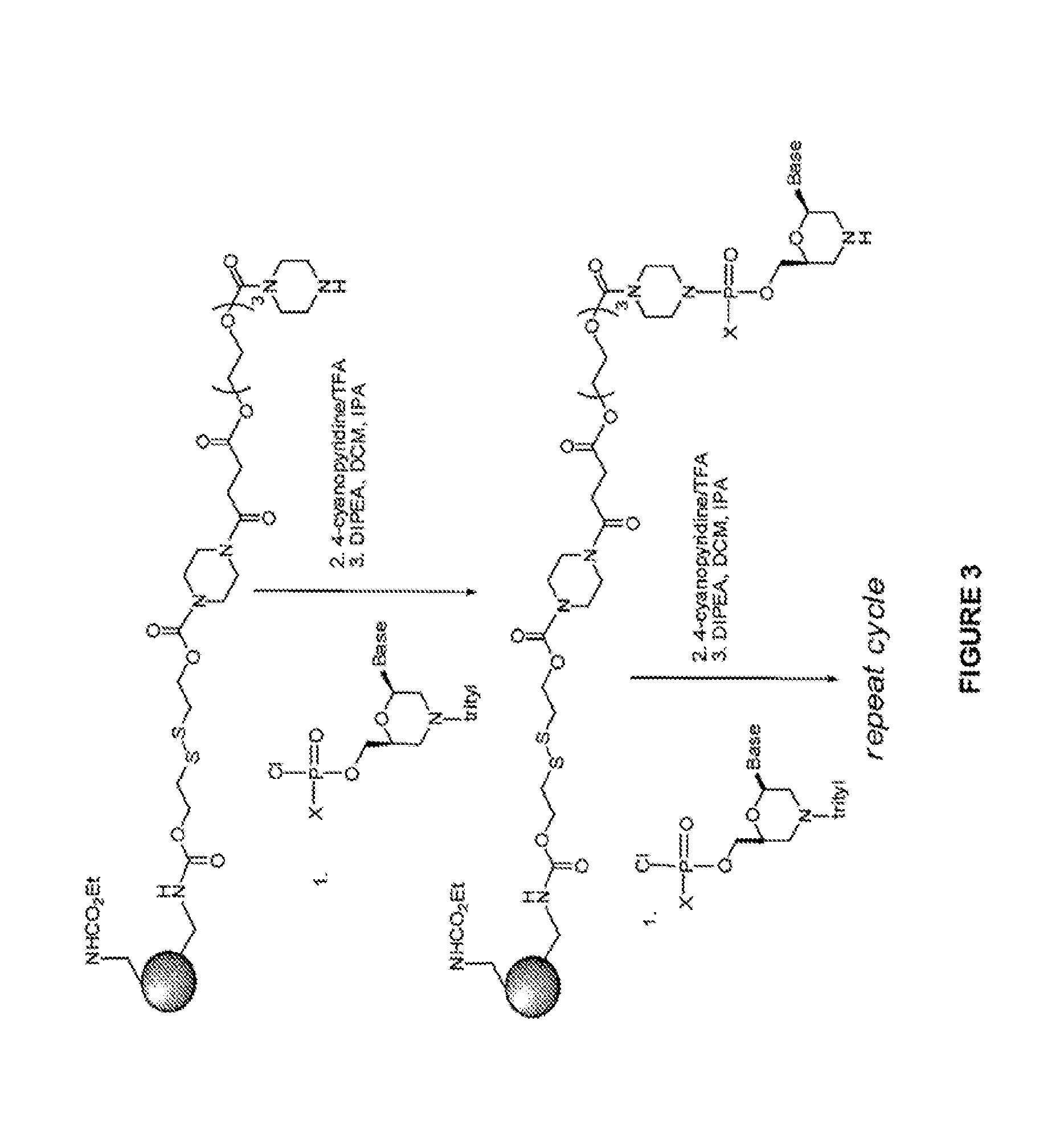
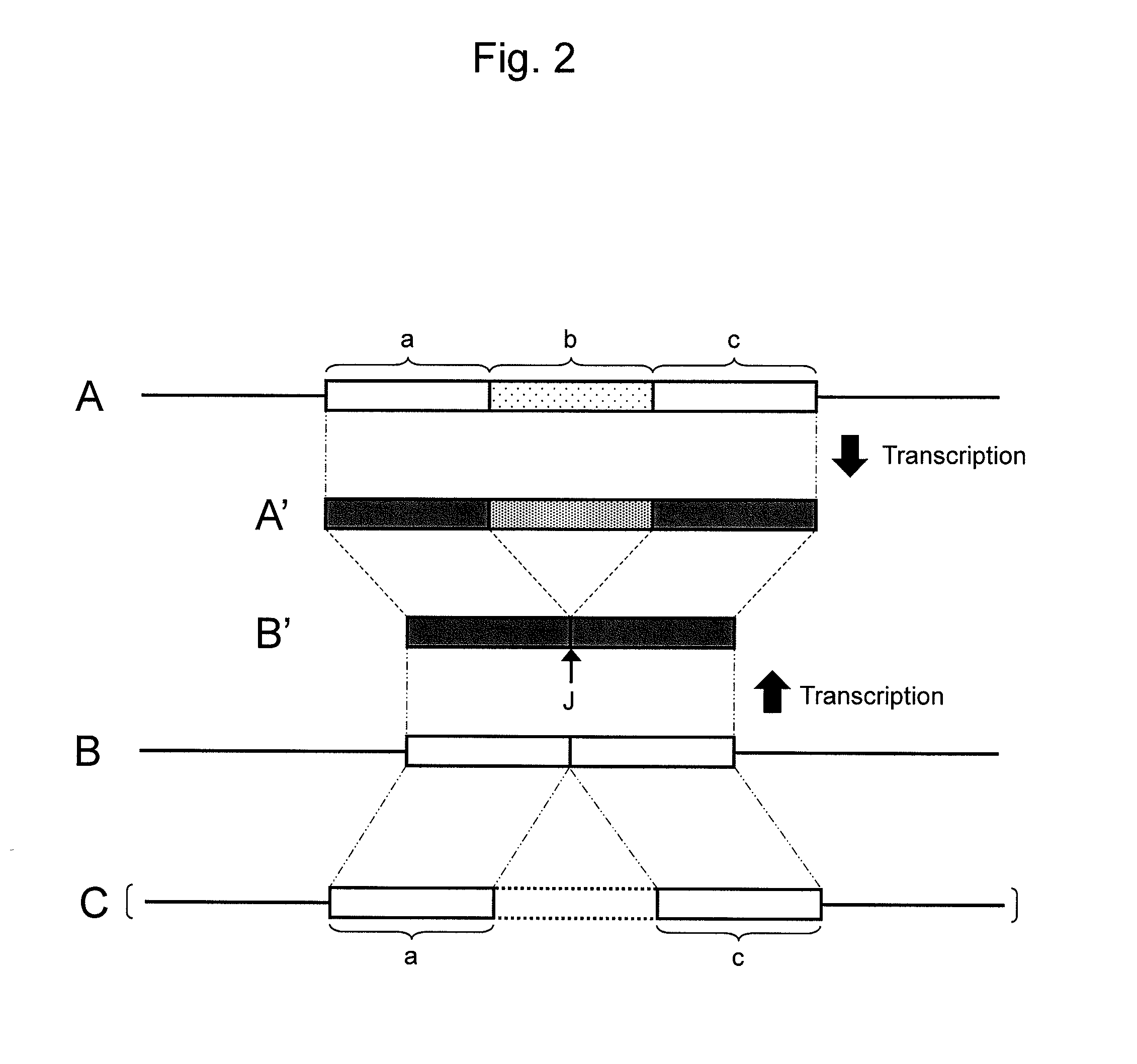
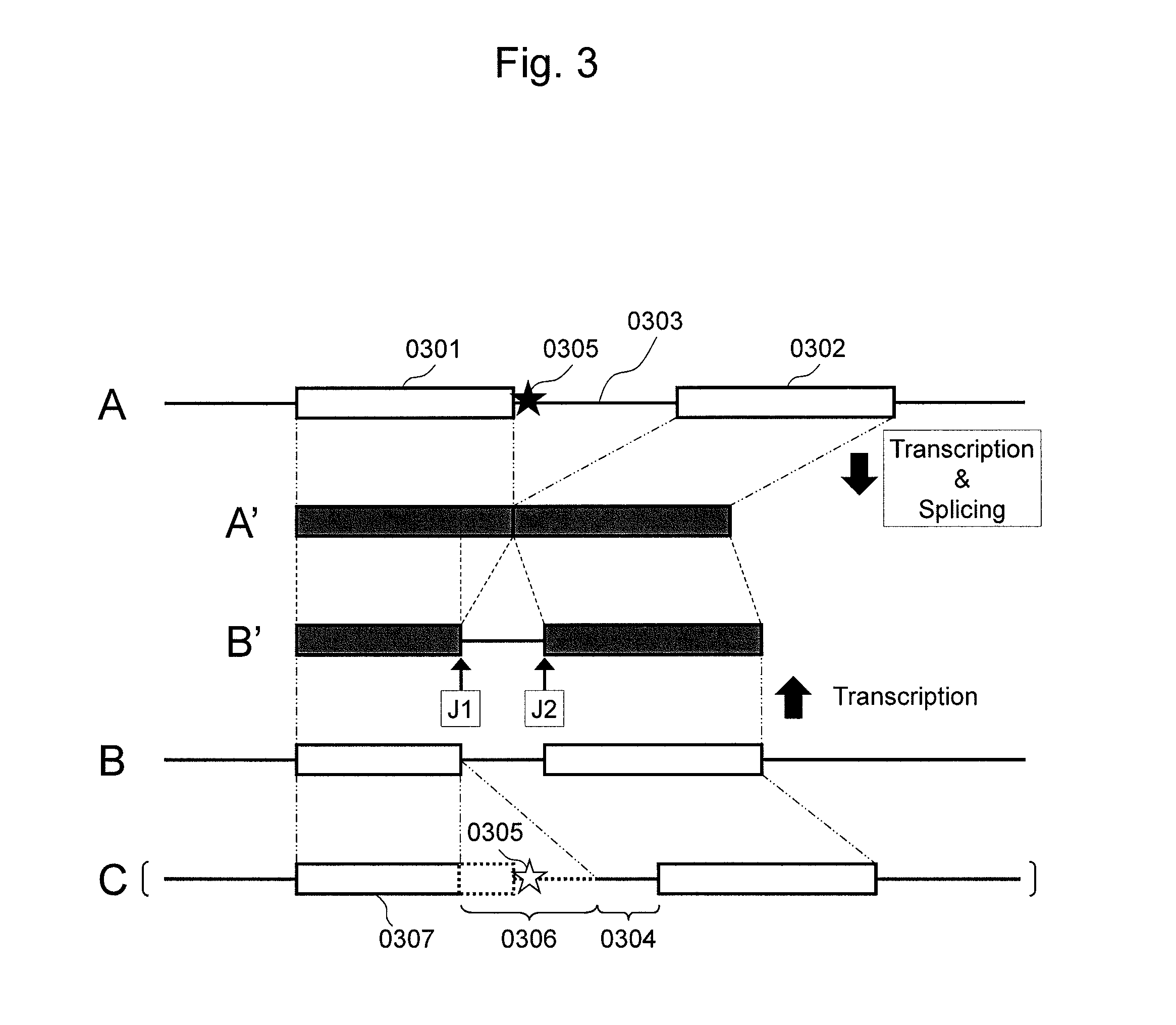
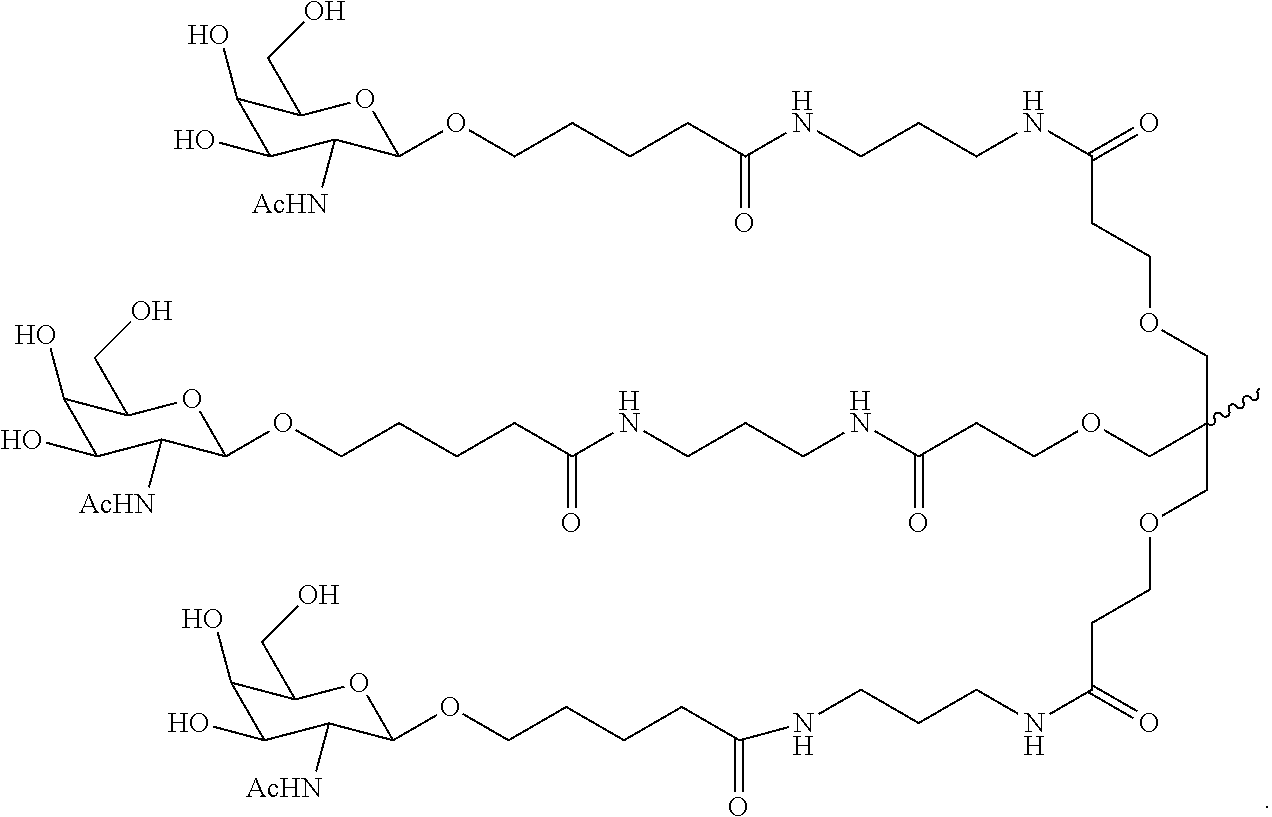
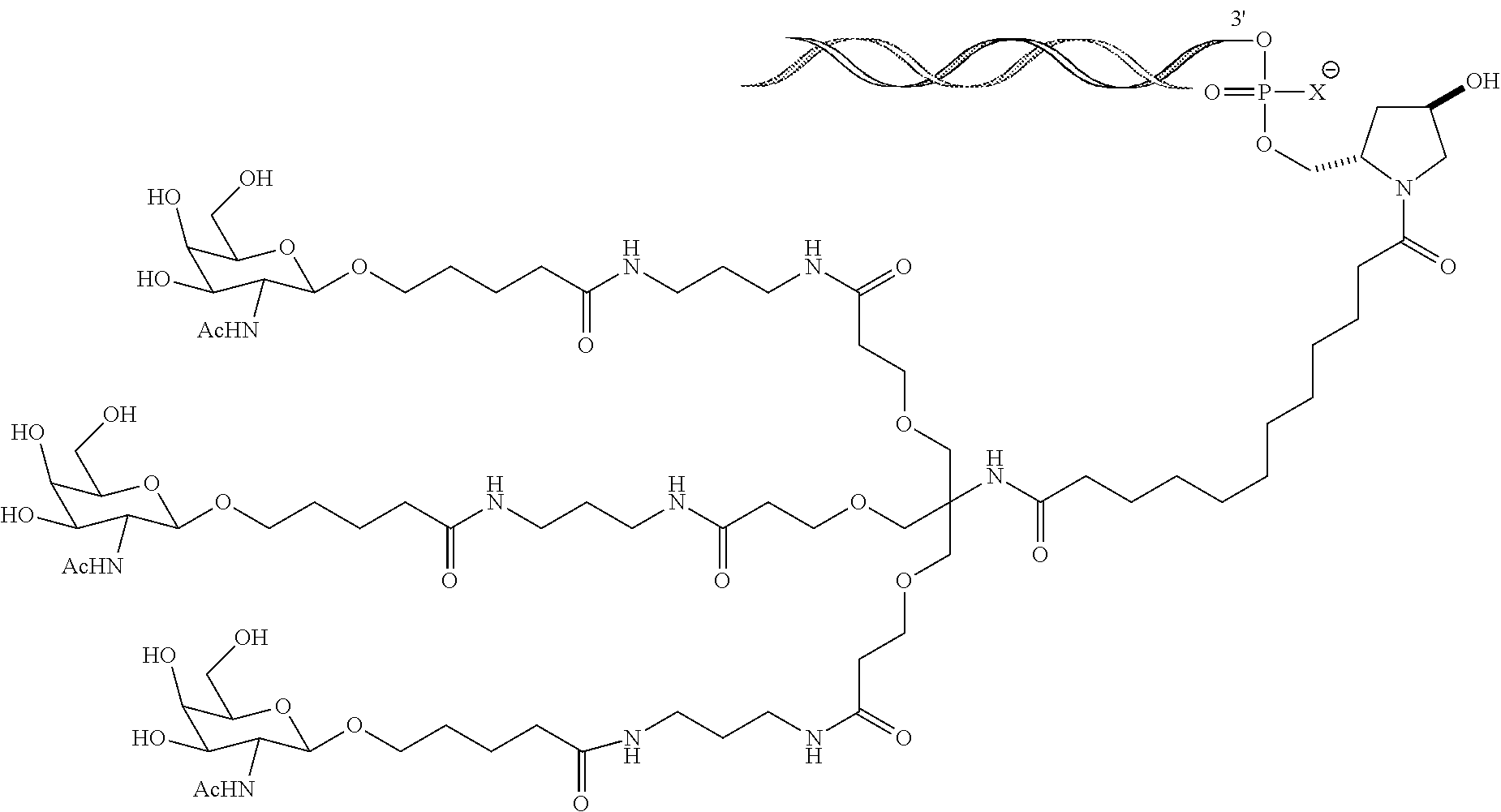
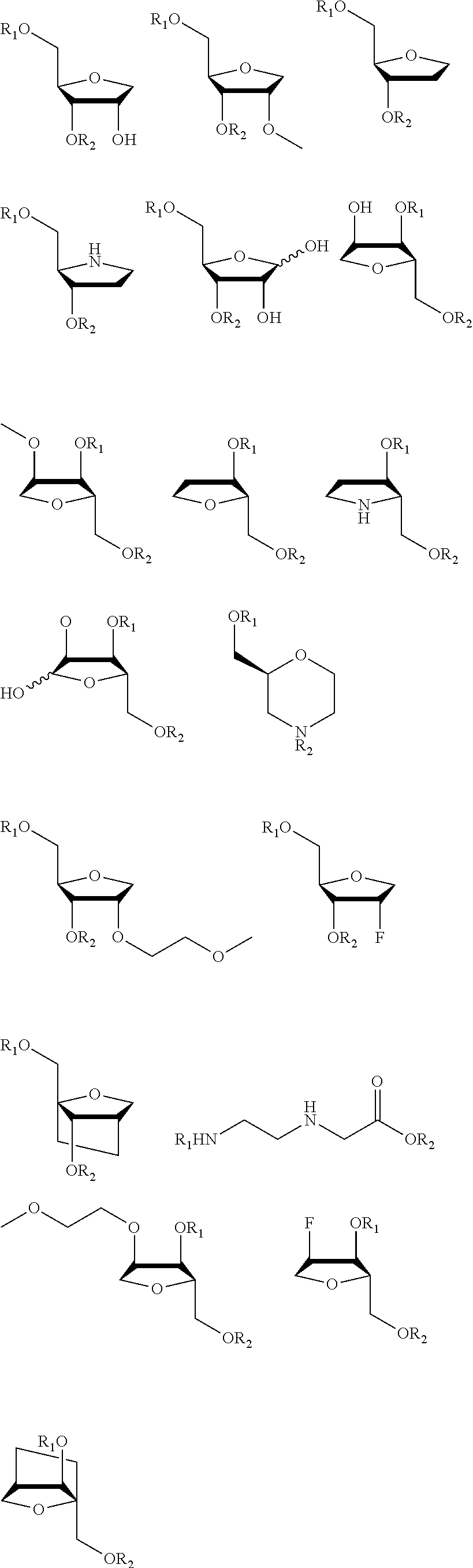
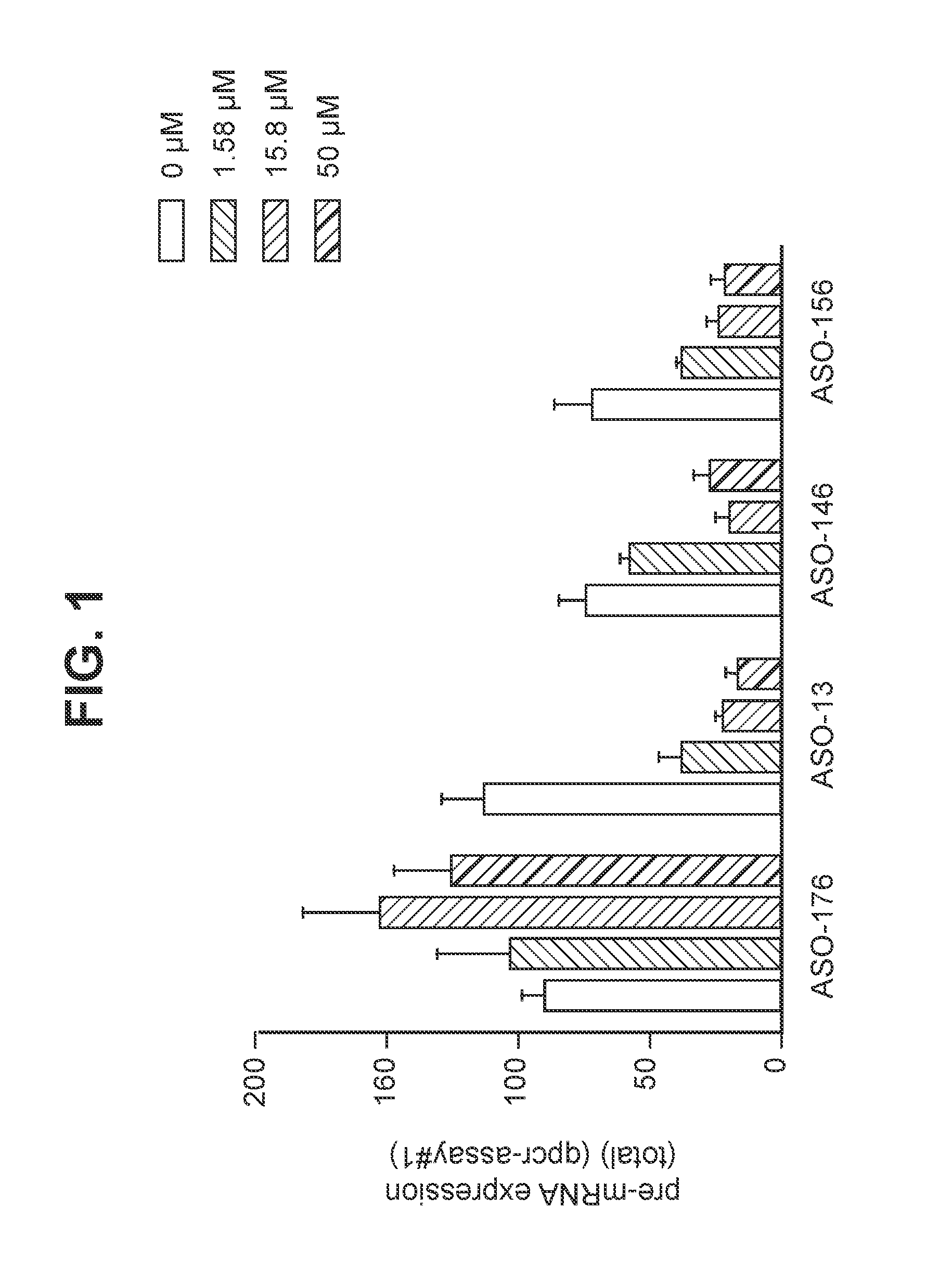
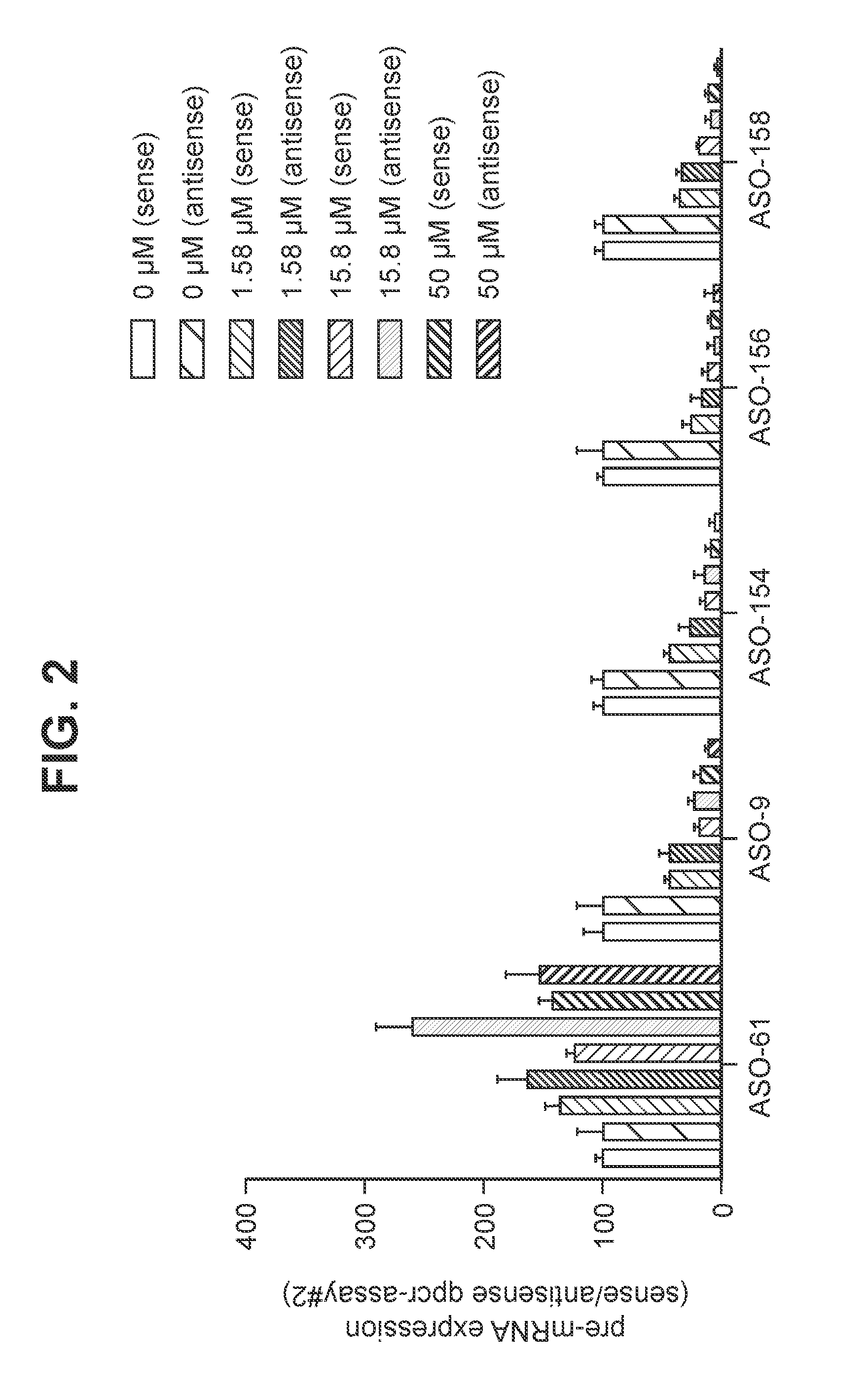
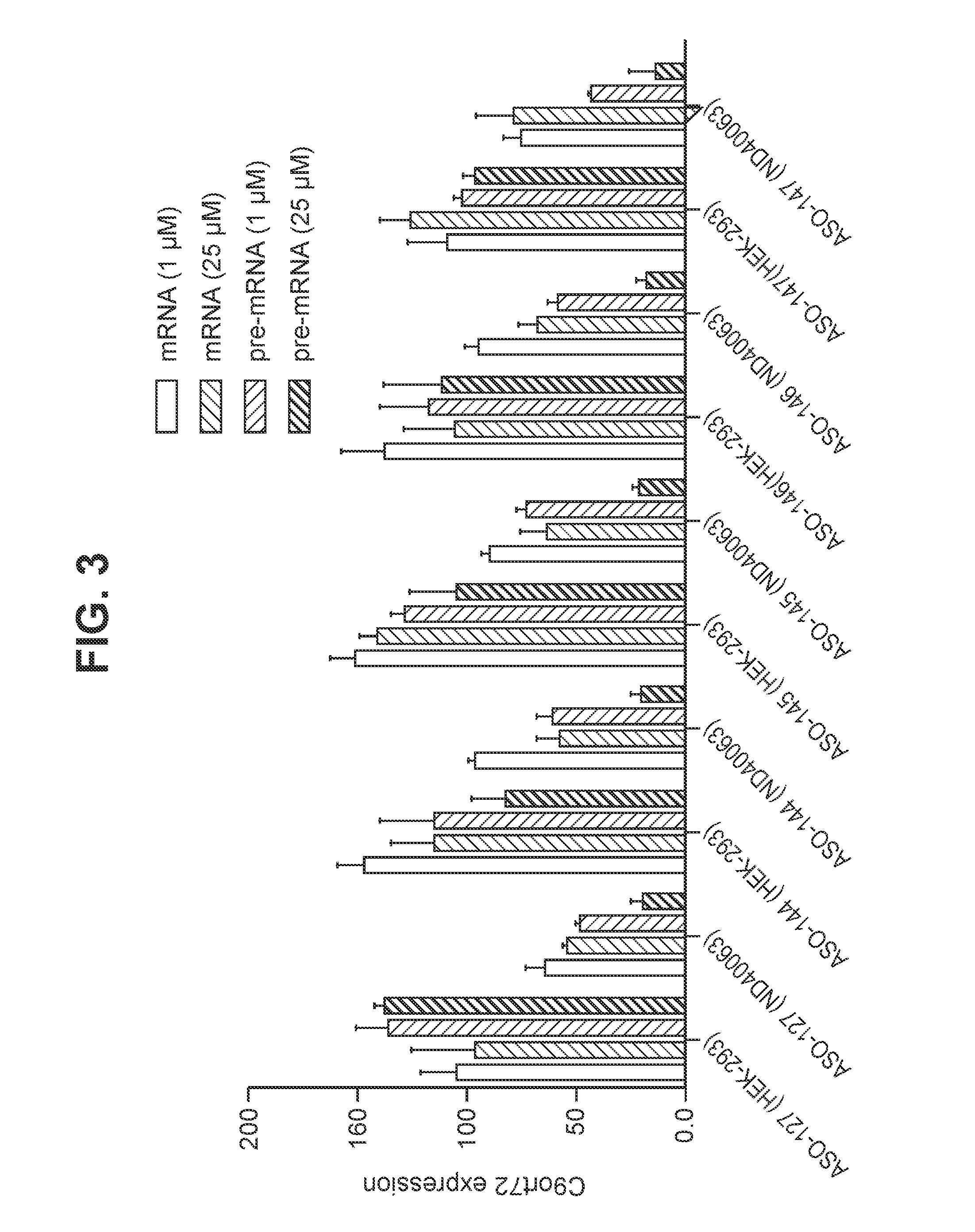
Patents
Literature
164results about "Polymorphism uses" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
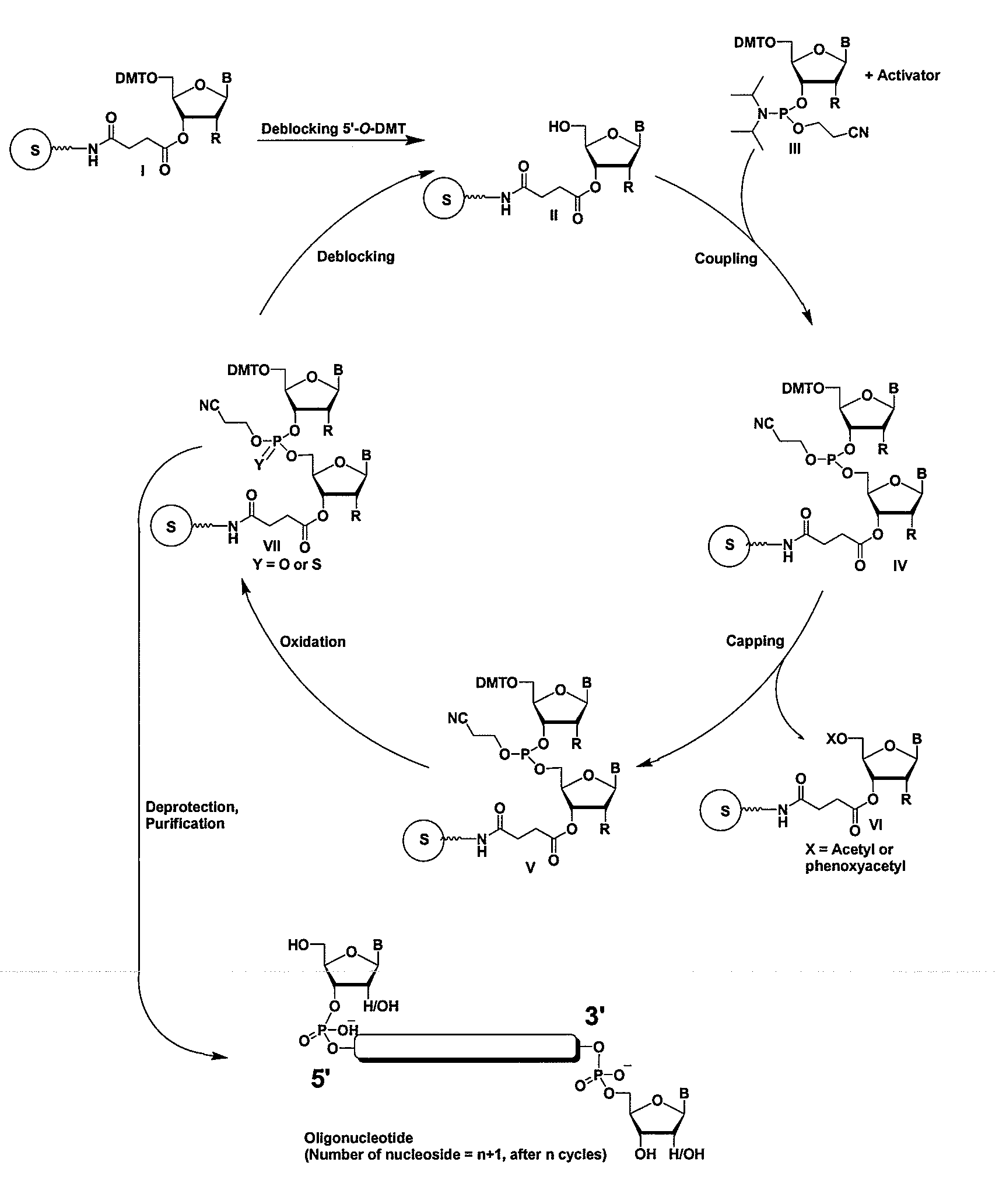
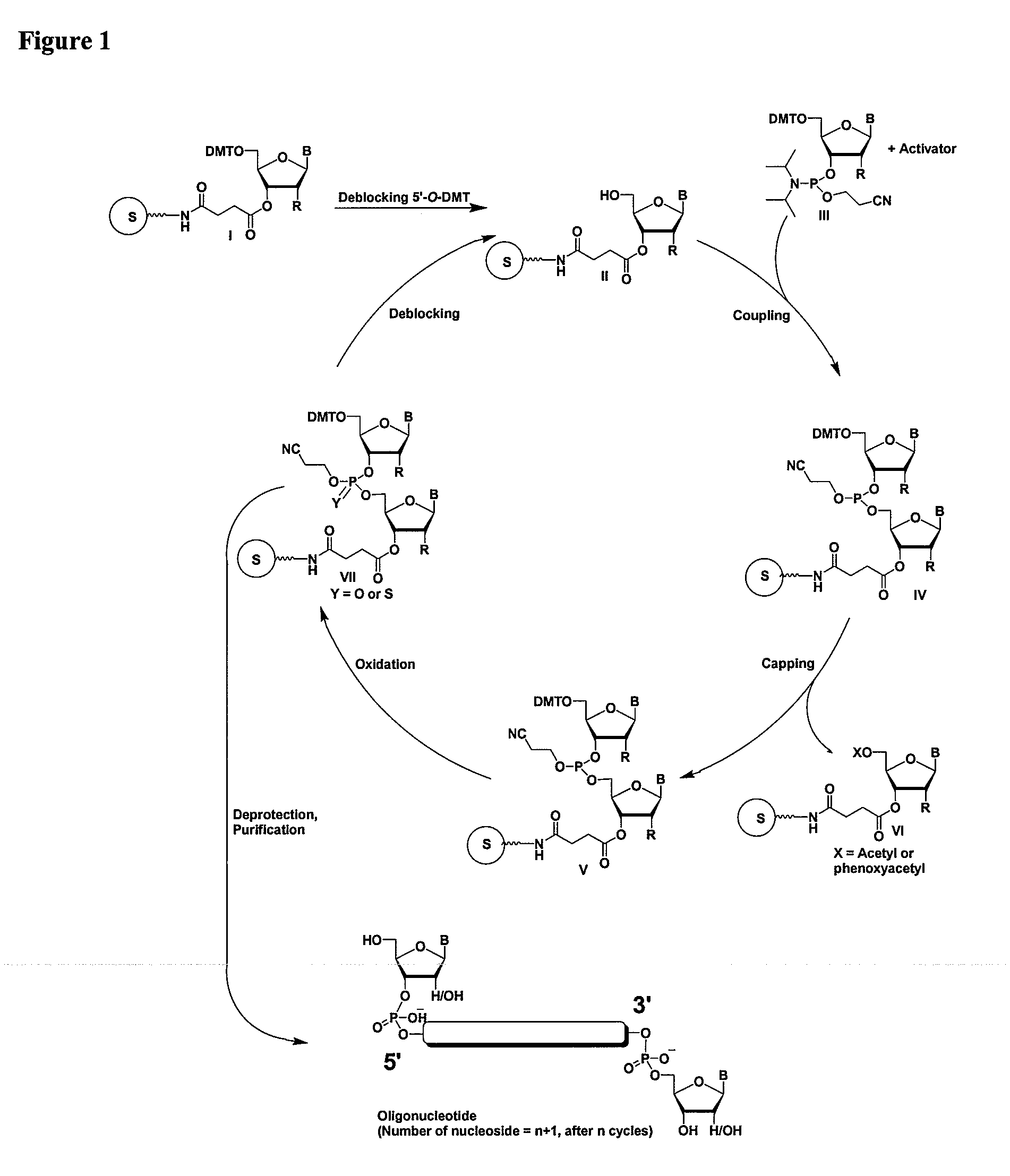
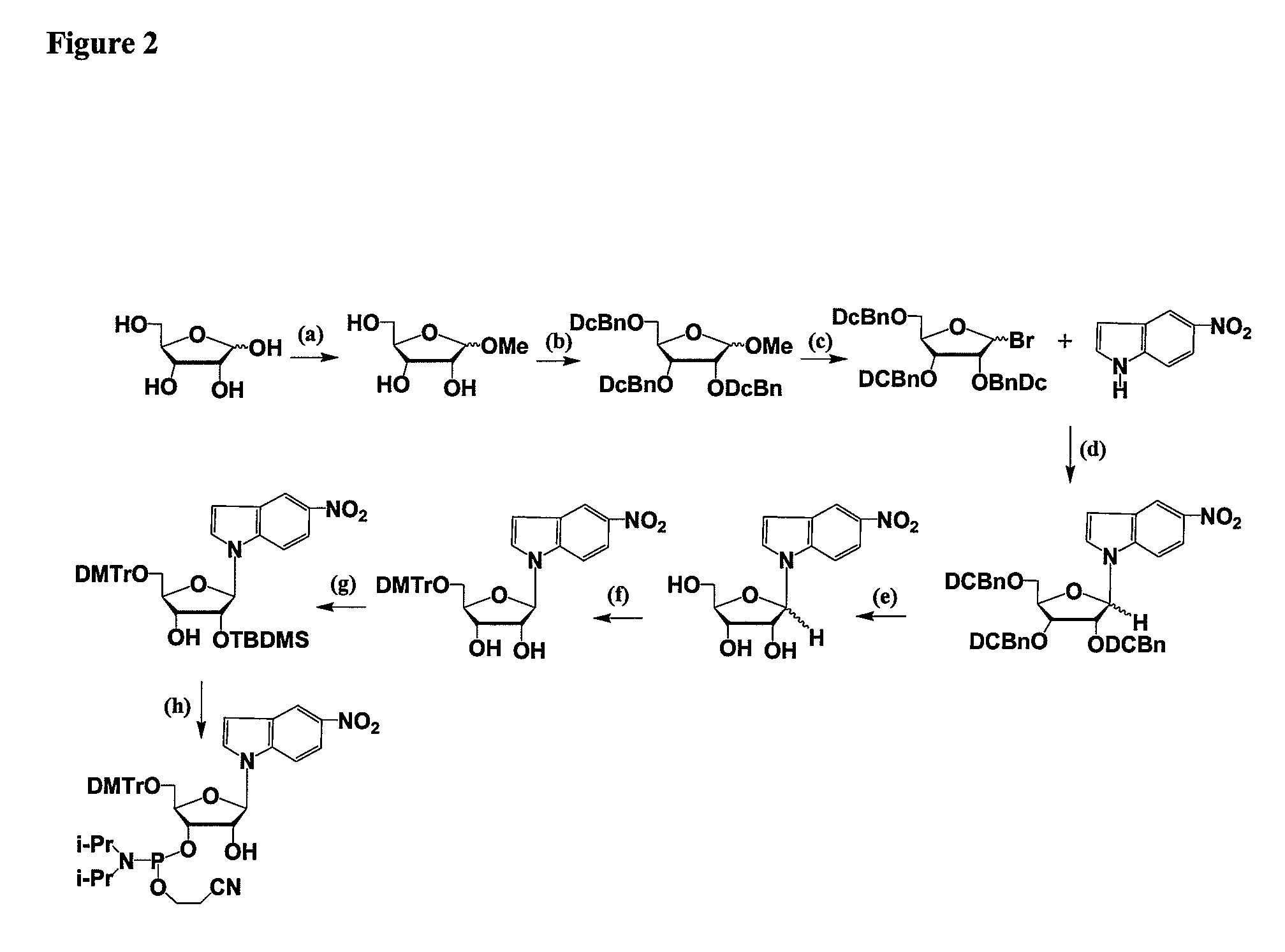
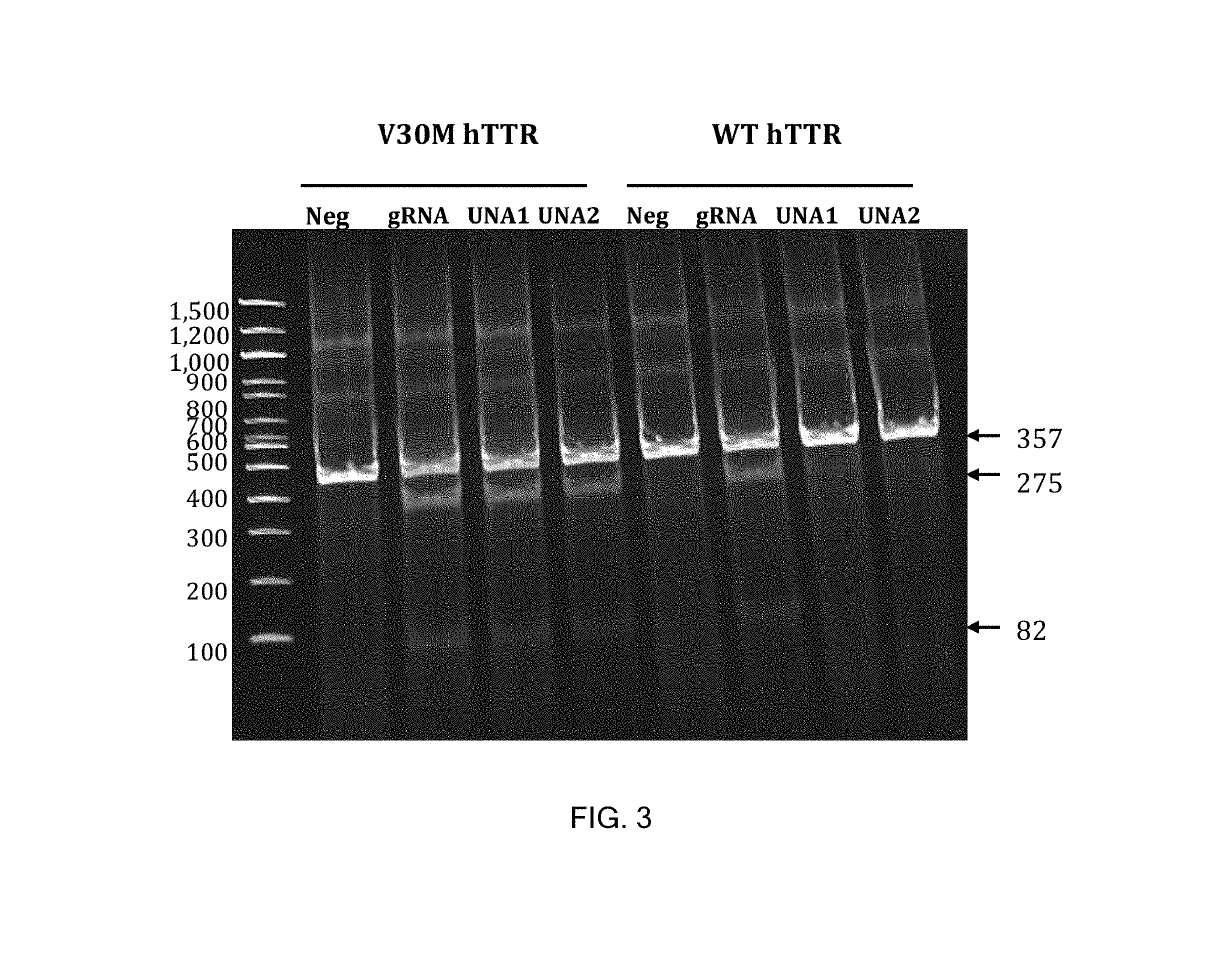
RNAi Agents Comprising Universal Nucleobases
InactiveUS20080213891A1Broad scopeReduce needSugar derivativesPolymorphism usesNitroimidazoleViral Genes
One aspect of the present invention relates to an oligonucleotide agent comprising at least one universal nucleobase. In certain embodiments, the universal nucleobase is difluorotolyl, nitroindolyl, nitropyrrolyl, or nitroimidazolyl. In a preferred embodiment, the universal nucleobase is difluorotolyl. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide is double-stranded. In certain embodiments, the oligonucleotide is single-stranded. Another aspect of the present invention relates to a method of altering the expression level of a target in the presence of target sequence polymorphism. In a preferred embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression of different alleles of a gene. In another preferred embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression level of two or more genes. In another embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression level of a viral gene from different strains of the virus. In another embodiment, the oligonucleotide agent alters the expression level of genes from different species.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
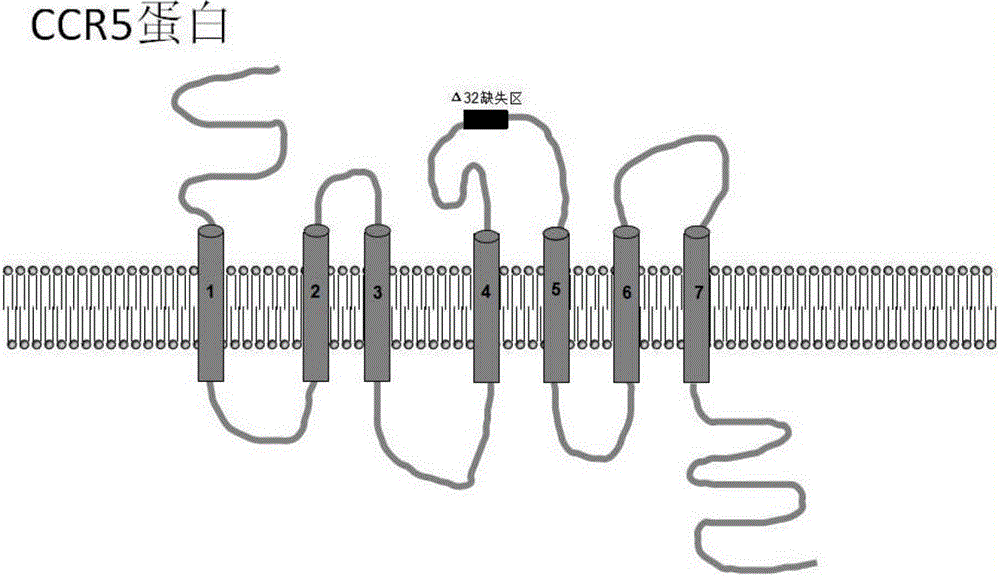
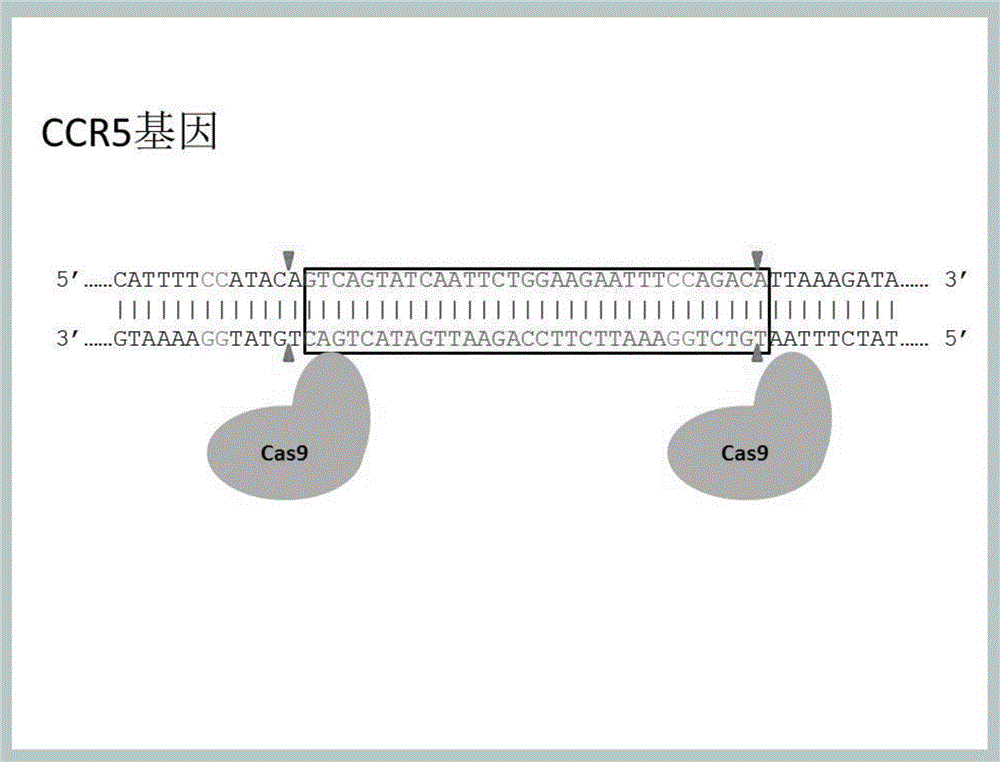
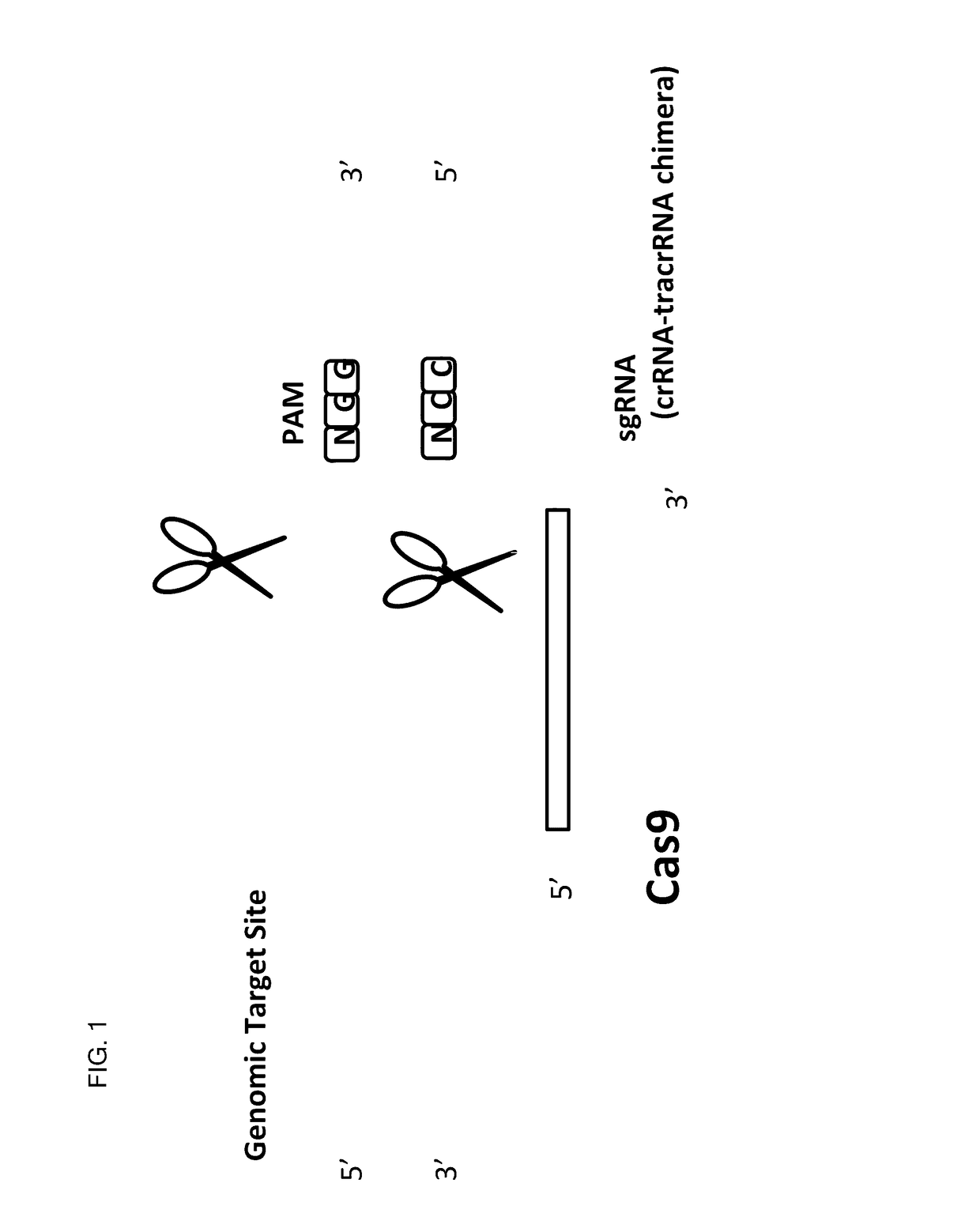
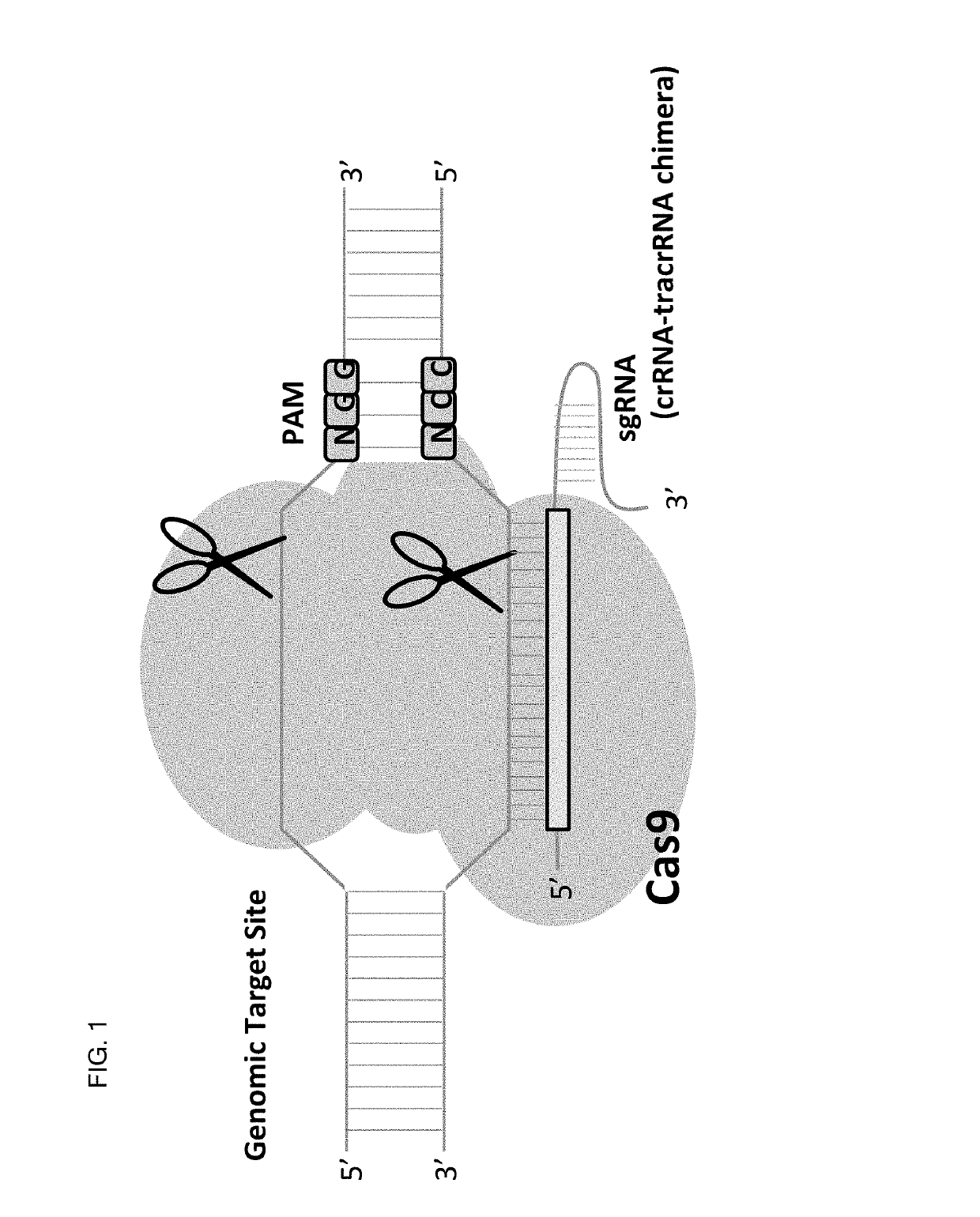
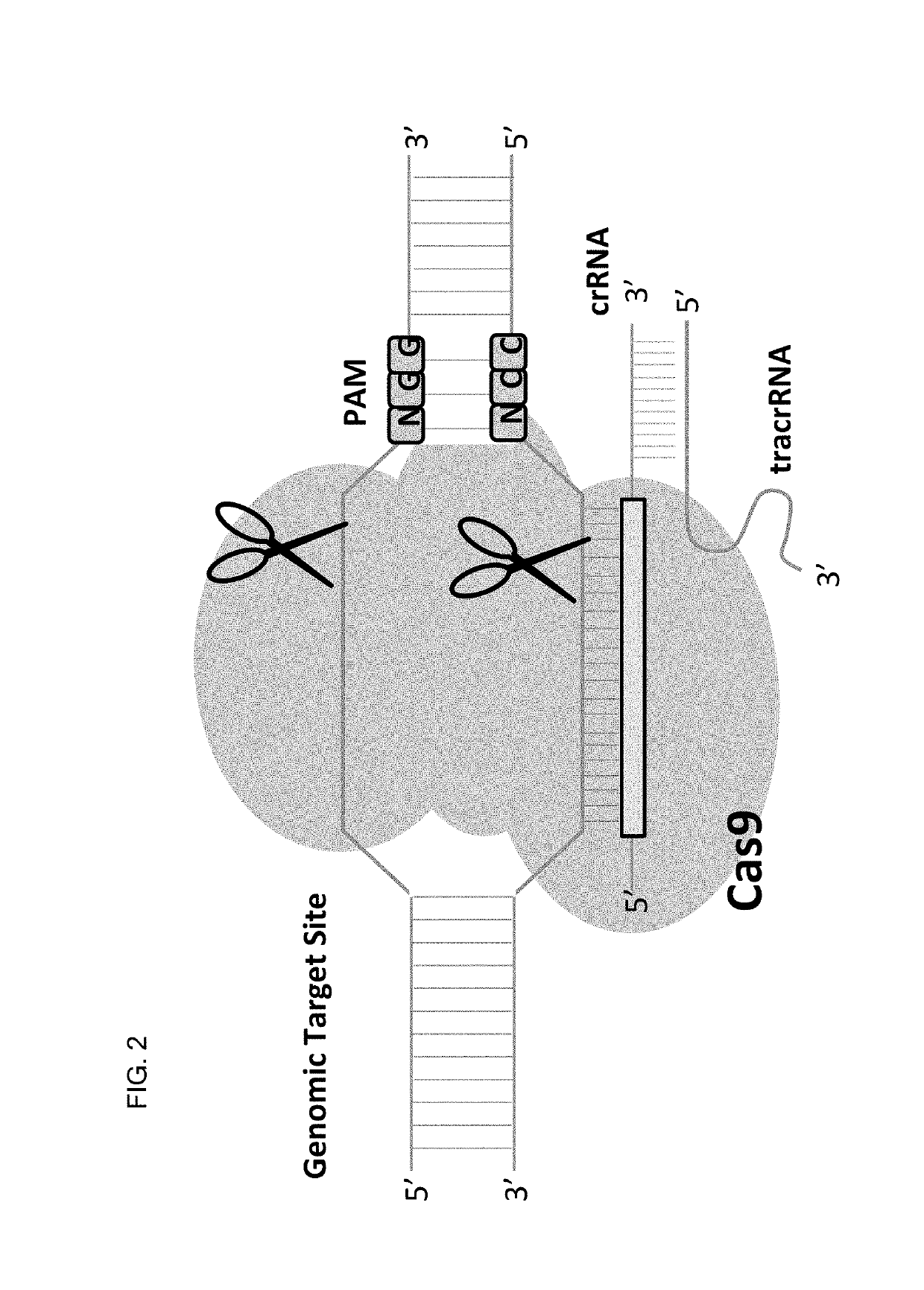
Method for inducing CCR5-delta32 deletion with genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9
The invention relates to a method for successfully inducing cell chemokine receptor CCR5 genes to be mutated into CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes with a new genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9. CCR5 is an important receptor for human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) to invade personal host cells. CCR5-delta32 deletion means deletion of 32 basic groups occurs in a CCR5 coding region, so that the sequence after the 185th amino acid is changed, and early termination occurs. CCR5-delta32 biallelic-gene homozygous deletion has natural resistance to HIV infection, and can not be infected by HIV. By means of the method, a slow virus packaging system and the CRISPR technology are used at the same time; as the slow virus infecting host range is wide, the method can be applied to cells such as bone marrow stem cells and CD4T cells, and the CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes hopefully become medicine for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome or other diseases.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Oligonucleotides for treating expanded repeat diseases
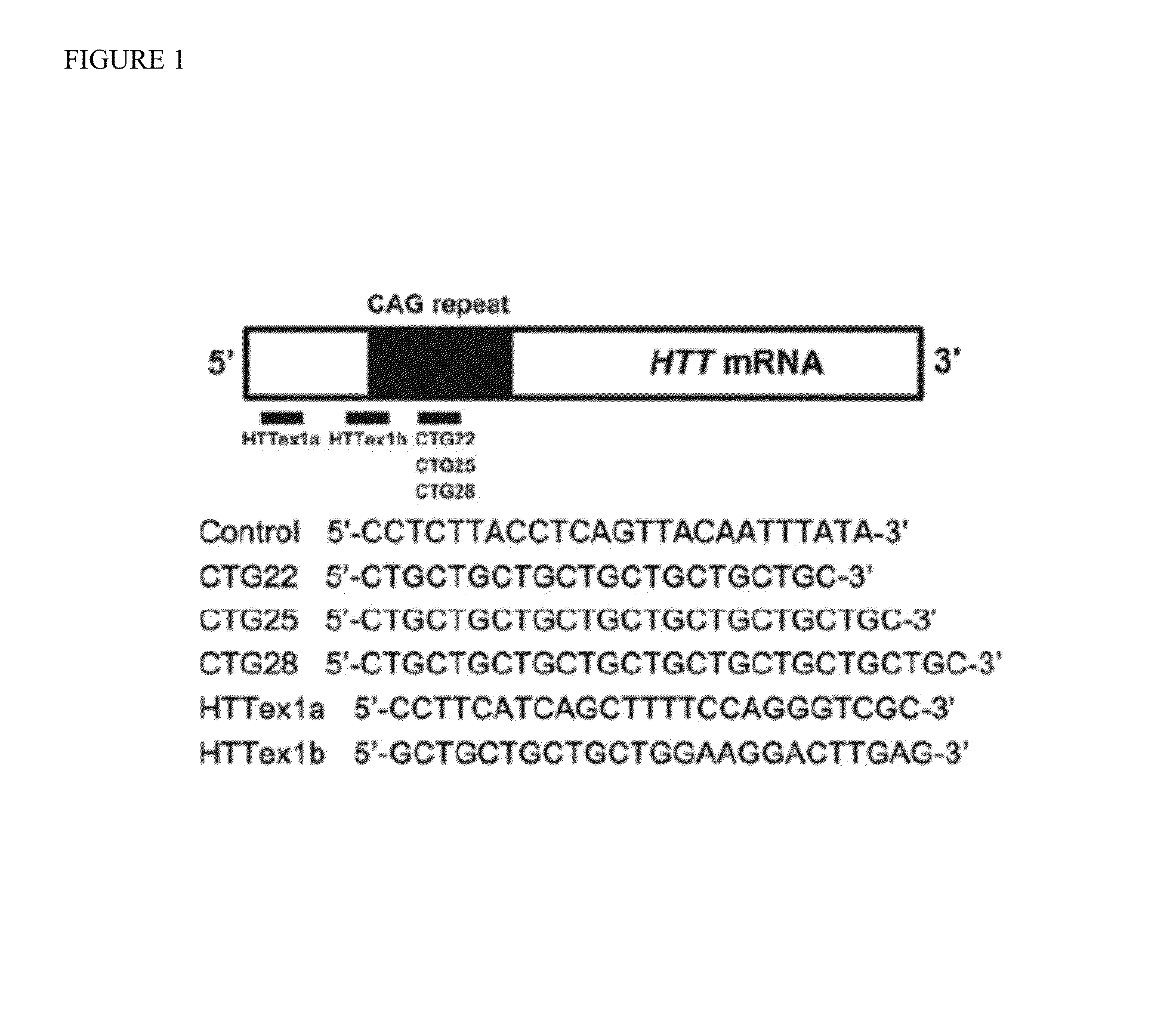
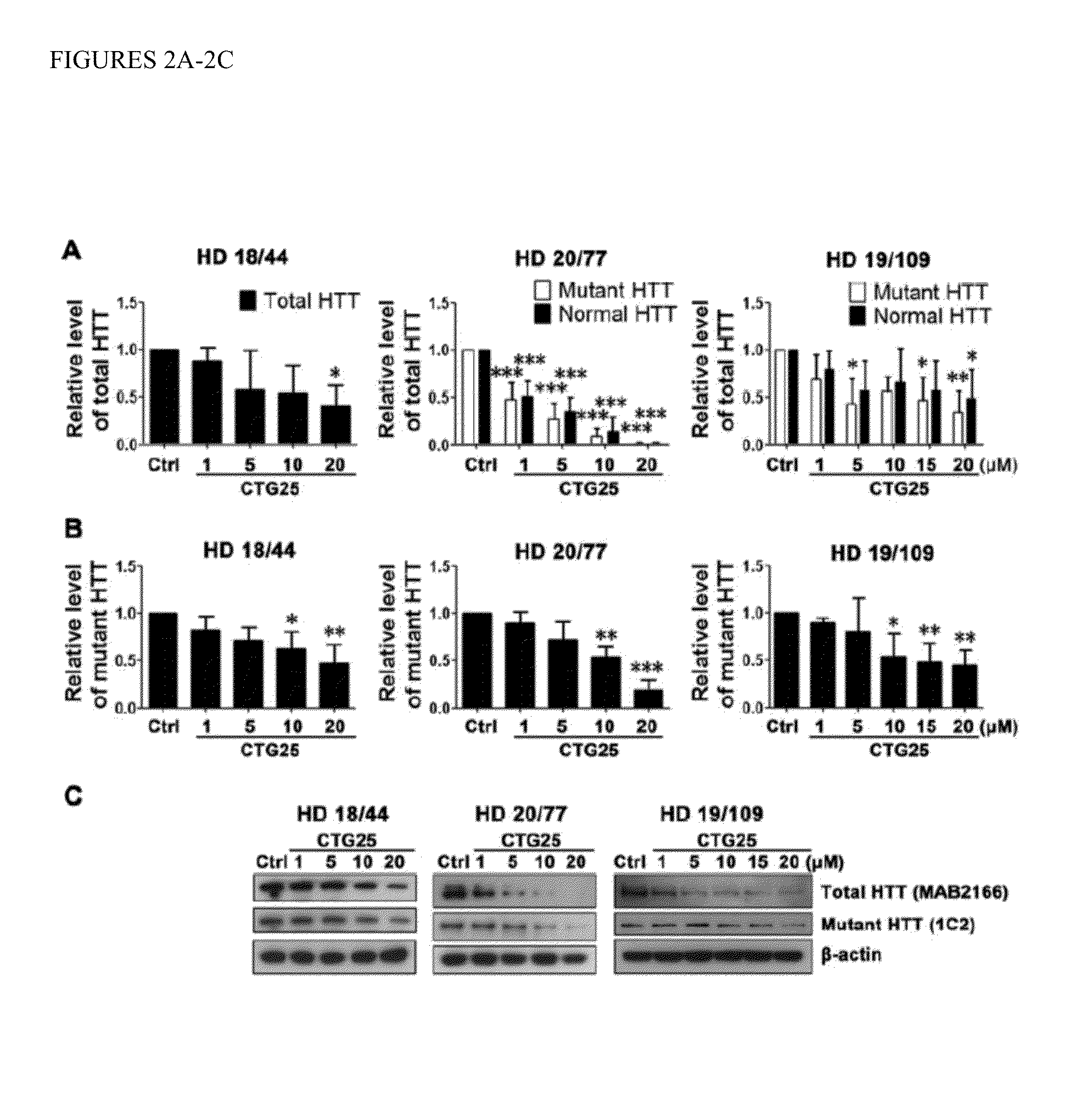
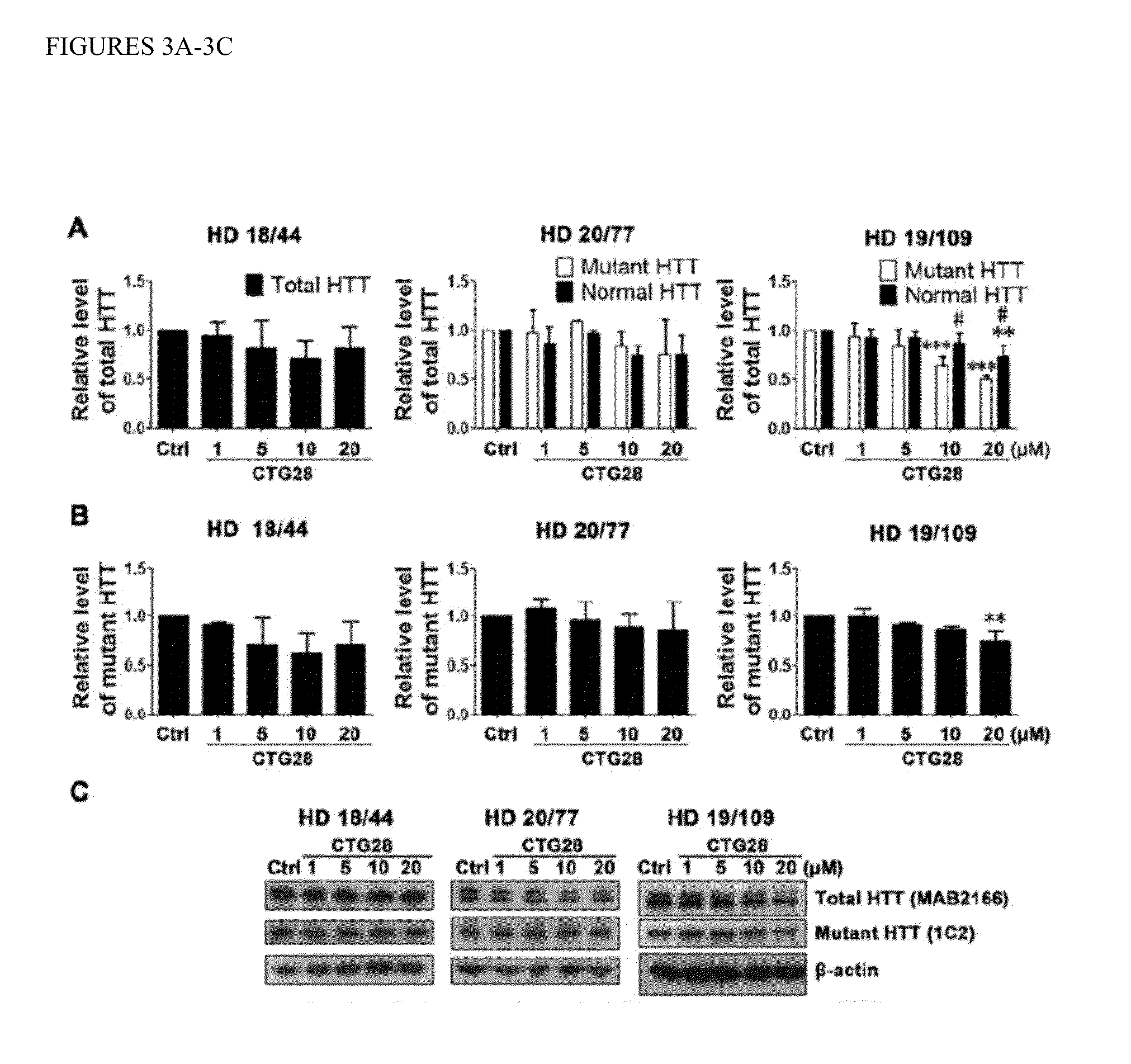
The invention provides for a method for selectively reducing the expression of a mutant mRNA and / or protein having an expanded nucleotide repeat relative to a wild-type mRNA, comprising contacting a cell with an antisense oligonucleotide of sufficient length and complementarity to the expanded nucleotide repeat. More particularly it relates to selectively reducing the expression of mutant Huntington protein associated with Huntington's disease. The antisense oligonucleotide comprising either a nucleotide or a repeated three nucleotide sequence as defined in the claims.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Shared neoantigens
ActiveCN108025048ATumor rejection antigen precursorsPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical drugPharmaceutical medicine
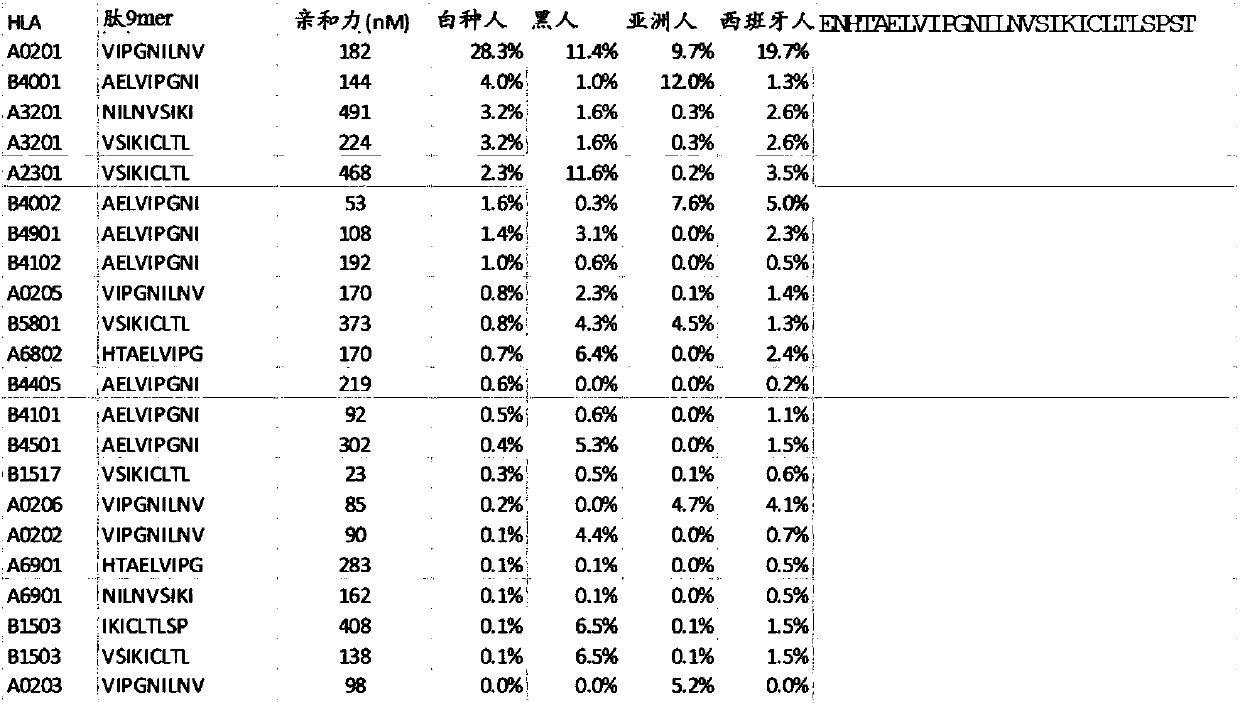
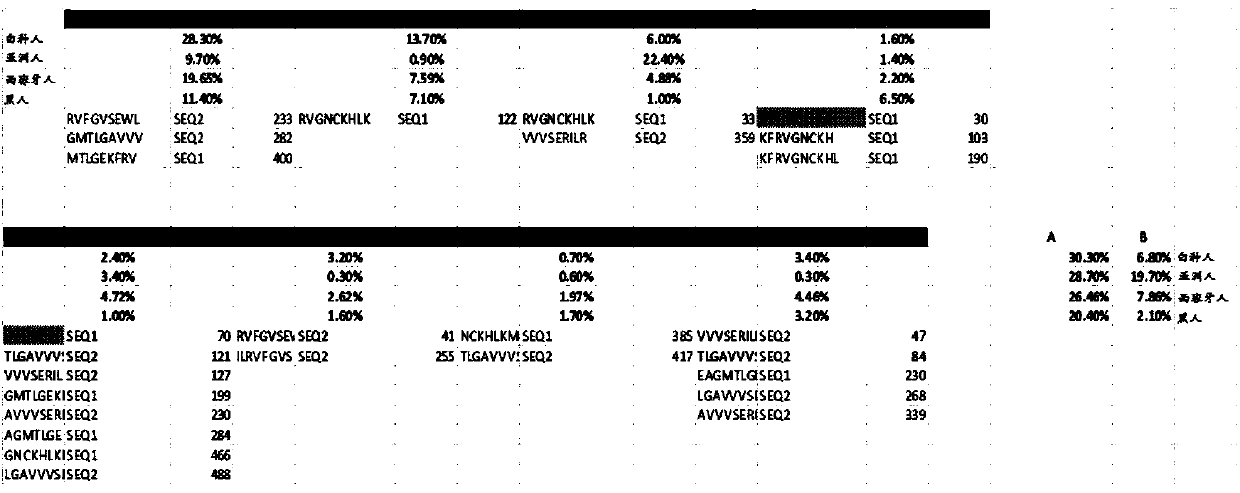
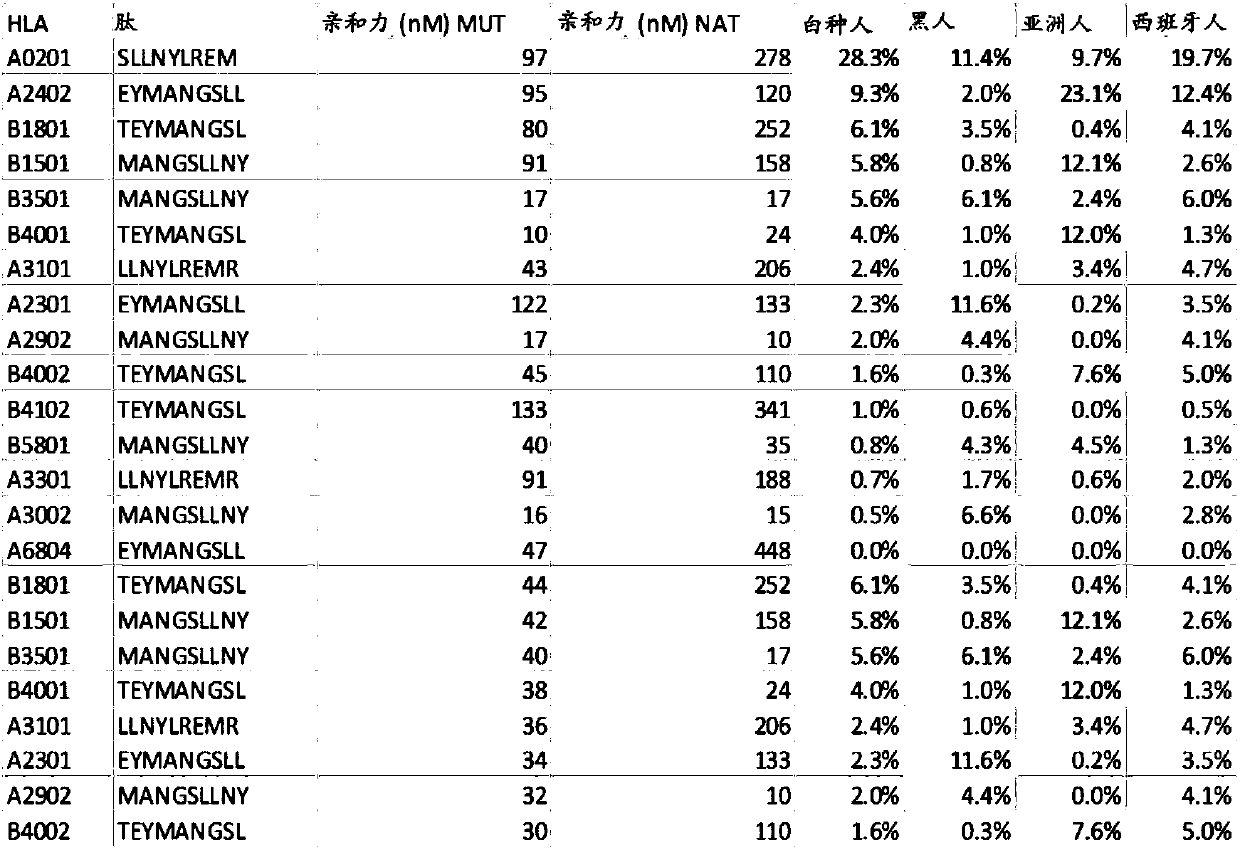
Disclosed herein in one aspect is a pharmaceutical composition comprising a plurality of neoantigenic peptides and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier, each neoantigenic peptide comprising a tumor-specific neoepitope capable of binding to an HLA protein in a subject, each tumor-specific neoepitope comprising a tumor-specific mutation present in a tumor, wherein (a) the composition comprises neoantigenic peptides comprising tumor-specific mutations present in at least 1% of subjects in a population of subjects suffering from cancer; (b) the composition comprises neoantigenic peptides comprising tumor-specific neoepitopes which bind to HLA proteins present in at least 5% of subjects in the population; and (c) the composition comprises at least one neoantigenic peptide capable of elicitingan immune response against a tumor present in at least 5% of the subjects in the population of subjects suffering from cancer.
Owner:THE BROAD INST INC +2
Methods and compositions for manipulating translation of protein isoforms from alternative initiation of start sites
InactiveUS20140296321A1High sensitivityImprove translationSugar derivativesPolymorphism usesStart codonStart site
Provided herein are antisense oligonucleotides, compositions comprising antisense oligonucleotides, and methods for the use of antisense oligonucleotides in manipulating translation. Expression of isoforms of proteins expressed from different start codons of the same transcript are inhibited by antisense oligonucleotides, which may also enhance expression of non-target isoforms.
Owner:SAREPTA THERAPEUTICS INC
Agent for suppressing expression of dominant mutant gene
InactiveUS20130197061A1Inhibit expressionMaintain expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesWild typeGene
Owner:LSIP
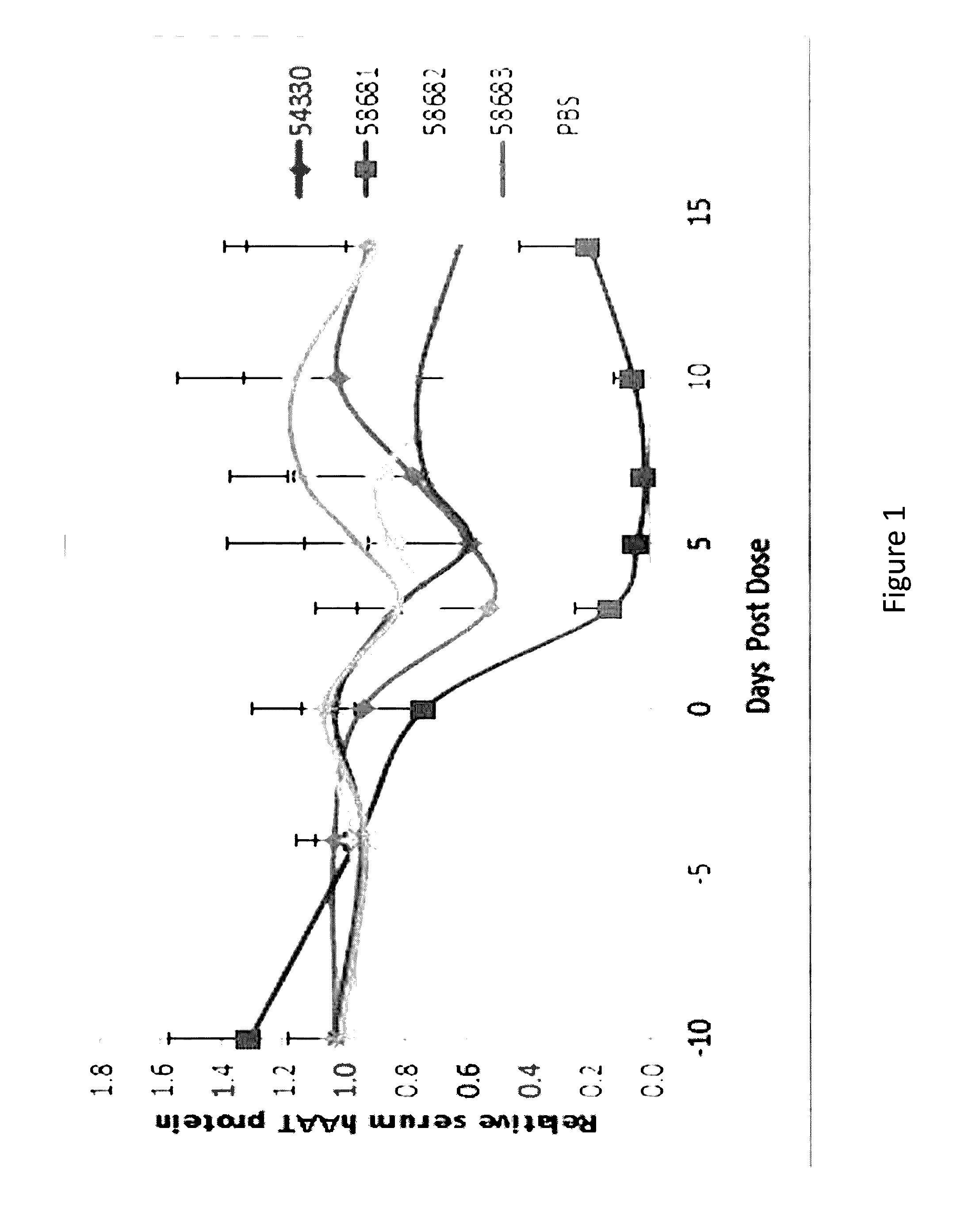
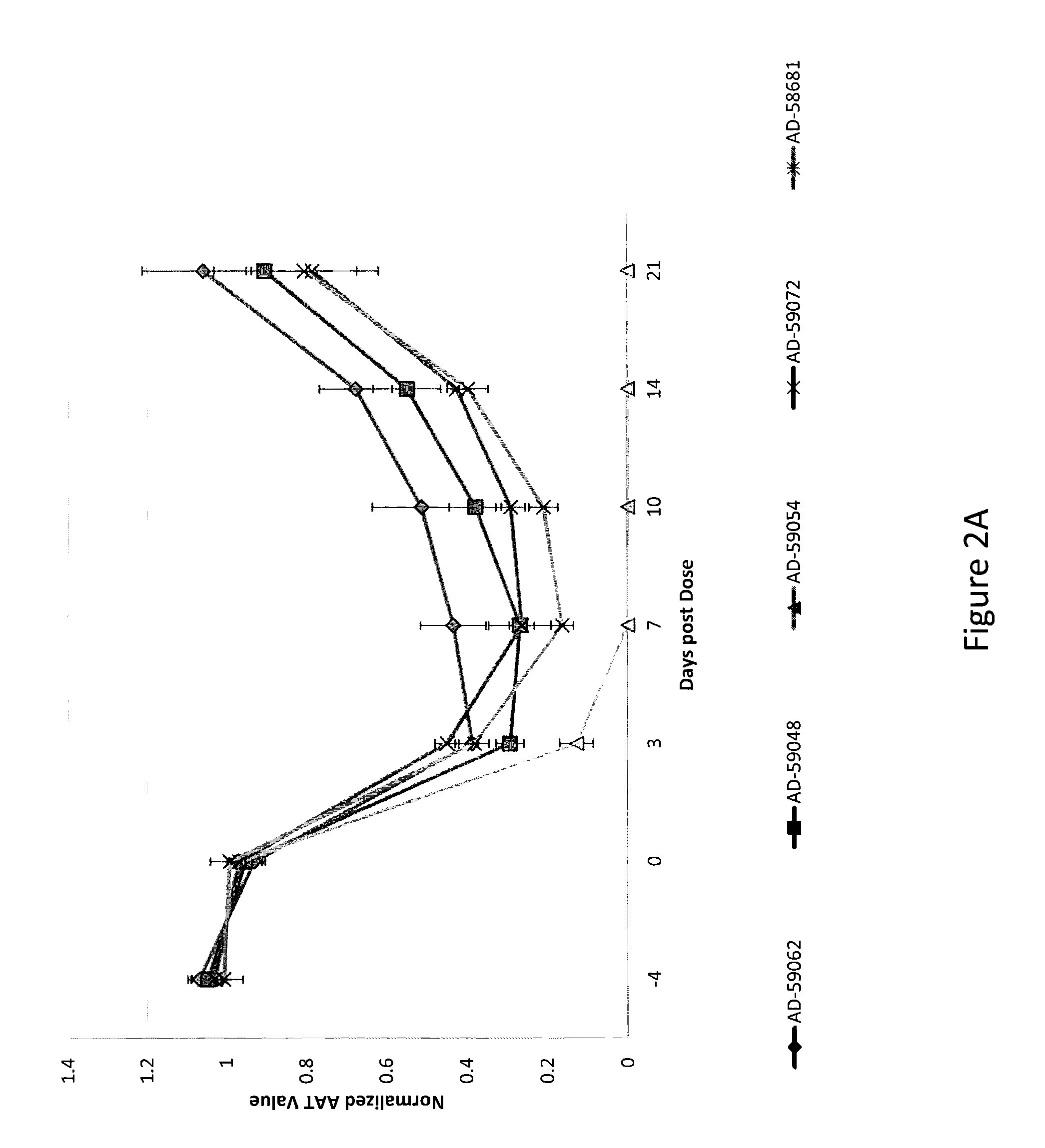
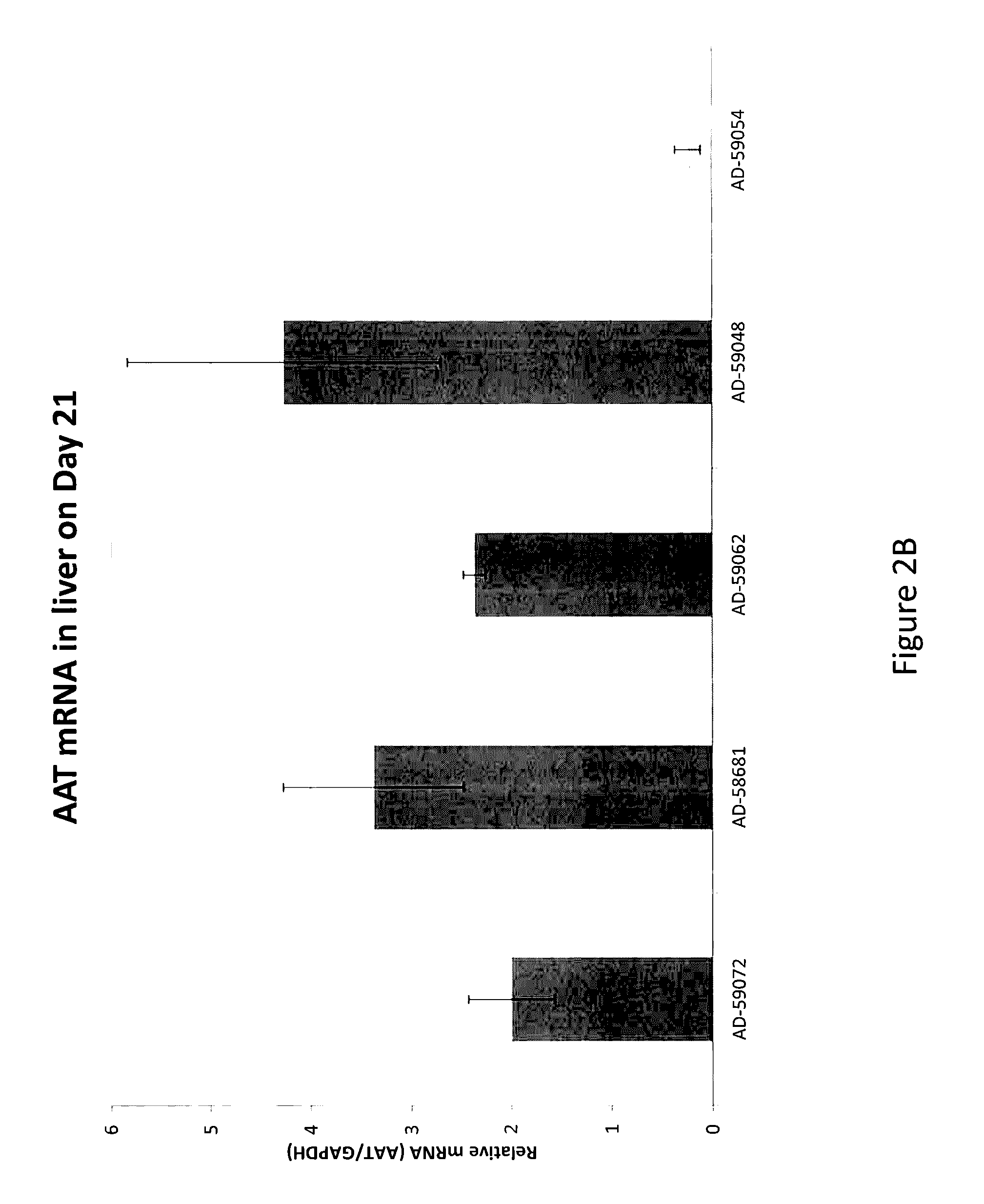
SERPINA1 iRNA COMPOSITIONS AND METHODS OF USE THEREOF
ActiveUS20140350071A1Reduce accumulationAvoid developmentOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryBiotechnologyDisease
The invention relates to RNAi agents, e.g., double-stranded RNAi agents, targeting the Serpina1 gene, and methods of using such RNAi agents to inhibit expression of Serpina1 and methods of treating subjects having a Serpina1 associated disease, such as a liver disorder.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARM INC
Methods and compositions for the treatment of huntington's disease
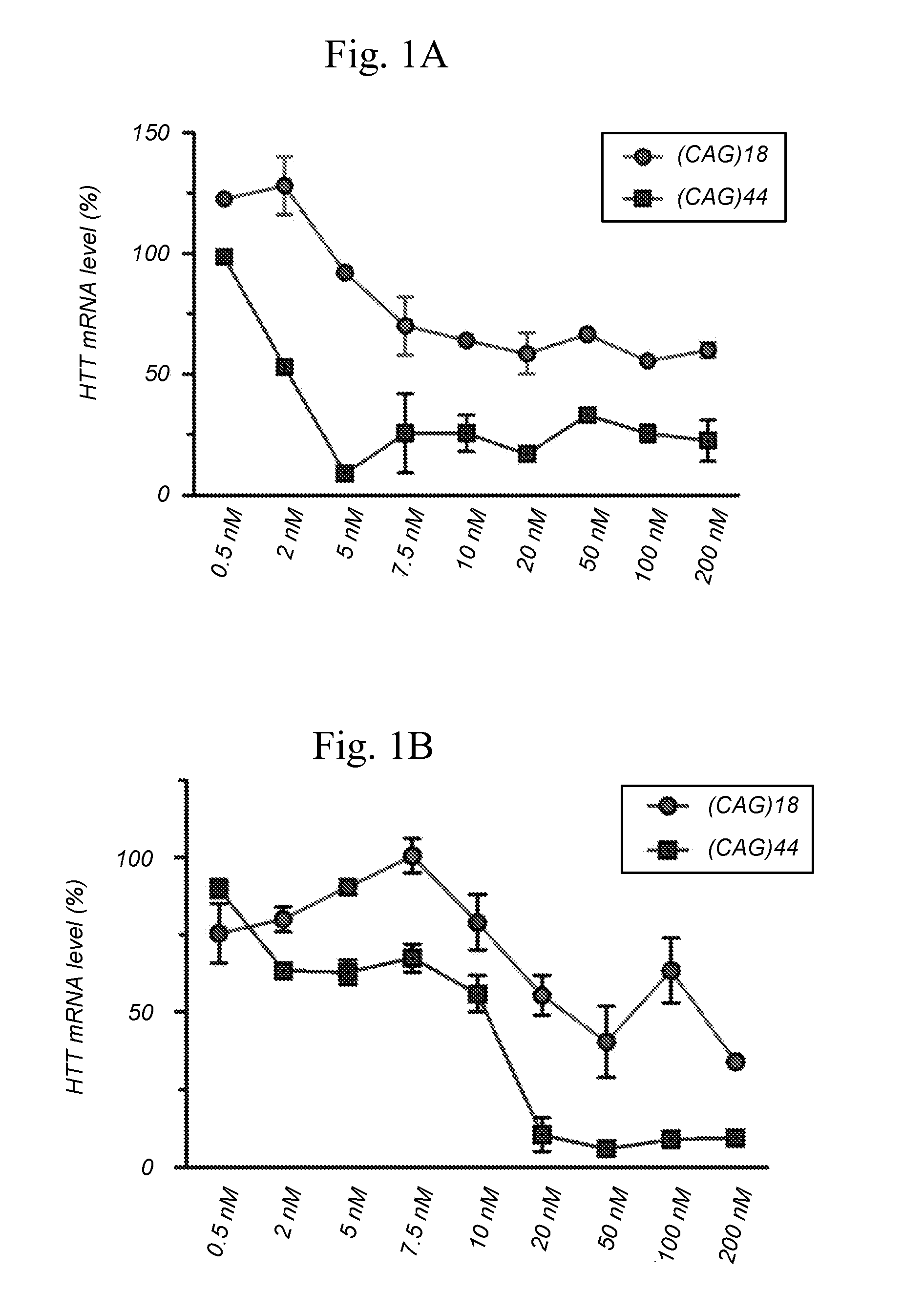
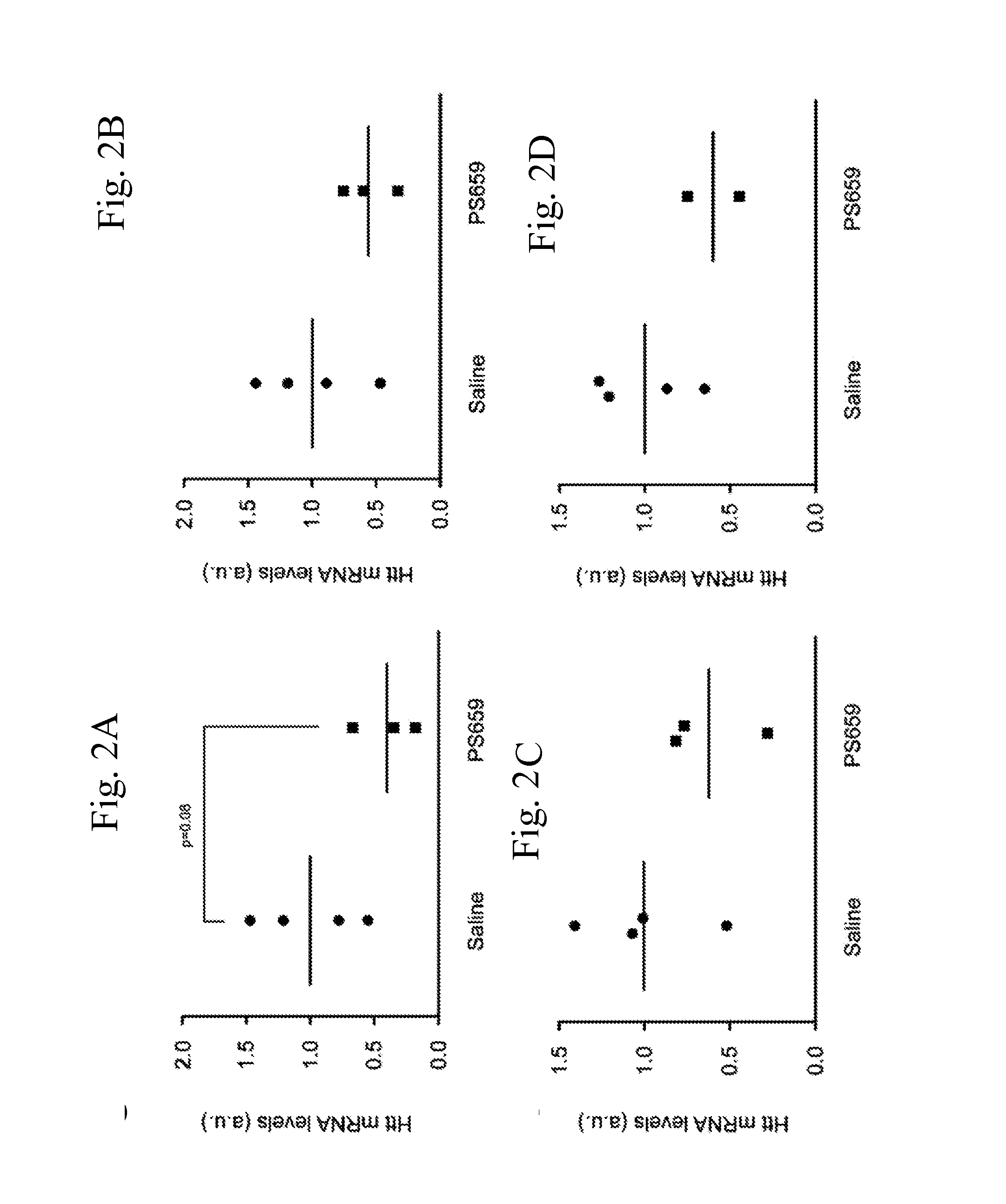
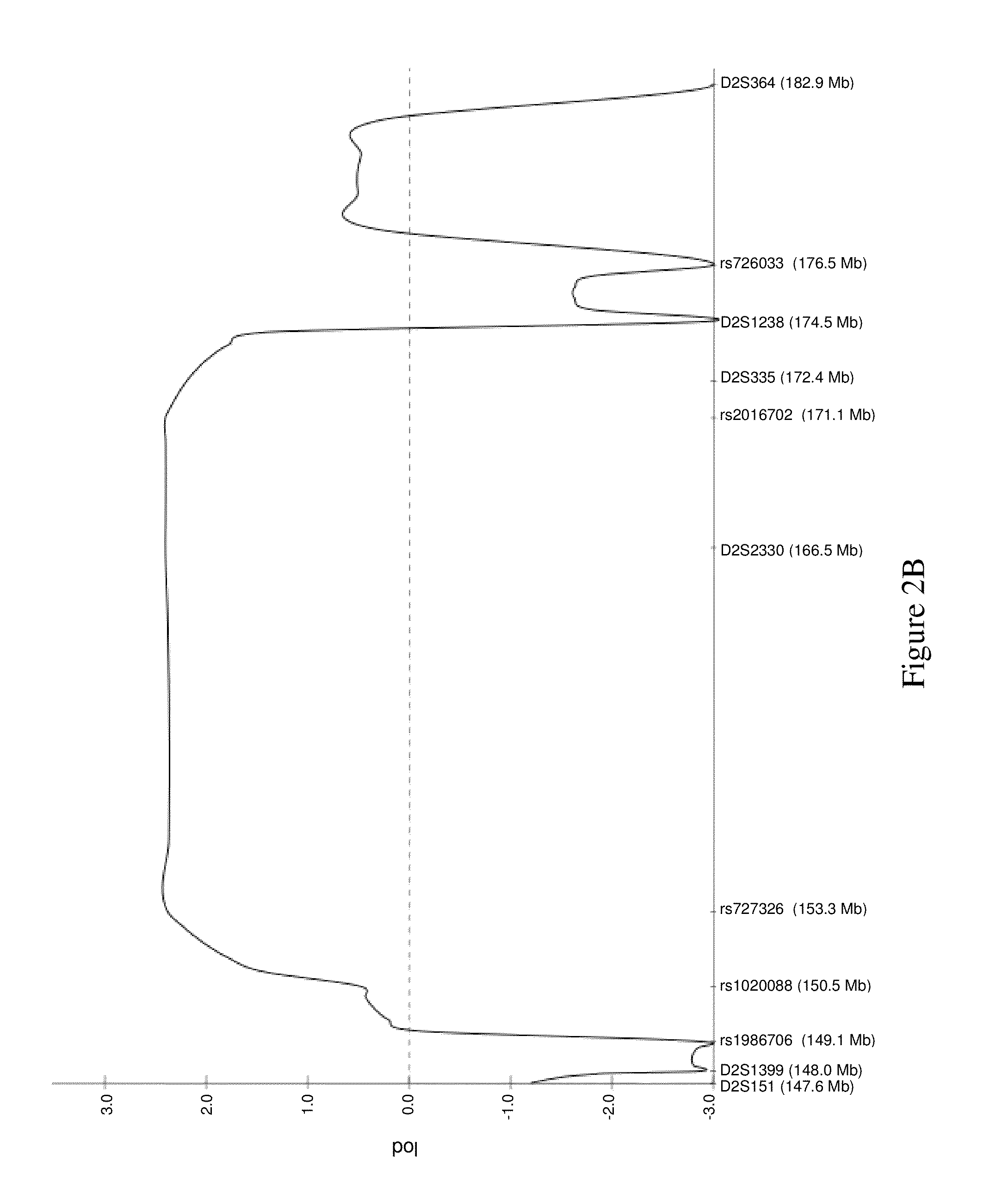
Methods and compositions for reducing expression of a mutant huntingtin (mHTT) protein in a cell are provided. Such methods include contacting the cell with an effective amount of a nucleic acid silencing agent targeting a differentiating polymorphism in RNA encoding the mHTT.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Methods and compositions for the treatment of Huntington'S disease
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA
Allele selective gene editing and uses thereof
ActiveUS20170080107A1Improve efficiencyHigh frequencySenses disorderNervous disorderDiseaseGene selection
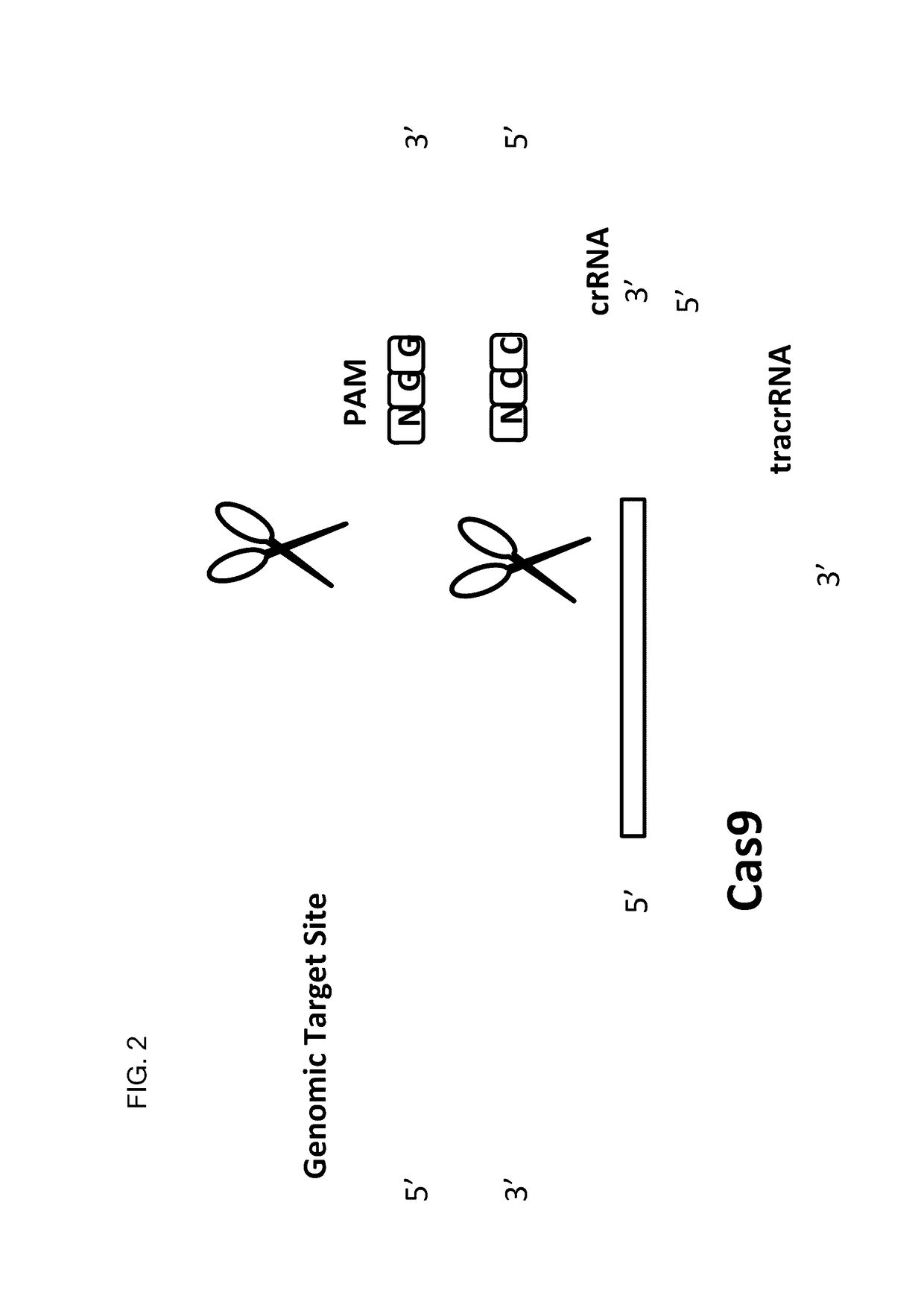
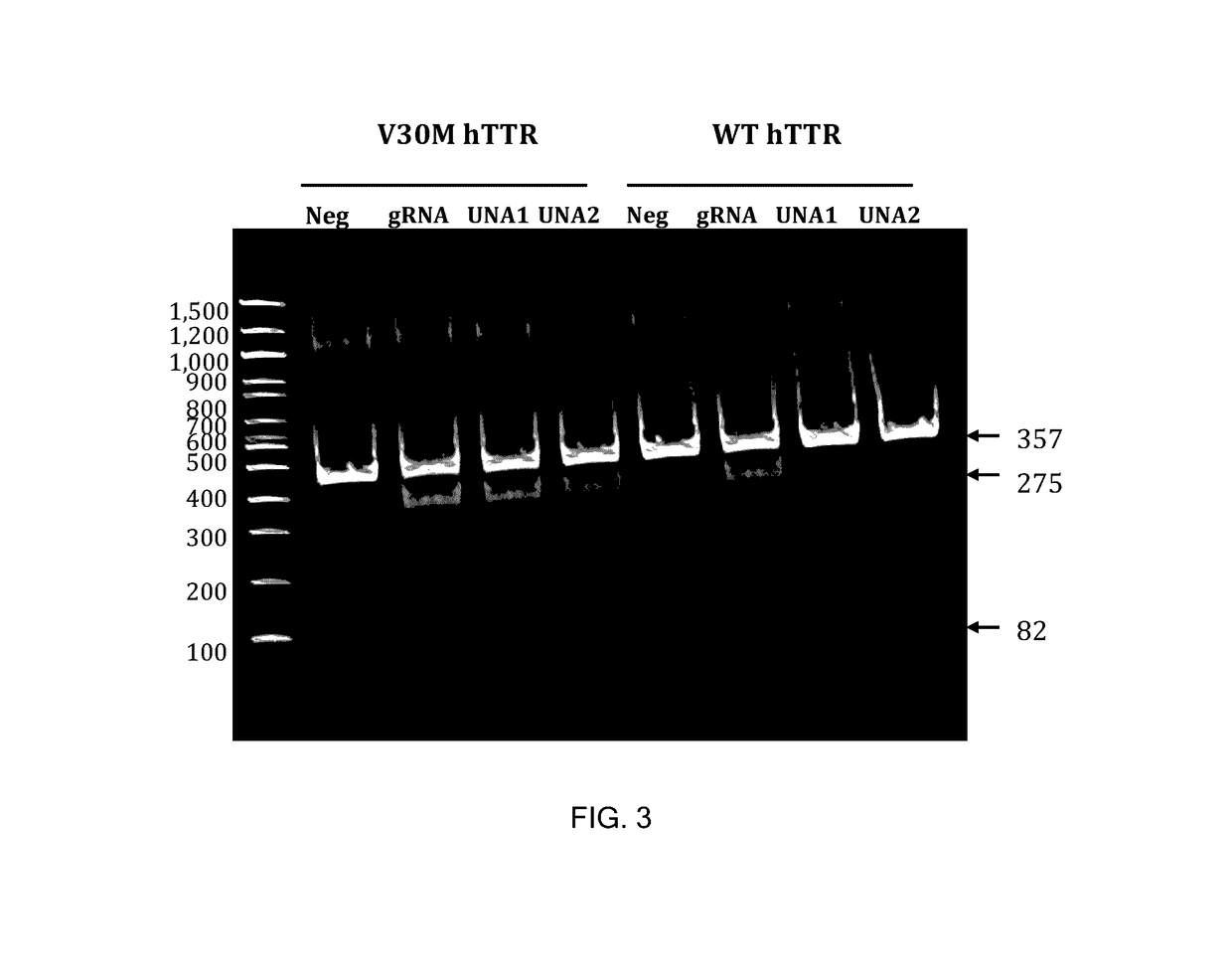
This invention encompasses compounds, structures, compositions and methods for therapeutic guide molecules that direct CRISPR gene editing. A guide molecule for directing gene editing can be allele selective, or disease allele selective, and can exhibit reduced off target activity. A guide molecule can be composed of monomers, including UNA monomers, nucleic acid monomers, and modified nucleotides, wherein the compound is targeted to a genomic DNA. The guide molecules of this invention can be used as active ingredients for editing or disrupting a gene in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
RNA interference for the treatment of gain-of-function disorders
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
RNA Modulating Oligonucleotides with Improved Characteristics for the Treatment of Neuromuscular Disorders
ActiveUS20150148404A1High affinityHigh melting temperatureNervous disorderSugar derivativesDiseaseInstability
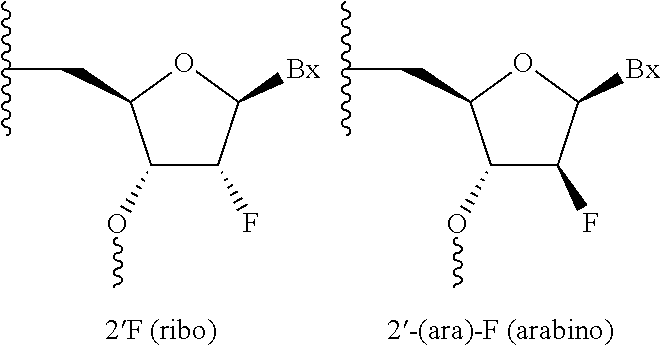
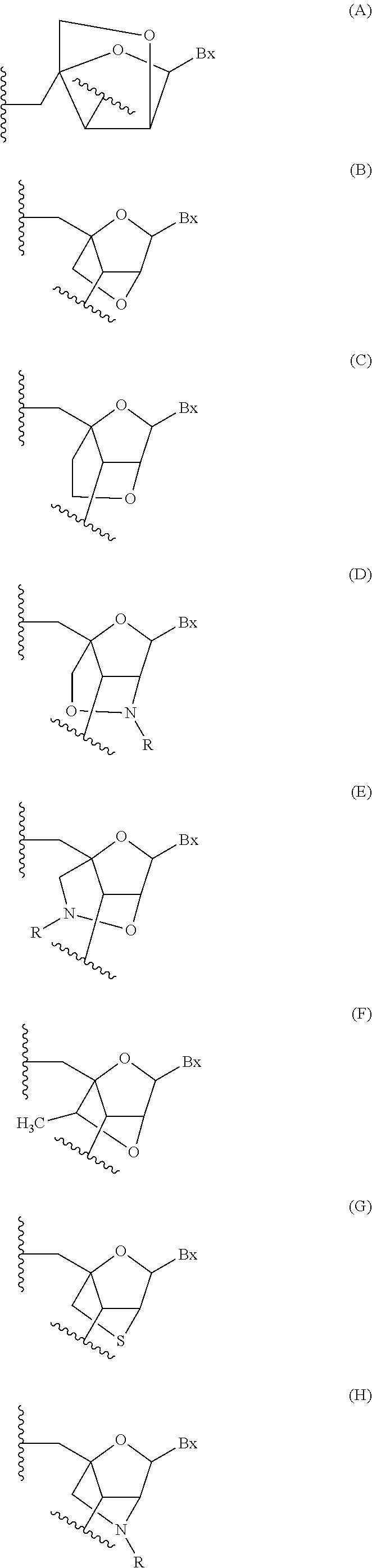
The current invention provides an improved oligonucleotide and its use for treating, ameliorating, preventing, delaying and / or treating a human cis-element repeat instability associated genetic neuromuscular or neurodegenerative disorder.
Owner:VICO THERAPEUTICS BV
Selective reduction of allelic variants
ActiveUS20130046008A1Easy to processInhibit expressionOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaHuntingtin Gene
Disclosed herein are antisense compounds and methods for selectively reducing expression of an allelic variant of a huntingtin gene containing a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). Such methods, compounds, and composition are useful to treat, prevent, or ameliorate Huntington's Disease (HD).
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC +1
Oligomers targeting hexanucleotide repeat expansion in human c9orf72 gene
InactiveUS20160108396A1Reduce the amount requiredReduce expressionSugar derivativesPolymorphism usesOligomerNucleotide
The disclosure relates to oligomers capable of targeting RNA expressed from the human C9ORF72 gene containing a pathogenic hexanucleotide repeat expansion. Such oligomers are useful for, among other things, reducing or eliminating C9ORF72 RNA and / or proteins translated therefrom, and treating or preventing diseases or disorders caused by, or associated with, hexanucleotide repeat expansion, including familial frontotemporal dementia (FTD) and familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS).
Owner:PFIZER INC
Selective antisense compounds and uses thereof
ActiveUS20150376625A1Many symptomModulate expressionNervous disorderSugar derivativesNucleic acid hybridisationNon targeted
The present disclosure provides oligomeric compounds. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell. In certain embodiments, certain oligomeric compounds selectively reduce the expression of a target nucleic acid transcript relative to a non-target nucleic acid transcript.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
RNA interference for the treatment of gain-of-function disorders
ActiveUS20110172291A1Increased nuclease resistanceIncrease resistanceOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderDiseaseHuntingtons chorea
The present invention relates to the discovery of an effective treatment for a variety of gain-of-function diseases, in particular, Huntington's disease (HD). The present invention utilizes RNA Interference technology (RNAi) against polymorphic regions in the genes encoding various gain-of-function mutant proteins resulting in an effective treatment for the gain-of-function disease.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Selective reduction of allelic variants
ActiveUS20130046007A1Treat and prevent and ameliorate diseaseReduce expressionSenses disorderNervous disorderHuntingtons choreaDisease
Disclosed herein are antisense compounds and methods for selectively of reducing expression of an allelic variant of a gene containing a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). Such methods, compounds, and composition are useful to treat, prevent, or ameliorate diseases, including neurodegenerative, such as Huntington's Disease (HD).
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
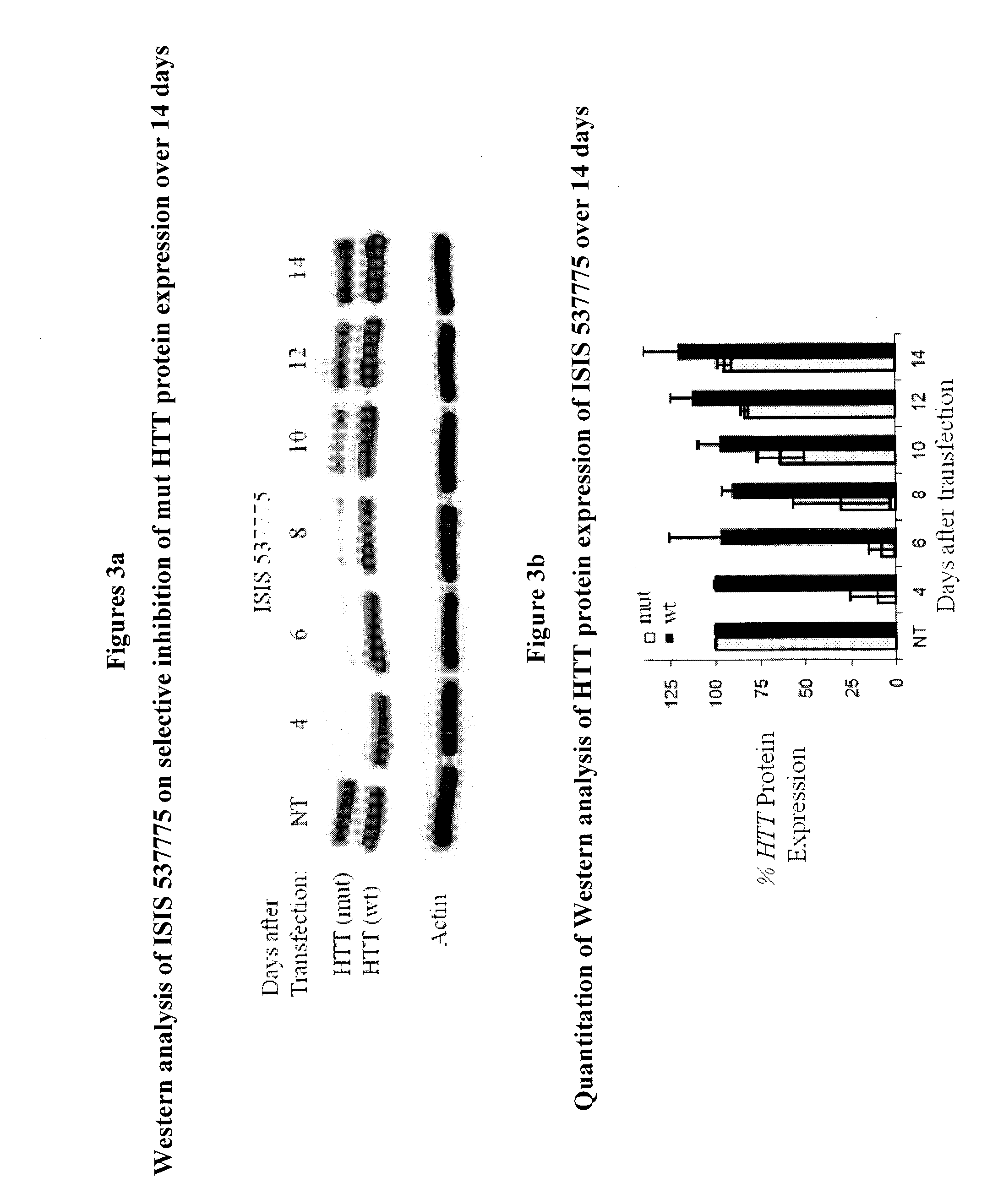
Phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers (PMOS) and their use in suppression of mutant huntingtin expression and attenuation of neurotoxicity
InactiveUS20160017327A1Improve neurotoxicityDecrease HTT protein expressionOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesHuntingtons choreaADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides antisense phosphorodiamidate morpholino oligomers which are useful for the suppression or inhibition of the HTT gene involved in Huntington's disease. The oligomers can selectively suppress mutant forms of the HTT protein while allowing the normal protein to be expressed in sufficient quantity to retain its function in the cell. Methods for treatment of Huntington's disease are also provided.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Selective antisense compounds and uses thereof
The present disclosure provides oligomeric compounds. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell. In certain embodiments, certain oligomeric compounds selectively reduce the expression of a target nucleic acid transcript relative to a non-target nucleic acid transcript.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating pompe disease
PendingUS20210317226A1Reducing glycogen levelSpecial deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseInternalization
Aspects of the disclosure relate to complexes comprising a muscle-targeting agent covalently linked to a molecular payload. In some embodiments, the muscle-targeting agent specifically binds to an internalizing cell surface receptor on muscle cells. In some embodiments, the molecular payload reduces glycogen levels in a cell.
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Linkage modified gapped oligomeric compounds and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140303235A1Loss of normal functionHigh selectivitySugar derivativesPolymorphism usesModified nucleosidesToxicity profile
The present invention provides gapped oligomeric compounds. More particularly the gapped oligomeric compounds provided herein comprise at least one modified intemucleoside linkage in the gap region. Such gapped oligomeric compounds have one or more improved properties such as selectivity, potency, improved toxicity profile and or improved proinflammatory profile. Certain such oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited, to nucleic acids in a cell. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Selective reduction of allelic variants
Disclosed herein are antisense compounds and methods for selectively reducing expression of an allelic variant of a huntingtin gene containing a single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP). Such methods, compounds, and composition are useful to treat, prevent, or ameliorate Huntington's Disease (HD).
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Modulation of RNA by repeat targeting
Disclosed herein are antisense compounds, compositions and methods for modulating an RNA target by targeting a repetitive sequence in the RNA target and modulating an associated disease, disorder and / or condition related to such RNA target. Also disclosed herein are methods of identifying such compounds and compositions.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Sirna-based therapy of fibrodyplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP)
This invention is directed to mutated Activin A type I receptor proteins (ACVR1) and isolated nucleic acids encoding same. The invention also relates to compositions and methods for siRNA-based regulation of mutated ACVR1 expression in the treatment of Fibrodysplasia Ossificans Progressiva (FOP).
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Methods and compounds useful in conditions related to repeat expansion
ActiveUS20140316121A1Reduced activityReduce the amount requiredOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesDisease causeStereochemistry
Described are compounds and methods useful for the treatment and investigation of diseases and disorders associated with expanded repeat-containing RNA molecules.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Muscle targeting complexes and uses thereof for treating hypertrophic cardiomyopathy
Aspects of the disclosure relate to complexes comprising a muscle-targeting agent covalently linked to a molecular payload. In some embodiments, the muscle-targeting agent specifically binds to an internalizing cell surface receptor on muscle cells. In some embodiments, the molecular payload inhibits expression or activity of a MYH7 allele comprising a disease-associated mutation, e.g., for the treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. In some embodiments, the molecular payload is an oligonucleotide, such as an antisense oligonucleotide or RNAi oligonucleotide.
Owner:DYNE THERAPEUTICS INC
Gapped oligomeric compounds comprising 5'-modified deoxyribonucleosides in the gap and uses thereof
ActiveUS20140309279A1Loss of normal functionHigh selectivitySugar derivativesPolymorphism usesNucleic acid hybridisationOrganic chemistry
The present invention provides gapped oligomeric compounds comprising at least one 5′-substituted P-D-2′-deoxyribonucleoside in the gap region. Certain such gapped oligomeric compounds are useful for hybridizing to a complementary nucleic acid, including but not limited to, nucleic acids in a cell. The oligomeric compounds provided herein have improved properties such as selectivity, potency and improved proinflammatory profile. In certain embodiments, hybridization results in modulation of the amount of activity or expression of the target nucleic acid in a cell.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Serapina1 iRNA compositions and methods of use thereof
ActiveUS9574192B2Avoid developmentReduce accumulationOrganic active ingredientsSpecial deliveryMedicine
The invention relates to RNAi agents, e.g., double-stranded RNAi agents, targeting the Serpina1 gene, and methods of using such RNAi agents to inhibit expression of Serpina1 and methods of treating subjects having a Serpina1 associated disease, such as a liver disorder.
Owner:ALNYLAM PHARMA INC
Allele selective gene editing and uses thereof
ActiveUS10369232B2Efficient gene editingReduce off-target effectsSenses disorderNervous disorderNucleotideGenomic DNA
This invention encompasses compounds, structures, compositions and methods for therapeutic guide molecules that direct CRISPR gene editing. A guide molecule for directing gene editing can be allele selective, or disease allele selective, and can exhibit reduced off target activity. A guide molecule can be composed of monomers, including UNA monomers, nucleic acid monomers, and modified nucleotides, wherein the compound is targeted to a genomic DNA. The guide molecules of this invention can be used as active ingredients for editing or disrupting a gene in vitro, ex vivo, or in vivo.
Owner:ARCTURUS THERAPEUTICS
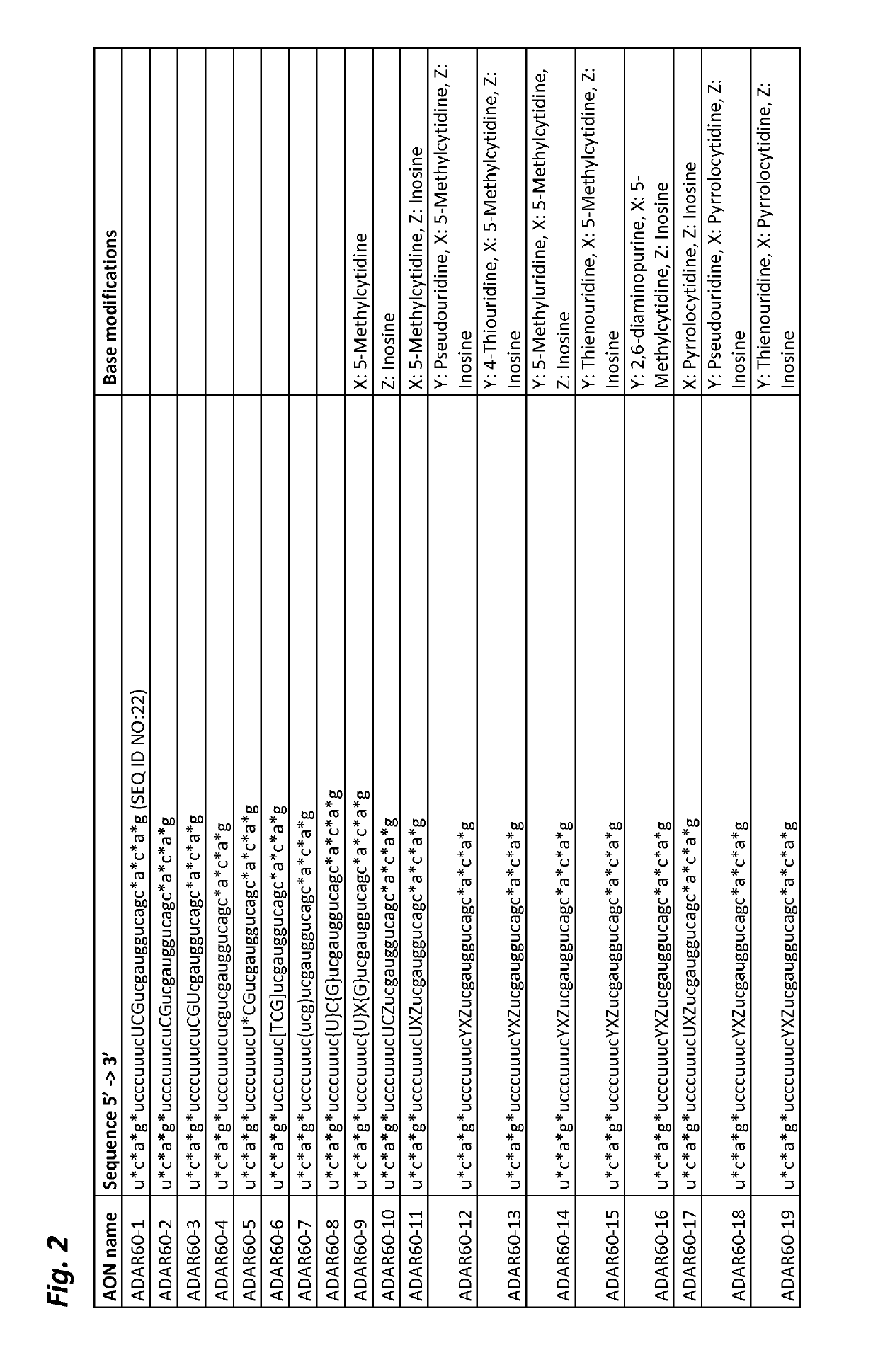
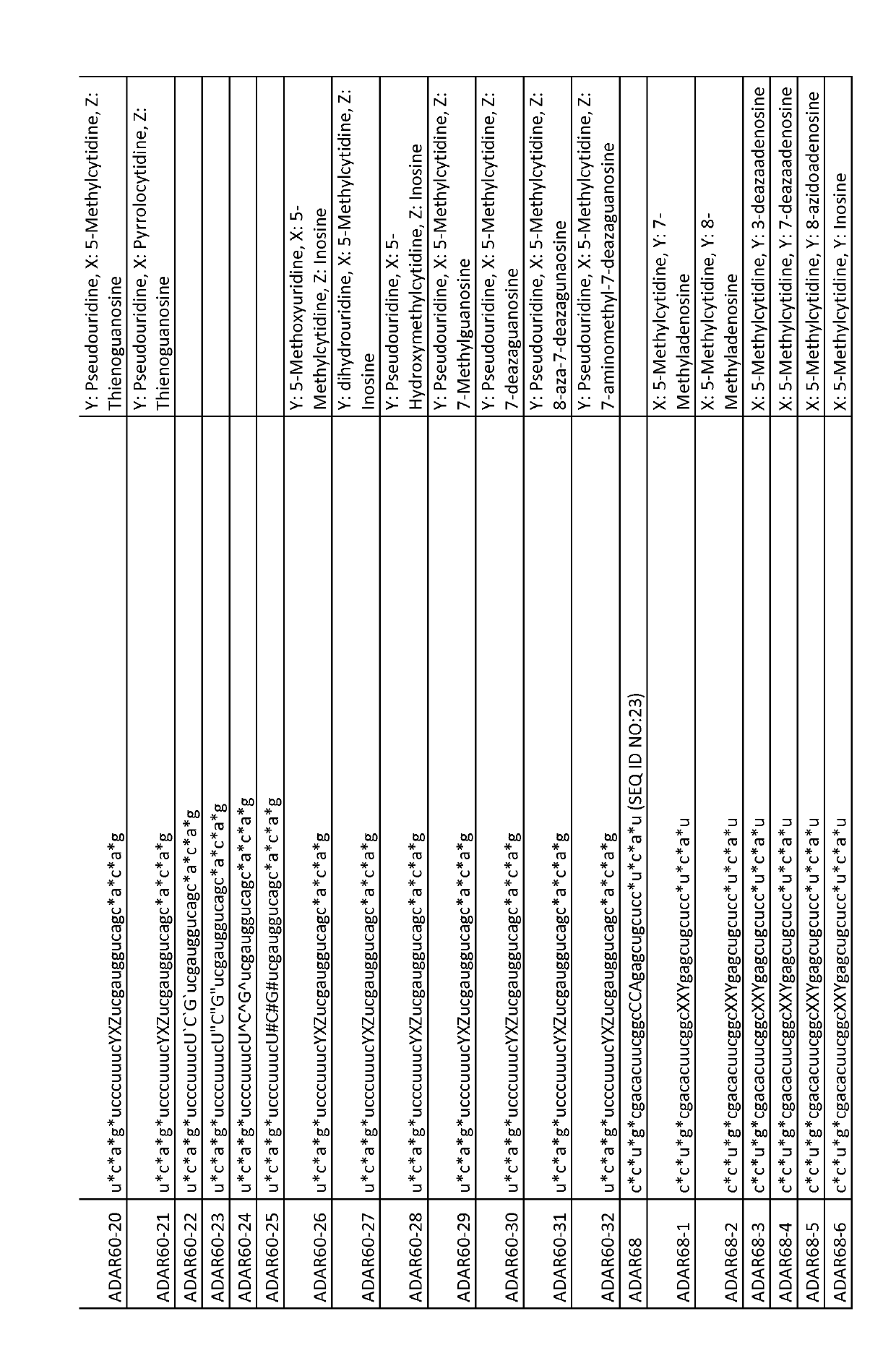
Chemically modified single-stranded rna-editing oligonucleotides
ActiveUS20190218552A1Ameliorate organ function.Disease reliefSenses disorderNervous disorderSingle-Stranded RNAAdenosine
The invention relates to antisense oligonucleotides that are capable of bringing about specific editing of a target nucleotide (adenosine) in a target RNA sequence in a eukaryotic cell, wherein said oligonucleotide does not, in itself, form an intramolecular hairpin or stem-loop structure, and wherein said oligonucleotide comprises a non-complementary nucleotide in a position opposite to the nucleotide to be edited in the target RNA sequence.
Owner:PROQR THERAPEUTICS II BV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com