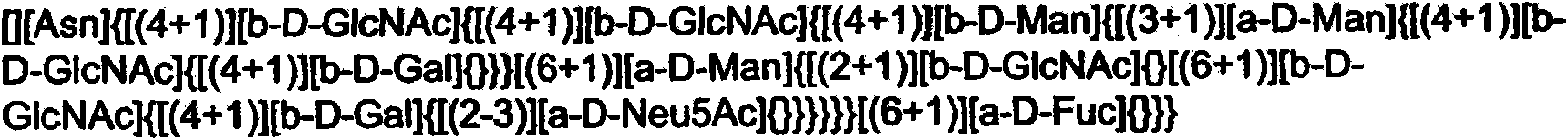Patents
Literature
33 results about "N linked glycans" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
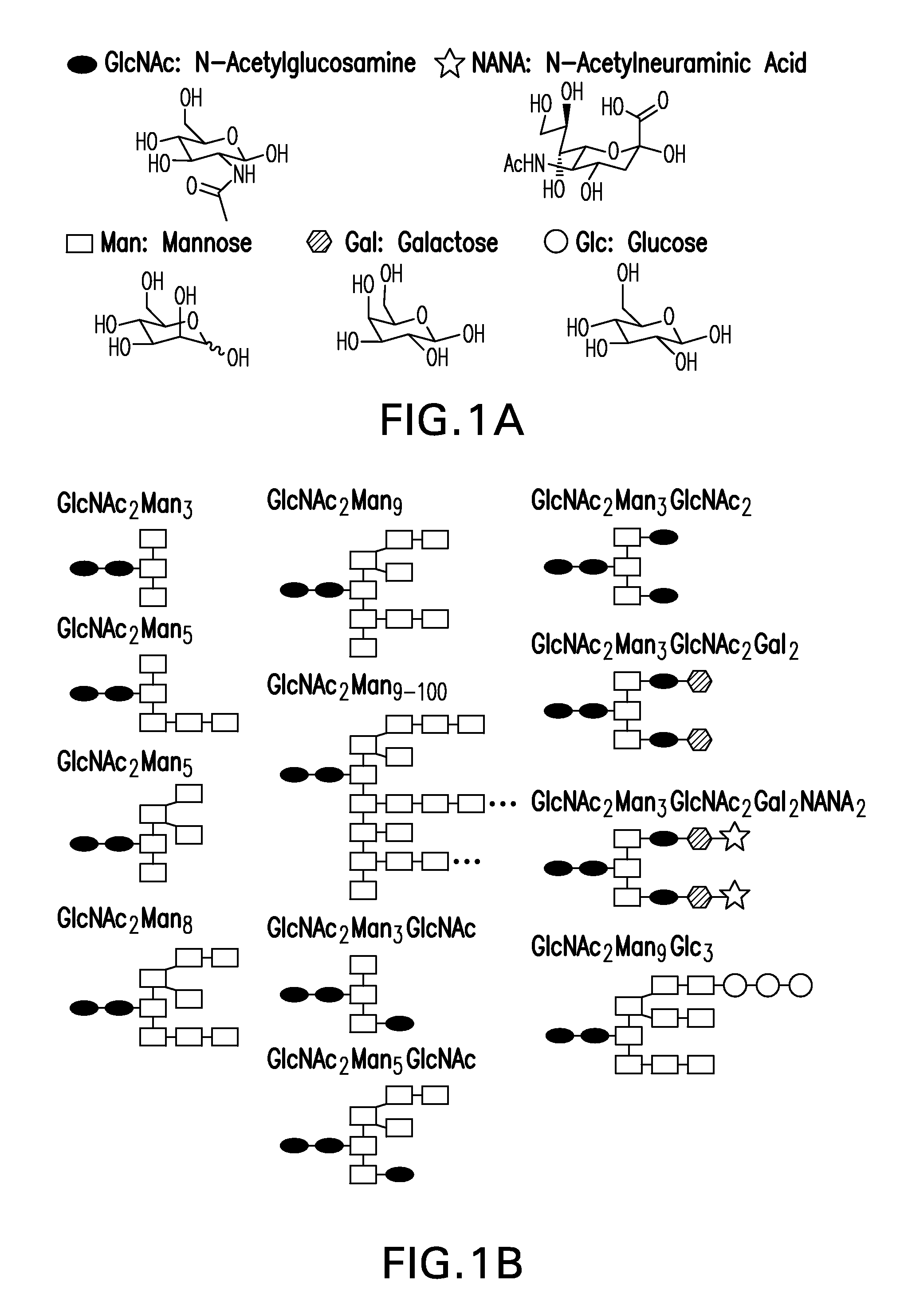
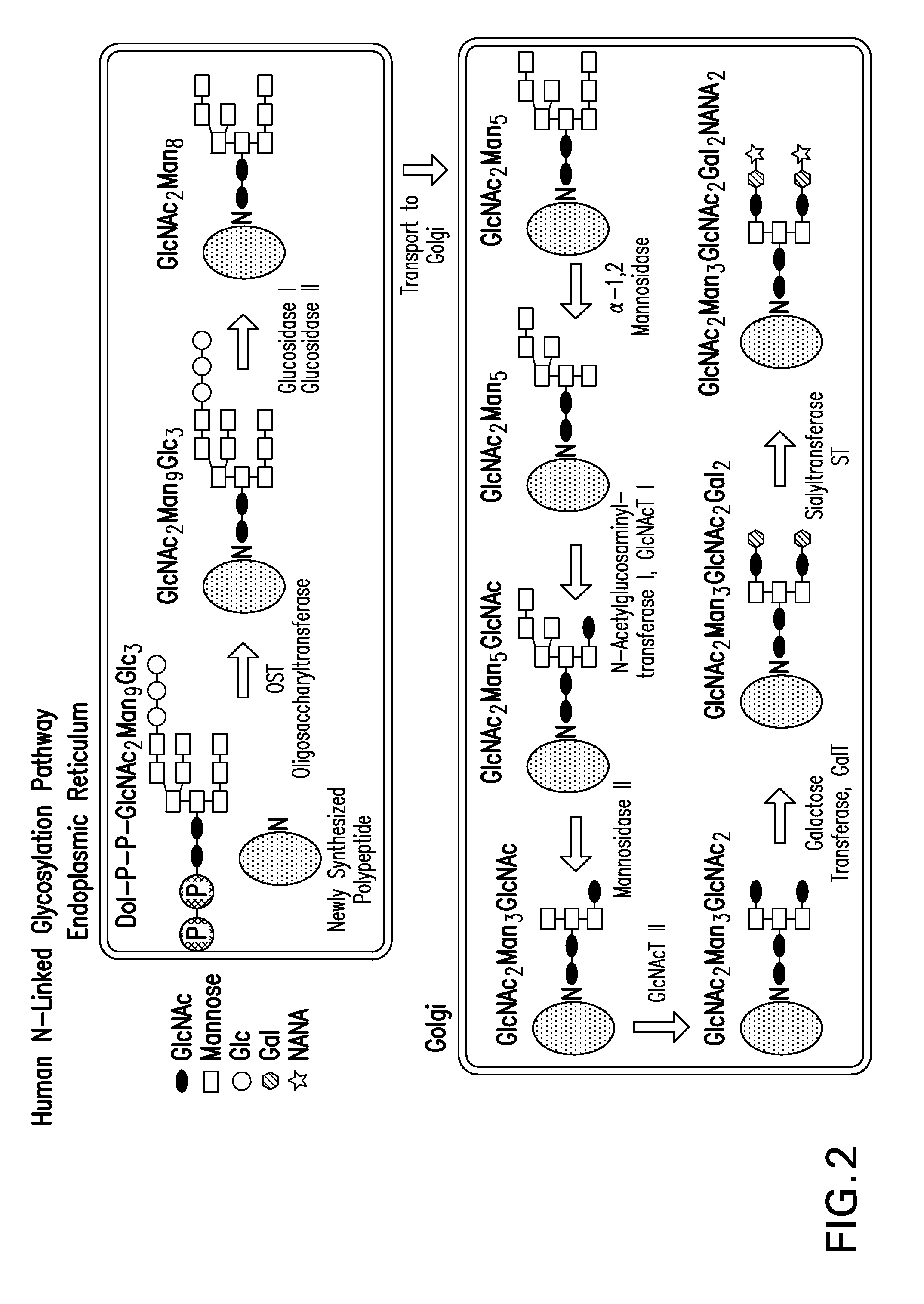
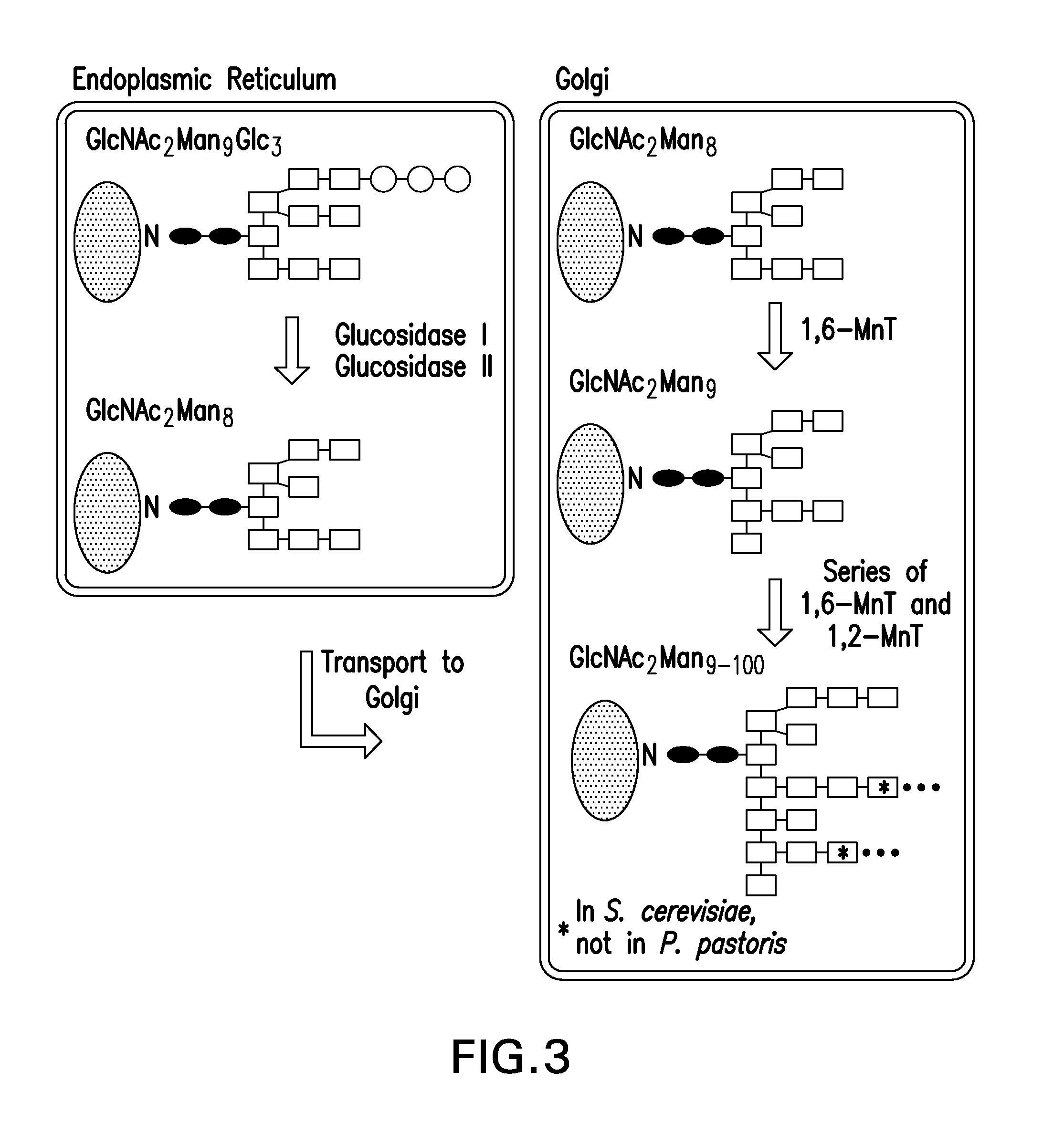
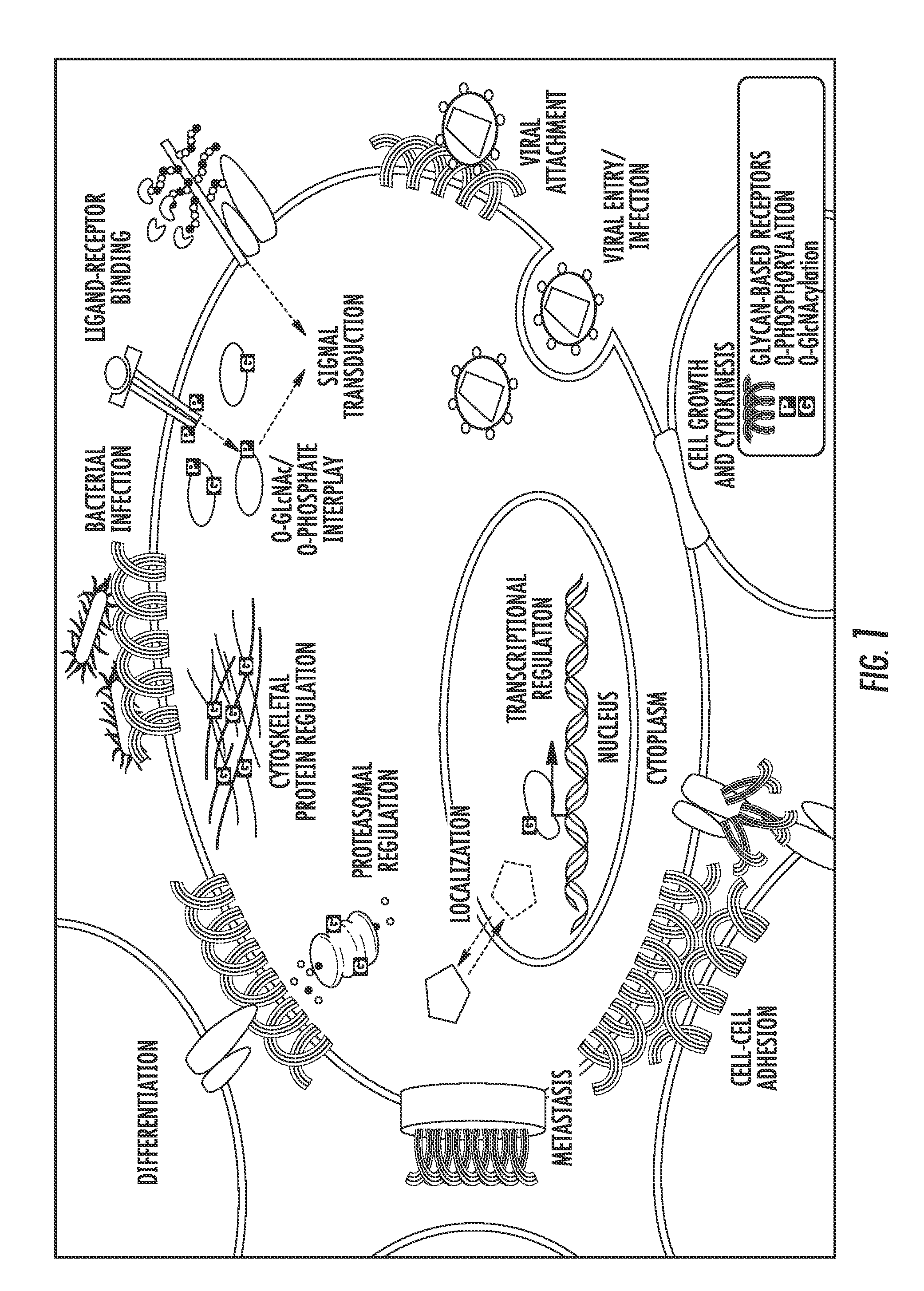
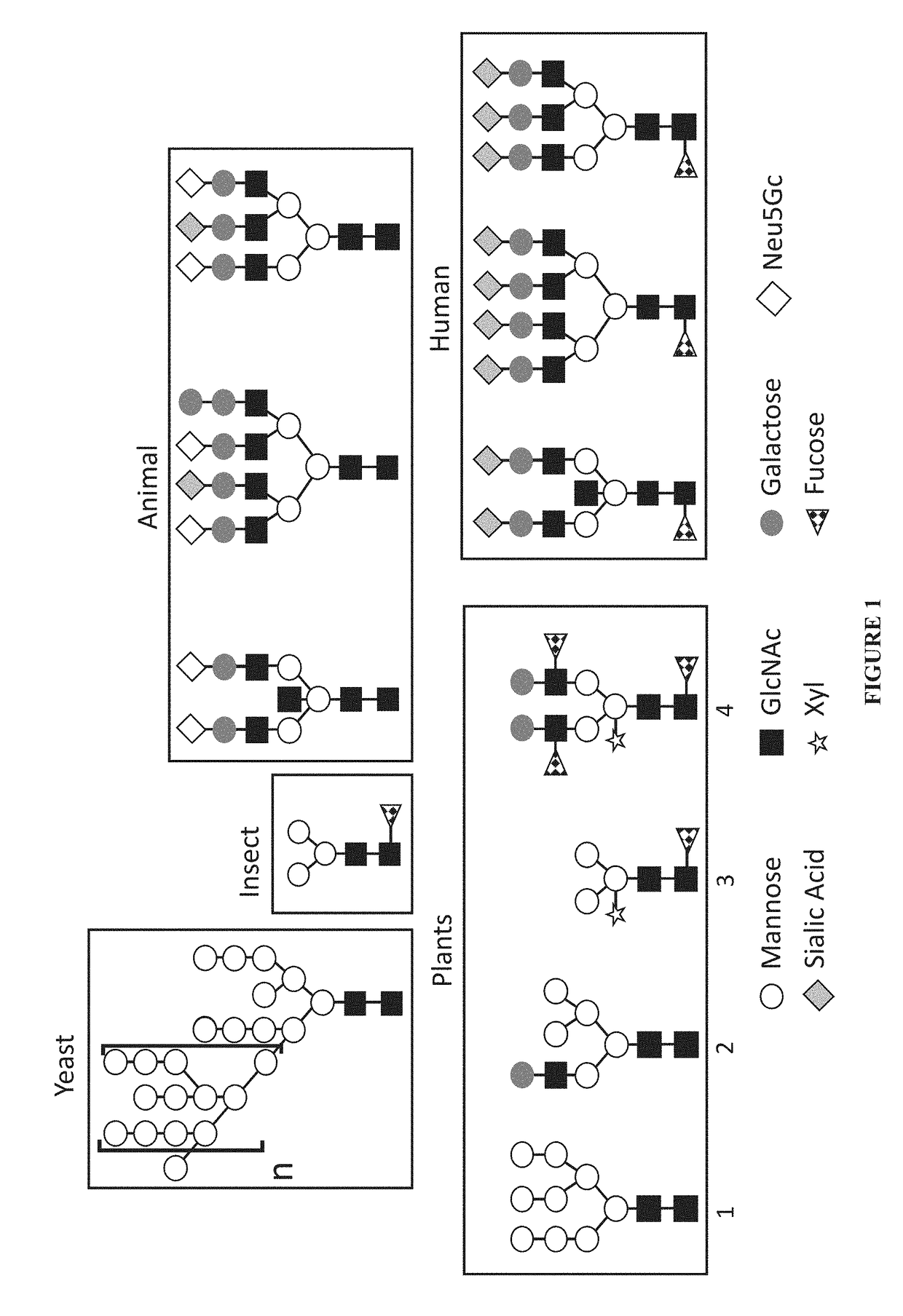
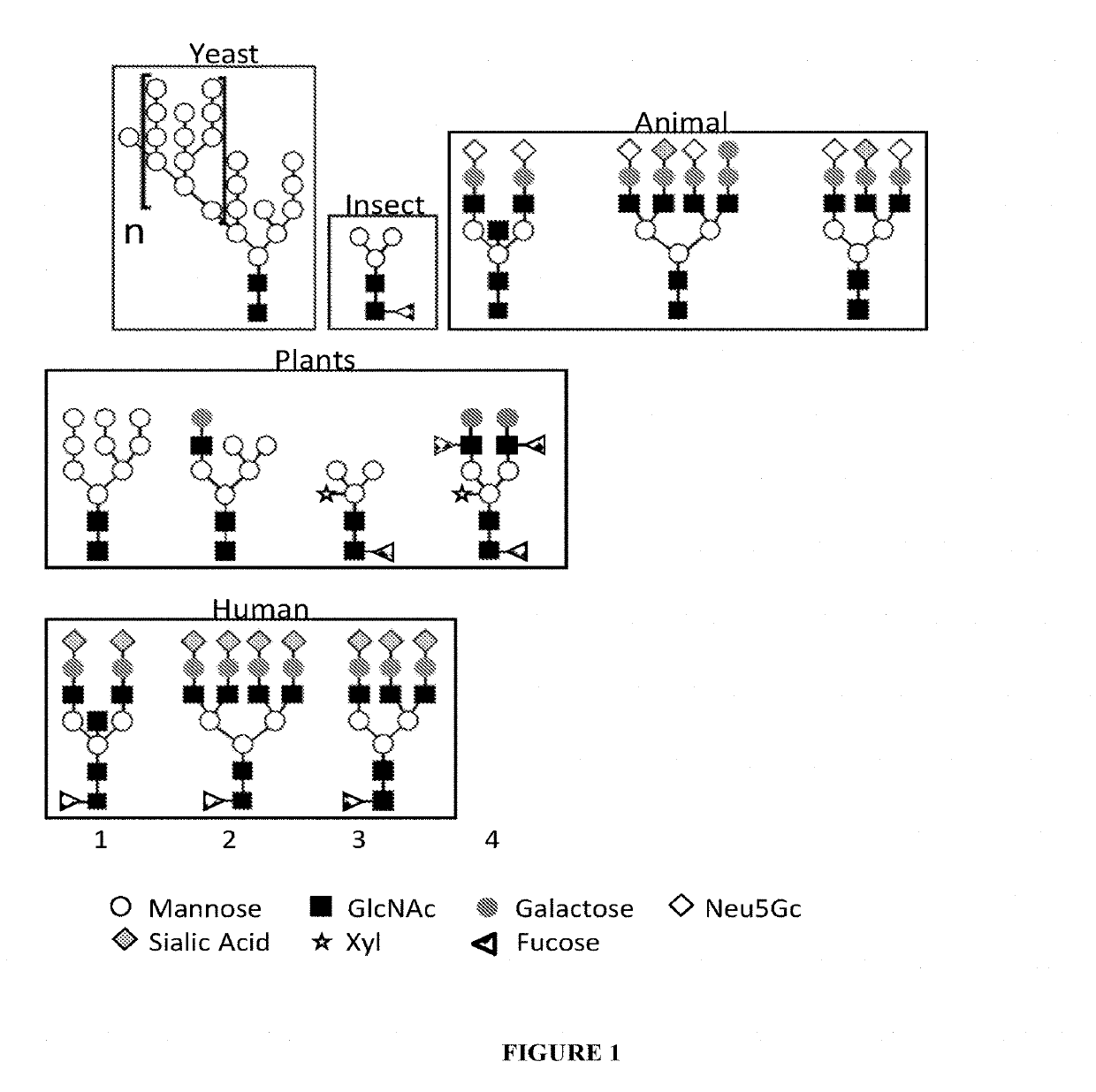
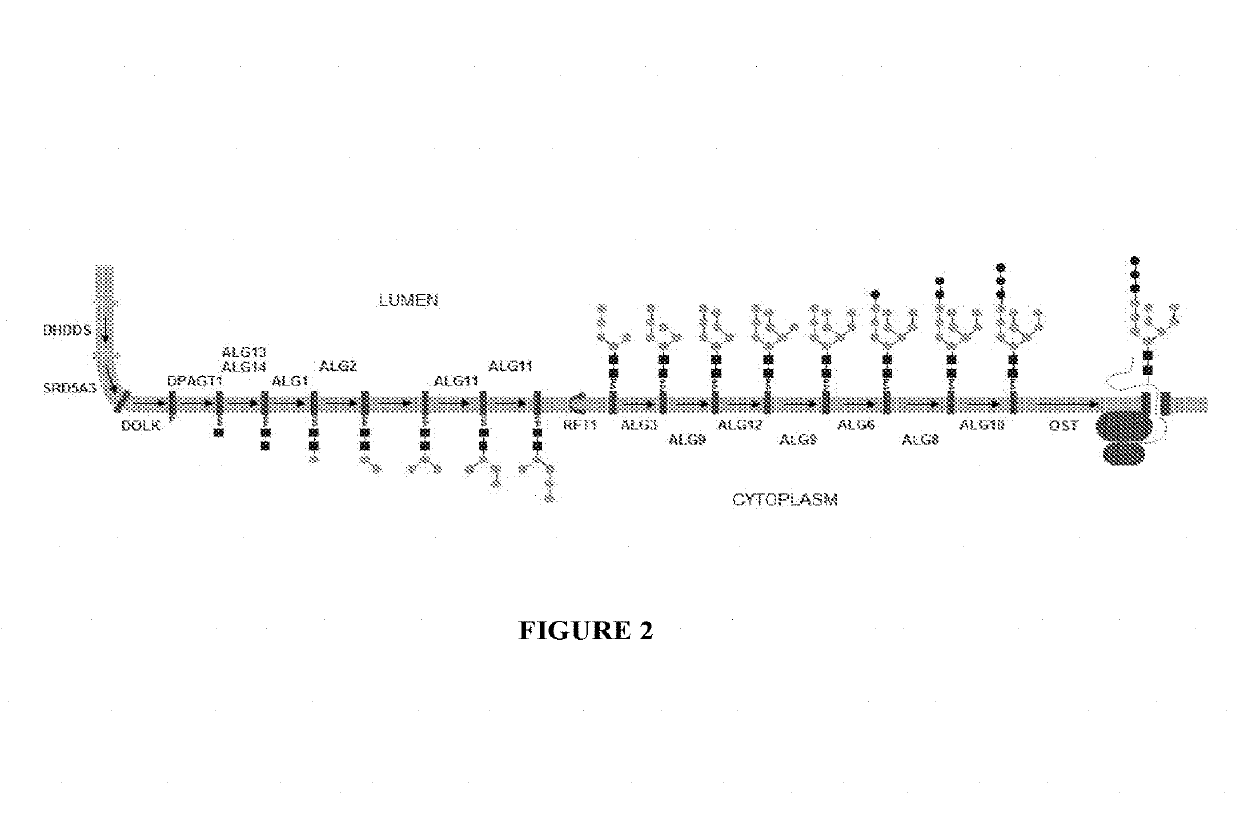
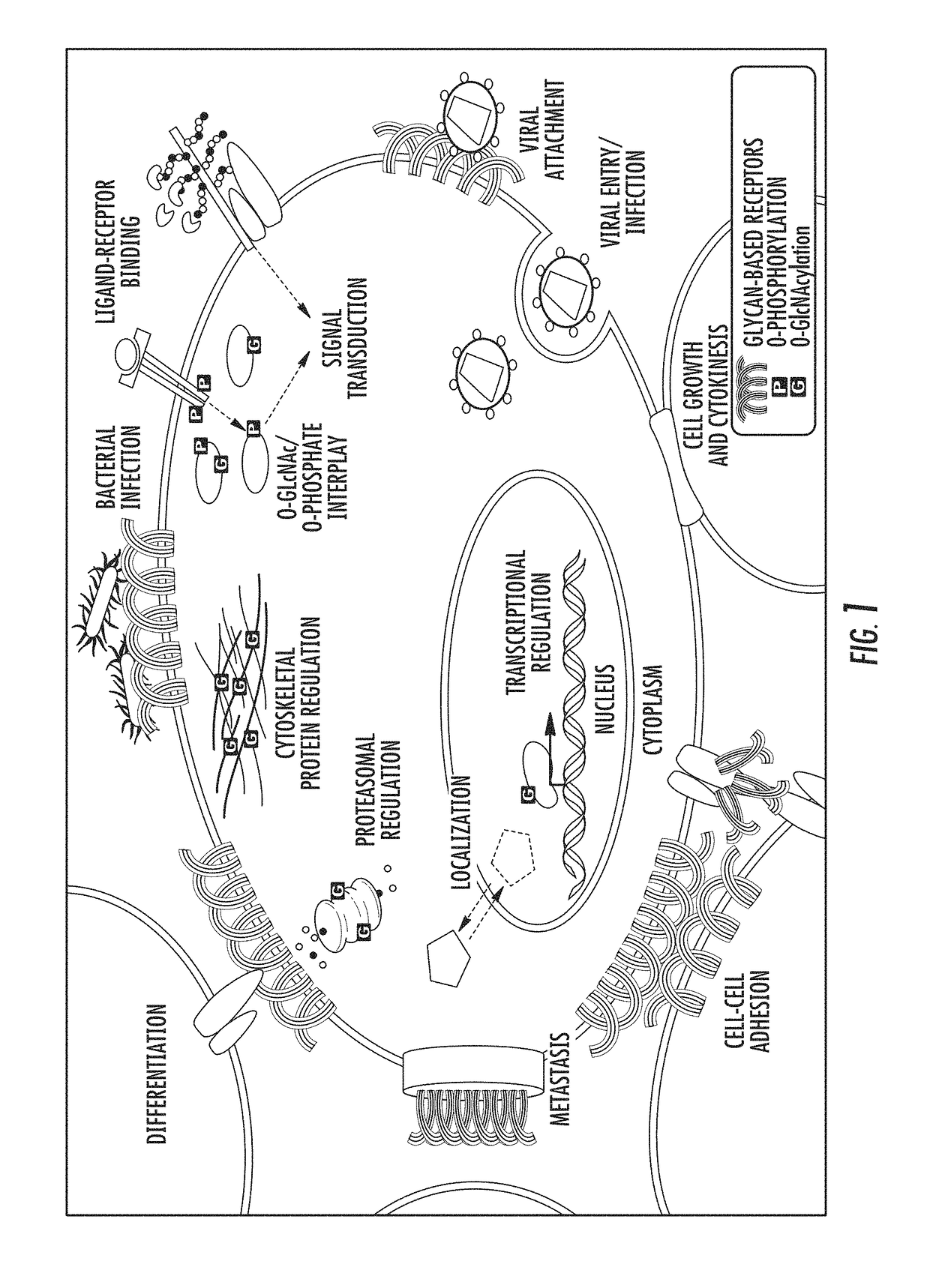
N-linked glycans are found attached to asparagine amino acids on proteins. They are responsible for many structural and functional aspects of glycoproteins, including cell-cell interactions, intracellular trafficking, and affecting the solubility and stability of proteins in vivo.
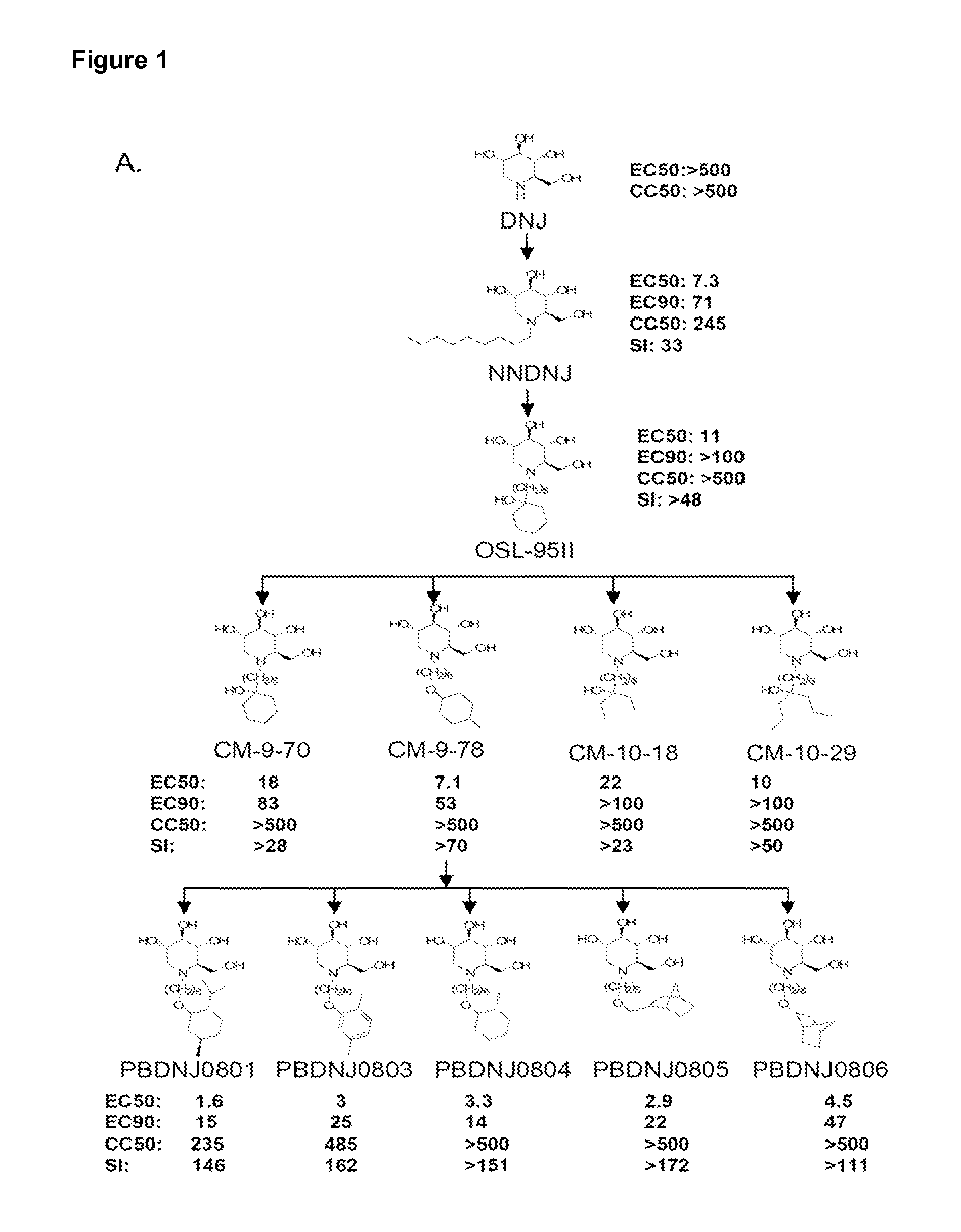
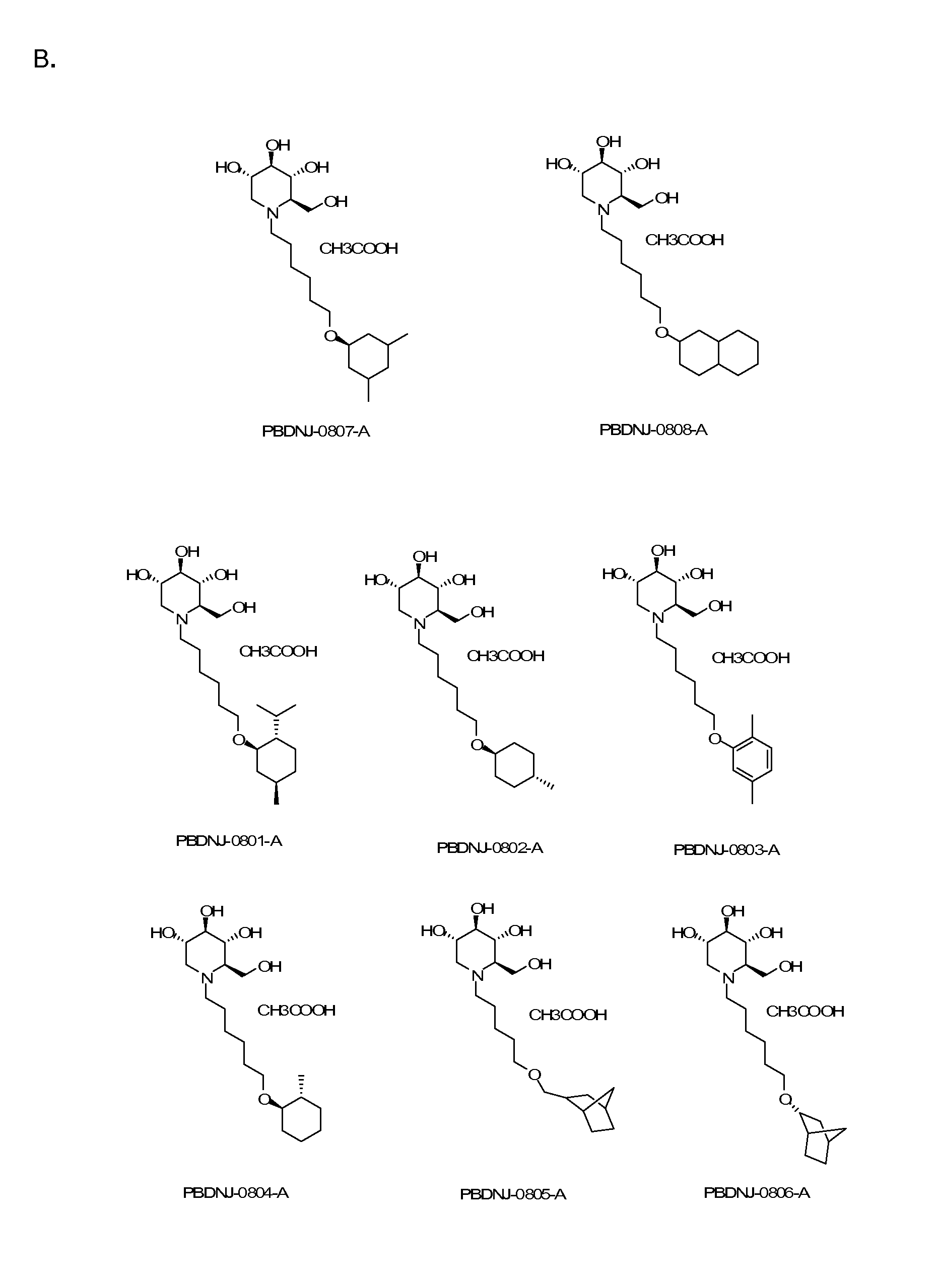
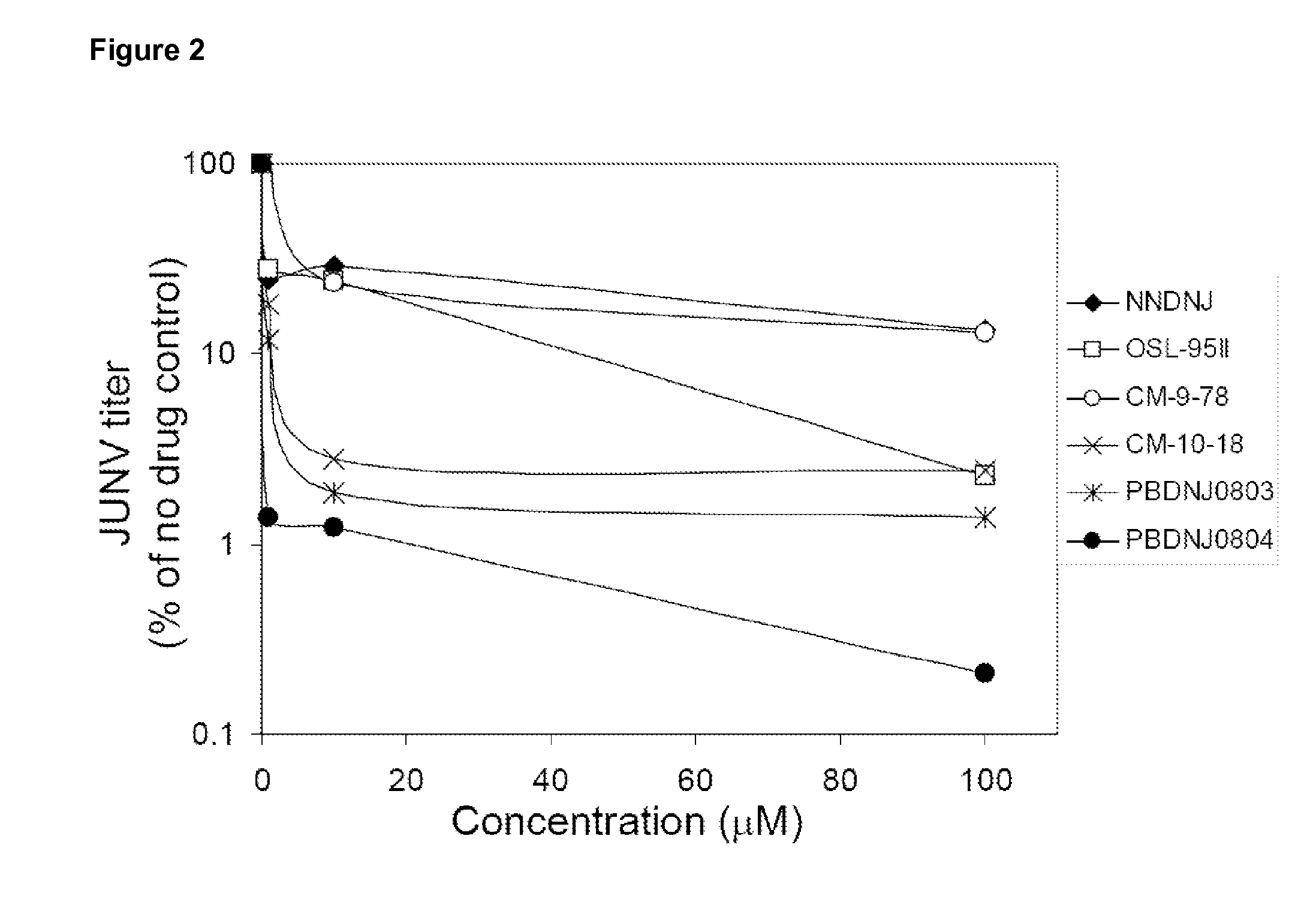
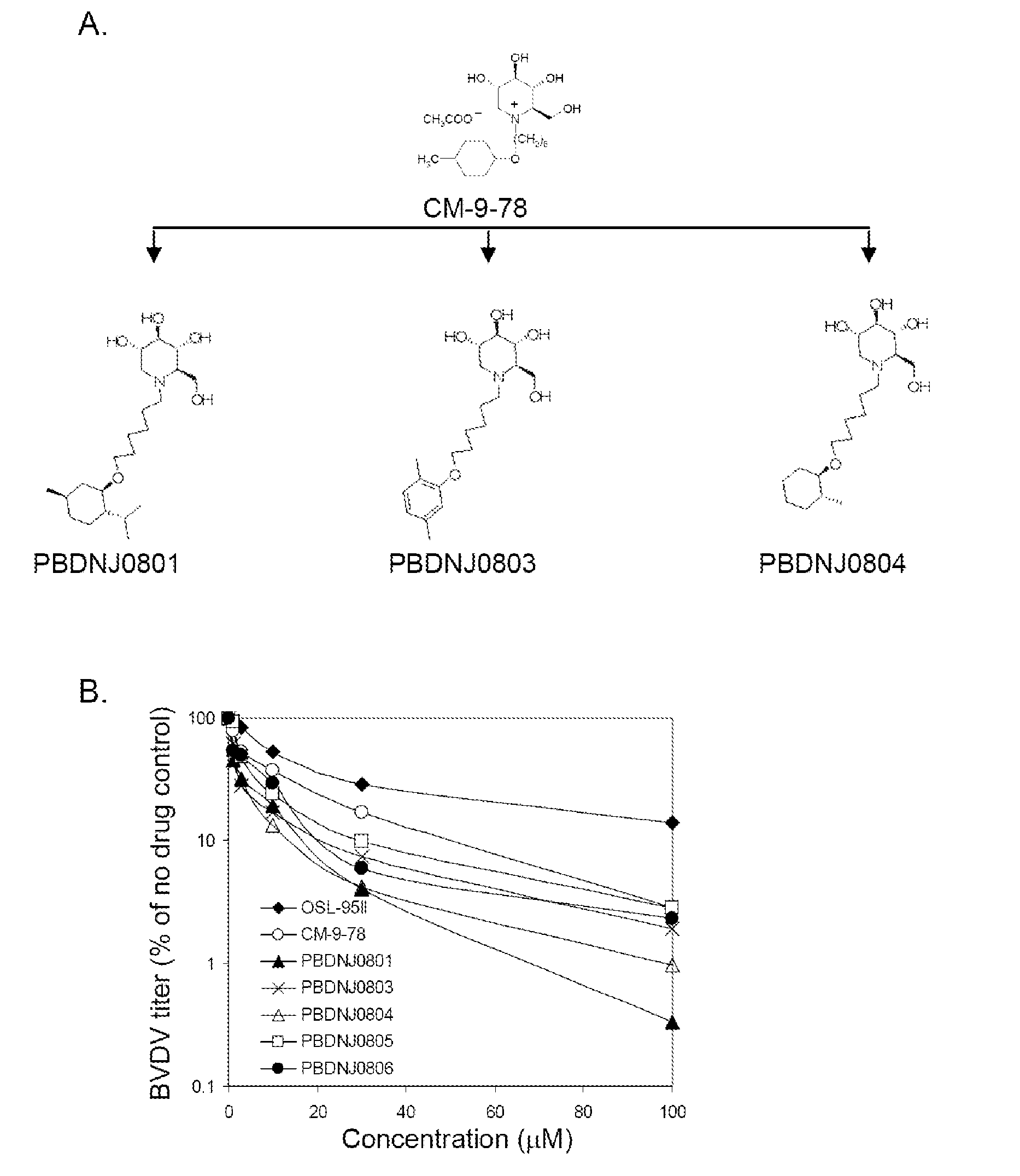
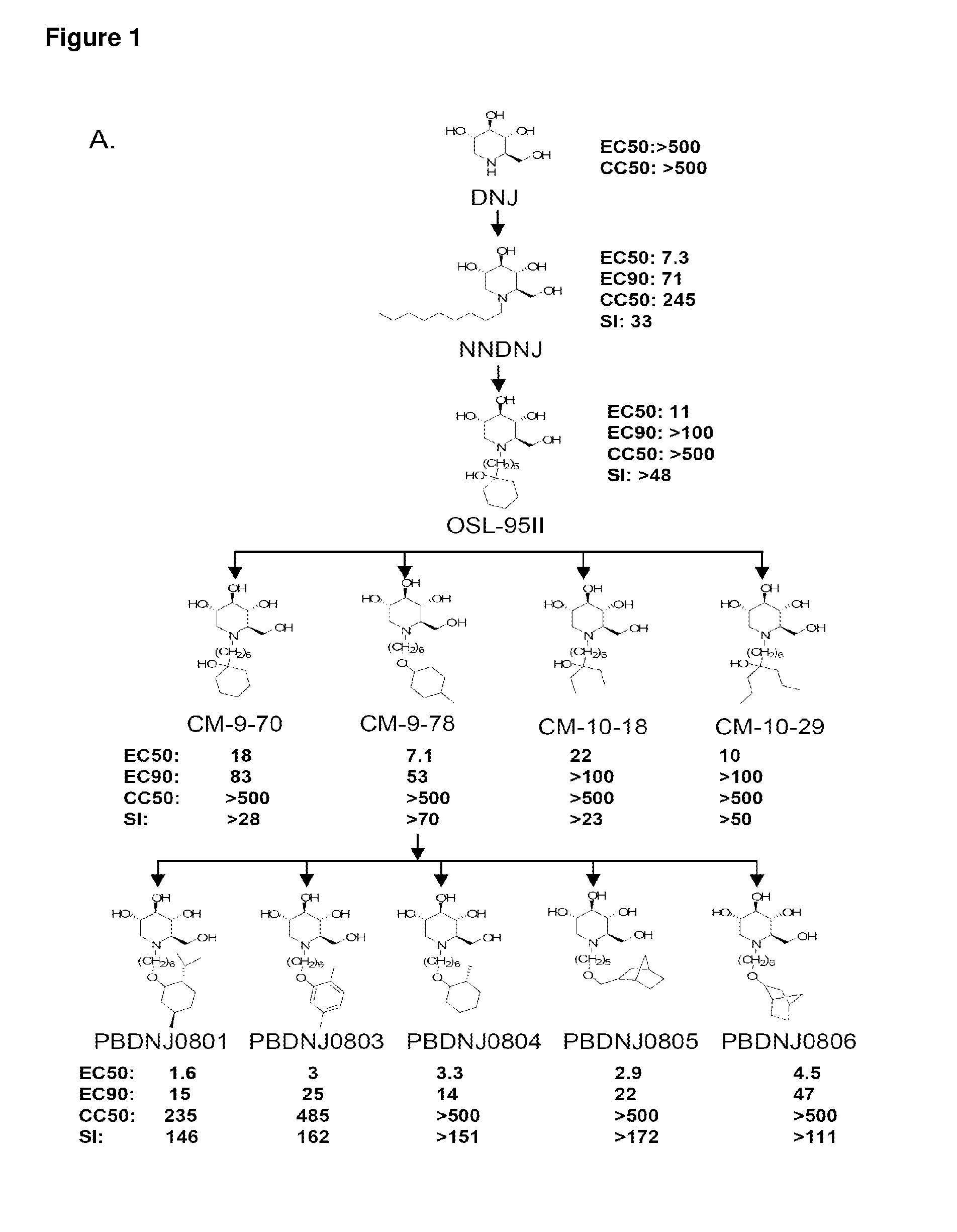
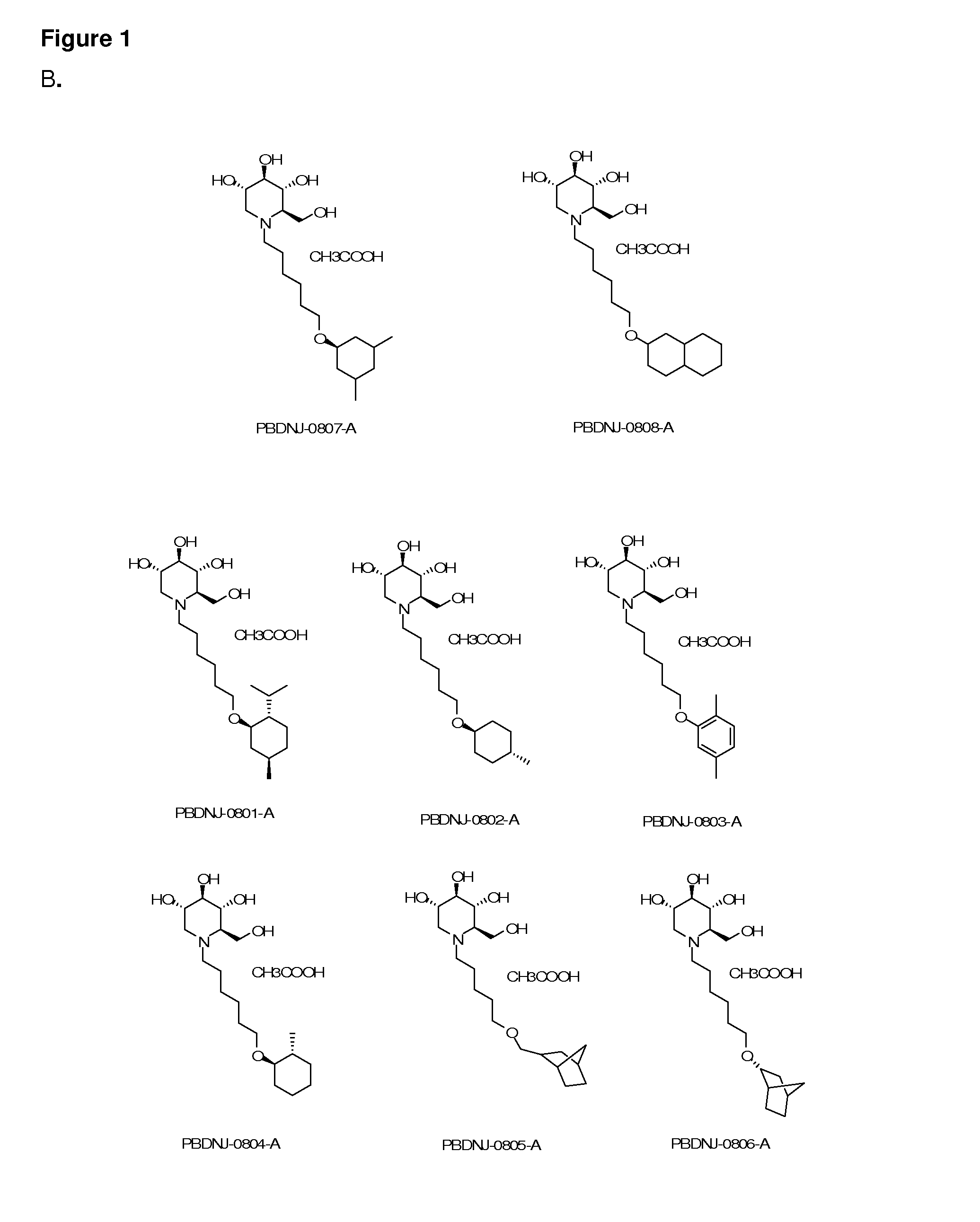
Novel Imino Sugar Derivatives Demonstrate Potent Antiviral Activity and Reducted Toxicity
InactiveUS20110189771A1Good effectImprove performanceOrganic chemistryTissue cultureBovine Viral Diarrhea VirusesSide chain
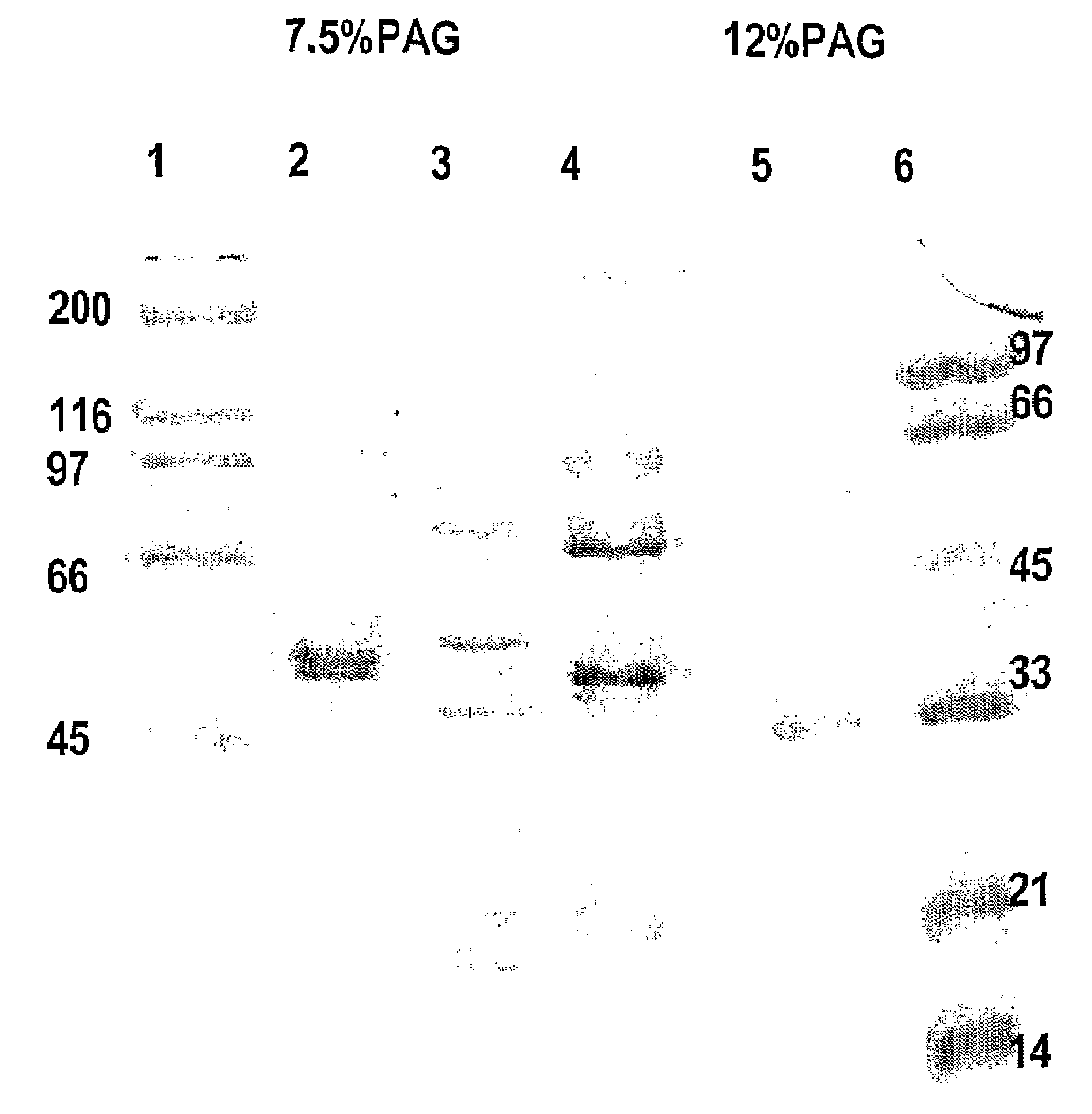
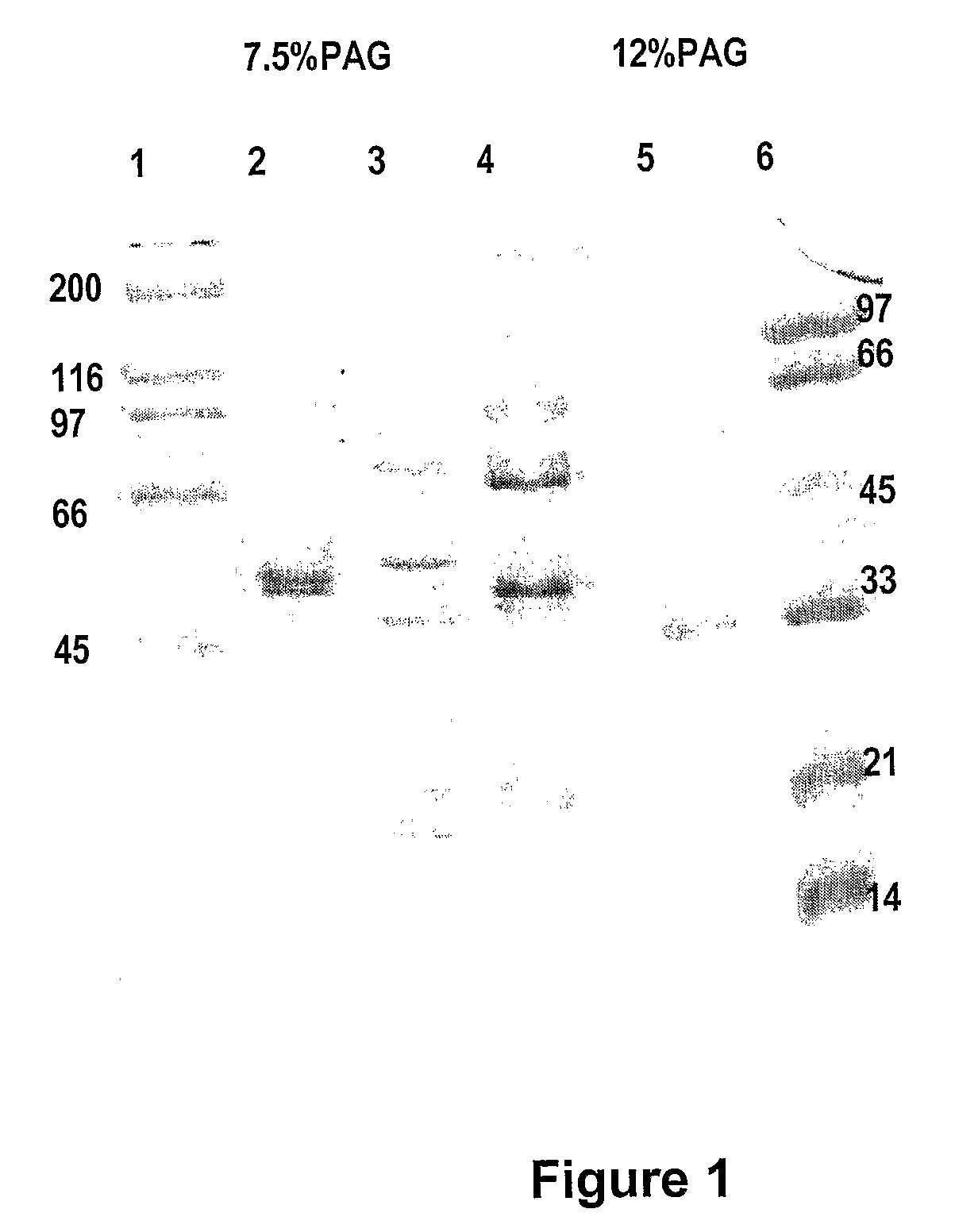
Imino sugars, such as deoxynojirimycin (DNJ), are glucose analogues that selectively inhibit cellular α-glucosidase I and II (enzymes that process N-linked glycans in glycoprotein) and exhibit broad spectrum antiviral activities against many enveloped viruses. Previously we have reported a novel DNJ derivative, OSL-95II, with antiviral activity and reduced cytotoxicity. In order to develop imino sugars with more potent antiviral activity as well as improved toxicity profile, OSL-95II was modified by diversifying the nitrogen linked alkylated side chain. The antiviral activities were initially tested in bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) infected MDBK cells, yielding several imino sugar derivatives with novel structure and superior antiviral activity and toxicity profile. Furthermore, these new compounds were shown to be active against Dengue virus (DV) and West Nile virus (WNV) infection in BHK cells where potent anti-DV activity having submicromolar EC50 values and SI of greater than 900. These compounds represent a new generation of iminio sugars and their analogues, having application in the clinical treatment of infection of DV and other members of flaviviridae.
Owner:INST FOR HEPATITS & VIRUS RES +1
Recombinantly expressed insulin polypeptides and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides recombinantly expressed insulin polypeptides that comprise an N-linked glycan motif. The N-linked glycan motif is not present in wild-type insulins and enables the recombinant expression of glycosylated insulin polypeptides (e.g., in yeast cells). Based on results obtained with synthetic glycosylated insulin conjugates we predict that when these recombinant glycosylated insulin polypeptides are administered to a mammal, at least one pharmacokinetic or pharmacodynamic property of the glycosylated insulin polypeptide will be sensitive to serum concentrations of glucose (or an exogenous saccharide such as alpha-methyl mannose). Exemplary insulin polypeptides, polynucleotides encoding these insulin polypeptides, glycosylated insulin polypeptides, pharmaceutical formulations and sustained release formulations are provided in addition to methods of use and preparation.
Owner:SMARTCELLS
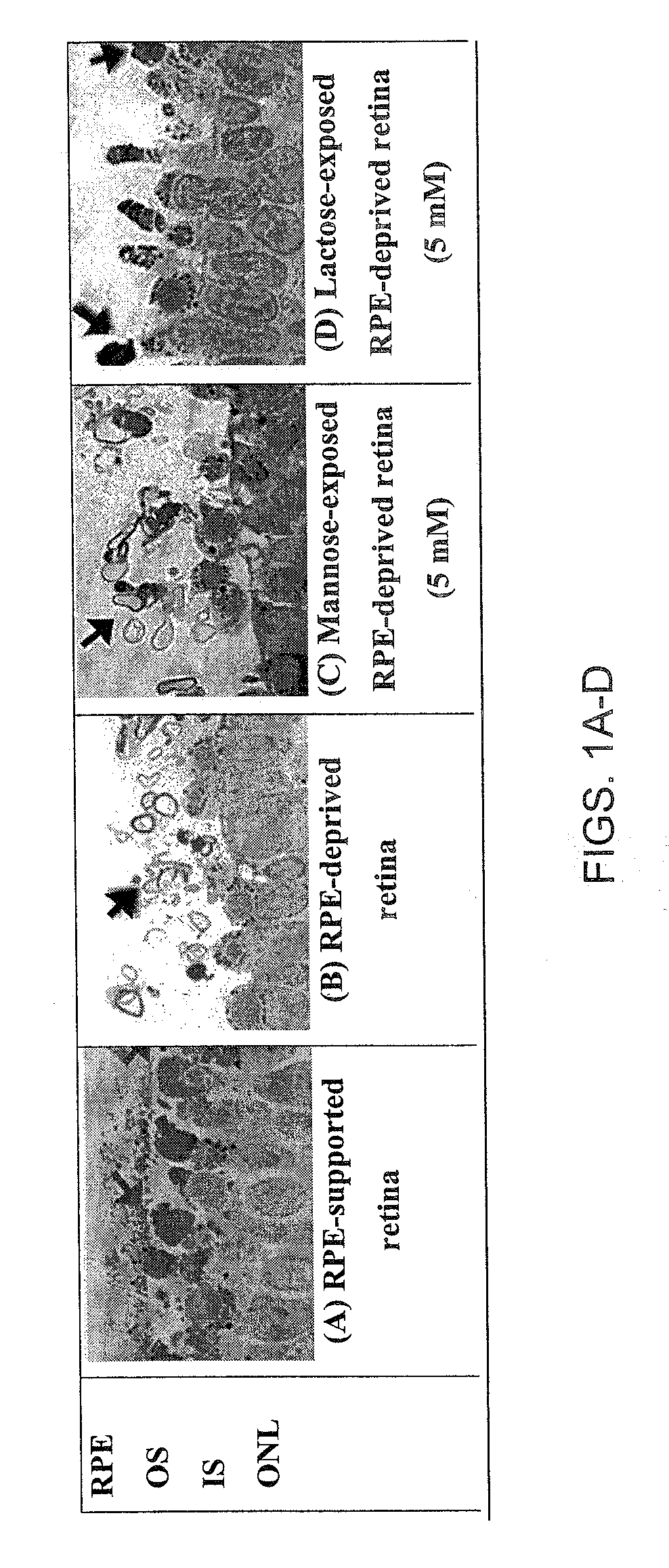
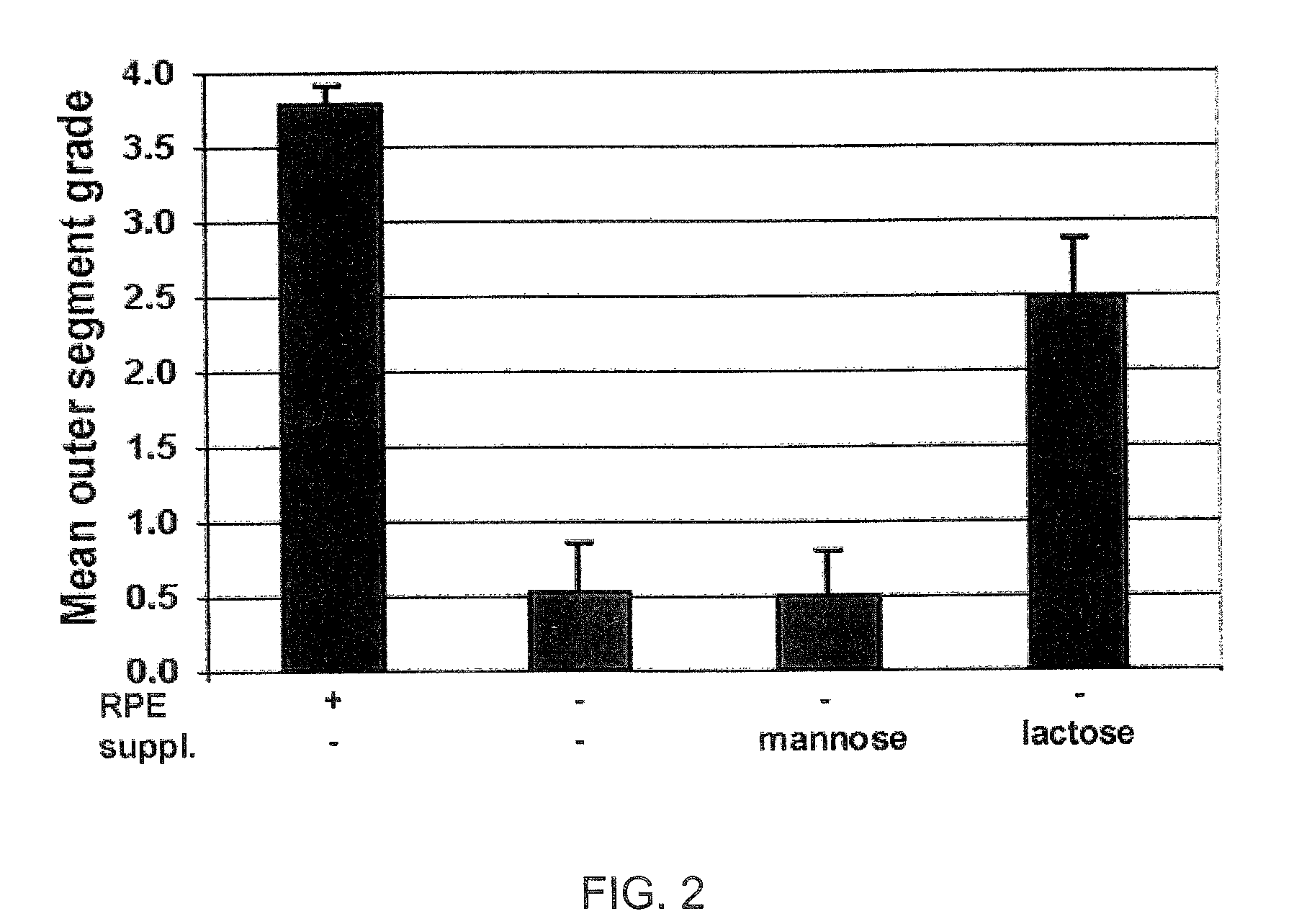
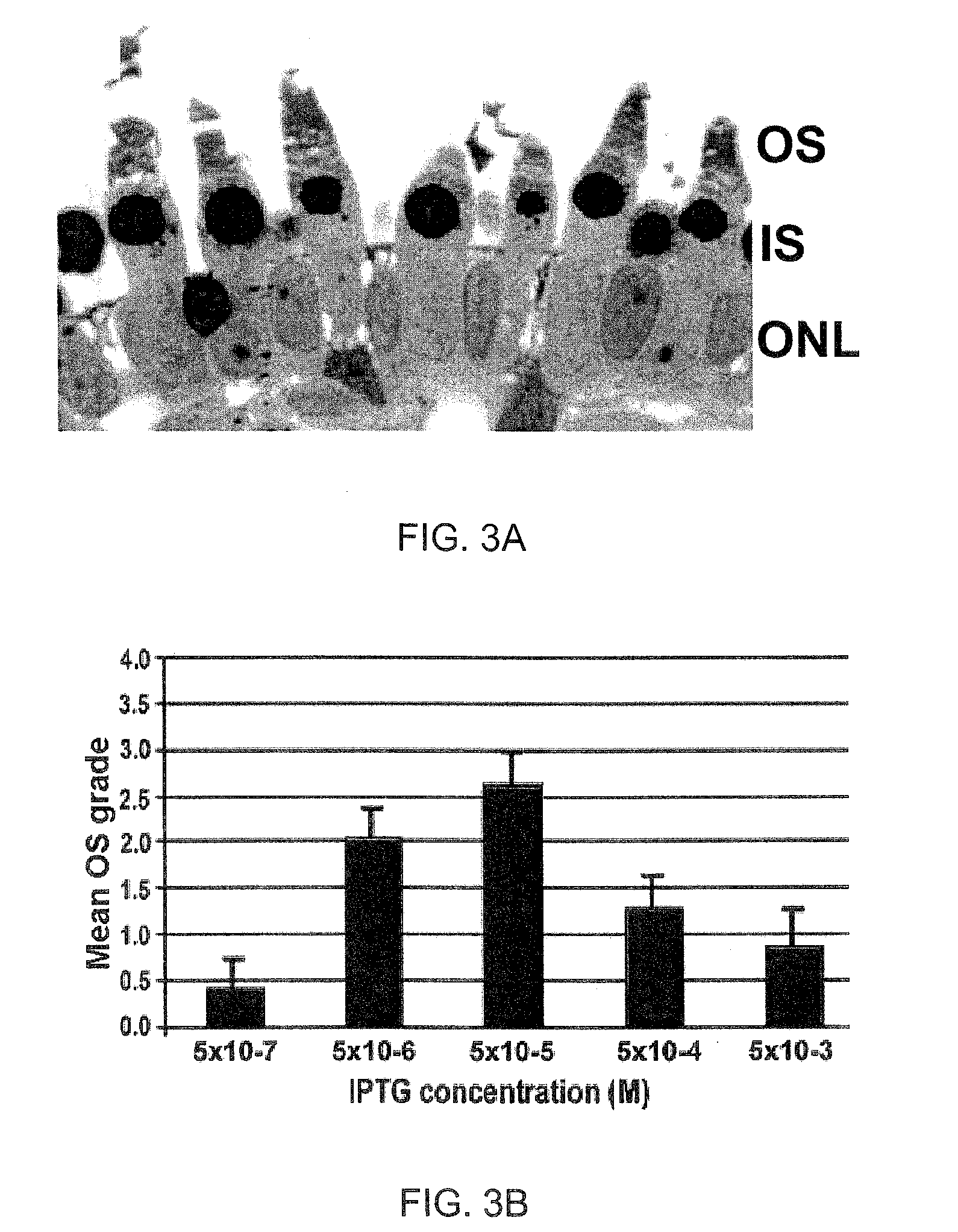
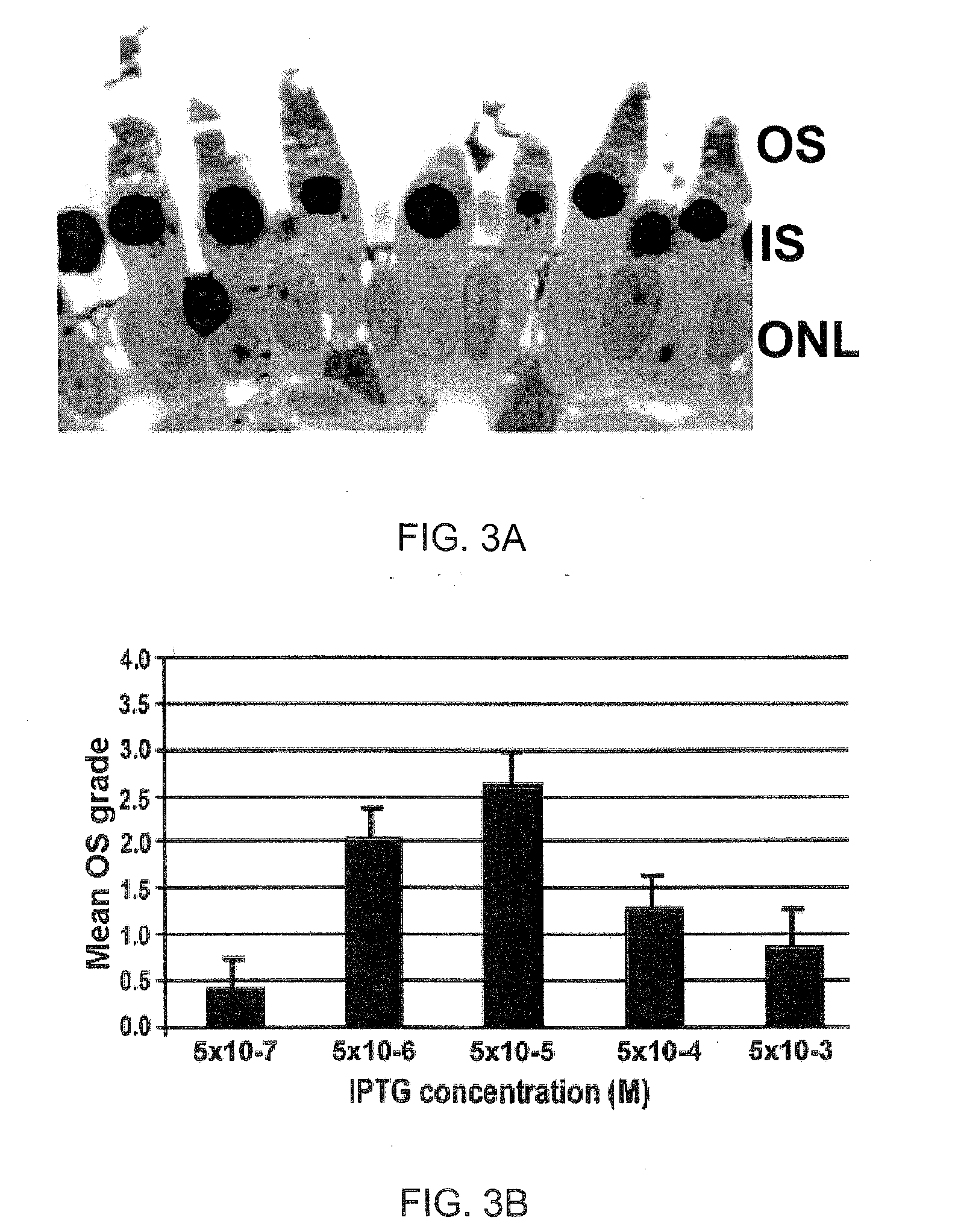
Glycan binding proteins as therapeutic targets for retinal disorders and treatment methods based thereon
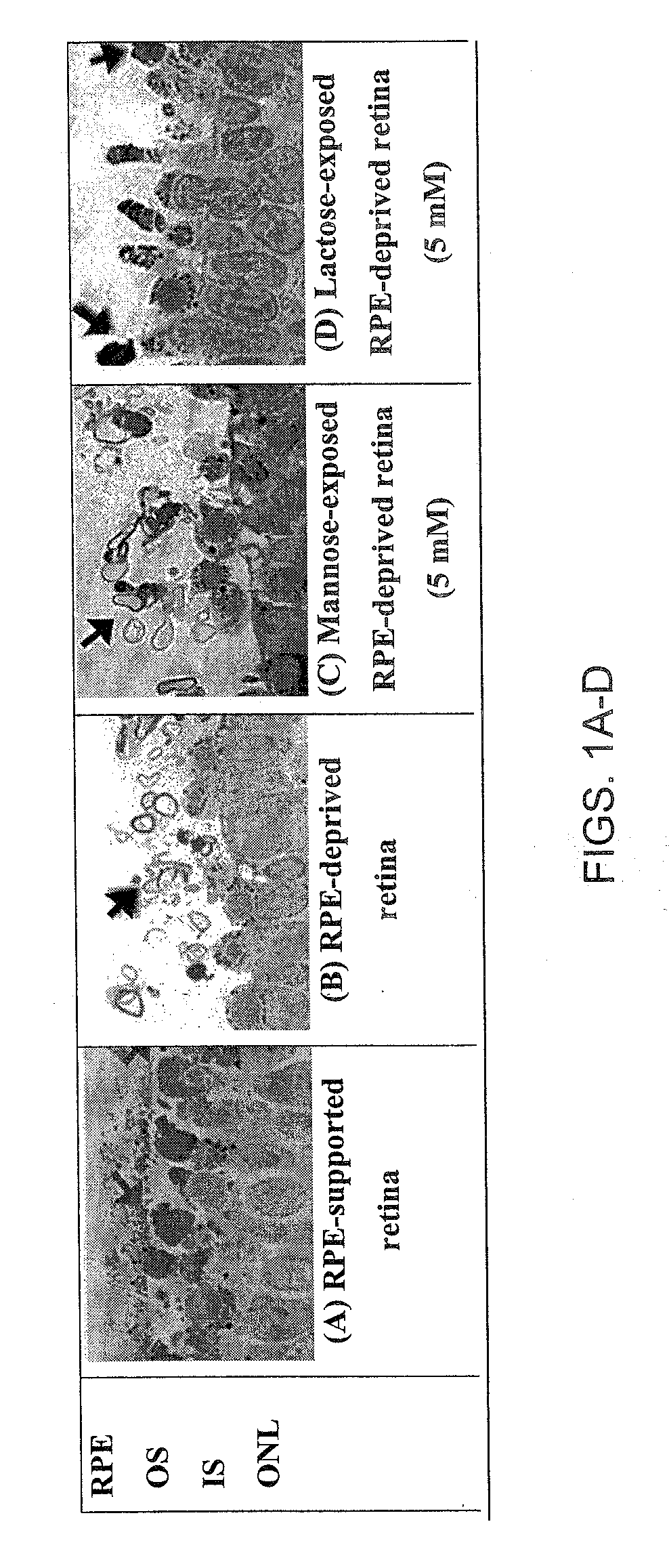
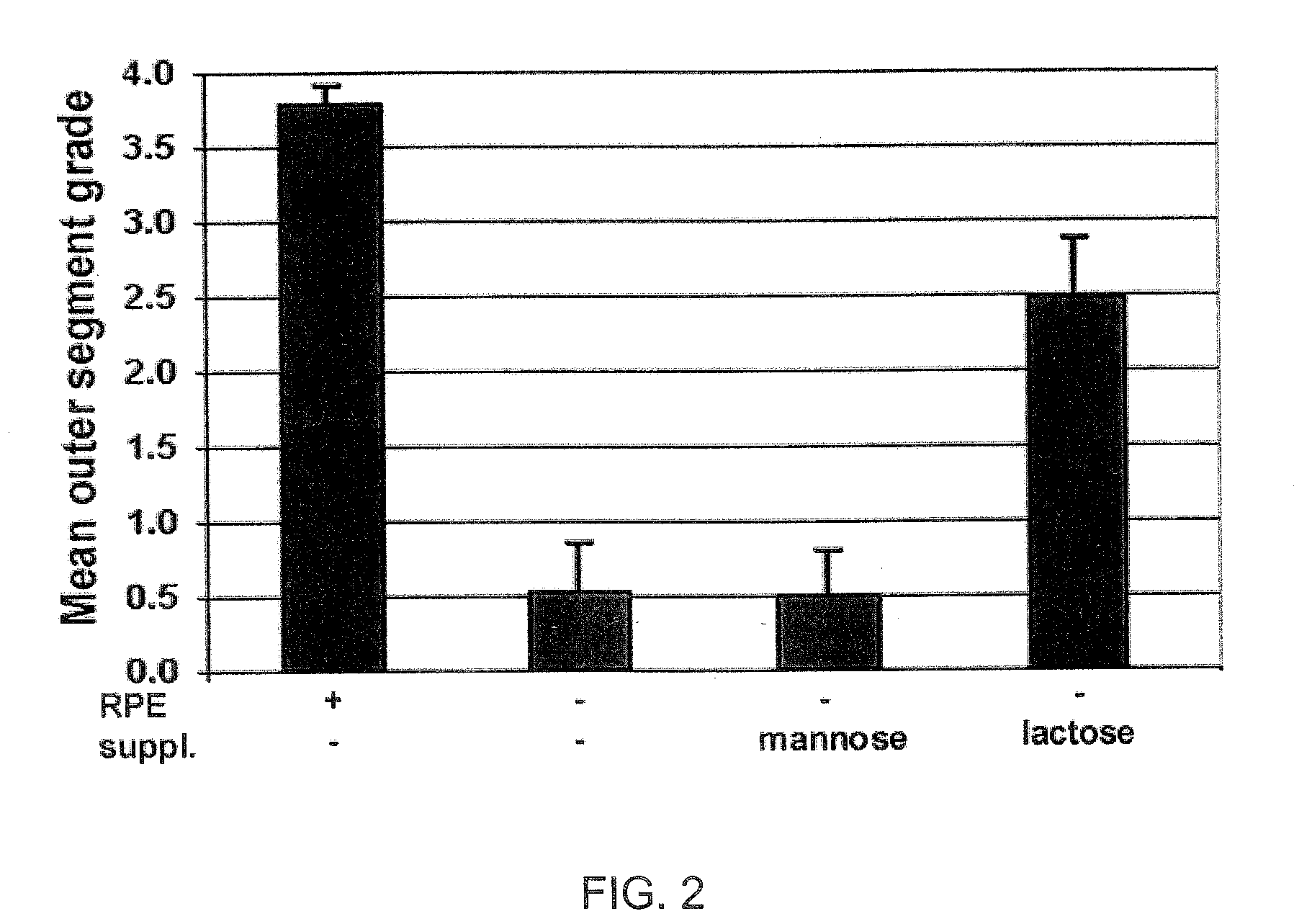
Disclosed are novel methods of treatment for retinal diseases and conditions including age-related macular degeneration, genetic-based retinal degenerations and retinal detachment. A novel glycan binding protein thought to be a cell surface receptor has been discovered in the retina. The retinal glycan binding receptor is shown to play an important role in promoting assembly of outer segment (OS) membranes by the photoreceptor cells of the eye, a process that is essential for vision. Based on the finding that certain sugars can bind with very high affinity to the retinal glycan receptor and stimulate its function, the invention provides novel therapeutic agents for treatment of retinal diseases that are multivalent N-linked glycans. Preferred pharmaceutical compositions in accordance with the present invention comprise active agents having the general formula: (Gal-GlcNAc)n-Man3-GlcNAc2, where n is 1-4. Particularly preferred multivalent glycans are galactosylated, biantennary (NA2), and asialo, galactosylated, triantennary (NA3) oligosaccharides.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
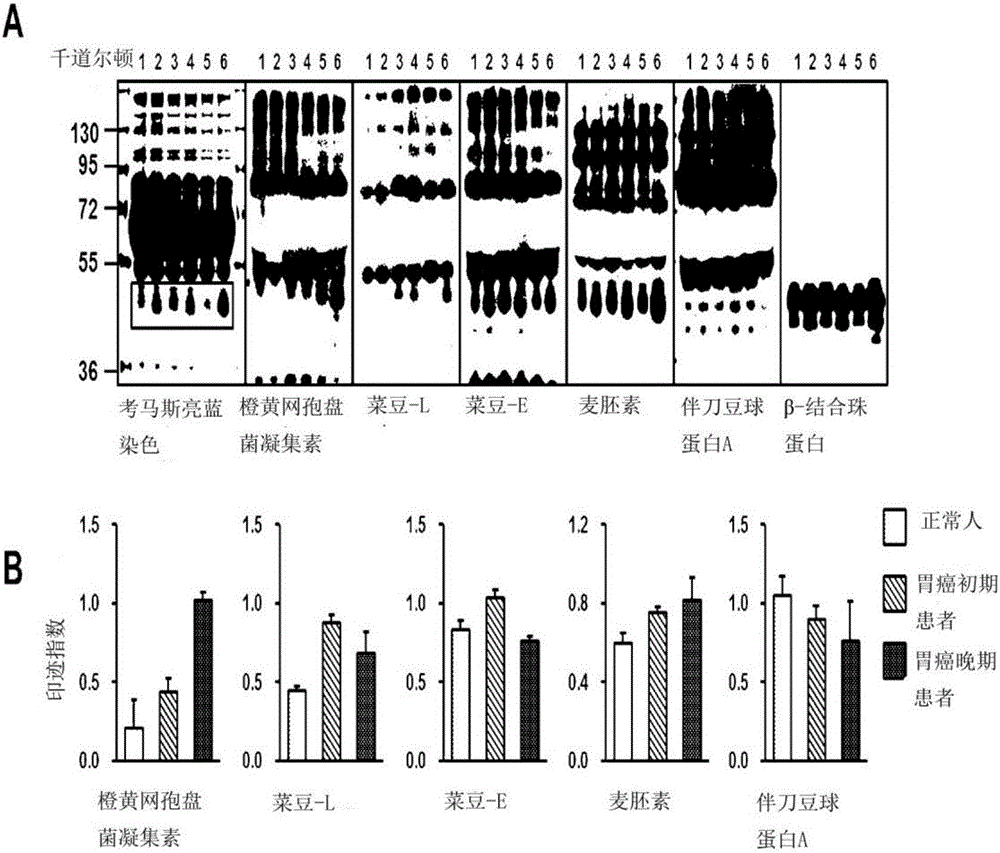
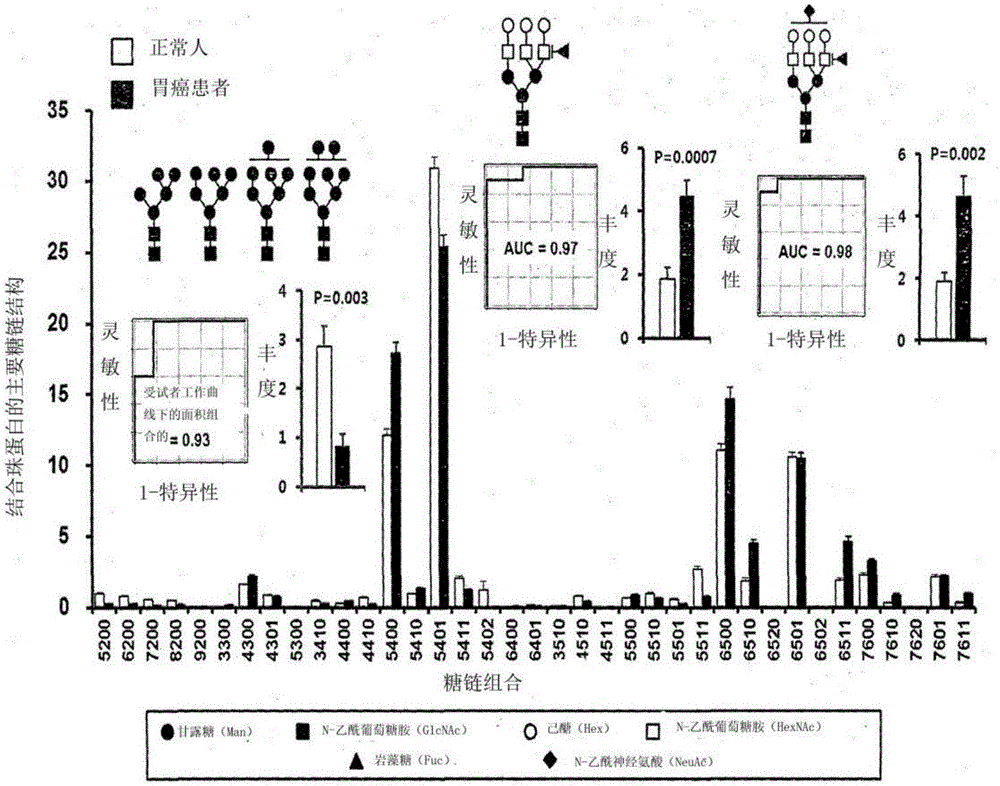
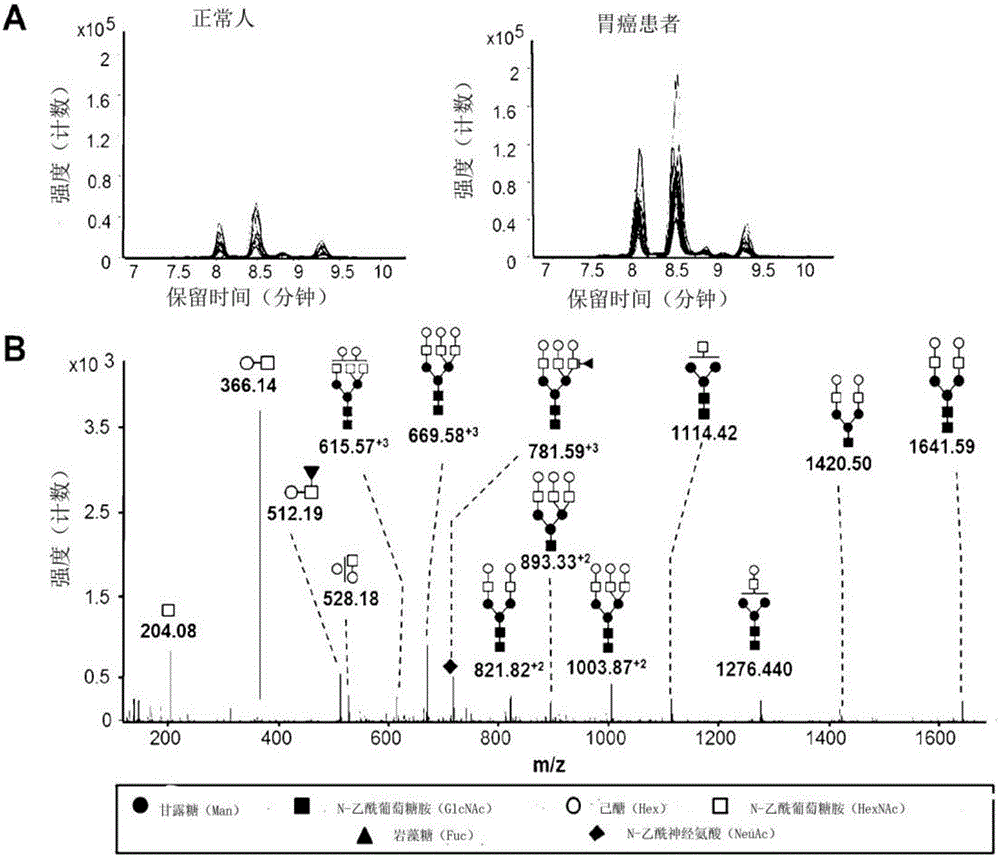
Novel method for gastric cancer diagnosis
InactiveCN106029906AIncreased sensitivityStrong specificityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingFucosylationHigh mannose
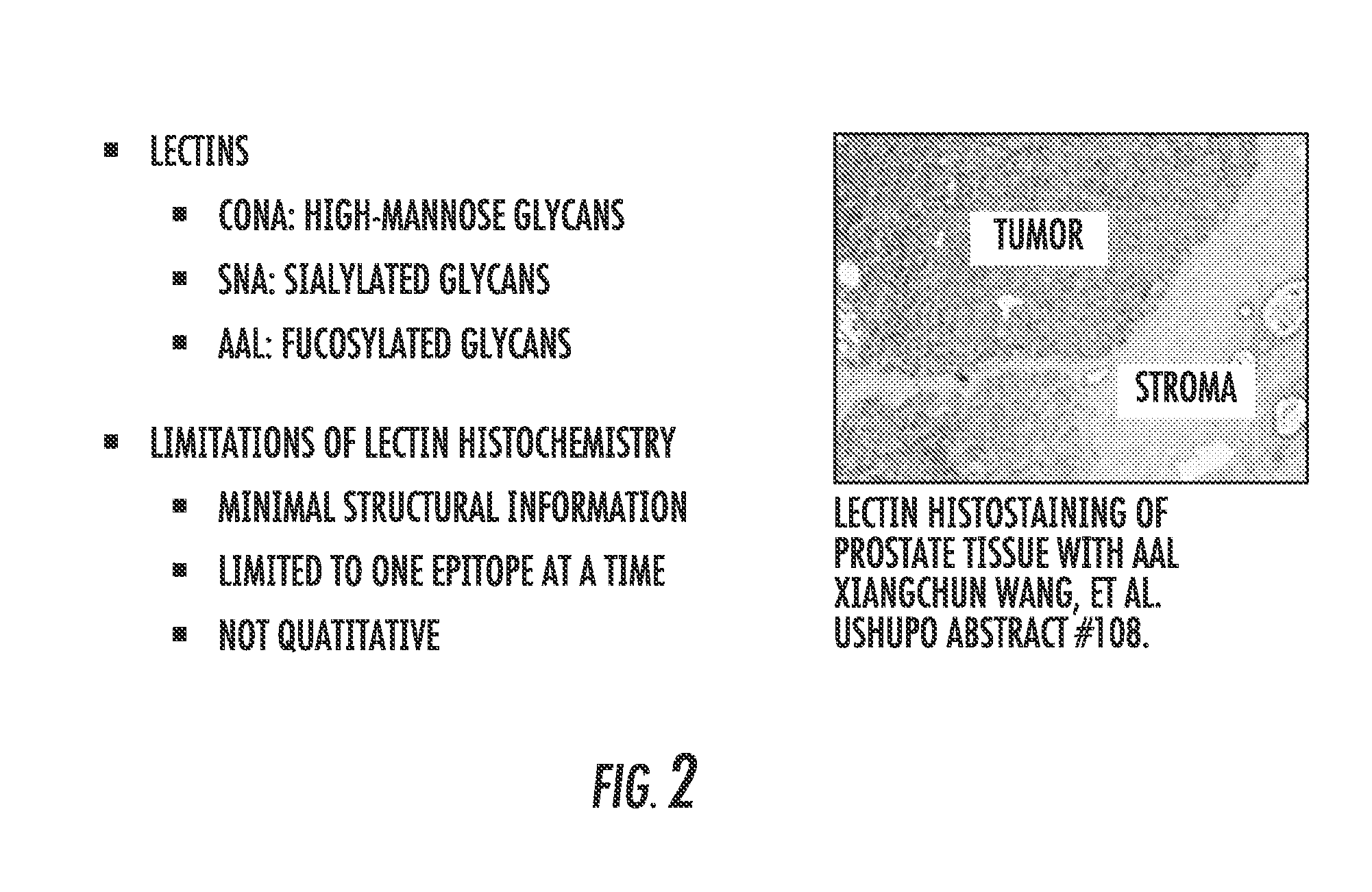
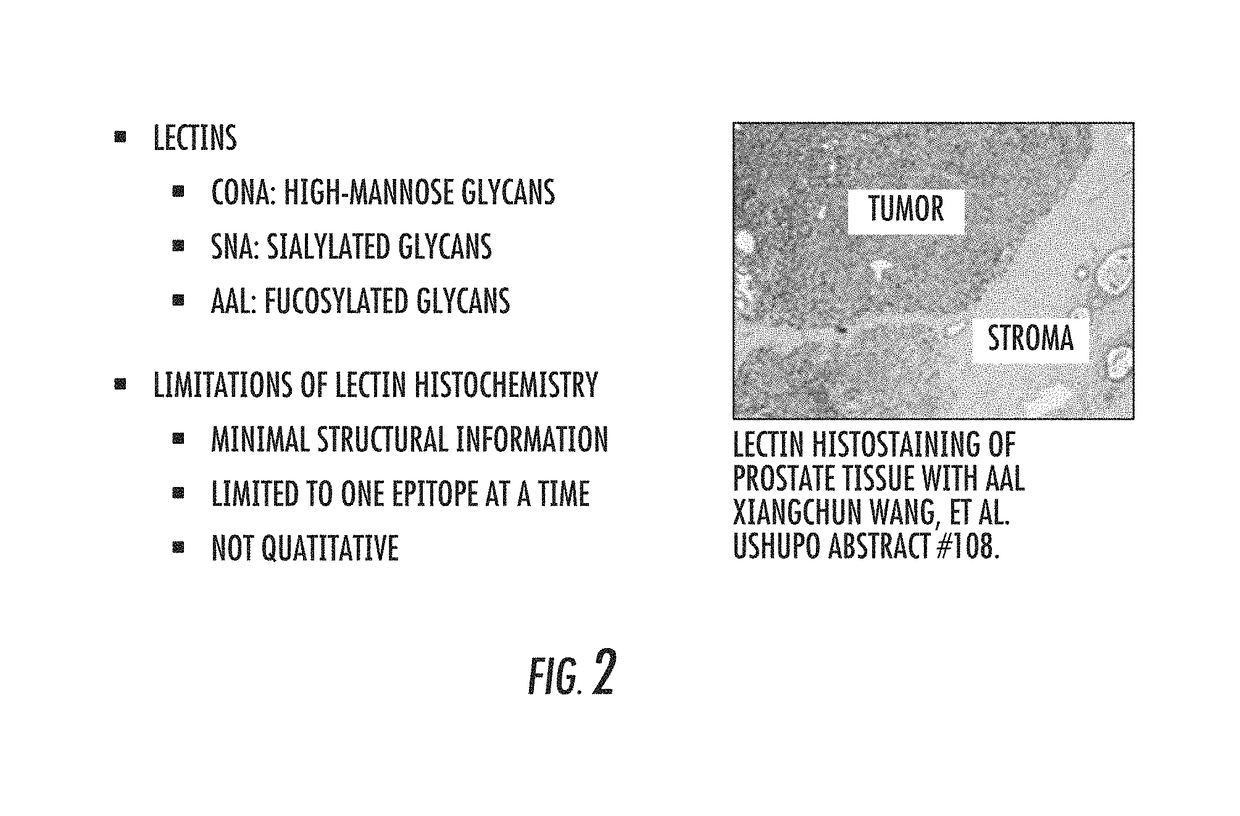
The present invention relates to a method for gastric cancer diagnosis through the detection of glycan changes, and to a kit for gastric cancer diagnosis. More specifically, based on, among the changes in N-linked glycosylation of the gastric cancer patient-derived haptoglobin, which are detected through lectin and mass spectrometry, the increase in fucosylation, the increases or significant changes in particular glycan structures according to the classification of antennary, or the reduction in high-mannose structure of the N-linked glycan compared with normal persons, the discovered N-glycosylation structures can be favorably used for a method for gastric cancer diagnosis using lectin, as a diagnostic marker, or mass spectrometry, and a kit for diagnosing gastric cancer.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Method for fast and high throughput detection of N-linked glycans in glycoprotein based on membrane separation
InactiveCN106525986AImprove throughputShorten the timeComponent separationCell culture supernatantThroughput
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology, and in particular relates to a method for fast and high throughput detection of N-linked glycans in a glycoprotein sample based on membrane separation. A hydrophobic membrane porous plate and a hydrophilic membrane porous plate are used to process the glycoprotein sample, the glycoprotein sample processing flux is improved, and steps are simplified. In addition, by changing the reaction conditions of PNGase F enzyme, and the sample processing time is successfully shortened. The detection time of the N-linked glycans in the glycoprotein sample can be shortened from 2 days of a traditional method to within 4-6 hours. In addition, the method successfully solves the problem that in traditional experiments only a purified glycoprotein sample can be used to carry out the experiments, and by use of the method, cell culture supernatant can be directly used for experiments. A strong support is provided for fast qualitative analysis of the N-linked glycans in the glycoprotein for screening of early cell lines.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAOZHE INFORMATION TECH LTD +1
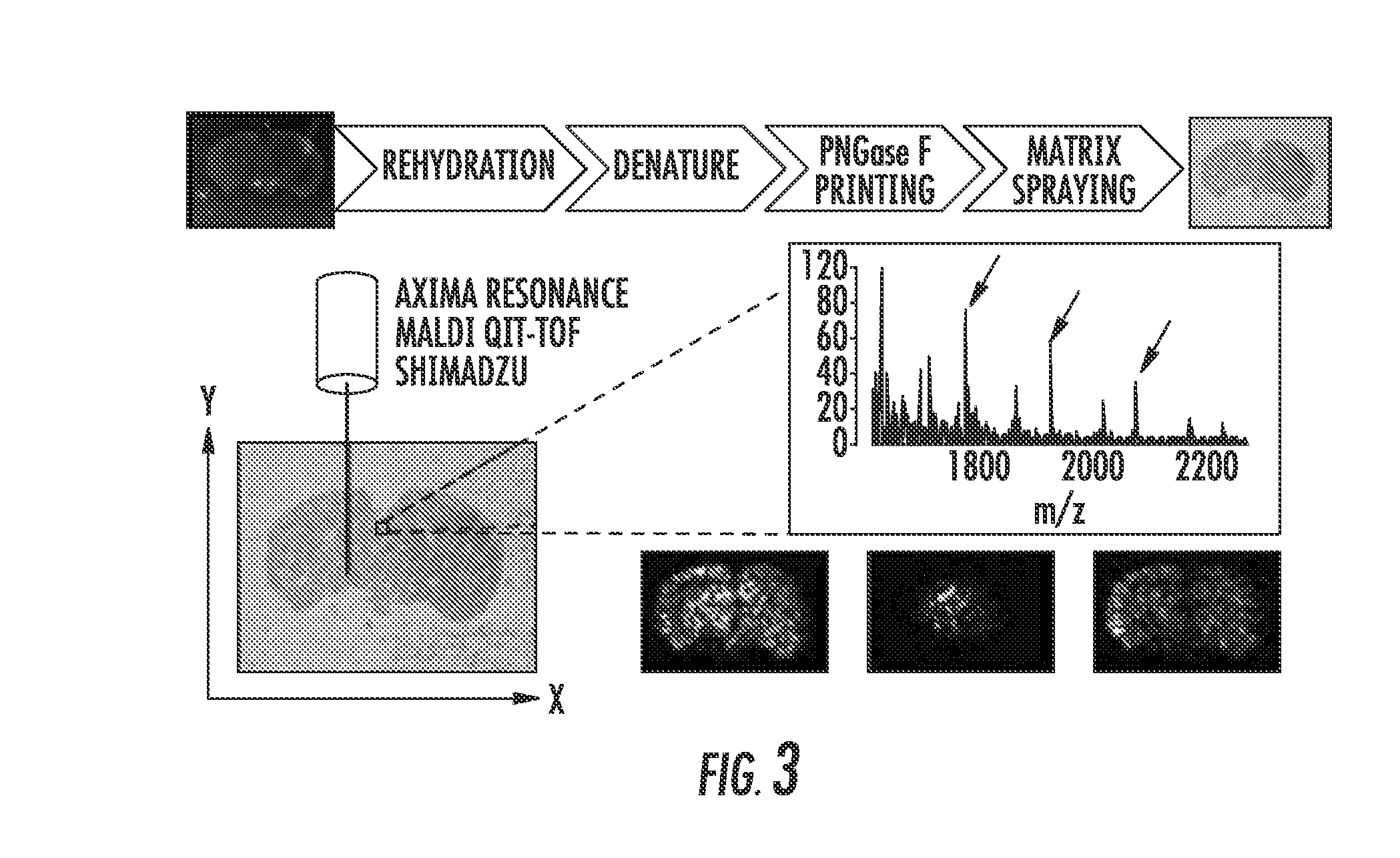
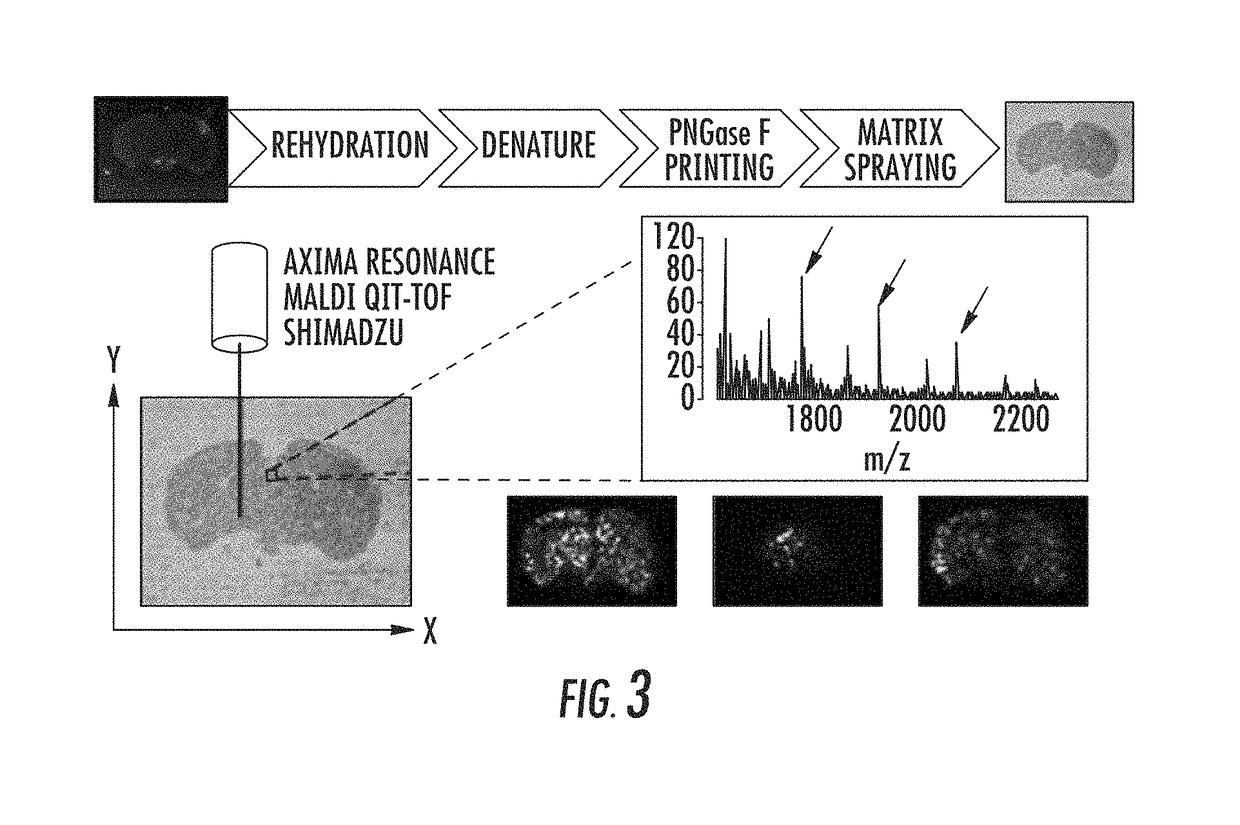
Mass spectrometry imaging of glycans from tissue sections and improved analyte detection methods
InactiveUS20150099669A1Improve detection limitKeep the distanceMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningMass spectrometry imagingMaldi ms
The presently disclosed subject matter provides methods using mass spectrometry for direct profiling of N-linked glycans from a biological sample. In addition, the embodiments of the present invention also disclose novel methods, known as targeted analyte detection (TAD), for improving the detection limit of MALDI-MS. These methods take advantage of the carrier effect of the added standard analytes, which occurs due to the generic sigmoidal shape of the calibration curve. The functionality of TAD depends on the relative enhancement of sensitivity over the increase of the standard deviation at the analysis of target analytes with spiking in exogenous concentration. At certain ranges of exogenous concentration, the increment in the sensitivity overcomes the standard deviation, resulting in an improved LOD. Theoretically, exogenous concentrations approximately at 1 LODorig would generate the optimum LOD improvement. TAD is a cost-effective LOD improvement method, which is not limited to a certain group of analytes, or detection methods or instruments. It can be applied to enhance the detection of any analyte with different detection methods, provided that the analyte of interest can be extracted or is available in synthetic form.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
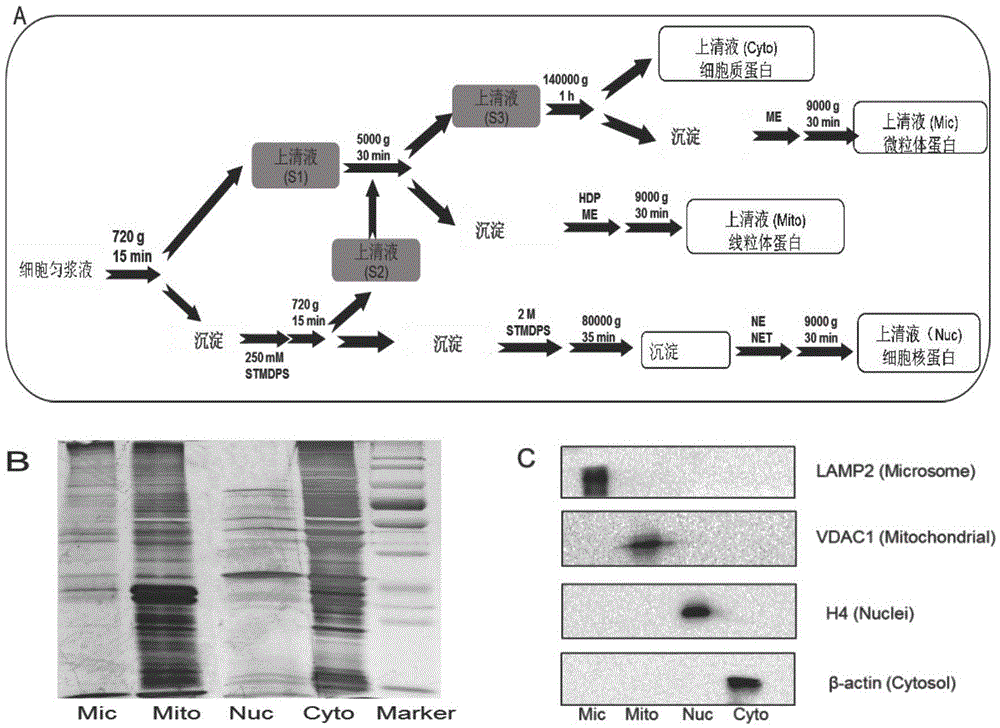
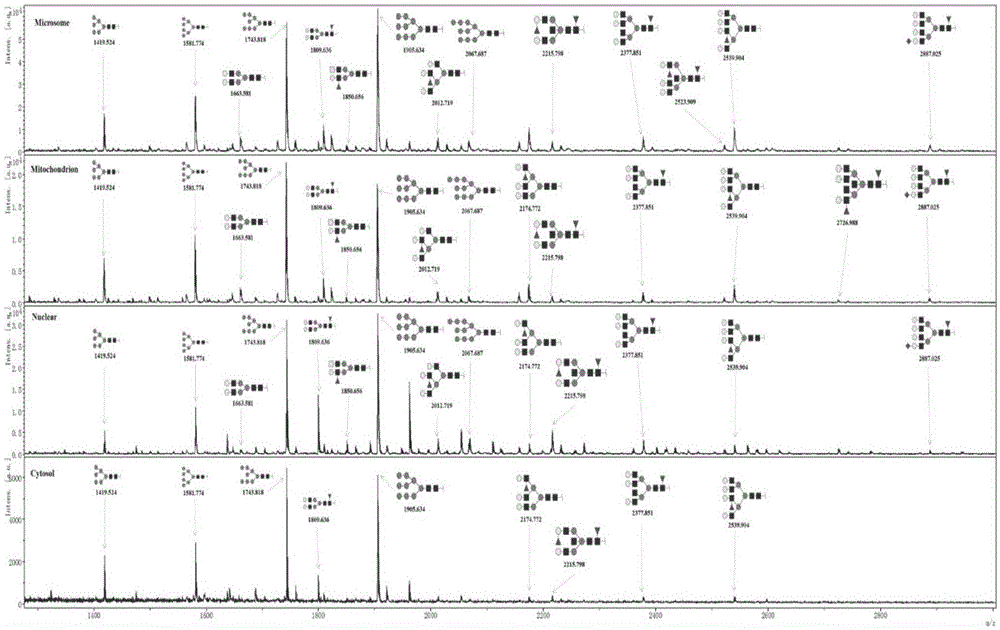
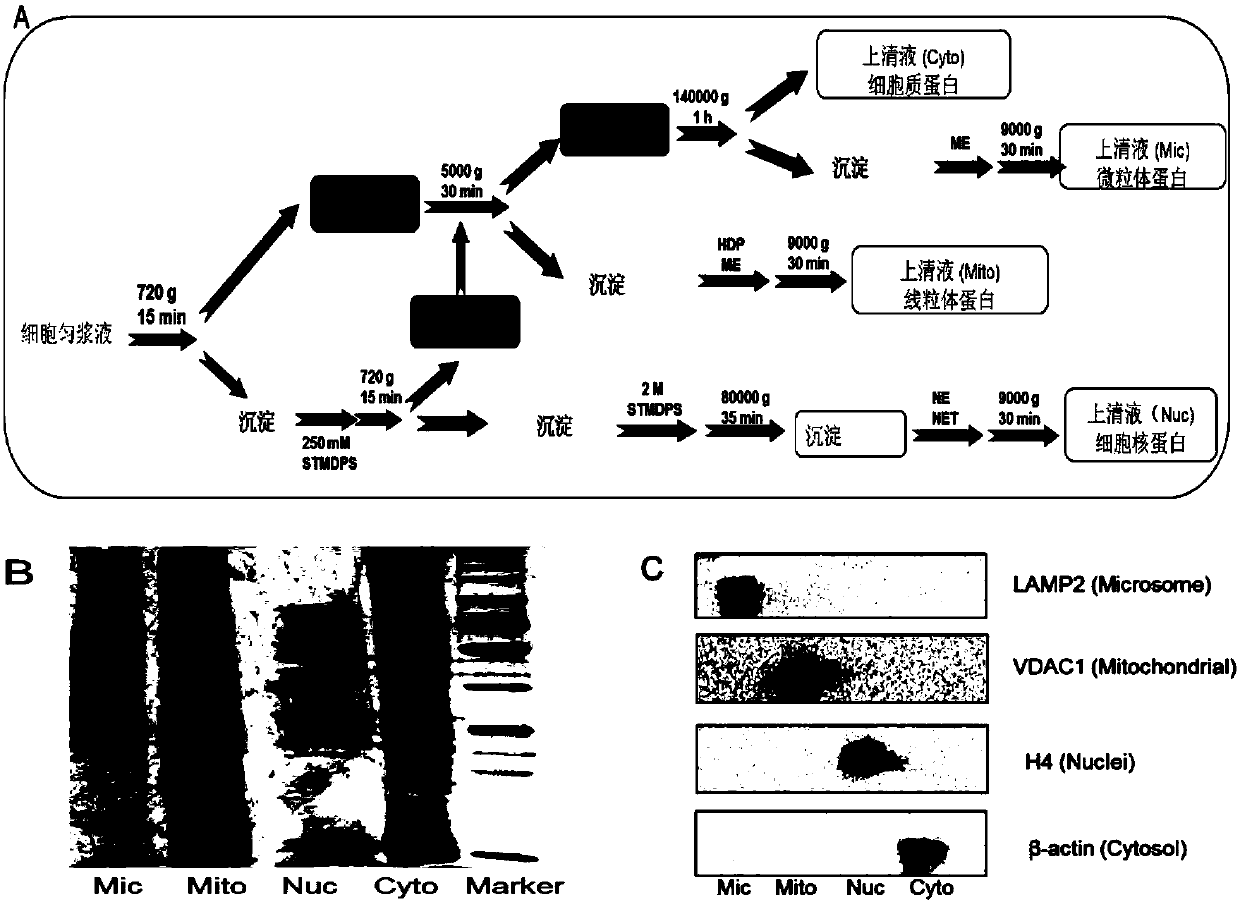
Subcellular structure characteristic N-linked carbohydrate chain and application thereof
ActiveCN105651853AImplement indirect detectionEasy to detectMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDetection of post translational modificationsBiologySubcellular structure
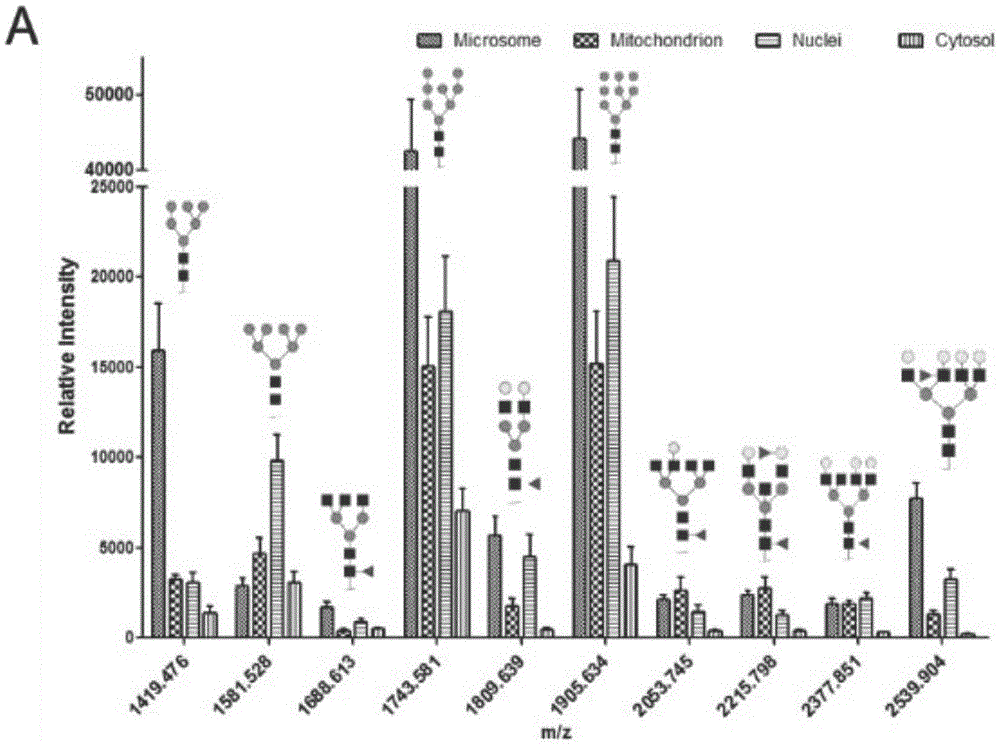
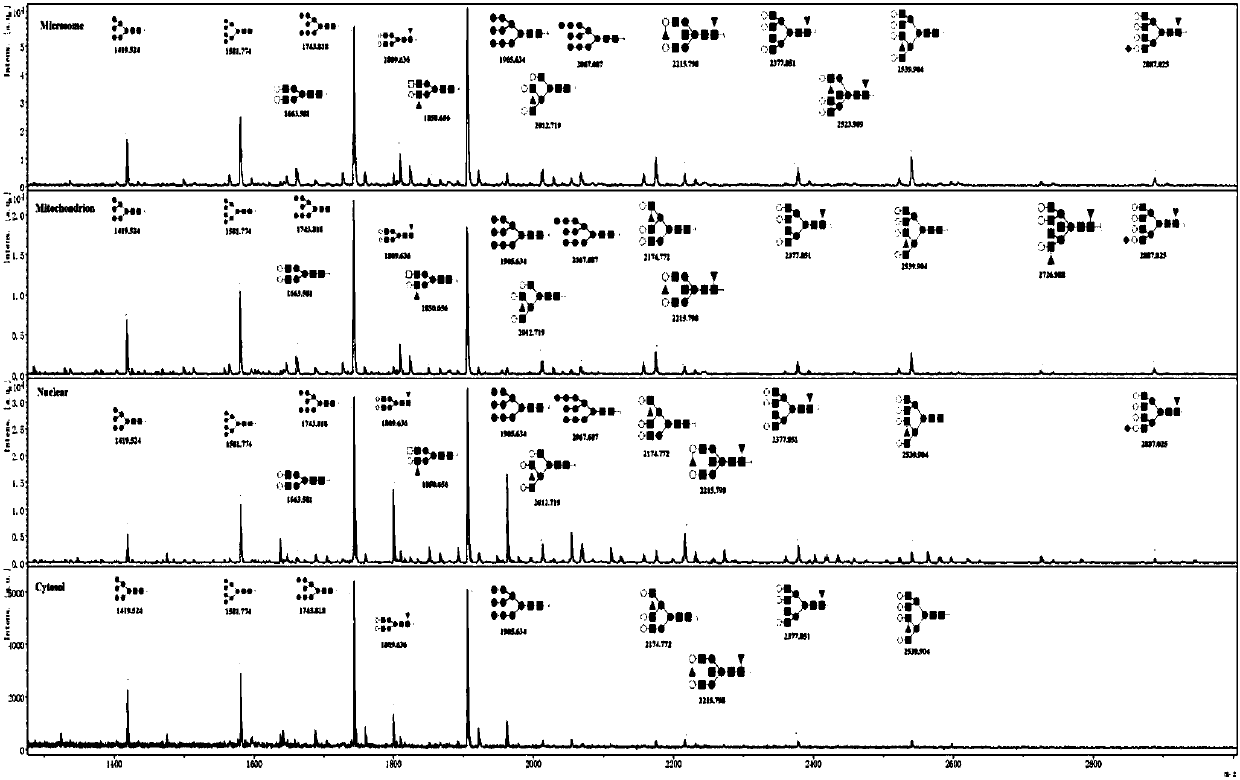
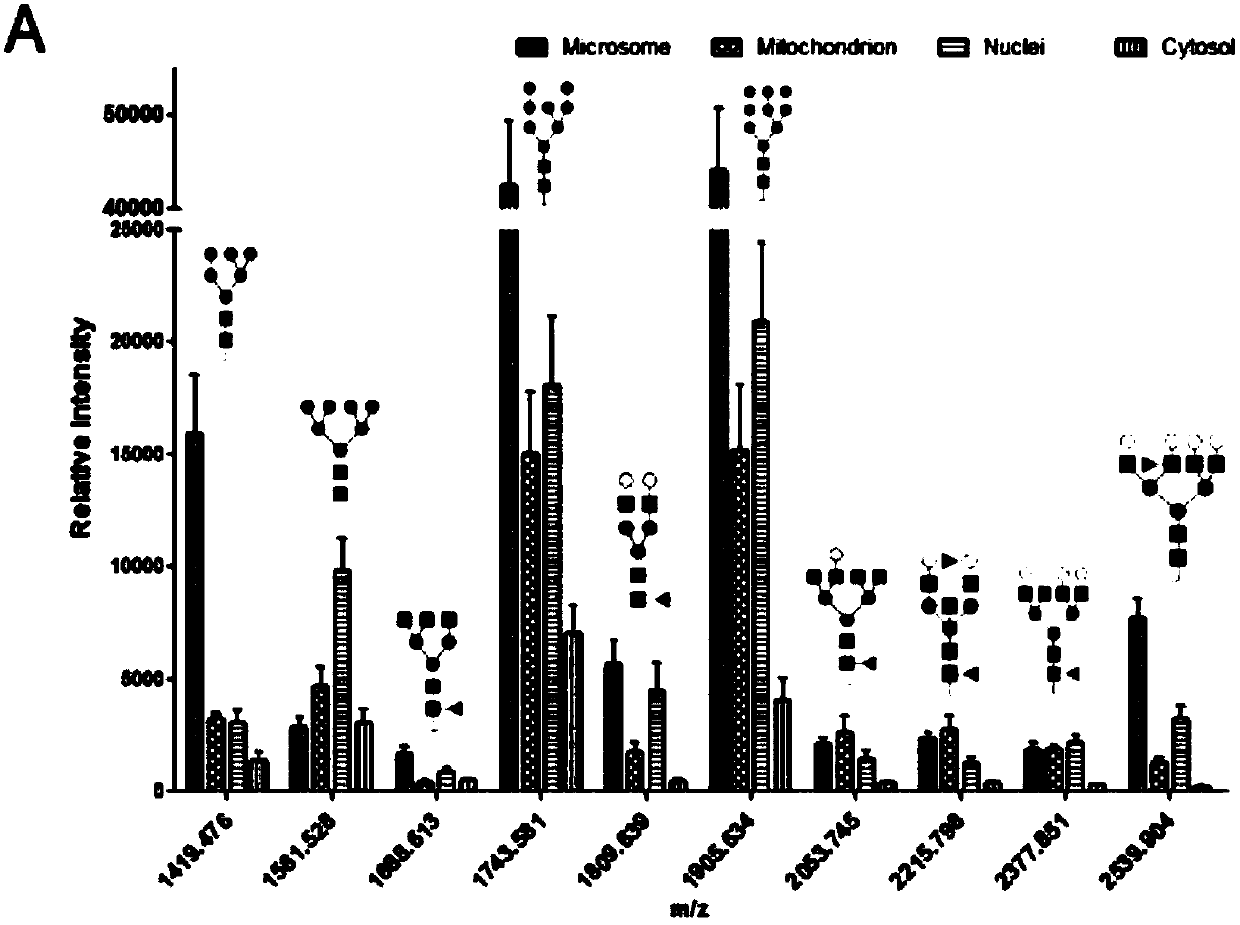
The invention discloses a subcellular structure characteristic N-linked carbohydrate chain and the application thereof and belongs to the technical field of glycobiology. Bladder YTS1 cells are used as the experiment material, the protein components of four subcellular structures (microsome, chondriosome, cell nucleus and cytoplasm) are obtained with the differential centrifugation method, and subcellular structure difference carbohydrate chain distribution is displayed through the change of the type and structure of subcellular structure protein galactosylated modification identified through a united lectin chip and a mass spectrum (PS) respectively. Subcellular structure characteristic N-linked glycan of ten kinds of human bladder YTS1 cells is obtained. By means of characteristic N-linked glycan, indirect detection and qualitative or quantitative detection of other target substances in corresponding subcellular structures can be achieved.
Owner:上海微江生物技术有限公司
Methods to obtain recombinant proteins with increased sialylation from cells that express adenovirus E1A protein, and proteins obtained thereby
InactiveUS7642078B2Reduce contentIncrease contentDepsipeptidesPeptide preparation methodsHeterologousE1A Protein
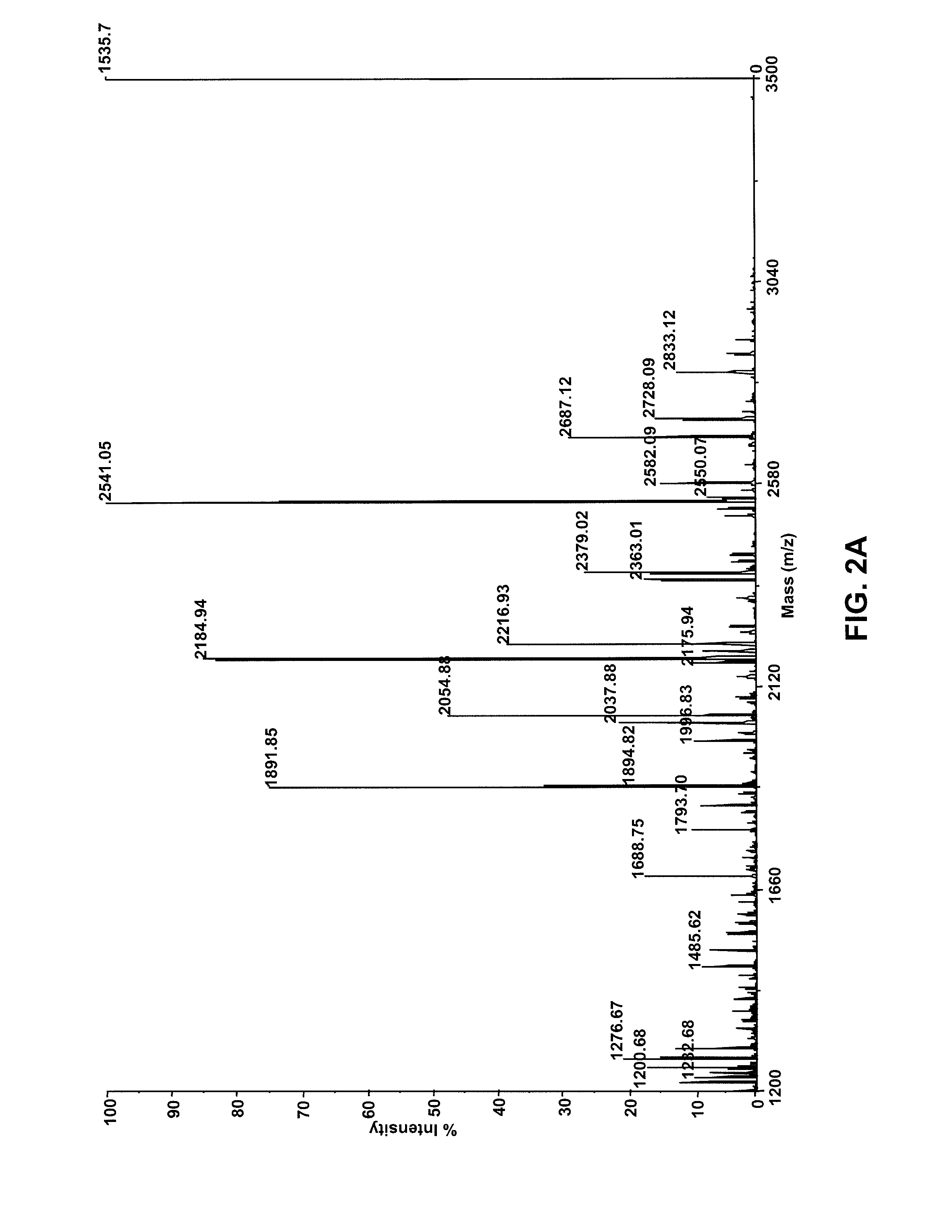
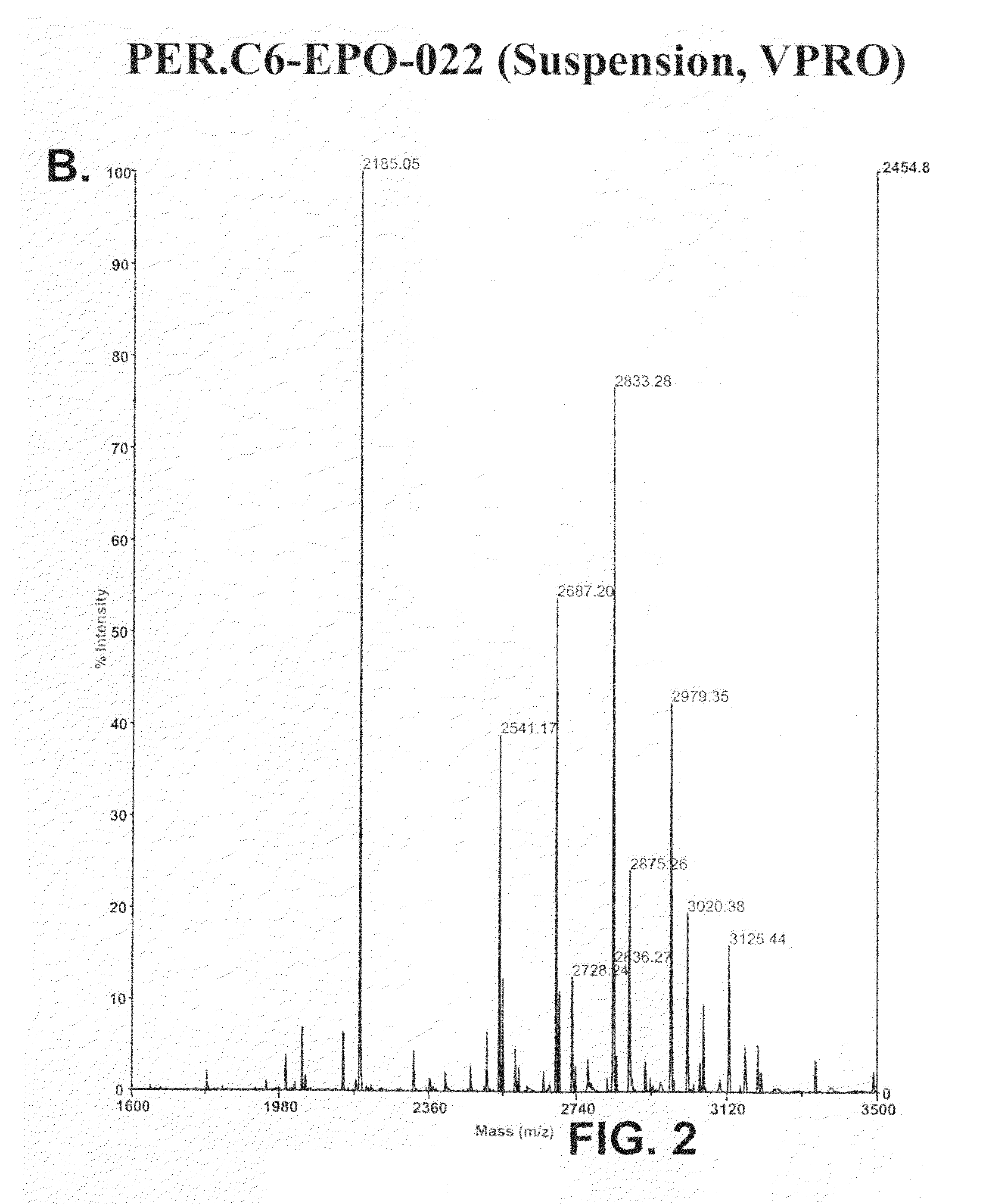
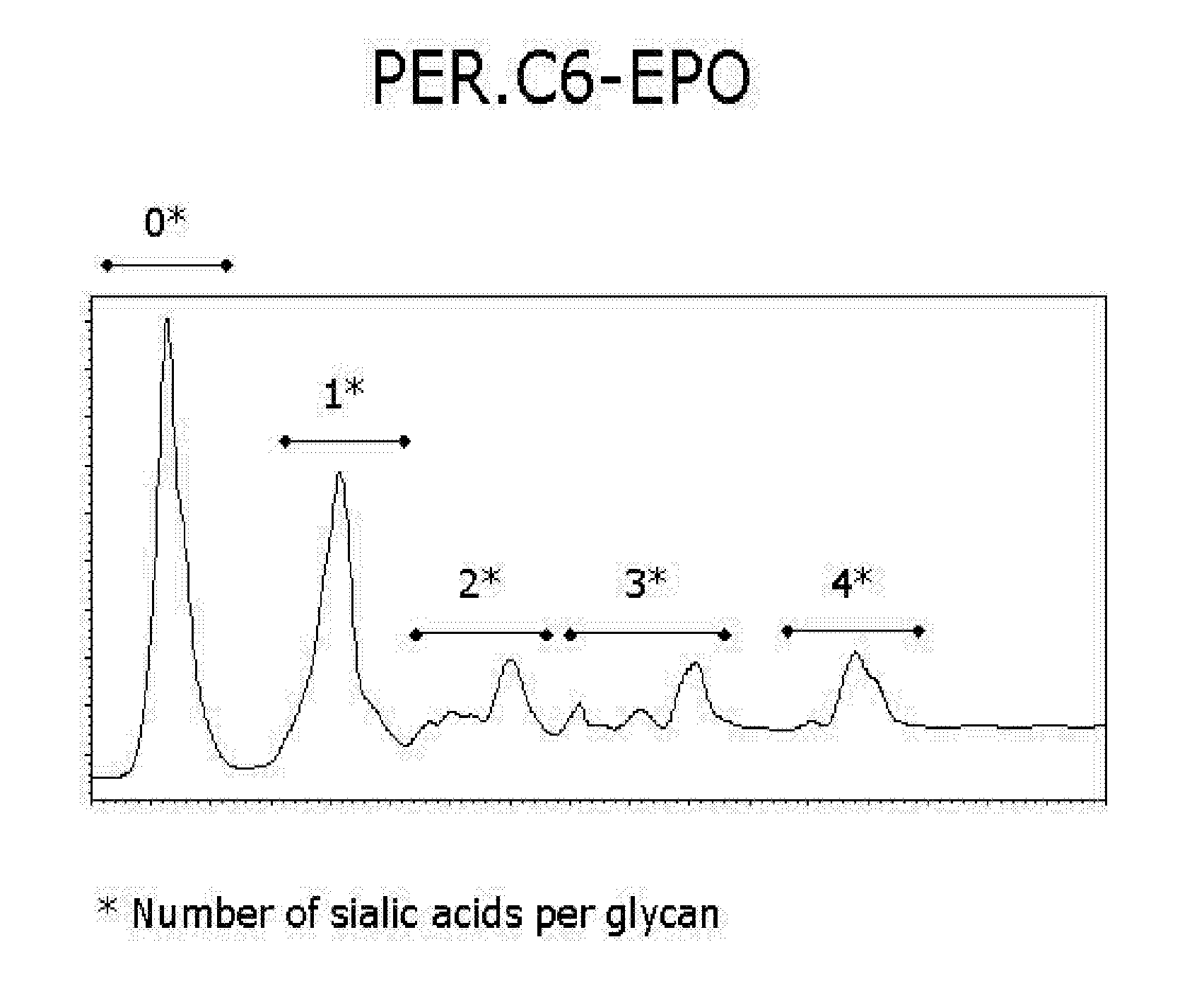
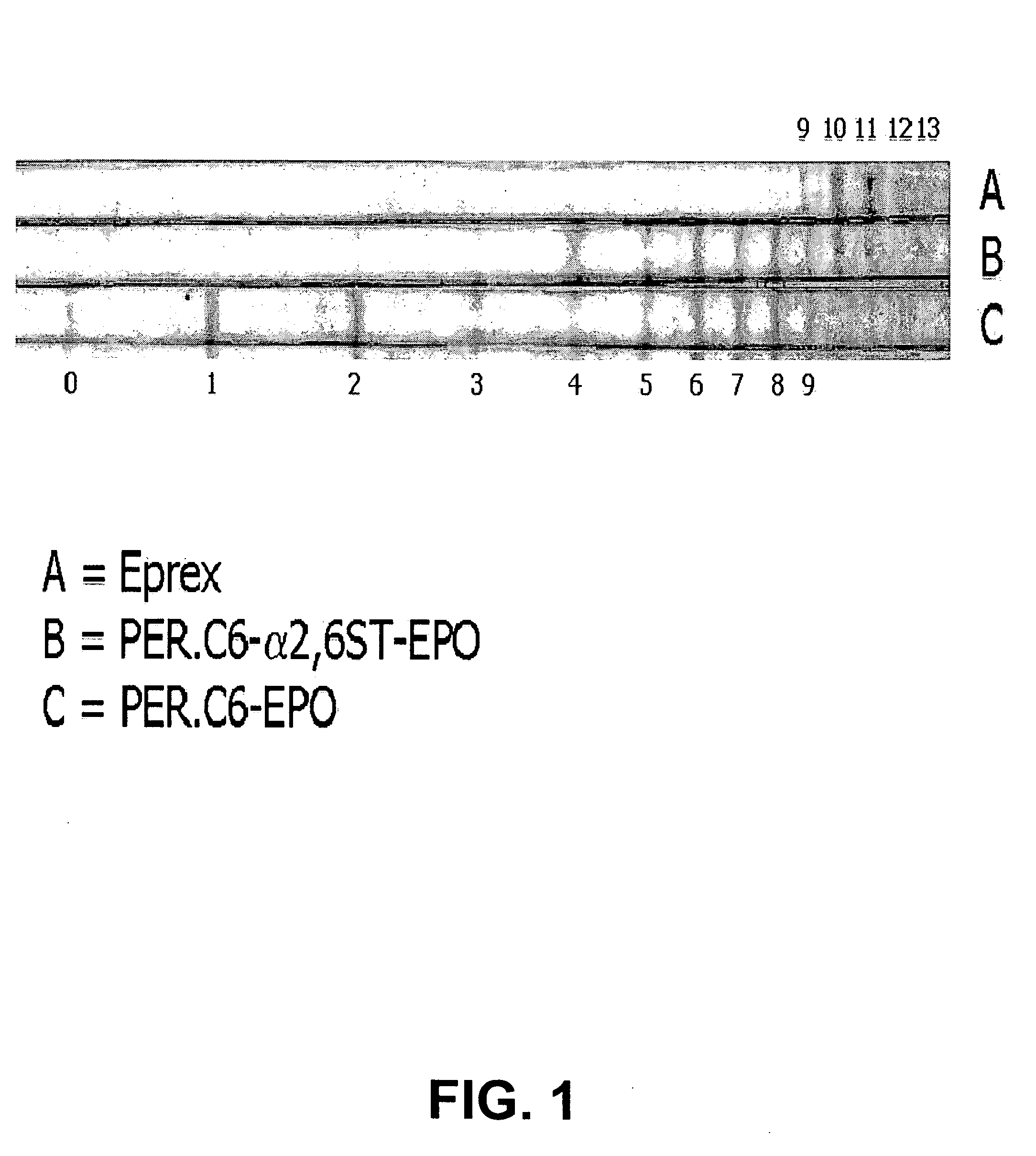
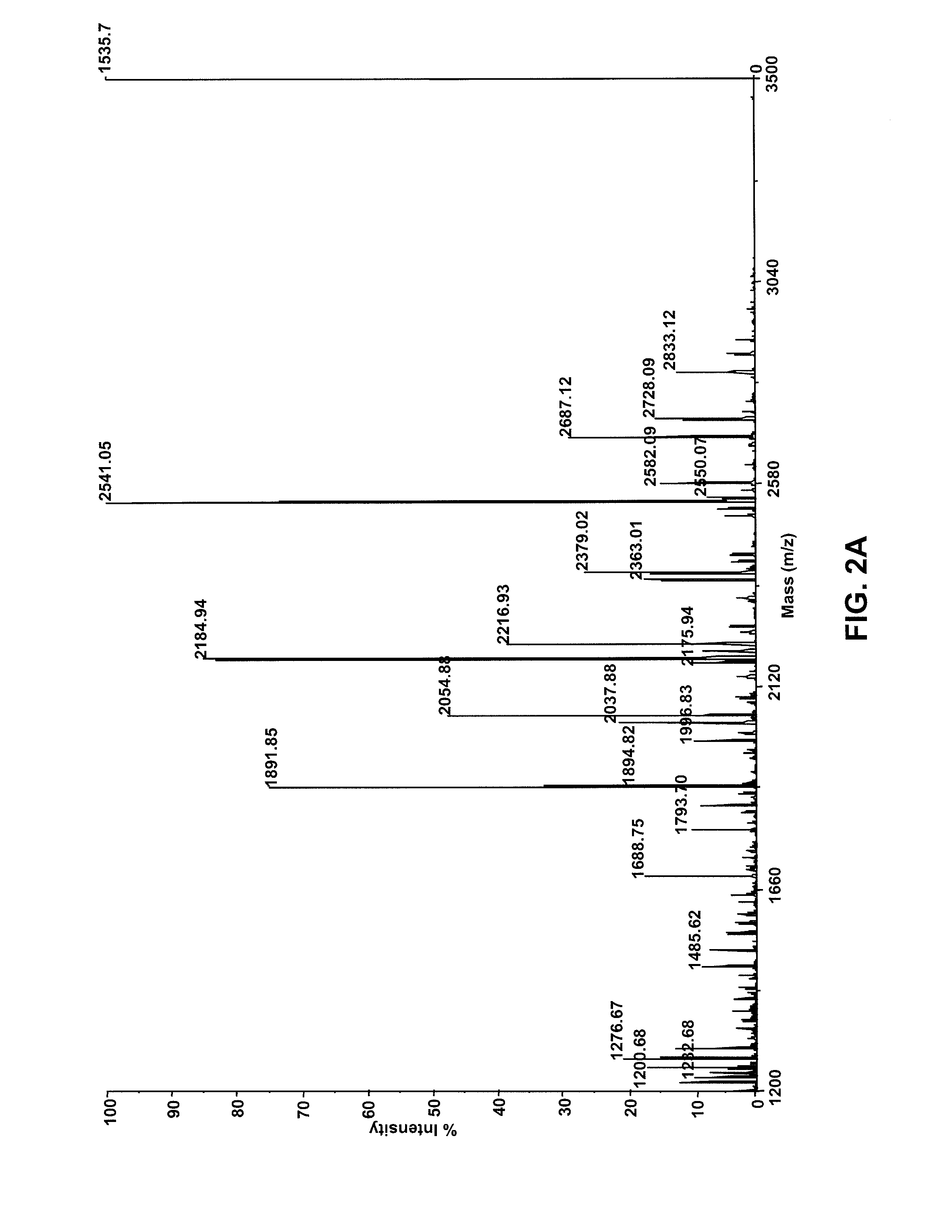
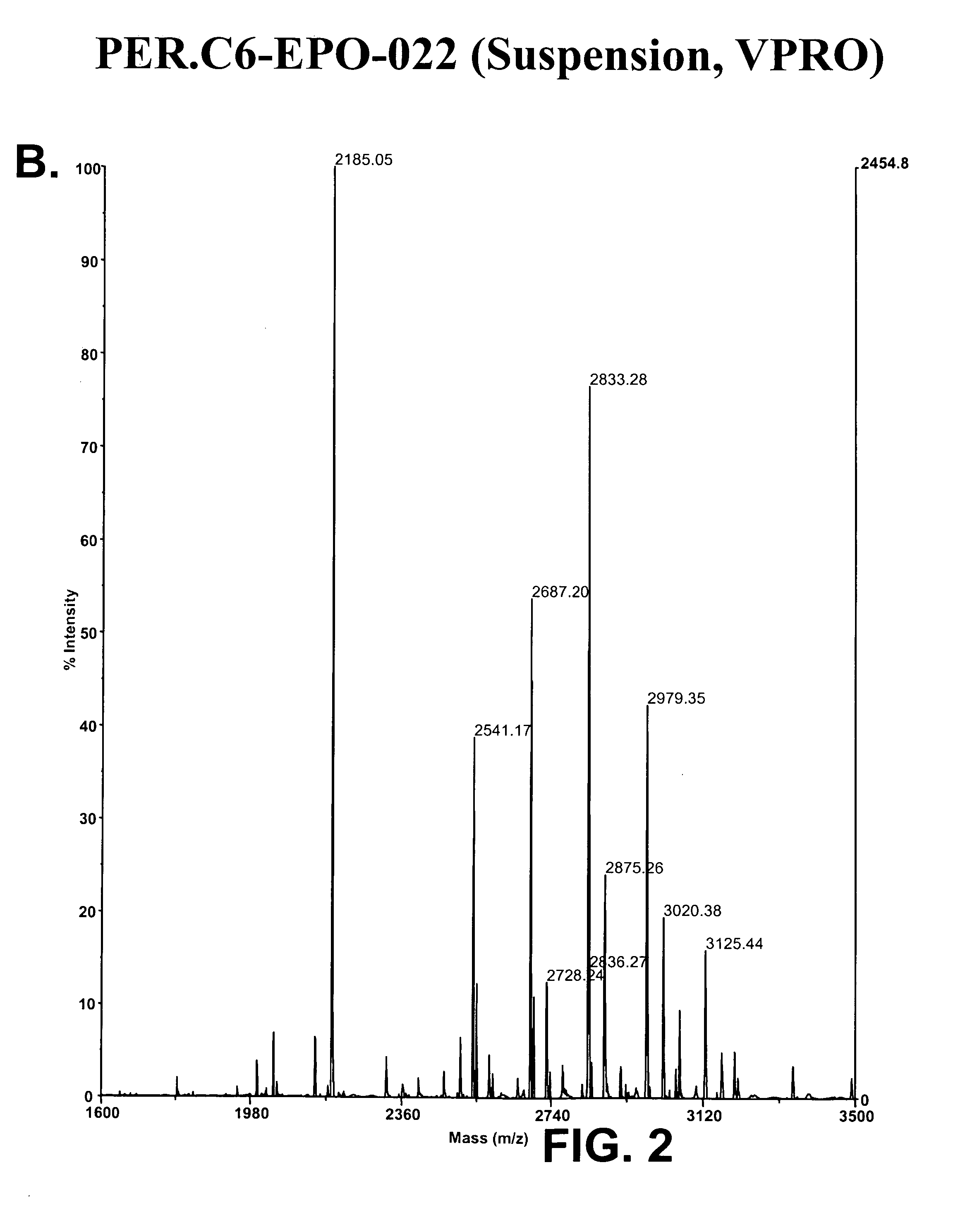
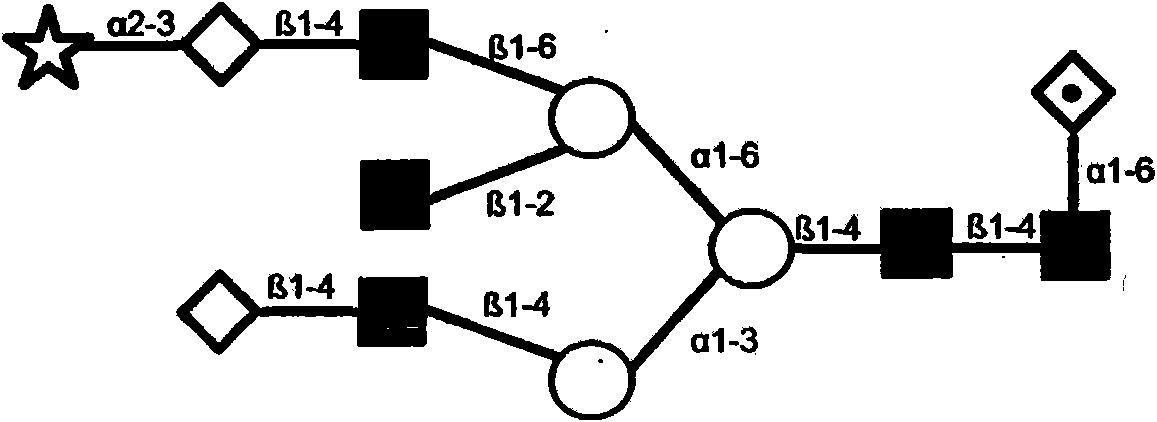
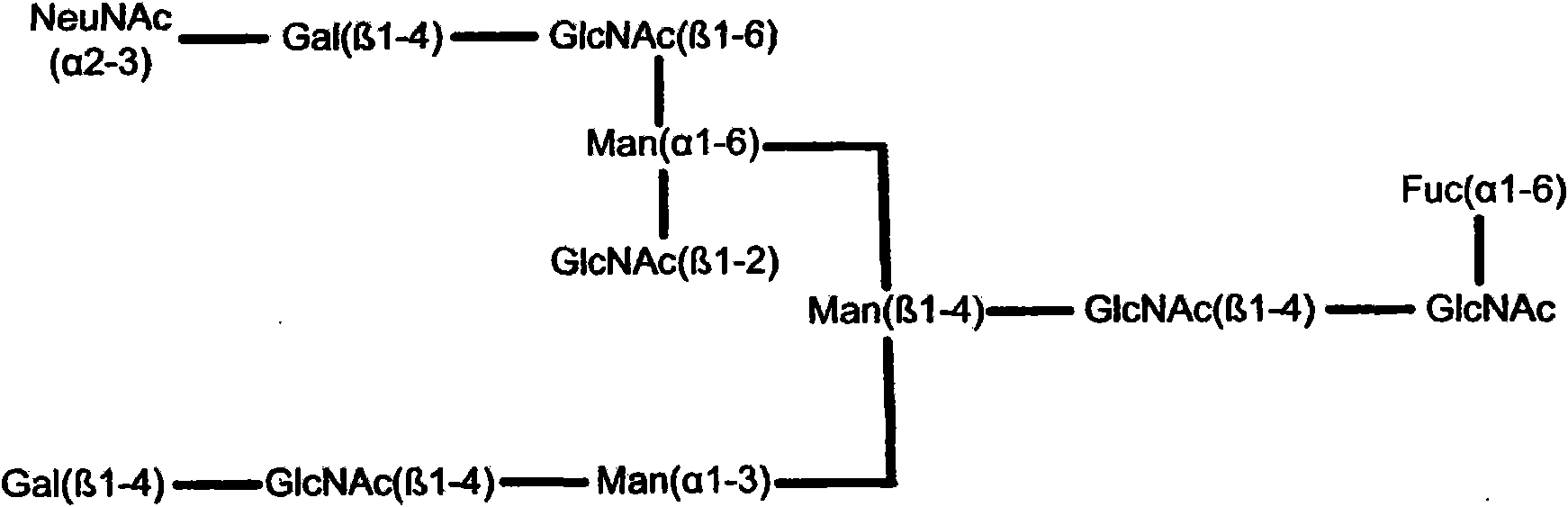
The invention provides compositions comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto, characterized in that said glycans comprise LewisX structures and on average at least 6 sialic acid moieties per EPO molecule. The invention further provides methods for obtaining a composition comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures, said method comprising: a) providing a eukaryotic cell containing a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein in expressible format and further containing a nucleic acid encoding an EPO in expressible format, wherein said cell further contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a sialyltransferase, preferably an alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase or an alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase, under control of a heterologous promoter; b) culturing said cell in a serum-free culture medium and allow expression of an EPO in said cell; c) harvesting the expressed EPO from said cell and / or from the culture medium; and d) purifying and fractionating the EPO to obtain fractions which have an increased average sialic acid content of the N-linked glycans per EPO molecule, to obtain a composition comprising one or more iso forms of an EPO comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Methods to obtain recombinant proteins with increased sialylation from cells that express adenovirus E1A protein, and proteins obtained thereby
InactiveUS8524477B2Reduce contentIncrease in sialic acid contentOxidoreductasesErythropoietinHeterologousE1A Protein
Provided are compositions comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (“EPO”) comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans have Lewis x structures and on average at least six sialic acid moieties per EPO molecule. Further provided are methods for obtaining a composition comprising one or more isoforms of EPO comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans comprise on average at least six sialic acids per EPO molecule and from zero to two Lewis x structures, the method comprising: a) providing a eukaryotic cell containing a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein in expressible format and a nucleic acid encoding EPO in expressible format, wherein the cell further contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a sialyltransferase, e.g., an α-2,6-sialyltransferase or an α-2,3-sialyltransferase, under control of a heterologous promoter; b) culturing the cell in a serum-free culture medium and allowing expression of EPO in the cell; c) harvesting the expressed EPO from the cell and / or from the culture medium; and d) purifying and fractionating the EPO to obtain fractions that have an increased average sialic acid content of the N-linked glycans per EPO molecule, to obtain a composition comprising one or more isoforms of an EPO comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans comprise on average at least six sialic acids per EPO molecule and from zero to two Lewis x structures.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
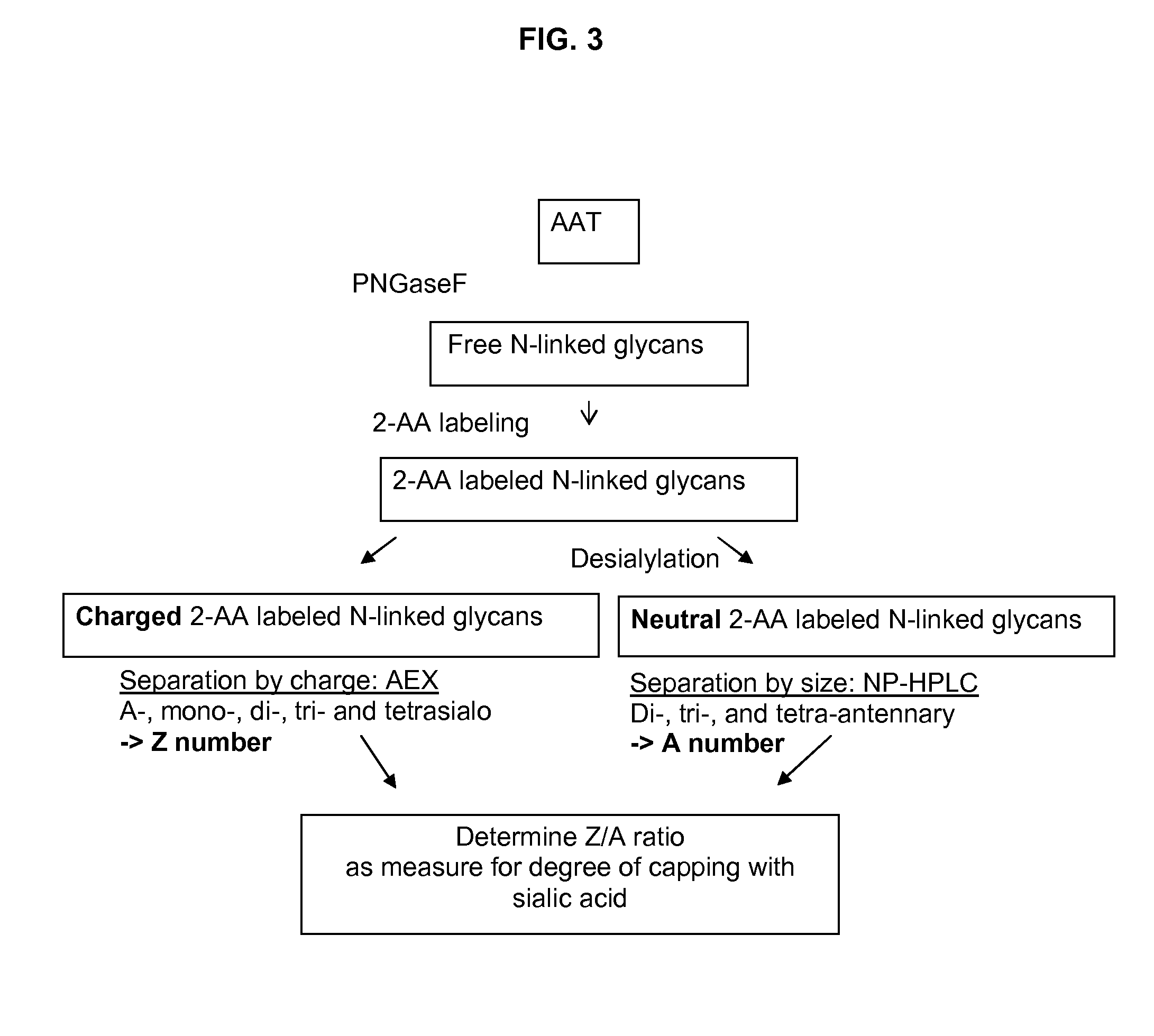
Recombinant human alpha1- antitrypsin
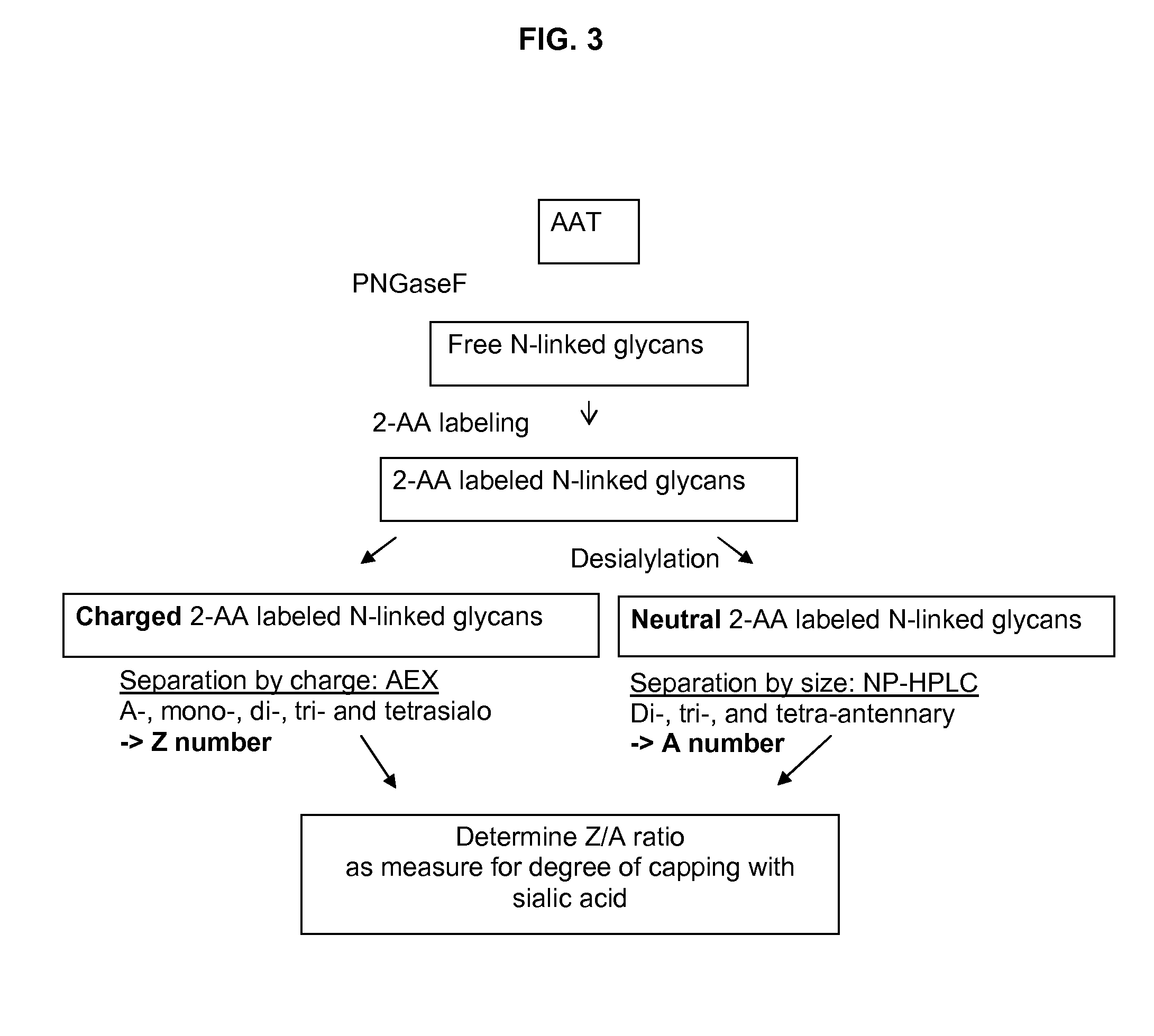
ActiveUS20120214747A1Suitable pharmacokinetic profileBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseNeutrophil granulocyte
The present invention relates recombinant human α1-antitrypsin (rhAAT) comprising N-linked glycans, wherein at least 10% of said N-linked glycans are tetra-antennary glycans; and the degree of capping with sialic acid on said N-linked glycans (Z / A) is at least 50%. The invention further relates to rhAAT for use as a medicament, in particular for use in the prevention and / or treatment of a disease associated with AAT deficiency, and / or a disease involving neutrophil-mediated tissue damage.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Methods To Obtain Recombinant Proteins With Increased Sialylation From Cells That Express Adenovirus E1a Protein, And Proteins Obtained Thereby
InactiveUS20070275439A1Reduce contentIncrease contentPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesHeterologousE1A Protein
The invention provides compositions comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto, characterized in that said glycans comprise LewisX structures and on average at least 6 sialic acid moieties per EPO molecule. The invention further provides methods for obtaining a composition comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (EPO) comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures, said method comprising: a) providing a eukaryotic cell containing a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein in expressible format and further containing a nucleic acid encoding an EPO in expressible format, wherein said cell further contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a sialyltransferase, preferably an alpha-2,6-sialyltransferase or an alpha-2,3-sialyltransferase, under control of a heterologous promoter; b) culturing said cell in a serum-free culture medium and allow expression of an EPO in said cell; c) harvesting the expressed EPO from said cell and / or from the culture medium; and d) purifying and fractionating the EPO to obtain fractions which have an increased average sialic acid content of the N-linked glycans per EPO molecule, to obtain a composition comprising one or more iso forms of an EPO comprising glycans linked thereto wherein said glycans comprise on average at least 6 sialic acids per EPO molecule and from 0 to 2 Lewis x structures.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Endo-N-Acetyl-Beta-D-Glucosaminidase Enzymes of Filamentous Fungi
InactiveUS20080220473A1Increased glycosylationImprove stabilityFungiSugar derivativesBiotechnologyTrichoderma reesei
The present invention discloses mannosyl-glycoprotein endo-beta-N-acetylglucosamidase (E.C.3.2.1.96, endo-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase acting on the di-N-acetylchitobiosyl part of N-linked glycans) from filamentous fungi such as Trichoderma reesei.
Owner:UNIV GENT
Glycan binding proteins as therapeutic targets for retinal disorders and treatment methods based thereon
ActiveUS20090060980A1Promote formationImprove integrityBiocideSenses disorderActive agentRetinal Disorder
Disclosed are novel methods of treatment for retinal diseases and conditions including age-related macular degeneration, genetic-based retinal degenerations and retinal detachment. A novel glycan binding protein thought to be a cell surface receptor has been discovered in the retina. The retinal glycan binding receptor is shown to play an important role in promoting assembly of outer segment (OS) membranes by the photoreceptor cells of the eye, a process that is essential for vision. Based on the finding that certain sugars can bind with very high affinity to the retinal glycan receptor and stimulate its function, the invention provides novel therapeutic agents for treatment of retinal diseases that are multivalent N-linked glycans. Preferred pharmaceutical compositions in accordance with the present invention comprise active agents having the general formula: (Gal-GlcNAc)n-Man3-GlcNAc2, where n is 1-4. Particularly preferred multivalent glycans are galactosylated, biantennary (NA2), and asialo, galactosylated, triantennary (NA3) oligosaccharides.
Owner:UNIV OF TENNESSEE RES FOUND
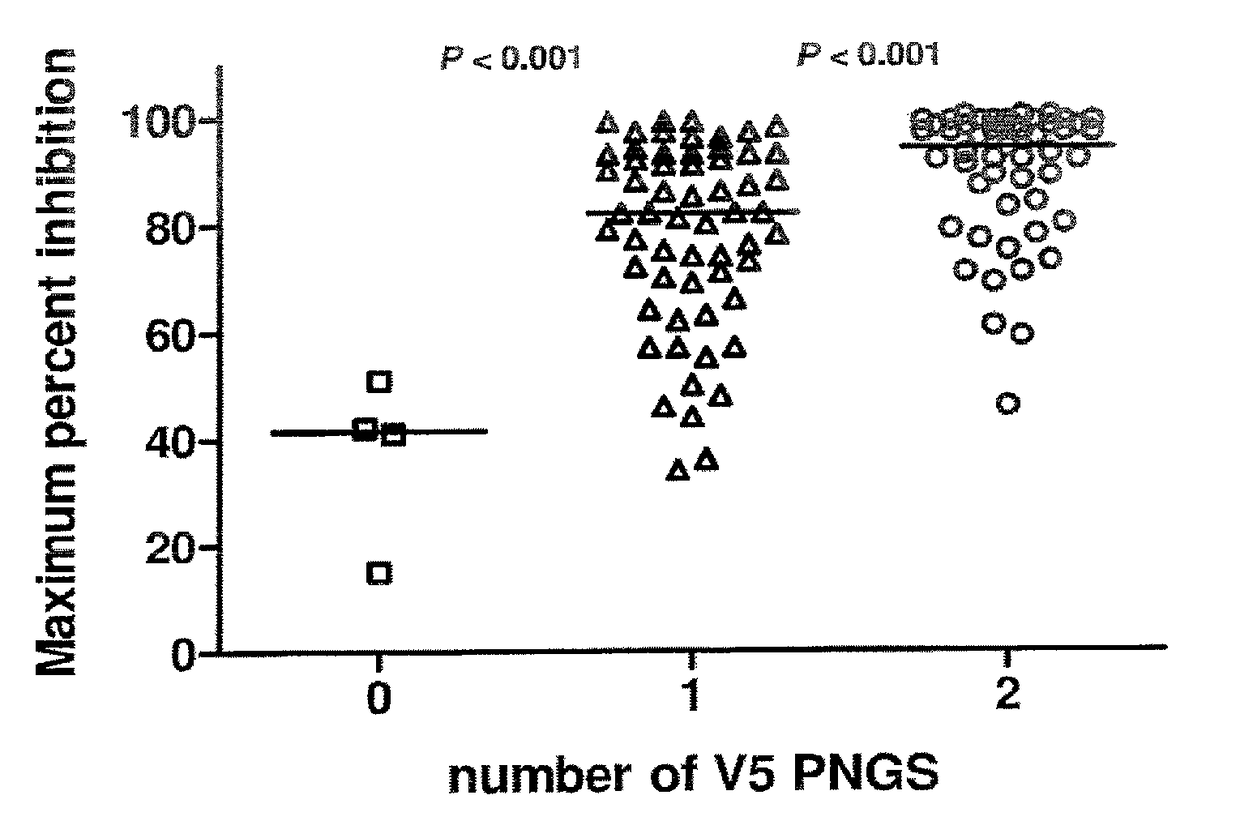
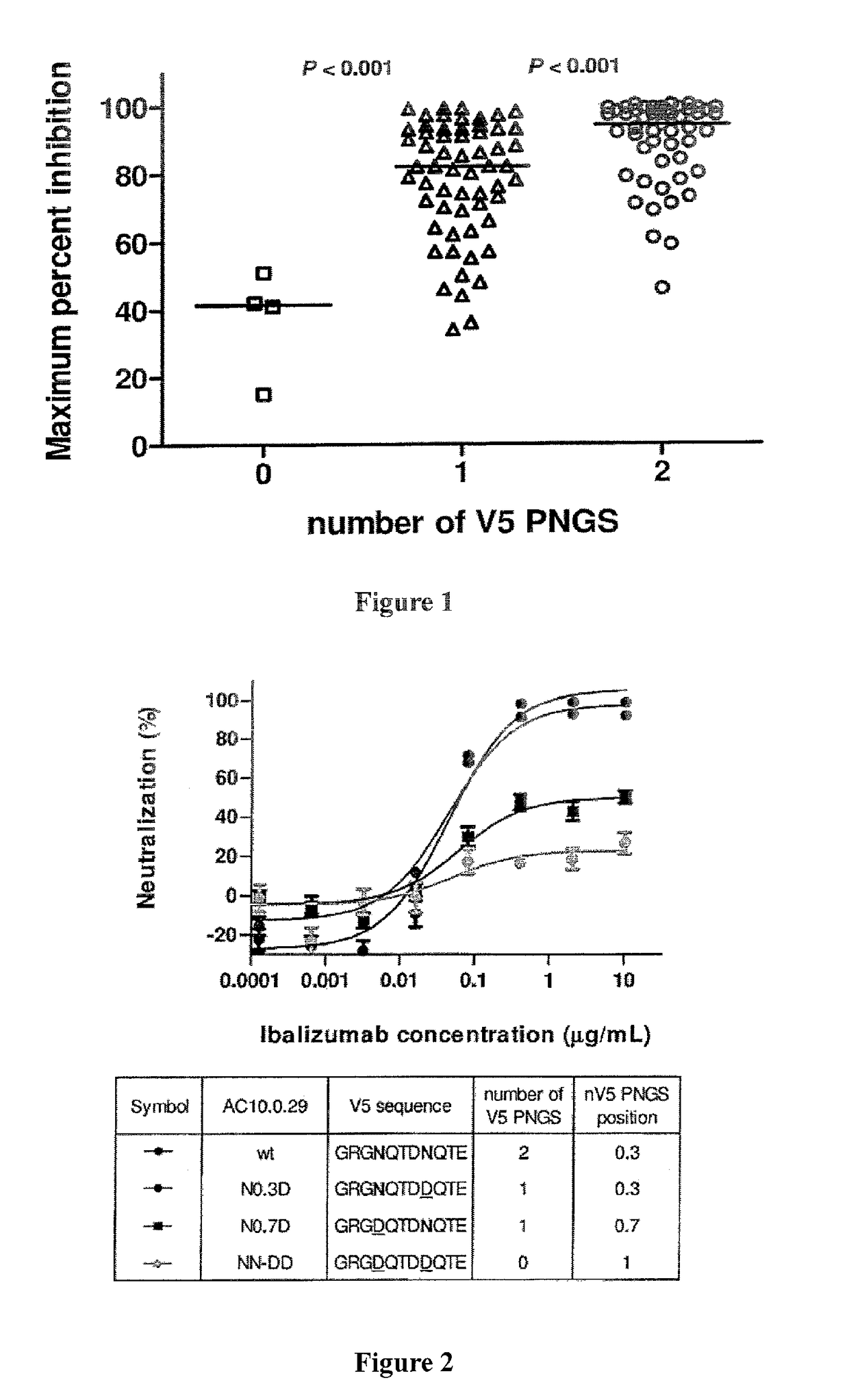
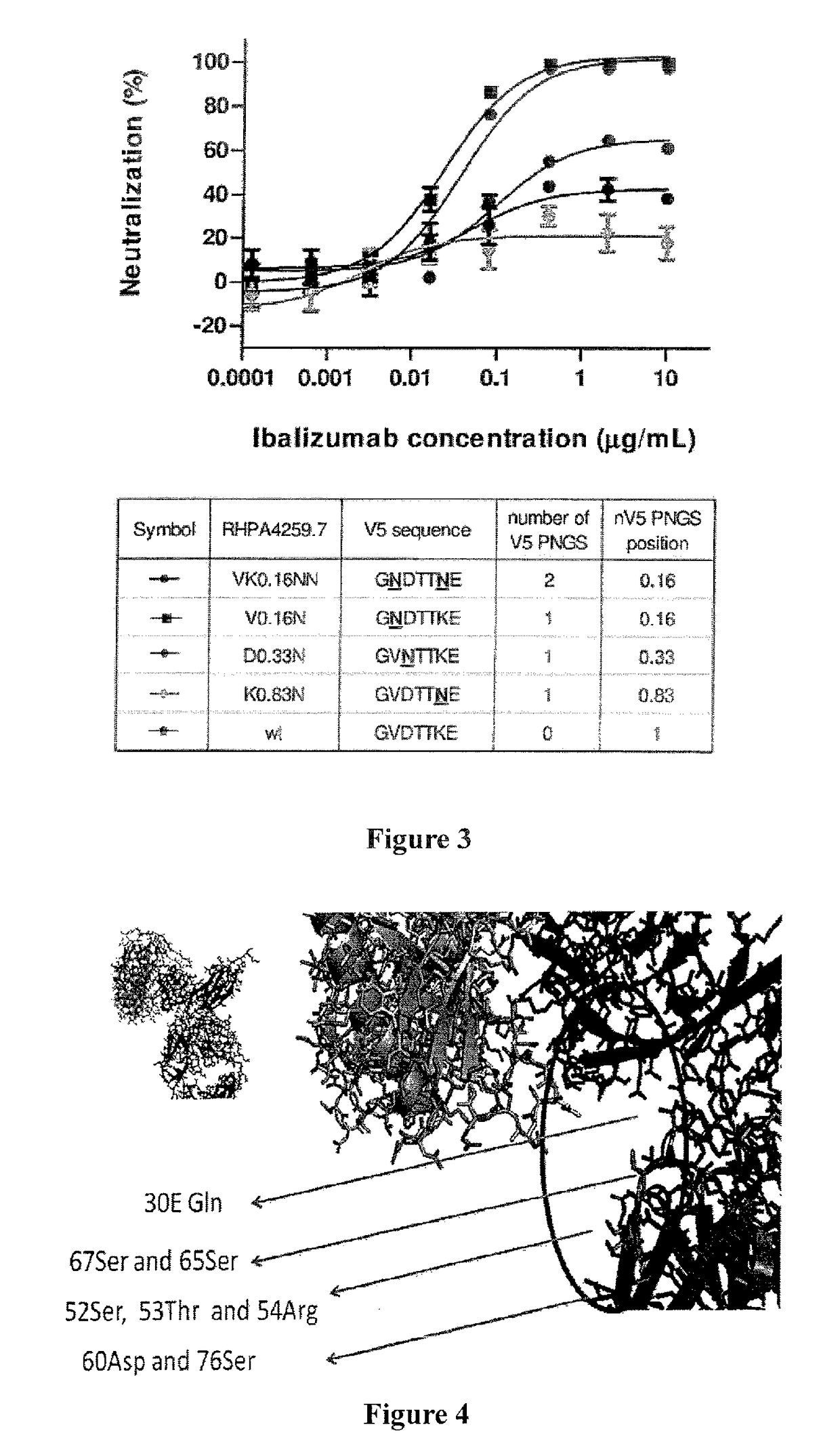
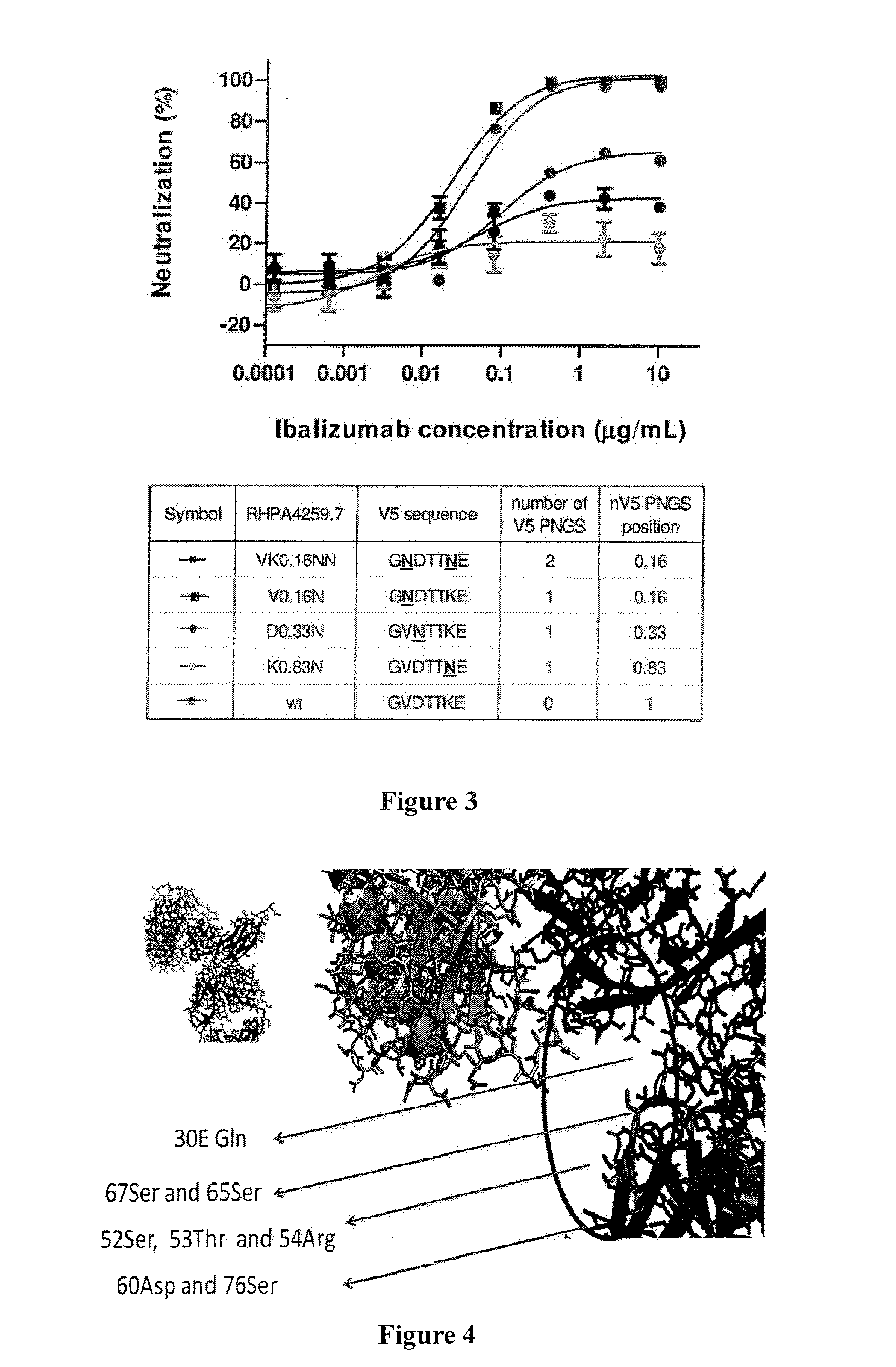
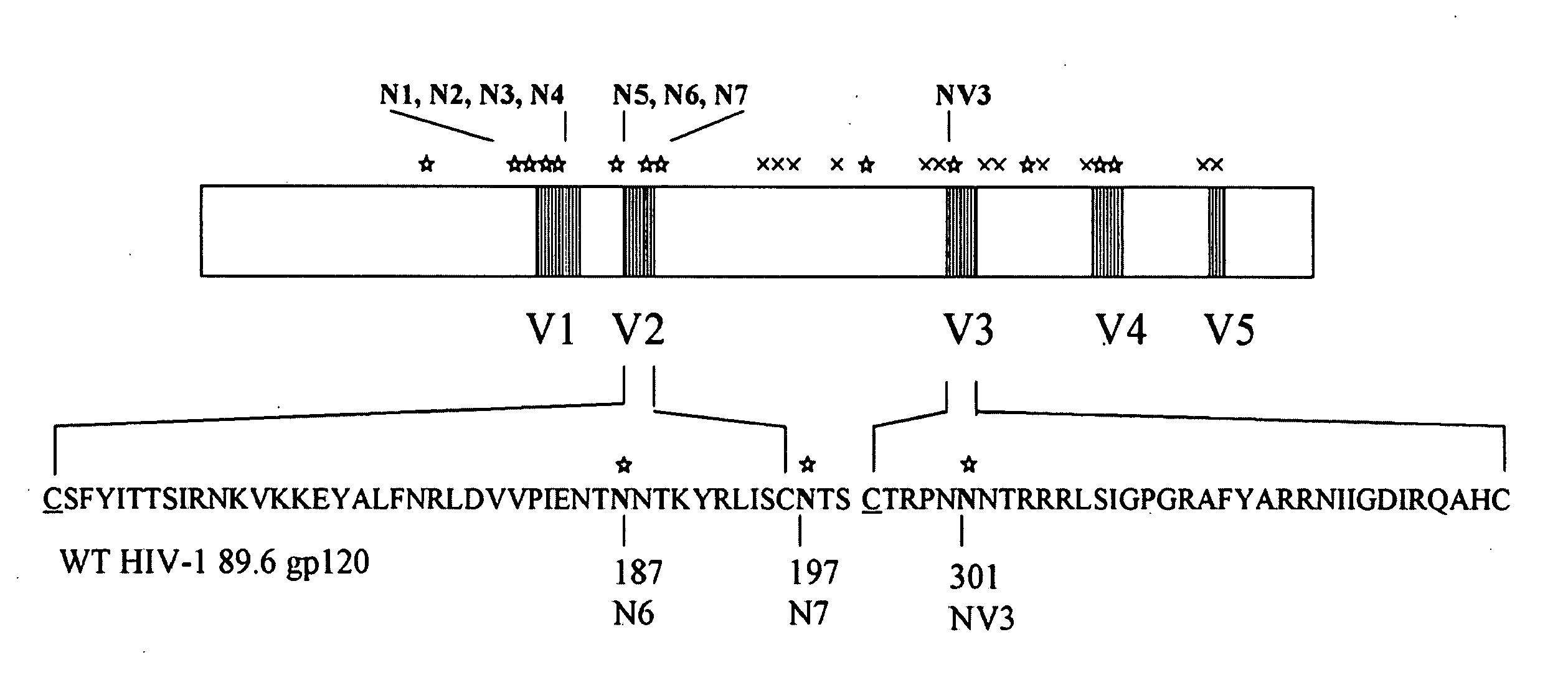
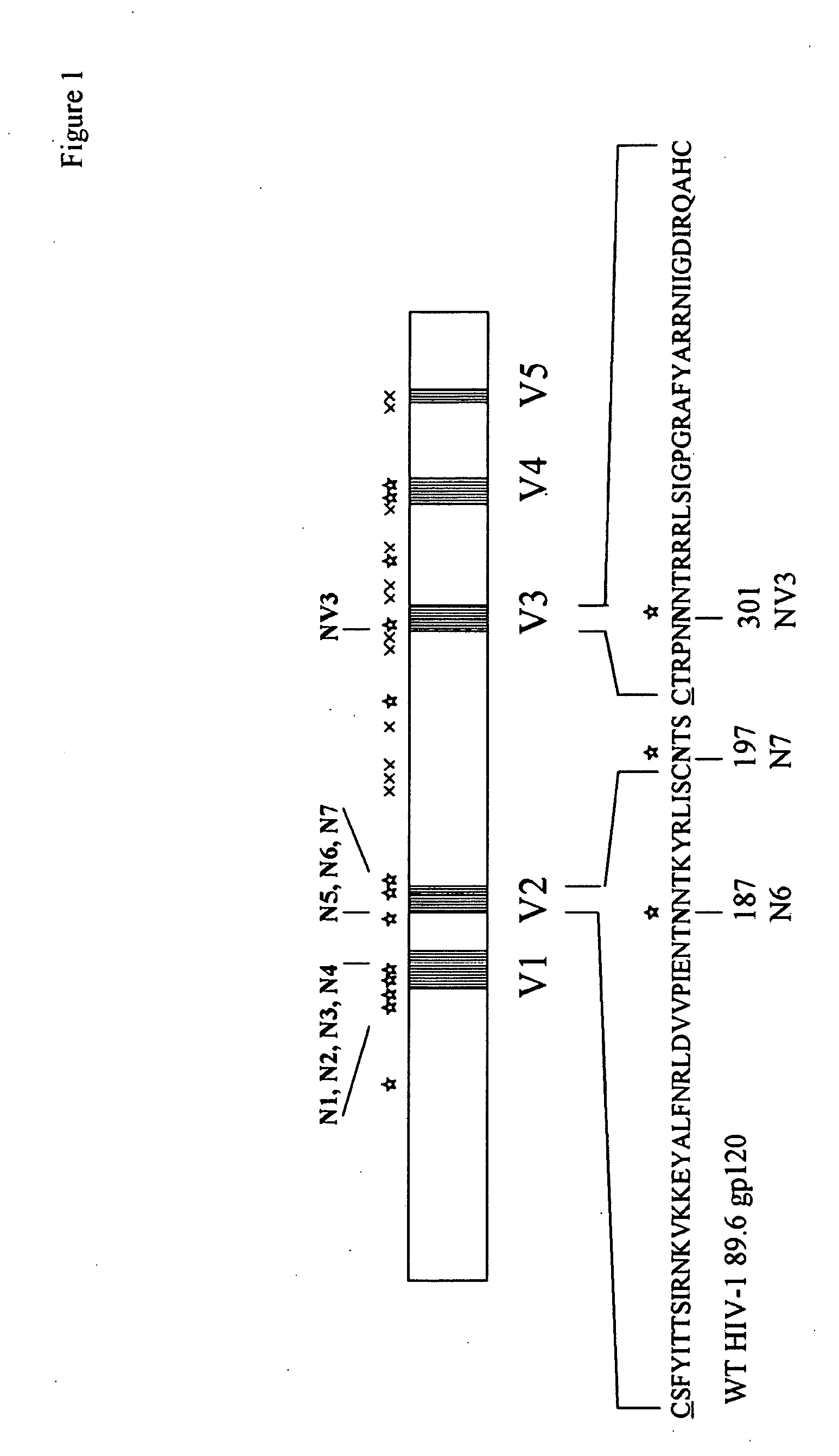
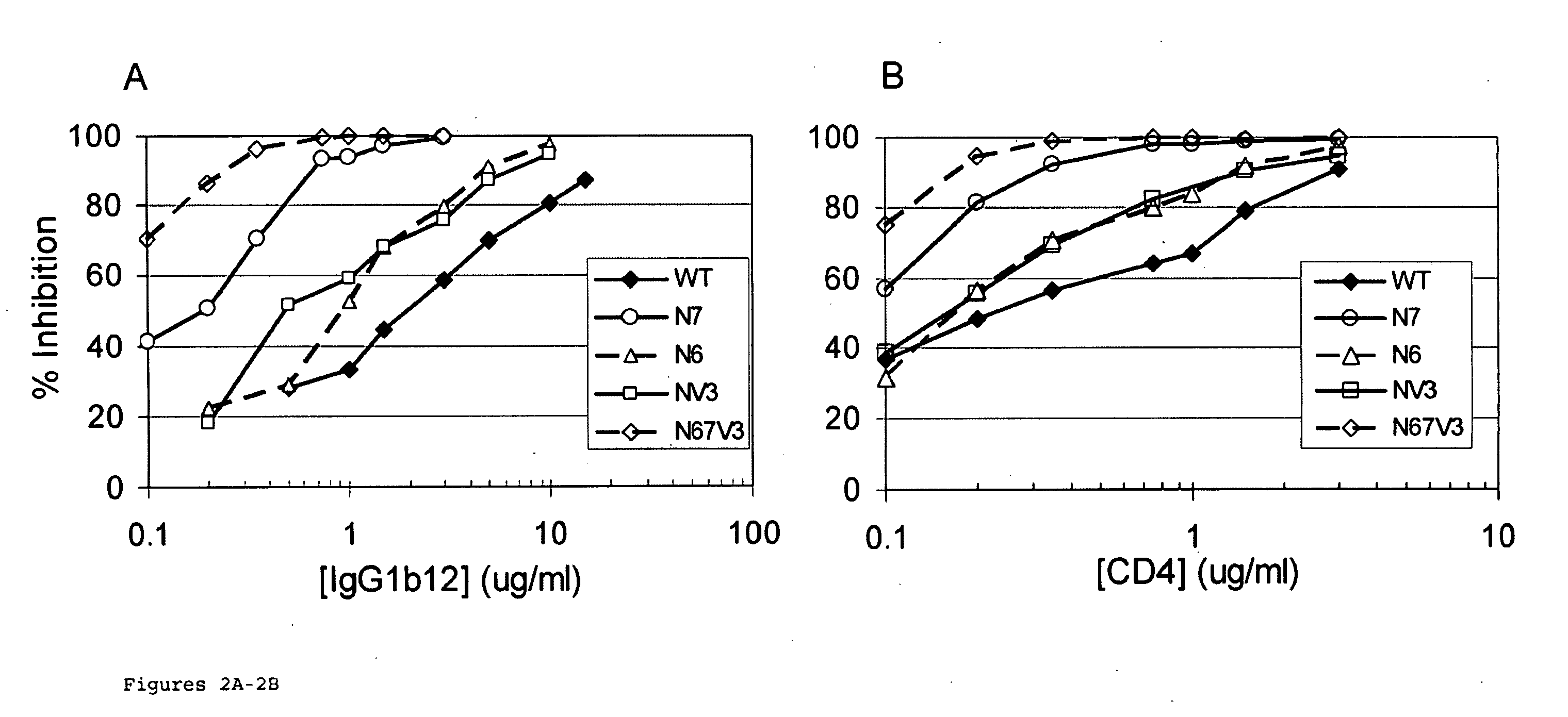
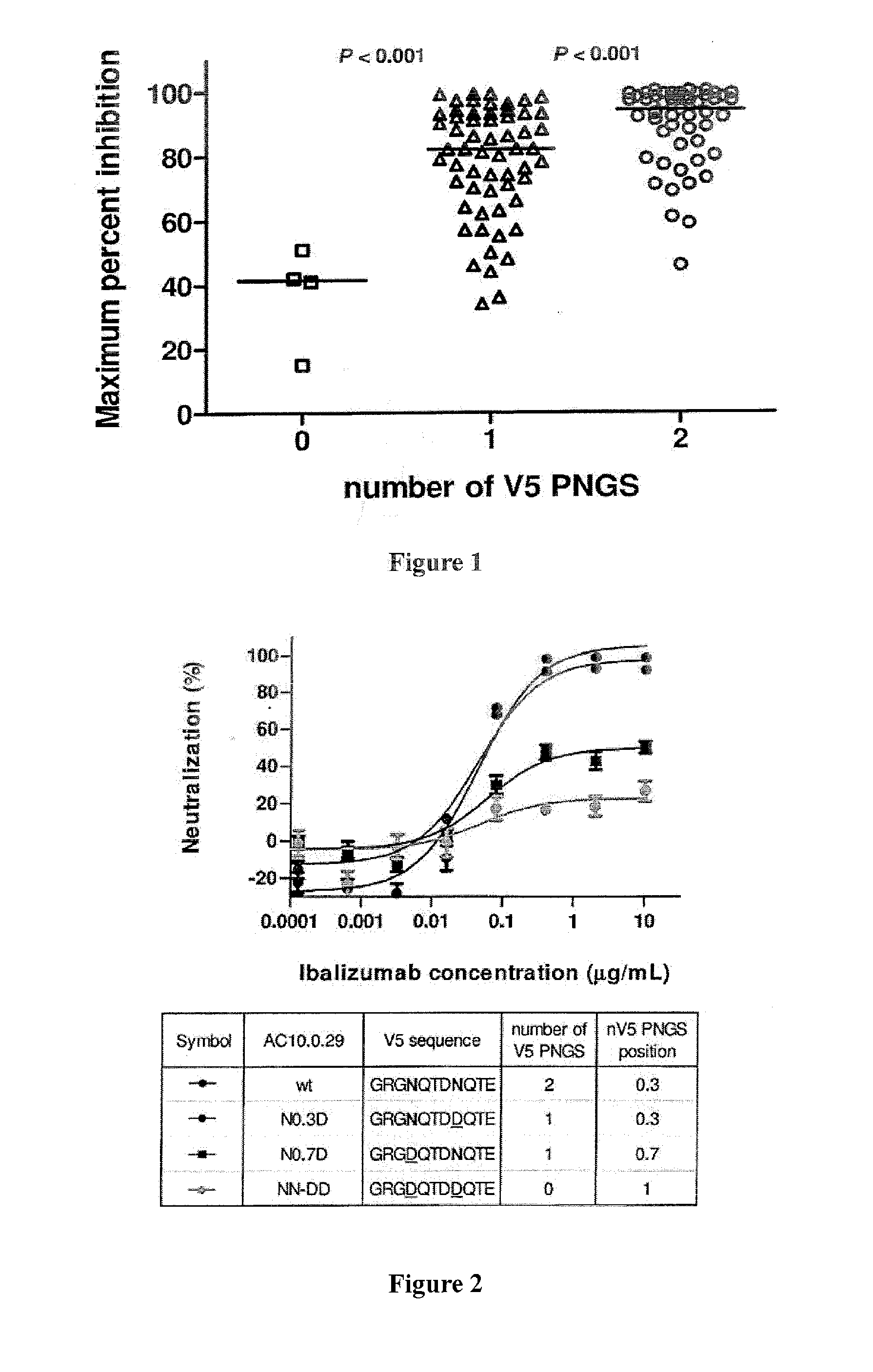
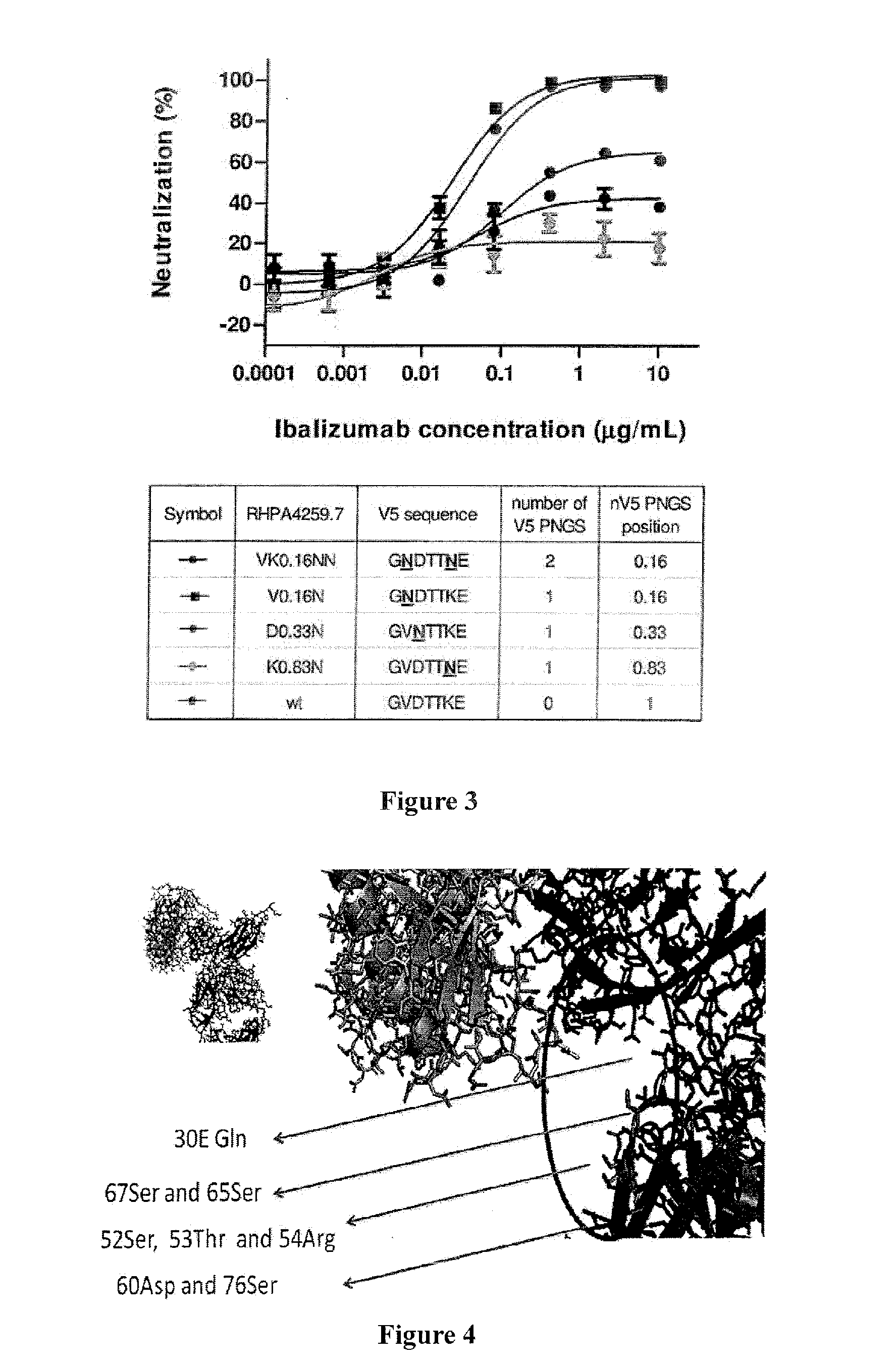
Glycan-modified anti-CD4 antibodies for HIV prevention and therapy
ActiveUS9790276B2High activityEasy to recycleImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiviralsAnti-CD4 Monoclonal AntibodyAnti cd4
Disclosed herein are glycan-modified anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies with N-linked glycans attached to the variable region. Expression vectors and cell lines useful for the production of such antibodies, and use of such antibodies for HIV prevention and therapy are also disclosed.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Expression of modified glycoproteins and glycopeptides
ActiveUS20180251569A1Improve scalabilitySimple structureImmunoglobulinsGlycosyltransferasesHigh mannoseMannosyltransferase
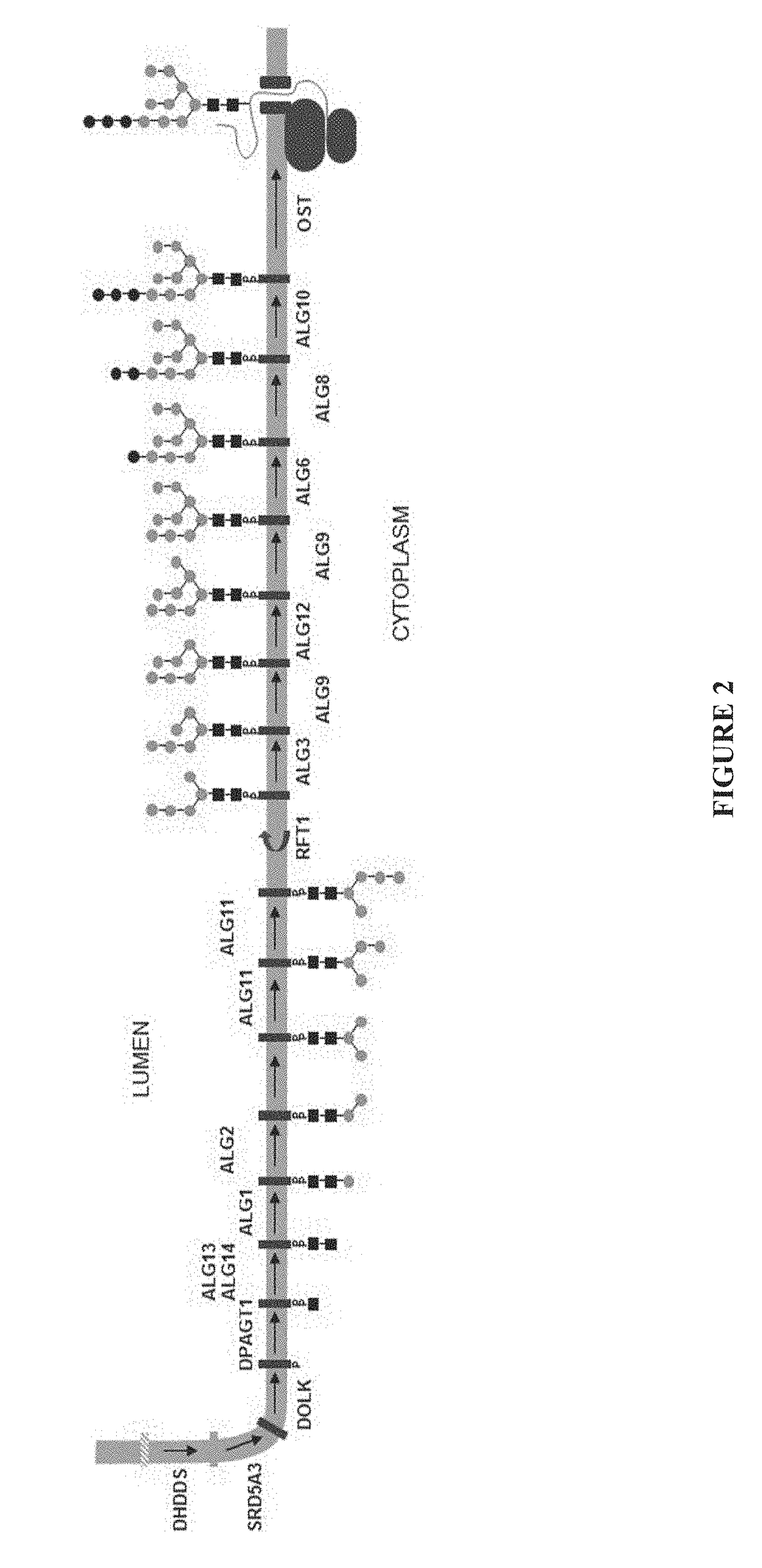
The present invention provides recombinant cells that contain a genetic modification to at least one mannosyl transferase gene. As a result of the modification the cells produce a glycoprotein or glycopeptide that has an N-linked glycan profile that is simplified or more easily humanized. The glycoprotein or glycopeptide can have at least 25% fewer high mannose structures on than the glycoprotein or glycopeptide produced by a reference cell. In some embodiments the modification is a deletion or disruption of a mannosyl transferase gene, which can be in an alg3 gene. Therefore, the proteins produced are more useful for the production of therapeutic glycoproteins than those produced by species having foreign or plant-like patterns of glycosylation. The invention also provides compositions of the glycoproteins or glycopeptides and methods of making them.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
Glycan-modified Anti-cd4 antibodies for HIV prevention and therapy
ActiveUS20150166662A1High activityInhibiting and treating or/and preventing infectionAnimal cellsMicroorganismsAnti-CD4 Monoclonal AntibodyAnti cd4
Disclosed herein are glycan-modified anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies with N-linked glycans attached to the variable region. Expression vectors and cell lines useful for the production of such antibodies, and use of such antibodies for HIV prevention and therapy are also disclosed.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
HIV vaccine
InactiveUS20090175889A1Well formedImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsInfected cellNucleotide
The invention provides a polynucleotide encoding an envelope protein comprising gp120 of human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1) having a mutation at amino acid residues 197-199 whereby a single N-linked glycan is removed. In a typical embodiment, the mutation replaces the asparagine (N) at residue 197 with another amino acid, such as glutamine (Q), creating an N197Q mutation. Because the N197 glycan is highly conserved among HIV-1 subtypes, this approach is applicable across HIV-1 isolates. The invention provides polypeptides, polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides, vectors, and recombinant viruses containing the polynucleotides, antigen-presenting cells (APCs) presenting the polypeptides, immune cells directed against HIV, and pharmaceutical compositions. The invention additionally provides methods, including methods for preventing and treating infection, for killing infected cells, for inhibiting viral replication, for enhancing secretion of antiviral and / or immunomodulatory lymphokines, and for enhancing production of neutralizing antibody.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON
Expression of modified glycoproteins and glycopeptides
ActiveUS10457970B2Avoid problemsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsHydrolasesHigh mannoseMannosyltransferase
The present invention provides recombinant cells that contain a modification causing altered expression or function of at least one mannosyl transferase enzyme. As a result of the modification the cells produce a glycoprotein or glycopeptide that has an N-linked glycan profile that is simplified or humanized. The glycoprotein or glycopeptide can have at least 25% fewer high mannose structures on than the glycoprotein or glycopeptide produced by a cell that does not have the modification. In some embodiments the modification is a deletion, knock out, or disruption of a gene encoding a mannosyl transferase, which can be in an Alg3 gene. Therefore, the proteins produced avoid many of the problems associated with the therapeutic use of glycoproteins from species having foreign or plant-like patterns of glycosylation. The invention also provides compositions of the glycoproteins or glycopeptides and methods of making them.
Owner:CONAGEN INC
Methods to obtain recombinant proteins with increased sialylation from cells that express adenovirus E1A protein, and proteins obtained thereby
InactiveUS20100221774A1Reduce contentIncrease in sialic acid contentOxidoreductasesErythropoietinHeterologousE1A Protein
Provided are compositions comprising one or more isoforms of an erythropoietin (“EPO”) comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans have Lewis x structures and on average at least six sialic acid moieties per EPO molecule. Further provided are methods for obtaining a composition comprising one or more isoforms of EPO comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans comprise on average at least six sialic acids per EPO molecule and from zero to two Lewis x structures, the method comprising: a) providing a eukaryotic cell containing a nucleic acid sequence encoding an adenoviral E1A protein in expressible format and a nucleic acid encoding EPO in expressible format, wherein the cell further contains a nucleic acid sequence encoding a sialyltransferase, e.g., an α-2,6-sialyltransferase or an α-2,3-sialyltransferase, under control of a heterologous promoter; b) culturing the cell in a serum-free culture medium and allowing expression of EPO in the cell; c) harvesting the expressed EPO from the cell and / or from the culture medium; and d) purifying and fractionating the EPO to obtain fractions that have an increased average sialic acid content of the N-linked glycans per EPO molecule, to obtain a composition comprising one or more isoforms of an EPO comprising glycans linked thereto, wherein the glycans comprise on average at least six sialic acids per EPO molecule and from zero to two Lewis x structures.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
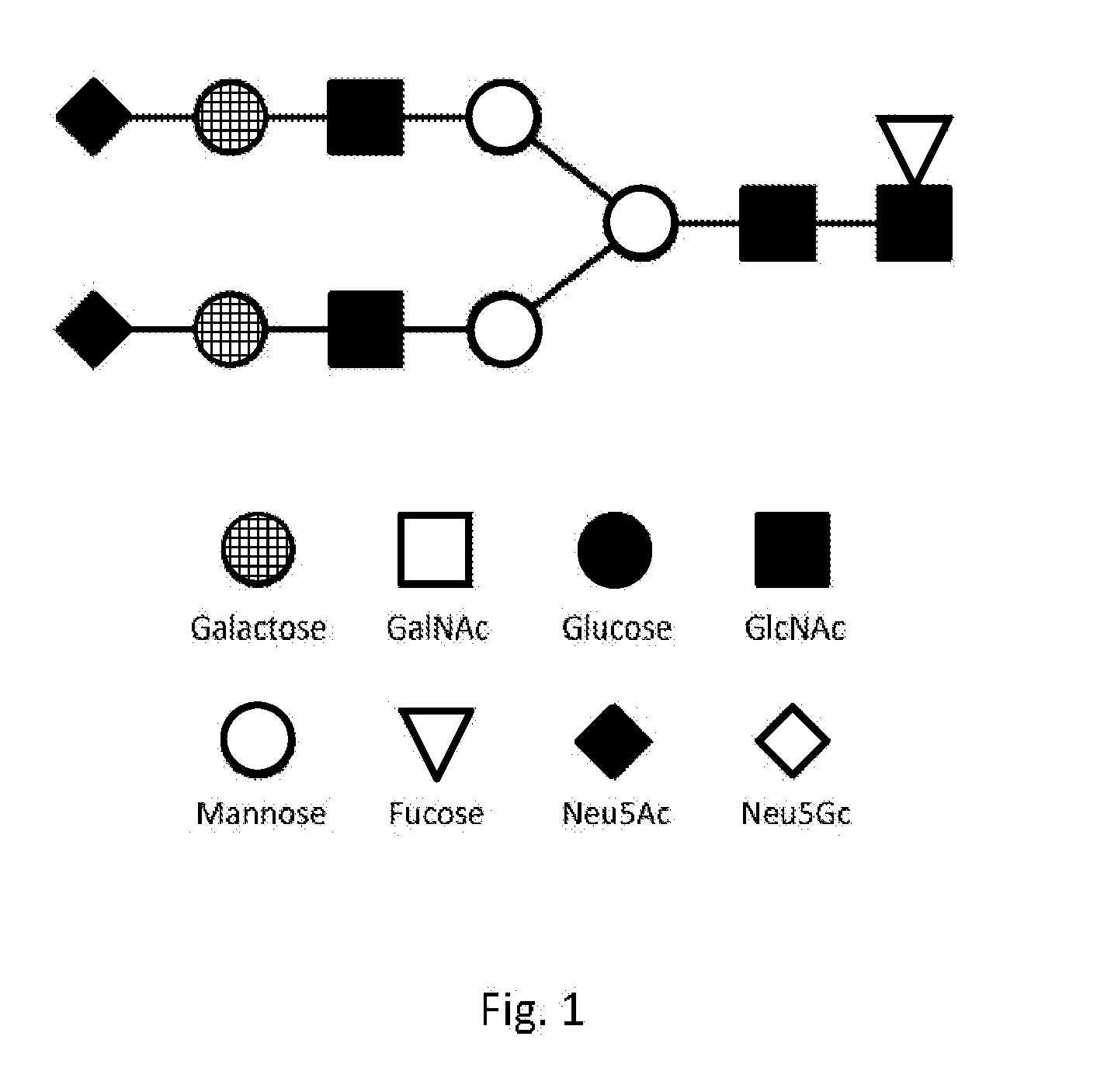
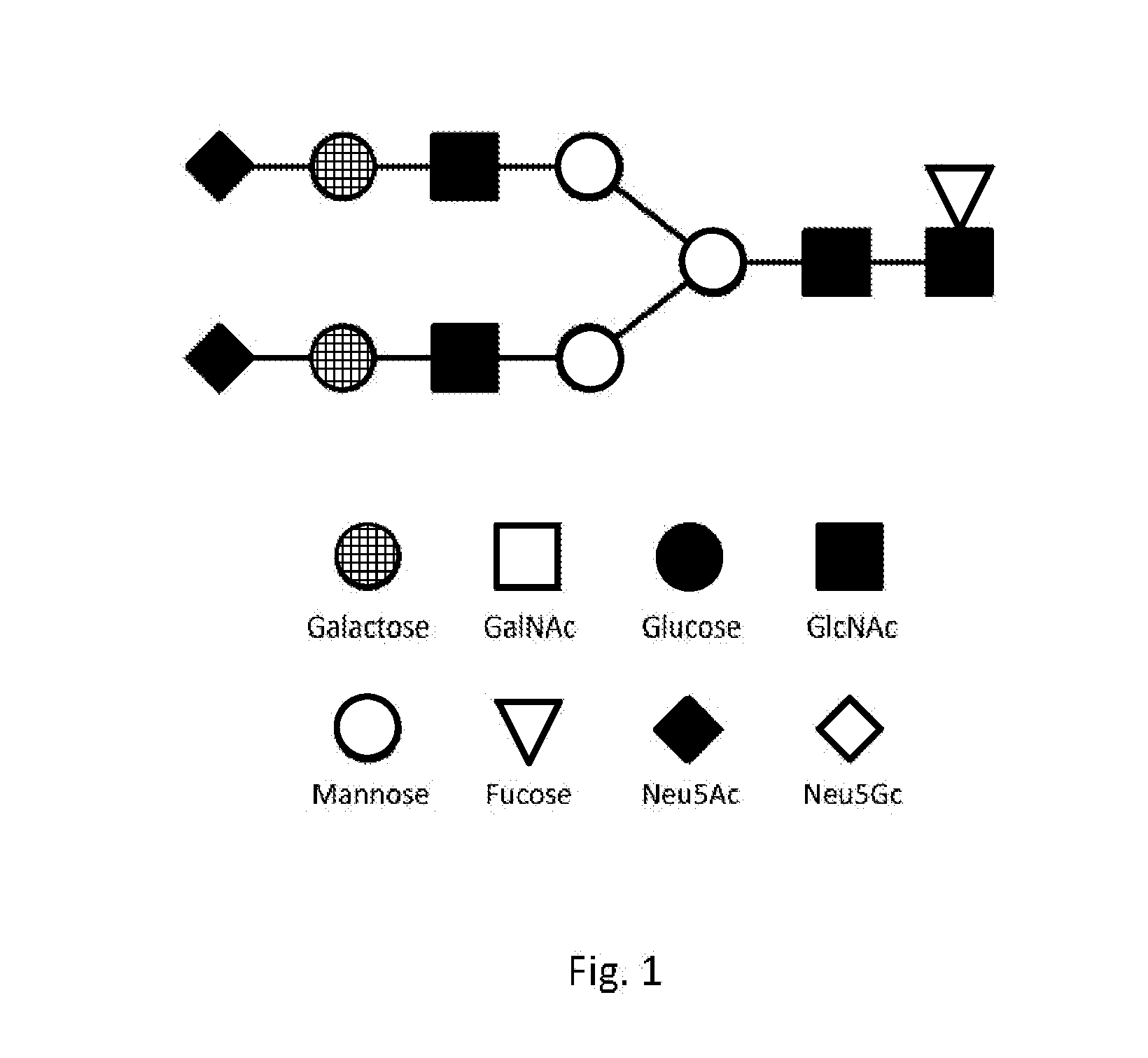
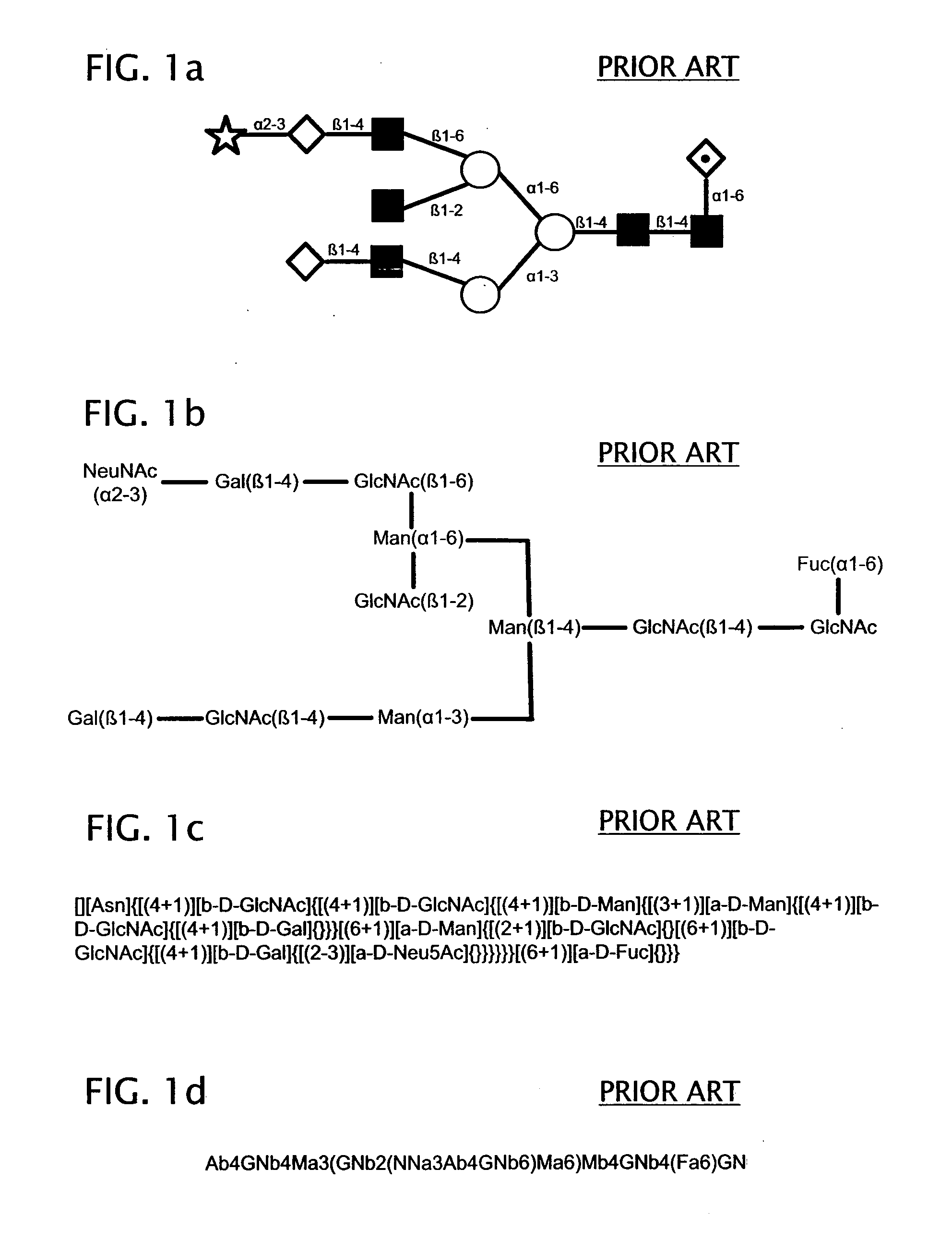
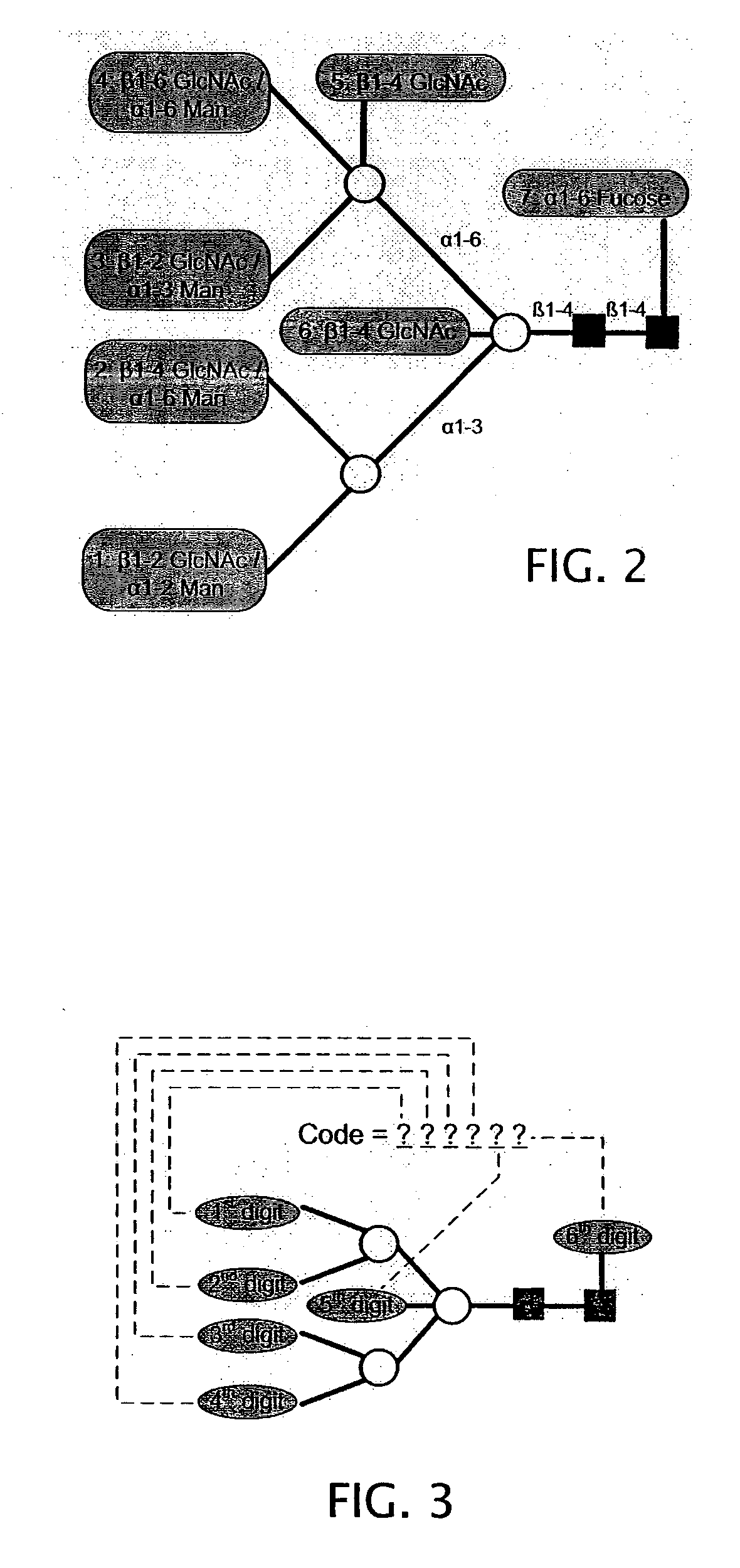
System and method for representing n-linked glycan structures
InactiveCN101785003AData visualisationSpecial data processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceOligosaccharide
A fixed-length alpha-numeric code for representing N-linked glycan structures commonly found in secreted glycoproteins from mammalian cell cultures. The code employs a pre-assigned alpha-numeric index to represent the monosaccharides attached in different branches to the core glycan structure. The present branch-centric representation allows visualization of the structure while the numerical nature of the code makes it machine readable. A difference operator can be defined to quantitatively differentiate between glycan structures for further analysis. The code can be incorporated in a retrievable format into an information management system. A method is also provided for representing the structure of at least a portion of an oligosaccharide, using the fixed-length alpha-numeric code.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Biomarkers For Diagnosis Of Diabetes And Monitoring Of Anti-Diabetic Therapy
InactiveUS20150204881A1Electrolysis componentsVolume/mass flow measurementDiabetes mellitusBlood component
The present invention relates to the use of N-linked glycan profiles of blood or blood component proteins as biomarkers for diagnosing diabetes mellitus and for monitoring the efficacy of anti-diabetic therapy. Specifically, the present invention relates to detecting changes in the amounts of N-linked glycans as diagnostic biomarkers for diabetes mellitus and as indicators of the efficacy of anti-diabetic therapy over time.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Biomarkers For Diagnosis Of Diabetes And Monitoring Of Anti-Diabetic Therapy
InactiveUS20150072888A1Easy to separateImprove statistical significanceAnalysis using chemical indicatorsSugar derivativesDiabetes mellitusBlood component
The present invention relates to the use of N-linked glycan profiles of blood or blood component proteins as biomarkers for diagnosing diabetes mellitus and for monitoring the efficacy of anti-diabetic therapy. Specifically, the present invention relates to detecting changes in the amounts of N-linked glycans as diagnostic biomarkers for diabetes mellitus and as indicators of the efficacy of anti-diabetic therapy over time.
Owner:SUMITOMO BAKELITE CO LTD
Imino sugar derivatives demonstrate potent antiviral activity and reduced toxicity
InactiveUS9040488B2Good effectImprove performanceBiocideOrganic chemistryBovine Viral Diarrhea VirusesSide chain
Imino sugars, such as deoxynojirimycin (DNJ), are glucose analogues that selectively inhibit cellular α-glucosidase I and II (enzymes that process N-linked glycans in glycoprotein) and exhibit broad spectrum antiviral activities against many enveloped viruses. Previously we have reported a novel DNJ derivative, OSL-95II, with antiviral activity and reduced cytotoxicity. In order to develop imino sugars with more potent antiviral activity as well as improved toxicity profile, OSL-95II was modified by diversifying the nitrogen linked alkylated side chain. The antiviral activities were initially tested in bovine viral diarrhea virus (BVDV) infected MDBK cells, yielding several imino sugar derivatives with novel structure and superior antiviral activity and toxicity profile. Furthermore, these new compounds were shown to be active against Dengue virus (DV) and West Nile virus (WNV) infection in BHK cells where potent anti-DV activity having submicromolar EC50 values and SI of greater than 900. These compounds represent a new generation of iminio sugars and their analogues, having application in the clinical treatment of infection of DV and other members of flaviviridae.
Owner:INST FOR HEPATITS & VIRUS RES +1
Glycan-modified Anti-cd4 antibodies for HIV prevention and therapy
ActiveUS20160362493A9High activityEasy to recycleImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntiviralsAnti-CD4 Monoclonal AntibodyAnti cd4
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Mass spectrometry imaging of glycans from tissue sections and improved analyte detection methods
ActiveUS20180196060A1Improve detection limitOmicsBiological testingMass spectrometry imagingMaldi ms
The presently disclosed subject matter provides methods using mass spectrometry for direct profiling of N-linked glycans from a biological sample. In addition, the embodiments of the present invention also disclose novel methods, known as targeted analyte detection (TAD), for improving the detection limit of MALDI-MS. These methods take advantage of the carrier effect of the added standard analytes, which occurs due to the generic sigmoidal shape of the calibration curve. The functionality of TAD depends on the relative enhancement of sensitivity over the increase of the standard deviation at the analysis of target analytes with spiking in exogenous concentration. At certain ranges of exogenous concentration, the increment in the sensitivity overcomes the standard deviation, resulting in an improved LOD. Theoretically, exogenous concentrations approximately at 1 LODorig would generate the optimum LOD improvement. TAD is a cost-effective LOD improvement method, which is not limited to a certain group of analytes, or detection methods or instruments. It can be applied to enhance the detection of any analyte with different detection methods, provided that the analyte of interest can be extracted or is available in synthetic form.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
System and method for representing n-linked glycan structures
InactiveUS20100185699A1Easy to interpretEasy to storeSugar derivativesDigital data processing detailsTheoretical computer scienceOligosaccharide
A fixed-length alpha-numeric code for representing N-linked glycan structures commonly found in secreted glycoproteins from mammalian cell cultures. The code employs a pre-assigned alpha-numeric index to represent the monosaccharides attached in different branches to the core glycan structure. The present branch-centric representation allows visualization of the structure while the numerical nature of the code makes it machine readable. A difference operator can be defined to quantitatively differentiate between glycan structures for further analysis. The code can be incorporated in a retrievable format into an information management system. A method is also provided for representing the structure of at least a portion of an oligosaccharide, using the fixed-length alpha-numeric code.
Owner:AGENCY FOR SCI TECH & RES
Recombinant human Alpha1-antitrypsin
The present invention relates recombinant human α1-antitrypsin (rhAAT) comprising N-linked glycans, wherein at least 10% of said N-linked glycans are tetra-antennary glycans; and the degree of capping with sialic acid on said N-linked glycans (Z / A) is at least 50%. The invention further relates to rhAAT for use as a medicament, in particular for use in the prevention and / or treatment of a disease associated with AAT deficiency, and / or a disease involving neutrophil-mediated tissue damage.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
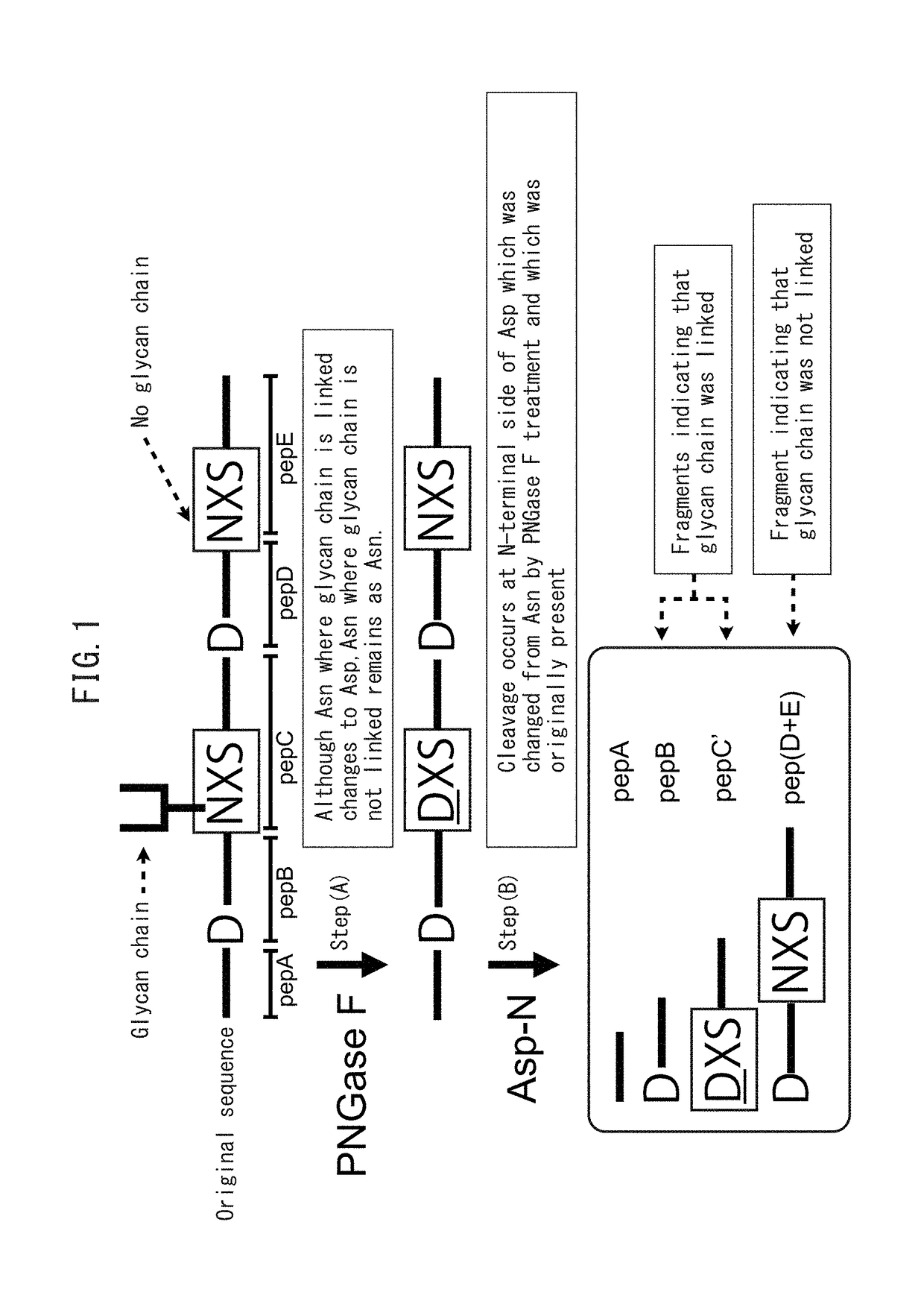
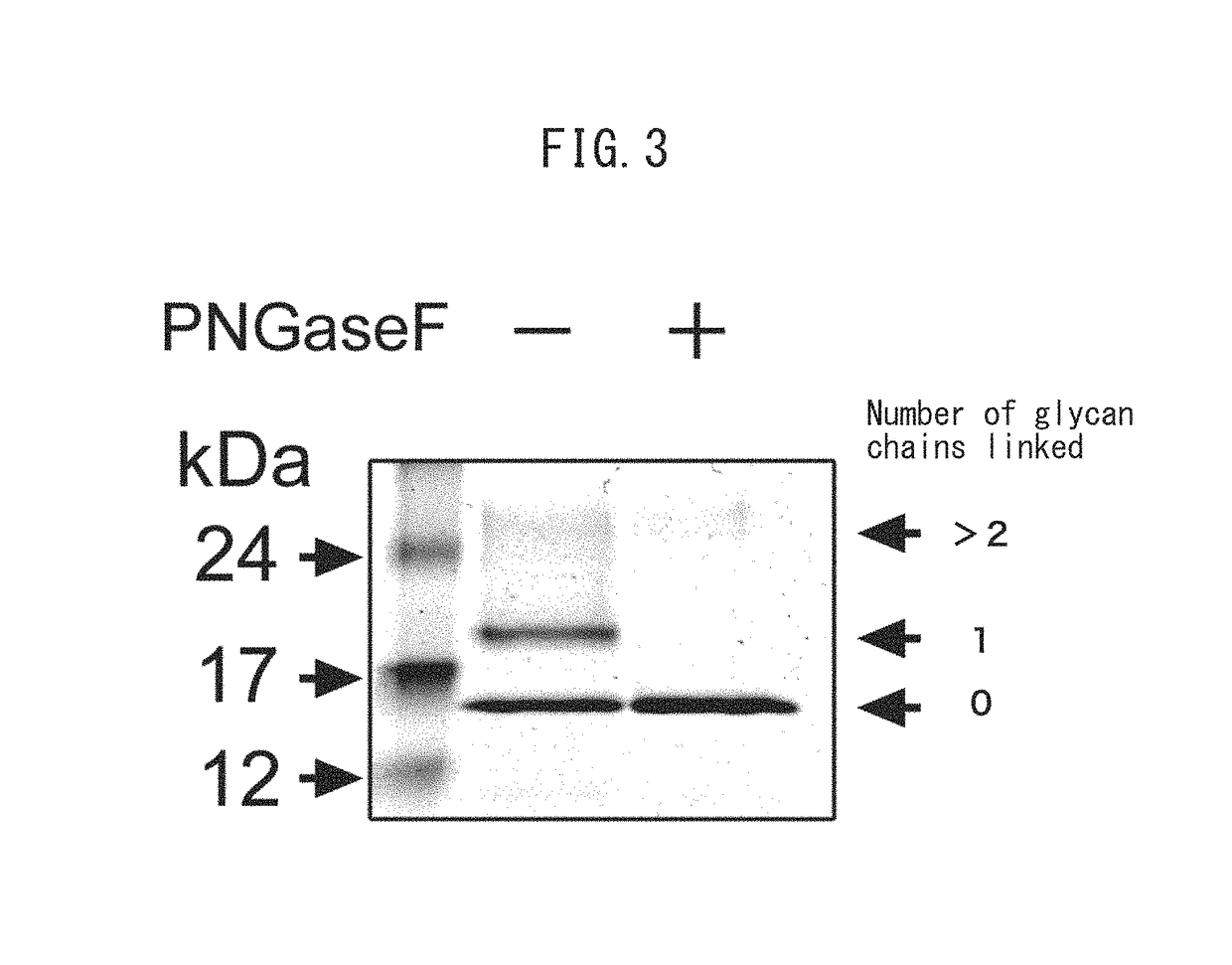
Method for determining site having N-linked sugar chain added thereto or proportion of said addition
ActiveUS9896713B2Easy to analyzeEasy to detectHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementSugarPeptide-N-Glycanase
A method for detecting a site which can be modified with an N-linked glycan chain and to which an N-linked glycan chain is actually linked in a glycoprotein; and a method for determining the state of an N-linked glycan chain addition at the site are provided. A glycoprotein having an N-linked glycan chain linked thereto is subjected to an N-linked glycan chain removal treatment with a peptide N-glycanase, subsequently a site capable of being modified with an N-linked glycan chain, in which an Asn residue has been changed to an Asp residue by the action of the peptide N-glycanase, is treated with an endo-type peptidase capable of recognizing an Asp residue to thereby produce peptide fragments, and subsequently the mass of the fragments is detected. In this manner, a site which can be modified with an N-linked glycan chain and to which an N-linked glycan chain is actually linked can be detected. Furthermore, the proportion or state of of the N-linked glycan chain addition at the site can be determined from the intensity of a signal generated upon the detection.
Owner:TOSOH CORP
A characteristic n-linked sugar chain of subcellular structure and its application
ActiveCN105651853BImplement indirect detectionEasy to detectMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDetection of post translational modificationsSubcellular structureProteome
The invention discloses a characteristic N-linked sugar chain of a subcellular structure and an application thereof, belonging to the technical field of glycobiology. In the present invention, the bladder YTS1 cells are used as experimental materials, and the protein components of four subcellular structures (microsomes, mitochondria, nuclei and cytoplasm) are obtained by using differential centrifugation, and the method of combining lectin chip and mass spectrometry (MS) The glycosylation modification types and structural changes of identified subcellular structural proteins showed the distribution of sugar chains in subcellular structural differences. The present invention obtains the characteristic N-linked glycans of the subcellular structure of 10 kinds of human bladder YTS1 cells; using the characteristic N-linked glycans, the indirect detection, qualitative or quantitative of other target substances in the corresponding subcellular structure can be realized detection.
Owner:上海微江生物技术有限公司
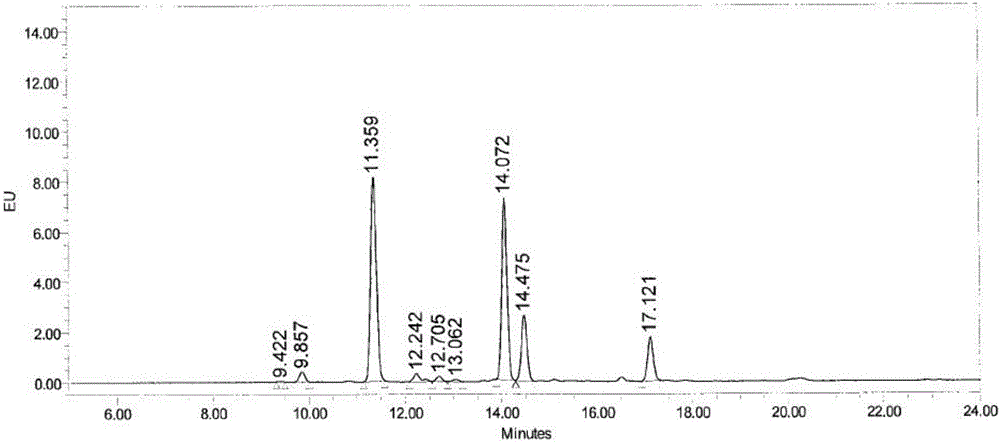
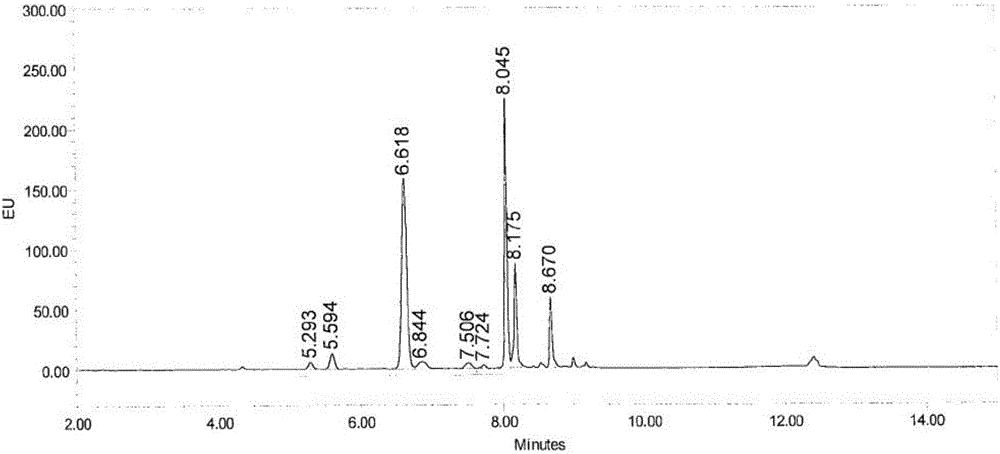
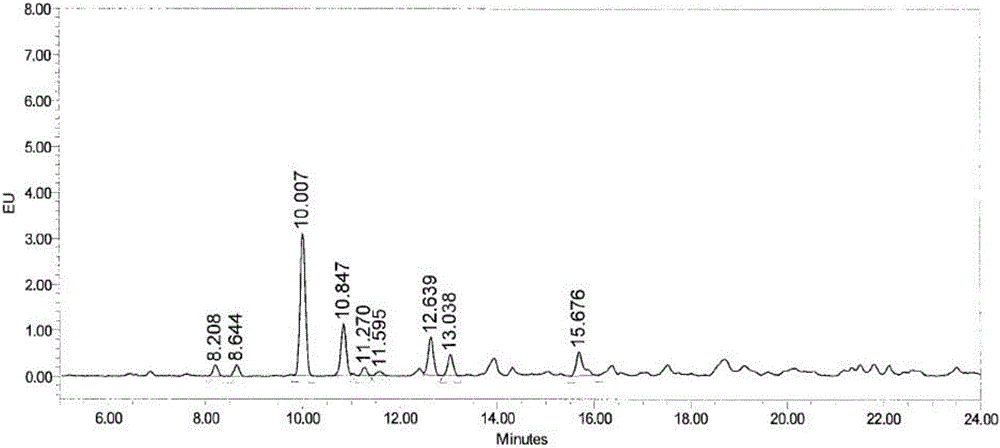
Efficient Separation and Preparation of N-Linked Glycans from Ovalbumin and Glycans
The invention provides a high-efficiency separation preparation method for preparing an N-linked polysaccharide from ovalbumin. The main component of the N-linked polysaccharide is an N-linked polysaccharide component linked with only one amino acid asparagine (Asn). The method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis on the ovalbumin by using a non-specific protease, centrifuging the obtained enzymatic hydrolysis solution, concentrating the centrifuged solution, removing polypeptides and residual proteins obtained after the ovalbumin enzymatic hydrolysis on the concentrated solution through using a one-dimensional chromatographic column, and collecting the target fraction; and centrifuging the collected fraction, concentrating the centrifuged fraction, and allowing the concentrated fraction to go through a two-dimensional chromatographic column to remove salt, 2-4 amino acids-linked N-connected polysaccharide components and micro-molecular amino acids in the fraction in order to obtain the N-linked polysaccharide component only linked with asparagines. A result of high resolution mass spectrum identification of the Asn linked N-linked polysaccharide component prepared in the invention shows that the N-linked polysaccharide component has clear composition, and the extraction and separation method has the advantages of high repeatability and good maneuverability, and is suitable for large-scale separation and preparation of the N-linked polysaccharide component from the ovalbumin.
Owner:TAIZHOU GUOKEHUAWU BIOMEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com