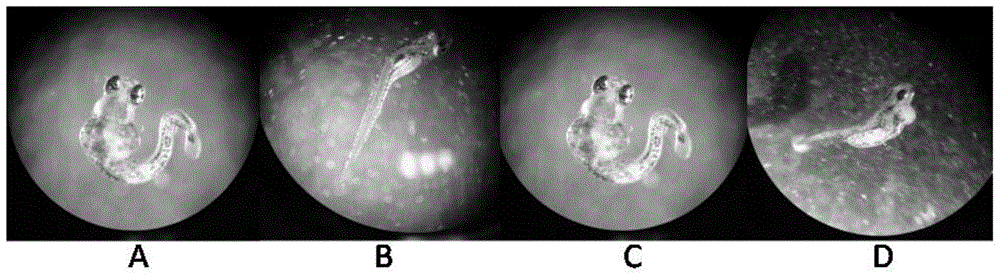
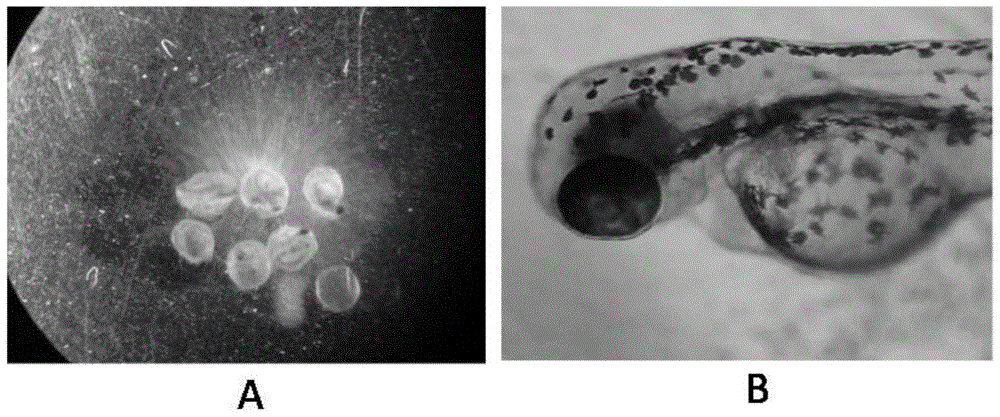
[0020] Example 1: Evaluation of three typical non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and novel pollutants (diclofenac, acetaminophen and ibuprofen) on the embryo toxic effects of zebrafish in early life stages
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
The invention discloses a method for predicating the embryotoxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants on an early-phase life stage of zebra fish. The method comprises the following steps: exposing zebra fish embryos in the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants which have equal logarithm space concentrations; recording the death rate and the aberration rate of the zebra fish embryos 7 days after exposing; and calculating by using SPSS software to obtain corresponding LC50 and teratogenetic EC50, which are used for evaluating the toxicity of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants. With the adoption of the method, the toxicity feature and the toxicity level of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants are subjected to an analytical test and quantitative description; and meanwhile, the method also can be used as an index for monitoring and evaluating the wastewater biological toxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and reference is provided for risk predication and evaluation of the potential biological toxicity of the pollutants in a water body.
Description
Technical field [0001] The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental toxicology, and in particular relates to a method for predicting the embryo toxicity of novel non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to zebrafish in the early life stage. Background technique [0002] The widely used non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) not only relieve human suffering, but also bring many environmental pollution and hazards. Exposure to lower concentrations will cause adverse effects on aquatic organisms, and they may also be synergistic and additive. Such interactions lead to increased joint toxicity when a large amount of coexistence occurs, and the potential risks cannot be ignored. However, the current toxicological studies of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are still mainly focused on the acute toxicity of short-term high-dose exposures simulated in the laboratory, and there are few studies on the toxicity that may be caused by exposure to their actual enviro...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More IPC IPC(8): G01N33/48
Inventor 杜娟钟玉鸣许玫英孙国萍
Owner GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com