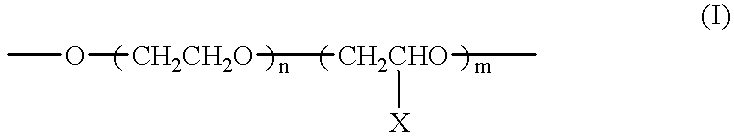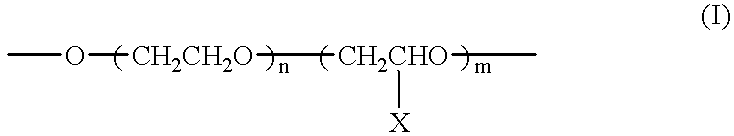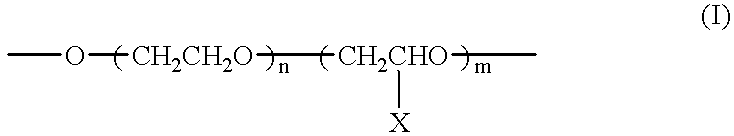Patents
Literature
923 results about "Static Charges" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
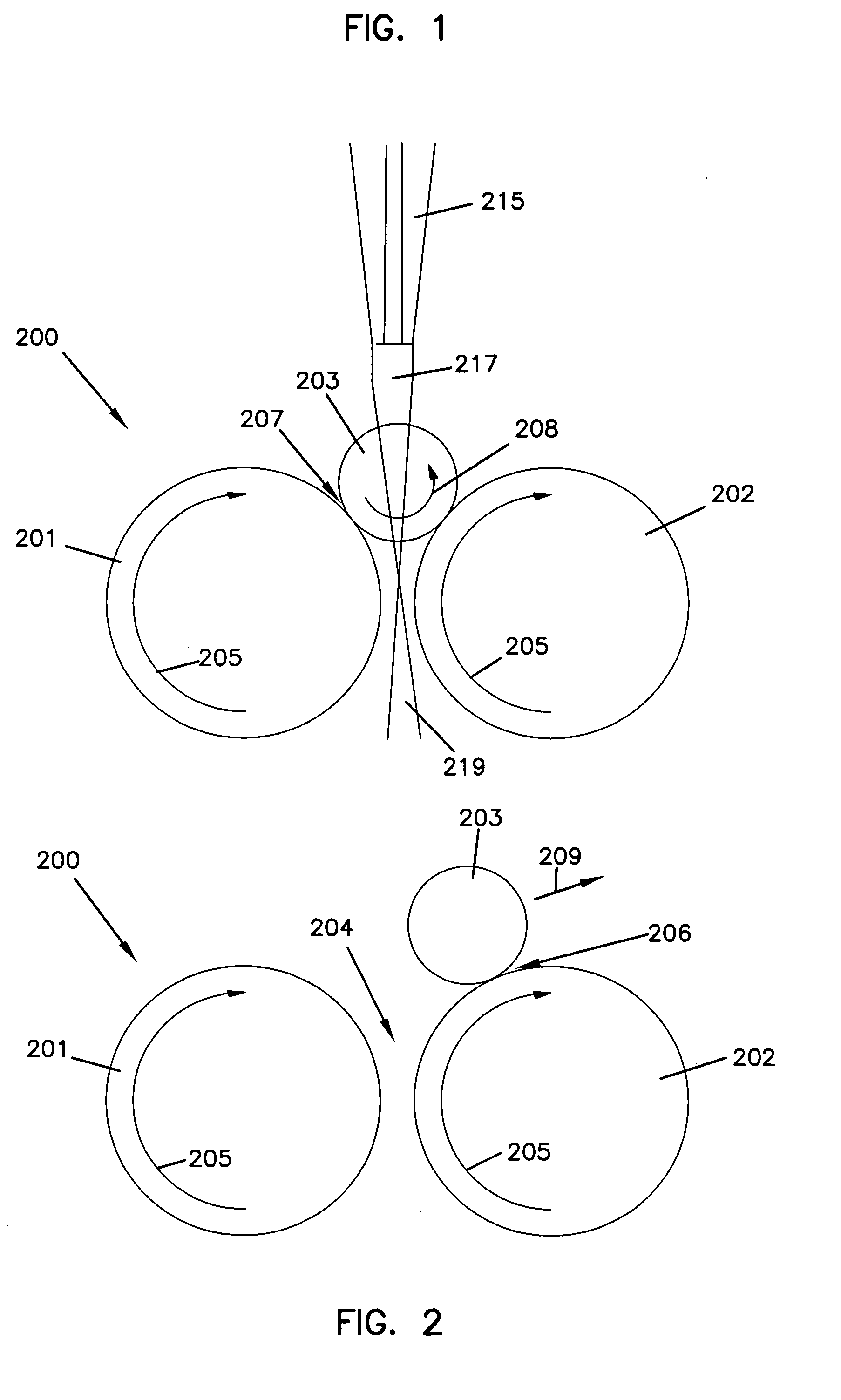
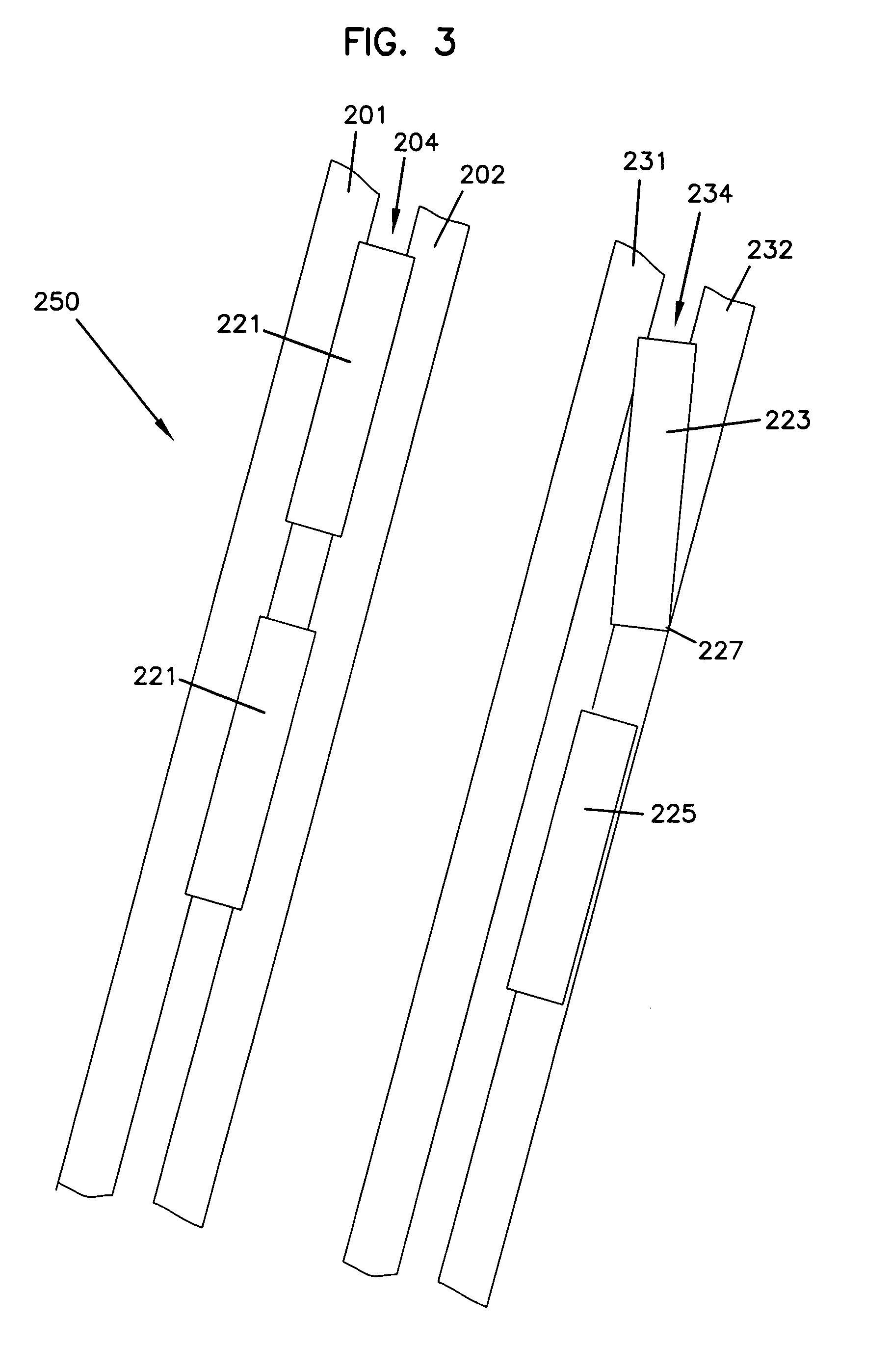
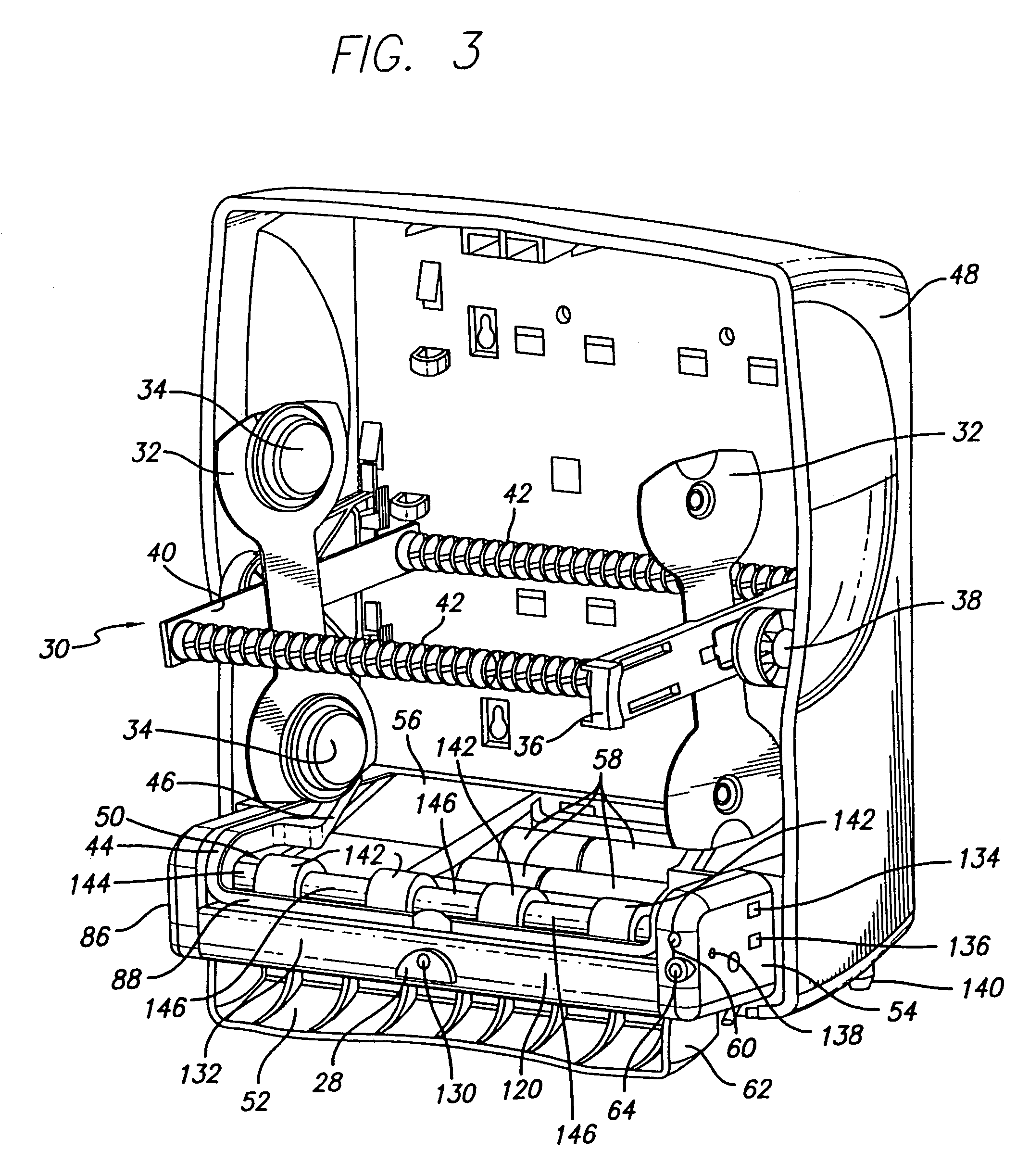
Static build up control in electronic dispensing systems
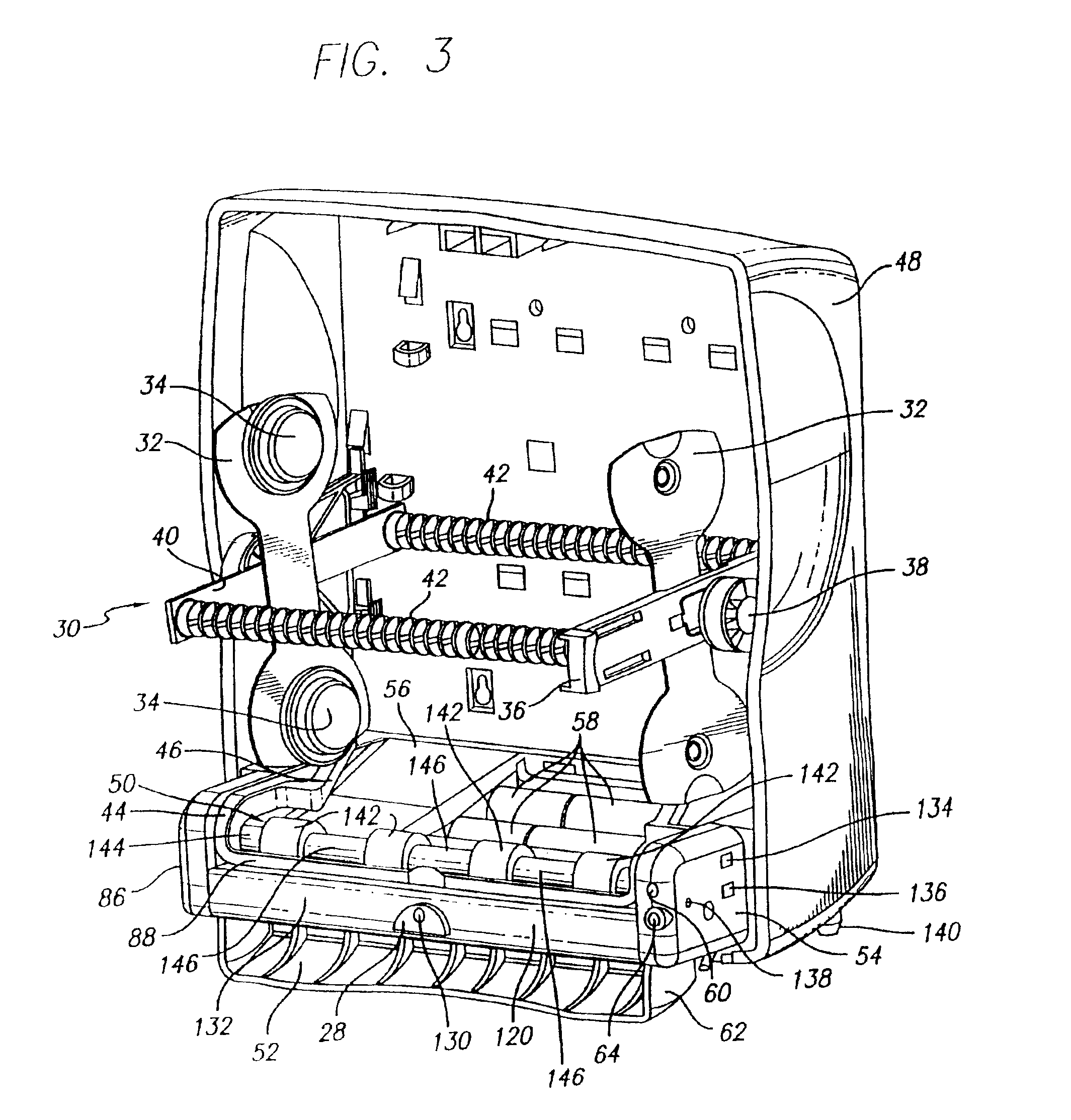
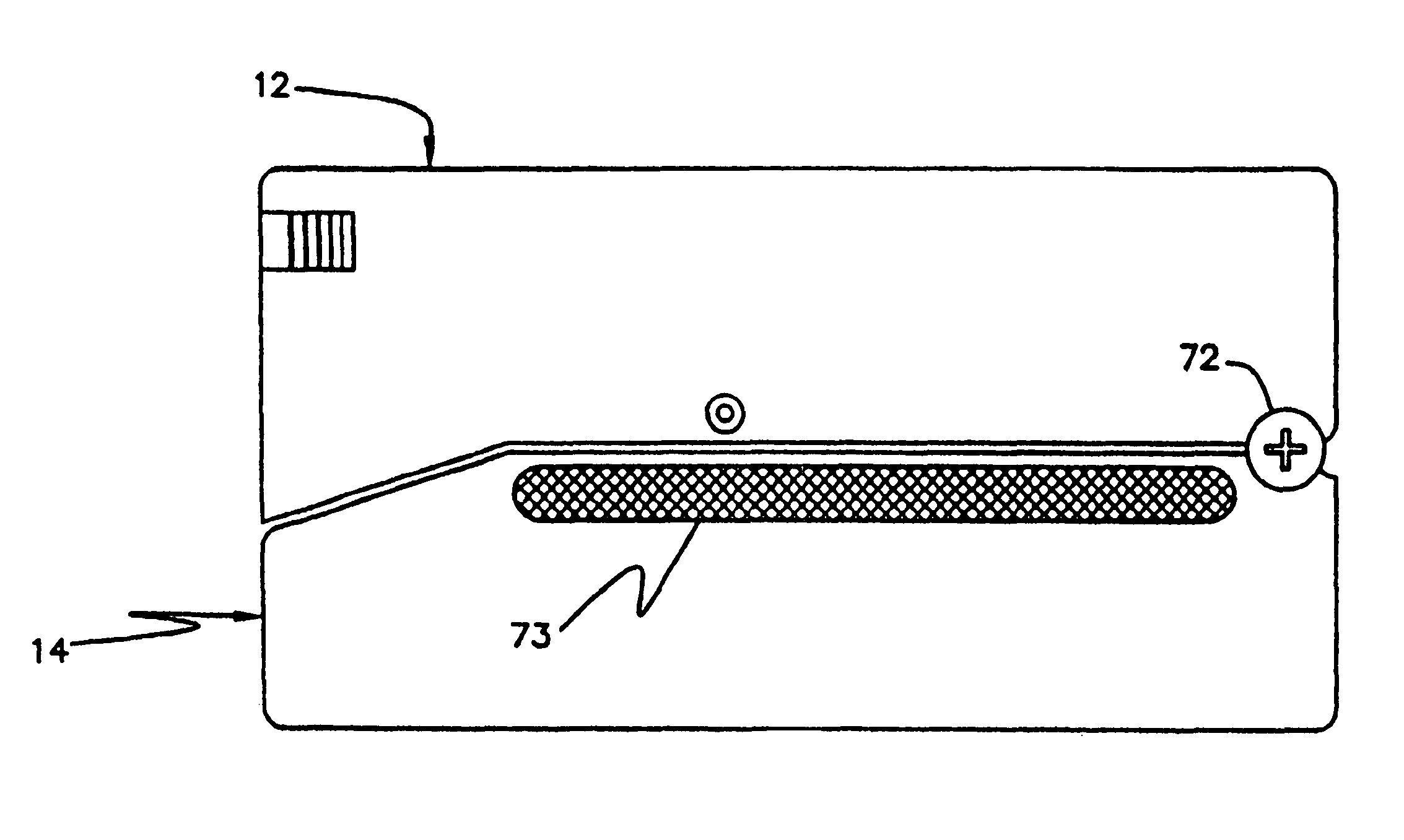
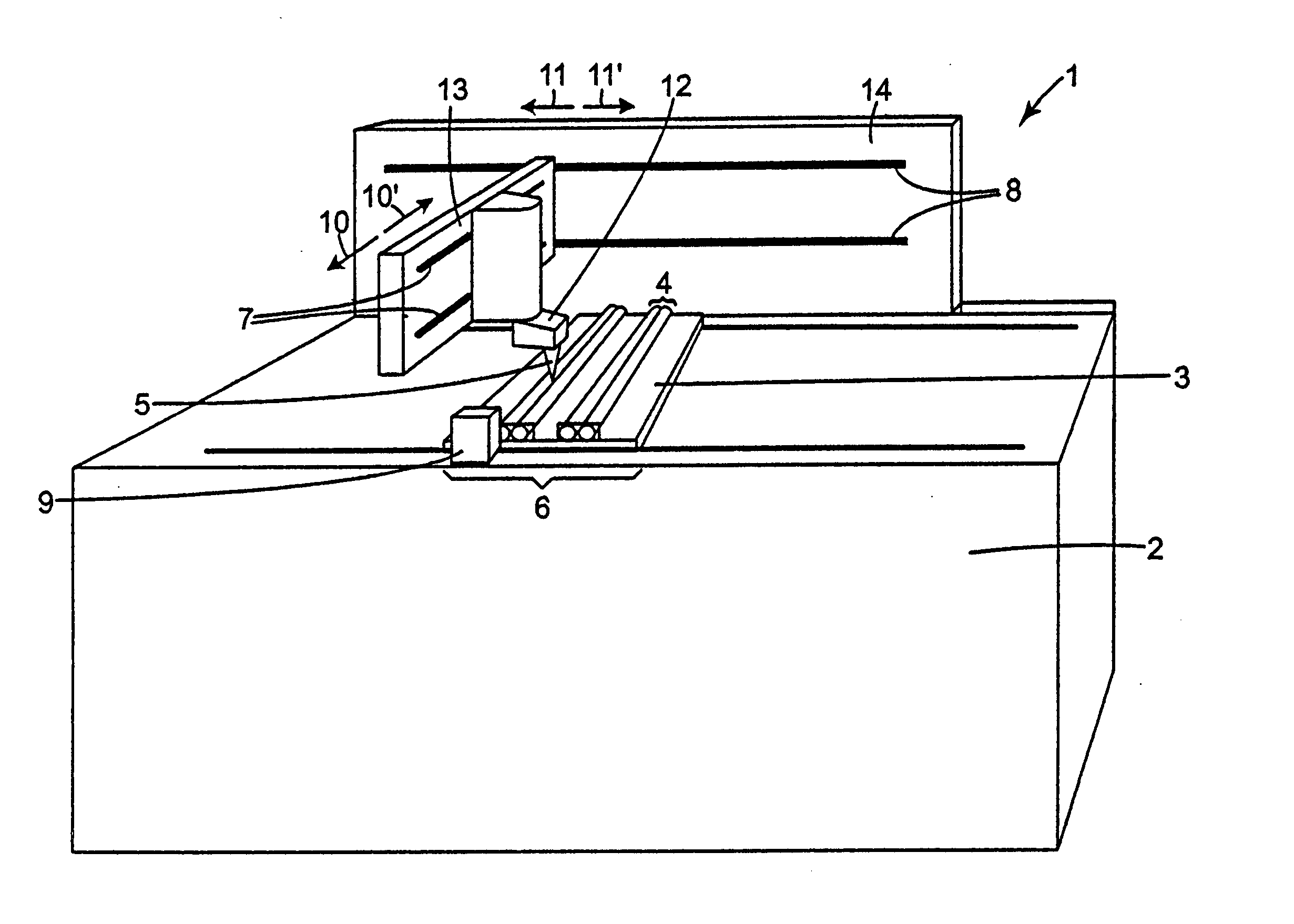
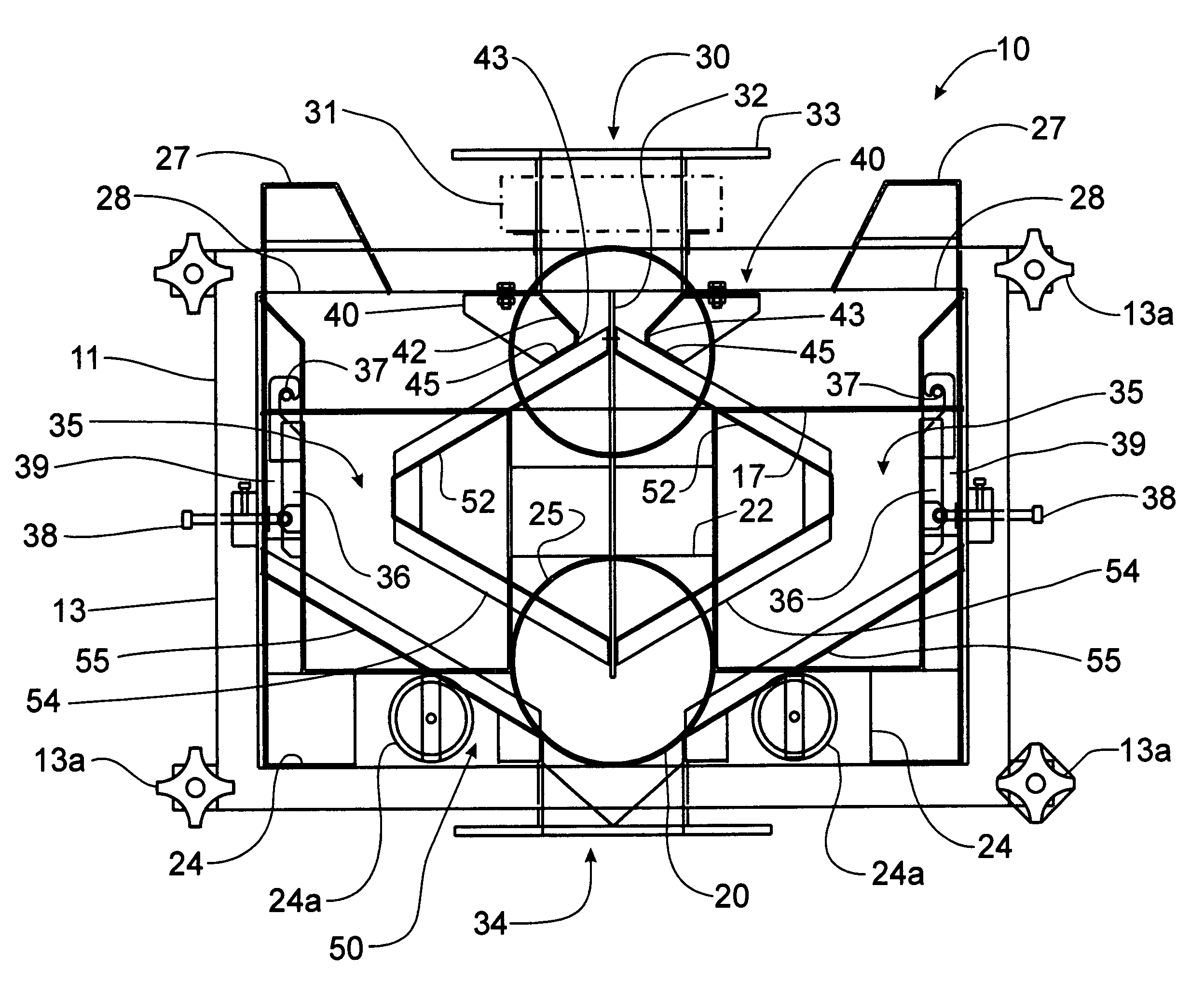
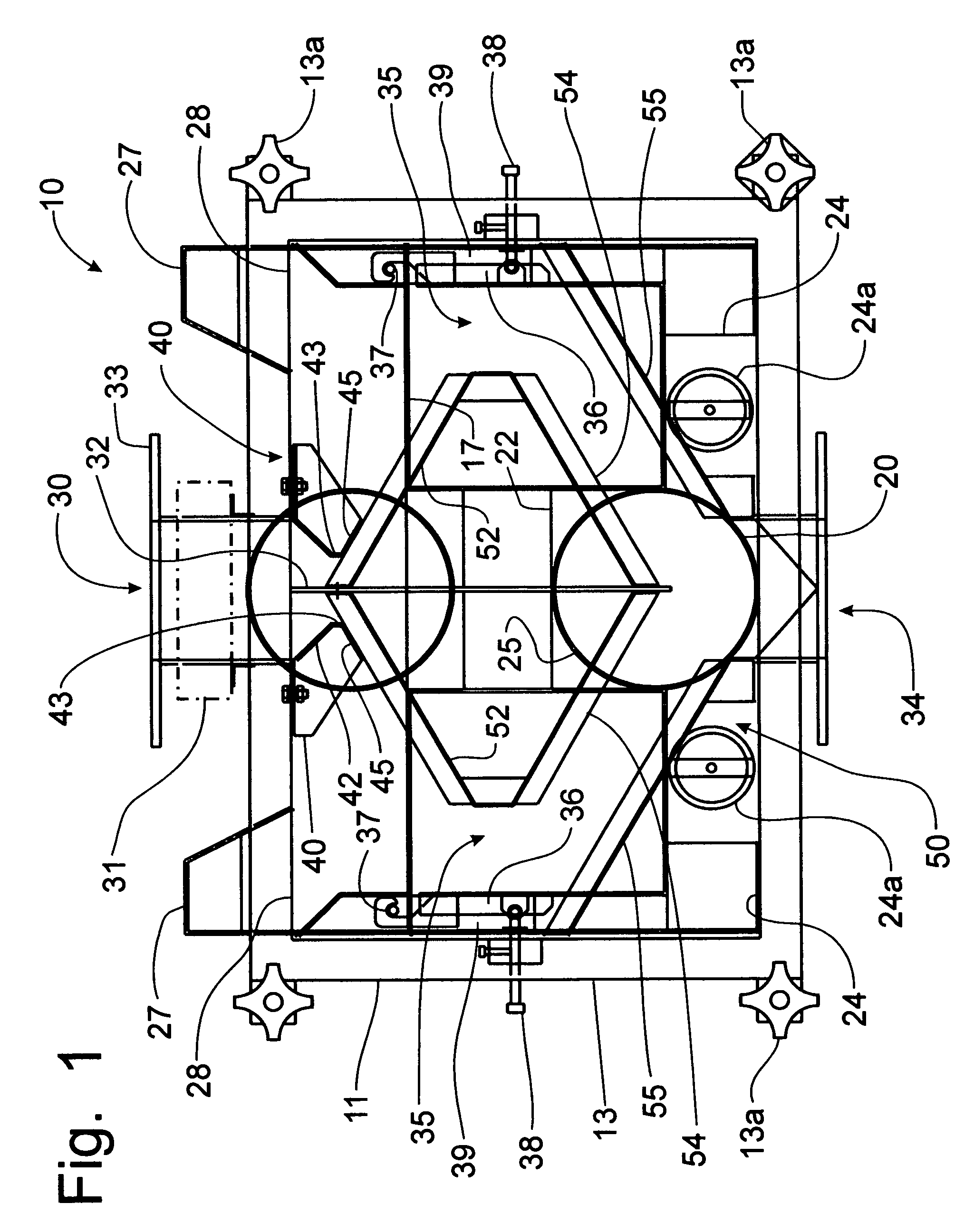
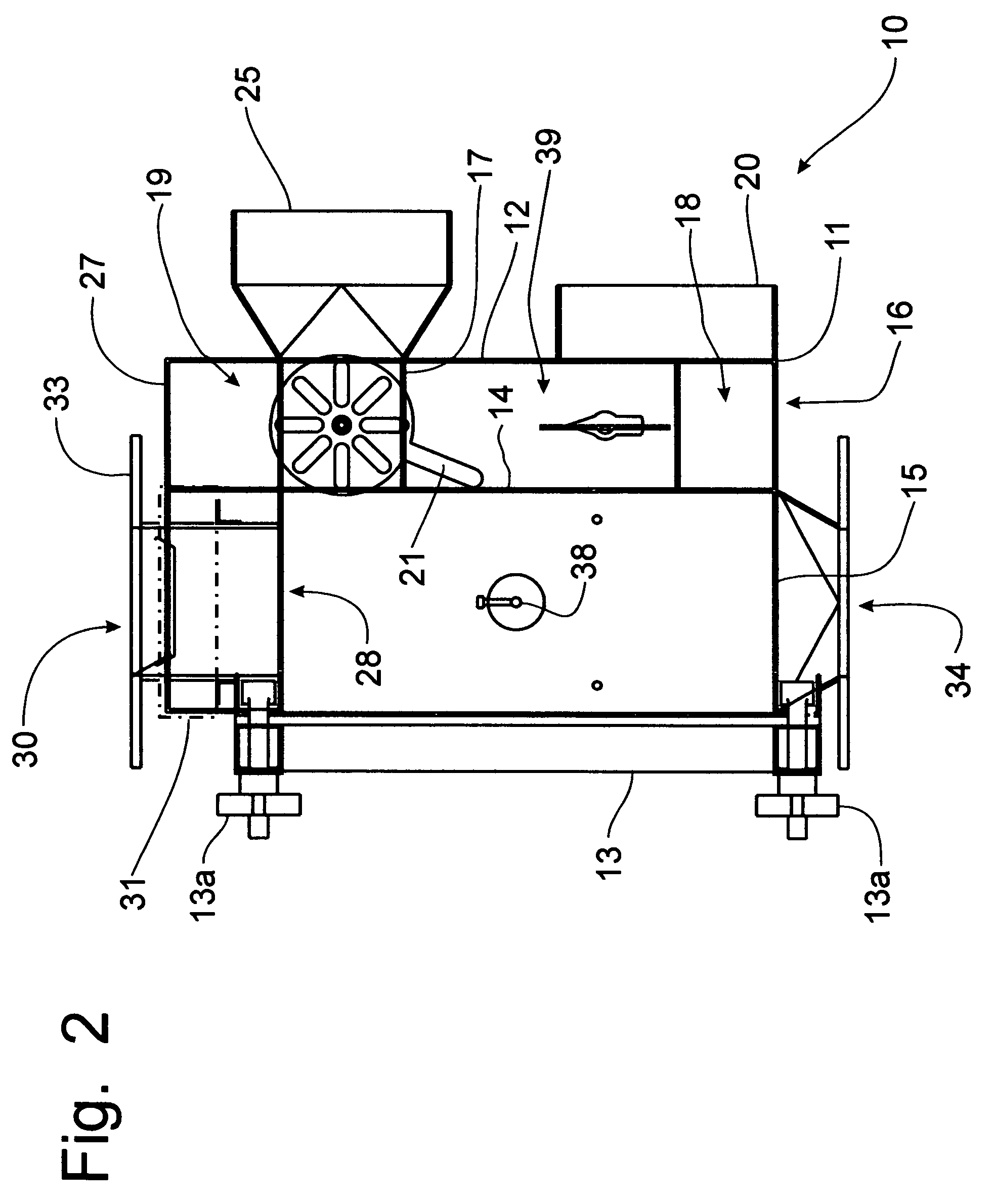
Apparatus for dispensing paper from rolls which feeds continuously, roll to roll, and does not require extra procedure to bring stub roll into position. The apparatus has device for holding and positioning at least first and second rolls of paper with respect to each other; device for dispensing paper from the first roll; device for dispensing paper from the first and second rolls simultaneously when the first roll reduces to a predetermined diameter of paper, device for positioning the depleted first roll for replacement without the necessity of removing the second roll; and device for dispensing from the second and replacement rolls simultaneously when the second roll reduces to a predetermined diameter of paper. The apparatus also has a proximity sensor, which senses when a hand is placed near the dispenser, and thereupon dispenses a set amount of towel. The dispenser incorporates device for dissipating static charges to a local ground.
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
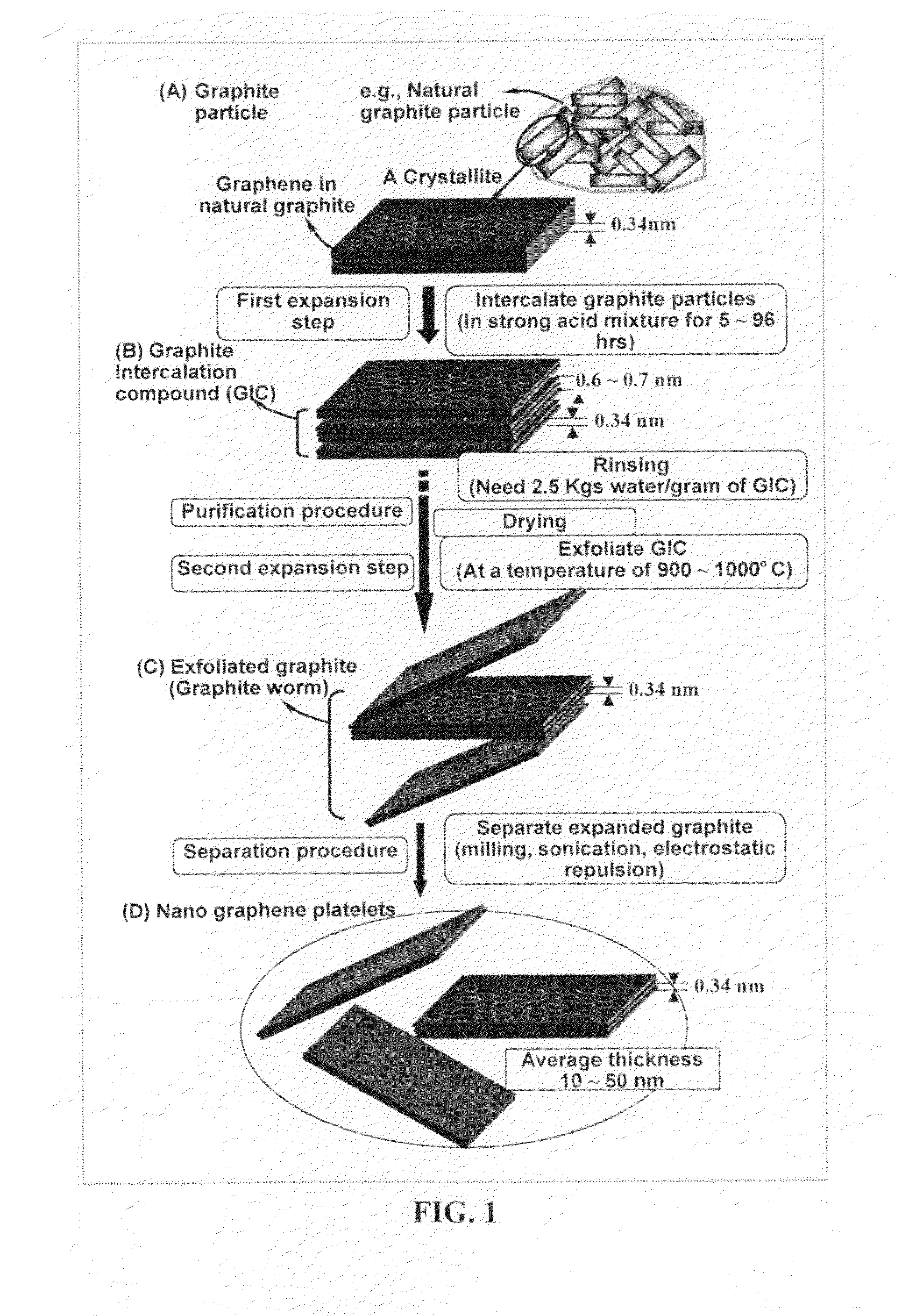
Process for producing dispersible Nano Graphene Platelets from oxidized graphite
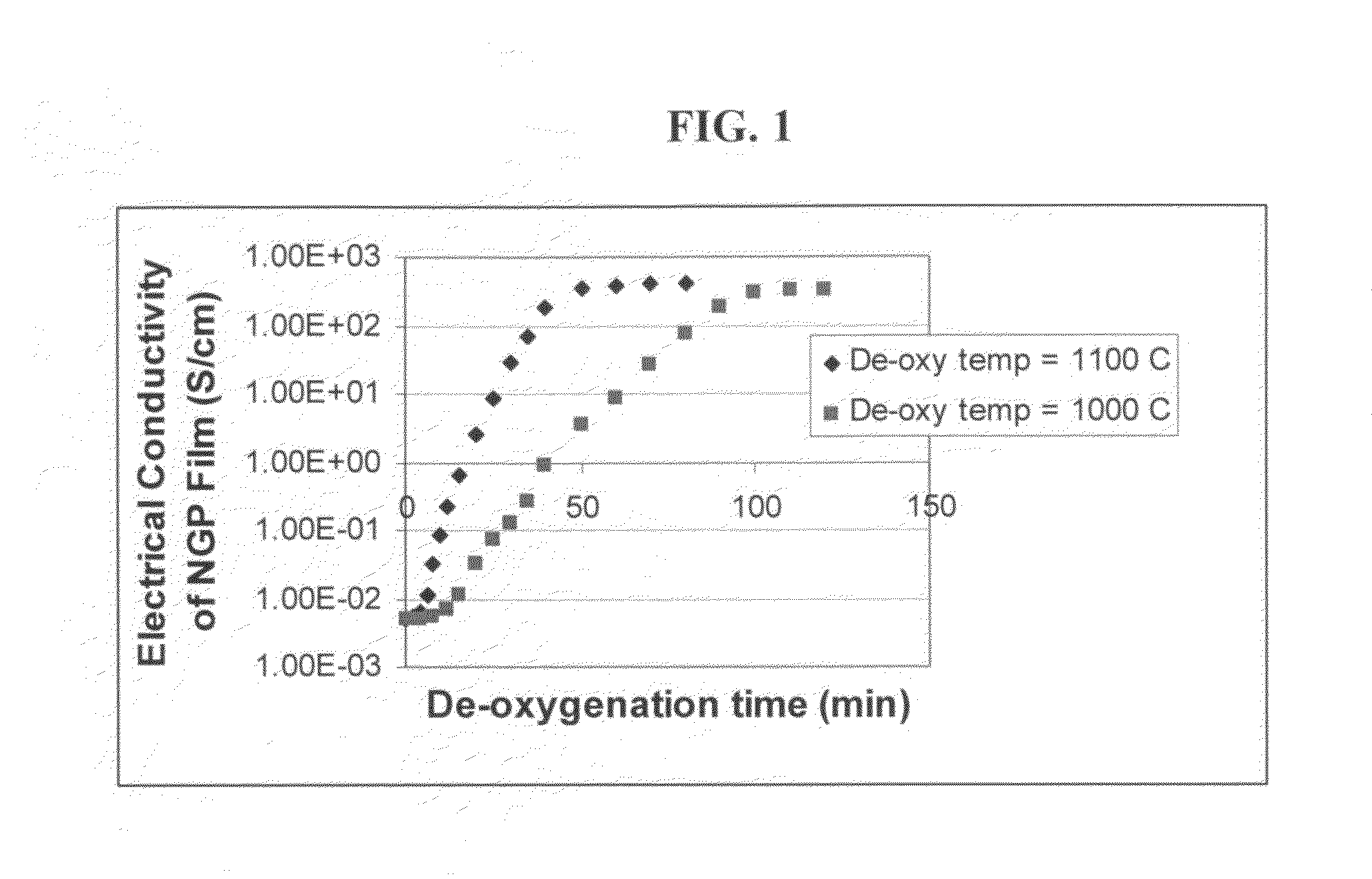
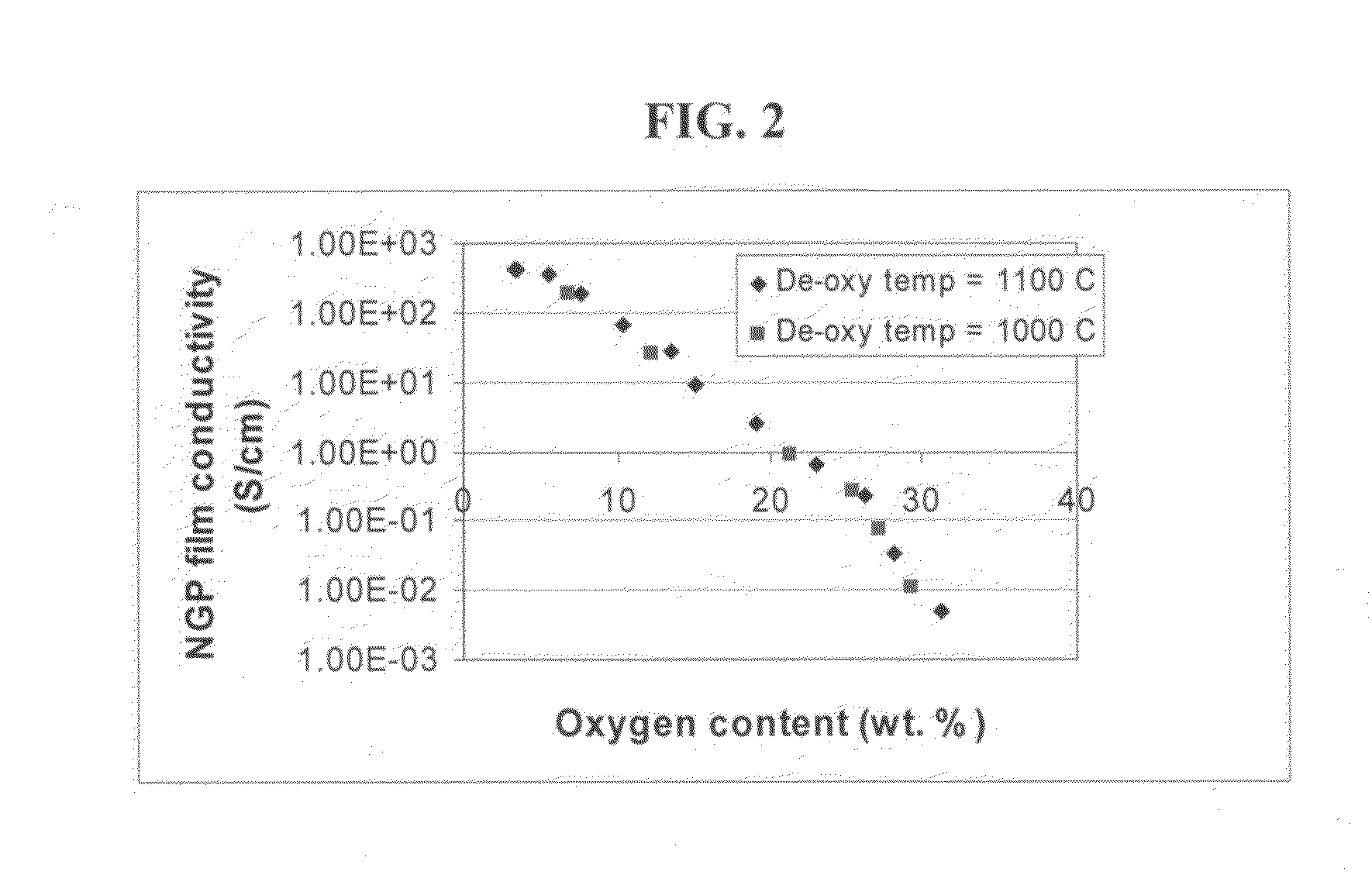
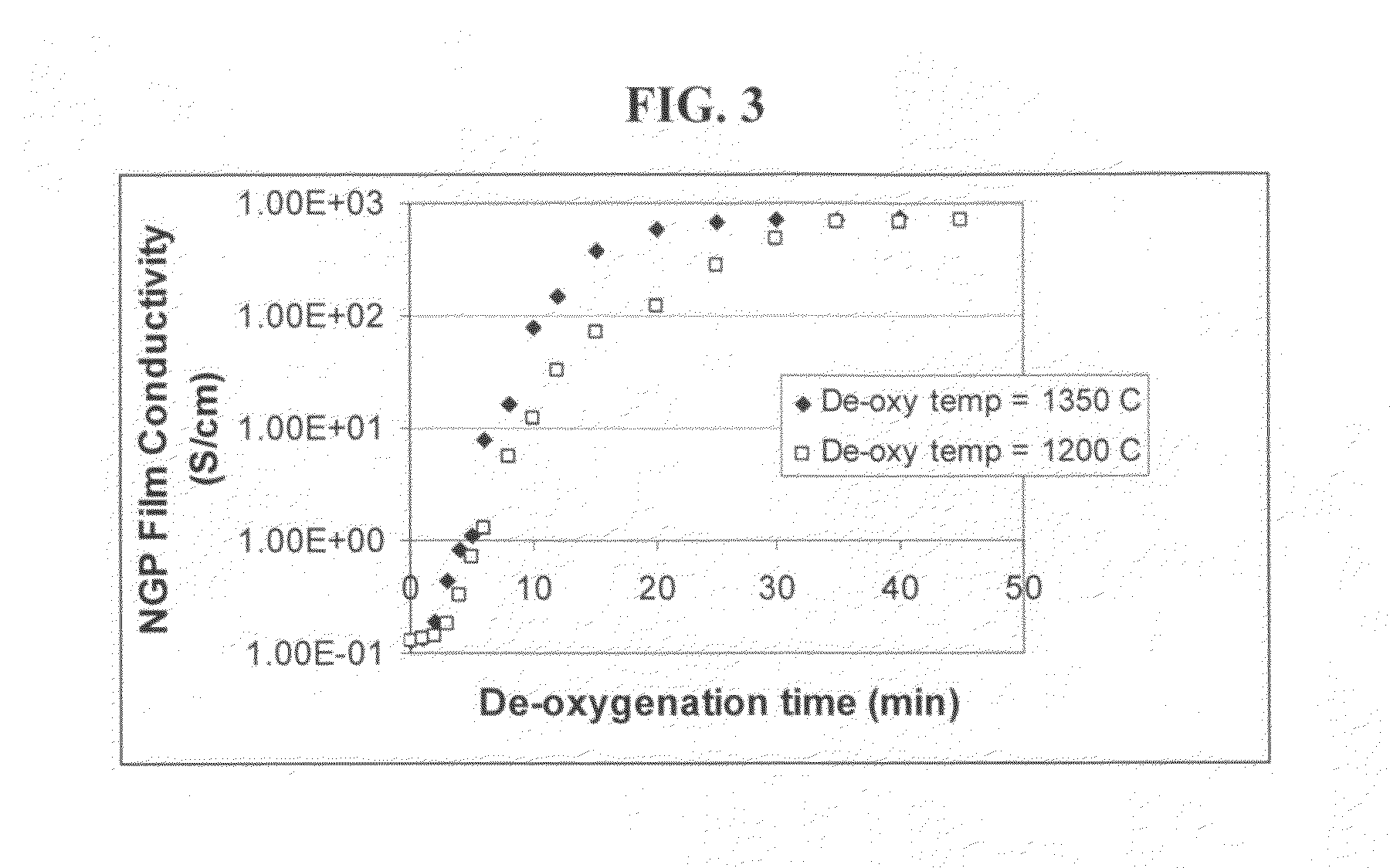
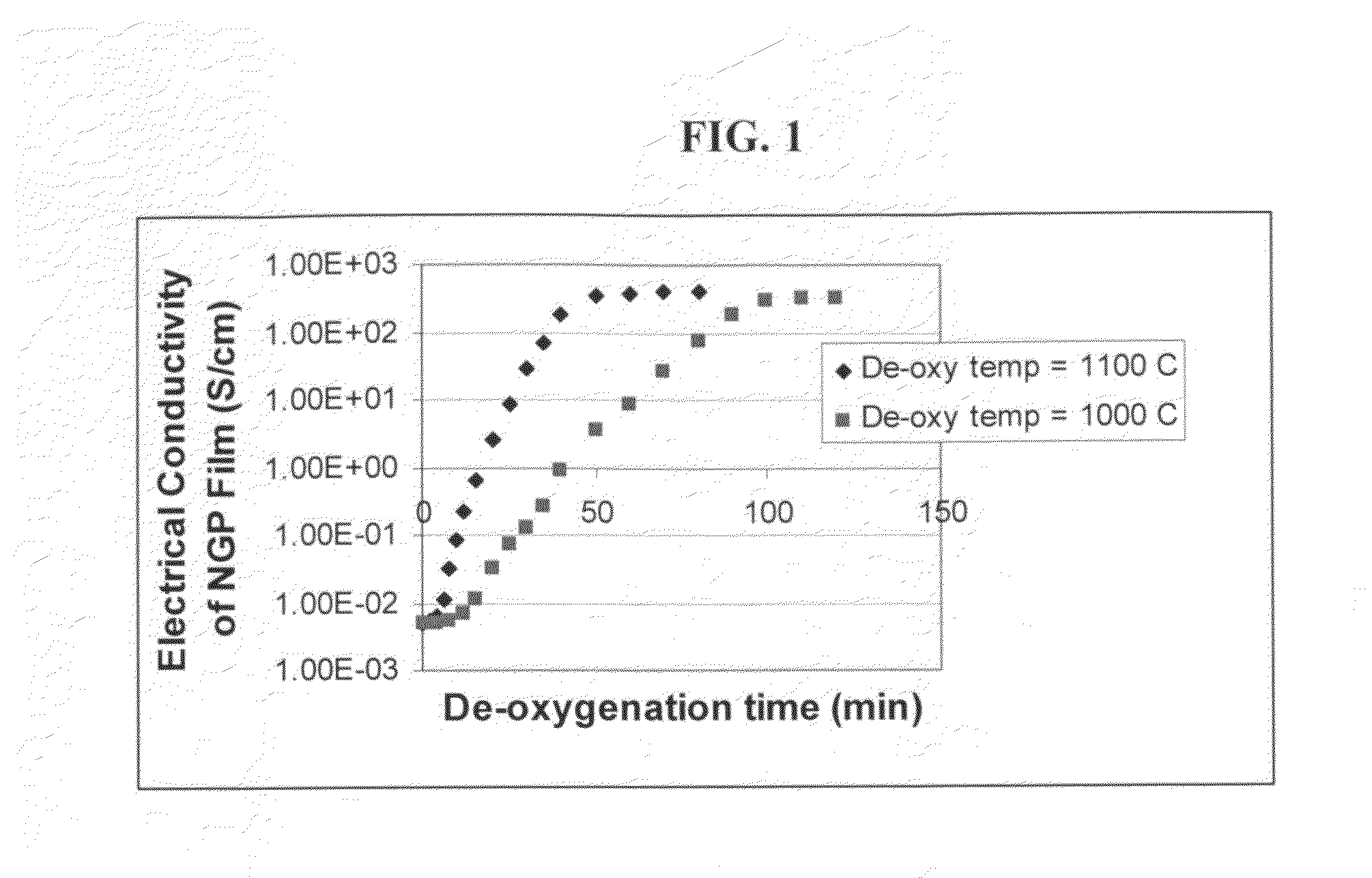
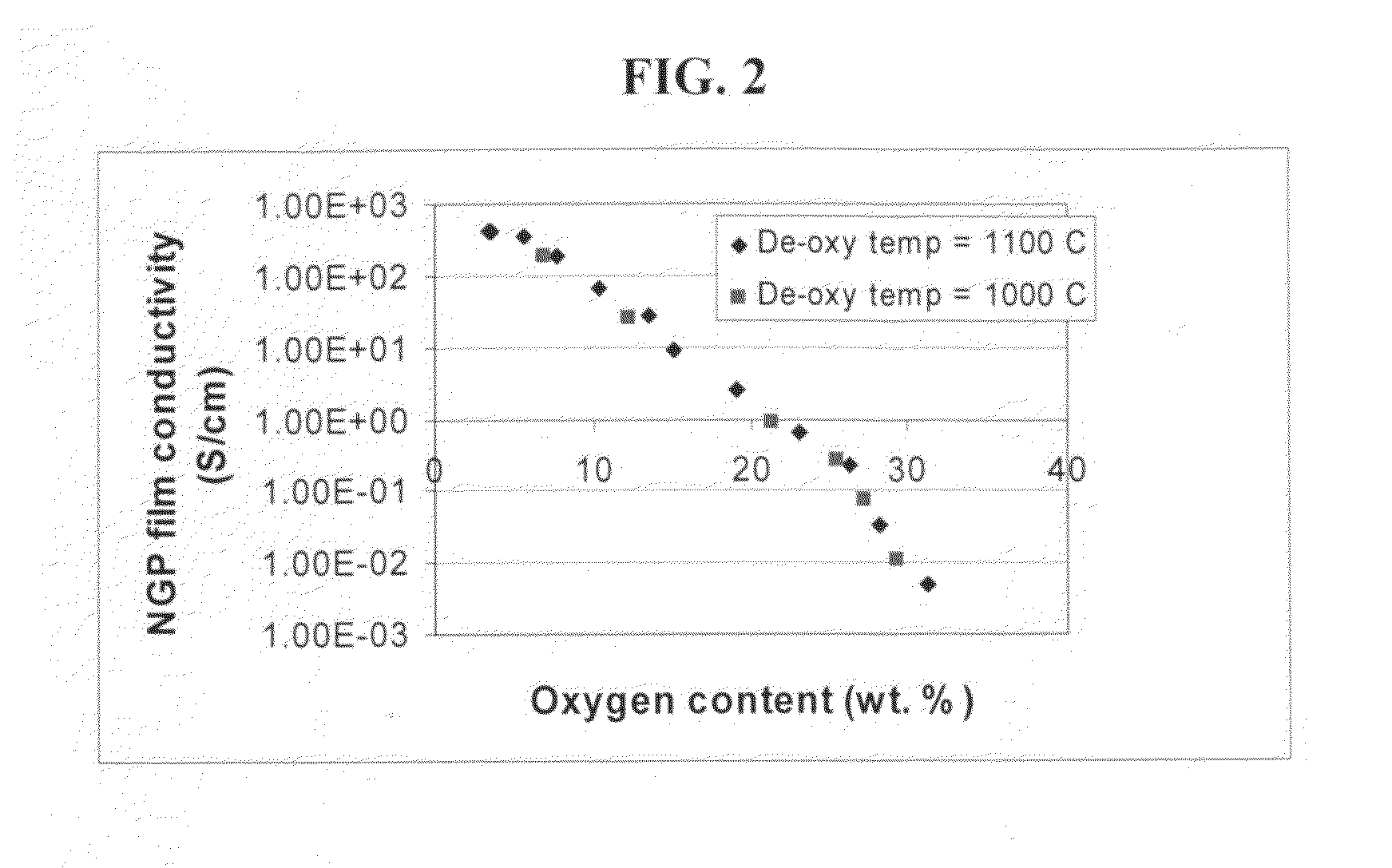
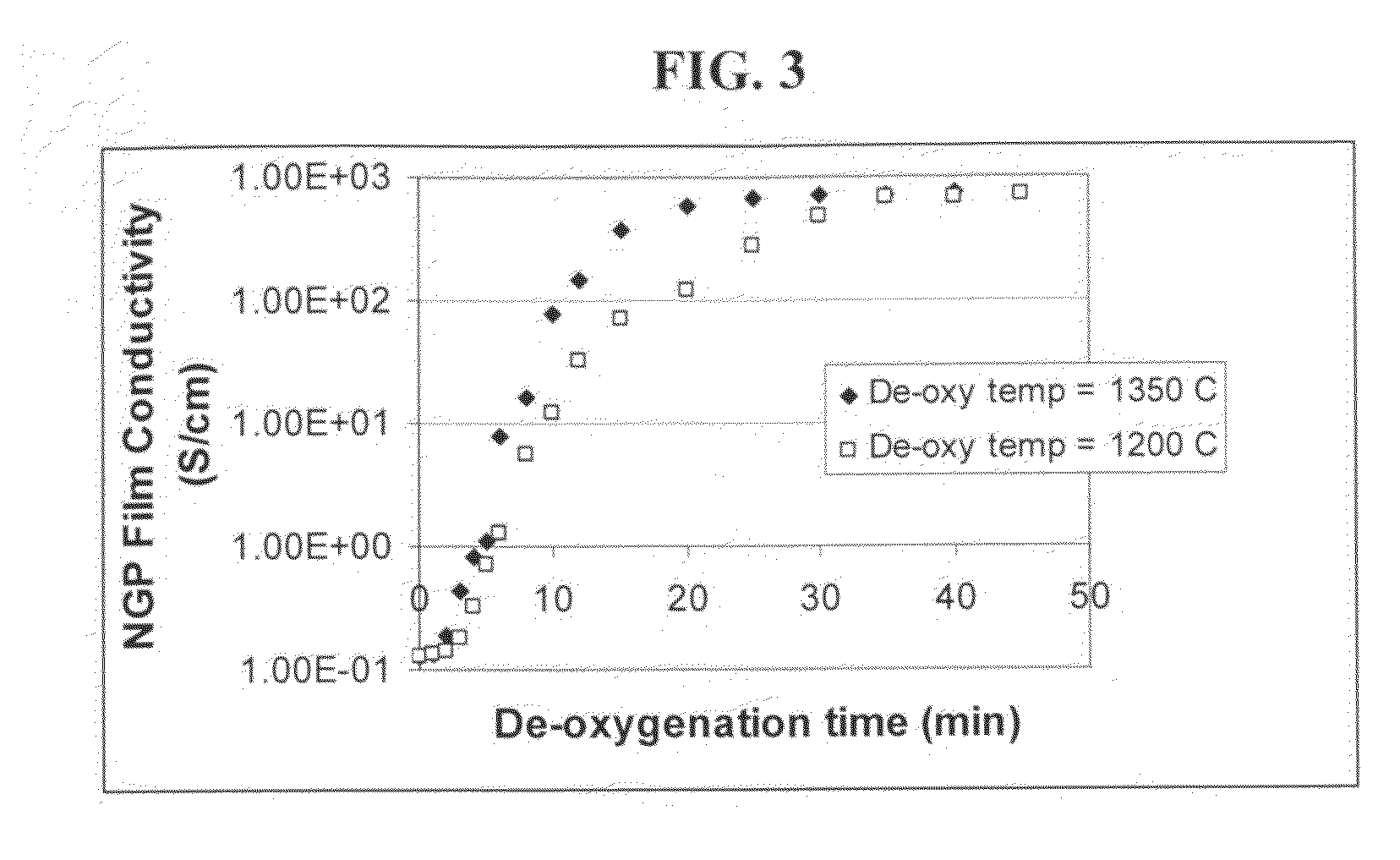
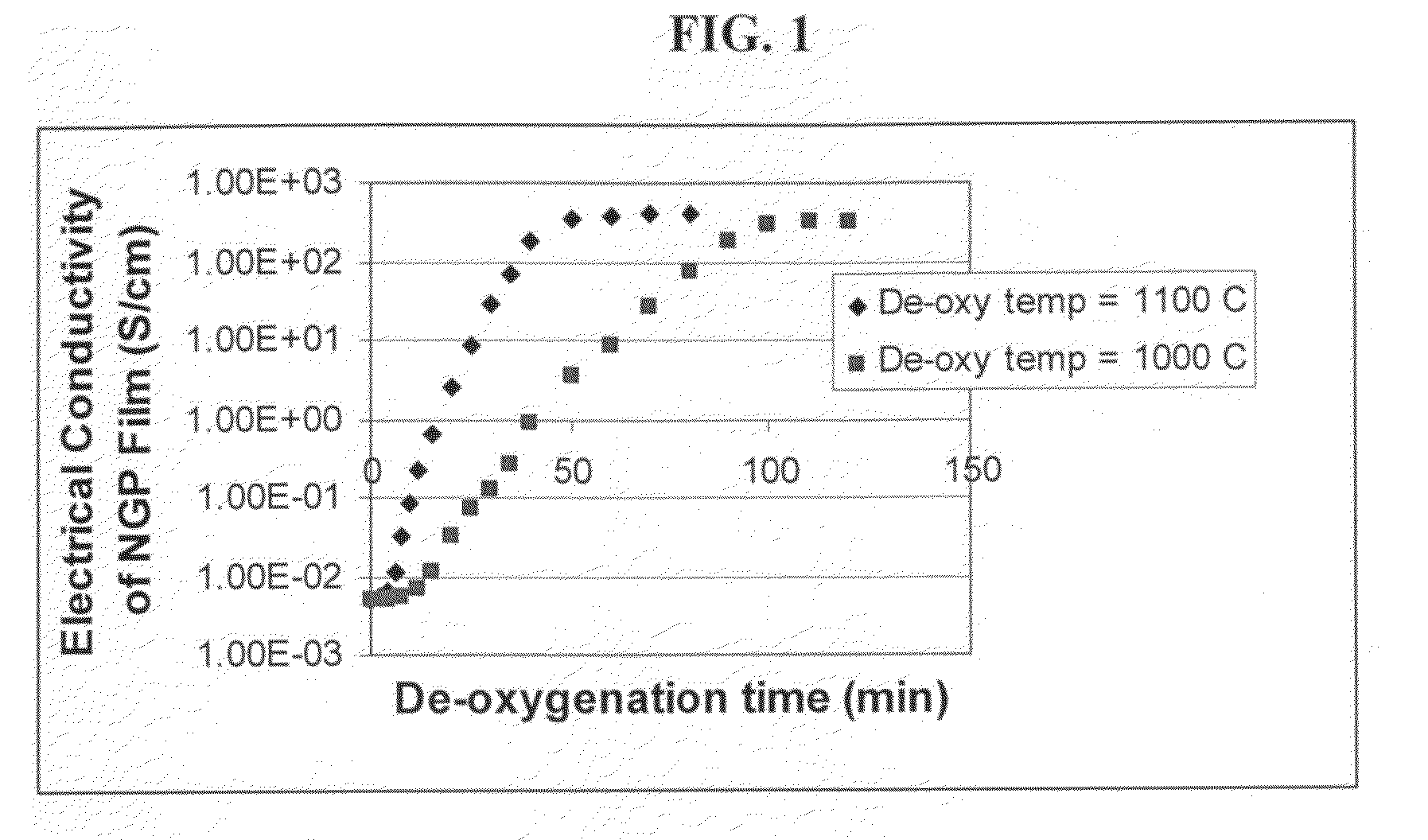
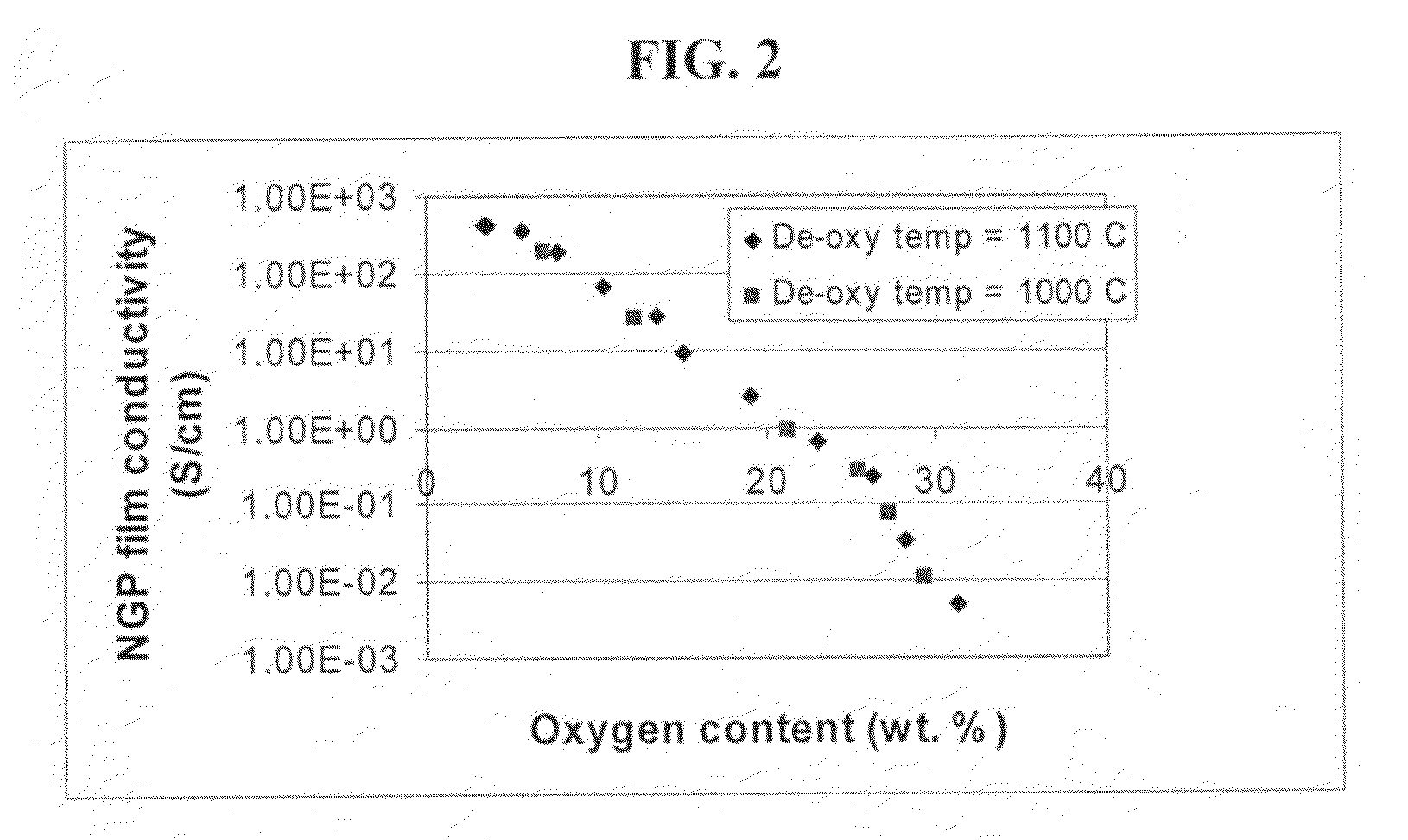
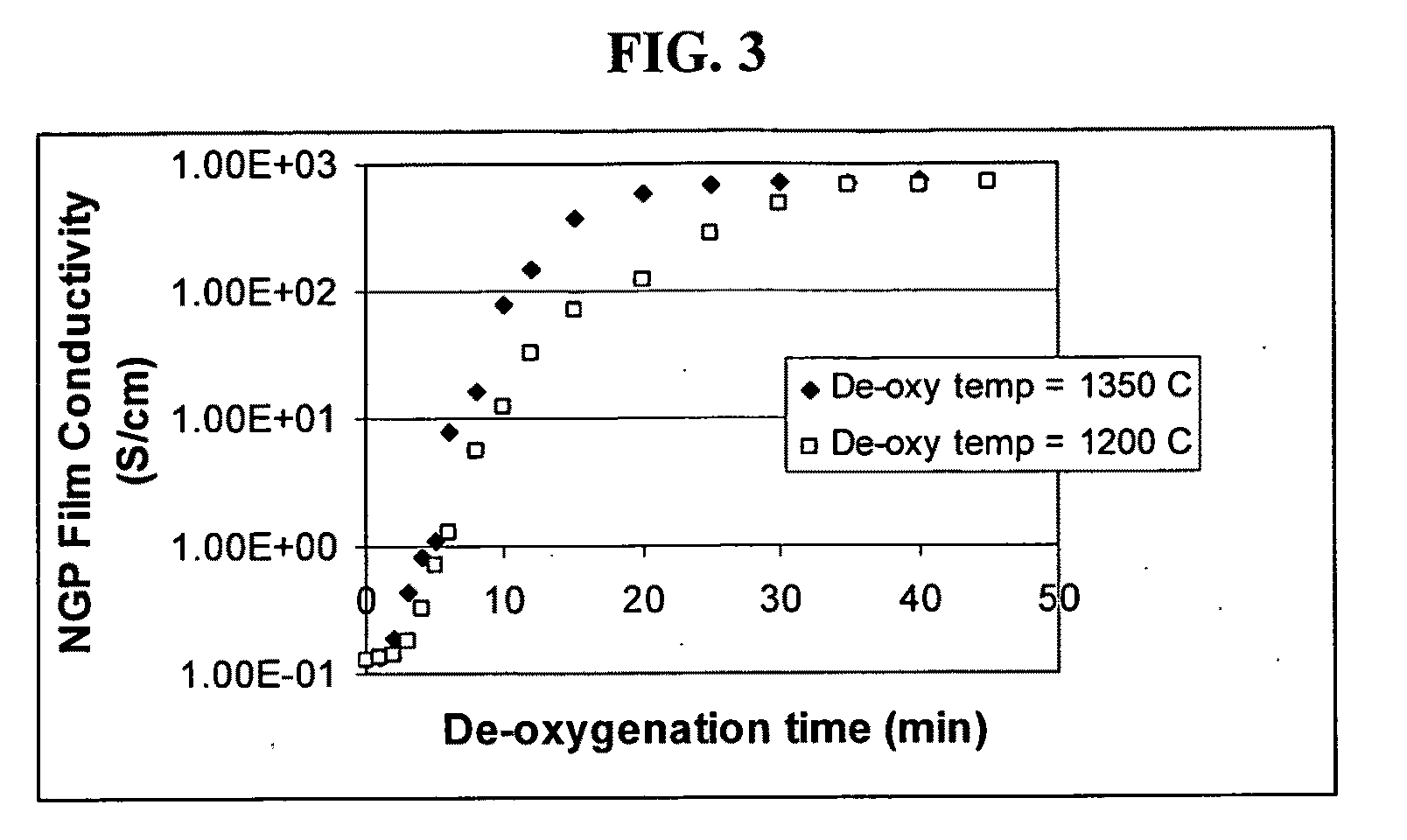
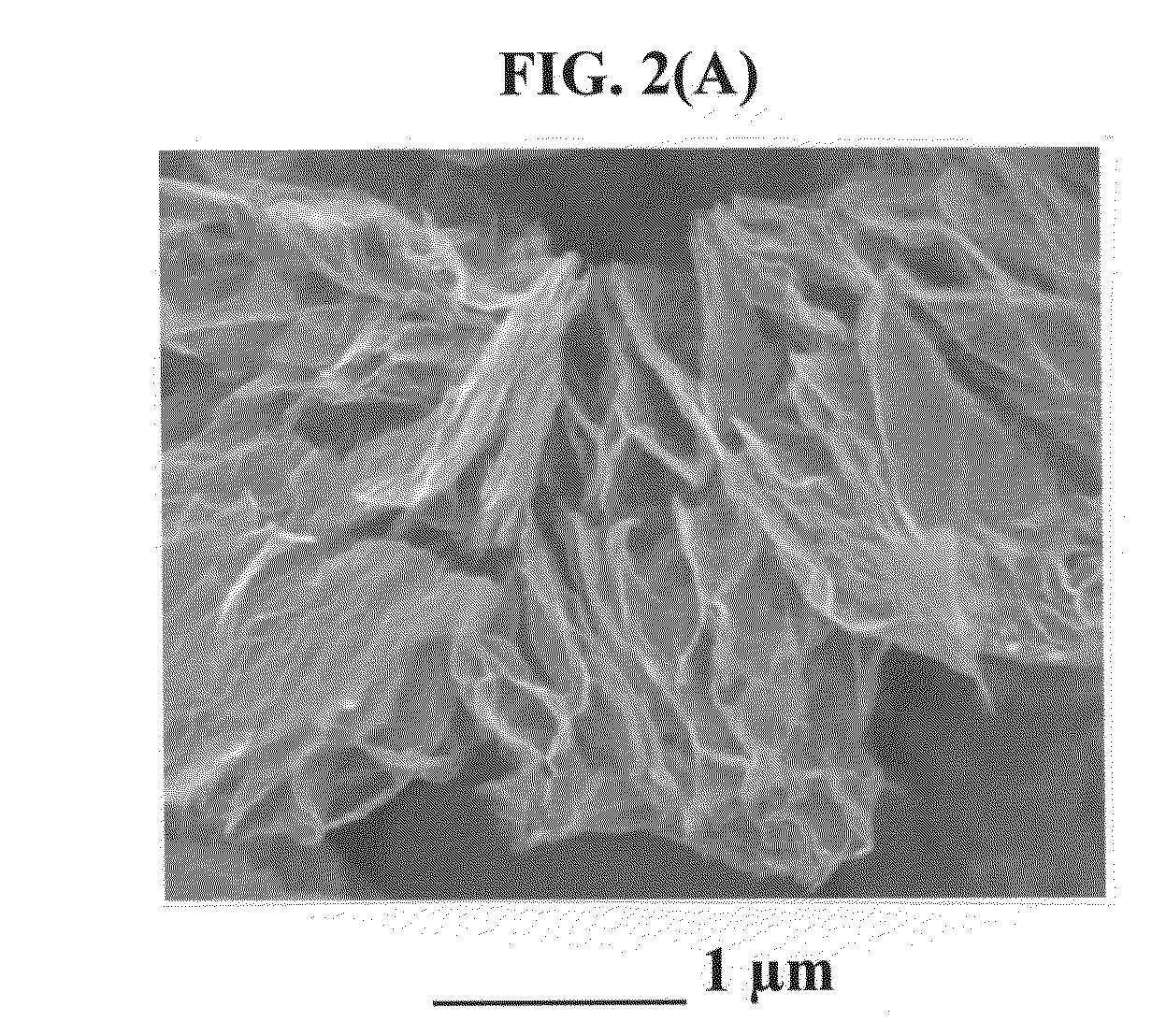
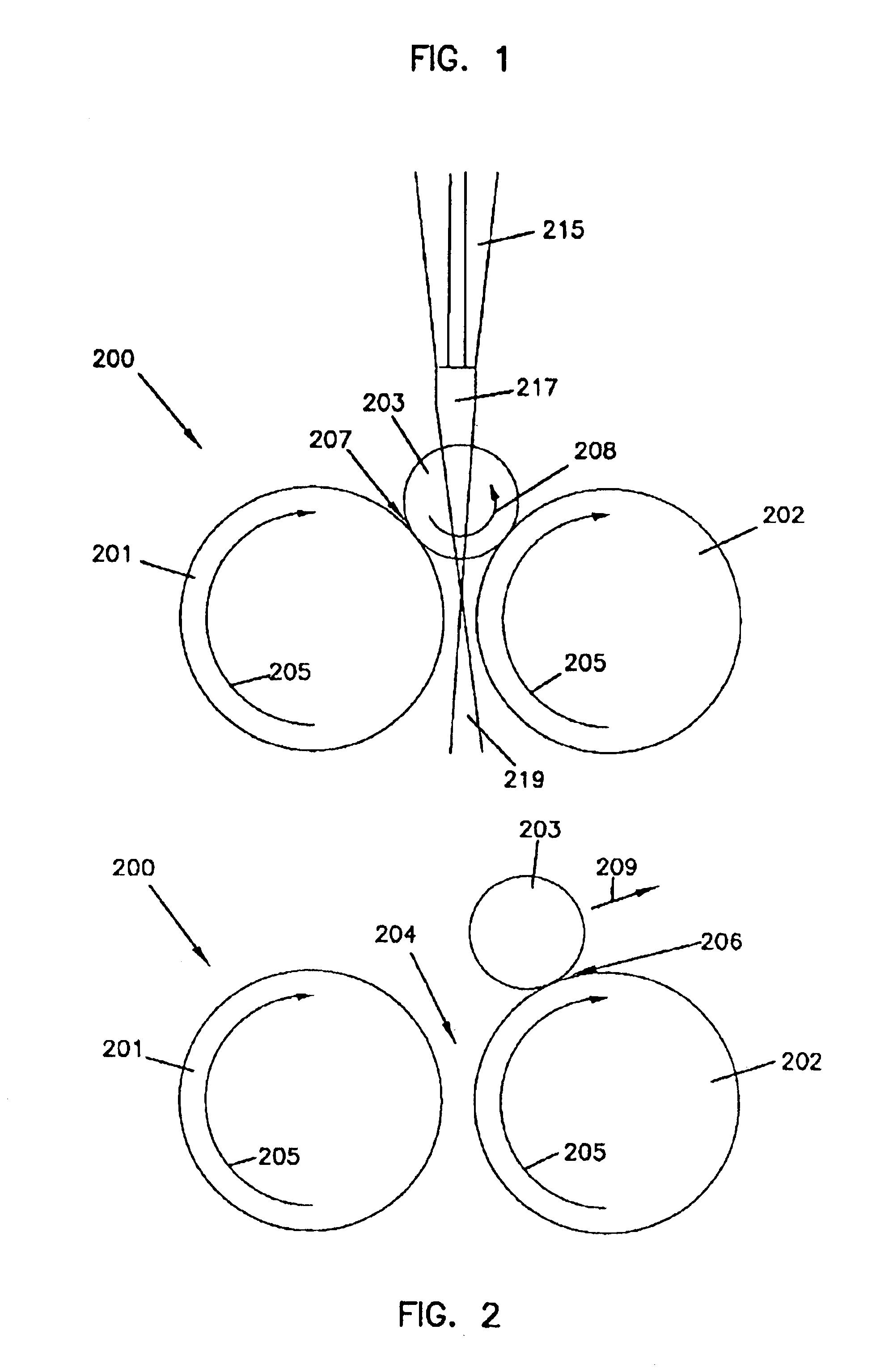
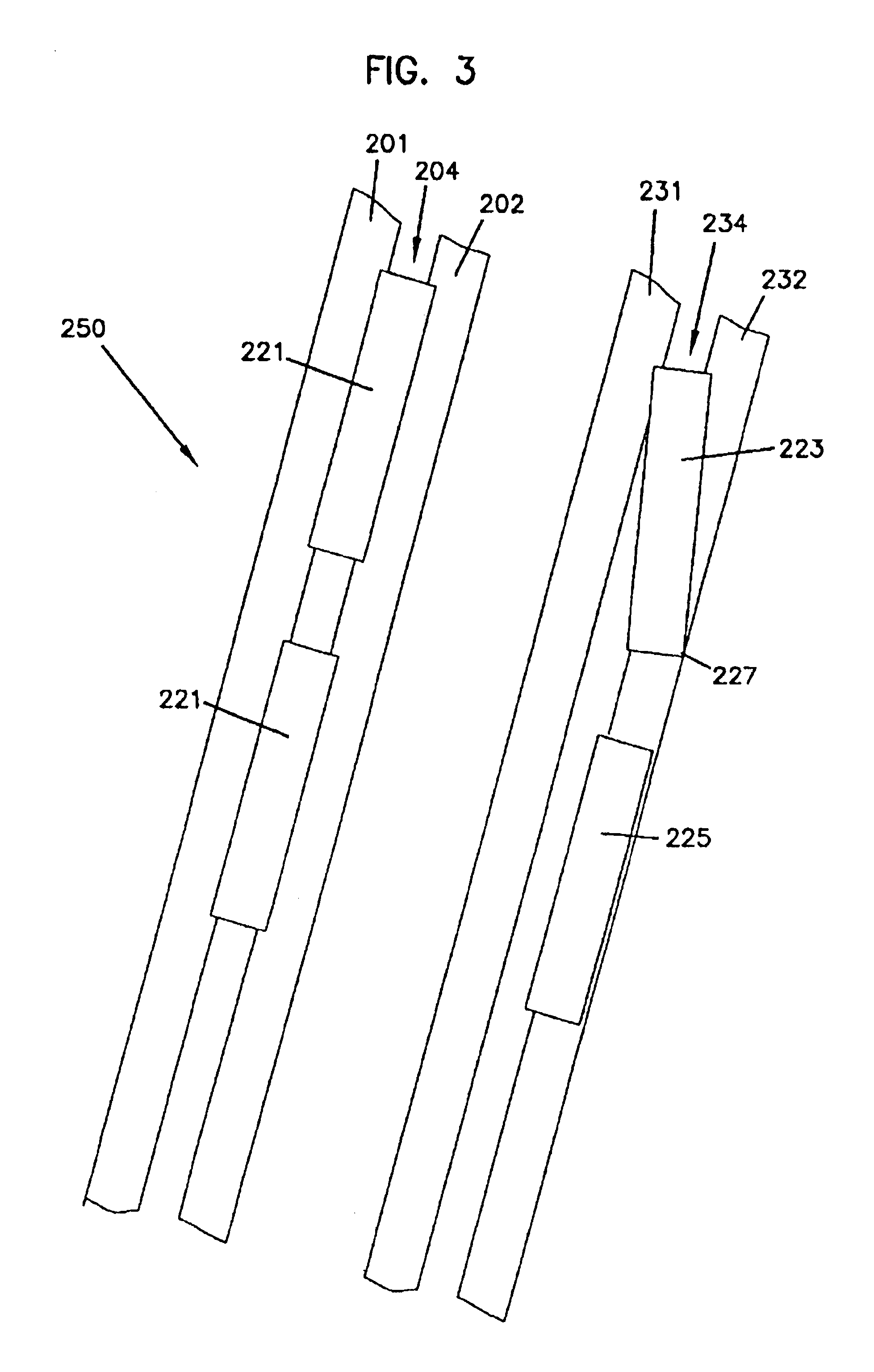
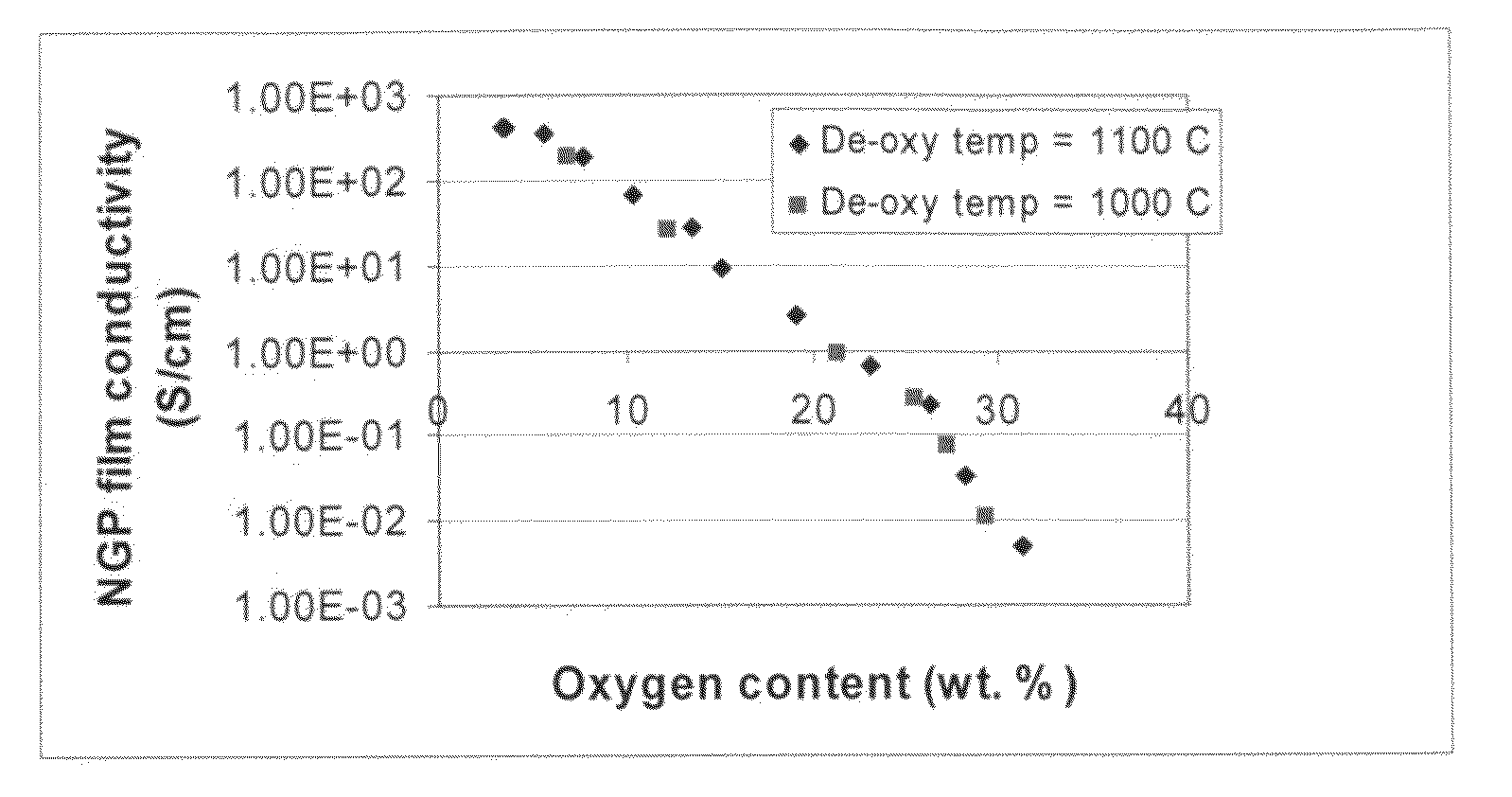
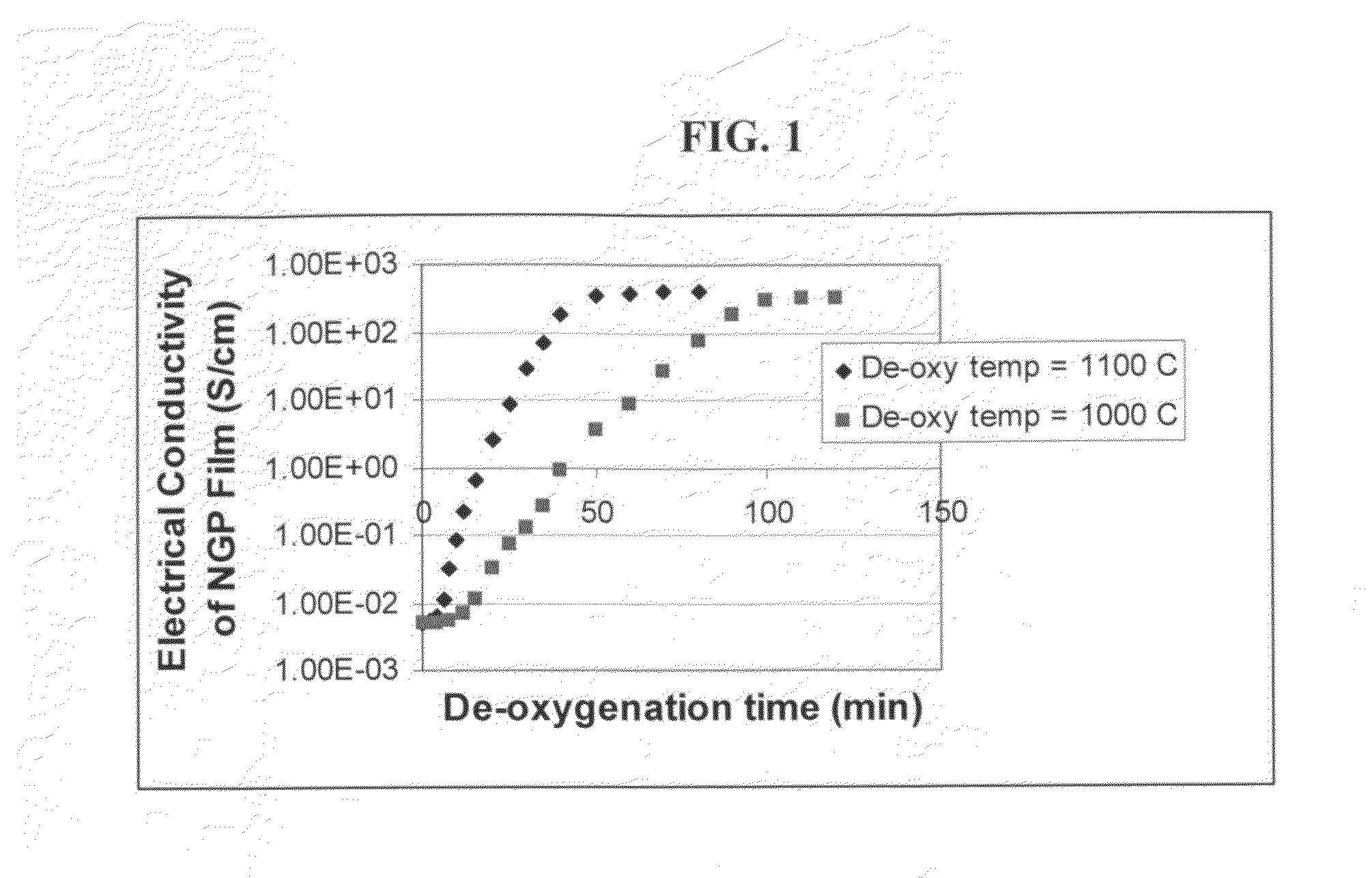
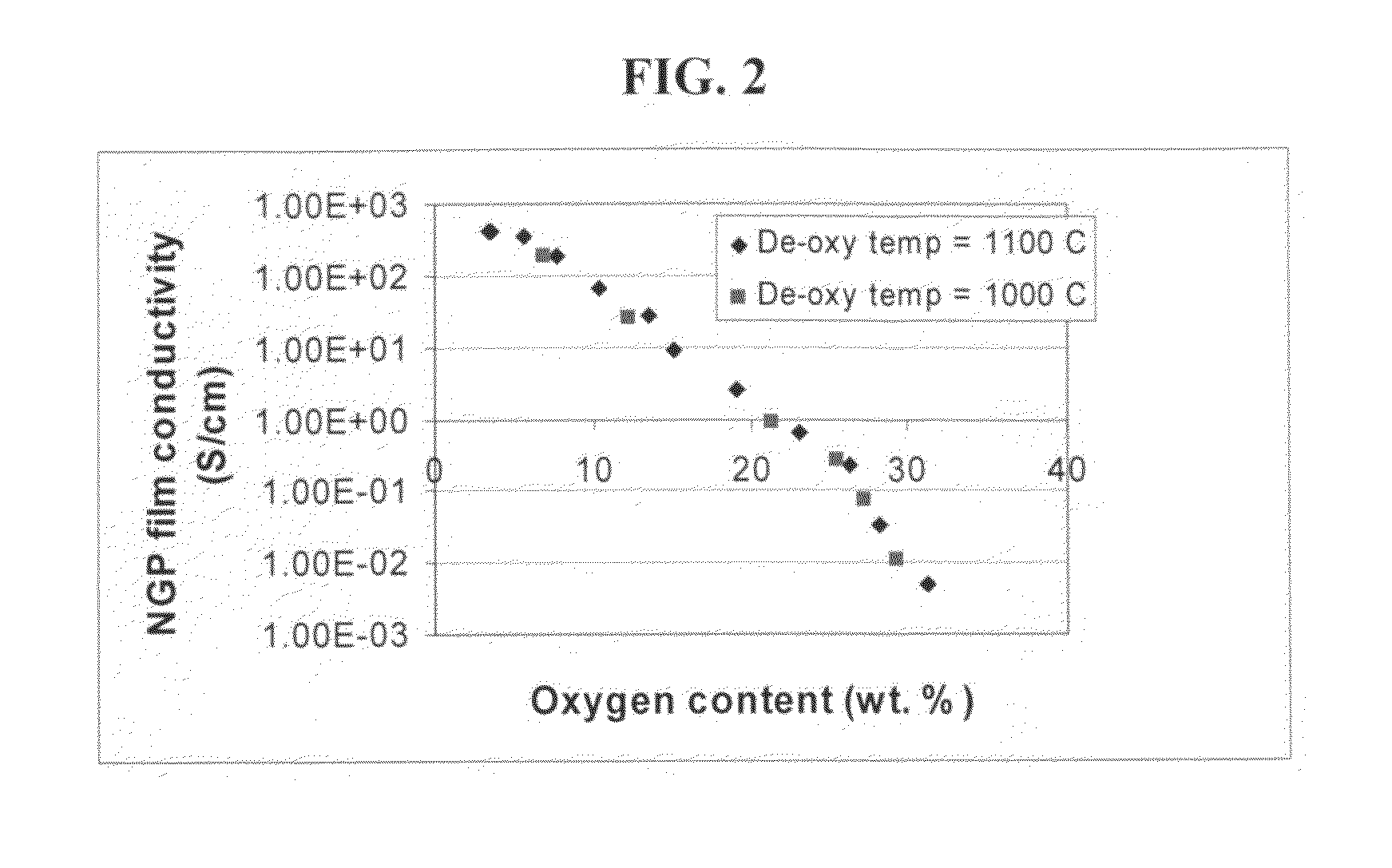
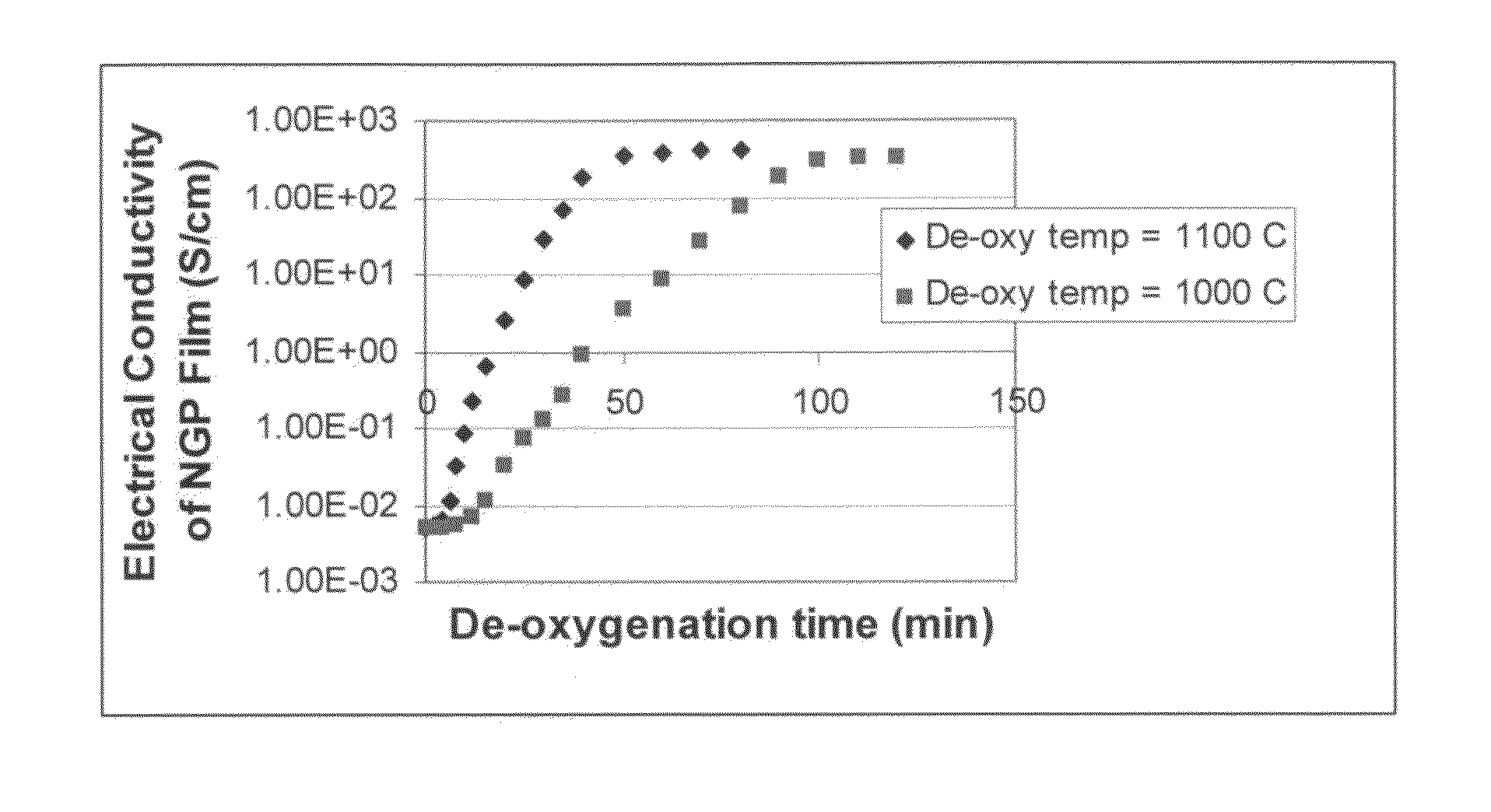
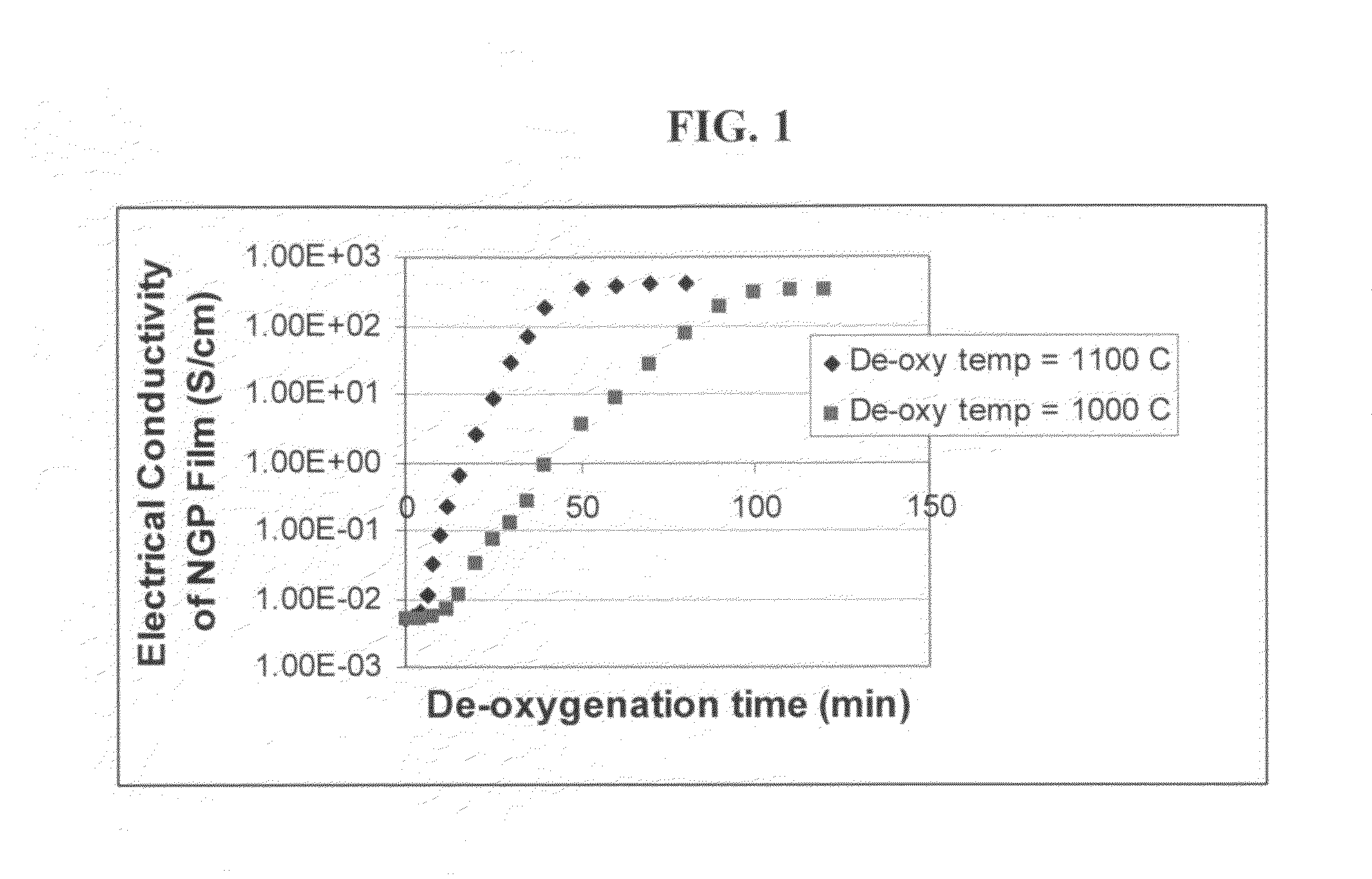
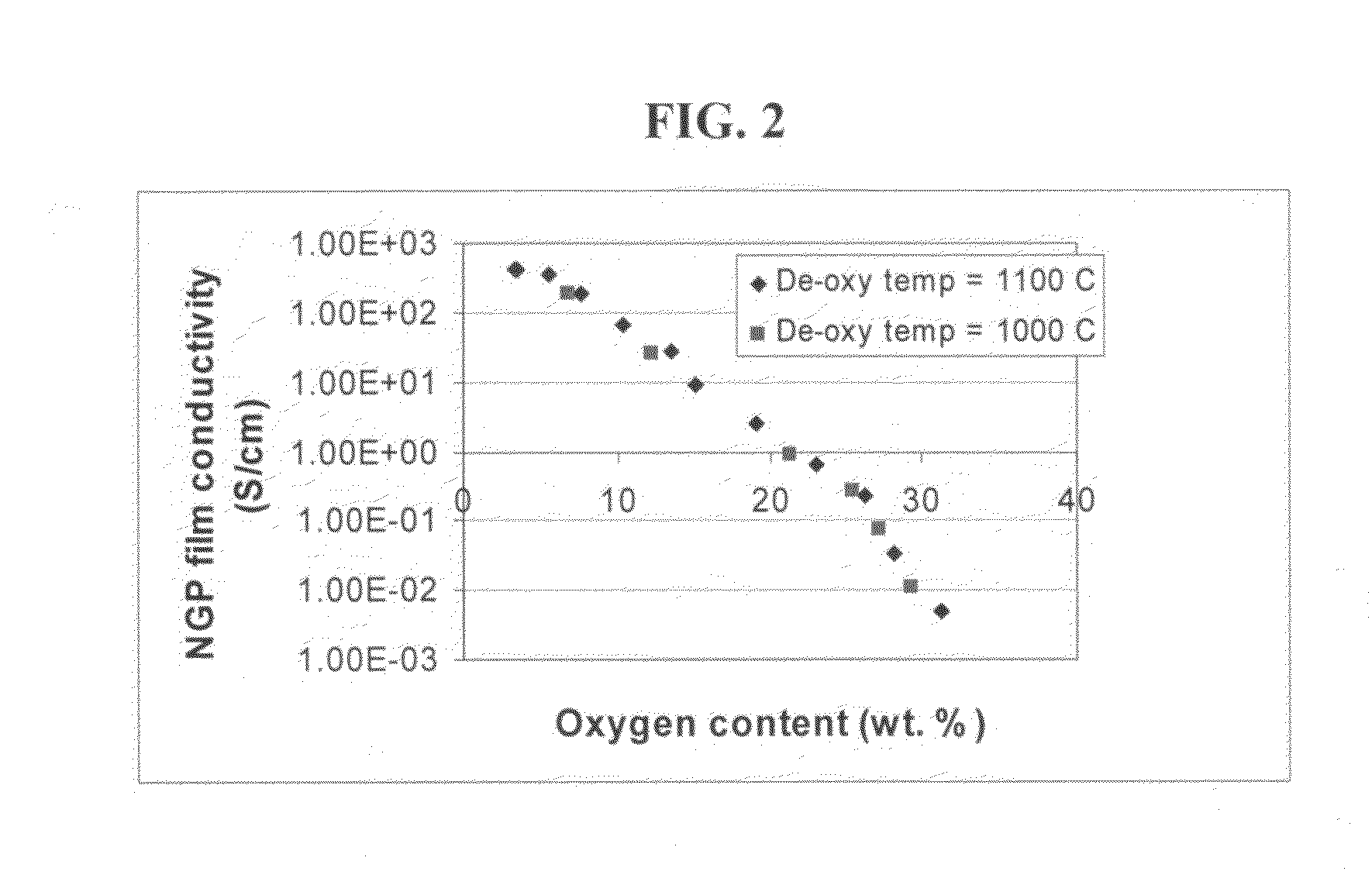
The present invention provides a process for producing nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are dispersible and conducting. The process comprises: (a) preparing a graphite intercalation compound (GIC) or graphite oxide (GO) from a laminar graphite material; (b) exposing the GIC or GO to a first temperature for a first period of time to obtain exfoliated graphite; and (c) exposing the exfoliated graphite to a second temperature in a protective atmosphere for a second period of time to obtain the desired dispersible nano graphene platelet with an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight, preferably below 20% by weight, further preferably between 5% and 20% by weight. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Severe weather detector and alarm
InactiveUSRE45514E1Protection lifeProtect propertyHuman health protectionWeather condition predictionExtreme weatherRadio receiver
A compact, portable weather station for predicting local extreme weather conditions and for reporting remote weather conditions. The weather station has sensors for determining local temperature, barometric pressure, humidity, ambient light, and ambient static charge. A microprocessor has memory for storing data relating to past weather conditions and data processing apparatus and algorithms for determining probable developing weather conditions responsive to sensed local conditions. The weather station has a radio receiver for communicating with global weather reporting communications systems utilizing cellular communications. Operating commands, predicted local weather conditions, and remote weather conditions are annunciated in synthesized voice in any one of a variety of predetermined languages. The weather station includes voice synthesizing and recognition apparatus for annunciating verbal prompts and weather conditions, and for responding to vocal control. The weather station is formed in two separable components, one having sensors and the other having radio communications apparatus.
Owner:LA CROSSE TECH IP HLDG
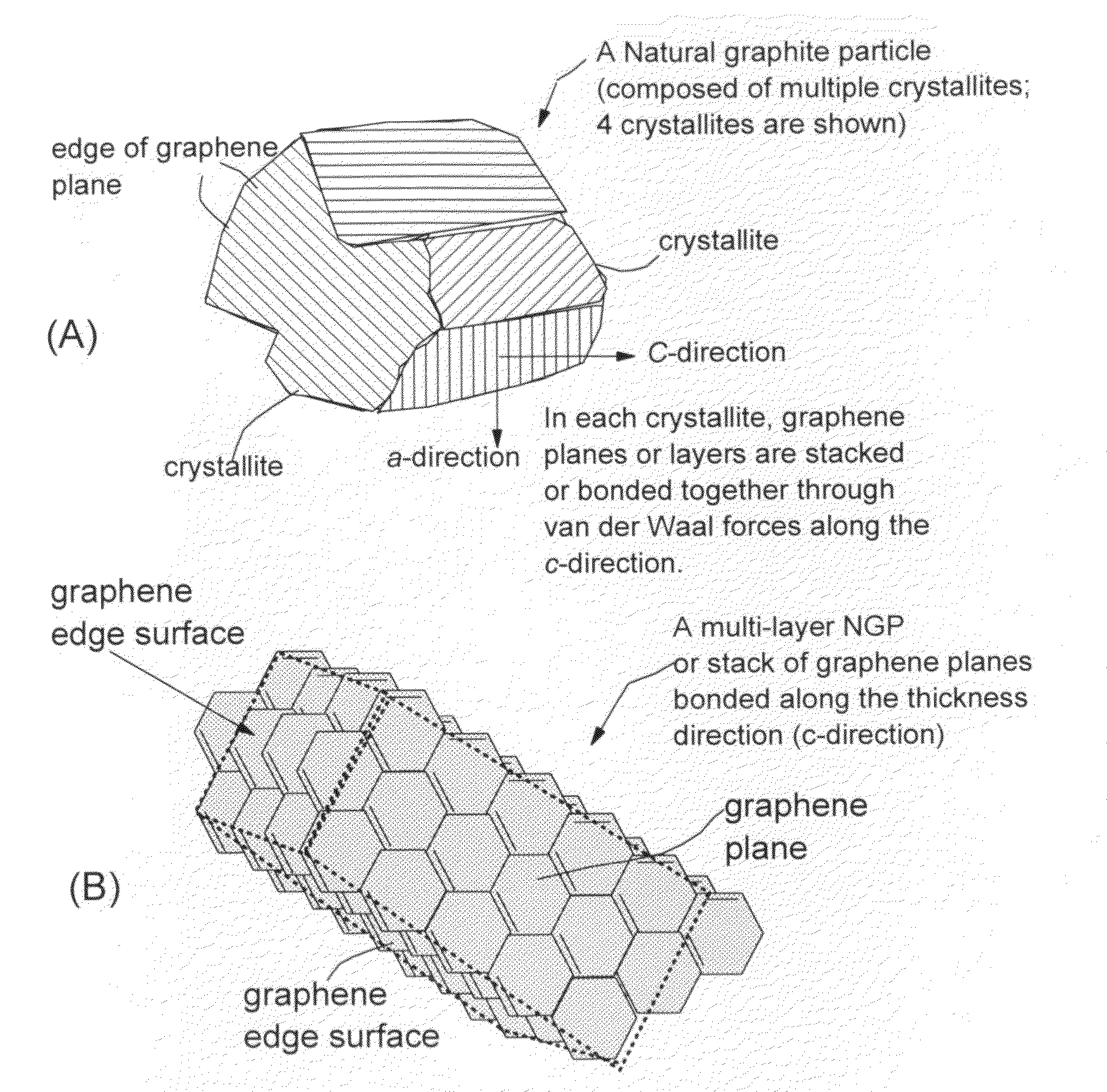
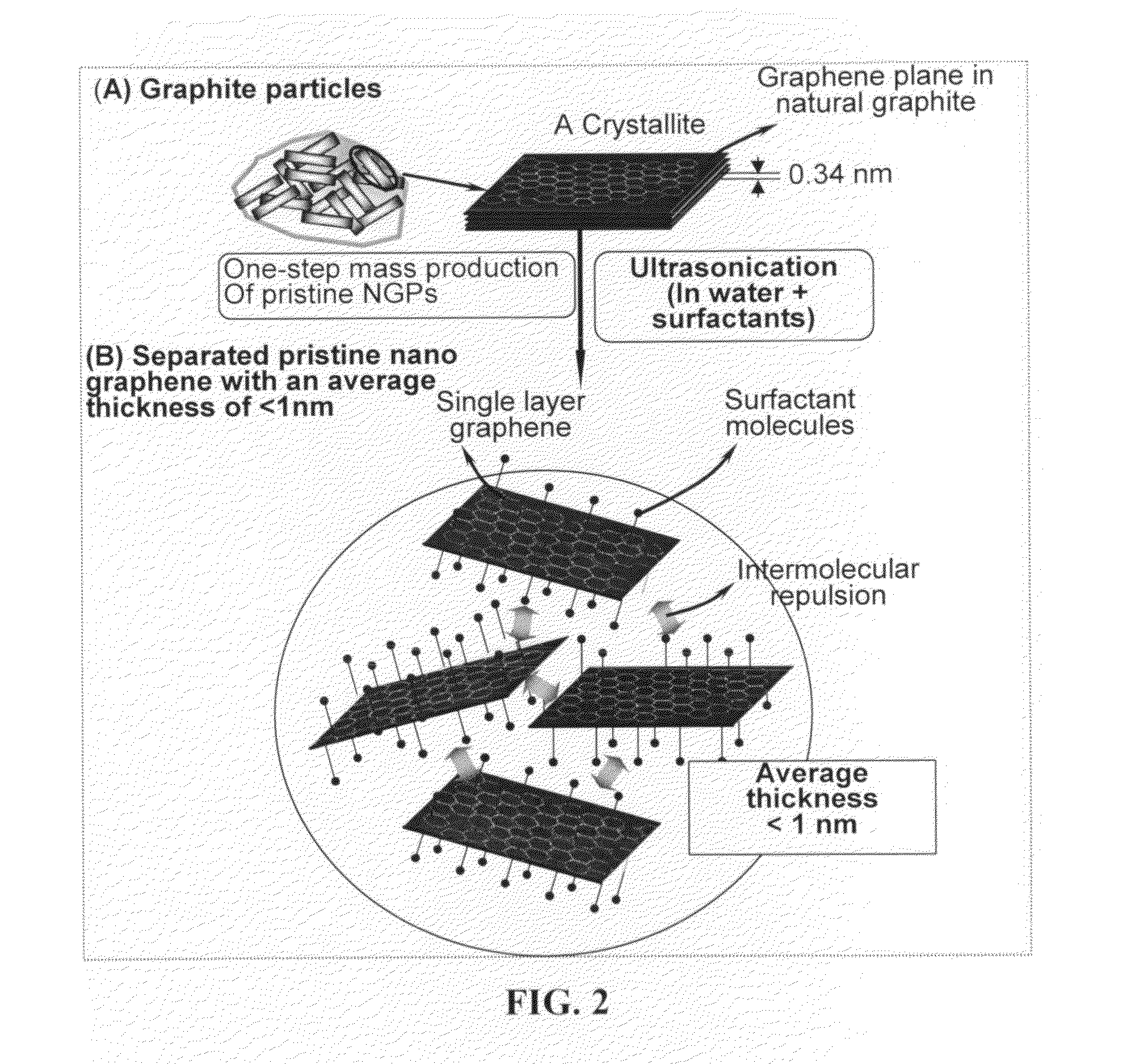
Mass production of pristine nano graphene materials
ActiveUS20110017585A1Reduce surface tensionImprove production yieldMaterial nanotechnologyGrapheneLiquid mediumDisplay device
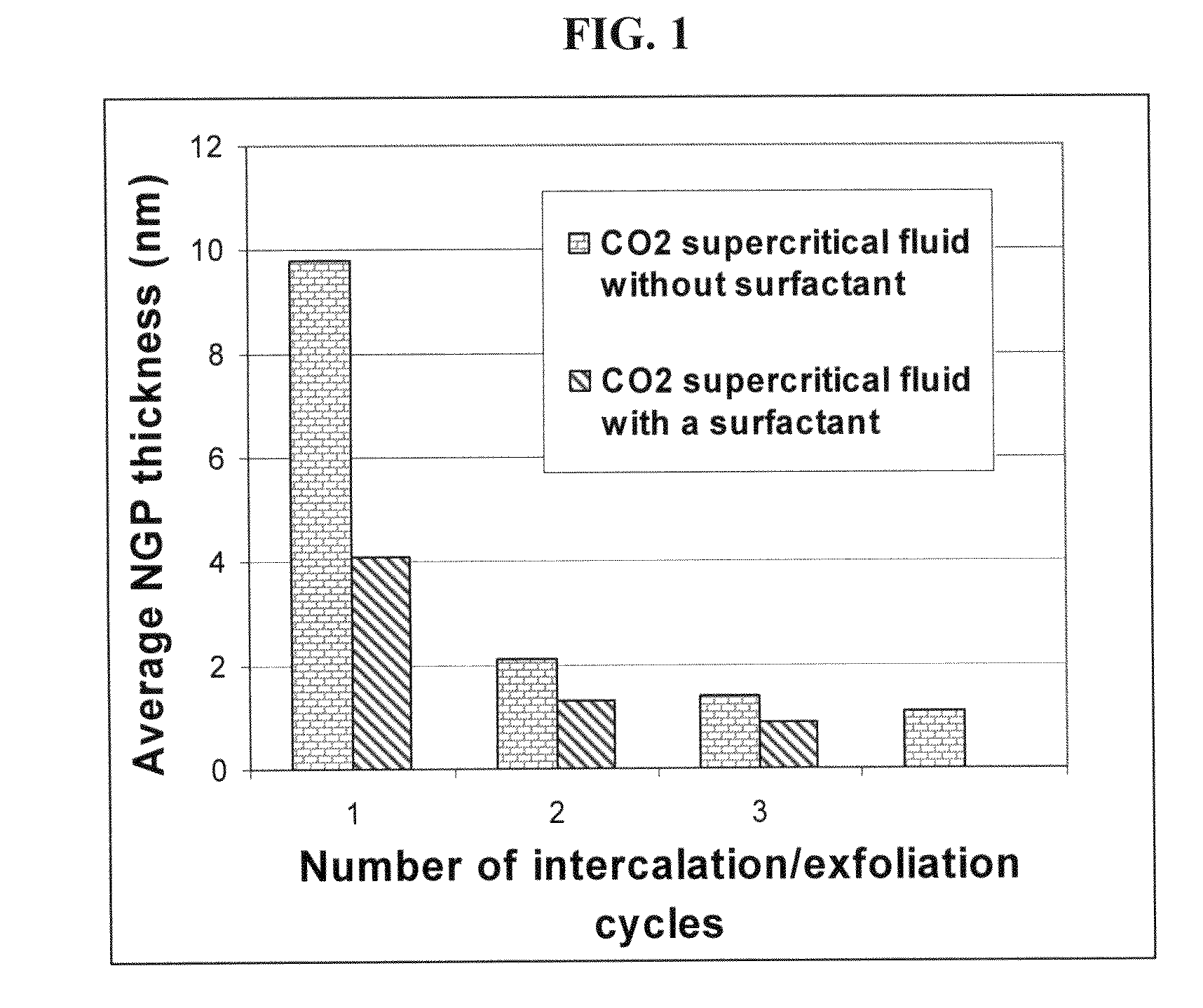
The present invention provides a method of producing pristine or non-oxidized nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are highly conductive. The method comprises: (a) providing a pristine graphitic material comprising at least a graphite crystallite having at least a graphene plane and an edge surface; (b) dispersing multiple particles of the pristine graphitic material in a liquid medium containing therein no surfactant to produce a suspension, wherein the multiple particles in the liquid have a concentration greater than 0.1 mg / mL and the liquid medium is characterized by having a surface tension that enables wetting of the liquid on a graphene plane exhibiting a contact angle less than 90 degrees; and (c) exposing the suspension to direct ultrasonication at a sufficient energy or intensity level for a sufficient length of time to produce the NGPs. Pristine NGPs can be used as a conductive additive in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays (e.g., to replace expensive indium-tin oxide), battery and supercapacitor electrodes, and nanocomposites for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding, static charge dissipation, and fuel cell bipolar plate applications.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
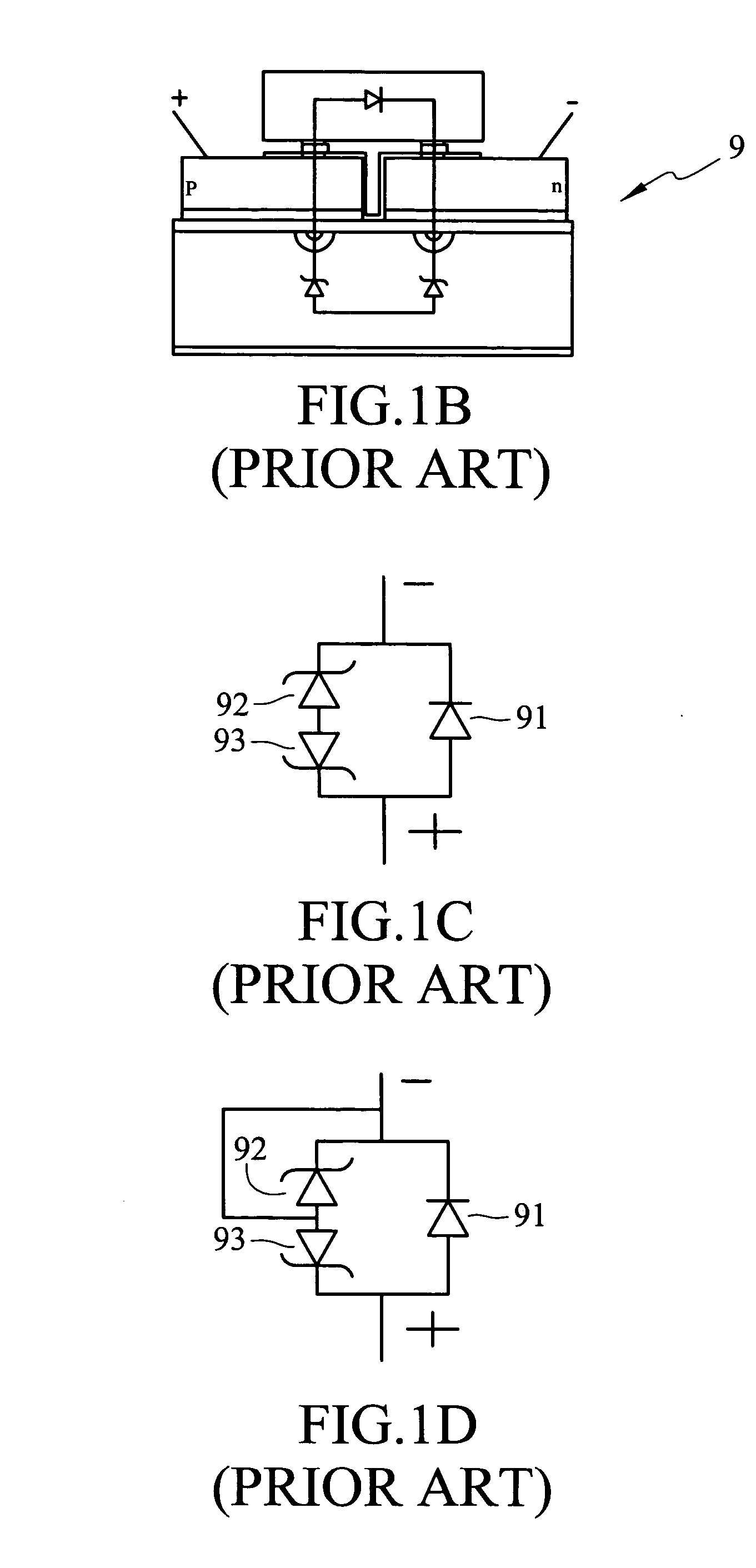
Structure of AC light-emitting diode dies
ActiveUS20060044864A1Increase the scope of applicationSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringAC power
A structure of light-emitting diode (LED) dies having an AC loop (a structure of AC LED dies), which is formed with at least one unit of AC LED micro-dies disposed on a chip. The unit of AC LED micro-dies comprises two LED micro-dies arranged in mutually reverse orientations and connected with each other in parallel, to which an AC power supply may be applied so that the LED unit may continuously emit light in response to a positive-half wave voltage and a negative-half wave voltage in the AC power supply. Since each AC LED micro-die is operated forwardly, the structure of AC LED dies also provides protection from electrical static charge (ESD) and may operate under a high voltage.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Process for producing dispersible and conductive Nano Graphene Platelets from non-oxidized graphitic materials
ActiveUS20100056819A1Impart dispersibilityImpart solubilityMaterial nanotechnologyPigmenting treatmentDisplay deviceSolar cell
The present invention provides a process for producing nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are both dispersible and electrically conducting. The process comprises: (a) preparing a pristine NGP material from a graphitic material; and (b) subjecting the pristine NGP material to an oxidation treatment to obtain the dispersible NGP material, wherein the NGP material has an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Method and system for desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
ActiveUS7544933B2Minimizing chanceHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsSolvent vaporDesorption
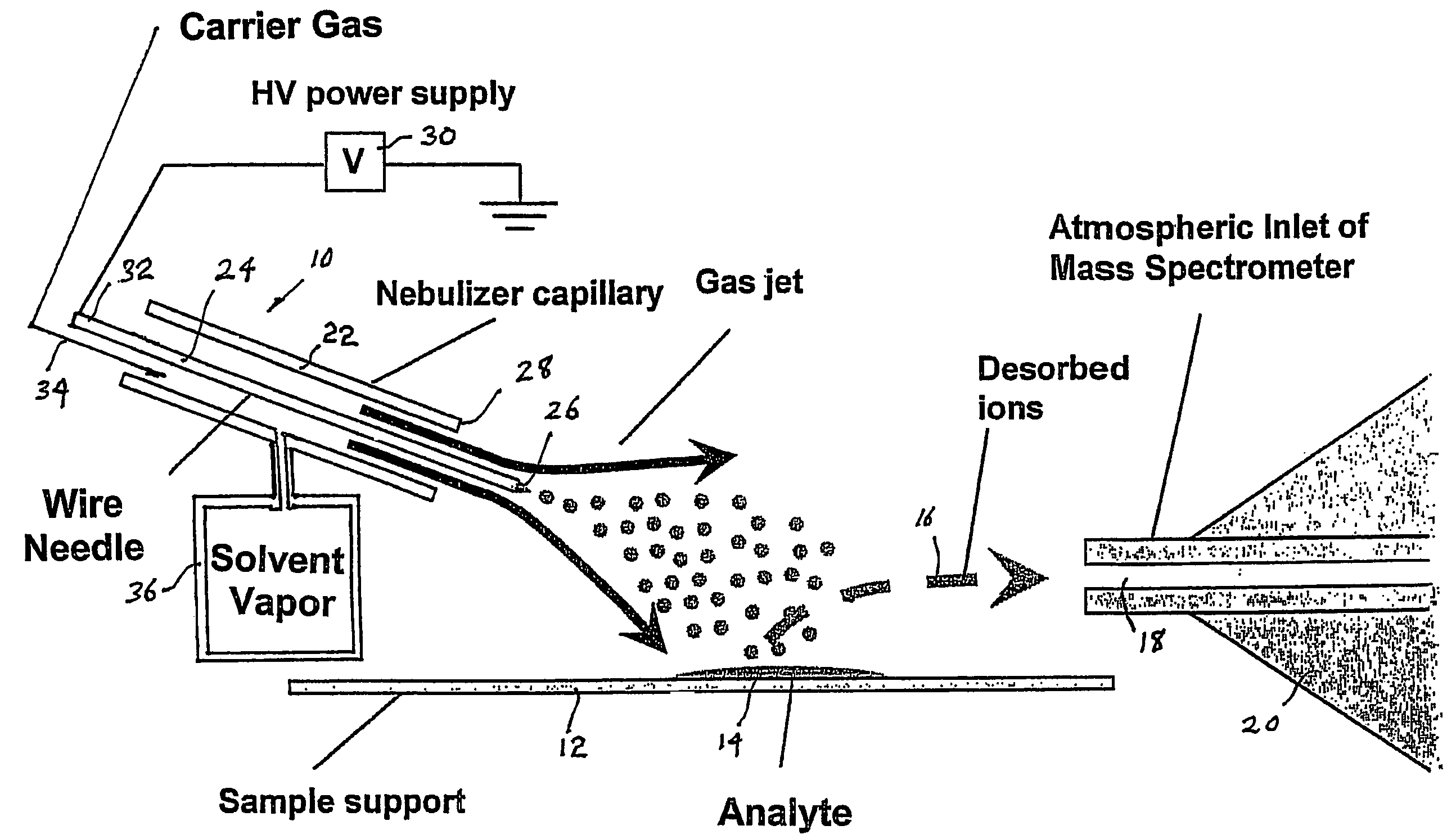
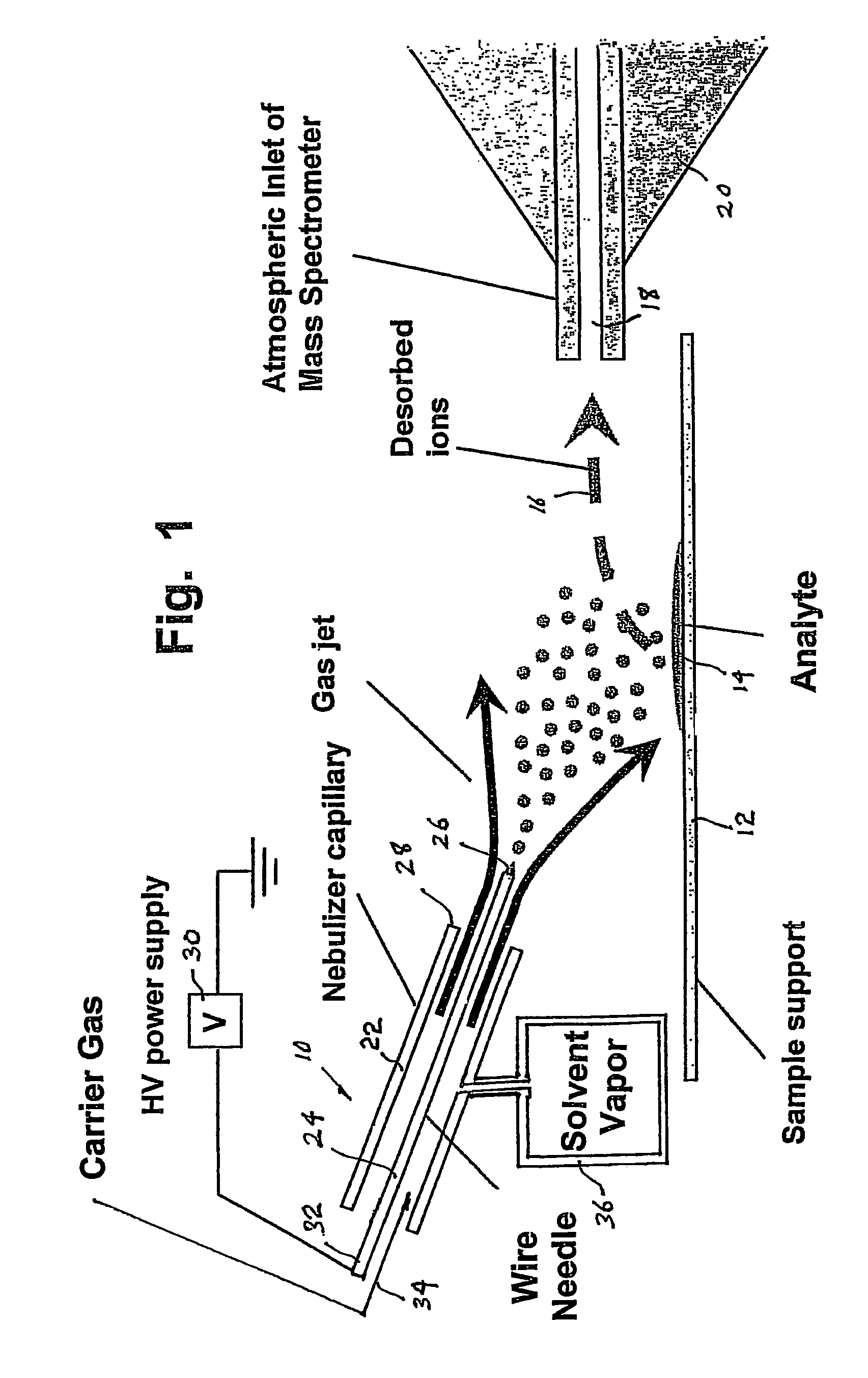
A desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI) system delivers a primary ion beam composed of an inert, high velocity gas and solvent ions to a surface to effect desorption and ionization of both volatile and non-volatile species present on surfaces. A electrode having a tapered tip is connected to a high voltage power supply. The tapered tip projects outward from a capillary carrying a high-speed flow of gas. A vapor of a solvent is mixed into the annular gas flow surrounding the needle. The gaseous solvent vapor is ionized in close proximity to the tapered tip by virtue of the high voltage applied to the electrode. The high-speed flow of gas and solvent vapor ions extending outward from the capillary is directed toward a substrate on which an analyte of interest may have been deposited. The solvent vapor ions can blanket the surface of the analyte causing a static charge build up that facilitates ion desorption and additionally can provide positive ion adducts of the analyte freed from the substrate surface that can be directed toward an atmospheric intake of a mass spectrometer or other instrument capable of studying the analyte.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Dispersible and conductive Nano Graphene Platelets
ActiveUS20100055458A1Impart dispersibilityImpart solubilityMaterial nanotechnologySynthetic resin layered productsDisplay deviceSolar cell
The present invention provides a dispersible and electrically conductive nano graphene platelet (NGP) material comprising at least a single-layer or multiple-layer graphene sheet, wherein the NGP material has an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight and no less than 5% by weight. This NGP material can be produced by: (a) preparing a pristine NGP material from a graphitic material; and (b) subjecting the pristine NGP material to an oxidation treatment. Alternatively, the production process may comprise: (A) preparing a graphite oxide (GO) from a laminar graphite material; (b) exposing the GO to a first temperature for a first period of time to obtain exfoliated graphite; and (c) exposing the exfoliated graphite to a second temperature in a protective atmosphere for a second period of time. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Supercritical fluid process for producing nano graphene platelets
ActiveUS20100044646A1Improve conductivityPigmenting treatmentNon-metal conductorsDisplay deviceSolar cell
The present invention provides a process for producing pristine or non-oxidized nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are highly conductive. The process comprises: (i) subjecting a graphitic material to a supercritical fluid at a first temperature and a first pressure for a first period of time in a pressure vessel and then (ii) rapidly depressurizing the fluid at a fluid release rate sufficient for effecting exfoliation of the graphitic material to obtain the NGP material. Conductive NGPs can be used as a conductive additive in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays (e.g., to replace expensive indium-tin oxide), battery and supercapacitor electrodes, and nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Method and apparatus for coating of substrates
The invention relates to methods and apparatuses that reduce problems encountered during coating of a device, such as a medical device having a cylindrical shape. In an embodiment, the invention includes an apparatus including a bi-directional rotation member. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method with a bi-directional indexing movement. In an embodiment, the invention includes a coating solution supply member having a major axis oriented parallel to a gap between rollers on a coating apparatus. In an embodiment, the invention includes a device retaining member. In an embodiment, the invention includes an air nozzle or an air knife. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method including removing a static charge from a small diameter medical device.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Compact dedusting apparatus
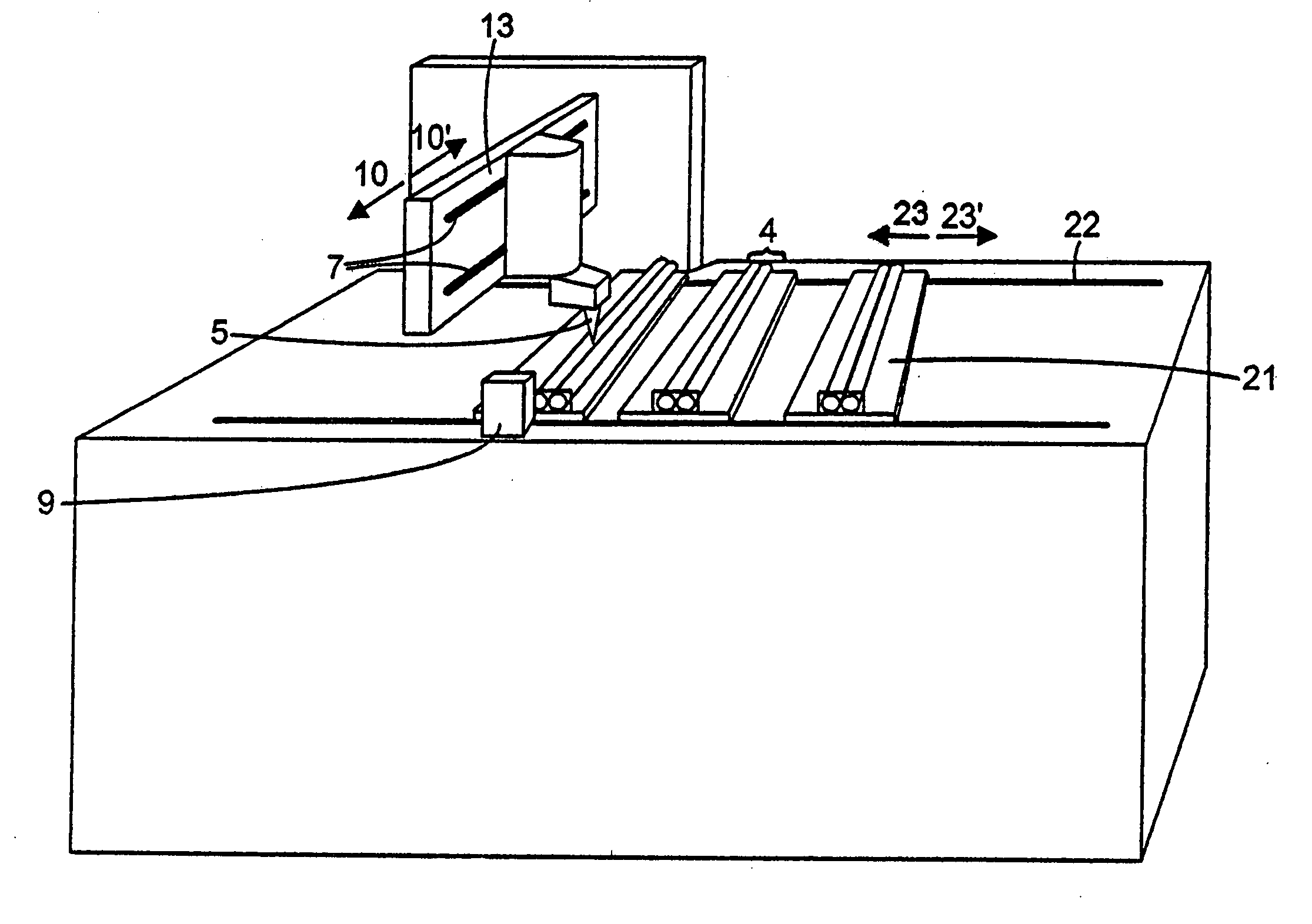
ActiveUS7380670B2Improved airflow characteristicsClean thoroughlyGas current separationMagnetic separationMagnetic fluxDust particles
A compact housing for a dedusting apparatus utilizes a magnetic flux field to disrupt the static charge attracting dust particles to product particles, which along with fluidization and counter current airflow principles that are proven to dislodge dust particles from the product, provides a highly efficient, compact deduster. The housing supports a double wash deck with product flow separated between the back-to-back primary wash decks. A deflector directing the flow of product onto the primary wash decks is provided with an extension that extends parallel to the wash deck to eliminated product bouncing off of the wash deck. The lower air outlets are eliminated, while the upper air outlets are positioned in extensions to the main housing above the product inlet opening. Air flow through the Venturi zone is enhanced by re-directing clean air directly to the backside of the Venturi panels, thereby eliminating the extraneous by-pass boxes.
Owner:PELLETRON CORP
Filter media with improved conductivity
InactiveUS20070028767A1Improve filtering effectImprove efficiencyCombination devicesAuxillary pretreatmentConductive coatingFilter media
Filter media are provided having improved conductivity to enhance filtration efficiency and / or dissipate static charge, and methods for making the same. In one exemplary embodiment, the filter media can include a filtration substrate, and at least one conductive coating disposed on at least a portion of the filtration substrate. In use, the conductive coating is coupled to an energy source and it is effective to emit ions when energy is delivered thereto to increase the efficiency of the filtration substrate and / or to dissipate or eliminate static charge generated during filtration.
Owner:HOLLINGSWORTH VOSE
Method and apparatus for coating of substrates
The invention relates to methods and apparatuses that reduce problems encountered during coating of a device, such as a medical device having a cylindrical shape. In an embodiment, the invention includes an apparatus including a bi-directional rotation member. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method with a bi-directional indexing movement. In an embodiment, the invention includes a coating solution supply member having a major axis oriented parallel to a gap between rollers on a coating apparatus. In an embodiment, the invention includes a device retaining member. In an embodiment, the invention includes an air nozzle or an air knife. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method including removing a static charge from a small diameter medical device.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
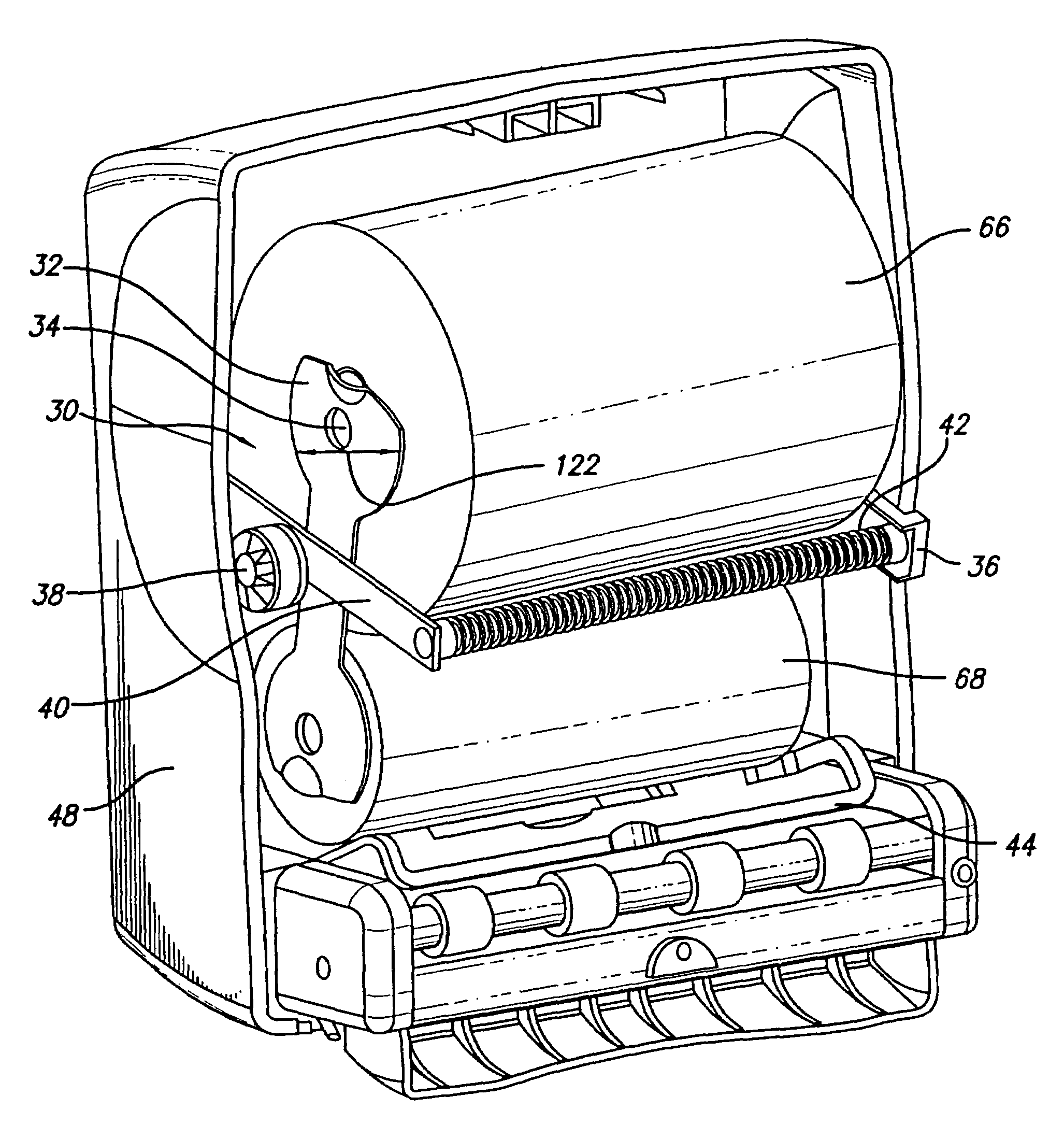
Static build-up control in dispensing system
Owner:GPCP IP HLDG LLC
Resin composition and jig for use in transportation
InactiveUS6344513B1Excellent static charge dissipating performanceLittle changeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSpecial tyresFiberCarbon fibers
Owner:TEIJIN LTD
Cleaner and control method thereof
InactiveUS20120047676A1Prevent malfunction and breakageBowling gamesLine/current collector detailsElectricityControl theory
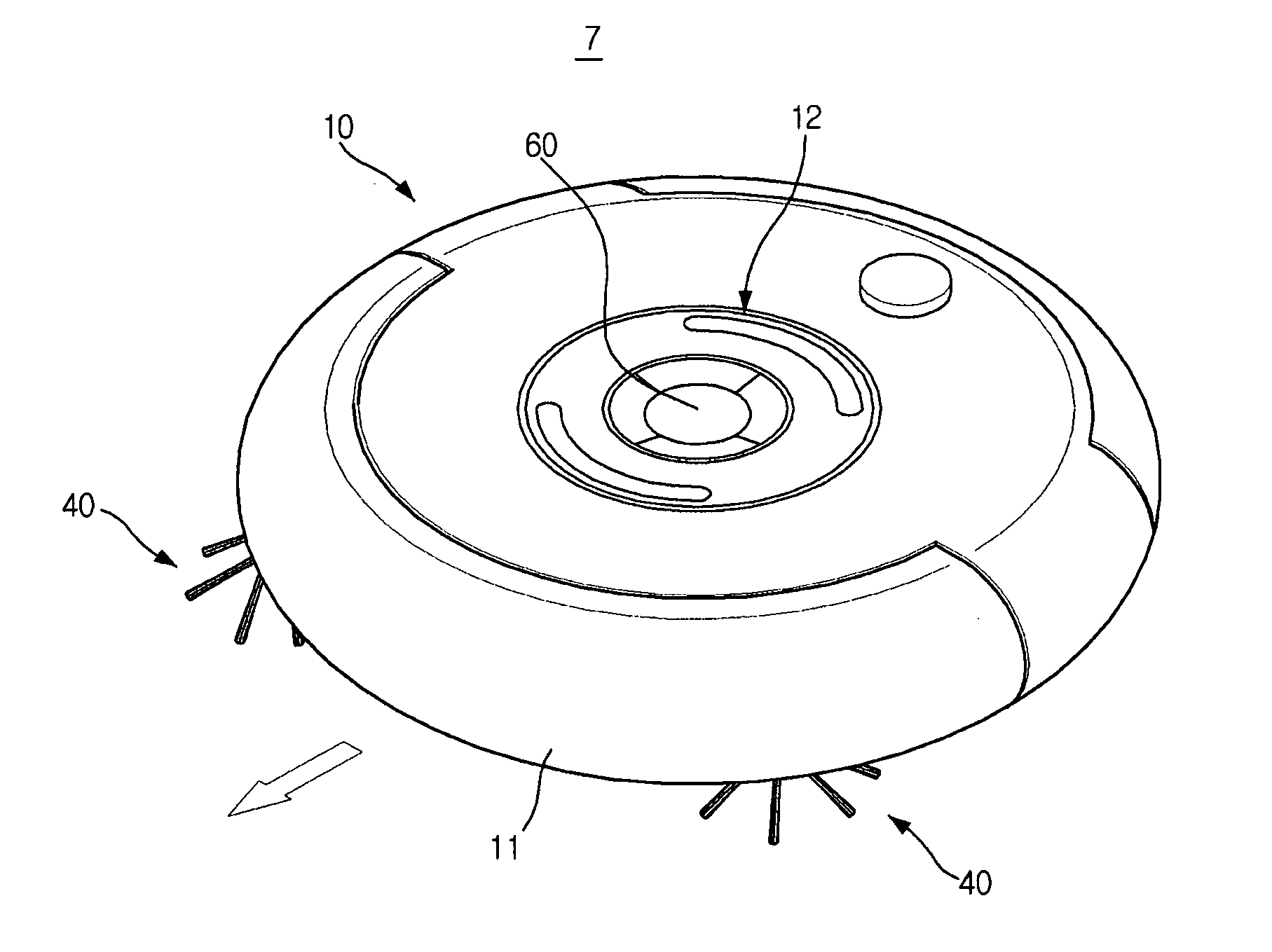
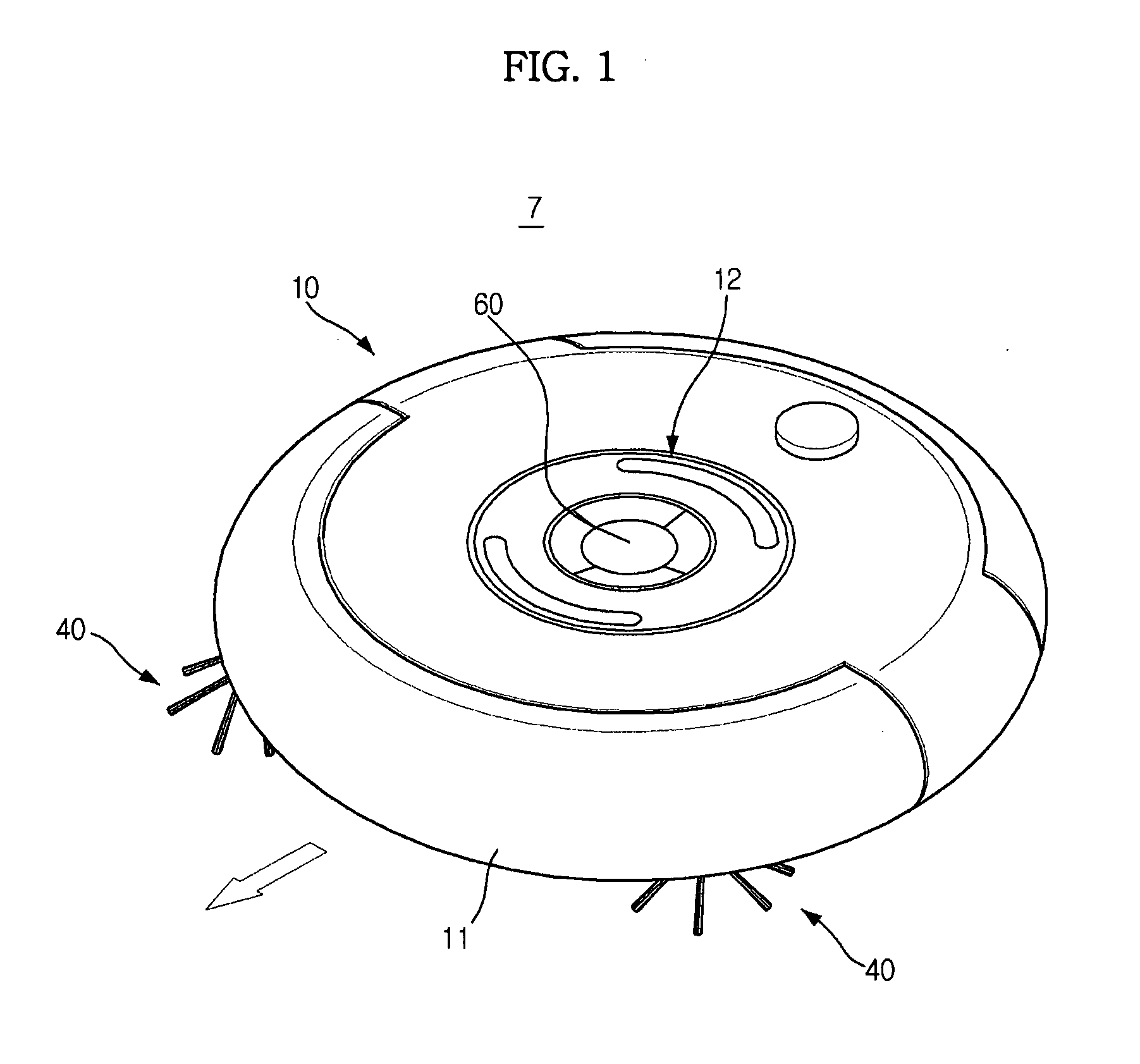
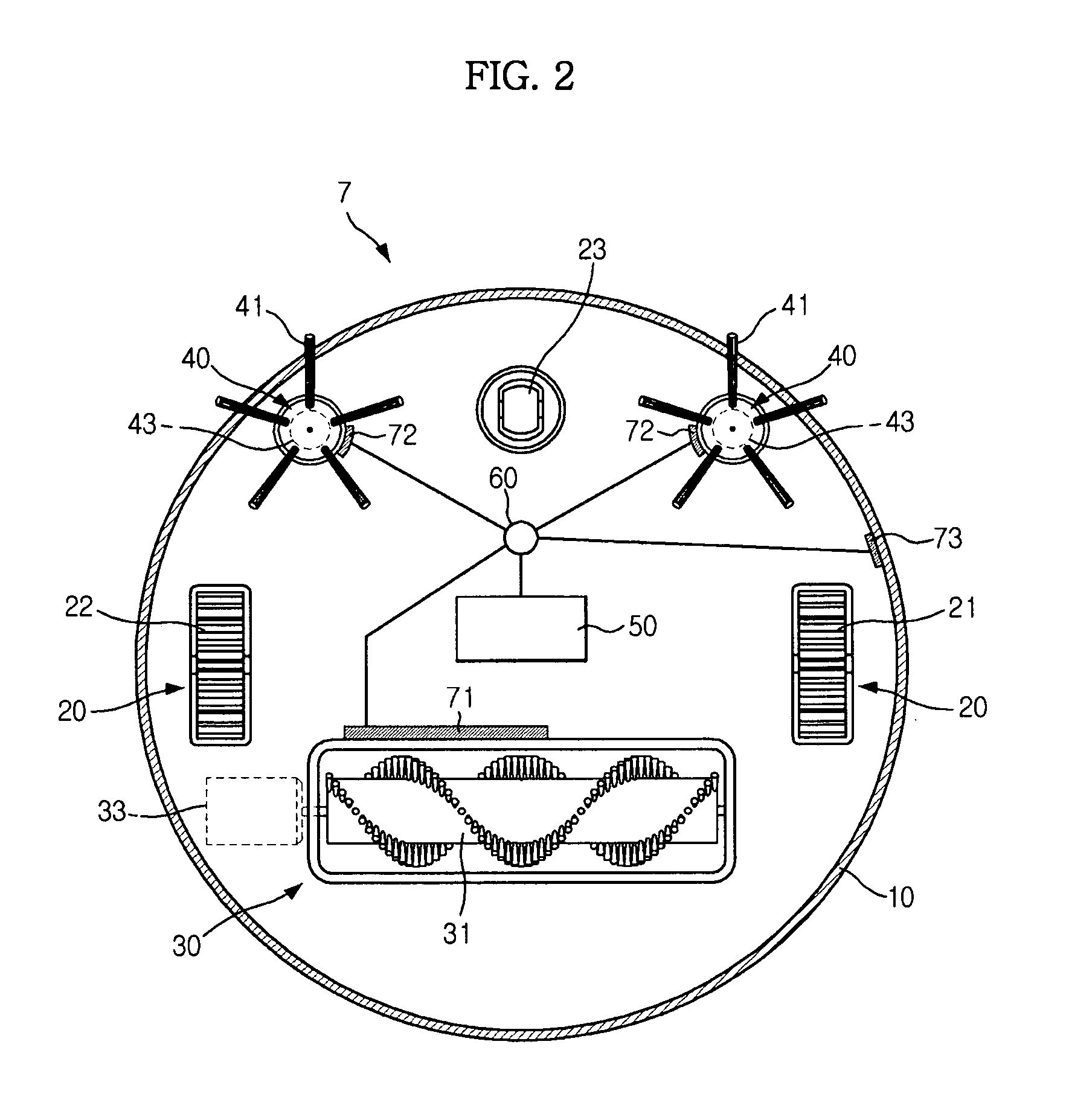
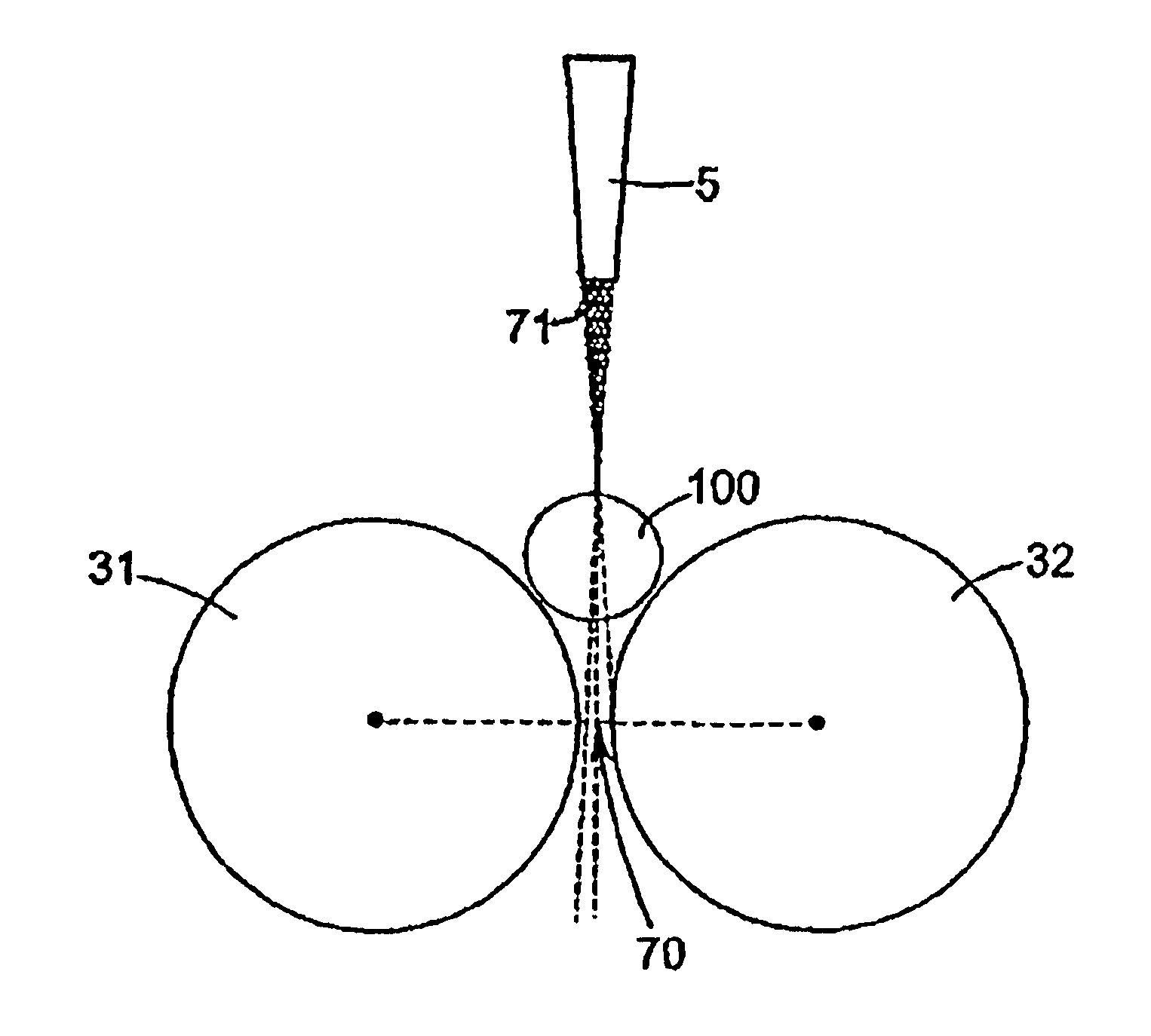
A robot cleaner having a static-charge removal device to prevent deterioration in performance or damage to an interior circuit of the cleaner due to static charge. The robot cleaner includes a conductive trap member to trap frictional static charge, a discharge member electrically connected to the trap member to discharge the static charge, trapped by the trap member, into another kind of energy, for example, light, sound, or kinetic energy, and a ground member located on the robot cleaner while being connected to the discharge member. The robot cleaner prevents adherence of dust, loose debris, etc. as well as damage to an interior circuit thereof due to static charge, thereby efficiently performing a cleaning operation.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Structure of AC light-emitting diode dies
A structure of light-emitting diode (LED) dies having an AC loop (a structure of AC LED dies), which is formed with at least one unit of AC LED micro-dies disposed on a chip. The unit of AC LED micro-dies comprises two LED micro-dies arranged in mutually reverse orientations and connected with each other in parallel, to which an AC power supply may be applied so that the LED unit may continuously emit light in response to a positive-half wave voltage and a negative-half wave voltage in the AC power supply. Since each AC LED micro-die is operated forwardly, the structure of AC LED dies also provides protection from electrical static charge (ESD) and may operate under a high voltage.
Owner:EPISTAR CORP
Method and apparatus for coating of substrates
The invention relates to methods and apparatuses that reduce problems encountered during coating of a device, such as a medical device having a cylindrical shape. In an embodiment, the invention includes an apparatus including a bi-directional rotation member. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method with a bi-directional indexing movement. In an embodiment, the invention includes a coating solution supply member having a major axis oriented parallel to a gap between rollers on a coating apparatus. In an embodiment, the invention includes a device retaining member. In an embodiment, the invention includes an air nozzle or an air knife. In an embodiment, the invention includes a method including removing a static charge from a small diameter medical device.
Owner:SURMODICS INC
Process for producing dispersible and conductive nano graphene platelets from non-oxidized graphitic materials
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Adhesive film and image display device
InactiveUS20070031660A1Improve bindingImprove adhesionSynthetic resin layered productsLaminationAntistatic agentWater dispersible
An adhesive film prevents static charge on peeling generated when removed from an adherend and also improves adhesion between a base material and an adhesive layer, where an under coat layer containing an organometallic is formed on the base material and then an adhesive layer is formed on the base material. Alternatively, an adhesive film showing high adhesion with a glass substrate, and including an antistatic layer, which prevents static charge on peeling generated when the surface protective film is removed, and improves adhesion between a base material and an adhesive layer, where the adhesive film includes a base material, an adhesive layer made of a water dispersible adhesive including, and an antistatic layer, containing a water soluble or water dispersible conductive material, interposed between them, and the adhesive film is stuck onto an image display device.
Owner:NITTO DENKO CORP
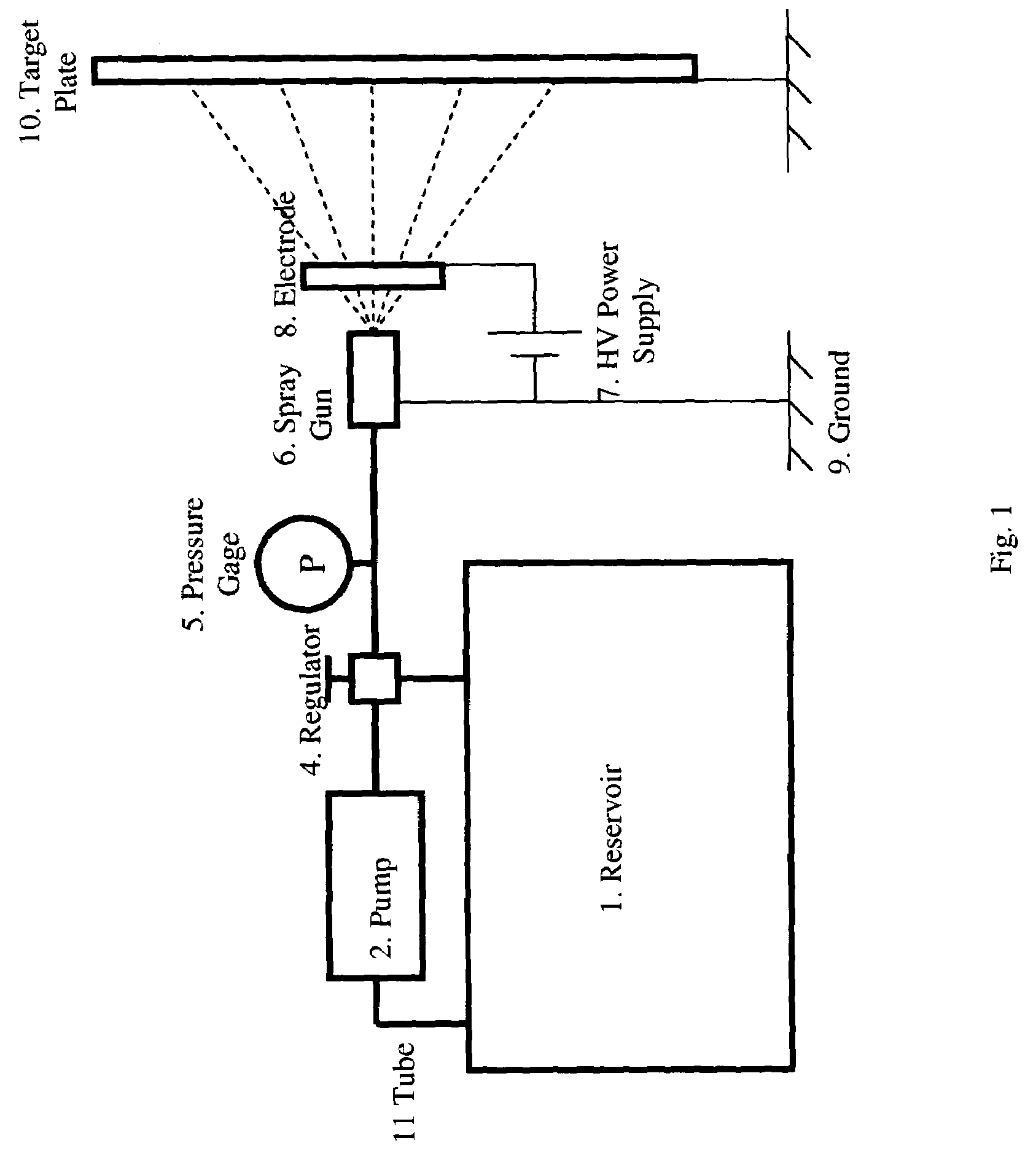
Method and apparatus for electrostatic spray
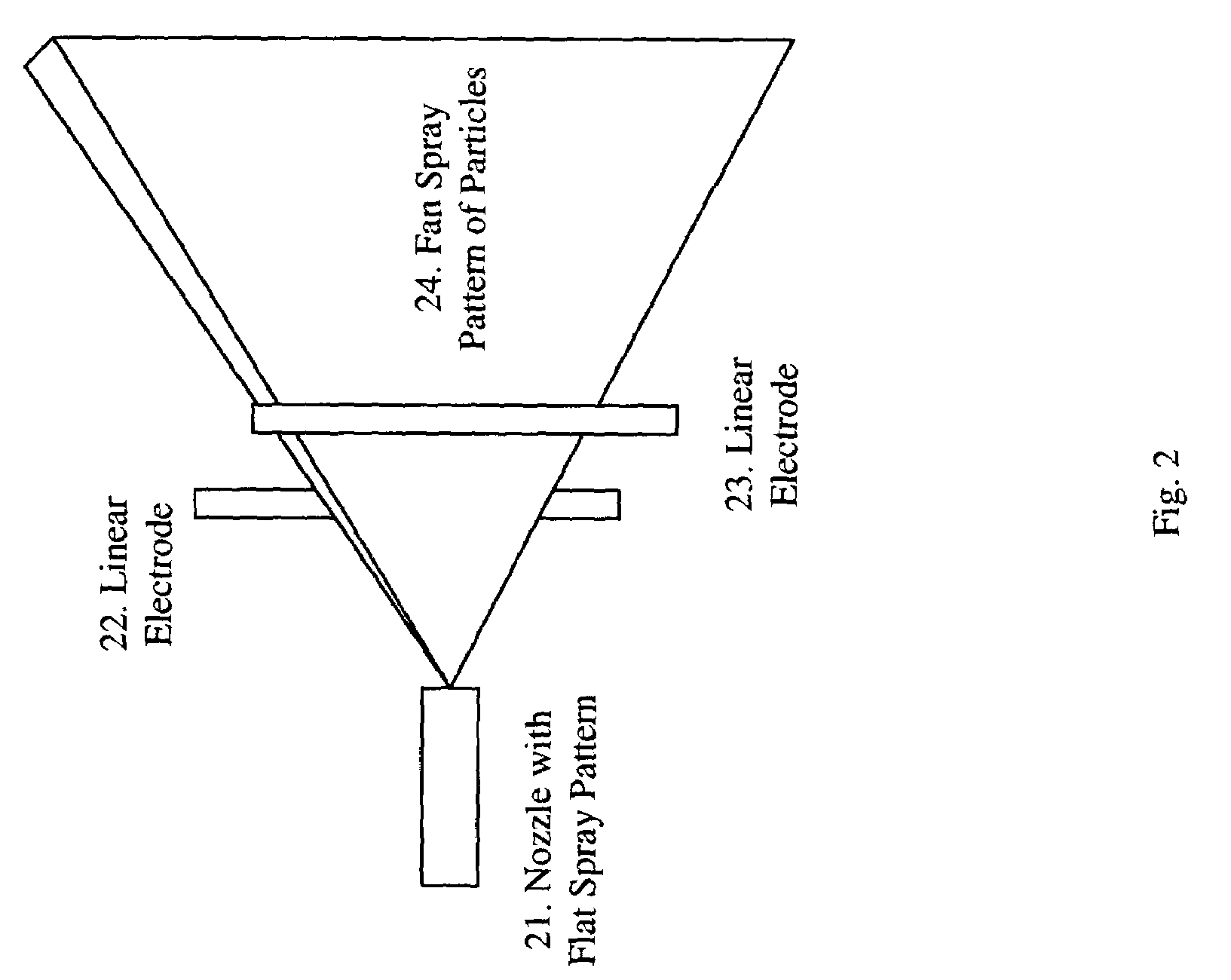
InactiveUS7150412B2High currentLeakage currentBurnersMovable spraying apparatusSpray nozzleEngineering
A method and apparatus to improve the atomization of liquid and the efficiency of depositing liquid particles onto target objects, or to coat the target object with a thin film of liquid, to reduce the risk of high-voltage electrical shock, and to reduce the weight of an electrostatic spray system has been developed by inducing electrostatic charges onto the atomized liquid particles sprayed from a grounded metal nozzle.
Owner:BIOMED PROTECT
Electrical micro-optic module with improved joint structures
InactiveUS20060103953A1Good ESD protectionImprove the immunityTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesElectricityOptical Module
An electrical micro-optic module (eMOM) includes a structure having zigzag contact surfaces and variable thread pitches. The structure elongates the path of contaminated particles and effectively reduces the amount of contamination to almost one order of magnitude due to the exponential decay of contamination versus path. Moreover, an electrostatic discharge (ESD) protection ring and conductive painting are used for static charge removal.
Owner:NSMC HLDG INT CORP
Process for producing dispersible nano graphene platelets from oxidized graphite
The present invention provides a process for producing nano graphene platelets (NGPs) that are dispersible and conducting. The process comprises: (a) preparing a graphite intercalation compound (GIC) or graphite oxide (GO) from a laminar graphite material; (b) exposing the GIC or GO to a first temperature for a first period of time to obtain exfoliated graphite; and (c) exposing the exfoliated graphite to a second temperature in a protective atmosphere for a second period of time to obtain the desired dispersible nano graphene platelet with an oxygen content no greater than 25% by weight, preferably below 20% by weight, further preferably between 5% and 20% by weight. Conductive NGPs can find applications in transparent electrodes for solar cells or flat panel displays, additives for battery and supercapacitor electrodes, conductive nanocomposite for electromagnetic wave interference (EMI) shielding and static charge dissipation, etc.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
Breaking and high tension electrostatic separating method for worn-out printed circuit board
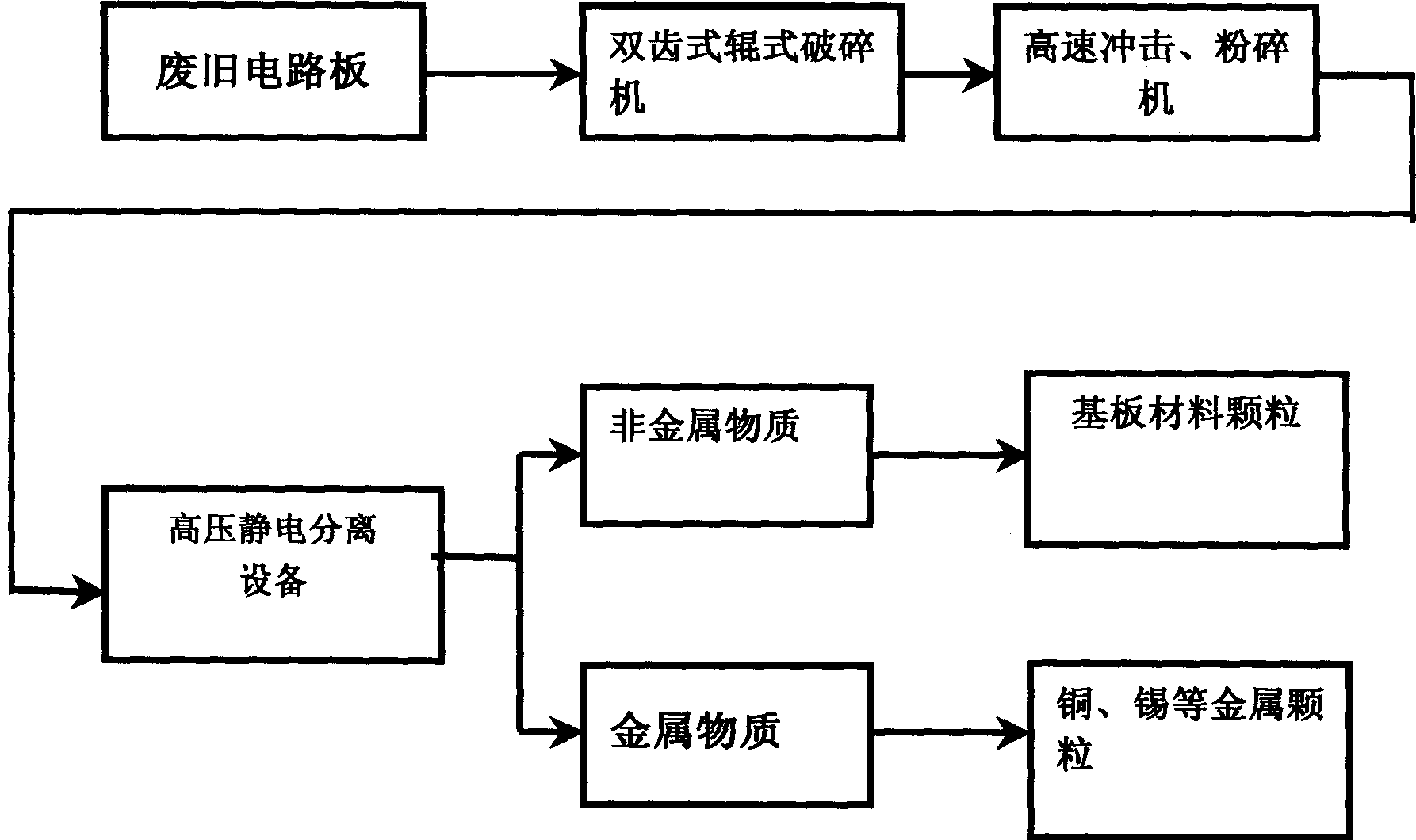
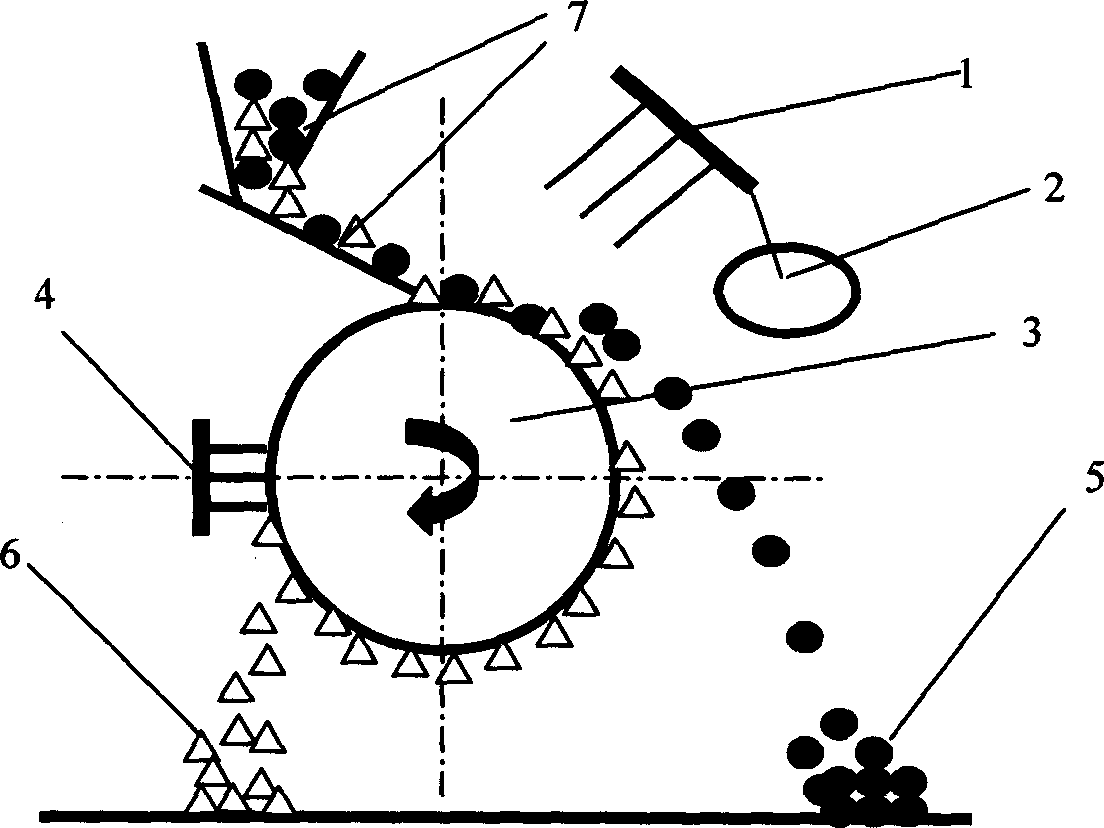
InactiveCN1654124ANo pollution in the processReduce pollutionElectrostatic separationGrain treatmentsElectrostatic separationEngineering
The crushing and high voltage electrostatic separation process of waste printed circuit board includes first crushing waste printed circuit board into 5-20 mm fragments, then pulverized into 0.06-0.5 mm grains and final separating metal grains from non-metal grains. The pulverized grains are fed to separating roller in high voltage electrostatic separating apparatus homogeneously and bombarded with negative ions the corona electrode generates to be charged. The metal grains are discharged fast in the earthing roller and electrostatically attracted with the static charge the electrostatic electrode generates to separate from the separating roller and fall into the metal collecting area, while the negatively charged non-metal grains are repelled electrically by the electrode to maintain on the surface of the metal roller before being brushed with a brush to fall into the non-metal collecting area. Thus, non-metal grains are separated from the metal grains in low cost, high efficiency and no pollution.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
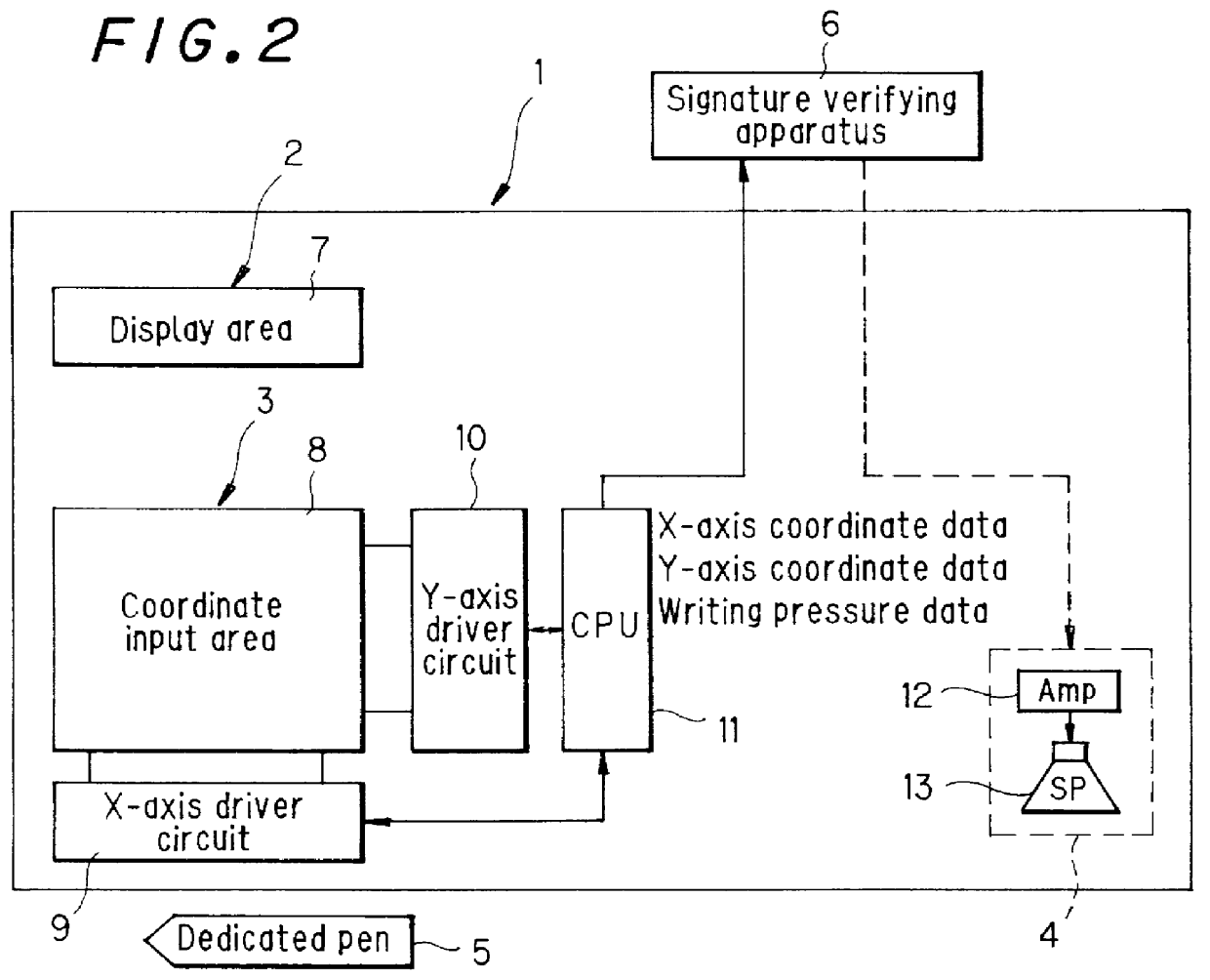
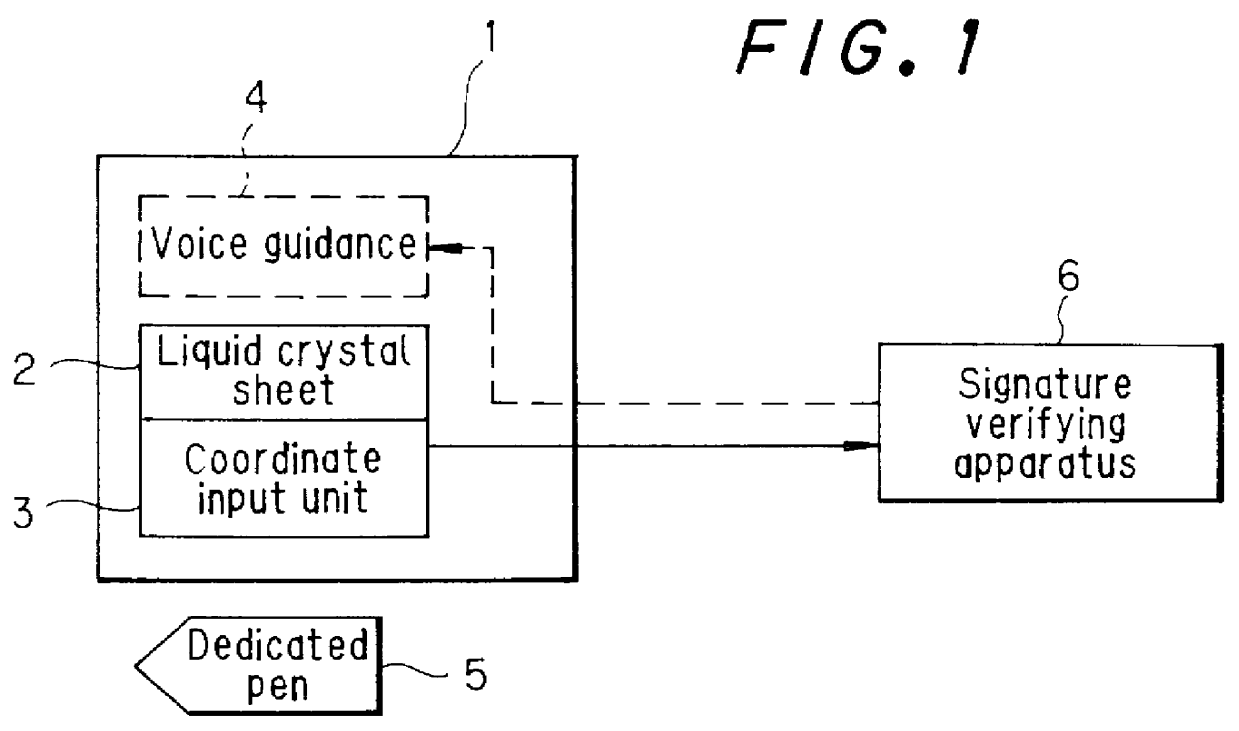
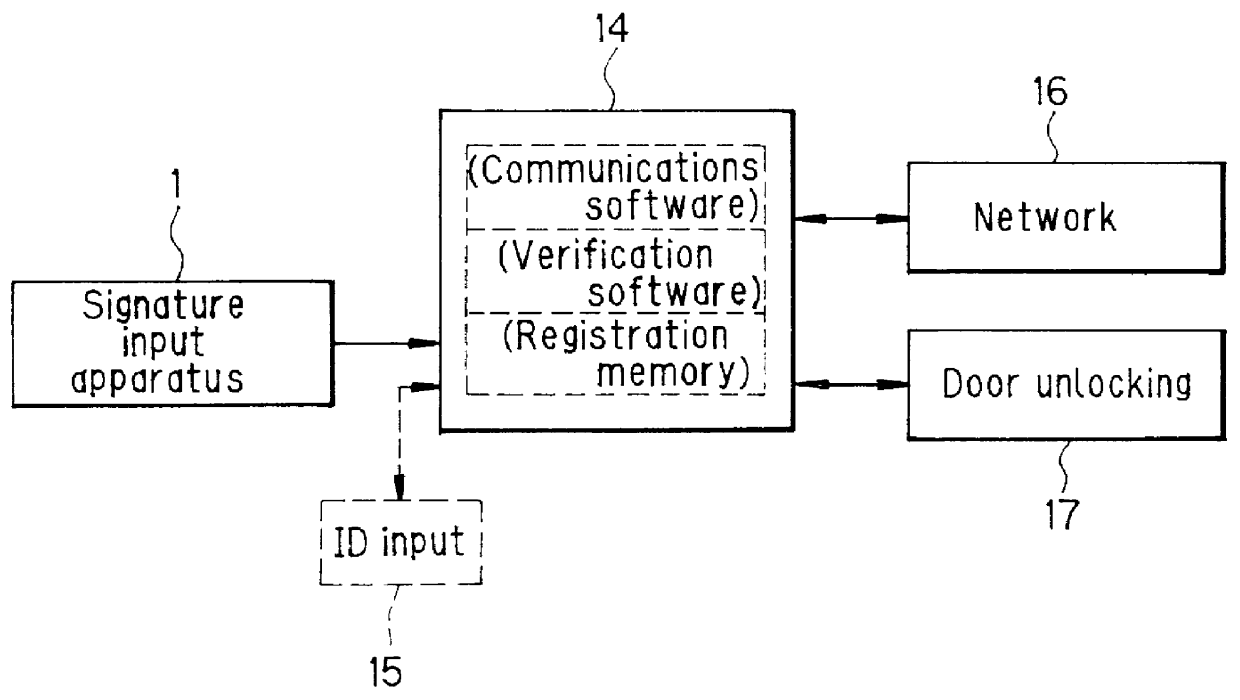
Signature input apparatus and a signature verification system
InactiveUS6118889AImprove securityEasy to changeImage analysisTransmission systemsHandwritingVerification system
PCT No. PCT / JP97 / 02403 Sec. 371 Date Mar. 23, 1998 Sec. 102(e) Date Mar. 23, 1998 PCT Filed Jul. 10, 1997 PCT Pub. No. WO98 / 05001 PCT Pub. Date Feb. 5, 1998The object is to improve the accuracy of signature input and signature verification and improve security by causing the handwriting of a signature to disappear by itself. The signature verification system includes a signature input apparatus 1 and a signature verifying apparatus 6. Signature input apparatus 1 has an externally charged type liquid crystal sheet 2 which has an underside being adhesive and is placed on a coordinate input unit 3. When a dedicated pen 5 having the function of applying static charge onto this liquid crystal sheet 2 is used to write a signature, the handwriting of the signature is liquid crystal representation on the display area of liquid crystal sheet 2 and this handwriting of the signature will disappear by itself after a predetermined period of time. Further, signature verifying apparatus 6 reads the handwriting coordinate information of a signature output from coordinate input unit 3 for detecting the handwriting coordinate information of a signature and verifies this handwriting coordinate information with the handwriting coordinate information of signatures which have been registered beforehand.
Owner:PILOT PEN CO LTD
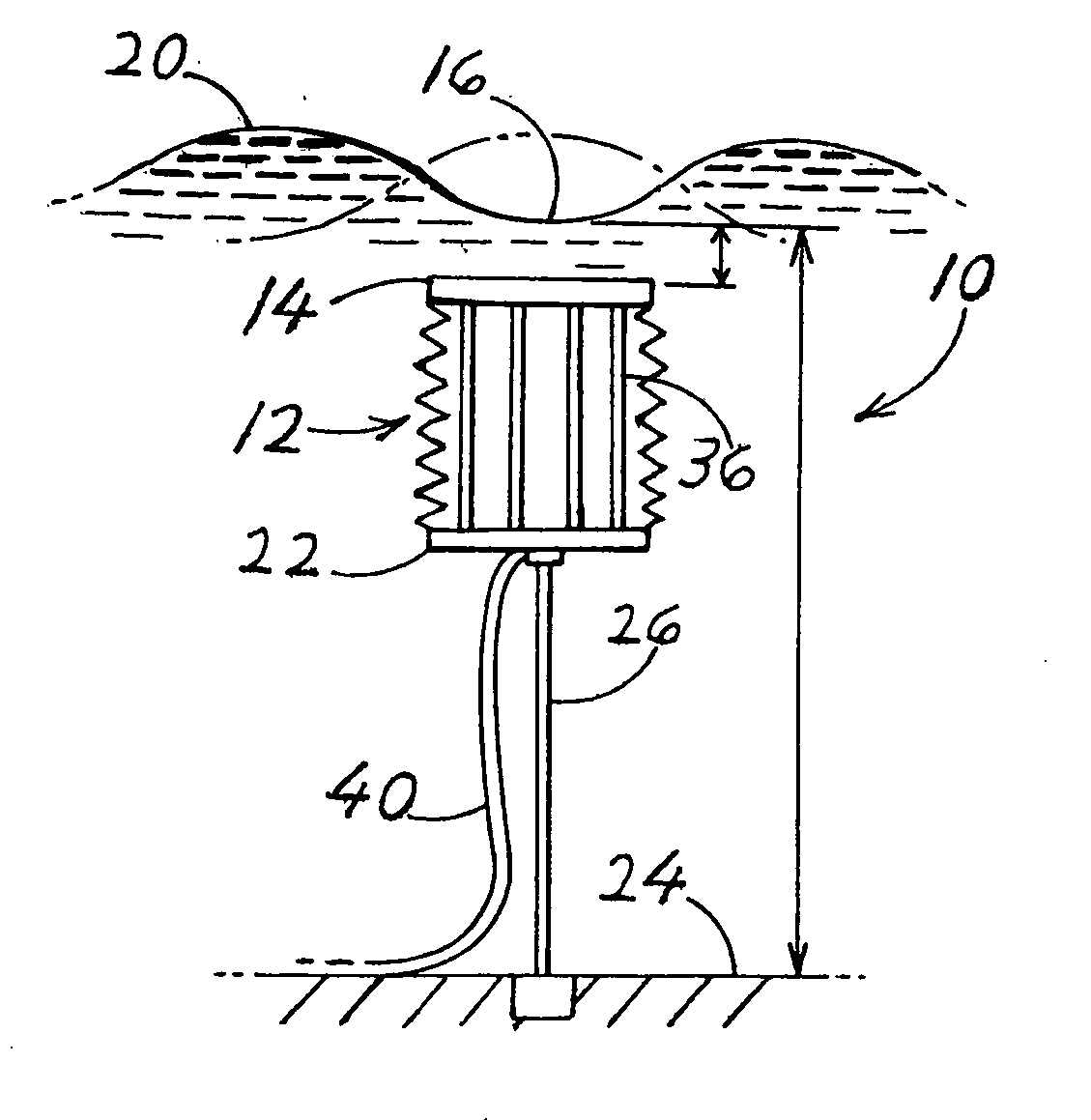
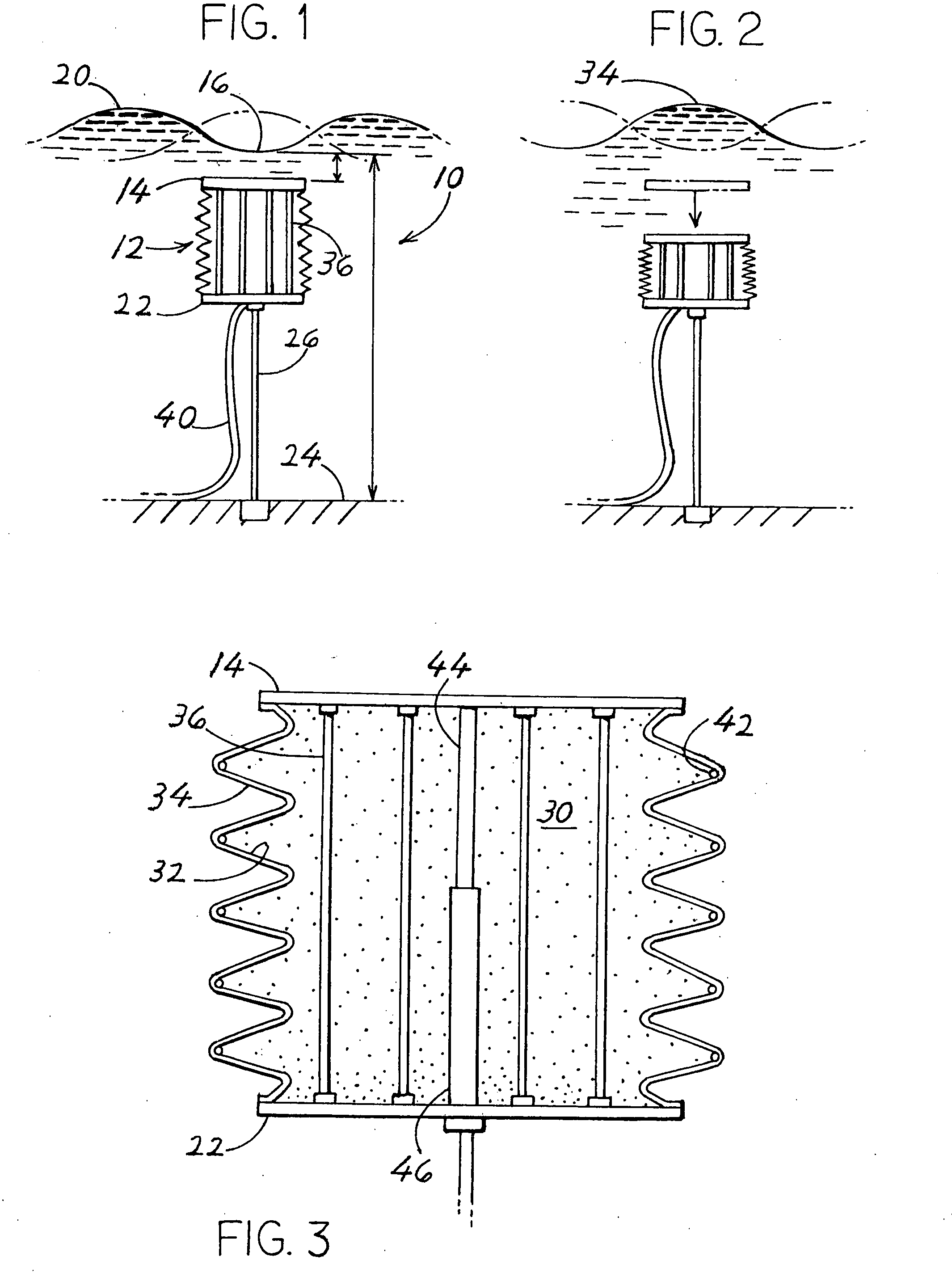
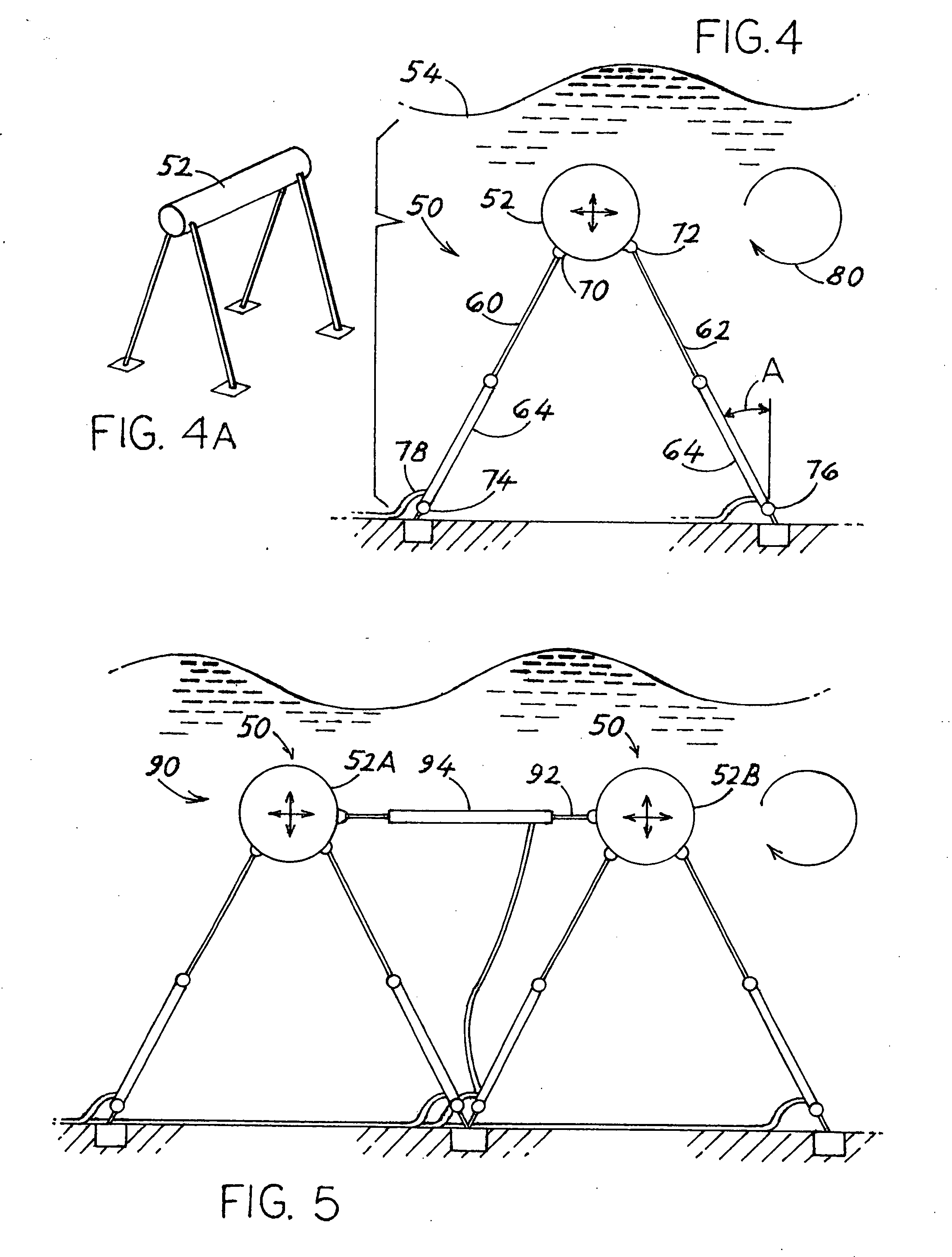
Wave power generator systems
ActiveUS20080267712A1Damps waveLengthened and shortenedWater-power plantsMachines/enginesActive polymerElectricity
Systems are provided for obtaining electrical energy from sea waves using deflectable material, especially EAP (electro-active polymers) type SSM (stretchable synthetic material) that generates electricity when an electrostatic charge is applied to the polymer and it is stretched. In one system (10), a buoyant element (12) has upper and lower parts (14, 22) connected by a quantity (36) of SSM, with the lower part anchored at a fixed height above the sea floor (24) and with the upper part movable vertically to stretch and relax the SSM as waves pass over. In another system (50) the buoy is rigid, but is anchored to the sea floor by at least one line (60) that includes, or is connected to at least a length (64) of SSM material. In still another system (160) a plurality of rigid buoys (162) that float on the sea surface, are connected in tandem by SMM (166, 172) that is stretched and relaxed as the buoys pivot relative to each other in following the waves. The buoys preferably lie with at least 80% of their volume below the average sea surface.
Owner:SINGLE BUOY MOORINGS INC
Intrinsically conductive thermoplastic composition and compounding processing for making conductive fiber
InactiveUS20080139065A1Effective static charge dissipationSafe dissipation of charge into the atmosphereElectroconductive/antistatic filament manufactureLayered productsFiberMaterials science
A conductive thermoplastic composition capable of forming conductive fibers including monofilaments, methods of making these compositions, and fibers including these compositions. The conductive thermoplastic compositions may be formed using any method capable of forming the compositions into fibers. The fibers are substantially smooth and / or are capable of being woven into fabrics or other articles to provide conductive properties to the fabric or article. These fibers provide effective static charge dissipation that may be imparted into applications such conveying belts or protective clothing for clean room operation.
Owner:SABIC INNOVATIVE PLASTICS IP BV
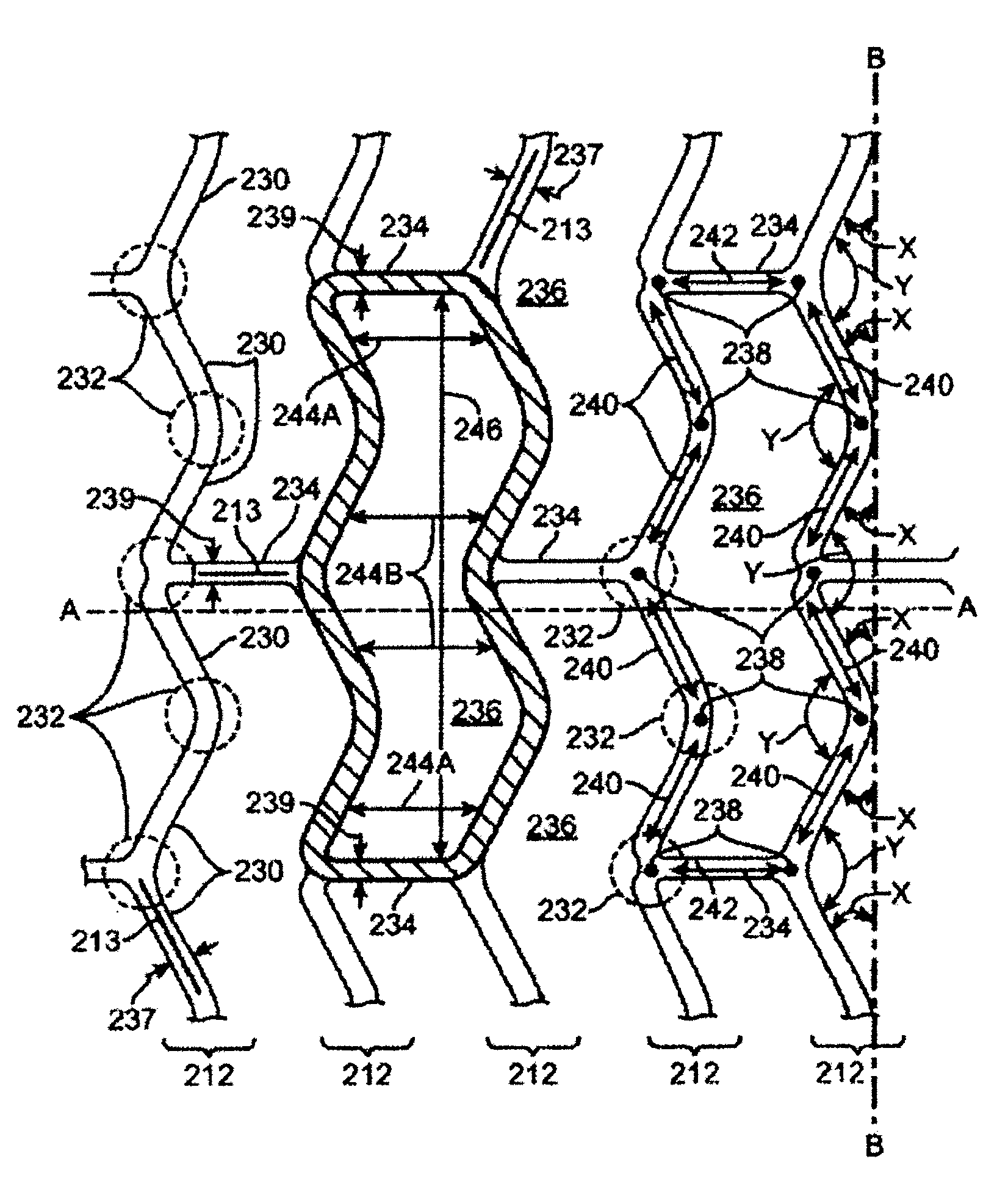
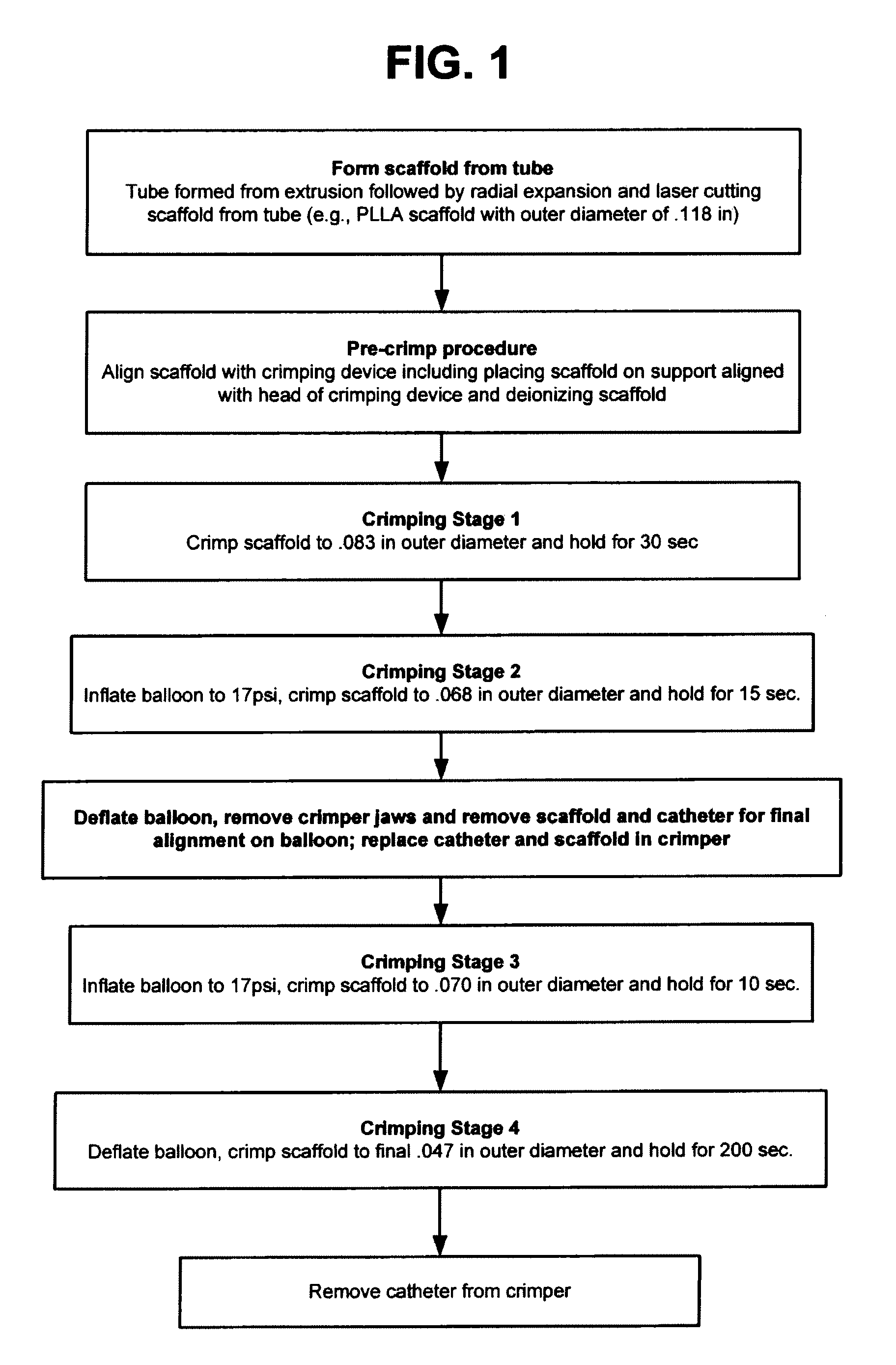
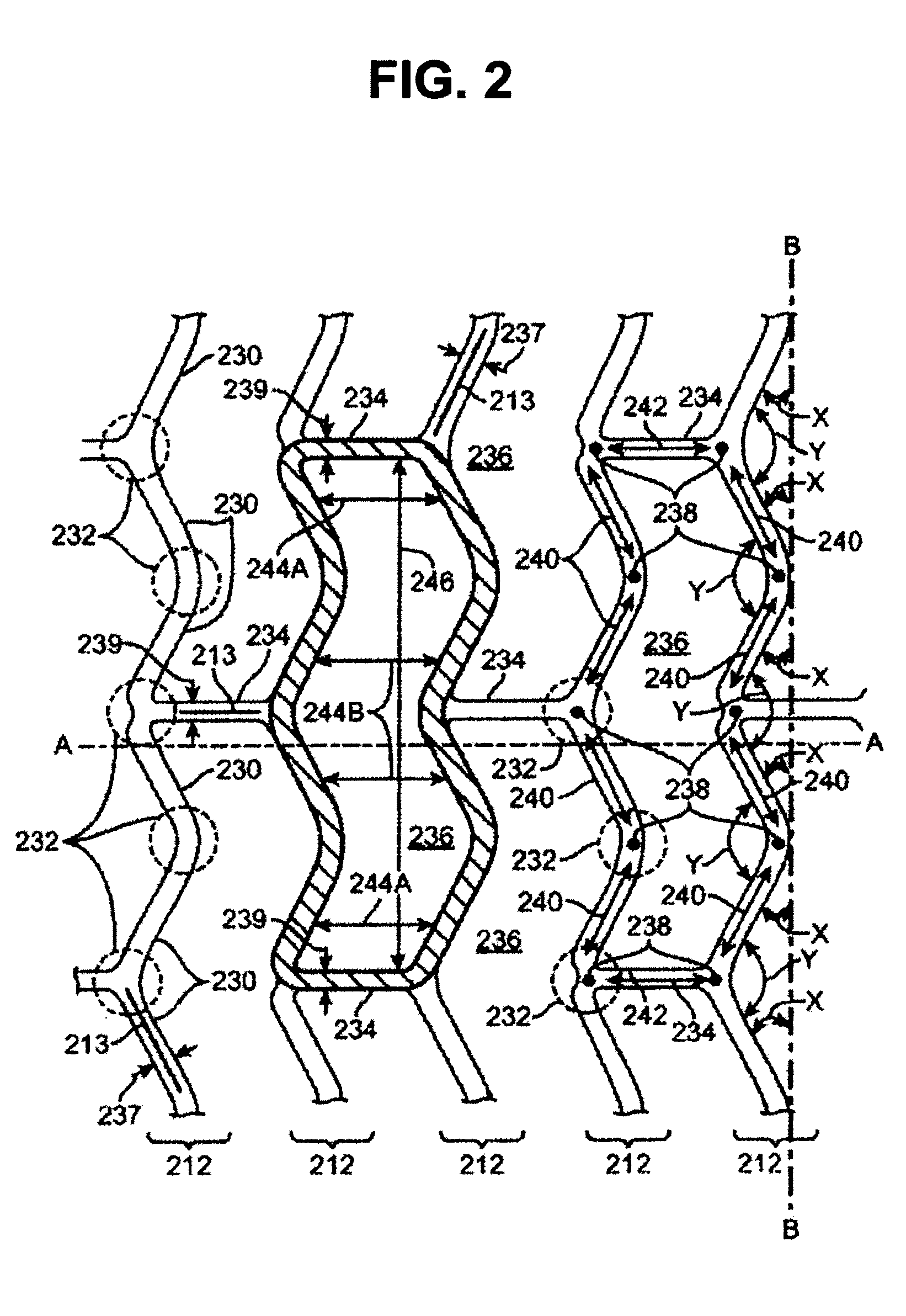
Methods for Crimping a Polymeric Stent Scaffold Onto a Delivery Balloon
ActiveUS20110271513A1Easy alignmentEliminates static buildupStentsMetal working apparatusInsertion stentPolymer scaffold
A medical device includes a polymer stent scaffold crimped to a catheter having an expansion balloon. A process for forming the medical device includes placing the scaffold on a support supported by an alignment carriage, and deionizing the scaffold to remove any static charge buildup on the scaffold before placing the scaffold within a crimper to reduce the scaffold's diameter. The polymer scaffold is heated to a temperature below the polymer's glass transition temperature to improve scaffold retention without adversely affecting the mechanical characteristics of the scaffold when deployed to support a body lumen.
Owner:ABBOTT CARDIOVASCULAR
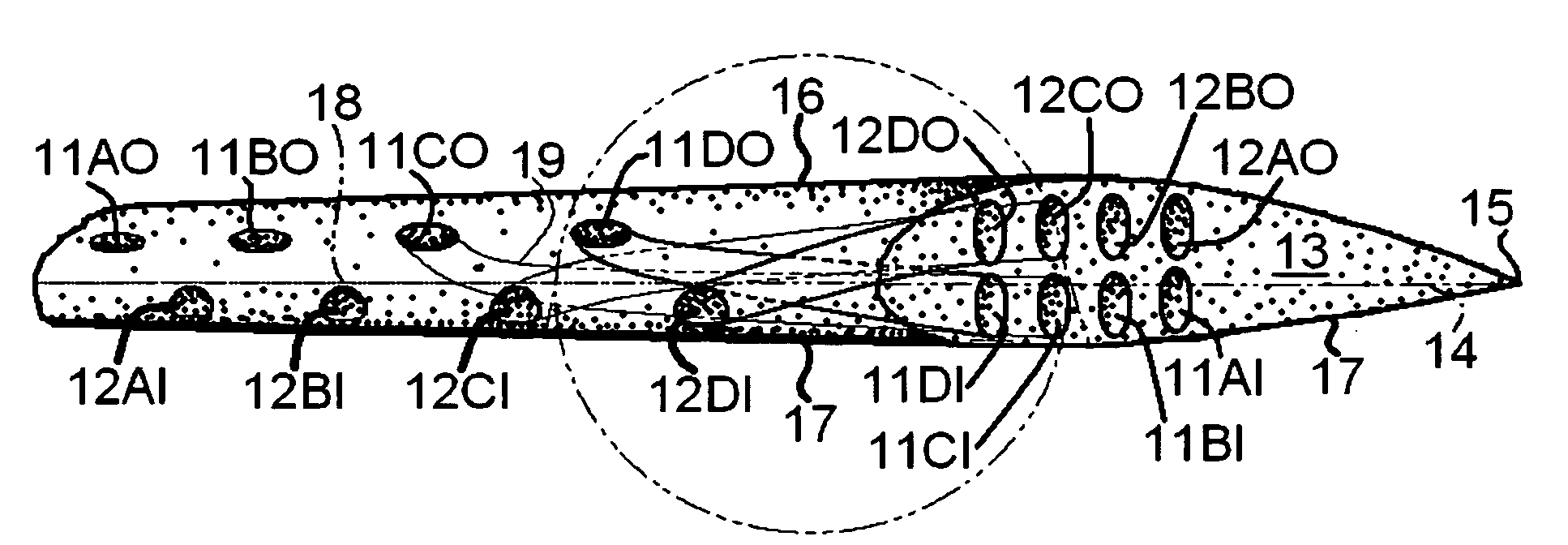
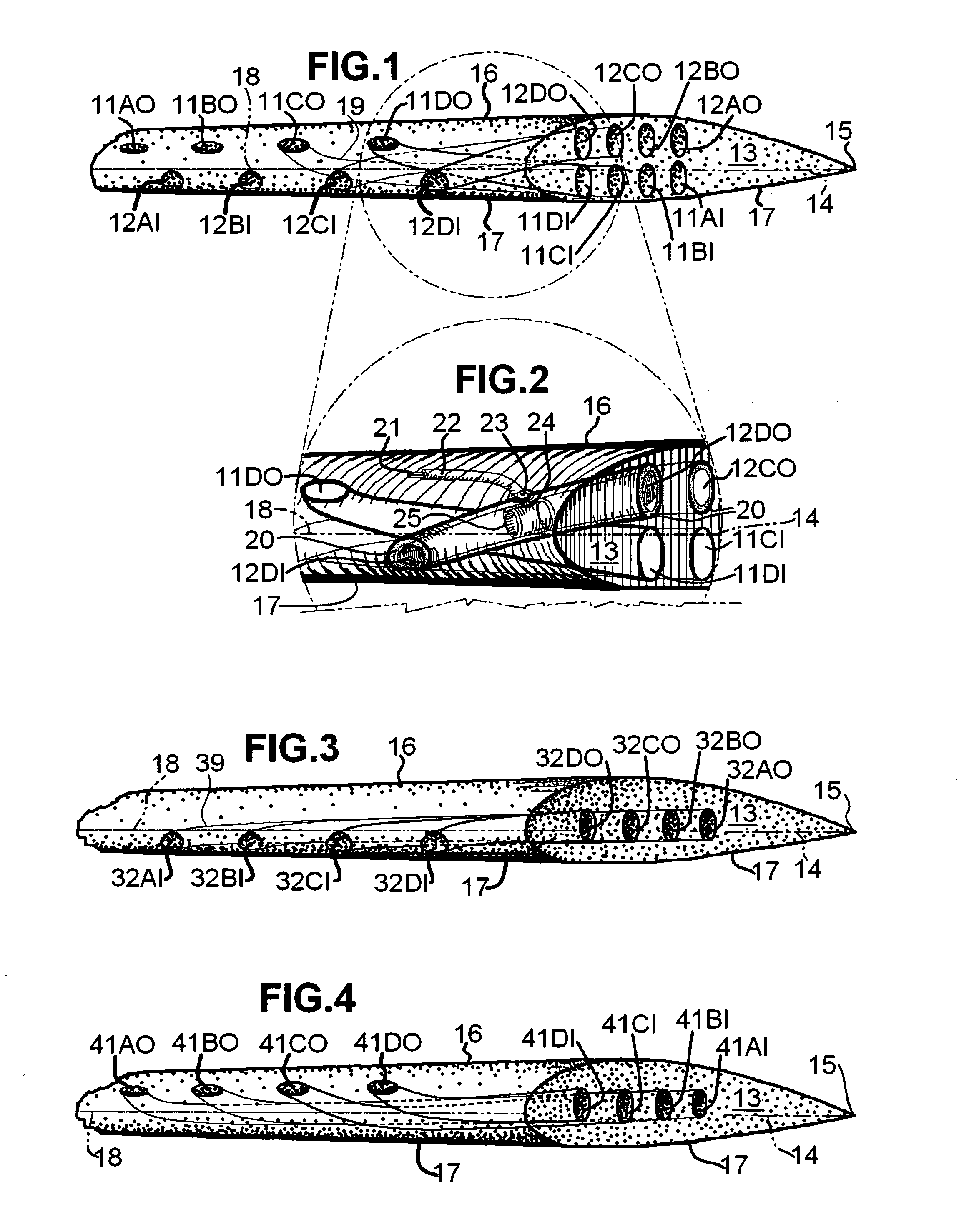
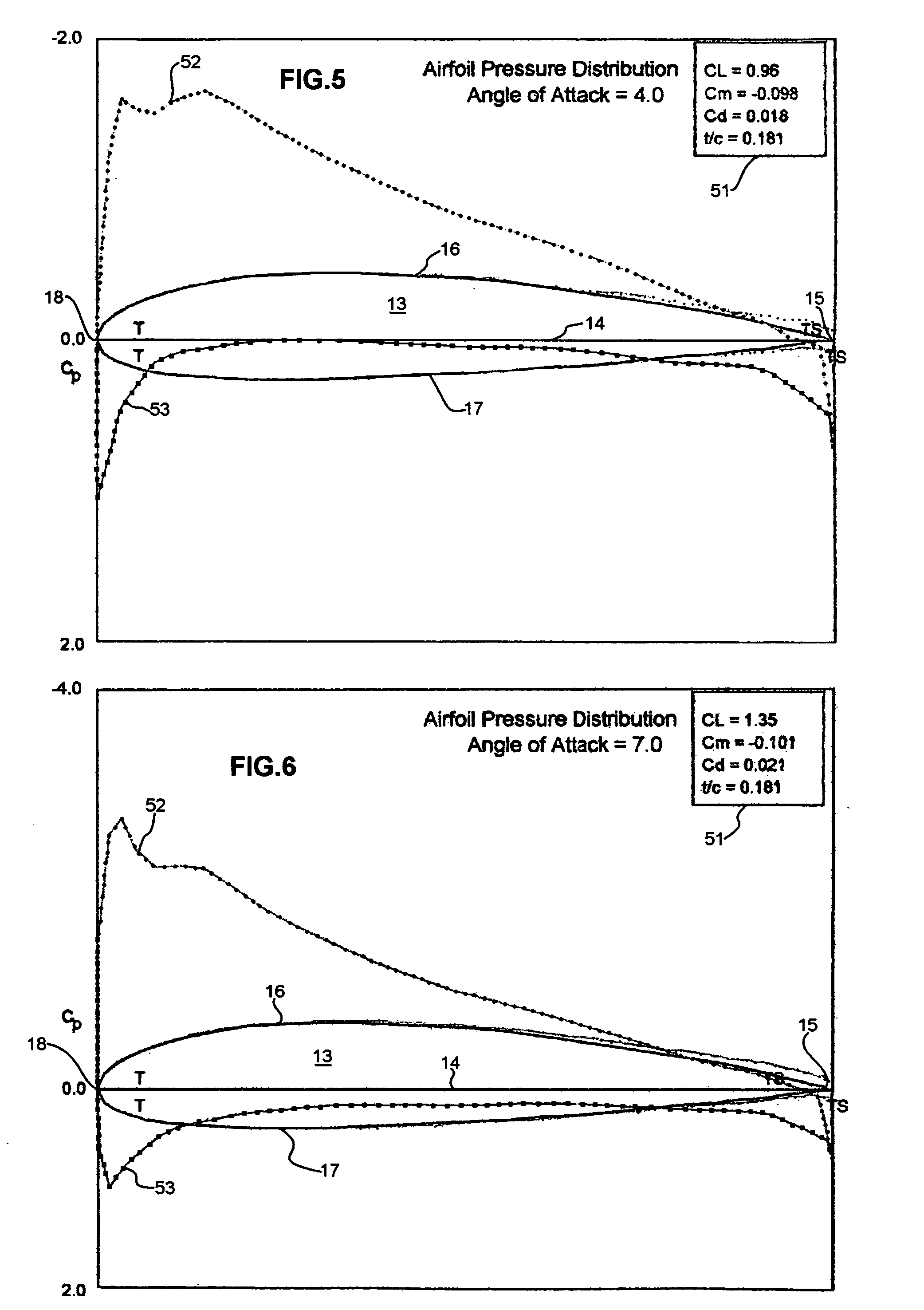
Surface flow diverting and static charging ducted pores on wing or blade tip to reduce wake and BVI noise
InactiveUS20070252047A1Promoting interlayer movementInfluencers by generating vorticesWing shapesElectricityLeading edge
Air pressure distribution for airfoil lower and upper surfaces is utilized to divert airflow using ducts formed in space-curve shapes placed inside the airfoil volume, through span-wise located inlets from high pressure areas on the airfoil lower surface near the leading edge and through chord-wise spaced inlets on the side face of the airfoil wing tip correspondingly to the side face of the airfoil wing tip through chord-wise spaced outlets on the side face of the airfoil wing tip and to span-wise located outlets to the low pressure areas on the airfoil upper surface. Triboelectric materials on the wing surfaces are employed to static charge the air in drag. Inside the ducts, the employment of either triboelectric linings and materials, or HV-supplied electrodes, or both, help to static charge the diverted air flow to and from the airfoil wing tip side face to diffuse wing tip vortex core early.
Owner:PAL ANADISH KUMAR
Conductive multilayer stack
InactiveUS20100028684A1Increased durabilityImprove functionalitySynthetic resin layered productsThin material handlingIr reflectionUltrasound attenuation
An electrically conductive multilayer stack having good IR reflection, radar attenuation, static discharge, and other desirable properties includes a coated substrate, a primary conductive layer, and a secondary protective stack having greater durability and functionality then conventional multilayer stacks used to protect aircraft canopies and other substrates. The secondary protective stack includes at least one conductive layer that helps dissipate static charge.
Owner:PPG IND INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com