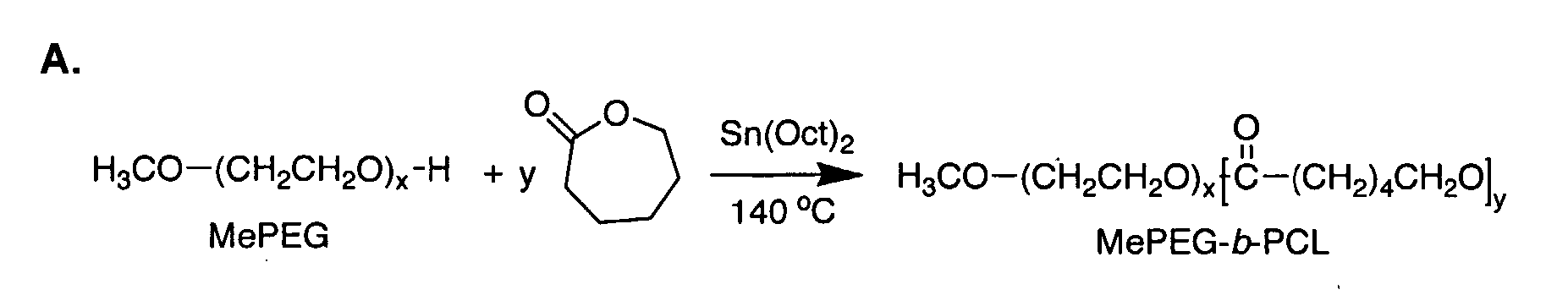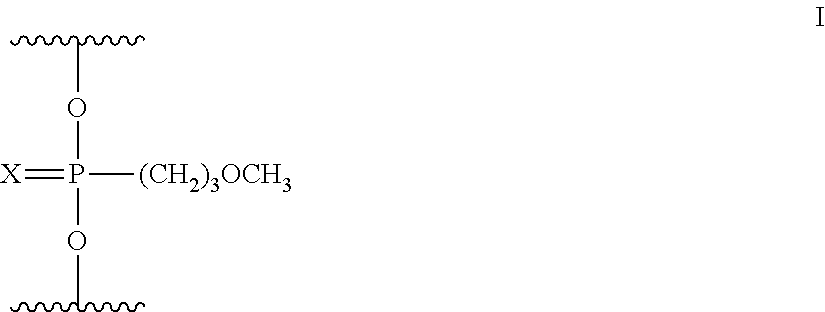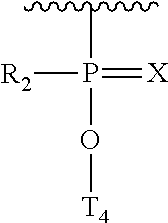Patents
Literature
31 results about "Toxicity profile" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Toxicological profile ( toxicity profile ) An examination, summary, and interpretation of a hazardous substance to determine levels of exposure and associated health effects.
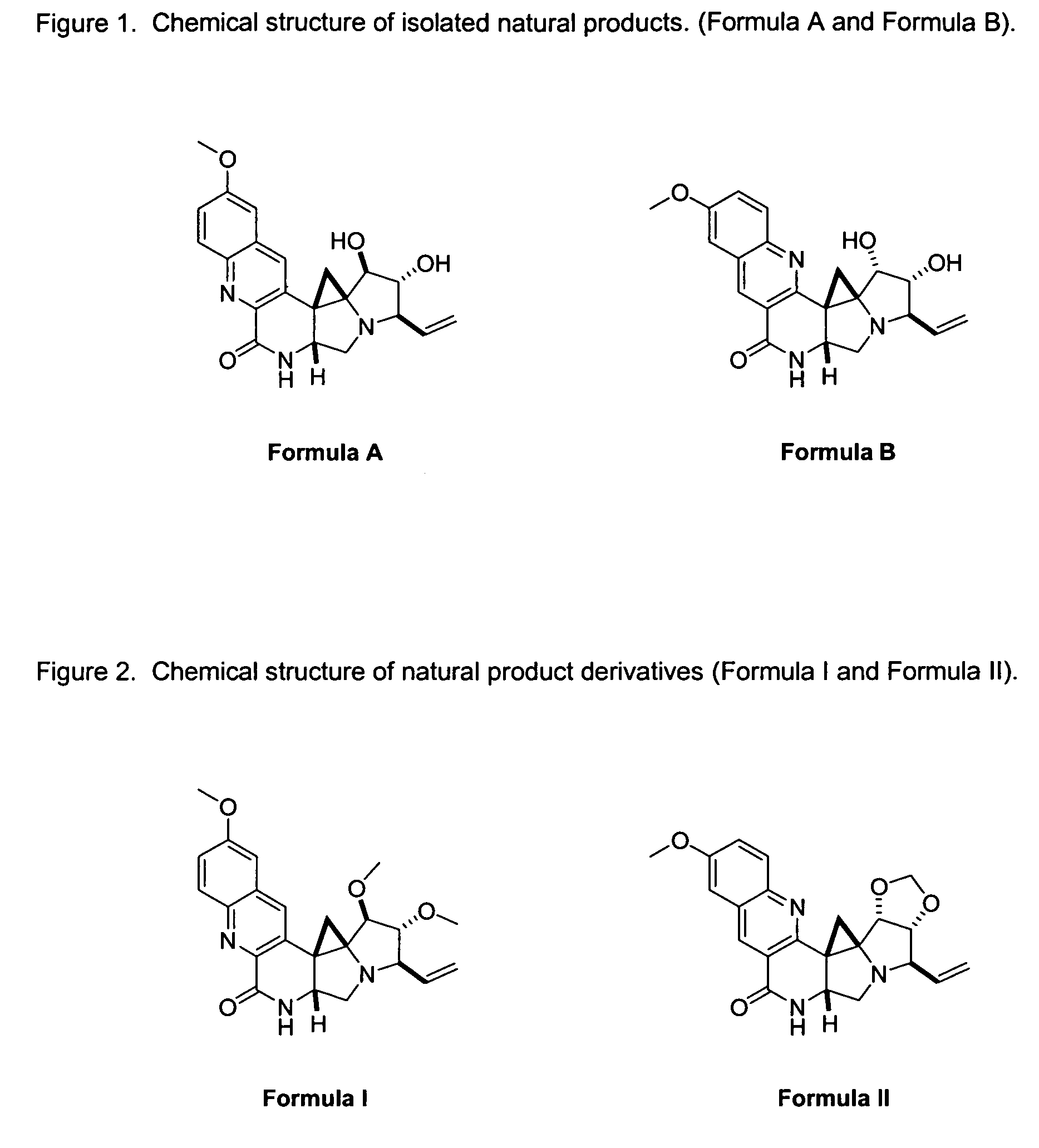
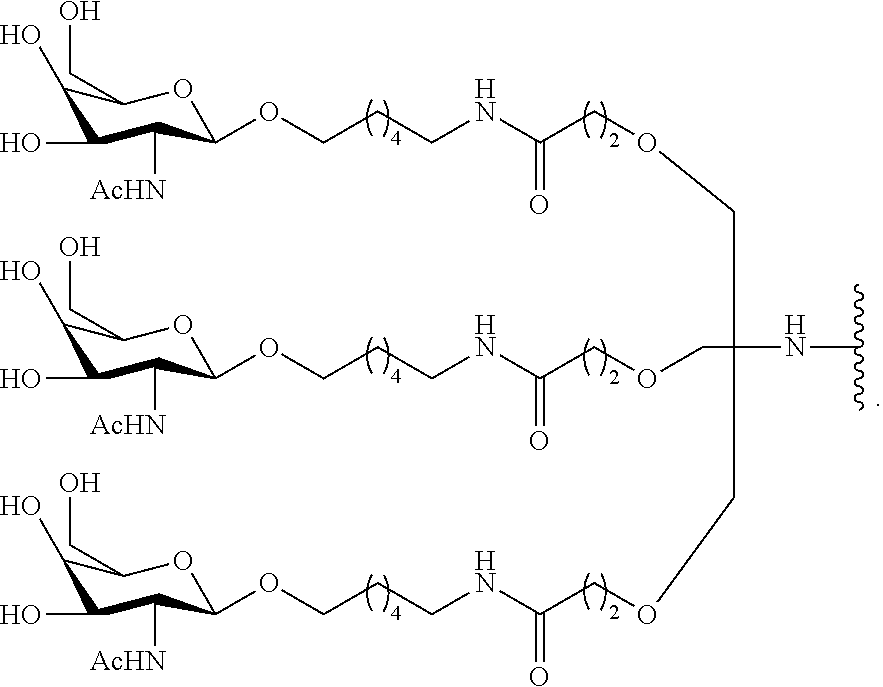
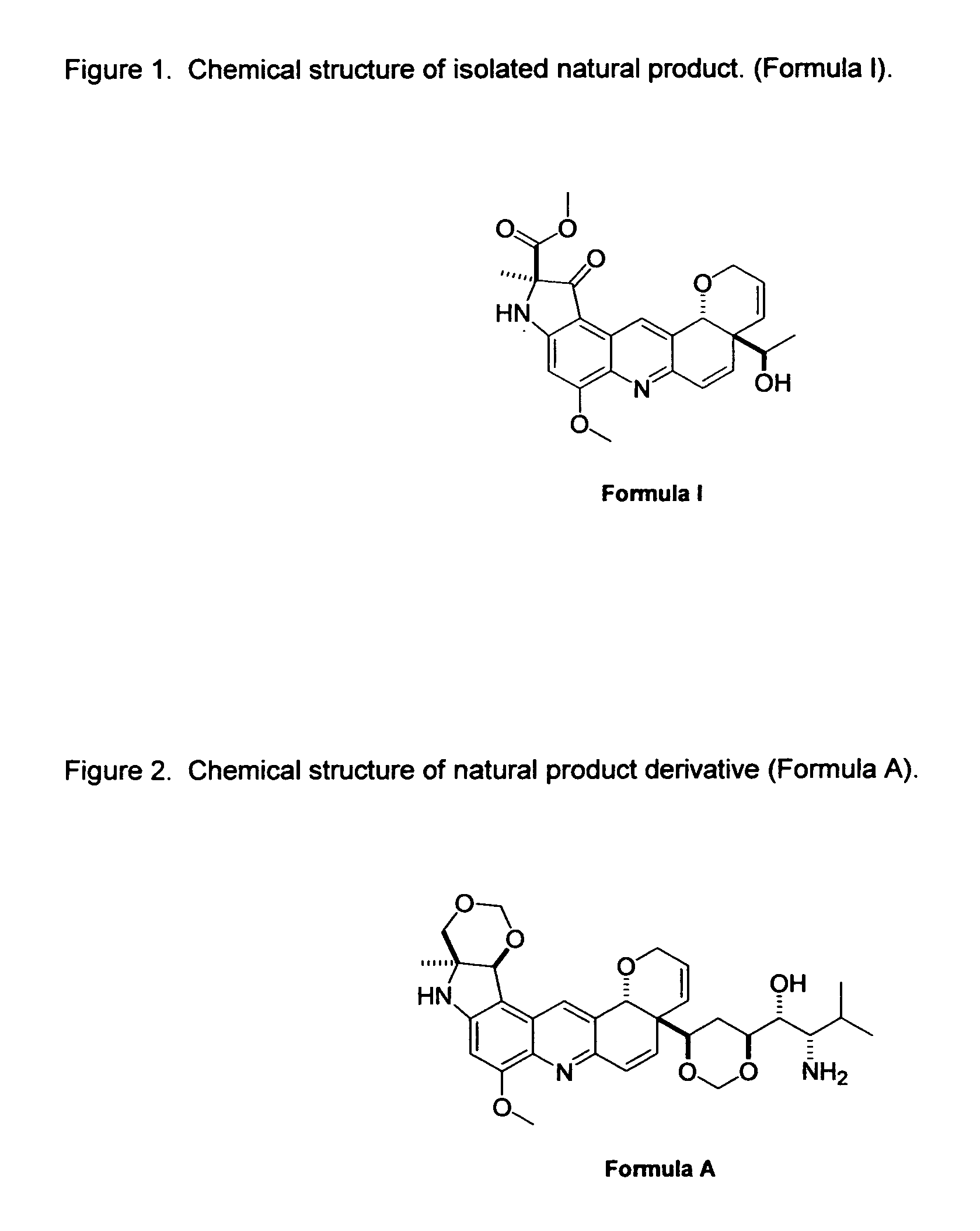
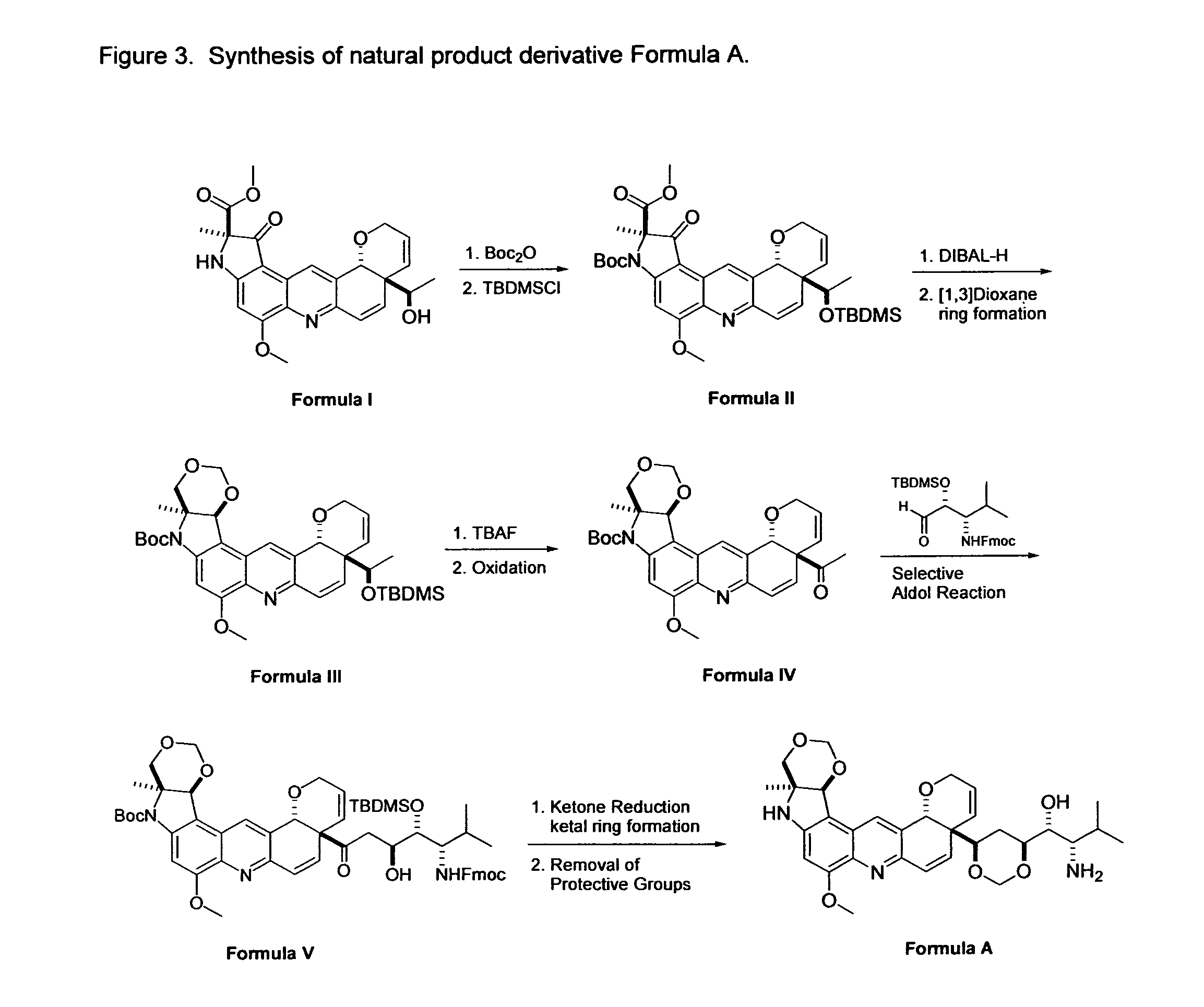
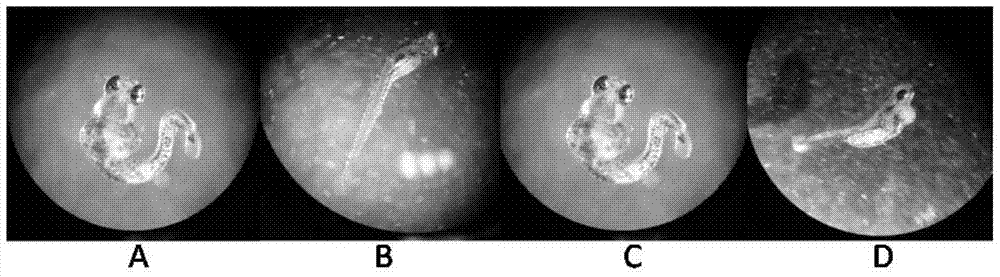
Novel Imino Sugar Derivatives Demonstrate Potent Antiviral Activity and Reducted Toxicity
InactiveUS20110189771A1Good effectImprove performanceOrganic chemistryTissue cultureBovine Viral Diarrhea VirusesSide chain
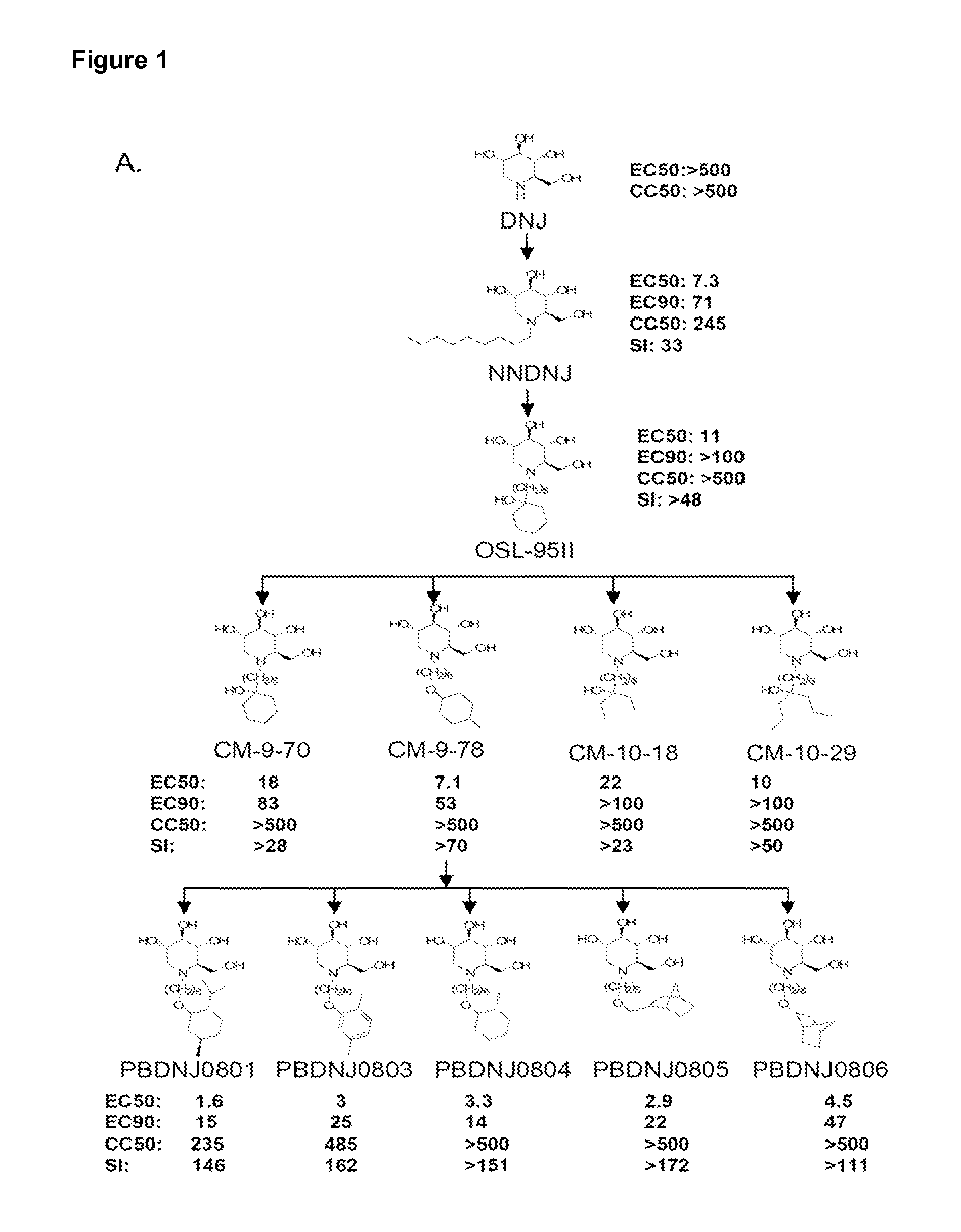
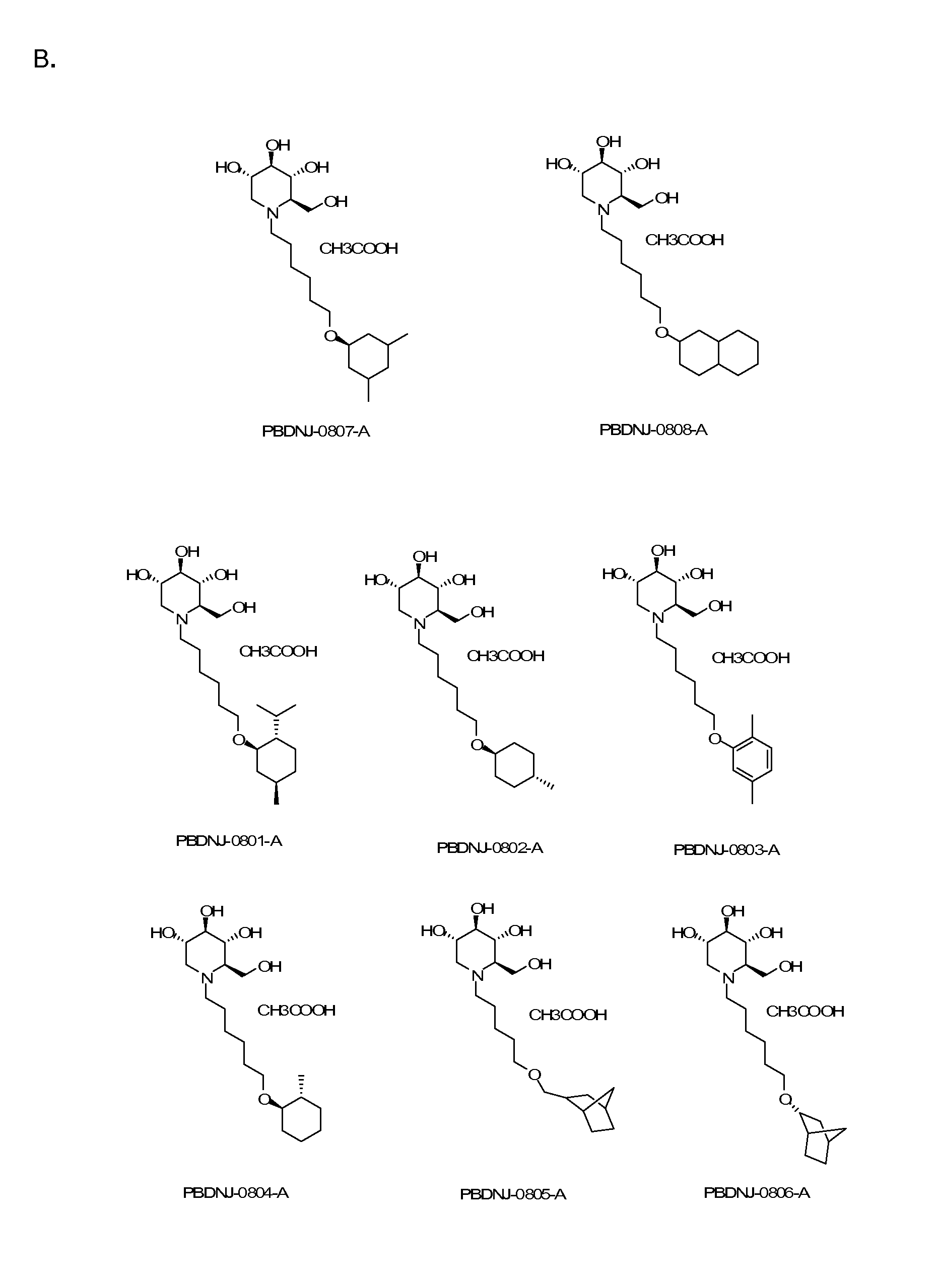
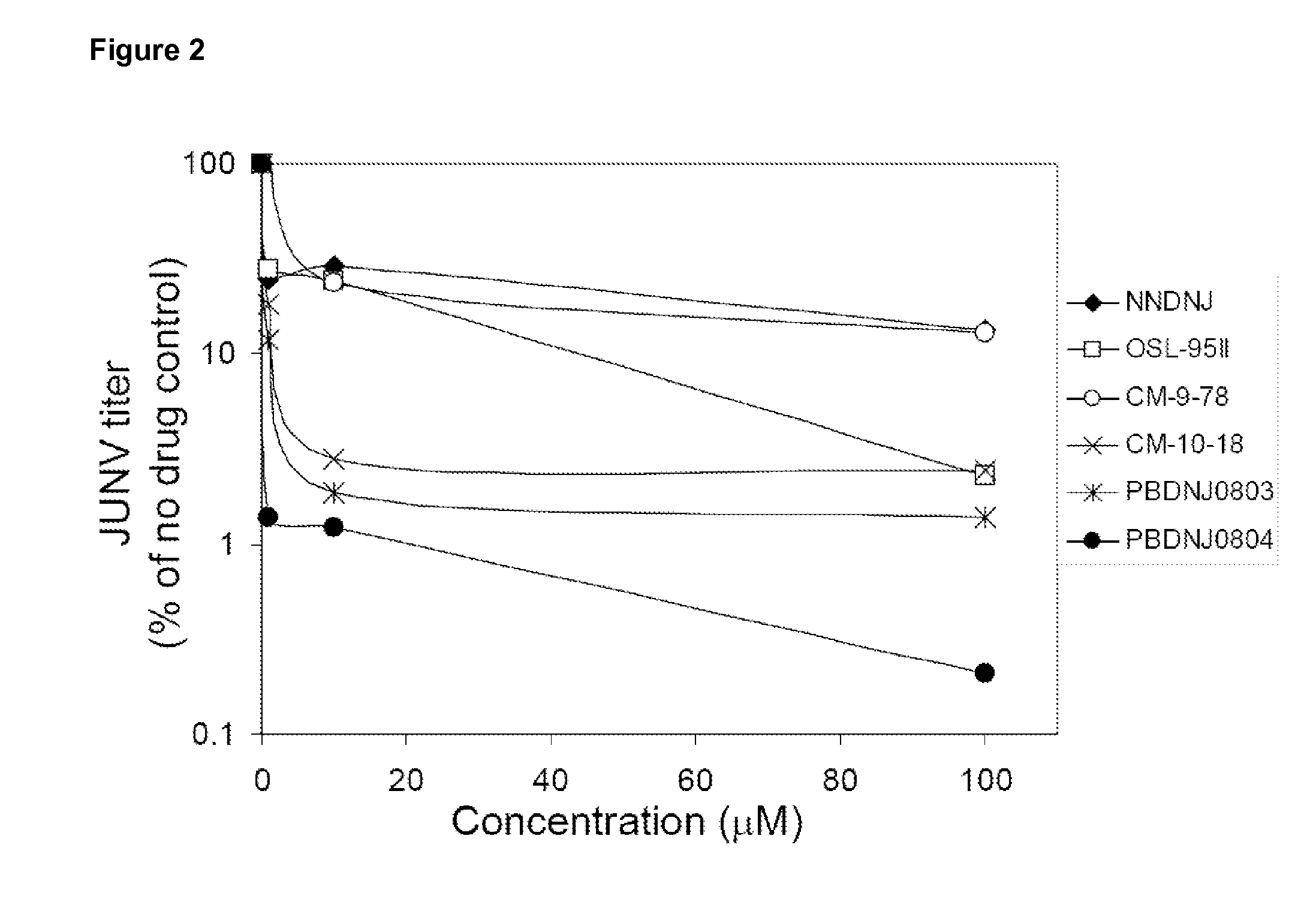
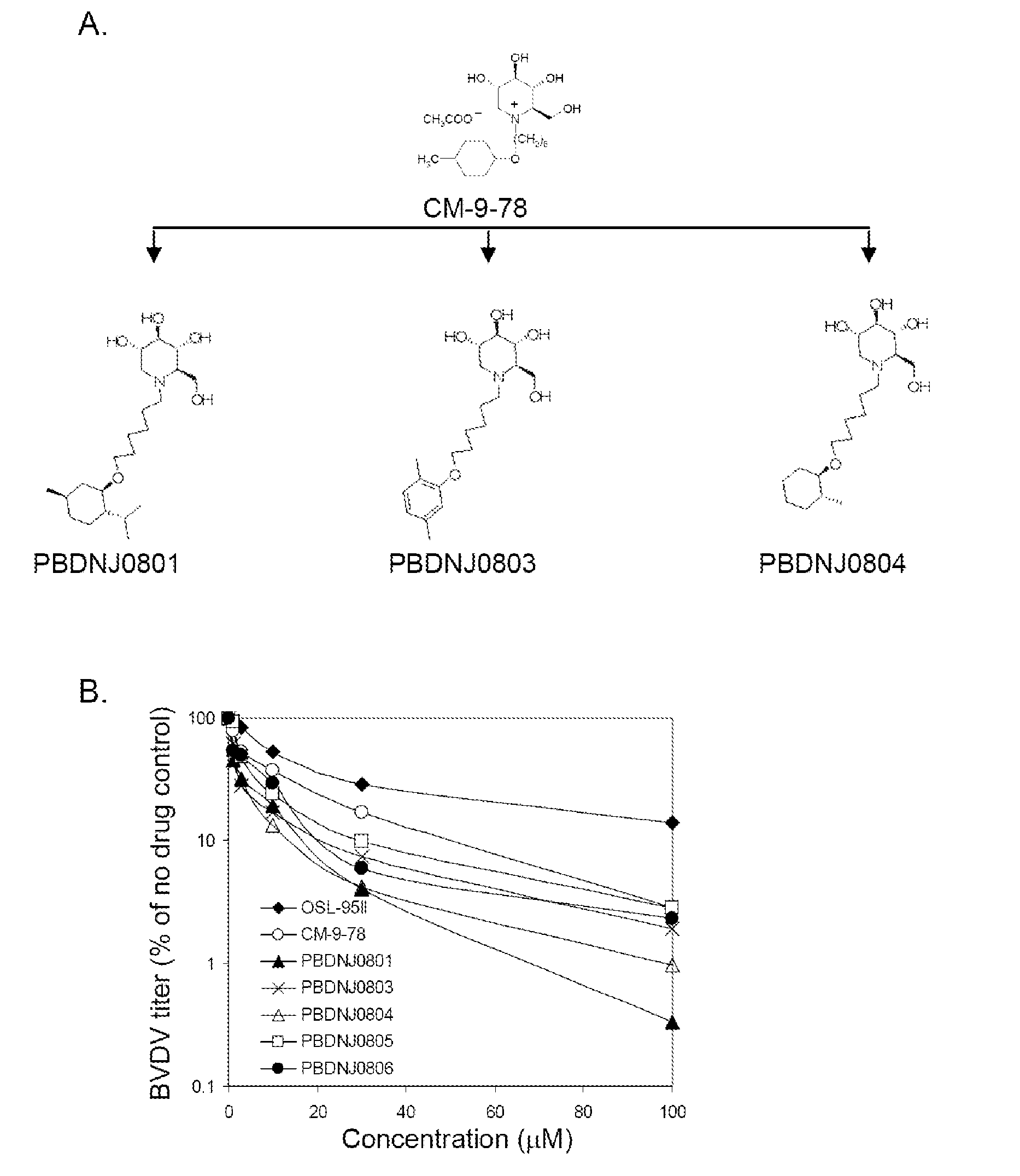
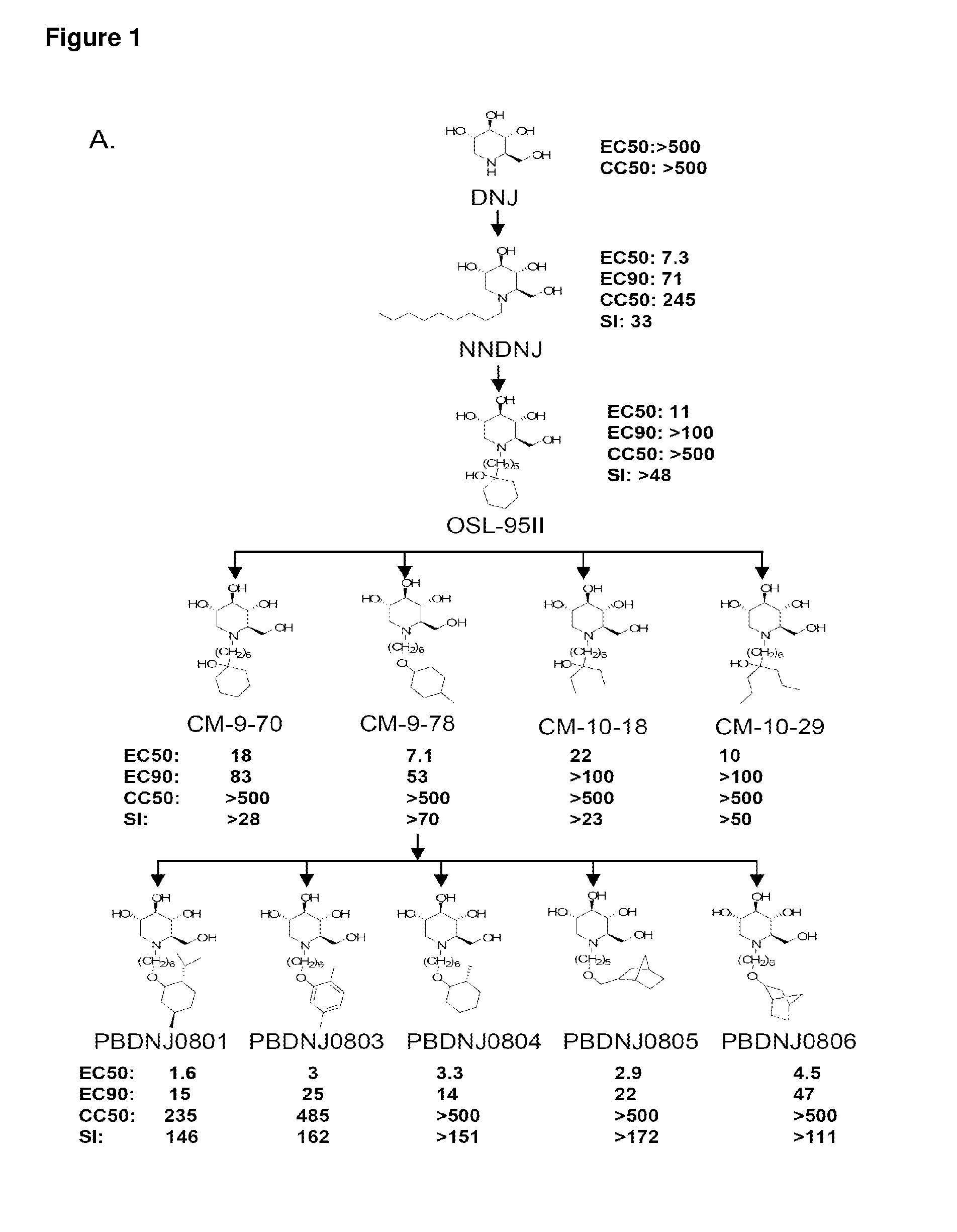
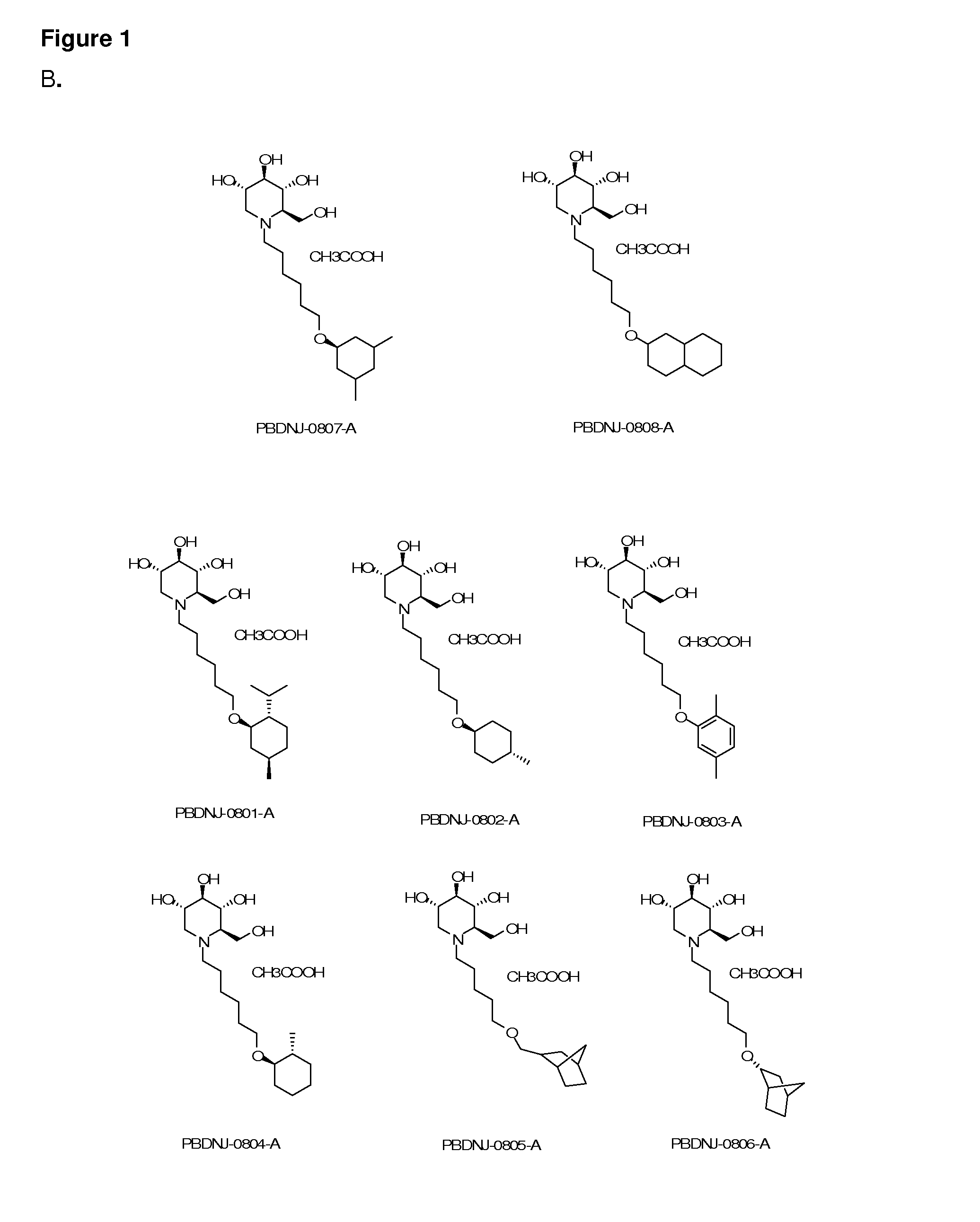
Imino sugars, such as deoxynojirimycin (DNJ), are glucose analogues that selectively inhibit cellular α-glucosidase I and II (enzymes that process N-linked glycans in glycoprotein) and exhibit broad spectrum antiviral activities against many enveloped viruses. Previously we have reported a novel DNJ derivative, OSL-95II, with antiviral activity and reduced cytotoxicity. In order to develop imino sugars with more potent antiviral activity as well as improved toxicity profile, OSL-95II was modified by diversifying the nitrogen linked alkylated side chain. The antiviral activities were initially tested in bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) infected MDBK cells, yielding several imino sugar derivatives with novel structure and superior antiviral activity and toxicity profile. Furthermore, these new compounds were shown to be active against Dengue virus (DV) and West Nile virus (WNV) infection in BHK cells where potent anti-DV activity having submicromolar EC50 values and SI of greater than 900. These compounds represent a new generation of iminio sugars and their analogues, having application in the clinical treatment of infection of DV and other members of flaviviridae.
Owner:INST FOR HEPATITS & VIRUS RES +1
Pyridopyrimidinone compounds with antimalarial activity
The present invention provides pyridopyrimidinone compounds with desirable biological activity and toxicity profiles for the enhanced treatment and prevention of malaria. The invention also relates to methods of making such molecules.
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
Linkage modified gapped oligomeric compounds and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140303235A1Loss of normal functionHigh selectivitySugar derivativesPolymorphism usesModified nucleosidesToxicity profile
The present invention provides gapped oligomeric compounds. More particularly the gapped oligomeric compounds provided herein comprise at least one modified intemucleoside linkage in the gap region. Such gapped oligomeric compounds have one or more improved properties such as selectivity, potency, improved toxicity profile and or improved proinflammatory profile. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
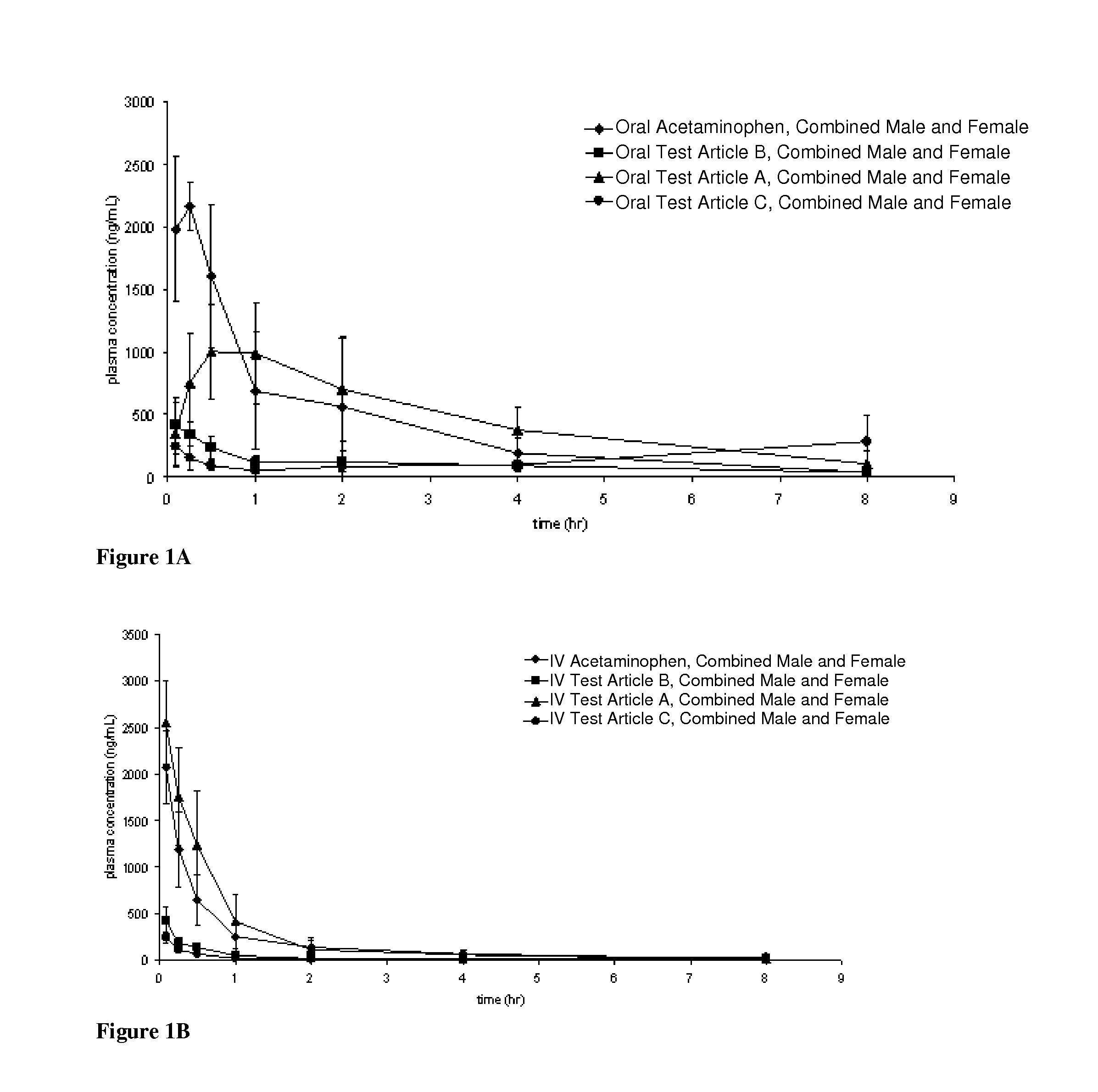
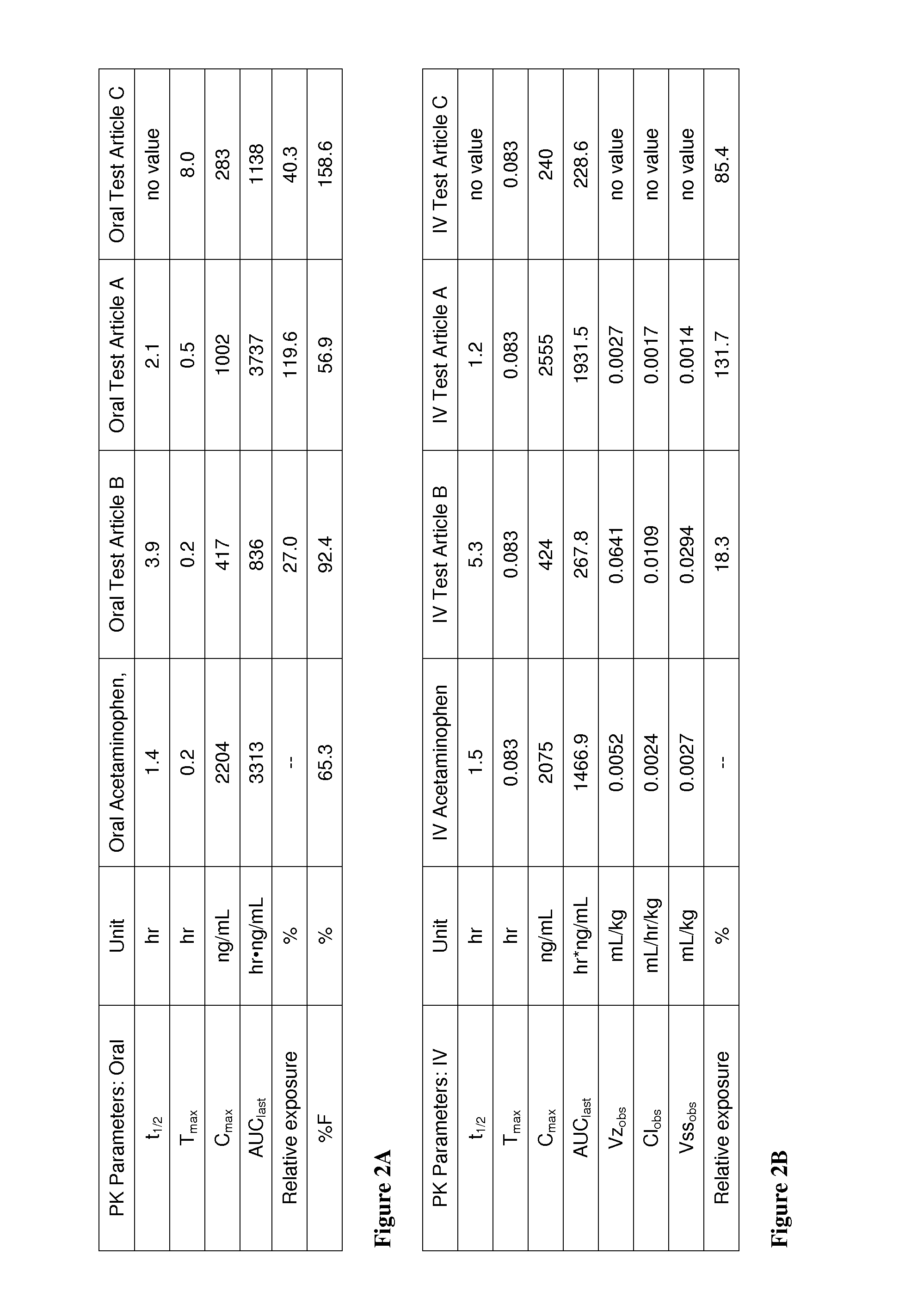
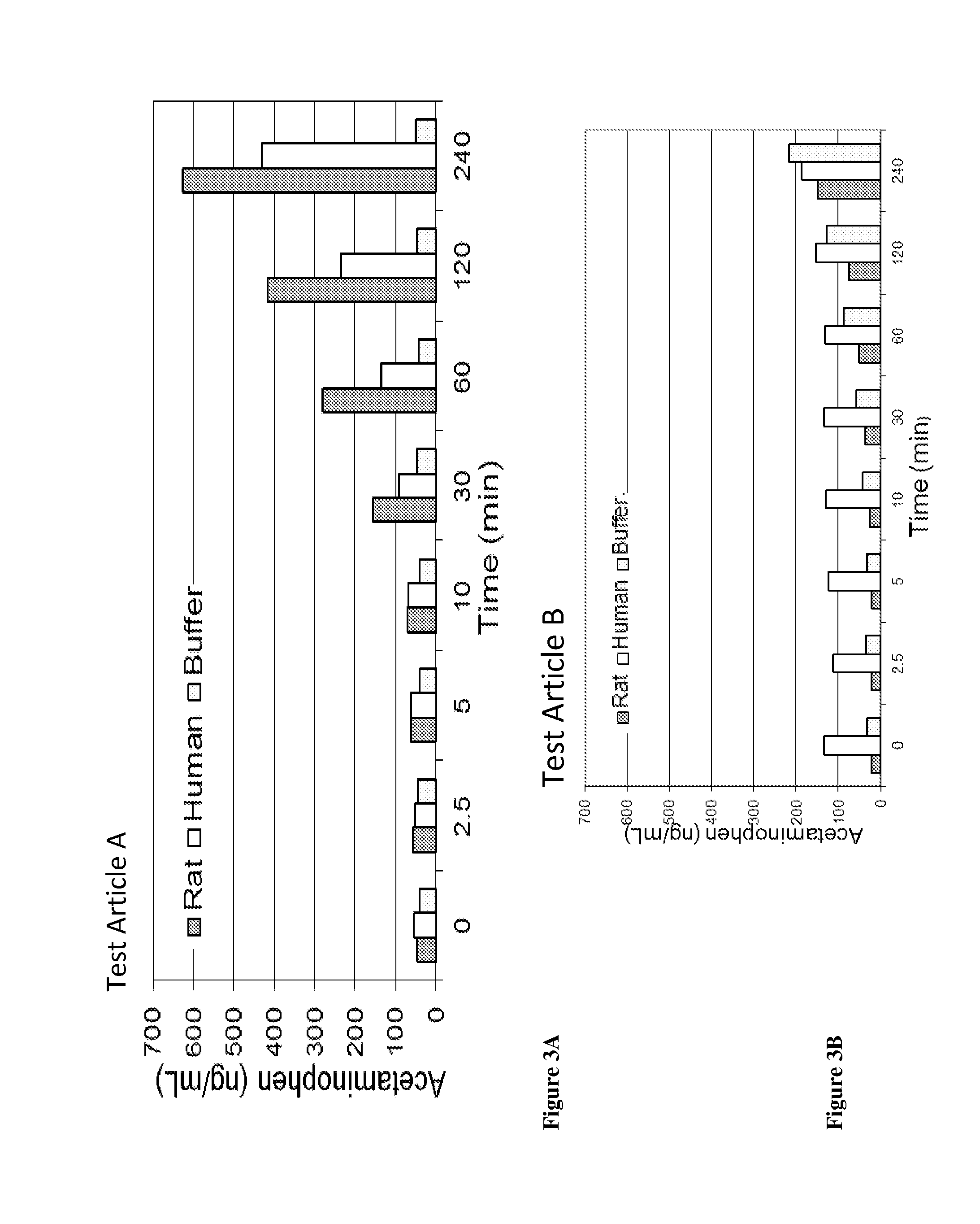
Acetaminophen conjugates, compositions and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20140243407A1Rapid onset of acetaminophen actionAct quicklyBiocideNervous disorderSolubilityWater soluble
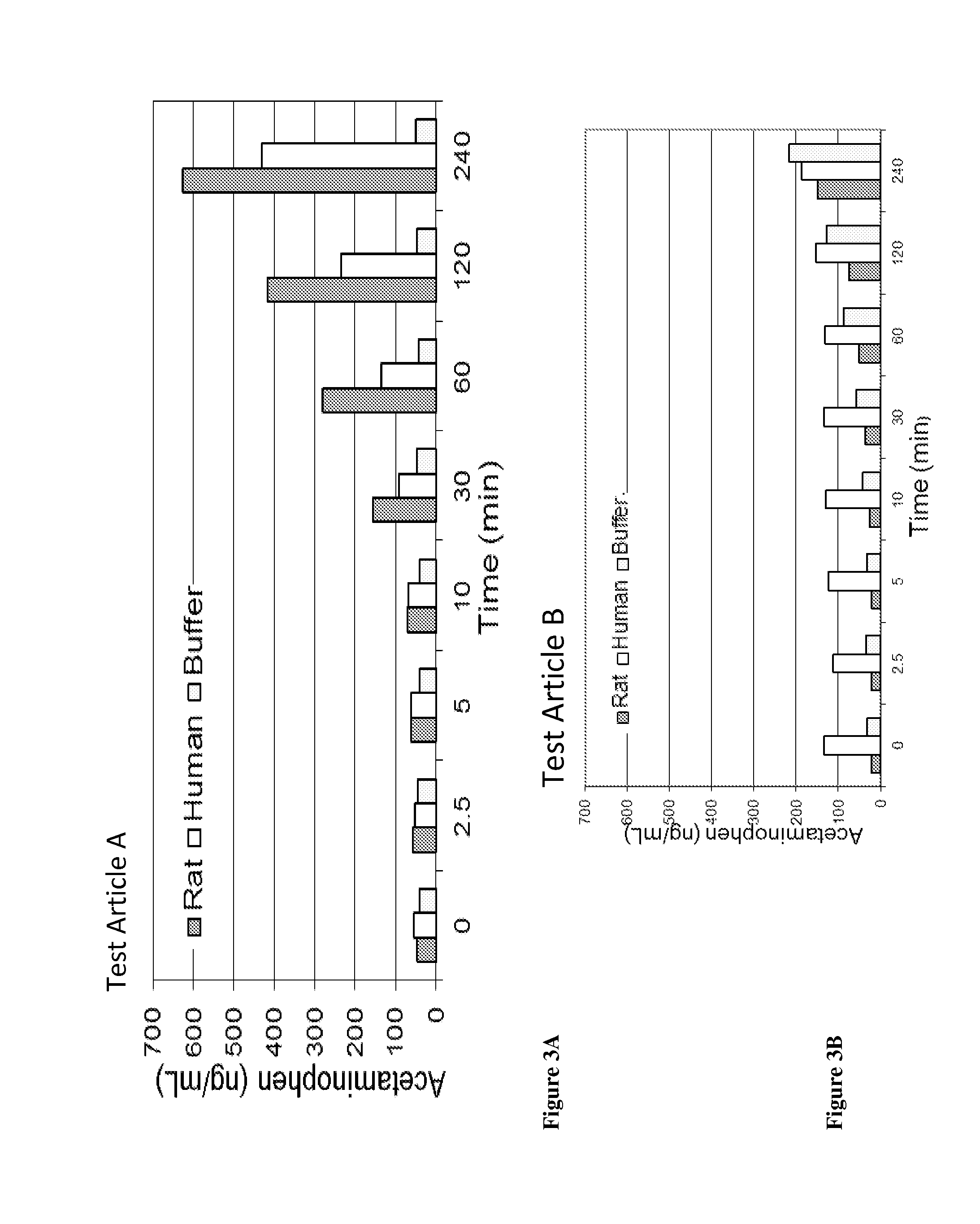
Acetaminophen conjugates are provided, which have an acetaminophen moiety covalently linked to a second moiety. The conjugates provided may have one or more advantageous properties, including increased water solubility as compared to acetaminophen, reduced toxicity profile as compared to acetaminophen and an altered pharmacokinetic profile. Formulations comprising the conjugates are also provided, as are methods of using the conjugates and kits comprising the conjugates.
Owner:ACORDA THERAPEUTICS INC
Polymer Based Nano-Carriers For The Solubilization And Delivery Of Hydrophobic Drugs
InactiveUS20080038353A1Easy to controlLess toxicityBiocideMaterial nanotechnologyNanocarriersBiodistribution
The present invention is in the field of polymer-based nano-carriers for the solubilization and delivery of hydrophobic drugs, and relates to methods of making said carriers, and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising said carriers. Novel PEO-b-PCL micelles and micelles containing cyclosporine A or analogs thereof are provided as well as a novel method for making said micelles that reduces aggregation and enhances delivery, the toxicity profile and biodistribution of hydrophobic drugs.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
Acetaminophen conjugates, compositions and methods of use thereof
Acetaminophen conjugates are provided, which have an acetaminophen moiety covalently linked to a second moiety. The conjugates provided may have one or more advantageous properties, including increased water solubility as compared to acetaminophen, reduced toxicity profile as compared to acetaminophen and an altered pharmacokinetic profile. Formulations comprising the conjugates are also provided, as are methods of using the conjugates and kits comprising the conjugates.
Owner:ACORDA THERAPEUTICS INC
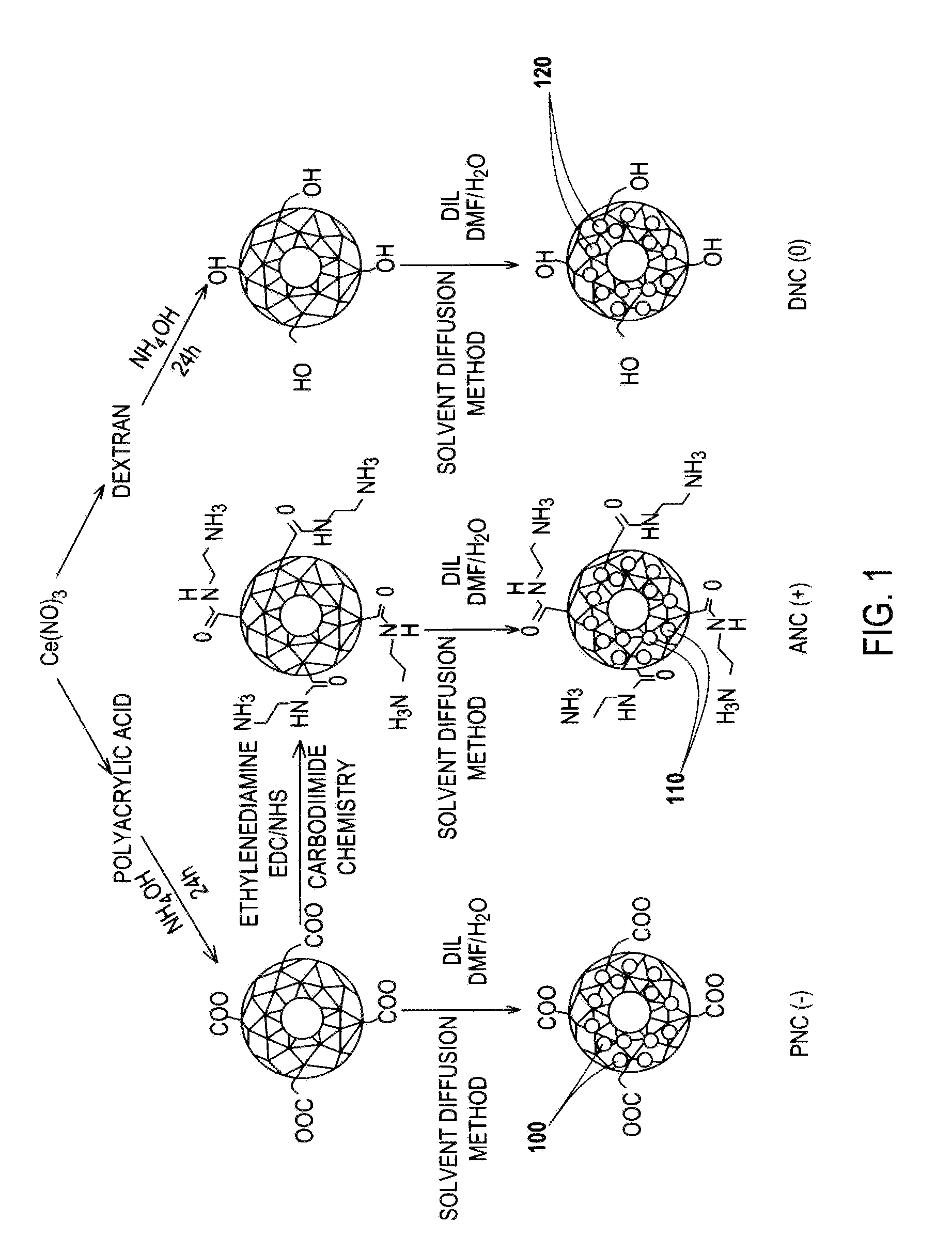
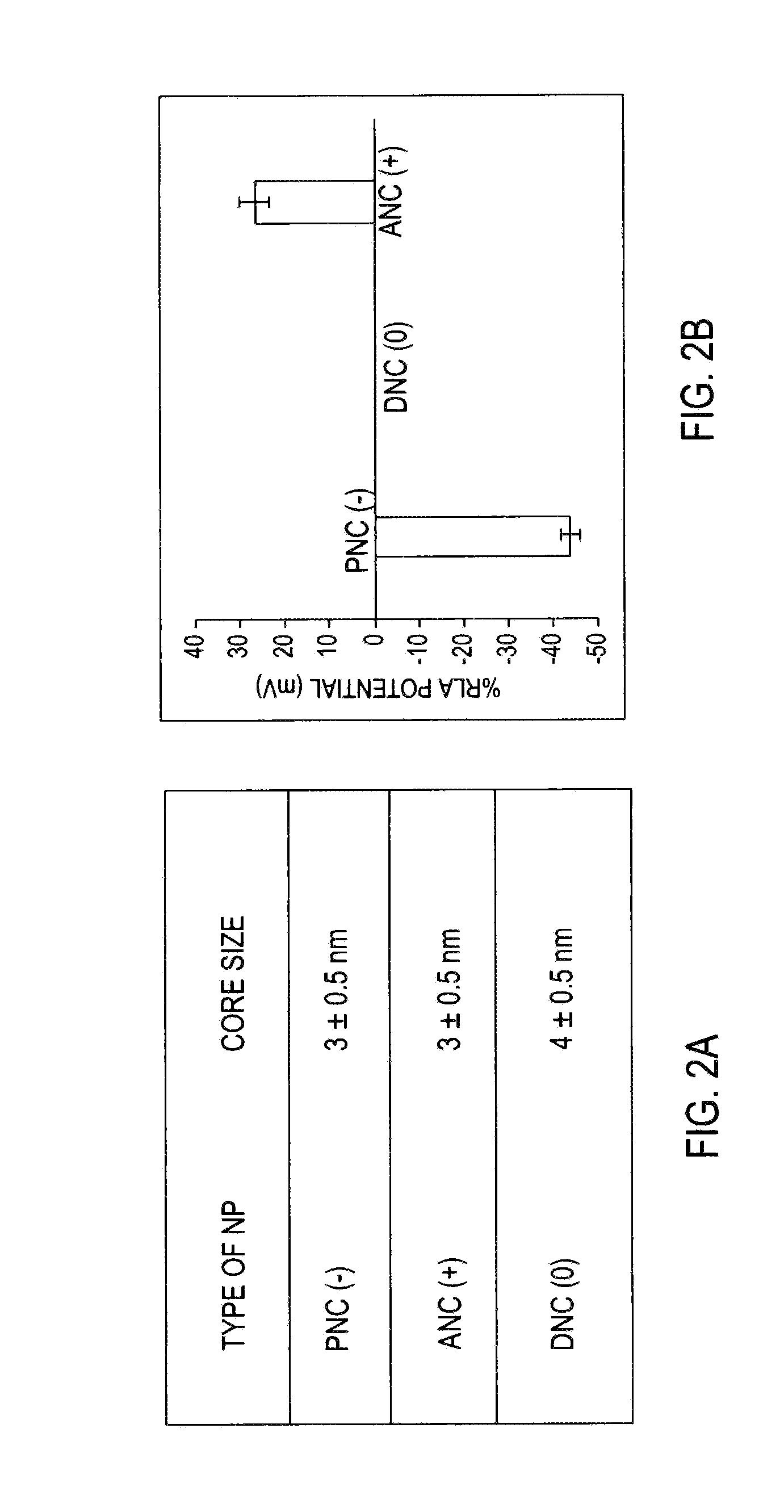
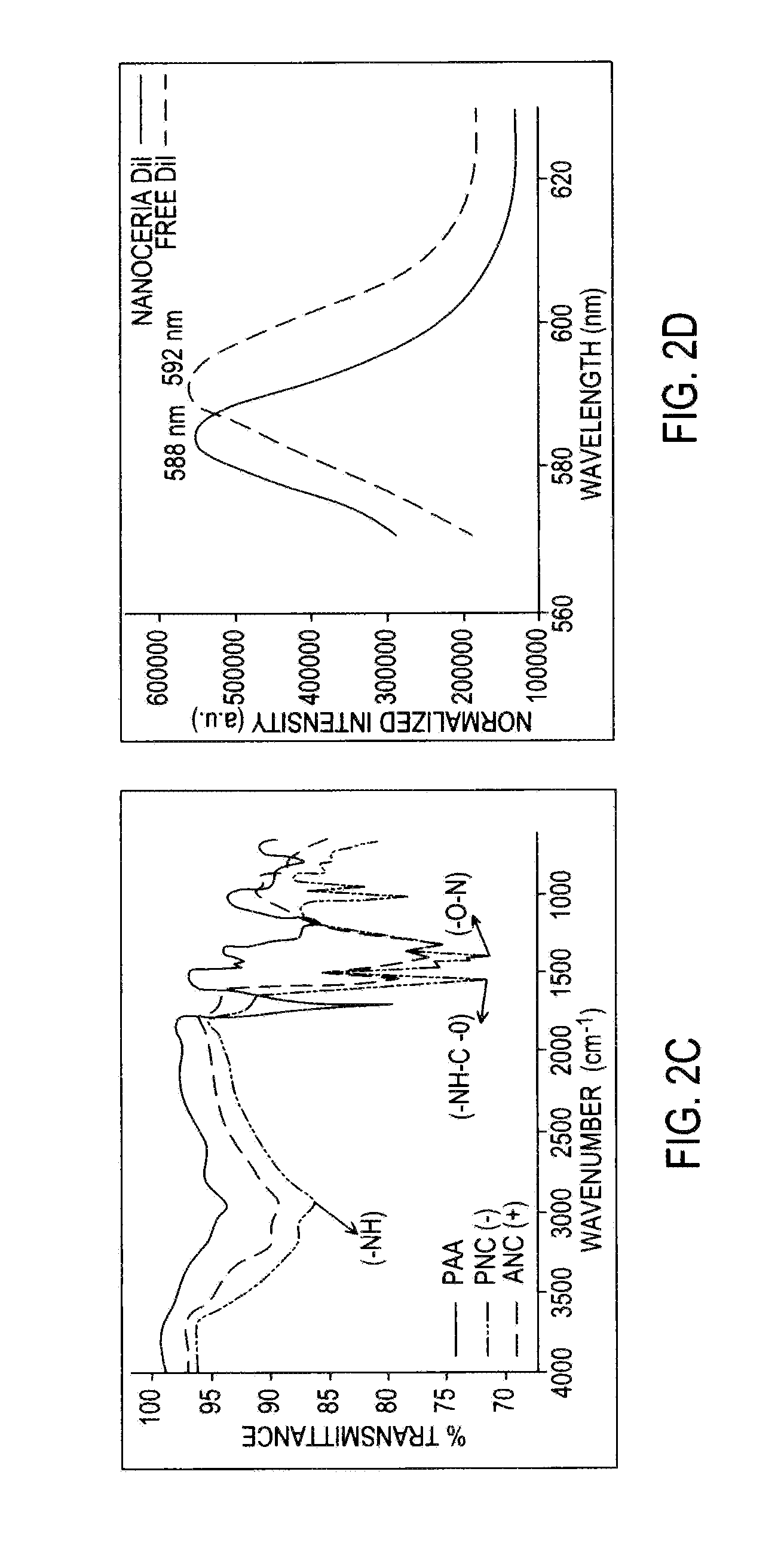
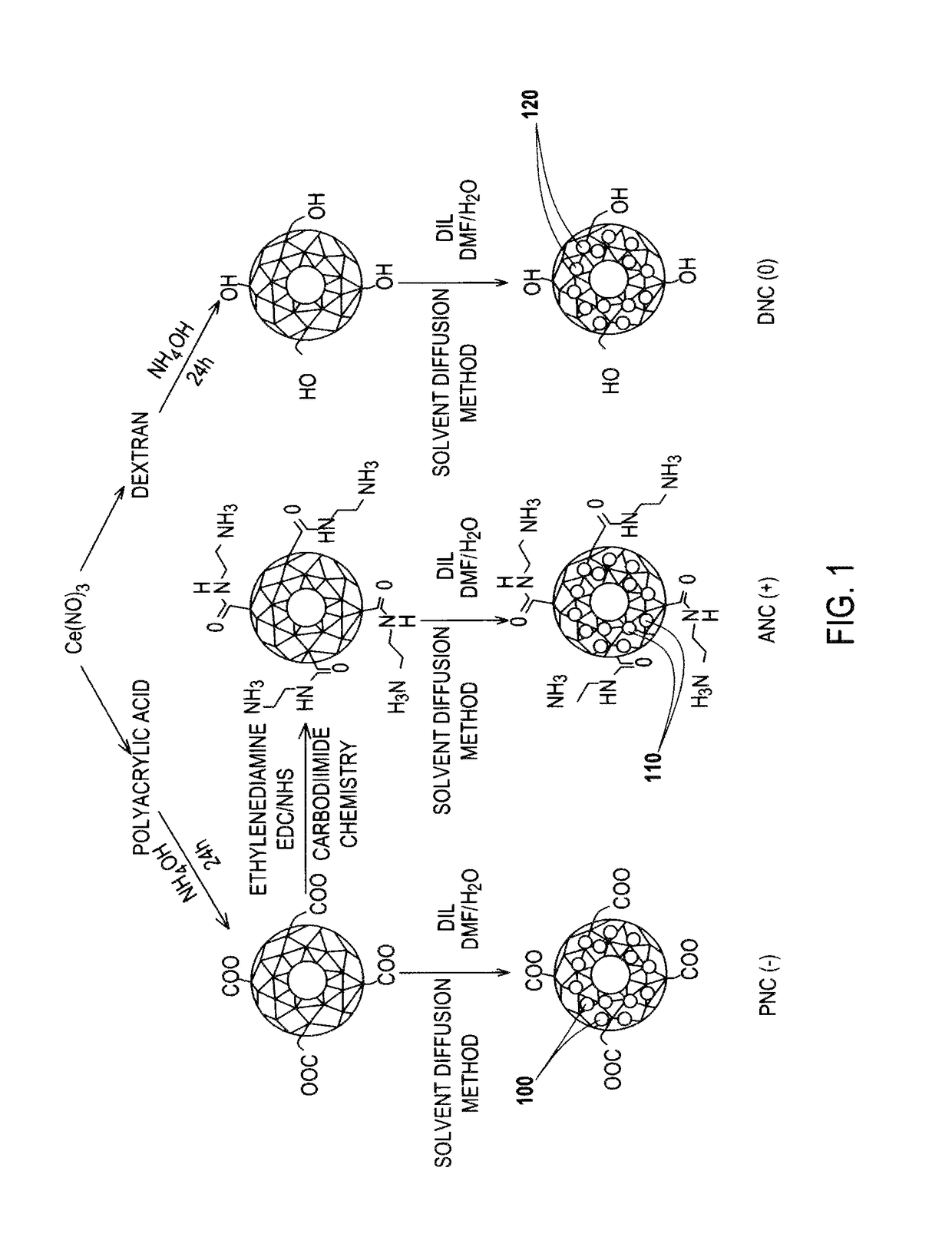
Application Device for Inducing Cytotoxicity to Tumor Cells Via Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20160074434A1Without compromising solubilityReduce in quantityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCancer cellLysosome
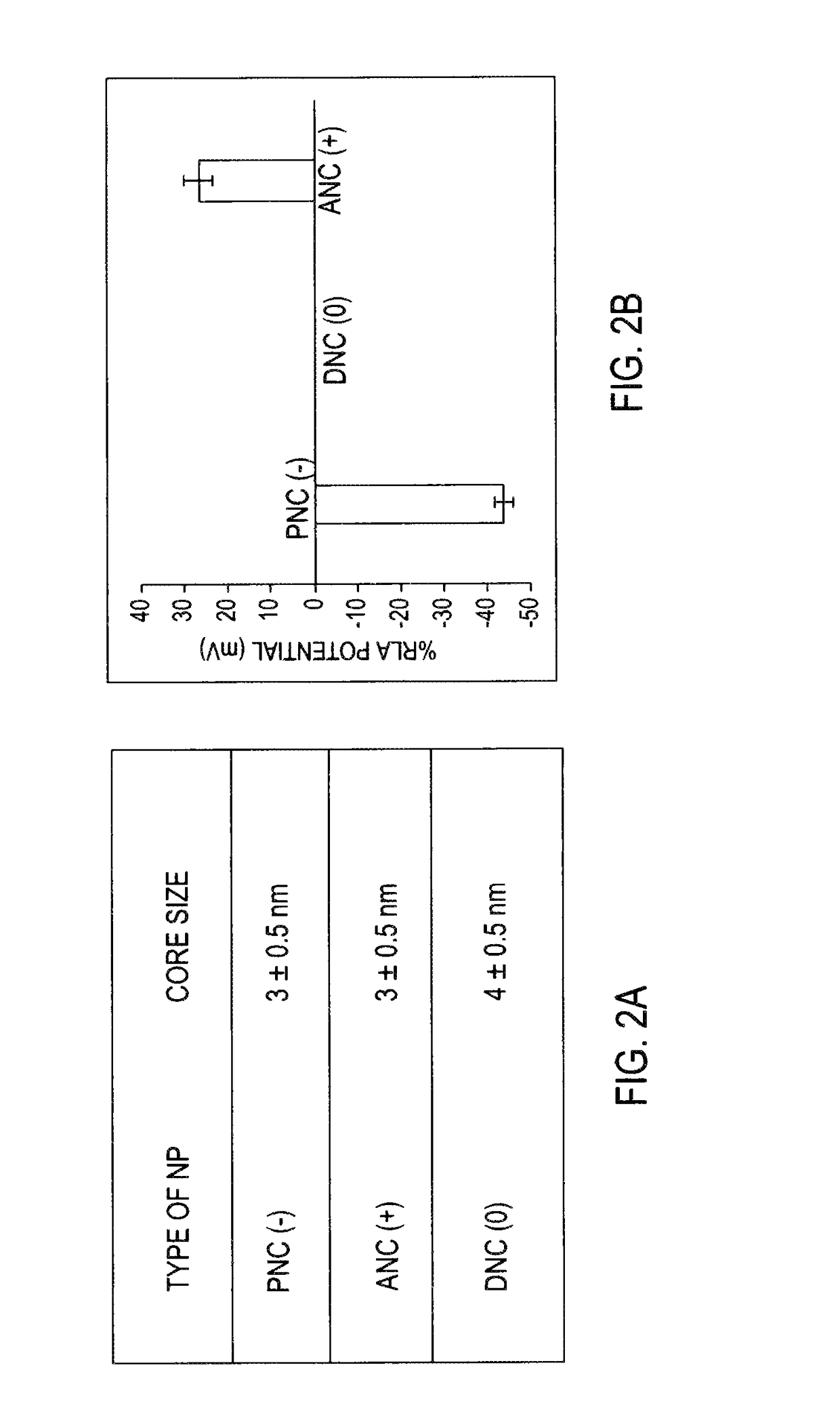
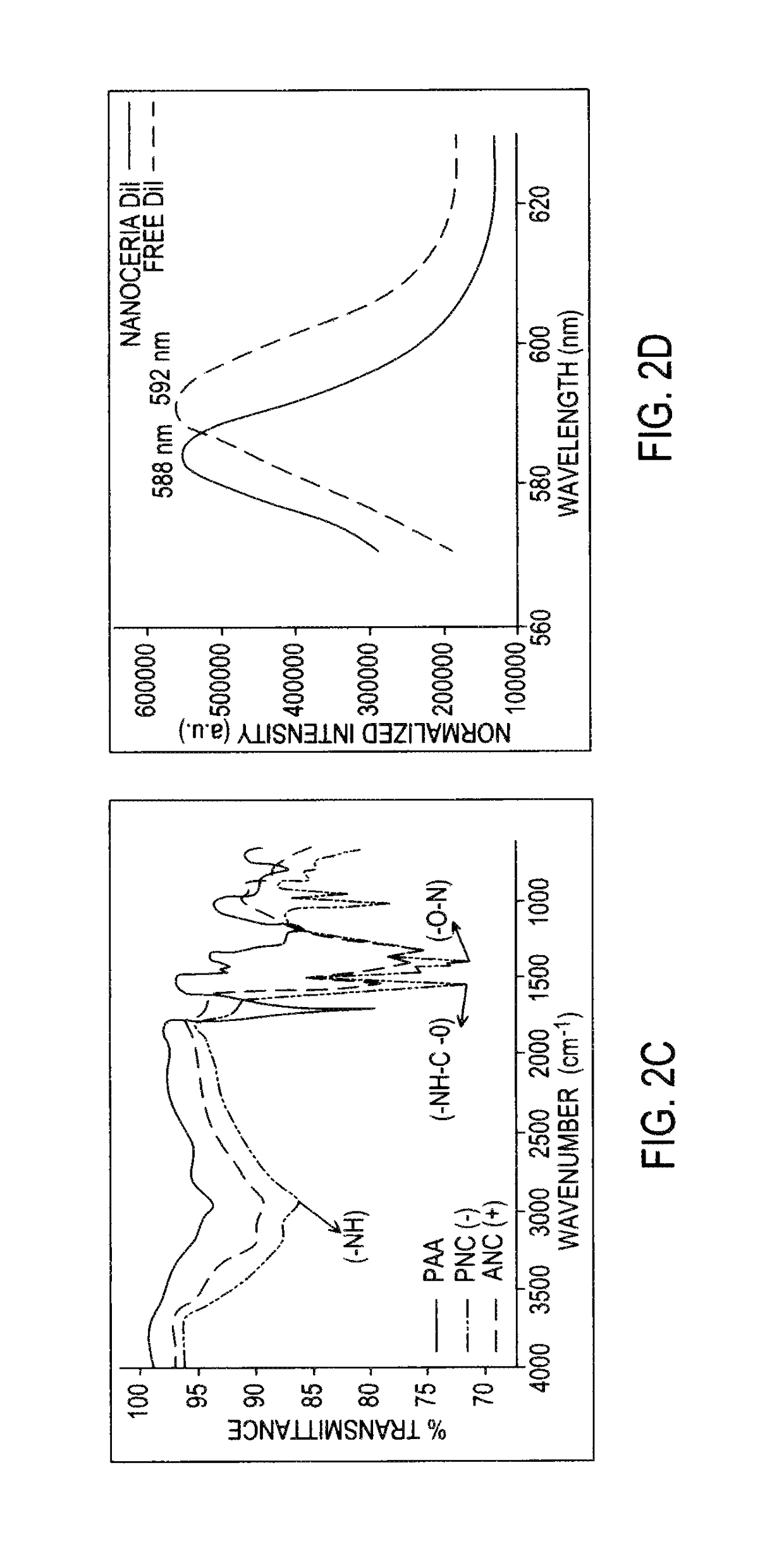
Differential surface-charge-dependent localization of nanoceria in normal cells and cancer cells plays a critical role in the toxicity profile of a nanoceria particle. Engineered surface-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles with different surface charges that are positive, negative and neutral provide therapeutic results for normal and cancer cell lines. Results show that nanoceria with a positive or neutral charge enters most of the cell lines studied, while nanoceria with a negative charge internalizes mostly in the cancer cell lines. Moreover, upon entry into the cells, nanoceria is localized to different cell compartments (e.g. cytoplasm and lysosomes) depending on the nanoparticle surface charge. The internalization and subcellular localization of nanoceria plays a key role in the nanoparticle cytotoxicity profile, exhibiting significant toxicity when they localize in the lysosomes of the cancer cell lines. In contrast, minimal toxicity is observed when they localize into the cytoplasm or do not enter the cells.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Small molecules with antiprotozoal activity
InactiveUS20100292264A1Modest inhibitory activityEffective inhibitory activityBiocideAntiparasitic agentsChemical compositionMalaria
The present invention provides new chemical compositions with desirable biological activity and toxicity profiles for the enhanced treatment of malaria.
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
Targeted Drug-Formaldehyde Conjugates and Methods of Making and Using the Same
InactiveUS20070275911A1Effective treatmentMake fastAntibacterial agentsBiocideCancer cellAntibiotic Y
The invention provides a prodrug platform technology for improving the therapeutic value of a variety of parent drug compounds by altering and improving drug characteristics such as aqueous solubility, hydrolytic stability, therapeutic index, toxicity profile, pharmacolcinetics and selectivity while allowing the potential for synthetic elaboration. The prodrug platform is particularly well suited for targeting therapeutic drugs, including anti-tumor drugs and antibiotics, to specific receptors on target cells (e.g., cancer cells and bacteria). The platform is a technology for providing an improved, preactivated form of a therapeutic drug, and for optionally targeting such drug to target cells or biological molecules. The invention is broadly applicable to many different therapeutic drugs, as well as to a variety of diseases and conditions, including a variety of forms of cancer and bacterial infections.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
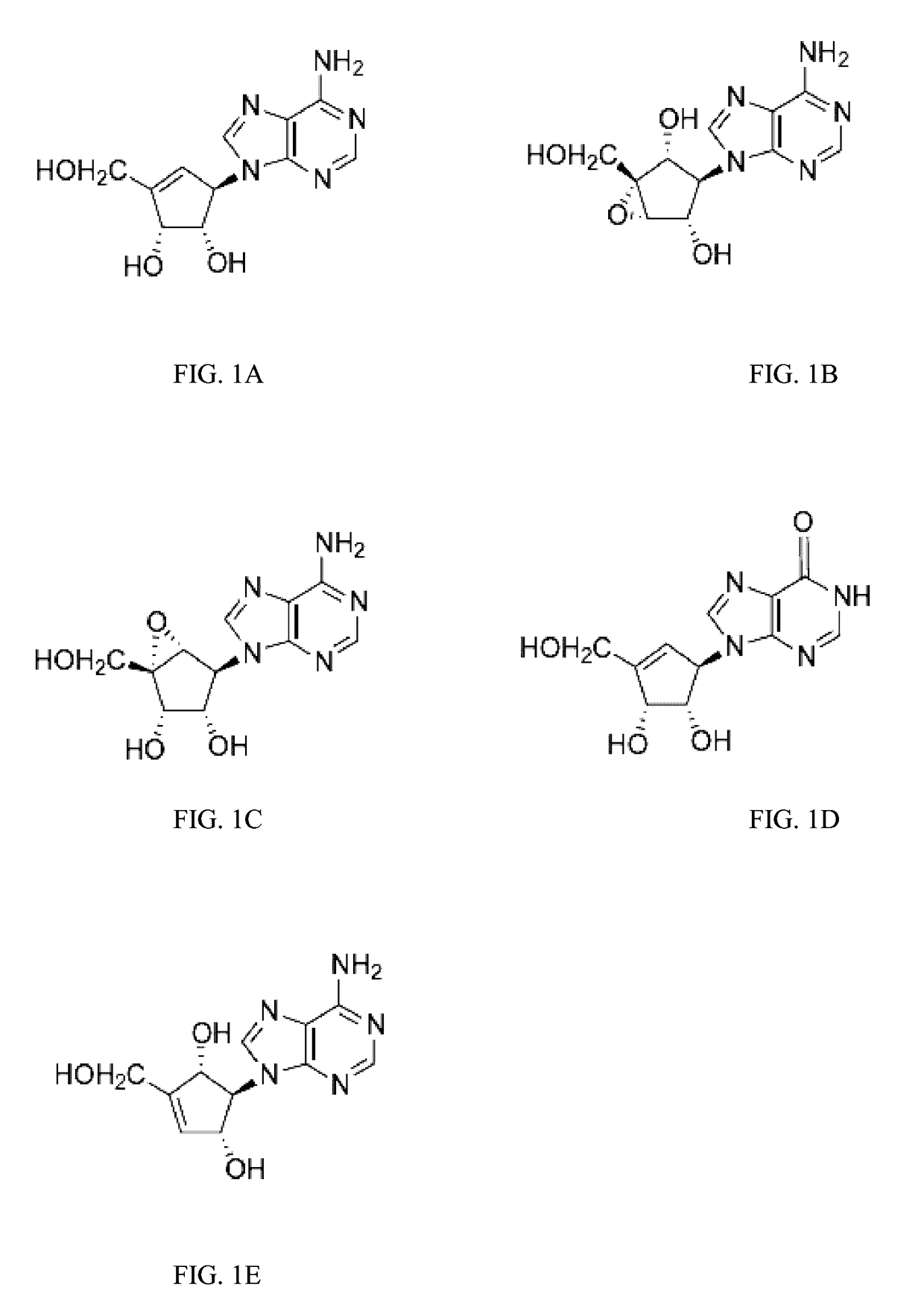
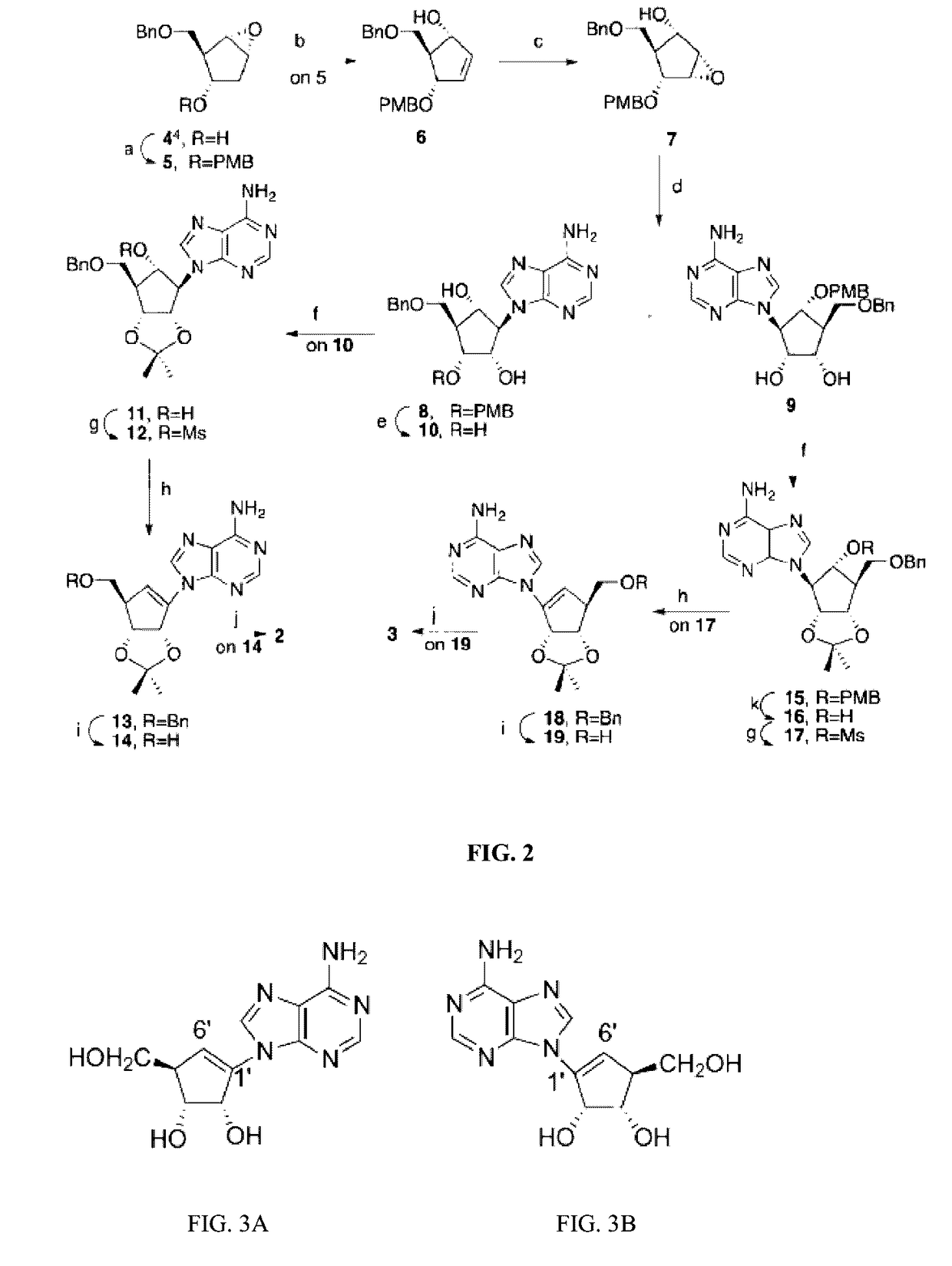
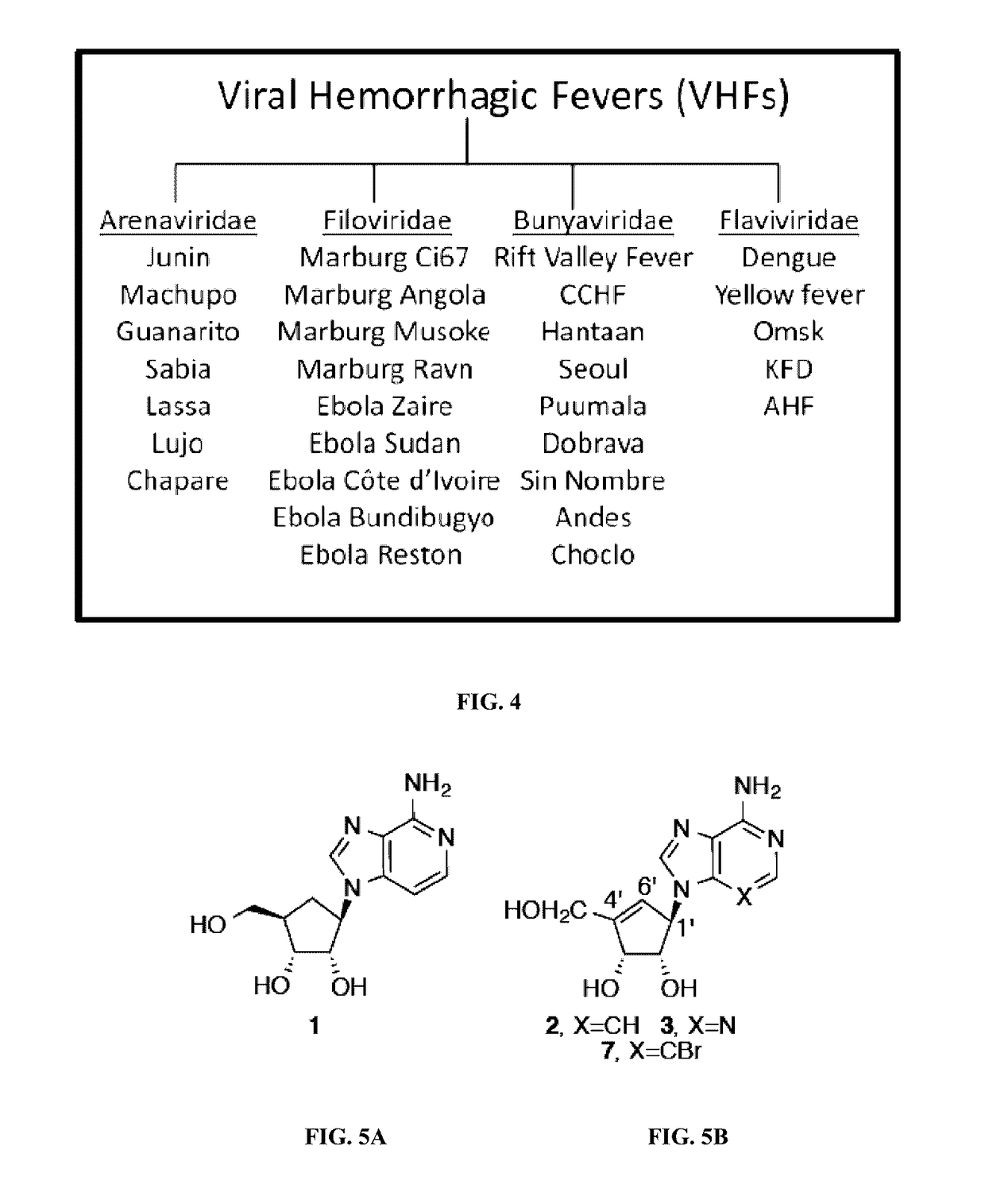
Enantiomers of the 1′,6′-isomer of neplanocin A
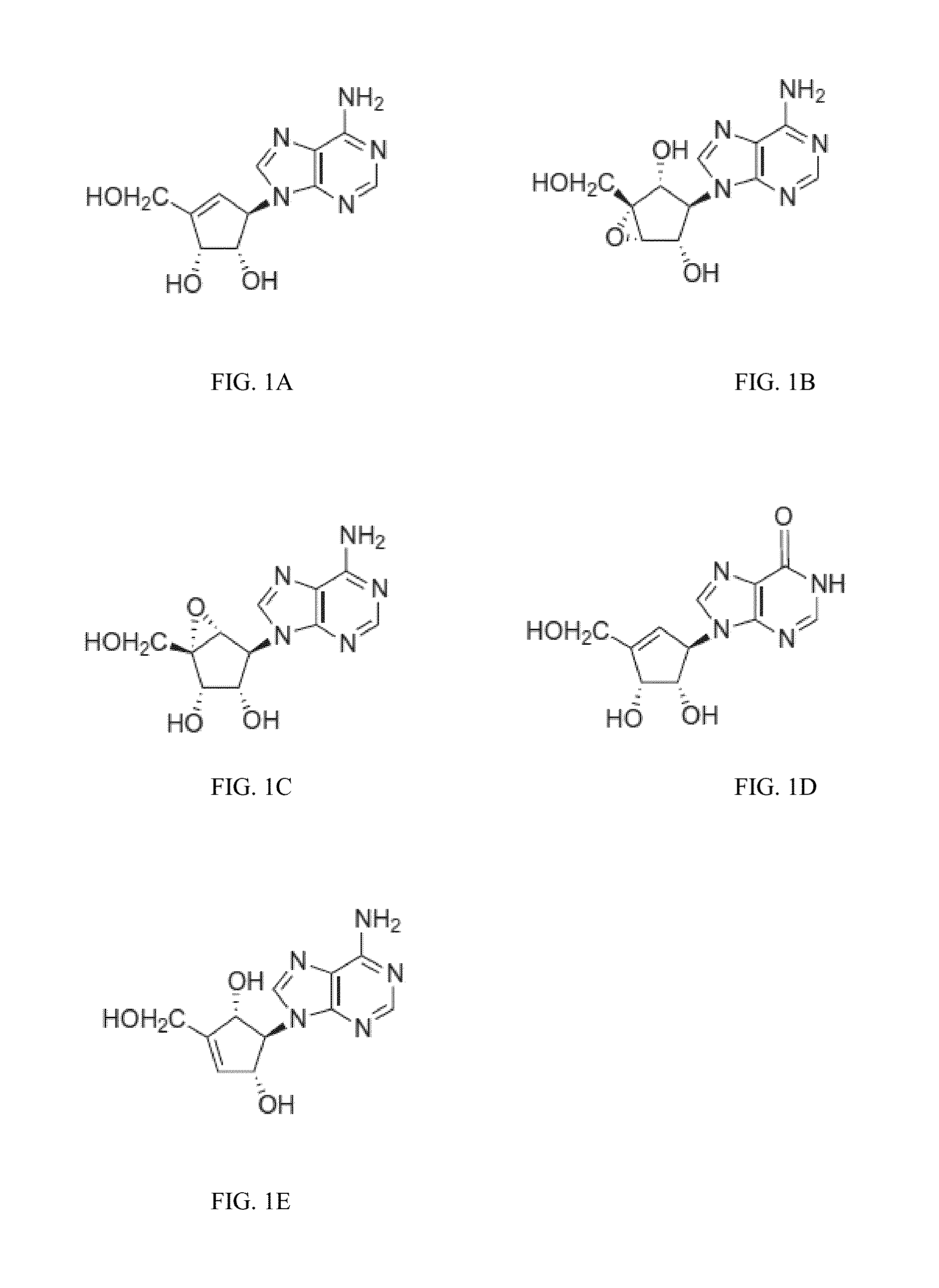
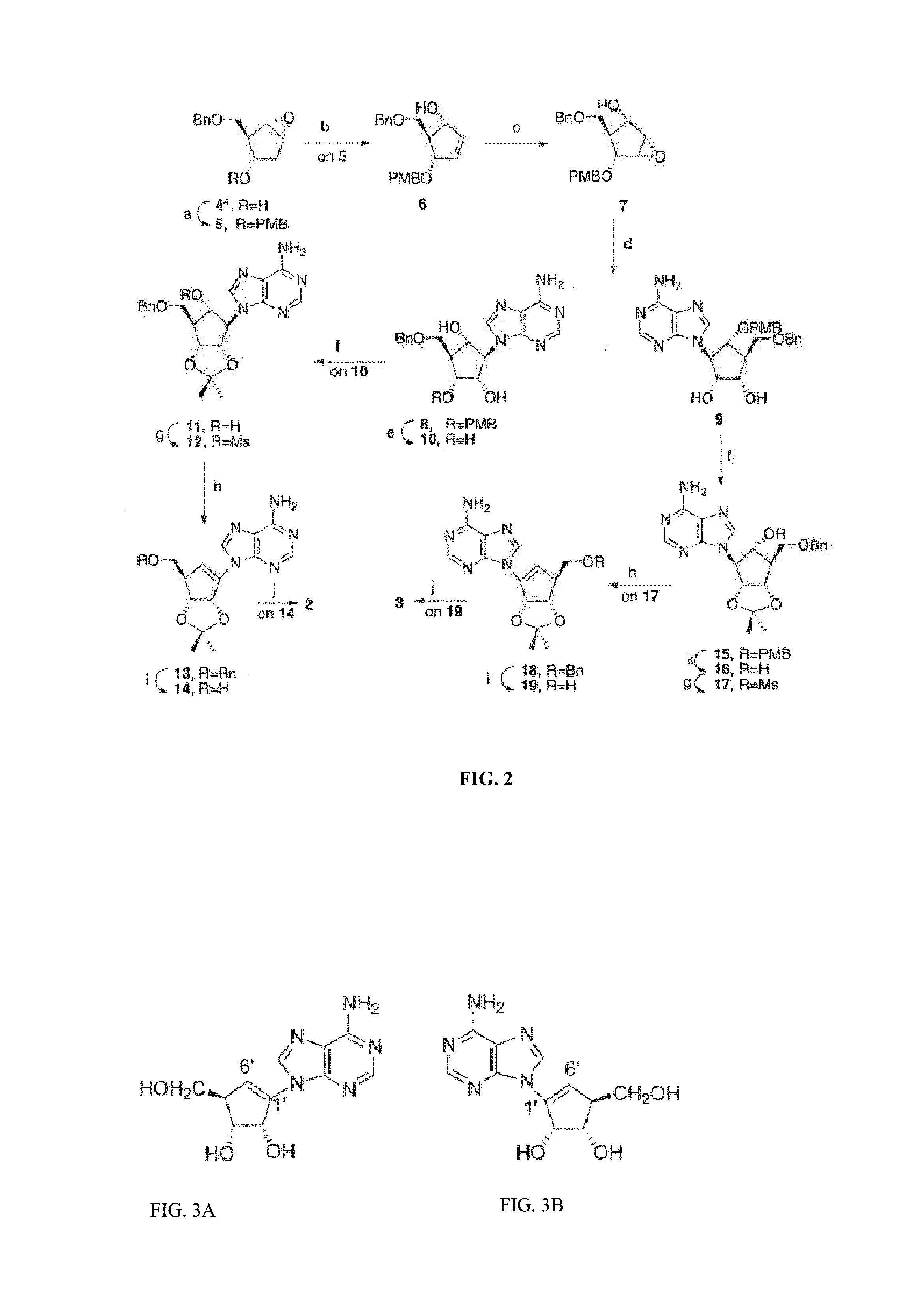
Enantiomers of 1′,6′-isoneplanocin, including derivatives of the enantiomers of 1′,6′-isoneplanocin, are disclosed along with novel synthetic methods. In particular, a substituted cyclopentane epoxide is synthesized into the enantiomers of 1′,6′-isoneplanocin. Enantiomers of carbocyclic nucleoside analogs of 3-deazaneplanocin to provide D- and L-like 1′,6′-iso-3-deazaneplanocin are also disclosed. The small molecule chemotherapeutic compounds beneficially provide DNA and RNA antiviral activity, demonstrating activity towards, for example, human cytomegalovirus, measles, Ebola, norovirus, dengue, vaccinia and HBV. Compounds exhibiting reduced S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inhibitory effects are disclosed and provide improved toxicity profiles in comparison to neplanocin. The invention provides improved prophylactic and / or therapeutic antiviral efficacy.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
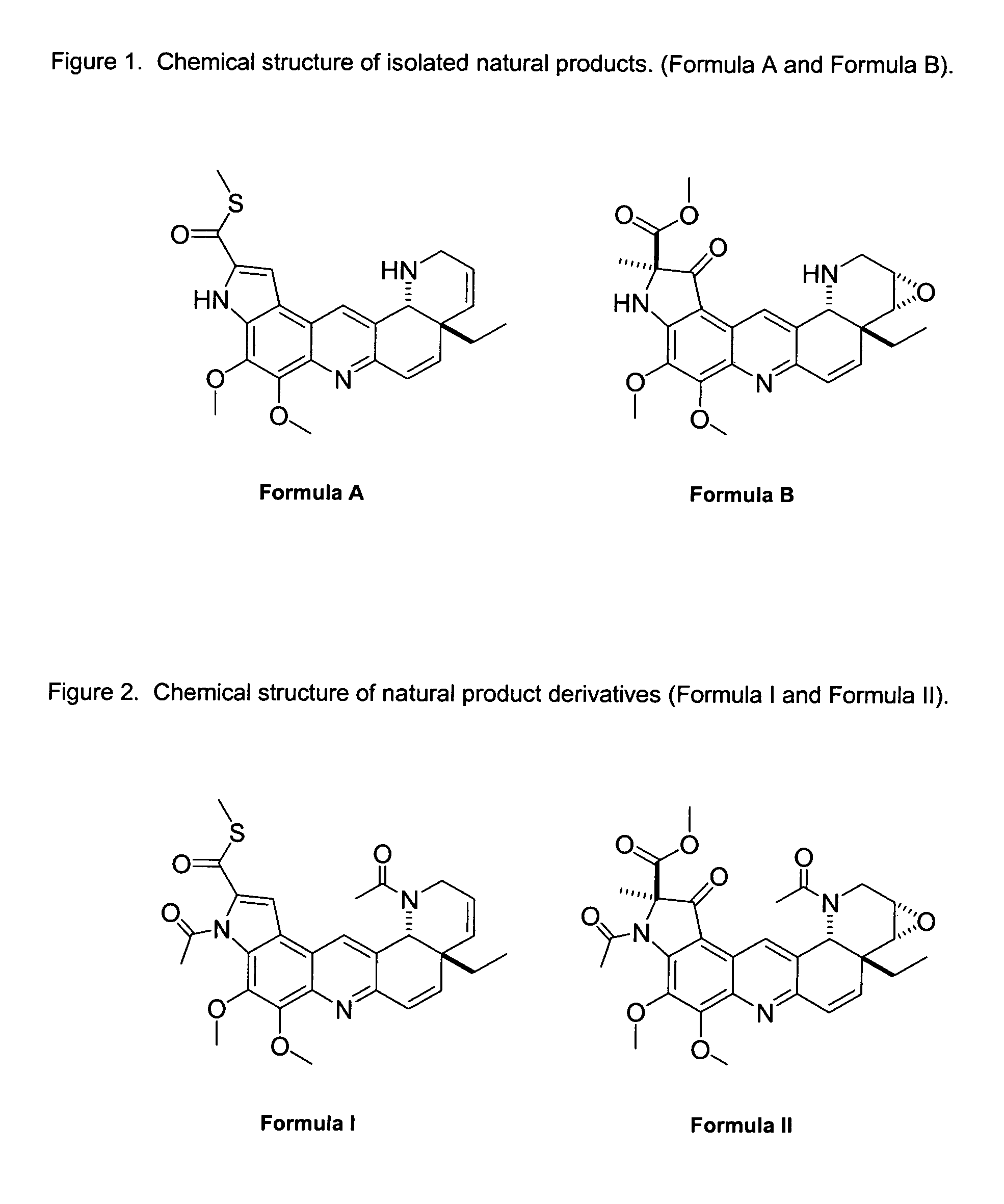
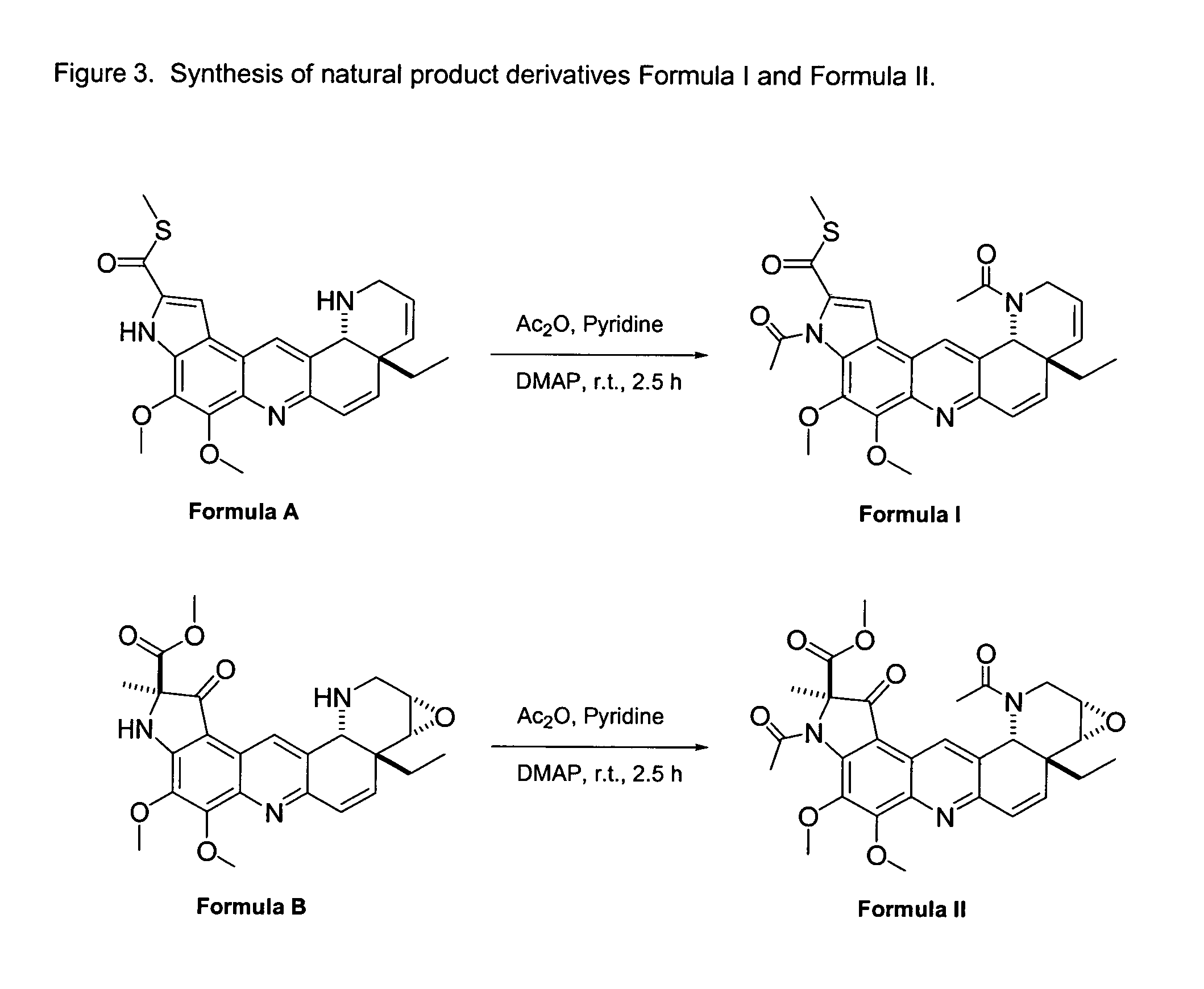
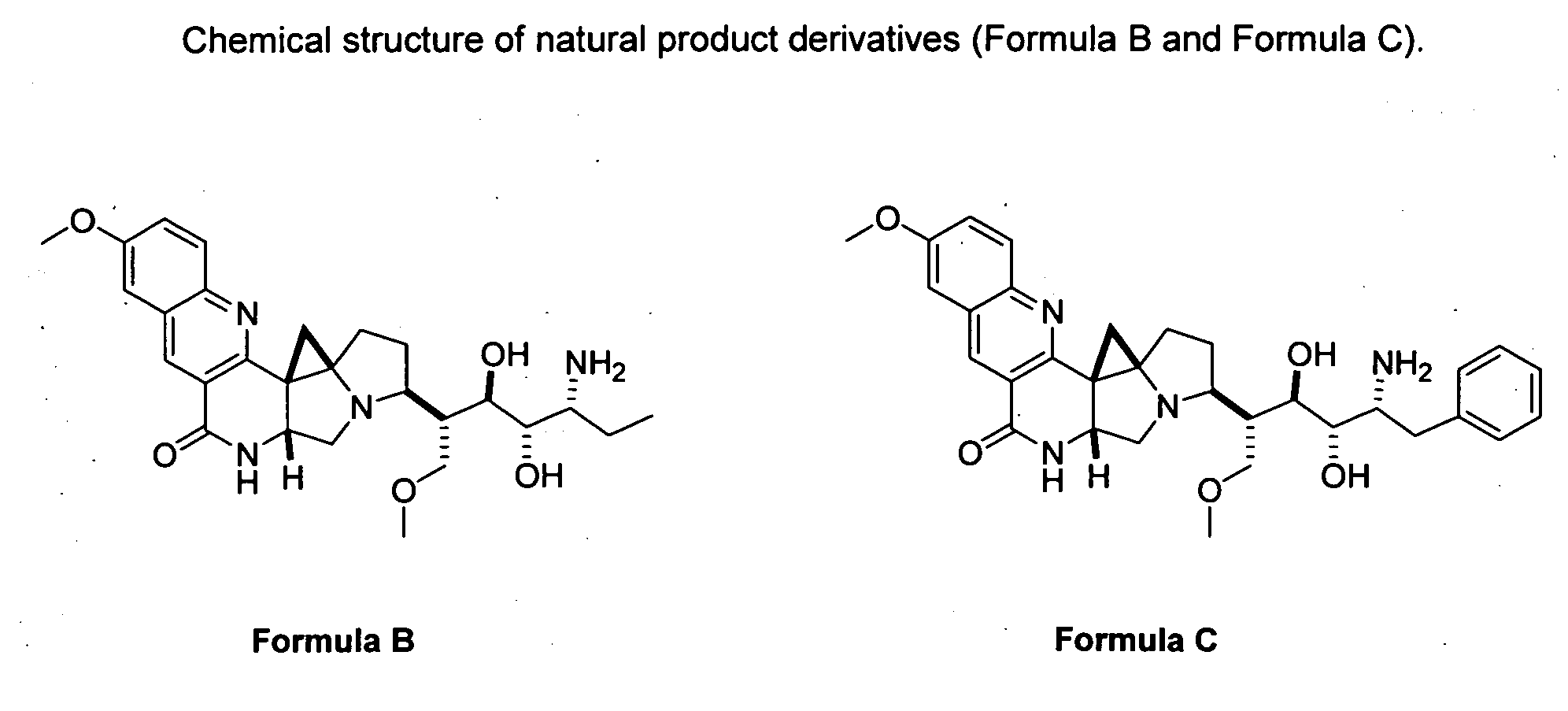
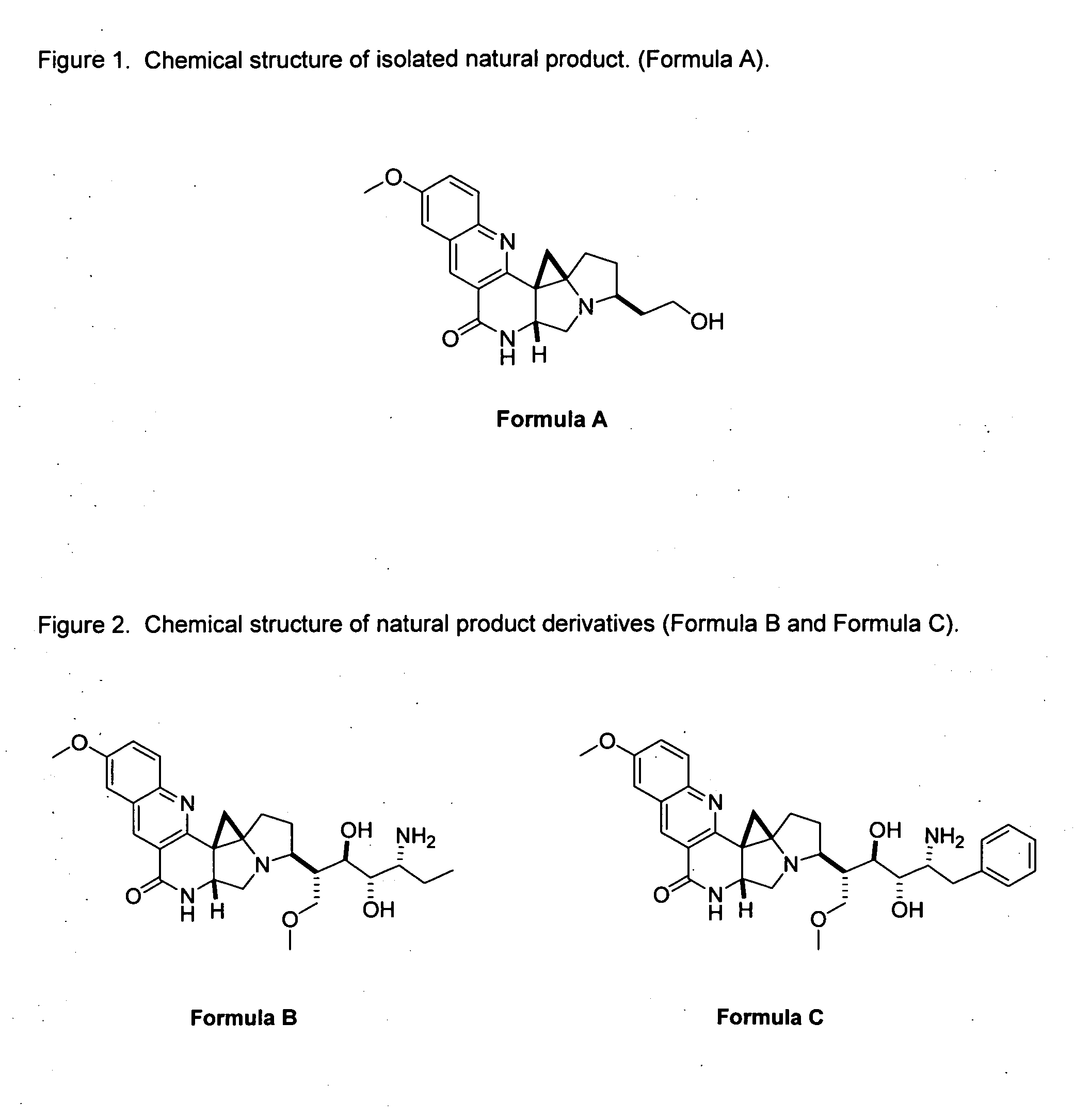
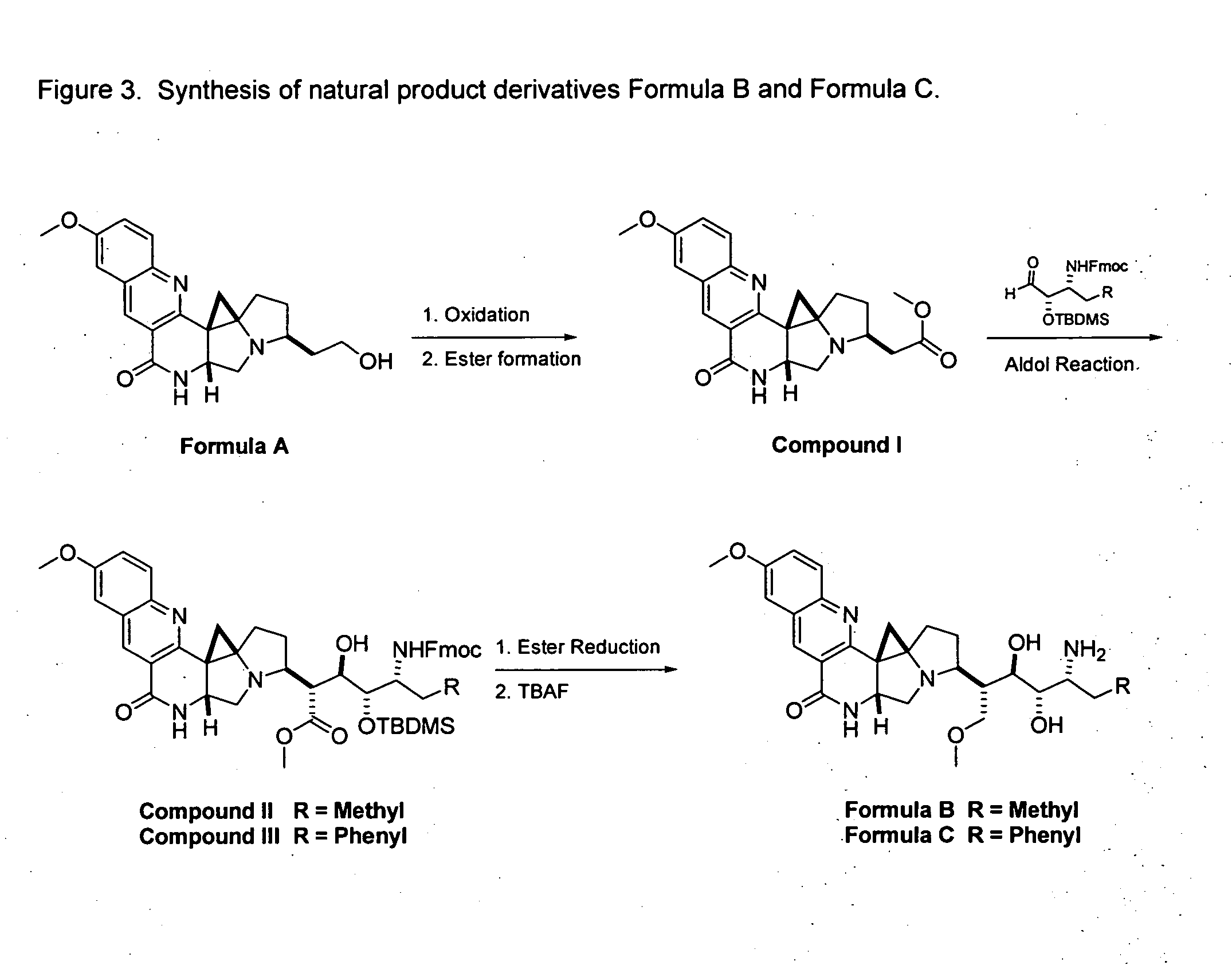
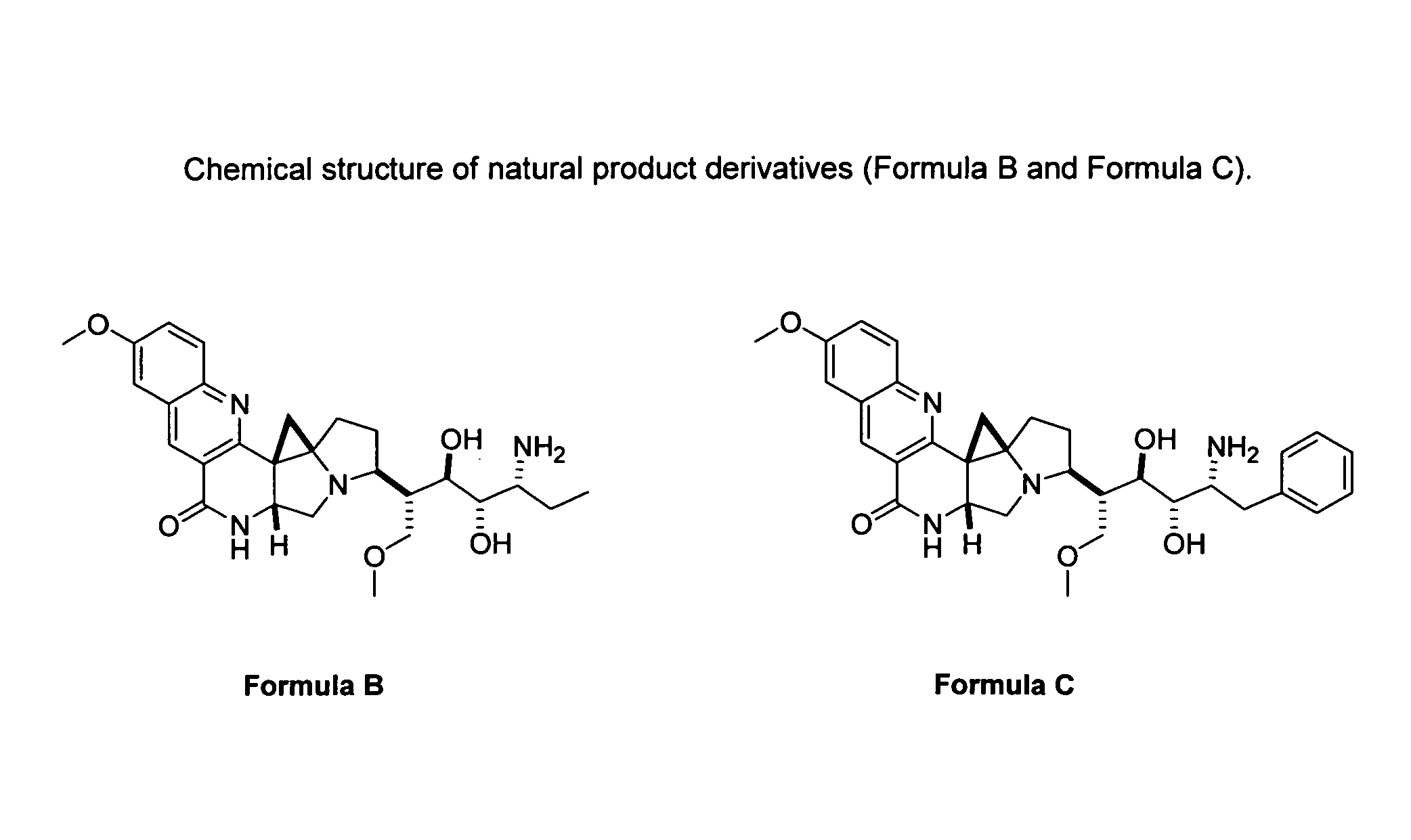
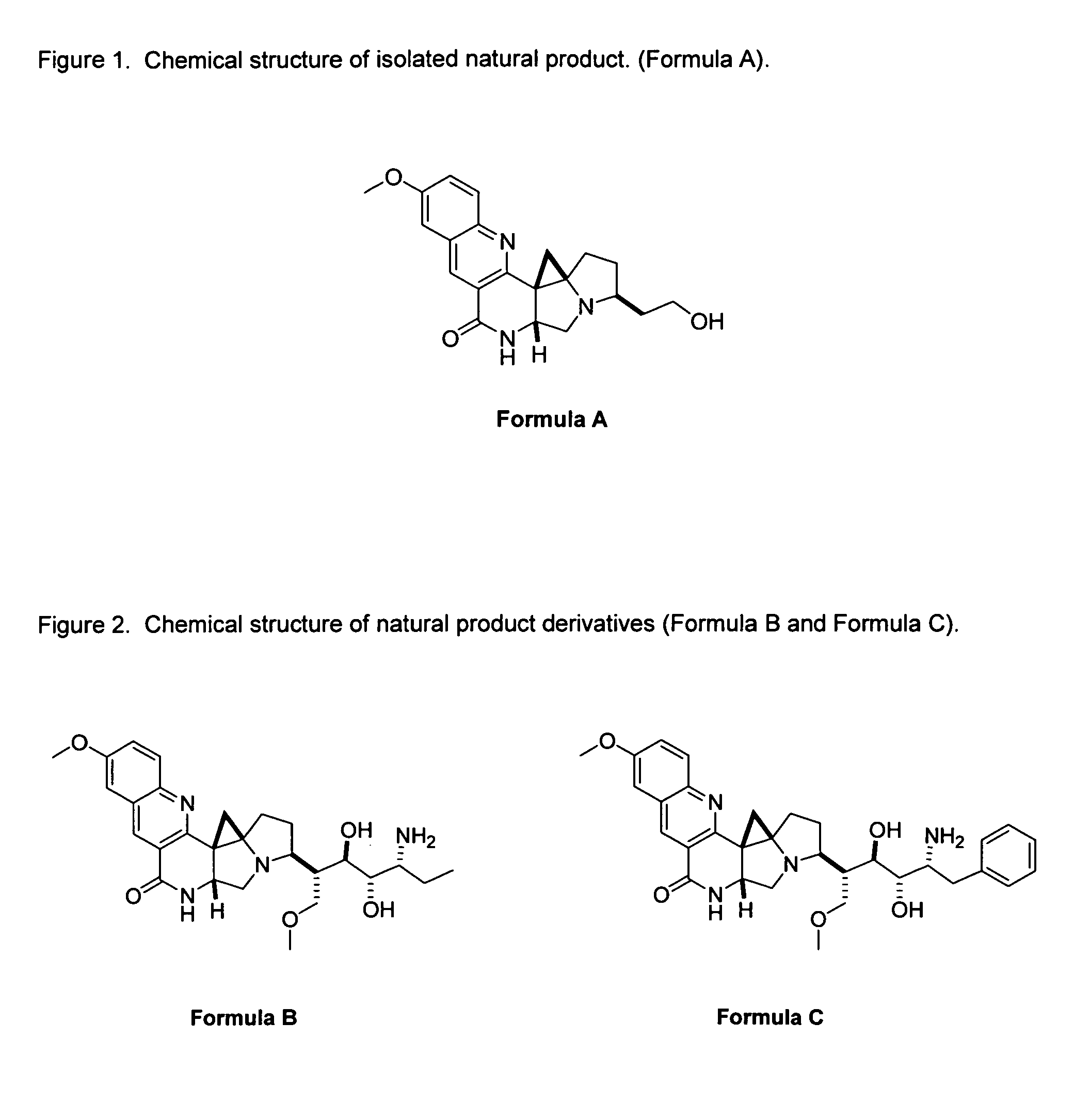
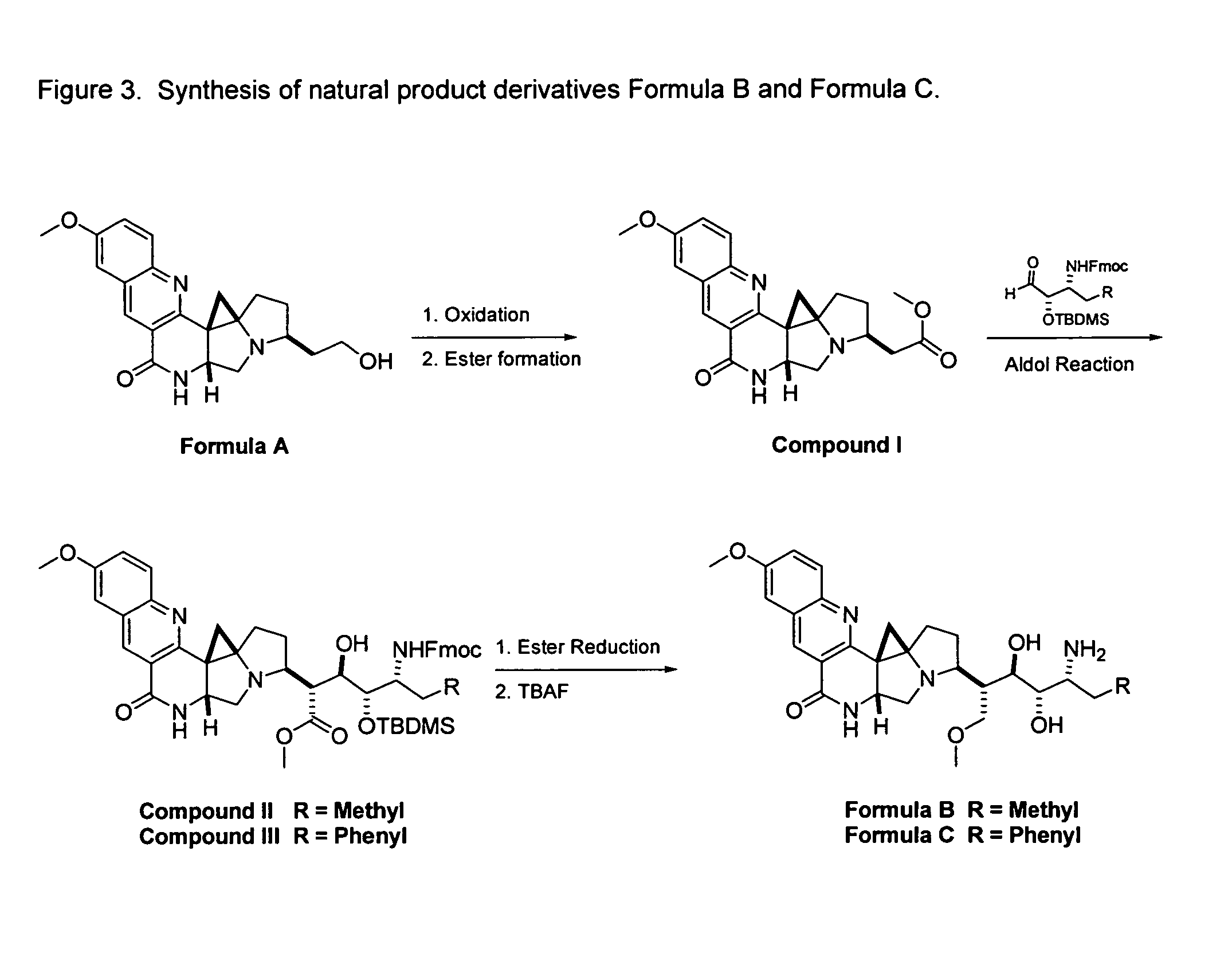
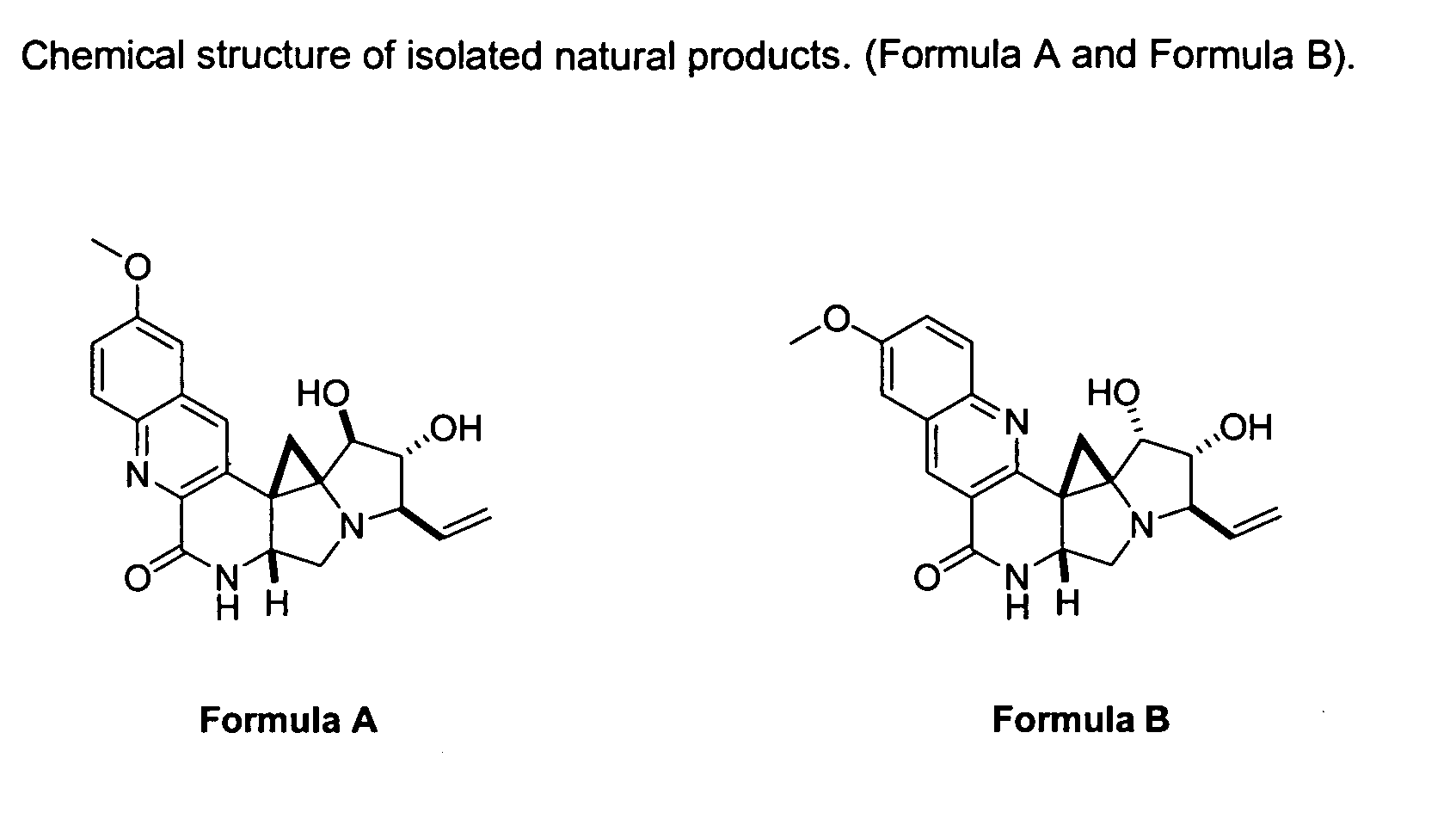
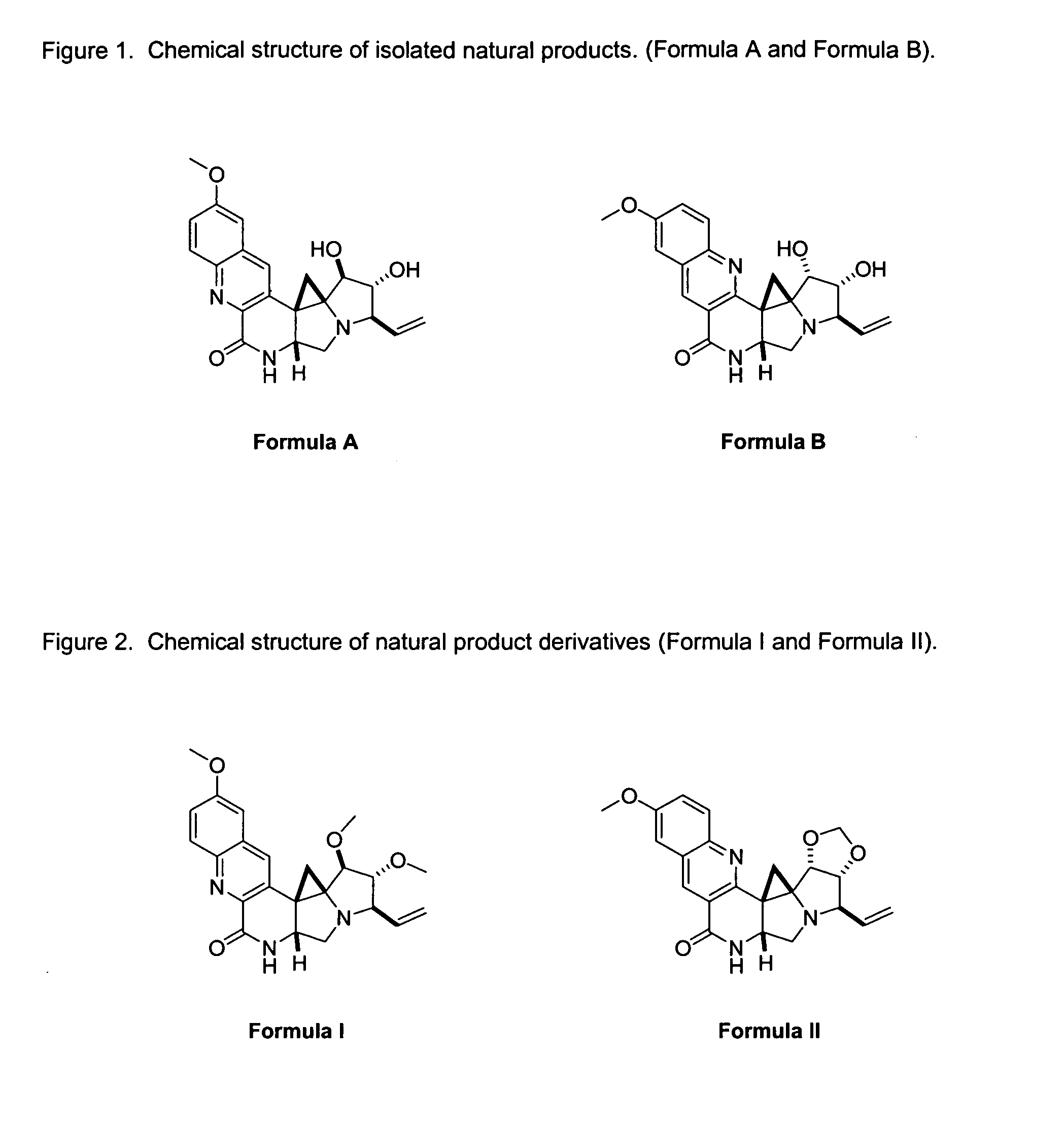
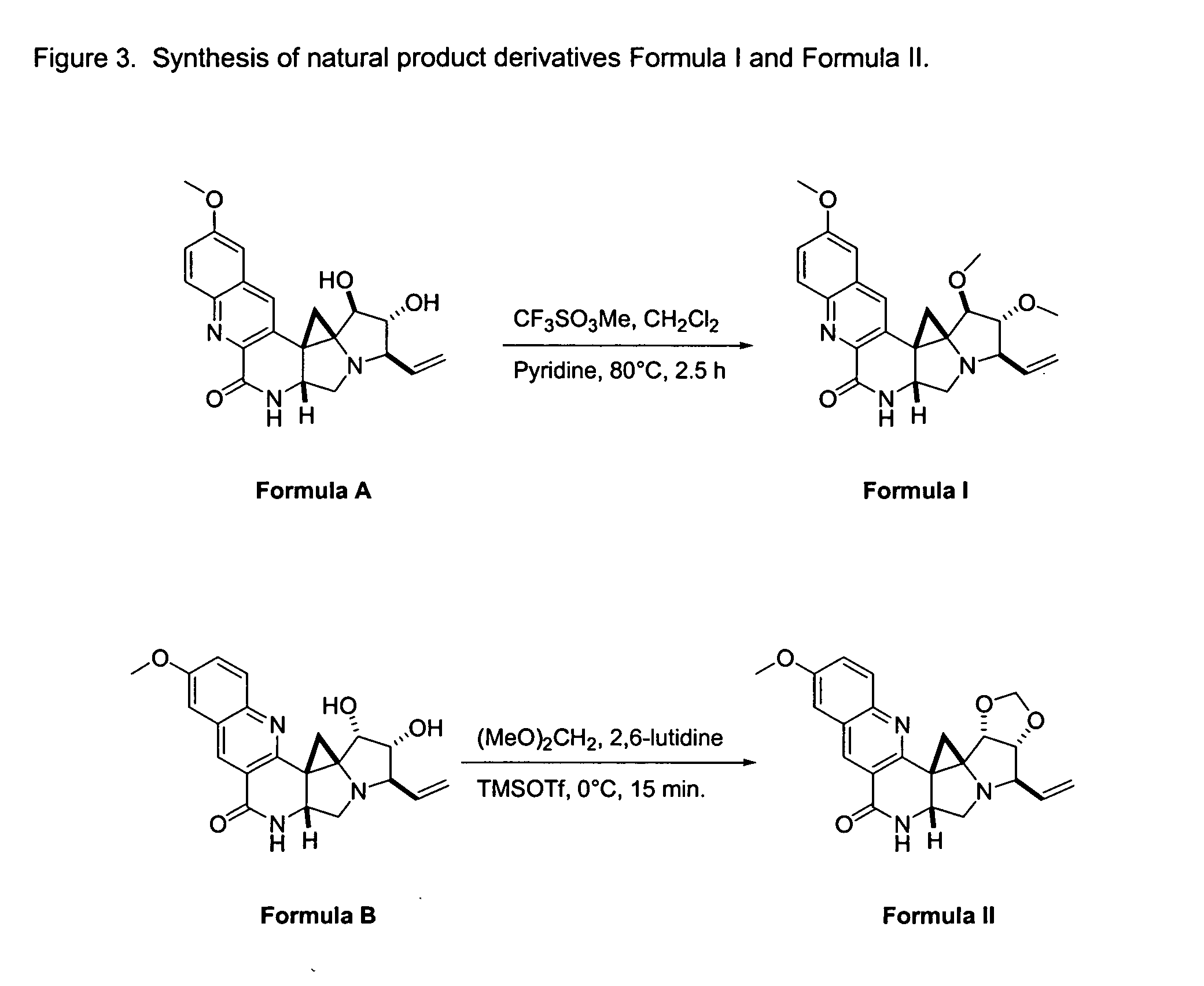
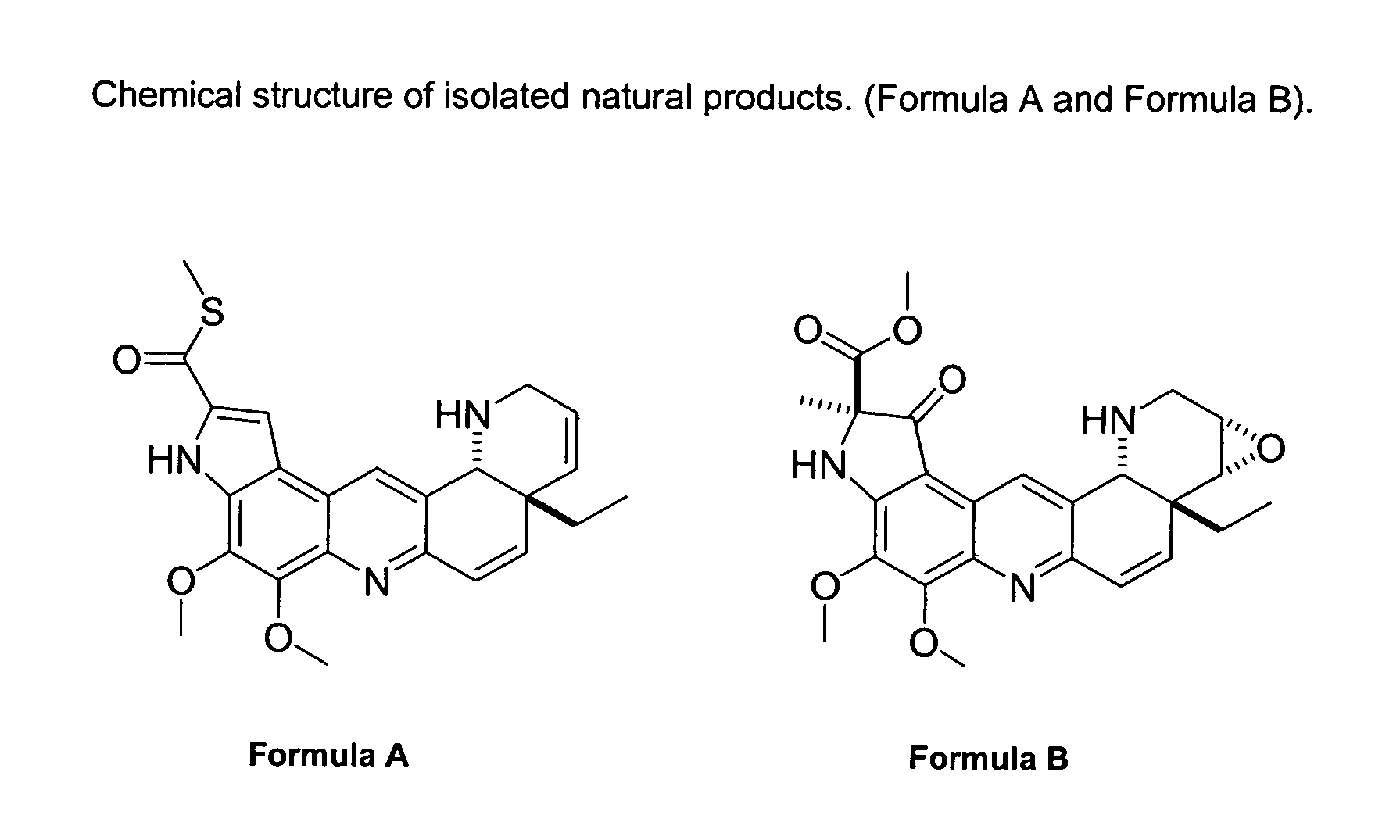
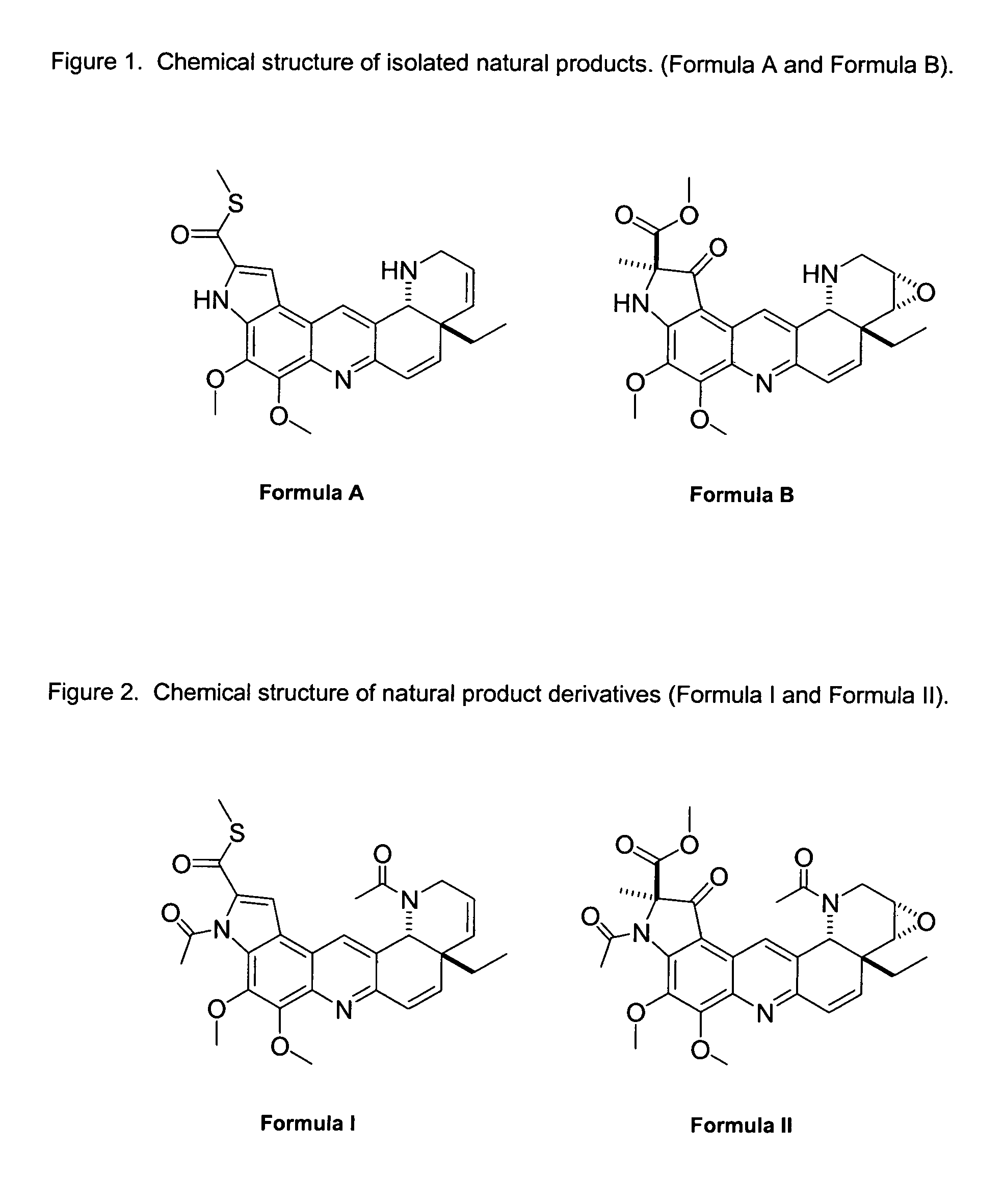
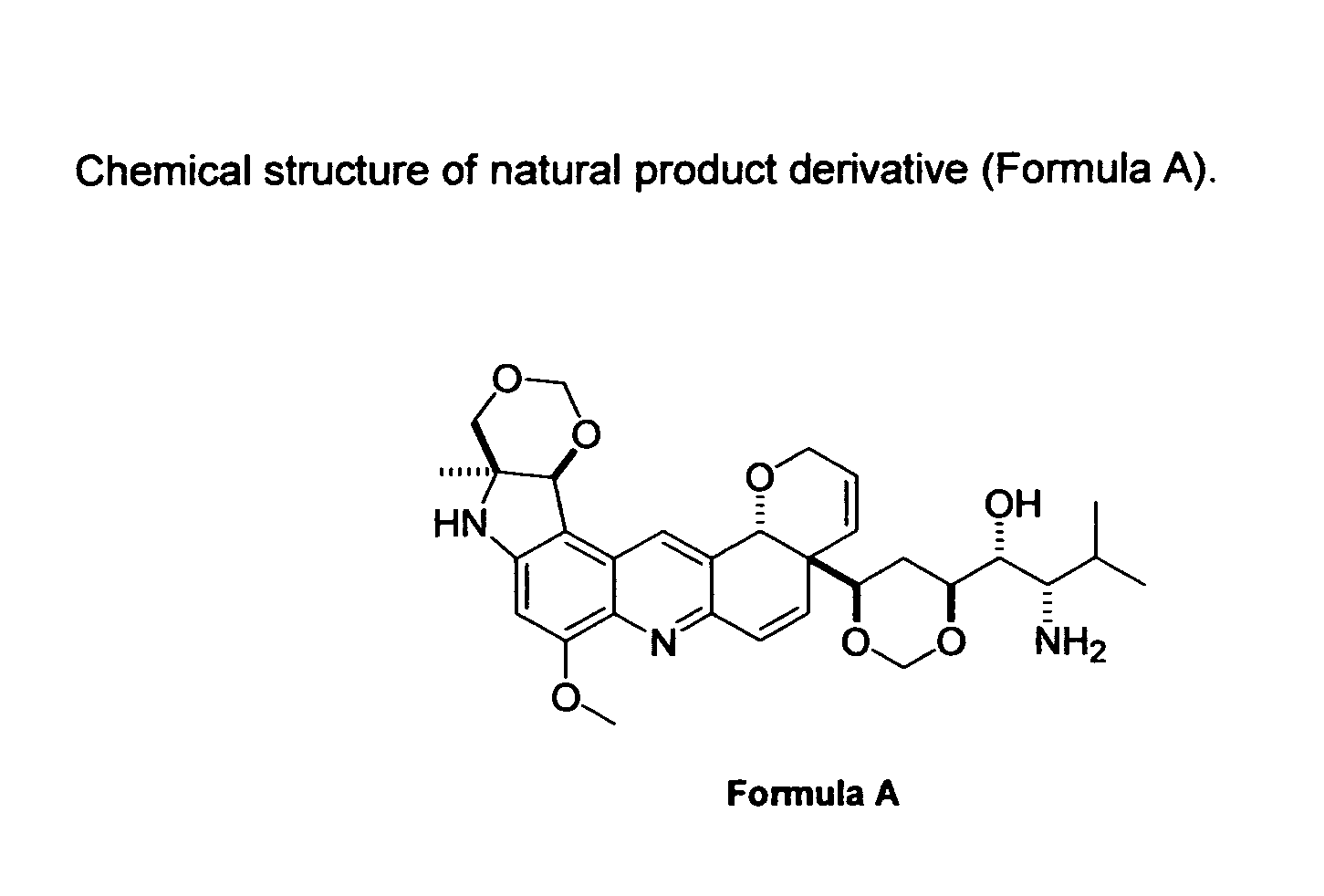
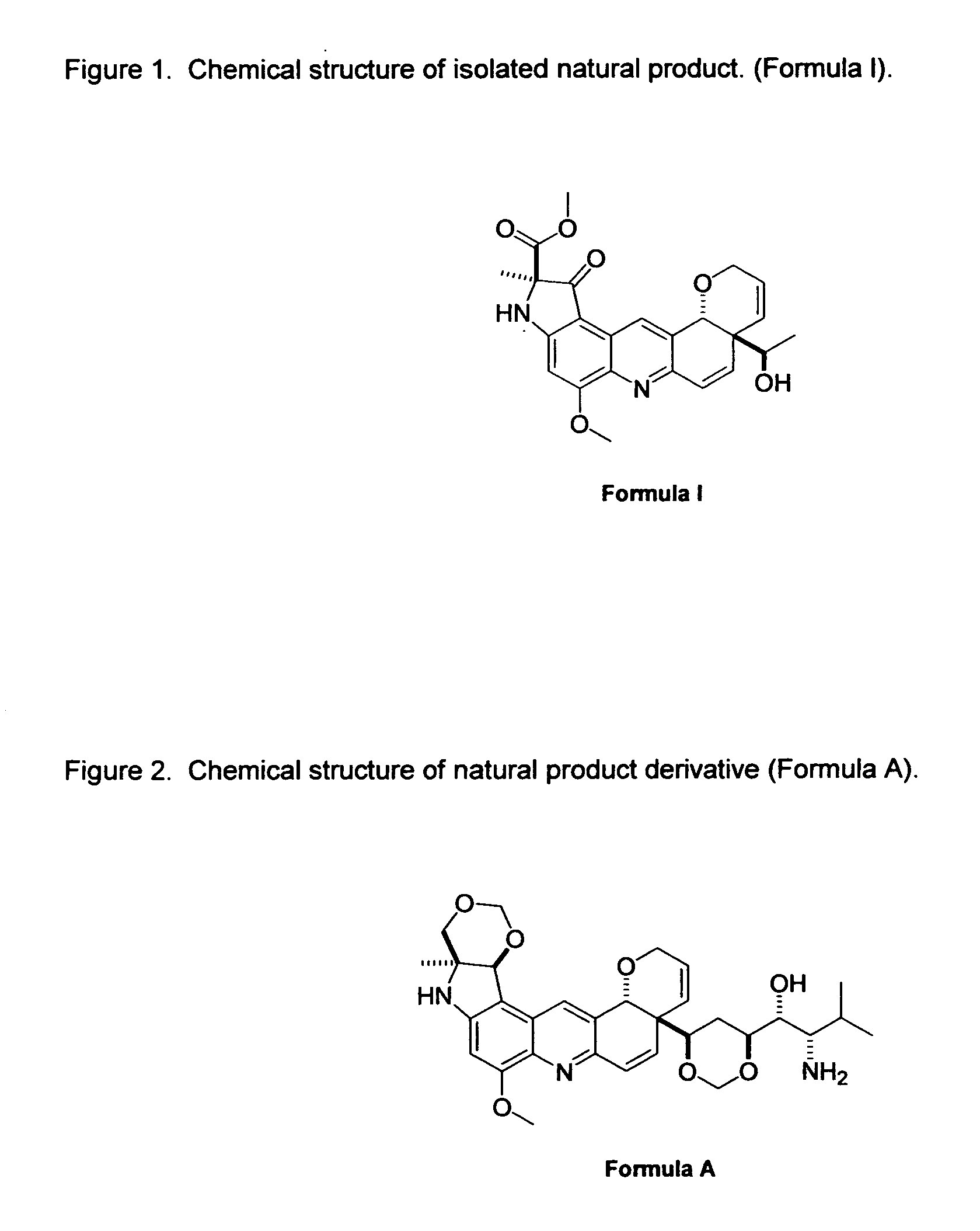
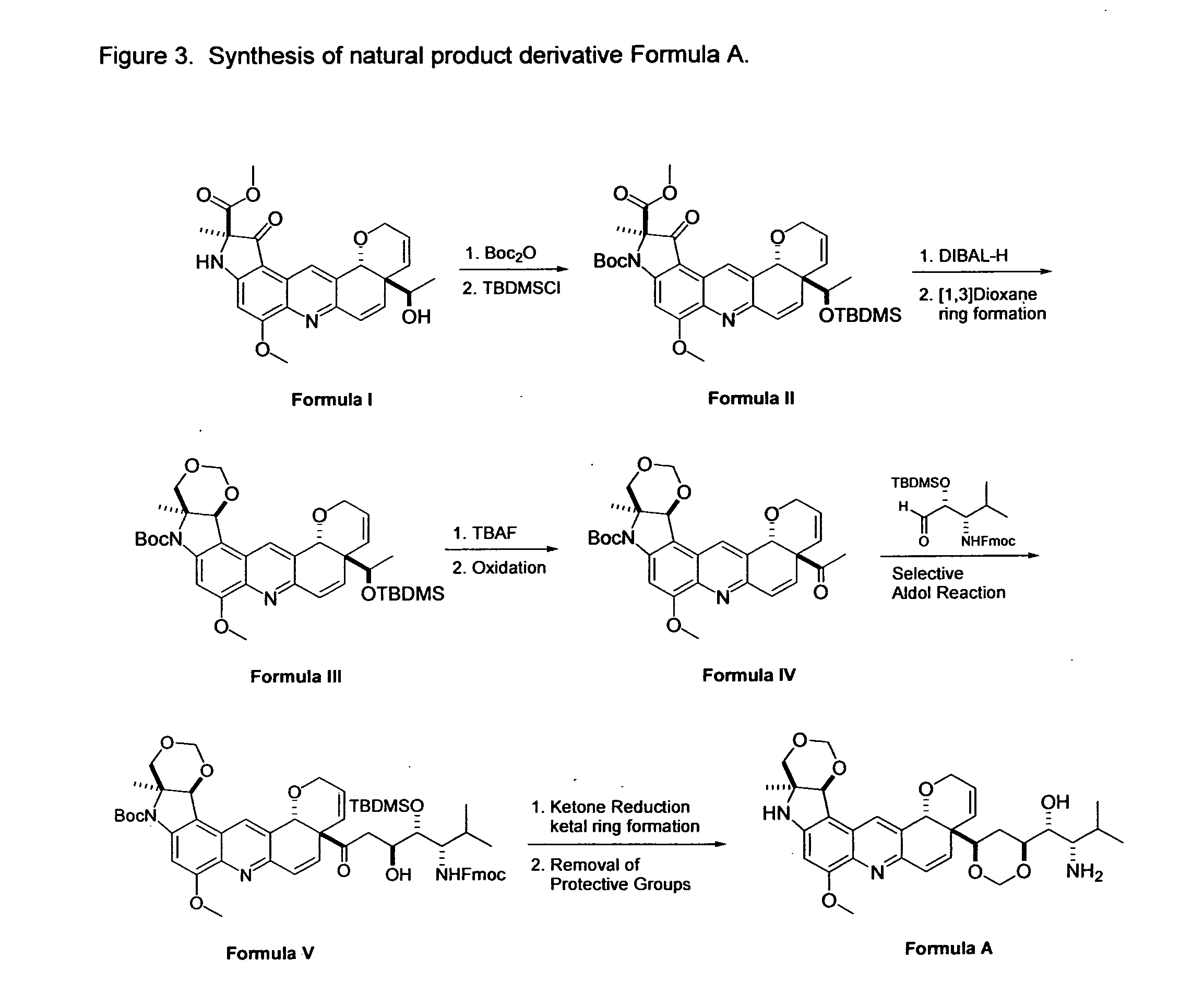
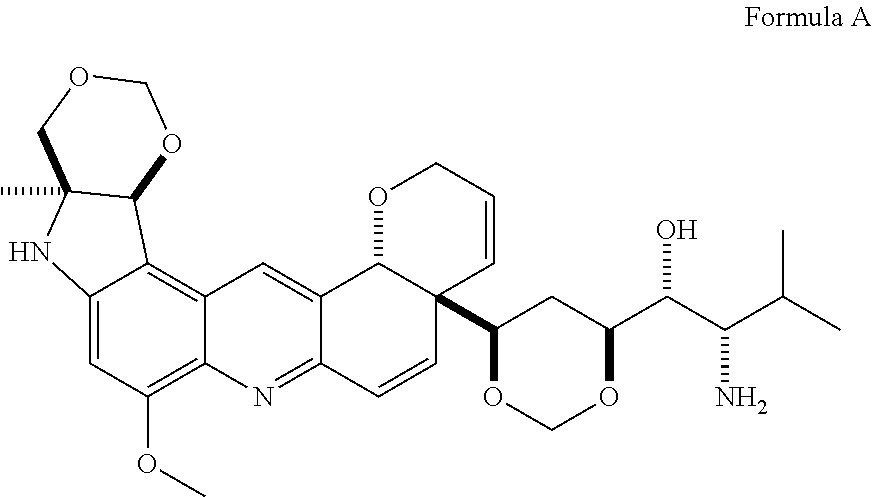
Natural product derivatives with antimalarial activity
The present invention provides new chemical compositions with desirable biological activity and toxicity profiles for the enhanced treatment of malaria.
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
Linkage modified oligomeric compounds
ActiveUS9926556B2Loss of normal functionHigh selectivitySugar derivativesDNA/RNA fragmentationModified nucleosidesToxicity profile
The present invention provides oligomeric compounds comprising at least one neutral methoxypropyl phosphonate modified internucleoside linkage. Such oligomeric compounds have one or more improved properties such as selectivity, potency, improved toxicity profile and or improved proinflammatory profile. Such oligomeric compounds have enhanced stability to exposure to base during synthesis. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Small molecules with antimalarial activity
The present invention provides new chemical compositions with desirable biological activity and toxicity profiles for the enhanced treatment of malaria.
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
Imino sugar derivatives demonstrate potent antiviral activity and reduced toxicity
InactiveUS9040488B2Good effectImprove performanceBiocideOrganic chemistryBovine Viral Diarrhea VirusesSide chain
Imino sugars, such as deoxynojirimycin (DNJ), are glucose analogues that selectively inhibit cellular α-glucosidase I and II (enzymes that process N-linked glycans in glycoprotein) and exhibit broad spectrum antiviral activities against many enveloped viruses. Previously we have reported a novel DNJ derivative, OSL-95II, with antiviral activity and reduced cytotoxicity. In order to develop imino sugars with more potent antiviral activity as well as improved toxicity profile, OSL-95II was modified by diversifying the nitrogen linked alkylated side chain. The antiviral activities were initially tested in bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) infected MDBK cells, yielding several imino sugar derivatives with novel structure and superior antiviral activity and toxicity profile. Furthermore, these new compounds were shown to be active against Dengue virus (DV) and West Nile virus (WNV) infection in BHK cells where potent anti-DV activity having submicromolar EC50 values and SI of greater than 900. These compounds represent a new generation of iminio sugars and their analogues, having application in the clinical treatment of infection of DV and other members of flaviviridae.
Owner:INST FOR HEPATITS & VIRUS RES +1
Intrapulmonary Administration Of Polynucleotide Toll-Like Receptor 9 Agonists For Treating Cancer Of The Lung
The present disclosure relates to methods for treating cancer by intrapulmonary administration of a polynucleotide Toll-like receptor 9 agonist. The methods of the present disclosure are suitable fortreating primary cancer of the lung, as well as metastatic cancer to the lung and extra pulmonary cancers thereof. Additionally, the present disclosure provides polynucleotide Toll-like receptor 9 agonists with immune stimulatory and toxicity profiles suitable for intrapulmonary administration.
Owner:DYNAVAX TECH CORP
Transgenic mice knockouts of BACE-1
InactiveUS7309811B2Improve bindingIncreased activationAnimal cellsMicrobiological testing/measurementGeneticsFunctional allele
The invention provides transgenic animals that are heterozygous or homozygous for a nonfunctional allele of BACE-1. These animals show normal development indicating that BACE-1 is not necessary for development and hence is an appropriate therapeutic target. The transgenic animals are useful in various screening assays including identifying inhibitors of other enzymes involved in processing of APP to Aβ and determining a toxicity profile of inhibitors of BACE-1.
Owner:PHARMACIA & UPJOHN CO +1
Small molecules with antimalarial activity
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
Natural product derivatives with antimalarial activity
The present invention provides new chemical compositions with desirable biological activity and toxicity profiles for the enhanced treatment of malaria.
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
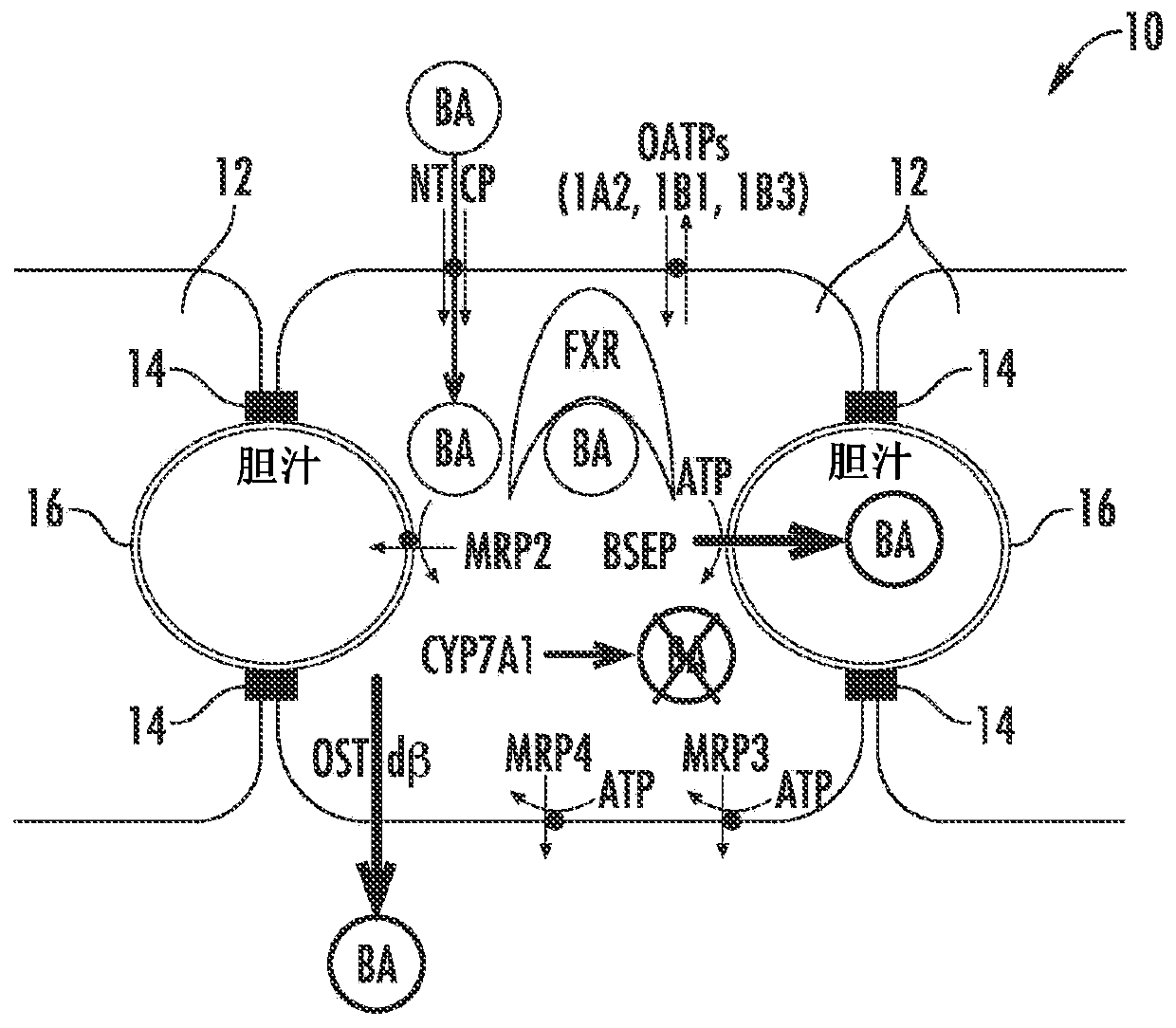
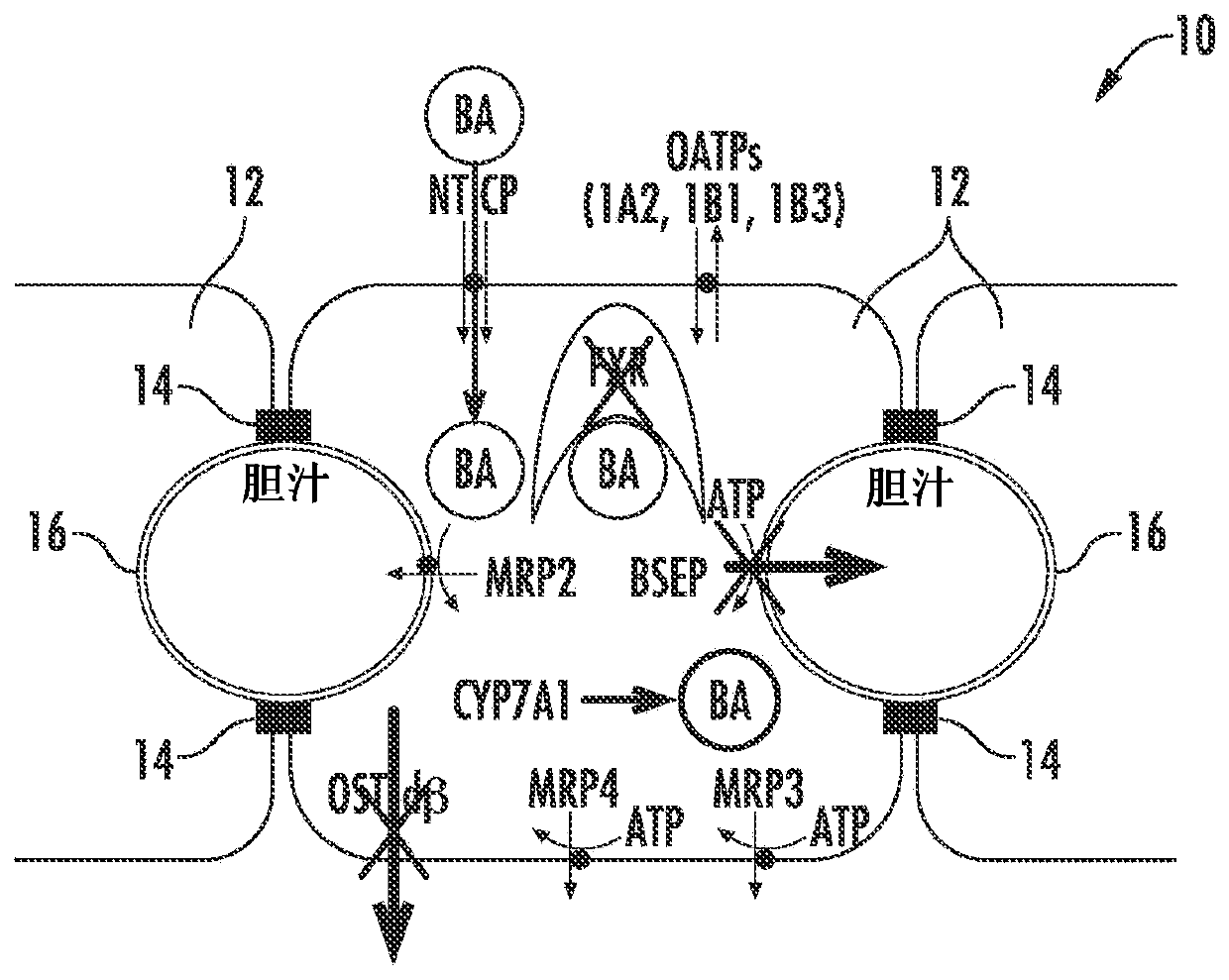
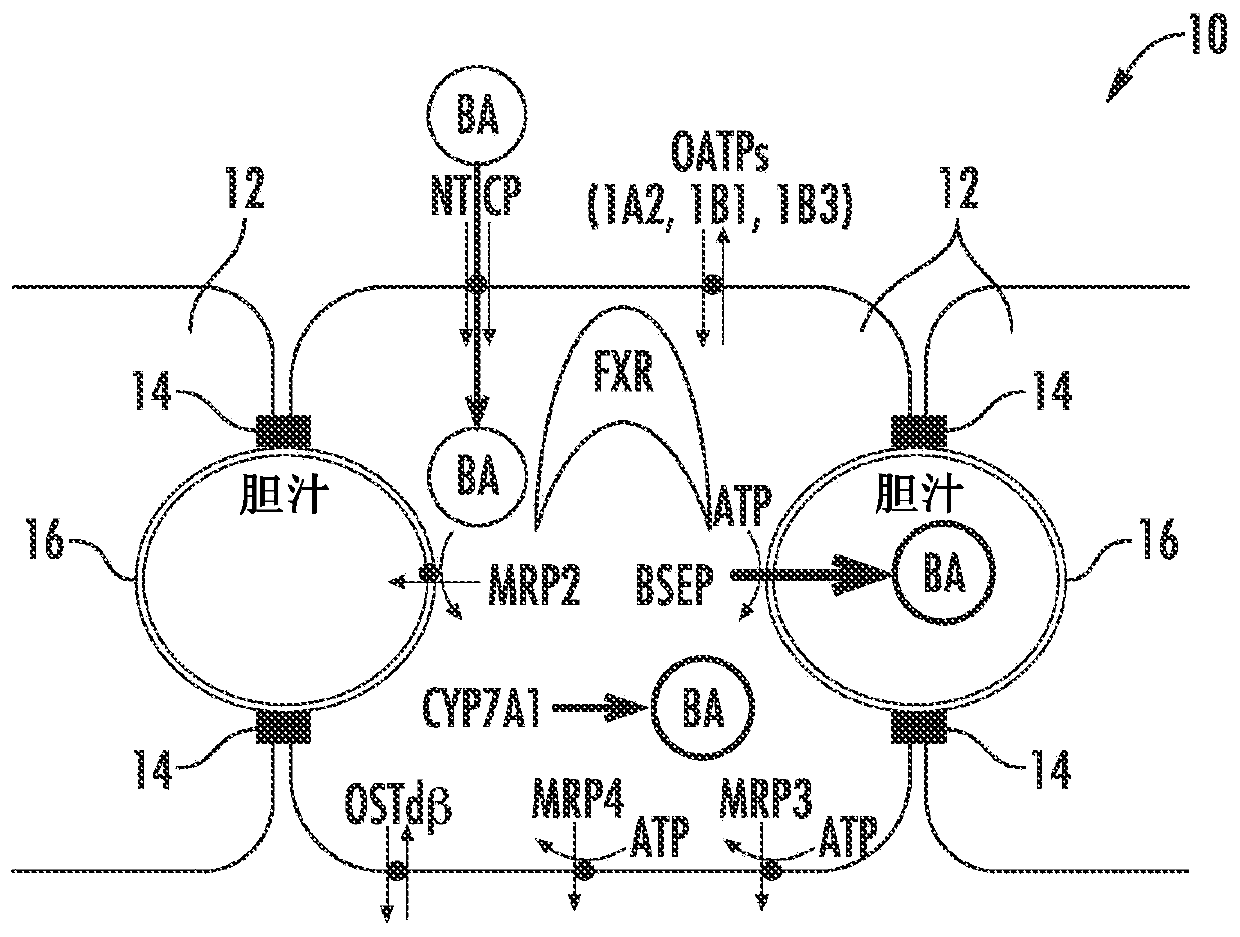
Methods and systems for screening candidate compounds for their potential to cause systemic or hepatic toxicity
Methods of screening a compound for susceptibility to causing systemic or hepatic toxicity, using a hepatic cell system exposed to a range of concentrations of a bile acid in the absence or presence of a compound to determine a toxicity profile. In vitro systems for predicting in vivo hepatotoxic potential of a compound are also provided, and include in vitro cultured hepatic cell systems with a capacity for bile acid synthesis, bile acid transport and bile acid regulation.
Owner:QUALYST TRANSPORTER SOLUTIONS
Small molecules with antiprotozoal activity
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
ANF-RGC in-gene knock-out animal
InactiveUS20130291132A1Reduced activityLittle and no ANF-RGC activityCompounds screening/testingOrganic active ingredientsBiological activationZoology
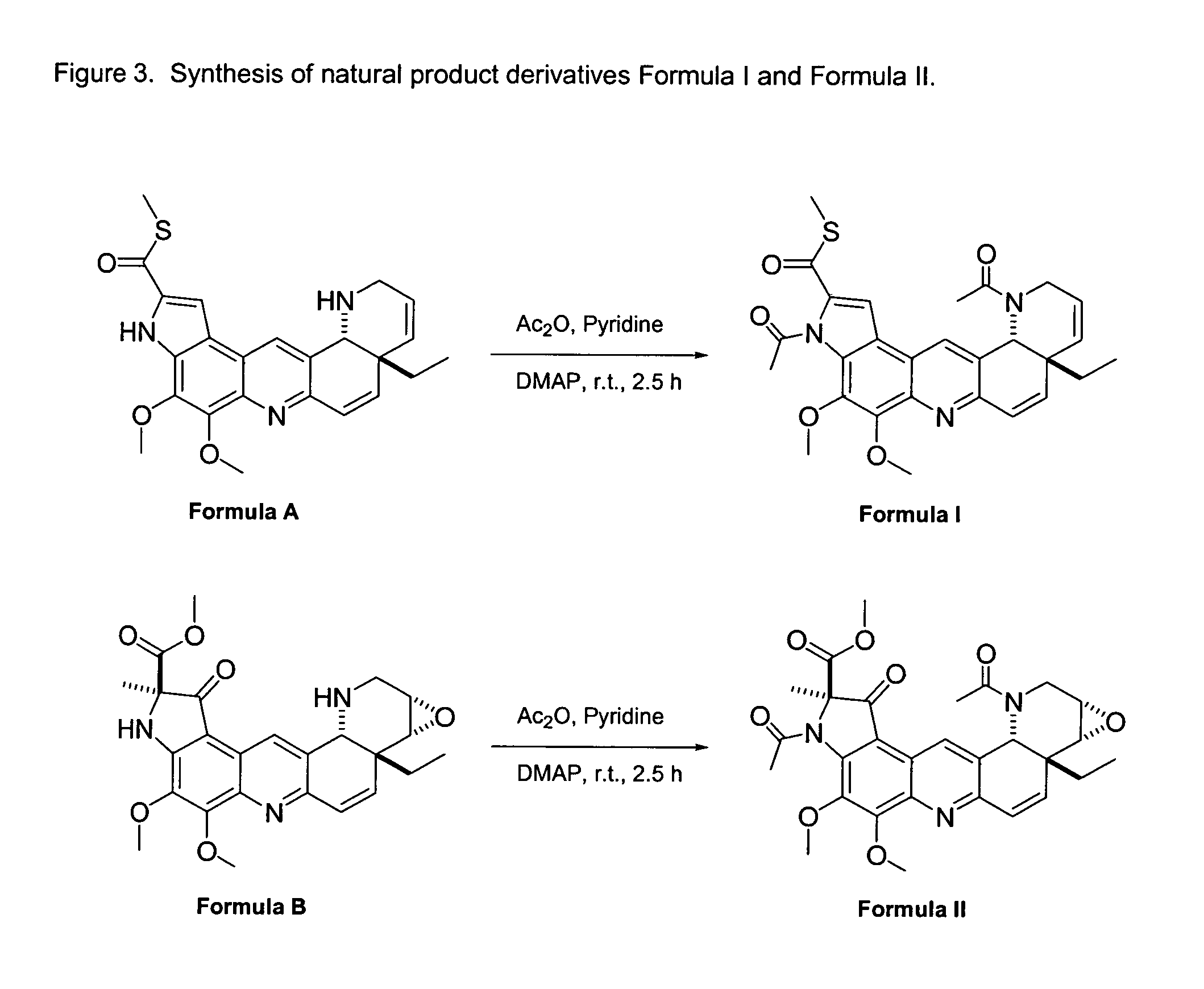
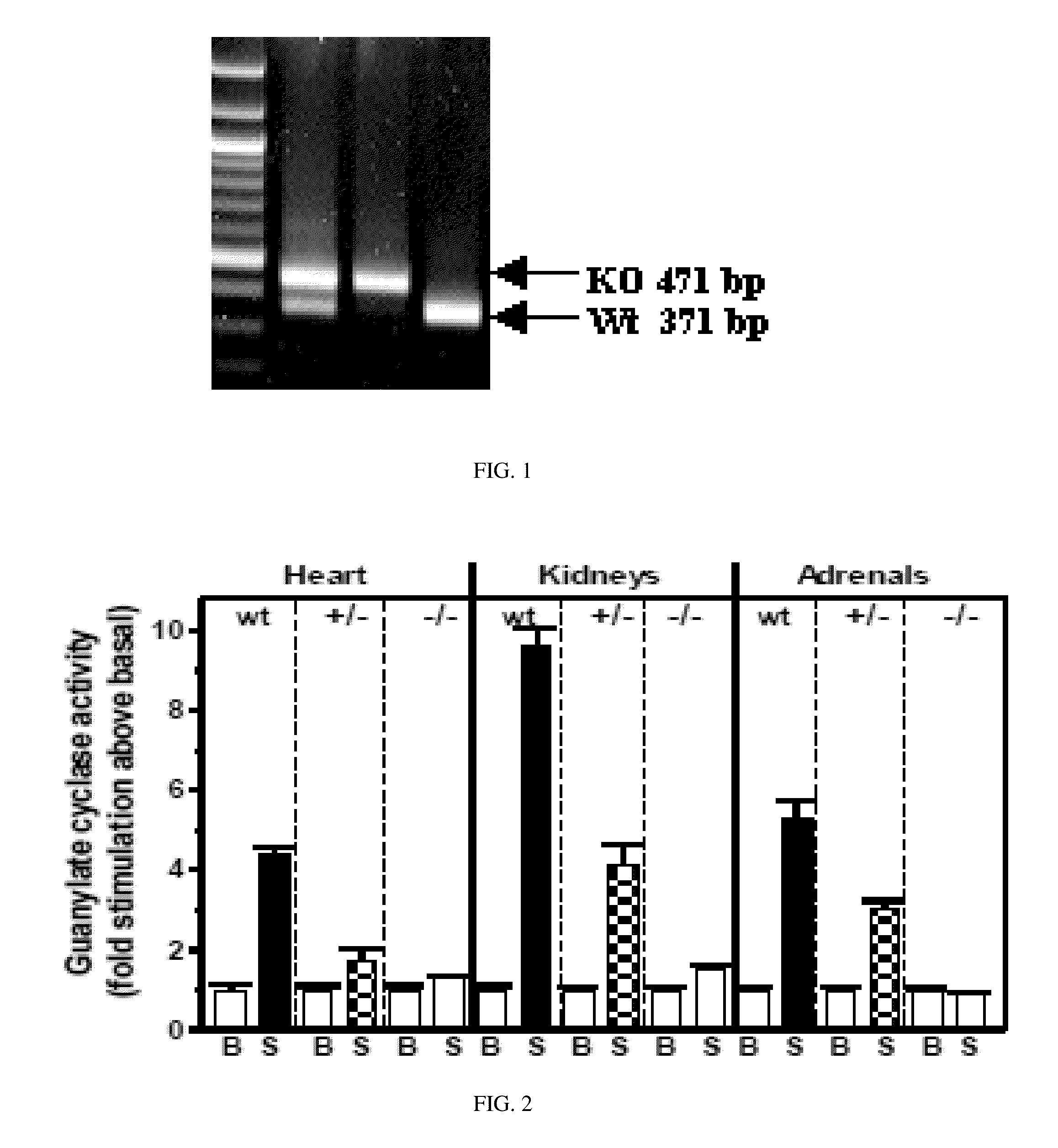
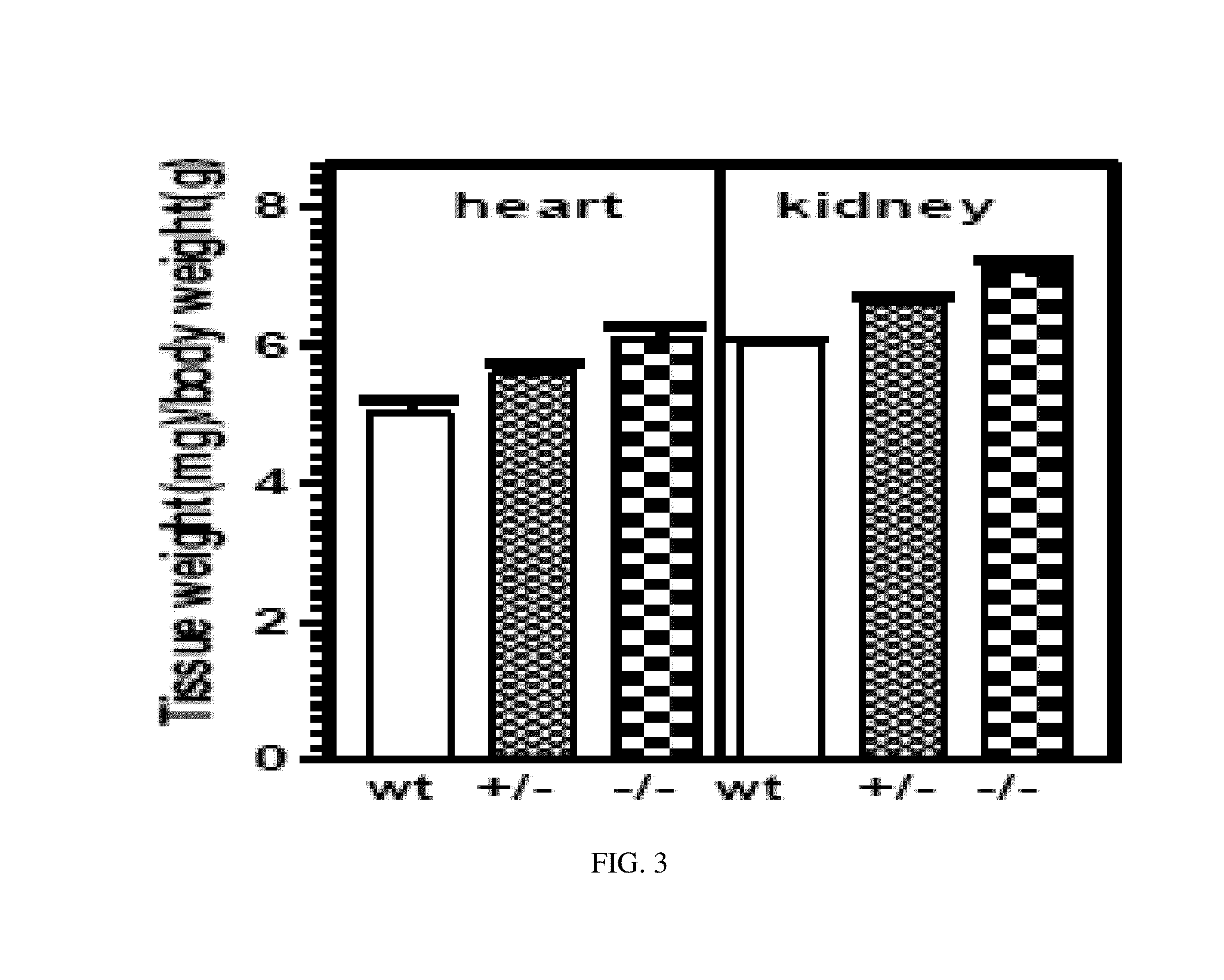
The present invention relates to transgenic animals comprising a mutation or deletion to the ANF-RGC protein, particularly to its ARM and / or its ATS-ST region. Such animals may be used to study the effects on pathways associated with ANF-RGC activation, including, but not limited to, hypertension. Such animals may also be used in drug screen assays, to establish toxicity profiles, or other similar methods discussed herein known in the art.
Owner:SALUS UNIVERSITY
Natural product derivatives with antiprotozoal activity
The present invention provides new chemical compositions with desirable biological activity and toxicity profiles for the enhanced treatment of malaria.
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
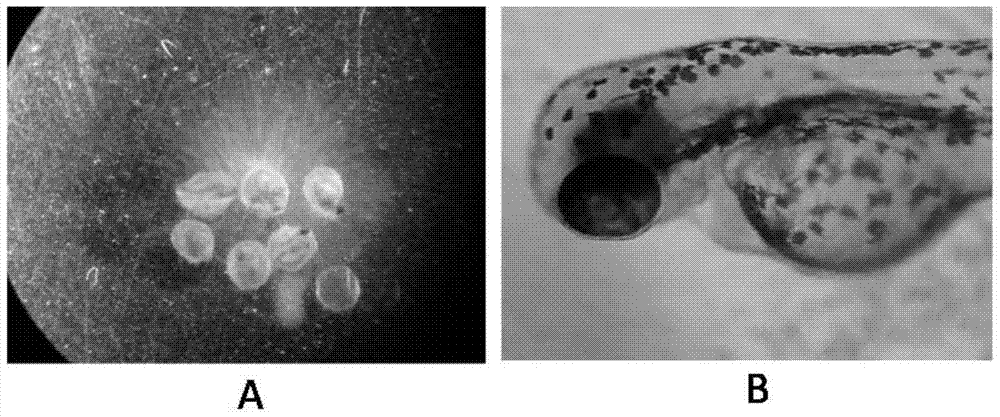
A method for predicting early life-stage embryotoxicity of zebrafish from novel pollutants from nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The invention discloses a method for predicting the toxicity of novel pollutants of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to embryos in the early life stage of zebrafish. The present invention records the mortality and distortion rate of zebrafish embryos after exposure for 7 days by exposing the zebrafish embryos to the new pollutants of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in an equal logarithmic interval concentration; and then uses SPSS software to calculate the corresponding LC 50 and teratogenic EC 50 To evaluate the toxicity of novel pollutants of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The method of the invention realizes the analysis, testing and quantitative description of the toxicity characteristics and toxicity levels of the new pollutants of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and can be used as an index for monitoring and evaluating the biological toxicity of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug sewage. It provides a reference for the prediction and assessment of the potential ecotoxicity risk of such pollutants in China.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Natural product derivatives with antiprotozoal activity
The present invention provides new chemical compositions with desirable biological activity and toxicity profiles for the enhanced treatment of malaria.
Owner:RADIX PHARMA
Differential tumor cell cytotoxicity via contact with coated cerium oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS10213458B2Without compromising solubilityReduce in quantityHeavy metal active ingredientsMicrocapsulesCancer cellLysosome
Differential surface-charge-dependent localization of nanoceria in normal cells and cancer cells plays a critical role in the toxicity profile of a nanoceria particle. Engineered surface-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles with different surface charges that are positive, negative and neutral provide therapeutic results for normal and cancer cell lines. Results show that nanoceria with a positive or neutral charge enters most of the cell lines studied, while nanoceria with a negative charge internalizes mostly in the cancer cell lines. Moreover, upon entry into the cells, nanoceria is localized to different cell compartments (e.g. cytoplasm and lysosomes) depending on the nanoparticle surface charge. The internalization and subcellular localization of nanoceria plays a key role in the nanoparticle cytotoxicity profile, exhibiting significant toxicity when they localize in the lysosomes of the cancer cell lines. In contrast, minimal toxicity is observed when they localize into the cytoplasm or do not enter the cells.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Enantiomers of the 1',6'-isomer of neplanocin a
Enantiomers of 1′,6′-isoneplanocin, including derivatives of the enantiomers of 1′,6′-isoneplanocin, are disclosed along with novel synthetic methods. In particular, a substituted cyclopentane epoxide is synthesized into the enantiomers of 1′,6′-isoneplanocin. Enantiomers of carbocyclic nucleoside analogs of 3-deazaneplanocin to provide D- and L-like 1′,6′-iso-3-deazaneplanocin are also disclosed. The small molecule chemotherapeutic compounds beneficially provide DNA and RNA antiviral activity, demonstrating activity towards, for example, human cytomegalovirus, measles, Ebola, norovirus, dengue, vaccinia and HBV. Compounds exhibiting reduced S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase inhibitory effects are disclosed and provide improved toxicity profiles in comparison to neplanocin. The invention provides improved prophylactic and / or therapeutic antiviral efficacy.
Owner:AUBURN UNIV
Pokeweed antiviral protein polypeptides with antiviral activity
InactiveUS20060128941A1Inhibits viral replicationBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsEscherichia coliHiv 1 rna
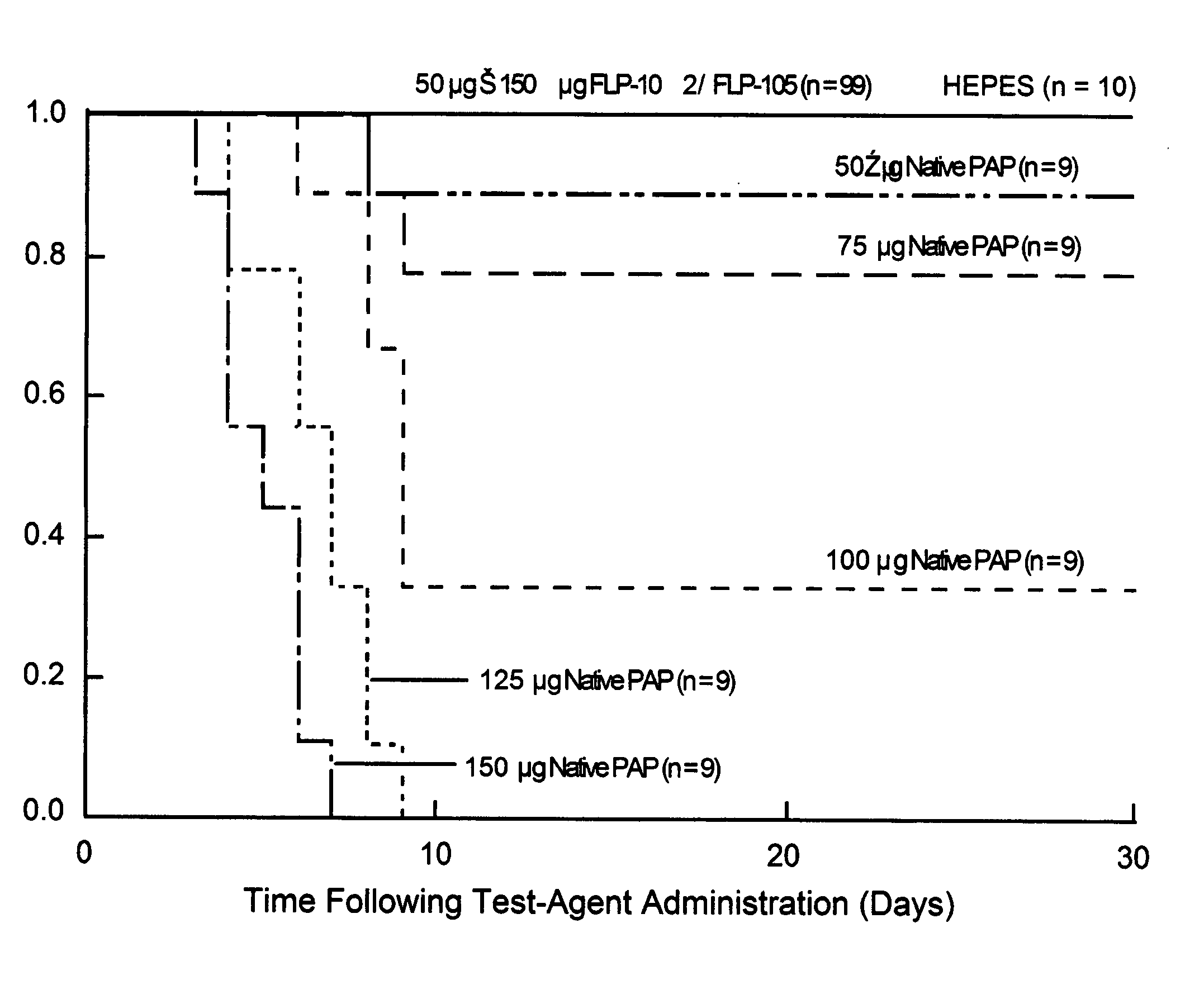
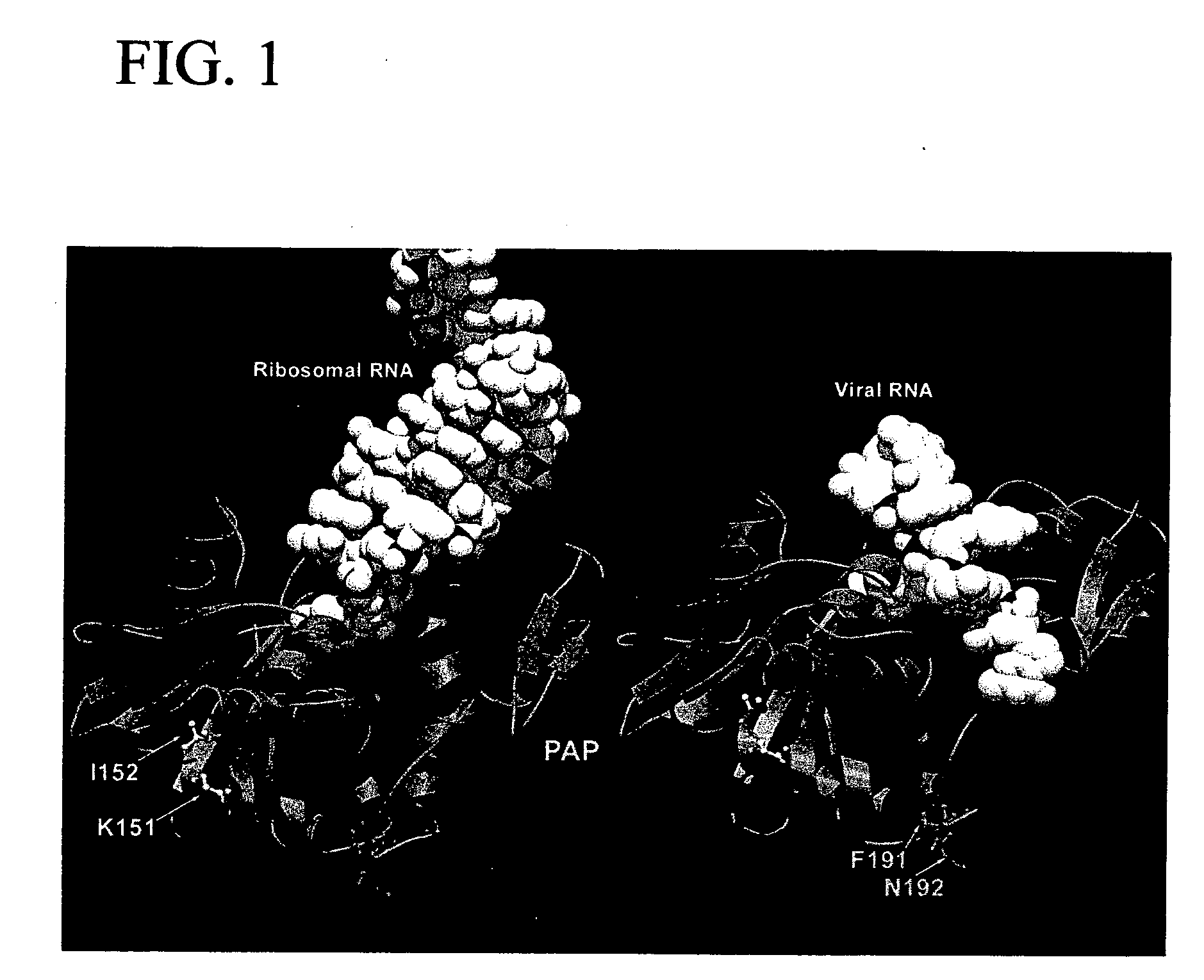
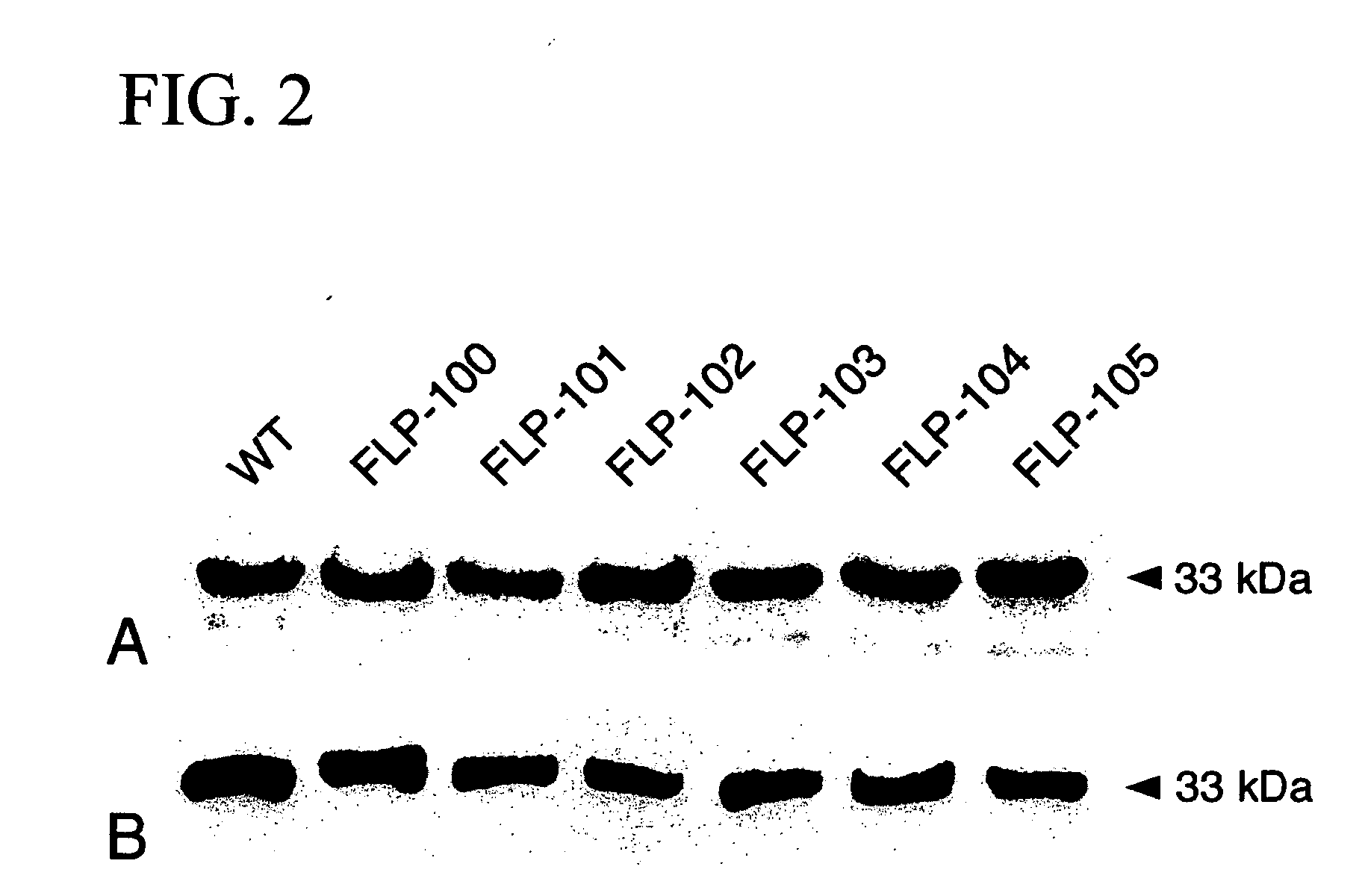
A molecular model of pokeweed antiviral protein (PAP)-RNA interactions was used to rationally engineer FLP-102 (151AA152) and FLP-105 (191AG192) as nontoxic PAP proteins with potent anti-HIV activity. FLP-102 and FLP-105 have been produced in E. coli and tested both in vitro as well as in vivo. These proteins depurinate HIV-1 RNA much better than ribosomal RNA and are more potent anti-HIV agents than native PAP or recombinant wild-type PAP. They are substantially less toxic than native PAP in BALB / c mice and exhibit potent in vivo activity against genotypically and phenotypically NRTI-resistant HIV-1 in a surrogate Hu-PBL-SLID mouse model of human AIDS. Rationally engineered nontoxic recombinant PAP proteins such as FLP-102 and FLP-105 may provide the basis for effective salvage therapies for patients harboring highly drug resistant strains of HIV-1. The documented in vitro potency of FLP-102 and FLP-105, their in vivo antiretroviral activity in HIV-infected Hu-PBL SCID mice, and their favorable toxicity profile in BALB / c mice warrant the further development of these promising new biotherapeutic agents.
Owner:UCKUN FAITH M +1
Morpholino modified oligomeric compounds
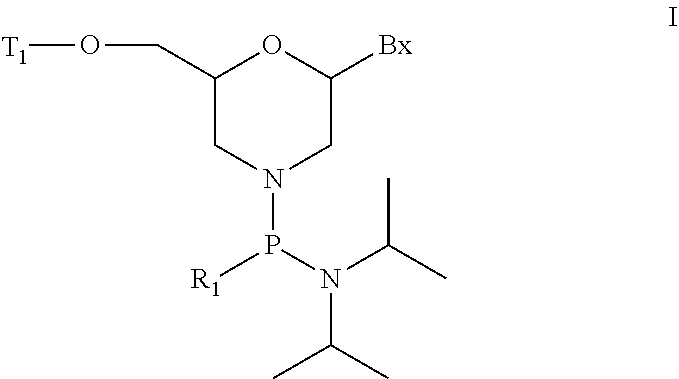
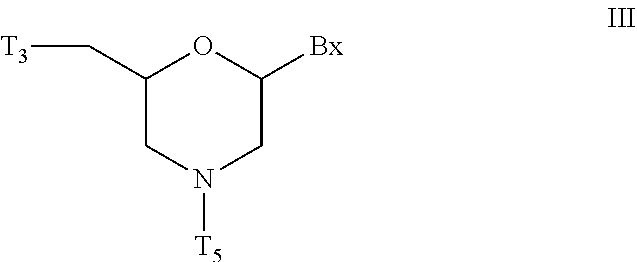
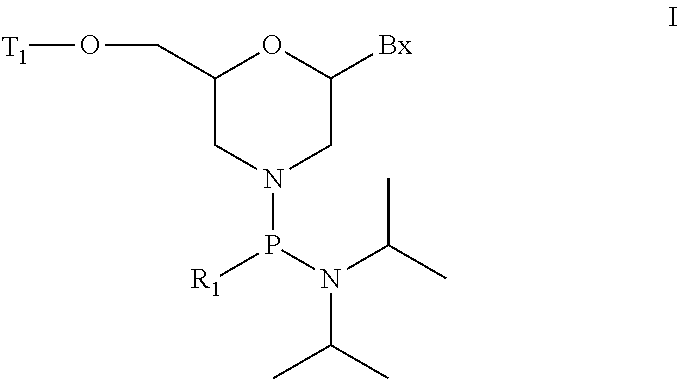
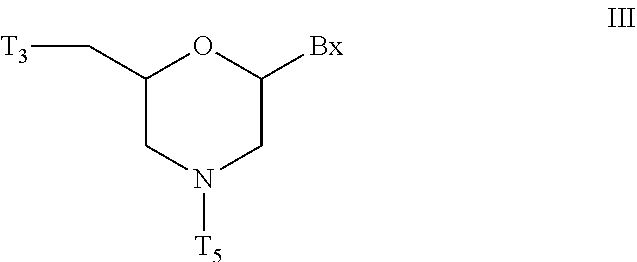
ActiveUS20200239881A1Sugar derivativesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsChemical compoundMorpholine
The present invention provides morpholino modified oligomeric compounds having at least one monomer subunit having Formula III, compounds having Formula I useful for making certain of the morpholino modified oligomeric compounds and methods of using the oligomeric compounds. In certain embodiments, the oligomeric compounds provided herein provide for an improved toxicity profile. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount of activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
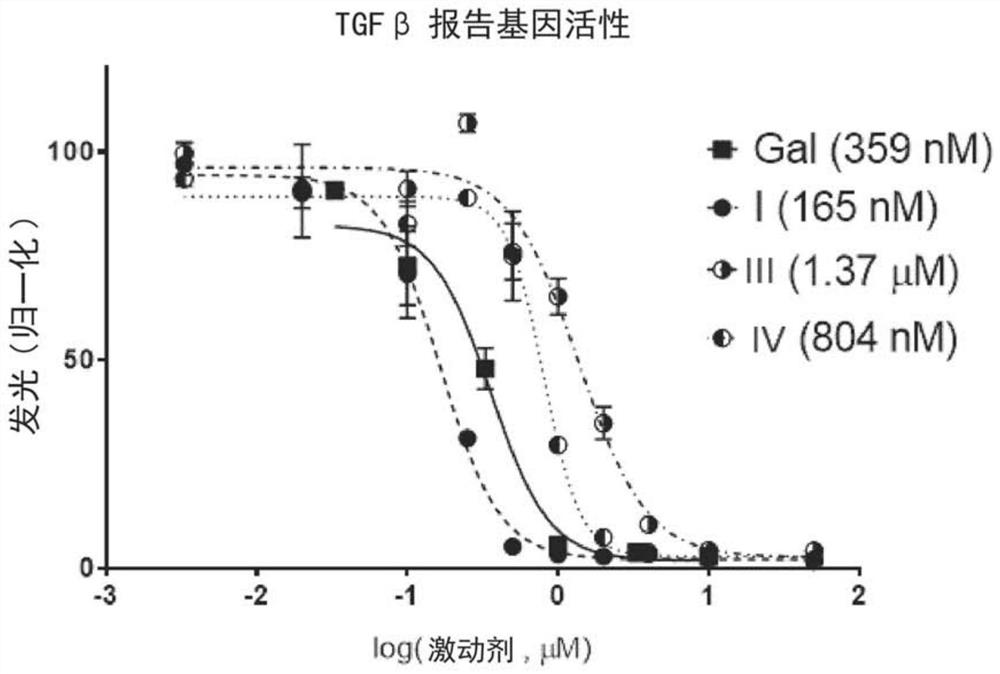
TGF Beta INHIBITOR AND PRODRUGS
A compound of formula (I) with improved TGF Beta signaling pathway inhibitory activity, improved therapeutic efficacy and improved toxicity profile, as well as two prodrugs thereof are disclosed. Compositions comprising said TGF Beta signaling pathway inhibitor and prodrugs thereof are also disclosed. Additionally, present invention discloses said compound of formula (I) and prodrugs thereof for use in a method of treating diseases responsive to TGF Beta signaling pathway inhibition.
Owner:生物医学研究机构基金会 +2
Morpholino modified oligomeric compounds
The present invention provides morpholino modified oligomeric compounds having at least one monomer subunit having Formula III, compounds having Formula I useful for making certain of the morpholino modified oligomeric compounds and methods of using the oligomeric compounds. In certain embodiments, the oligomeric compounds provided herein provide for an improved toxicity profile. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount of activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com