Method for autocrine secretion of extracellular matrix by stem cells and induction of stem cells to become hepatocytes
A technology of stem cells and extracellular matrix, applied in the field of stem cell differentiation, can solve the problems of inability to meet basic research and clinical treatment, affect the physiological function of cultured cells, and poor differentiation effect, and achieve good urea synthesis ability, good differentiation effect, and glycogen. The effect of strong synthesis ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Induced production of hepatocytes
[0036] S1. Cross-linking modification of gelatin coating:
[0037] First, add 0.2% gelatin solution to the 12-well plate and place it at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Let stand in the incubator for 1 hour, then add 1% glutaraldehyde solution and 1M ethanolamine solution, and let stand at room temperature for 30 minutes.
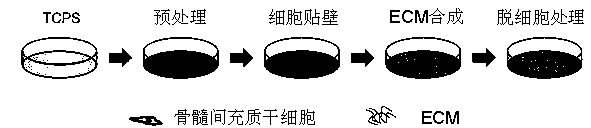
[0038] S2. Induce bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to secrete extracellular matrix, the process is as follows figure 1 Shown:
[0039] Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells were treated at 3,000 cells / cm 2 The density was inoculated into gelatin cross-linked cell culture substrate containing complete medium, complete medium was (α-MEM basal medium, 10% fetal bovine serum, 100U / ml penicillin, 100U / ml streptomycin and 0.25 μg / ml amphotericin B). When the cell density reached 90% confluence, 50 μg / mL ascorbic acid was added to the culture medium to continue the culture. To obtain decellularized ECM, the ECM secreted by b...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Microscopic observation of extracellular matrix
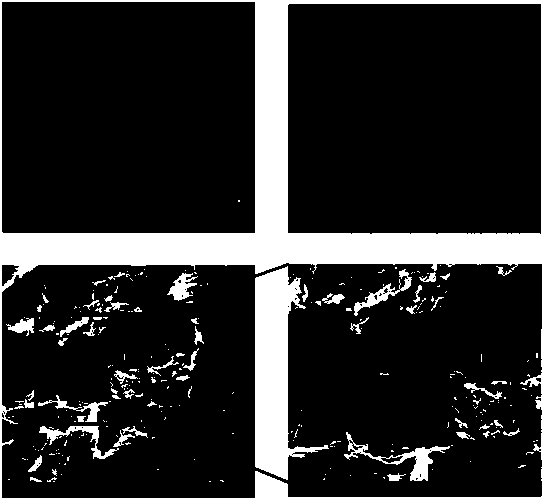
[0044] The ECM was first observed and photographed under a light microscope, and then after being fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde and dehydrated with gradient alcohol (50%, 75%, 80%, 95%, 100%), the morphology and structure were observed under an electron microscope. The results are as follows image 3 shown.
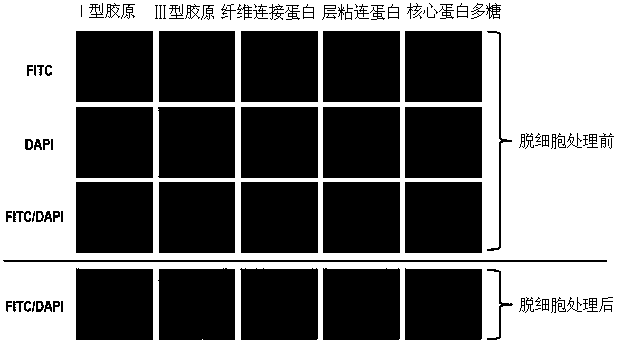
[0045] Example 2 Fluorescence staining of extracellular matrix
[0046] Before and after the decellularization treatment, the ECM was first fixed with ice methanol, then blocked with 1% bovine serum albumin, and added primary antibodies of type I collagen, type III collagen, fibronectin, decorin, and laminin antibodies. After incubation and washing with PBS for three times, the secondary antibody was added and observed with an immunofluorescence microscope. The results were as follows: image 3 shown.
Embodiment 4
[0047] Example 4 Identification of Differentiated Cells
[0048] 1. Identification of Differentiated Hepatocytes Using Glycogen Synthesis Capacity
[0049] Cells were collected on the 14th and 28th day of induction of differentiation, first fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde, then incubated with 1% periodic acid solution at room temperature for 5 minutes, then washed with PBS, stained with magenta reagent for 15 minutes, and observed under the microscope , the result is as Figure 4 shown
[0050] 2. Identification of Differentiated Hepatocytes Using Urea Synthesis Capacity
[0051] The culture supernatants were collected on the 7th, 14th, 21st, and 28th days of induction of differentiation, and placed in a -80°C low-temperature refrigerator. After the experiment was over, the concentration of urea in the supernatant was detected by spectrophotometry. The results were as follows: Figure 5 shown.
[0052] 3. Using Real-time RT-PCR to identify the expression...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com