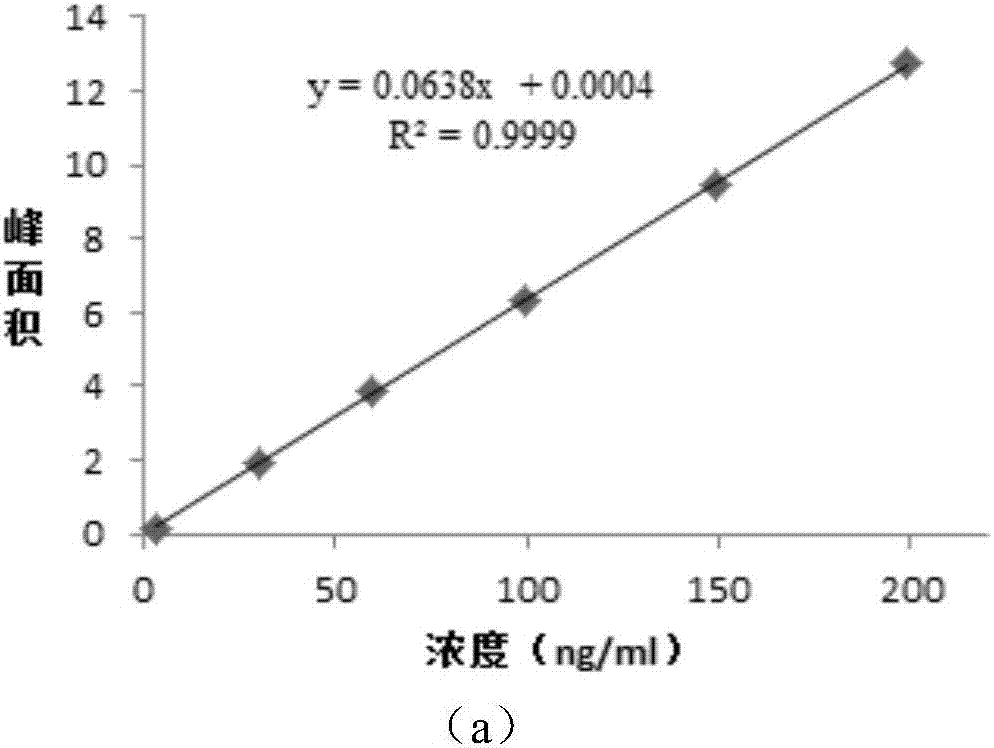
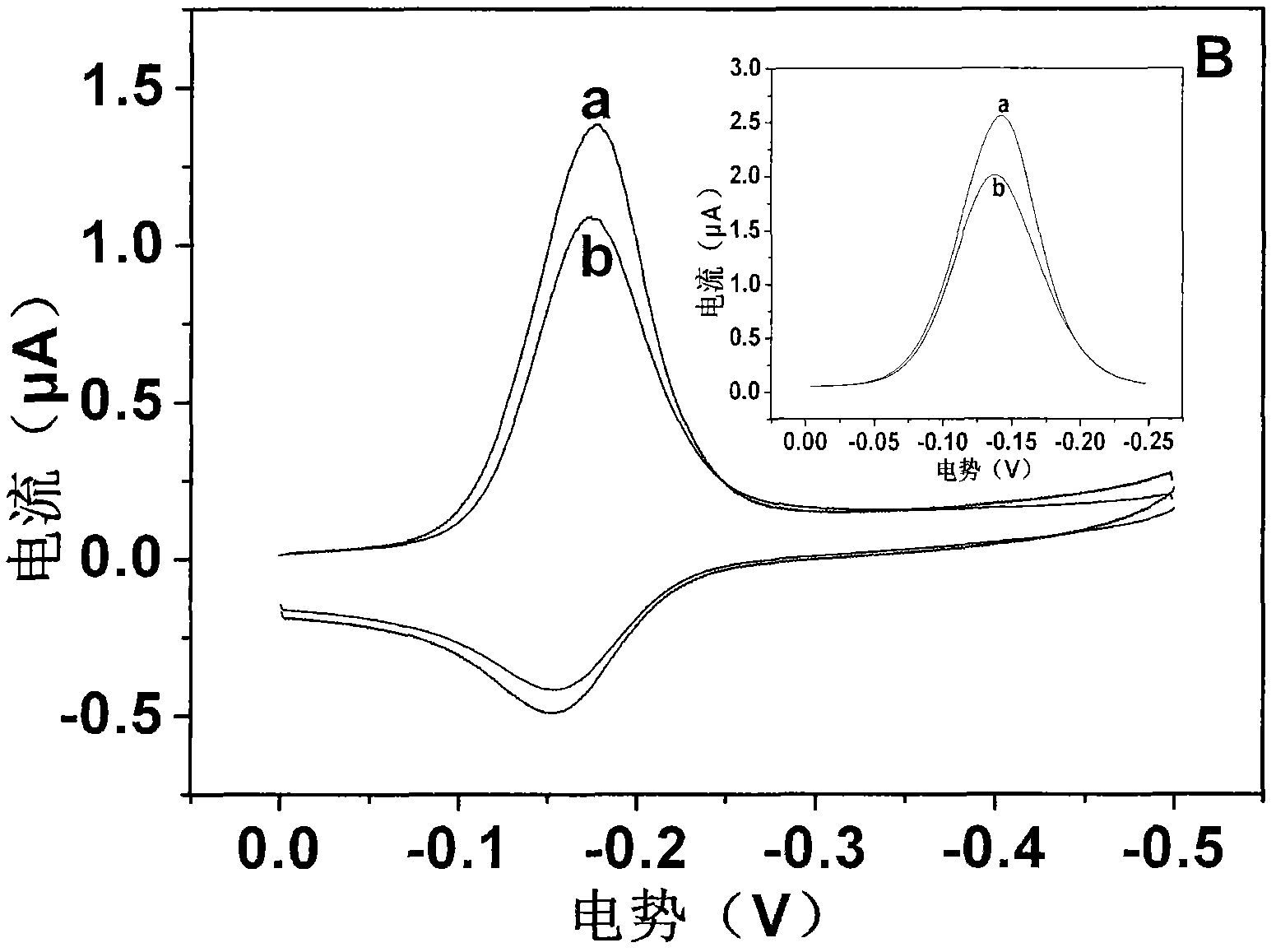
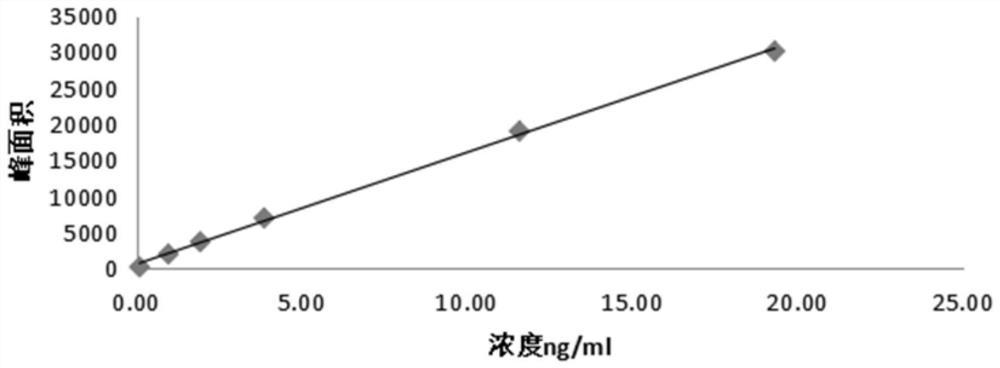
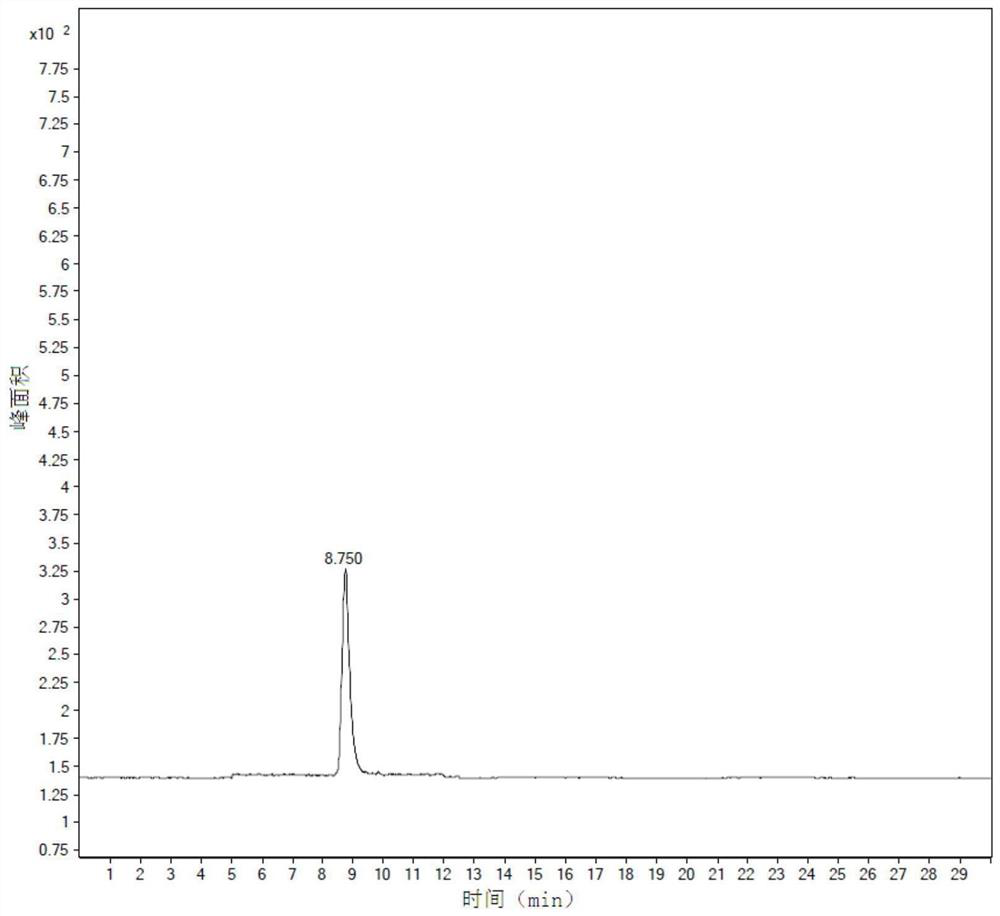
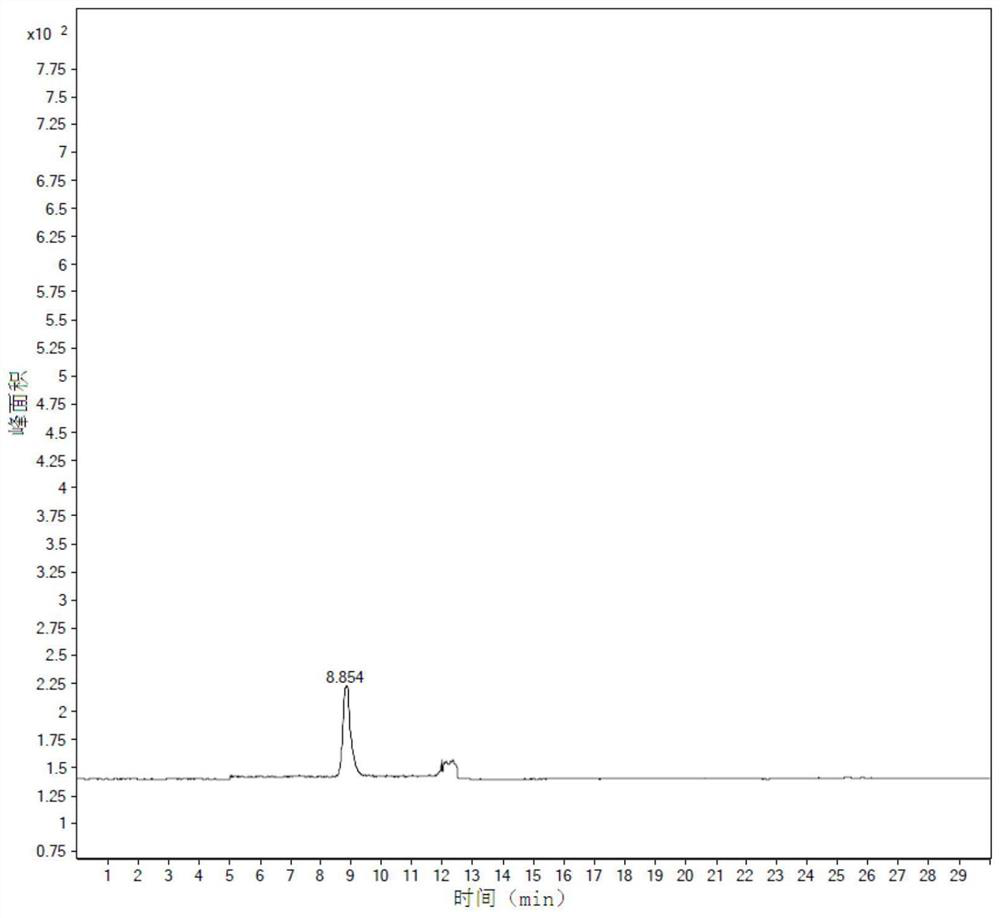
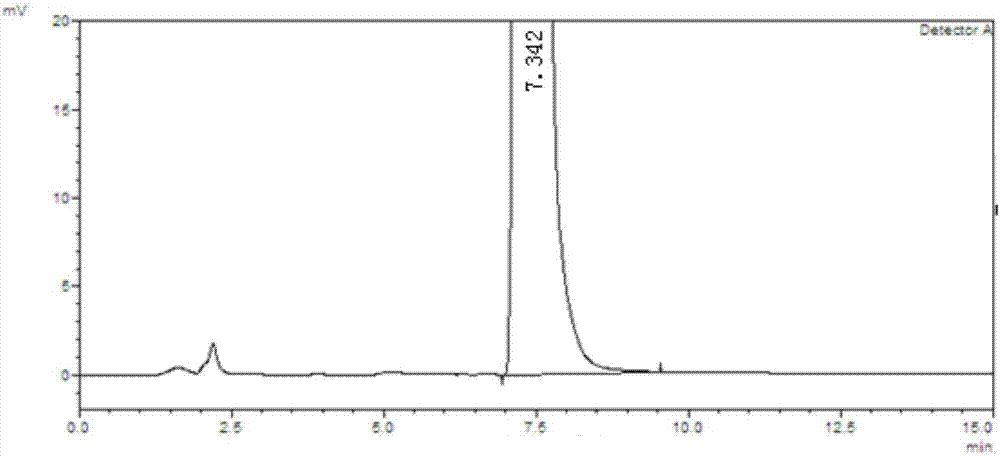
Patents
Literature
305 results about "Genotoxicity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In genetics, genotoxicity describes the property of chemical agents that damages the genetic information within a cell causing mutations, which may lead to cancer. While genotoxicity is often confused with mutagenicity, all mutagens are genotoxic, whereas not all genotoxic substances are mutagenic. The alteration can have direct or indirect effects on the DNA: the induction of mutations, mistimed event activation, and direct DNA damage leading to mutations. The permanent, heritable changes can affect either somatic cells of the organism or germ cells to be passed on to future generations. Cells prevent expression of the genotoxic mutation by either DNA repair or apoptosis; however, the damage may not always be fixed leading to mutagenesis.
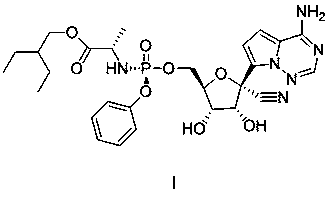
Preparation method of remdesivir
InactiveCN111116656AReduce usageReduced risk of genotoxic impuritiesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAcid hydrolysisOrganic base
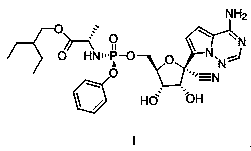
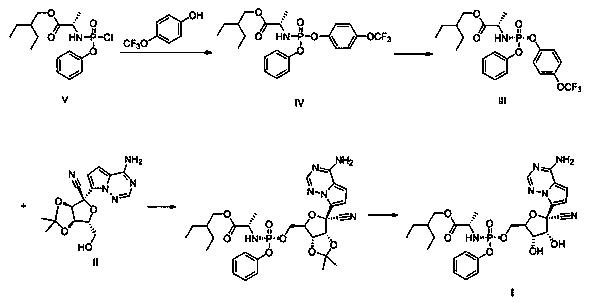
The invention discloses a preparation method of remdesivir, and belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemicals; the preparation method comprises the steps: carrying out a reaction on a compound V with pentafluorophenol under the action of an alkali to obtain a compound IV; further splitting the compound IV to obtain a compound III; carrying out a reaction on the compound III with a compound II under the action of organic base with large steric hindrance, and carrying out acid hydrolysis to obtain a compound I. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the use of genotoxic nitro substitutes is avoided, the risk of genotoxic impurities is reduced, and the method is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:江苏阿尔法集团福瑞药业(宿迁)有限公司
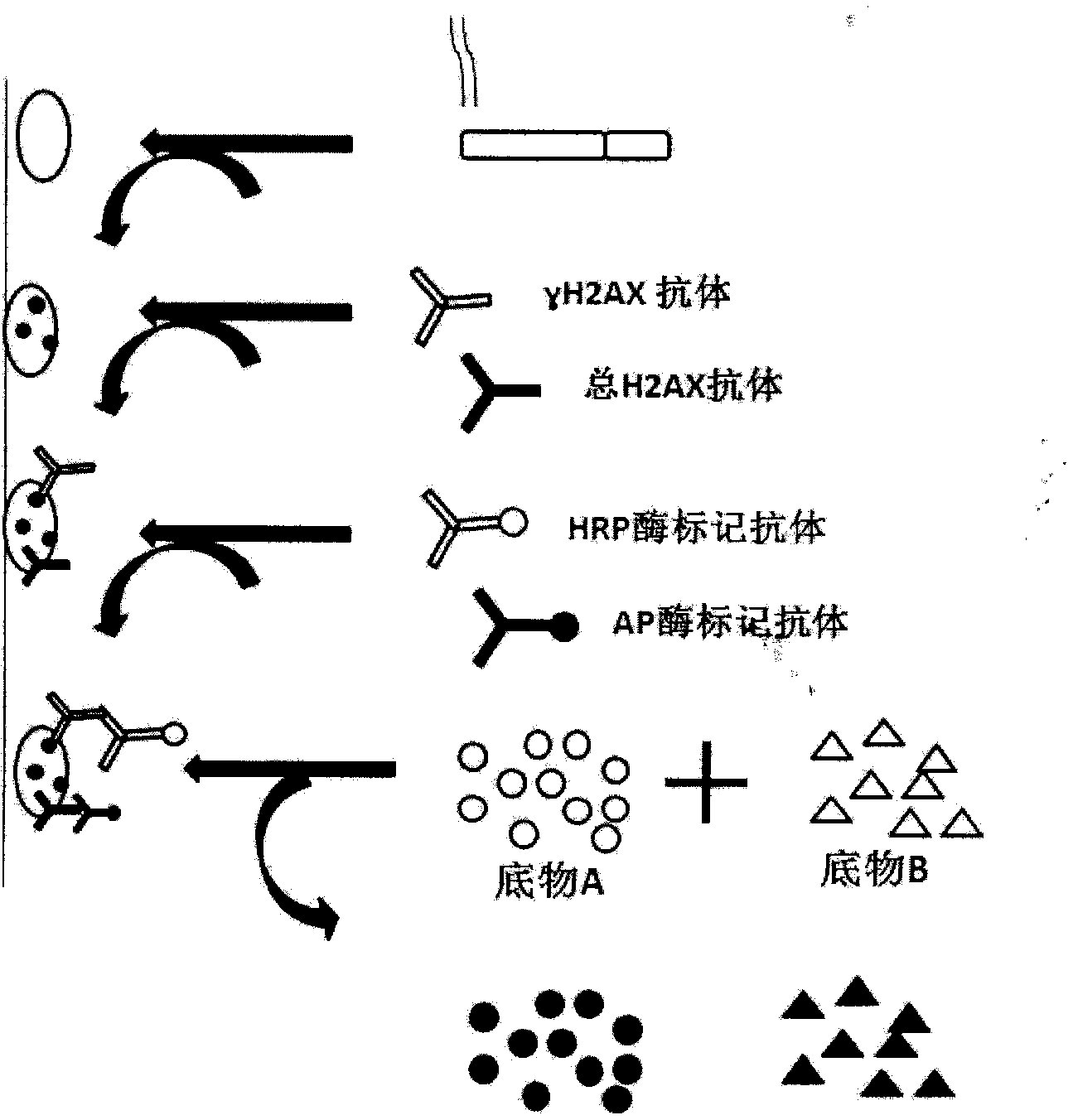
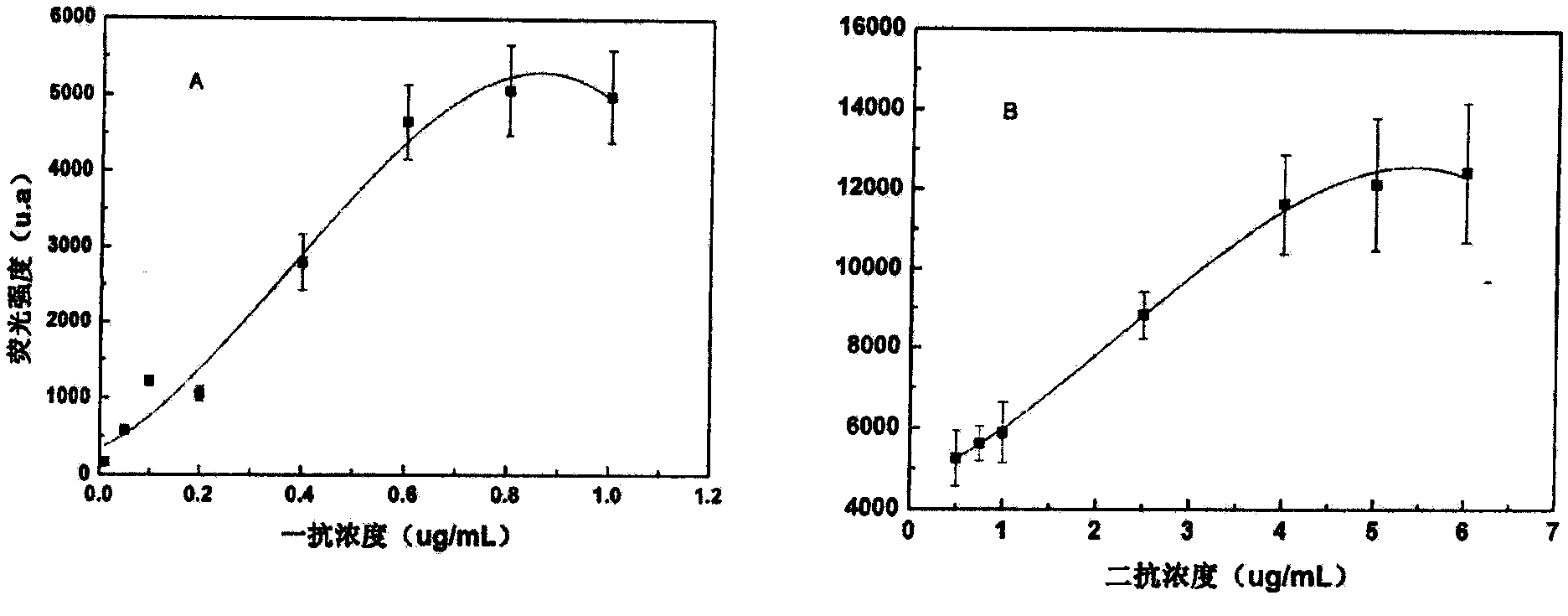
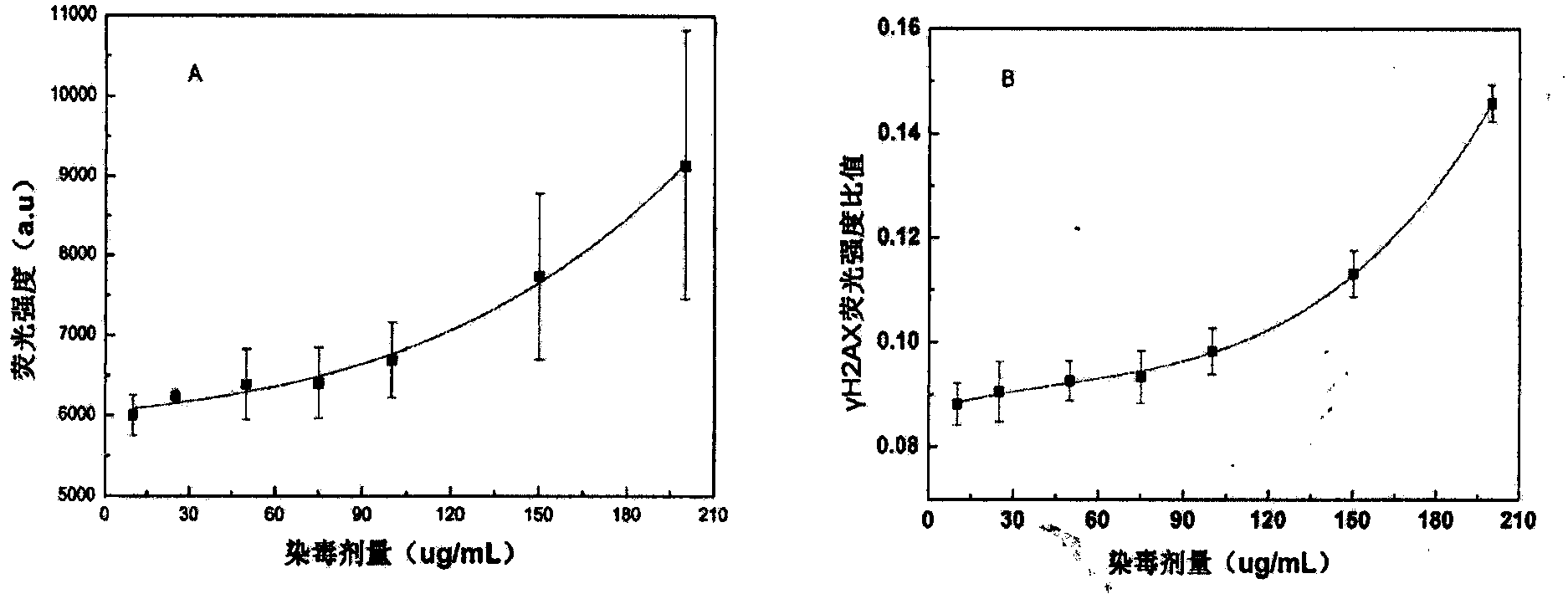
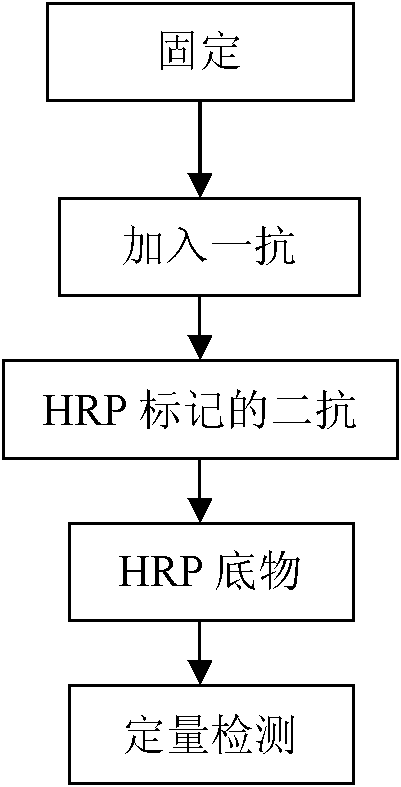
Enzyme-linked immunoassay method for determining content of cell DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) injury marker H2AX
ActiveCN103645327AAchieve accurate quantificationFewer extraction stepsBiological testingFluorescenceOrganic dye
The invention provides an enzyme-linked immunoassay method for determining the content of a cell DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) injury marker H2AX. The enzyme-linked immunoassay method is characterized by comprising the steps that sandwich recognition on the specificity of a target protein H2AX is carried out by using a specific H2AX antibody and an enzyme-linked second antibody, a substrate after enzyme reaction is added, then the substrate is subjected to enzyme catalysis to be changed into a fluorescence product, wherein quantitative determination for the H2AX content can be realized according to a fluorescence value of the substrate. According to the method, the content change of the H2AX in the cells, caused by the fact that cigarette smoke is exposed, is quantitatively determined so that the aim of evaluating the virulence of cigarette smoke genes is realized. Compared with a traditional organic dye, the enzyme-linked antibody has the advantages that the catalyzing frequency of an enzyme is high, an amplification reaction effect is amplified and the detection sensitivity is improved; the enzyme has a stable property at a room temperature, is low in price, and is suitable for a lot of analysis. An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay has the advantages of rapidness, accuracy, high throughput, high sensitivity and the like.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
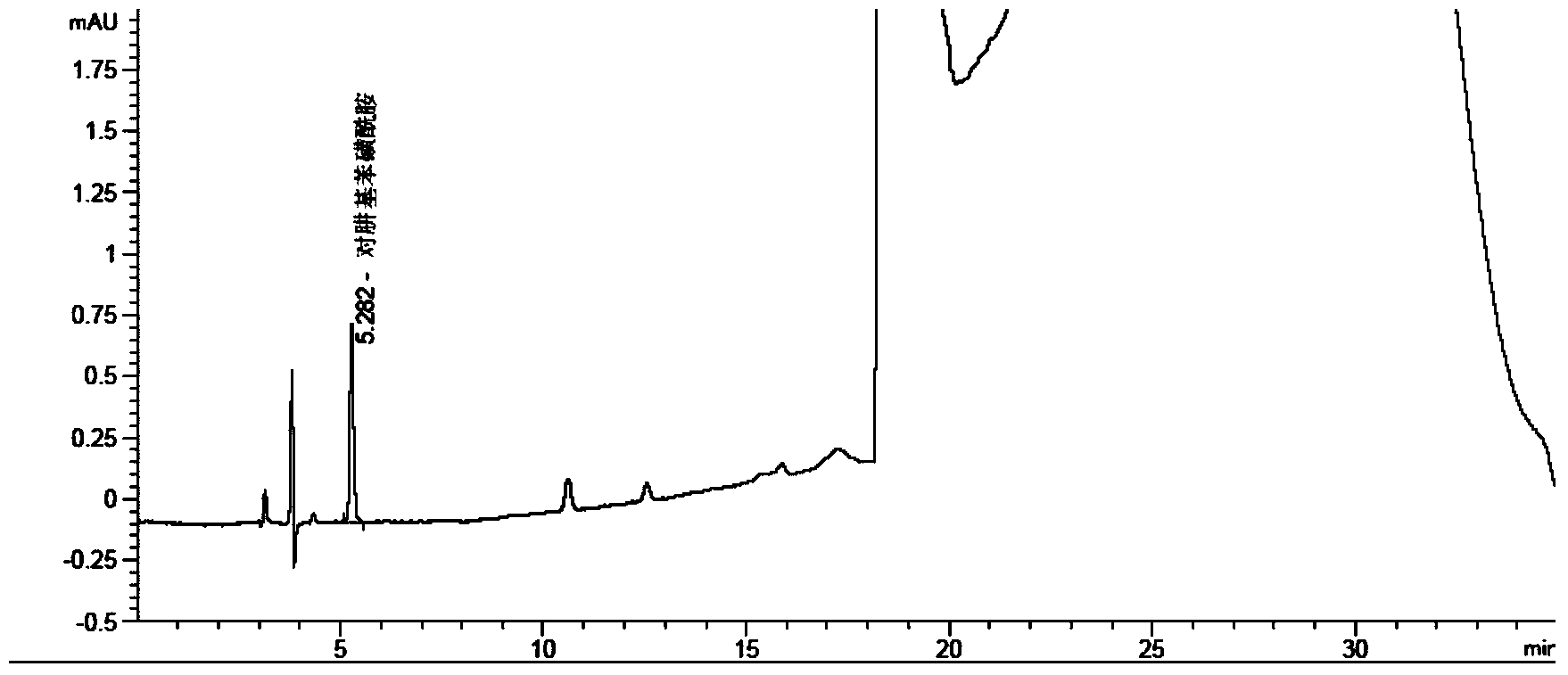
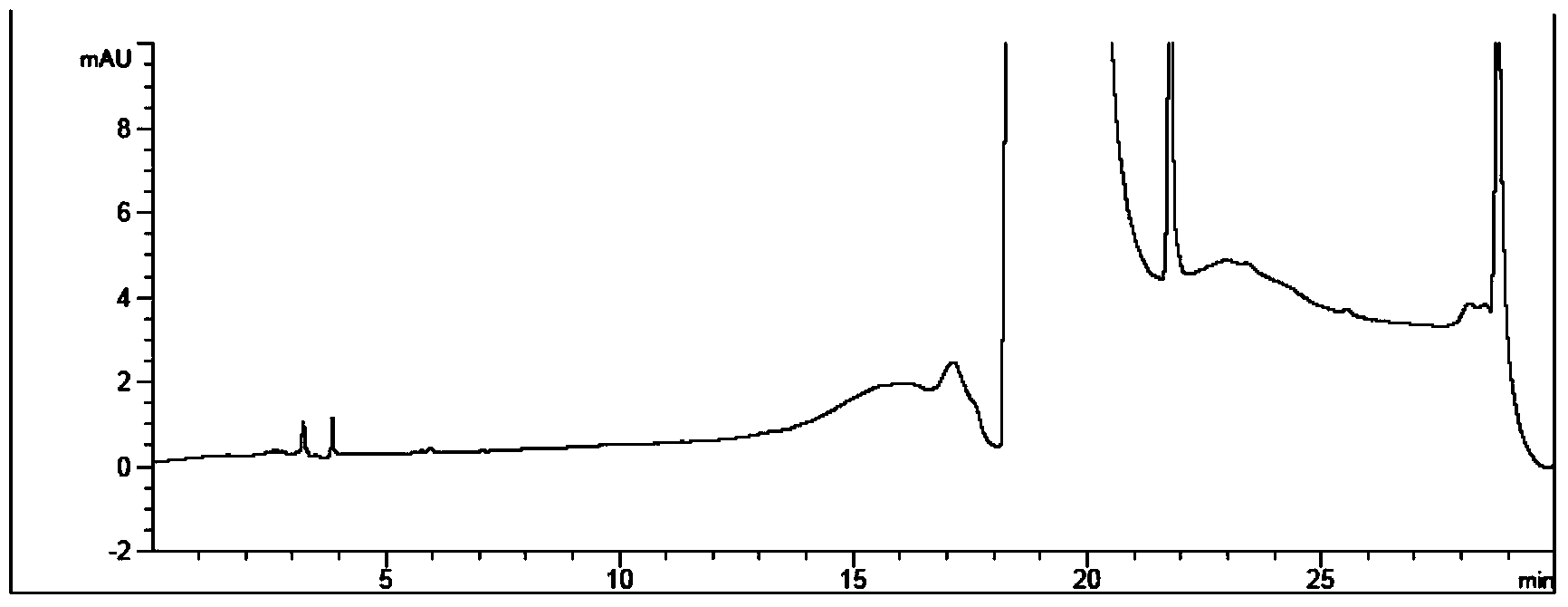
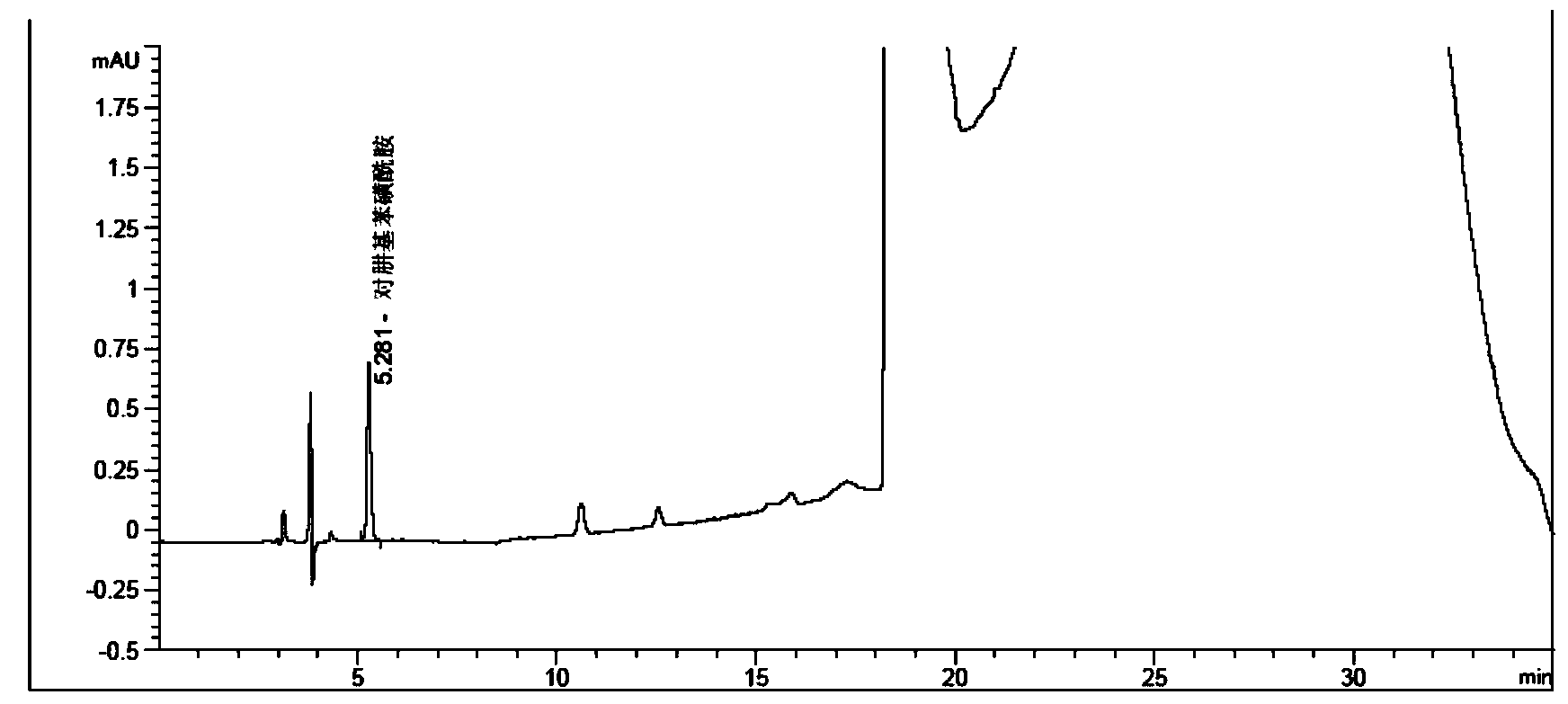
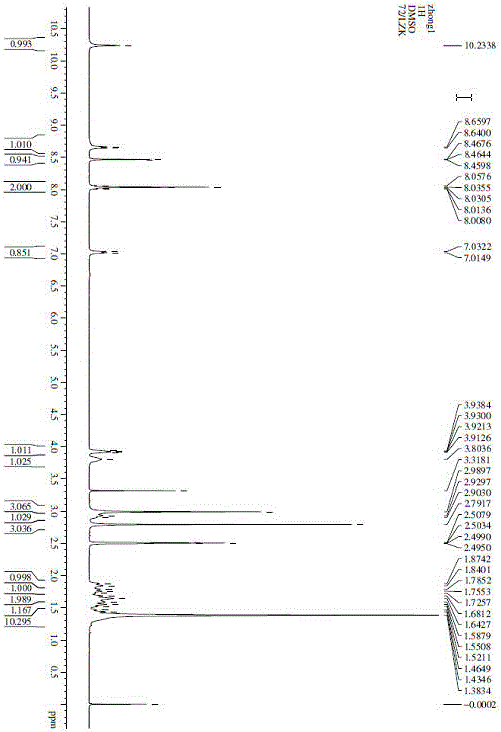
Method for measuring phenylhydrazine compound residues in crude drugs through HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography)
The invention discloses a method for measuring genotoxic impurities (or doubtful genotoxicity), namely phenylhydrazine compound residues, in crude drugs through the HPLC (high performance liquid chromatography). The detection is directly implemented by taking phenyl bonded silica gel as a chromatographic column of a solid phase and organic phase and buffer solution mixed solvent gradient elution as a mobile phase. The detection method is high in detection sensitivity, strong in specificity, high in precision, high in accuracy, convenient to operate and strong in adaptability and can be used for detecting phenylhydrazine compounds in various crude drugs, and the quality of the crude drugs can be effectively controlled.
Owner:WATERSTONE PHARMA WUHAN
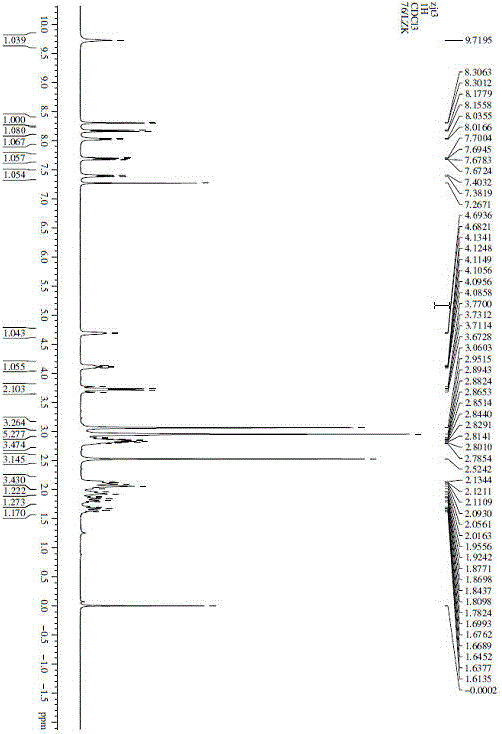
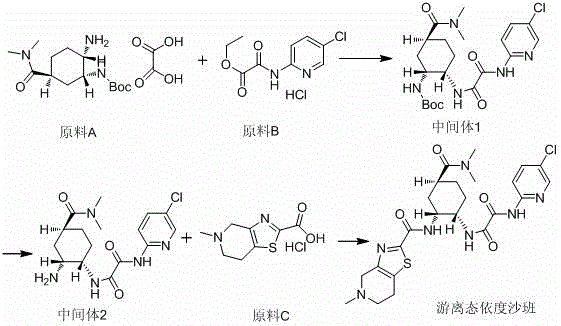
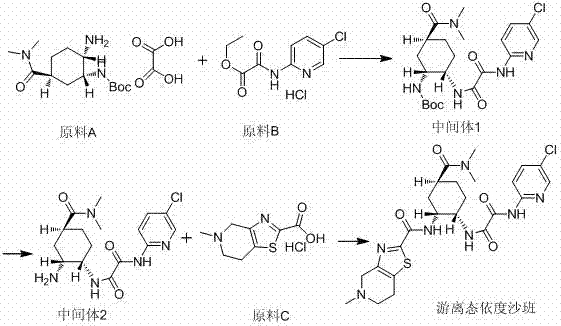
Preparation method for free-state edoxaban
The invention discloses a preparation method for free-state edoxaban.The synthetic route is shown in the description.According to the preparation method, the charging sequence is changed, and a curing problem caused by a traditional method is reduced; according to an existing method, a starting material A and triethylamine are added at first, a starting material B is added, a large amount of solid will appear in the temperature increasing process, and the stirring uniformity is greatly affected, so that the yield is greatly lowered, and the method is adopted for greatly solving the problem and improving the yield; when the compound free-state edoxaban is synthetized, a first amount of a saturated sodium bicarbonate water solution is added at first, the phenomenon that a product is rapidly separated out and impurities are included due to the fact that the added saturated sodium bicarbonate water solution is excessive is avoided, and meanwhile introduction of genotoxicity impurity methanesulfonate is effectively avoided; after the impurities are completely hydrolyzed, a second amount of the saturated sodium bicarbonate water solution is added so that the product can be separated out thoroughly; the method improves the crystallization way, the yield is improved, and generation of impurities is reduced.
Owner:LEPU PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Detection method of parecoxib sodium genotoxicity impurity and application thereof
ActiveCN105372376AAchieve separationHigh sensitivityComponent separationPhosphateReversed-Phase Liquid Chromatography
The present invention provides a detection method of parecoxib sodium genotoxicity impurity and application thereof. The method uses a reversed-phase liquid chromatography method. The chromatography conditions are as follows: the chromatographic column comprise a C18 column, a C8 column, a phenyl column and a Hilic column; a mobile phase consists of water-acetonitrile, dilute phosphoric acid-acetonitrile, and phosphate-acetonitrile; a flow phase comprises an aqueous phase and an organic phase in the ratio of 90:10-10:90; the column temperature is 25-40 DEG C; the flow rate of the mobile phase is 0.2-2ml / min; detection wavelength is 205-290nm; a detector is a UV detector or a photodiode array (PDA) detector; and the sample size is 0.1-40 mul. The detection method of parecoxib sodium genotoxicity impurity achieves the separation of parecoxib sodium and three genotoxicity impurities in a short period of time, has high sensitivity and specificity, and simple operation, reaches the separation rate of the main component and genotoxicity impurities, and the separation rate of genotoxicity impurities both greater than 1.5; and the method can be used for quality control of parecoxib sodium, and has practical value.
Owner:TIANJIN INSTITUTE OF PHARMA RESEARCH
Antitumor 3,5-diphenylmethylene-4-piperidone derivative and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to an antitumor 3,5-diphenylmethylene-4-piperidone derivative and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical fields of antitumor drugs and preparation methods thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: performing a Claisen-Schmidt condensation reaction on a 4-piperidone derivative having antitumor activity and 4-trifluoromethyl through 4-piperidone hydrochloride to obtain an intermediate a; and reacting the intermediate a with an acylation or sulfonylation reagent to obtain N-R-3,5-di(4-trifluoromethyl benzylidene)-4-piperidone b-5. The 3,5-diphenylmethylene-4-piperidone derivative is novel in structure, has the advantage of combination of a plurality of molecular targets, and has multidrug resistance activity; and the genotoxicity of currently-used antitumor drugs can be avoided. Compared with normal cells, the derivative has higher antitumor activity to tumor cells, so that the derivative has a great application prospect in the field of antitumor drugs.
Owner:BINZHOU MEDICAL COLLEGE
Photo-electro-chemical method for detecting nucleic acid
InactiveCN1885036AEasy Photoelectrochemical DetectionEfficient photoelectrochemical detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansRedoxNucleic acid hybridisation
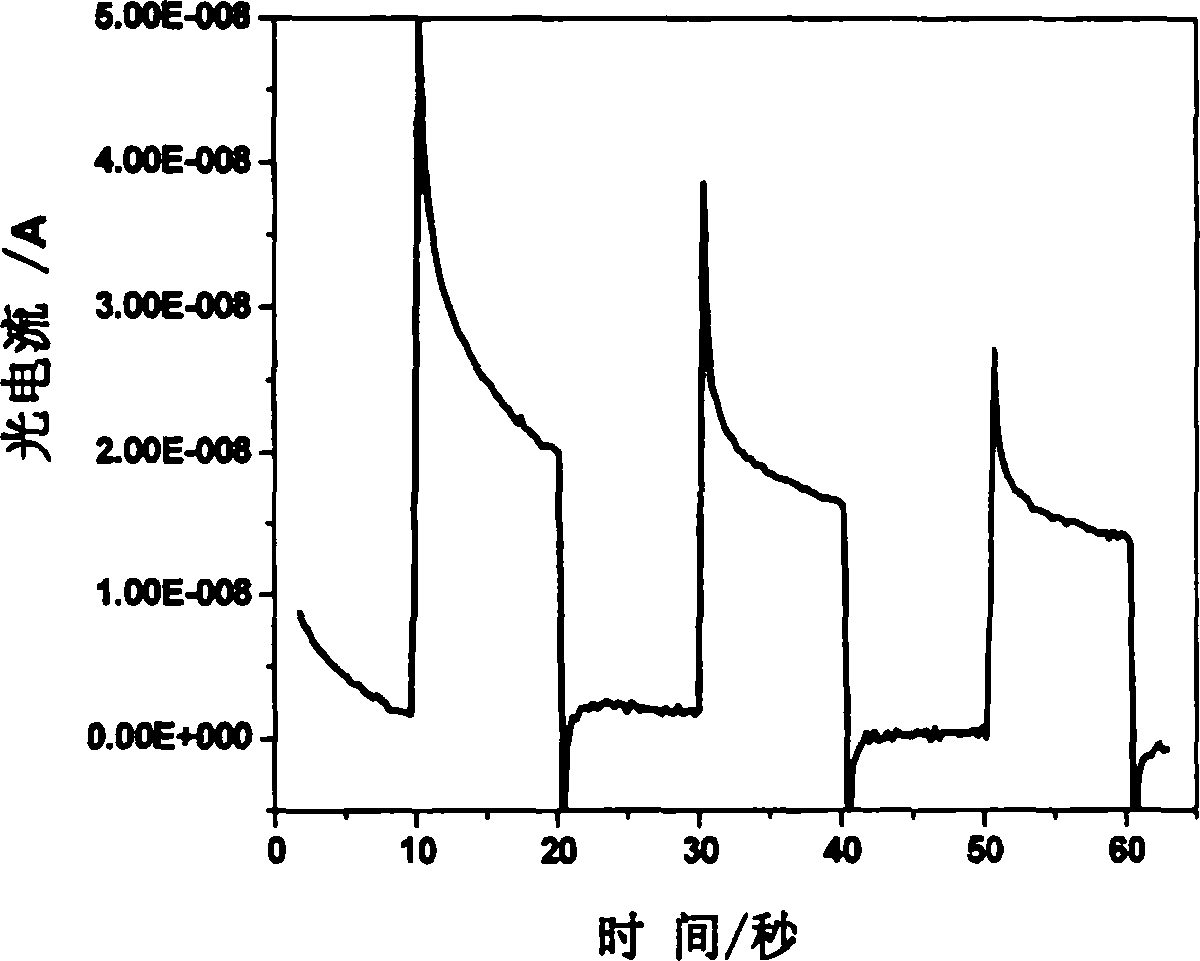
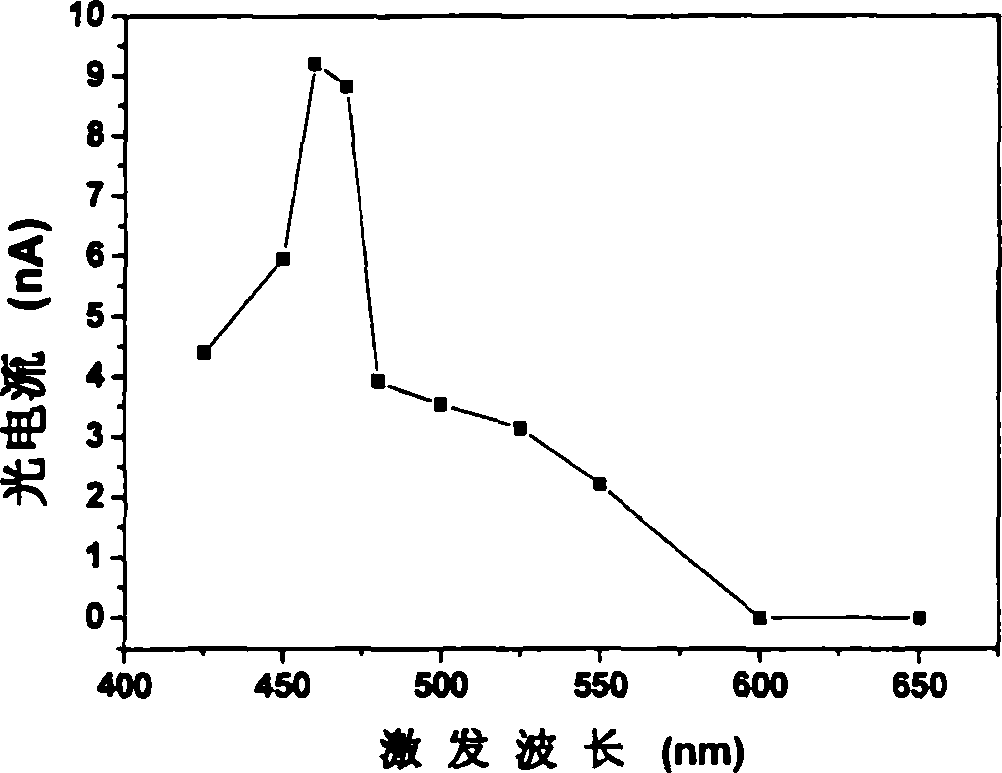
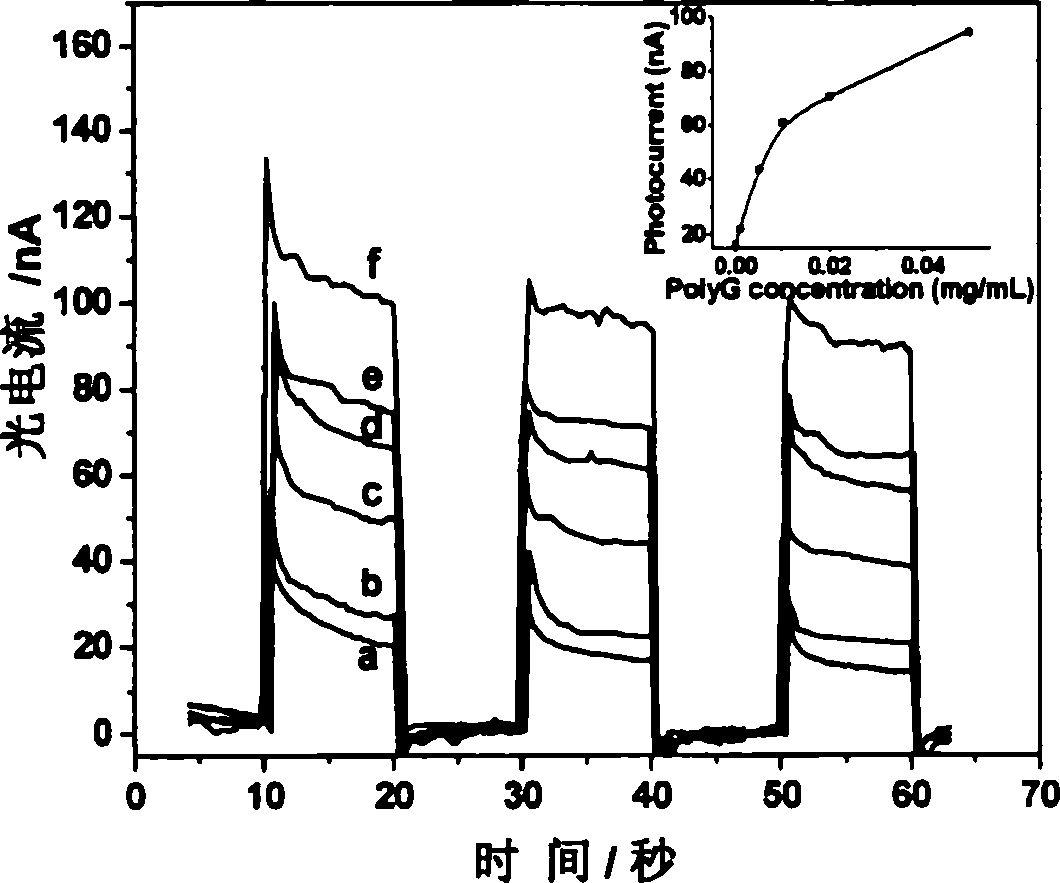
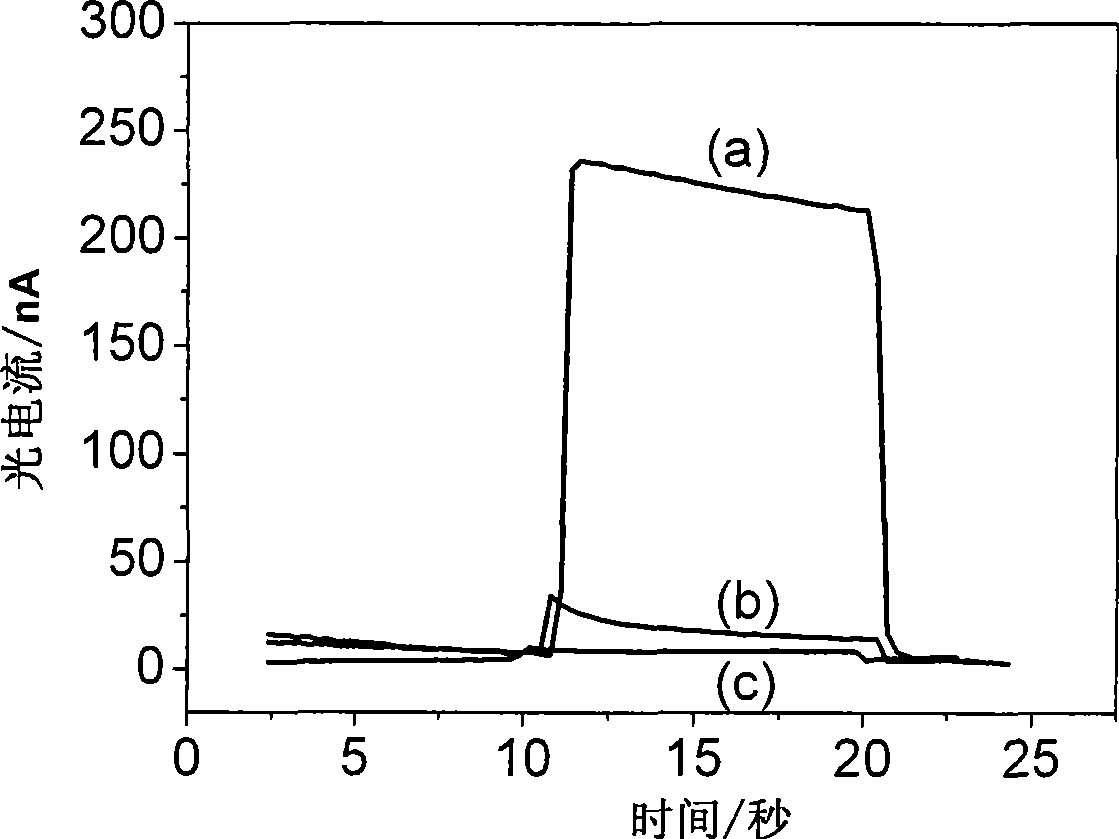
The invention relates to a method for detecting nucleic acid alkali group with optical electric chemical technique, wherein said method comprises: a, contacting the tested sample and the material with optical electric chemical activity; b, evaluating the oxidization and reduction reaction between the nucleic acid alkali group and said optical electric chemical material, that using light to transform the optical electric chemical material into exciting state with existed electrode, and processing oxidization reduction reaction with nucleic acid alkali group when the excited material loses electrons, to evaluate the current generated in oxidization reduction reaction; c, based on said current, analyzing the sample qualitative or quantitatively. The invention can be used in biological detection, as nucleic acid cross detection, nucleic hurt detection and chemical material gene toxicity detection.
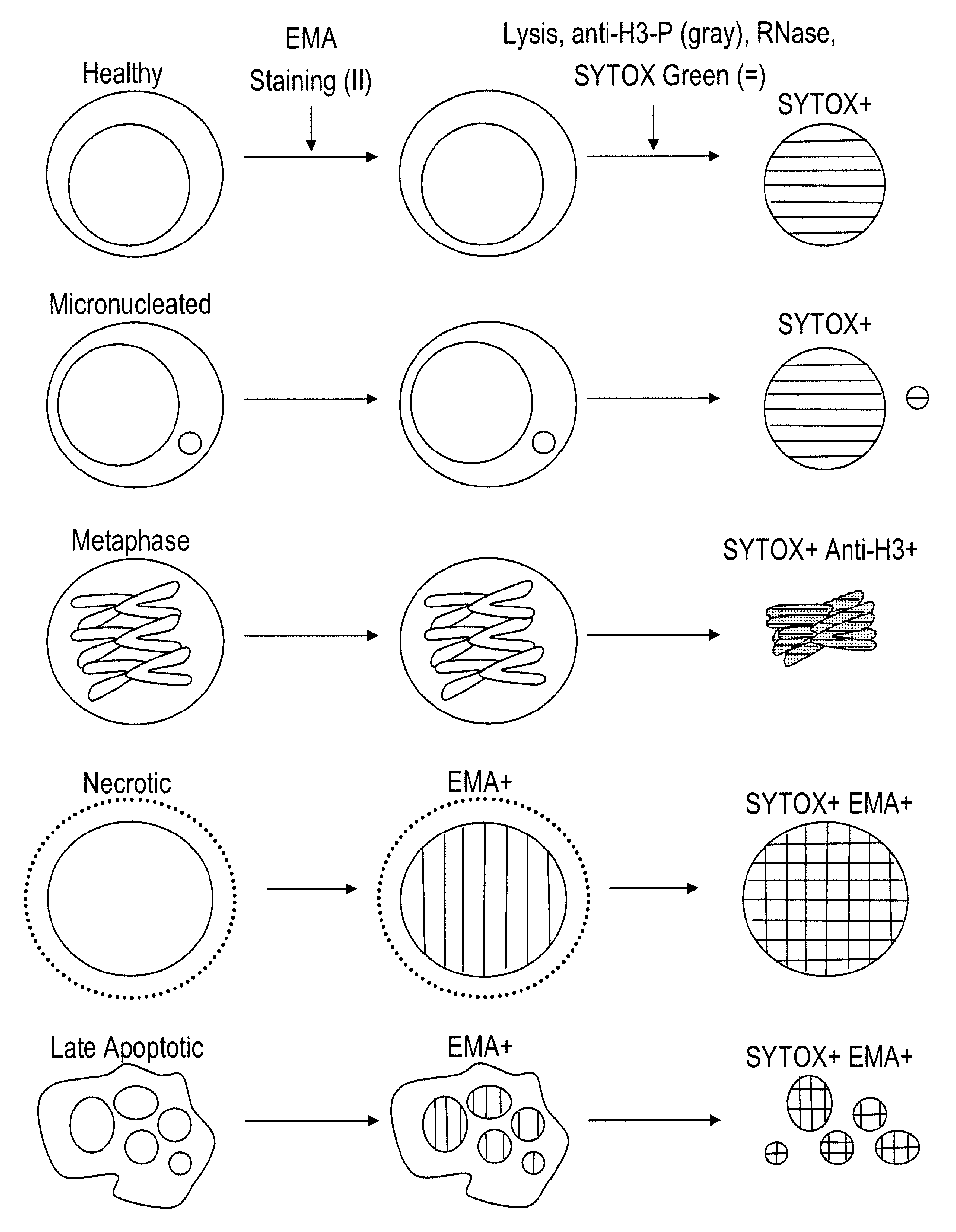
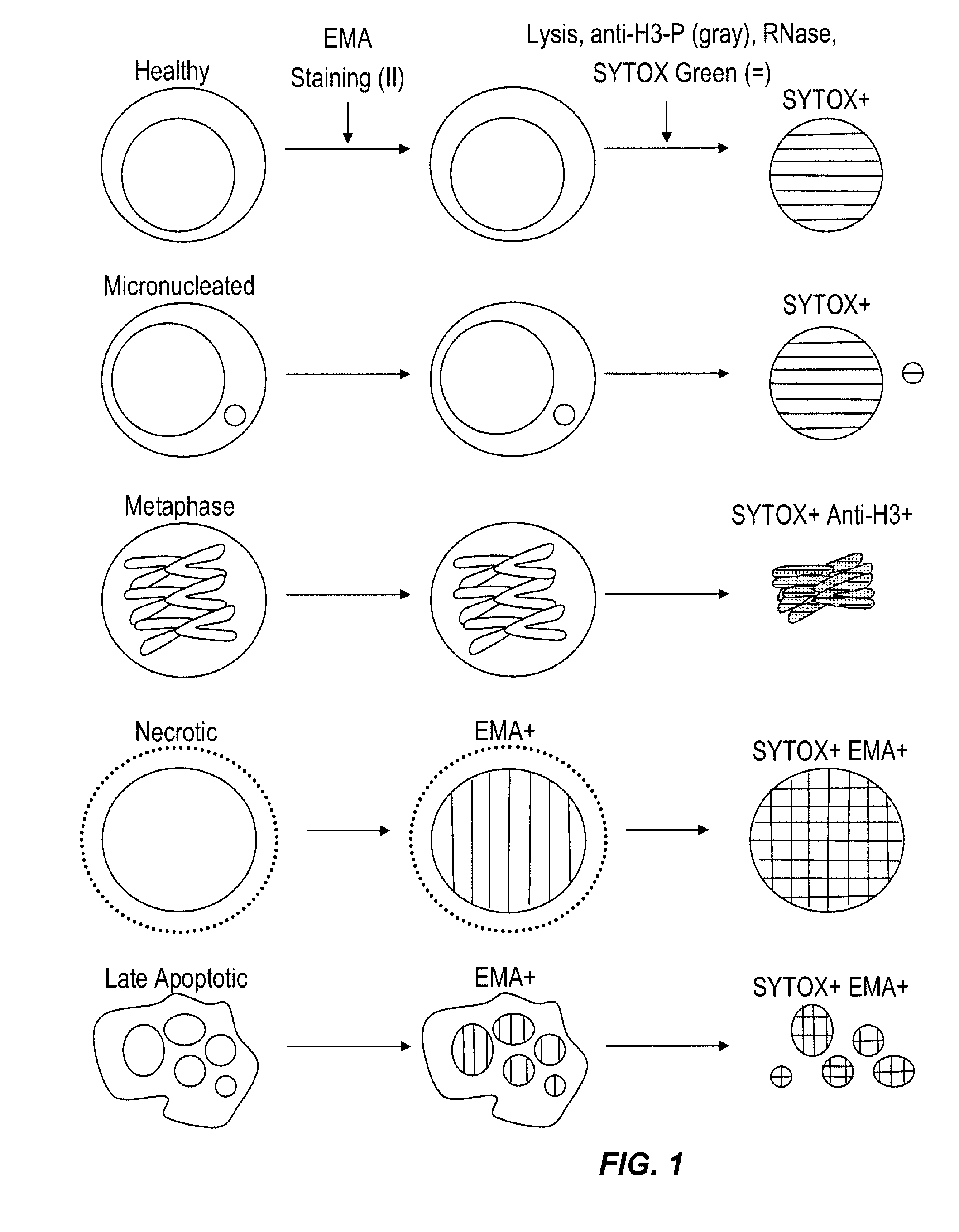
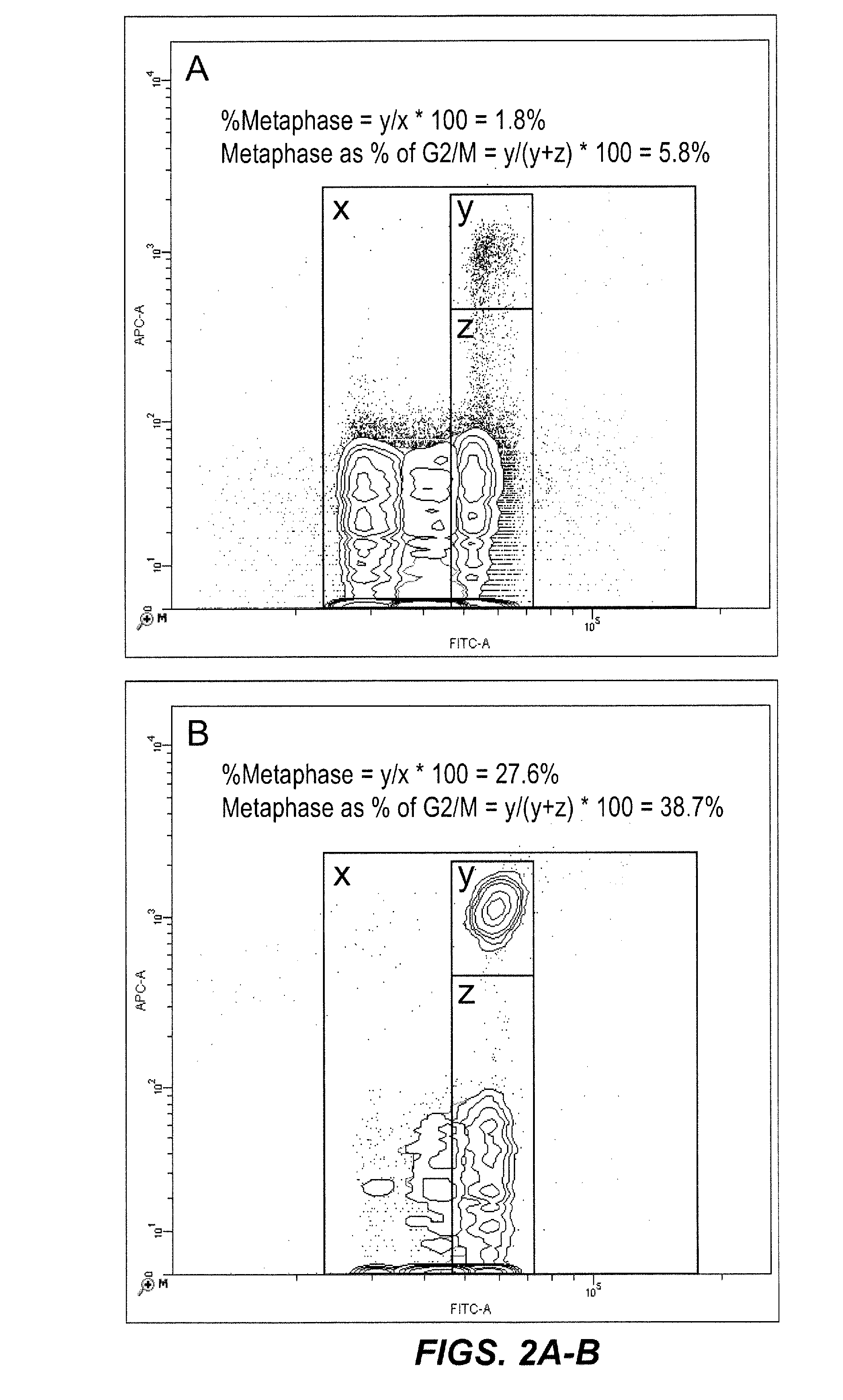
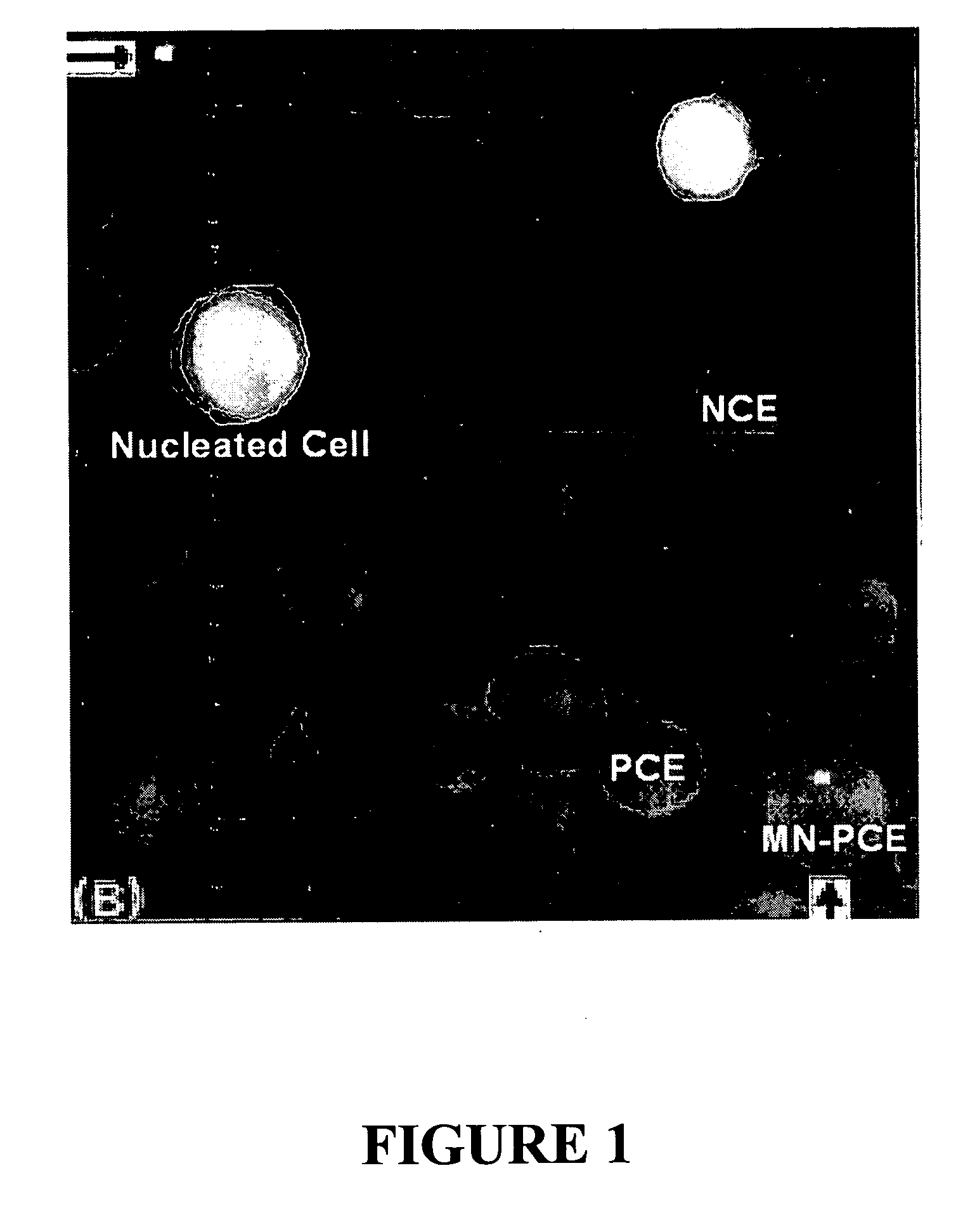
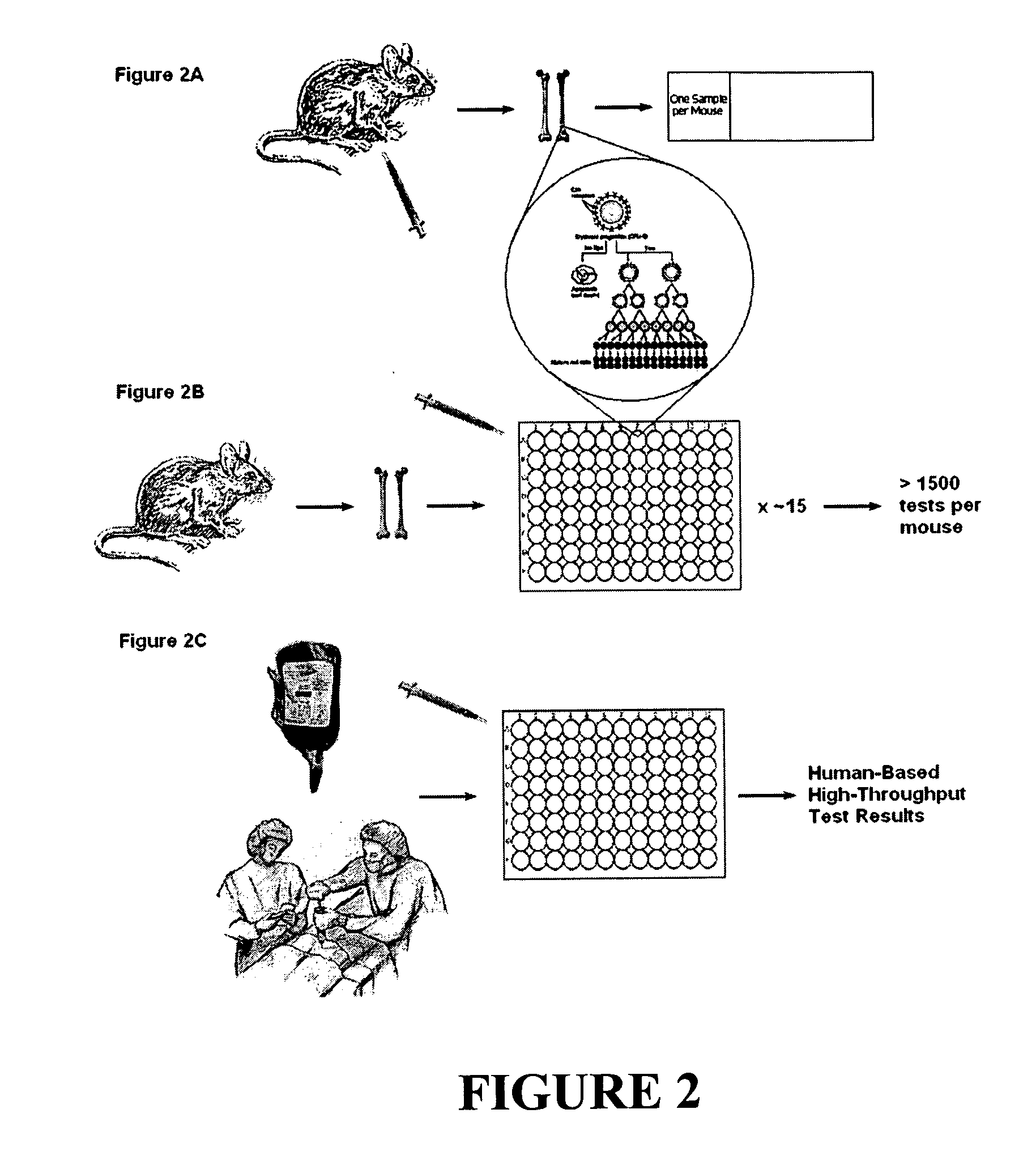
Method for enumerating eukaryotic cell micronuclei with an emphasis on simultaneously acquiring cytotoxicity and mode of action information
InactiveUS20140017673A1Fast and reliable and accurateLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological testingMode of actionMetaphase chromosome
The present invention relates a method for the enumeration of eukaryotic cell micronuclei, while simultaneously acquiring cytotoxicity and mode of action information. The method utilizes differential labeling of chromatin from dead and dying cells to distinguish the chromatin from micronuclei, nuclei, and metaphase chromosomes, and differential labeling of metaphase events to provide additional information regarding cytotoxicity and genotoxic modes of action. Counting of micronuclei events relative to the number of nuclei and quantifying perturbations to the proportion of metaphase events can be used to assess the DNA-damaging potential of a chemical agent, the DNA-damaging potential of a physical agent, the effects of an agent which can modify endogenously-induced DNA damage, the effects of an agent which can modify exogenously-induced DNA damage, and genotoxic mode of action.
Owner:LITRON LAB
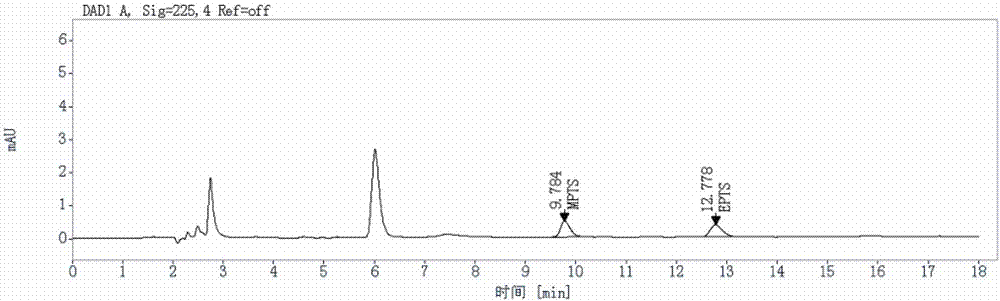
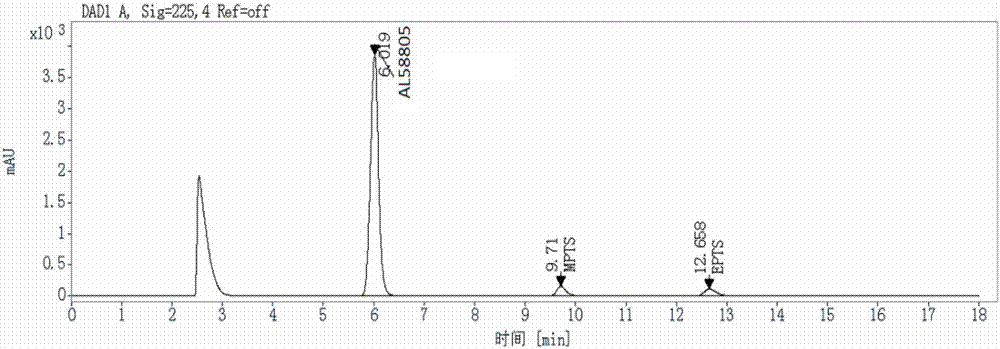
Method for detecting genotoxic impurities in AL58805 bulk drug or medicinal preparation by using high-performance liquid chromatography
ActiveCN107037153AEfficient separationDo not interfere with detectionComponent separationPhosphoric acidColumn temperature
The invention relates to a method for detecting genotoxic impurities in an AL58805 bulk drug or medicinal preparation by using high-performance liquid chromatography. The method is directed at methyl p-toluenesulfonate (MPTS) and ethyl p-toluenesulfonate (EPTS); a sample undergoes pre-treatment at first; and then high-performance liquid chromatography is employed for determination, wherein a C18 chromatographic column is employed; detection wavelength is 225 nm; an aqueous acetonitrile-phosphoric acid solution is used as a mobile phase; flow velocity is 0.8 to 1.2 mL / min; column temperature is 30 to 40 DEG C; a sample size is 20 [mu]L; and elution time is 18 min. Results show that the detection limit of MPTS is 0.3 ppm and the limit of quantitation of MPTS is 1 ppm; and the detection limit of EPTS is 0.5 ppm and the limit of quantitation of EPTS is 1.4 ppm. The method has the advantages of good specificity, simple operation, high sensitivity and accurate results and is applicable to determination of MPTS and EPTS in AL58805.
Owner:常州佳德医药科技有限公司
Lactobacillus salivarius and method for preparing metabolite thereof, composition of lactobacillus salivarius and metabolite thereof and use of the composition
InactiveUS20130309212A1Effective treatmentEffective preventionBiocideBacteriaMetaboliteLactobacillus salivarius
Provided is a Lactobacillus salivarius belonging to Lactobacillus salivarius subsp. Salivarius and deposited in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with an accession number CGMCC No: 3606. Further provided is a method for preparing a metabolite of the Lactobacillus salivarius, wherein the Lactobacillus salivarius is as described above. Further provided is a composition, comprising viable strains of the Lactobacillus salivarius and / or the metabolite of the Lactobacillus salivarius prepared as described above. Further provided is a use of the composition in preparation of drugs for prevention and / or treatment of cancers and a method for treating and / or preventing cancers. The viable strains of Lactobacillus salivarius and the metabolite of Lactobacillus salivarius provided in the present invention can both remove the genotoxicity of 4-NQQ in vivo, thus exerting an effect of effectively preventing and / or treating cancers.
Owner:REN FAZHENG
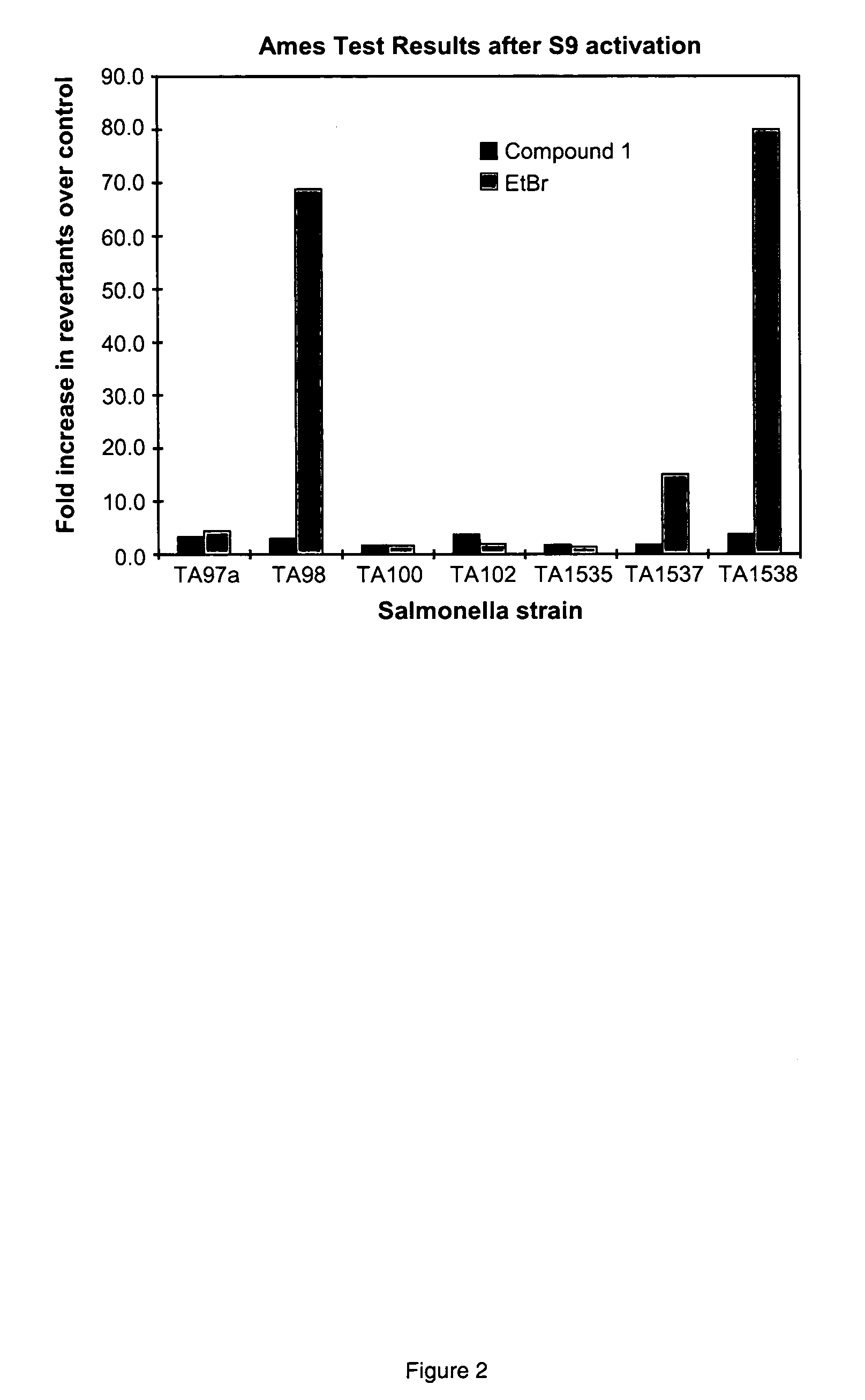
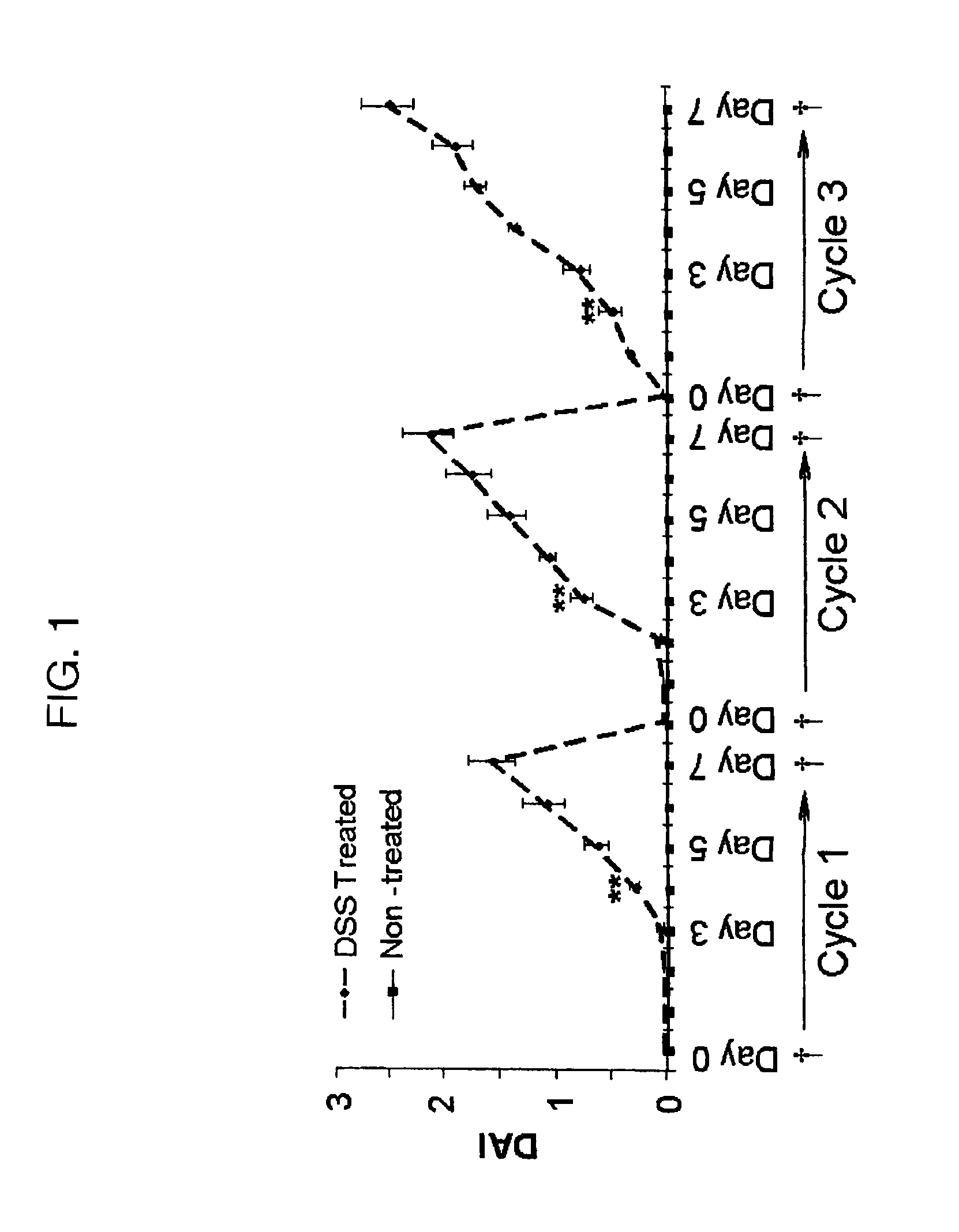
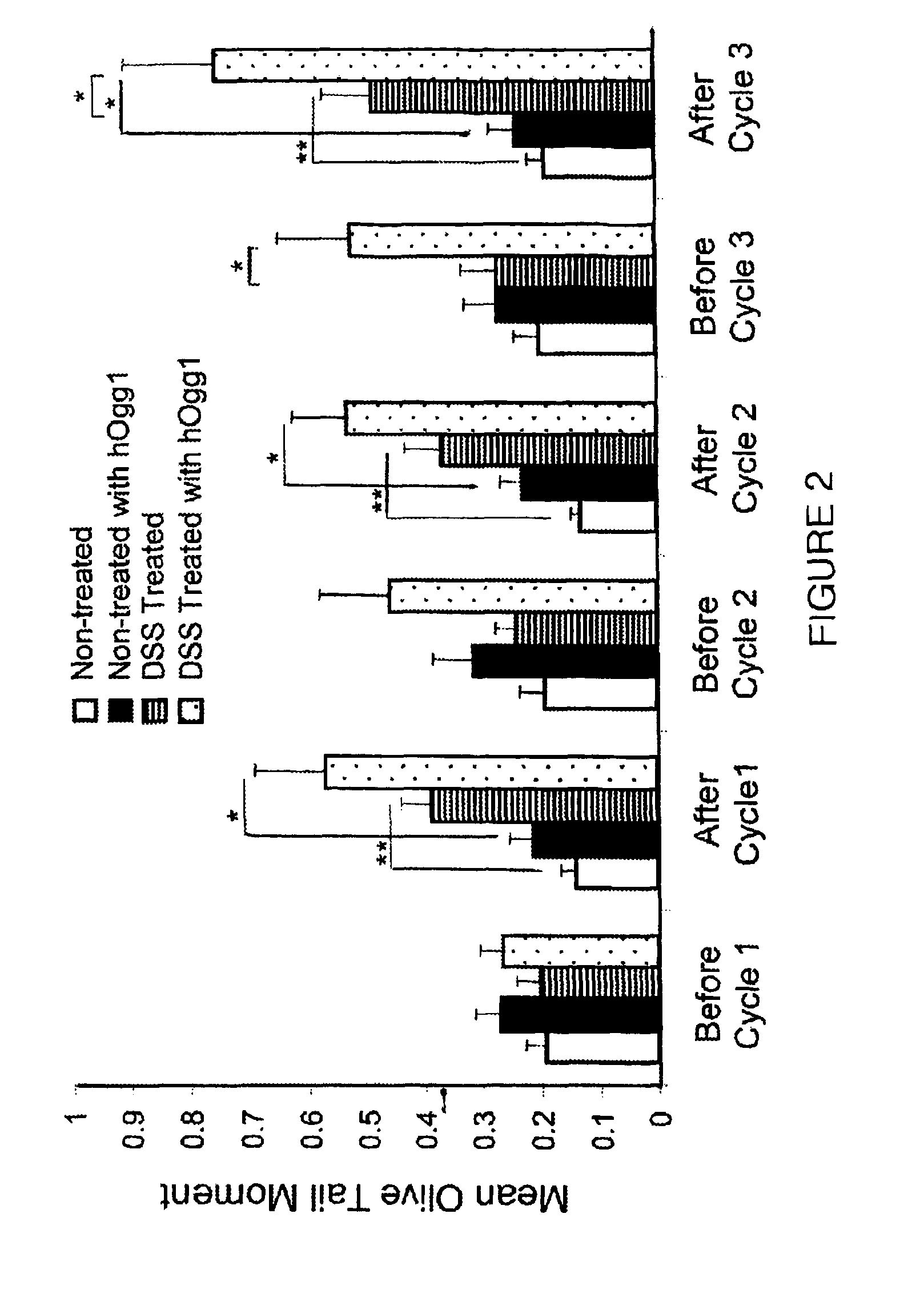
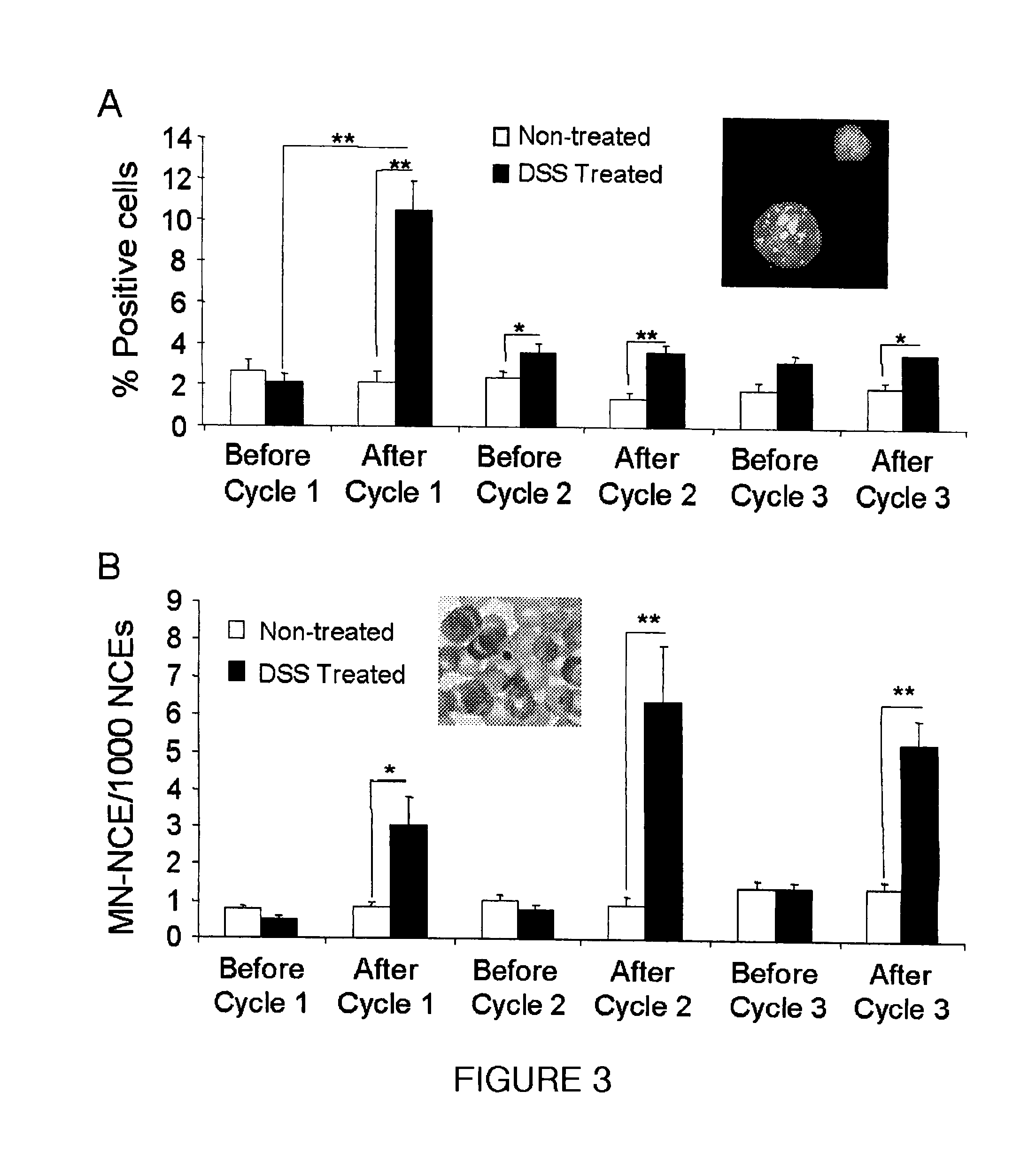
Genotoxicity as a biomarker for inflammation
InactiveUS20100267037A1Efficacy of treatmentDecreased amount of presentMicrobiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUveitisAutoimmune condition
The invention provides a method for detection of inflammatory disease in a subject that comprises assaying a test sample of peripheral blood from the subject for a marker of DNA damage. An elevated amount of marker present in the test sample compared to control sample is indicative of inflammatory disease activity, including sub-clinical inflammation. The method can be adapted for quantitatively monitoring the efficacy of treatment of inflammatory disease in a subject. Markers of DNA damage include single- and / or double-stranded breaks in leukocytes, oxidative DNA damage in leukocytes, or a marker of nitric oxide oxidative activity (protein nitrosylation in leukocytes). The inflammatory disease can be inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease). The invention may also be used for detection of other types of inflammatory disease, such as non-immune intestinal inflammatory disease (diverticulitis, pseudomembranous colitis), autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, uveitis, vasculitis), or non-immune lung diseases (asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, and interstitial pneumonitis). This unexpected discovery of markers of genotoxicity present in circulating leukocytes enables detection of inflammation occurring at a localized site with a relatively simple and minimally invasive assay using peripheral blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Test system for determining gene toxicities
InactiveUS20040197855A1Maximize sensitivityBroad spectrumVectorsSugar derivativesFluorescenceGenotoxic Stress
The subject matter of the invention is a method which makes it possible to detect genotoxic stress in living mammalian cells by the detection of all previously documented types of DNA recombination and also of mutations in response to noxae. The detection is based on the detection of the fluorescence from intact autofluorescent proteins or of luminescence by means of intact bioluminescent enzymes or enzymes that convert chemoluminescent substrates. It is characterised by a short reaction time in the scope of hours and permits the transfer of the test system to different mammalian cells and to living experimental animals, particularly by using a retroviral vector system.
Owner:WIESMULLER LISA
Method for treating azide ions, non-genotoxic impurity Sartan raw material medicine and immediate thereof
The invention discloses a method for treating azide ions in a system and application thereof to the preparation of a compound with a tetrazolium group and without genotoxic impurities. The method is that the azide ions contained in the hydrogen peroxide treatment system are used. The method is used for preparing the compound with the tetrazolium group and comprises the following preparation steps:enabling a compound containing a cyano group to react with an azide, adding hydrogen peroxide after the reaction to quench and remove excessive sodium azide and further obtaining the compound with the tetrazolium group. The compound prepared by the method does not contain the genotoxic impurities. The method is simple in operation, mild in reaction conditions and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:珠海润都制药股份有限公司
Electrochemical method employing DNA as probe to detect environmental pollutant
ActiveCN102375021AImprove stabilityReliable test resultsMaterial electrochemical variablesPotential toxicitySignalling molecules
An electrochemical method employing DNA as a probe to detect environmental pollutants. A biosensor detector comprises a working electrode, an auxiliary electrode, a reference electrode, a detection cell and an electrochemical working station. The working electrode is modified with nucleic acid probes on a surface thereof, and a genotoxicity compound in an environment sample is detected in a buffer system. When a detection result is positive, a signal of the sensor is changed obviously. Compared with an existing biosensor, the method has main advantages of: 1. high sensitivity; combination of an electrical active molecule and nucleic acid probes to increase a response current; 2. miniature and cheap apparatus and equipment, large detection flux, simple sample pre-treatment, and suitabilityfor on spot rapid screening detection. The method can not only carry out screening detection on a known genotoxicity compound but also evaluate potential toxicity effect of a newly synthesized compound; and the method can screen whether an actual sample contains a genotoxicity compound.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Linezolid injection and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN111686072AImprove quality and safetyImprove medication safetyAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsUse medicationMorpholine
The invention provides a linezolid injection and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method of the linezolid injection comprises the steps of weighing, preparation, filtration, encapsulationand sterilization, and nitrogen filling protection is carried out on liquid medicine in the steps of preparation and / or encapsulation. The content of 3-fluoro-4-(4-morpholinyl) aniline in the linezolid injection product can be obviously reduced by performing nitrogen charging protection on the liquid medicine in the steps of preparation and / or encapsulation, so that the product quality and the medication safety of the linezolid injection are favorably improved, and the medication risk of the variety is also obviously reduced by reducing the content of genotoxic impurities.
Owner:SUZHOU SIXTH PHARMA PLANT OF JIANGSU WUZHONG PHARMA GROUP
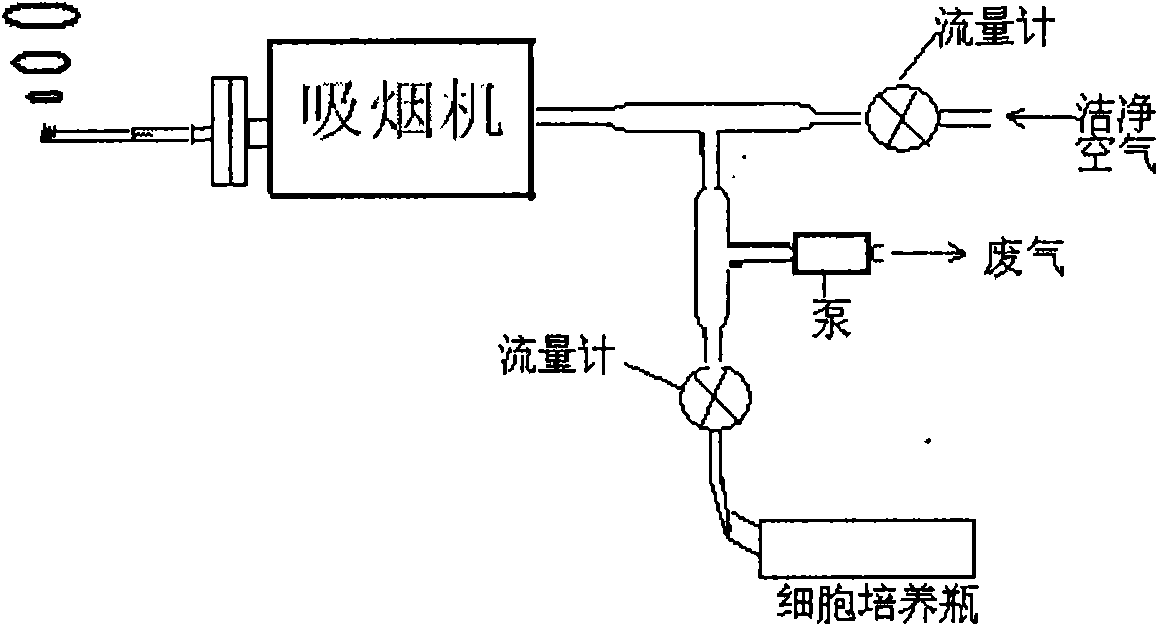
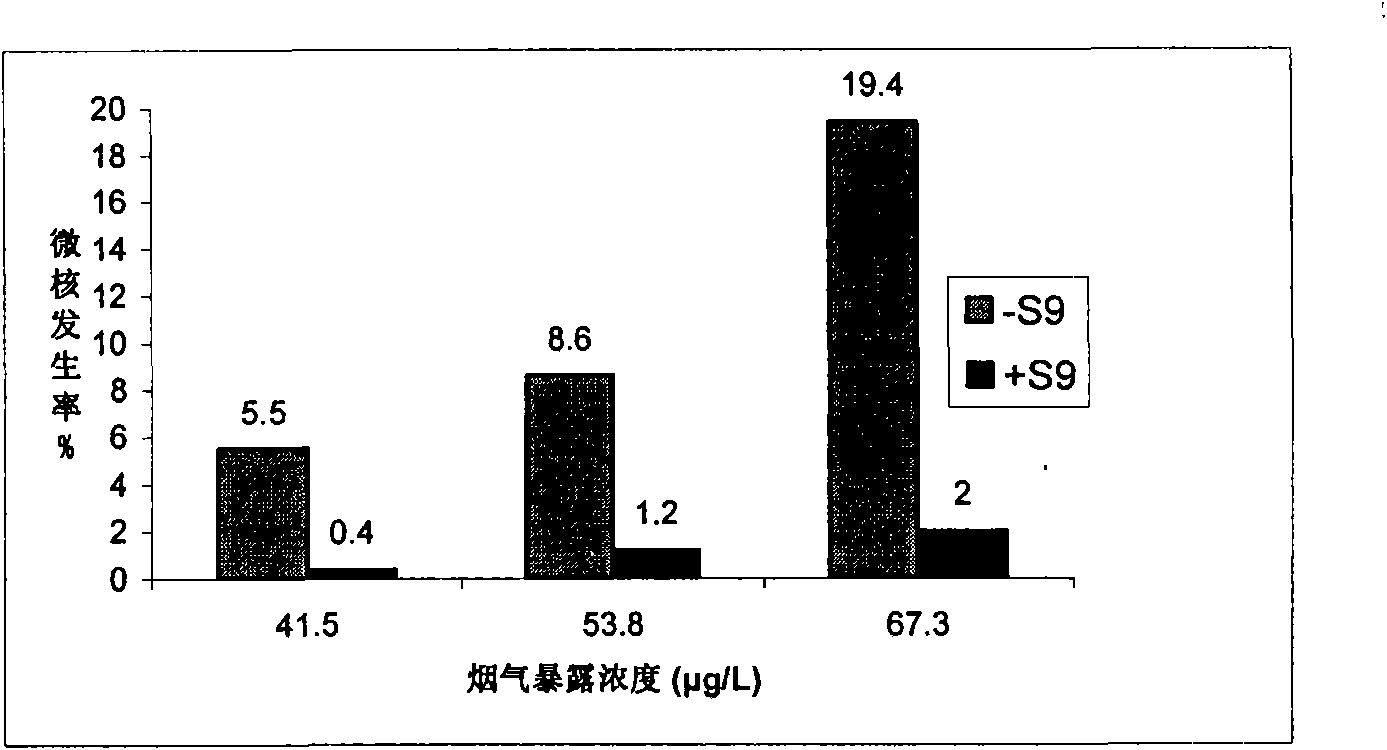
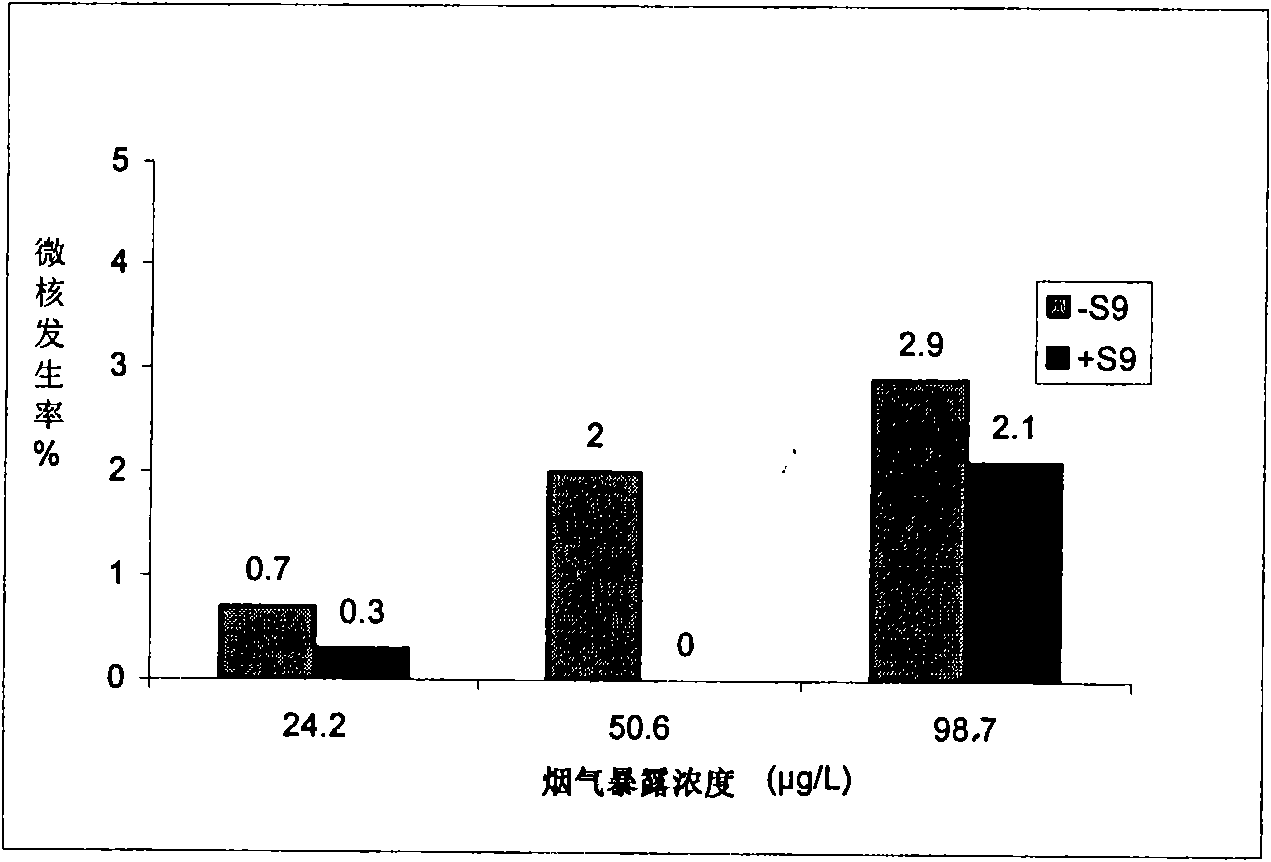
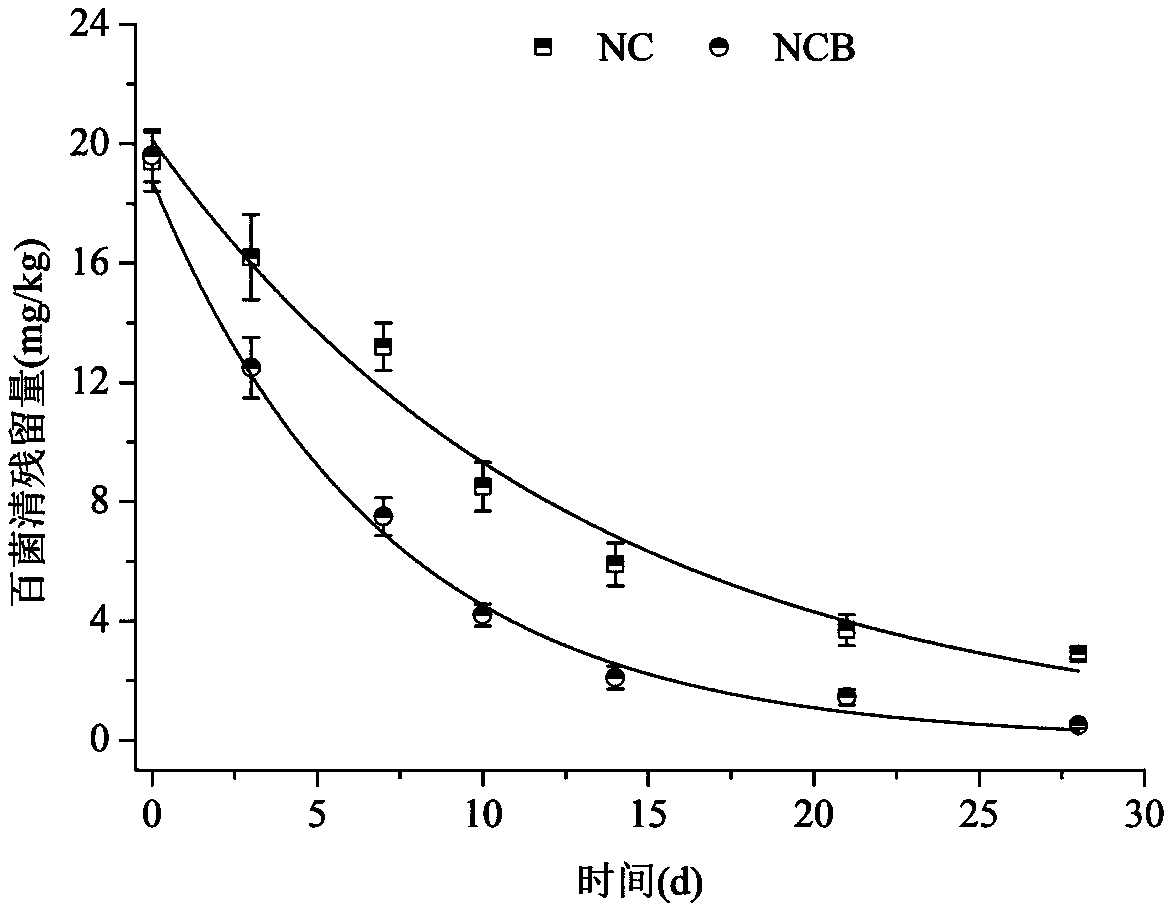
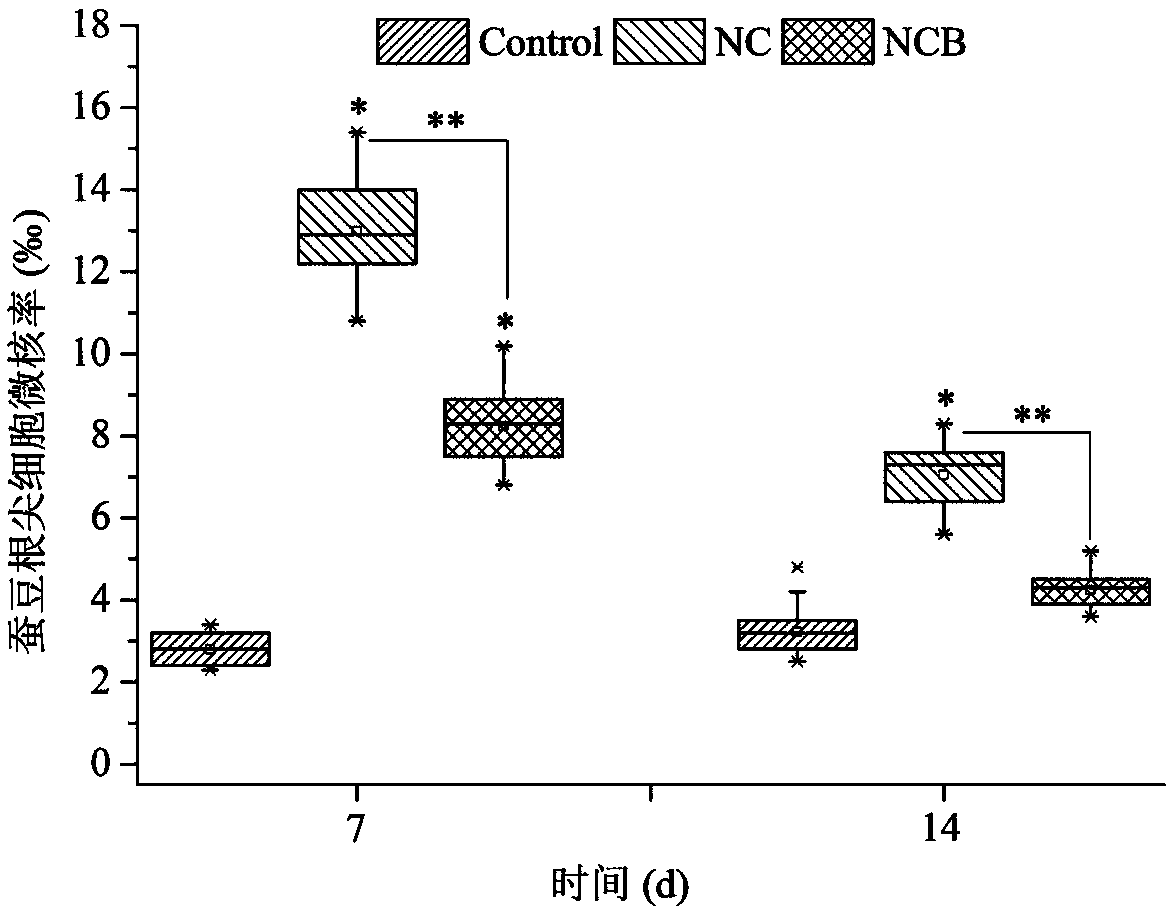
Cigarette mainstream smoke genotoxicity measurement method
ActiveCN101580869AEasy to operateHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMultinucleateFluorescence
A cigarette mainstream smoke genotoxicity measurement method is characterized in that: the cultured cells are directly placed in cigarette mainstream smoke diluted by pure air to expose, the exposed cells are cultured, centrifuged and fixed by cold methanol, acridine orange solution is used for the fluorescent staining for the cells, the stained cells are observed in low power lens to select the region which is distributed evenly and stained well and calculate the number of cells with microkernel(including mononuclear, binuclear and multinuclear) of 500 cells in each sample under fluorescent microscope, the samples is compared with the control sample exposed in pure air to judge whether the cigarette mainstream smoke can increase the cell micronucleus and judge the genotoxicity of the cigarette mainstream smoke. The genotoxicity of the cigarette mainstream smoke can be quantitative evaluated by the invention and the invention has simple operation, high sensitivity and reliable result, thus establishing a new method for measuring cigarette mainstream smoke genotoxicity.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU TOBACCO RES INST OF CNTC
Method for carrying out enzyme-linked immunoadsorption detection on integral zebra fish and application thereof
ActiveCN102023207ATrue reflection absorptionTrue reflection distributionBiological testingDiseaseFood additive
The invention relates to a method for carrying out enzyme-linked immunoadsorption detection on an integral zebra fish and application of the method in drugs for identifying genotoxic compounds, screening anti-tumor drugs and repairing DNA damage. On one hand, the invention can be used for evaluating the genotoxicity of the compounds including environmental compounds, drugs, cosmetics, food additives and the like, and on the other hand, the invention can be used for screening new drugs, such as the anti-tumor drugs, antioxidants, anti-aging drugs, anti-neurodegenerative disease drugs and the like. The invention has very important guiding significance on diagnosing and treating certain diseases and novel drug research and development and compound toxicity screening. By applying the zebra fish to evaluate the compound toxicity and screen the novel drugs, the advantages of low cost, low use level of samples, automatic operation and the like can be achieved, and an in vivo physiological environment of a live animal can be provided, therefore, the goals of simple and convenient evaluating and screening works, rapidness, economy, high efficiency and high flux can be achieved.
Owner:南京新环检测科技有限公司
Method and sensor for detecting nucleic acid on-site damage by photoelectrochemistry
InactiveCN101393146AEasy to makeMade practicalMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMicrobiological testing/measurementSignalling moleculesEnvironmental toxicology
The invention relates to a method and a sensor for detecting on-site damage of nucleic acid in photo-electrochemistry, and provides a method for detecting gene toxicity of chemical substances simply, quickly and sensitively. The method comprises the following steps: (a) an analyte possibly having gene toxicity is contacted with the nucleic acid; (b) if the analyte to be detected expresses the gene toxicity after being activated, a corresponding enzyme is used as an activating agent; (c) photo-electrochemical active molecules are used as a signal indicator; and (d) the combination and / or reaction between the analyte and the nucleic acid is elevated, that is, in the presence of electrodes, current generated by electron transfer between the photoelectrical signal molecules and the electrodes under the action of light is evaluated, and qualitative analysis or quantitative analysis for the gene toxicity of the analyte is carried out according to the difference of photocurrent response before and after the nucleic acid contacts with the analyte. The method and the sensor are applied in the fields of toxicity screening for industrial chemicals, toxicity detecting for environmental pollutants, toxicity testing for synthetic drugs, environmental toxicology research, and the like.
Owner:RES CENT FOR ECO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI THE CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
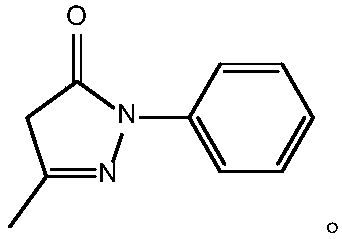
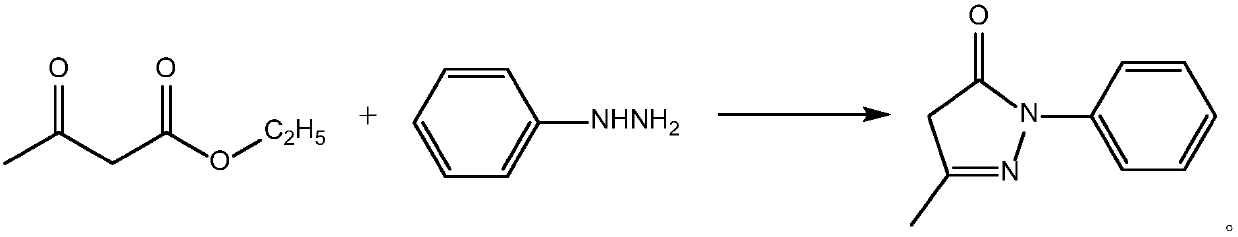
Preparing method of edaravone
The invention relates to a preparing method of edaravone, and belongs to the technical field of preparation of heterocyclic compounds. The preparing method of edaravone comprises the steps of carryingout a reaction between phenylhydrazine and ethyl acetoacetate at 25-30 DEG C for 1-4 h in an organic solvent, and then removing the solvent to obtain an oily substance, wherein the mole ratio of phenylhydrazine to ethyl acetoacetate is 1:(1.019-1.080); uniformly mixing the obtained oily substance with acetic acid, carrying out a reflux reaction at 105-115 DEG C for 6-10 h, then removing unreactedacetic acid, then adding an alcohol solvent for uniform mixing, and conducting soil-liquid separation to obtain edaravone. According to the preparing method of edaravone, by controlling the reactioncondition, stepwise reactions are carried out, the reaction process is more easily controlled, the content of impurities in the product is also greatly reduced, particularly, the contents of residualphenylhydrazine and derivative impurities thereof can be reduced, the genotoxicity of the product is greatly lowered, and the safety of using edaravone is improved.
Owner:HENAN RUNHONG PHARMA
Efficient degrading strain for chlorothalonil, and application of efficient degrading strain in greenhouse soil environment
ActiveCN107916238AReduced genotoxicityLow costBacteriaContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentGreenhouse soil
The invention relates to a degrading strain BJ1 capable of efficiently degrading a bactericide-chlorothalonil, and application of the degrading strain in greenhouse soil environment, belonging to thetechnical field of biodegradation. The degrading strain is identified as stenotrophomonas acidaminiphila and has a strain preservation number of CCTCC No. M2011475. The strain can use the chlorothalonil as an only carbon source; after the degrading strain is cultured in an inorganic salt culture solution for seven days, the degradation rate of the 50mg / L chlorothalonil can reach 93.2%. In the high-temperature and high-humidity greenhouse environment, the application of strain BJ1 can promote the degradation of the chlorothalonil in the soil, and the degradation rate can be increased by 45.6%;furthermore, the strain BJ1 can significantly reduce chlorothalonil-induced soil genotoxicity. The degrading stain is mainly used for the biological purification of chlorothalonil residues in the soil, especially in the soil in the greenhouse environment, thus reducing the harm, caused by the chlorothalonil, to the environment, and realizing functions of repairing the chlorothalonil-contaminated soil and protecting the ecological environment.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
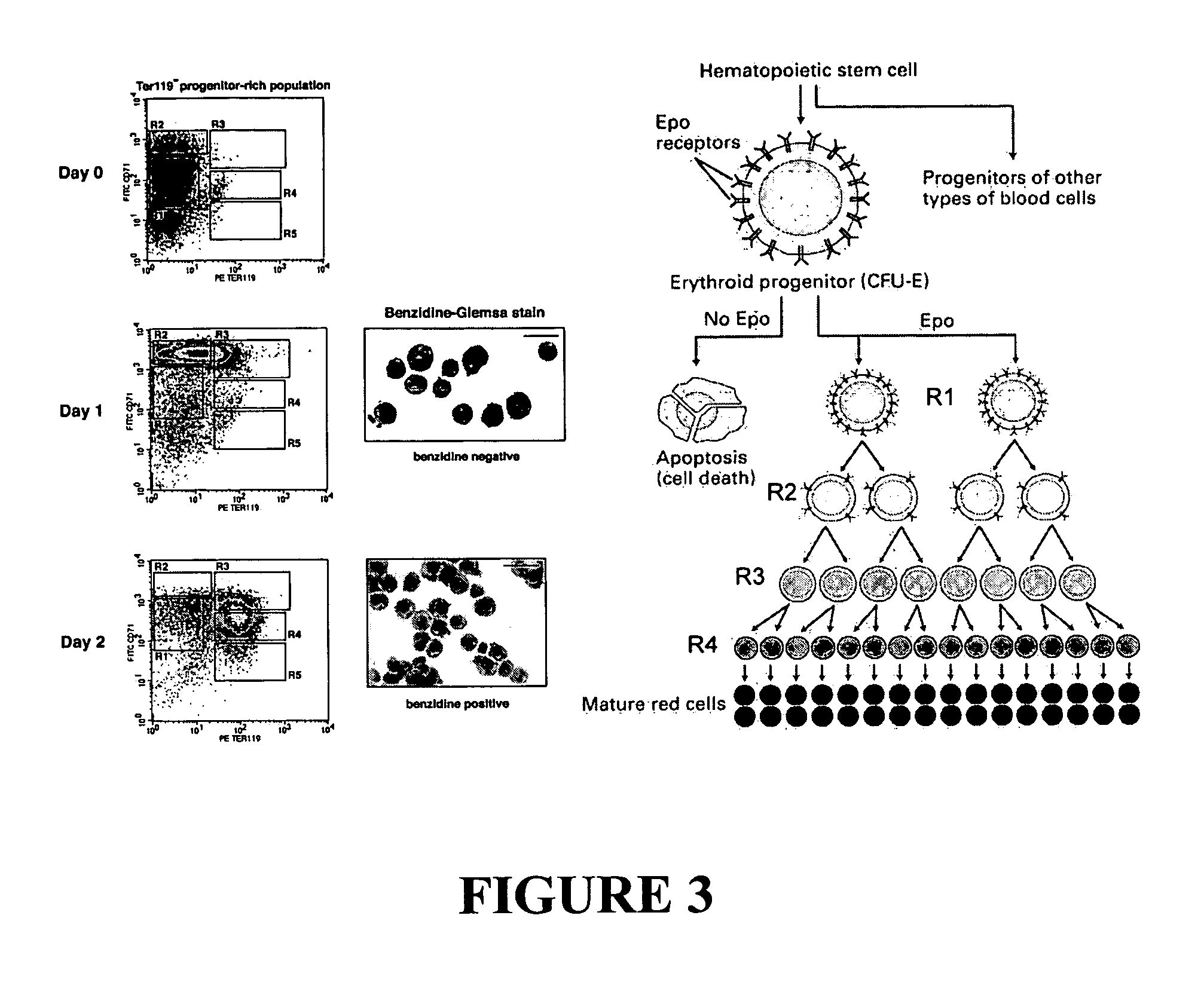
In vitro erythroid micronucleus assay for genotoxicity
InactiveUS20070087364A1Accurate responseIncreased proliferationMicrobiological testing/measurementDisease diagnosisErythroid cellGenotoxicity
The present invention is directed to novel assays to measure the genotoxic effects of compounds on erythroid cells in vitro.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
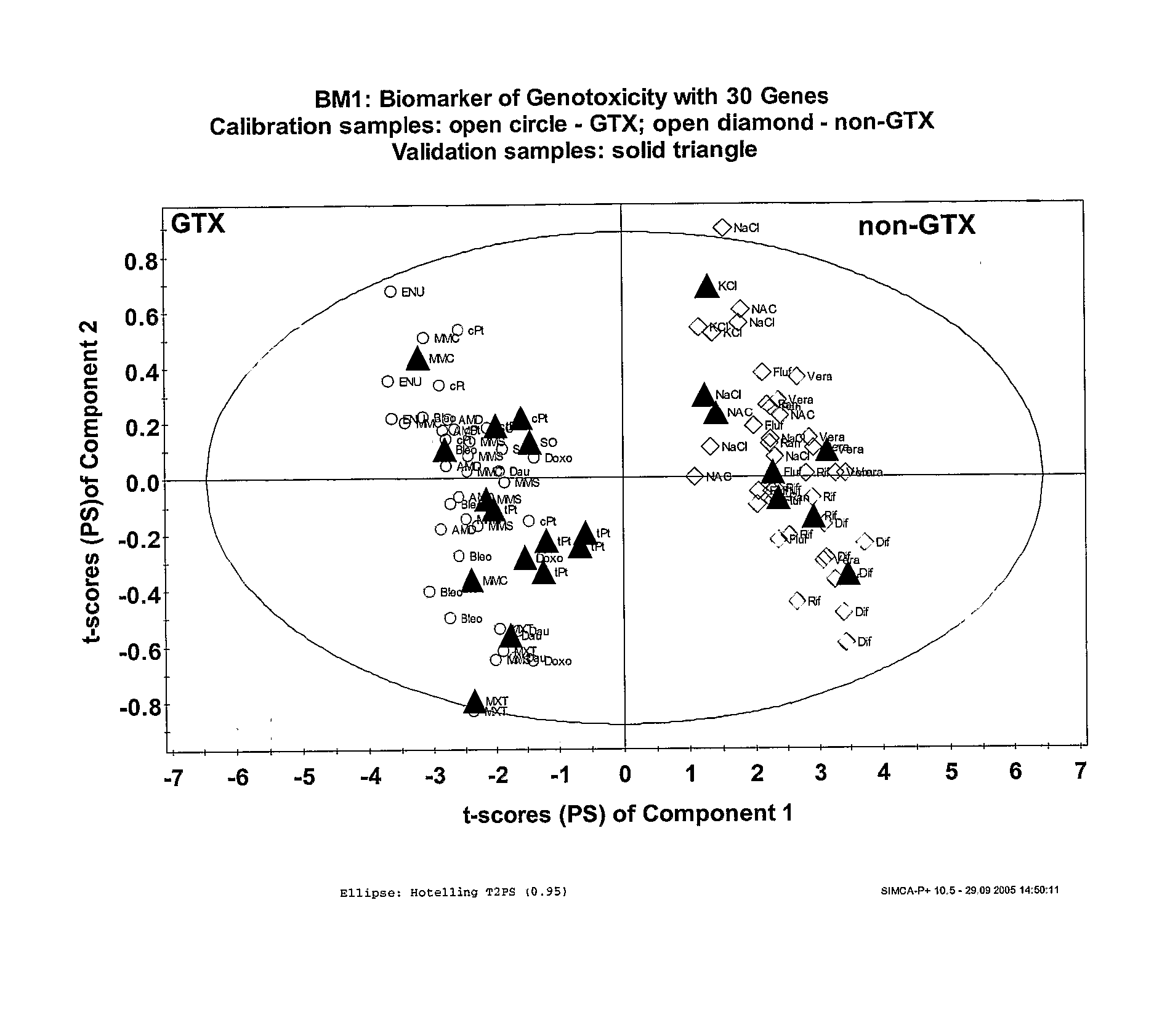
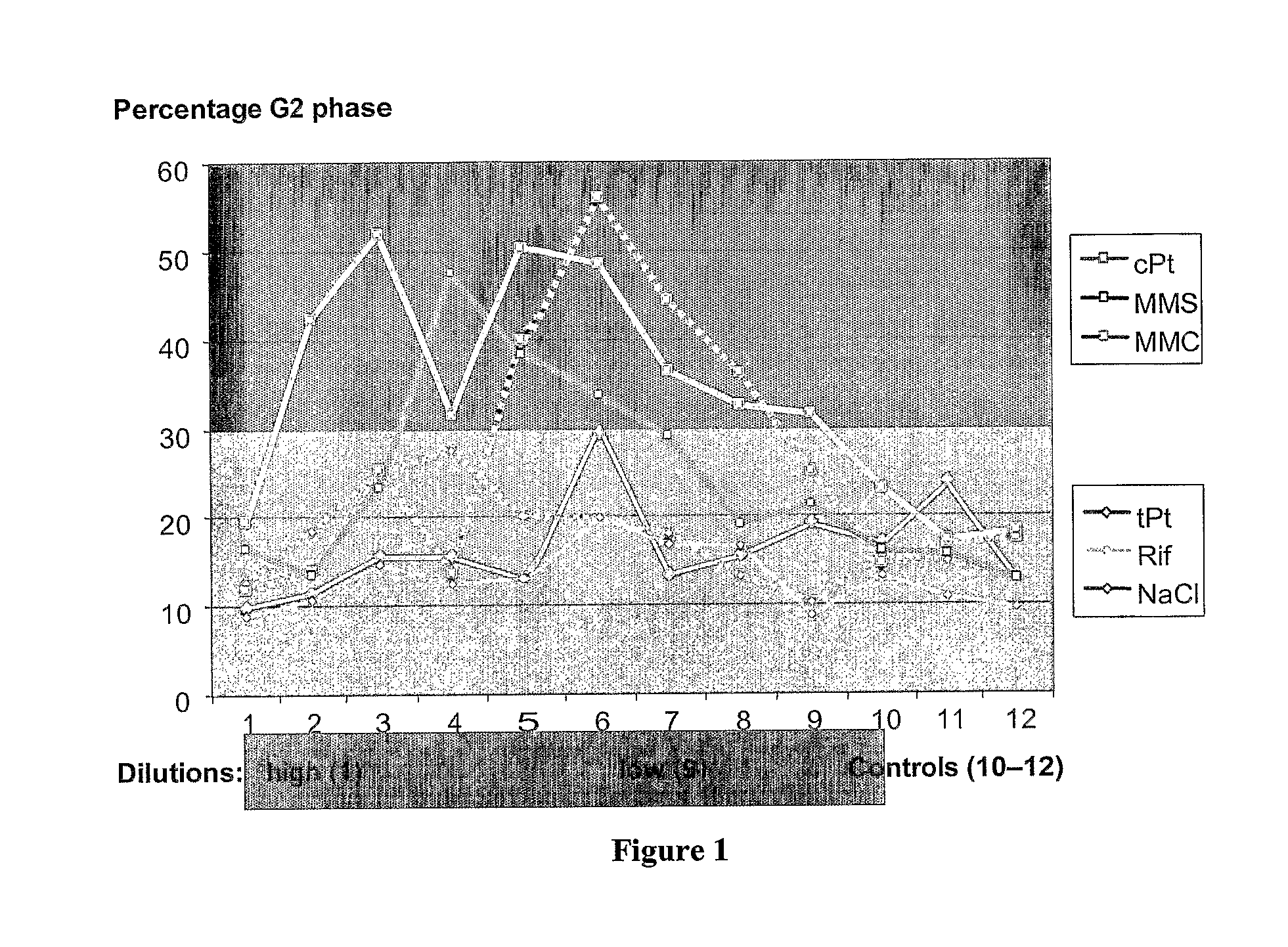
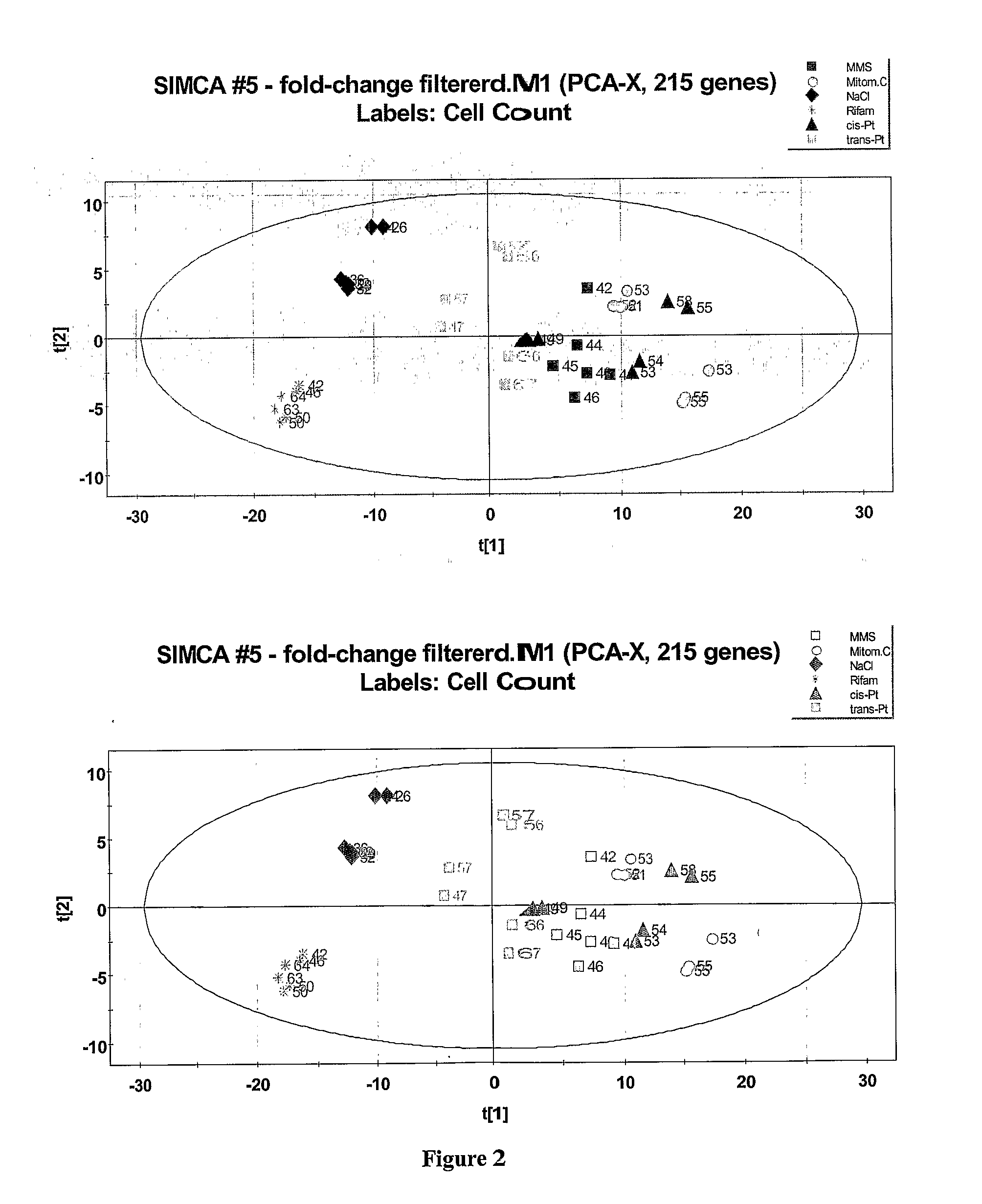
Evaluation of the Toxicity of Pharmaceutical Agents
InactiveUS20080096770A1Rapid high throughput screening processMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsNon genotoxic
The invention provides a rapid high throughput screening process to identify genotoxic compounds. This is accomplished by using a set of biomarker predictor genes that selectively screen for genotoxic or non-genotoxic compounds.
Owner:MCGINNIS CLAUDIA +3
Detection of immobilized nucleic acid
The present invention provides methods for determining the presence of immobilized nucleic acid employing unsymmetrical cyanine dyes that are derivatives of thiazole orange, a staining solution and select fluorogenic compounds that are characterized as being essentially non-genotoxic. The methods comprise immobilizing nucleic acid, single or double stranded DNA, RNA or a combination thereof, on a solid or semi solid support, contacting the immobilized nucleic acid with an unsymmetrical cyanine dye compound and then illuminating the immobilized nucleic acid with an appropriate wavelength whereby the presence of the nucleic acid is determined. The cyanine dye compounds are typically present in an aqueous staining solution comprising the dye compound and a tris acetate or tris borate buffer wherein the solution facilitates the contact of the dye compound and the immobilized nucleic acid. Typically the solid or semi-solid support is selected from the group consisting of a polymeric gel, a membrane, an array, a glass bead, a glass slide, and a polymeric microparticle. Preferably, the polymeric gel is agarose or polyacrylamide. The methods employing the non-genotoxic compounds represent an improvement over commonly used methods employing ethidium bromide wherein the present methods retain the advantages of ethidium bromide, ease of use and low cost, but without the disadvantageous, known mutagen requiring special handling and waste procedures.
Owner:LIFE TECH CORP
Genotoxicity as a biomarker for inflammation
InactiveUS8445200B2Microbiological testing/measurementMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansUveitisInflammatory Bowel Diseases
The invention provides a method for detection of inflammatory disease in a subject that comprises assaying a test sample of peripheral blood from the subject for a marker of DNA damage. An elevated amount of marker present in the test sample compared to control sample is indicative of inflammatory disease activity, including sub-clinical inflammation. The method can be adapted for quantitatively monitoring the efficacy of treatment of inflammatory disease in a subject. Markers of DNA damage include single- and / or double-stranded breaks in leukocytes, oxidative DNA damage in leukocytes, or a marker of nitric oxide oxidative activity (protein nitrosylation in leukocytes). The inflammatory disease can be inflammatory bowel disease (ulcerative colitis or Crohn's disease). The invention may also be used for detection of other types of inflammatory disease, such as non-immune intestinal inflammatory disease (diverticulitis, pseudomembranous colitis), autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, uveitis, vasculitis), or non-immune lung diseases (asthma, chronic obstructive lung disease, and interstitial pneumonitis). This unexpected discovery of markers of genotoxicity present in circulating leukocytes enables detection of inflammation occurring at a localized site with a relatively simple and minimally invasive assay using peripheral blood.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
A kind of preparation method of free state edoxaban
Owner:LEPU PHARMACEUTICAL CO LTD
Preparation method of retegravir
ActiveCN111233930AReduce usageReduced risk of genotoxic impuritiesGroup 5/15 element organic compoundsAcid hydrolysisOrganic base
The invention discloses a preparation method of retegravir, which belongs to the field of pharmaceutical chemicals, and comprises the following steps: reacting a compound V with 4-trifluoromethoxyphenol under the action of alkali to obtain a compound IV; further performing chiral resolution on the compound IV to obtain a compound III; and carrying out an acid hydrolysis reaction on the compound III and the compound II under the action of organic base with large steric hindrance to obtain a compound I. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the use of genotoxic nitro substitutes isavoided, the risk of genotoxic impurities is reduced, and the method is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:JIANGSU ALPHA PHARM CO LTD
Separation and determination method of apremilast and potential genotoxic impurities thereof
ActiveCN107014910AEfficient separationAccurate determination of contentComponent separationElutionSilica gel
The invention belongs to the field of analytic chemistry, and concretely relates to a separation and determination method of apremilast and potential genotoxic impurities thereof. The method comprises the steps of adopting a chromatographic column taking octadecyl silane bonded silica gel as filler, and concretely comprises the steps of adding a diluting agent for dissolving each potential genotoxic impurity reference substance so as to prepare a reference substance solution with known concentration; adding a diluting agent for dissolving a sample for test so as to prepare a solution of the sample for test; taking the reference substance solution and the solution of the sample for test respectively for sample injection; adopting a moving phase for carrying out high performance liquid chromatography elution analysis, and recording a chromatogram map; comparing peak areas of impurities, corresponding to peak appearance times, in the reference substance solution and the solution of the sample for test, and calculating the contents of the apremilast and the potential genotoxic impurities contained in the sample for test. The method is high in specificity, high in sensitivity (the limit of detection of the potential genotoxic impurities of SM1 is 0.0004 percent), and simple to operate, and has the advantages of convenience and quickness.
Owner:CHONGQING HUAPONT PHARMA
Method for determining genotoxicity
InactiveUS20060110768A1Cell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsMicrobiological testing/measurementCompound (substance)Genotoxicity
Methods and reagents for determining the genotoxicity of a compound based on genomic responses to contact therewith are provided.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Method for detecting 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinooxy with high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry
InactiveCN109632981AEasy to operateThe test result is accurateComponent separationConcentration gradientLinear regression
The invention discloses a method for detecting 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinooxy with high performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. The method comprises the steps that 1, a test solution and a reference stock solution is prepared; 2, the test solution and the reference stock solution with a certain concentration gradient are subjected to sample introduction, a high performance liquid chromatograph mass spectrometer is used for detecting and recording a chromatogram; and 3, linear regression analysis is performed on the mass concentration of the reference stock solution and chromatogram peak area, a regression equation and correlation coefficients are obtained, and a standard curve is manufactured; and the peak area of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinooxy in the chromatogram of the test solution is utilized to calculate the content of 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinooxy by an external standard method. The method provided by the invention is the first method for detecting 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidinooxy developed in the field. The method has accurate detection result, high sensitivity, good stability, and low detection limit, and totally meets detection requirements for genotoxic impurities in the field.
Owner:CHANGZHOU HEQUAN PHARMA CO LTD
Methods of identifying and using chemotherapeutic agents
The disclosure includes methods for the identification of chemotherapeutic agents that selectively reduce the growth or the survival of genotoxically stressed DNA damage checkpoint deficient tissue, such as irradiated cancerous tissue. The methods involve the use of genotoxically-stressed tissue(s) that are deficient in one or more DNA damage checkpoints. The disclosure also provides kits for performing the disclosed methods. The disclosure also includes chemotherapeutic agents that selectively reduce the growth or the survival of genotoxically stressed DNA damage checkpoint deficient tissue, such as irradiated cancerous tissue. The disclosure also includes methods of treatment or management of cancer, tumor formation, other conditions involving abnormal proliferation, or cell-cycle diseases or disorders.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com