Composition containing conducting polymer particle
A technology of conductive polymer and composition, applied in the field of photography and thermal imaging photography, which can solve the problems of caking, increased pigment pollution, and small degree of triboelectric electrification.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0029] According to the present invention, the method for preparing the composition for use as a conductive composition comprises: preparing a stable aqueous colloidal dispersion consisting of one or more conductive polymeric materials. Preferably, these colloidal dispersions are combined with at least one neutrally charged conductivity enhancer, one or more film-forming polymeric binders, thickeners, and other additives. The composition can be incorporated into the imaging element in the form of a thin antistatic sublayer.
[0030] Conductive polymer particles may be coated on top of the water soluble coating composition. The polymer may be selected from any conductive polymer or a combination of conductive polymers, such as substituted or unsubstituted pyrrole-containing polymers (mentioned as examples in U.S. Patents 5,665,498 and 5,674,654), substituted or unsubstituted Thiophene-containing polymers (mentioned in U.S. Pat. Patents 5,716,550, 5,093,439 and 4,070,189 are m...
Embodiment 1
[0053] Embodiment 1. is suitable for the preparation method of a kind of coating composition that is used to prepare conductive layer and comprises with 173.9g demineralized water, 0.2g gelatin, 0.3g content is 1.0% chromium alum (gelatin hardener) aqueous solution, 0.19g content 10.6% aqueous solution of coating aid (10G surfactant provided by Olin Corp.), 0.22g content of 2% aqueous dispersion of polymethylmethacrylate particles and 15.39g content of 1.3% Baytron P TM Aqueous dispersions of colloidal PDET / PSS were mixed together. The coating composition described above was applied by means of a coating hopper to a 4 mil thick polyethylene terephthalate film support which had been previously coated with 1,1-dichloroethylene / acrylonitrile / itaconic acid. Copolymer coating. The wet laydown of the coating composition applied to the film support was 16.1 ml / m 2 , equivalent to a dry weight coverage of PDET / PSS of 16.1mg / m 2 . The surface resistivity (SER) of the conductive lay...
Embodiment 2-46
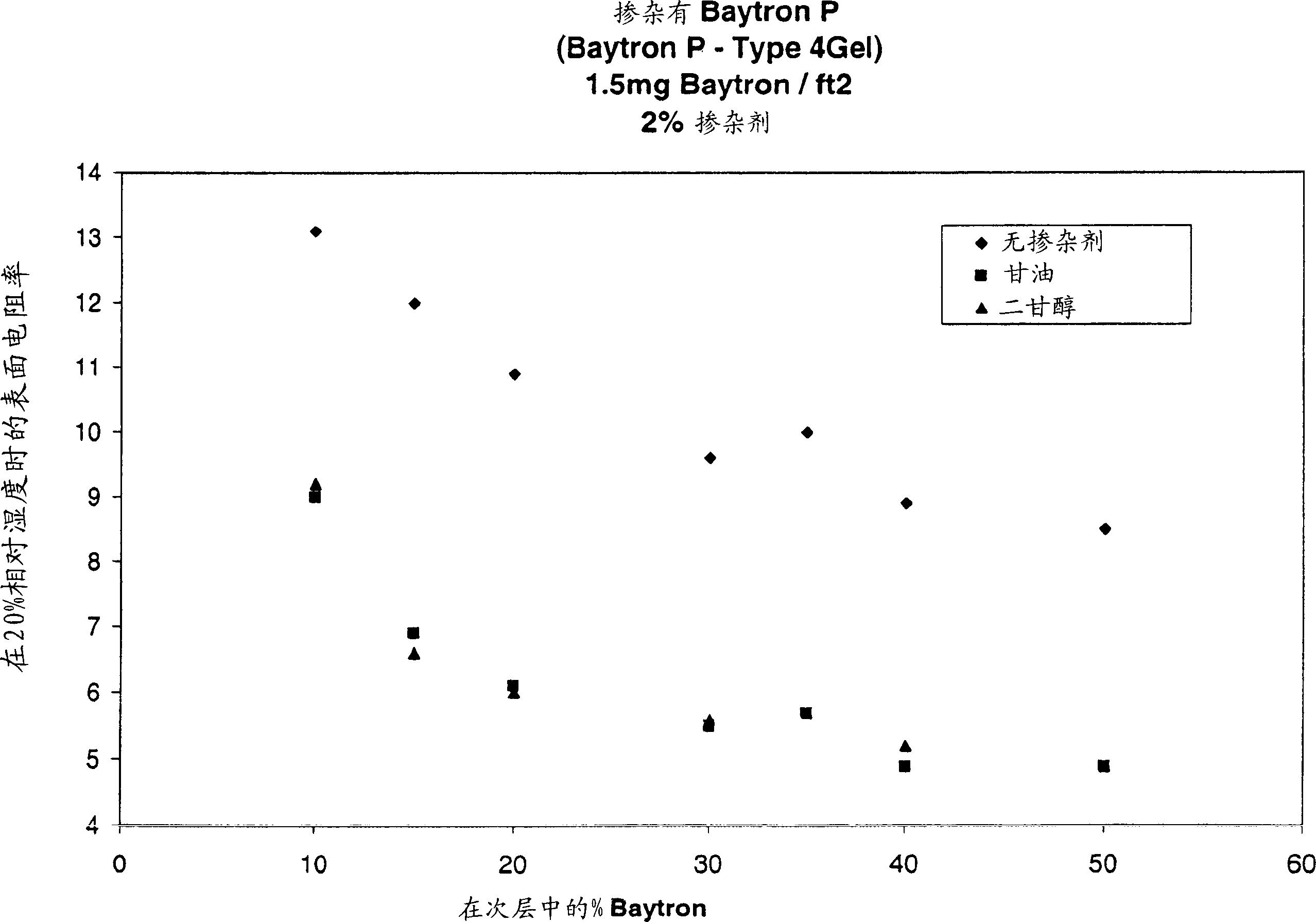
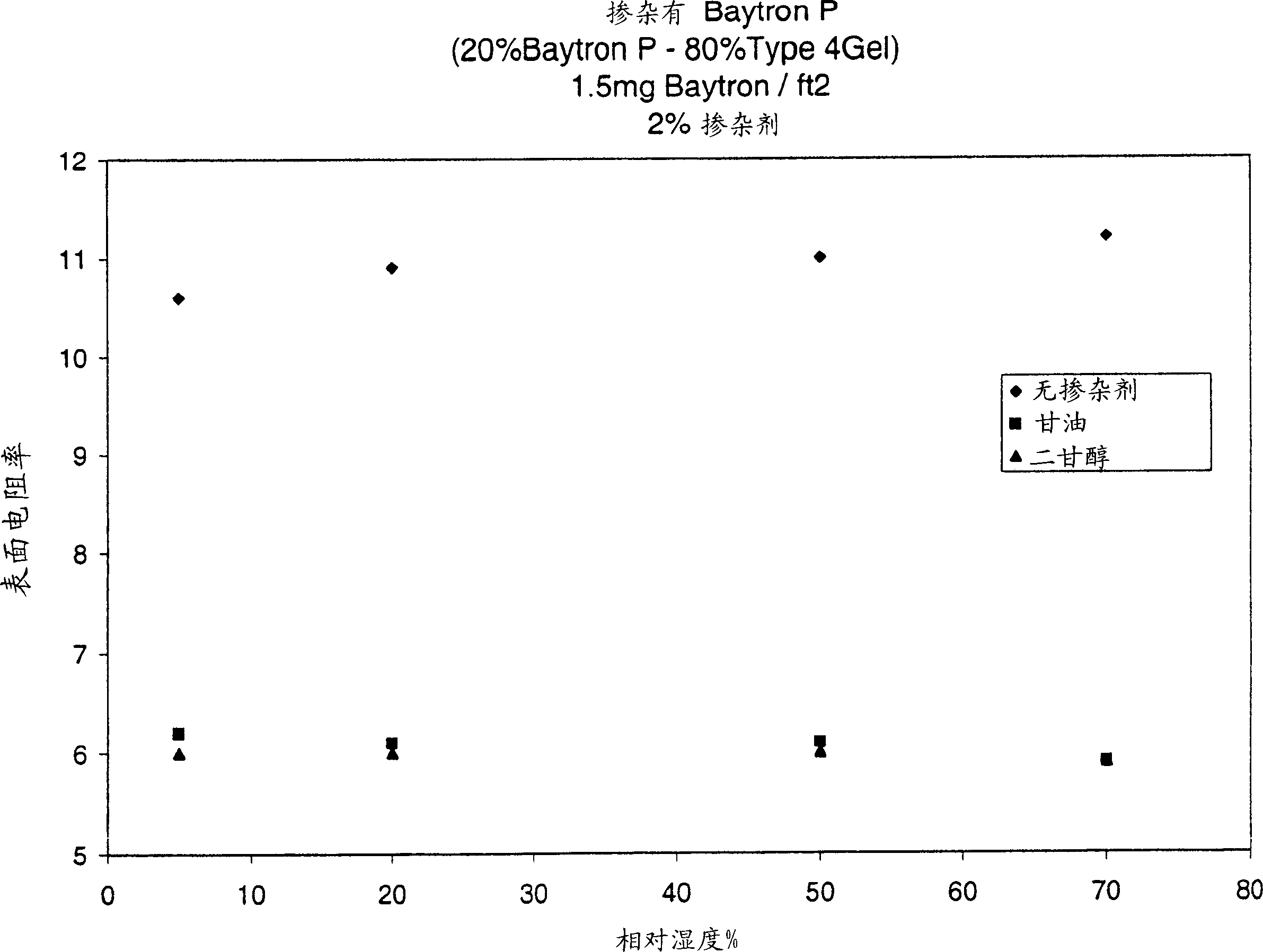
[0056] Also contains an organic neutrally charged conductivity enhancer and / or different Baytron P TM The preparation of the conductive coating at the ratio of gelatin involves mixing the neutrally charged conductivity enhancer at the concentration shown in Table 1 and adjusting the amount of gelatin in the molten state to obtain the Baytron P as shown in Table 1. TM Ratio to gelatin. The preparation method of the coating is as described in Example 1. The surface resistivity and net optical density of these conductive layers were measured by the above-mentioned method, and the results are listed in Table 1.
[0057] As shown in the data in Table 1, compared with only Baytron P TM Compared with the antistatic layer composition of gelatin, Baytron P TM The use of neutrally charged conductivity enhancer organic compounds in antistatic layer formulations mixed with gelatin can provide superior performance in terms of surface resistivity. In order to clearly show the improvemen...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| The average diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com