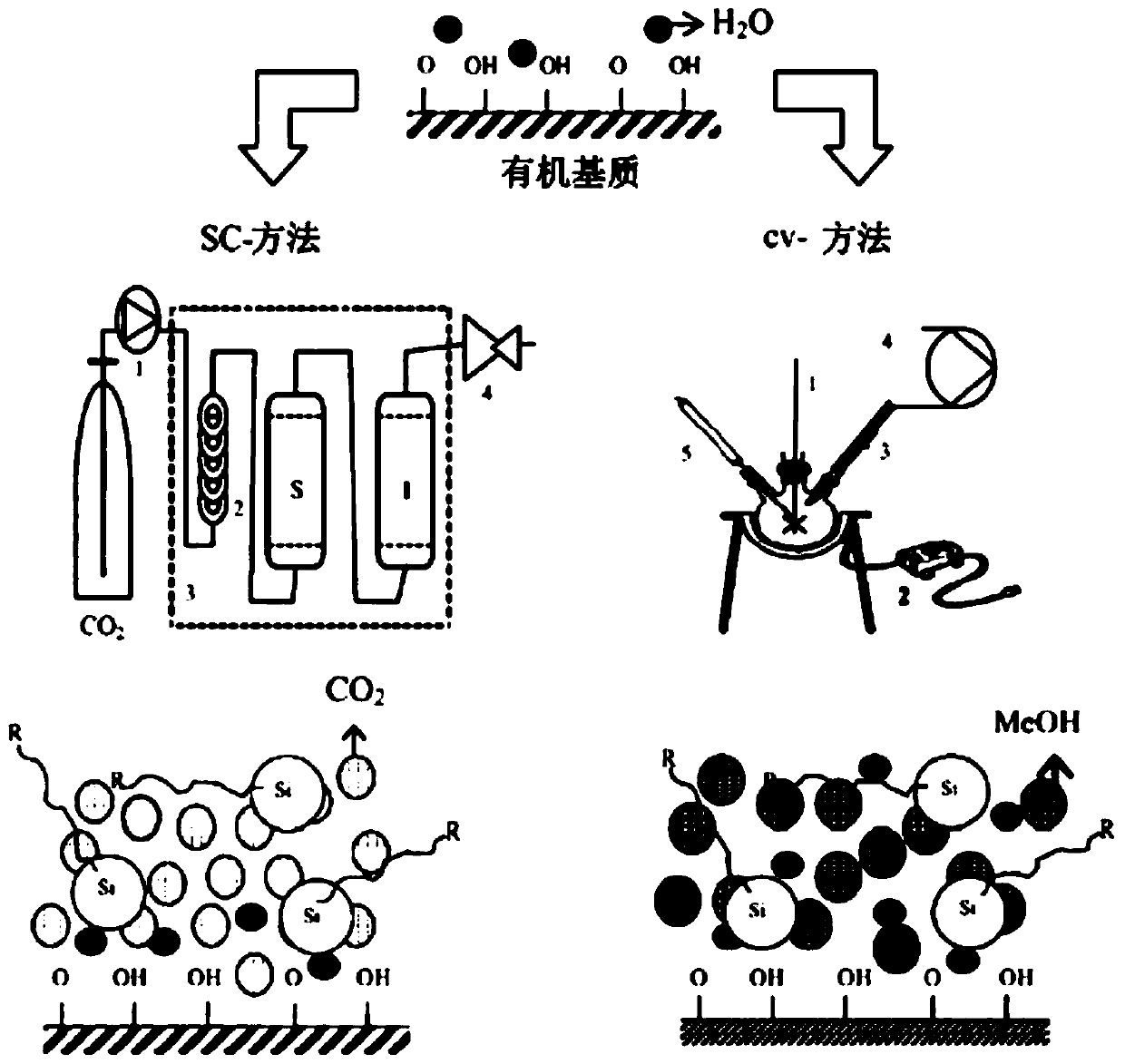
Supercritical/sub-critical fluid blocking method of HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography) reversed phase bonded stationary phase
A high-performance liquid chromatography and subcritical fluid technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, and other chemical processes, to achieve the effects of reducing pollution, mild process reaction conditions, and realizing semi-automation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Example 1: 5 μm C18 bonded phase supercritical fluid capping
[0047] Traditional solid-liquid reflux capping method: Japan Daiso Company 5 μm B-type spherical silica gel and silane reagent octadecyldimethylchlorosilane are used as raw materials, toluene is used as solvent, imidazole and pyridine are used as catalysts, reflux at toluene reflux temperature with nitrogen protection for 24 hours, and C18 bonded phase is obtained after washing. Technical parameters: specific surface area 300m 2 / g, bonding density 3.2μmol / m 2 .
[0048] 100g C18 bonded phase uses trimethylchlorosilane as the end-capping reagent, and 1,1,1,3,3,3-hexamethyldisilazimide, N,N-dimethyltrimethylsilylamine, etc. As a catalyst, it was refluxed for 24 hours at the reflux temperature of toluene with nitrogen protection. After the reaction, use toluene, dichloromethane, acetonitrile, methanol and water (50:50), wash with acetone in sequence, dry under nitrogen protection at 80°C, and use after co...
Embodiment 2
[0050] Example 2: Surface Charge Titration
[0051] Surface charge titration and Zeta potential are two of the most important surface characterization techniques in the field of colloid and interface science. Titration method: 10 grams of chromatographic bonded phase is placed in the potentiometric titration chamber, with 10mM sodium chloride (80%) and methanol (20%) as the liquid phase, with 0.1M hydrochloric acid to adjust the pH value to 3.0, from pH value 3.0 in nitrogen Under protection, it was titrated to pH8 with 0.1M NaOH, back-titrated to pH3.0 with 0.1M hydrochloric acid, and again titrated to pH8.0 with 0.1M NaOH.
[0052] The raw potentiometric titration data is transferred to the computer and converted into a pH-surface charge curve.
[0053] The pH-surface charge curve as a new dimension test platform can clearly reveal the surface charge of many reversed phase chromatography products on the market.
[0054] Type B spherical silica itself has 8μmol / m 2 Of the ...
Embodiment 3
[0059] Example 3: Zeta Potential
[0060] The pH-surface charge density curve alone makes it difficult to determine the isoelectric point (i.e.p) of a bonded phase. This is accompanied by a Zeta potential measurement. Zeta potential of Supelco HS C18 and Supelco ABZ Plus as image 3 shown.
[0061] The isoelectric point of Supelco HS C18 is at pH2.7, which is similar to that of silica gel itself. Supelco ABZ Plus due to residual NH 2 functional group, the isoelectric point shifts to pH4.4.
[0062] Since the supercritical fluid capping seals the active silanol groups to the greatest extent, the surface charge density of Novel C18 is almost zero, and the surface charge cannot be observed by Zeta potential measurement.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com