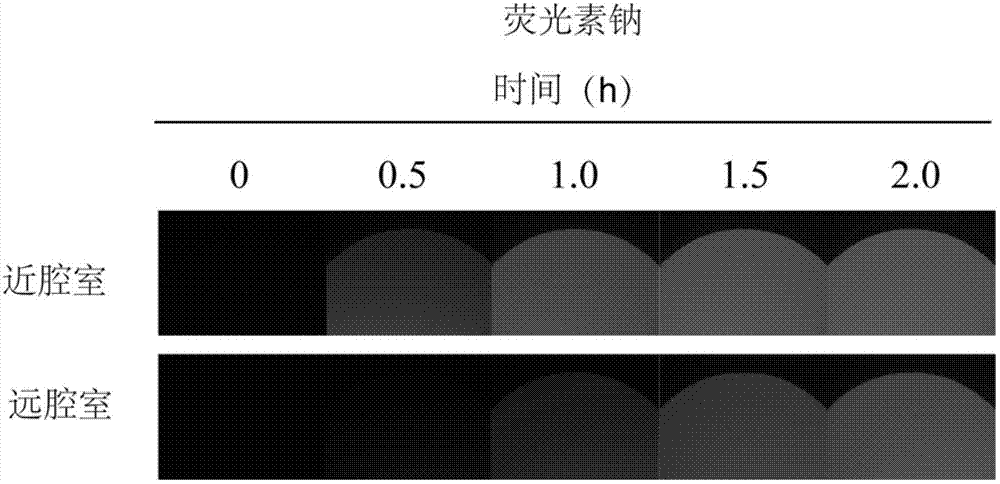
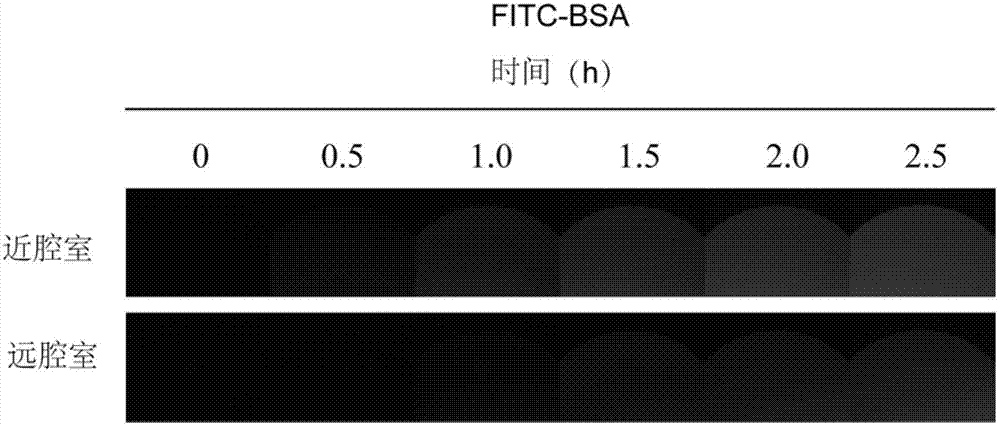
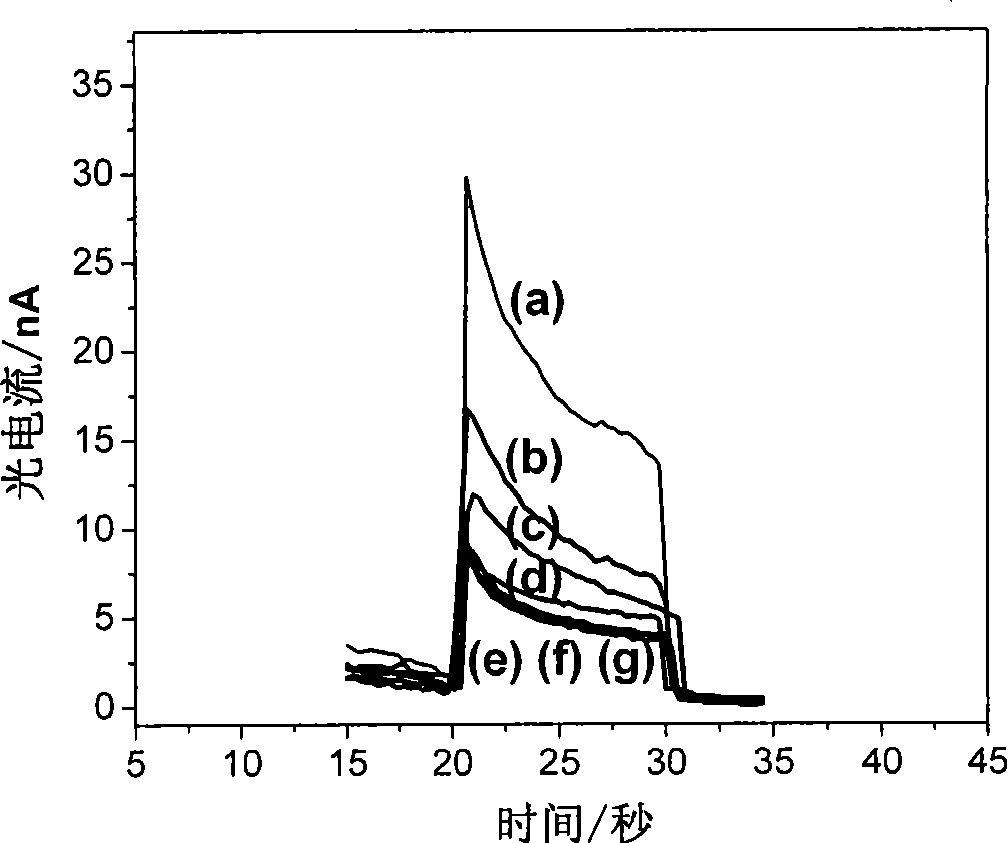
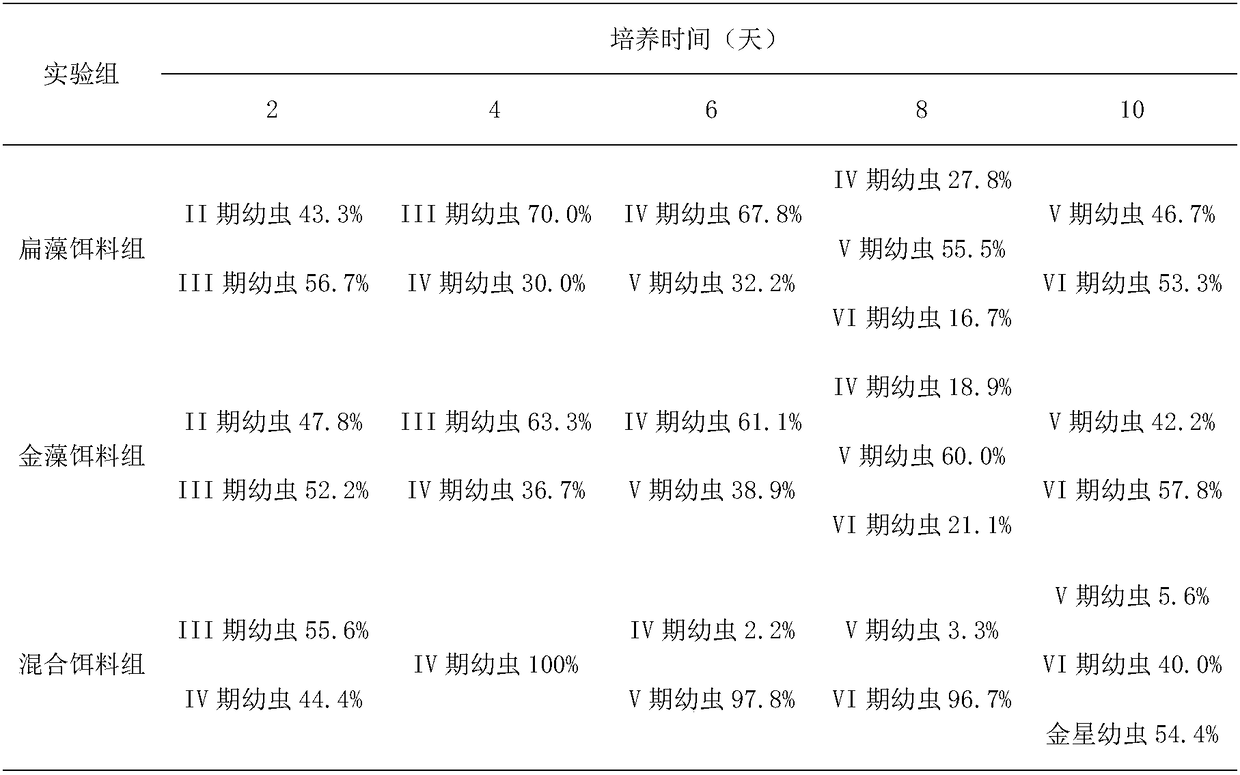
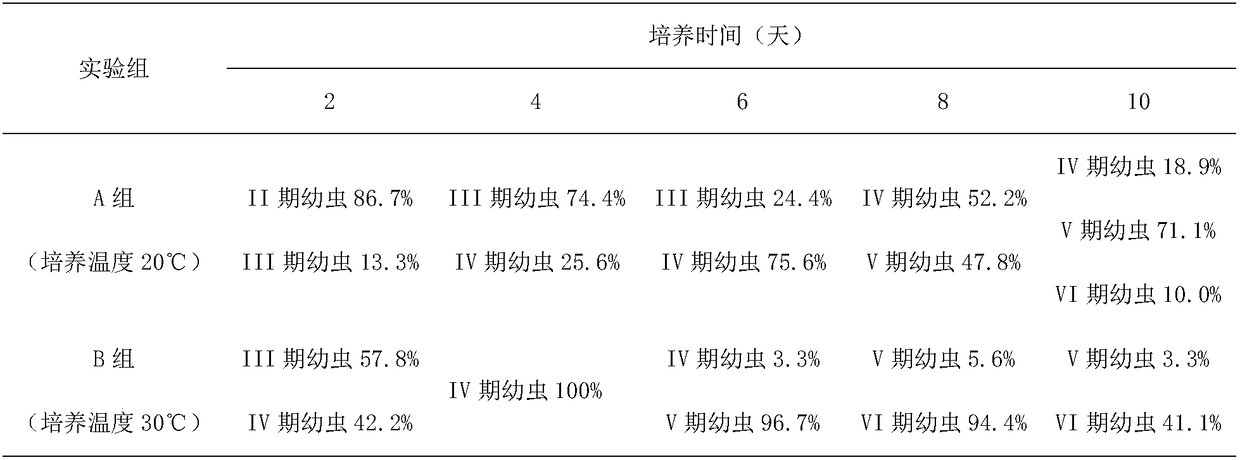
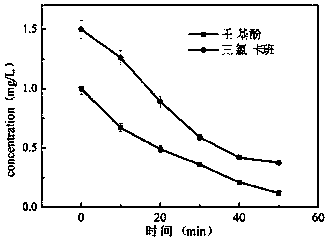
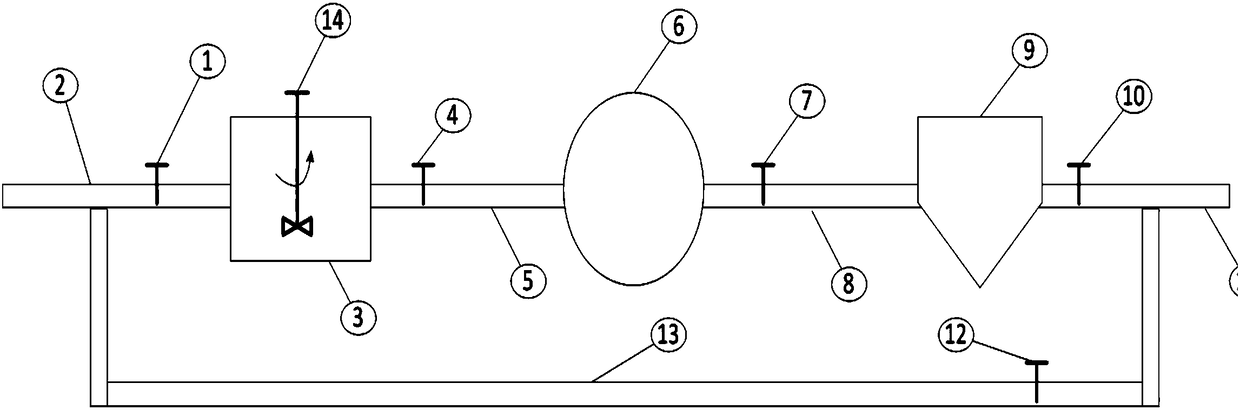
Patents
Literature
34 results about "Environmental toxicology" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Environmental toxicology is a multidisciplinary field of science concerned with the study of the harmful effects of various chemical, biological and physical agents on living organisms. Ecotoxicology is a subdiscipline of environmental toxicology concerned with studying the harmful effects of toxicants at the population and ecosystem levels.
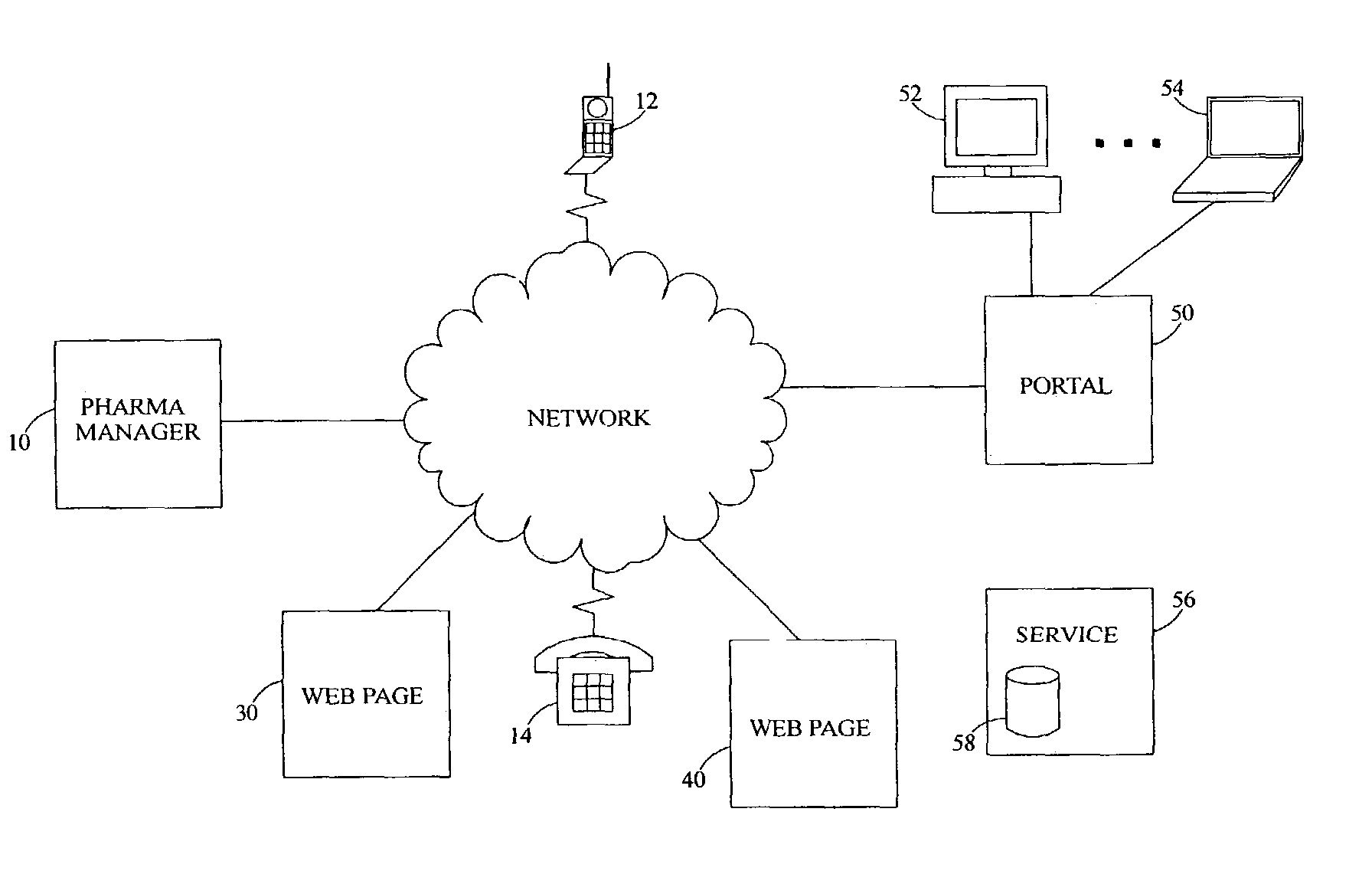
Pharmaceutical hazardous waste identification and management system
InactiveUS7096161B2Solid waste disposalDigital data processing detailsInformation repositoryEnvironmental toxicology
A pharmaceutical hazardous waste identification and management system integrates disparate information regarding pharmaceuticals to provide an indication of which pharmaceuticals are hazardous wastes as defined by respective national, international and state regulations and / or which are hazardous materials as defined by the US OSHA regulations. A subset of this information offers a global repository with respect to the occurrence, concentrations, and ecotoxicologic data of pharmaceuticals based on peer reviewed data provided by environmental toxicologists and related scientists.
Owner:WASTE MANAGEMENT NAT SERVICES INC
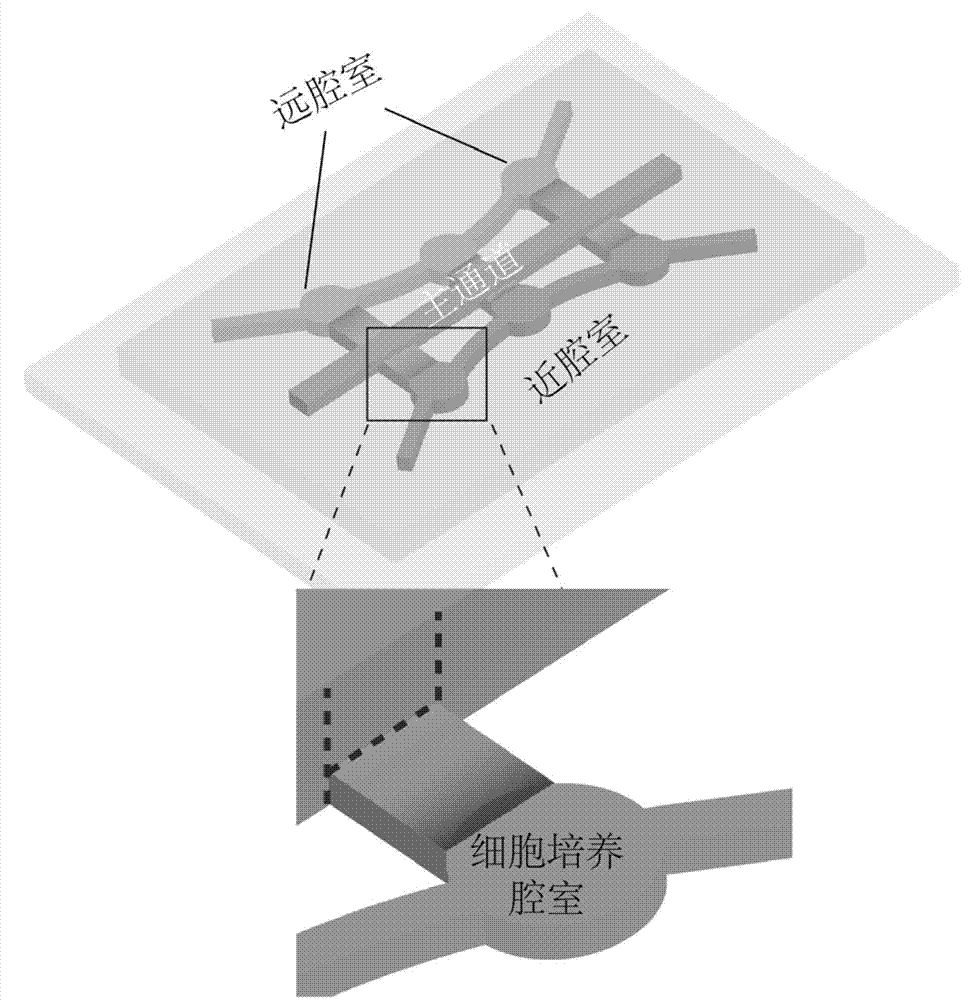
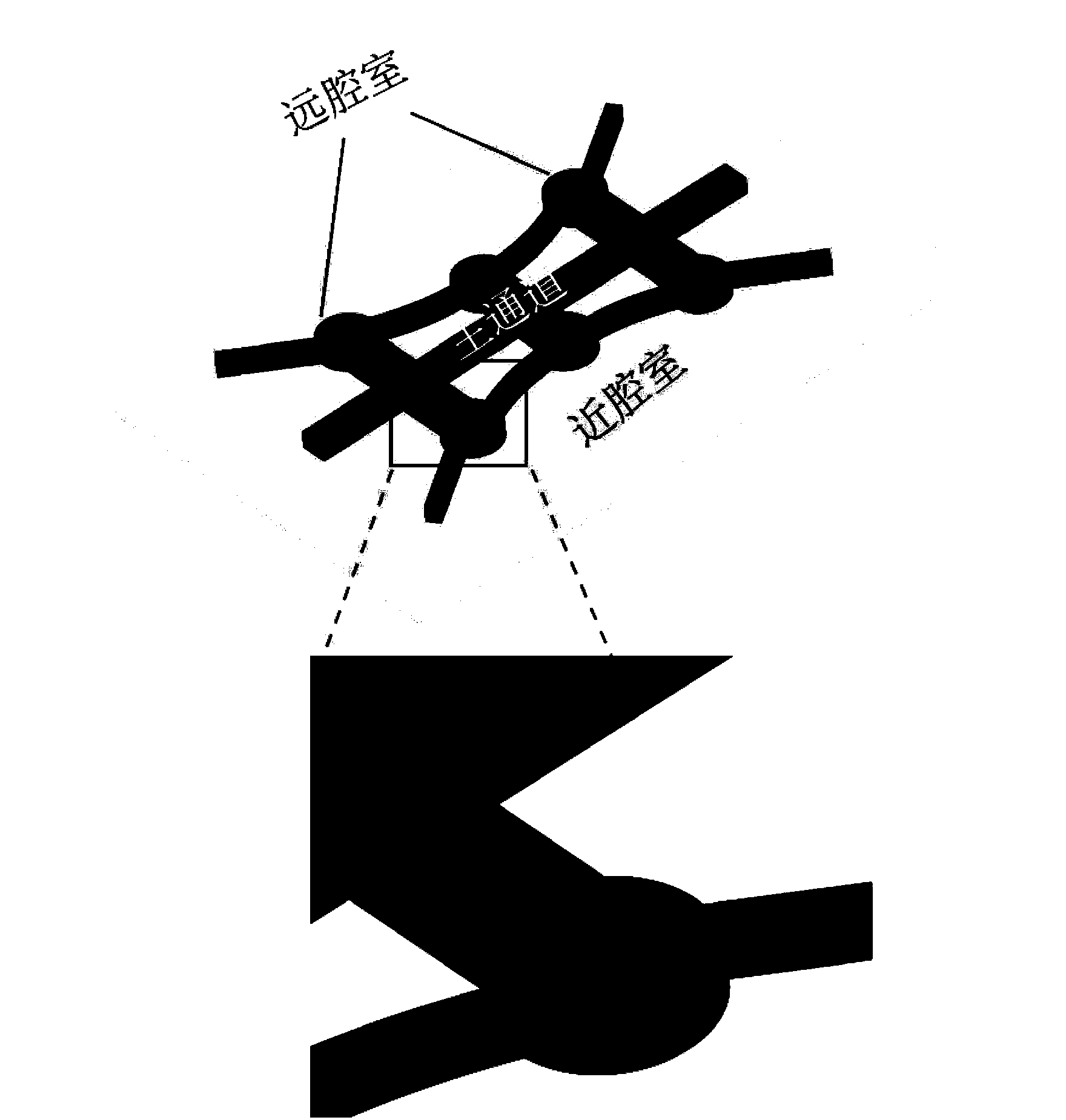
Microfluidic chip apparatus and application thereof
ActiveCN102728422AGood biocompatibilityEasy to makeMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresEnvironmental toxicologyQuantum dot
The invention provides a three-dimensional cultivation microfluidic chip apparatus used for quantum dot cytotoxicity detection. The microfluidic chip apparatus is manufactured by bonding a dimethyl silicone polymer chip and a glass substrate. The chip has two parts, which are a main channel and cell cultivation chambers. The main channel is used for simulating a blood vessel. The cell cultivation chambers communicate with the main channel with different distances, and are used for simulating adjacent tissues with different distances from the blood vessel. The heights of the main channel and the cell cultivation chambers are different, such that a mixture of cells and a three-dimensional cultivation substrate is prevented from leaking to the main channel when injected into the cell cultivation chambers. The apparatus can further be used for proofing that one of the quantum dot cytotoxicity cell mechanisms is the cell autophagia effect. The microfluidic chip apparatus provided by the invention is advantaged in simple manufacturing and easy operation. The apparatus can be used for simulating the diffusion process of the blood vessel and the adjacent tissues. With the apparatus, three-dimensional cultivation and quantum dot cytotoxicity detection of cells can be realized. Therefore, the apparatus is suitable for medicine screening and environmental toxicology analysis.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Construction method of Epinephelus fuscoguttatus heart cell line
InactiveCN101451121AIdeal for in vitro studiesSkeletal/connective tissue cellsInsulin-like growth factorLiquid medium
The invention relates to a method for constructing a heart cell system of blotchy rockcod, which comprises: taking a heart tissue of the blotchy rockcod as a material, adopting a trypsin digestion method to start primary culture, and culturing the heart tissue in a DMEM / F12 liquid medium which contains fetal calf serum, basic fibroblast growth factors, I-type insulin-like growth factors, chondroitin sulfate and culture supernatant of fin cells of the blotchy rockcod in the log phase and has a pH value of between 7.0 and 7.4; and adopting the trypsin digestion method for subculturing. The heart cell system of the blotchy rockcod constructed by the method is subcultured for 70 generations currently. The technology is scientific and reasonable, is hopeful to be applied to separation and breeding of fish viroids, preparation of virus vaccines and research in the aspects of interaction of viruses and host cells, and so on, can also be taken as a model for researching environmental pollutants in environmental toxicology, and performs pollution monitoring and safety evaluation on various environmental pollutants in the sea such as genic toxins, mutagen, carcinogens, environmental hormones and endocrine disruptors.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Construction method for anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line
ActiveCN102766595AGood growthEasy to operateSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAnabarilius grahamiFresh water organism
The invention relates to a construction method for a anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line and belongs to the technical field of freshwater organism cell culture. The method includes using anabarilius grahami heart tissue as a material, washing and shearing the heart tissue, using hyaluronidase and II type collagenase to perform a joint digestion to obtain free heart cells and loose tissue blocks, inoculating the free heart cells and the loose tissue blocks in a culture flask of 25 square centimeters, adding an L-15 culture solution containing fetal calf serum, human basic fibroblast growth factor and chondroitin sulfate in the culture flask, and placing the culture flask in a culture box of 28 DEG C to culture. The culture solution is replaced at an interval of three and half days, and when cells grow into monolayers, a trypsin digestive method is utilized to perform cell passage. The construction method for the schizothorax taliensis cardiac cell line has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the cell growth state of the constructed anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line is good, the cells are fibroblast-like, more than 40 generations can be continuously achieved during the cell passage, the constructed anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line can be directly used for models of an environmental toxicology for studying environmental pollutants to perform pollution detection and safety evaluation, and the method is also suitable for the construction of cardiac cell lines of other fishes.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
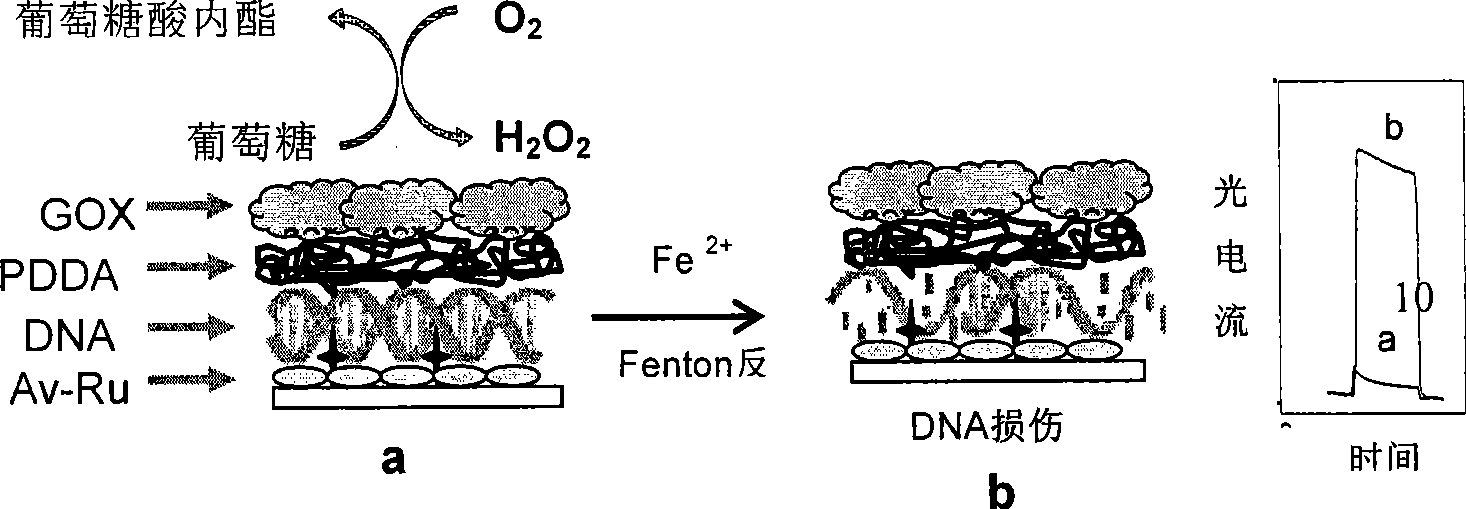
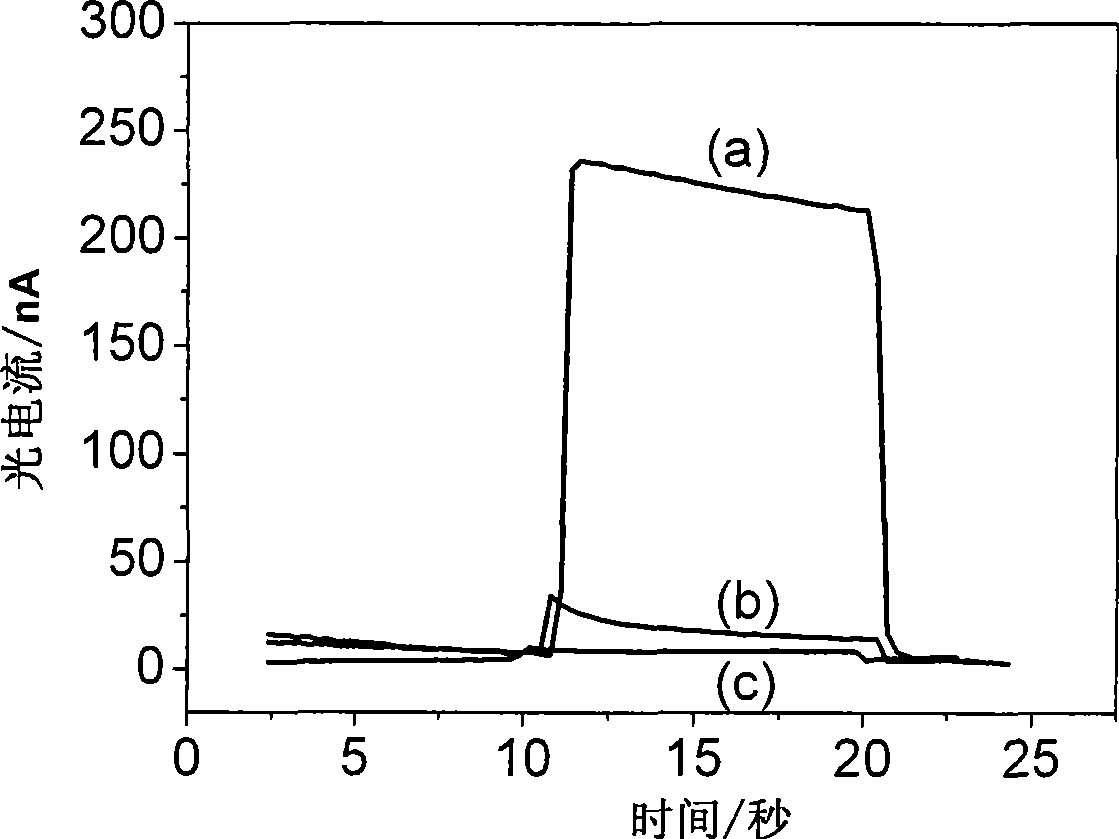
Method and sensor for detecting nucleic acid on-site damage by photoelectrochemistry
InactiveCN101393146AEasy to makeMade practicalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicrobiological testing/measurementSignalling moleculesEnvironmental toxicology
The invention relates to a method and a sensor for detecting on-site damage of nucleic acid in photo-electrochemistry, and provides a method for detecting gene toxicity of chemical substances simply, quickly and sensitively. The method comprises the following steps: (a) an analyte possibly having gene toxicity is contacted with the nucleic acid; (b) if the analyte to be detected expresses the gene toxicity after being activated, a corresponding enzyme is used as an activating agent; (c) photo-electrochemical active molecules are used as a signal indicator; and (d) the combination and / or reaction between the analyte and the nucleic acid is elevated, that is, in the presence of electrodes, current generated by electron transfer between the photoelectrical signal molecules and the electrodes under the action of light is evaluated, and qualitative analysis or quantitative analysis for the gene toxicity of the analyte is carried out according to the difference of photocurrent response before and after the nucleic acid contacts with the analyte. The method and the sensor are applied in the fields of toxicity screening for industrial chemicals, toxicity detecting for environmental pollutants, toxicity testing for synthetic drugs, environmental toxicology research, and the like.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method and device for analyzing toxic effect of pesticide on lobsters bred in rice field
PendingCN111903593ATroubleshooting issues that cannot be guaranteedSolve problems where the security posture cannot be guaranteedClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaEnvironmental toxicologyPaddy field
Owner:NANJING INST OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI MINIST OF ECOLOGY & ENVIRONMENT OF THE PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA
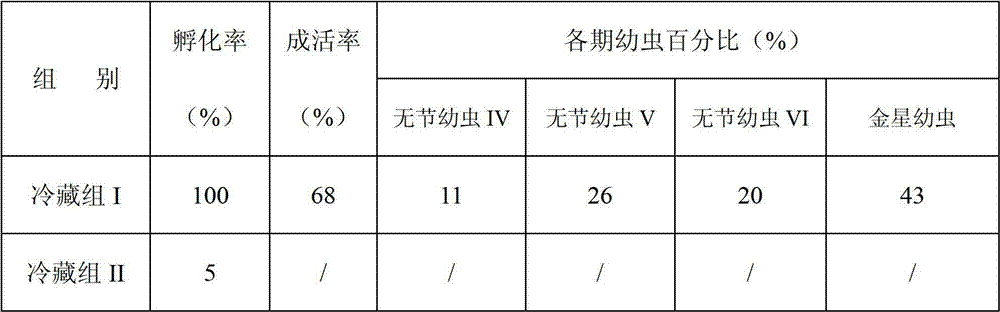
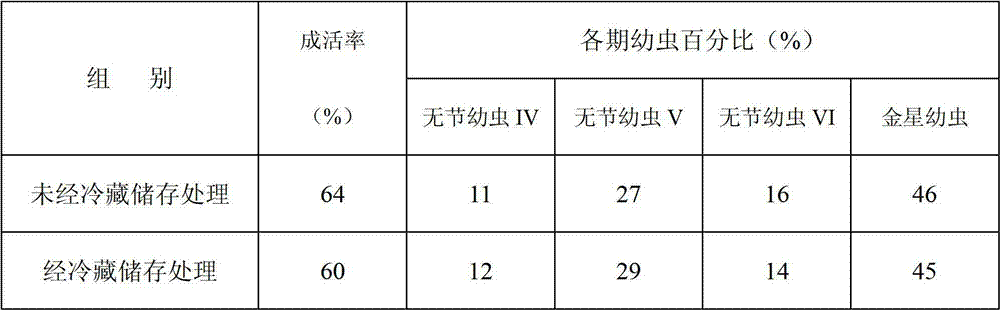
Method for storing mature egg mass of balanus reticulatus utinomi
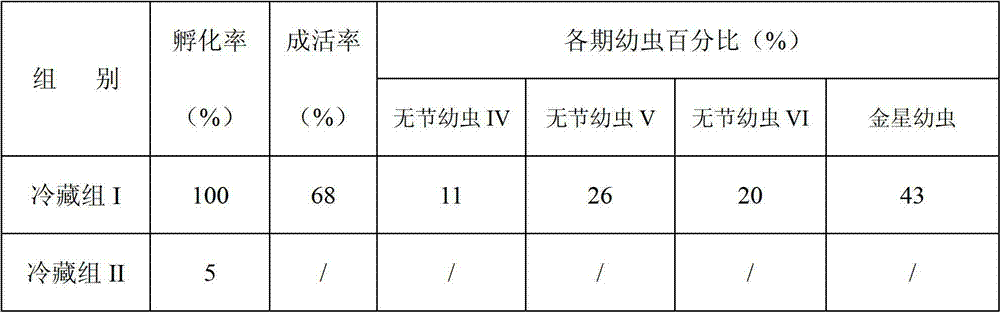
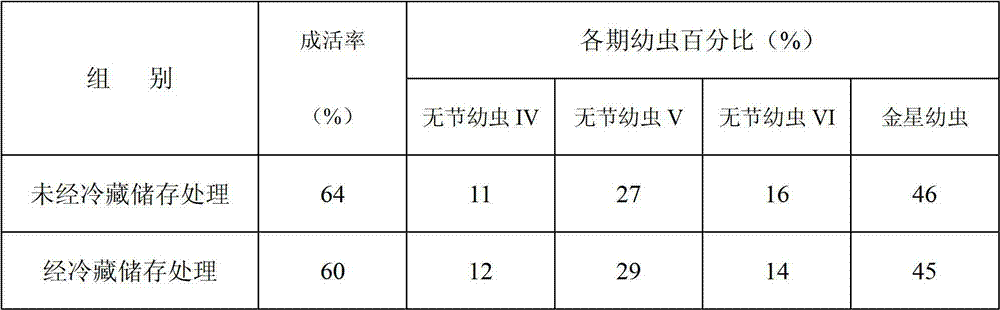
InactiveCN102812932AImpact on survival rateDoes not affect growth and developmentAnimal husbandryEnvironmental toxicologyRefrigeration
The invention discloses a method for storing mature egg mass of balanus reticulatus utinomi. The method comprises collecting mature-gonad individuals of the balanus reticulatus utinomi, selecting intact individuals, using sea water to clean the individuals, then placing the individuals in the environment at 4-6 DEG C, and performing refrigeration storage. The method for storing the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi is simple, convenient and practical, the storing standby time of the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi is effectively prolonged on the premise that hatched nauplius can grow and develop normally, the storing time of the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi can be over 24h, the problems that the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi is difficult to store and reserve and fresh samples need collecting prior to larva cultivation each time are solved, the gap is the technical field is filled, times and costs of field sampling operation are reduced, sample utilization rate is improved, development of larva cultivation work is facilitated, a foundation is laid for development of large-scale balanus larva cultivation work, and the method has wide application prospect in the fields of antifouling agent screening, coating testing, adhesion mechanism study and environmental toxicology research and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for efficient transfection of turbot muscle cells
ActiveCN106222202AHigh transfection efficiencyPromote growthOther foreign material introduction processesGenomicsFluorescence
The invention discloses a method for efficient transfection of turbot muscle cells. The transfection is realized by performing a nucleofection method on a constructed turbot muscle cell line serving as a material and a plasmid which is connected with a green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene which serves as an exogenous gene; the transfection efficiency is detected by a fluorescence inversion microscope and a flow cytometer. By the adoption of the transfection method disclosed by the invention, the transfection efficiency of the constructed turbot muscle cell line for the GFP gene can reach 65 percent, and cells have good growing states. The method is configured to supply a powerful tool to research the fields such as fish cell signal transduction, fish functional genomics, fish threpsology and aquatic environmental toxicology.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Method for evaluating influence of ionic liquid on lipid metabolism by using zebra fish
PendingCN111370066AQuick checkEasy to detectMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsEcological environmentEnvironmental toxicology
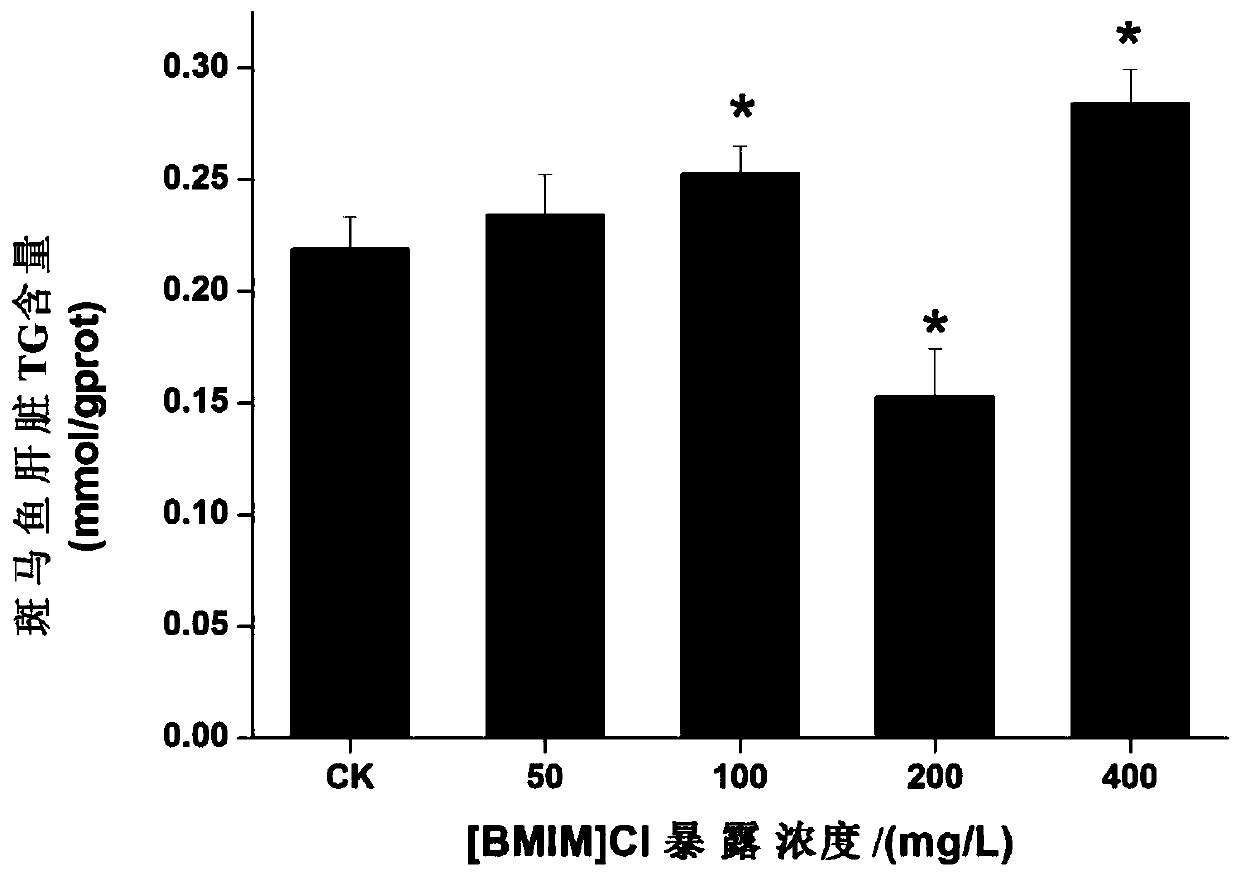
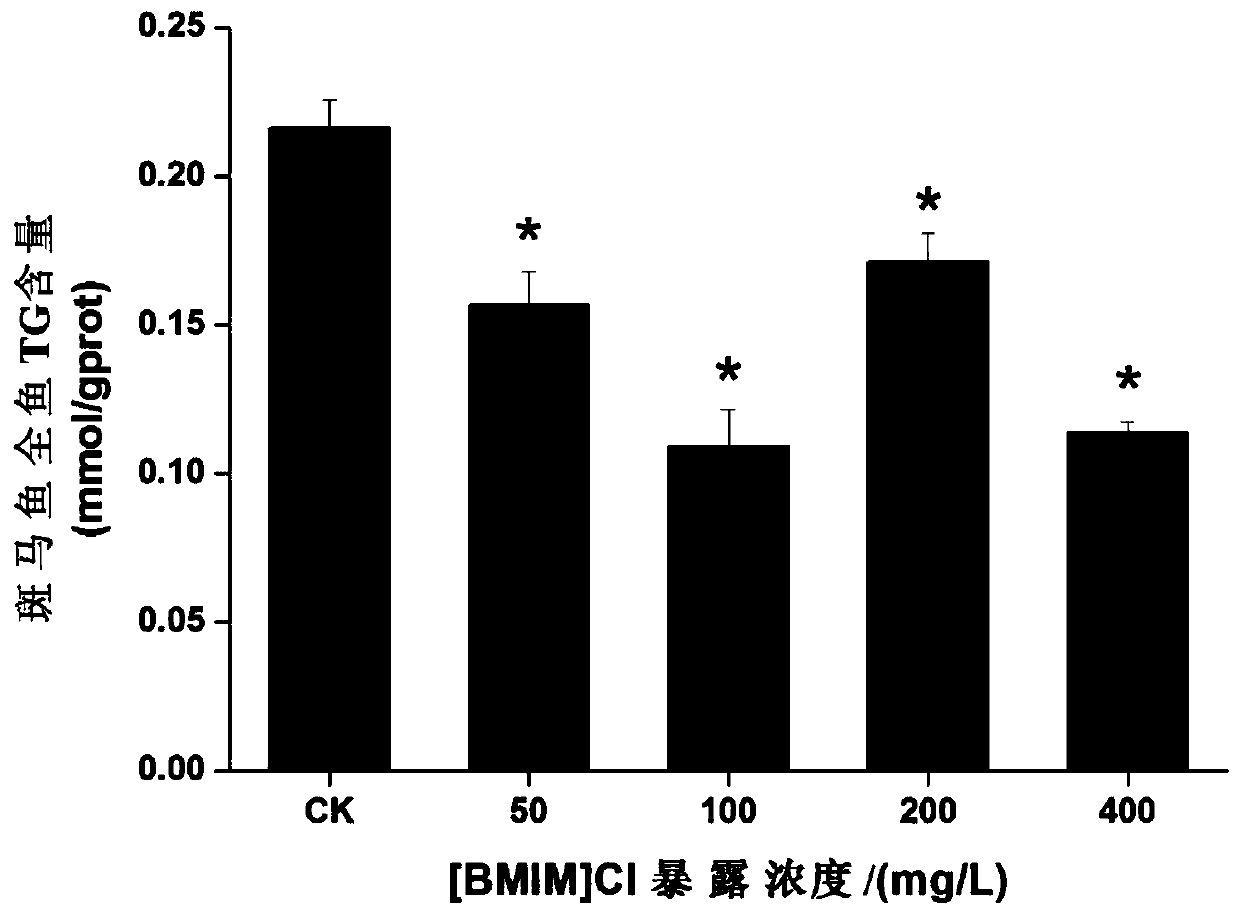
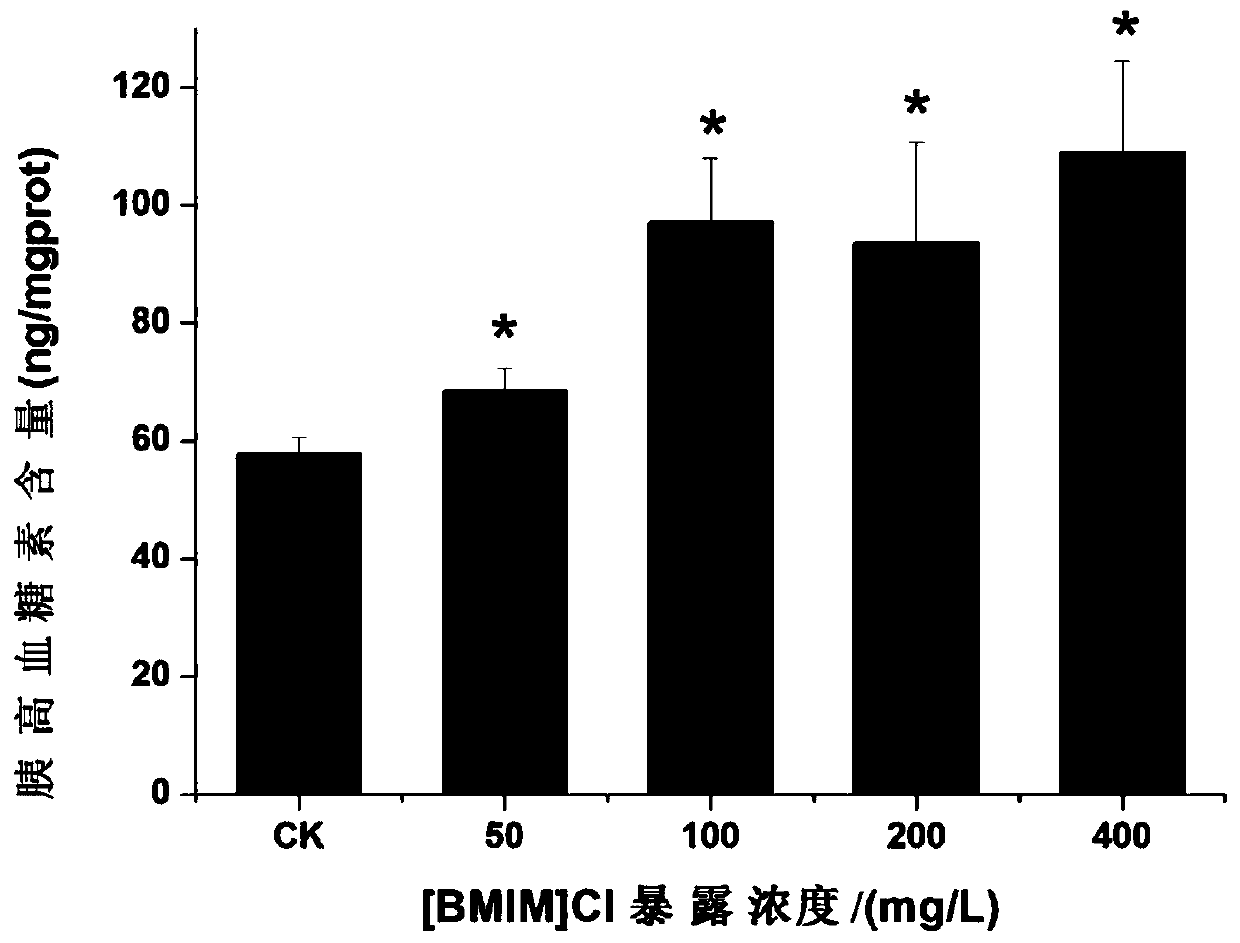
The invention relates to the field of environmental toxicology models, in particular to a method for evaluating the influence of ionic liquid on lipid metabolism by using zebra fish. According to theinvention, zebra fish is used as an experimental object; and after acute exposure of the zebra fish in an ionic liquid with a certain concentration, related hormones influencing liver metabolism, physiological and biochemical indexes related to liver metabolism and expression of liver lipid metabolism related genes are determined, and histological slices of the liver are observed. By analyzing thechange of the indexes of the exposed zebra fish, the influence of the ionic liquid on the liver lipid metabolism toxicity is comprehensively and accurately evaluated. Thus, a basis is provided for formulating aquatic ecological environment pollutant standards.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
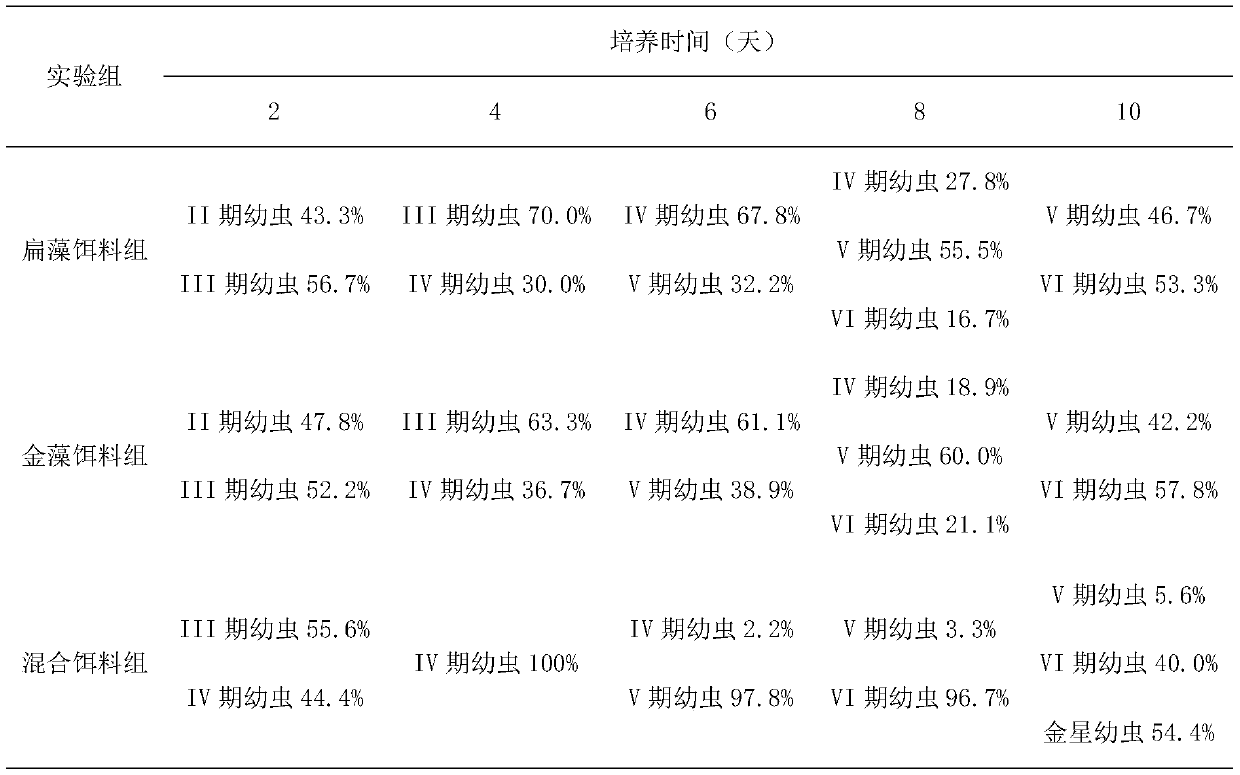
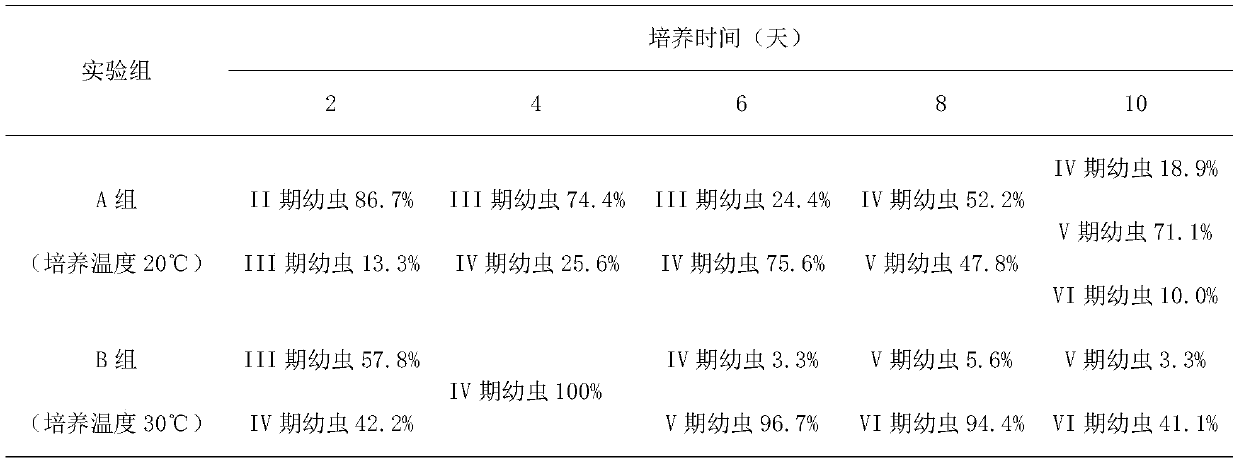
Simple and quick method for cultivating larvae of Tetraclita squamosa squamosa
ActiveCN108157297AIncrease growth rateReduce incubation timeAnimal husbandryEnvironmental toxicologyDicrateria
The invention discloses a simple and quick method for cultivating larvae of Tetraclita squamosa squamosa. After the nauplius larvae are hatched from eggs of Tetraclita squamosa squamosa, Platymonas subcordiformis and Dicrateria zhanjiangensis are added as bait for cultivation. Through the method, the development speed of the nauplius larvae of Tetraclita squamosa squamosa can be improved, the cultivation time can be shortened, and experimental steps can be simplified, so that convenience is provided for research of marine basic ecology and environmental toxicology; therefore, the method has awide application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for pretreating waste water containing emerging pollutants by adopting oxidation of calcium peroxide
InactiveCN109133316AReduce the content of harmful and toxic substancesLow ecotoxicityMultistage water/sewage treatmentWater/sewage treatment by neutralisationEnvironmental toxicologyWastewater
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental toxicology and ecological restoration, and particularly discloses a method for pretreating and degrading emerging pollutants in waste water by adopting a new oxidizing agent. The method comprises the steps that waste water containing the emerging pollutants passes through an adjusting pond before entering a traditional biological treating system, and then through a traditional treating measure, the pollutants in the waste water are finally removed to achieve safe discharging. Calcium peroxide of a certain amount is thrown in the adjusting pond, by adjusting the p H value to be best, it is achieved that the rate of releasing H2O2 by the calcium peroxide is balanced with the utilization rate of H2O2, and it is avoided that the toohigh p H value influences later biological activity. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the application range is wide, and the oxidizing agent is safe, stable, effective andeconomic and cannot cause secondary pollution.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
Method for analyzing metabolic behaviors of PCB95 and metabolites thereof in chicken liver microsomes
The invention provides a method for analyzing metabolic behaviors of PCB95 and metabolites thereof in chicken liver microsomes, and relates to the technical field of environmental toxicology. The method comprises the steps of (a) establishing a chicken liver microsome incubation system; (b) performing incubation metabolism on PCB95 with different concentrations and metabolites thereof in the chicken liver microsome incubation liquid; (c) determining the contents of PCB95 and metabolites thereof in the incubation liquid by using a gas chromatograph and an electron capture detector; and (d) analyzing and evaluating characteristic metabolic behaviors and toxicity differences of PCB95 and metabolites thereof in chicken liver microsomes according to quantitative results. The method can be used for simultaneously analyzing the metabolism conditions of PCB95 and metabolites thereof in chicken liver microsomes, and is simple to operate and high in analysis speed.
Owner:INST OF QUALITY STANDARD & TESTING TECH FOR AGRO PROD OF CAAS
Anuran cross-species molecular sensors
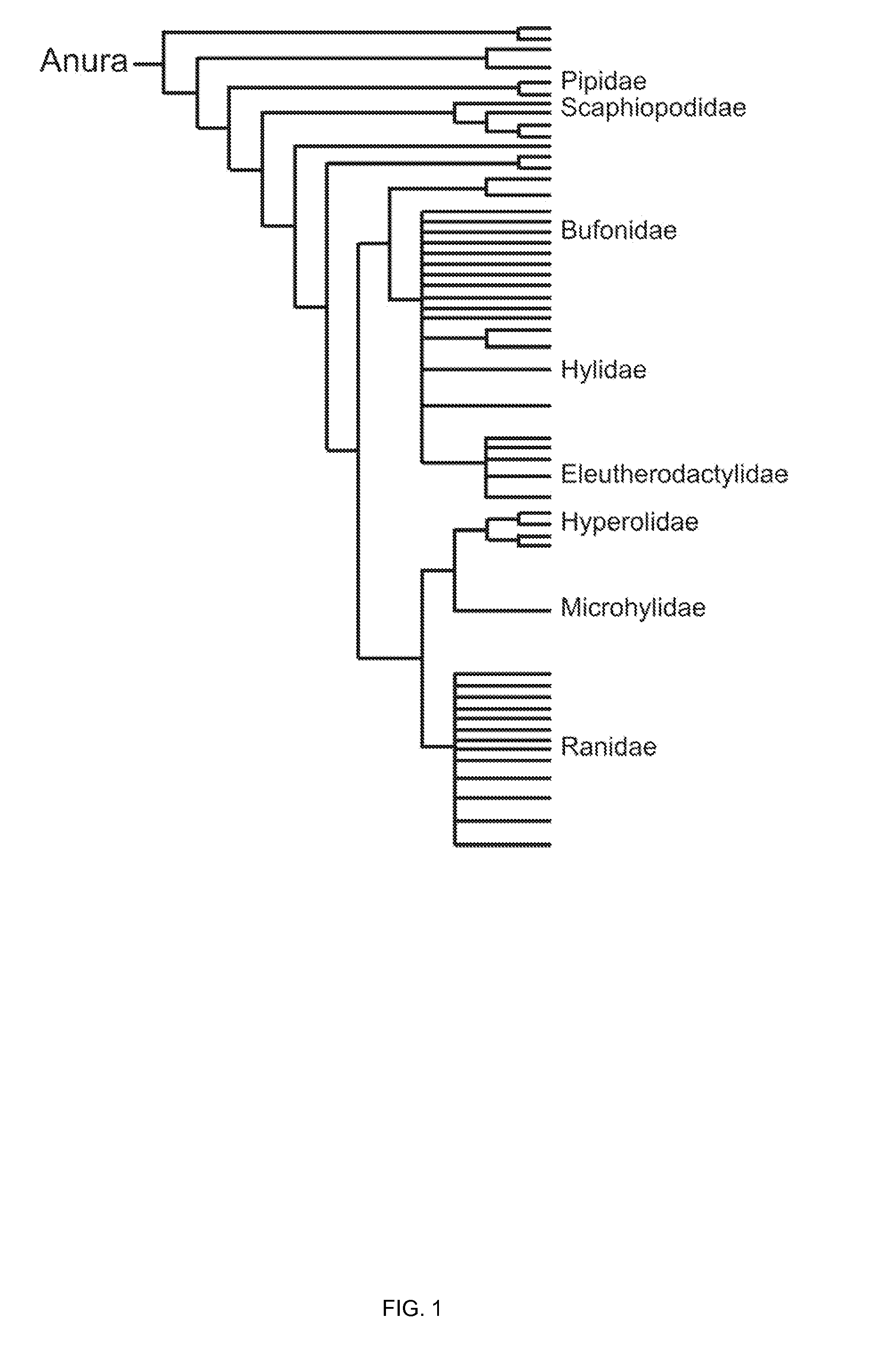
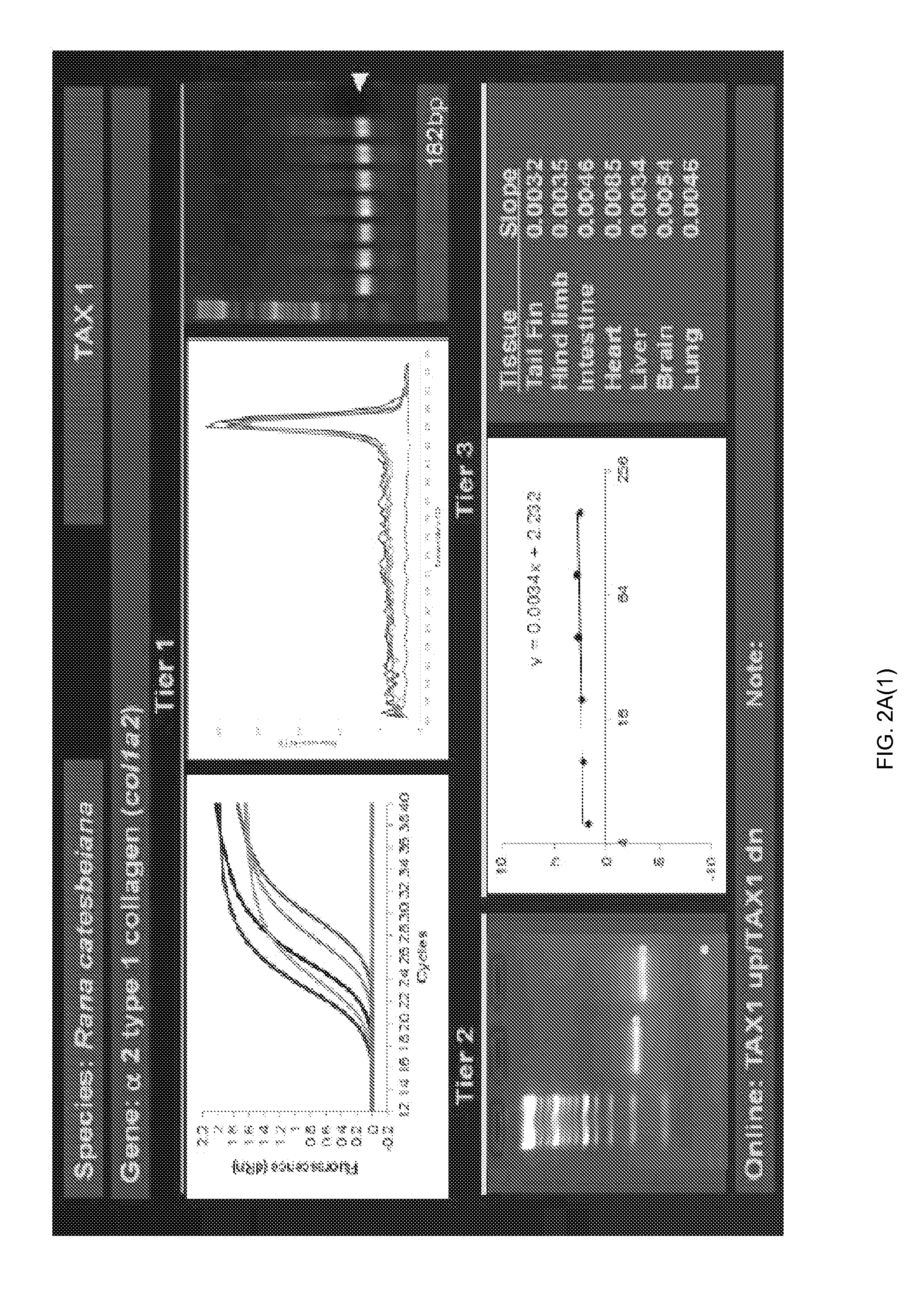
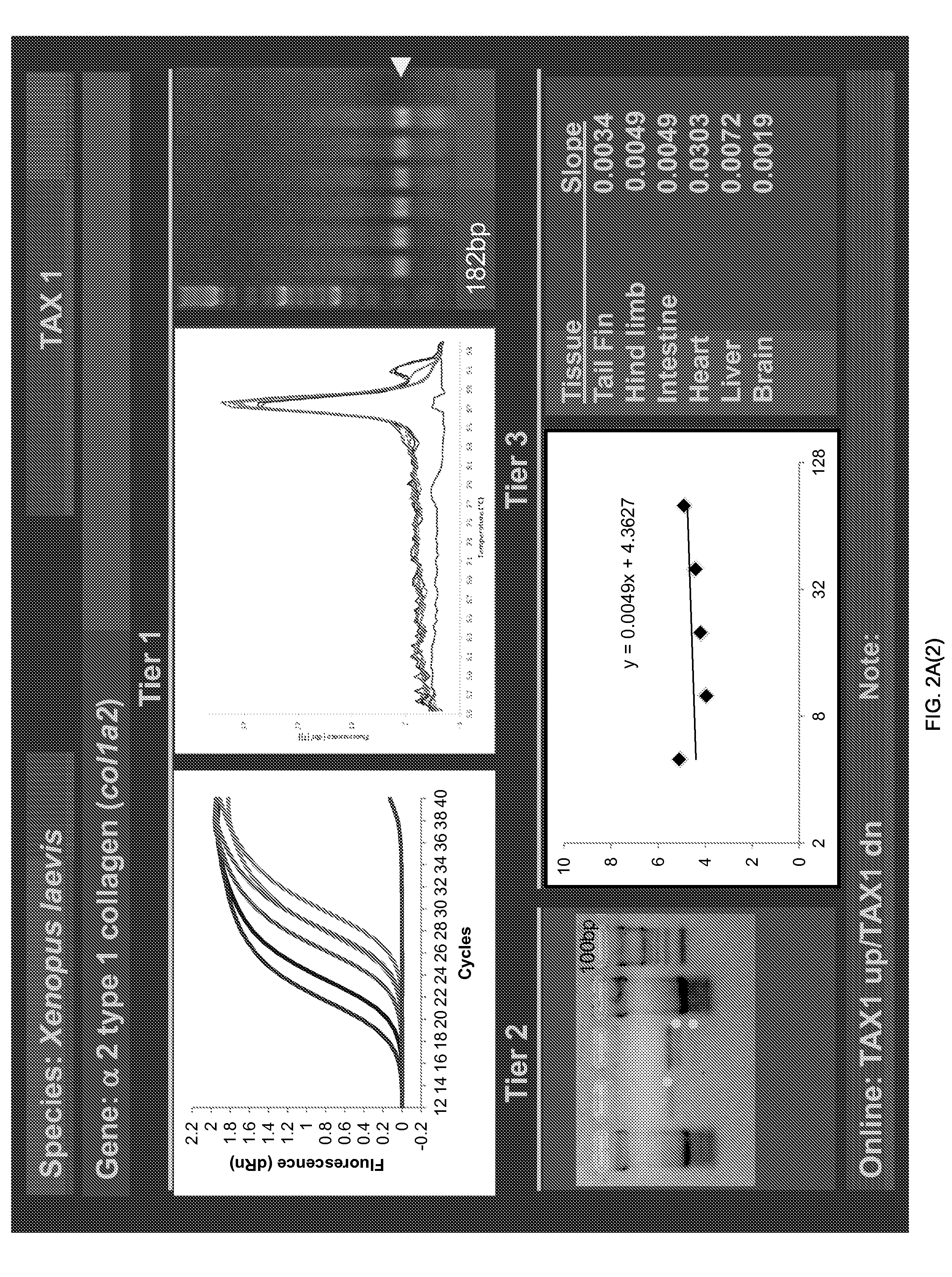
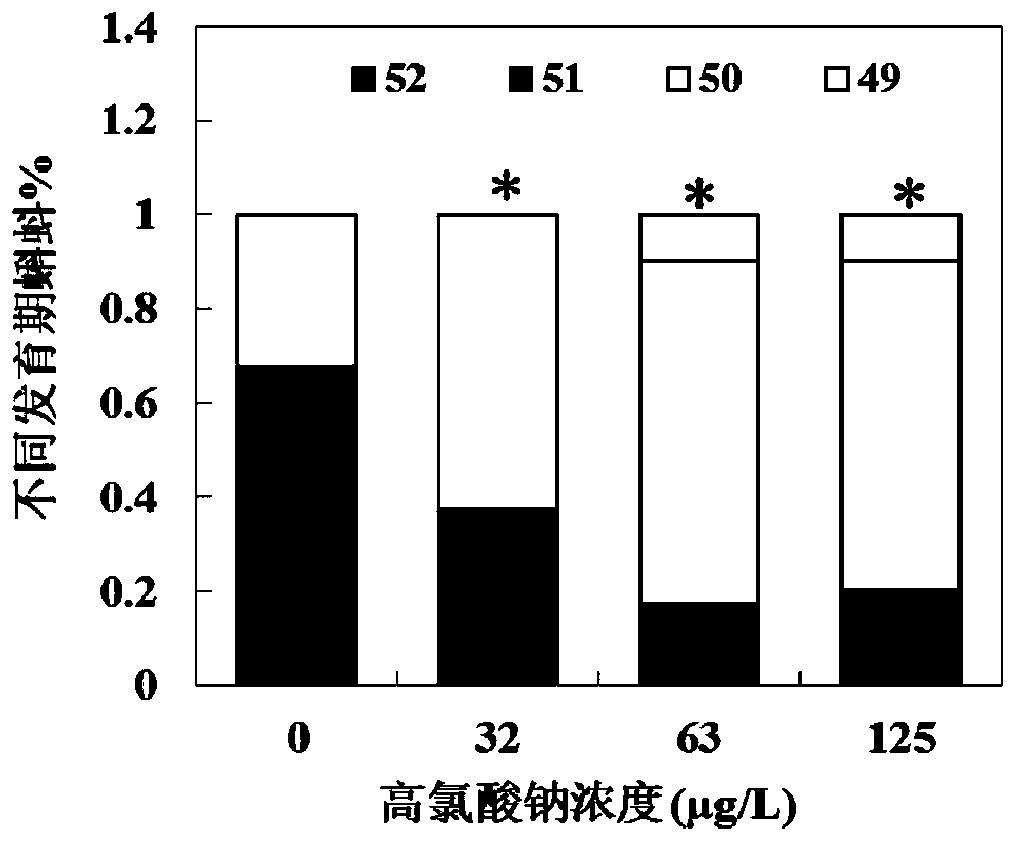
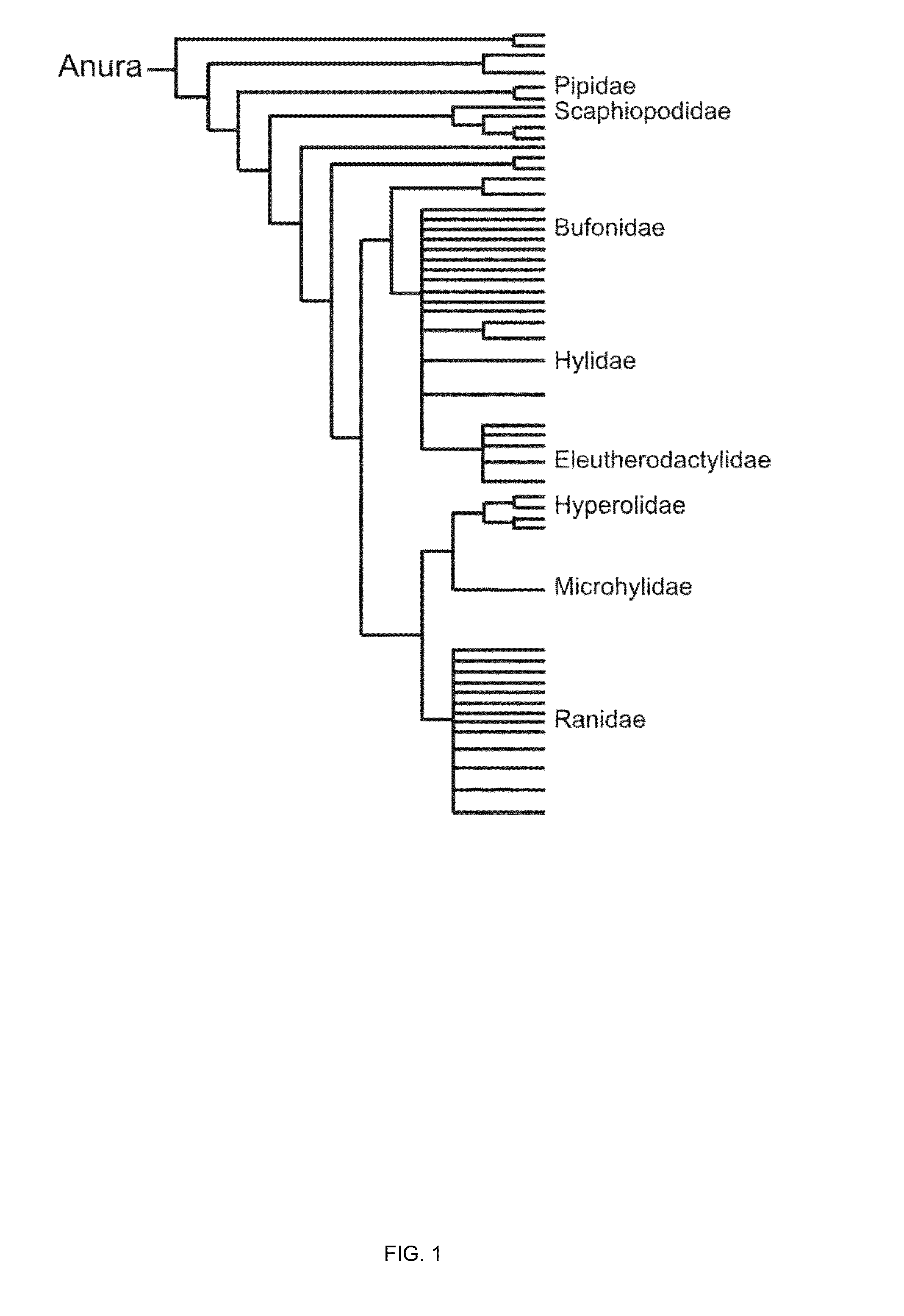
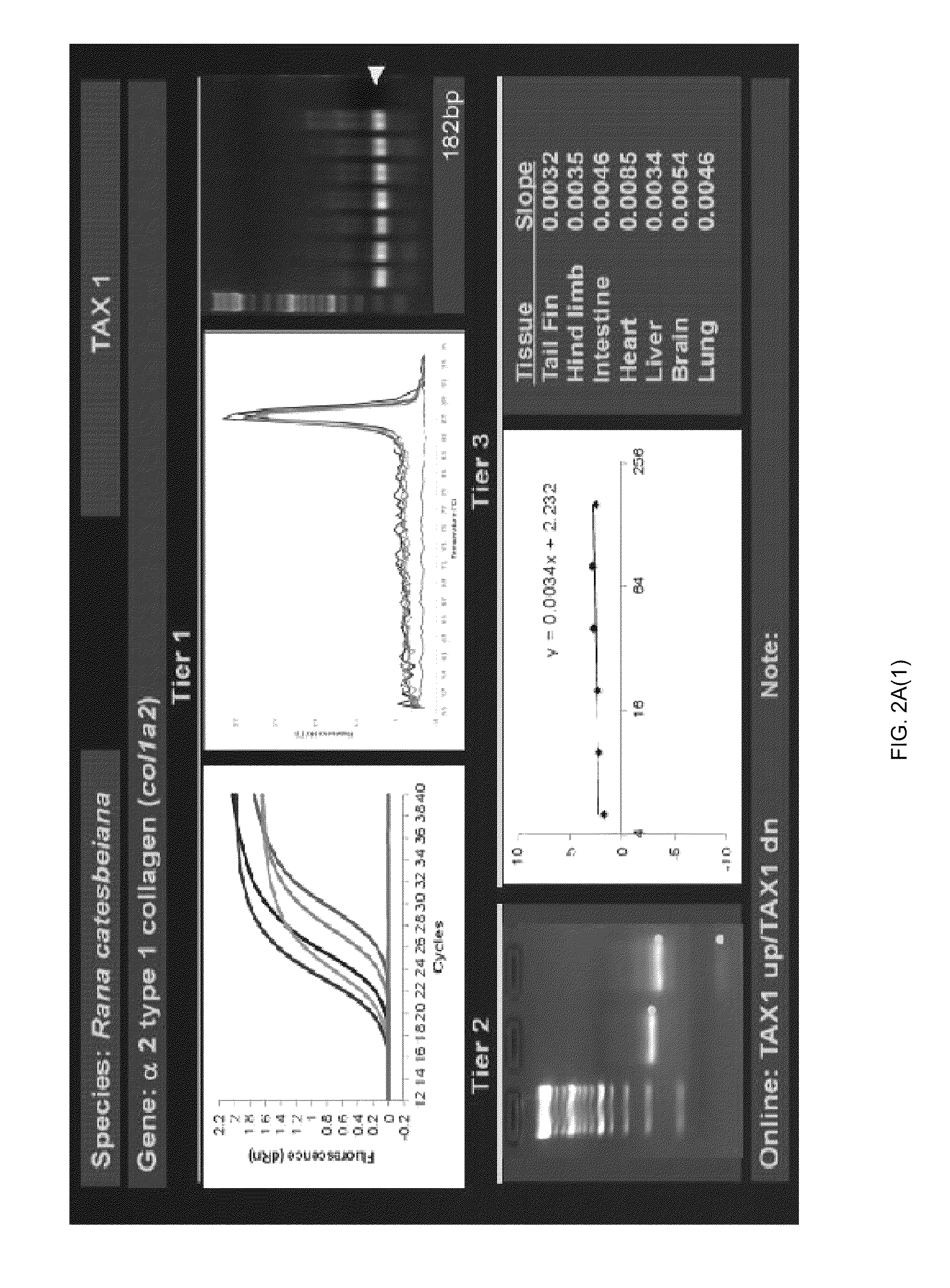
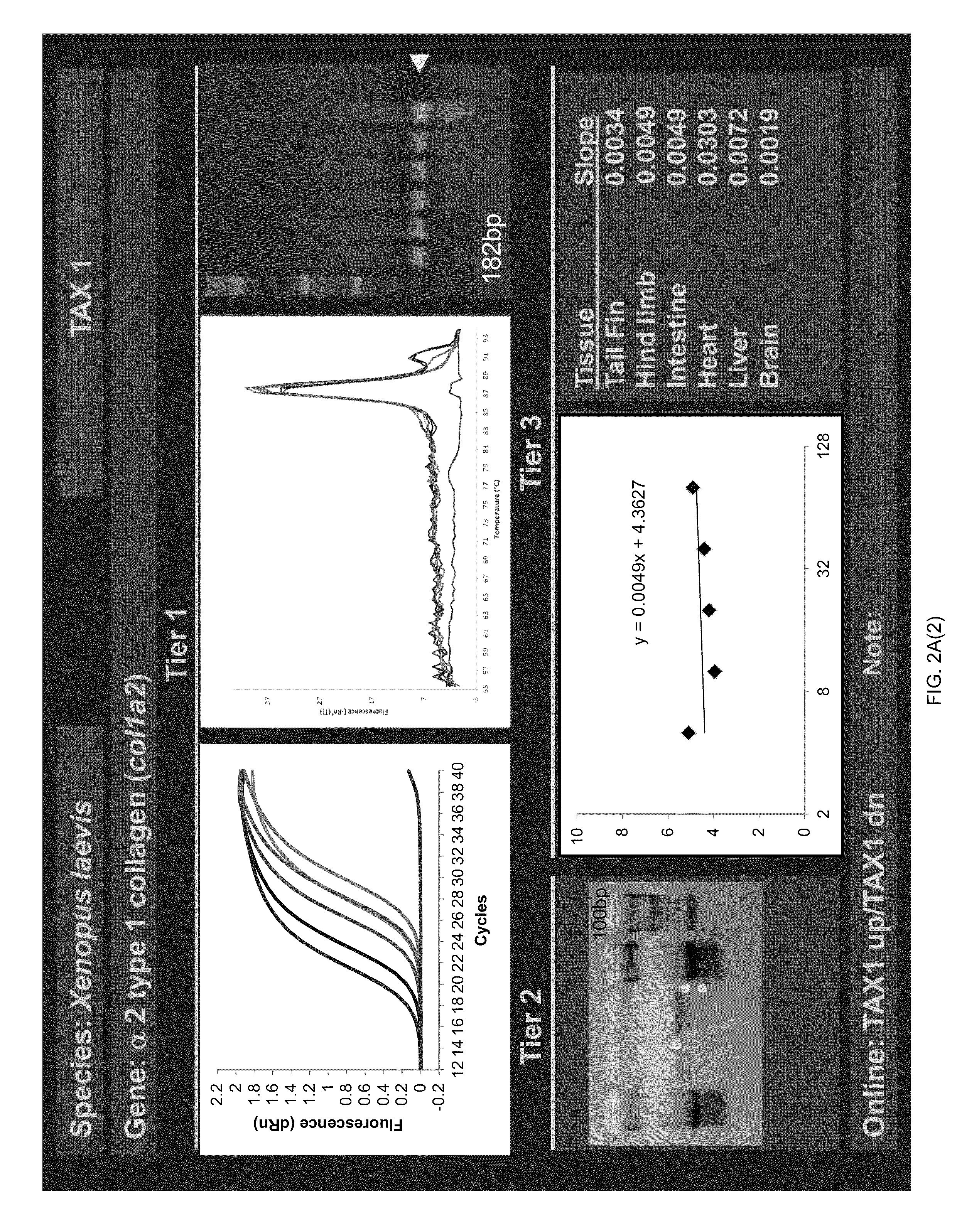
ActiveUS20150094228A1Sufficient genomic resourceExtensive resourcesNucleotide librariesPollution detectorsSequence designEnvironmental toxicology
Described herein are DNA primer sequences designed for the determination of gene or transcript information from Anuran species, and which may be used in studies for developmental and / or toxicity testing and for environmental toxicology or ecological assessment. Also described herein is a rapid, sensitive, high-throughput assay useful for supporting potential risk assessment across vertebrate clades, and that is also useful for evaluation of complex contaminant mixtures.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF NORTHERN ARIZONA UNIV
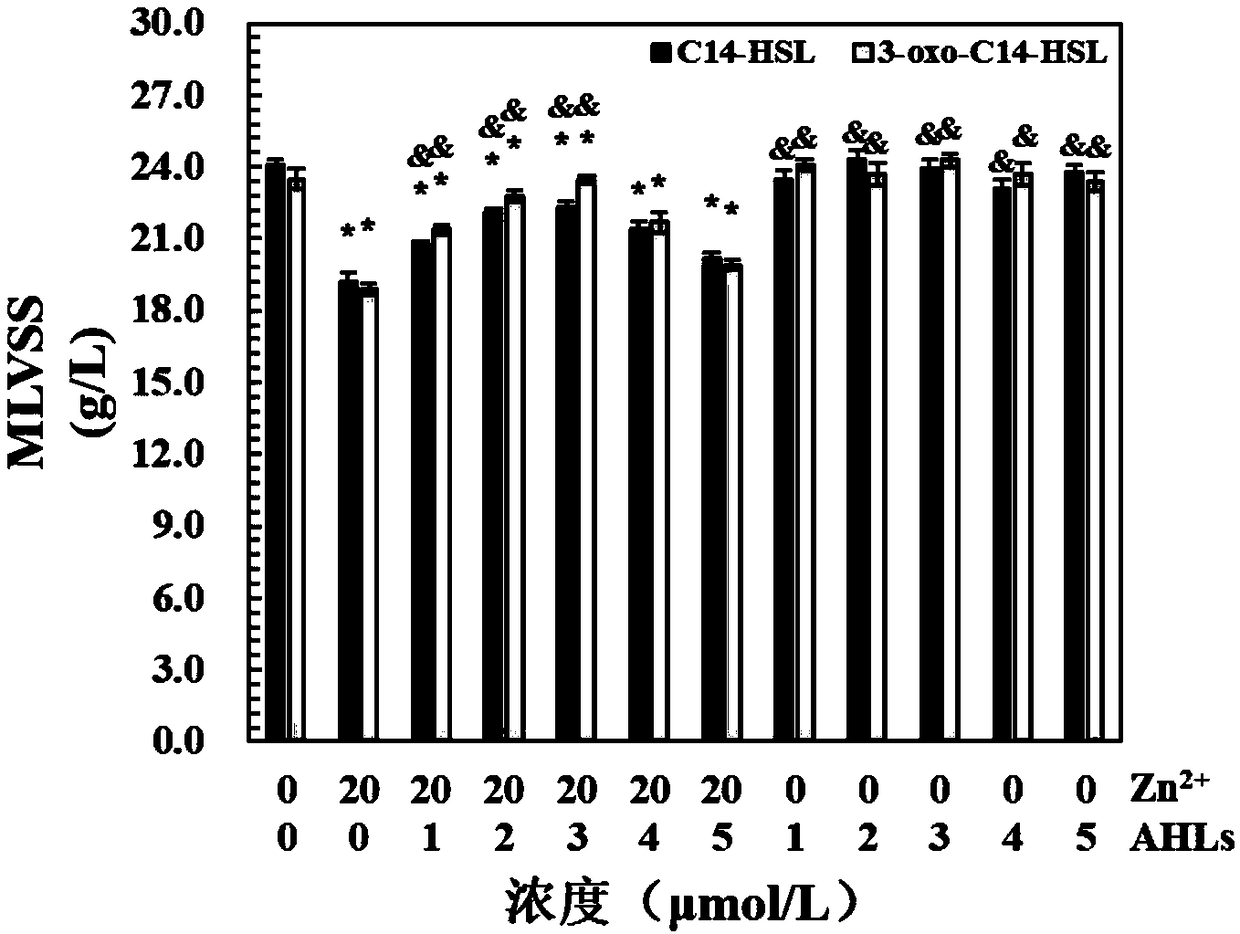
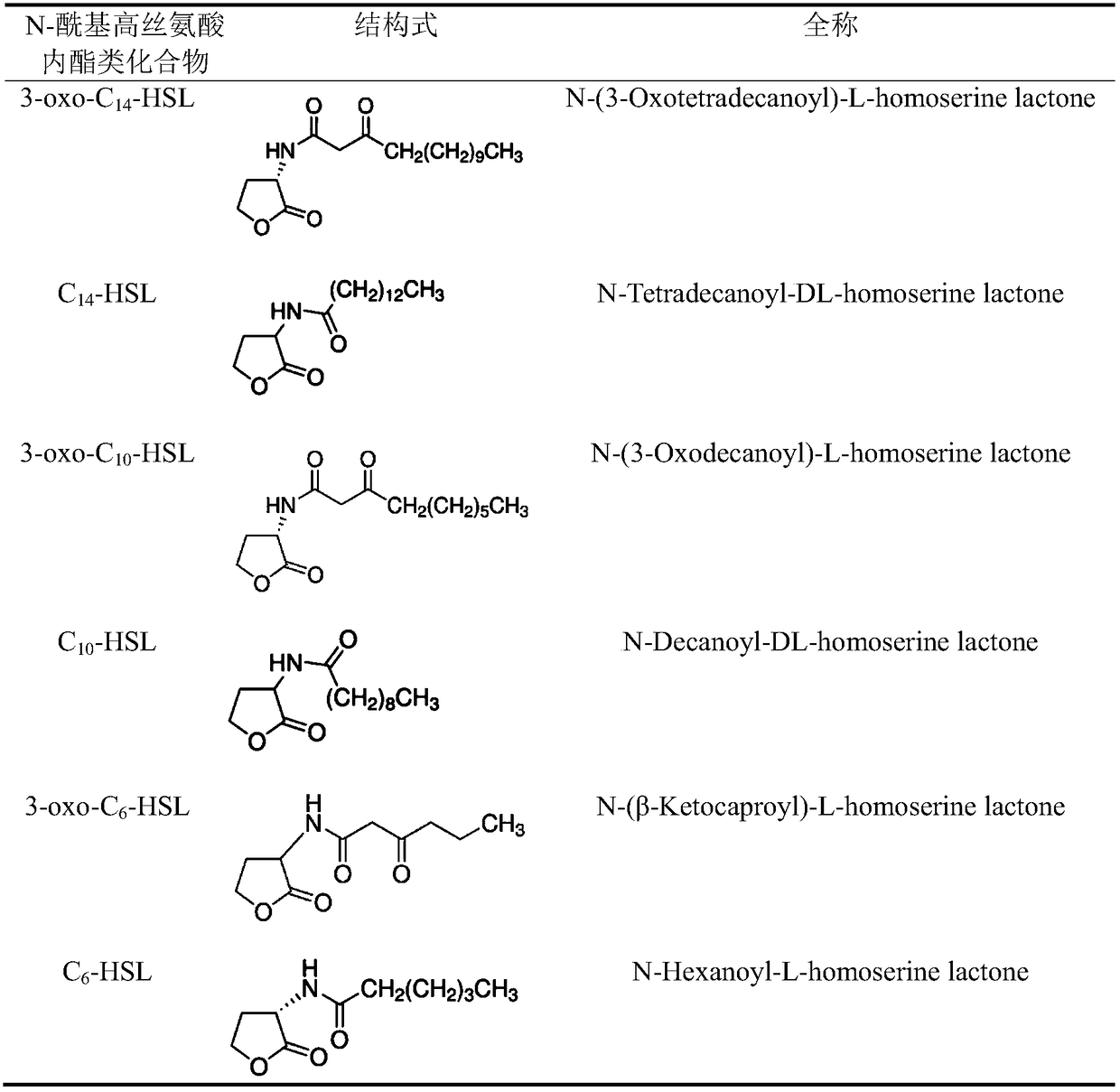
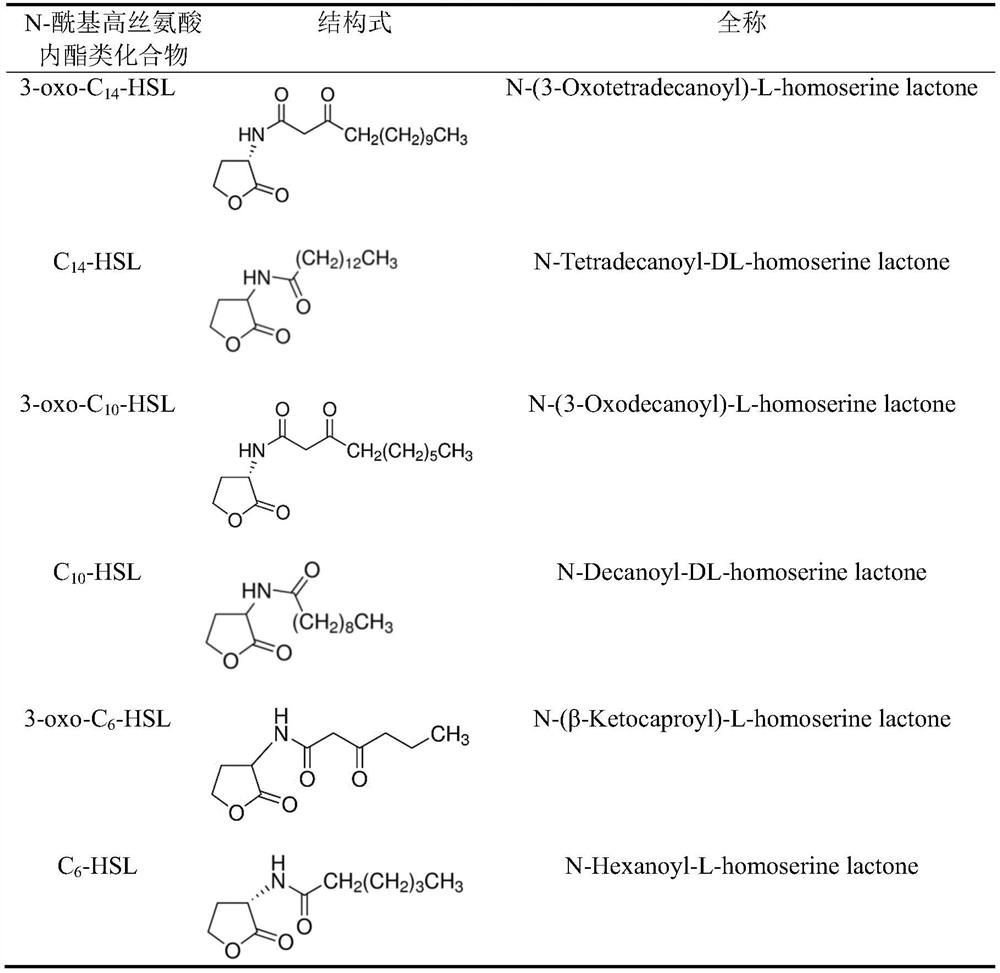
Method for improving heavy metal pollution impact load resistance of biological nitrogen removal system for sewage
ActiveCN109354184AImproved shock load capabilityImprove effluent qualityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesCarbon numberEnvironmental toxicology
The invention belongs to the fields of environmental toxicology and biological sewage treatment, and particularly relates to a method for improving the heavy metal pollution impact load resistance ofa biological nitrogen removal system for sewage. The method comprises the step that in the biological nitrogen removal system for the sewage containing heavy metal pollutants, a N-acylated homoserinelactone compound which is composed of the lactonized homoserine part and acyl side chains with the carbon number of 6-14 is added into an exterior source. The method has the advantages that the operation is simple, the treatment efficiency is high, the heavy metal pollution impact load resisting capacity of microorganisms can be obviously improved by using a small amount of an agent, the outlet water quality of the biological nitrogen removal system for the sewage under heavy metal pollution stress can be effectively improved, and the method is economical, environmentally friendly and free ofsecondary pollution; when the biological sewage treatment system is impacted by toxicities of the heavy metal pollutants, the system stability and the system performance recovery capability can be effectively improved in time, and the method can be called as an emergent sewage treatment technology under a sudden heavy metal pollution accident.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
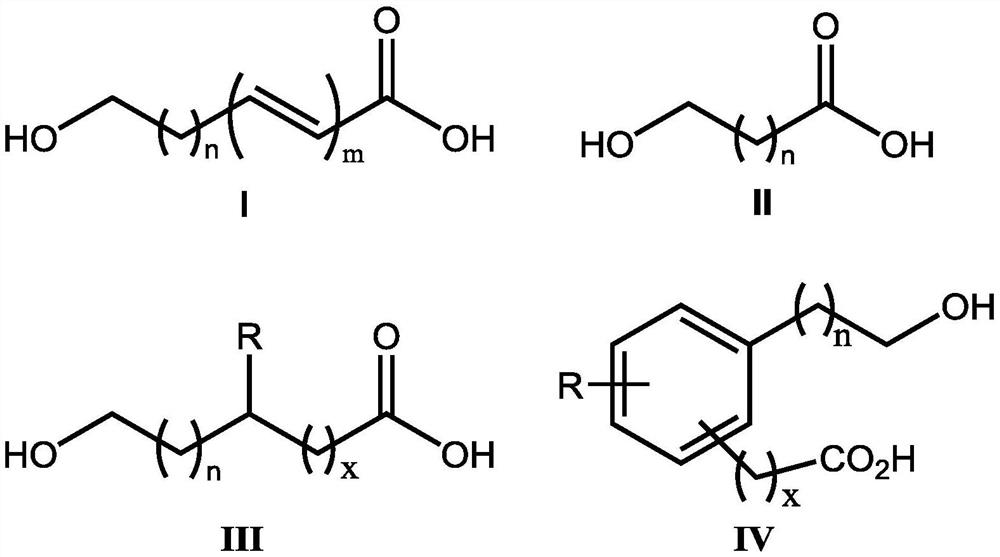
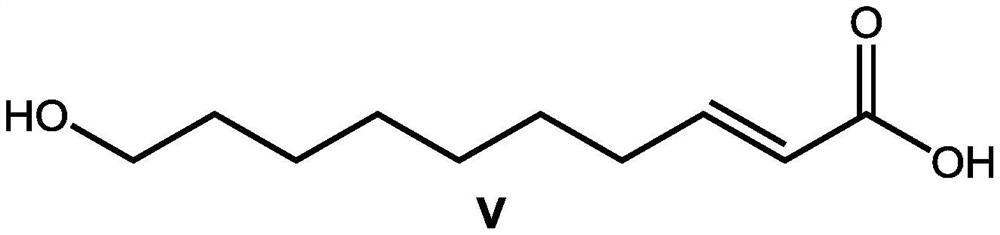
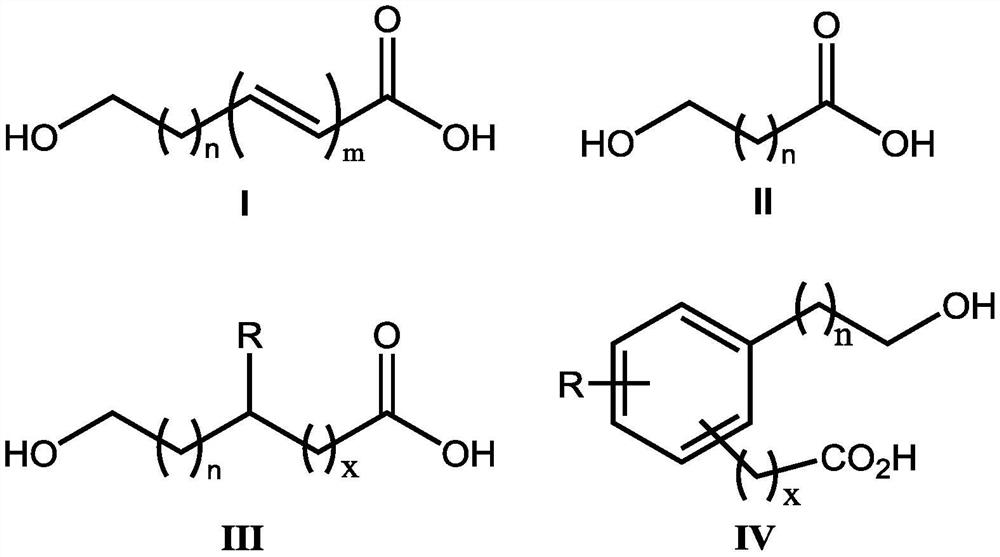
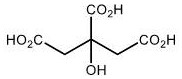
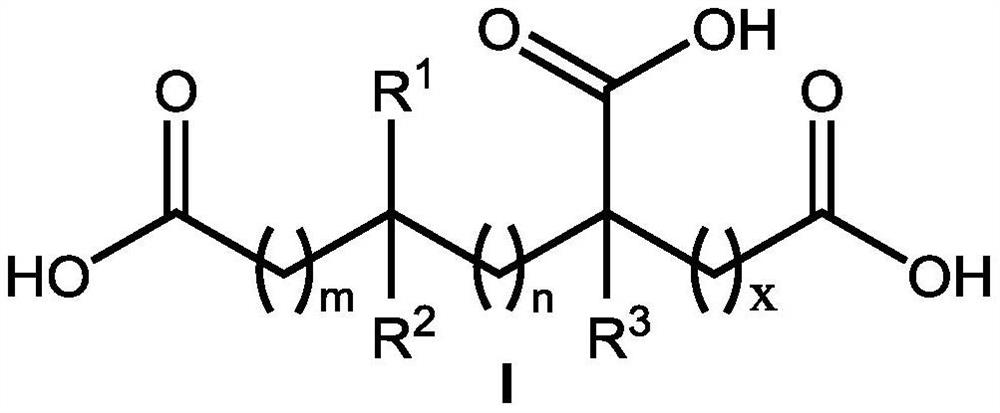
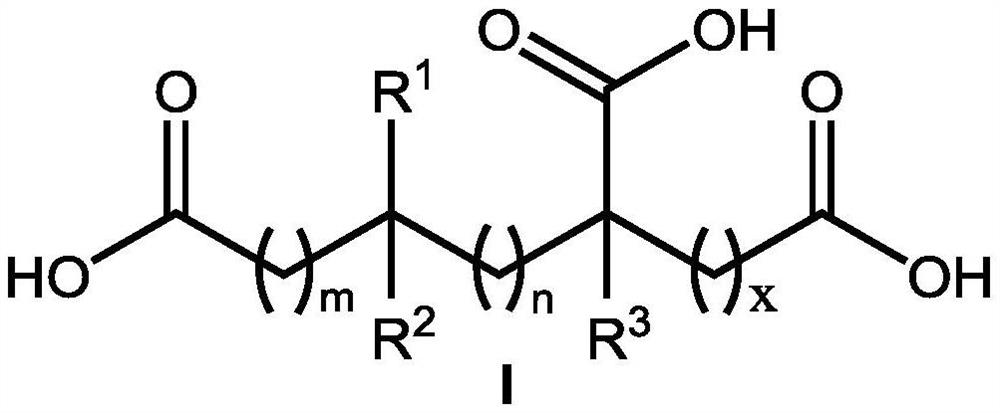
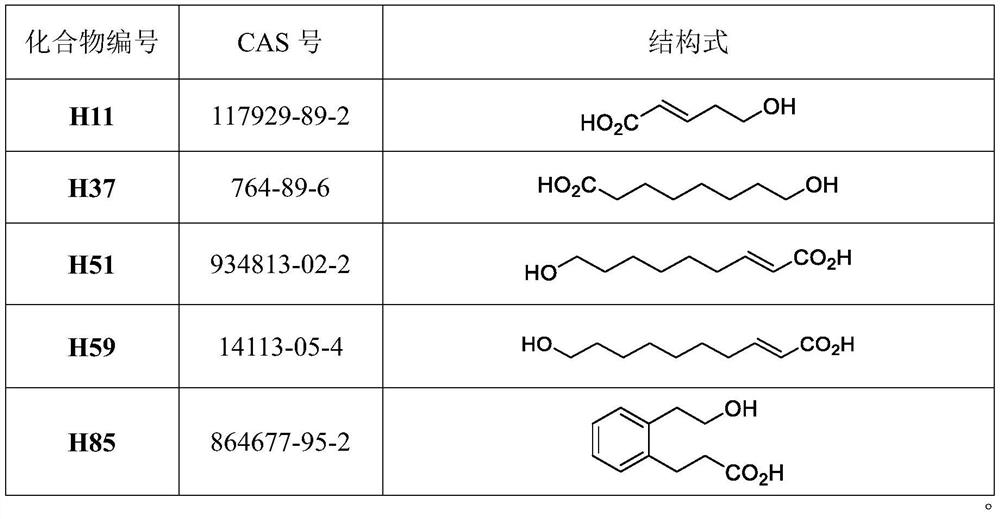
Application of hydroxy carboxylic acid compound in preventing and treating plant diseases
ActiveCN112106775AInhibition formationAvoid infectionBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyEnvironmental toxicology
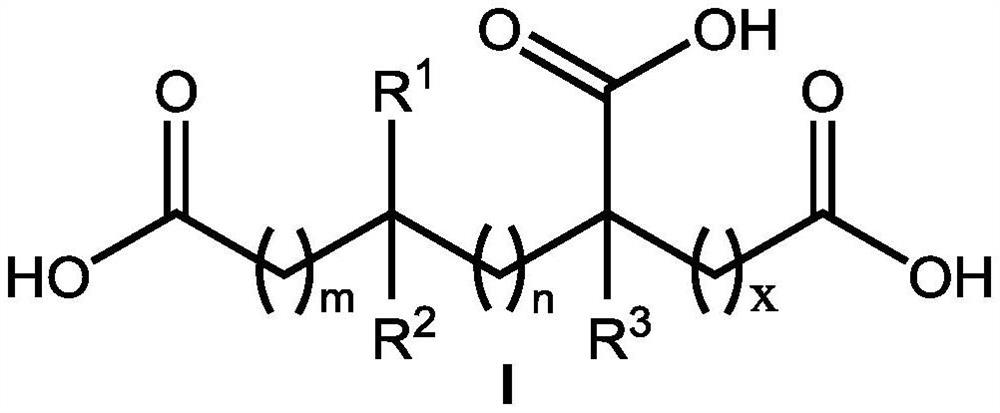
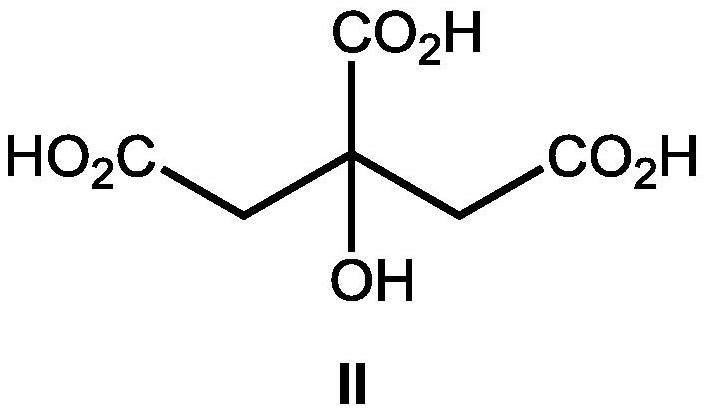
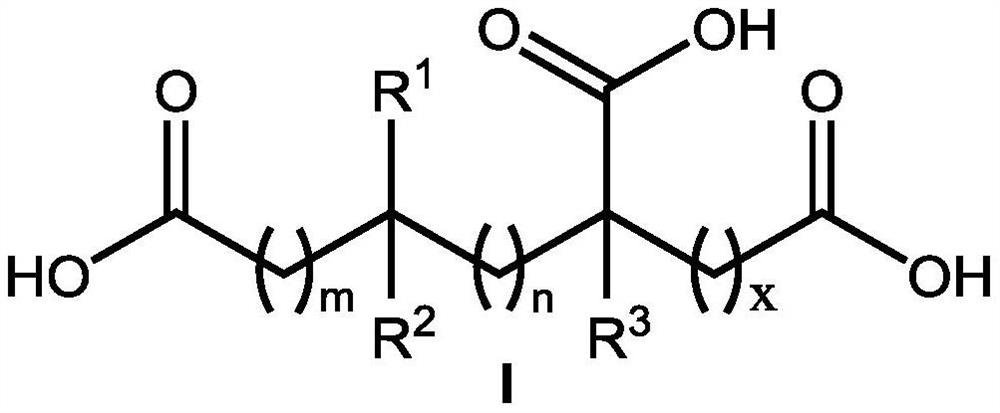
The invention discloses an application of a hydroxy carboxylic acid compound in preventing and treating plant diseases. The hydroxyl carboxylic acid compound is selected from compounds represented byformulas I, II, III and IV, and isomers, hydrates or salts thereof. The hydroxy carboxylic acid compound has a remarkable effect in the aspect of inhibiting the activity of fungus or oomycete appressorium formation, can be used for preventing plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew and phytophthora, and is free of obvious phytotoxicity and good in safety. Compared with an existing compound for preventing and treating the plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew and phytophthora, the hydroxyl carboxylic acid compound has the characteristics of good prevention effect, environmental protection, no toxicity, low residue and safety, and as the compound is known and widely used, the raw materials are easy to obtain, the synthesis process is mature, and environmental toxicology and effects are well-studied. Therefore, the advantages of being convenient, easy to obtain, environment-friendly and safe are achieved.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
A method for improving the impact load resistance of heavy metal pollution in sewage biological denitrification system
ActiveCN109354184BImprove resistance to heavy metal pollution impact loadImproved shock load capabilityWater contaminantsTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesEnvironmental toxicologySide chain
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Method for culturing cyprids of balanus reticulates on large scale
The invention discloses a method for culturing cyprids of balanus reticulates on a large scale, which comprises the following steps: after ovum of the balanus reticulates is bred into naupliar larva, putting the naupliar larva into a culture medium with bait for constant temperature culture in dark environment; performing intermittent lighting on the naupliar larva in the constant temperature culture process; and performing cold storage on the appeared cyprids. The method can overcome the defects of high death rate, small and unstable yield, quick settlement and metamorphosis processes, incapacity of storage and accumulation and the like in the breeding process of the cyprids, greatly improve the yield of the cyprids, effectively prolong the time of a drifting stage of the cyprids, promotethe settlement synchrony of the cyprids, and provide required experimental materials for screening marine fouling organism antifouling compositions and studying environmental toxicology, along with wide application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
A Simple and Quick Method for Cultivating Barnacle Larvae
ActiveCN108157297BIncrease growth rateReduce incubation timeAnimal husbandryEnvironmental toxicologyMogulones larvatus
The invention discloses a simple and quick method for cultivating larvae of Tetraclita squamosa squamosa. After the nauplius larvae are hatched from eggs of Tetraclita squamosa squamosa, Platymonas subcordiformis and Dicrateria zhanjiangensis are added as bait for cultivation. Through the method, the development speed of the nauplius larvae of Tetraclita squamosa squamosa can be improved, the cultivation time can be shortened, and experimental steps can be simplified, so that convenience is provided for research of marine basic ecology and environmental toxicology; therefore, the method has awide application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for storing mature egg mass of balanus reticulatus utinomi
InactiveCN102812932BImpact on survival rateDoes not affect growth and developmentAnimal husbandryEnvironmental toxicologyRefrigeration
The invention discloses a method for storing mature egg mass of balanus reticulatus utinomi. The method comprises collecting mature-gonad individuals of the balanus reticulatus utinomi, selecting intact individuals, using sea water to clean the individuals, then placing the individuals in the environment at 4-6 DEG C, and performing refrigeration storage. The method for storing the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi is simple, convenient and practical, the storing standby time of the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi is effectively prolonged on the premise that hatched nauplius can grow and develop normally, the storing time of the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi can be over 24h, the problems that the mature egg mass of the balanus reticulatus utinomi is difficult to store and reserve and fresh samples need collecting prior to larva cultivation each time are solved, the gap is the technical field is filled, times and costs of field sampling operation are reduced, sample utilization rate is improved, development of larva cultivation work is facilitated, a foundation is laid for development of large-scale balanus larva cultivation work, and the method has wide application prospect in the fields of antifouling agent screening, coating testing, adhesion mechanism study and environmental toxicology research and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
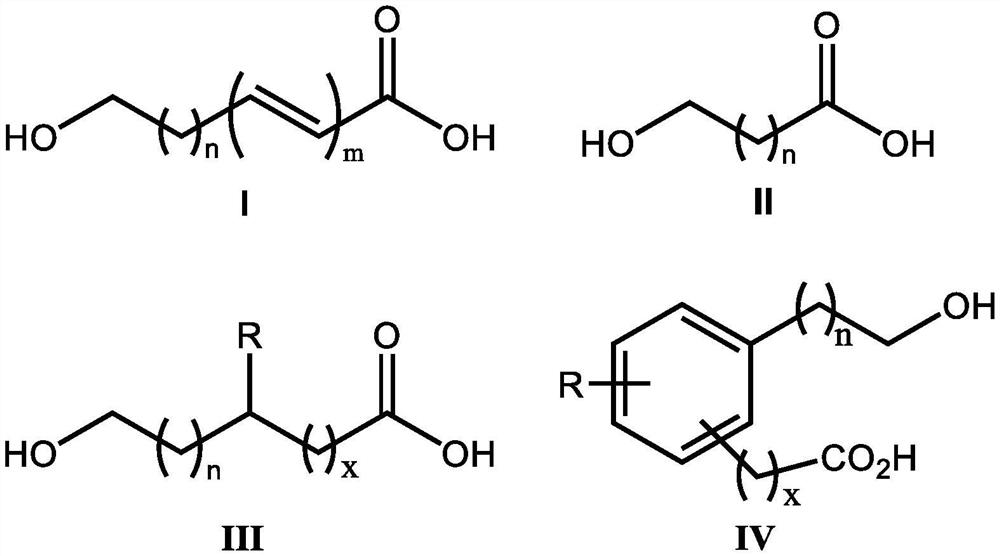
Inhibitory activity of polycarboxylic acid compounds against appresses of fungi and oomycetes and their use in the control of plant diseases
ActiveCN112400879BInhibition formationAvoid infectionBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyEnvironmental toxicology
The invention discloses the inhibitory activity of polycarboxylic acid compounds on phytopathogenic fungi and oomycete appresses and their application in the prevention and treatment of plant diseases; the polycarboxylic acid compounds are selected from compounds of formula I, their isomers, hydrated food or salt. The polycarboxylic acid compound involved in the present invention can significantly inhibit the formation of appresses of fungi and oomycetes, and can be used for the prevention of various plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew, phytophthora, powdery mildew, etc. , no obvious harm, good safety. Compared with the existing compounds for preventing and controlling plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew, phytophthora, and powdery mildew, the polycarboxylic acid compound of the present invention has good preventive effect, environmental protection, and nontoxicity. , low residue, safety features. Because these compounds are known and widely used compounds, and the environmental toxicology and impact research is thorough, therefore, they have the advantages of convenience, easy availability, environmental protection and safety.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
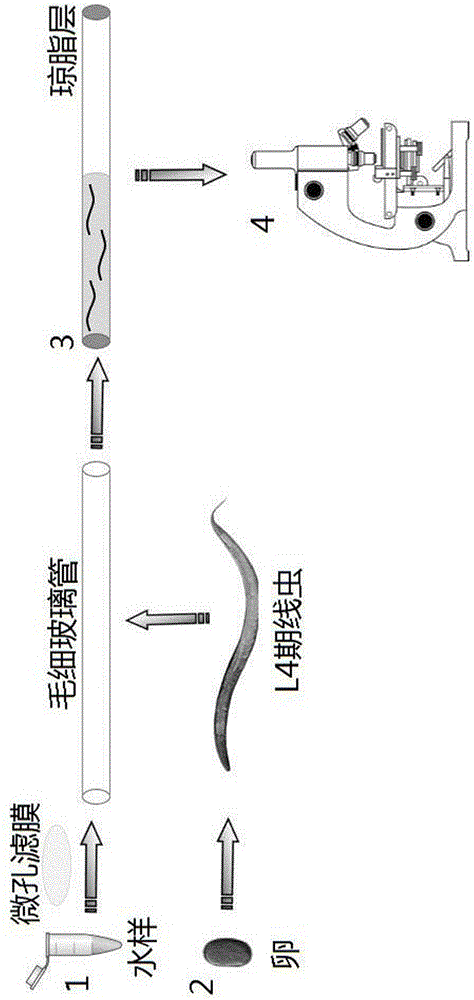
A Toxicological Detection Method of Trace Water Samples Based on Caenorhabditis elegans
InactiveCN104569330BEasy to trainReduce the use volumeTesting waterBiological testingBiological bodyNematode
The invention discloses a Caenorhabditis elegans based micro water sample toxicology detection method, belonging to the technical field of the environmental toxicology detection on water samples. The method mainly comprises the steps of carrying out sterilization treatment on an environment water sample, culturing nematode, exposing a biological sample of the environment water sample, and performing toxicology detection on the water sample. The Caenorhabditis elegans based micro water sample toxicology detection method is characterized in that the complexity effect of a multi-kind polyvalent mixture in the environment water sample on a living body is evaluated comprehensively, the required water sample amount is low, the operation is simple, and the method can be used for solving the problems that the waste liquid amount in an existing pollutant toxicologic study is high and can be treated difficultly and secondary pollution can be caused, overcoming the experimental error caused by change of the concentration of substances in the water sample due to water evaporation, achieving rapid detection of the toxicology of the living body in the water sample, solving the problems that the existing water sample toxicology detection time is long, the cost is high and the like, and improving the accuracy and the precision of the environmental water sample evaluation.
Owner:AGRI ENG INST ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Microfluidic chip apparatus and application thereof
ActiveCN102728422BGood biocompatibilityEasy to makeMicrobiological testing/measurementLaboratory glasswaresEnvironmental toxicologyQuantum dot
The invention provides a three-dimensional cultivation microfluidic chip apparatus used for quantum dot cytotoxicity detection. The microfluidic chip apparatus is manufactured by bonding a dimethyl silicone polymer chip and a glass substrate. The chip has two parts, which are a main channel and cell cultivation chambers. The main channel is used for simulating a blood vessel. The cell cultivation chambers communicate with the main channel with different distances, and are used for simulating adjacent tissues with different distances from the blood vessel. The heights of the main channel and the cell cultivation chambers are different, such that a mixture of cells and a three-dimensional cultivation substrate is prevented from leaking to the main channel when injected into the cell cultivation chambers. The apparatus can further be used for proofing that one of the quantum dot cytotoxicity cell mechanisms is the cell autophagia effect. The microfluidic chip apparatus provided by the invention is advantaged in simple manufacturing and easy operation. The apparatus can be used for simulating the diffusion process of the blood vessel and the adjacent tissues. With the apparatus, three-dimensional cultivation and quantum dot cytotoxicity detection of cells can be realized. Therefore, the apparatus is suitable for medicine screening and environmental toxicology analysis.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
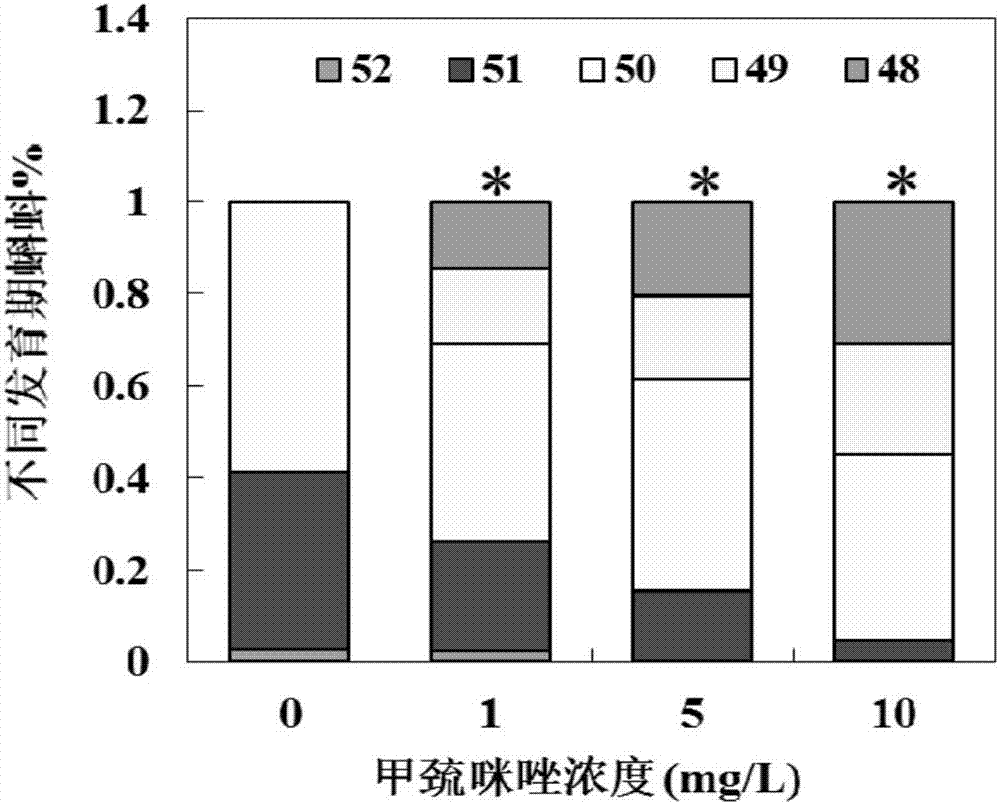
In-vivo screening method for examining thyroid disruption and application
ActiveCN107091922AIncreased sensitivityReduce mistakesBiological testingMedicineEnvironmental toxicology
The invention provides an in-vivo screening method for examining thyroid disruption and application, which relate to the technical field of environmental toxicology. The in-vivo screening method for examining thyroid disruption provided by the invention exposes xenopus laevis tadpoles at the stage of NF48 to chemical contaminant to examine the metamorphic development index of the xenopus laevis tadpoles, the in-vivo screening method for examining thyroid disruption is highly efficient and highly sensitive, the error is small, and the examination result is accurate.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Fluorescent biosensing method for detection of interaction between small organic molecules and binding proteins based on restriction endonuclease foki inhibition assay
InactiveCN101717824BSimple designSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceEnvironmental toxicology
The invention is a fluorescent biosensing method for detecting the interaction between organic small molecules and binding proteins based on restriction endonuclease inhibition analysis, including the interaction between the oligonucleotide DNA chain modified by the intermediate organic small molecules and the protein, restriction Conditions for the formation of endonuclease FokI dimers, selection of inhibitory sites, and real-time fluorescent quantitative detection technology based on Taqman probes. It utilizes the specific combination of small organic molecules modified in the middle of the oligonucleotide DNA chain and its binding protein or antibody, based on the inhibition of restriction endonuclease FokI digestion by the interaction between small organic molecules and proteins or antibodies, through the The cleaved Taqman probe is used for quantitative real-time fluorescence analysis to detect the interaction between small organic molecules and proteins and the small organic molecules or their binding proteins. The method has high sensitivity, simple operation and strong specificity, and can be used in the study of signal transduction and molecular regulation mechanism in biomedicine, food and agricultural product safety detection, environmental toxicant detection, drug screening, etc.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV
In vivo screening method and application for detection of thyroid disturbance
ActiveCN107091922BIncreased sensitivityReduce mistakesBiological testingEnvironmental toxicologyRadiology
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Anuran cross-species molecular sensors
ActiveUS9448227B2Pollution detectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence designEnvironmental toxicology
Described herein are DNA primer sequences designed for the determination of gene or transcript information from Anuran species, and which may be used in studies for developmental and / or toxicity testing and for environmental toxicology or ecological assessment. Also described herein is a rapid, sensitive, high-throughput assay useful for supporting potential risk assessment across vertebrate clades, and that is also useful for evaluation of complex contaminant mixtures.
Owner:ARIZONA BOARD OF REGENTS ACTING FOR & ON BEHALF OF NORTHERN ARIZONA UNIV
A method for efficiently transfecting turbot muscle cells
ActiveCN106222202BHigh transfection efficiencyPromote growthOther foreign material introduction processesEnvironmental toxicologyGenetics genomics
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
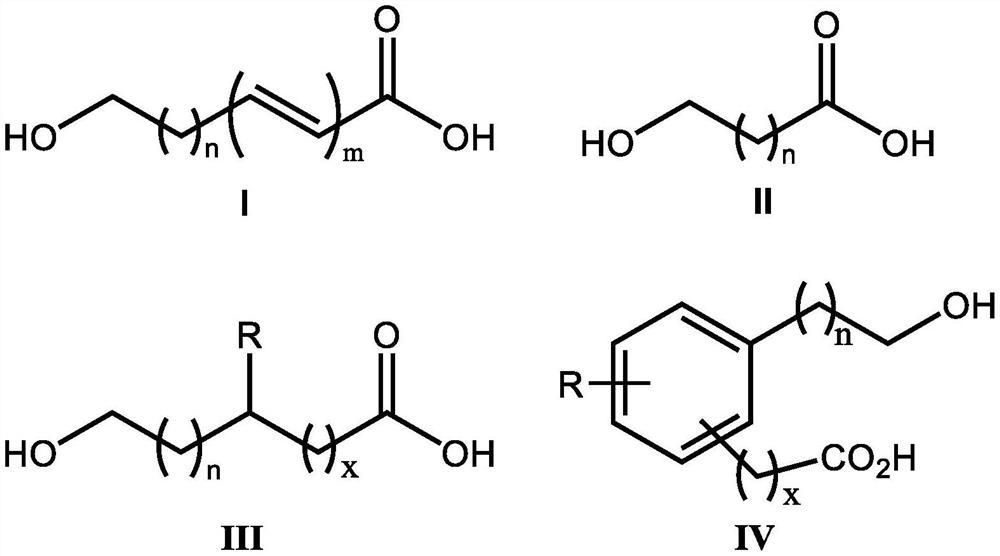
Inhibitory activity of polycarboxylic acid compounds on fungi and oomycete appressorium and application of polycarboxylic acid compounds in prevention and treatment of plant diseases
ActiveCN112400879AInhibition formationAvoid infectionBiocideFungicidesBiotechnologyEnvironmental toxicology
The invention discloses inhibitory activity of polycarboxylic acid compounds on plant pathogenic fungi and oomycetes appressorium and an application of the polycarboxylic acid compounds in preventionand treatment of plant diseases. The polycarboxylic acid compound is selected from a compound shown as a formula I, and an isomer, hydrate or salt thereof. The polycarboxylic acid compound disclosed by the invention remarkably inhibits the formation of appressorium of fungi and oomycetes, can be used for preventing various plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew, phytophthora root rot and powdery mildew, and is free of obvious phytotoxicity and good in safety. Compared with an existing compound for preventing and treating plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew, phytophthora root rot and powdery mildew, the polycarboxylic acid compound has the advantages of being good in prevention effect, environmentally friendly, free of toxicity, low in residue and safe. The compounds are known and widely used, and environmental toxicology and influence research is thorough, so that the compounds have the advantages of convenience, easiness in obtaining, environmental protection and safety.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Construction method for anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line
ActiveCN102766595BEasy to operateGood growthSkeletal/connective tissue cellsAnabarilius grahamiFresh water organism
The invention relates to a construction method for a anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line and belongs to the technical field of freshwater organism cell culture. The method includes using anabarilius grahami heart tissue as a material, washing and shearing the heart tissue, using hyaluronidase and II type collagenase to perform a joint digestion to obtain free heart cells and loose tissue blocks, inoculating the free heart cells and the loose tissue blocks in a culture flask of 25 square centimeters, adding an L-15 culture solution containing fetal calf serum, human basic fibroblast growth factor and chondroitin sulfate in the culture flask, and placing the culture flask in a culture box of 28 DEG C to culture. The culture solution is replaced at an interval of three and half days, and when cells grow into monolayers, a trypsin digestive method is utilized to perform cell passage. The construction method for the schizothorax taliensis cardiac cell line has the advantages that the operation is simple and convenient, the cell growth state of the constructed anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line is good, the cells are fibroblast-like, more than 40 generations can be continuously achieved during the cell passage, the constructed anabarilius grahami cardiac cell line can be directly used for models of an environmental toxicology for studying environmental pollutants to perform pollution detection and safety evaluation, and the method is also suitable for the construction of cardiac cell lines of other fishes.
Owner:KUNMING INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Application of Hydroxycarboxylic Acid Compounds in Controlling Plant Diseases
ActiveCN112106775BInhibition formationAvoid infectionBiocideFungicidesEnvironmental toxicologyChemical compound
The invention discloses the application of hydroxycarboxylic acid compounds in preventing and treating plant diseases; the hydroxycarboxylic acid compounds are selected from compounds of formulas I, II, III and IV, their isomers, hydrates or salts. The hydroxycarboxylic acid compounds of the present invention have remarkable effects in inhibiting the formation of fungi or oomycetes, and can be used for the prevention of plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew, and phytophthora. Obvious injury and good safety. Compared with the existing compounds for preventing and treating plant diseases such as rice blast, anthracnose, gray mold, downy mildew, and phytophthora, the hydroxycarboxylic acid compound of the present invention has good preventive effect, environmental protection, non-toxicity, and low residual , safety features, because this kind of compound is known and widely used compound, the raw material is easy to get, the synthesis process is mature, and the environmental toxicology and impact research is thorough, therefore, it has the advantages of convenience, easy to get, environmental protection and safety.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com