Method and sensor for detecting nucleic acid on-site damage by photoelectrochemistry
A photoelectrochemical and sensor technology, applied in the field of detection, can solve the problems of long time, no parallelism, complex optical detection instruments, etc., and achieve the effect of simple production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Catalytic photocurrents of the signaling molecule bipyridylruthenium.
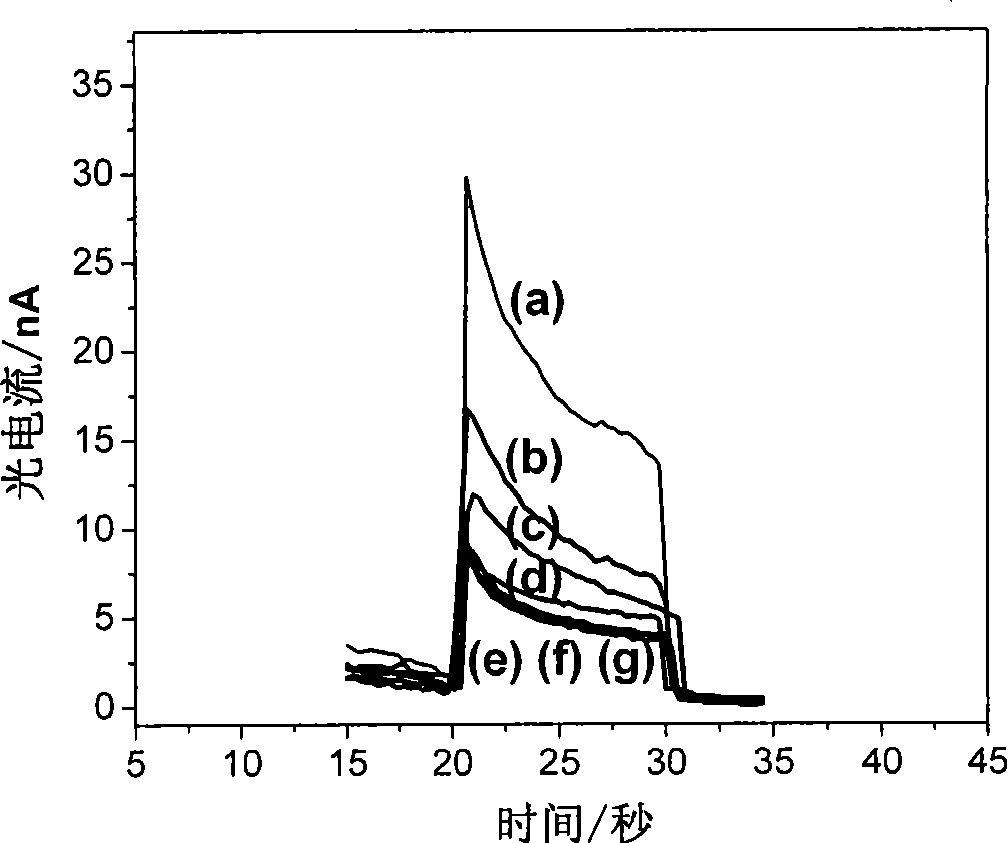
[0058] The succinamide (NHS)-activated bipyridyl ruthenium signal molecule was covalently labeled on avidin to form avidin-Ru. Spread 10 μL of avidin-Ru solution evenly on the prepared nano-SnO at room temperature 2 Electrode surface, static adsorption for 1 hour, take out water and shake for 5 minutes, blow dry with nitrogen, get avidin-Ru modified semiconductor electrode, SnO 2 / avidin -Ru. Use the same method to modify different nucleotides on the electrode surface, such as: double-stranded DNA (ds-DNA), single-stranded DNA (ss-DNA), polyguanine nucleotide (polyG), polythymidine acid (polyA), polycytosine nucleotide (polyC), polyuracil nucleotide (polyU). Then various nucleotide-modified semiconductor electrode sensors are placed in the electrolytic cell, and the photocurrent is detected in the phosphate buffer solution. The electrochemical workstation used is CHI 630A, and the detection is ba...
Embodiment 2
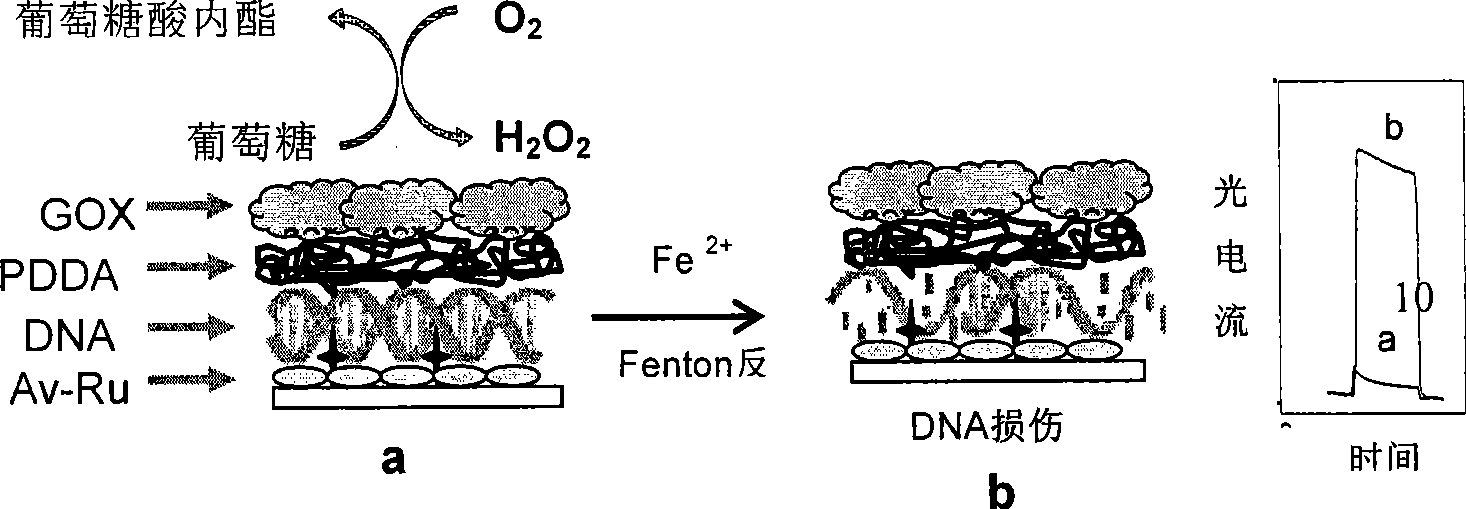
[0060] Modified electrode SnO 2 / avidin-Ru / ds-DNA / PDDA / GOx detection of metal ion Fe 2+ genotoxicity.
[0061] Avidin-Ru, ds-DNA, polydiallyldimethylamine hydrochloride (PDDA), and glucose oxidase (GOx) were sequentially assembled on the surface of the semiconductor electrode according to the method described in Example 1 to obtain a modified sensor Electrode: SnO 2 / avidin-Ru / ds-DNA / PDDA / GOx, see figure 2 . Place the modified sensor in 1mM FeSO 4 / 50mM glucose solution, react at 37°C for 1h. The glucose in the solution is used here to react with the glucose oxidase assembled on the electrode to produce hydrogen peroxide, which can react with Fe 2+ The Fenton reaction produces highly active oxygen and damages nucleic acids, which is the main way for metal ions to exhibit genotoxicity in the body. After the reaction, the electrode was taken out, rinsed with water, dried with nitrogen gas, and placed in 20mM phosphate buffer to detect the photocurrent. Separate FeSO 4 A...
Embodiment 3
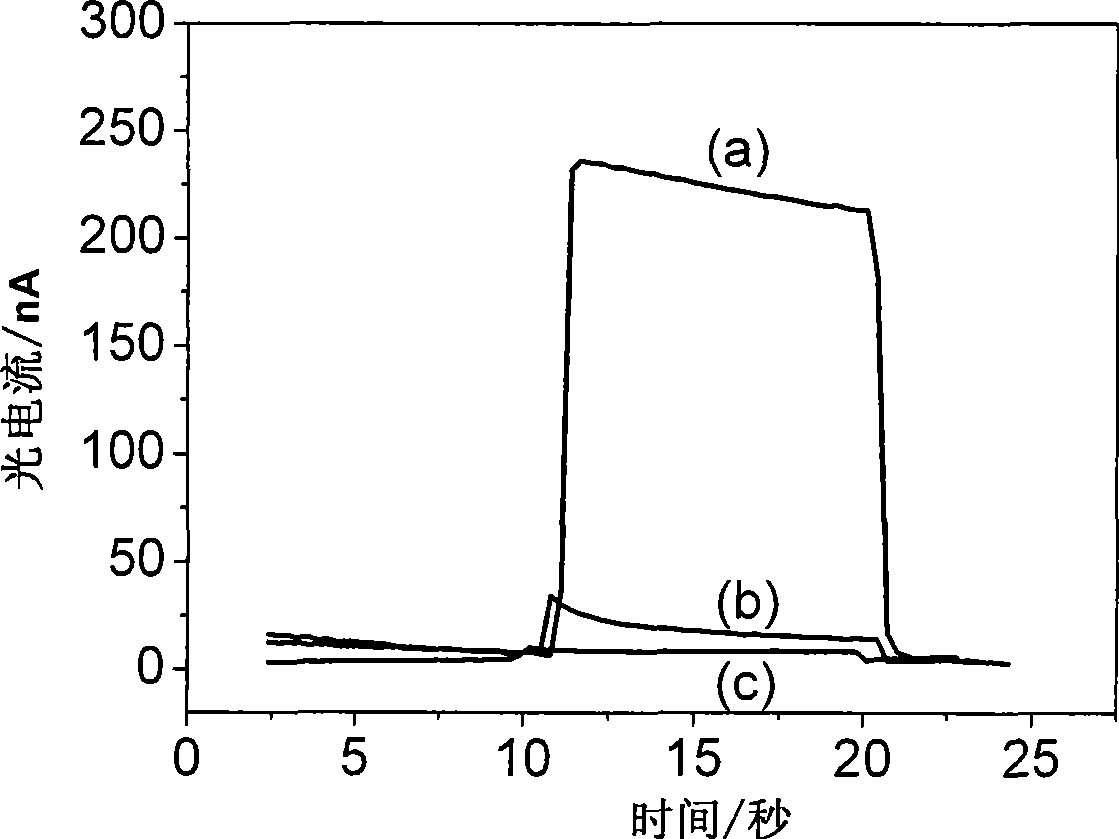
[0063] Modified electrode SnO 2 / avidin-Ru / ds-DNA / Hb was used to detect the potential genotoxicity of styrene.
[0064] Avidin-Ru, ds-DNA, and hemoglobin (hemoglobin, Hb) were sequentially assembled on the surface of the semiconductor electrode according to the method described in Example 1 to obtain a modified sensor electrode SnO 2 / avidin-Ru / ds-DNA / Hb, see Figure 4 . Here, hemoglobin can convert styrene into genotoxic styrene oxide under the action of hydrogen peroxide, causing nucleic acid damage, similar to the metabolism of styrene in the human liver, which is also the nucleic acid damage pathway of most organic substances in the body. That is, in the living body, it is first catalyzed by the cytochrome P450 enzyme in the liver and converted into an active metabolite, and then covalently combined with the base of the nucleic acid to form an adduct, causing damage to the nucleic acid. The prepared sensor electrode SnO 2 / avidin-Ru / ds-DNA / Hb placed in 2mM H 2 o 2 / 2...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com