A characteristic n-linked sugar chain of subcellular structure and its application
A subcellular and sugar-linked technology, applied in the field of glycobiology, can solve the problems of lack of organelle sugar chain structure data and the inability to reveal the overall glycome characteristics of subcellular structure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Extraction of Cell Broken Total Protein
[0045] Place 15mL centrifuge tubes, pipettes and other test materials in a biological safety cabinet for ultraviolet sterilization for 15 minutes; take the cell culture bottle and pour out the old medium, add 1.5mL trypsin to quickly clean the bottom of the bottle, and then add 1.5mL trypsin after suction , placed in a 37°C cell incubator to react for 3 minutes, after the reaction was completed, microscopic examination ensured that the cells were fully digested and released from the wall; adding 1.5mL of cell culture medium to remove the enzyme effect, fully blowing and aspirating the bottom of the culture bottle, after mixing, aspirate and move to a 15mL centrifuge Centrifuge the tube at 1000r / min for 5min; remove the supernatant after centrifugation, add 5mL 1×PBS, carefully blow and aspirate to resuspend the cells for washing, then centrifuge at 1000r / min for 5min, repeat 3 times; add 1mL T-PER to the obtained cell ...
Embodiment 2
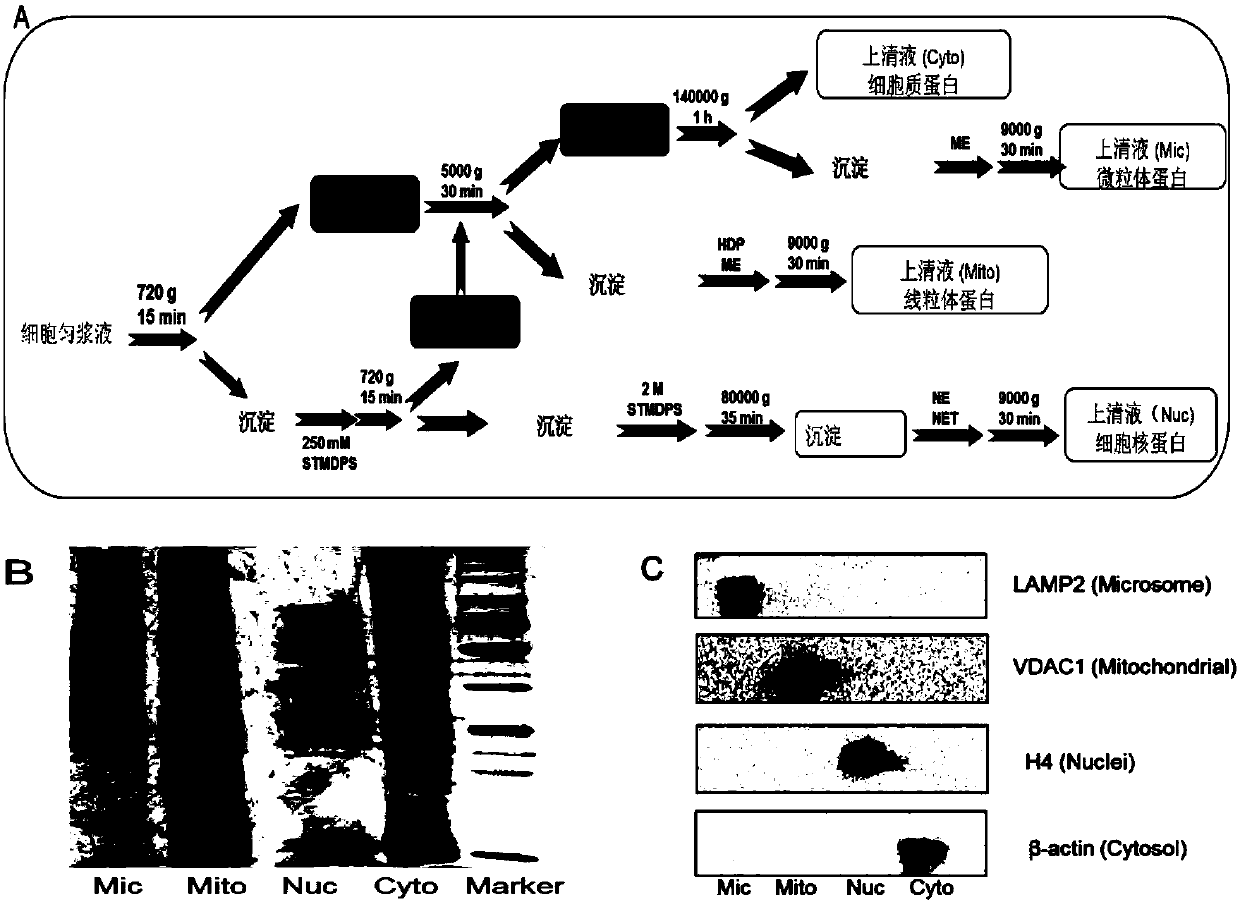
[0046] Example 2: Extraction of subcellular structural proteins
[0047] The separation method of the subcellular structure adopted in the present invention is an experimental scheme established after modification on the basis of the previous separation method. cells (~1×10 7 ) was digested with trypsin, and washed twice with pre-cooled PBS (0.01M phosphate buffer saline, 0.15M NaCl, pH 7.4). Add 500ul homogenate (50mM HEPES pH 7.4, 3mM MgCl 2 , 1mM EGTA) on ice for ultrasound (ultrasonic time 3s, interval time 15s, working frequency 10 times, power 400w). After centrifugation at 720 g for 15 min, the supernatant was transferred to a new tube and recorded as (S1). 500 μL of 250 mM STMDPS buffer solution (250 mM sucrose, 50 mM Tris-HCl) was added to the pellet, centrifuged at 720 g for 15 min, and the supernatant was transferred to a new tube, which was recorded as (S2). Add 2M STMDPS buffer (2M sucrose, 50mM Tris-HCl (pH 7.4), 5mM MgCl 2 , 1 mM DTT, 1 mM PMSF, 25 mg / ml sp...
Embodiment 3
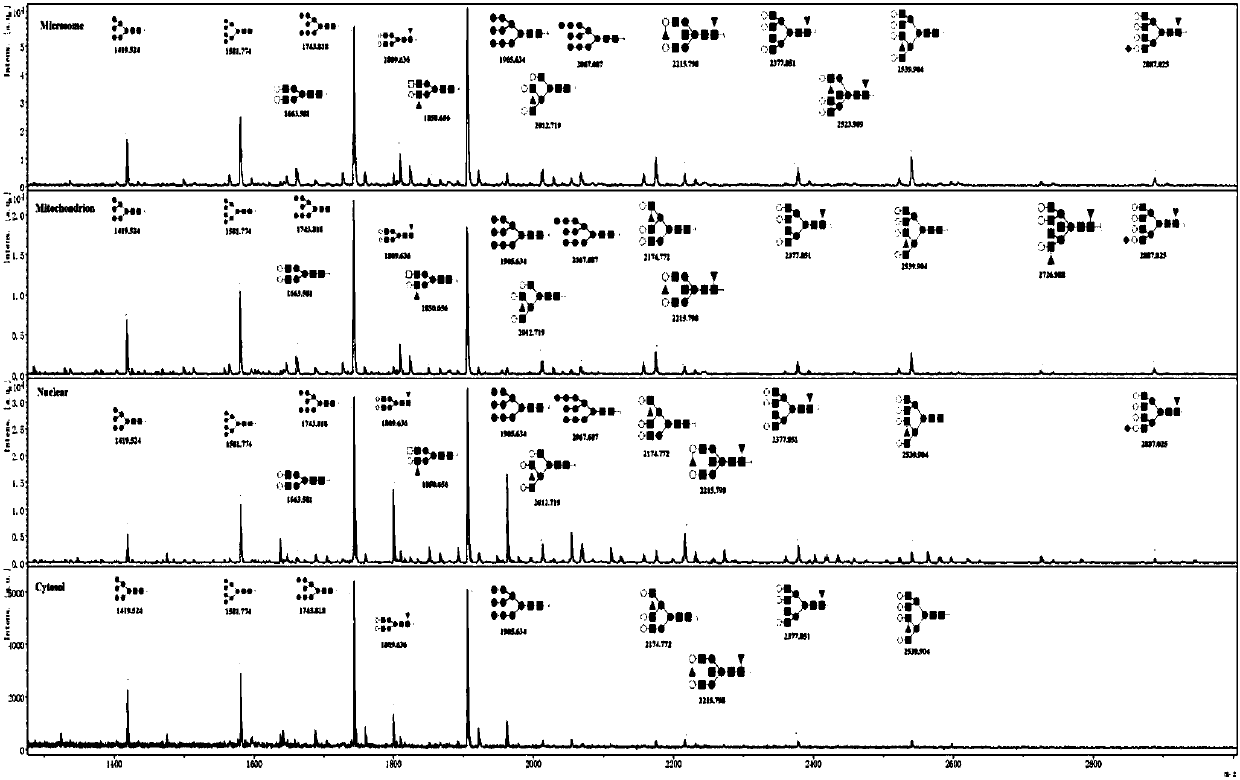
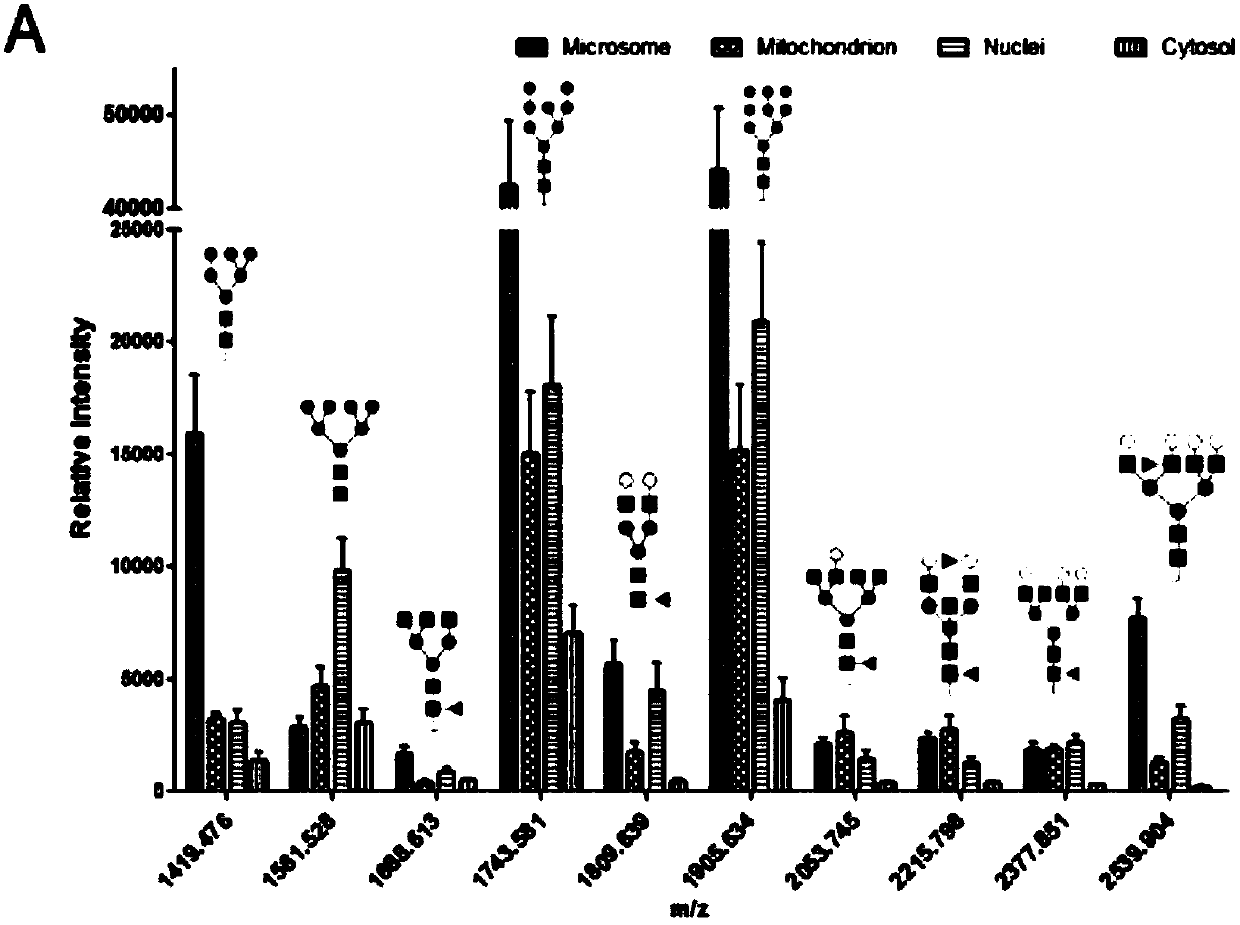
[0049] Example 3: Mass spectrometric analysis of N-linked glycans of YTS1 subcellular structure
[0050] (1) Acethydrazide modification and release of sugar chain sialic acid extracted from subcellular structural protein samples by enzymatic method
[0051] After the 10kD ultrafiltration membrane is assembled into a collection tube for collecting waste liquid during the ultrafiltration process, add a sample protein solution corresponding to a volume of 1 mg of protein, fill up the liquid surface of each tube with 8M urea, and mix well. Centrifuge at 14000g for 15min, concentrate the solution to the bottom of the ultrafiltration membrane tube, discard the effluent; add 300μL of 8mol / L urea, centrifuge at 14000g for 15min, add 200μL of 8M urea, centrifuge, discard the effluent; add 150μL of 10mM DTT solution Mix well, and incubate at 56°C in a dry-type thermostat for 45 minutes. After the reaction, centrifuge at 14,000 g in a desktop centrifuge for 15 minutes, discard the efflue...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com