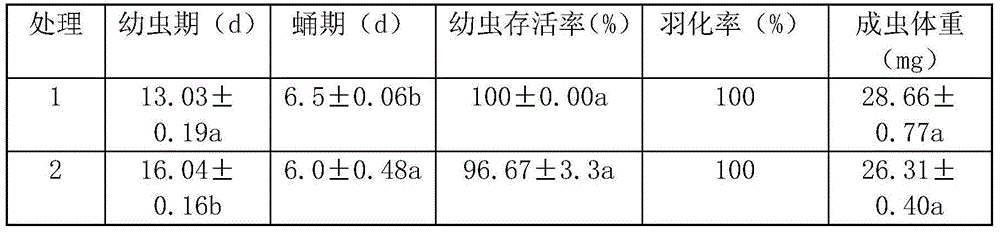
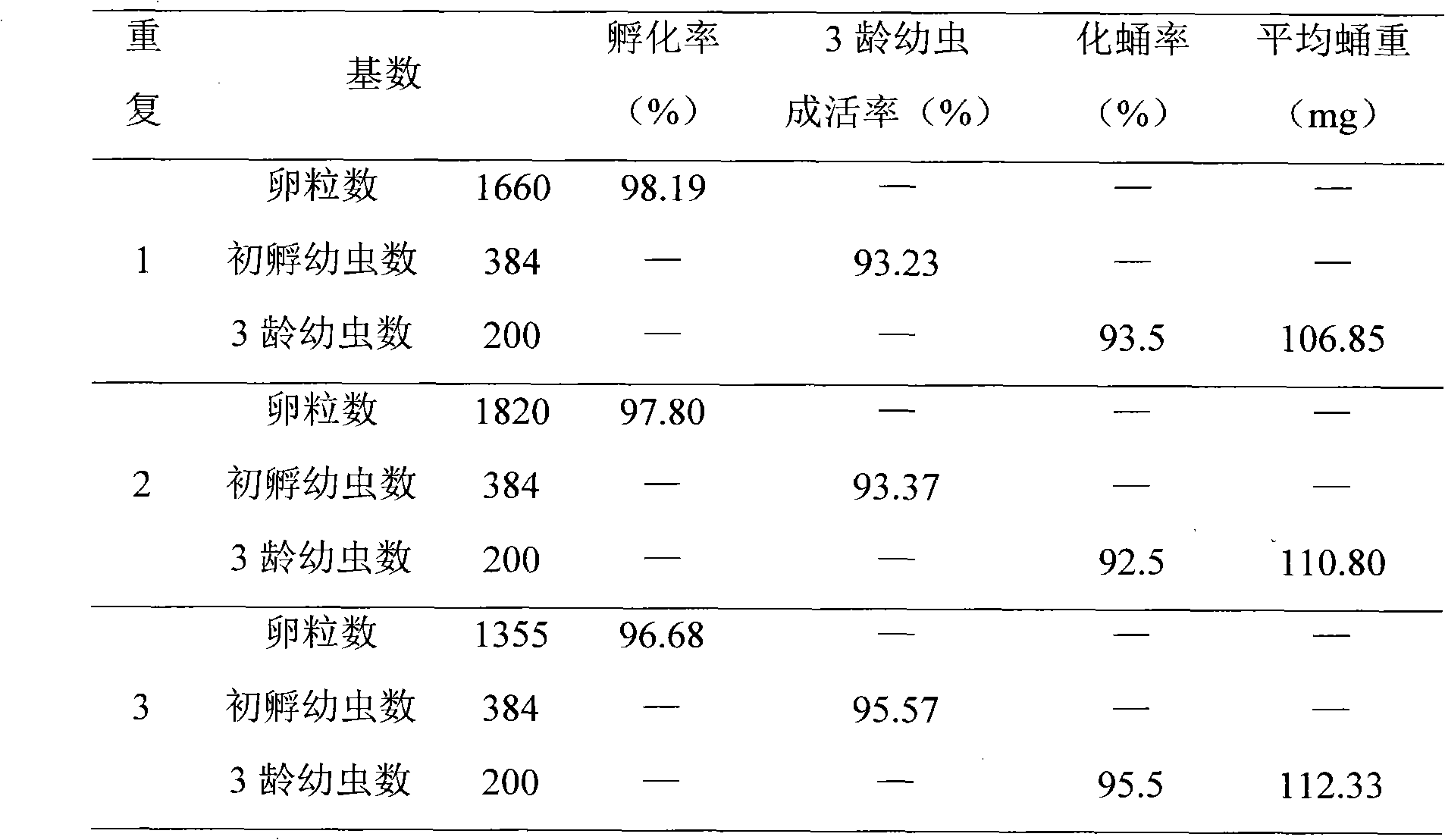
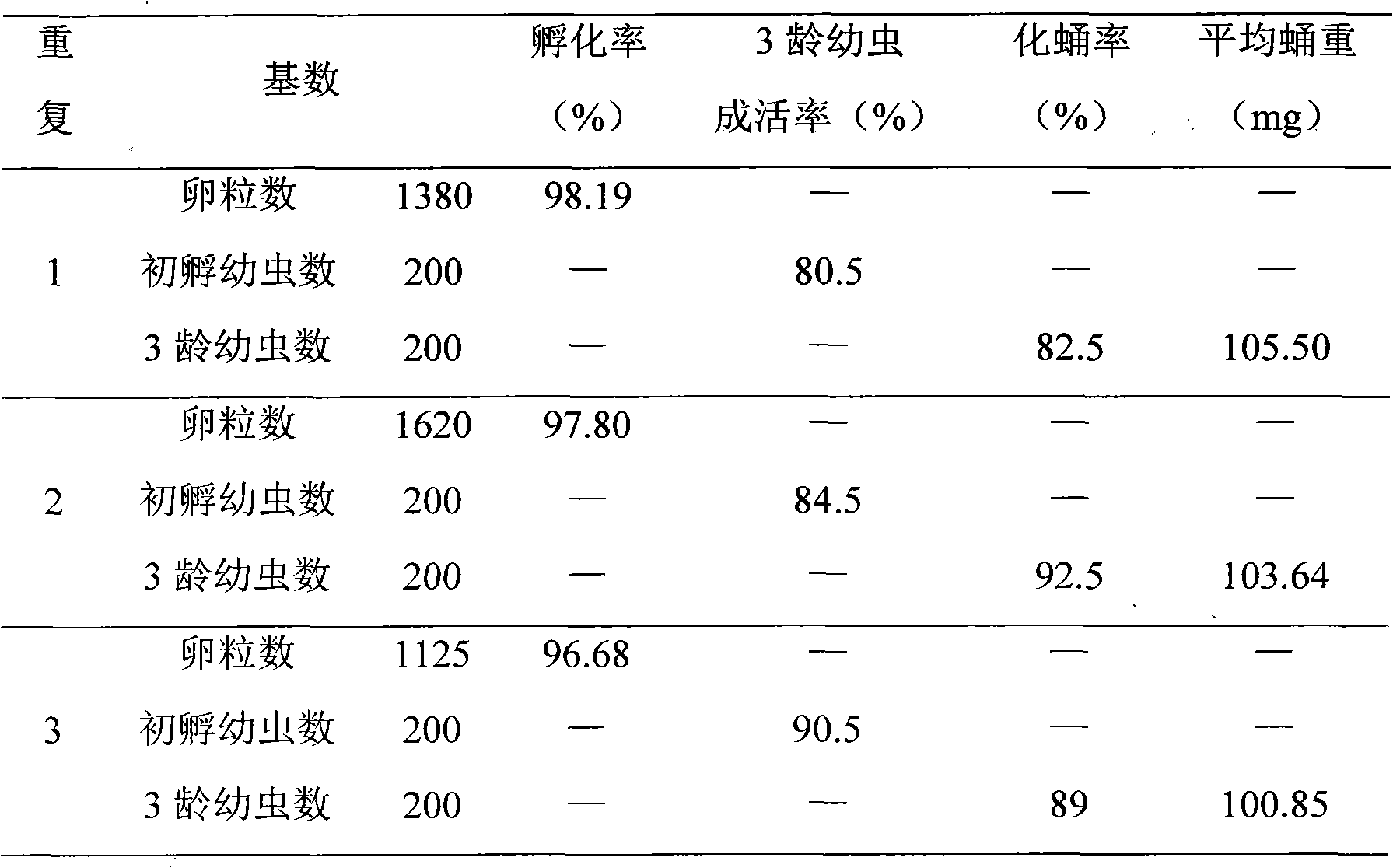
Patents
Literature
207 results about "Mogulones larvatus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
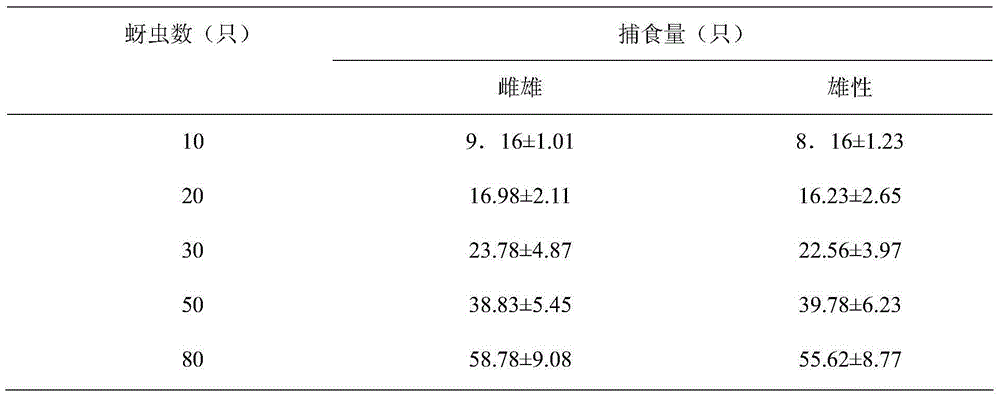
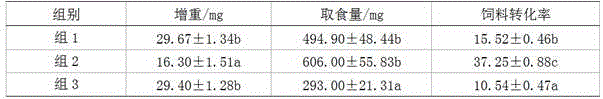
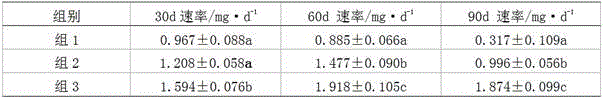
The number of weevil eggs and larvae and all plant reproductive parameters measured per unit biomass were independent of plant size. This study compared the effects of pasture competition and the root-crown feeding weevil, Mogulones larvatus Goeze, on Australia's economically most important ...
Method for processing inapplicable tobacco leaves by musca domestica larva to prepare biological protein feed
ActiveCN103109972ARealize resource utilizationIncrease profitAnimal feeding stuffAnimal scienceResource utilization
The invention discloses a method for processing inapplicable tobacco leaves by musca domestica larvae to prepare a biological protein feed, and belongs to the technical field of environmental protection. The method for processing the inapplicable tobacco leaves by the musca domestica larvae to prepare the biological protein feed comprises the steps of: crushing fresh inapplicable tobacco leaves until the grain size of the crushed leaves is 1-5mm; adding bran, mixture of rice chaff and husk, feather meal and spray-dried animal blood cells to prepare compost; and inoculating housefly eggs at the surface of the compost, cultivating the housefly eggs for 5 days at 25-35 DEG C, collecting the compost containing the musca domestica larvae, drying and preparing the biological protein feed. The method disclosed by the invention is strong in handling capacity, small in floor area, and low in energy consumption in the processing process, achieves the resource utilization of the inapplicable tobacco leaves, changes waste into precious resources, improves the environmental health, simultaneously produces the biologic protein feed, and has a good application prospect.
Owner:胡新军 +2
Industrial golden cicada breeding method
The invention relates to an inset breeding technology, in particular to an artificial golden cicada breeding method. The method includes the steps of industrial hatching workshop building, wood planting and specific breeding methods. The industrial hatching workshop building includes the steps that (1) a cicada egg branch storage chamber is built, wherein the cicada egg branch storage chamber is a plastic greenhouse, greenhouse cloth of the cicada egg branch storage chamber is double layers of plastic films, one layer of the plastic film is black, and multi-layer storage racks used for storing cicada egg branches are arranged in the cicada egg branch storage chamber; (2) a larvae hatch room is built, wherein the larvae hatch room is built beside the cicada egg branch storage chamber or integrally connected with the cicada egg branch storage chamber, the larvae hatch room is a common plastic greenhouse, a plurality of hatch pools are built in the larvae hatch room, and the dimension of an inner cavity of each hatch room is 100 cm*100 cm*50 cm. The industrial golden cicada breeding method enables the growth period of golden cicadas to be 18 months ahead of the growth period of original wide golden cicadas, the hatching period is shortened to about 35 days from original one year, and the survival rate can reach above 80%. The golden cicadas bred through the method are large in size, meaty, full and high in yield.
Owner:XUZHOU GUANGQIN RICE IND
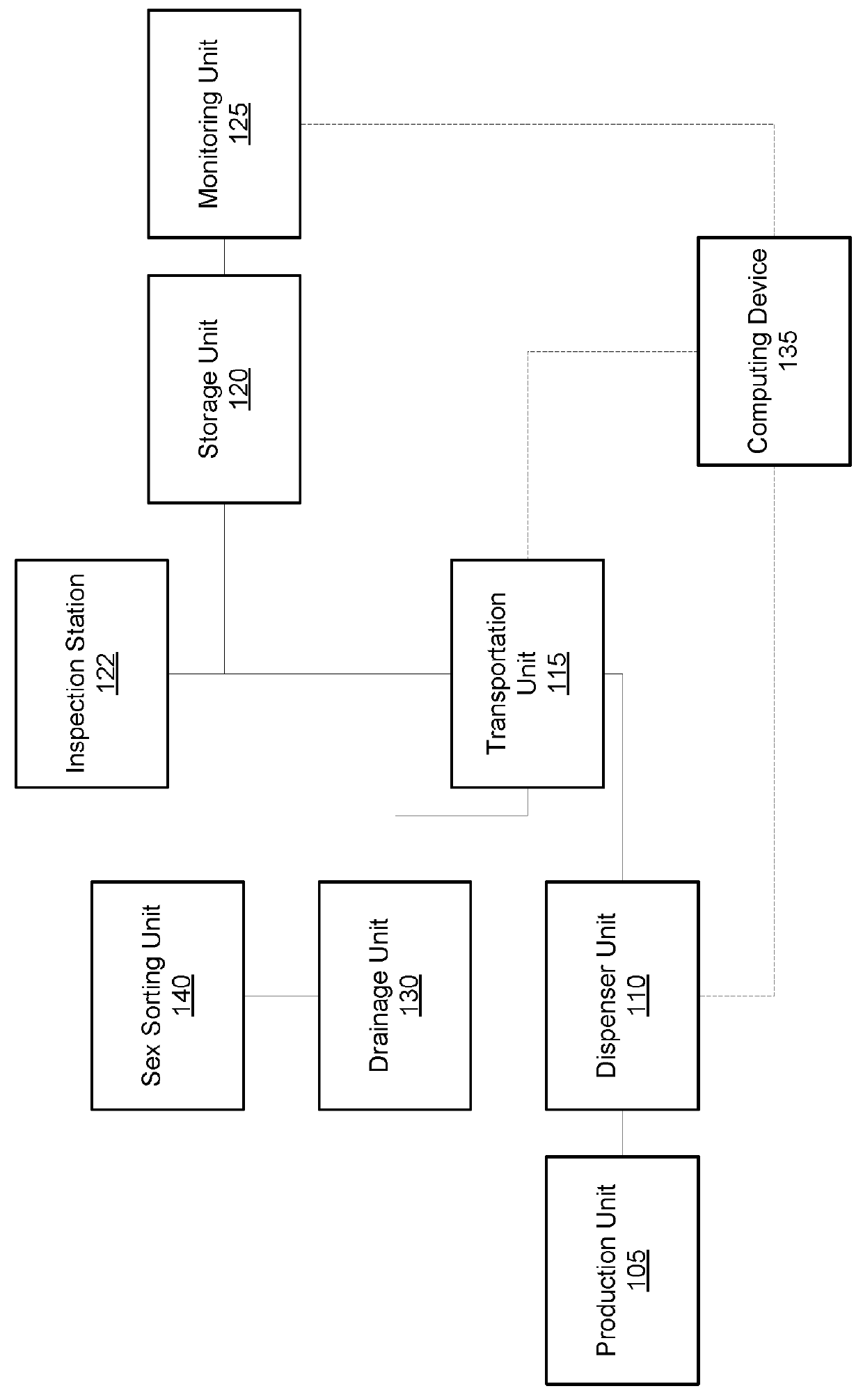
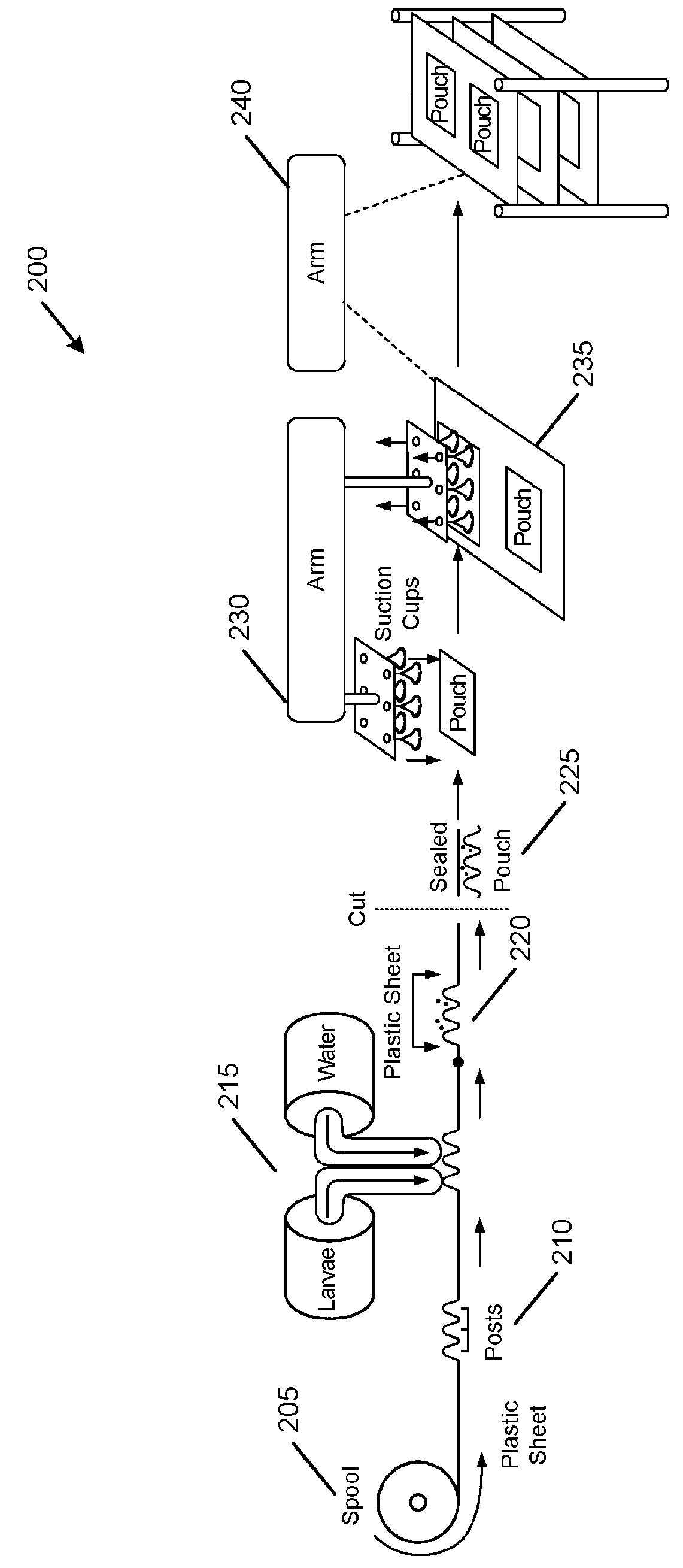
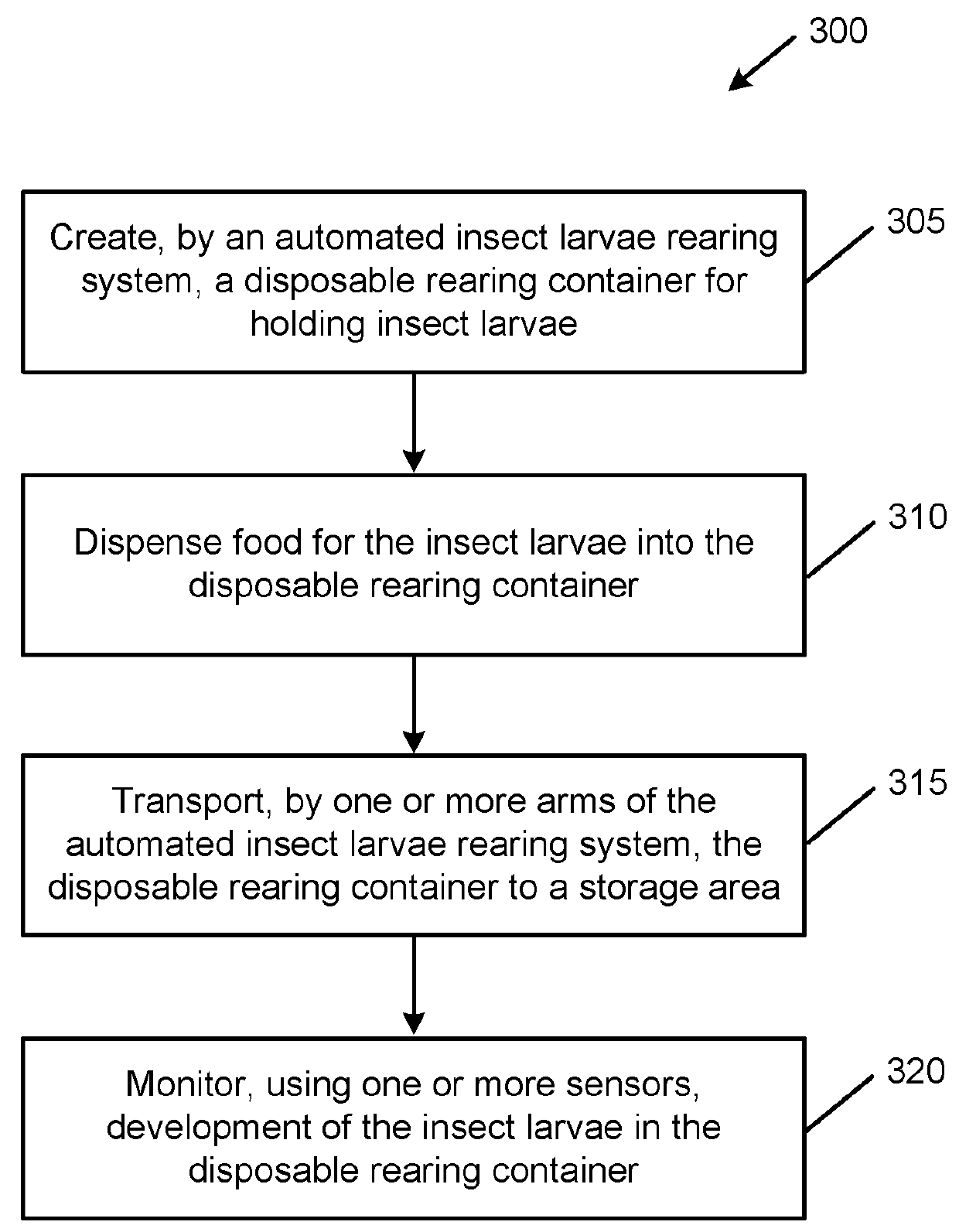
Automated mass rearing system for insect larvae
Embodiments of the present disclosure can provide an automated mass rearing system for insect larvae. The automated mass rearing system can facilitate hatching, feeding, monitoring the growth and emergence of insect larvae and pupae. In some embodiments, the automated mass rearing system can include a production unit, a transportation unit, a storage unit, a dispensing unit, and a monitoring unit. In some embodiments, this automated mass rearing system can facilitate mass mosquito growth from egg hatching all the way through to full adults or certain stages in between such as the larvae rearing process (i.e., from larvae to pupae) with little or no human intervention. By automating the rearing and transportation of insect eggs, larvae, and pupae, deaths or developmental issues can be minimized. Various techniques and apparatuses are used in this automation that causes minimal disturbance to the insects during development, and thereby maximizing survival rate and fitness of the insects.
Owner:VERILY LIFE SCI LLC
Method for producing fly maggots for feeding chickens in chicken farm
The invention relates to a method for producing fly maggots for feeding chickens in a chicken farm. The method includes the following steps of (1) laying eggs, placing aseptic fly pupae in a fly house to incubate for 4 to 5 days to form imagoes, enabling the imagoes to reach to sexual maturity after 2 to 5 days, starting mating, and maintaining the temperature of the fly house in a range from 22 DEG C to 30 DEG C; (2) receiving the eggs, placing egg collecting substances prepared by wheat bran and water through effective microorganisms (EM) in a white plastic box, forming egg clusters by laid eggs, and incubating the egg clusters for 16 hours at the temperature of 60 DEG C; (3) preparing nutrient mediums by 80% of wheat bran and water, EM and pig blood, placing the nutrient mediums in a maggot growing house, spreading the nutrient mediums, placing the egg collecting substances and the eggs on the nutrient mediums uniformly, growing the eggs into larvae after 4 days, and separating out the larvae; and (4) maintaining the room temperature in a range from 20 DEG C to 30 DEG C and the humidity to be 60%, enabling the larvae to be transformed into pupae after 2 to 3 days, and incubating the pupae for 4 to 6 days to form flies. By means of the method, after the produced fly maggots are fed to the chickens, the laying rate of the chickens is increased, eggs laid by the chickens are physically beneficial and environment-friendly, drug residues are absent, and the bred chickens are fresh and tender in meat quality and free of tranig.
Owner:刘建东
Method for increasing yield of natural cordyceps sinensis
The invention provides a method for increasing the yield of natural cordyceps sinensis. The method comprises the following steps of (1) selecting a base for increasing the yield of natural cordyceps sinensis; (2) placing a trapping lamp; (3) preparing trapping liquid; (4) screening and preparing culture medium of hepialidae hirsutella sinensis and paecilomyces hepialid; and (5) controlling yield increase conditions. According to the method, at the adult stage, a high pressure mercury vapor lamp is used for trapping, so the imagoes of hepialus armoricanus around the lamp fly to the base, and the egg-laying amount is increased; ethanol, vinegar and sugar solution are sprayed on meadows beneficial to larva growth, so the larvae gather together; and the hepialidae hirsutella sinensis and the liquefied paecilomyces hepialid are sprayed on the gathering area of larvae to raise the infection rate of the larvae of hepialus armoricanus, so the aim of increasing the yield of cordyceps sinensis is achieved and the industrialized production is realized.
Owner:瓜州亿得生物科技有限公司
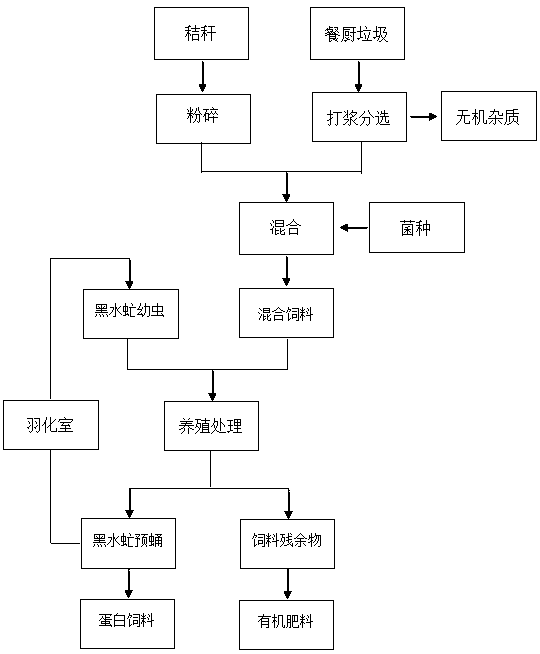
Method for treating and utilizing kitchen wastes and straws by using black soldier fly larvae
InactiveCN110201972AFull of nutritionMeet the requirements of farmingBio-organic fraction processingFood processingBacillus licheniformisHermetia illucens
The invention discloses a method for treating and utilizing kitchen wastes and straws by using black soldier fly larvae. The method comprises the following steps: mixing crushed straws with slurry prepared from the kitchen wastes, and adding bacillus subtilis and bacillus licheniformis to form mixed feed; paving the mixed feed in a black soldier fly larvae breeding trough for breeding the black soldier fly larvae; sieving the black soldier fly larvae and feed residues in the black soldier fly larvae breeding trough when the larvae enter the pre-pupa stage; directly using the black soldier flylarvae as feed for fishes and poultry or preparing the black soldier fly larvae into dried insects to serve as a protein feed raw material; fermenting and composing the feed residues to obtain organicfertilizer by an aerobic composting process. According to the method disclosed by the invention, cooperative treatment and utilization of the kitchen wastes and the straws can be realized; and the kitchen wastes and the straws meet the growth demand of the black soldier fly larvae and are transformed into animal protein feed and the organic fertilizer, so that a disposal method is greatly simplified and the efficiency is improved.
Owner:江苏绿博生物科技有限公司
System and method for breeding and harvesting insects
In an aspect, a system for breeding and harvesting insects is provided and includes an egg-producing chamber structure configured to receive insect pupae for pupation and to permit emerged adult insects to mate and oviposit insect eggs, at least one oviposition region in the egg-producing chamber structure configured to receive the insect eggs and apertured to permit at least one of the insect eggs and neonates of the insect eggs to pass therethrough, at least one larvae-growth chamber in communication with the at least one oviposition region so as to be configured to receive the at least one of the insect eggs and neonates of the insect eggs, wherein the larvae-growth chamber is further configured to permit the at least one of the insect eggs and neonates of the insect eggs to transition into larvae and to hold feed material for the larvae, a harvesting receptacle positioned to hold larvae, and an inclined surface positioned to receive larvae from the at least one larvae-growth chamber, and to provide a passageway for the larvae to travel to the harvesting receptacle.
Owner:LIVIN FARMS LTD
Method for breeding medical ground beetles
InactiveCN103609532AIn line with the original wild life habitsReproduce fastAnimal husbandryDiseaseGround beetle
The invention provides a method for breeding medical ground beetles and belongs to the technical field of medical animal breeding. The method for breeding the medical ground beetles comprises the steps of control over a place of a breeding party, temperature and humidity, management of breeding fodder, breeding soil of the ground beetles, an egg reservation of the ground beetles and incubation of eggs, management of larvae of the ground beetles and medium-sized ground beetles, management of copulation, management of adults, prevention and treatment of diseases and pests, collection and processing of the ground beetles and finished product storage of the ground beetles. The method for breeding the medical ground beetles accords with the original wild life habits of the ground beetles, the growth and breeding speed of the ground beetles is greatly increased, and the ground beetles are good in medical property, strong in efficacy, good in quality and high in market selling price.
Owner:张国平
Method for breeding larva of lepidoptera insects indoor and device thereof
InactiveCN102388843ASolve Xi crawling (crawling) away from foodAddressing Difficulty Getting Food AgainAnimal husbandryOrder LepidopteraZoology
The invention discloses a method for breeding larva of lepidoptera insects indoor. The breeding box using in the method has no bottom, and the lower part of the inner wall of the breeding box is fixedly connected with at least two support blocks. A leaking frame is arranged on the support blocks, at least one fixing device of a cutting transplanting pipe is arranged on the leaking frame, and at least one cutting transplanting pipe is arranged in the fixing device of the cutting transplanting pipe. The lateral wall of the breeding box or the box cover is provided with at least one ventilating window. The leaking frame comprises a cross rod and a grid. The branches of the host plant are inserted in the cutting transplanting pipe, the leaves of the plant branches cannot touch the inner wall of the breeding box, and clean water or plant culture medium is put in the cutting transplanting pipe. The invention solves the technical problems that the larva difficultly eats food caused by disorderly climbing, and the larva groups are easy to crossly infect by pathogen caused by that excrement of the larva pollutes the leaves. The invention can adjust the temperature and the humidity in the breeding box, has long fresh keeping period, can conveniently change the branches and clean the box body, can easily disinfect, and has a simple and smart structure, low cost and little labour input, so it is suitable for breeding the larva of large insects indoor.
Owner:云南省农业科学院蚕桑蜜蜂研究所
Method for breeding and feeding Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd in floating seedling raising shed
The invention relates to a method for breeding and feeding Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd in a floating seedling raising shed and belongs to the field of insect feeding. According to the biological and ecological behaviors of the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd and the modern agricultural science and technology, by using the existing floating seedling raising shed and the time difference between Myzus periscae (Sulzer) breeding period and the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd larva growth and development period, breeding Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd required for Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd breeding is obtained at the same time when the Myzus periscae (Sulzer) is bred. The method for breeding and feeding the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd in the floating seedling raising shed has the advantages that the operation is simple to conduct, the cost is low, the repetitive investment is not required, the survival rate is high, the scale breeding is facilitated and the popularization is facilitated. Compared with the method for breeding and feeding the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd in a seedling raising greenhouse, on the premise that the bred and fed quantity is not affected, the cost per mu is reduced by RMB4.5, the quantity of bred and fed adult Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd and the parasitism rate are respectively improved by 21.3 percent and 3.8 percent, the number of parasitic aphids on each plant in the field and the control rate of the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd to the aphids are improved by 4.75 percent, the economic benefit, the social benefit and the ecological benefit are good, and a good foundation is laid for the large-scale breeding and feeding of the Aphidius gifuensis Ashmesd.
Owner:云南省烟草公司保山市公司
Method for large-scale indoor artificial breeding of Hong Kong oysters in coastal region of South China
ActiveCN103798166ALow breeding densityGuaranteed growth rateClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaLow salinityTerra firma
The invention discloses a method for large-scale indoor artificial breeding of Hong Kong oysters in the coastal region of South China. According to the method, a large number of healthy oyster larvae are bred indoors by means of parent maturation, parturition hastening, incubation, larva breeding, adhering transformation, juvenile mollusk breeding and other processes. In combination with the ecological habits of the Hong Kong oysters and the coastal regional characteristics of South China, the step-by-step salinity-reduction breeding pattern that parent maturation of the Hong Kong oysters in a high-salinity environment, the larvae are bred in a medium-salinity environment, and juvenile mollusks are bred in a medium / low-salinity environment is realized, and a solid foundation is laid for production of the larvae of the Hong Kong oysters, development of aboriginal varieties and industrial popularization of the Hong Kong oysters.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Aspergillus fungus with nematode-killing vitality, and its preparing method and use
The invention relates to a cultivation of epiphyte that has plant infestation wireworm poisoning function and the metabolite manufacture method and the application. The strain of the epiphyte is Asipergillus. niger snf0407009 and the conserving code is CGMCC No.1714. It is made up from normal liquid fermenting and cultivating, and its metabolite has high poisoning function to plant infestation wireworm, especially root wireworm. The influence to the Meloidogyne incognita has been measured indoor. Different thickness fermenting liquid would have obviously influence to Meloidogyne incognita. One time fermenting liquid has the similar function as 10ug / mL aldicarb. It has good application prospect.
Owner:SHENYANG AGRI UNIV
Feeding substrate and artificial feeding method for increasing later-period survival rate of larvae of hepialus armoricanus which is host of cordyceps sinensis
InactiveCN103688761AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of reproductionHorticultureAnimal husbandryHand rearingPlant disease
The invention discloses a feeding substrate and an artificial feeding method for increasing a later-period survival rate of larvae of hepialus armoricanus which is a host of cordyceps sinensis. The feeding substrate is a mixed substrate comprising to-be-processed feeding soil and soil with hyphae of pleurotus eryngii. The to-be-processed feeding soil is mixed soil comprising highland humus soil from cordyceps sinensis producing areas and coarse sand, particles of pleurotus eryngii solid mother strains are cultured in highland humus soil from the cordyceps sinensis producing areas and then are smashed to form the soil with the hyphae of the pleurotus eryngii, and the highland humus soil for culturing the particles contains saw dust and coarse sand. The feeding substrate and the artificial feeding method have the advantages that the hyphae of the pleurotus eryngii is fixedly planted and grown in the soil of the larva feeding substrate, so that nutrition can be provided for the larvae via zero distance, pleurotus eryngii fungi are used as antagonistic bacteria for preventing diseases and contaminating microorganisms, growth and reproduction of pathogenic bacteria can be competitively inhibited, the diseases can be effectively reduced, and the feeding substrate and the artificial feeding method have obvious features, merits and important practical significance on artificial cultivation of the cordyceps sinensis.
Owner:浙江天使生物工程有限公司
Outdoor cultivation of clam in factory
The invention is concerned with the outdoor manufactory raising seedling method for cyclina sinensis, the characteristic is: puts the spats into the pool that the water temperature is 25 centigrade to 28 centigrade, the salinity is 20 per mill to 25 per mill , the water level is 0.8cm to 1.2cm and the water is dark deposit filtration, puffs under the mesh box; processes dark processing of the pool; the incubation water temperature is 27 centigrade to 30 centigrade, the salinity is 20 per mill to 30 per mill , the light irradiation is under 500lux; moves the D larva into the pool that is same with the incubation water quality, the light irradiation is under 1000lux; the cultivating density of the larva is 10 to 15 per milliliter, feeds the single-cell alga, changes the water at each morning or evening; moves the anaphase larva into the outdoor pool that is with bottom mud, the water deep is 50 cm, the water temperature is 25 centigrade to 32 centigrade, the salinity is 5 per mill to 32 per mill , and with gas head, feeds the single-cell alga, the light irradiation is under 3000lux; changes water every day after the adhesion of the larva; cleans the bottom of the pool once two days; evacuates the spats when the density of the spats is over 100 per cm2.
Owner:EAST CHINA SEA FISHERIES RES INST CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
Fly maggot cultivating method using bean dregs
The invention discloses a fly maggot cultivating method using bean dregs. The fly maggot cultivating method includes the following steps: (1) breeding fly larvae; (2) obtaining eggs: an egg obtaining plate is put in a fly larva cage from the third day after the fly larvae start mating, and inducing materials are put in the egg obtaining plate; the egg obtaining plate is replaced every 12 hours; the inducing materials are composed of an inducing material main ingredient and an odor agent, and the inducing material main ingredient is composed of fresh bean dregs, wheat bran and water; (3) covering the eggs and cultivating fly maggots: fly maggot feed is scattered on an egg obtaining basin taken out from the fly larva cage evenly, then the egg obtaining basin is put into a cultivating chamber to be cultivated; the temperature in the cultivating chamber is 25-35 DEG C, and relative humidity is 60%-70%; the fly maggot feed is composed of fresh bean dregs, wheat bran and water; after the eggs are cultivated for 96 hours (adding the fly maggot feed every 48 hours), cultivation mixture containing fly maggot larvae is contained; and (4) collecting the fly maggots to obtain the fly maggots.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Diffusion breeding and releasing method for preventing myzus persicae through harmonia axyridis
ActiveCN103478117AMake up for the lack of slightly poor drug resistanceSimultaneous releaseAnimal huntingMyzus persicaeRoom temperature
The invention discloses a diffusion breeding and releasing method for preventing myzus persicae through harmonia axyridis. The myzus persicae is bred in a diffusion breeding shed, and an insect-proof net (7) covers the diffusion breeding shed; a tobacco seedling is cultivated through a floating method; when the tobacco seedling has five to six true leaves, tobacco leaves with the myzus persicae are put on the tobacco seedling to breed the myzus persicae; male and female harmonia axyridis adults captured in the wild are put into the insect-proof net, eat the myzus persicae and then mate to lay eggs; the eggs are incubated into larvae, or low-age larvae are directly collected, or after the larvae are pupated, pupae are taken back for eclosion at room temperature; the eclosion adults are fed with the myzus persicae and are put into a refrigerator for refrigeration and storage; the low-age larvae or the adults of the harmonia axyridis are put into a low-age larva transporting and releasing device (9) or an adult transporting and releasing device (10); the low-age larvae or the adults of the harmonia axyridis are released to a field according to a ratio of the harmonia axyridis to the myzus persicae of 1:(100-120) in a preliminary forming stage of the myzus persicae in the field. According to the method, the breeding speed rate of the harmonia axyridis can be remarkably improved, and the field pest control efficiency is improved in a mode of preventing the myzus persicae through the harmonia axyridis.
Owner:YUNNAN REASCEND TOBACCO TECH GRP
Artificial feed for harmonia axyridis larvae and preparation method thereof
The invention belongs to the field of feeding of natural enemy insects and in particular relates to an artificial feed for harmonia axyridis larvae and a preparation method of the artificial feed. The artificial feed for harmonia axyridis larvae is prepared from the following components in parts by weight: 5 parts of pork liver, 0.5-1.5 parts of dried powder of housefly larvae, 1-2 parts of yeast extract, 1-3 parts of saccharose and 1-2 parts of honey. The preparation method comprises the steps of preparing pasty pork liver, preparing dried powder of housefly larvae and mixing all the components. The components of the artificial feed are readily available, the investment is low, the production cost is low, and the preparation method is simple, can be operated easily and is suitable for feeding harmonia axyridis larvae in a large-scale manner.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Artificial rearing method of larvae of beet armyworm
InactiveCN102113471AImprove hatchabilityOvercome the disadvantage of high mortalityAnimal husbandryArtificial rearingAlcohol
The invention discloses an artificial rearing method of larvae of beet armyworm, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) placing eggs of the beet armyworm in a ground glass hatching jar, placing fresh young cabbage leaves after surface disinfection by 75% of alcohol in the jar and sealing by using three-layer gauze till hatching; (2) selecting the freshly hatched larvae of the beet armyworm into a 24-hole insect rearing plate loaded with artificial feed, and rearing till 3 ages; and (3) transferring the 3-age larvae of the beet armyworm into flat bottom glass finger-shaped pipes loaded with the artificial feed, enabling each pipe to contain two larvae, and rearing till pupation. The method is simple, the rearing process occupies small space, the survival rate of the larvae is high, and a large number of standard test insects can be obtained.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Method for artificially and largely raising Dioryctria pryeri indoors
InactiveCN105028333ARich sourcesSolve the technical bottleneck that cannot be raised in the cones after pickingAnimal husbandryAdult femaleParaffin oils
The invention discloses a method for artificially and largely raising Dioryctria pryeri indoors and application of the method. The method comprises the following steps of wrapping various coniferous tree cones with paraffin to prepare feed for the Dioryctria pryeri; collecting, culturing and raising provenances, i.e., pupae of the Dioryctria pryeri, in the field; pairing newly emerged adult females and males to mate, and isolating female moths after mating for laying eggs; collecting and culturing the eggs of the Dioryctria pryeri until larvae hatch; transferring the hatched larvae to the cones wrapped by the paraffin and raising. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the Dioryctria pryeri is raised by the natural feed which is rich in source and low in cost, cannot be influenced by seasons and does not need a complicated processing course; the method is simple and easy, and can be suitable for largely raising the Dioryctria pryeri; a large amount of stable insect sources are provided for studies on the control technique for the Dioryctria pryeri and other injurious insects similar to the Dioryctria pryeri in injurious feature and production of parasites.
Owner:JILIN CITY ACADEMY OF FORESTRY
Cockroach and eupolyphaga large-scale mixed breeding technique
InactiveCN102144615AIn line with the original wild life habitsPromote growthAnimal husbandryDiseaseHabit
The invention relates to a cockroach and eupolyphaga large-scale mixed breeding technique and belongs to a method for breeding specific animals. A cockroach and eupolyphaga mixed breeding method is characterized in that: 1, breeding environment, a pool which is a precursor of a three-dimensional greenhouse feeding pond is adopted; 2, food stuffs feeding, wherein adults and larvae of the eupolyphaga and the cockroach have the same food stuffs such as wheat bran, rice chaff, green vegetables, carrots, rice paste, pumpkins, pericarp, leaves and the like; and the food stuffs based on the green materials are fed for one time every 2 to 3 days and more dried materials such as the wheat bran are fed; 3, management of larval and middle-aged cockroaches, wherein larvae are not required to be separated from eggmass at the early stage after reproduction of the cockroach; and management of larval and middle-aged eupolyphaga is that the larvae are separated from eggmass after being incubated; and 4, prevention and control of diseases and insect damage, wherein the natural enemies of the cockroach and the eupolyphaga during artificial culture are ants, mice, spiders, chickens, ducks, birds and the like; and the diseases and insect damage are prevented in advance and treated actively. The cockroach and eupolyphaga large-scale mixed breeding technique has the advantages of accordance with the original wild life habit of the cockroach and greatly increasing growth speed and reproductive speed of the cockroach, along with high medicament properties, strong effect, excellent quality and high market price.
Owner:鞠芳
Method for completely converting poultry excrement step by step through hermetia illucens and potosia brevitarsis
InactiveCN106070067APromote improvementHigh economic valueClimate change adaptationExcrement fertilisersFecesEcological environment
The invention discloses a method for completely converting poultry excrement step by step through hermetia illucens and potosia brevitarsis. A small amount of saw powder is added to the poultry excrement to be mixed, the water content of the poultry excrement is adjusted, microbial inoculums are added for fermentation for 12-24 hours, hermetia illucens larvae are introduced, and conversion treatment is conducted. Commodity larvae are separated from materials, larva bodies are high-protein insects and can be used as feed or deeply processed, after waste is fermented, potosia brevitarsis larvae are introduced for further conversion treatment, and potosia brevitarsis larva bodies and particle frass are obtained. The method is high in treatment and conversion capacity and high in efficiency and benefit, the treatment process is low in energy consumption, secondary high-efficiency utilization of the poultry excrement is achieved, two types of produced larvae have high economic value, particle organic fertilizer can be directly used for agricultural production, a great significance is achieved in solving ecological environment pollution and raising incomes of farmers, and thus the method has wide market prospects.
Owner:天津农垦渤海农业集团有限公司 +5
Method for rearing litchi fruit borers
The invention relates to the field of insect rearing technologies and particularly discloses a method for rearing litchi fruit borers. The method includes the steps of adult moth rearing and larva rearing. According to the method, kinds of factors, such as temperature, humidity, feed, a photoperiod and oviposition media, limiting the survival rate of litchi fruit borer bodies are comprehensively considered, and influences generated by interaction among the factors on the litchi fruit borers are comprehensively considered, so that the rearing method according to the characteristic of the rearing period of the litchi fruit borers is researched. The method can improve the survival rate of the reared litchi fruit borers, reduce the use amount of the feed, save cost and improve efficiency, and is high in rearing efficiency.
Owner:PLANT PROTECTION RES INST OF GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Agasicles hygrophila experimental population raising method
InactiveCN102499188AGuaranteed survival rateSame incubation timeAnimal husbandryArtificial rearingEgg masses
The invention discloses an agasicles hygrophila experimental population raising method. The agasicles hygrophila experimental population raising method includes steps that filter paper with the size equal to that of a bottle bottom is placed in an insect breeding bottle I, and is wetted, and 20-30 adult insects which are just subjected to the eclosion are placed in the insect breeding bottle I and are fed by three fresh alternanthera philoxeroides; alternanthera philoxeroides leaves with egg masses in the insect breeding bottle I are placed in insect breeding bottles II, each insert breeding bottle II holds ten alternanthera philoxeroides leaves, and then the insect breeding bottles II are placed in an artificial incubator; fresh alternanthera philoxeroides is placed in the incubator on the first day of incubation, and the alternanthera philoxeroides is continuously replaced by other fresh alternanthera philoxeroides until larvas are matured; and when about to pupate, the agasicles hygrophila matured larvas are transferred into pupating devices, each pupating device contains 100 matured larvas, the matured larvas enter straws of alternanthera philoxeroides to pupate, and pupating rate can reach 80% to 95%. The agasicles hygrophila experimental population raising method is simple in artificial raising, easy to control, small in occupied space and low in cost, and can be used for raising a controllable quantity of neat and consistent agasicles hygrophila with different insect development stages and different insect ages according to different experimental needs.
Owner:SHANXI AGRI UNIV
Artificial breeding and intensive cultivation method for tylorrhynchus heterochaetus
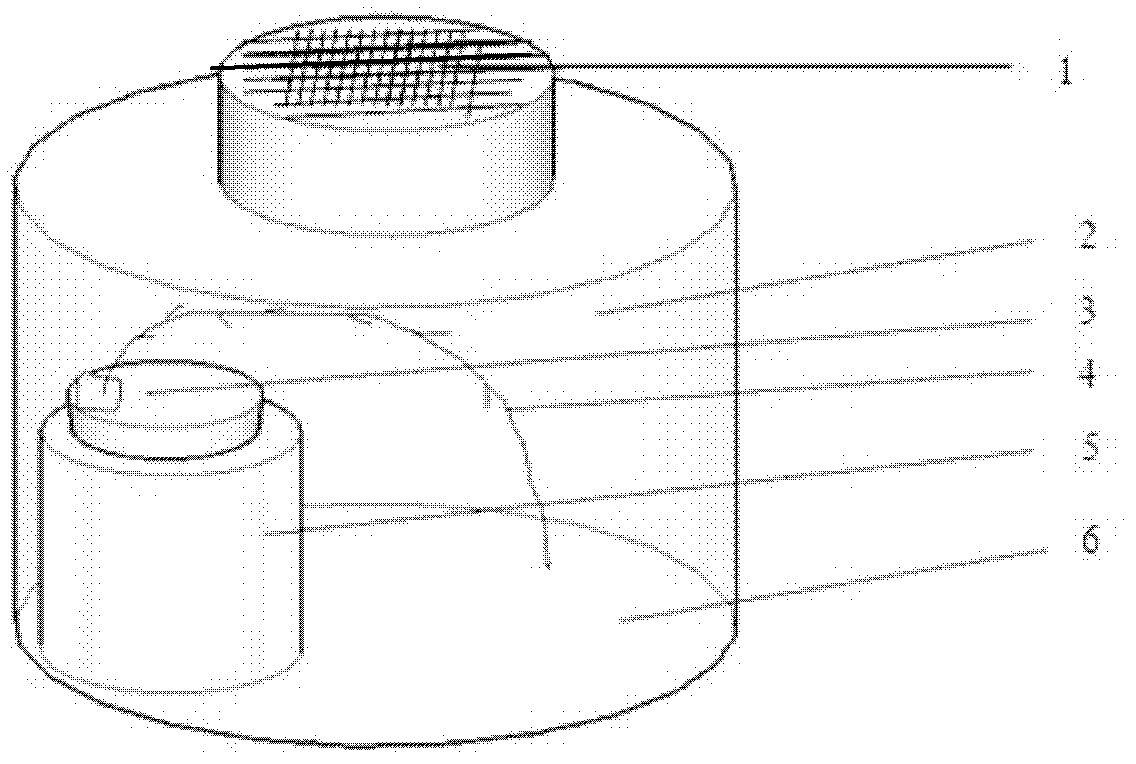
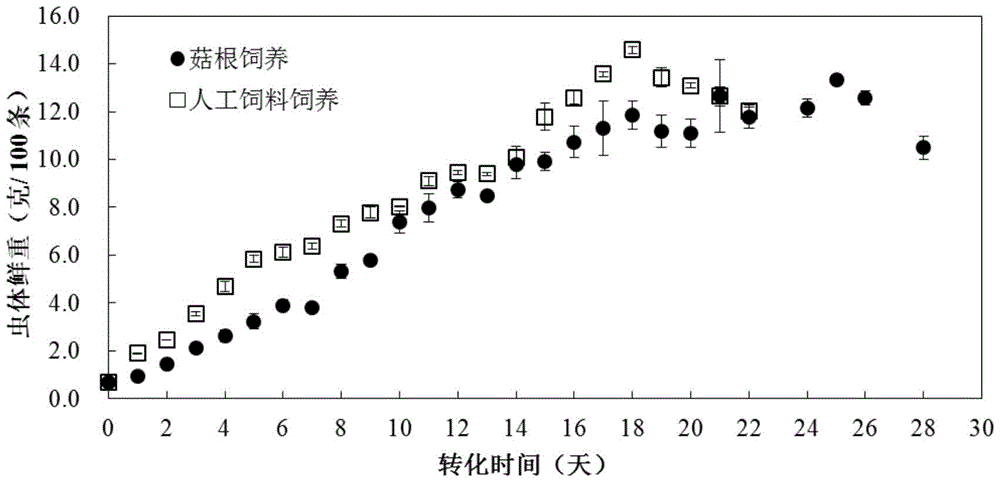
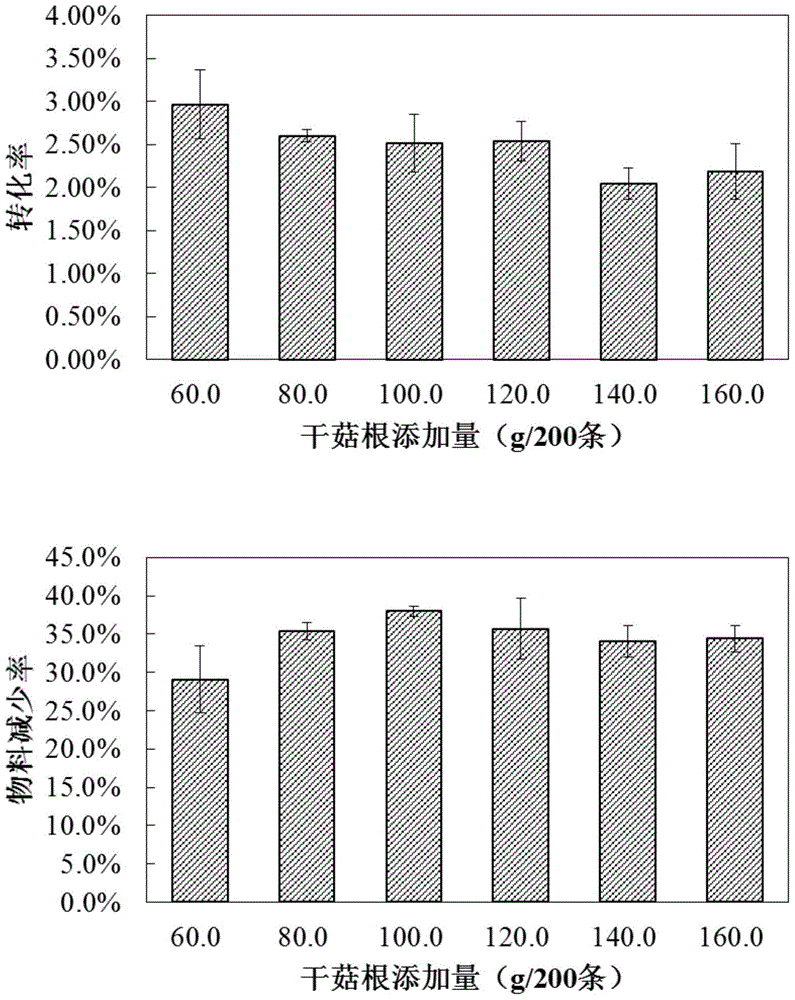
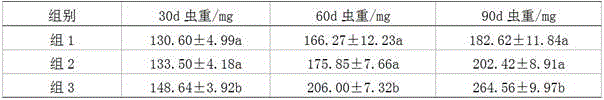
ActiveCN105994052AImprove farming outputProtect natural resourcesClimate change adaptationAnimal feeding stuffMogulones larvatusArtificial fertilization
The invention provides an artificial breeding and intensive cultivation method for tylorrhynchus heterochaetus. The artificial breeding and intensive cultivation method includes the steps of parent selecting, artificial fertilization, artificial incubation, nursery pond preparing, artificial breeding and intensive cultivation. The technical problems of the tylorrhynchus-heterochaetus breeding male-female proportion, breeding water environment conditions, young tylorrhynchus heterochaetus food intake, tylorrhynchus-heterochaetus pond cultivation and the like are solved, and therefore artificial breeding and intensive cultivation of tylorrhynchus heterochaetus are achieved; seed resources can be provided for large-scale cultivation of tylorrhynchus heterochaetus, the cultivation yield of tylorrhynchus heterochaetus can be increased, and the artificial breeding and intensive cultivation method is of great significance in protecting natural tylorrhynchus heterochaetus resources and meeting the consumption requirement of the market for tylorrhynchus heterochaetus.
Owner:珠海市斗门区河口渔业研究所
Application of black soldier fly larvae to feed for improving meat quality of aquatic products
InactiveCN108576485AImprove intestinal microbial environmentImprove qualityFood processingClimate change adaptationFinless eelAquatic animal
The invention discloses an application of black soldier fly larvae to a feed for improving meat quality of aquatic products. Black soldier fly larva powder is added to a feed for aquatic products, andthe black soldier fly larva powder is rich in various nutrient components and functional components, so that the intestine environment of the aquatic animals can be improved, the absorption of the nutrient components in the feed by the aquatic animals can be strengthened, meat quality texture indexes of the muscle elasticity, the adhesiveness, the chewiness, the hardness, the adhesiveness, the cohesion, the recoverability and the like, of the aquatic animals of finless eels, pelteobagrus fulvidraco, japanese sea perches and the like are notably improved, and the application has favorable application prospect and market value.
Owner:ANIMAL SCI RES INST GUANGDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI +1
Propylaea japonica artificial breeding, breed conservation and propagation production method
InactiveCN104396881AFacilitated releaseImprove reproductive efficiencyAnimal husbandryLeafhopperAdult stage
The invention discloses a propylaea japonica artificial breeding, breed conservation and propagation production method. According to the invention, a host plant species and an aphid large-amount breeding technology which are used in high-efficiency host aphid propagation are selected; propylaea japonica are bred according to four development stages which are an egg stage, a larva stage, a pupa stage and an adult stage; an appropriate breeding technology is adopted according to biological and ecological characteristics of propylaea japonica; breeding equipment is tested and developed, such that propagation efficiency is improved; propylaea japonica is trapped for spawning with physical and chemical methods, such that centralized collection and breeding is facilitated; breeding and storing conditions are determined through tests; and box packages are adopted for adults and paper bag packages are adopted for larvas and eggs, such that field release and popularization are facilitated. According to the invention, a key technology for propylaea japonica large-scale propagation by using live aphids is explored, and high-quality, high-efficiency and large scale propagation of propylaea japonica is realized. The propylaea japonica is used for controlling agricultural and forestry pests such as aphids, plant hoppers and leafhoppers, such that production needs can be satisfied.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
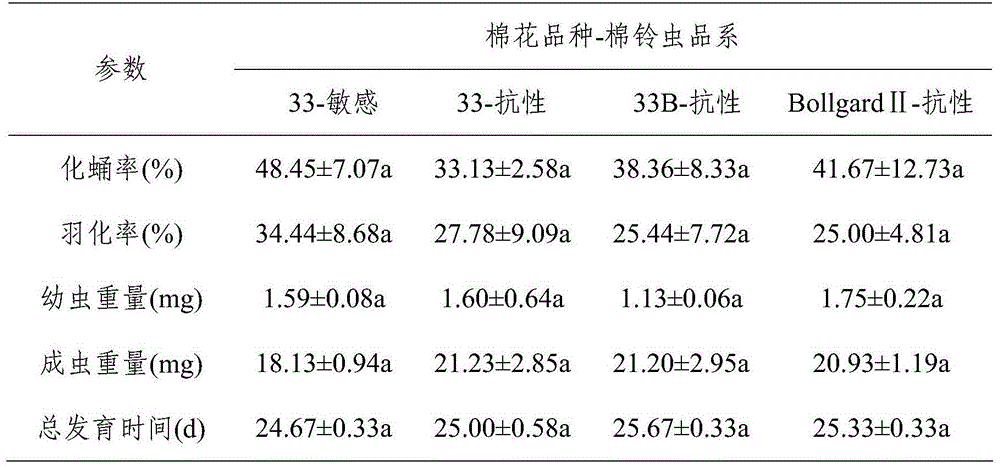
Biological assaying method for evaluating effect of transgene cotton on chrysopa pallens
ActiveCN104133054AWide applicabilitySolve the preservation problemBiological testingChrysopa pallensHigh doses
The invention provides a biological assaying method for evaluating the effect of transgene cotton on chrysopa pallens. The method comprises the following steps: paving agar on the bottom of a culture dish; placing transgene cotton leaves on the surface of the agar, inoculating newly-hatched helicoverpa armigera larvae; feeding newly-hatched chrysopa pallens larvae for 1 to 3 days with pea aphid, then feeding the chrysopa pallens larvae with the helicoverpa armigera larvae which has been fed by the transgene cotton leaves for 1 to 3 days; observing the growth situation of the chrysopa pallens larvae since the first day when the chrysopa pallens larvae is fed with the helicoverpa armigera larvae until the chrysopa pallens larvae pupate and perform eclosion; setting a reference group; comparing the differences of the experiment group and the reference group on the indexes of pupation rate, eclosion rate, larva weight, imago weight, and total growth time, and analyzing the difference significance through variance analysis so as to evaluate the effect of transgene cotton on chrysopa pallens. The application range of the biological assaying method is wide. The effect of high dose protein in transgene plants on predators can be effectively measured by utilizing the nutrition relationship evaluation of transgene plant-pest-predator.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
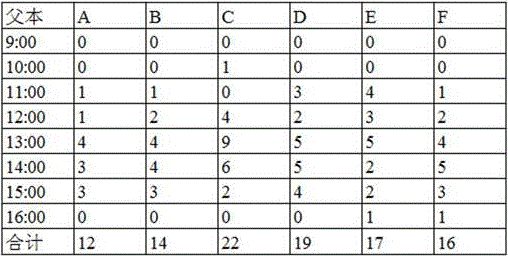
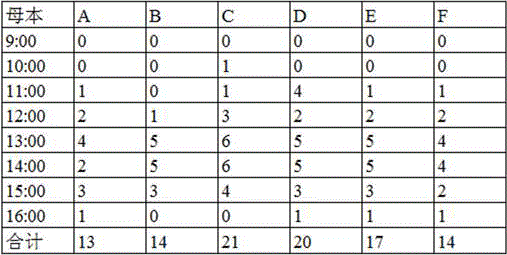
Method for increasing flower visiting rate of bees for hybrid soybean seed production
ActiveCN106069732AIncrease the number of flower visitsThe number of flower visits increasedBiocidePest attractantsPollenSource orientation
The invention relates to the field of pollination of crops, in particular to an effective method for increasing the flower visiting rate of bees. The flower visiting frequency and the number of flowers visited by the bees are increased by combining bee colony control and spraying of an attractant on plants. The method comprises steps as follows: a hybrid soybean field adopting bee pollination is selected; the structure of a bee colony is adjusted; the bee colony for pollination is transported to the soybean field, and the selected bee colony for pollination is transported to the hybrid soybean seed production field in the early stage of flowering of the soybeans; the attractant to be sprayed to the plants is prepared from linalool, benzyl alcohol, ocimene, geraniol, nerol, mushroom alcohol and 2-heptanone. The bee colony is released in the pollination field after being prepared, and the attractant is sprayed on flowers of crops in the flowering period of the crops to attract the bees to visit the flowers. The biological characteristic that pollen and smell are taken as one of approaches to food-source orientation of bee larva is utilized, a large quantity of bees are attracted, the number of the flowers visited by the bees and the natural pollination rate are increased, the yield of the crops is increased, and the method has the characteristics that the method is scientific, simple, convenient and easy to operate, low in cost and remarkable in effect and materials are low in price and easy to obtain.
Owner:SHANXI ACAD OF AGRI SCI GARDENING RES INST
Method for converting edible mushroom root wastes through stratiomyiidae larvae
InactiveCN105693296ARealize secondary useIncrease added valueBio-organic fraction processingFood processingAquaculture industryFeces
The invention discloses a method for converting edible mushroom root wastes through stratiomyiidae larvae.The method comprises the steps that mushroom roots and mushroom bran of edible mushrooms or compounding materials prepared by mixing the mushroom roots and mushroom bran of the edible mushrooms and organic waste such as livestock excrement, kitchen leftovers and bran according to different proportions are prepared into stratiomyiidae feed by adding tap water, the 5-8-day-old stratiomyiidae larvae are inoculated, converting is performed for 20-25 days under the condition that the temperature is 25 DEG C-30 DEG C, separated live larvae are used for directly feeding animals or prepared into dried stratiomyiidae larva bodies to serve as larva body protein, and remaining fecula and residues can be prepared into organic fertilizer through conventional composting.According to the method, not only is pollution of the organic wastes such as the mushroom roots of the edible mushrooms to the environment solved, but also the requirement of livestock and poultry and aquaculture industries for feed protein and the requirement of planting industry for organic fertilizer can be met; in addition, the food safety can be guaranteed, waste materials are changed into things of value in waste cyclic utilization, and the considerable economic benefit is achieved.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Artificial feed for bat moth larvae and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105795168ANutritious and comprehensiveImprove feeding effectAnimal feeding stuffAnimal fodder preservationMicrochiropteraAnimal science
The invention provides artificial feed for bat moth larvae and a preparation method thereof. The feed is prepared from the following raw materials in parts by weight: 180 to 220 parts of wheat bran, 230 to 260 parts of fish meal, 40 to 60 parts of corn flour, 60 to 90 parts of soybean meal, 100 to 140 parts of serpentgrass powder, 110 to 140 parts of yeast powder, 15 to 25 parts of agar, 4 to 6 parts of ethylparaben and 400 to 600 parts of sterile water. An insect source is hepialus menyuanicus or hepialus armoricanus, and the artificial feed is successfully prepared by virtue of the feeding practice of larvae in four years and by virtue of continuous preparation, feeding, formula improvement and experience summarizing.
Owner:ALPHA FUJIAN BIOTECH
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com