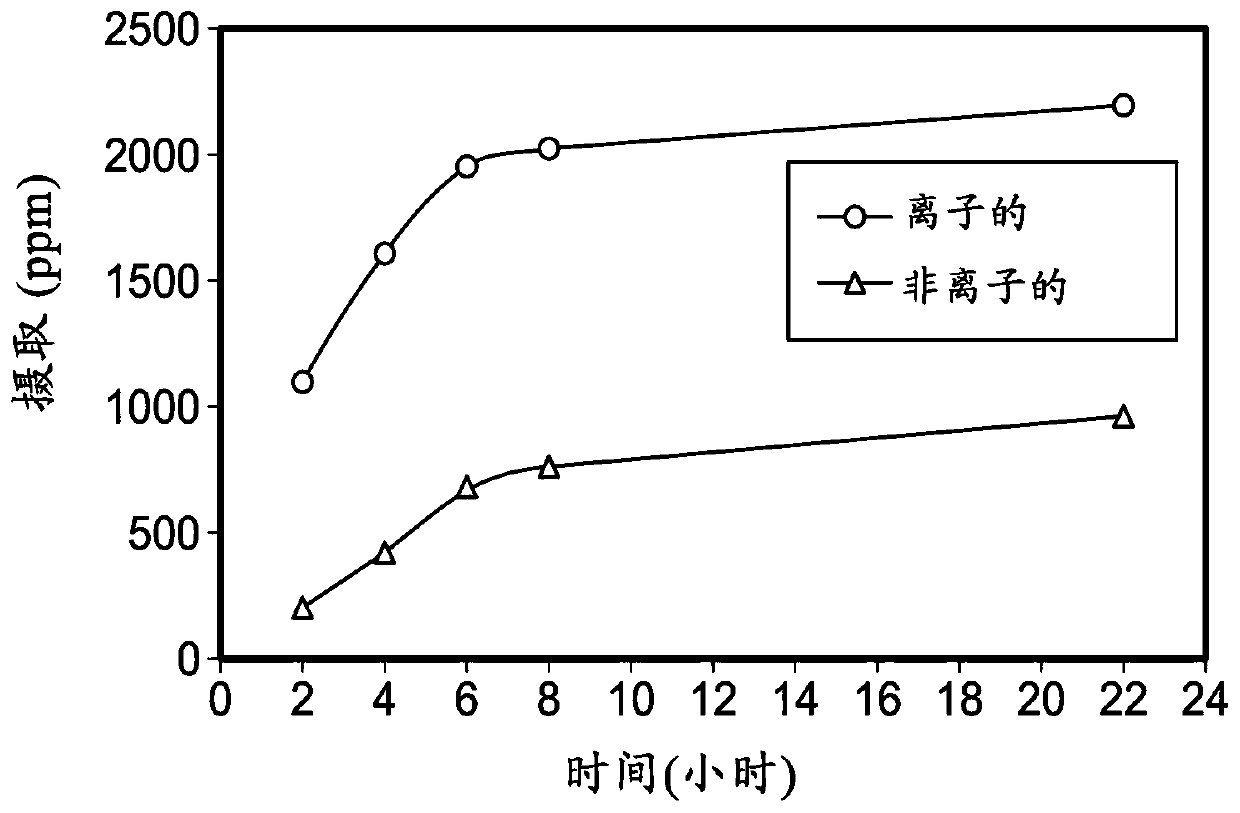
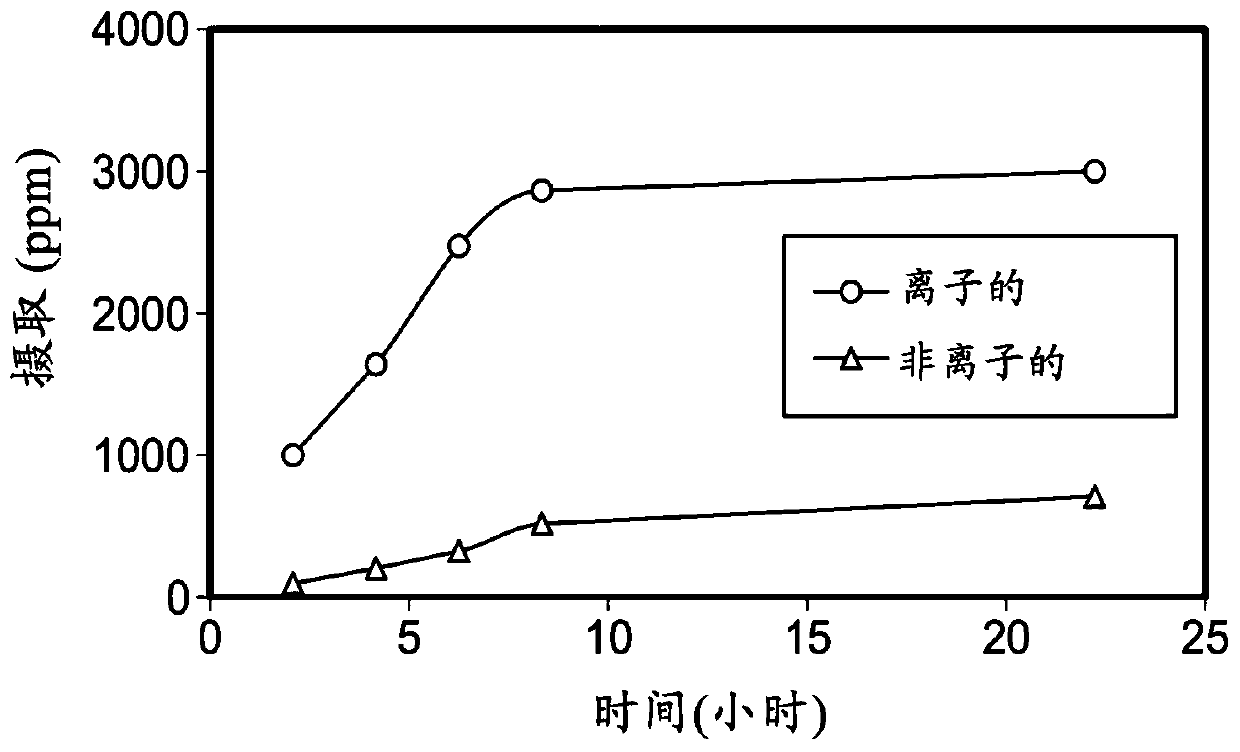
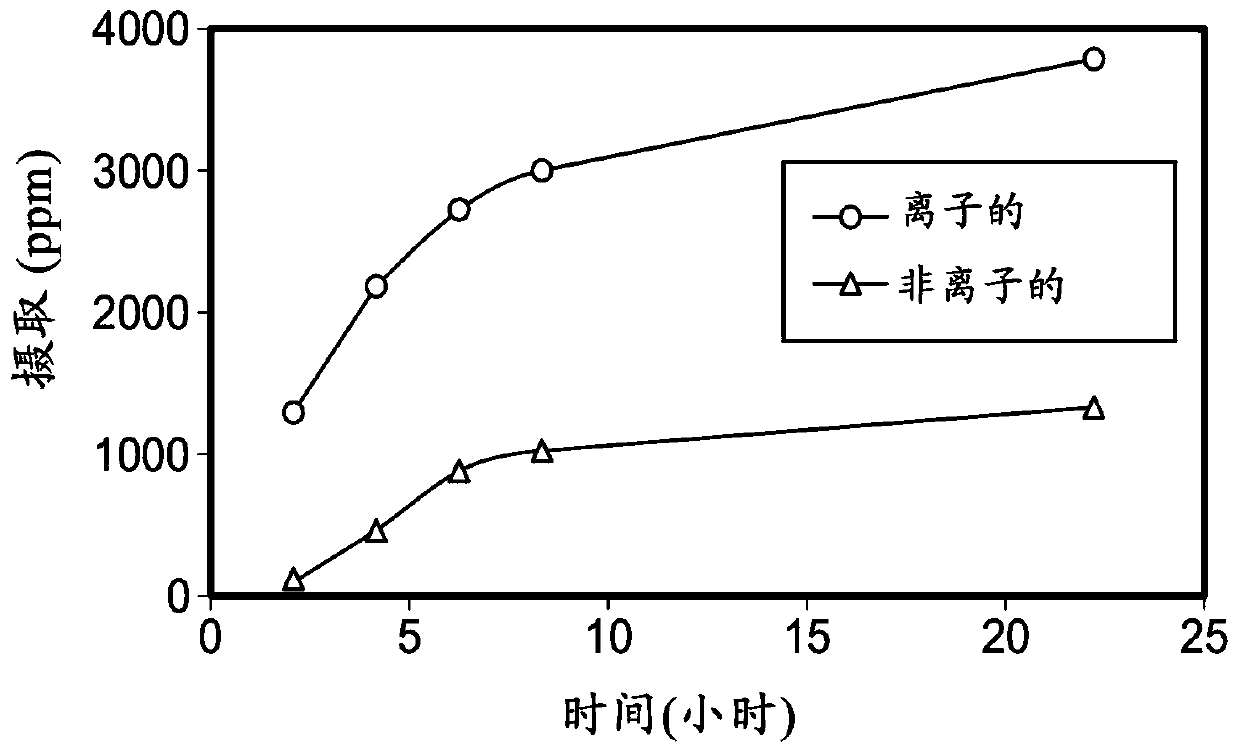
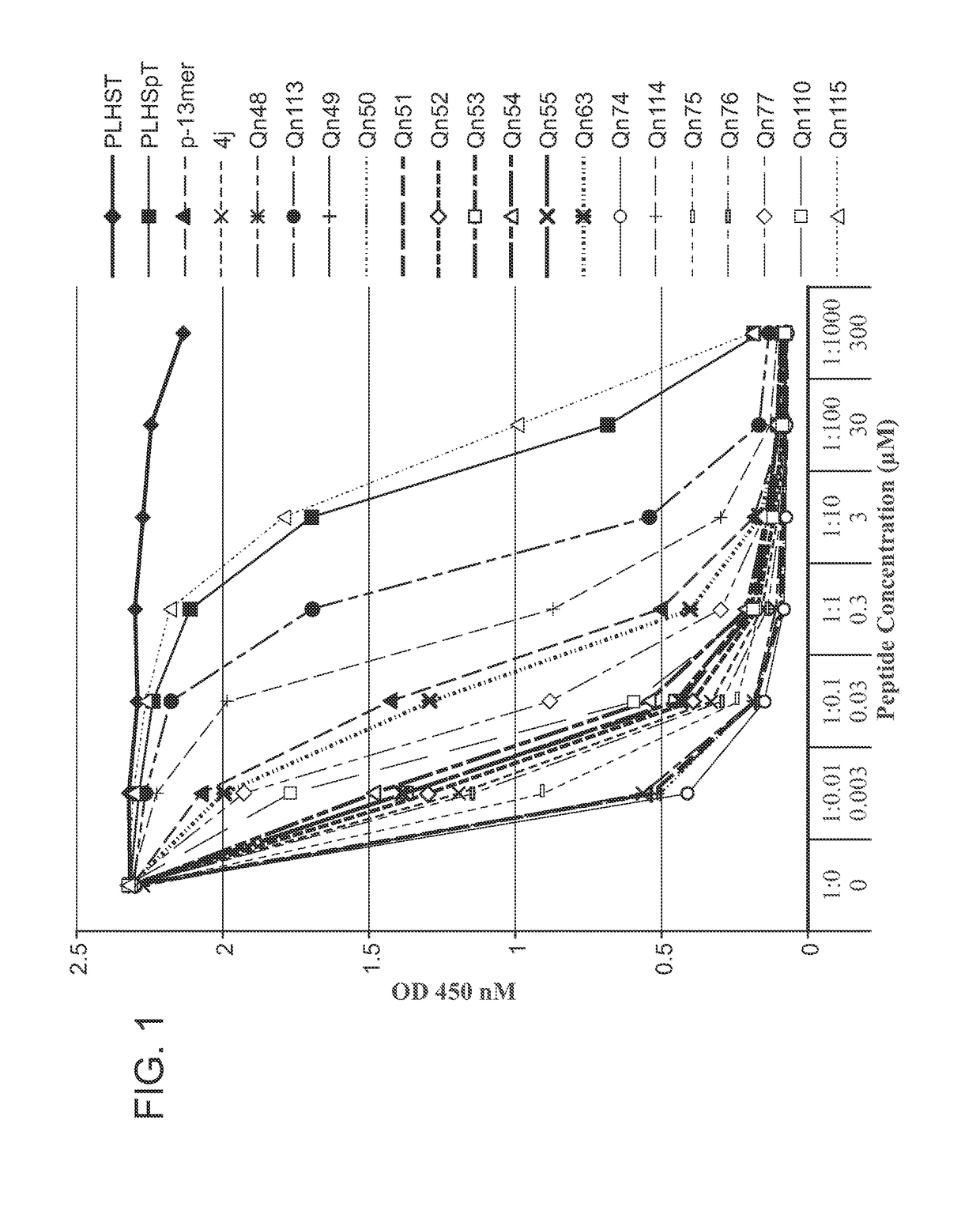
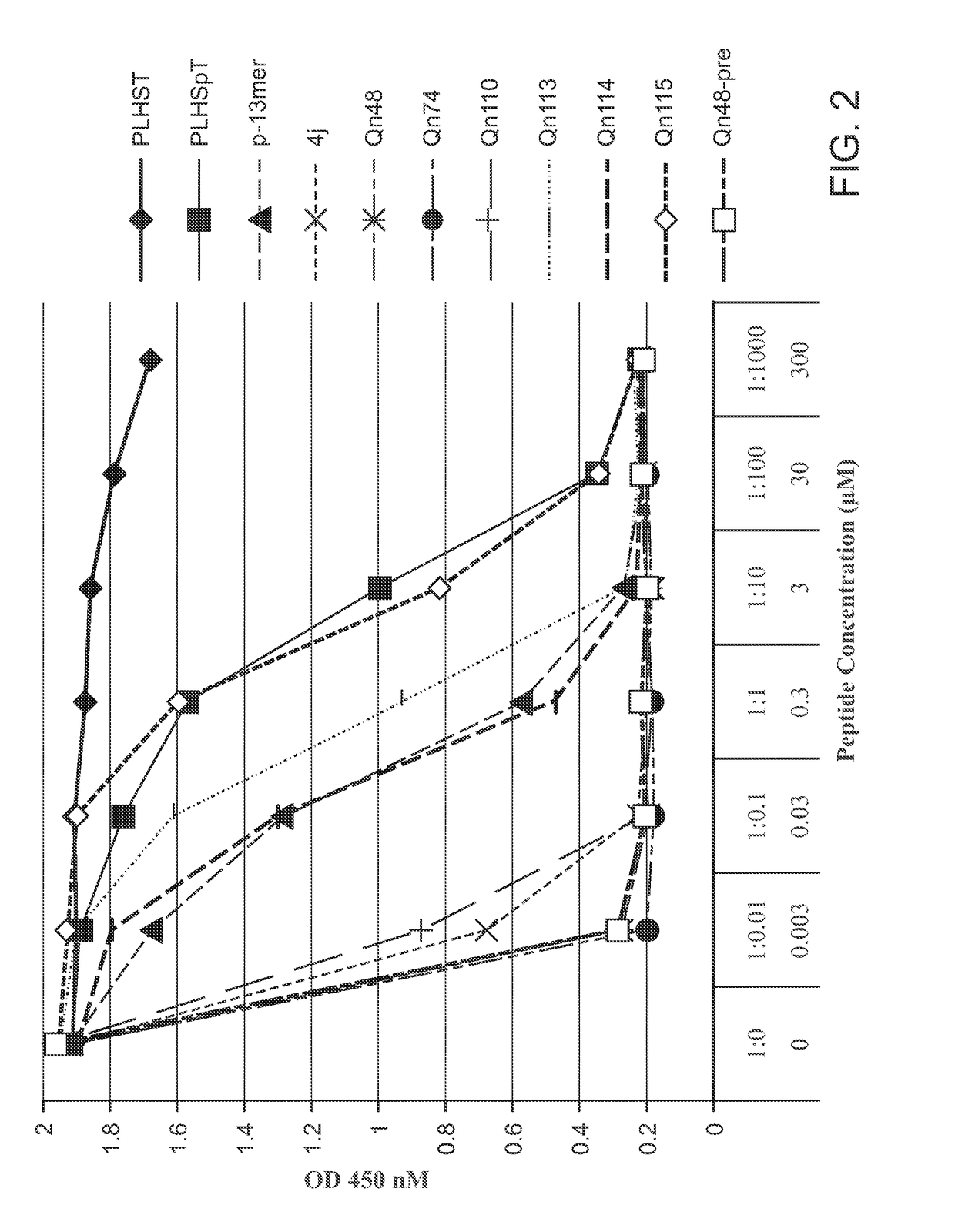
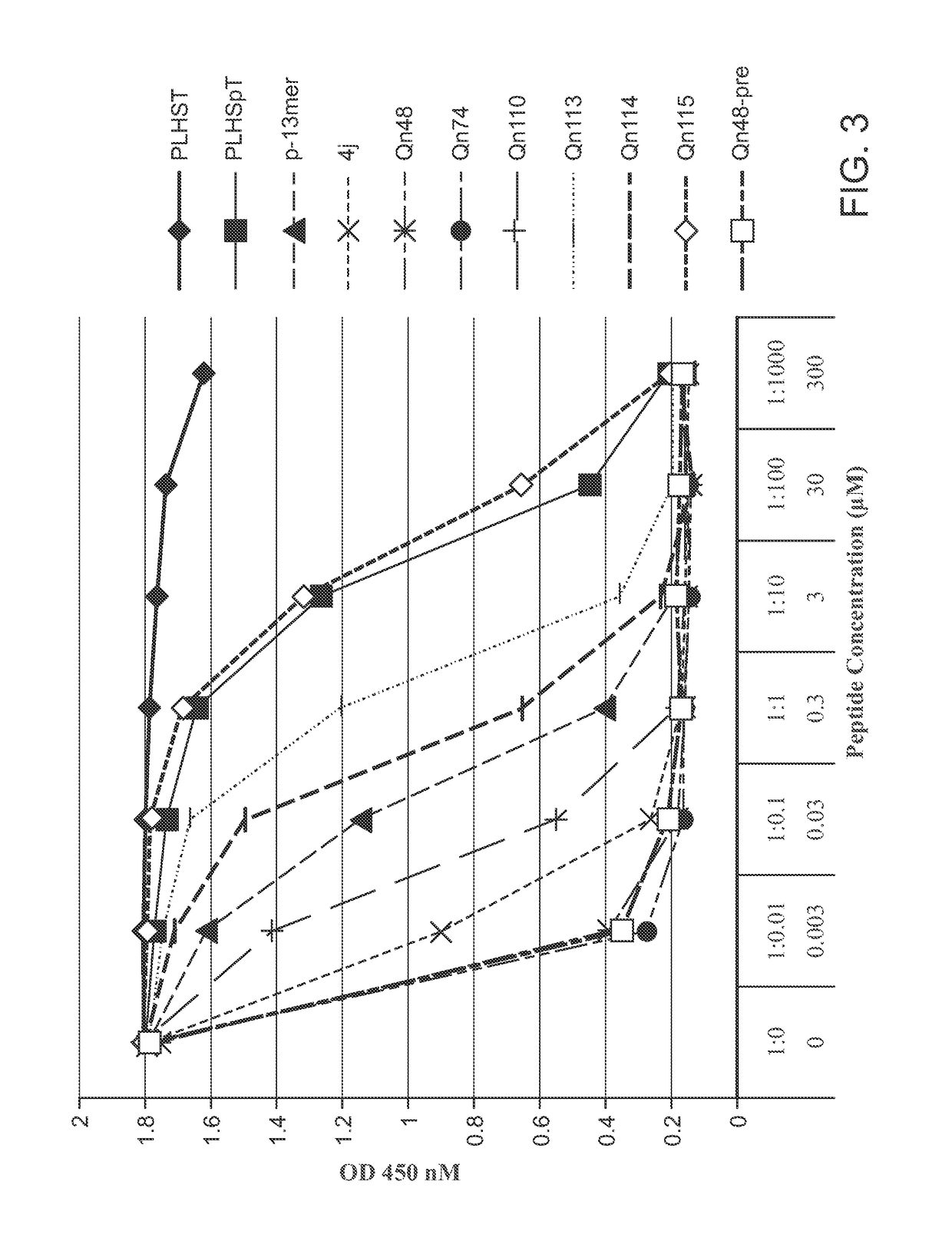
Patents
Literature
33 results about "Neutral Charge" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, the term "neutral charge" is used to refer to an atom or collection of atoms that contains neither a positive nor negative charge. To have a neutral charge, the atom must have an equal number of protons and electrons. Protons give an atom a positive charge, while electrons give it a negative charge.
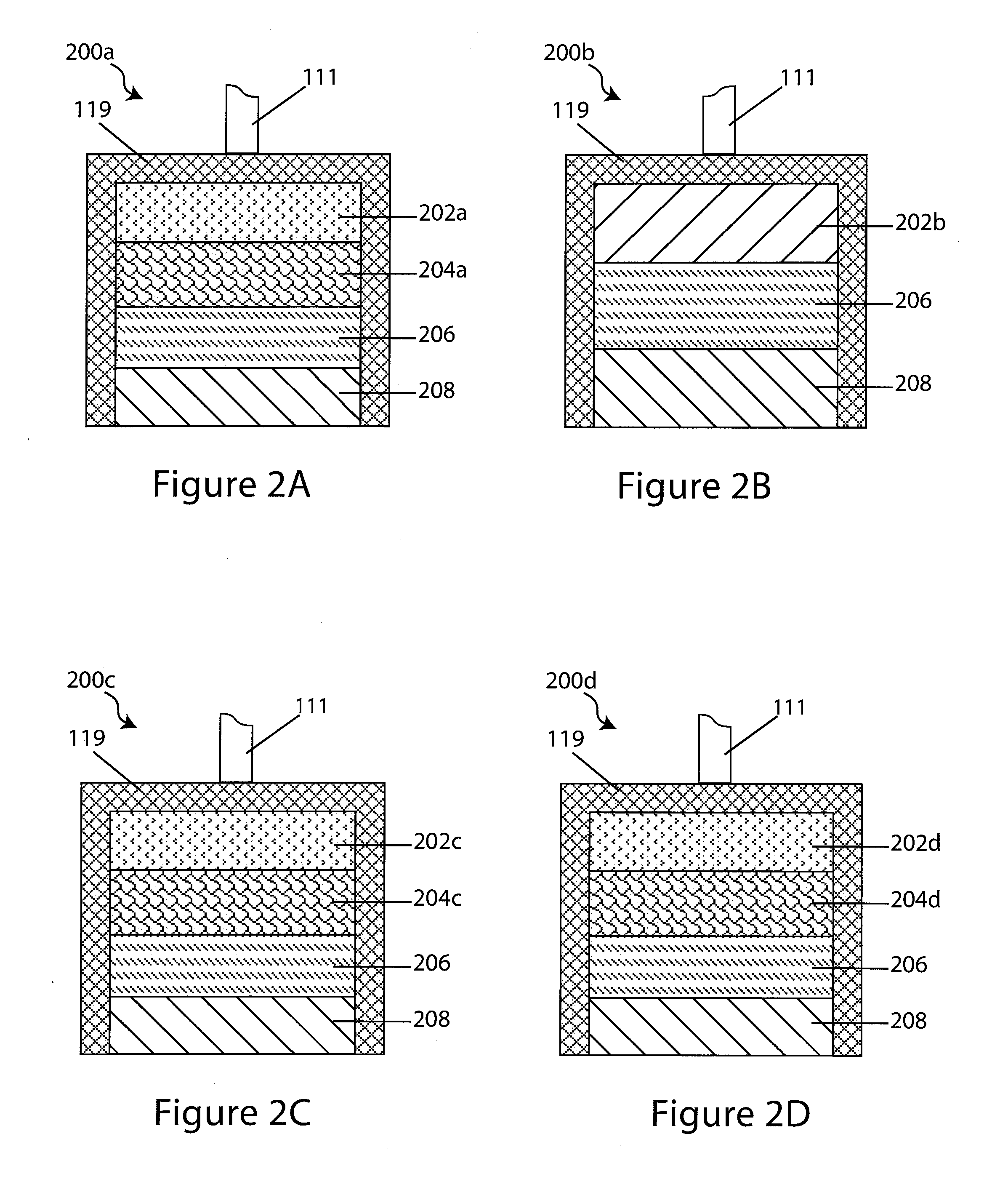
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
InactiveUS20070092759A1Reduce the driving voltageIncrease brightnessDischarge tube luminescnet screensLamp detailsLow voltageNeutral Charge
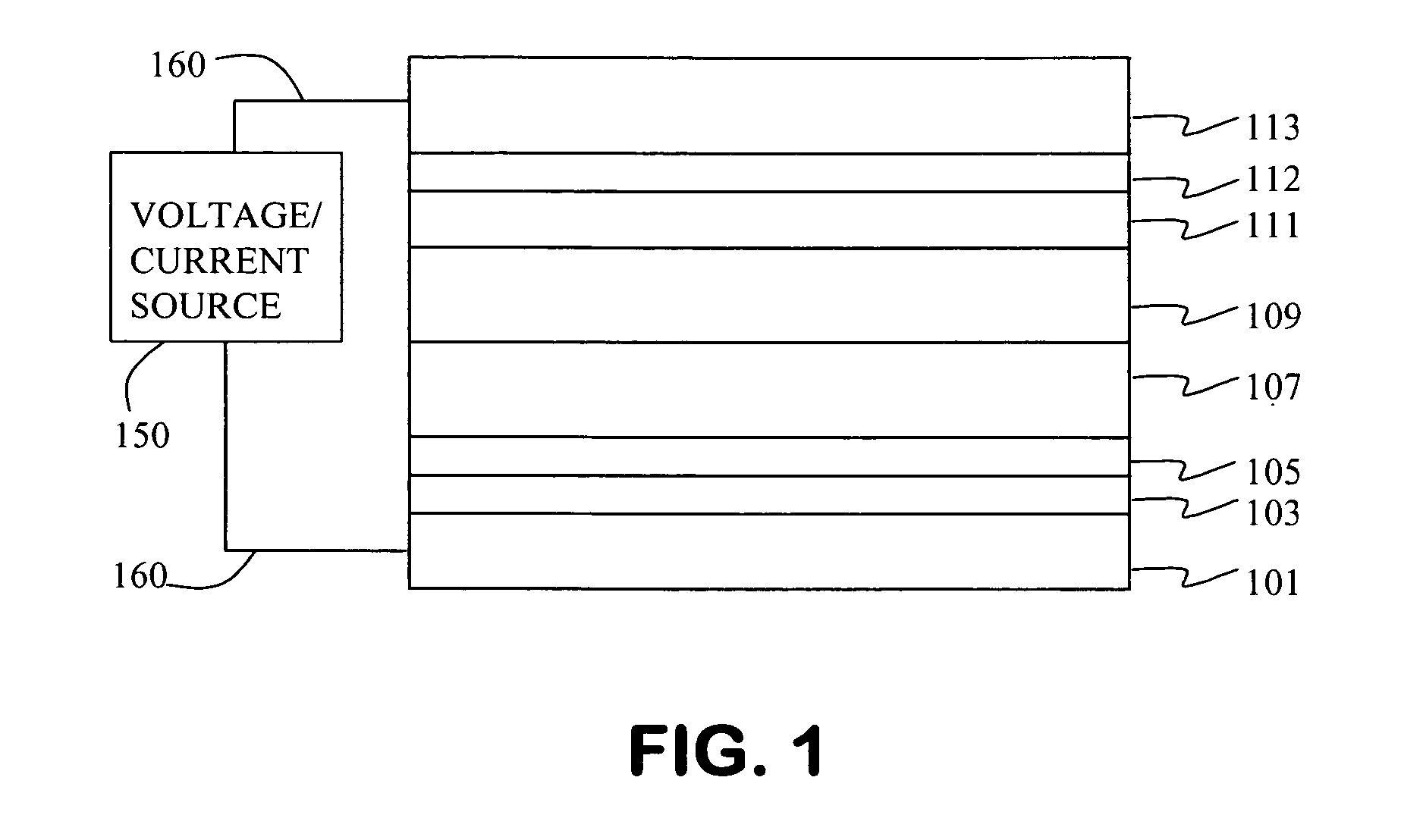
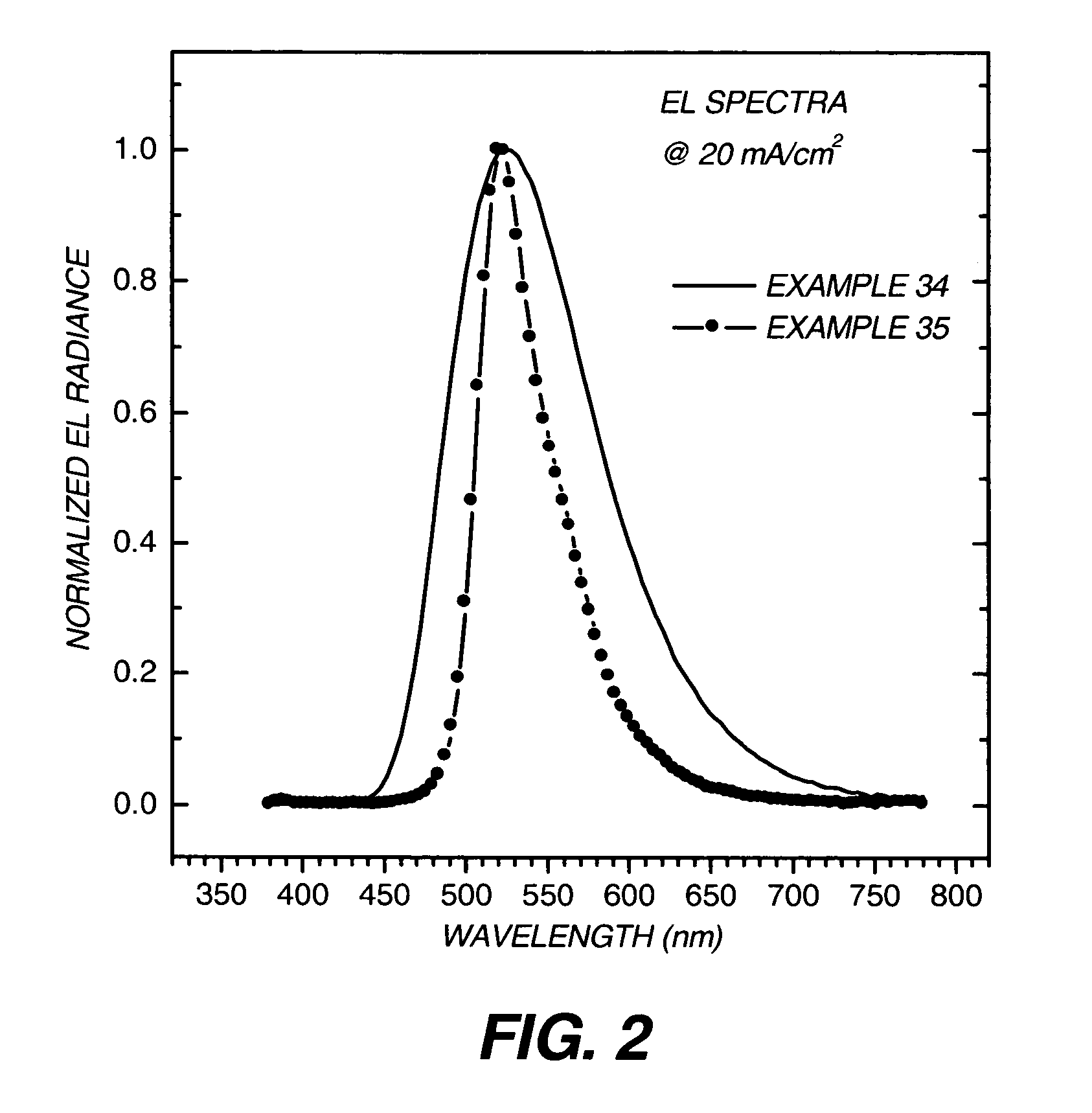
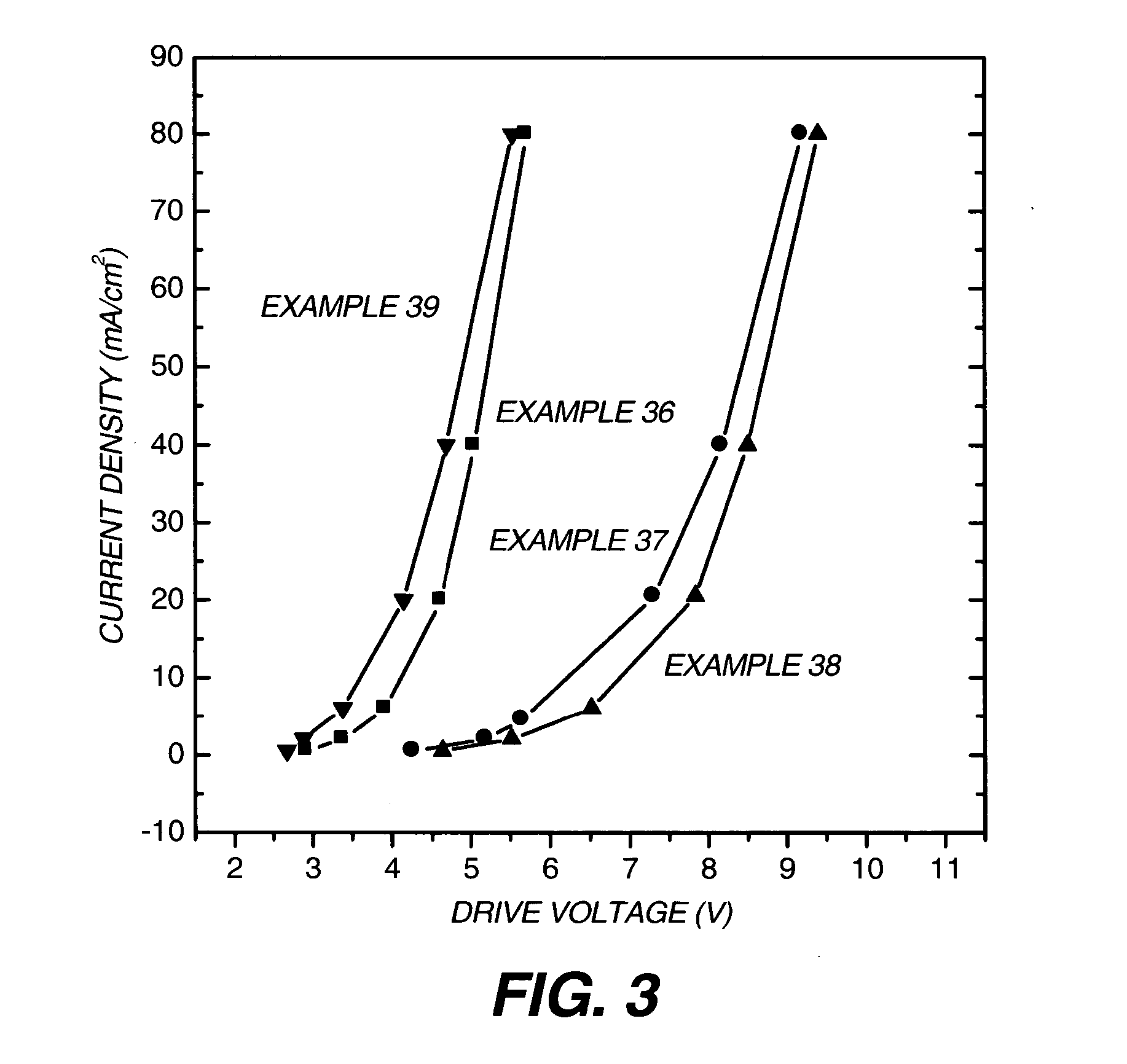
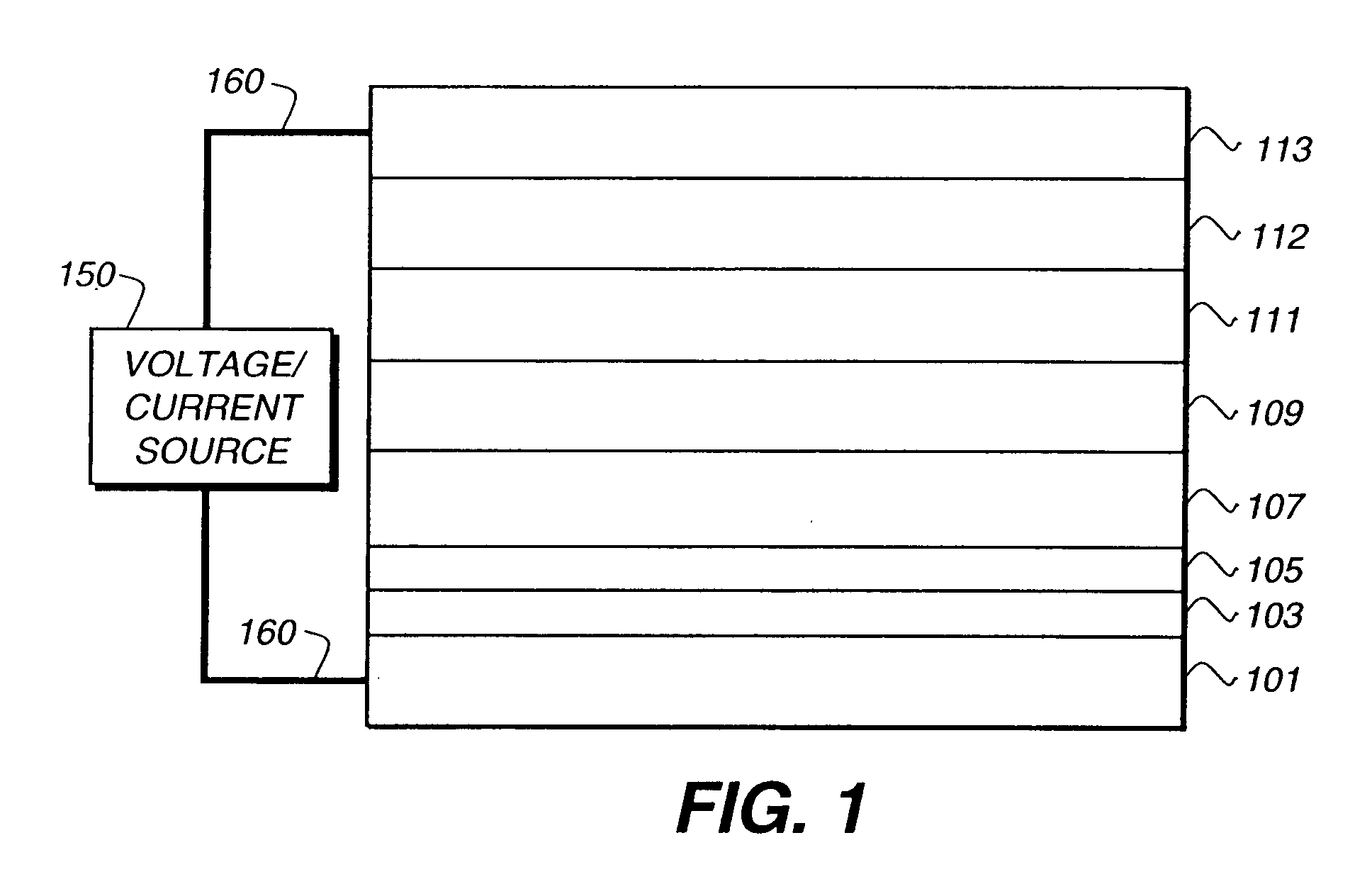
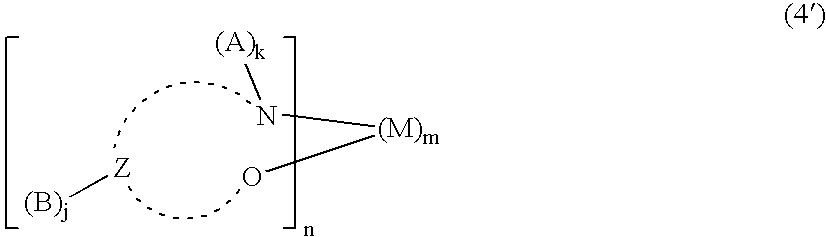
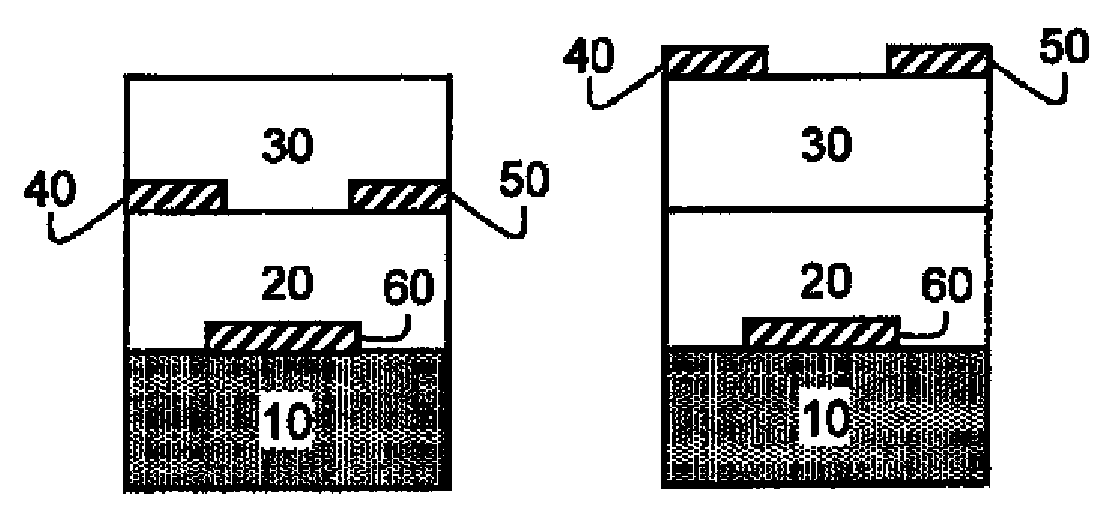
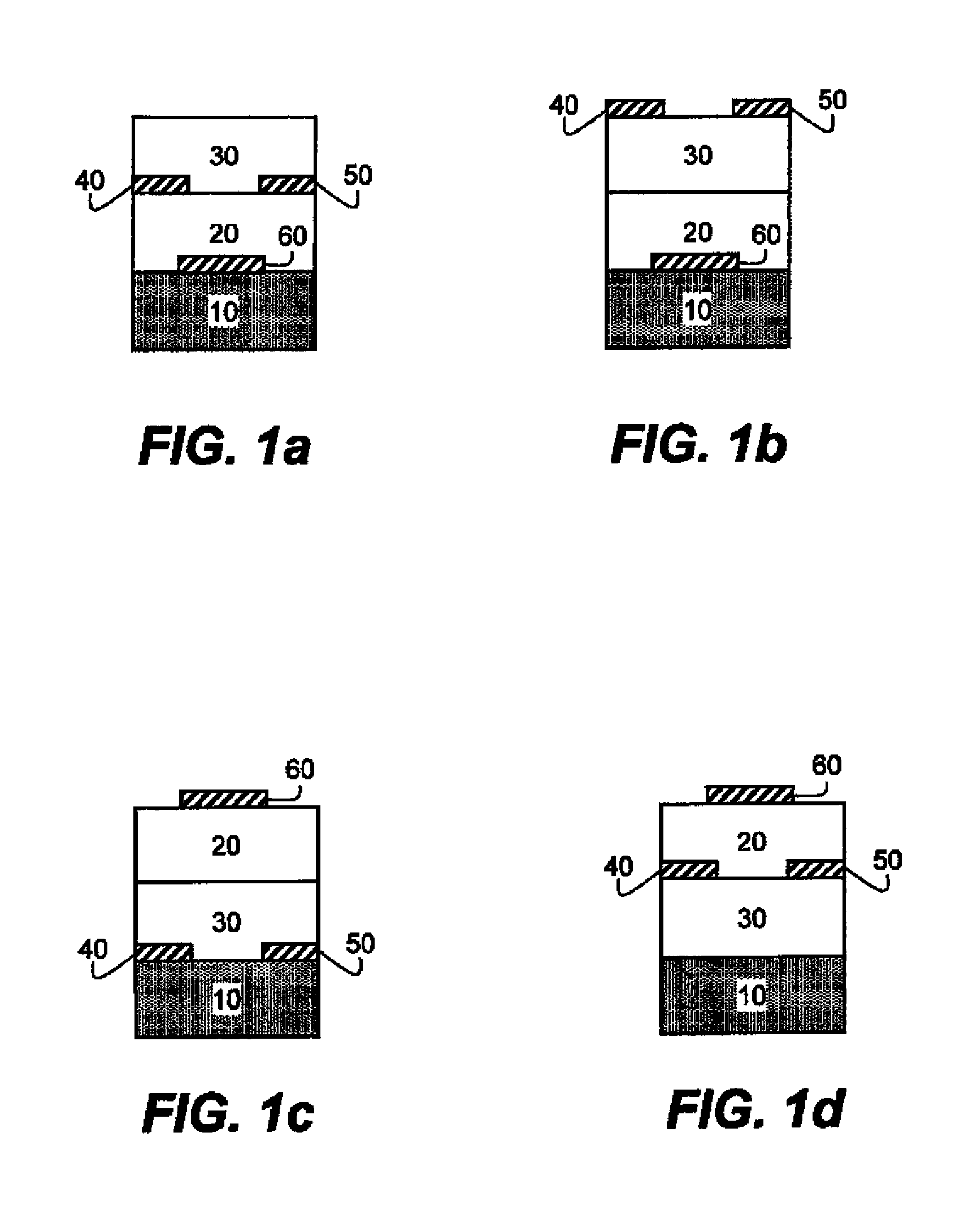
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, and, has located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, a further layer containing a cyclometallated complex represented by Formula (4′) wherein: Z and the dashed arc represent two or three atoms and the bonds necessary to complete a 5- or 6-membered ring with M; each A represents H or a substituent and each B represents an independently selected substituent on the Z atoms, provided that two or more substituents may combine to form a fused ring or a fused ring system; j is 0-3 and k is 1 or 2; M represents a Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB element of the Periodic Table; m and n are independently selected integers selected to provide a neutral charge on the complex; and provided that the complex does not contain the 8-hydroxyquinolate ligand. Such devices exhibit reduce drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, and, has located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, a further layer containing a cyclometallated complex represented by Formula (4′) wherein: Z and the dashed arc represent two or three atoms and the bonds necessary to complete a 5- or 6-membered ring with M; each A represents H or a substituent and each B represents an independently selected substituent on the Z atoms, provided that two or more substituents may combine to form a fused ring or a fused ring system; j is 0-3 and k is 1 or 2; M represents a Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB element of the Periodic Table; m and n are independently selected integers selected to provide a neutral charge on the complex; and provided that the complex does not contain the 8-hydroxyquinolate ligand. Such devices exhibit reduce drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
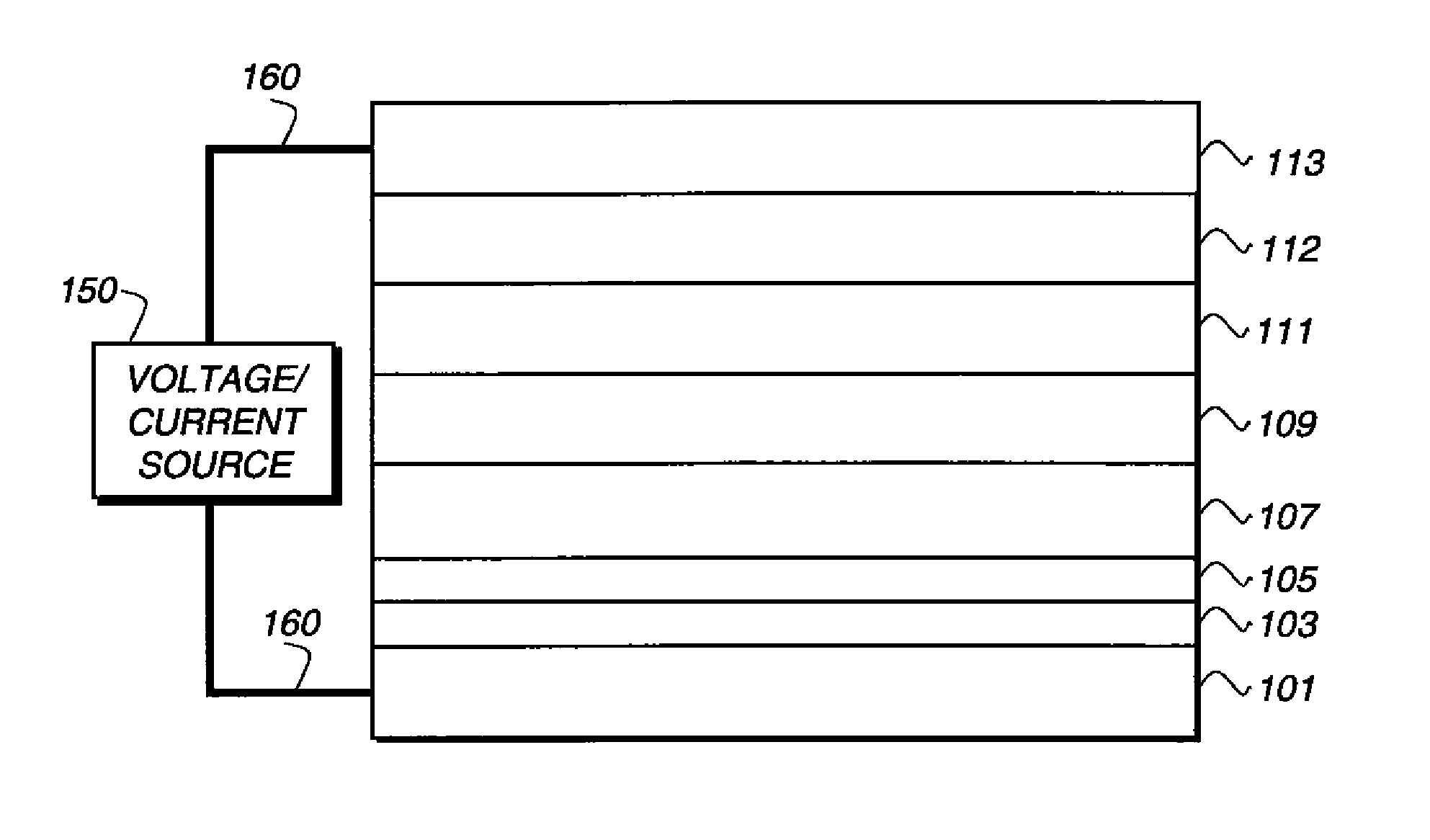
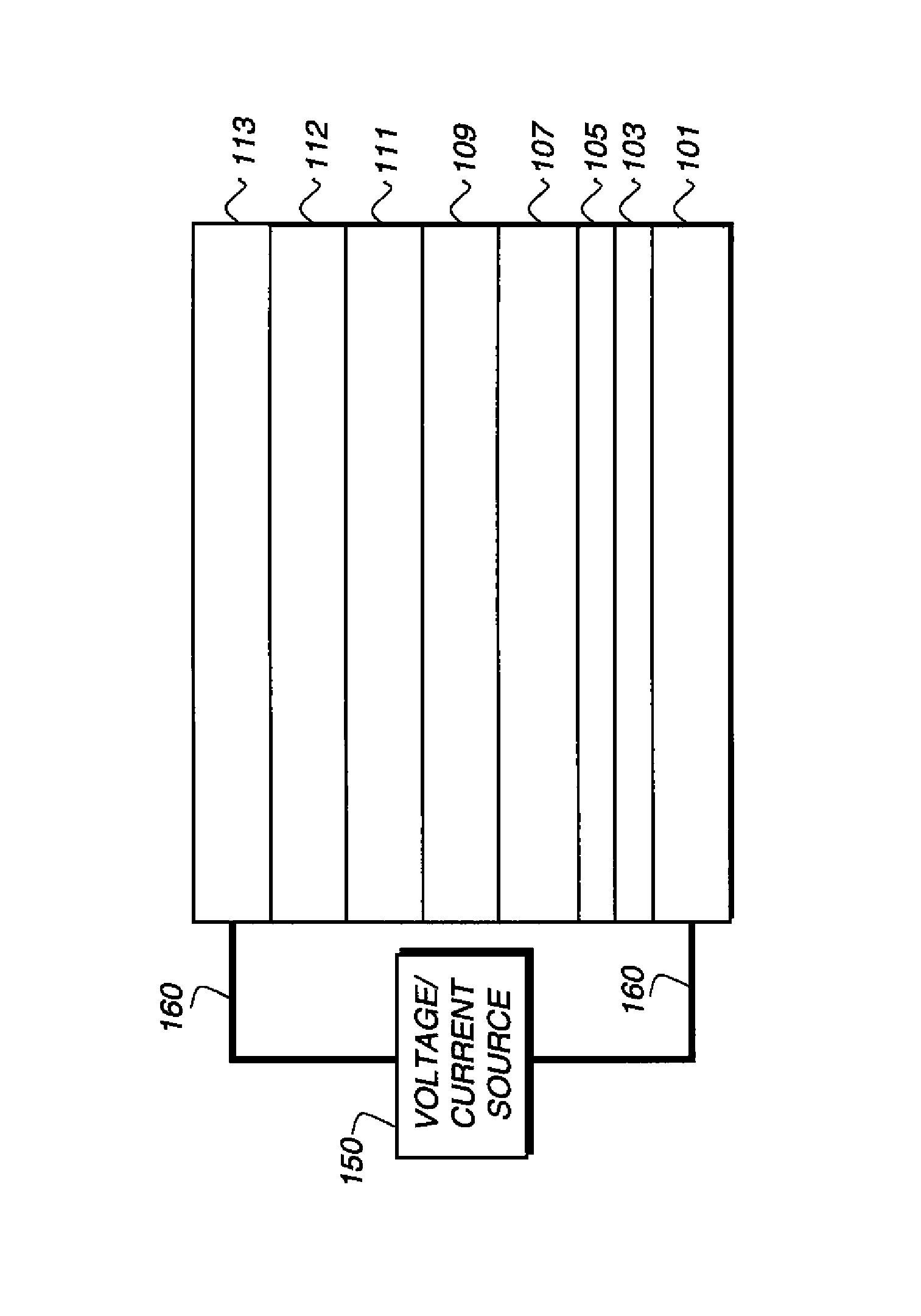
Electrotransport devices, methods and drug electrode assemblies
A drug electrode assembly usefully employed in an electrotransport device for the delivery of drugs across a tissue surface includes an electrode, a drug reservoir which stores the drug (including an ionized (e.g., anionic) or neutrally charged drug species), and a liquid impermeable solid-state assist ion conducting barrier layer interposed between the electrode and the drug reservoir. The barrier layer can be a single-ion conductor of a specific (unique) species of ion called the assist ion. During drug delivery, the assist ion moves across the barrier layer into or out of the drug reservoir, and as the assist ion crosses the barrier layer / drug reservoir interphase, the drug species moves to the tissue surface. The assist ion can be, for example, sodium ions (Na+), and the electrode can be an electrode of the assist ion (i.e., a sodium electrode).
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Organic element for low voltage electroluminescent devices
ActiveUS7767317B2Discharge tube luminescnet screensElectroluminescent light sourcesCrystallographyLow voltage
An OLED device comprises a cathode, a light emitting layer and an anode, in that order, and, having located between the cathode and the light emitting layer, a further layer containing;(a) 10 vol % or more of a carbocyclic fused ring aromatic compound, and (b) a cyclometallated complex represented by Formula (4′)wherein:Z and the dashed arc represent two or three atoms and the bonds necessary to complete a 5- or 6-membered ring with M;each A represents H or a substituent and each B represents an independently selected substituent on the Z atoms, provided that two or more substituents may combine to form a fused ring or a fused ring system;j is 0-3 and k is 1 or 2;M represents a Group IA, IIA, IIIA and IIB element of the Periodic Table; andm and n are independently selected integers selected to provide a neutral charge on the complex; andprovided that the complex does not contain the 8-hydroxyquinolate ligand. Such devices exhibit reduce drive voltage while maintaining good luminance.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Electrotransport devices, methods and drug electrode assemblies
InactiveUS20120289887A1Improve stabilityImprove performanceElectrotherapyMedical devicesElectrical conductorNeutral Charge
A drug electrode assembly usefully employed in an electrotransport device for the delivery of drugs across a tissue surface includes an electrode, a drug reservoir which stores the drug (including an ionized (e.g., anionic) or neutrally charged drug species), and a liquid impermeable solid-state assist ion conducting barrier layer interposed between the electrode and the drug reservoir. The barrier layer can be a single-ion conductor of a specific (unique) species of ion called the assist ion. During drug delivery, the assist ion moves across the barrier layer into or out of the drug reservoir, and as the assist ion crosses the barrier layer / drug reservoir interphase, the drug species moves to the tissue surface. The assist ion can be, for example, sodium ions (Na+), and the electrode can be an electrode of the assist ion (i.e., a sodium electrode).
Owner:POLYPLUS BATTERY CO INC
Mixed abrasive tungsten cmp composition
ActiveUS20150267082A1Other chemical processesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWater basedColloidal silica
A chemical mechanical polishing composition includes a water based liquid carrier and first and second silica abrasives dispersed in the liquid carrier. The first silica abrasive is a colloidal silica abrasive having a permanent positive charge of at least 10 mV. The second silica abrasive has a neutral charge or a non-permanent positive charge. A method for chemical mechanical polishing a substrate including a tungsten layer includes contacting the substrate with the above described polishing composition, moving the polishing composition relative to the substrate, and abrading the substrate to remove a portion of the tungsten from the substrate and thereby polish the substrate.
Owner:CMC MATERIALS INC
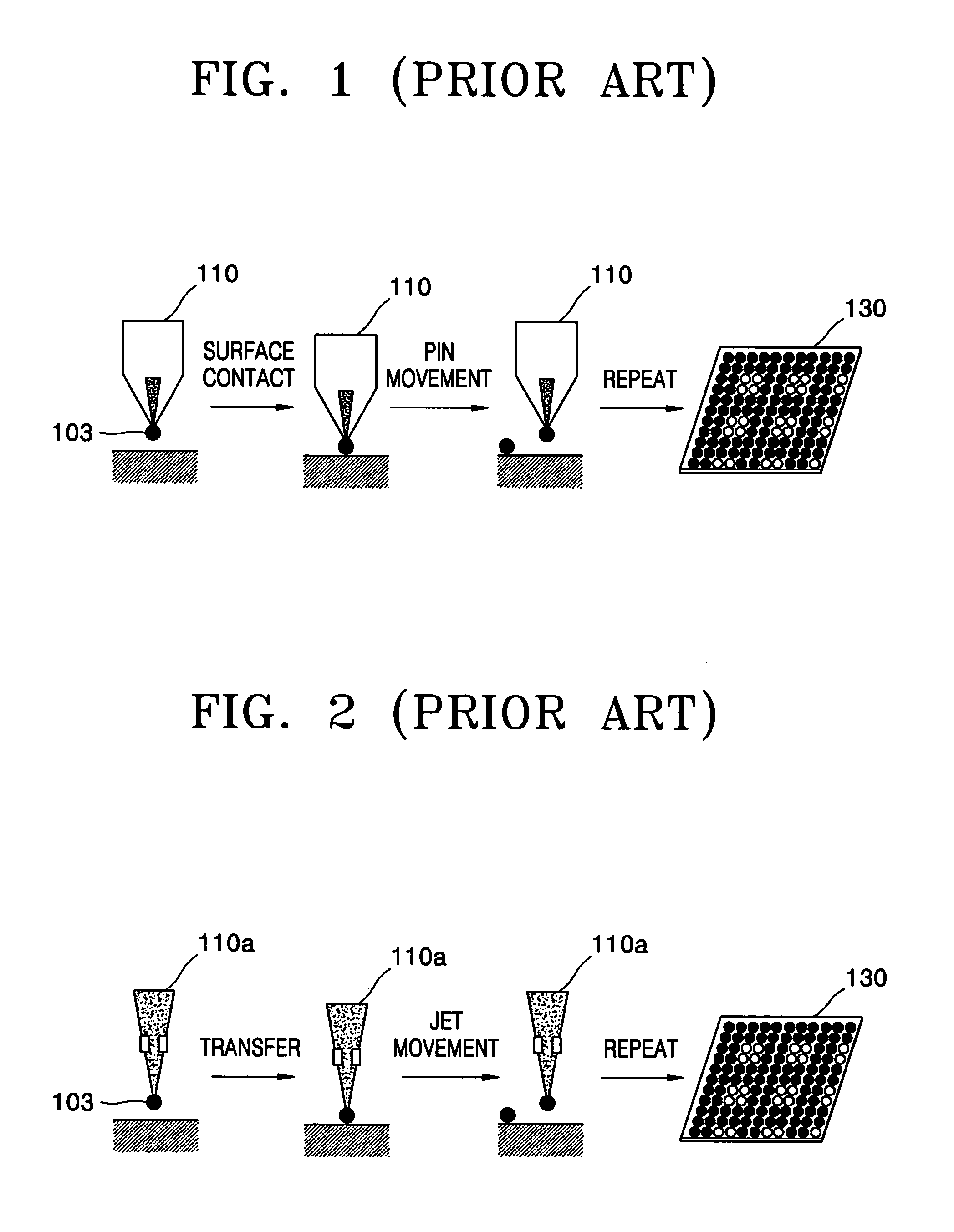
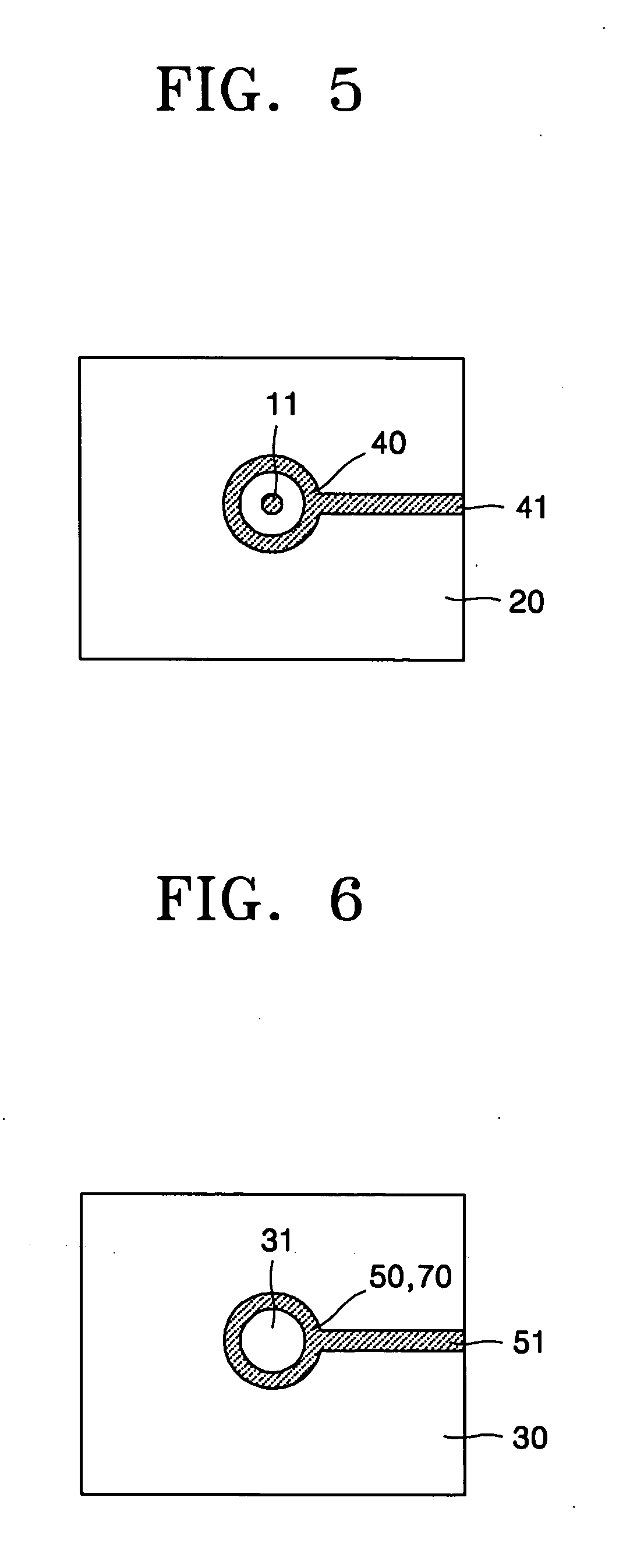
Device and method for printing biomolecules onto substrate using electrohydrodynamic effect
InactiveUS20050214799A1Easy alignmentEasy to handleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsPeptide librariesDielectricAntigen
A device and a method for printing biomolecules onto a substrate using an electrohydrodynamic (EHD) effect are provided. The device for printing biomolecules onto a substrate using an electrohydrodynamic (EHD) effect includes at least one capillary having an outlet through which a feeding solution of biomolecules selected from the group consisting of nucleic acids, proteins, and oligopeptides is discharged, the nucleic acids being selected from the group consisting of probe DNA, RNA, peptide nucleic acid (PNA), and LNA and the proteins being selected from the group consisting of antigen and antibody; a printer body supporting the at least one capillary; a substrate below the outlet having a target surface onto which the biomolecules are deposited; a first electric field forming electrode located on the printer body around the circumference of the outlet; a second electric field forming electrode spaced apart from the first electrode by a predetermined distance; and a voltage applying unit which is electrically connected to the first electrode and the second electrode to apply an alternating current (AC) voltage between the first electrode and the second electrode so that an electric field may be formed around the biomolecule solution suspended in the outlet, and due to the interaction of the electric field and a difference in dielectric constant between the biomolecule solution having a free surface and the surrounding atmosphere, the electric force acts inward on the biomolecule solution from the surroundings, thereby dropping a predetermined amount of the biomolecule solution onto the target surface of the substrate. By using an EHD effect, the advantages of the device and method are that the process is quick, the biomolecule spots are uniform and easily aligned, and especially it is possible to spot the biomolecules correctly and reproducibly even when the printer body is not fully aligned with the substrate. In addition, the device and method are applicable to proteins which are sensitive to heat and biomolecules which have neutral charges.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method of improving directional imaging ability of carbon dots to cell nucleolus
InactiveCN108152261AImprove imaging effectExcellent directional imaging effectFluorescence/phosphorescenceLuminescent compositionsEthylene diamineNeutral Charge
The invention discloses a method of improving directional imaging ability of carbon dots to cell nucleolus. The method includes: using citric acid and ethylene diamine as carbon sources to prepare carbon dots; adjusting the surfaces of the carbon dots from negative charge to close to neutral so as to improve directional imaging ability of the carbon dots to the cell nucleolus. Common organic saltis used as a carbon source and simply treated to prepare the carbon dots. Effect of the carbon dots on nucleolus imaging is improved by changing charge on the surfaces of the obtained carbon dots, andthe carbon dots with the surfaces in neutral charge have better directional imaging effect on the nucleolus.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Separation process and dyes for use therewith
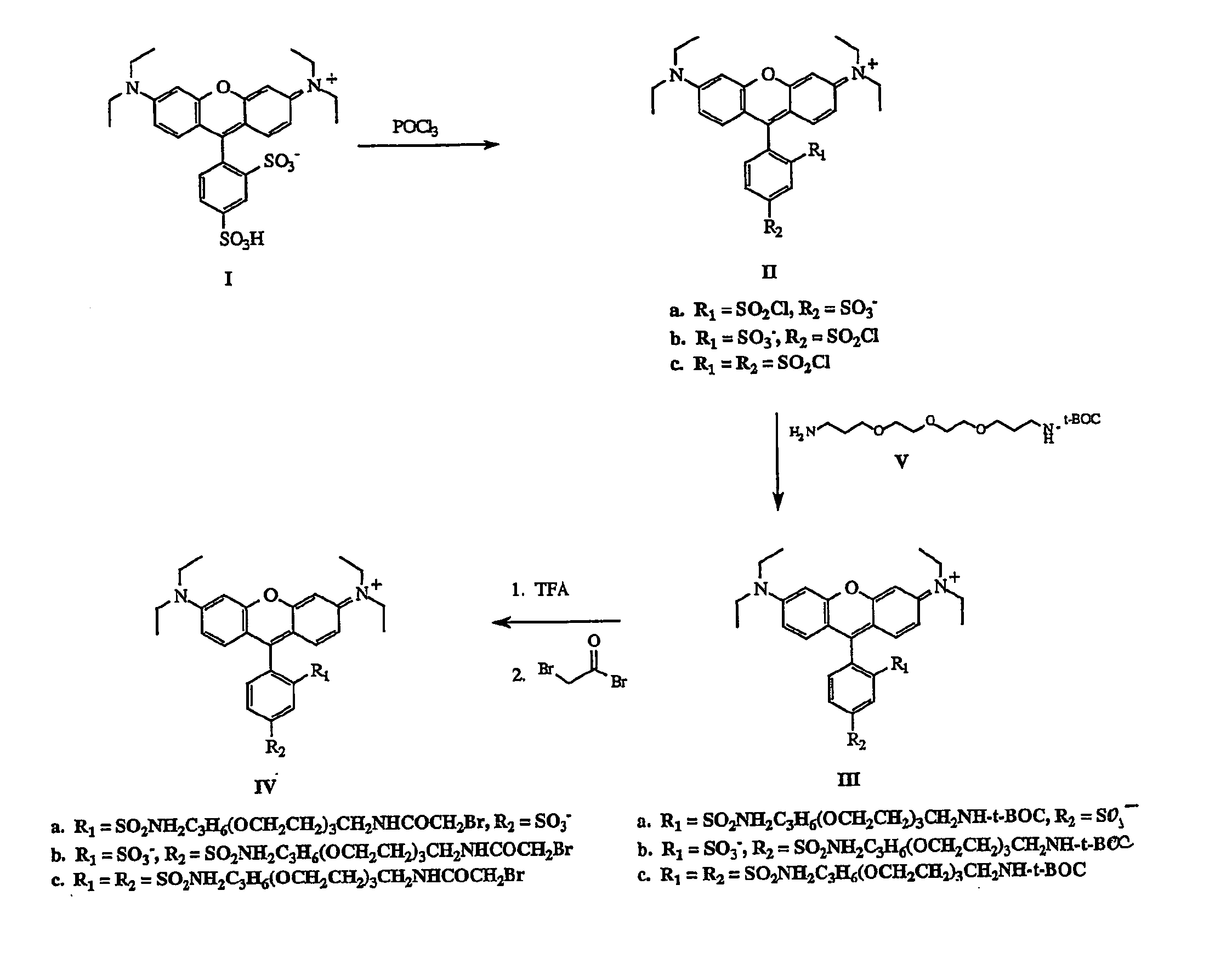
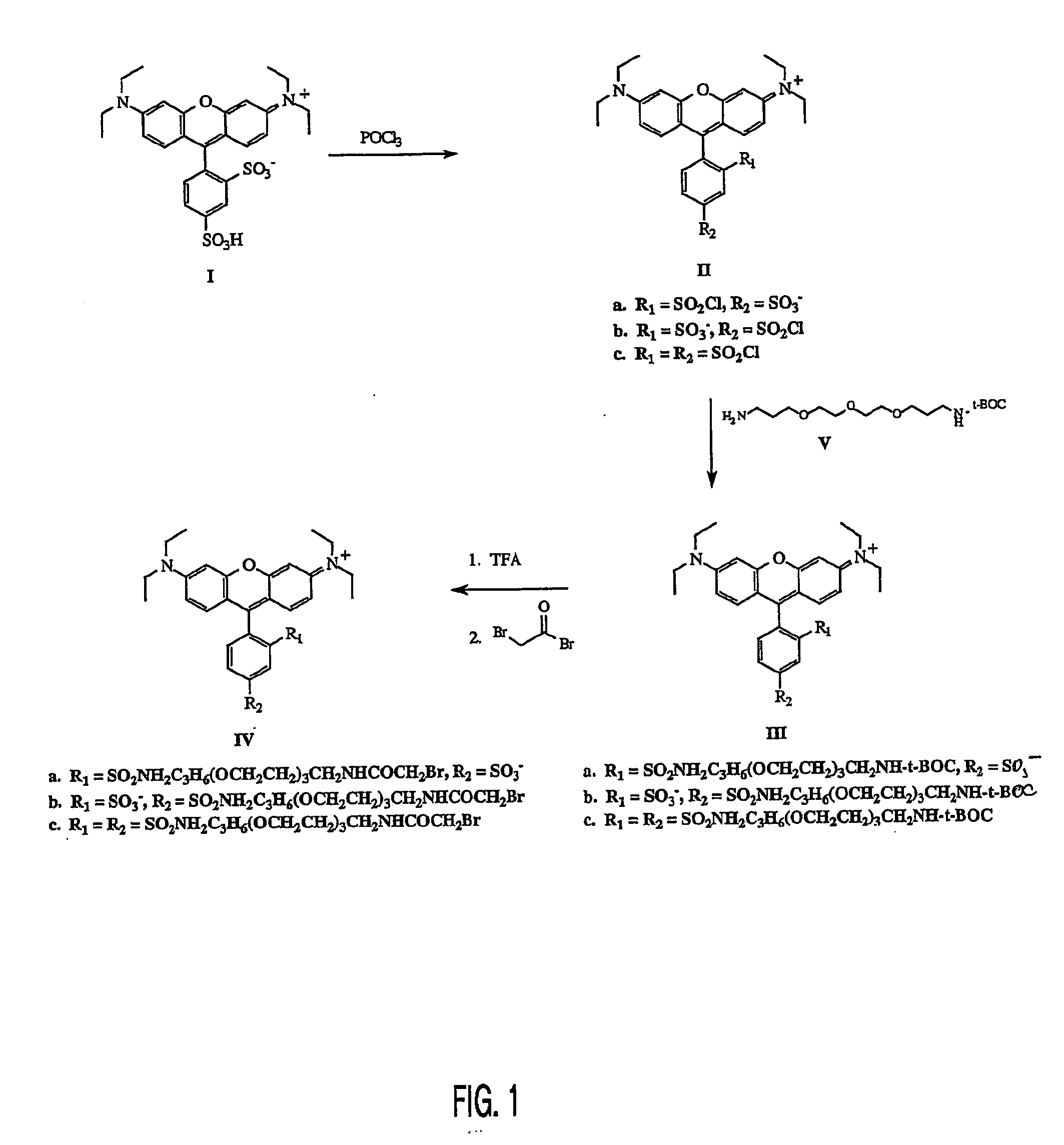
InactiveUS20050224354A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementNeutral ChargePhotochemistry
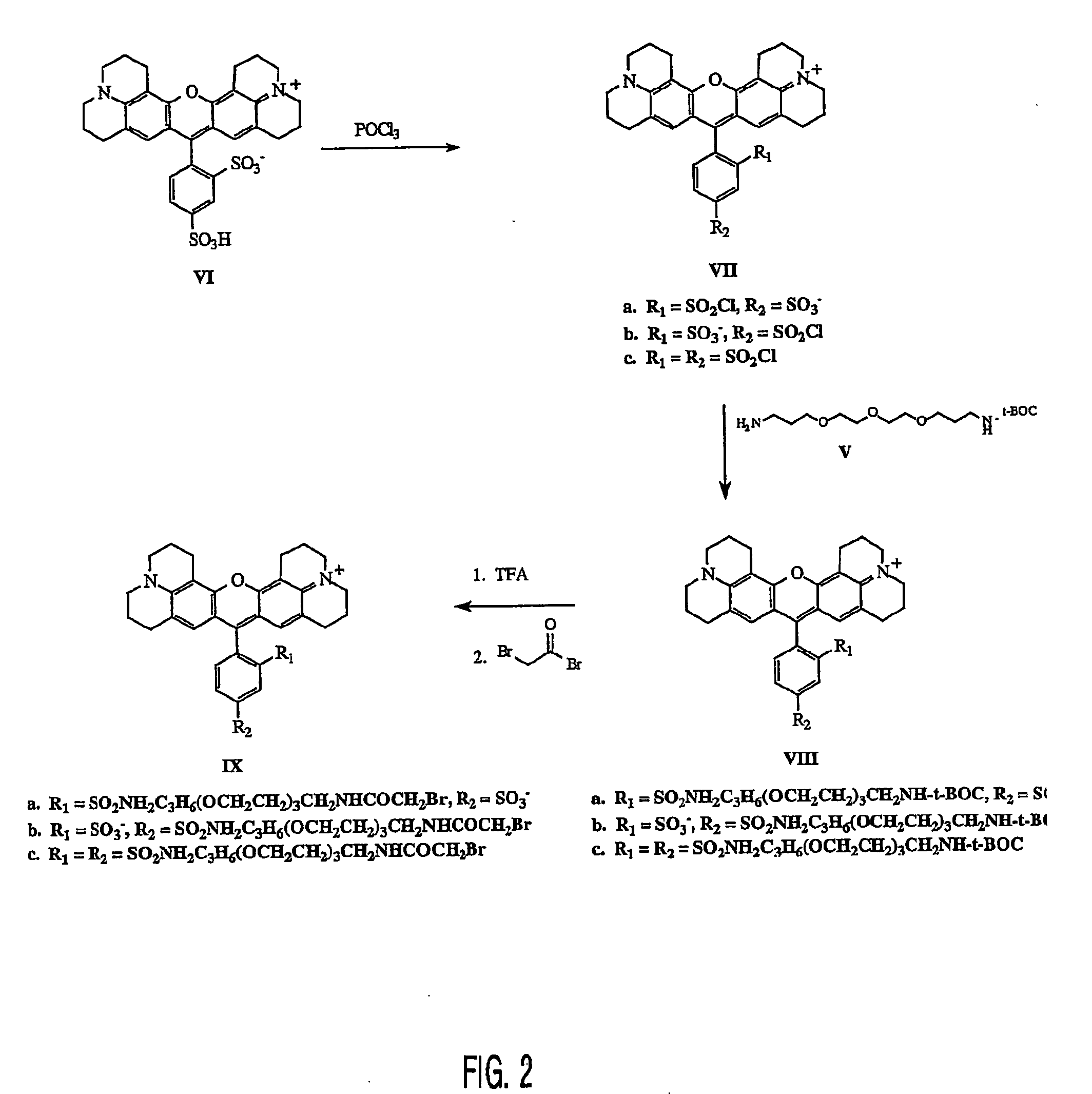
The present invention describes rhodamine compounds particularly well-suited for pre-labeling a protein that is then subjected to two-dimensional electrophoresis. Isomeric purification and synthesis of a dye having net neutral charge or no charge precludes interference with isoelectric electrophoretic separation.
Owner:PERKINELMER HEALTH SCIENCES INC
Application Device for Inducing Cytotoxicity to Tumor Cells Via Coated Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles
InactiveUS20160074434A1Without compromising solubilityReduce in quantityHeavy metal active ingredientsBiocideCancer cellLysosome
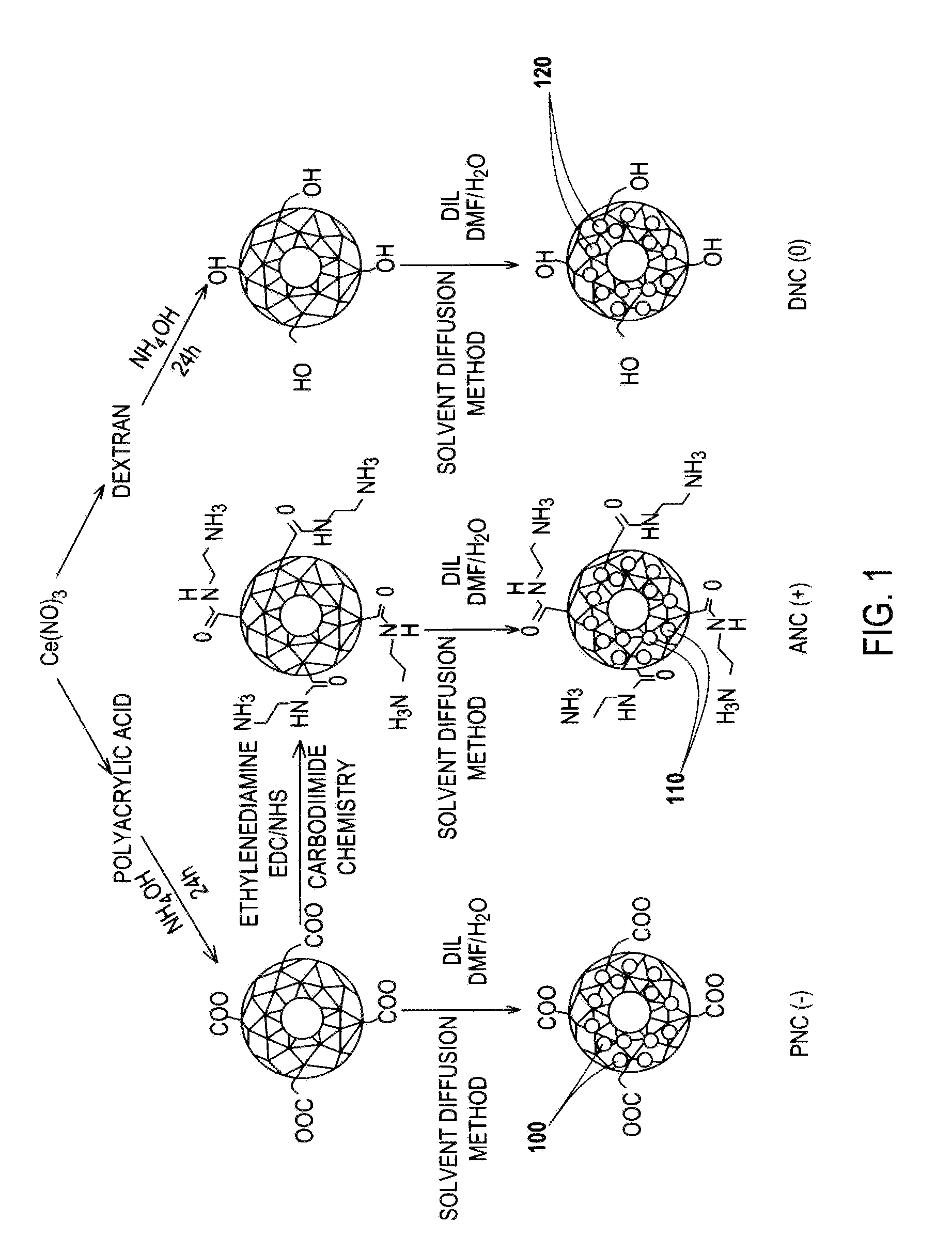
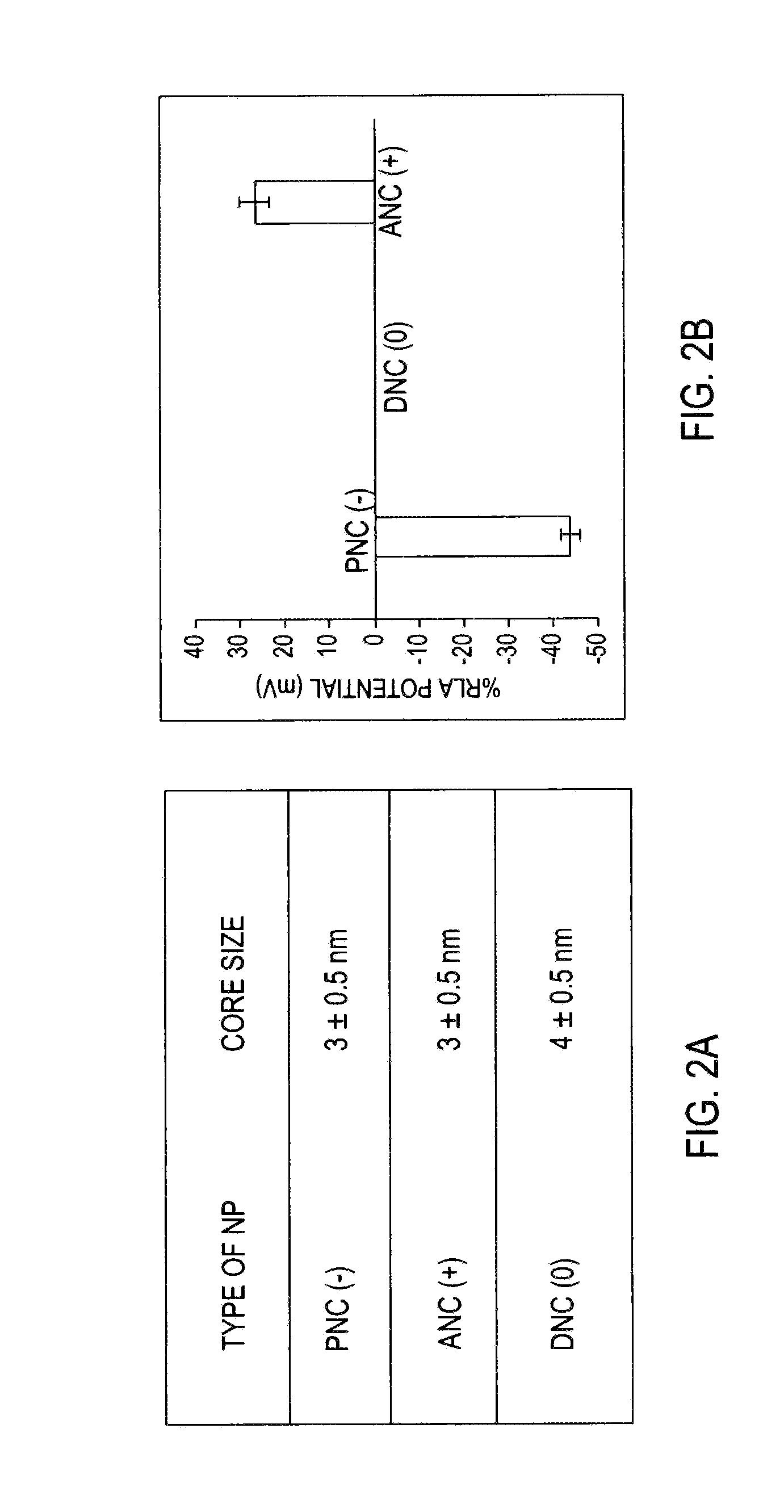
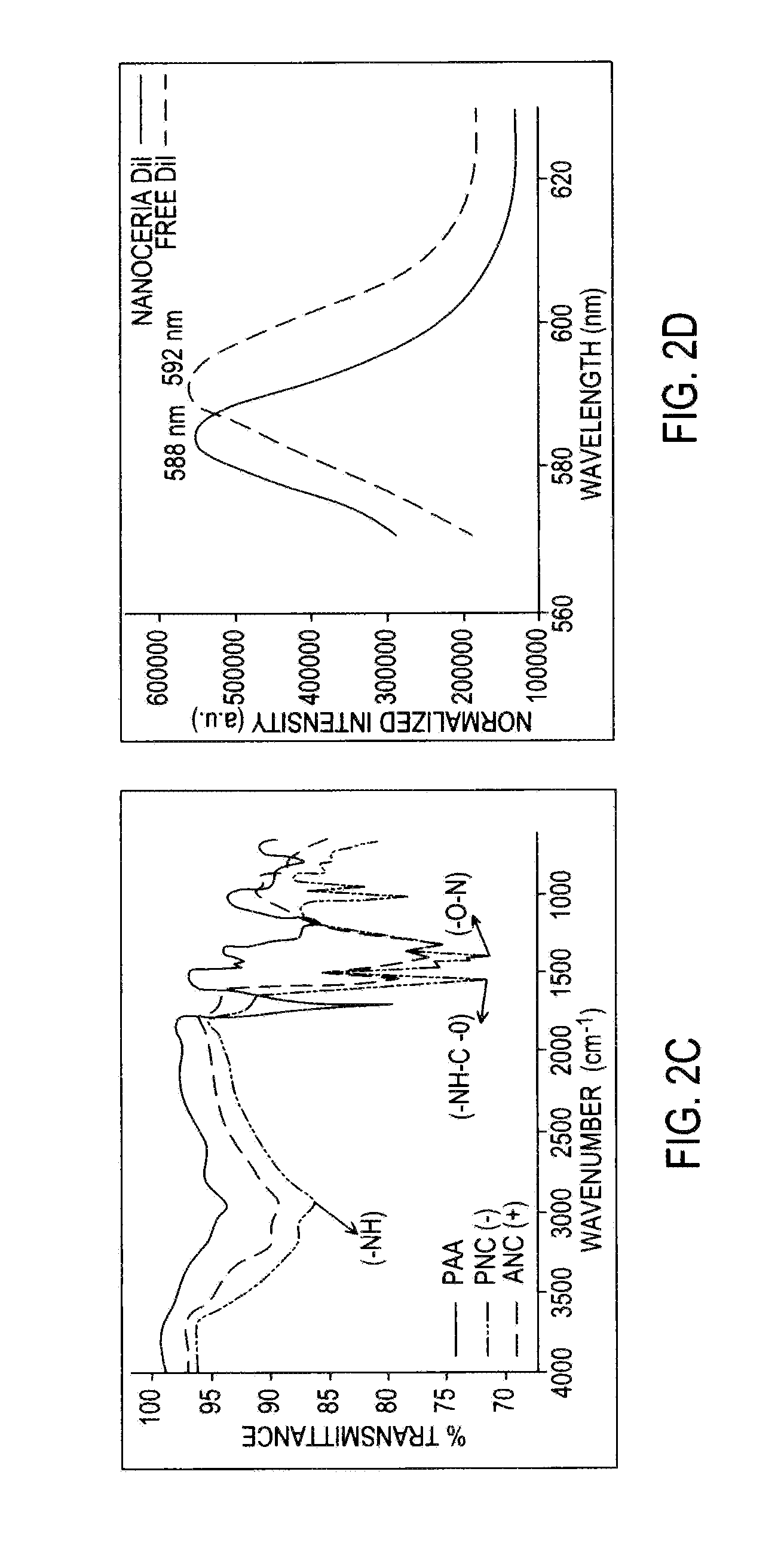
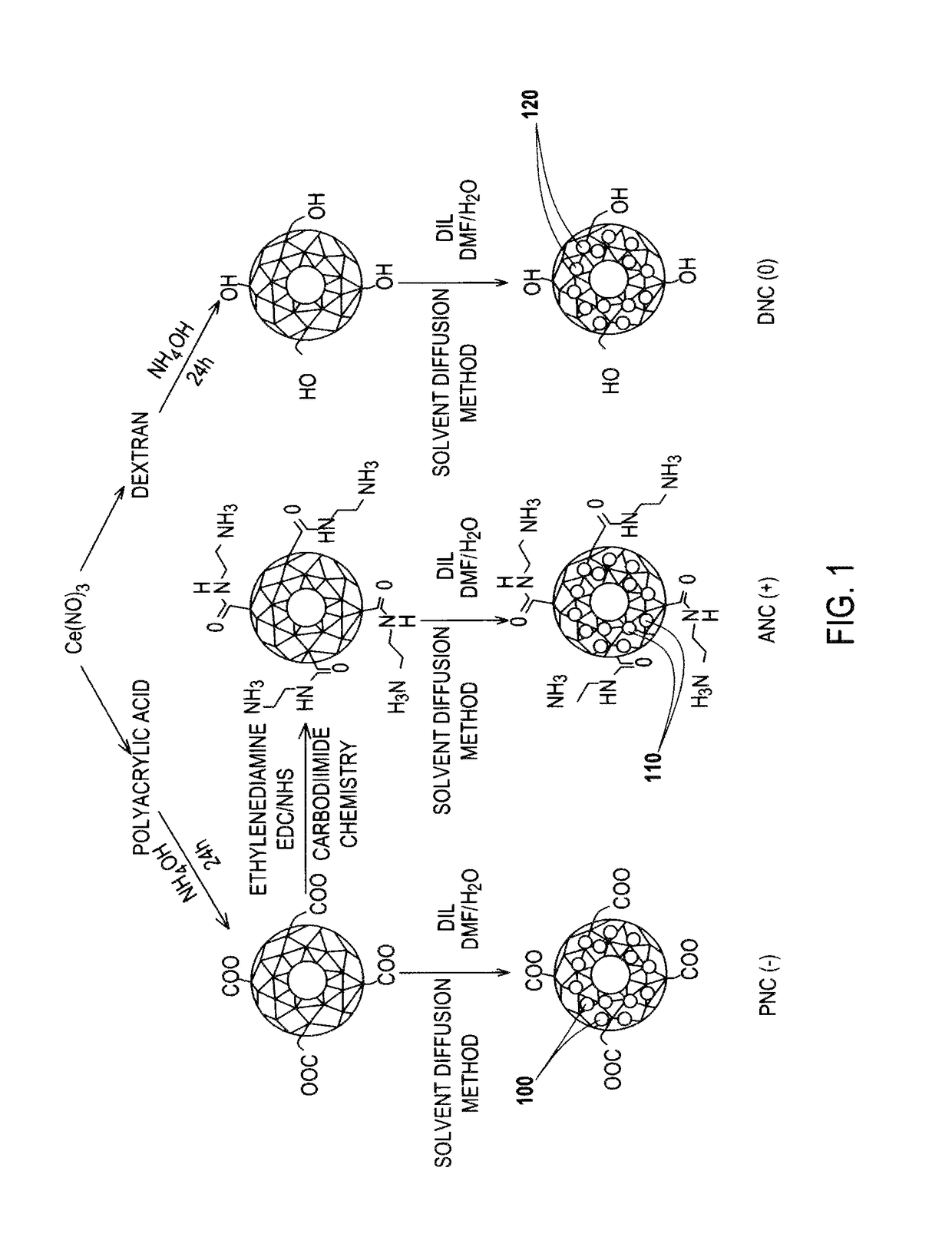
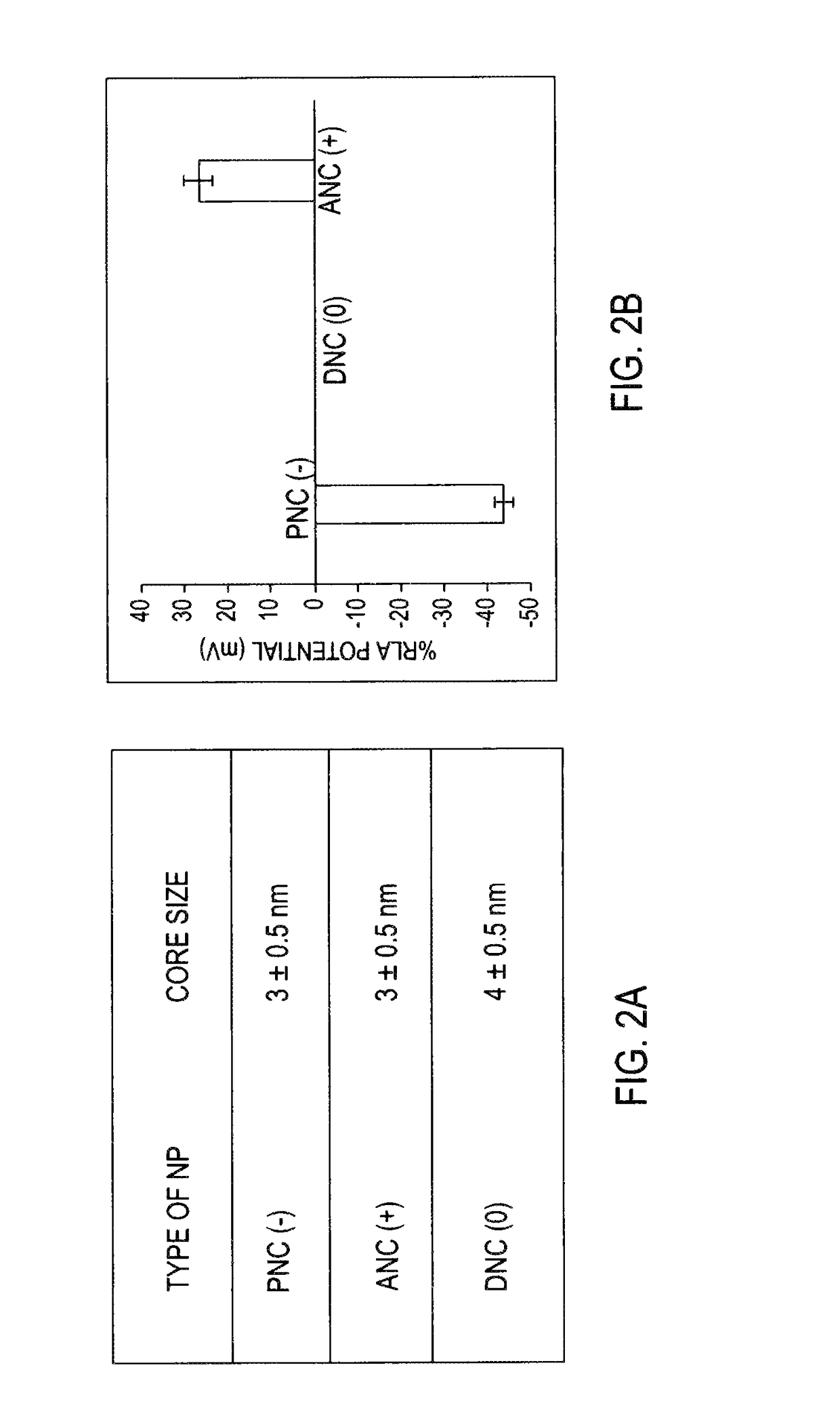
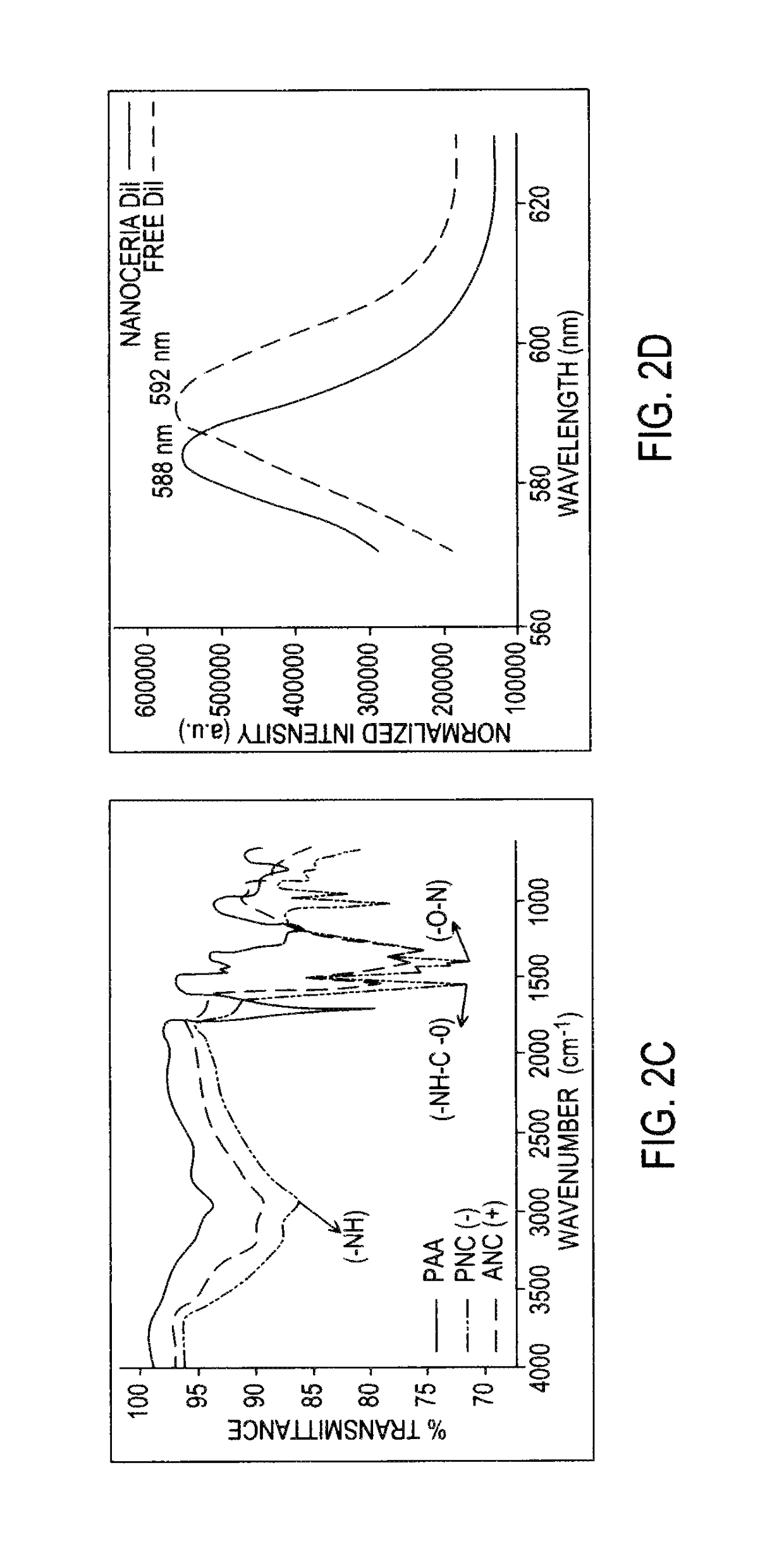
Differential surface-charge-dependent localization of nanoceria in normal cells and cancer cells plays a critical role in the toxicity profile of a nanoceria particle. Engineered surface-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles with different surface charges that are positive, negative and neutral provide therapeutic results for normal and cancer cell lines. Results show that nanoceria with a positive or neutral charge enters most of the cell lines studied, while nanoceria with a negative charge internalizes mostly in the cancer cell lines. Moreover, upon entry into the cells, nanoceria is localized to different cell compartments (e.g. cytoplasm and lysosomes) depending on the nanoparticle surface charge. The internalization and subcellular localization of nanoceria plays a key role in the nanoparticle cytotoxicity profile, exhibiting significant toxicity when they localize in the lysosomes of the cancer cell lines. In contrast, minimal toxicity is observed when they localize into the cytoplasm or do not enter the cells.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Photocurable and thermally curable thiosulfate-containing polymers
ActiveUS9453095B2Improve propertiesEasy to manufactureSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSulfateNeutral Charge
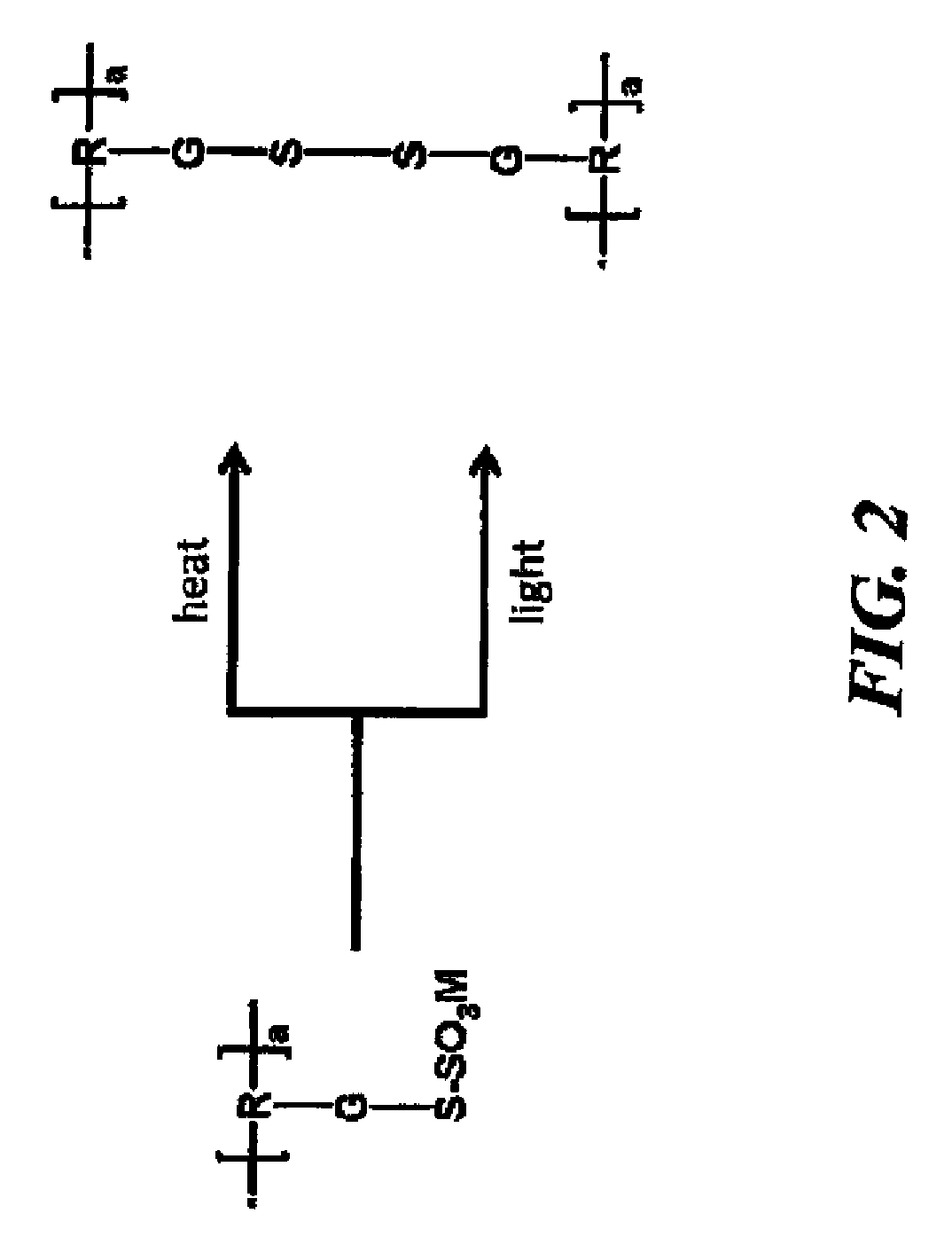
Photocurable or thermally curable thiosulfate-containing polymers have a Tg of at least 50° C. and (a) recurring units comprising pendant thiosulfate groups, and (b) recurring units comprising organic charge balancing cations that are associated with the (a) recurring units sufficiently to provide a net neutral charge with the pendant thiosulfate groups. These polymers can be represented by the following Structure (III):wherein R represents the organic polymer backbone, G is a single bond or a divalent linking group, M+ represents the organic charge balancing cation, and “a” represents at least 0.5 mol % and up to and including 50 mol % of (a) recurring units, and “b” represents the (b) recurring units and is at least equal to the “a” mol %, based on the total recurring units. These thiosulfate-containing polymers can be used to made dielectric compositions and gate dielectric layers in various devices.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
Intelligent leakage circuit breaker
InactiveCN100555785CWith leakage protection functionWith over-current protection functionArrangements responsive to excess currentMicrocontrollerLow voltage
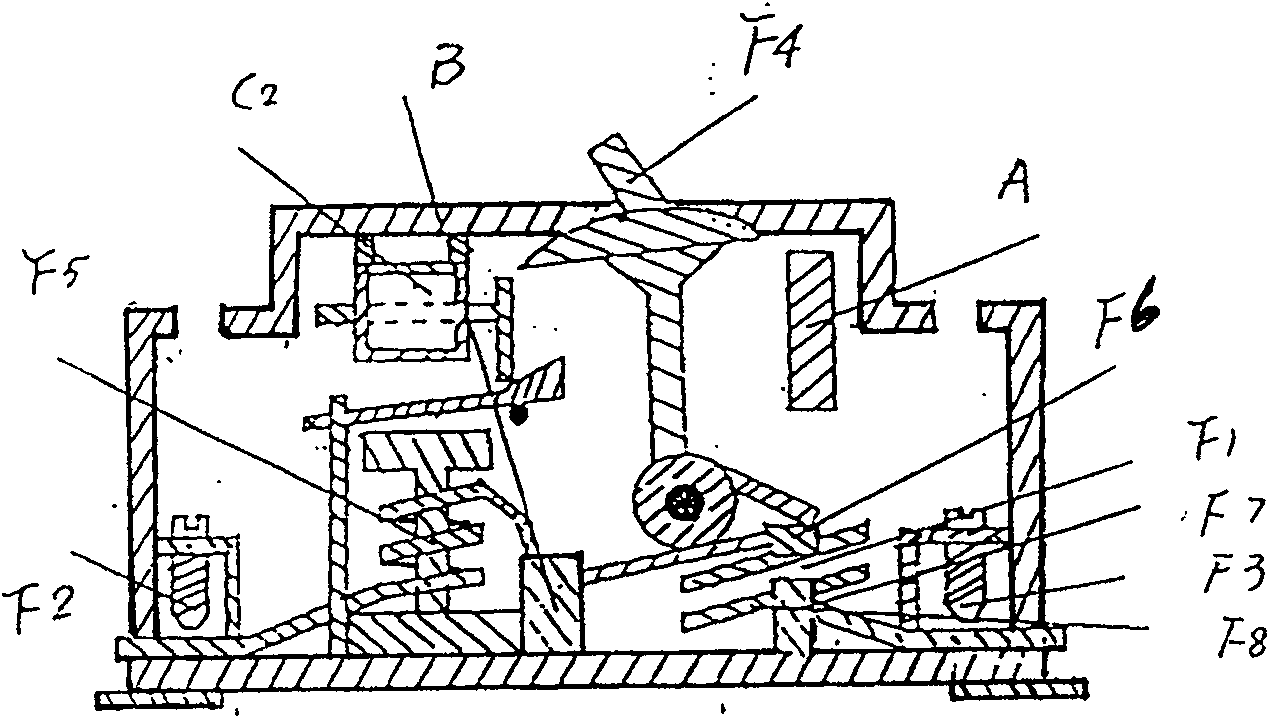
The intelligent leakage circuit breaker is mainly composed of: digital logic microcontroller A, fault sensing circuit B, electromagnetic trip circuit C, low-voltage power circuit D, ground circuit PE, accessories F, etc. Using digital logic microcontroller control, with leakage protection function, it also innovates the failure of ungrounded wire, live ground wire, live neutral wire, neutral wire and phase wire, and single-phase misconnection and two-phase faults in the controlled circuit. The intelligent and advanced protection function of non-electric shock protection can fundamentally eliminate electric shock and electrical fire between people. The invention has little power consumption, low cost and volume no larger than the existing leakage circuit breaker, and is a replacement product of the existing leakage circuit breaker.
Owner:钟汝祥
Nanoparticles comprised of shells associated with charged entities and formed from monomers and methods of making and using nanoparticles
InactiveUS20160367705A1Easy to manufactureCost constraintEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsNeutral ChargeHigh concentration
The present invention relates to relates to a nanoparticle that includes a shell formed from a first monomer having a first charge and a second monomer different than the first monomer. The first and second monomers are copolymerized, and the shell encapsulates a core region and is associated with a charged entity having a second charge of opposite sign to the first charge. The present invention further relates to a nanoparticle having a neutral charge. The present invention further relates to nanoparticle dispersions, methods of making the nanoparticle, methods of method of imaging, methods of delivering drugs, and methods of delivering a high concentration of contrast enhancing and / or imaging agents.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIVERSITY
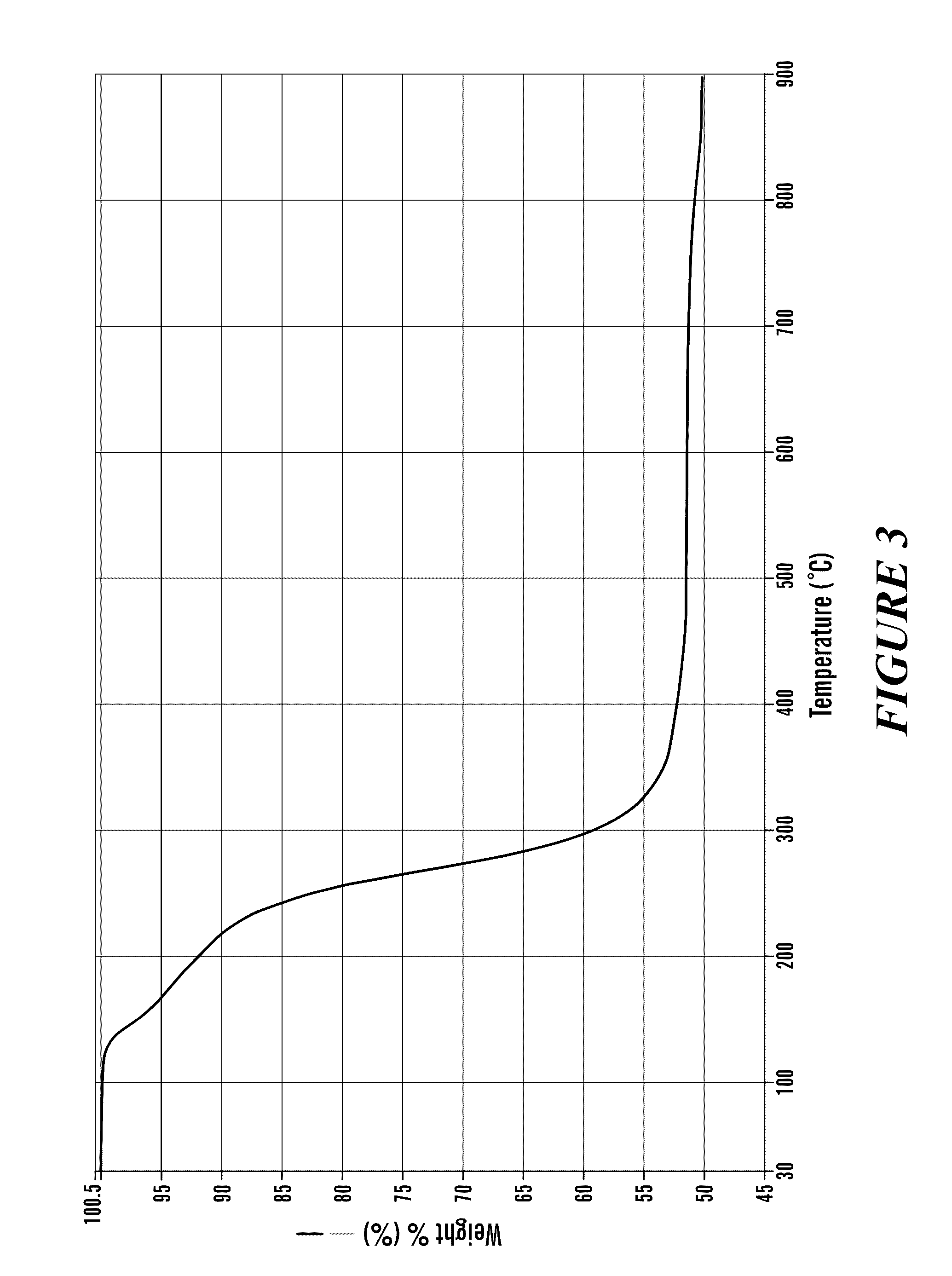
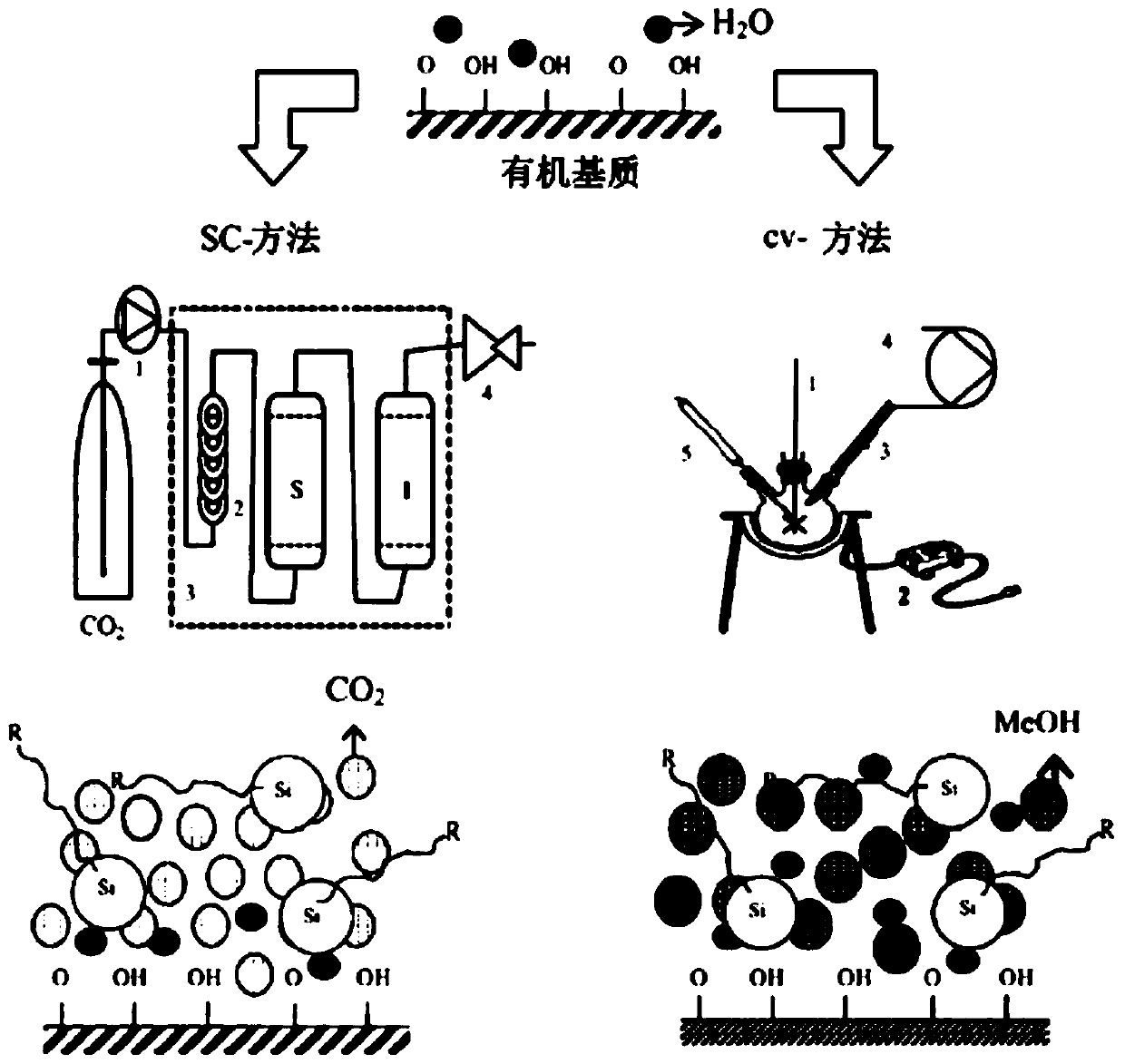
Supercritical/sub-critical fluid blocking method of HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) reversed phase bonded stationary phase
The invention discloses a supercritical / sub-critical water blocking method of HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) reversed phase bonded stationary phase, which comprises the steps of using carbon dioxide supercritical fluid and / or carbon dioxide sub-critical fluid as a carrier, bring a blocking reagent and a catalyst into a supercritical / sub-critical fluid reactor loaded with silica gel reversed phase bonded stationary phase, and carrying out blocking reaction under a closed condition. According to the method, residual active silanol groups can be thoroughly closed, and lyophobic reversed phase bonded stationary phase with complete neutral charge is produced; no residual active silanol groups exchanges side effects with alkali compound cations, so that alkali compound has a very symmetrical peak shape, and the retention time and mechanism fully follow the order from low to high of hydrophobicity of the compound. The method has the advantages that the reaction condition is mild, the reversed phase bonded stationary phase has no damage, the life of a chromatographic column is long, the repeatability of production batches is very good, the use amount of a toxic organic solvent, such as methylbenzene, is minimized, the pollution to the environment is reduced to the greatest extent, and the process continuity and semi-automatization can be realized.
Owner:WUHAN CHROM MATRIX BIOTECH CO LTD
Ionically modified silicones, compositions, and medical devices formed therefrom
A hydrophilic silicone, compositions comprising the same, and articles comprising the same are shown and described herein. The hydrophilic silicone is an ionically modified silicone compound wherein the compound has a net neutral charge. The hydrophilic silicone compounds may be provided as part of a composition, e.g., a composition suitable for forming a hydrogel, which may be employed to form afilm material and even an article (e.g., in a contact lens).
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
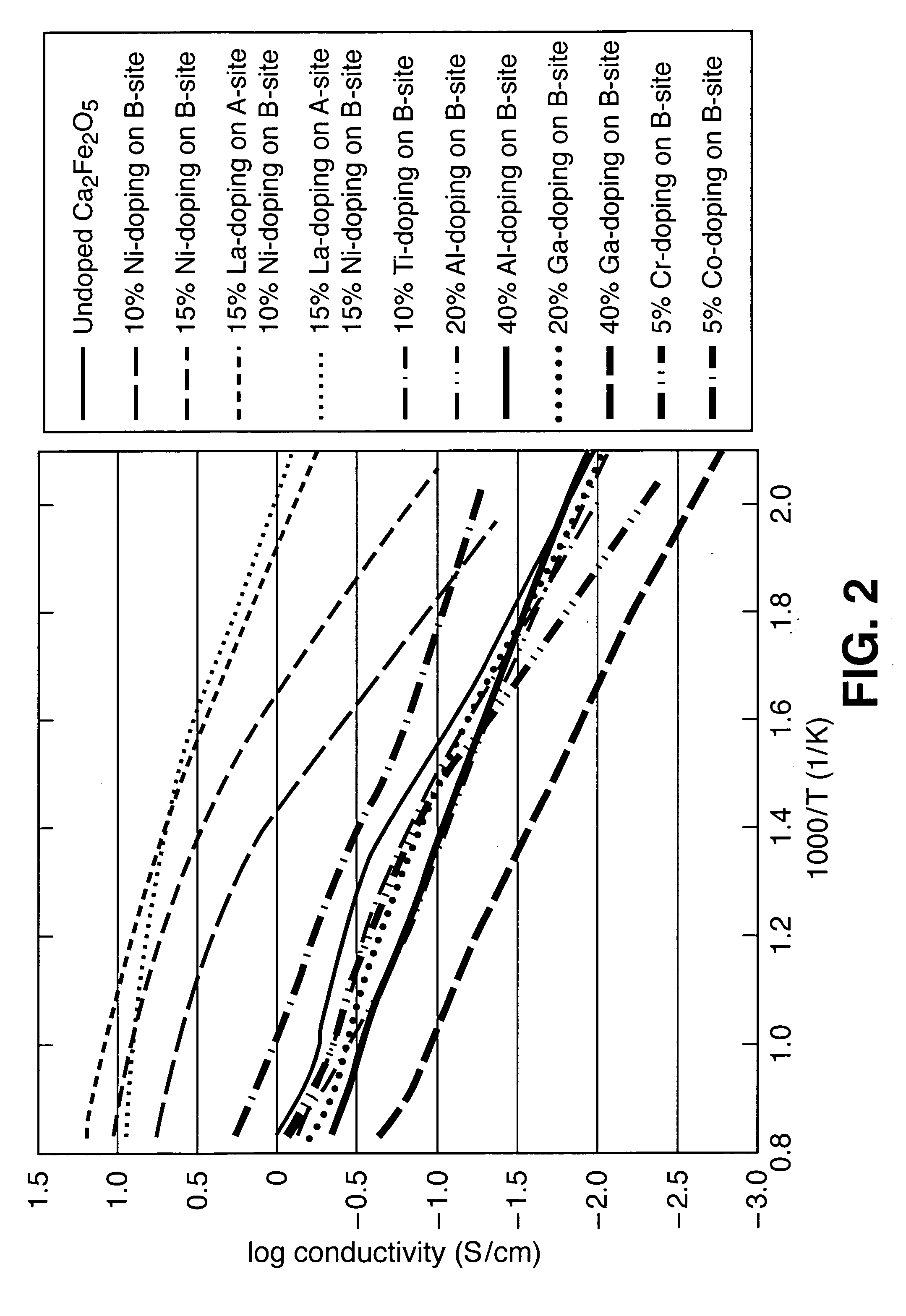
Solid oxide fuel cell cathode material
InactiveUS20070207373A1Low costHigh oxygen ion conductivityActive material electrodesSolid electrolyte fuel cellsRare-earth elementNeutral Charge
A solid oxide fuel cell includes a porous anode, a dense electrolyte in contact with the porous anode, and a porous cathode in contact with the dense electrolyte. The porous cathode is characterized by a single-phase structure of Brownmillerite or Srebrodolskite, the composition thereof having the formula (Ca2-xAx)(Fe2-yBy)O5±z wherein: A is at least one element selected from the group: rare earth elements, Bi, and alkaline elements; B is at least one element selected from the group: Al, Ga, In, Mg, Si, and transition metal elements; 0≦x<2; 0≦y<2; and z is a variable, the value of which is such that the overall composition has a generally neutral charge state.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Composition containing conducting polymer particle
A composition for forming an electrically conductive antistatic layer comprises: electronically conductive polymer particles; a neutral-charge conductivity enhancer; and a hydrophilic polymeric binder.
Owner:EASTMAN KODAK CO
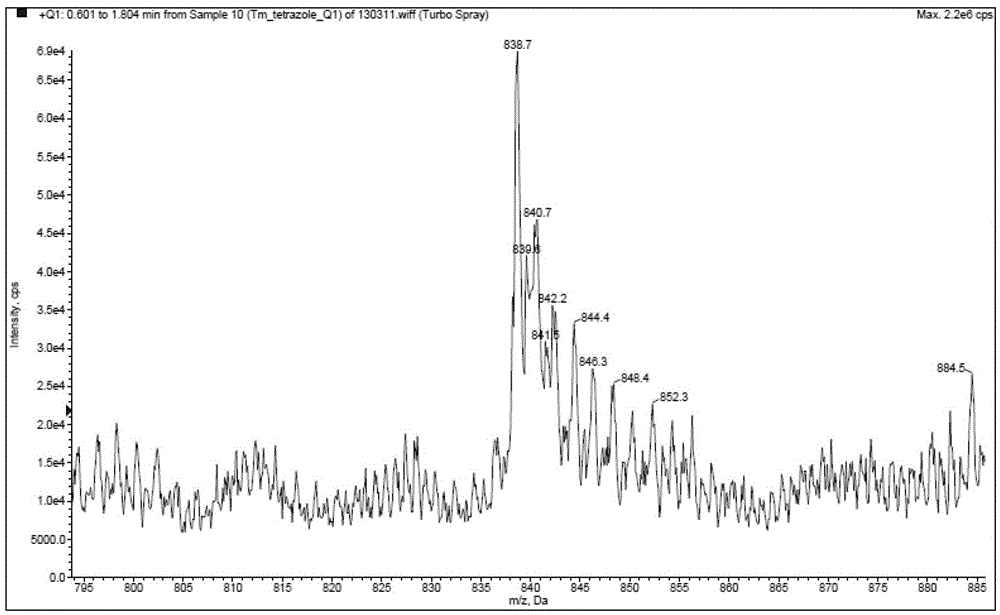
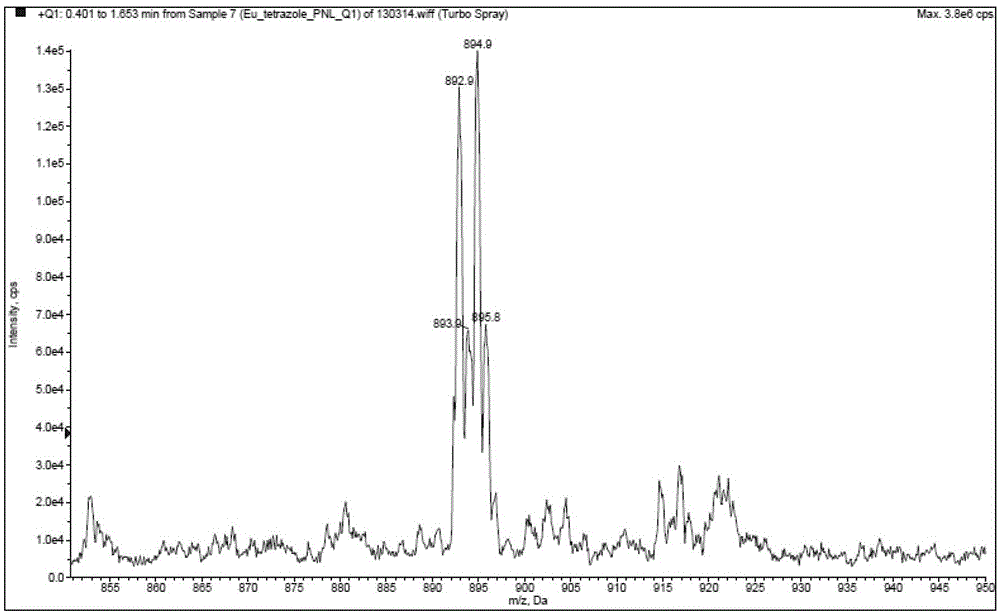
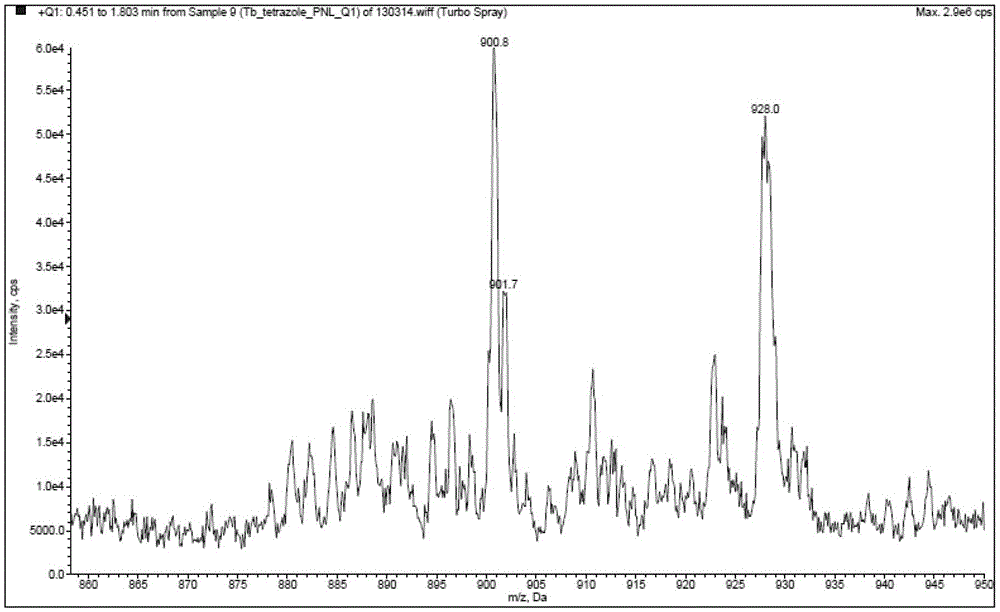
Nitrogen-containing bidentate heterocyclic substituted tetrazole rare earth complex and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103242354BHigh purityHigh yieldGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsLuminescent compositionsCeriumPhenanthroline
The invention provides a nitrogen-containing double-tooth heterocyclic ring substituted tetrazole type rare-earth complex LnL3 expressed by the formula I, wherein Ar is a nitrogen-containing double-tooth heterocyclic ring; the center rare-earth ion Ln is any one of yttrium, lanthanum, cerium, praseodymium, neodymium, samarium, europium, gadolinium, terbium, dysprosium, holmium, erbium, thulium, ytterbium and lutetium. The preparation method of the nitrogen-containing double-tooth heterocyclic ring substituted tetrazole type rare-earth complex LnL3 is characterized in that a nitrogen-containing double-tooth heterocyclic ring substituted tetrazole type three-tooth compound, namely a dipyridyl tetrazole type three-tooth compound or phenanthroline tetrazole type three-tooth compound, is taken as a single ligand, and simultaneously, coordination saturation is satisfied, and the tetrazole group in the complex serves as negative irons to realize electrically neutral charge balance together with center rare-earth metal cations. The obtained rare-earth complex is high in thermal stability, can be prepared into a device through an evaporation film-forming process or a solution film-forming process. Besides, the preparation method has the advantages of high yield, of the product has high purity, reaction time is short and operation is simple; and as a result, the cost is greatly reduced.
Owner:GUANGDONG SYNYOO NEW MATERIAL
Method and apparatus for label-free electronic real-time double-stranded nucleic acid detection
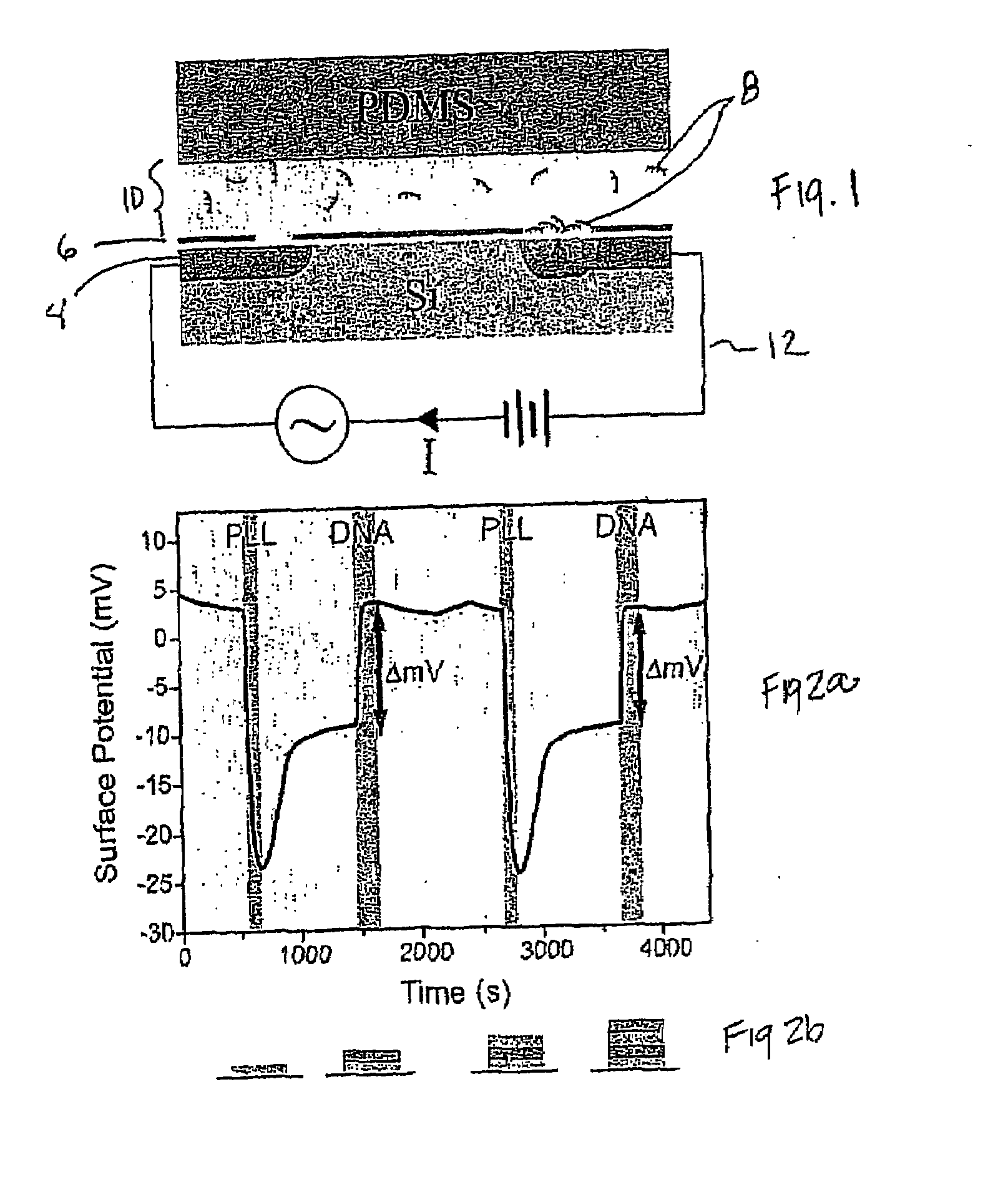
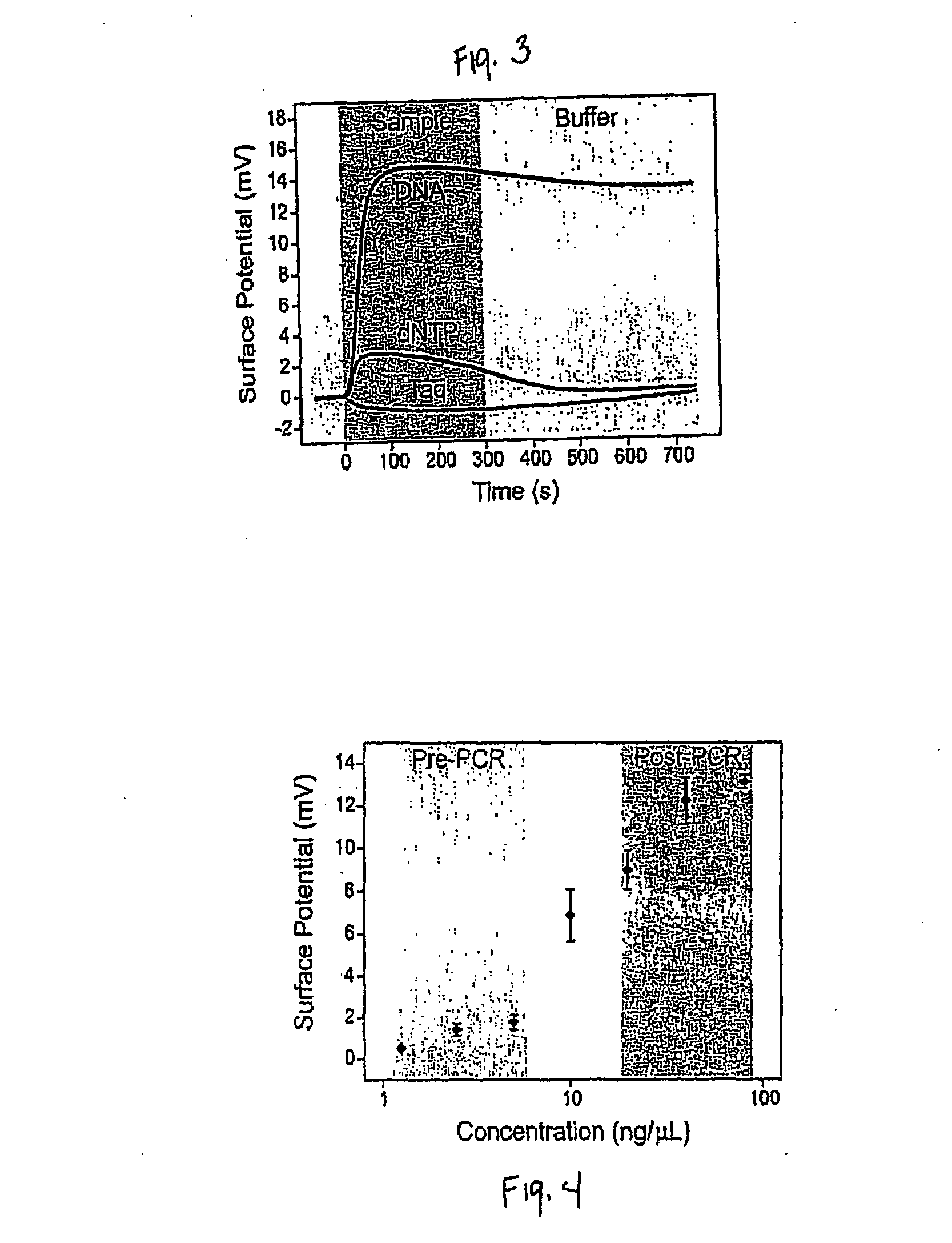
InactiveUS20080124717A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNucleic acid detectionNeutral Charge
In various embodiments, the present invention is a method and apparatus for label-free detection and optional quantification of double-stranded nucleic acid comprising binding a first layer comprising a charged species to a sensing surface having an associated first charge, wherein the first layer confers to the sensing surface a second charge or a neutral charge on a net basis, performing at least one cycle of DNA amplification to produce a double-stranded nucleic acid, and measuring a property of the interaction between the first layer and the double-stranded nucleic acid after the at least one cycle of DNA amplification. The present invention may be used in a cyclic manner, corresponding with the cyclic nature of DNA amplification processes.
Owner:MANALIS SCOTT +1
Polymer-Attached Inhibitors of Influenza Virus
InactiveUS20130280204A1Prevent and inhibit developmentPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsSynthetic polymeric active ingredientsDiseaseNeutral Charge
Antiviral compositions containing one or more antiviral agents coupled to a polymer and methods of making and using the compositions, are described herein. The one or more antiviral agents are covalently coupled to the polymer, and thereby prevent or decrease development of drug resistance. In some embodiments, the polymer is a biodegradable polymer. In particular embodiments, the polymer is a water-soluble, biodegradable polymer, which has an overall neutral charge (e.g., no charged groups or overall neutral charge). In a more particular embodiment, the neutral polymer is polyglutamine or a polymer having properties similar to polyglutamine, polyaspartate, and other homopolypeptides that can be modified to have no charge or no net charge. The compositions described herein are effective at treating a variety of viral infections, such as influenza, respiratory syncythial virus, rhinovirus, human metaneumovirus, and other respiratory diseases, while inhibiting or preventing the development of resistance.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
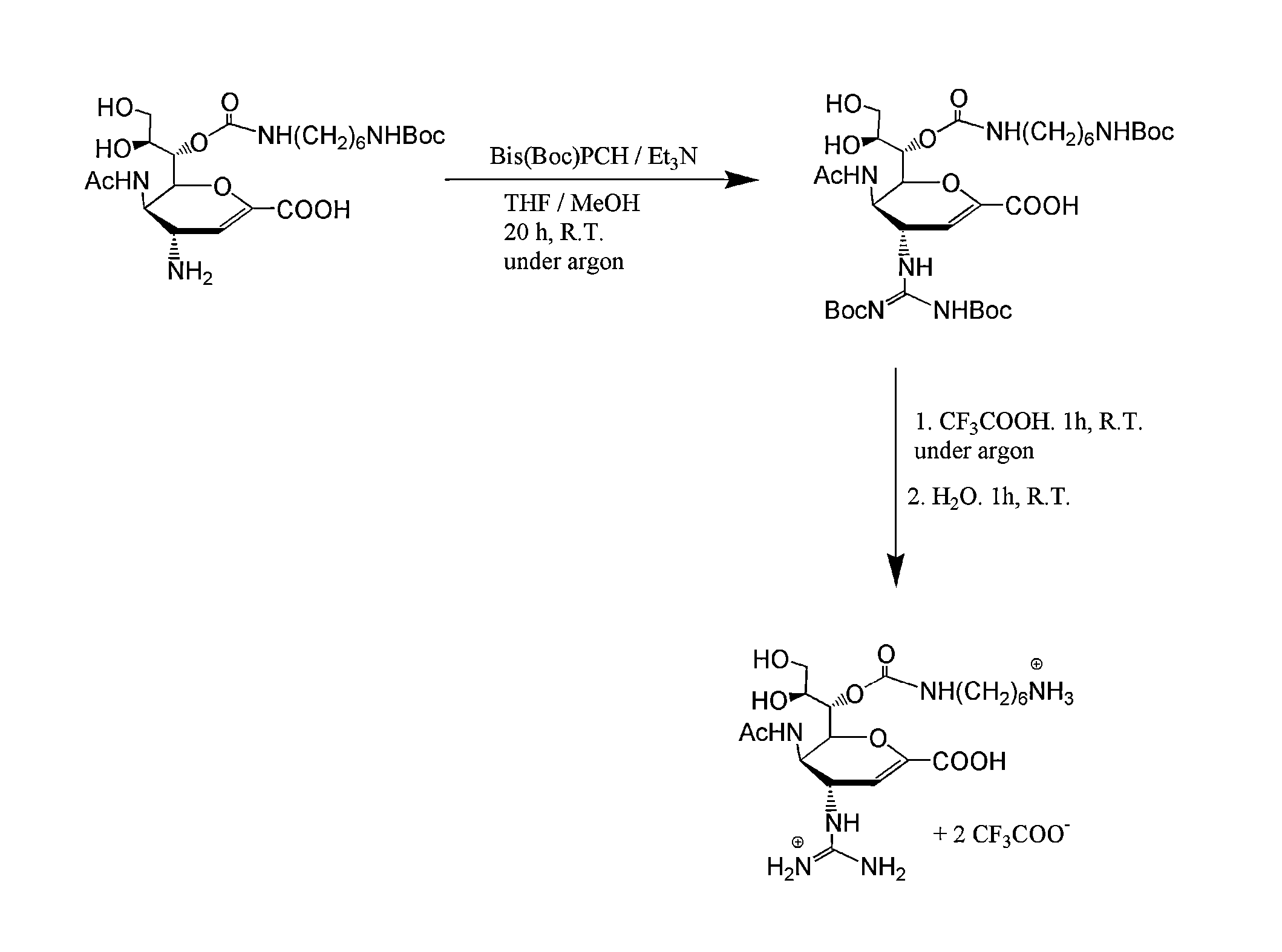
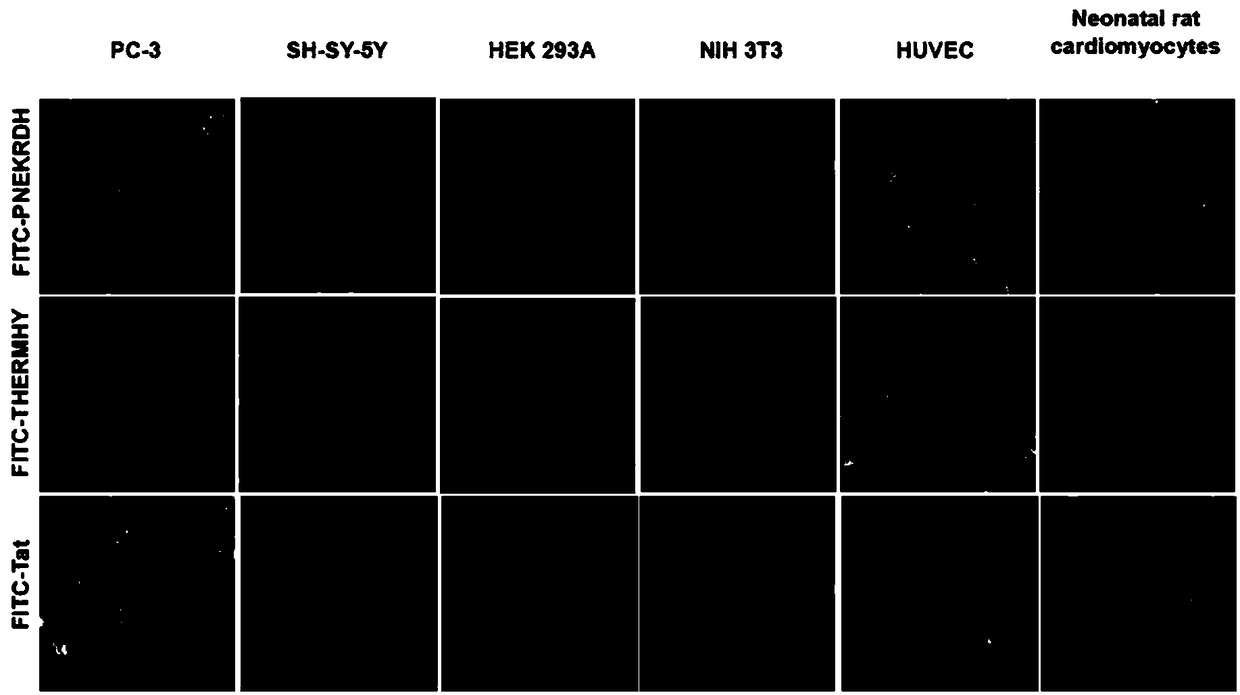
Cell penetrating peptide with neutral charge and application of cell penetrating peptide as delivery carrier in cells
InactiveCN108752426AEchographic/ultrasound-imaging preparationsPeptidesCrystallographyNeutral Charge
The invention provides a cell penetrating peptide with neutral charge, wherein the net charge of the cell penetrating peptide under physiological conditions is 0. The invention also provides a specific amino acid sequence. The invention also provides application of the cell penetrating peptide with neutral charge as a delivery carrier in cells, medical application of the cell penetrating peptide with neutral charge as the delivery carrier of therapeutic drugs in cells, and application of the cell penetrating peptide with neutral charge as a contrast agent in the medical imaging technology of the delivery carrier in cells. Furthermore, homologues of the cell penetrating peptide with neutral charge also have cell penetrating performance and can medically serve as the delivery carrier in cells as well as serve as the delivery carrier of the therapeutic drugs in cells.
Owner:SOUTHERN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Cyanine compound and optical recording material
InactiveUS8206806B2Suitable characteristicMethine/polymethine dyesLayered productsNeutral ChargeOxygen
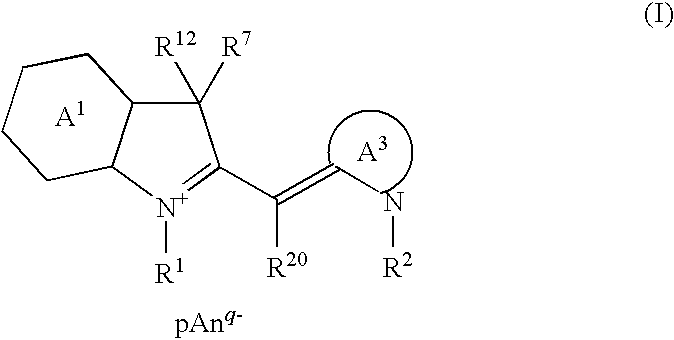
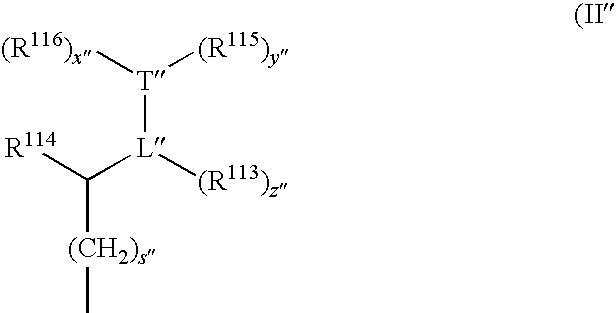
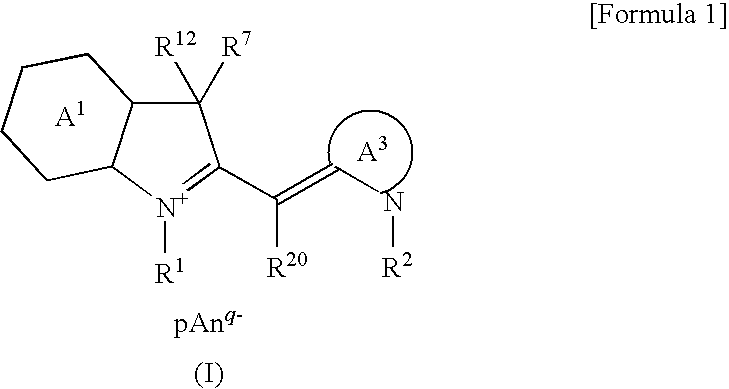
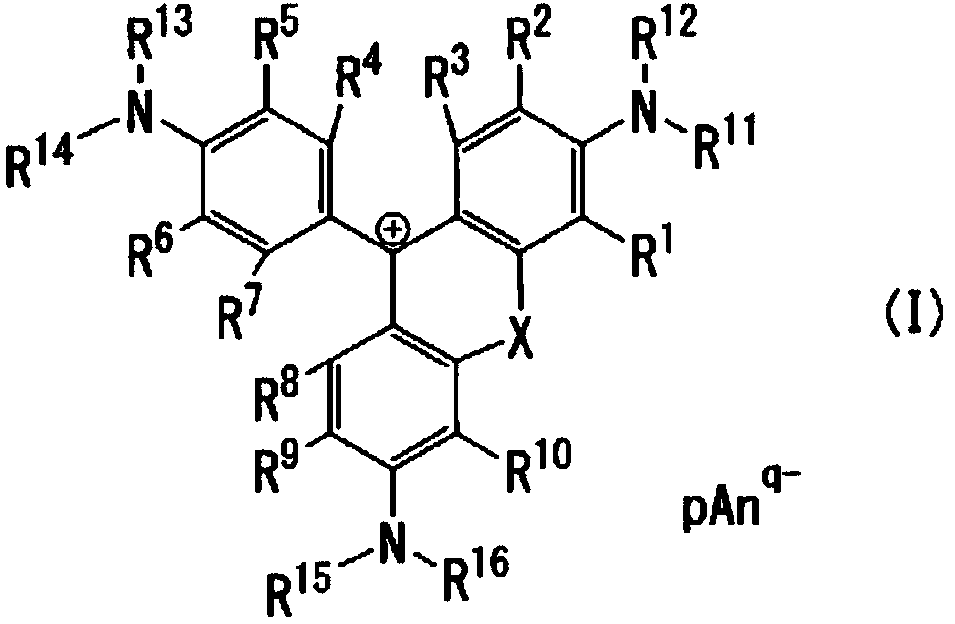
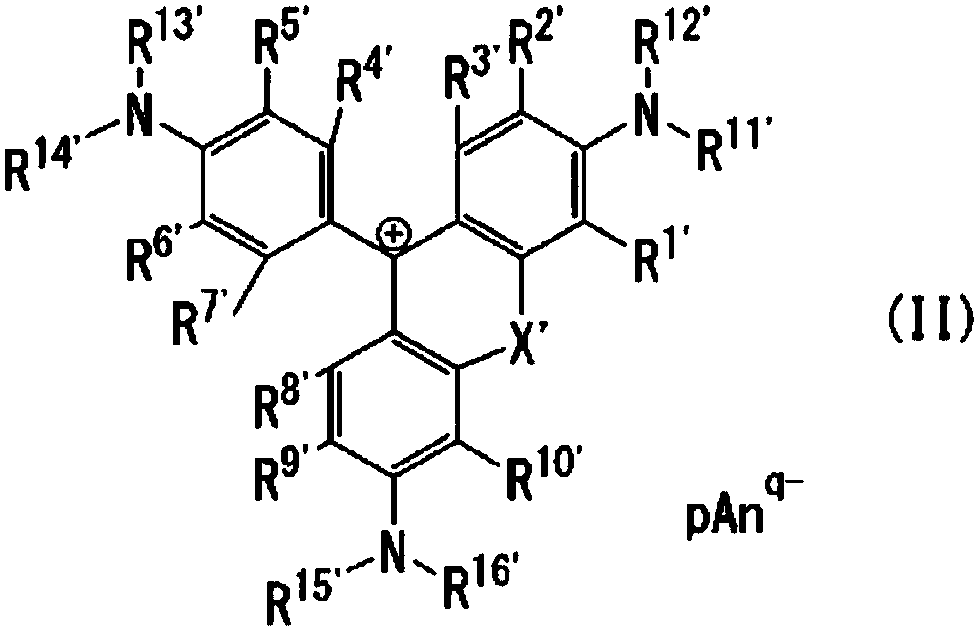
A cyanine compound is represented by formula (I):A1: benzene or naphthalene ring. A3: 5- or 6-membered ring. R1, R2: hydrogen atom and the like. R7: an alkyl group and the like. R12: a substituent by formula (II) or (II′). R20: a hydrogen atom and the like. Anq-: a q-valent anion. q: 1 or 2; p: a coefficient for neutral charge. In formula (II): bond between L and T is a double, conjugated double, or triple bond. L: carbon atom. T: carbon, oxygen, sulfur, or nitrogen atom. x, y, z: 0 or 1. s: 0-4. R13: hydrogen atom and the like. R14, R15, and R16: hydrogen atom and the like. In formula (II′), the bond between L′ and T′ is a double or conjugated double bond. L′: carbon atom. T′:carbon, oxygen, nitrogen atom. s′: 0-4. Ring containing L′ and T′: 5-membered ring, may contain a heteroatom.
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Magnetoelectric composite gas purification method
ActiveCN111420804AImprove charging efficiencyReduce power consumptionVapor flow controlElectric supply techniquesParticulatesPurification methods
Owner:湖北玖恩智能科技有限公司
CVD single crystal diamond material
ActiveCN102770588BPolycrystalline material growthBraking element arrangementsRefractive indexSingle crystal
Owner:ELEMENT SIX LTD
Indolium compound and optical recording material
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Coloring photosensitive compositions and compounds
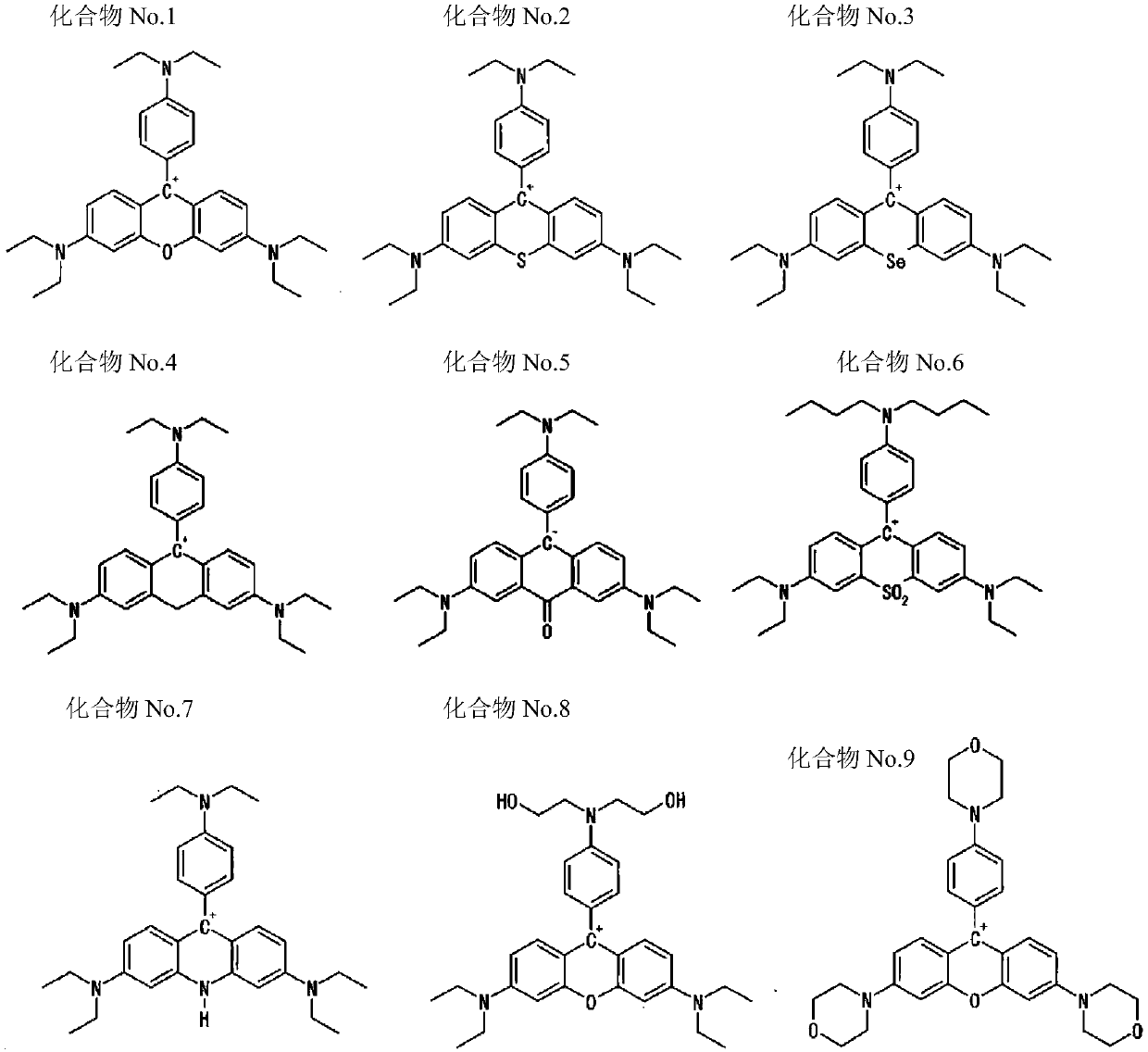
ActiveCN104871045BImprove solubilityImprove heat resistancePyronine/xanthon/thioxanthon/selenoxanthan/telluroxanthan dyesDiaryl/thriaryl methane dyesCompound aNeutral Charge
A colored photosensitive composition containing a dye (A) comprising: a compound indicated by general formula (I); a polymerizable compound (B) having an ethylenically unsaturated bond; and a photopolymerization initiator (C). In the general formula (I), X is ideally an oxygen atom . Furthermore, at least one type of coloring materials (excluding the dye (A)) ideally contains (D). (Refer to the Description for definitions of R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6, R7, R8, R9, R10, R11, R12, R13, R14, R15, R16, and X in the formula. Anq- indicates a q-valent anion, q indicates 1 or 2, and p indicates a coefficient for keeping a neutral charge.)
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Carrier system and photoelectric conversion device
InactiveUS20160329161A1Improve photoelectric conversion efficiencySuitableMethine/polymethine dyesLight-sensitive devicesO-Phosphoric AcidPhotopigment
This carrier carries a pigment (A) and a co-adsorbent (B) represented by the following general formula (1). (In the formula, ring A represents a 5- or 6-membered heterocycle which may be further condensed; the hydrogen atom in ring A may be substituted by a hydrocarbon group which may have a substituent, a halogen atom, a cyano group, a nitro group, a —OR2 group, or a —SR2 group; Z represents a divalent aliphatic hydrocarbon group interrupted 0-3 times by —O— or the like; Z1 represents a divalent aromatic group; R1 represents a carboxylic acid group, a sulfonic acid group, a phosphoric acid group, or a phosphonic acid group; R2 and R3 represent a hydrocarbon group which may have a hydrogen atom or a substituent; Anm− represents an m-valent anion; m represents an integer of 1 or 2; and p represents a coefficient for maintaining a neutral electric charge).
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Indolium compound and optical recording material
InactiveUS20090296554A1Improve light resistanceCombination recordingMethine/polymethine dyesOrganic groupNeutral Charge
An indolium compound is represented by formula (I):Ring A: a benzene or naphthalene ring. Ring B: 5- or 6-membered heterocyclic or aromatic ring. Z: alkyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms, may be substituted with a halogen atom or interrupted by —O—, —CO—, —OCO—, or —COO—, a sulfonyl group having a hydrocarbyl group having -8 carbon atoms, a sulfinyl group having a hydrocarbyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms, an alkylamino group having an alkyl group having 1-8 carbon atoms, a dialkylamino group having alkyl groups having 1-8 carbon atoms, a cyano group, a nitro group, a hydroxyl group, or a halogen group. R1: group represented by formula (II) or (II′). R2: organic group having 1-30 carbon atoms or group represented by formula (II), (II′), or (III). Y: group represented by formula (III). n: integer 0-4; Anm−: m-valent anion, m is 1 or 2. p: coefficient for neutral charge:
Owner:ADEKA CORP
Peptide and peptide mimetic binding antagonists of polo-like kinase 1 polo box domain and methods of use
ActiveUS10047122B2Improve bioavailabilityGood effectGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsTransferasesPeptide mimeticNeutral Charge
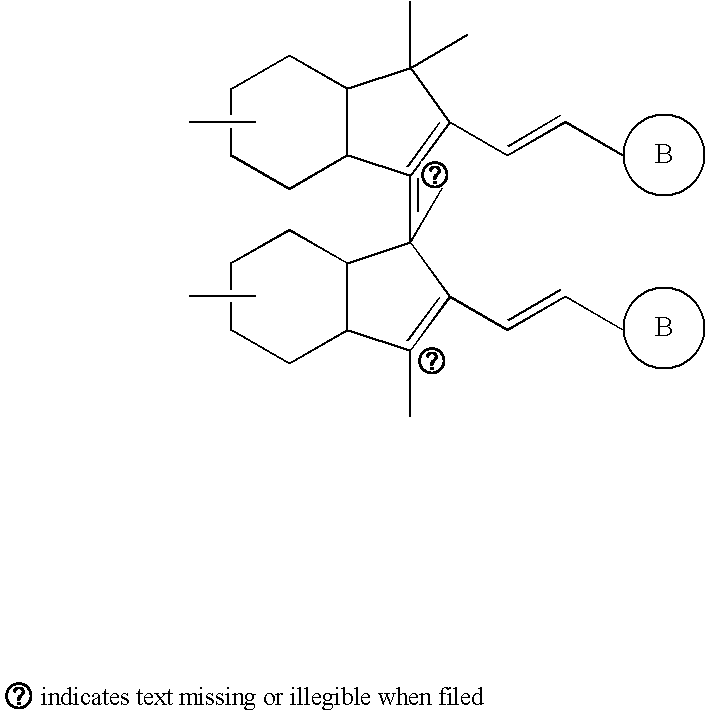
The invention provides novel compounds that may serve as anticancer therapeutics. The compounds of the invention bind to polo-like kinases through the polo-box domain. In certain embodiments, the compounds of the invention are POM-protected peptide derivatives. The use of cationic bis-alkyl his residues in combination with a mono POM-protected phophoryl group results in a peptide possessing an overall neutral charge. The peptide derivatives of the invention have achieved both good efficacy and an enhanced bioavailability. The invention also provides methods of use, compositions, and kits thereof. Further, the invention provides a novel method of design and / or synthesis of phosphoryl-derived peptide derivatives useful as therapeutic agents.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Differential tumor cell cytotoxicity via contact with coated cerium oxide nanoparticles
ActiveUS10213458B2Without compromising solubilityReduce in quantityHeavy metal active ingredientsMicrocapsulesCancer cellLysosome
Differential surface-charge-dependent localization of nanoceria in normal cells and cancer cells plays a critical role in the toxicity profile of a nanoceria particle. Engineered surface-coated cerium oxide nanoparticles with different surface charges that are positive, negative and neutral provide therapeutic results for normal and cancer cell lines. Results show that nanoceria with a positive or neutral charge enters most of the cell lines studied, while nanoceria with a negative charge internalizes mostly in the cancer cell lines. Moreover, upon entry into the cells, nanoceria is localized to different cell compartments (e.g. cytoplasm and lysosomes) depending on the nanoparticle surface charge. The internalization and subcellular localization of nanoceria plays a key role in the nanoparticle cytotoxicity profile, exhibiting significant toxicity when they localize in the lysosomes of the cancer cell lines. In contrast, minimal toxicity is observed when they localize into the cytoplasm or do not enter the cells.
Owner:UNIV OF CENT FLORIDA RES FOUND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com