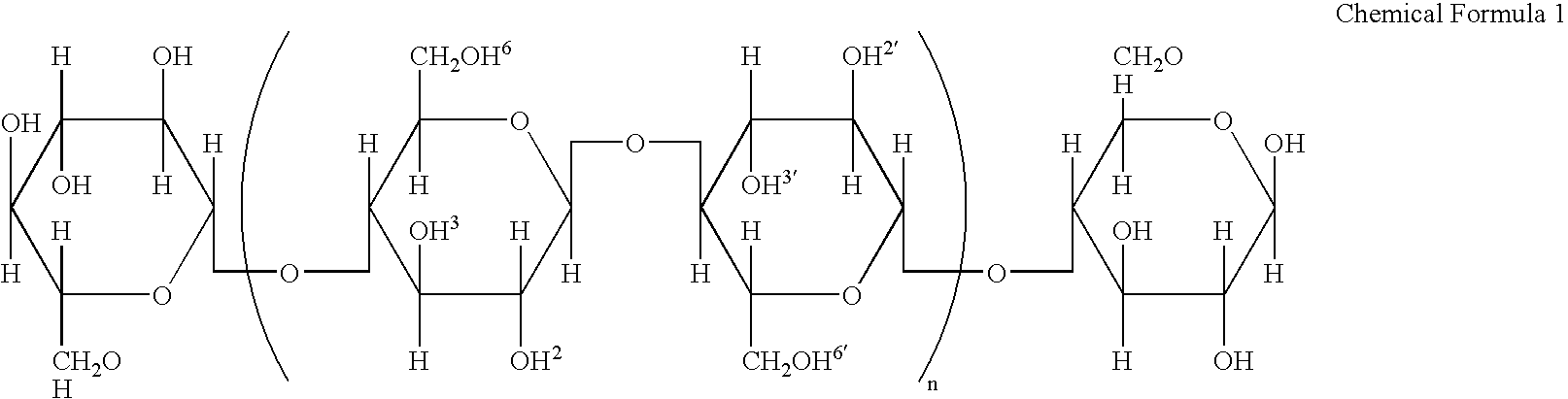
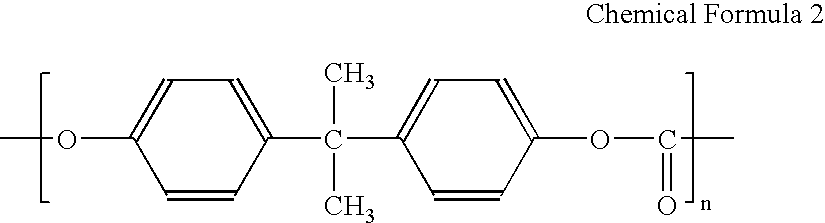
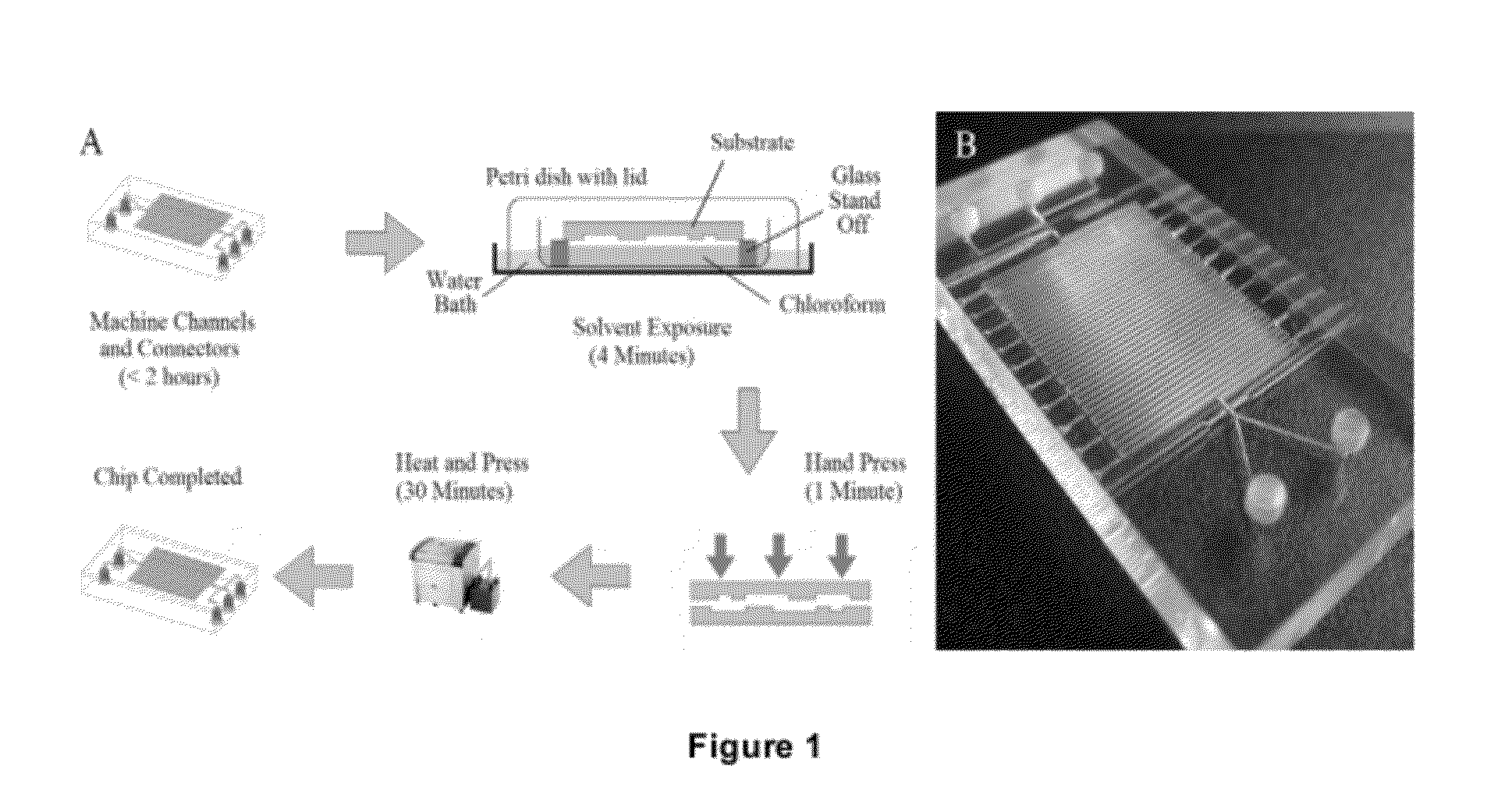
Patents
Literature
383 results about "Solvent vapor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
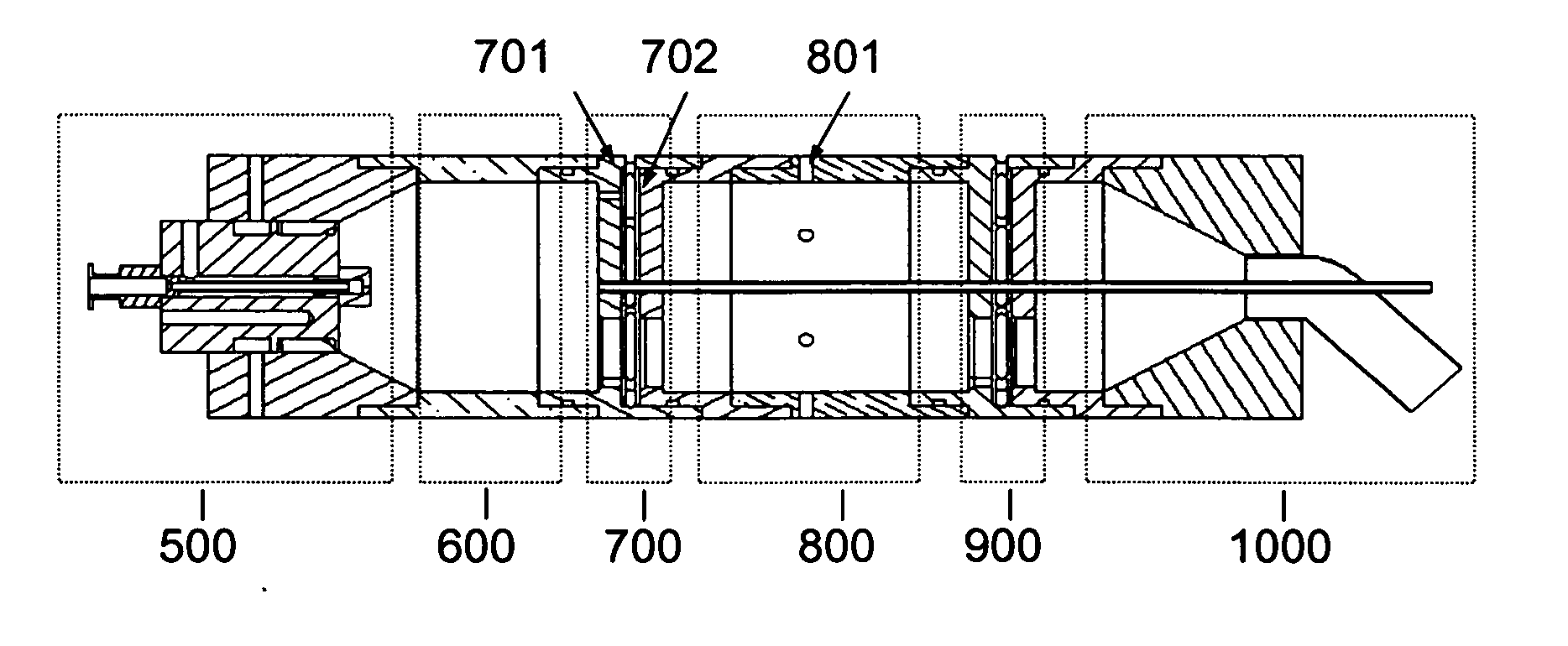
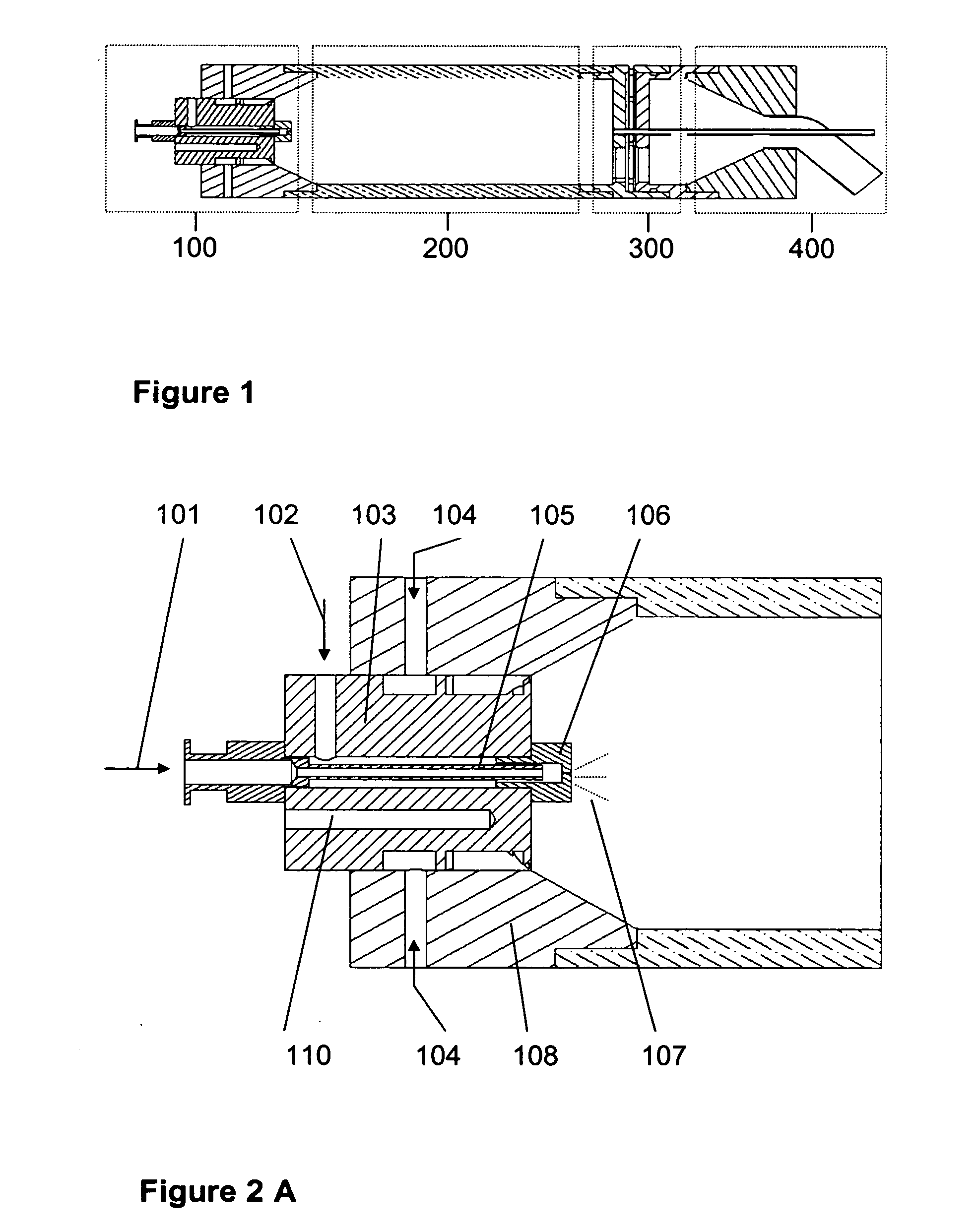
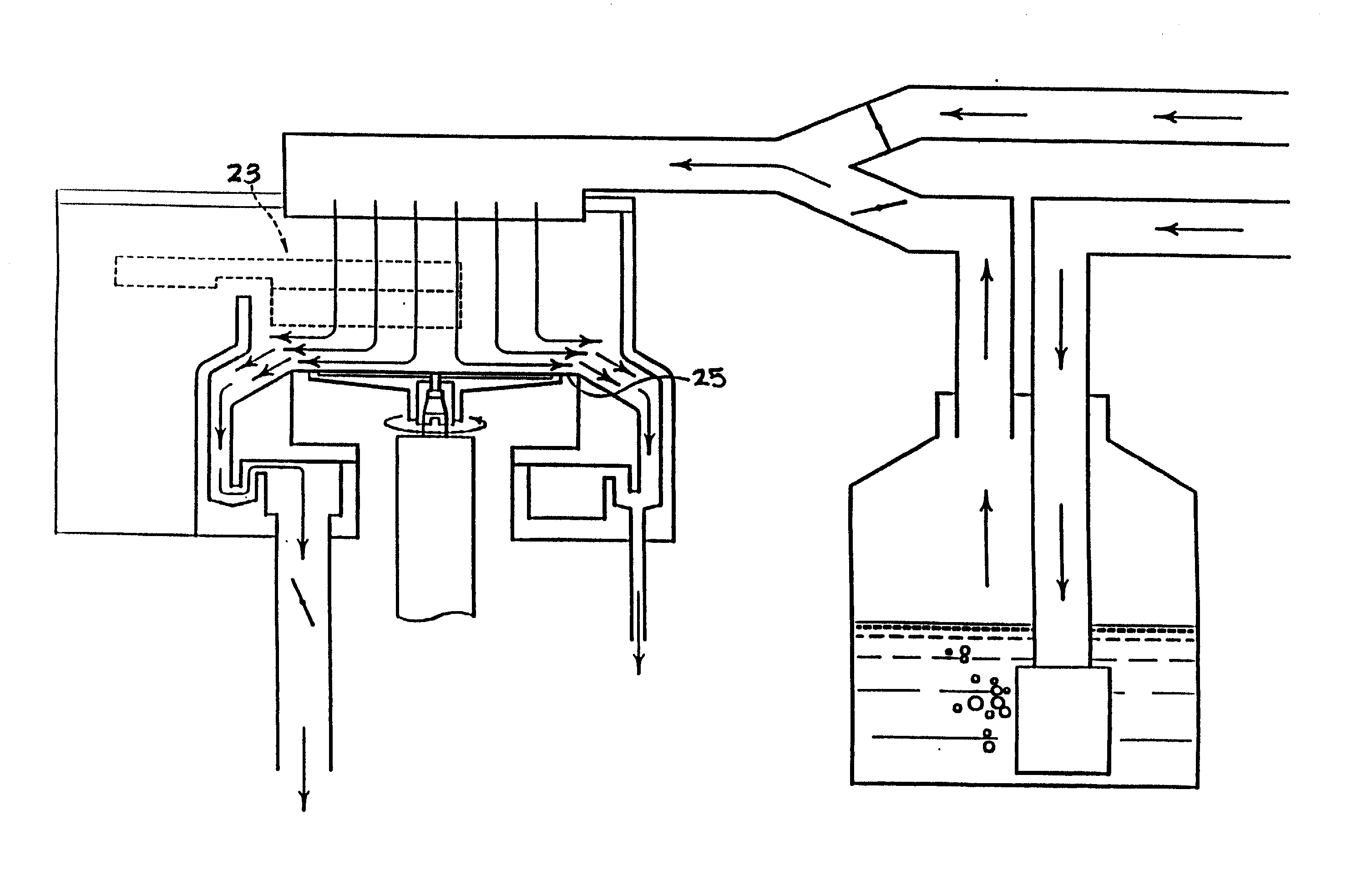
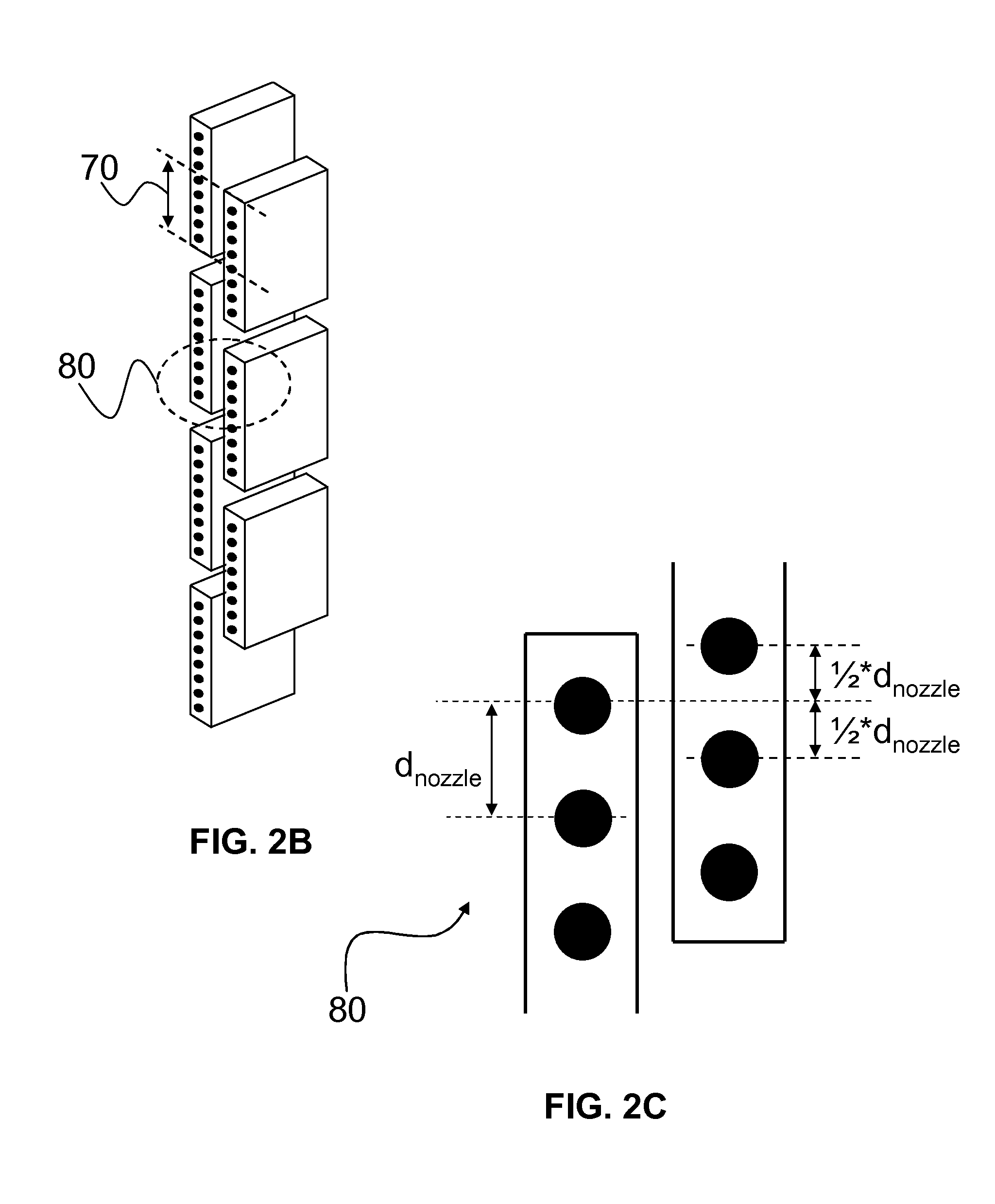
Aerosol processing and inhalation method and system for high dose rate aerosol drug delivery
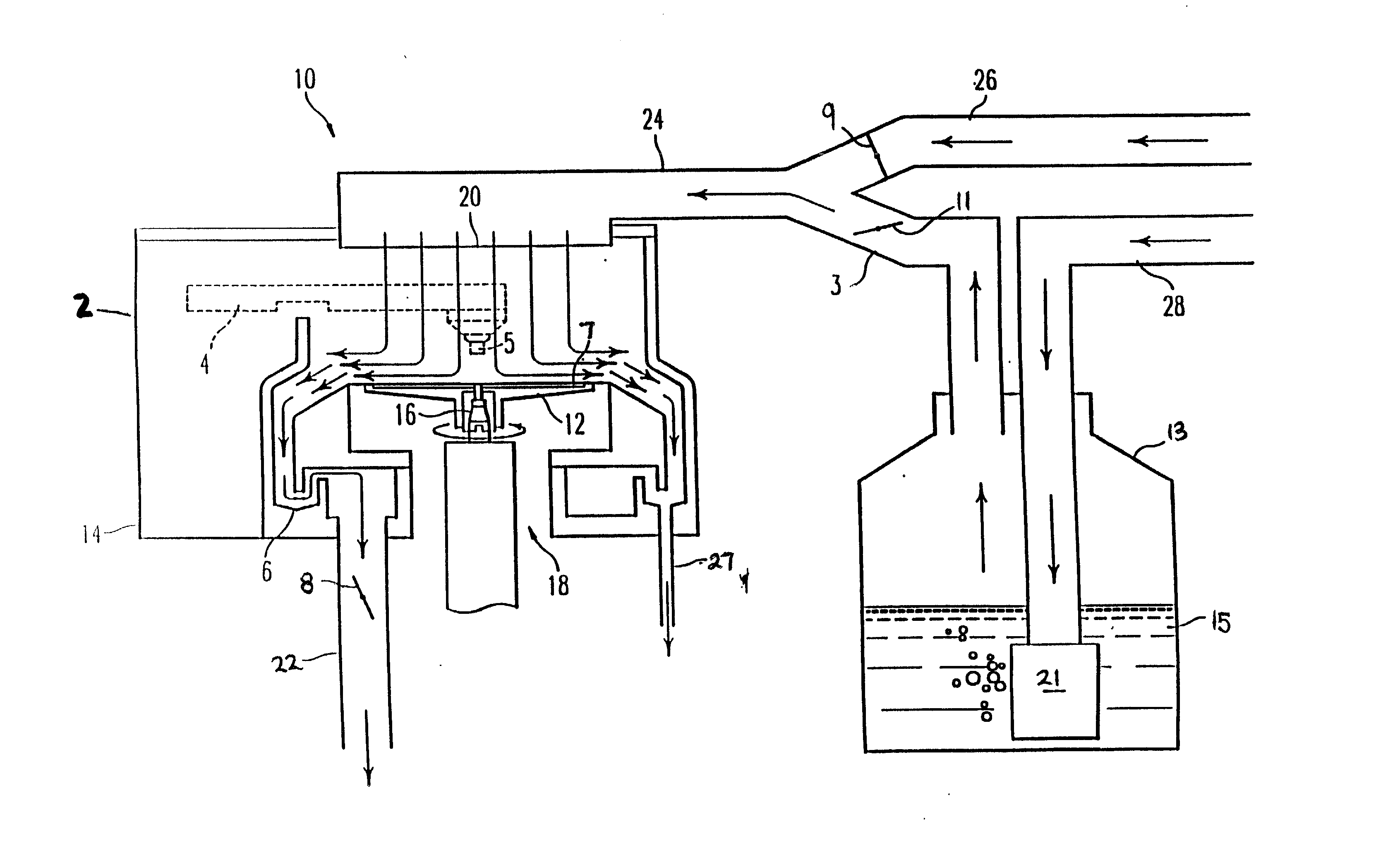
ActiveUS20070144514A1Increase dose rateRisk minimizationRespiratorsLiquid surface applicatorsSolvent vaporCounter flow
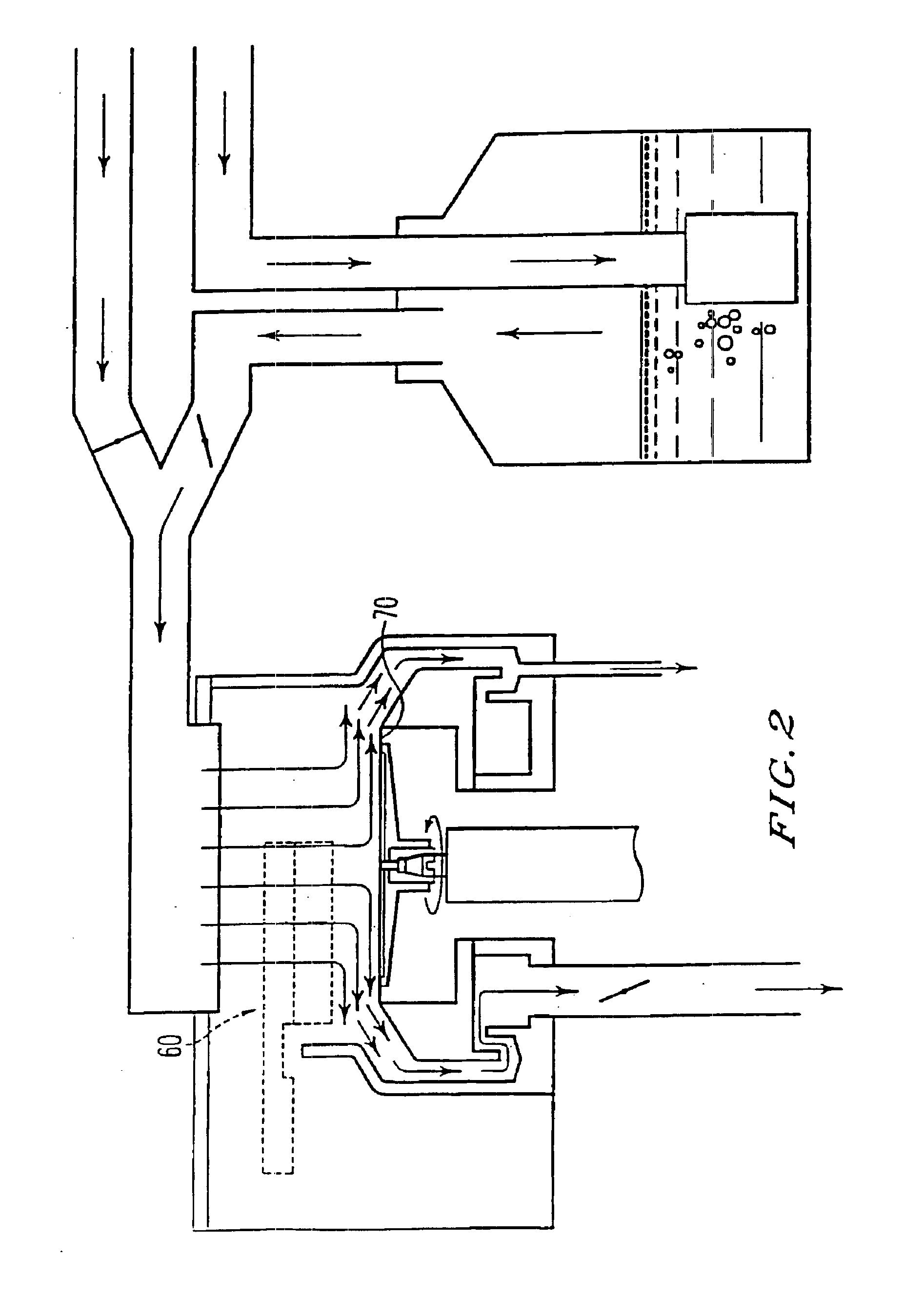
A method and system is disclosed which is capable of delivering at a high dose rate, respirable solid aerosols derived from aqueous- or nonaqueous-based solutions containing the desired therapeutic agent(s). The method and system comprises the integration of an aerosol generator, an aerosol evaporator, an aerosol concentrator, and an aerosol flow regulator. The aerosol generator generates 10-30 μm droplets, with a narrow size distribution. The aerosol jet is arrested by a coaxial counter-flow heated air jet, and evaporated rapidly by annular swirling heated air. Most of the air, together with the unwanted solvent vapor, is removed from the aerosol stream during the process of aerosol concentration. The output aerosol carries the dry particles to be inhaled by the patient. The respiratory-governed control of aerosol fluid generation system delivers fluid containing the test agent of interest (drug or toxin) to the aerosol generator throughout inhalation.
Owner:KAER BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
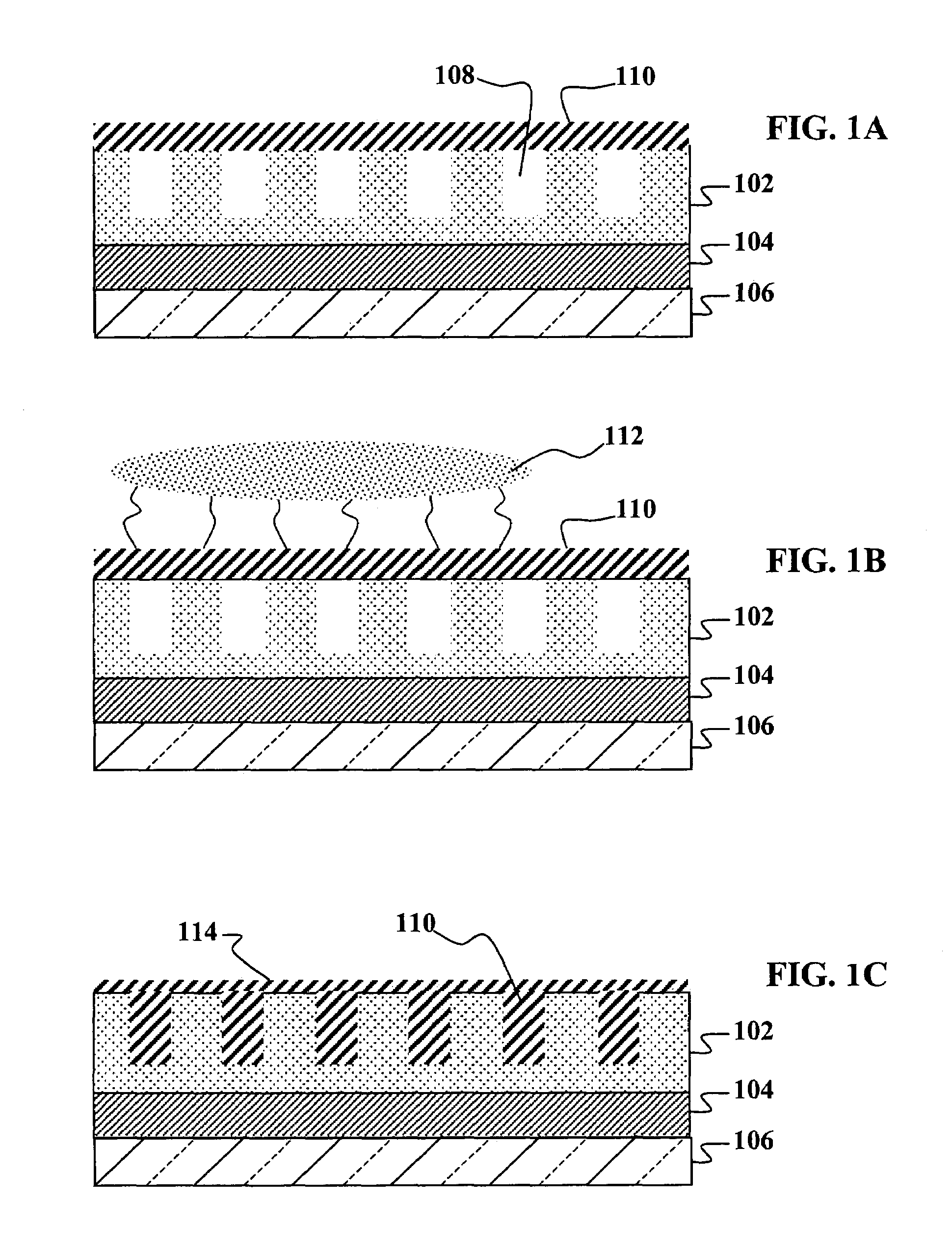
Solvent vapor infiltration of organic materials into nanostructures
Spaces in a nanostructure can be filled with an organic material while in the solid state below Tm (without heating) by exposing the organic material to solvent vapor while on or mixed with the nanostructured material. The exposure to solvent vapor results in intimate contact between the organic material and the nanostructured material without having to expose them to possibly detrimental heat to melt in the organic material. Solution processing methods need only to be employed to create bulk films while organic material infiltration can take place in the solid state after depositing the film.
Owner:AERIS CAPITAL SUSTAINABLE IP
Method and system for desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization
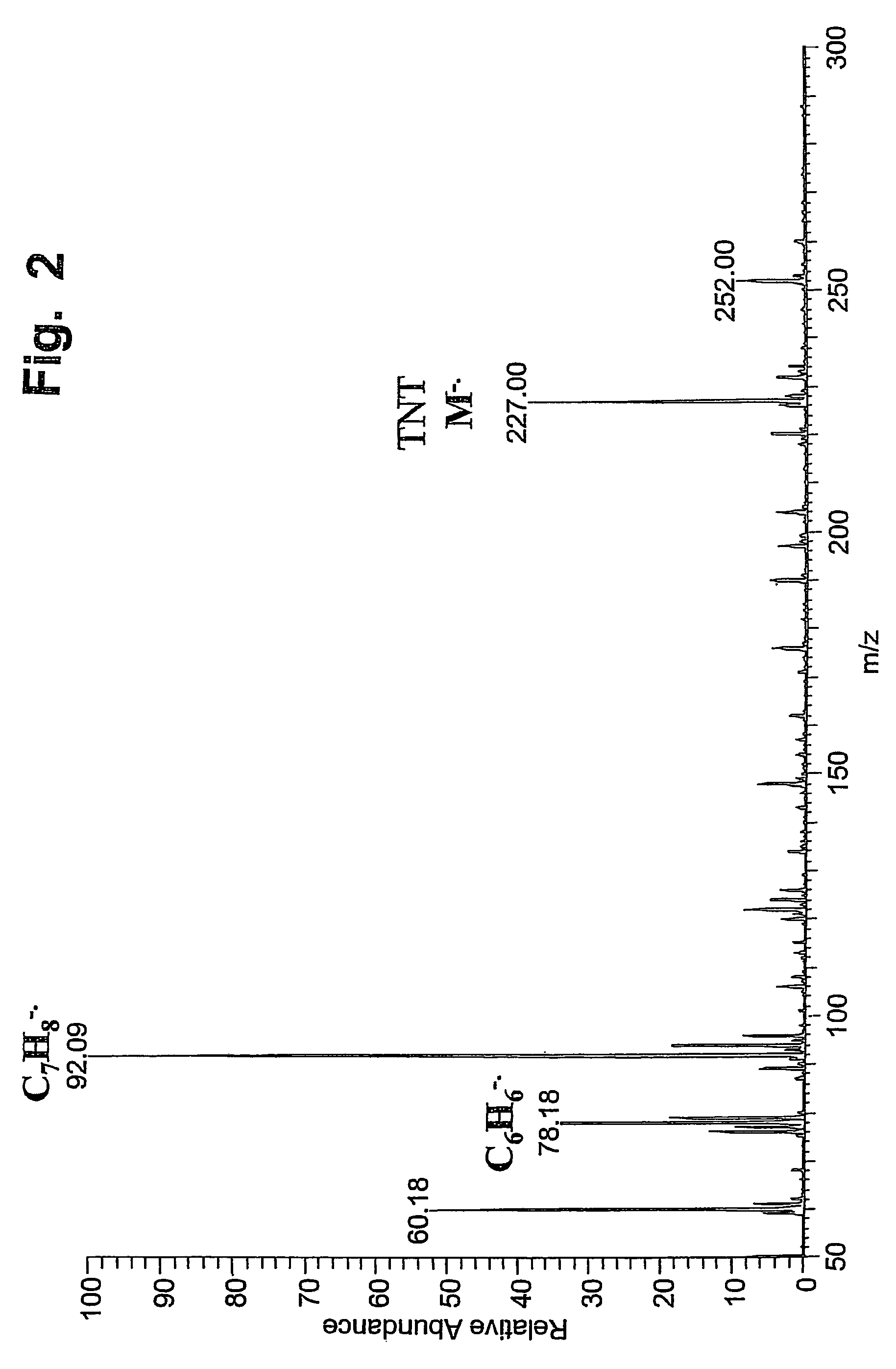
ActiveUS7544933B2Minimizing chanceHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by optical meansIon sources/gunsSolvent vaporDesorption
A desorption atmospheric pressure chemical ionization (DAPCI) system delivers a primary ion beam composed of an inert, high velocity gas and solvent ions to a surface to effect desorption and ionization of both volatile and non-volatile species present on surfaces. A electrode having a tapered tip is connected to a high voltage power supply. The tapered tip projects outward from a capillary carrying a high-speed flow of gas. A vapor of a solvent is mixed into the annular gas flow surrounding the needle. The gaseous solvent vapor is ionized in close proximity to the tapered tip by virtue of the high voltage applied to the electrode. The high-speed flow of gas and solvent vapor ions extending outward from the capillary is directed toward a substrate on which an analyte of interest may have been deposited. The solvent vapor ions can blanket the surface of the analyte causing a static charge build up that facilitates ion desorption and additionally can provide positive ion adducts of the analyte freed from the substrate surface that can be directed toward an atmospheric intake of a mass spectrometer or other instrument capable of studying the analyte.
Owner:PURDUE RES FOUND INC
Aerosol processing and inhalation method and system for high dose rate aerosol drug delivery
ActiveUS7802569B2Risk minimizationIncrease dose rateRespiratorsDispersed particle separationCounter flowSolvent vapor
Owner:KAER BIOTHERAPEUTICS CORP
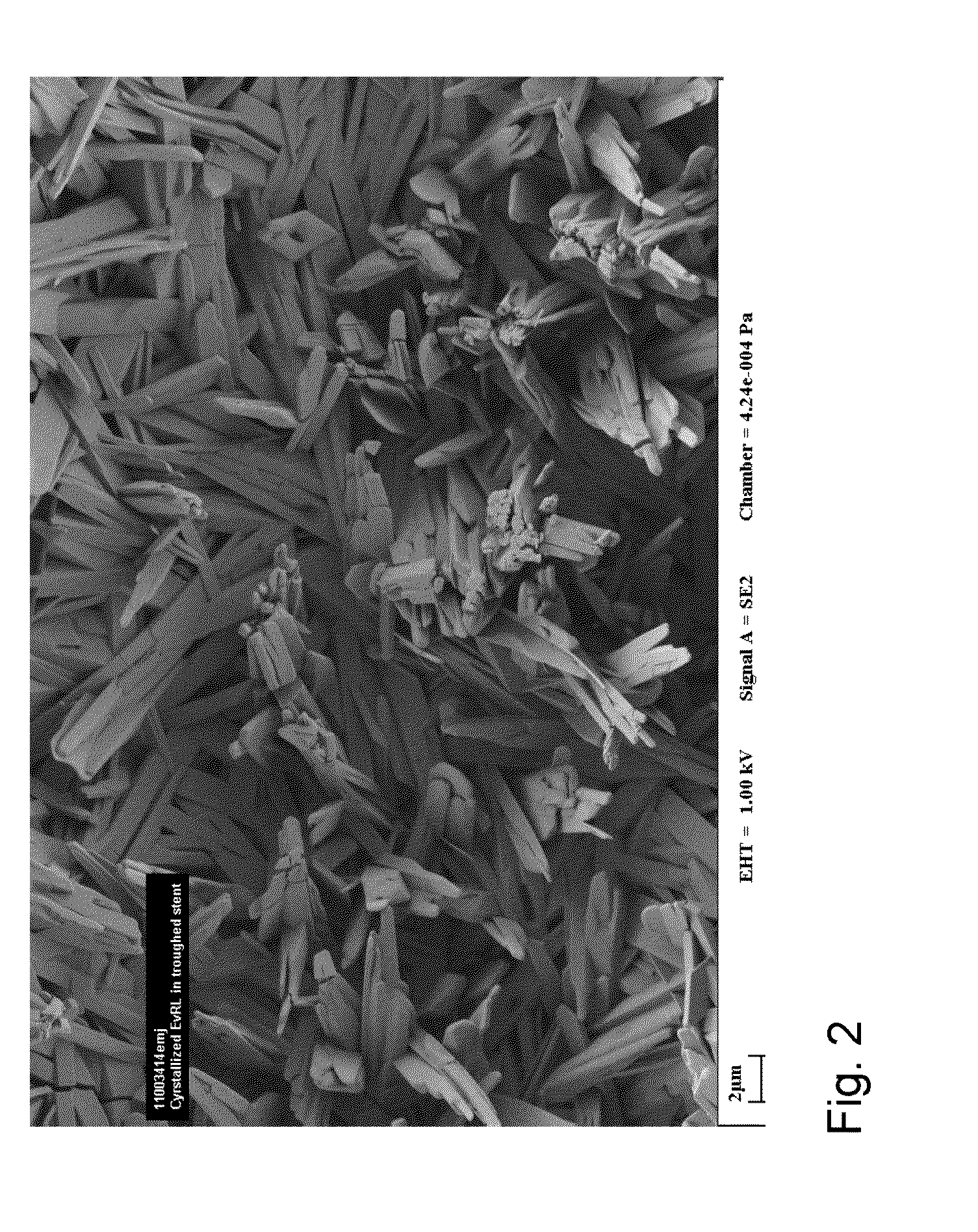
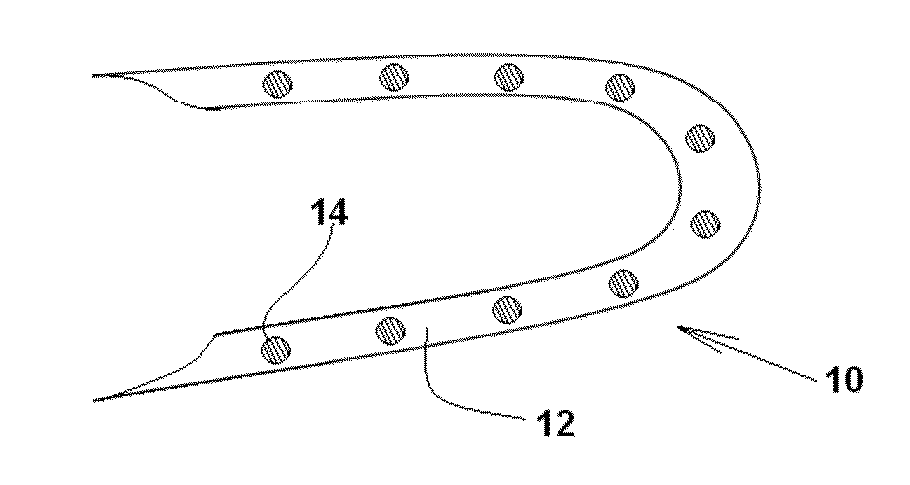
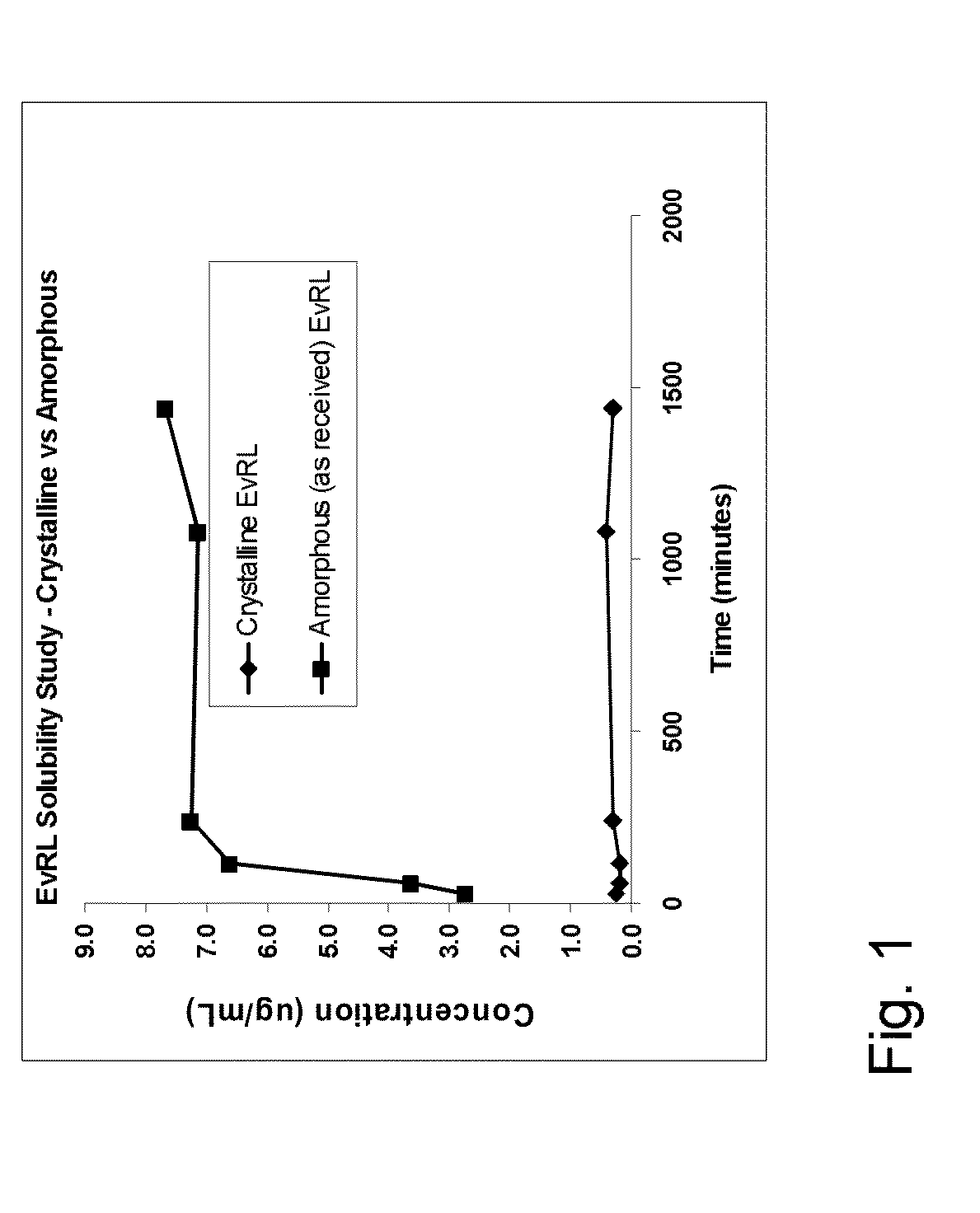
Medical Device with Crystalline Drug Coating
A medical device having a polymer-free outer surface layer comprising a crystalline drug selected from the group consisting of everolimus, tacrolimus, sirolimus, zotarolimus, biolimus, and rapamycin. The device may be produced by a method comprising the steps of providing a medical device; applying a solution of the drug to said portion of the outer surface to form a coating of amorphous drug; and vapor annealing the drug with a solvent vapor to form crystalline drug; wherein a seed layer of a crystalline form of said drug having a maximum particle size of about 10 μm or less is applied to at least said portion of the outer surface of the device before or after applying the drug solution, but before vapor annealing the amorphous coating.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Solvent extraction of hydrocarbons from inorganic materials and solvent recovery from extracted hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6207044B1No pollution to the environmentIncrease surface areaLiquid organic insulatorsWorking-up pitch/asphalt/bitumen by chemical meansHydrocarbon solventsSolvent vapor
A process for the solvent separation of hydrocarbons from tar sand or contaminated soils comprises extracting the hydrocarbons from the sand or soil in a solvent extraction means to form a hydrocarbon rich solvent solution. The rich solvent is separated from the hydrocarbon in a process that utilizes flashing of the solvent in a heated flashing column at ambient pressure. The hydrocarbon is withdrawn from the bottom of the column and the flashed solvent vapors are strategicly withdrawn and passed into a condensation column from which the condensed solvent may be recycled. The flashing column is divided by a series of horizontal, vertically aligned apertured trays. The solution is introduced into the top of the column and the flashing operation is facilitated by the increase in the surface area of the solution as it flows by gravity from tray to tray. The column is maintained at a temperature, preferably above the boiling temperature of the solvent. The process is particularly adapted to the use of chlorinated hydrocarbon solvents and most particularly to the use of methylene chloride.
Owner:LUCENT TECH INC
Capillary separated vaporization chamber and nozzle device and method
There is provided a capillary separated vaporization chamber and nozzle method and device for improved electron ionization liquid chromatography mass spectrometry of samples in a supersonic molecular beam. The device includes a vaporization chamber located upstream of a supersonic nozzle; a capillary separating the vaporization chamber and the supersonic nozzle, means for spray formation from sample in a flowing liquid; a vacuum system into which the supersonic nozzle induces supersonic expansion of the vaporized sample compounds and solvent vapor, for forming a supersonic molecular beam with vibrationally cold sample molecules and vaporized solvent; flythrough electron ionization ion source; mass analyzer; an ion detector and means for data processing of the resulting mass spectral information, for identifying and / or quantifying the chemical content of the sample.
Owner:AMIRAV AVIV
Manufacturing Process, Such as Three-Dimensional Printing, Including Solvent Vapor Filming and the Like
InactiveUS20080032083A1Improving dimensional resolutionControl spreadStampsWrappersPorosityCalcium biphosphate
Methods of manufacturing an article use three-dimensional printing for a portion of the manufacturing. Three-dimensionally printing is conducted onto a powder bed which contains both organic-solvent-soluble, water-insoluble particles and water soluble, organic-solvent-insoluble particles. The water-soluble particles which may be selected for properties such as size and may include more than one substance. The organic-solvent-insoluble particles may further include at least one substantially insoluble substance such as a member of the calcium phosphate family. Printing may be done using an aqueous binder liquid. After removal of unbound powder, the preform may be exposed to the vapor of an organic solvent which causes the particles of organic-soluble-polymer to fuse to each other. This may further be followed by dissolving out the water-soluble particles, if such particles were present in the powder. Solvent vapor fusing together with the use of porogen particles may also be used in manufacturing methods other than 3DP. Rather than using organic solvent, heat responsive particles can be used, and can be filmed by elevated temperatures. Articles that may be produced by the described methods exhibit features such as a high porosity and an ability to undergo large deformations without breaking, and by at least partial springback from such deformation. The springback may be substantially instantaneous or may be time-dependent involving a time period of at least several seconds.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for producing film from polymer solution, and optical polymer film
A dope containing cellulose acylate as a main content of polymer is cast on a front surface of a moving belt in a method of producing a film from a solution. A drying apparatus is confronted to a back surface of said belt to evaporate a solvent in the gel-like film. Further, a condensers are confronted to a cast surface of said gel-like film to condense a solvent vapor for recovery. A wind speed above and near the gel-like film is from 0.01 m / s to 0.5 m / s, and the belt is transported downwards at the casting position PS. When d (mm) is a distance between the casting surface and each condenser, Tw (° C.) is a temperature of each condenser, and Ts (° C.) is a temperature of the casting dope, conditions are satisfied: Q=(Ts-Tw) / d and 5<Q<100. The obtained film is excellent in thickness uniformity and optical properties, and therefore adequate for the optical film.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Solvent extraction of polyhydroxyalkanoates from biomass
ActiveUS7226765B2Quality improvementImprove practicalityFermentationSolid solvent extractionSolvent vaporSolvent extraction
Processes for the extraction of PHAs from biomass, said processes comprising: combining the biomass containing the PHAs with a single main solvent to form a biomass liquor; heating the biomass liquor to at least partially solubilize the PHAs from the biomass to form a PHA liquor; separating the biomass from the PHA liquor to form a PHA-enriched liquor; evaporating from 0% to about 50% of the single main solvent from the PHA-enriched liquor to form a solvent vapor and a concentrated PHA-enriched liquor; and cooling the concentrated PHA-enriched liquor to form precipitated PHAs and an impure solvent liquor. Optionally, further recovering the precipitated PHAs from the impure solvent liquor by filtration under pressure. A PHA-enriched liquor and a concentrated PHA-enriched liquor.
Owner:MEREDIAN BIOPLASTICS INC +2
Method and apparatus for recovering and/or recycling solvents
InactiveUS6159345AReduce transportationHeating safetyOrganic chemistrySolvent extractionSolvent vaporDistillation
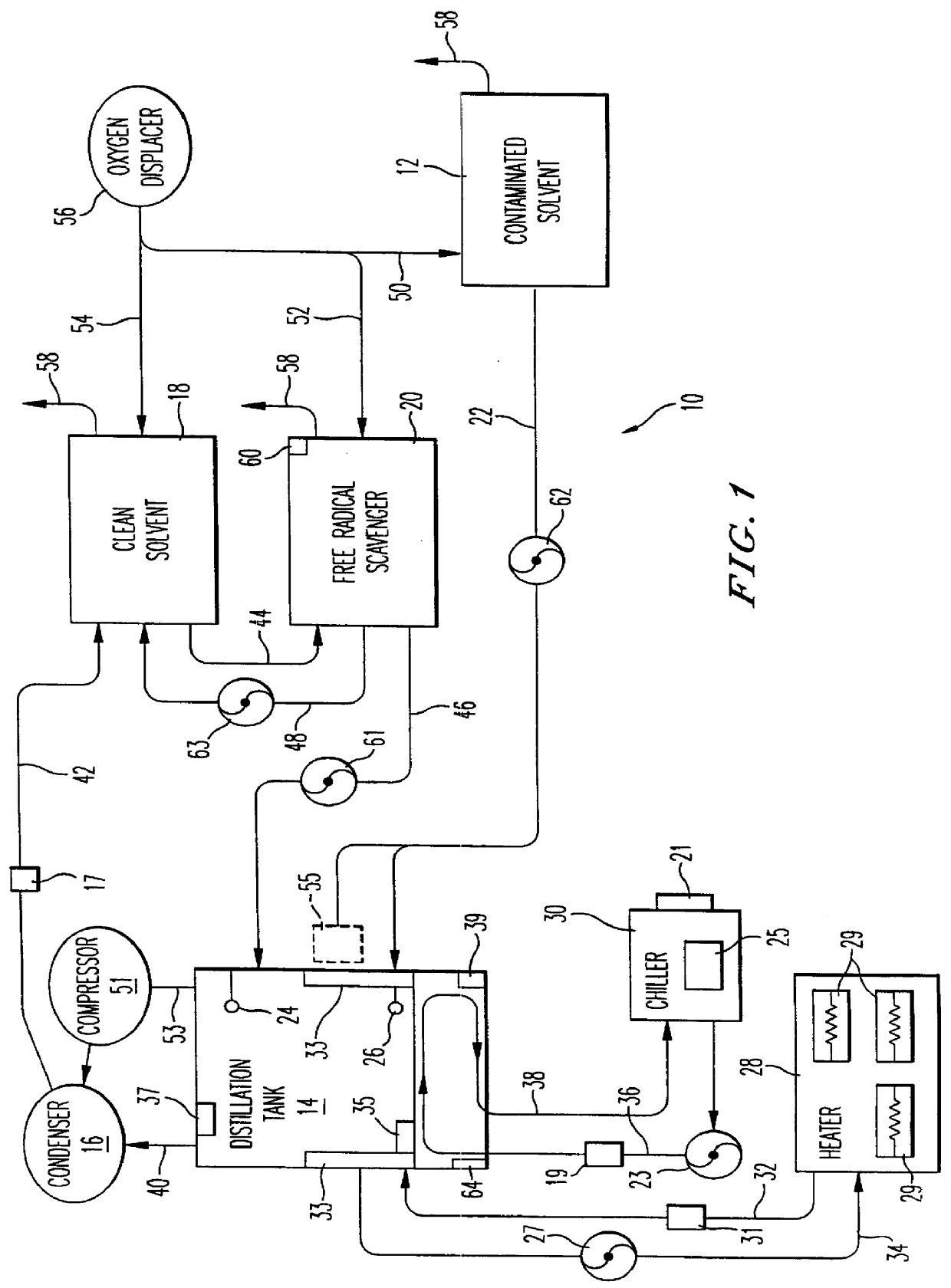
A method and apparatus for recycling and recovering potentially explosive solvents includes providing a contaminated solvent to a distillation tank, vaporizing the solvent in the distillation tank, thereby producing solvent vapor, condensing the solvent vapor, and adding a free radical scavenger substance to the distillation tank during the heating step. The vapor is then condensed and collected in a clean solvent tank where additional free radical scavenger substance is added to the clean solvent tank. Preferably, contaminated solvent is introduced into the solvent recovery system by providing contaminated solvent into contaminated solvent tank which is connected to the distillation tank, and an oxygen displacer substance is provided to the contaminated solvent tank and the clean solvent tank so as to minimize the amount of free oxygen in the tanks.
Owner:MITSUBISHI KAGAKU IMAGING
Preparation method of high purity bulleyaconitine A
ActiveCN101555227AHigh purityReduce manufacturing costNervous disorderOrganic chemistrySolvent vaporEthyl acetate
The invention relates to a preparation method of high purity bulleyaconitine A. The preparation method comprises the following steps: root of radix aconiti feri of Yunnan is crushed, and acid alcoholic solvent or alcohol water solution is used for diacolation, and supersound or thermal refluxing extraction. The extracting solution is decompressed and concentrated to be non-alcoholic at the temperature of 80 to 90 DEG C, cooled down to room temperature, to ensure the relative density to be 1.00 to 1.30; standing is performed for 10 to 20 hours; the extracting solution is filtered; the pH is adjusted to 6.0 to 8.0 with basifier; and then the extracting solution is extracted with ethyl acetate or chloroform. The ethyl acetate or chloroform liquid is contracted, column chromatography is performed to the obtained paste, silica gel or neutral alumina are used as fillers, any one of solvent vapor-acetone-diethylamine, ligarine-acetone-diethylamine or cyclohexane-acetone-diethylamine is used for eluation, the bulleyaconitine A in the collected liquid is constantly checked during the thin layer chromatography, the collected liquid containing the bulleyaconitine A is merged, the solvent is concentrated, carbinol or ethanol is dissolved, filtering is performed, crystallization is performed at room temperature, filtering is performed, the crystal is repeatedly rinsed with carbinol or ethanol, and the final product is obtained. The purity of the obtained product is high, the production cost is low, and the toxicity of the used organic solvent is low.
Owner:KPC PHARM INC
Method of uniformly coating a substrate
InactiveUS20020127334A1Improve thickness uniformityIncrease consumptionPretreated surfacesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolvent vaporProduct gas
A method of and an apparatus for coating a substrate with a polymer solution to produce a film of uniform thickness, includes mounting the substrate inside an enclosed housing and passing a control gas, which may be a solvent vapor-bearing gas into the housing through an inlet. The polymer solution is deposited onto the surface of the substrate in the housing and the substrate is then spun. The control gas and any solvent vapor and particulate contaminants suspended in the control gas are exhausted from the housing through an outlet and the solvent vapor concentration is controlled by controlling the temperature of the housing and the solvent from which the solvent vapor-bearing gas is produced. Instead the concentration can be controlled by mixing gases having different solvent concentrations. The humidity of the gas may also be controlled.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
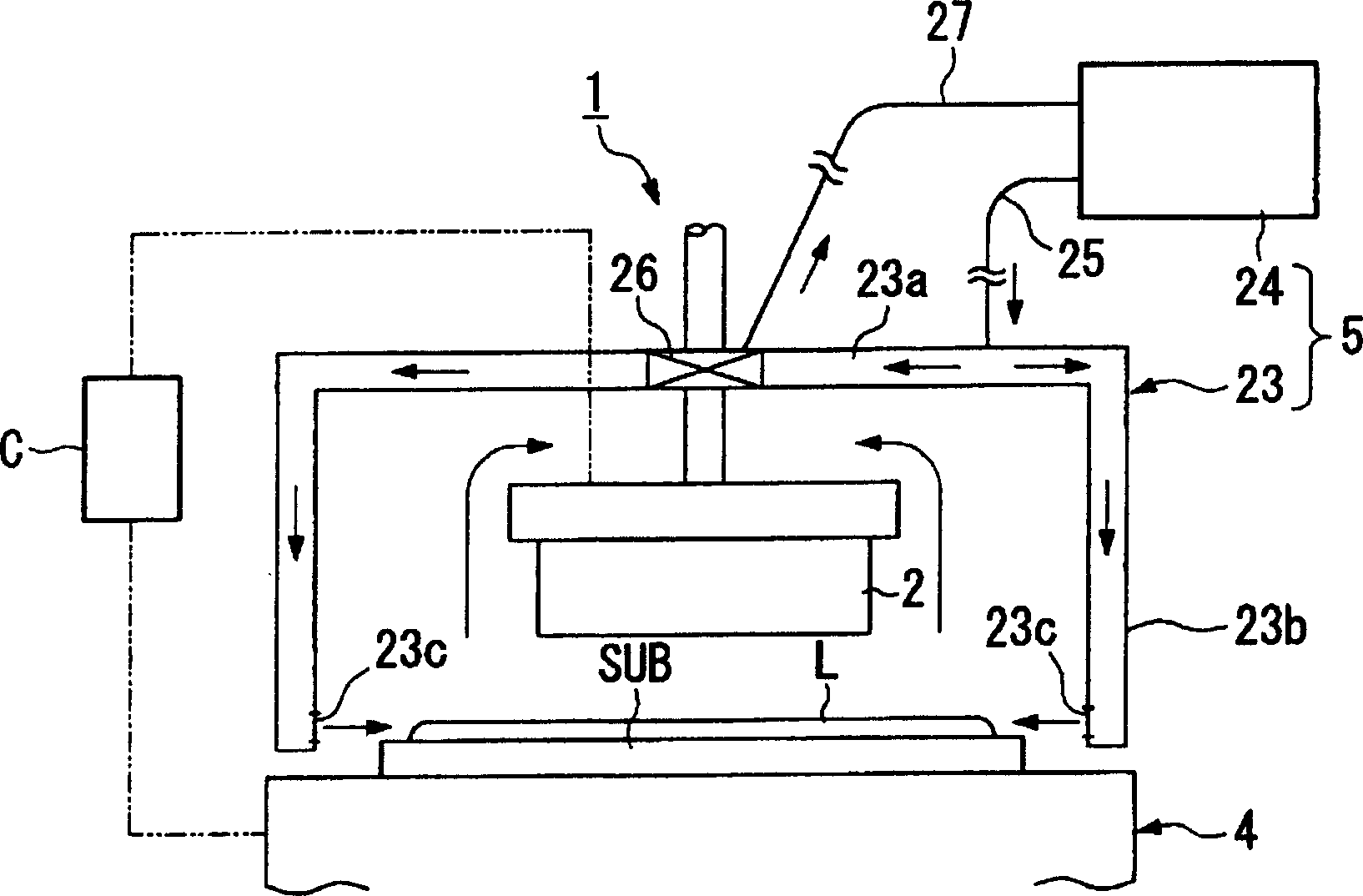
Substrate Treatment Method and Substrate Treatment Apparatus
An object of the present invention is to uniformly form a fine resist pattern with a desired dimension within a plane of a substrate. In a solvent vapor supply unit, a solvent vapor discharge nozzle is provided which can discharge a solvent vapor for swelling a resist pattern while moving above the front surface of a wafer. The wafer for which developing treatment has been finished and on which a resist pattern has been formed is carried into the solvent vapor supply unit, and the solvent vapor discharge nozzle is moved above the front surface of the wafer, so that the solvent vapor discharge nozzle supplies the solvent vapor onto the front surface of the wafer. This uniformly supplies a predetermined amount of solvent vapor to the resist pattern on the front surface of the wafer. As a result, the solvent vapor causes the resist pattern to evenly swell by a predetermined dimension, so that a resist pattern with a desired dimension is finally uniformly formed within the plane of the wafer.
Owner:TOKYO ELECTRON LTD
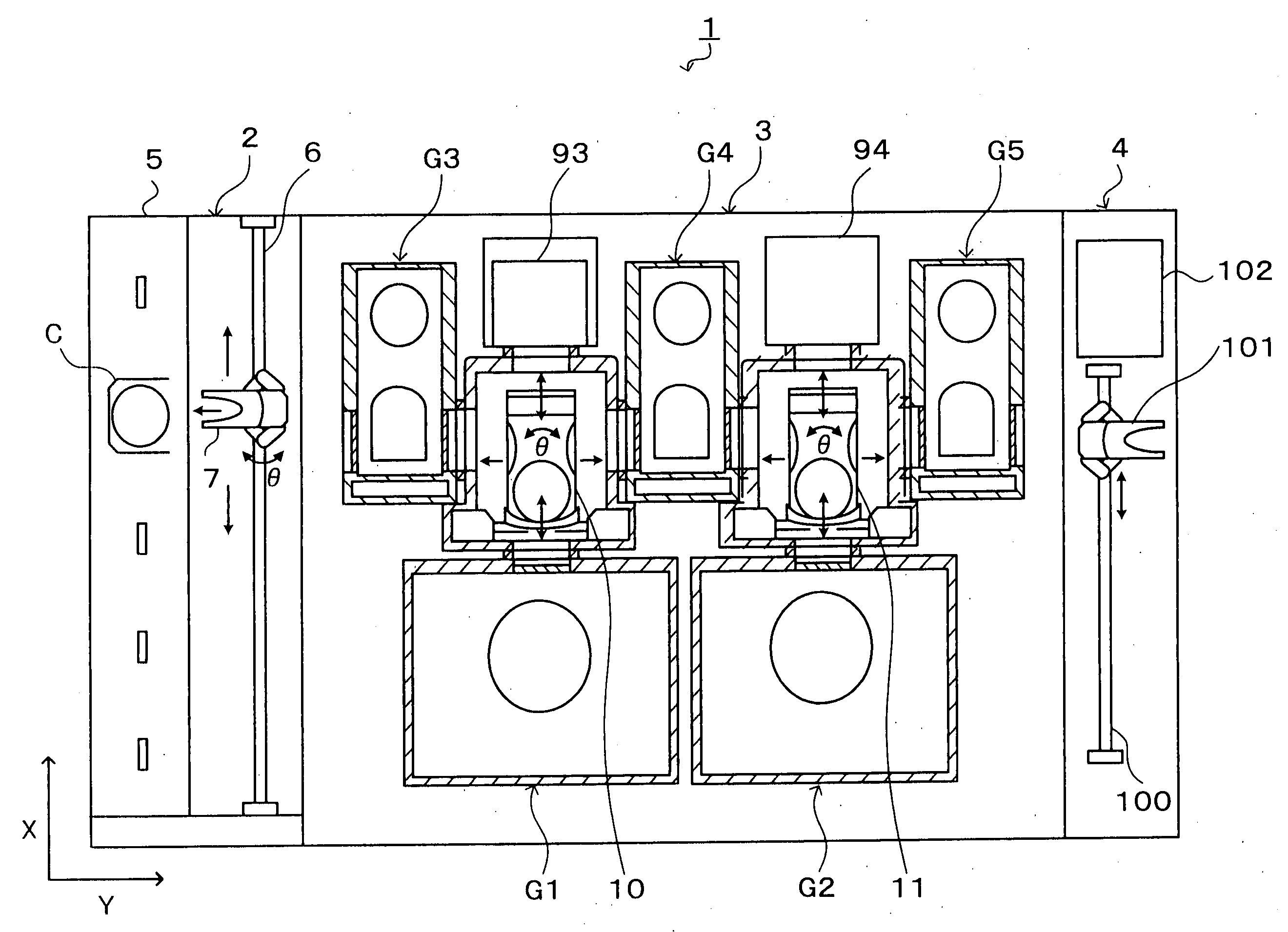
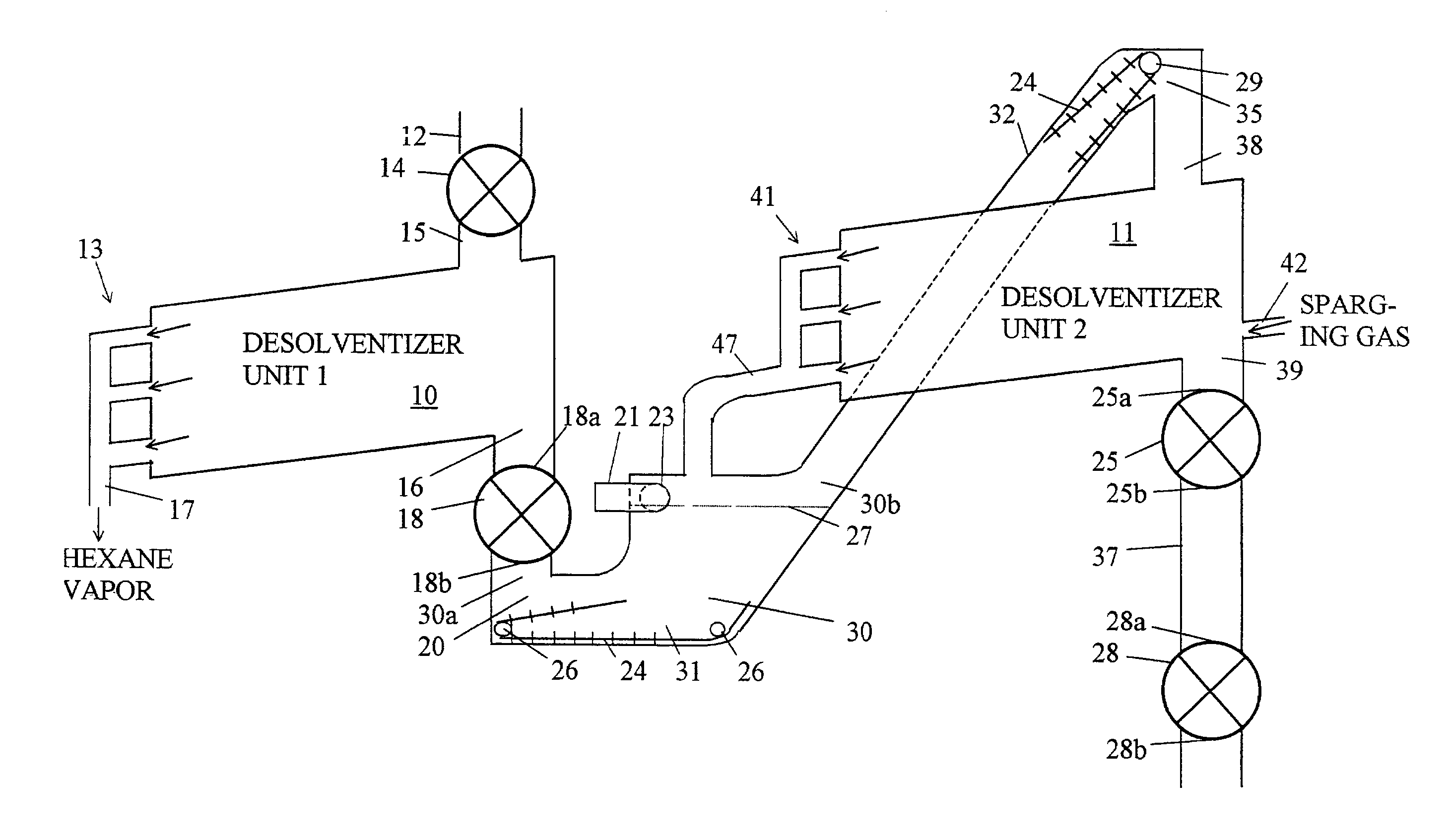
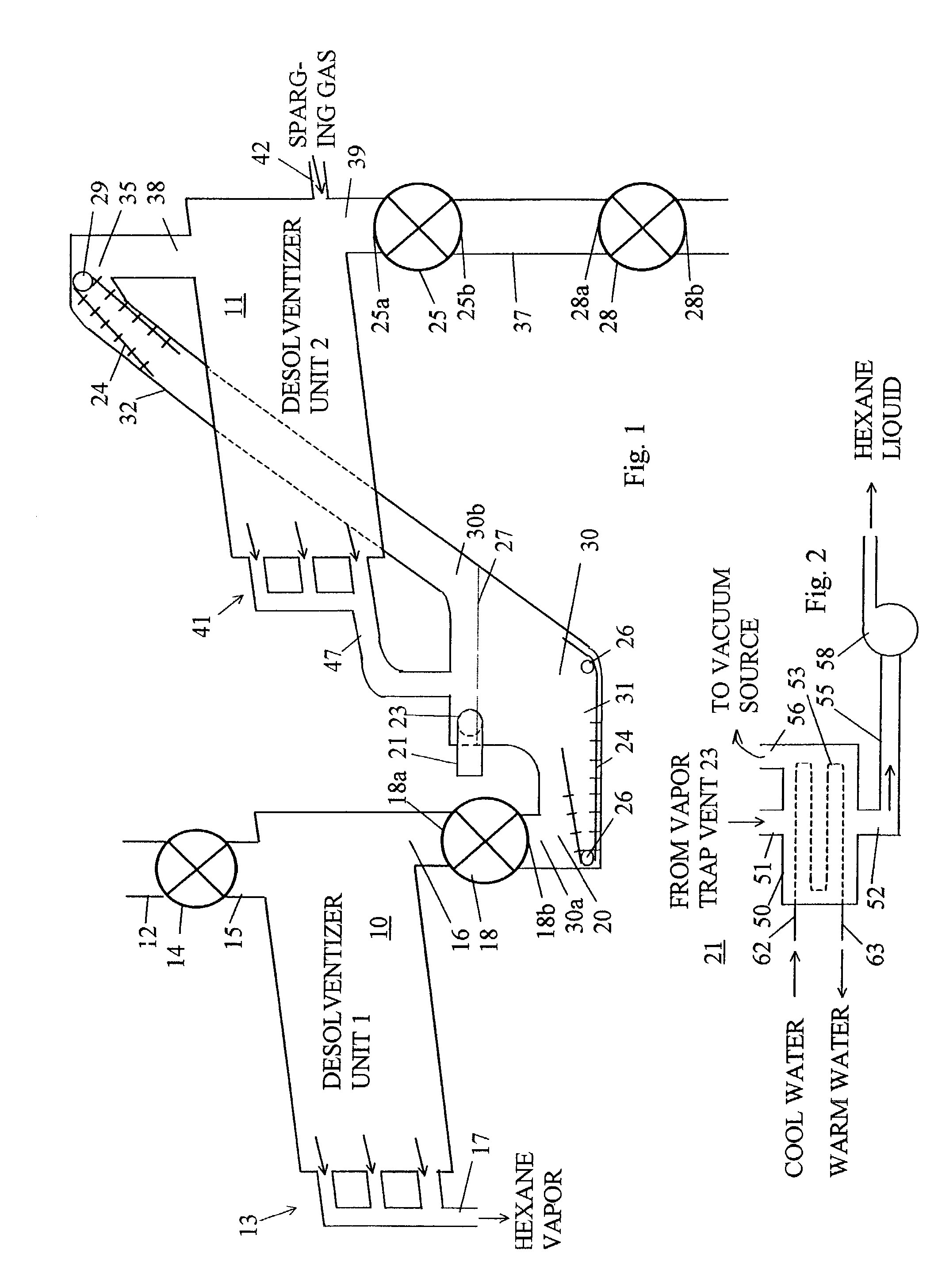
Two stage apparatus for desolventizing food grain meal
A desolventizing system for removing solvent from a quantity of solvent-laden particles such as flakes comprises first and second desolventizer units, each having an inlet port for receiving solvent-laden particles, an outlet port for discharging at least partially desolventized particles, and a solvent vapor port. A solvent trap is connected between the outlet port of the first desolventizer through a first airlock, and to the inlet port of the second desolventizer unit. Particles entering the solvent trap through the first airlock are conveyed to the inlet port of the second desolventizer. The second desolventizer unit has an airlock connected to the outlet port of the second desolventizer unit. The solvent trap has a vent preferably in the upper part of the trap for connection to a vacuum source that maintains a partial vacuum within both the solvent trap and the second desolventizer unit allowing liquid solvent and water permeating particles within the second desolventizer unit to vaporize efficiently at a relatively low temperature. Solvent vaporized in each desolventizer unit can be drawn out through the solvent vapor port of the desolventizer unit for further processing and later reuse.
Owner:CROWN IRON WORKS
Method and apparatus for desolvating flowing liquid
ActiveUS20100000943A1Quick releaseAvoid contactLiquid degasificationComponent separationTemporal resolutionSolvent vapor
Methods and apparatus for desolvating flowing liquid streams while retaining temporal resolution of dissolved substrates are disclosed. A novel small-scale self-regulating spray dryer preserves temporal resolution while desolvating a liquid chromatography eluent stream and depositing the solute onto an optical surface for infrared spectrographic analysis. The liquid eluent is pumped through a heated nebulizer to create a high-speed jet of solute containing liquid and solvent vapor. This jet is directed circumferentially inside a hot cylindrical cavity. Centrifugal force causes the larger liquid droplets to travel along the outer diameter of the cavity. The cavity surface is heated to cause the droplets to film boil. Film boiling reduces droplet contact with the cavity surface thereby retaining the solute in the droplets. The solute temperature is limited by controlling the pressure into which the solvent evaporates from the droplets. When the droplets are sufficiently small, Stokes drag from the exiting solvent vapor carries the droplets out through the center of the cylindrical cavity. After exiting, the superheated solvent vapor further dries the droplets. Solvent vapor is removed by condensation onto a cooled surface. A freezing point reducing agent may be added to improve removal of solvent condensate. Stokes drag from a non-condensable gas maintains the dried droplets in suspension. This suspension travels through an orifice that focuses the impaction of the dried droplets onto the optical surface for infrared analysis. The deposition surface is in an evacuated chamber and is temperature controlled to freeze liquid solutes yet allowing sublimation of residual solvent.
Owner:SPECTRA ANALYSIS INSTR
Method to improve post wafer etch cleaning process
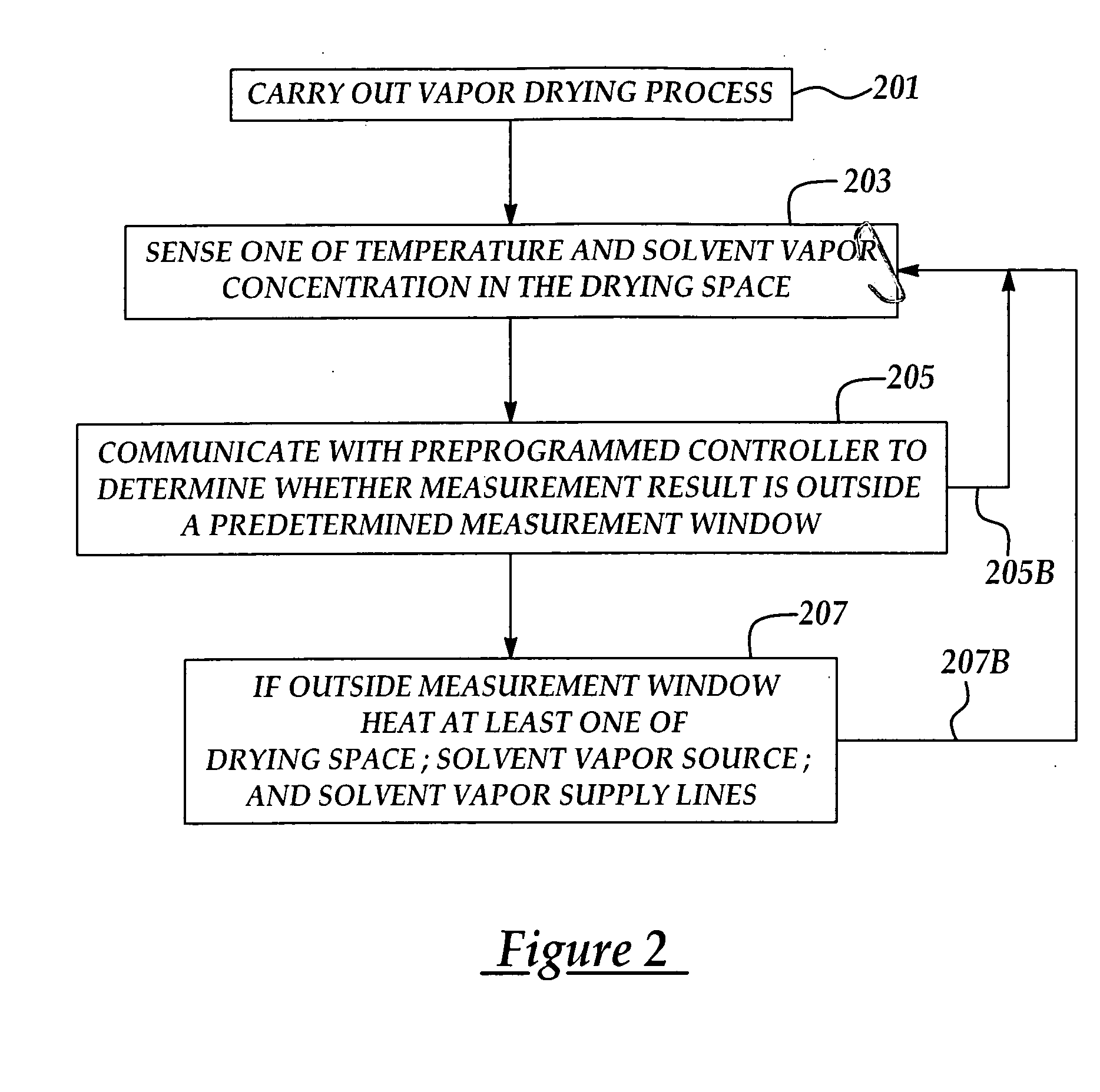
InactiveUS20050091874A1Drying solid materials with heatDrying gas arrangementsSolvent vaporPhysical chemistry
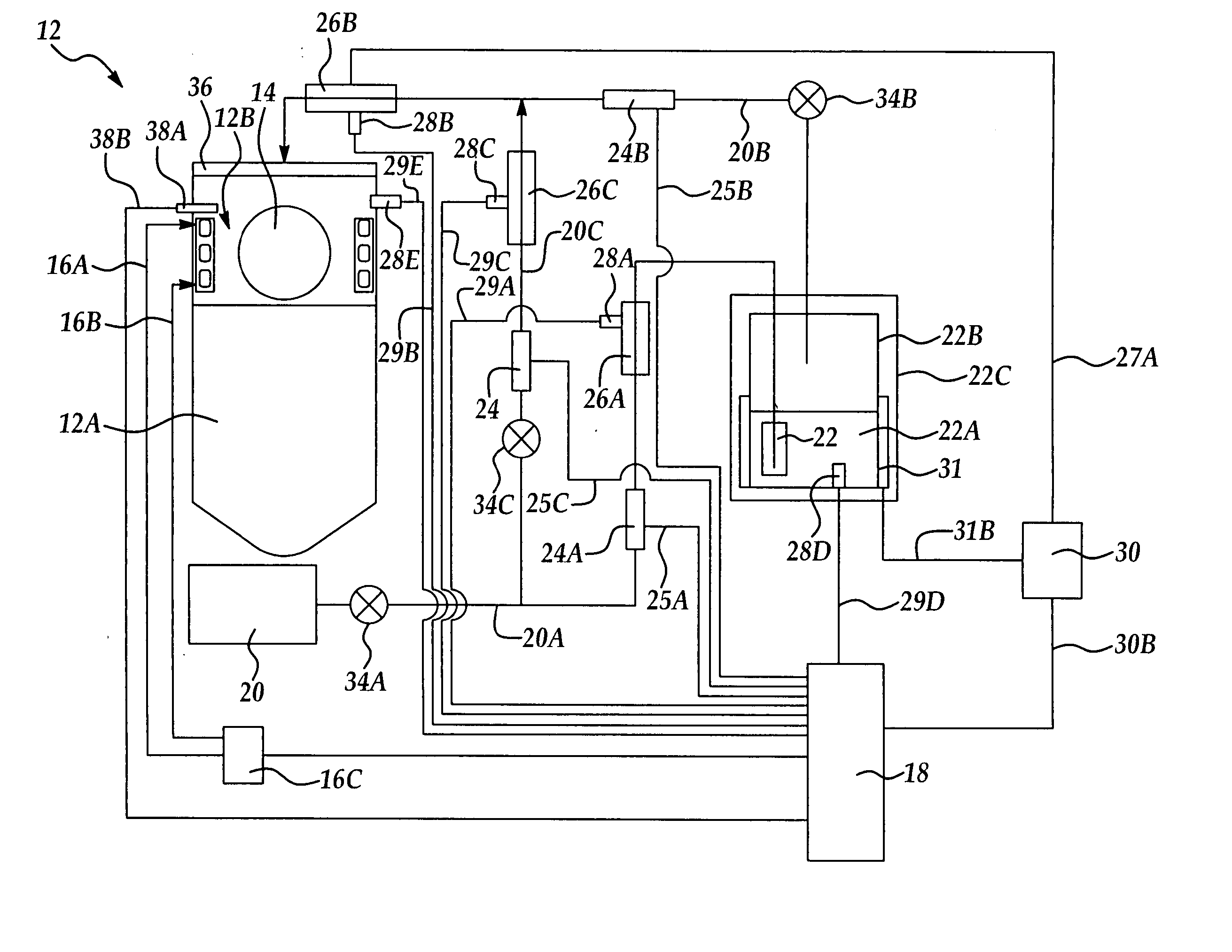
A method and apparatus for performing a semiconductor process wafer drying process, the method provides a semiconductor wafer having a process surface disposed in an enclosed drying space following exposure of the process surface to water; supplying a solvent vapor to the drying space at a predetermined concentration from a solvent vapor source and at least one solvent vapor supply line; determining at least one of a solvent vapor concentration and a solvent vapor temperature in the drying space; and heating in response to the determined solvent concentration at least one of at least a portion of one of the solvent vapor source, the at least one solvent vapor supply line, and at the drying space to alter the solvent vapor concentration in the drying space.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Solvent vapor bonding and surface treatment methods
The present invention relates to a method of producing a microstructured device, as well as a method of processing a microstructured substrate to heal surface defects therein, a method of bonding substrates and healing surface defects in a substrate, and microstructured devices produced by these methods.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Thin film spray coating machine and thin film preparation method
InactiveCN102553753AChange shapeGood modification effectPretreated surfacesLiquid spraying apparatusSolvent vaporHeat conducting
The invention discloses a thin film spray coating machine, which comprises a spray head, and is characterized in that: the spray head is fixed on a three-dimensional adjusting frame and can move in a three-dimensional way; a post-treatment tank is arranged below the spray head; the bottom of the post-treatment tank is provided with a heat conducting plate; an electric heating plate is arranged below the heat conducting plate; and the post-treatment tank and a cover plate form a closed space. The invention also discloses a thin film preparation method, which comprises the following steps of: spray coating in the post-treatment tank to form a thin film; and then directly performing solvent vapor infiltration post-treatment on the thin film in the post-treatment tank. The thin film spray coating machine provided by the invention can be used for preparing a large-area thin film with uniform thickness, small error, high accuracy and adjustable shape and has high filming repeatability. Heating and solvent infiltration treatment functions are integrated; and laboratory film preparation and small-scale industrial film preparation are facilitated.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
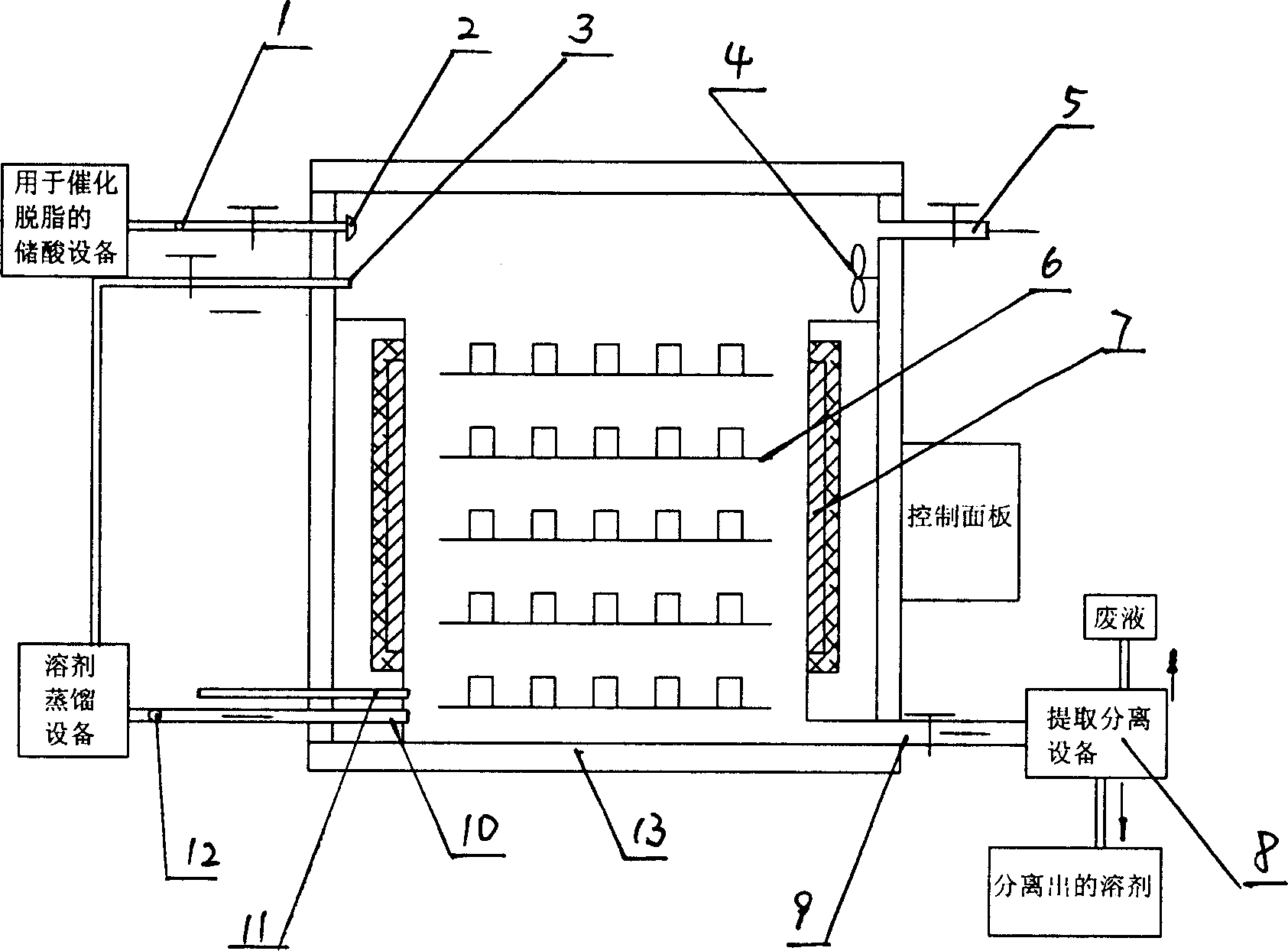
Mixed defatting stove and its mixed defatting process
The mixed defatting stove includes one stove body with a solvent inlet in the lower part and connected via a pump to a solvent storage device, a solvent outlet, a protecting gas inlet in the lower part, a gas exhaust port in the upper part, a solvent vapor inlet in the upper part and connected to solvent distiller, and has a heater on the side wall of the stove body, a blower on the upper part of the stove body to homogenize gas inside the stove, and an atomizer on the upper part of the stove and connected via a pump to a catalytic defatting acid storing device outside the stove body. The mixed defatting stove may meet the requirement of different defatting processes, including single or simultaneous solvent defatting, vapor defatting, condensed vapor defatting, catalytic defatting and siphonic defatting.
Owner:LIANYUNGANG DONGMU NEW MATERIALS CO LTD
Method of uniformly coating a substrate
InactiveUS20020098283A1Uniform solution layer thicknessReduce total usageSpraying apparatusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSolvent vaporProduct gas
A method of and an apparatus for coating a substrate with a polymer solution to produce a film of uniform thickness, includes mounting the substrate inside an enclosed housing and passing a control gas, which may be a solvent vapor-bearing gas into the housing through an inlet. The polymer solution is deposited onto the surface of the substrate in the housing and the substrate is then spun. The control gas and any solvent vapor and particulate contaminants suspended in the control gas are exhausted from the housing through an outlet and the solvent vapor concentration is controlled by controlling the temperature of the housing and the solvent from which the solvent vapor-bearing gas is produced. Instead the concentration can be controlled by mixing gases having different solvent concentrations. The humidity of the gas may also be controlled.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
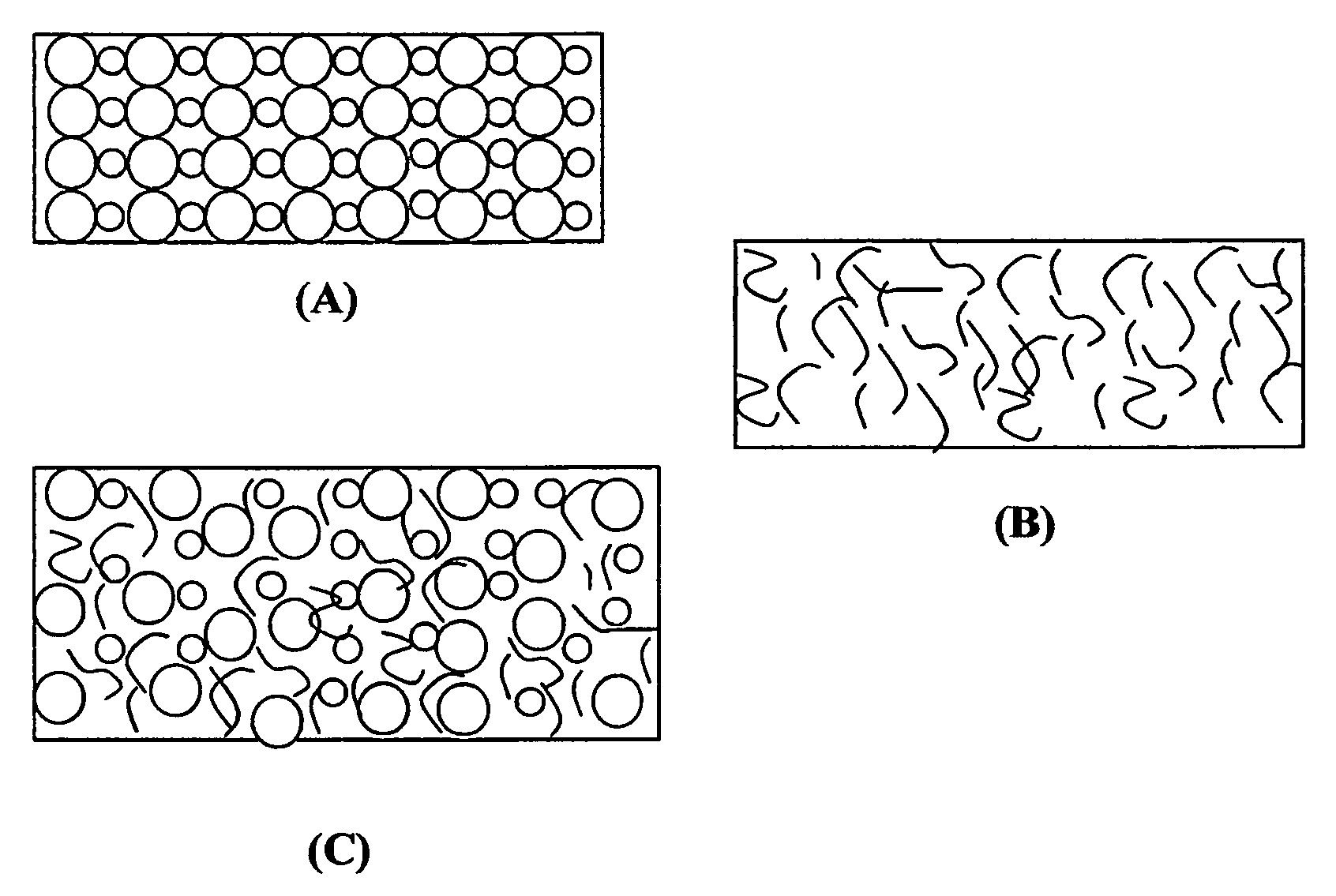
Non-flammable quasi-solid electrolyte and non-lithium alkali metal or alkali-ion secondary batteries containing same
ActiveUS9059481B2Improve solubilityFlammability of any organic solvent can be effectively suppressedNon-aqueous electrolyte accumulatorsCell electrodesSolid state electrolyteAlkali ions
A non-flammable quasi-solid electrolyte and a rechargeable non-lithium alkali metal cell containing this electrolyte. The electrolyte comprises an alkali metal salt dissolved in an organic liquid solvent with a concentration higher than 2.5 M (preferably >3.5 M) or a molecular ratio greater than 0.2 (preferably >0.3), wherein the alkali metal is selected from Na, K, a combination of Na and K, or a combination of Na and / or K with Li. The alkali metal salt concentration is sufficiently high so that the electrolyte exhibits a vapor pressure <0.01 kPa when measured at 20° C., a vapor pressure <60% of the vapor pressure of thet organic solvent when measured alone, a flash point at least 20 degrees Celsius higher than a flash point of the organic liquid solvent when measured alone, a flash point higher than 150° C., or no detectable flash point.
Owner:GLOBAL GRAPHENE GRP INC
System and method for freeze-drying and packaging
Systems and methods for protecting biological or other material from contamination through the steps of filling, freeze-drying, packaging, storing and use are disclosed. A system can include a flexible container, at least two membranes configured to transmit air or solvent vapor out of the flexible container, and a port to allow for the introduction or withdrawal of a material or substance into or out of the flexible container. The system can optionally further comprise a membrane frame supporting at least one of the membranes and engaged with at least one column member. The at least one column member can be configured to maintain the membranes and the membrane frame a spaced distance from one or more materials received within the flexible container. Upon application of a downward force, the at least one column member can assume a collapsed configuration. A method can include inserting a biological material into a flexible container, freeze-drying the biological material, moving the freeze-dried biological material to a portion of the flexible container that includes at least one port, and sealing the biological material within the portion.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Inkjet marking module and method for conditioning inkjet marking module
An inkjet marking module includes an inkjet marking device adapted to jet droplets of an inkjet marking material to form an image on recording substrate; and an evaporation device arranged for evaporating a solvent to a gaseous medium. The evaporation device includes an aerosol generator for creating an aerosol of the solvent in the gaseous medium; and a droplet eliminator for removing droplets from the aerosol, the droplet eliminator being arranged downstream of the aerosol generator. A printing system includes such an inkjet marking module and a method is disclosed for controlling the relative degree of saturation of a solvent vapor in a gaseous medium in an inkjet marking module.
Owner:OCE TECH
Composite nanofiber filter material with photocatalytic function and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107596791AIncrease spinning speedSolve problems such as easy blockageDispersed particle separationFilament/thread formingFiberSolvent vapor
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Film forming device and method, producing device and method for liquid-crystal device
InactiveCN1439517AShow clearlySolid-state devicesPretreated surfacesLiquid-crystal displaySolvent vapor
The invention can include a thin-film forming device that is a device for forming a thin-film by applying a coating solution onto a substrate, the coating solution containing a solvent and a film-forming material dissolved or dispersed therein. Also an ejection mechanism having a droplet ejection head for ejecting the coating solution onto the substrate, a moving mechanism capable of relatively moving the positions of the droplet ejection head and the substrate, and a control unit for controlling at least one of the ejection mechanism and the moving mechanism can be provided for the thin-film forming device. In addition, a solvent vapor supply mechanism for supplying the solvent vapor to the vicinity of the coating solution applied onto the substrate can also be provided for the thin-film forming device. Thereby, material losses are reduced by using a droplet ejection head, the thickness of the entire film can be made uniform, in addition, the patent provides also provides e a thin-film forming device and a thin-film forming method, a liquid crystal display and a device and method for manufacturing the same, and a thin-film structure and a device and method for manufacturing the same, in which material losses are reduced by using a droplet ejection head, and in addition, the thickness of the entire film can be made uniform.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
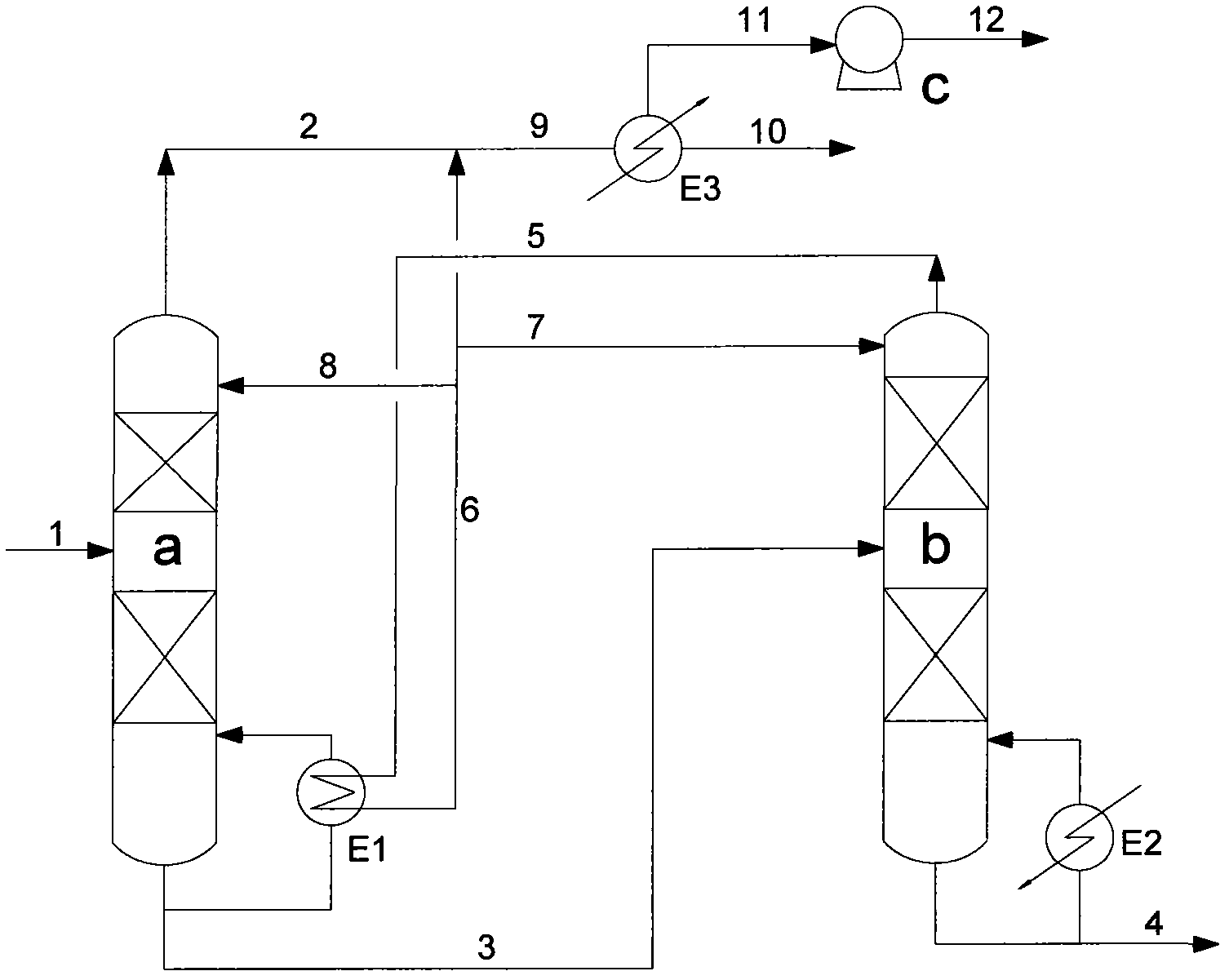
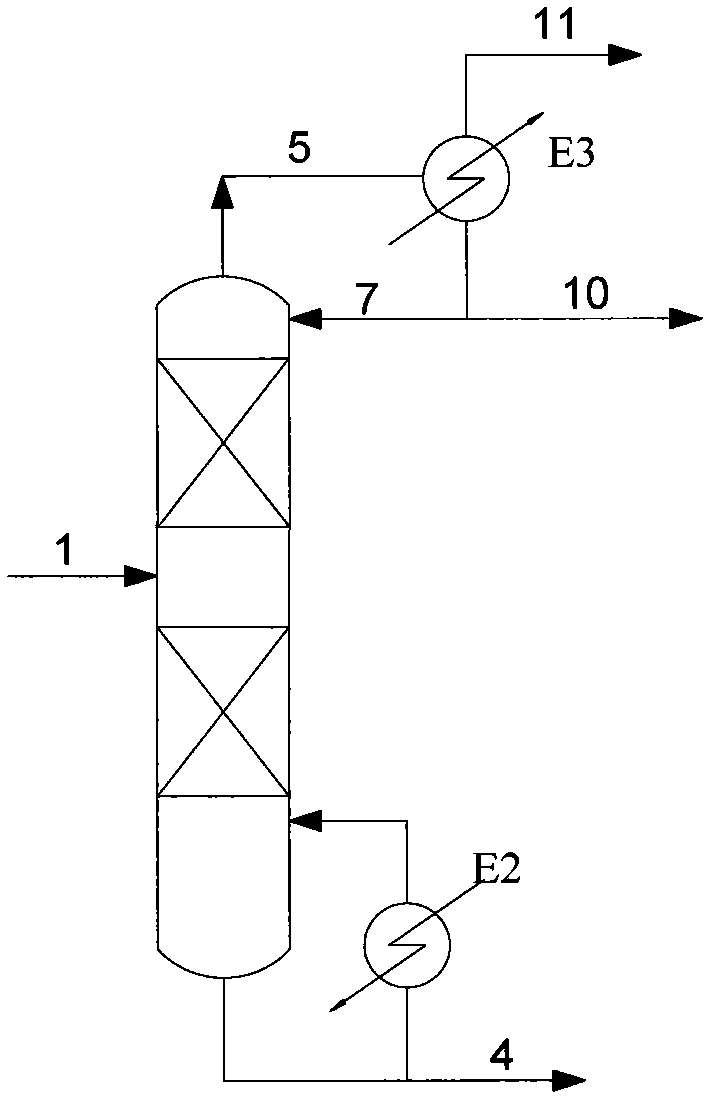
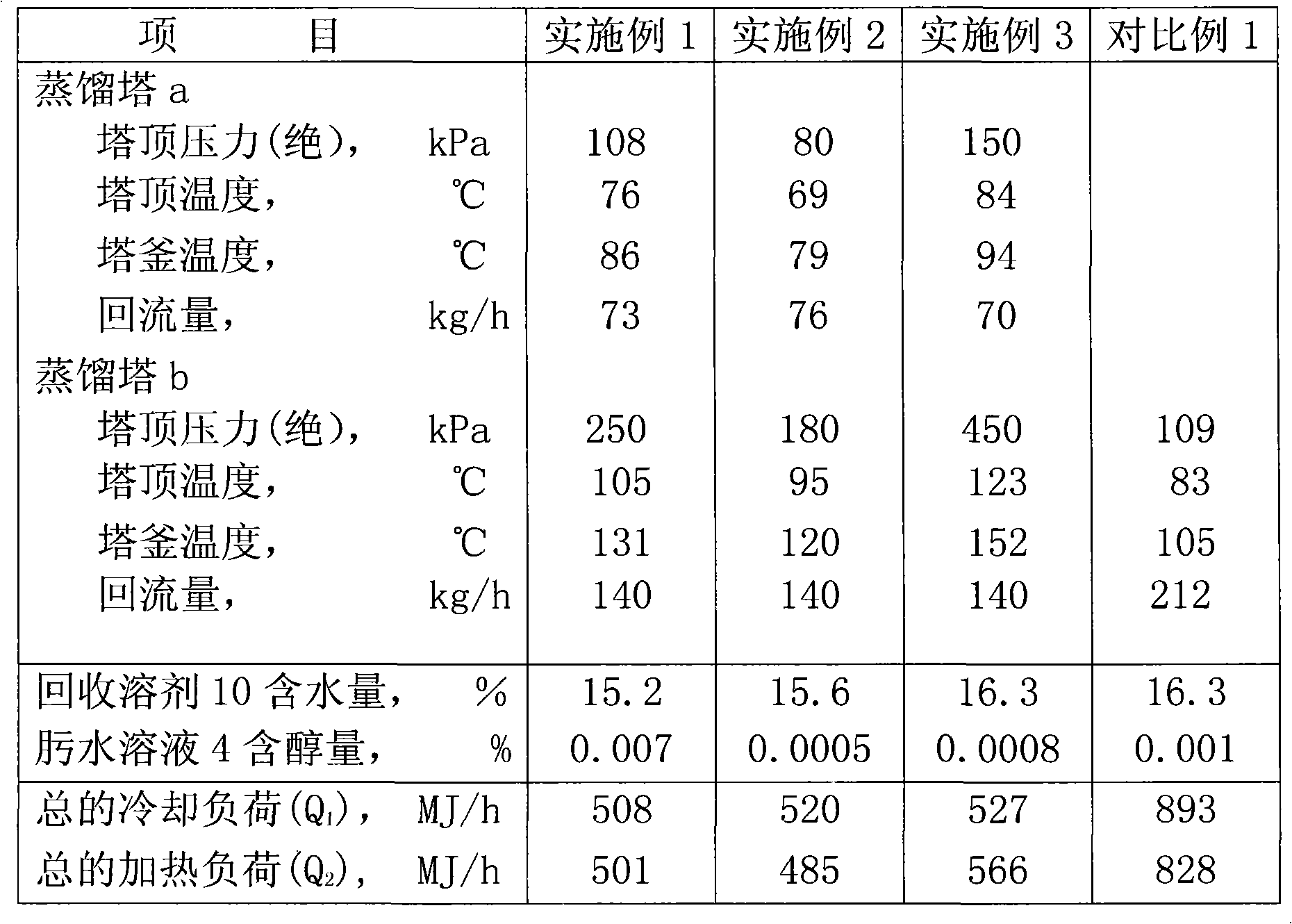
Method for recovering solvent from ammoximation reaction liquid
InactiveCN102633676AReduce dosageReduce manufacturing costOximes preparationSolvent vaporPhysical chemistry
The invention provides a method for recovering a solvent from an ammoximation reaction liquid. The method comprises the following steps: feeding a reaction liquid containing ammonia, the solvent, cyclohexanone oxime, water and cyclohexanone into a primary distillation tower (a), and evaporating out partial solvent containing ammonia and water from a tower top; and feeding materials in a tower kettle into a secondary distillation tower (b), and carrying out pressure distillation by utilizing exterior heat source so as to obtain high-temperature vapor containing the solvent from the tower top and obtain a material containing cyclohexanone oxime, water and cyclohexanone from the tower kettle, wherein the high-temperature vapor containing the solvent serves as the distillation heat source for the primary distillation tower (a). By using the method, the energy consumption for the solvent recovery can be reduced.
Owner:北京凯美信科科技开发有限责任公司
Reduced-pressure drying method, method of manufacturing functional film, method of manufacturing electro-optic device, electro-optic device, liquid crystal display device, organic el display device, and electronic apparatus
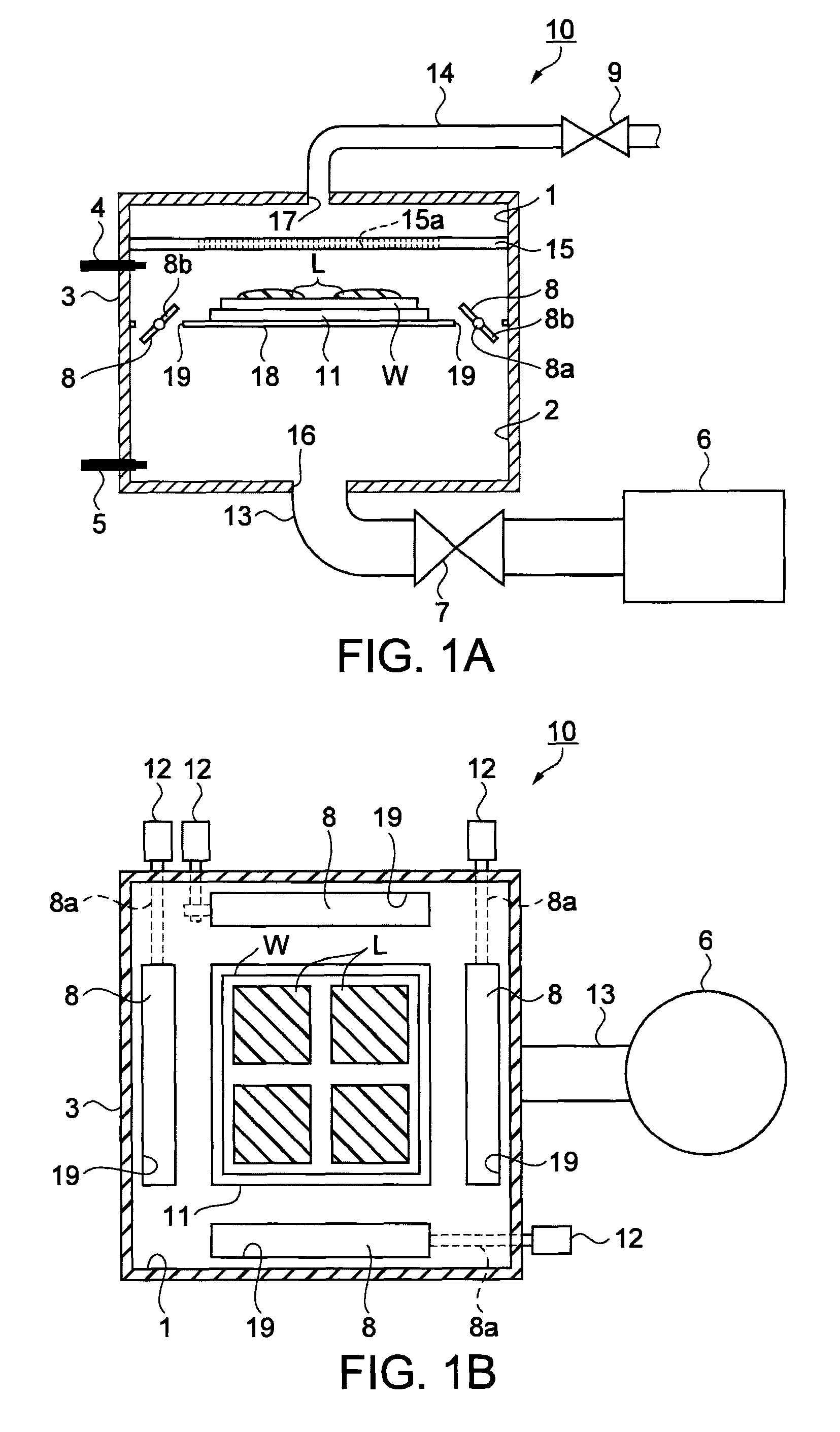
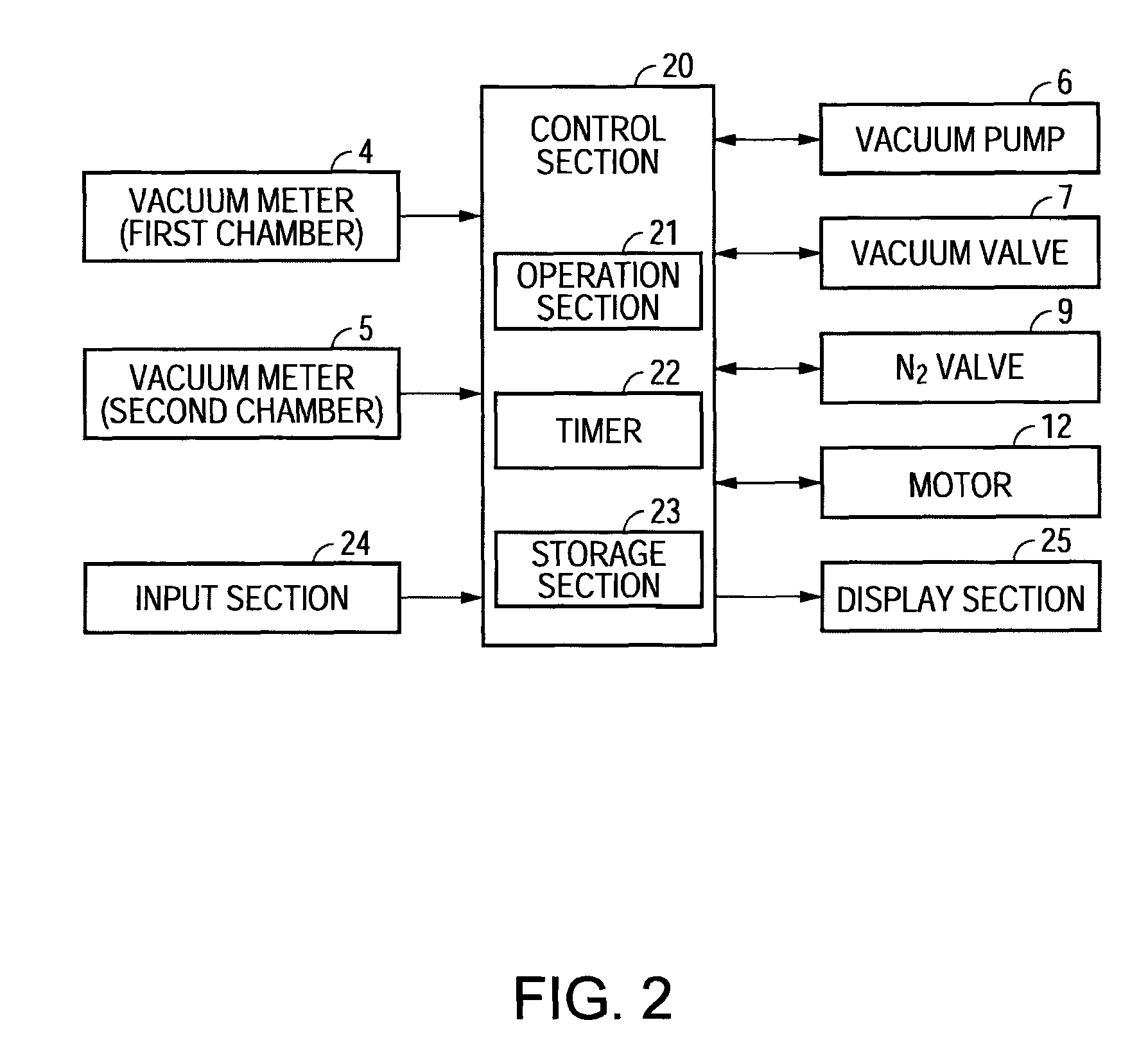
InactiveUS8203689B2Liquid crystal compositionsDrying solid materials without heatLiquid-crystal displayDisplay device
A reduced-pressure drying method includes: decompressing a second chamber communicated with a first chamber housing a base material coated with a liquid substance containing a solvent to predetermined operative pressure by a decompressing device; leaving the first chamber closed in response to reaching the predetermined operative pressure until the evaporated solvent raising the pressure in the first chamber to predetermined pressure; communicating the first chamber with the pressure raised to the predetermined pressure with the second chamber; and discharging the vapor of the solvent dispersed in the first and the second chambers by the decompressing device.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Method of uniformly coating a substrate
InactiveUS6977098B2Improve thickness uniformityIncrease consumptionSpraying apparatusPretreated surfacesSolvent vaporEngineering
A method of and an apparatus for coating a substrate with a polymer solution to produce a film of uniform thickness, includes mounting the substrate inside an enclosed housing and passing a control gas, which may be a solvent vapor-bearing gas into the housing through an inlet. The polymer solution is deposited onto the surface of the substrate in the housing and the substrate is then spun. The control gas and any solvent vapor and particulate contaminants suspended in the control gas are exhausted from the housing through an outlet and the solvent vapor concentration is controlled by controlling the temperature of the housing and the solvent from which the solvent vapor-bearing gas is produced. Instead the concentration can be controlled by mixing gases having different solvent concentrations. The humidity of the gas may also be controlled.
Owner:ASML HLDG NV
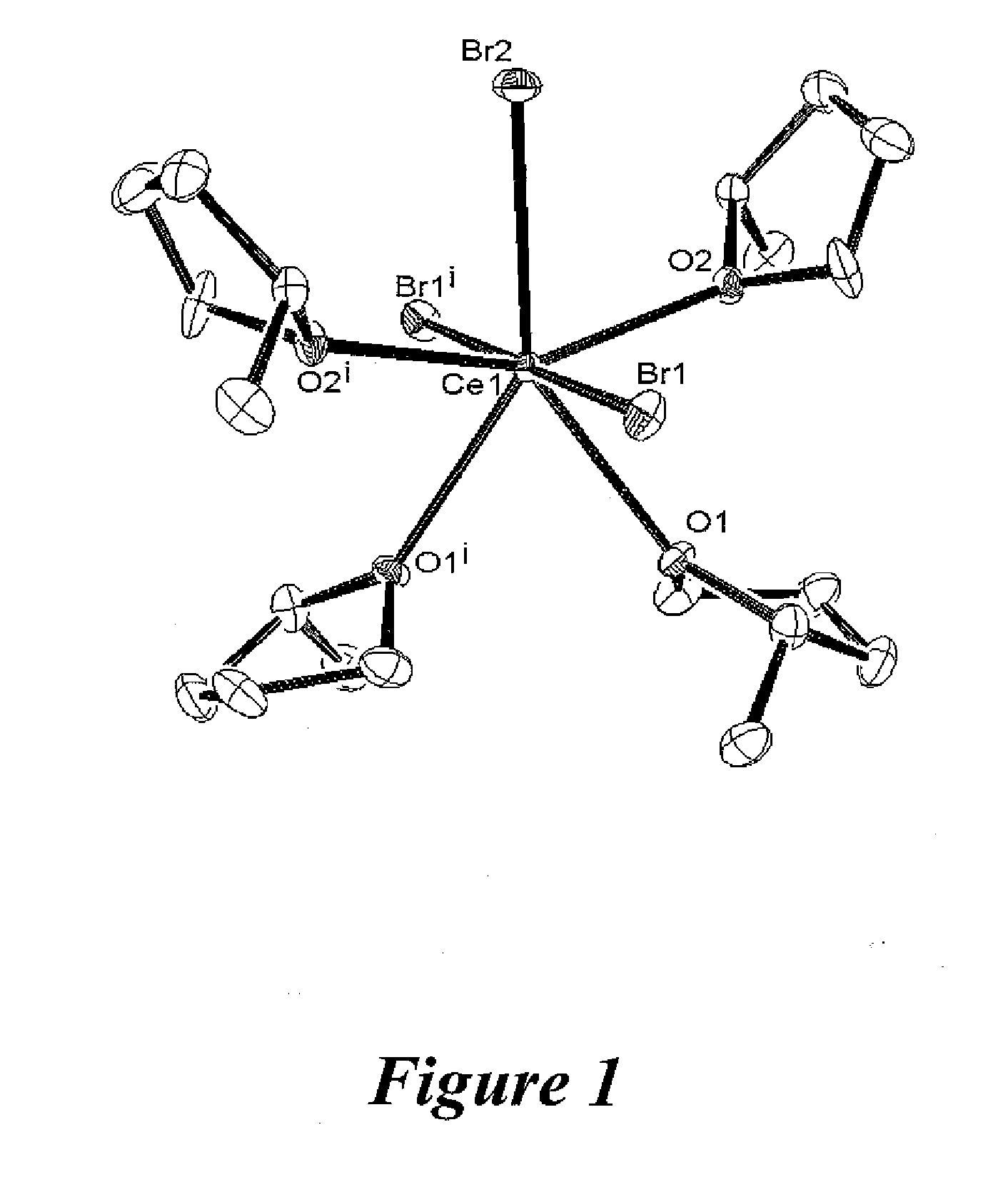
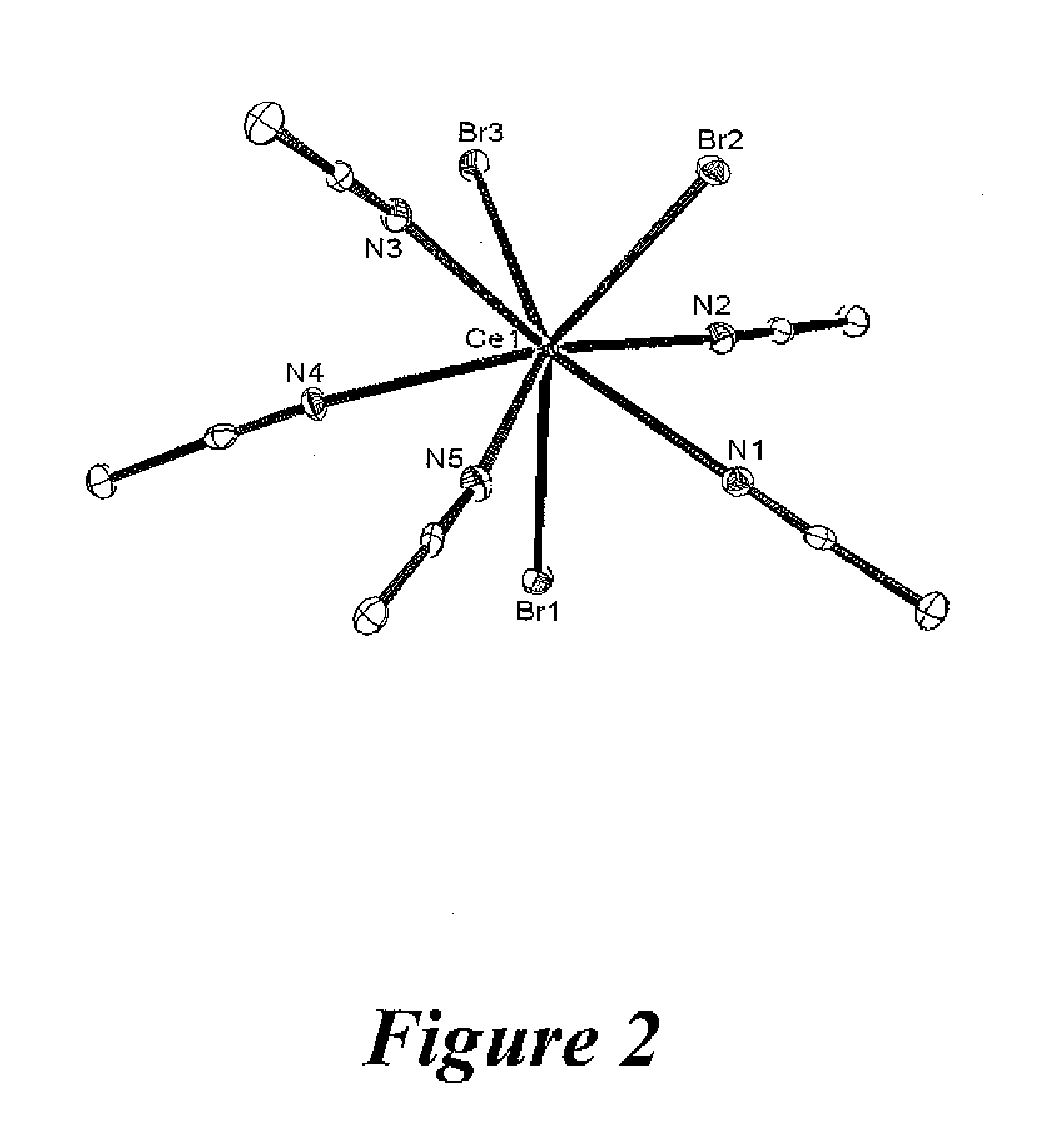
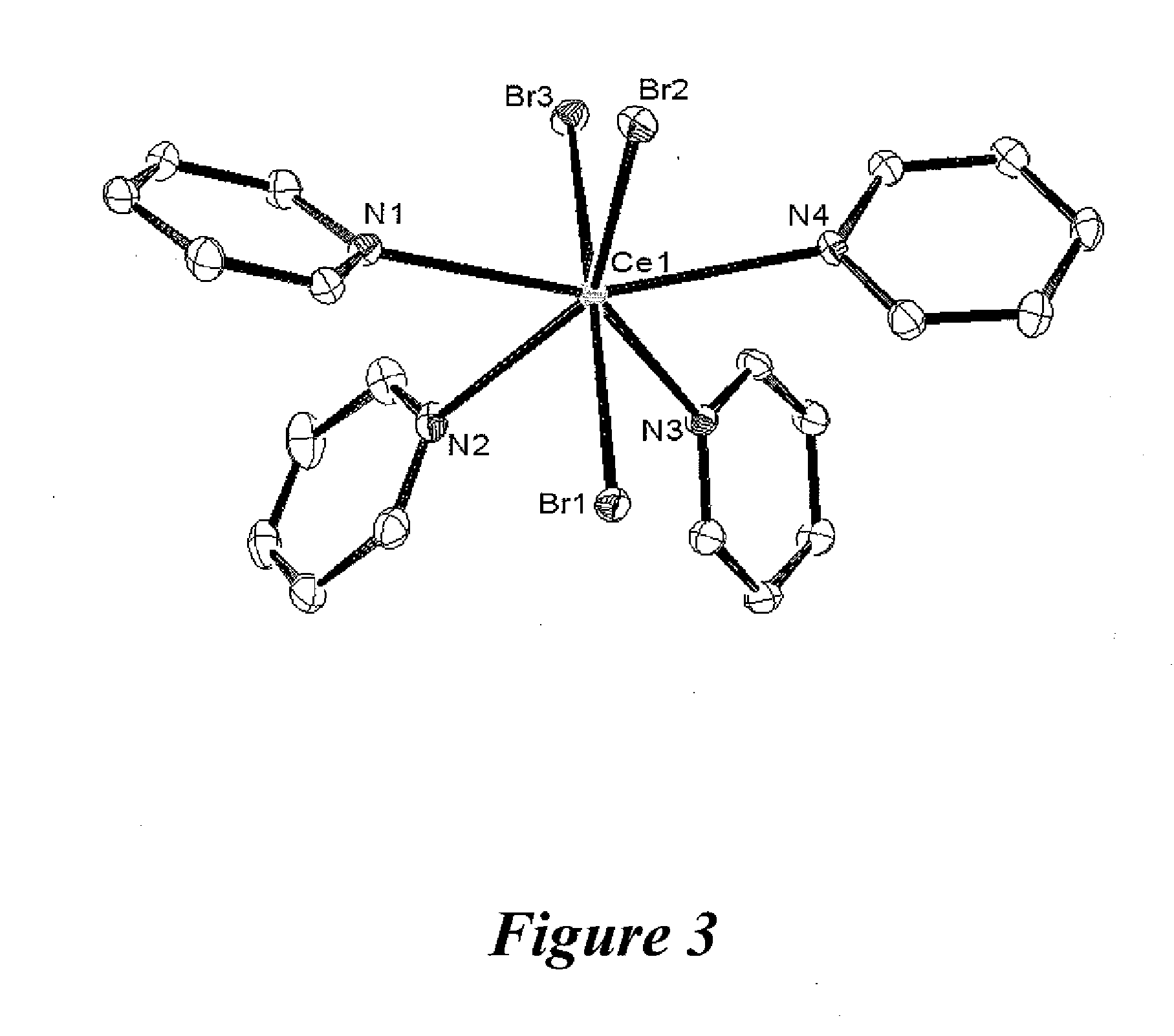
Preparation of cerium halide solvate complexes
InactiveUS20120238733A1Promote conversionGroup 3/13 organic compounds without C-metal linkagesBiological testingSolvent vaporCerium
Crystals of a solvated cerium(III) halide solvate complex resulted from a process of forming a paste of a cerium(III) halide in an ionic liquid, adding a solvent to the paste, removing any undissolved solid, and then cooling the liquid phase. Diffusing a solvent vapor into the liquid phase also resulted in crystals of a solvated cerium(III) halide complex.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com