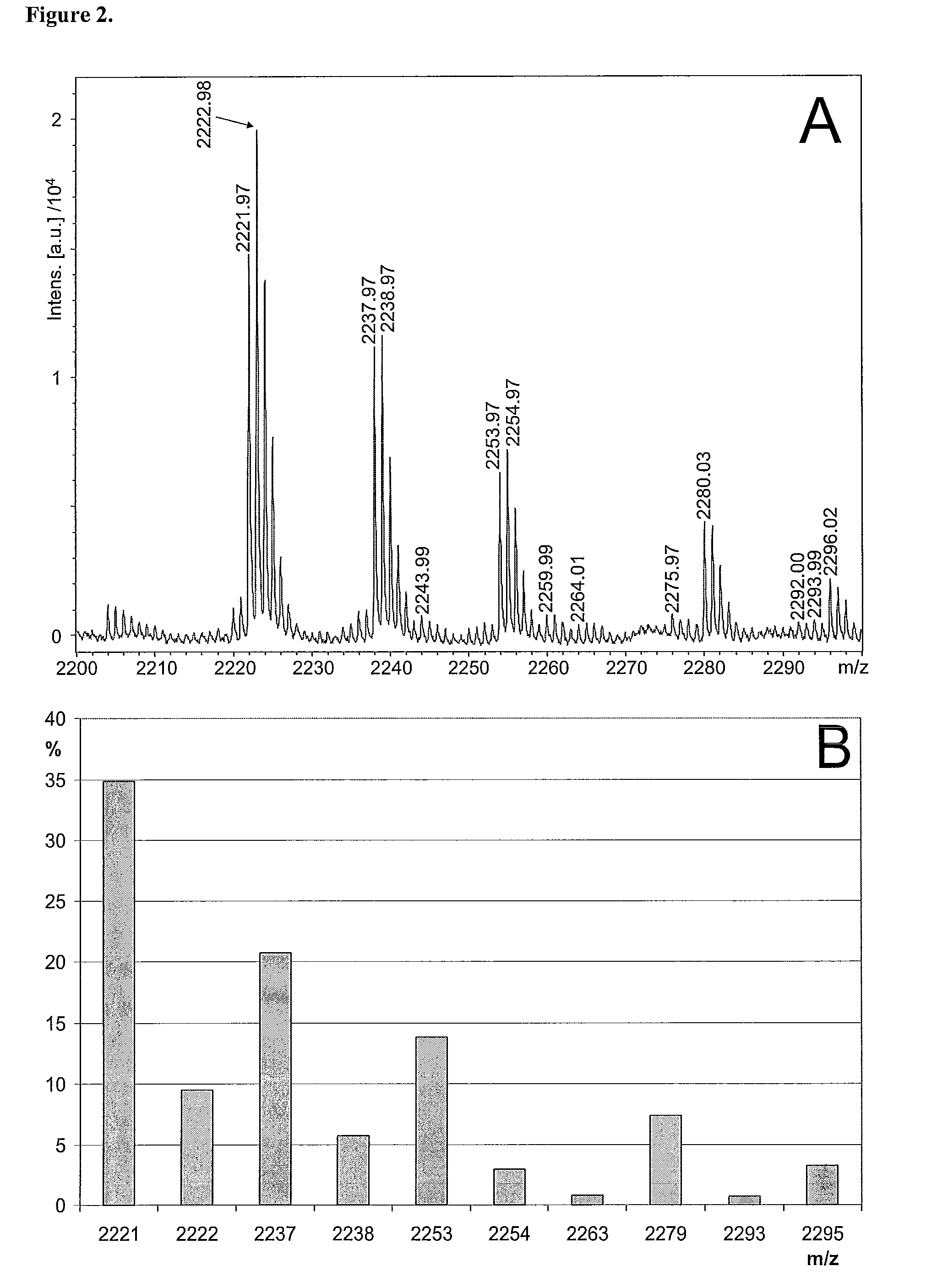
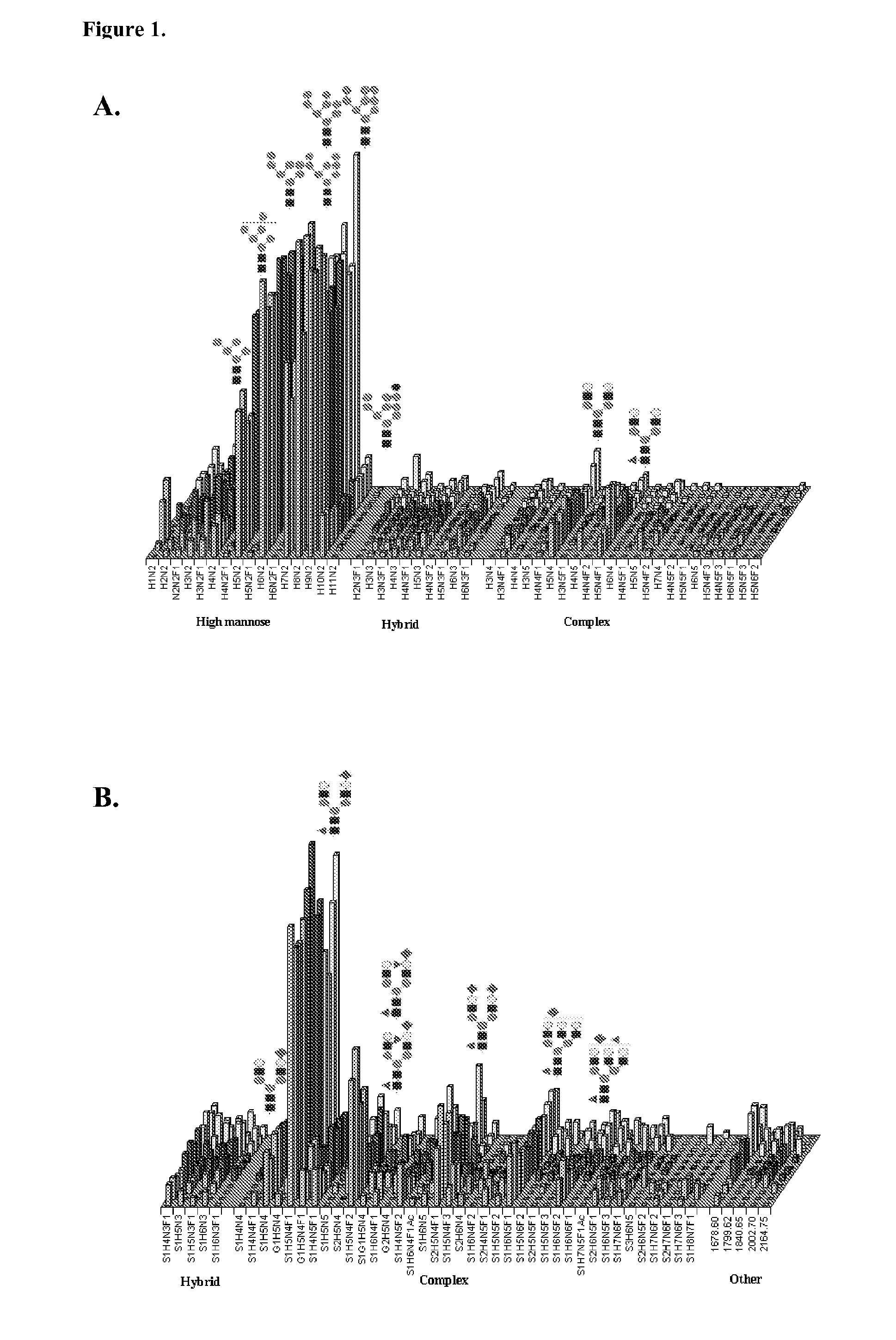
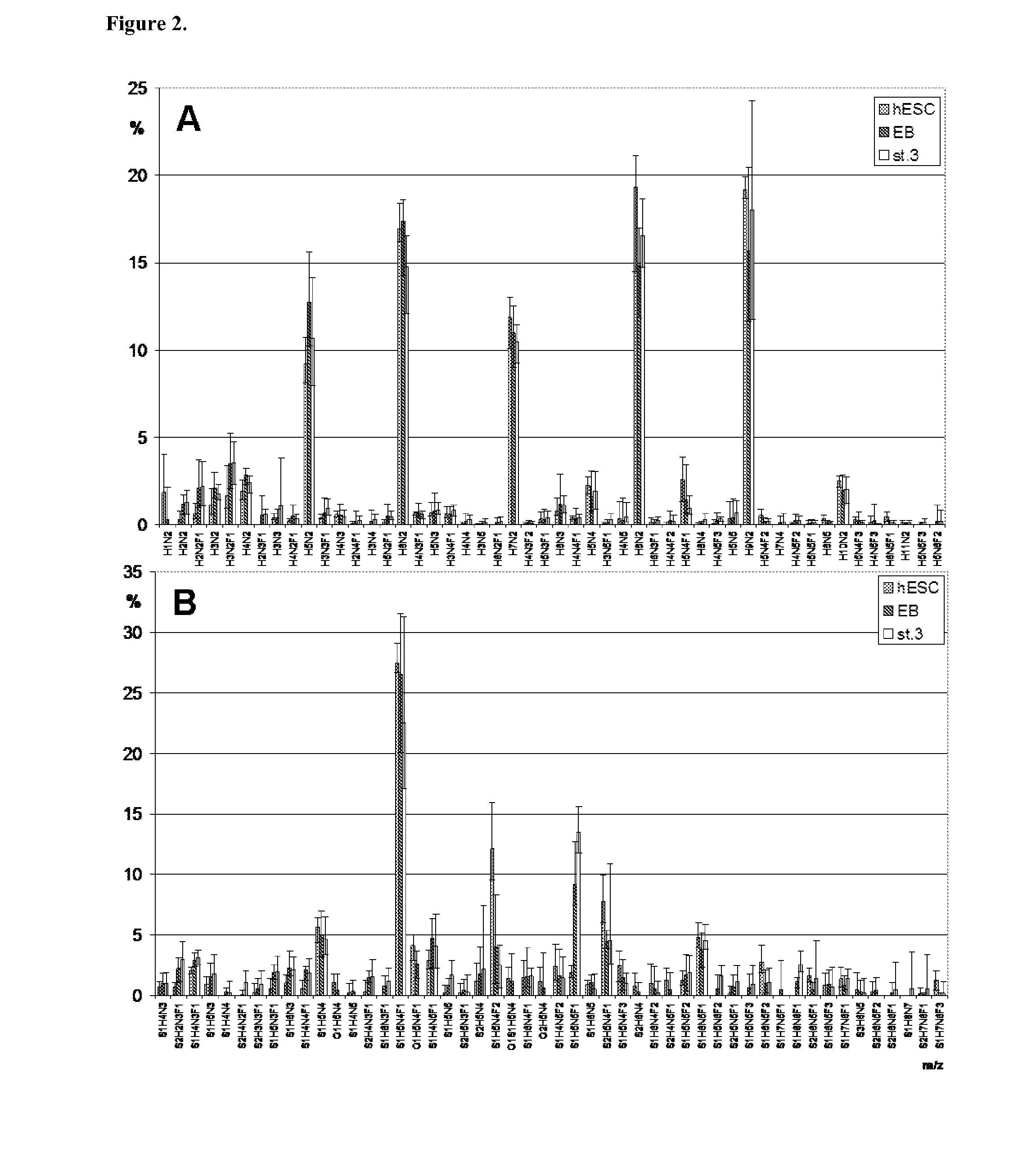
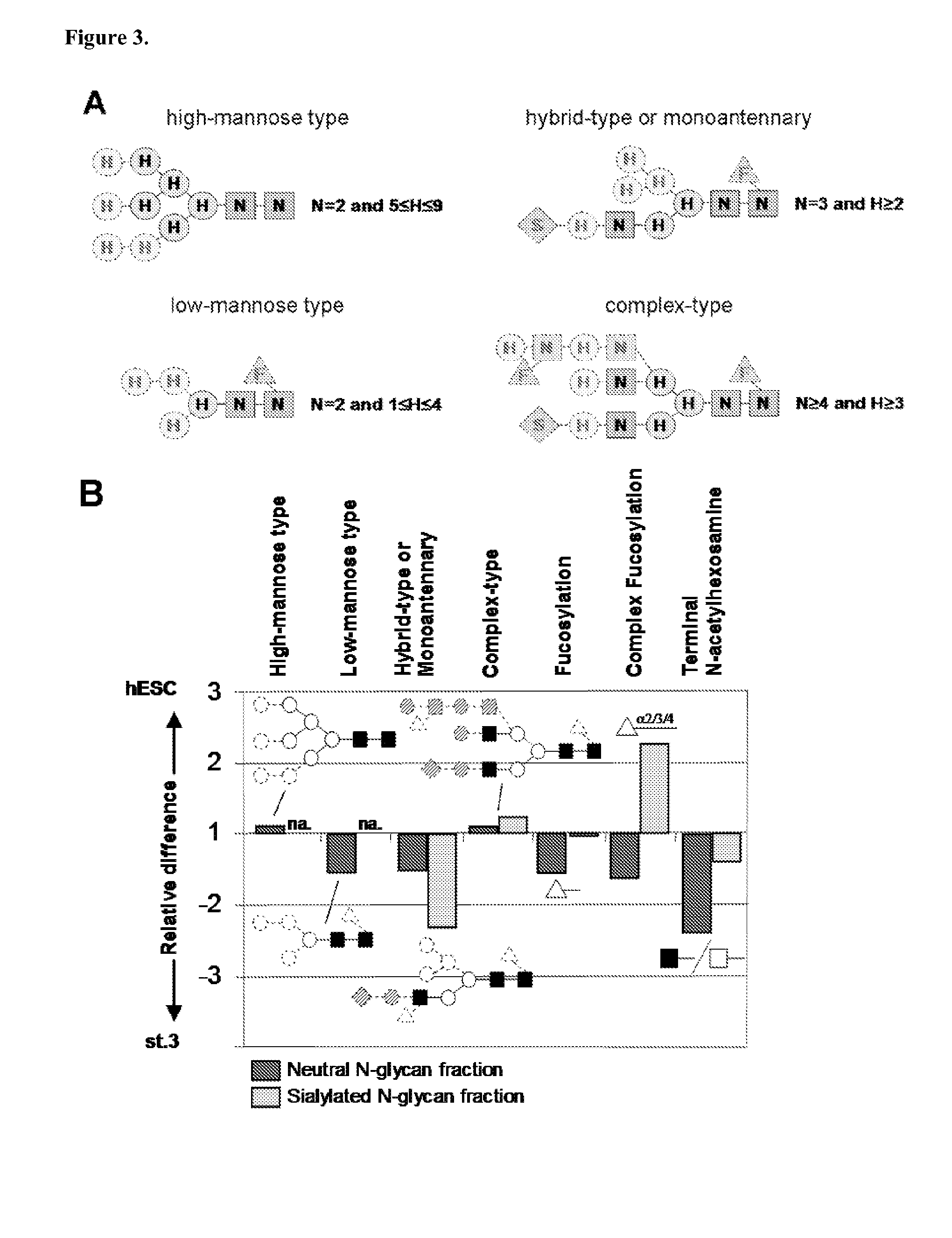
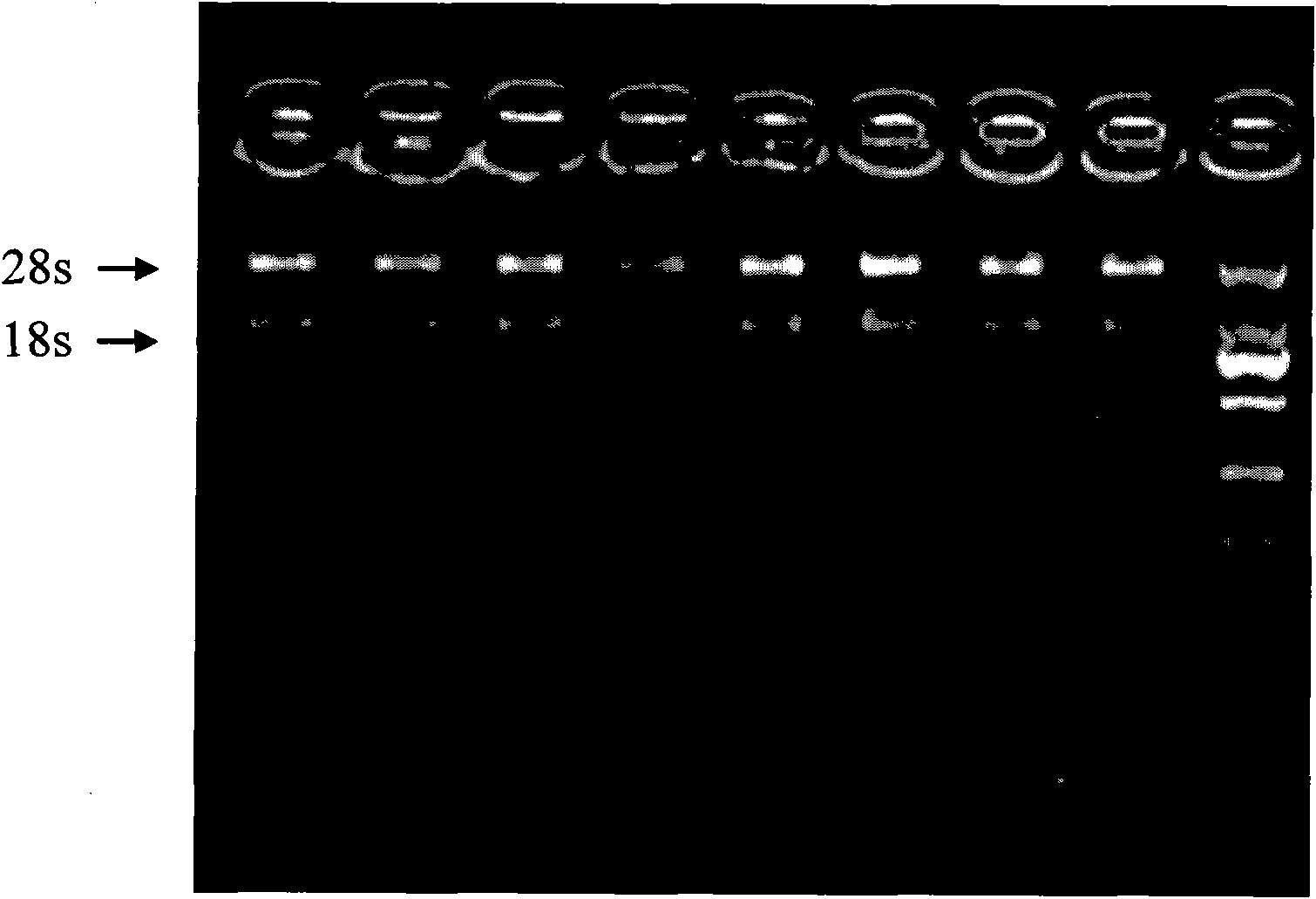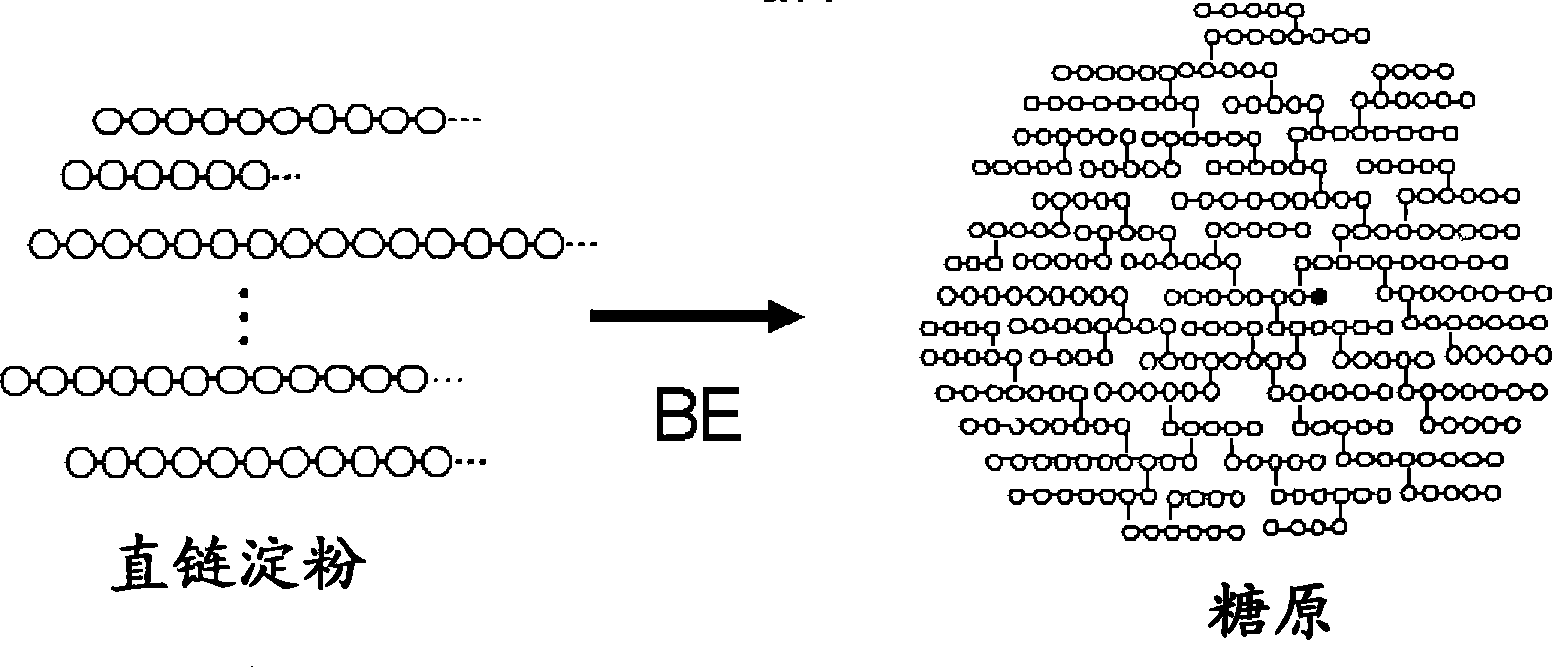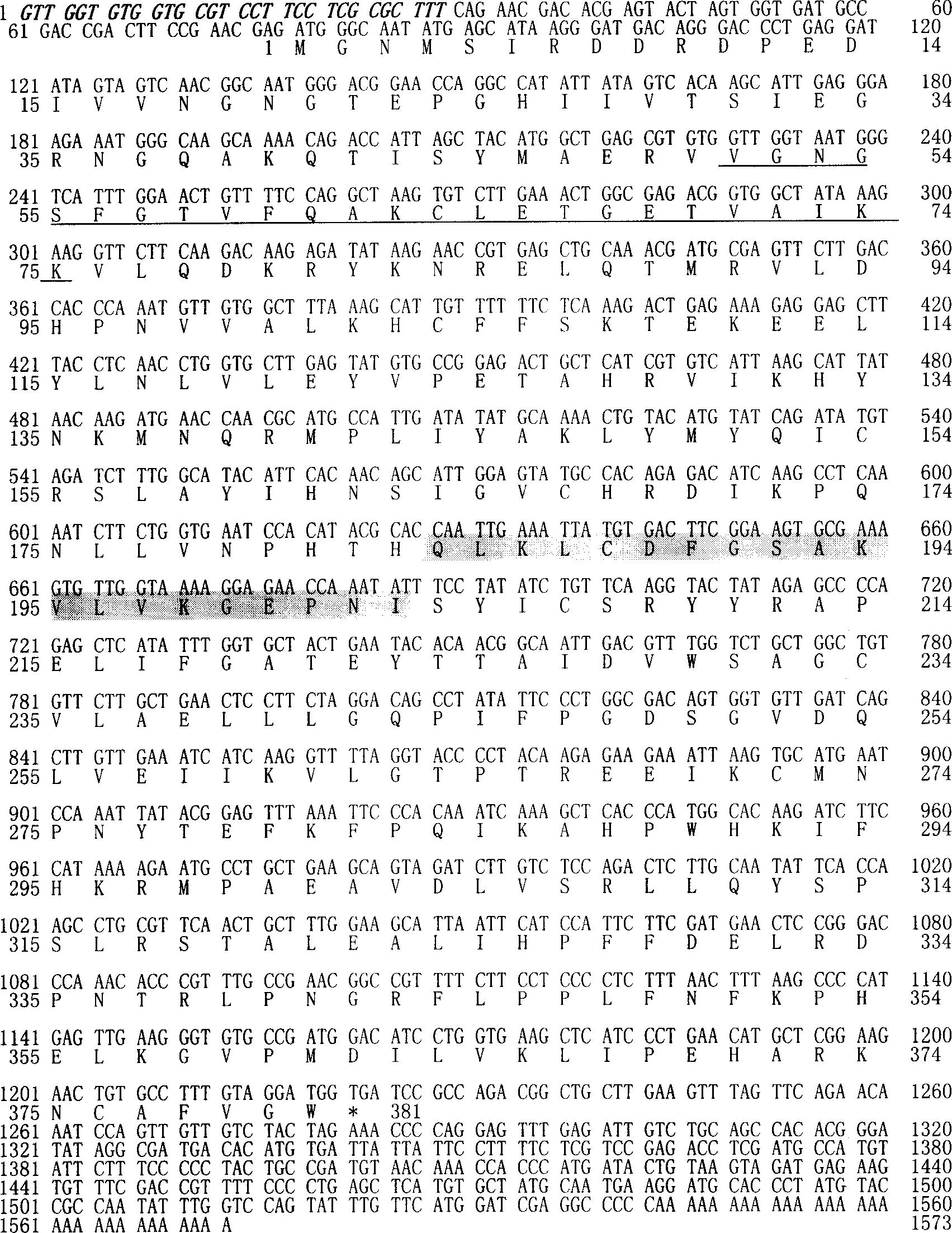Patents
Literature
88 results about "Glycome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The glycome is the entire complement of sugars, whether free or present in more complex molecules, of an organism. An alternative definition is the entirety of carbohydrates in a cell. The glycome may in fact be one of the most complex entities in nature. "Glycomics, analogous to genomics and proteomics, is the systematic study of all glycan structures of a given cell type or organism" and is a subset of glycobiology.
Plants and processes for obtaining them
InactiveUS6013861AIncrease depositionAlteration of fine structureOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationStarch synthaseStarch synthesis
Plants, particularly cereal plants, which have improved ability to synthesise starch at elevated or lowered temperatures and / or to synthesise starch with an altered fine structure are produced by inserting into the genome of the plant (i) a gene(s) encoding a form of an enzyme of the starch or glycogen biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which display an activity which continues to increase over a temperature range over which the activity would normally be expected to decrease, and / or (ii) a gene(s) encoding sense and anti-sense constructs of enzymes of the starch biosynthetic pathway, particularly soluble starch synthase and / or branching enzyme and / or glycogen synthase, which alters the natural ratios of expression of the said enzymes or inserts enzymes with special structural characteristics which alter the natural branching pattern in starch.
Owner:ZENECA LTD
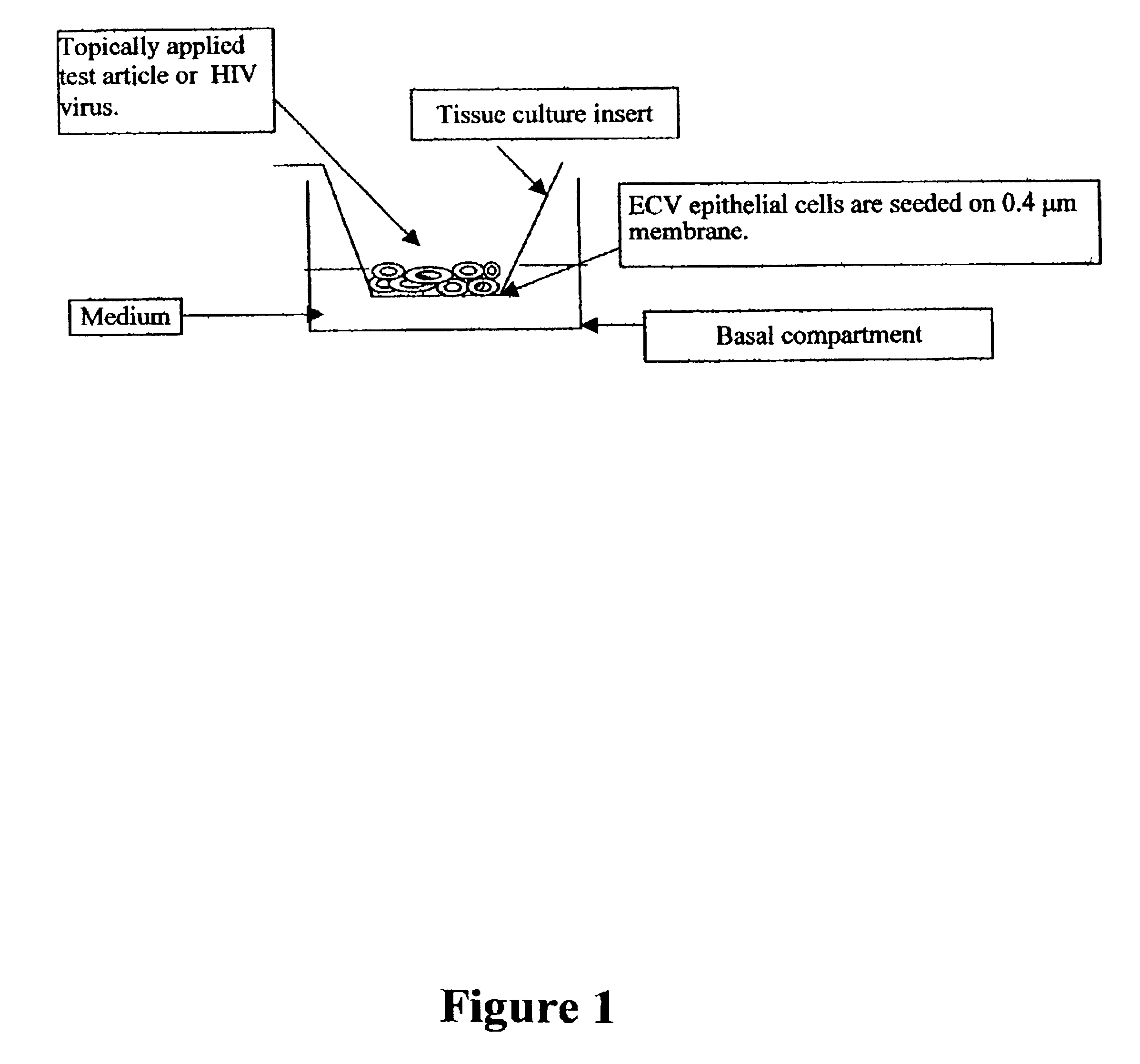
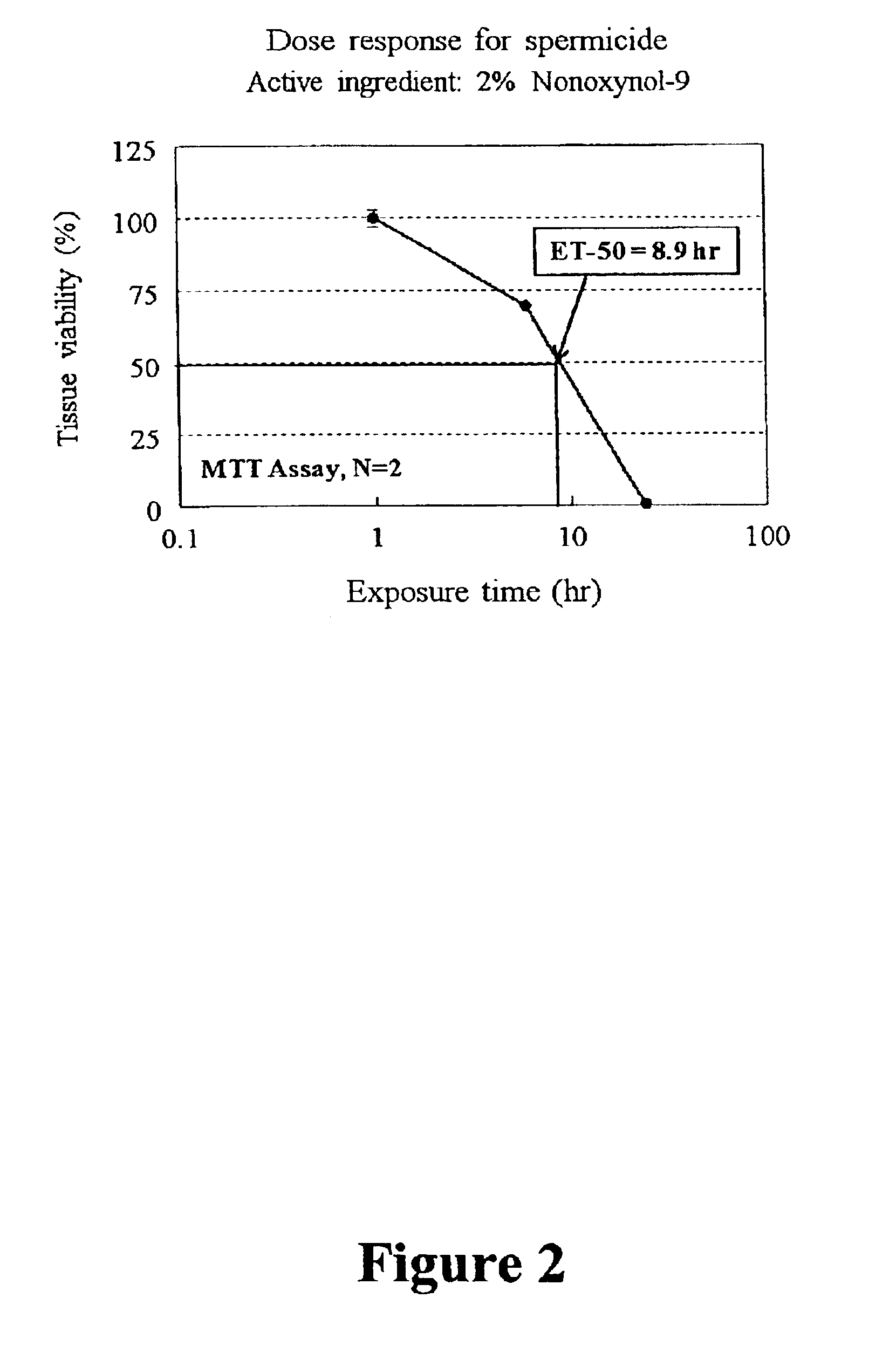
Three dimensional vaginal tissue model containing immune cells
InactiveUS6943021B2Improve survivabilityInduced proliferationBiocideEpidermal cells/skin cellsSerum free mediaAir liquid interface
Disclosed is a cervico-vaginal tissue equivalent comprised of vaginal epithelial cells and immune cells, cultured at the air-liquid interface. The tissue equivalent is capable of being infected with a sexually transmitted pathogen such as a virus (e.g., HIV), a bacteria, a helminthic parasite, or a fungus. The tissue equivalent is also capable of undergoing an allergic-type reaction or an irritant-type reaction. The tissue equivalent is characterized as having nucleated basal layer cells and nucleated suprabasal layer cells, and further as having cell layers external to the suprabasal layer progressively increasing in glycogen content and progressively decreasing in nuclei content. Immune cells of the tissue equivalent are primarily located in the basal and suprabasal layers. Also disclosed are methods for producing the tissue equivalent. The methods involve providing vaginal epithelial cells and immune cells, seeding the cells onto a porous support, and co culturing the seeded cells at the air-liquid interface under conditions appropriate for differentiation. One such method disclosed is for generation of the tissue equivalent in serum free medium. Specific cells from which the tissue equivalent is generated, and also specific preferred components of the medium in which the tissue equivalent is generated are provided. Also disclosed is a cervico-vaginal tissue equivalent produced by the methods disclosed herein.
Owner:MATTEK CORP
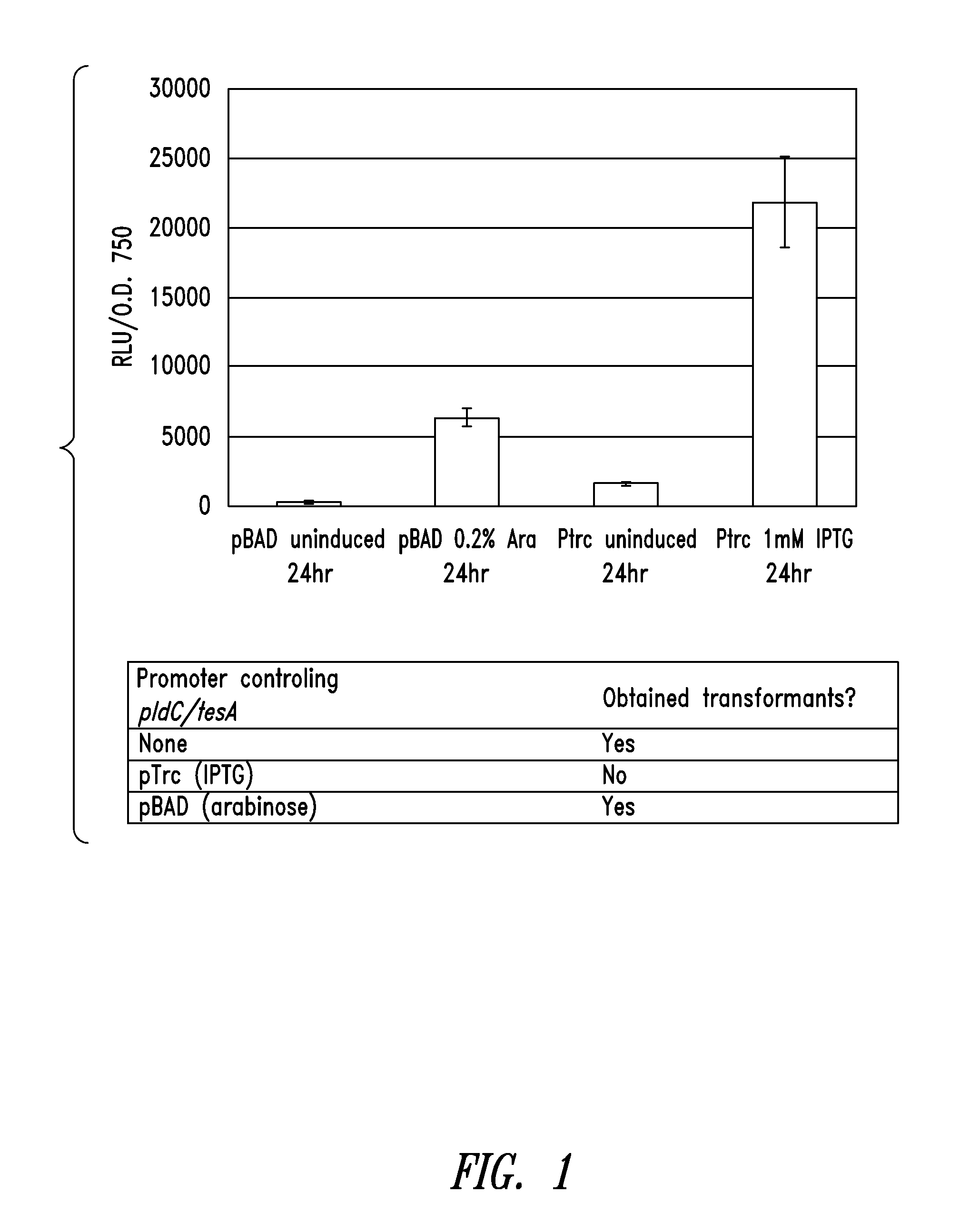
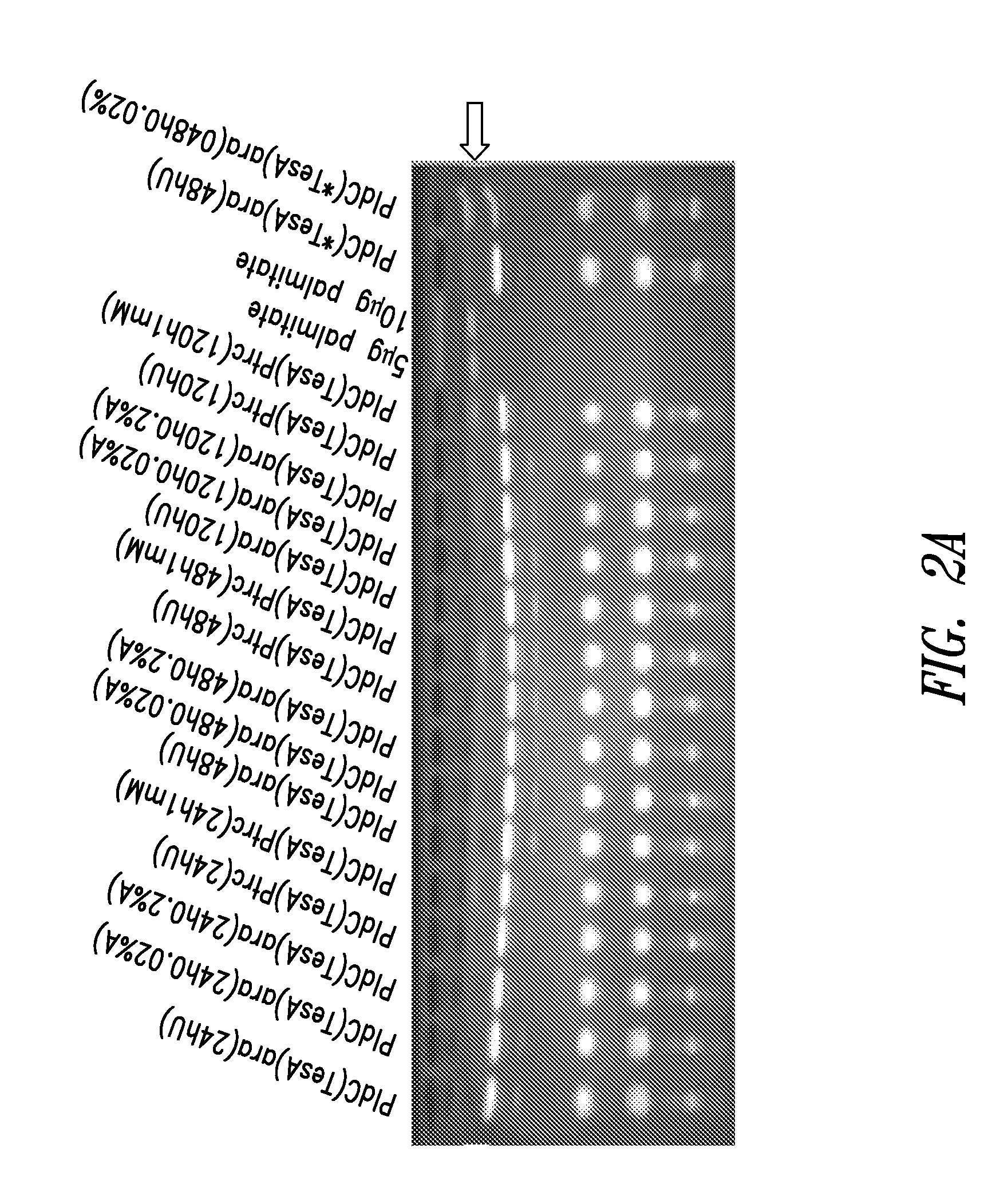
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing lipids
ActiveUS20110250659A1Reduce the amount requiredIncrease volumeHydrolasesUnicellular algaePhylum CyanobacteriaLipid formation
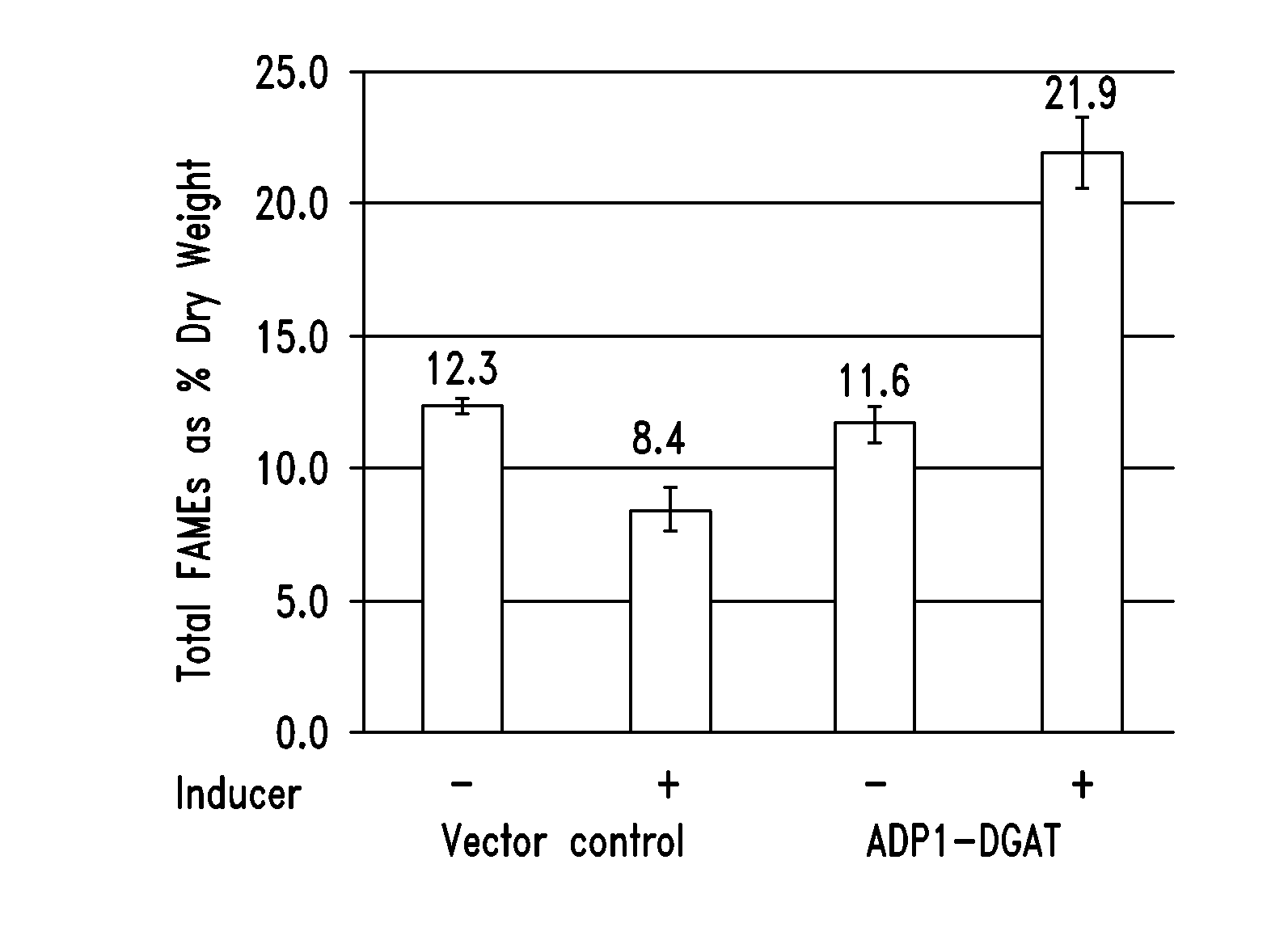
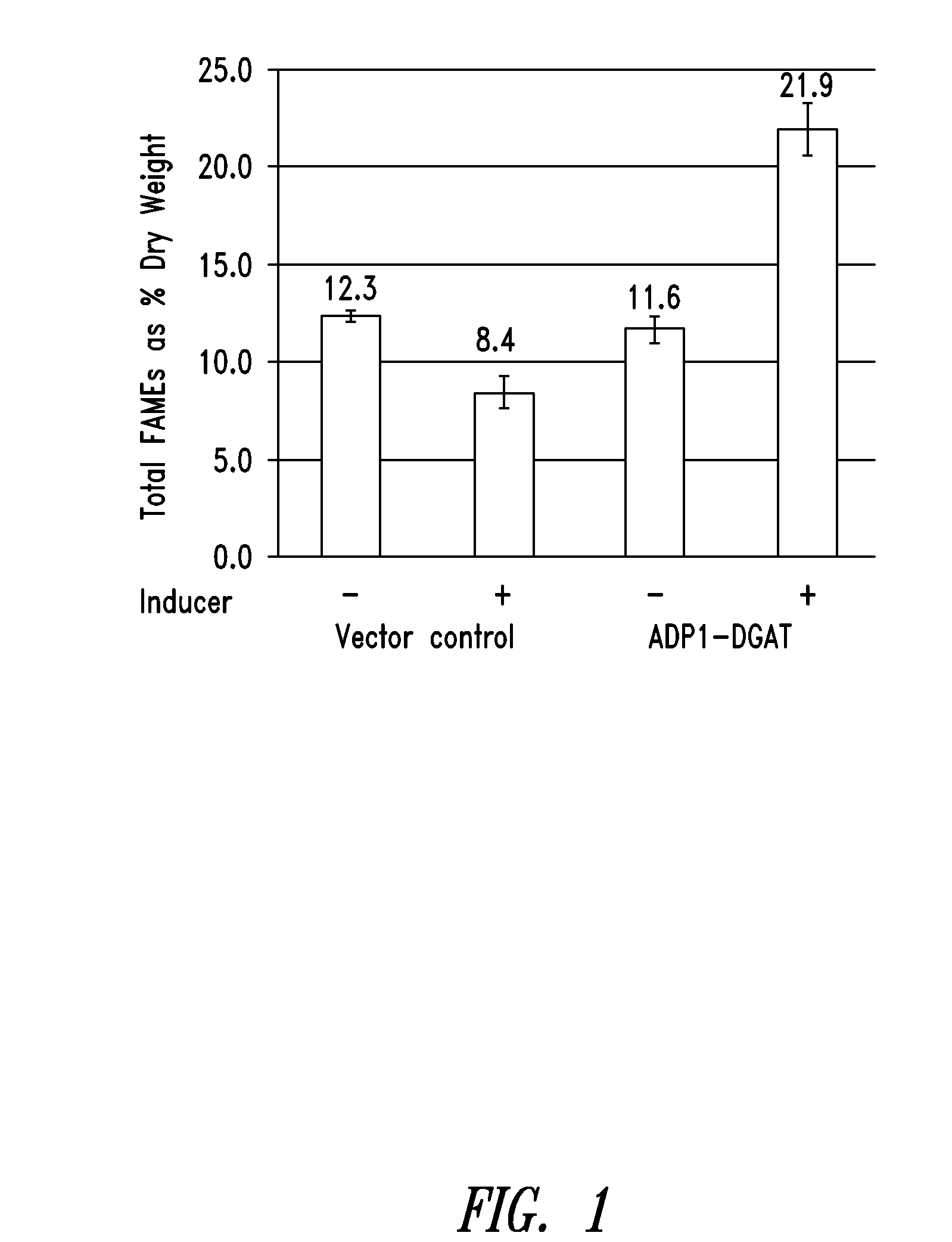
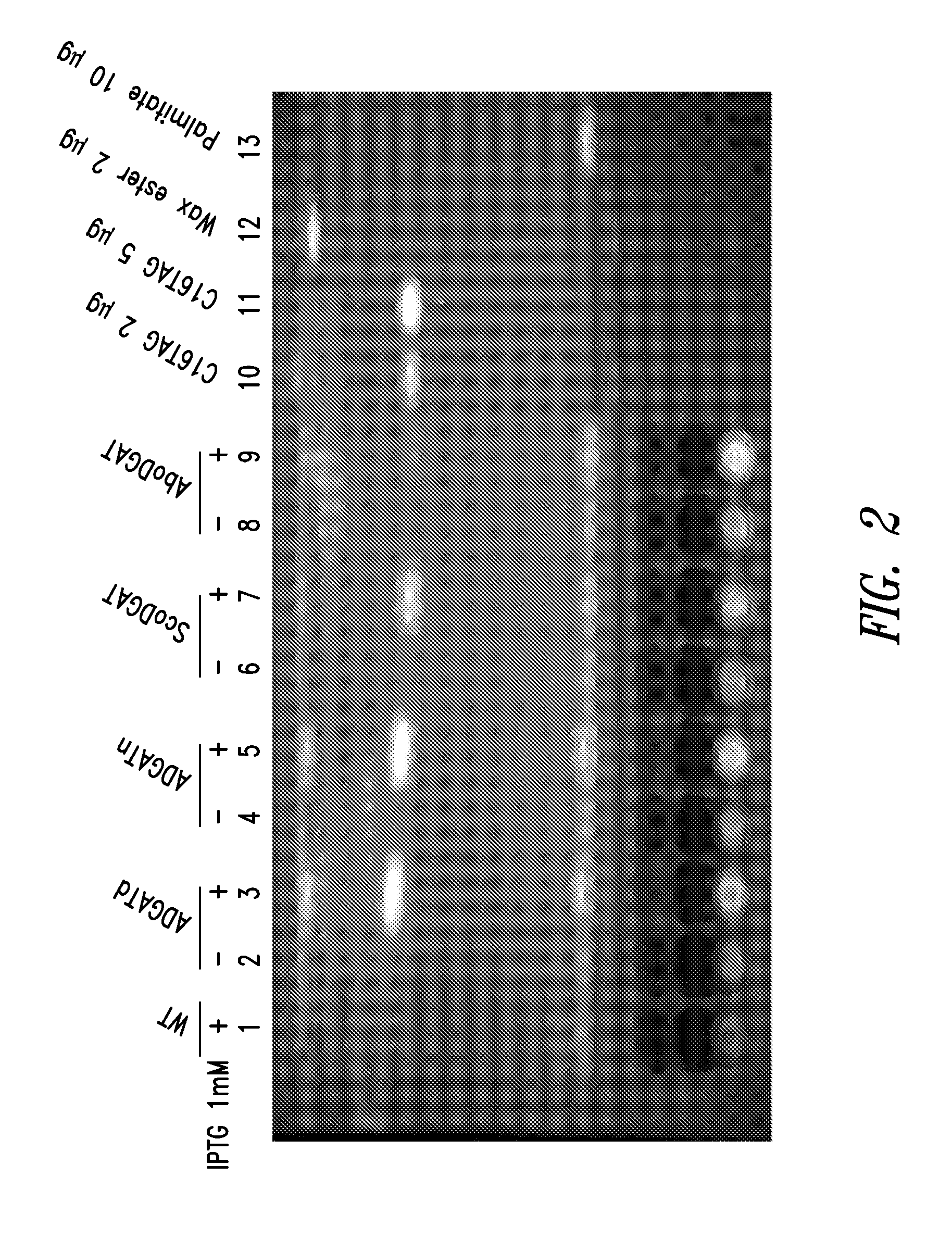
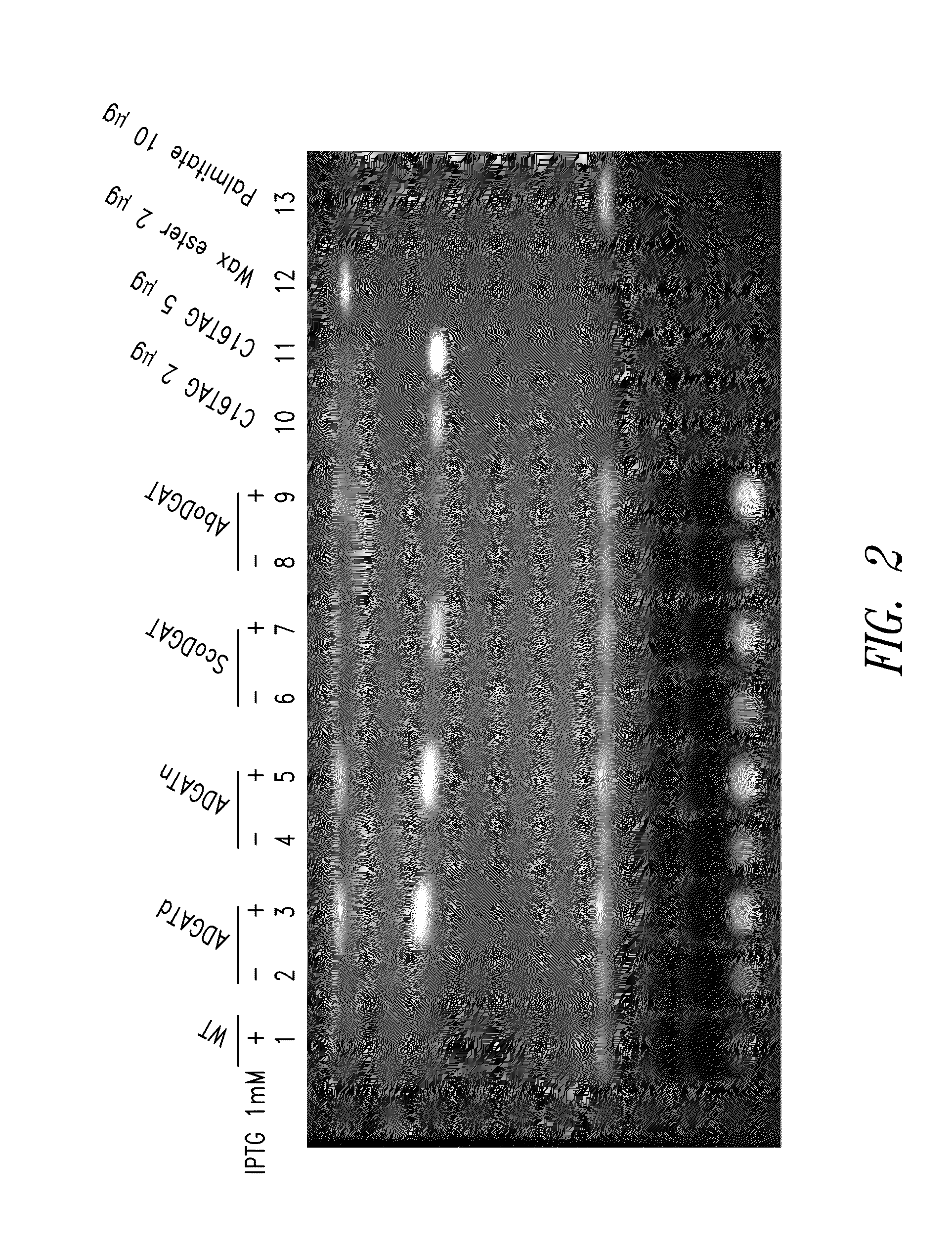
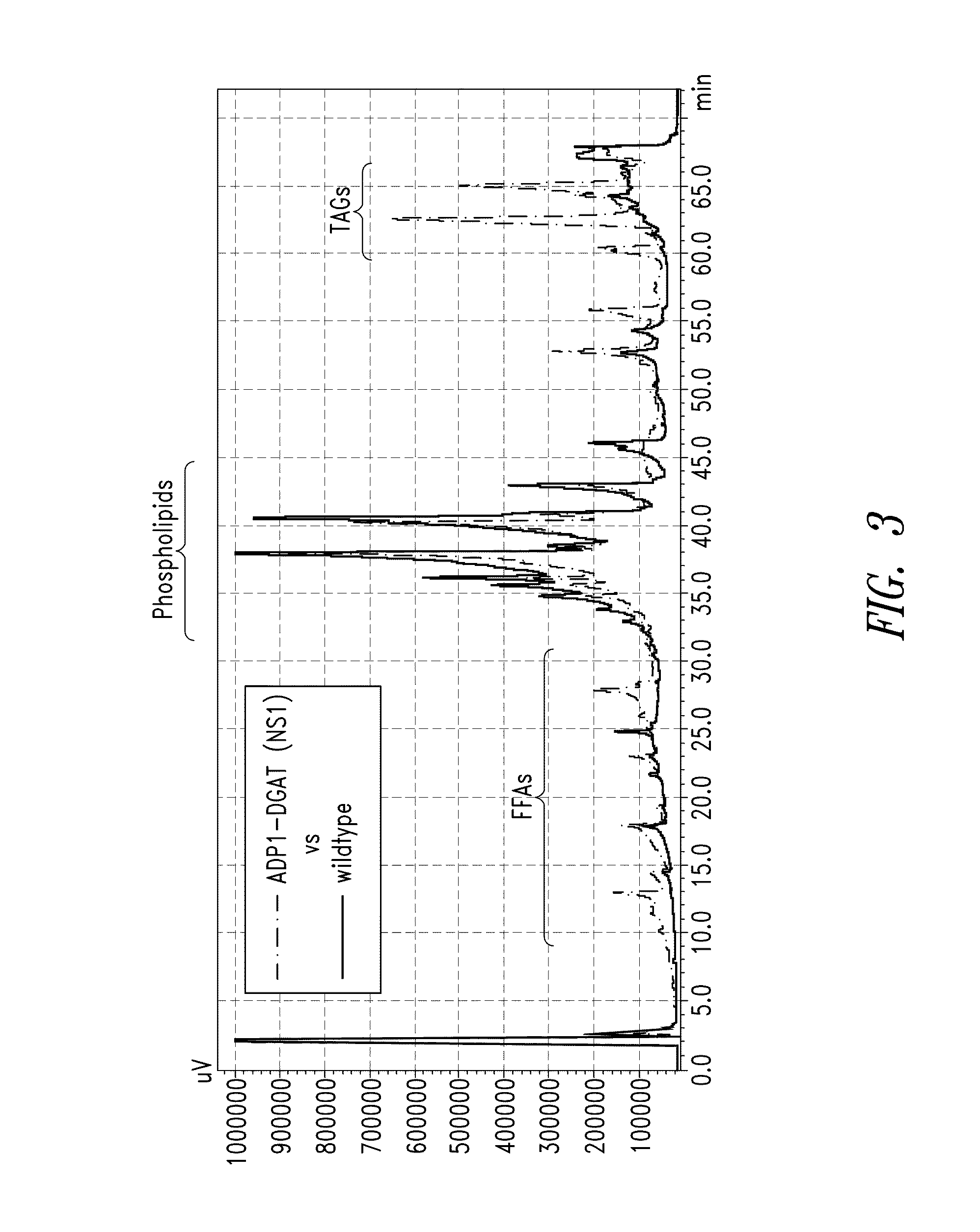
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, e.g., Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a phospholipase and / or thioesterase, which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. This disclosure also describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms that contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, which are capable of producing increased amounts of fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides, as well as photosynthetic microorganism comprising mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen under reduced nitrogen conditions as compared to a wild type photosynthetic microorganism.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
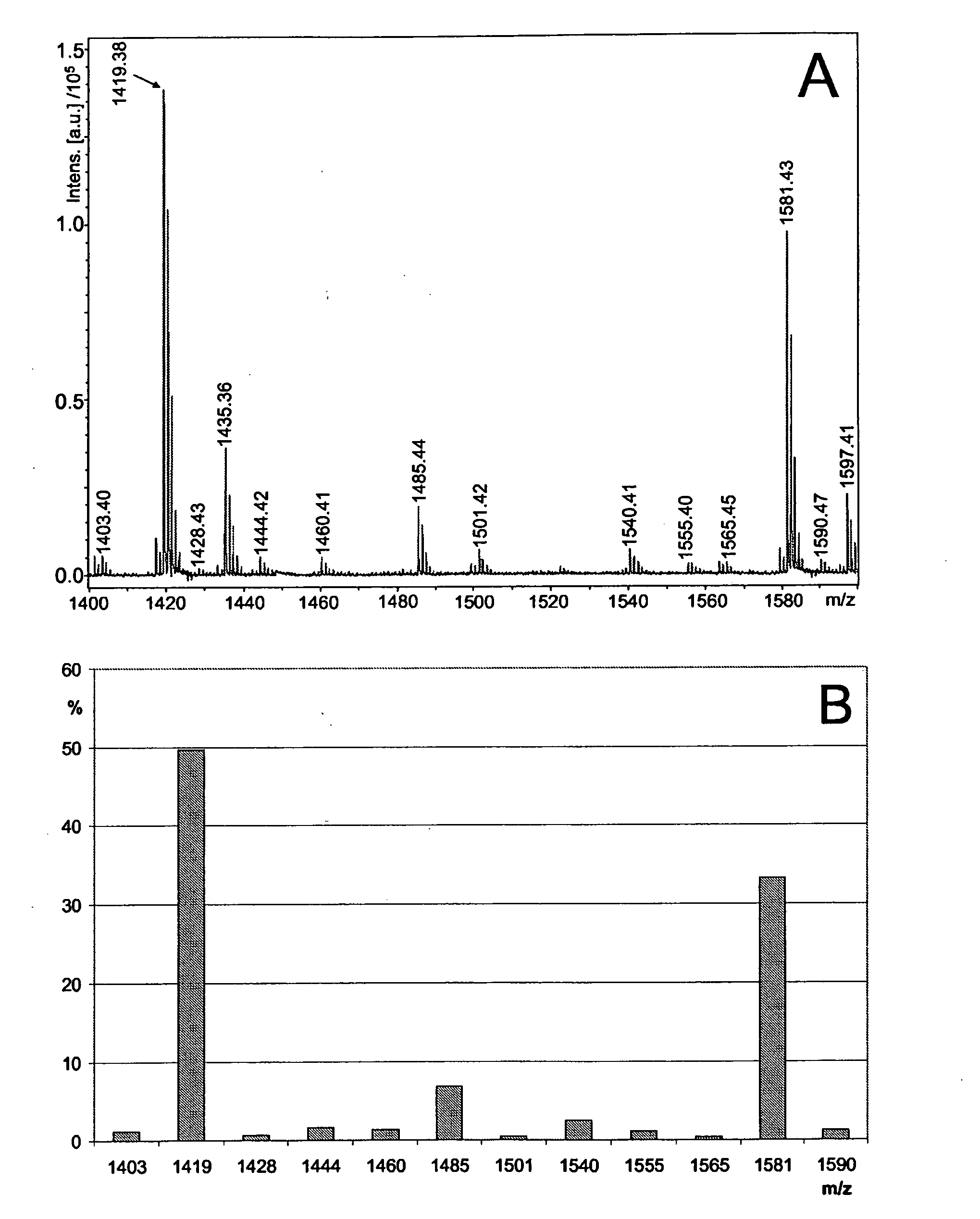
Tissue Carbohydrate Compositions and Analysis Thereof
InactiveUS20090104603A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTotal TissueMass spectrometric
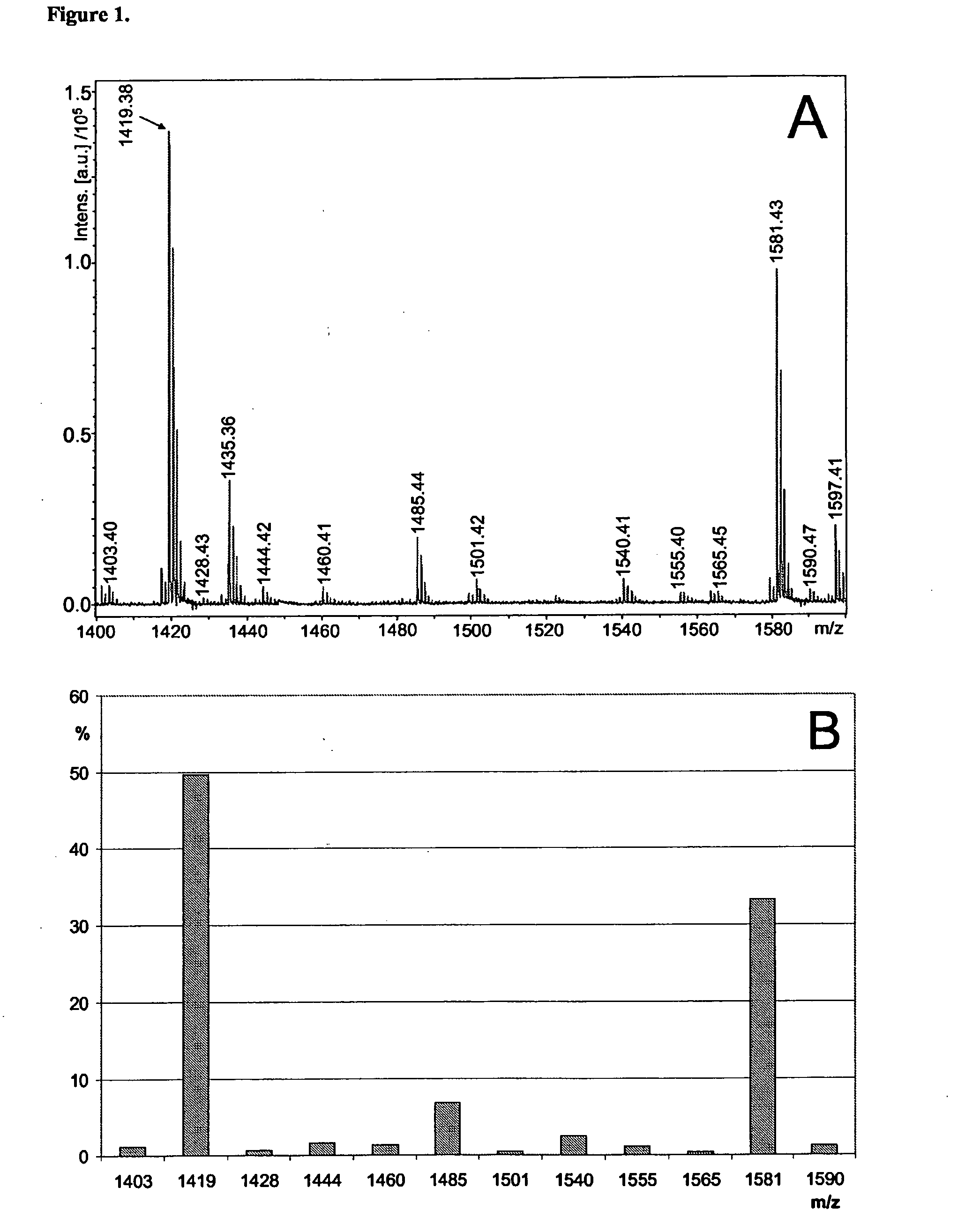
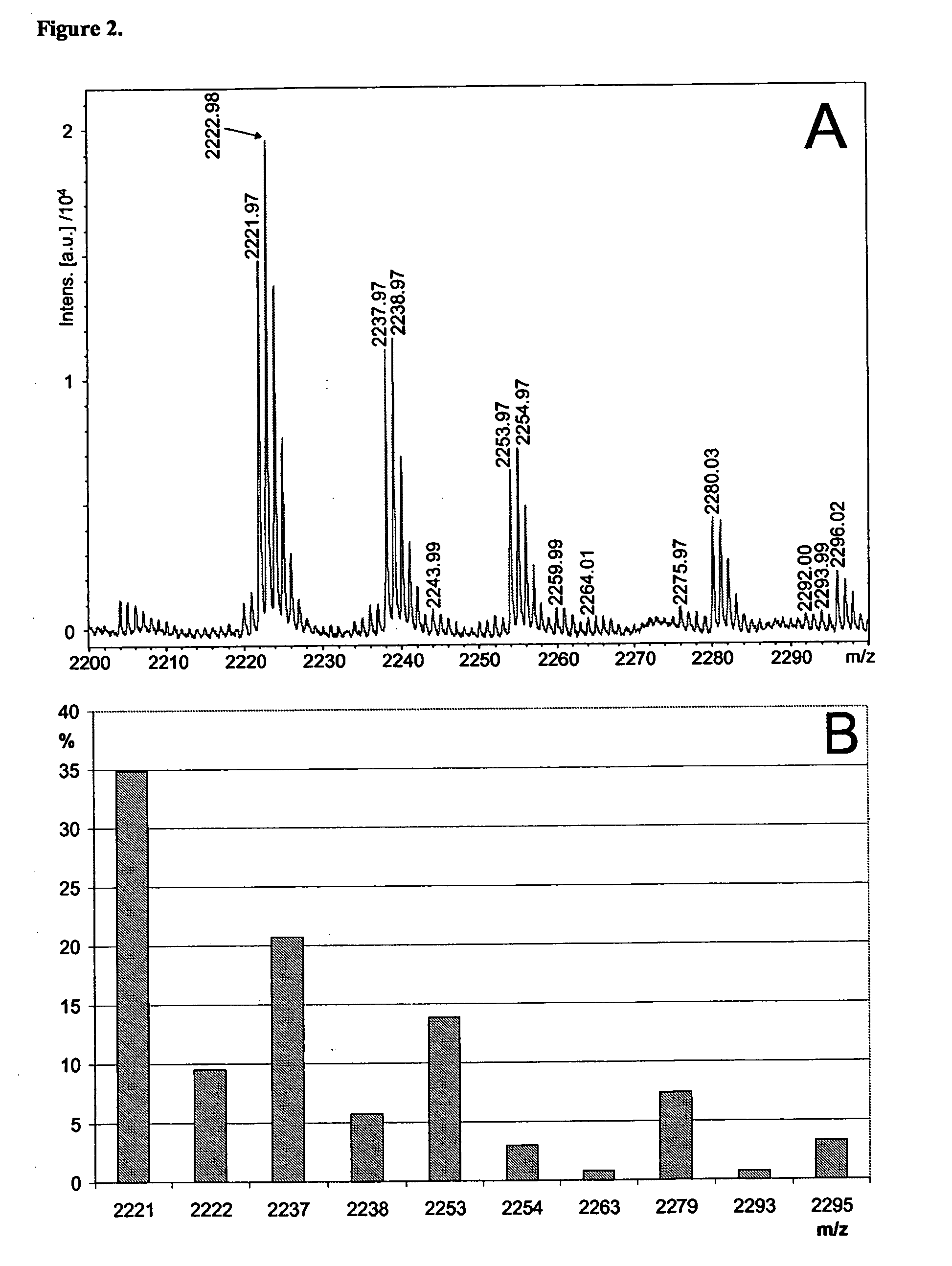
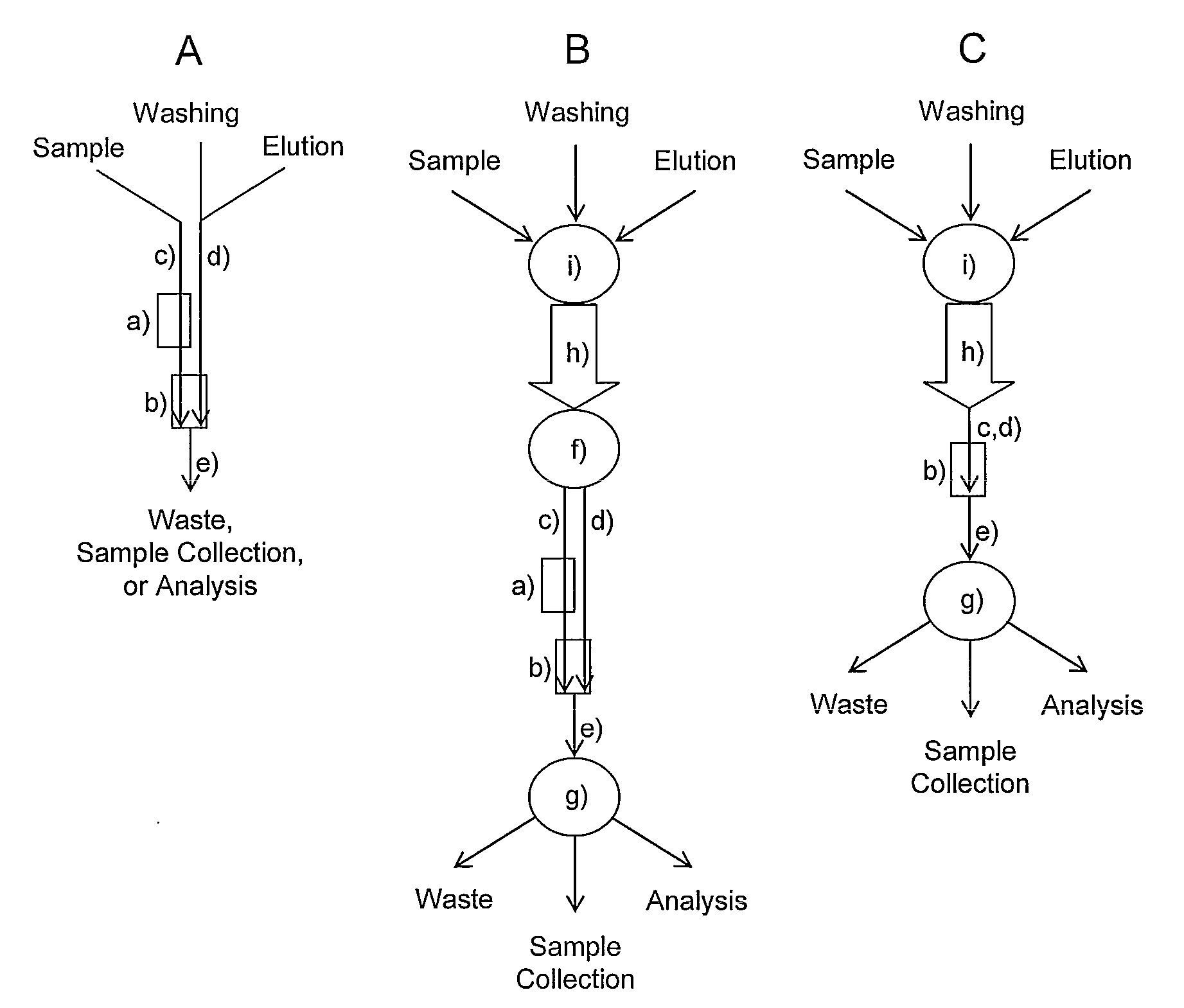
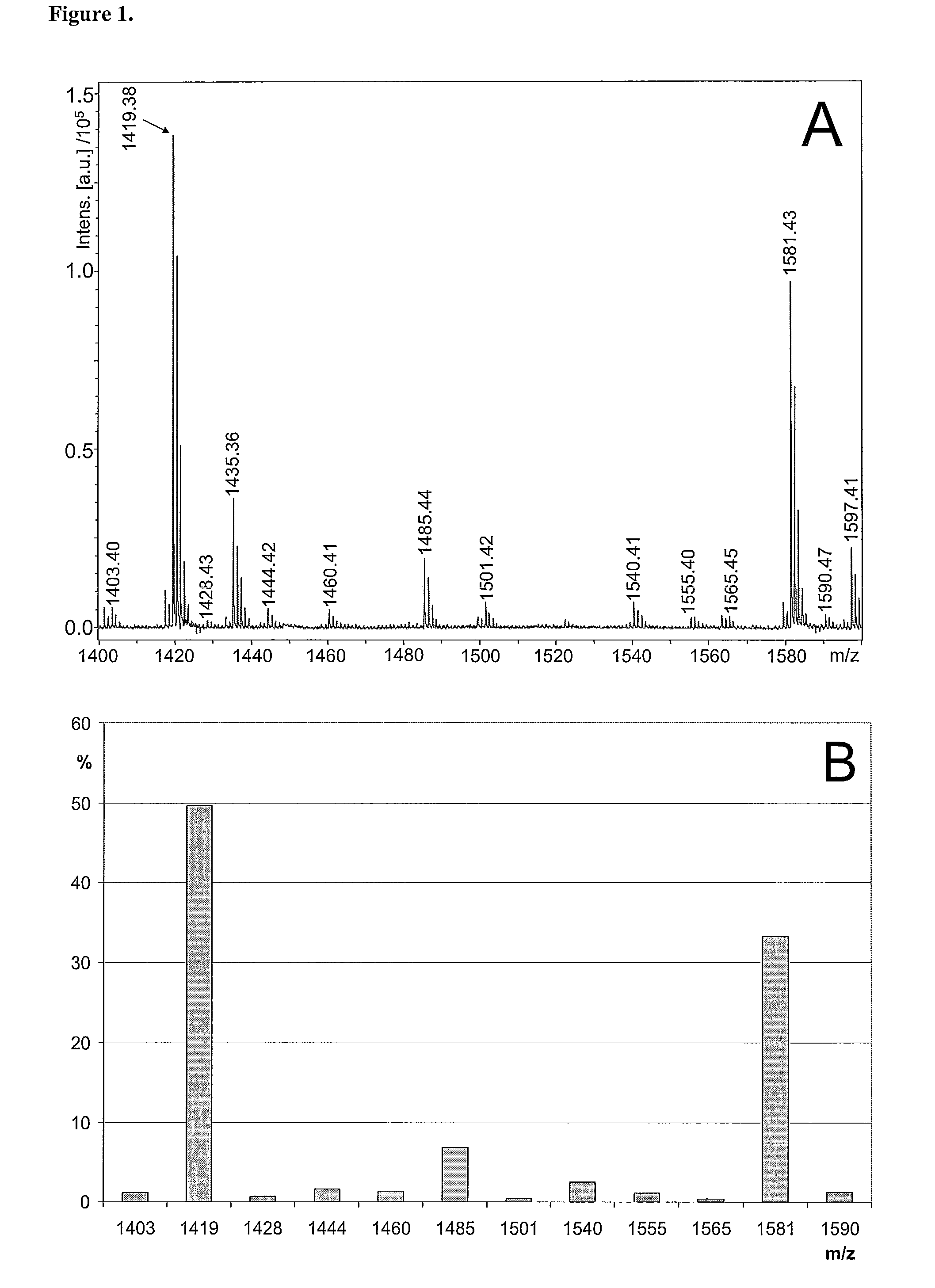
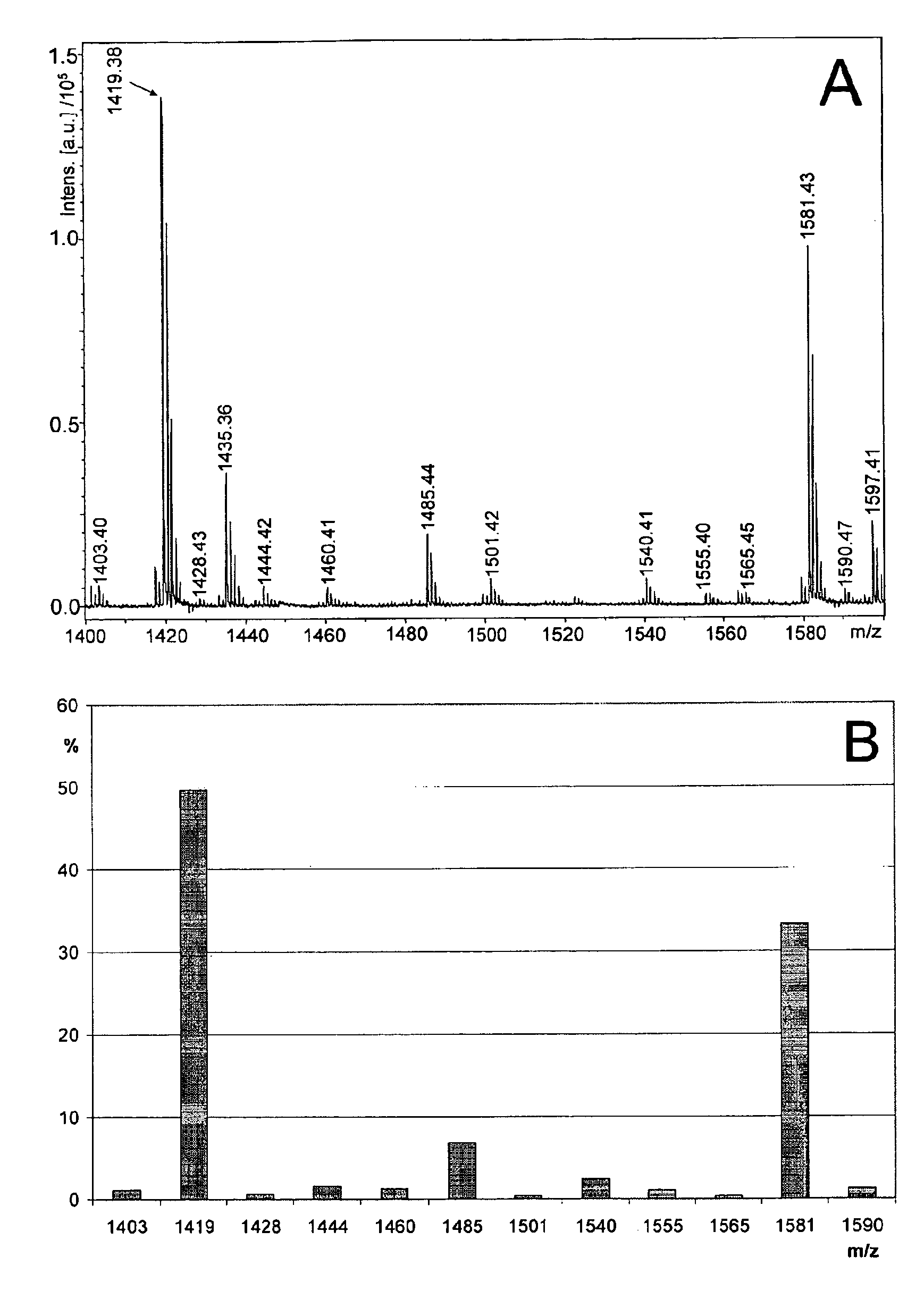
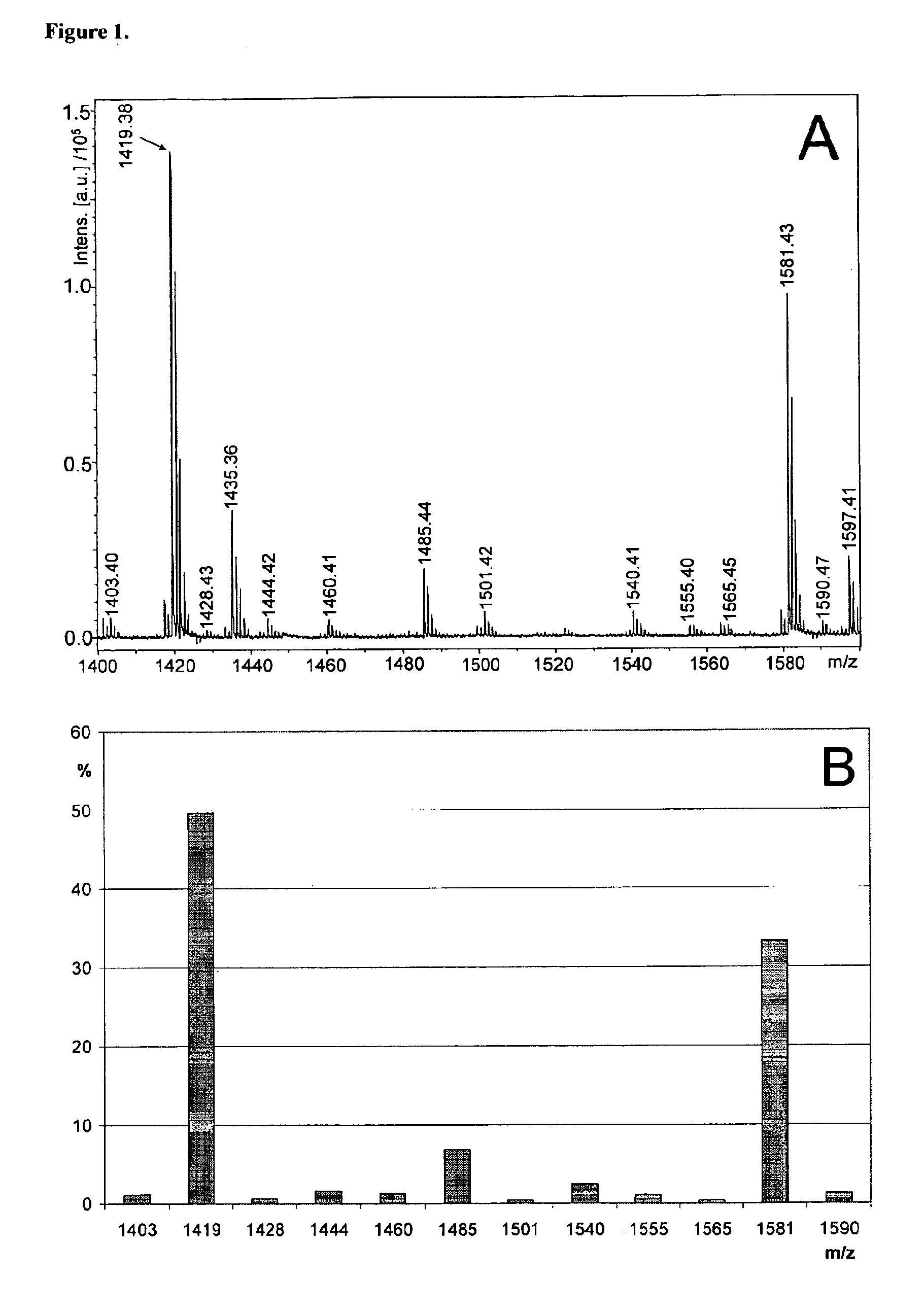
The present invention reveals novel methods for producing novel carbohydrate compositions, glycomes, from animal tissues. The tissue substrate materials can be total tissue samples and fractionated tissue parts, or artificial models of tissues such as cultivated cell lines. The invention is further directed to the compositions and compositions produced by the methods according to the invention. The invention further represent methods for analysis of the glycomes, especially mass spectrometric methods.
Owner:GLYKOS FINLAND
Tissue carbohydrate compositions and analysis thereof
InactiveUS20100003699A1Analysis using chemical indicatorsMicrobiological testing/measurementMass spectrometryTotal Tissue
The present invention reveals novel methods for producing novel carbohydrate compositions, glycomes, from animal tissues. The tissue substrate materials can be total tissue samples and fractionated tissue parts, or artificial models of tissues such as cultivated cell lines. The invention is further directed to the compositions and compositions produced by the methods according to the invention. The invention further represent methods for analysis of the glycomes, especially mass spectrometric methods.
Owner:GLYKOS FINLAND
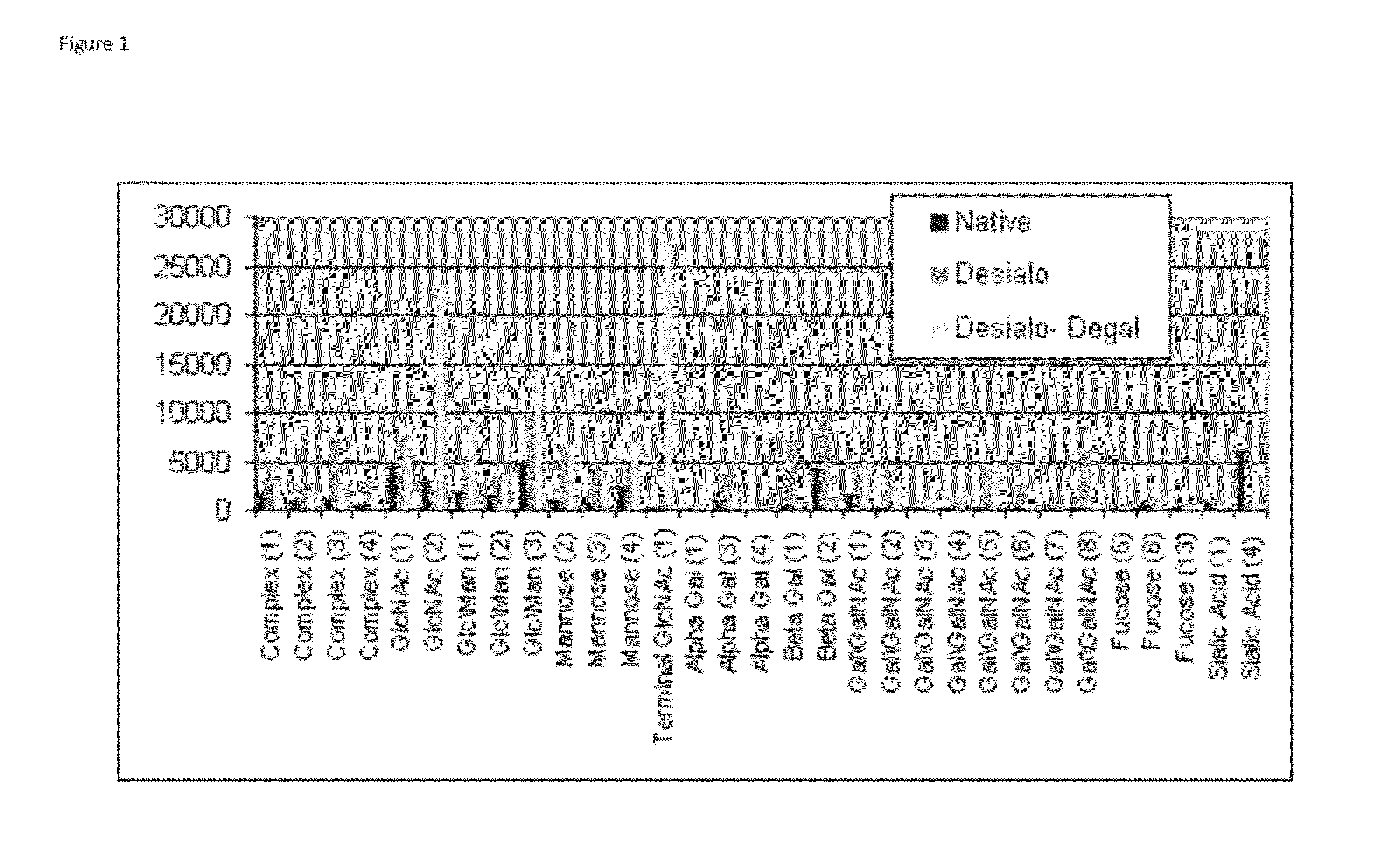
Novel cellular glycan compositions
InactiveUS20090317834A1Biological material analysisEmbryonic cellsMonosaccharide compositionMass spectrometric
The invention describes novel compositions of glycans, glycomes, from human embryonic stem cells, and especially novel subcompositions of the glycomes with specific monosaccharide compositions and glycan structures. The invention is further directed to methods for modifying the glycomes and analysis of the glycomes and the modified glycomes. Furthermore, the invention is directed to stem cells carrying the modified glycomes on their surfaces. The glycomes are preferably analysed by profiling methods able to detect reproducibly and quantitatively numerous individual glycan structures at the same time. The most preferred type of the profile is a mass spectrometric profile. The invention specifically revealed novel target structures and is especially directed to the development of reagents recognizing the structures.
Owner:GLYKOS FINLAND
Modified Photosynthetic Microorganisms With Reduced Glycogen and Their Use in Producing Carbon-Based Products
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen as compared to a wild type Cyanobacterium, and which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. In certain embodiments, the genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms also contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of lipids or fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
Production of modified polysaccharides
InactiveUS6639126B1Improve abilitiesSuppression of activityOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationBiotechnologyPullulanase
The invention alters the physical characteristics of storage polyglucans including starch. Methods are provided to modify the polyglucan biosynthesis pathway by simultaneously altering the activity of a pullulanase debranching enzyme and the activity of another polypeptide in the polyglucan biosynthesis pathway. Compositions of the invention include transgenic plants and seeds having a modified polyglucan structure and / or content and elevated phytoglycogen levels. Additional compositions include a grain with increased energy availability for improved feed quality and industrial uses. Further compositions include a polyglucan with improved functional properties useful in a wide range of food and industrial applications.
Owner:PIONEER HI BRED INT INC
Extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA
InactiveCN101864414AMeet Gene Expression AnalysisFulfil requirementsDNA preparationWater bathsTotal rna
The invention discloses a high-extraction-purity, good-integrity and high-yield extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The method comprises the following steps of: quickly freezing apostichopus japonicus body-wall tissue in liquid nitrogen; grinding and putting the frozen tissue in lysate to homogenate, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding chloroform to the supernatant fluid and centrifugating to take the supernatant fluid to another centrifuge tube; then, adding a high-salt solution and isopropyl alcohol and filtering precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the precipitation with DEPC (diethypyrocarbonate) treated water to have constant volume; sequentially adding a DNA enzyme buffer solution without RNA enzymes, DNA enzymes without RNA enzymes and an RNA enzyme inhibitor to the dissolved solution to mix; carrying out a water bath at 37 DEG C to obtain DNA lysate; adding phenol and chloroform in a ratio of 5:1 to the DNA lysate to mix, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding a glycogen solution, a potassium acetate solution and pre-cooling ethanol to the supernatant fluid; mixing and staying over night; centrifugating to discard the supernatant fluid; washing and dying the precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the solution with the DEPC treated water to have constant volume of 20 mu l; and storing at 80 DEG C below zero.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
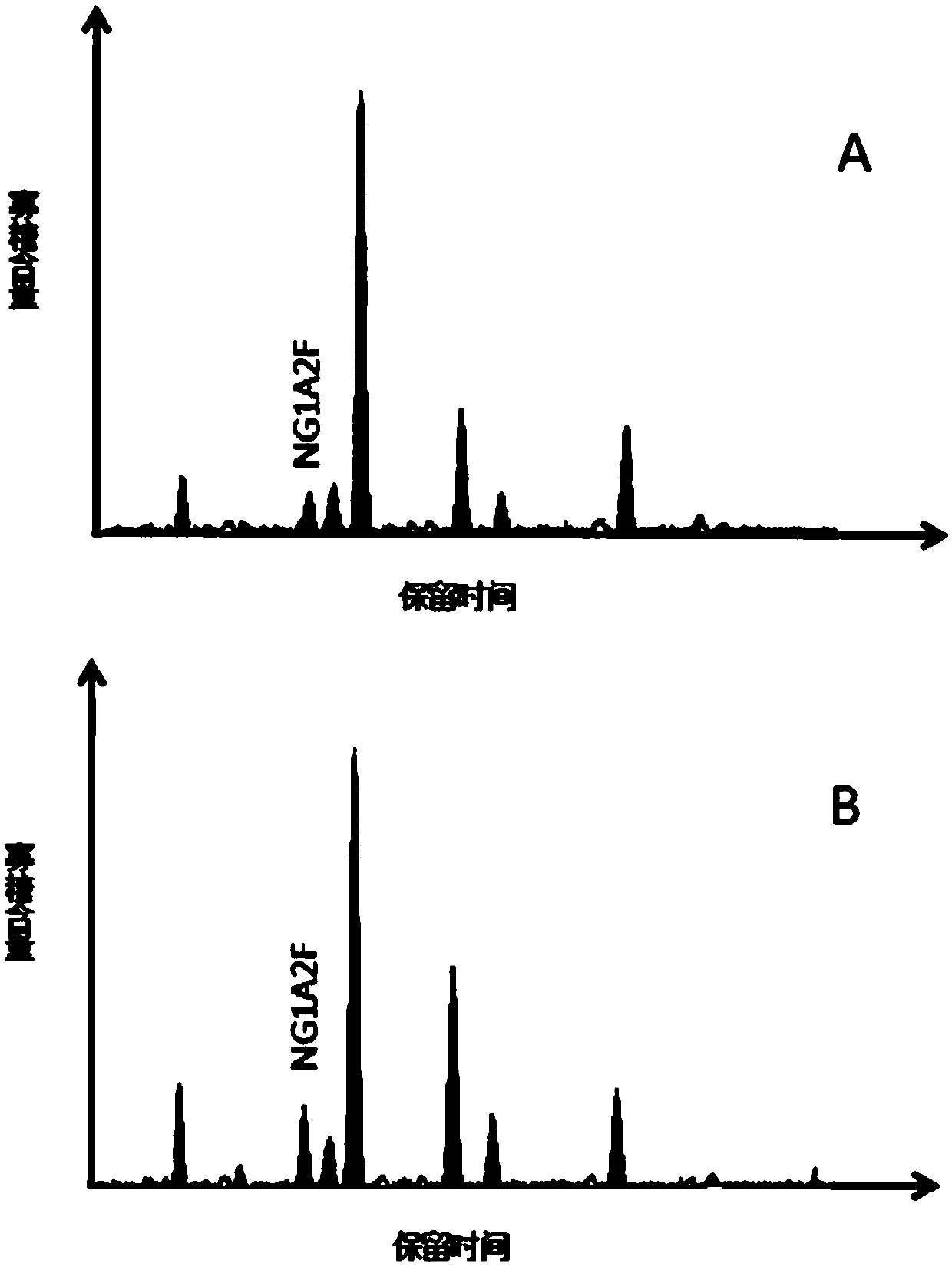
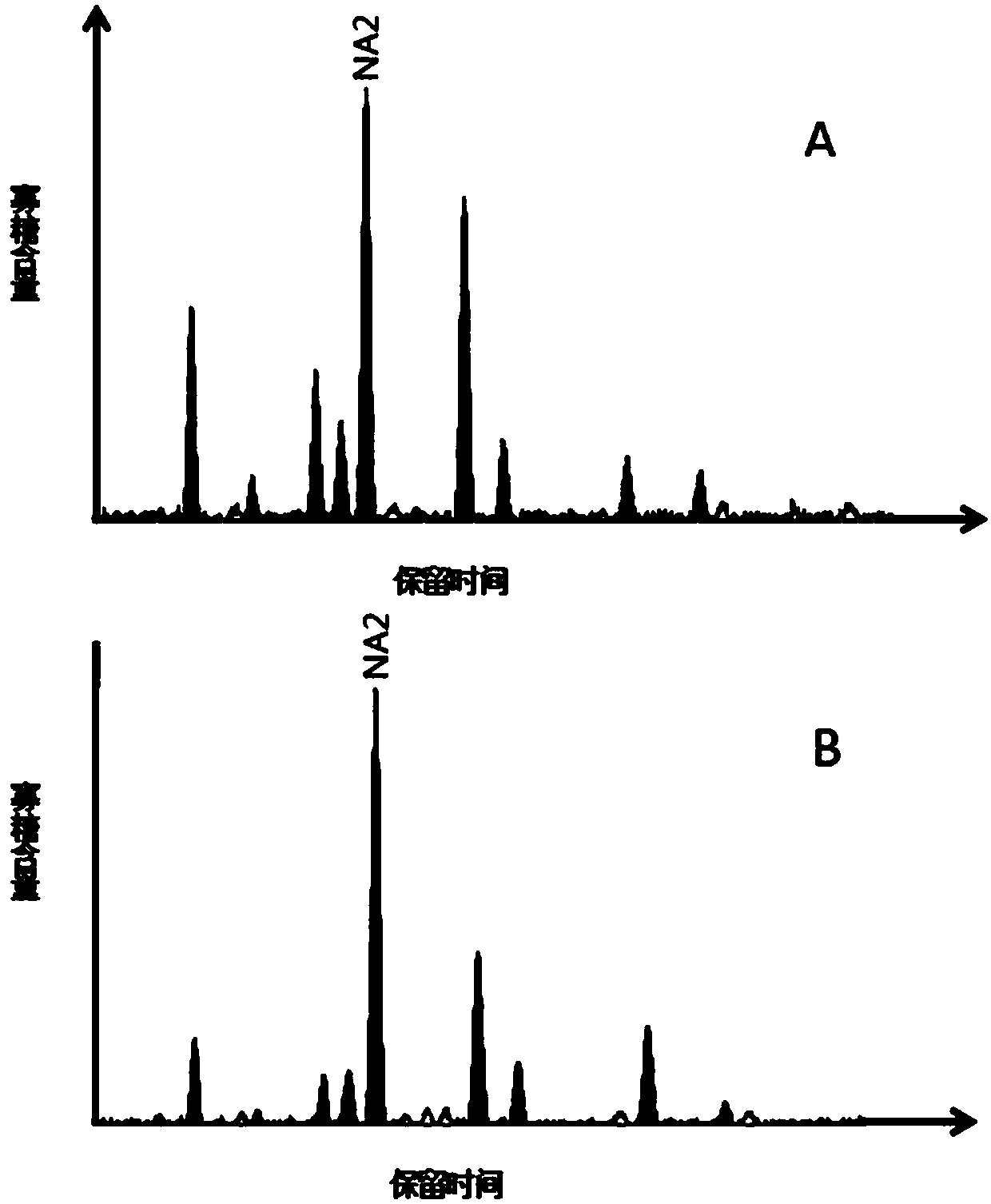
Method for establishing seroglycoid N-glycome atlas model of chronic hepatitis liver injury
PendingCN109100507ATimely monitoringHigh sensitivityMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingChronic hepatitisNormal control
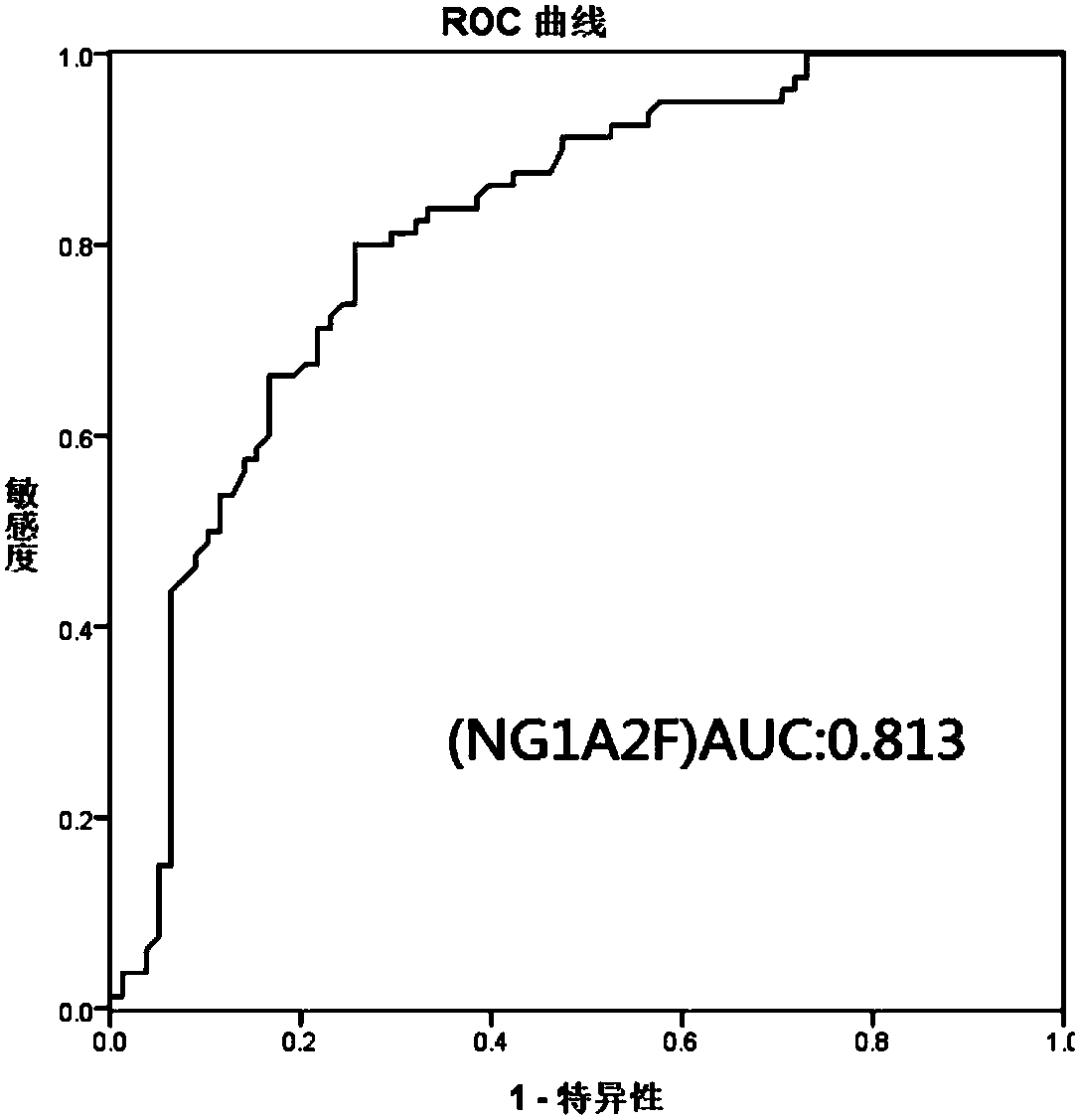
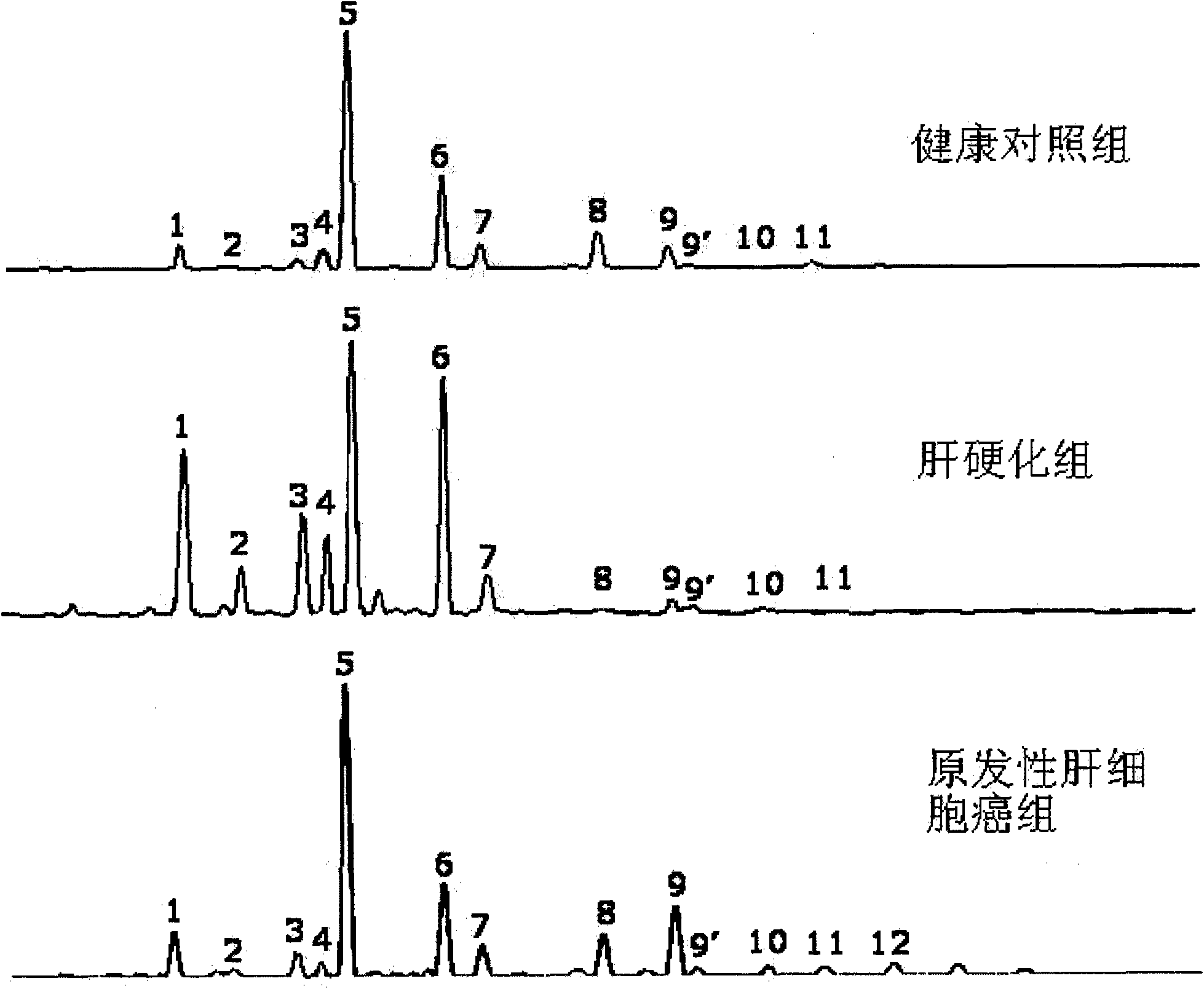
The invention discloses a method for establishing a seroglycoid N-glycome atlas model of chronic hepatitis liver injury. The method comprises the following steps: detecting a seroglycoid N-glycome atlas by using a G-Test detection method, establishing an N-glycome atlas model with significant difference between liver injury patients and normal control personnel, and screening NG1A2F with significant expression difference between a liver injury group and a normal control group. Based on the N-glycome atlas model established by the method disclosed by the invention, the detection sensitivity andspecificity of liver injury respectively reach 80.0% and 74.4%. In subsequent applications, the degree of liver injury of personnel to be detected can be detected by comparing the peak values of single peak NG1A2F in the N-glycome atlas of the serum of the personnel to be detected and in the atlas model established by the method. Based on the method disclosed by the invention, a plurality of patients with chronic hepatitis liver injury can be subjected to routine and non-invasive detection to help doctors and the patients to monitor the occurrence and progression of the chronic hepatitis liver injury in time, and the method is expected to be promoted and used in clinical practice.
Owner:JIANGSU XIANSIDA BIOTECH CO LTD +1
Separation and purification method of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome and application of human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome
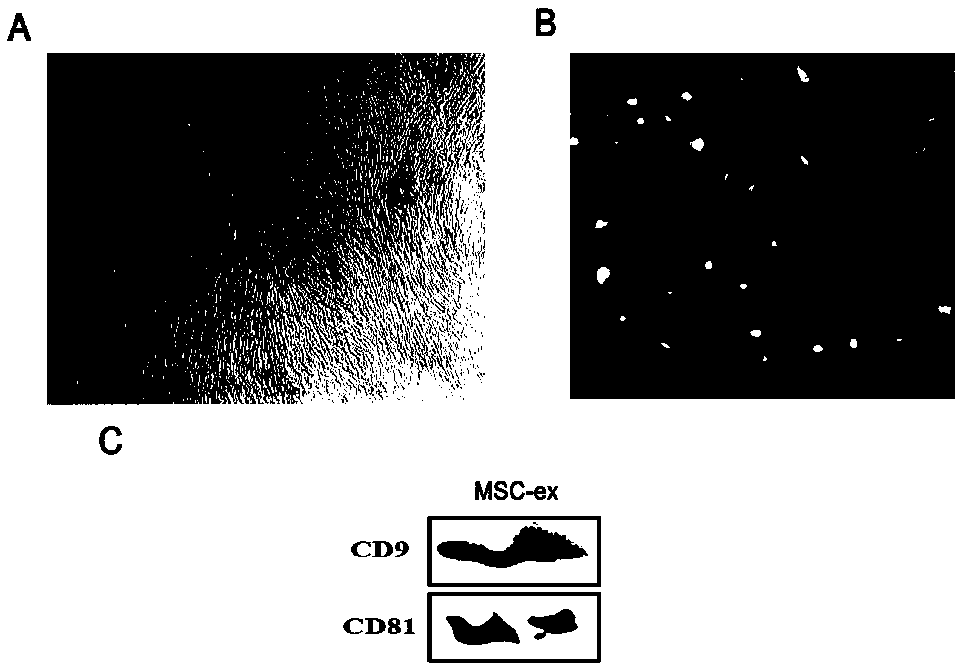
ActiveCN108103017AHigh protein purityGood repeatabilityMetabolism disorderSkeletal/connective tissue cellsSucrosePurification methods
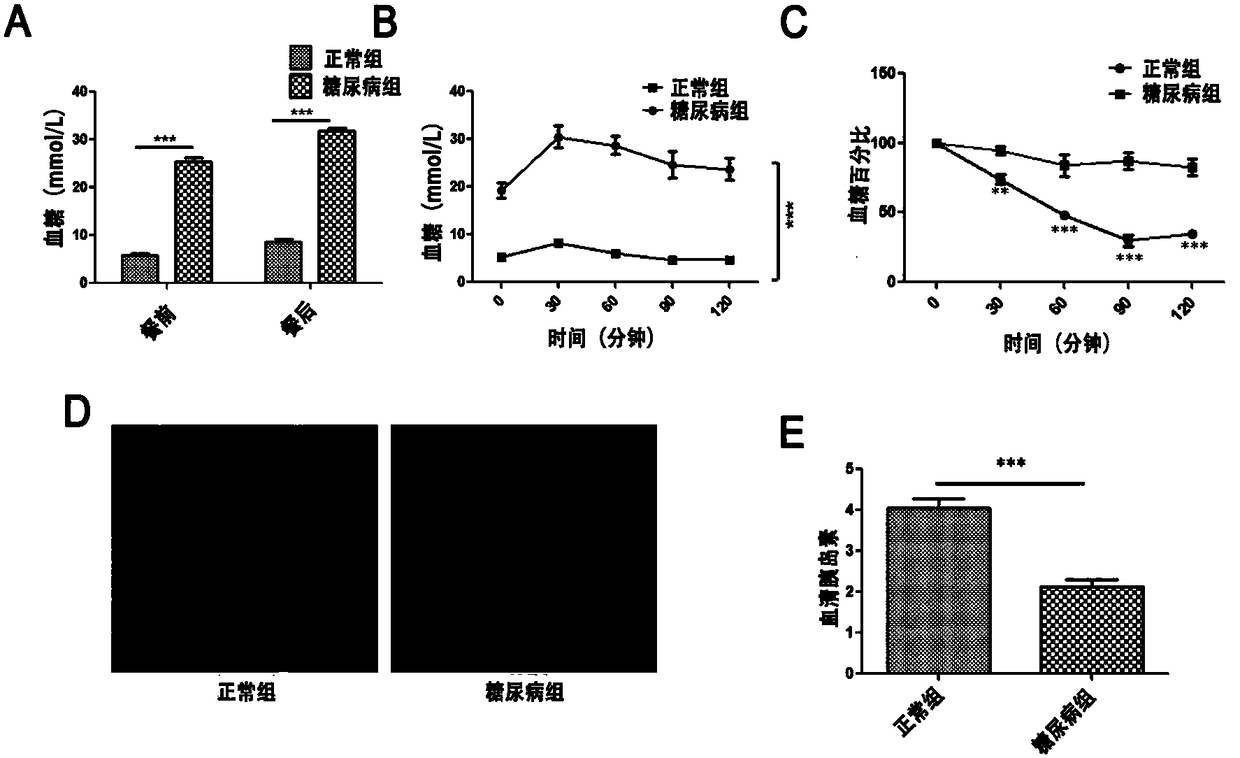
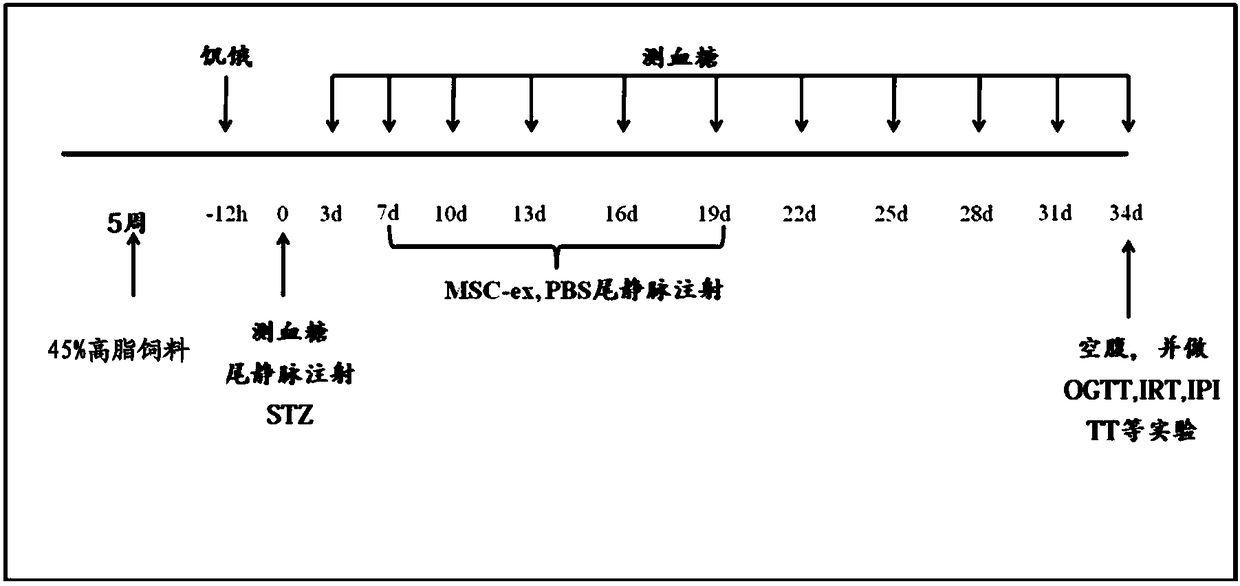
The invention provides a separation and purification method of a human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome and an application of the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome, and belongs to the technical field of medicines. The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome provided by the invention is prepared by cultivating human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via aserum-free medium, collecting supernatant liquid, implementing centrifuging as well as ultra-filtration and concentration, transferring a concentrated solution onto a 30% sucrose-heavy water densitypad and implementing further purification through sucrose density centrifuging, so that the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome is obtained. According to the separation and purificationmethod that the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome is obtained through separation and purification, immunoreactivity is effectively reduced, and a controllable dosage when the human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome is used is guaranteed. The human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell exosome, by improving a degree of activating an insulin signaling pathway of a type IIdiabetes animal model, can inhibit composition and decomposition of hepatic glycogen, so that glucose metabolism homeostasis can be achieved; and meanwhile, the sensitivity of the type II diabetes animal model to insulin and an insulin secretion function of pancreatic [beta] cells can be improved and a blood glucose concentration can be reduced, so that the application of the human umbilical cordmesenchymal stem cell exosome to the preparation of medicines for treating type II diabetes can be achieved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Novel Carbohydrate Profile Compositions From Human Cells and Methods for Analysis and Modification Thereof
Owner:GLYKOS FINLAND
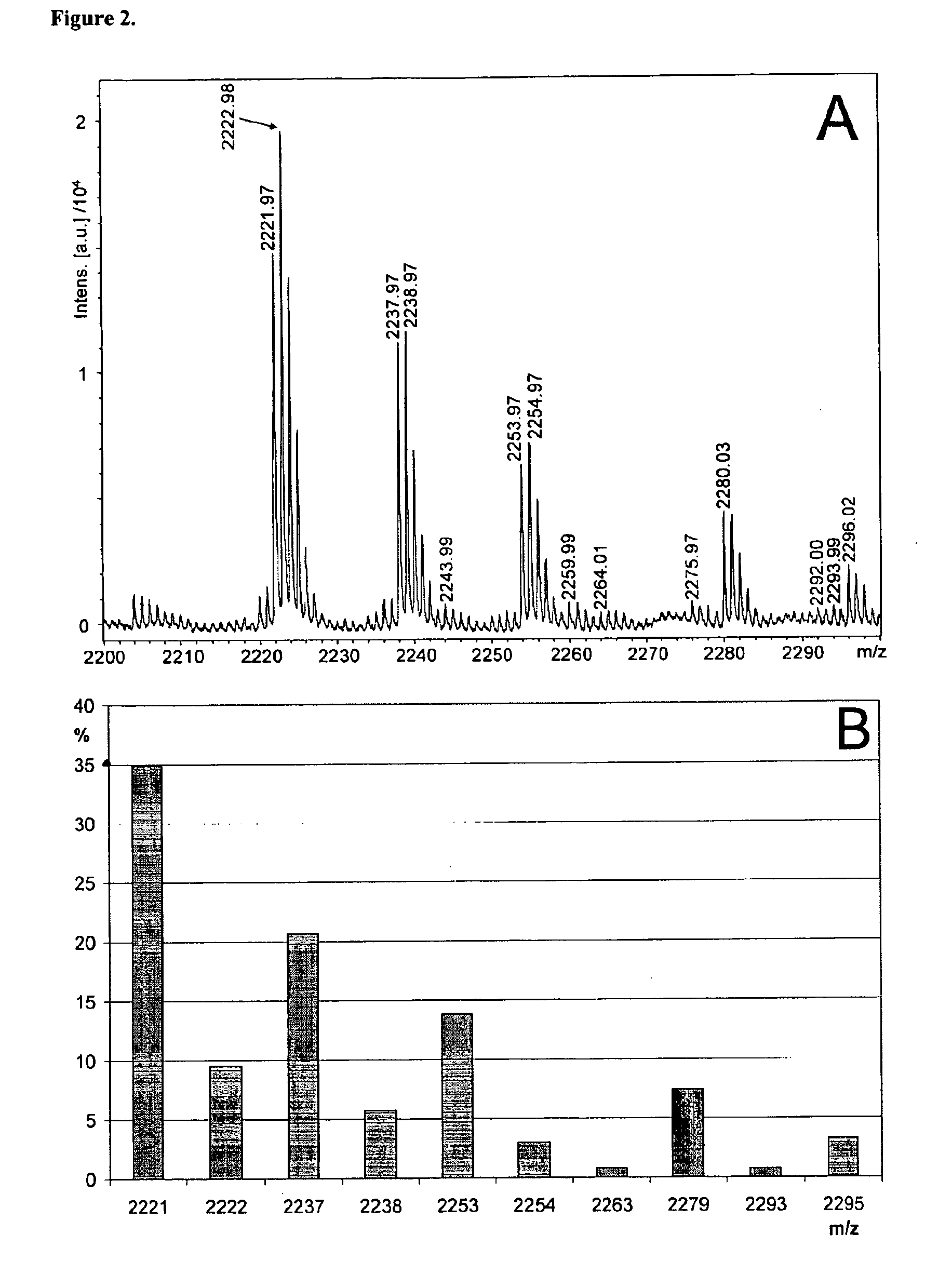
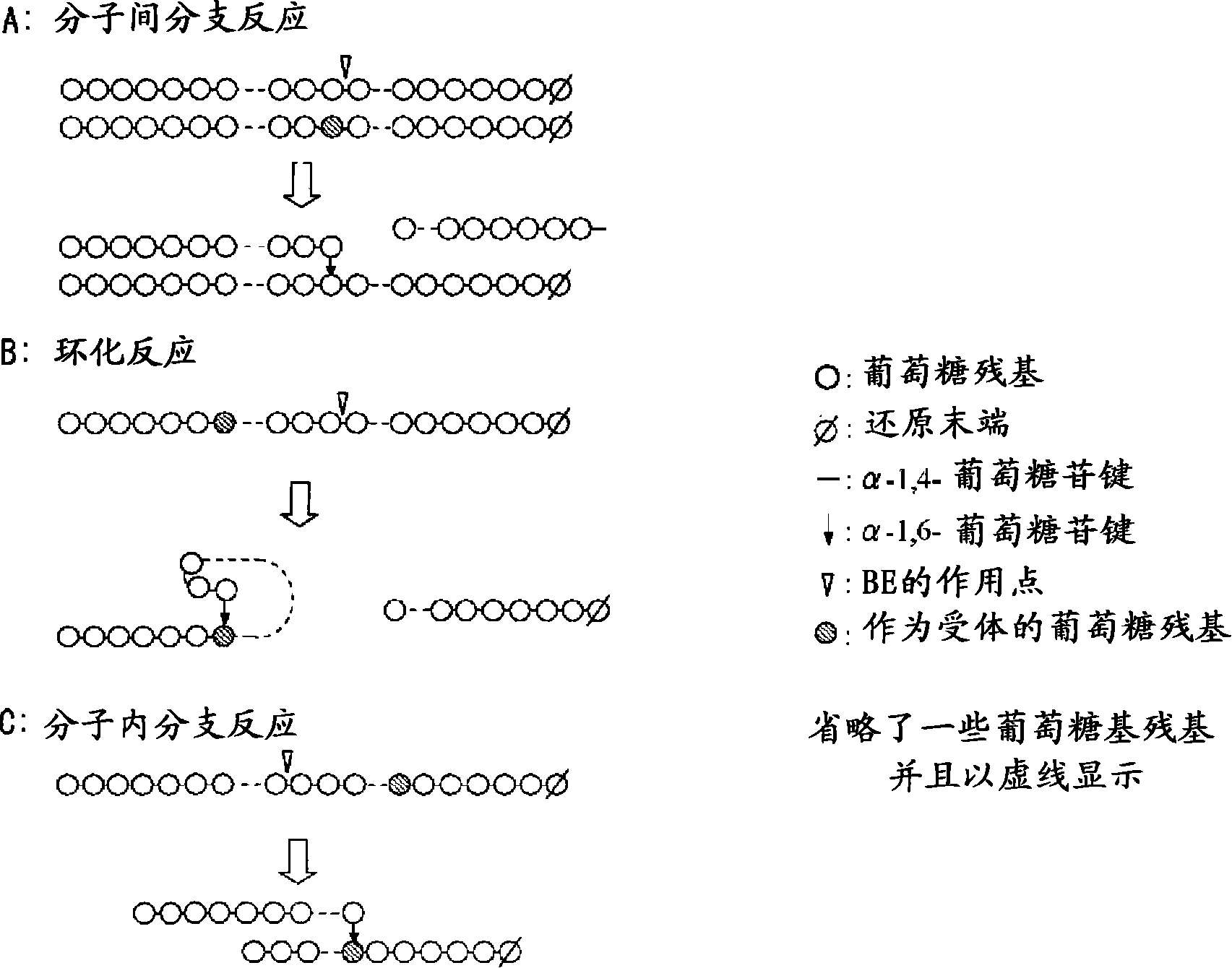
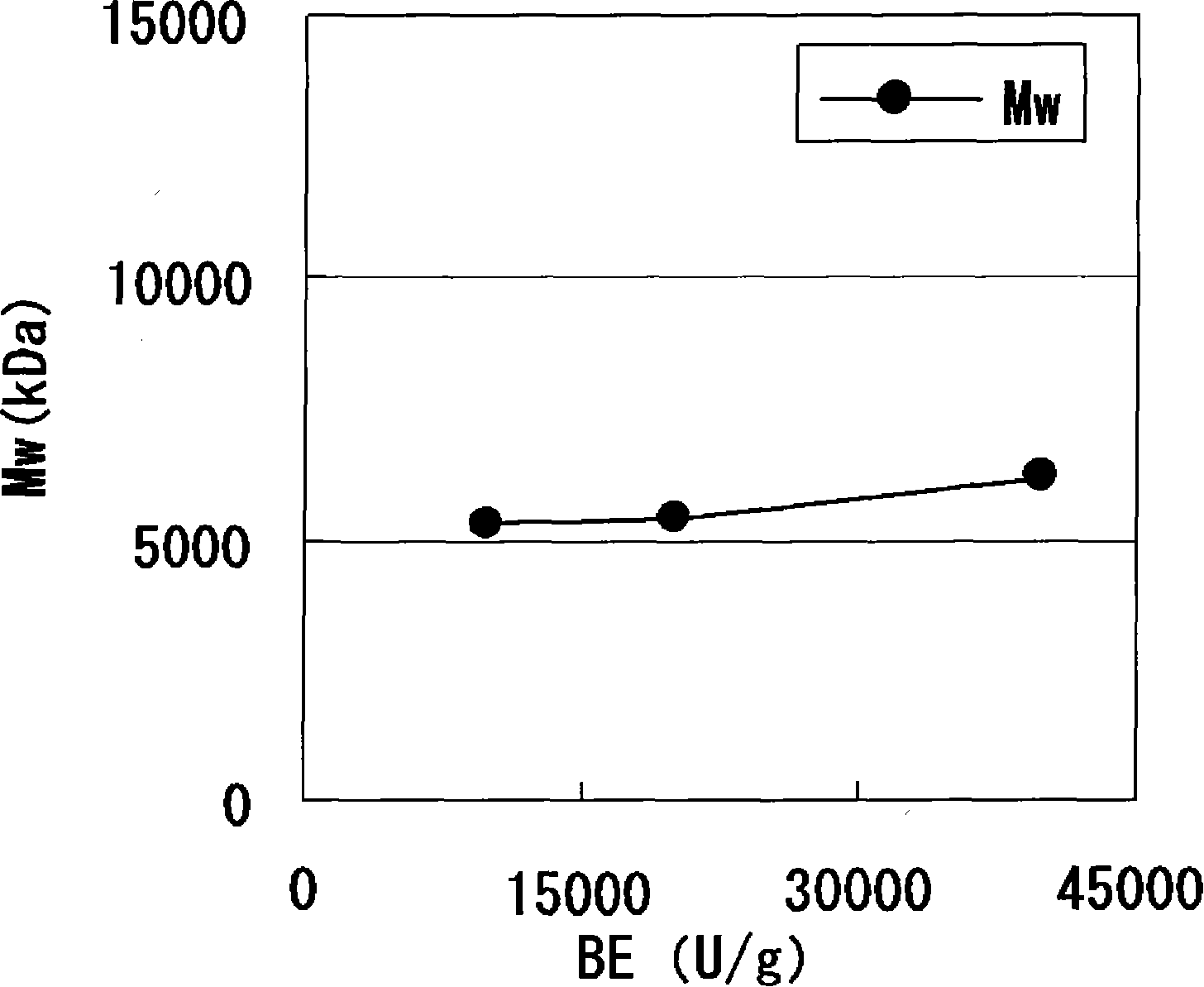
Method of producing glycogen
A method of producing glycogen comprising a step of: allowing a branching enzyme having the ability to synthesize glycogen to act on a substrate in a solution to produce a glycogen, wherein the substrate is an ±-glucan being linked mainly with ±-1,4-glucosidic bonds and having a degree of polymerization of 4 or more, and the number-average molecular weight of saccharides in the solution before initiation of the reaction is more than 180 but not more than 150,000. (The branching enzyme activity of the branching enzyme) / (the molecular-weight-decreasing activity of the branching enzyme) can be 500 or less. The branching enzyme can be a thermostable branching enzyme.
Owner:EZAKI GLICO CO LTD
SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker related to Crassostrea gigas glycogen content character and application thereof
ActiveCN104152444AAvoid the use of concentrated acid and alkaliSimple and safe operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDebranching enzyme activityCrassostrea
The invention relates to an SNP (single-nucleotide polymorphism) marker related to Crassostrea gigas glycogen content character and application thereof. The site of the SNP marker is named TY202 and positioned on the 3rd exon of the glycogen debranching enzyme gene, and the genotype is Y. The TY202 is positioned on the 7022nd base at the 5' end of the glycogen debranching enzyme gene. The 3rd exon is positioned on the 6446-7043 base pair at the 5' end of the glycogen debranching enzyme gene. The glycogen content of the individual with the SNP marker site genotype of T / T or T / C is higher than that of the individual with the genotype of C / C. The method for detecting the individual genotype can be utilized to predict the glycogen content of the individual. When being used in breeding, the SNP marker can be used for selecting the target individual and for molecular marker assisted selective breeding. The SNP marker avoids using concentrated acid or concentrated alkali in the glycogen detection process, thereby being safer and more convenient to operate.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms with reduced glycogen and their use in producing carbon-based products
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, including Cyanobacteria, that contain one or more mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen as compared to a wild type Cyanobacterium, and which are capable of producing an increased amount of lipids and / or fatty acids. In certain embodiments, the genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms also contain one or more exogenous genes encoding a diacyglycerol acyltransferase, a phosphatidate phosphatase, and / or an acetyl-CoA carboxylase, and which are capable of producing increased amounts of lipids or fatty acids and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:LUMEN BIOSCI INC
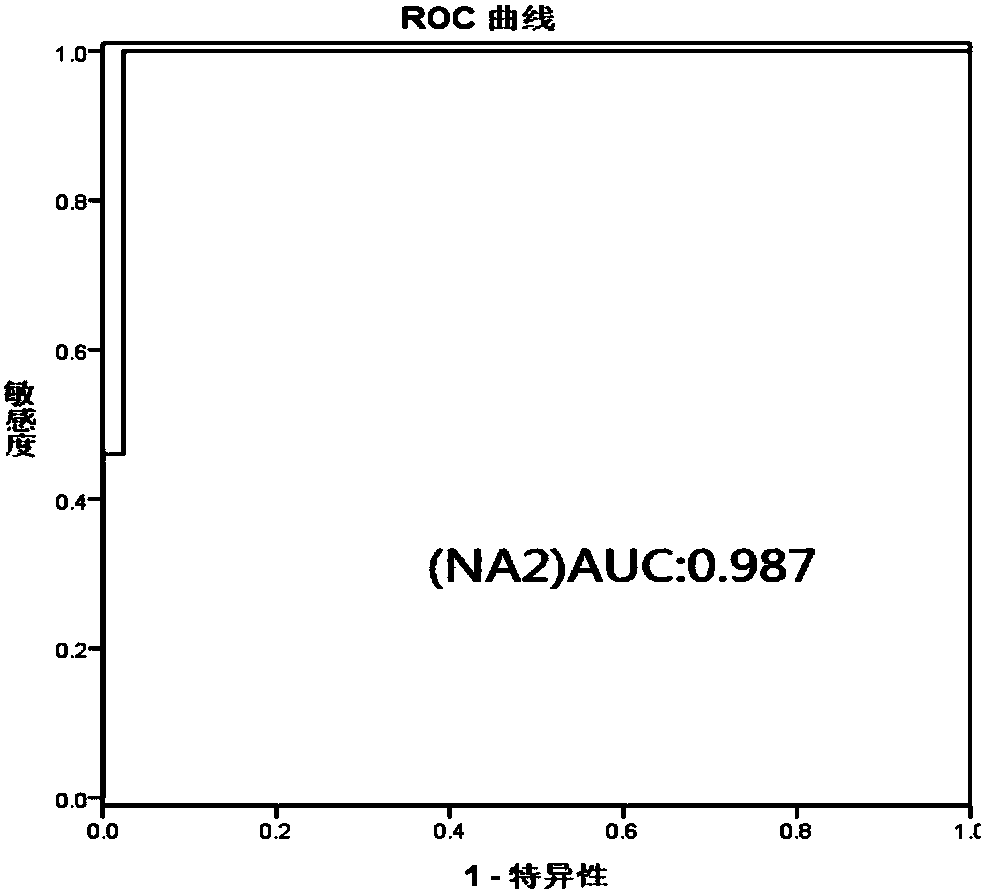
Hepatic failure serum glycoprotein N-glycome map model establishing method
The invention discloses a hepatic failure serum glycoprotein N-glycome map model establishing method, wherein a serum glycoprotein N-glycome map is detected by using a G-Test detection method, the N-glycome map model having significant difference between hepatic failure patients and normal control people is established, and the NA2 having significant expression difference between the hepatic failure group and the normal control group is screened. According to the present invention, the hepatic failure detection sensitivity and the hepatic failure detection specificity of the N-glycome map model constructed based on the method of the present invention respectively are 100.0% and 97.6%; in the subsequent applications, by comparing the peak value of the single-peak NA2 in the serum glycoprotein N-glycome map of the person to be detected and in the map model established by the method of the present invention, the hepatic failure degree of the person to be detected can be detected; and baseon the method of the present invention, a large number of hepatic failure patients can be subjected to conventional and non-invasive detection so as to help doctors and patients timely monitor the occurrence and the progression of hepatic failure, such that the method is expected to be popularized in clinical practice.
Owner:JIANGSU XIANSIDA BIOTECH CO LTD +1
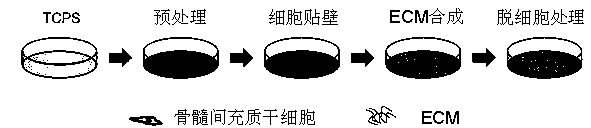
Method for autocrine secretion of extracellular matrix by stem cells and induction of stem cells to become hepatocytes
InactiveCN103396982AGood for mutual contactAchieve induced differentiationArtificial cell constructsVertebrate cellsCell-Extracellular MatrixECM Protein
The invention provides an application of a method for the autocrine secretion of an extracellular matrix by stem cells and the induction of the stem cells to become hepatocytes. The extracellular matrix is secreted by inducing bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and removes the matrix of the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. The invention concretely provides the method for inducing the bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes by the extracellular matrix according to actual demands. The method for generating the hepatocytes through induction has the advantages of high efficiency, practicality, high induction efficiency and good differentiation effect, and the glycogen synthesis capability and the urea synthesis capability of the hepatocytes obtained after the induction are strong.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
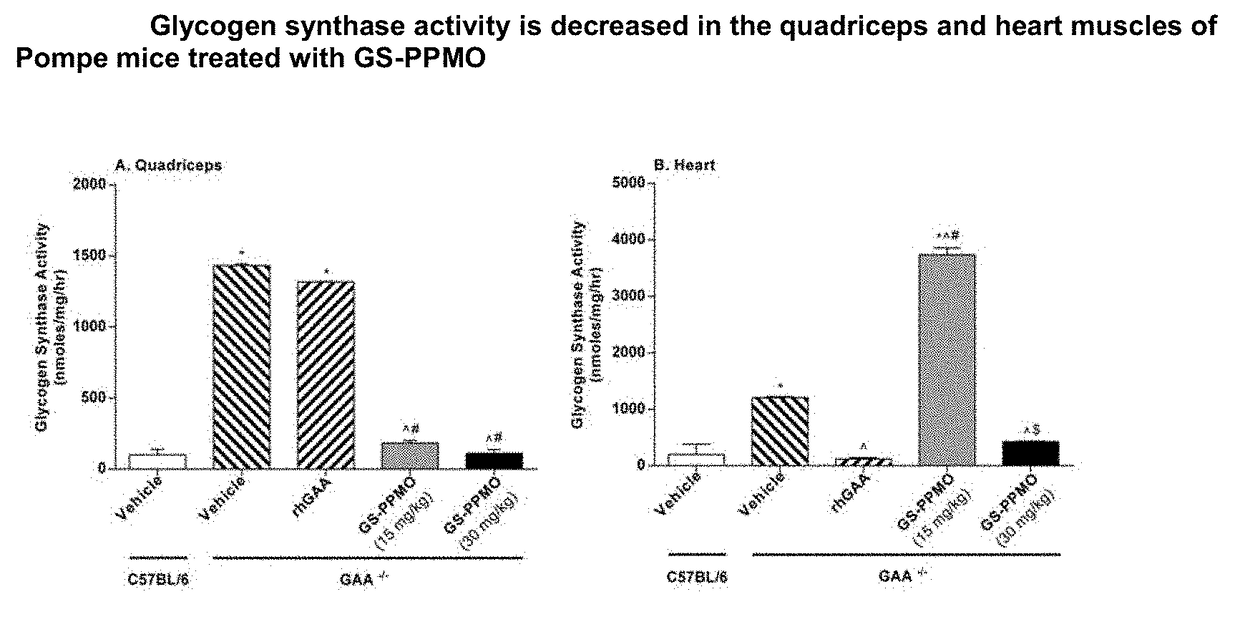
Inhibiting or downregulating glycogen synthase by creating premature stop codons using antisense oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20170182189A1Suppressed accumulation of glycogenDecreasing glycogen accumulationSplicing alterationMetabolism disorderDiseasePremature Stop Codon
The present disclosure relates to antisense oligonucleotides (AONs) for modulating the expression of glycogen synthase. AONs of the present disclosure may be useful in treating diseases associated with the modulation of the expression of the enzyme glycogen synthase, such as Pompe disease. Also provided by the present disclosure are compositions comprising AONs, as well as methods of down regulating mRNA coding for glycogen synthase, methods for reducing glycogen synthase in skeletal and cardiac muscle, and methods for treating Pompe disease.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Reagent composition for separating total RNA in plant or microorganism and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102443580AQuality improvementOvercoming selectivityDNA preparationSodium acetatePrecipitation
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology method and relates to a reagent composition for separating total RNA in a plant or a microorganism and a preparation method thereof. The high quality RNA can be obtained after a simple extraction by chloroform while guanidinium isothiocyanate and phenol are regarded as main components, positive ions are provided by NaCl, MgCl2 and the like, and a solution pH is stabilized by a sodium acetate-acetic acid buffer system. Glycogen serving as a nucleic acid precipitant is added in the RNA extraction reagent in the invention, so that the reagent disclosed by the invention, in comparison with reagents of the same type, greatly improves precipitation efficiency of the nucleic acid and also can efficiently separate the nucleic acid component which has a very low content in a tissue sample. Therefore, the nucleic acid precipitation process can be finished in a short period, the precipitation process at -20 DEG C for hours is avoided, and operating time is shortened greatly. The method is rapid as well as efficient and has wide applicable samples; and the reagent composition disclosed by the invention is cheaper than commercial TRIzol reagents. The disadvantages of high sample selectivity, fussy operation and relatively low efficiency of the traditional method are overcome. The operation is more flexible; and the sample after being homogenized can be stored at -20 DEG C and then used for the RNA extraction.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Preparation method for deer blood peptide and anti-fatigue effect of deer blood peptide
InactiveCN107164446AWorks well togetherHydrolysed protein ingredientsAntinoxious agentsFiltrationHydrolysis
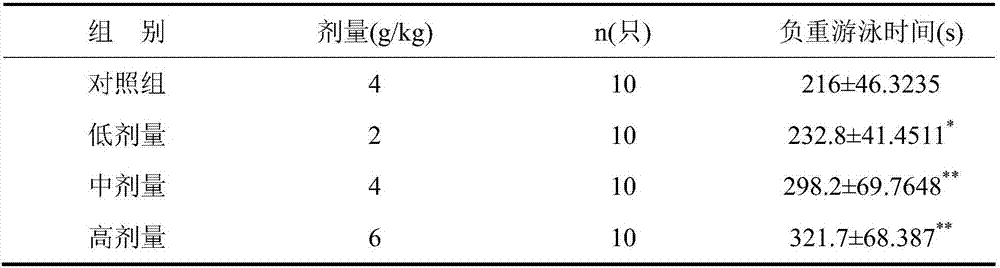
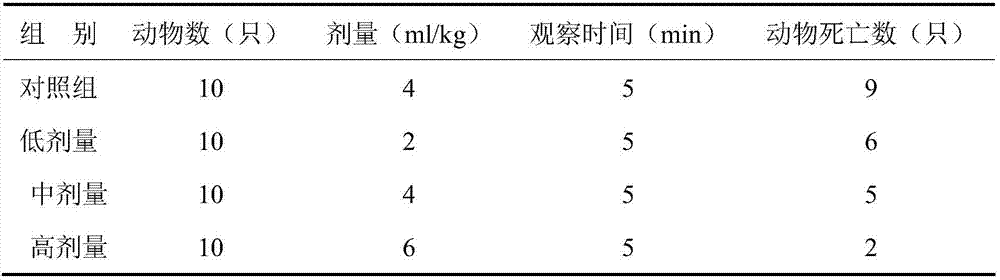
The invention relates to a preparation method of deer blood peptide and its anti-fatigue effect, belonging to the field of medicine. Drying of deer blood: use a spray dryer, adjust the inlet temperature to 180°C, the outlet temperature to 80°C, and the speed to 26,000-30,000 rpm; deer blood protein hydrolysis: the concentration of deer blood protein is 3%, and alkaline protease is used for hydrolysis , The hydrolysis conditions are: temperature 53°C, time 5.5h, pH 9.5, enzyme amount 1272u / g; purification of deer blood peptide: membrane filtration and gel chromatography. In the present invention, the anti-fatigue experiment of mice is used to study the activity of the deer blood peptide. Animal experiments show that the polypeptide produced by the optimal hydrolysis process can significantly prolong the swimming time and low-pressure hypoxia tolerance of mice, the content of liver glycogen is significantly higher than that of the control group, and the content of blood lactic acid is significantly lower than that of the control group; It has good anti-fatigue effect.
Owner:吉林省金鹿药业有限公司
Modified photosynthetic microorganisms for producing lipids
InactiveUS20140004580A1Promote cell growthIncrease productionUnicellular algaeOxidoreductasesPhylum CyanobacteriaWild type
This disclosure describes genetically modified photosynthetic microorganisms, e.g., Cyanobacteria, that overexpress an acyl-acyl carrier protein reductase (acyl-ACP reductase). These microorganisms may optionally overexpress one or more fatty acid synthesis proteins such as ACP and ACCase, and / or one or more polypeptides associated with glycogen breakdown. Also included are photosynthetic microorganisms comprising mutations or deletions in a glycogen biosynthesis or storage pathway, which accumulate a reduced amount of glycogen under reduced nitrogen conditions as compared to a wild type photosynthetic microorganism. The modified photosynthetic microorganisms provided herein are capable of producing increased amounts of lipids such as fatty acids or wax esters and / or synthesizing triglycerides.
Owner:MATRIX GENETICS
Reagent for extracting RNA or DNA virus in body fluid
The invention provides a reagent for extracting RNA or DNA virus in body fluid, which is characterized in that each liter of the reagent comprises the following compositions: 4 to 6 mols of guanidinium isothiocyanate, 1 to 2.5 mols of guanidine hydrochloride, 20 to 50 mmols of sodium citrate, 10 to 30 ml of beta-mercaptoethanol, 5 to 10 grams of sarcosyl, 1.5 to 3 mols of urea, 60 to 100 mg of glycogen, and the balance of water. The efficiency of extracting the RNA or DNA virus by the reagent is high, and high-purity RNA or DNA virus can be stably obtained only by 100 mu L of body fluid sample. When the obtained RNA or DNA is used for quantitative PCR detection, the detection sensitivity can reach 50 copies / mL.
Owner:GUANGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF CHINESE MEDICINE
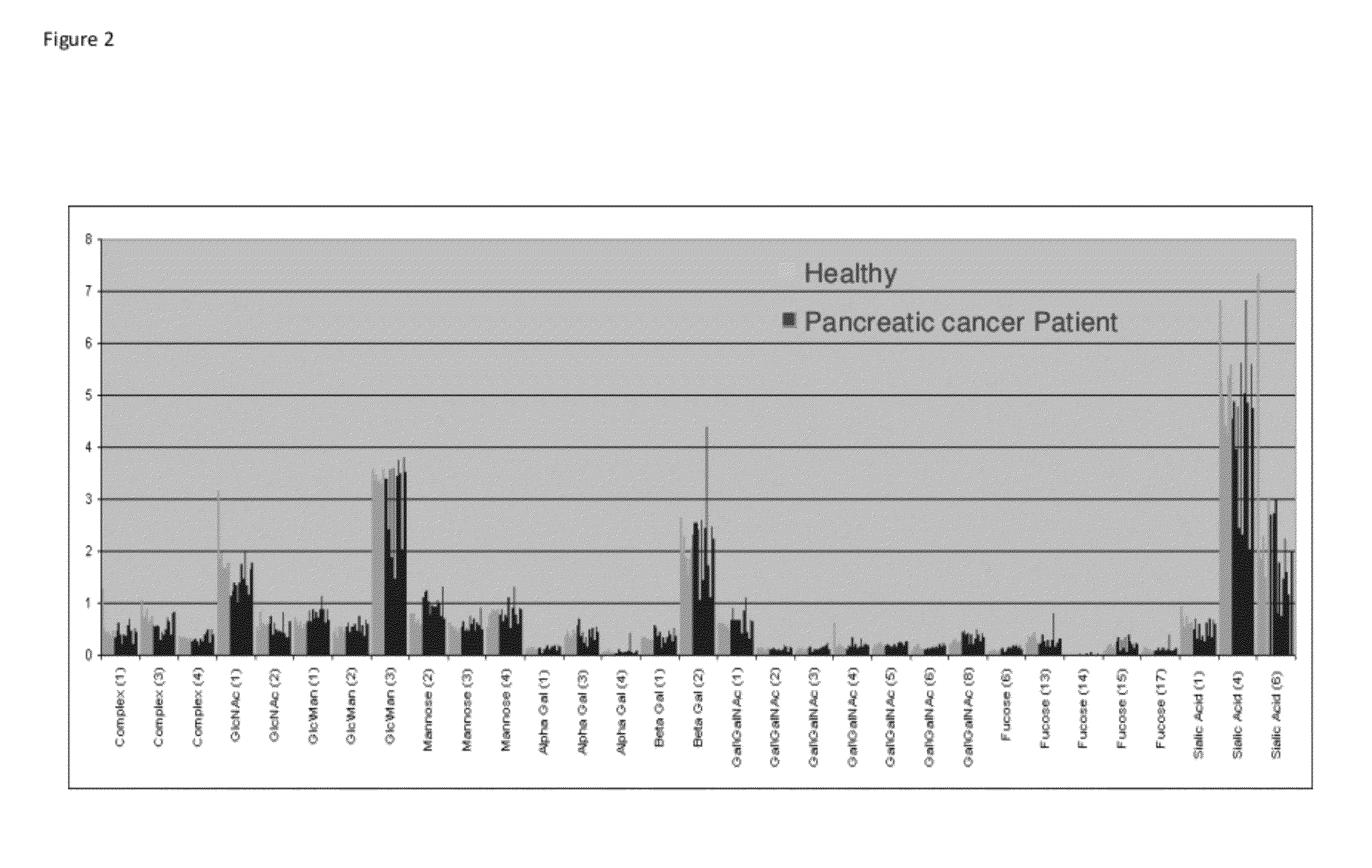
Diagnosis of cancers through glycome analysis
Owner:LANDSTEIN DORIT +8
Collagen peptide-containing lactic acid bacterium powder
InactiveCN101953468AFix stability issuesSolve the requestFood shapingFood preparationCalcium in biologyDigestion
The invention discloses collagen peptide-containing lactic acid bacterium powder, which is prepared from the following raw materials in part by weight: 10 to 30 parts of marine fish skin collagen oligopeptides powder, 10 to 20 parts of citric acid and 30 to 50 parts of multilayer microcapsule lactic acid bacterium powder. In the invention, the problems of low lactic acid bacterium stability and poor storage conditions are solved; the lactic acid bacterium powder is prepared by multilayer microcapsule embedding technology and therefore can be stored at normal temperature; in digestion and absorption, multiple glycome layers ensure the lactic acid bacteria are not damaged by gastric acid; and thus, the lactic acid bacteria can reach the small intestine smoothly so as to be absorbed by human body completely. The lactic acid bacterium powder and the marine collagen peptide are complementary to each other and can improve the immunity of human body and promote the absorption of calcium.
Owner:烟台鸿瑞集团生物科技园有限公司
Method for raising S-adenosyl-L-methionine production level by saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic engineering
ActiveCN105483153AImprove industrial production efficiencyStrong accumulation abilityFungiMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceS-Adenosyl-l-methionine
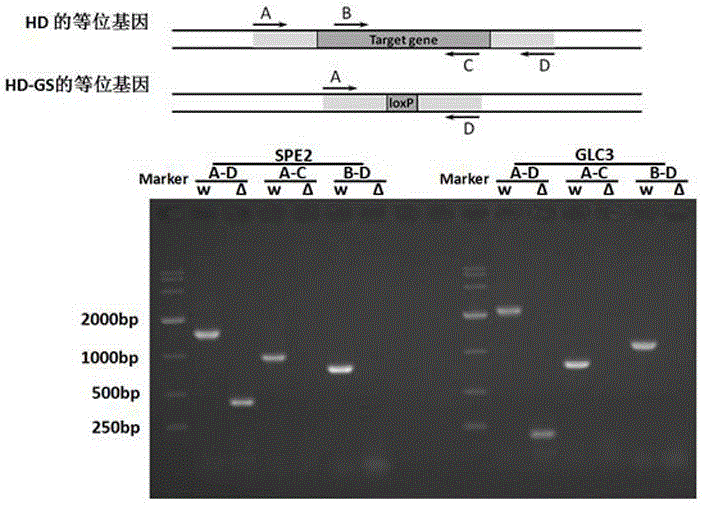
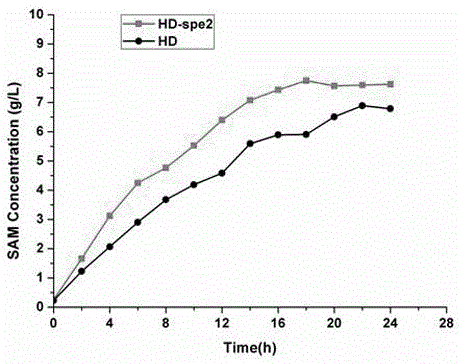
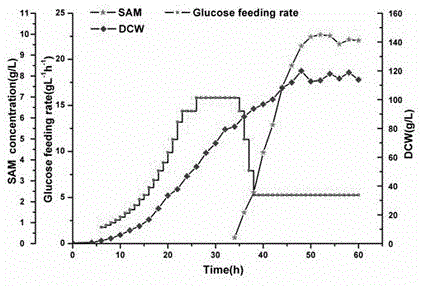
The invention discloses a method for raising S-adenosyl-L-methionine production level by saccharomyces cerevisiae metabolic engineering. By means of saccharomyces cerevisiae gene knockout, an S-adenosylmethionine decarboxylase coding gene SPE2 on a chromosome of saccharomyces cerevisiae is subjected to mutation inactivation to obtain SPE2 mutant strains. Compared with an original saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, the mutant strains have the advantages of high SAM (S-adenosyl-L-methionine) accumulation capability and evident improvement of SAM yield. Particularly, on the basis that the saccharomyces cerevisiae mutant strains are obtained after knockout of a glycogen branching enzyme gene GLC3, knockout of the gene SPE2 is further carried out, or knockout of the gene SPE2 is carried out before knockout of the gene GLC3, yield of ademetionine produced with the saccharomyces cerevisiae strains is evidently increased to be higher than 55.1%.
Owner:SHANDONG JINCHENG BIO PHARMA CO LTD +1
Inhibiting or downregulating glycogen synthase by creating premature stop codons using antisense oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20190117794A1Good effectReduce glycogen synthase enzyme activitySplicing alterationMetabolism disorderDiseasePremature Stop Codon
The present disclosure relates to antisense oligonucleotides (AONs) for modulating the expression of glycogen synthase. AONs of the present disclosure may be useful in treating diseases associated with the modulation of the expression of the enzyme glycogen synthase, such as Pompe disease. Also provided by the present disclosure are compositions comprising AONs, as well as methods of down regulating mRNA coding for glycogen synthase, methods for reducing glycogen synthase in skeletal and cardiac muscle, and methods for treating Pompe disease.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
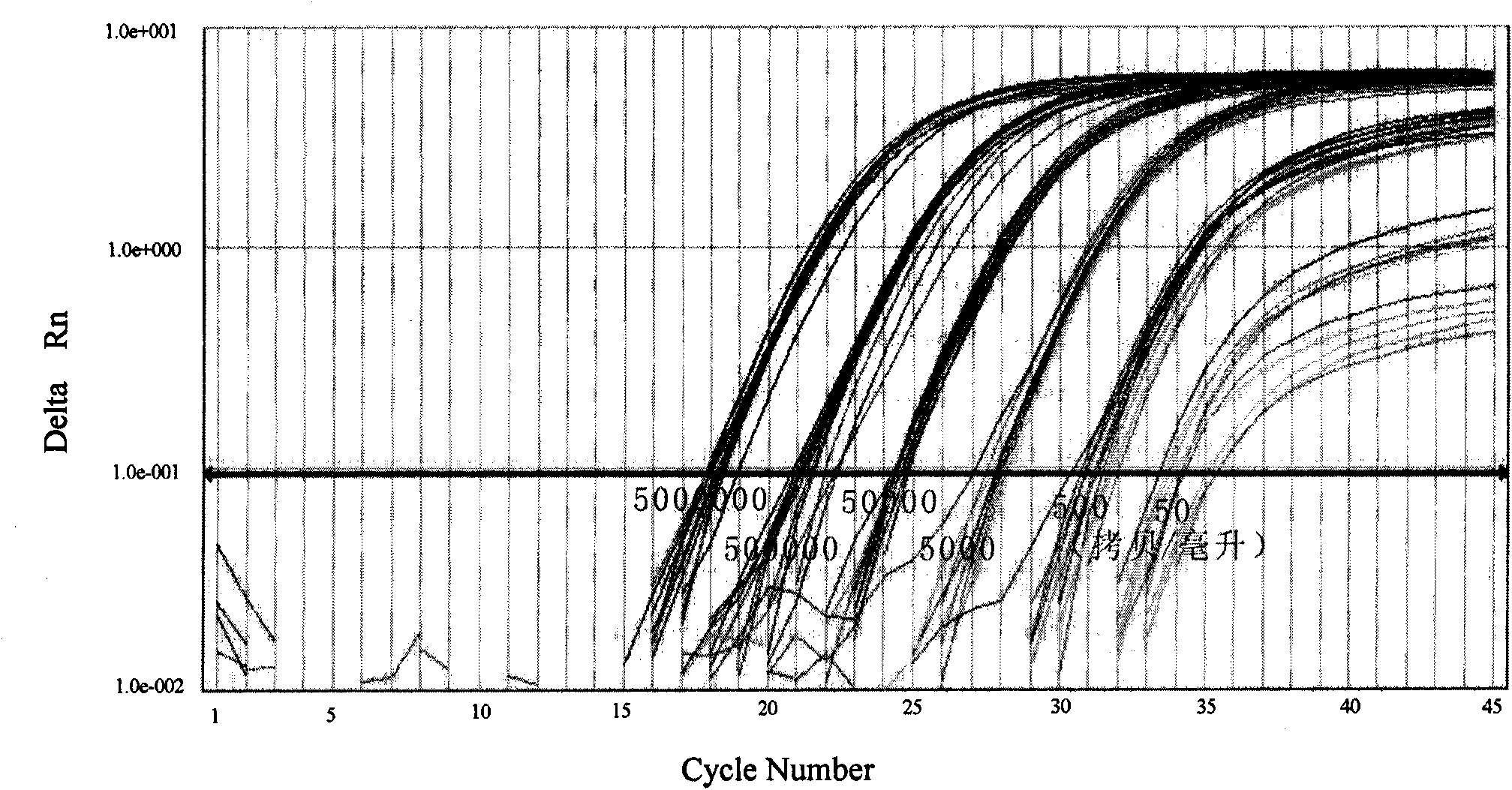
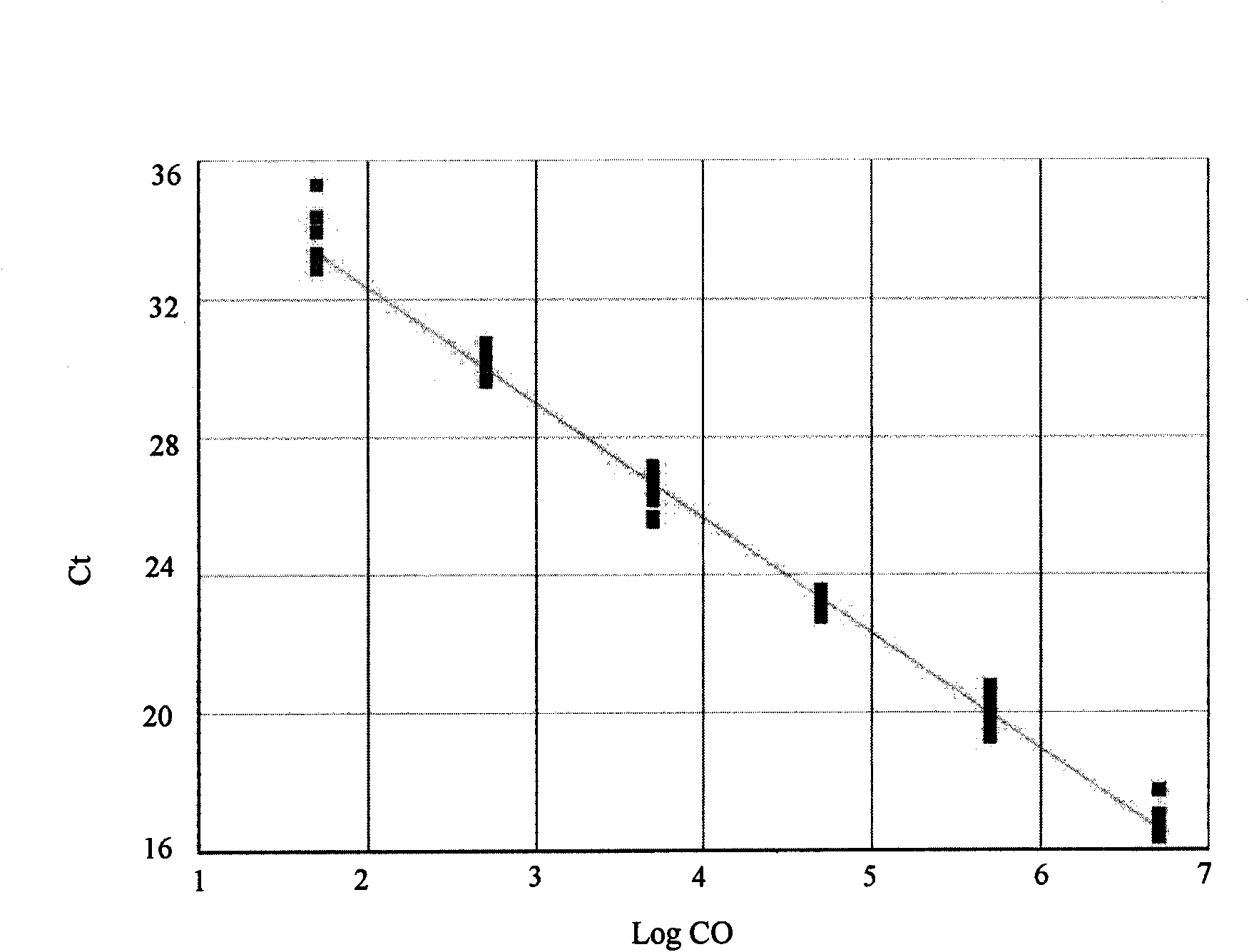
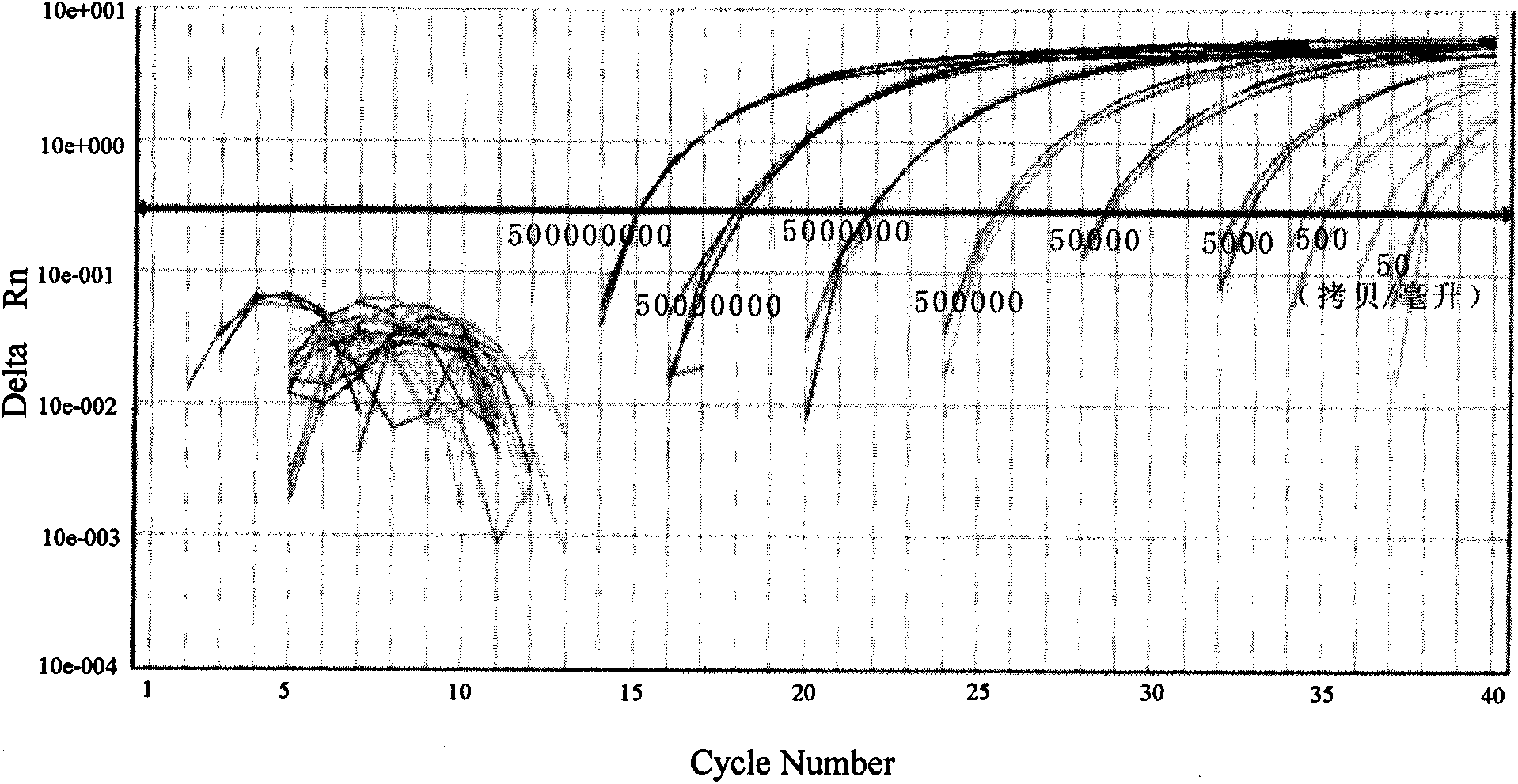
Method for detecting N-glycome log (P9/P4) in serum and detecting system and application thereof
ActiveCN101576495AStrong specificityImprove accuracyMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansBiological testingHigh risk populationsHepatic fibrosis
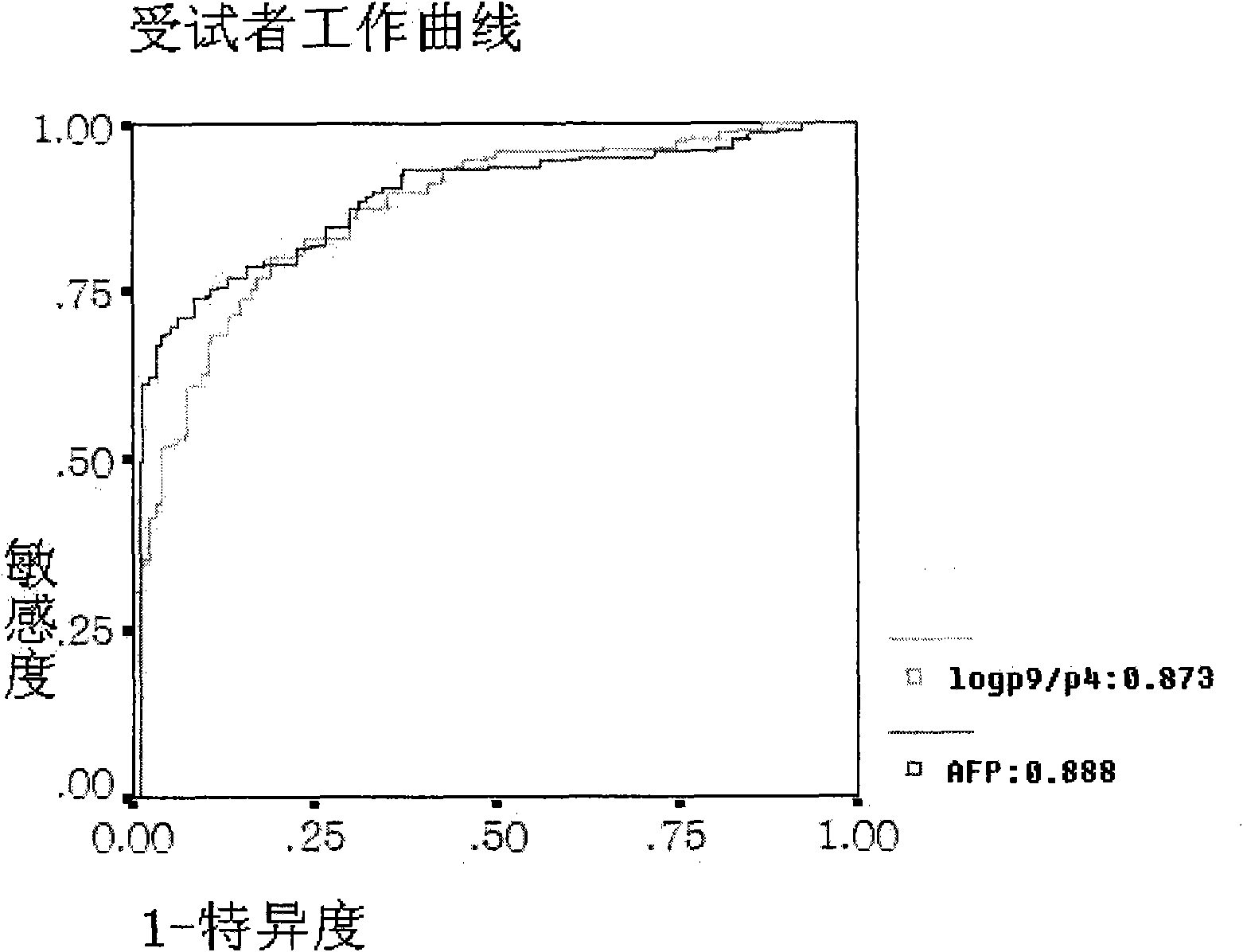
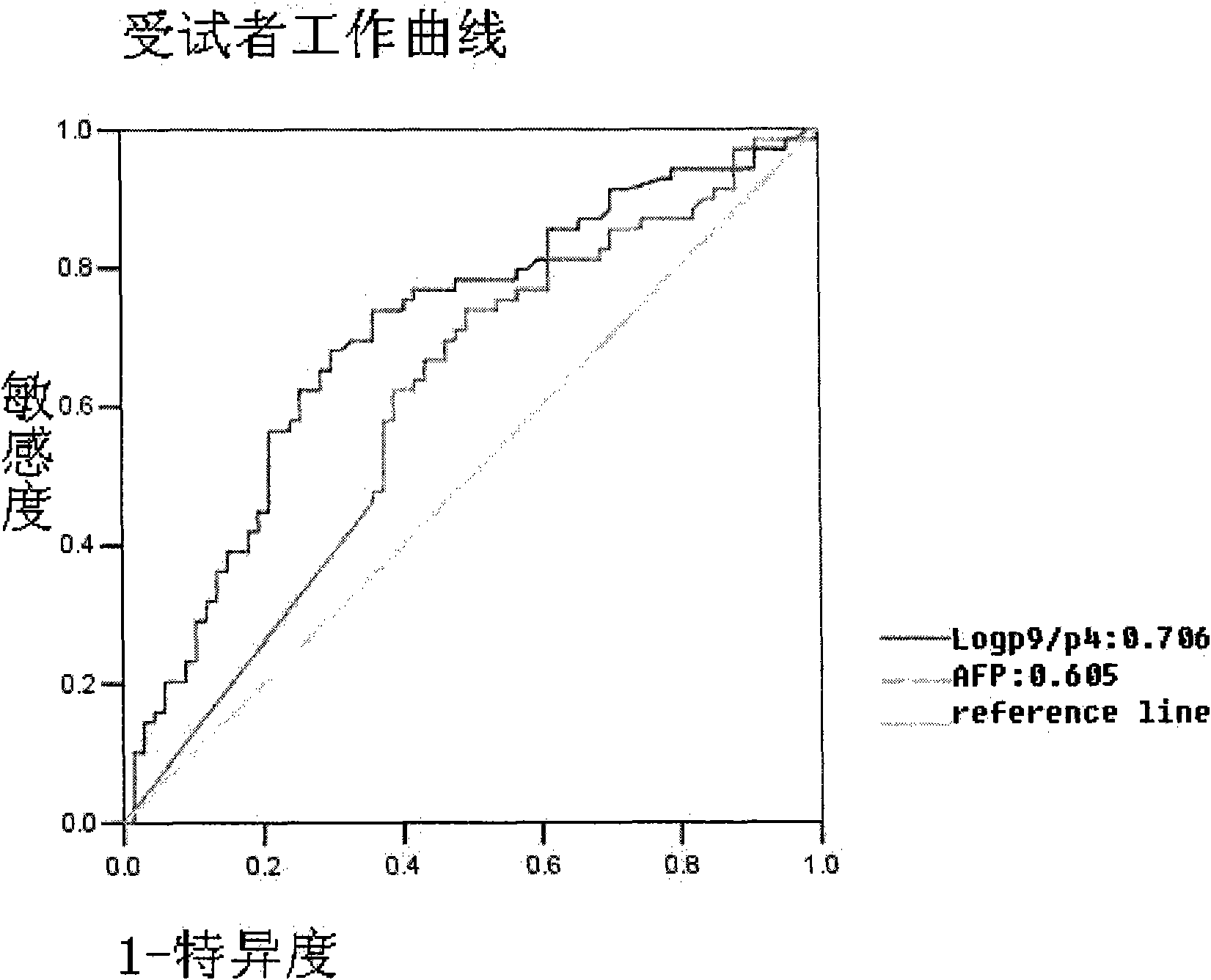
The invention belongs to the diagnostics field of clinical medicine and aims at providing a method for detecting N-glycome log (P9 / P4) in serum so as to overcome defects of prior art that both sensitivity and specificity of AFP detection and supersonic inspection which are adopted to screen high risk group of HCC which is the fifth common malignancy in the world are so low that HCC cannot be detected and treated early. The method is based on DSA-FACE of a DNA sequencer to detect distribution of glycan connected by N-glycosidic bond on glycosidoprotein in serum so as to calculate value of log (P9 / P4). The invention also provides a corresponding detecting system and applies the detecting method and the detecting system to the early screening and diagnosis of HCC, especially to the early screening and diagnosis of tendency of HCC and hepatic fibrosis relevant to HBV inflection. Compared with the AFP detection, the method provided by the invention can raise the specificity and accuracy respectively by 16 percent and 8 percent and has the similar sensitivity.
Owner:SECOND MILITARY MEDICAL UNIV OF THE PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY
Wheat glycogen synthetase kinase gene
InactiveCN1523110ASugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliOpen reading frame
The present invention relates to a wheat glycogen synthetase kinase gene obtained by utilizing cDNA-AFLP technique to clone the salt-stressed specific expression fragment of wheat salt-tolerant mutant, adopting sequence determinatio Blast identification and RACE method. The total length of said gene is 1573bp, in which its open reading frame (ORF) contains 1143 bp, coding 381 amino acids, its coded protein extensively participates in plant response reaction to drought, ABA induction and light induction, specially participates in salt-stressed signal conduction process. After said gene is cloned into prokaryotic expression vector, it can express out a prokaryotic expression product whose molecular weight is 43.6 KD in the colibacillus, i.e. glycogen synthetase kinase protein. Said invention also provides its application field.
Owner:HEBEI NORMAL UNIV
ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN105087516AImprove controllabilitySimple screening methodTransferasesFermentationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
The invention provides an ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant and a screening method and application thereof. The screening method includes the steps of firstly, synthesizing first chain cDNA; secondly, performing PCR amplification; thirdly, building AGPase large and small subunit cDNA prokaryotic expression vectors; fourthly, performing active screening. The method has the advantages that distant hybridization is performed on AGPase large subunit genes and small subunit genes from different species, and the recombinant gene expression vectors are obtained in a highly-controllable manner; escherichia coli glgC mutant strains are converted and inoculated to a Conberg enrichment solid culture medium, and iodine-potassium iodide dyeing is used to screen the high-activity ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant. The screening method is simple and practical and stable and reliable. The enzyme activity and glycogen content of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant are evidently higher than those of wild corn AGPase, evident change of the substrate affinity of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant is avoided, and the sensitivity of the ADP-glucose pyrophosphorylase mutant to activating agent is increased.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Sulphating grifola frondosa insoluble polysaccharide and application
ActiveCN105399849AHigh yieldImprove proliferative abilityImmunological disordersWater bathsN dimethylformamide
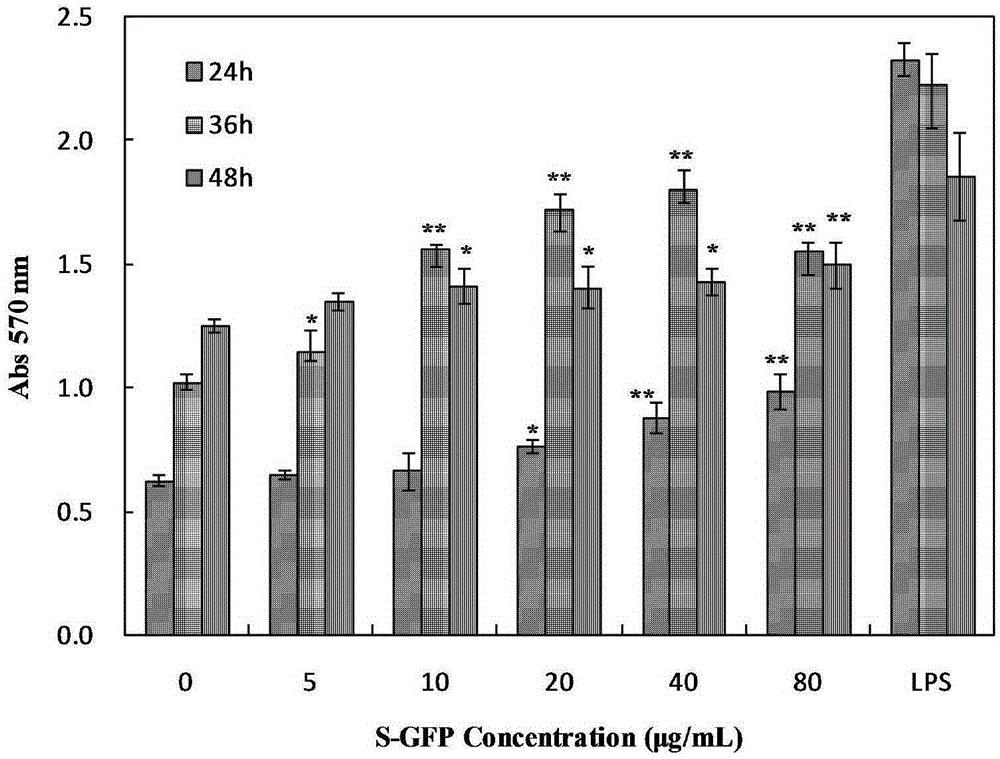
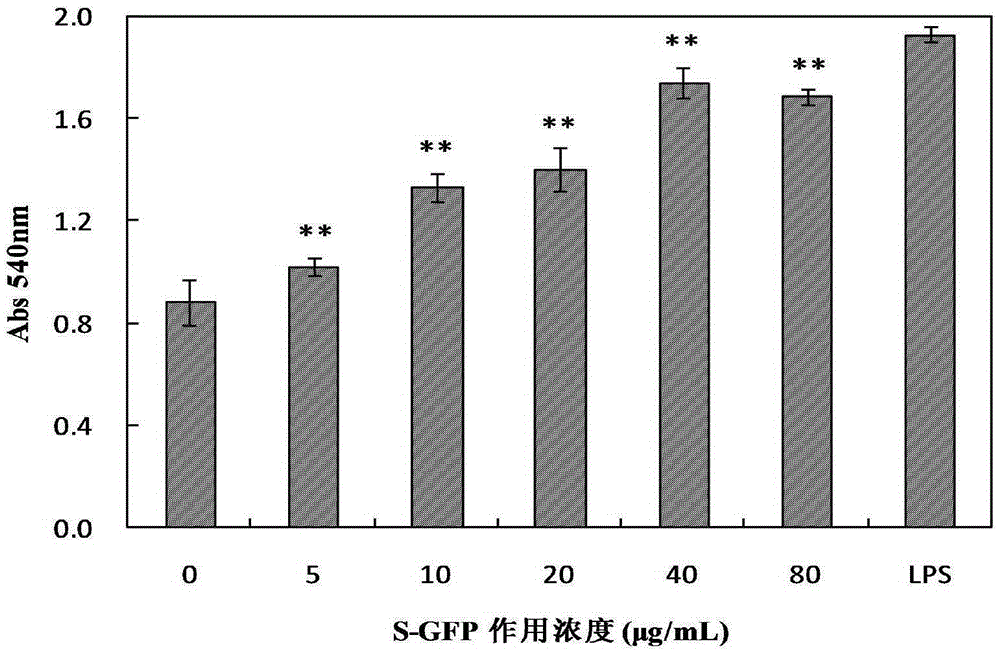
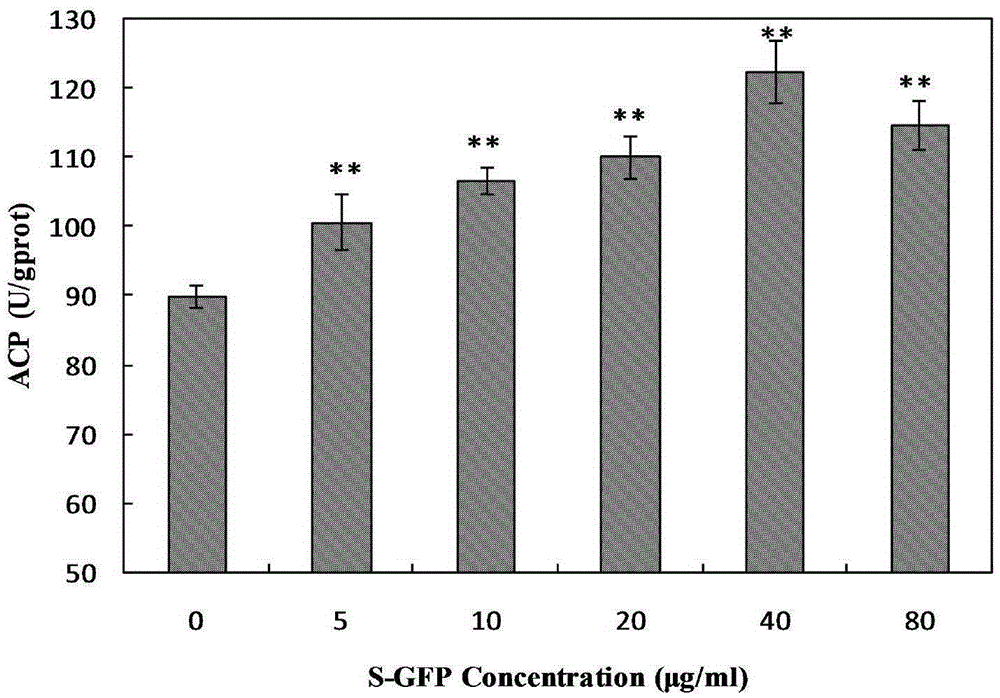
The invention relates to sulphating grifola frondosa insoluble polysaccharide. A preparation method comprises the steps of taking grifola frondosa polysaccharide as a raw material, using N,N-dimethylformamide for swelling, adding sulfur trioxide trimethylamine, and obtaining sulphating grifola frondosa insoluble polysaccharide through water bath reaction, cooling, centrifugation, washing and dialysis. When the polysaccharide is at a certain concentration and time range, an S-GFP can remarkably improve proliferation and phagocytic activity of RAW264.7 cells and have dosage dependence, the optimal action time is 36 h, the optimal action dosage is 40 [mu]g / mL, and secretion and activity of cell acid phosphatase, lysozyme and superoxide dismutase are improved remarkably. The expression of RAW264.7 cell iNOS genes is induced and up-regulated at the mRNA transcriptional level, the generation amount of cell NO is increased, the secretion of cytokines such as IL-2, IL-12, IFN-gamma and IL-6 is promoted, and the sulphating grifola frondosa insoluble polysaccharide is high in immune enhancement activities and can be applied to preparation of medicines or health care products for enhancing immunity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com