Methods and systems for screening candidate compounds for their potential to cause systemic or hepatic toxicity
A technology for screening compounds and compounds, applied in the fields of biochemical equipment and methods, microorganisms, biological testing, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] bile acid homeostasis
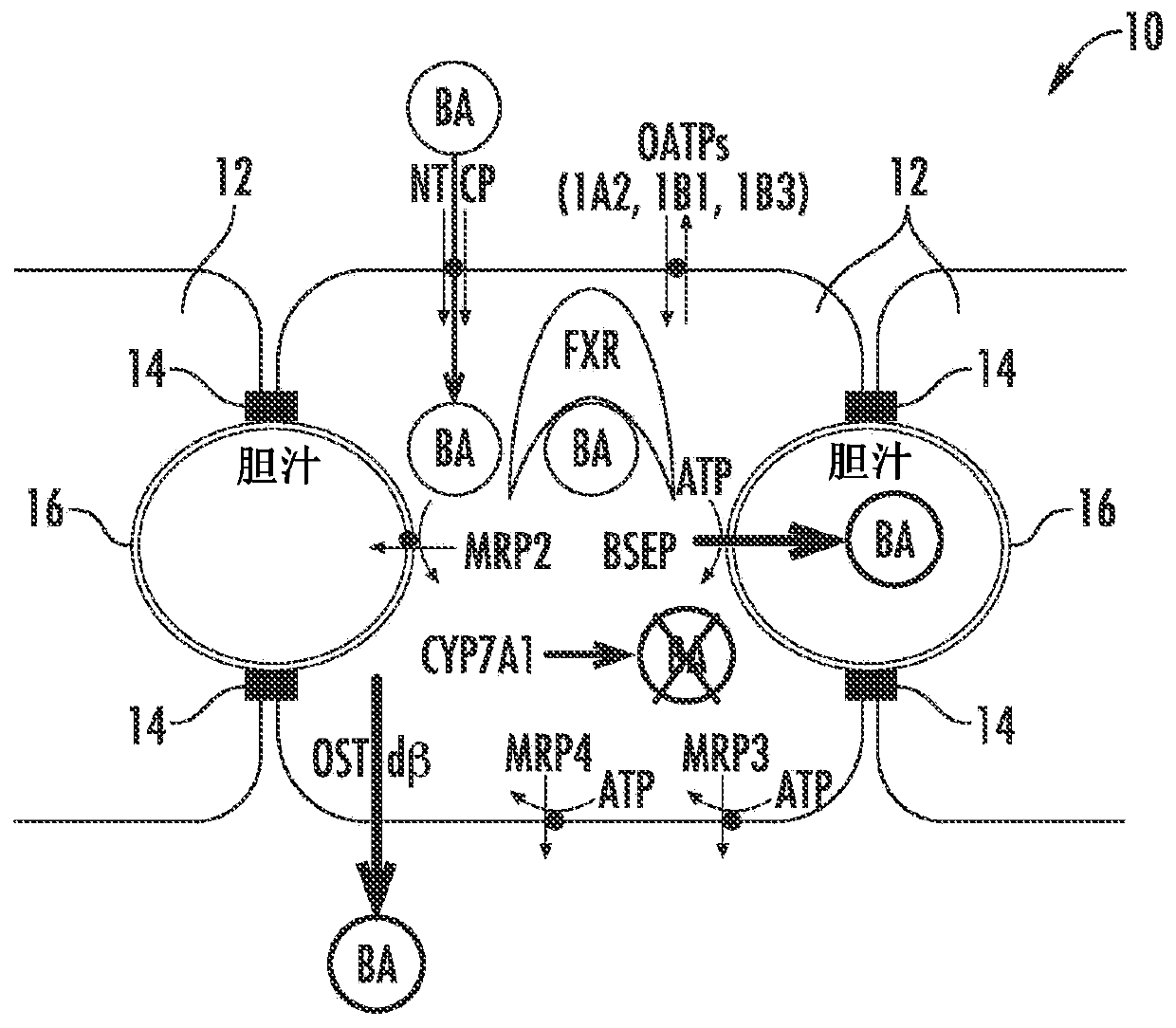
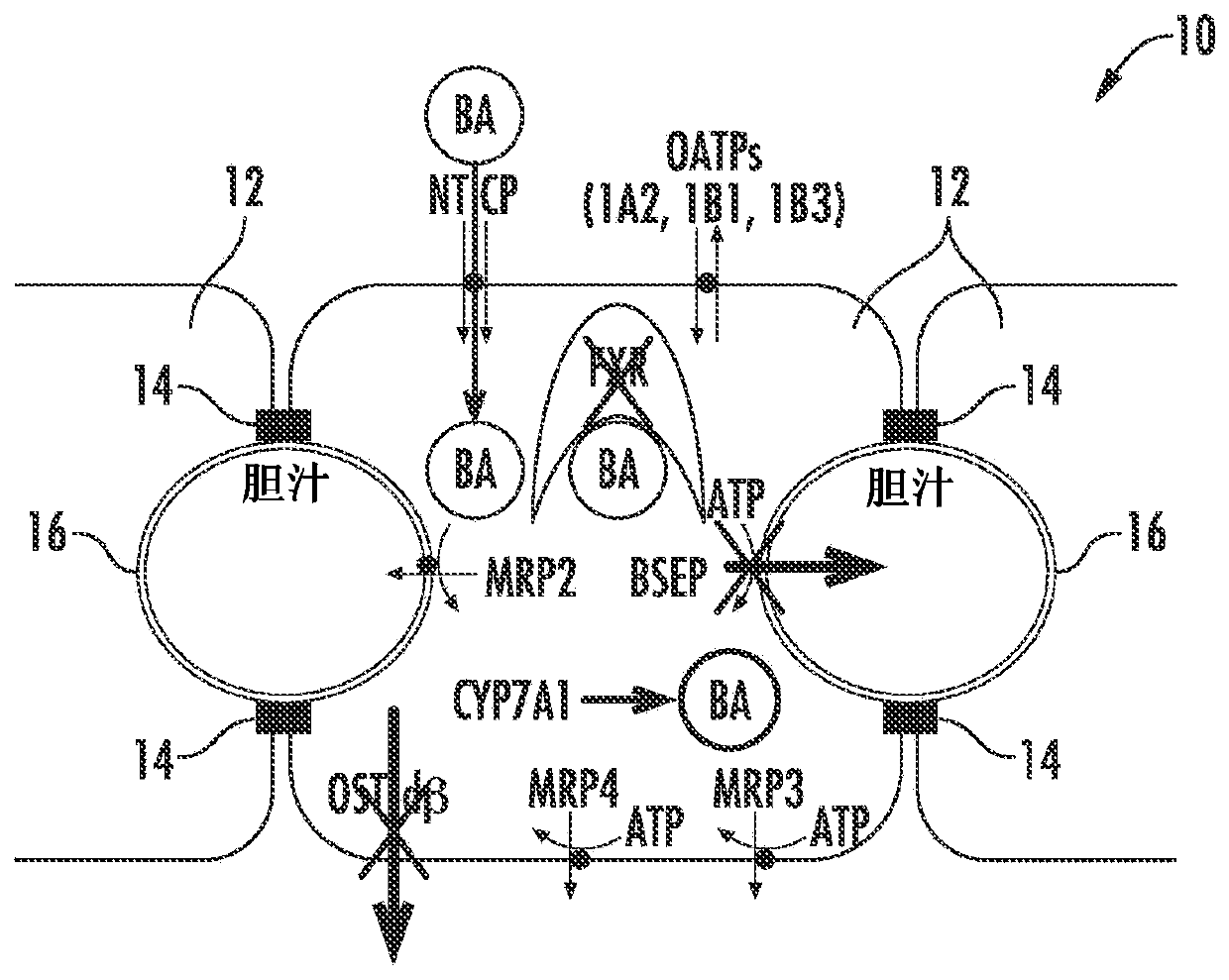
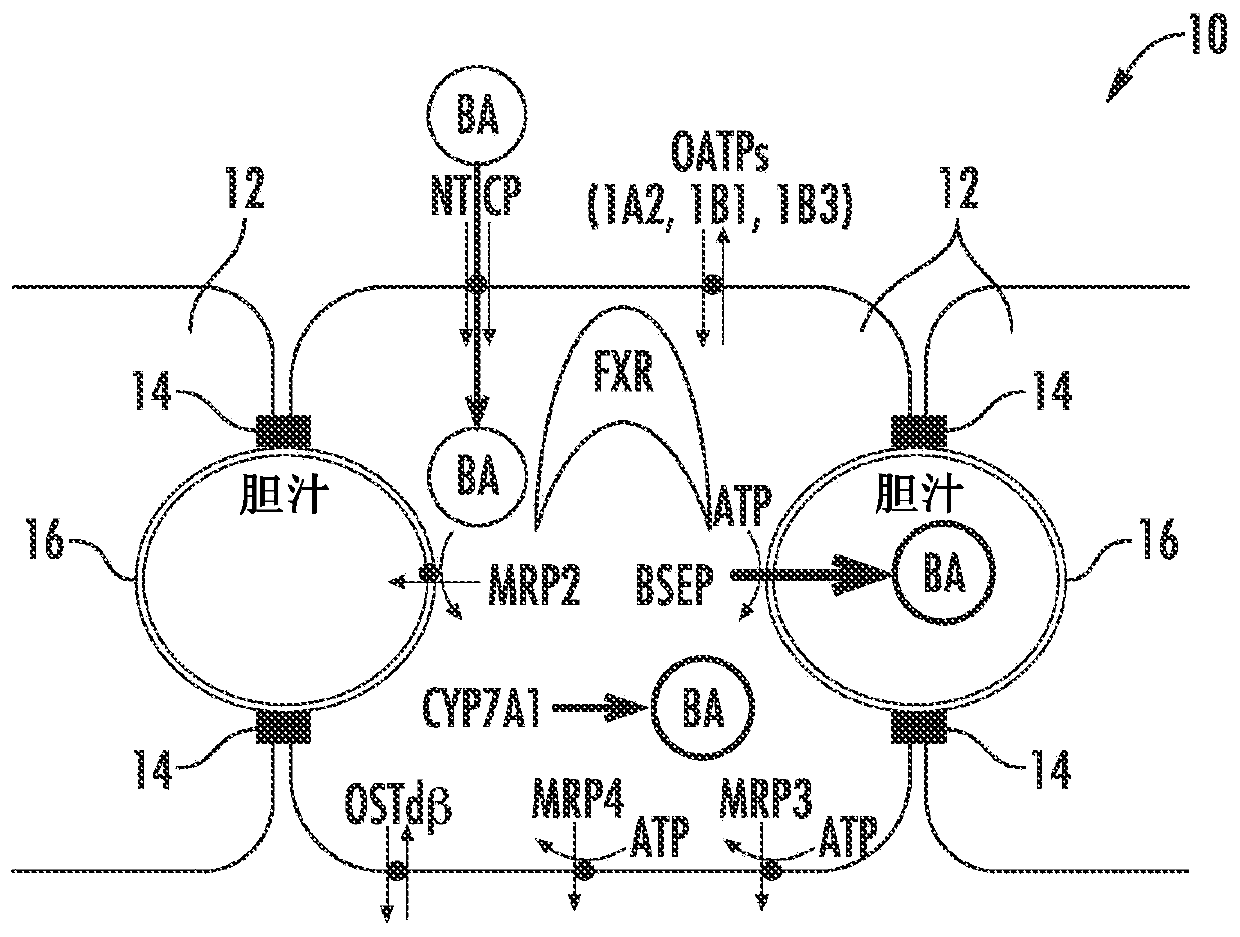
[0083] As demonstrated here, drug-induced cholestatic hepatotoxicity is a consequence of impaired bile acid inhibition of BSEP by NCE and impaired adaptive response of hepatocytes to bile acid homeostasis. A possible mechanism of action causing drug-induced cholestatic hepatotoxicity could include inhibition of cholestatic hepatotoxicity of BSEP function (initial injury) and 1) prevention (antagonism) of farnesoid X receptor (FXR) sensing of bile acid cells or 2) inhibition of all bile acid efflux pathways (basolateral and canalicular); or 3) a combination of both.
[0084] Figure 1A to Figure 6 is a schematic diagram of a hepatocyte system 10 (in vivo or in vitro) comprising hepatocytes 12 having tight junctions 14 and one or more bile canaliculi 16 therebetween. Components, enzymes and transporters in cellular systems include: bile acid BA; adenosine triphosphate ATP; farnesoid X receptor FXR; bile salt export protein BSEP; multidrug resista...
Embodiment 2
[0094] Feedback mechanism of bile acid homeostasis
[0095] figure 2 Normal bile acid uptake (NTCP), synthesis (CYP7A1 ) and export (BSEP) in vivo are exemplified. image 3The effect of NCE as a BSEP inhibitor to initiate feedback mechanisms of bile acid homeostasis (eg activation of FXR) leads to induction of compensatory mechanisms (eg basolateral efflux transporter OSTα / β) and reduction of bile acid intracellular concentrations. Initiation of the bile acid feedback mechanism prevents bile acid hepatotoxicity (aka cholestatic hepatotoxicity). Figure 4 The effects of NCE as BSEP inhibitors and FXR antagonists that prevent activation of the feedback mechanism of bile acid homeostasis, which leads to increased intracellular concentrations of bile acids, leading to bile acid hepatotoxicity (aka cholestatic hepatotoxicity) are exemplified. Figure 5 NCEs that inhibit the action of multiple bile acid efflux pathways, leading to hepatotoxicity, are exemplified. Bile acid feedb...
Embodiment 3
[0097] Development of an assay device for screening hepatotoxicity of cholestasis
[0098] Provided herein are assay devices, methods and systems to identify NCEs that may interfere with the bile acid processing capacity of hepatocytes. In some embodiments, such assays, methods and systems are configured to be based on toxicity assays (e.g. ATP / LDH / caspase 3 / 7 / 8) and / or by monitoring and clinical measurements (AST / ALT )-related LDH links cholestasis to hepatotoxicity, and the AST / ALT is commonly used to monitor liver function. In some embodiments, such assay devices, methods and systems are configured to classify NCE as cholestatic, ineffective, or cholestatic hepatotoxic.
[0099] In some embodiments, the potential outcome (BA in the presence of NCE) can be as follows Figure 7 and Figure 8 expression shown in . exist Figure 7 and Figure 8 In , dotted, dashed, and solid lines indicate the following:
[0100] -Dotted line
[0101] BA dose-appropriate to determine BA...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com