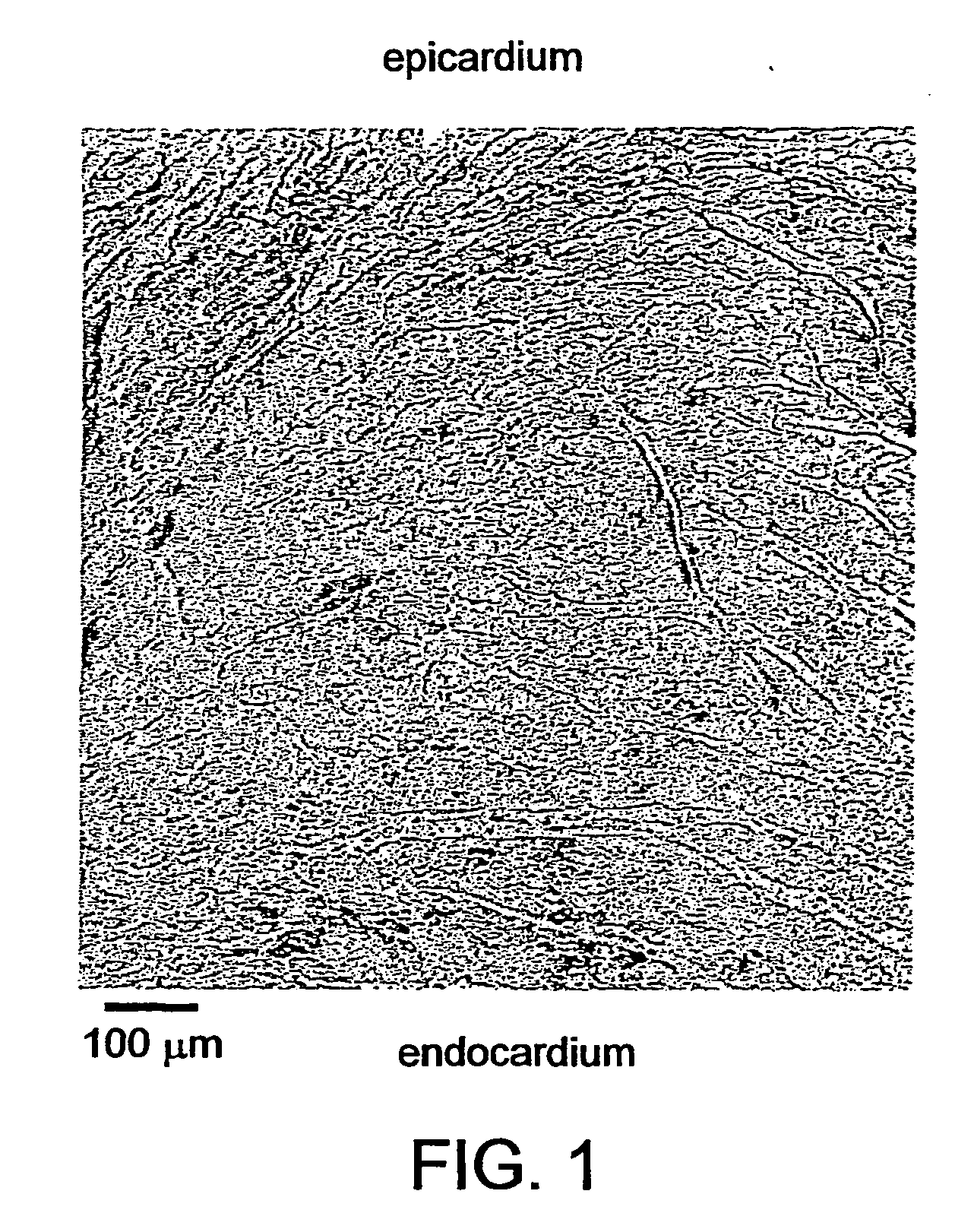
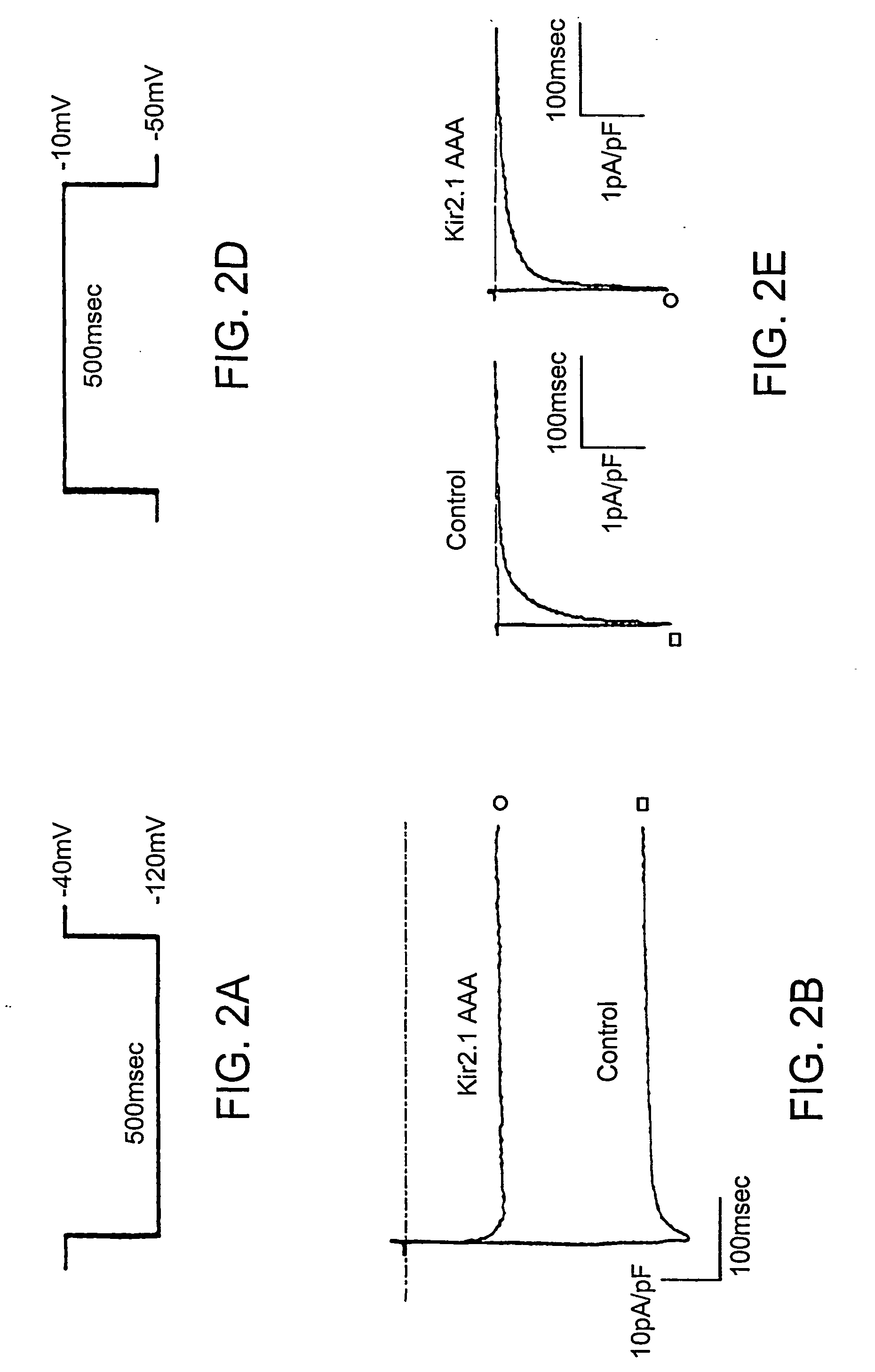
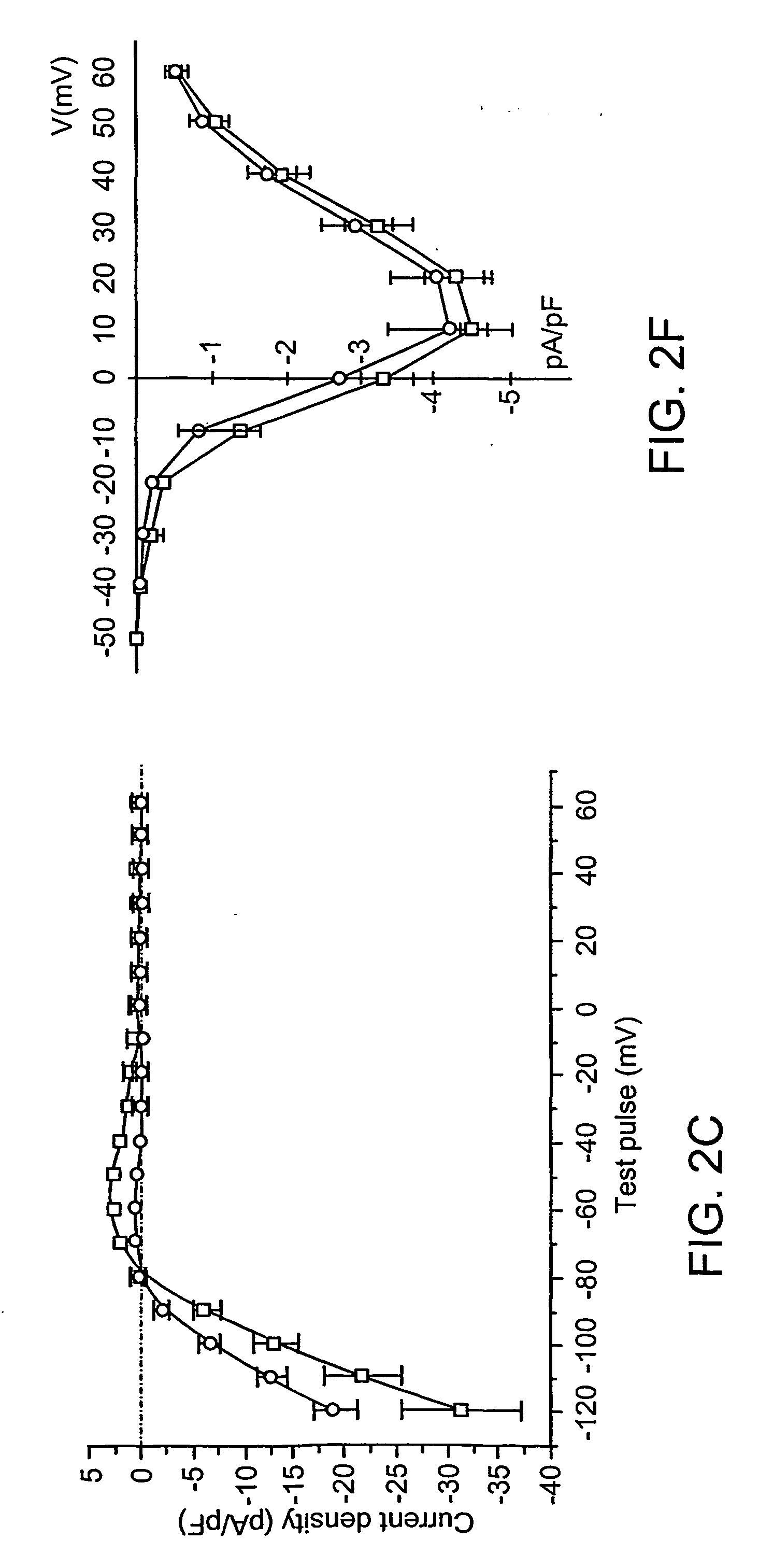
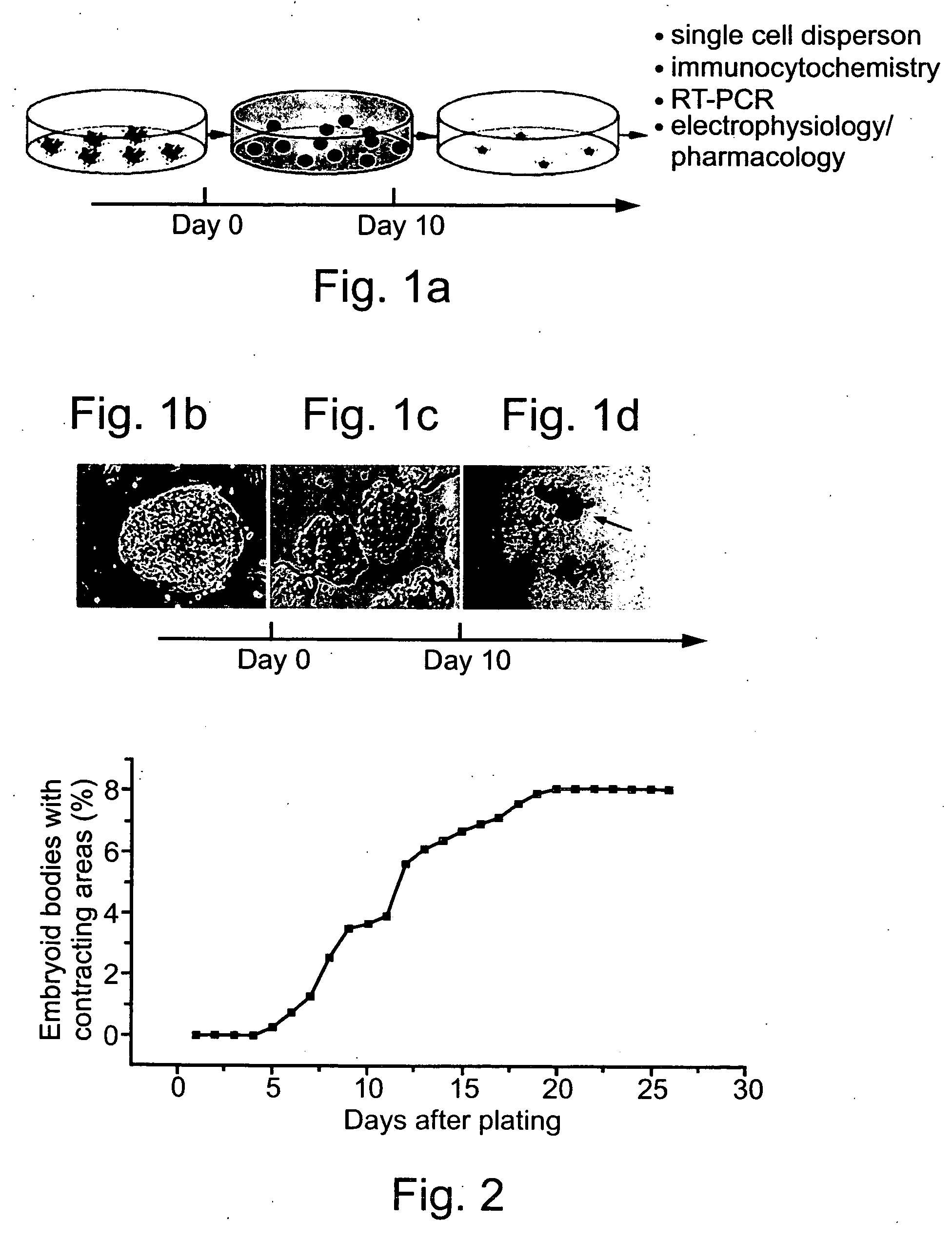
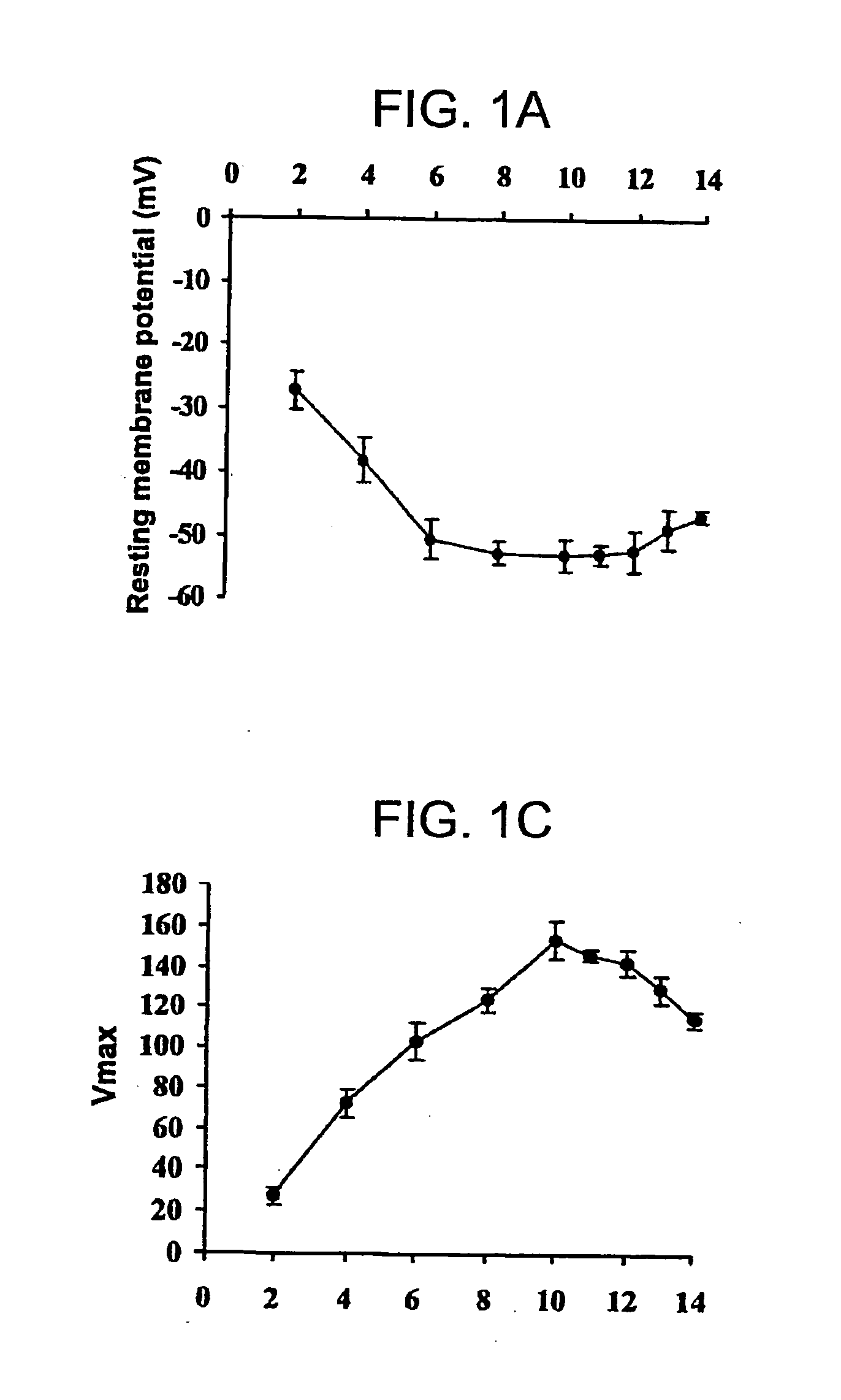
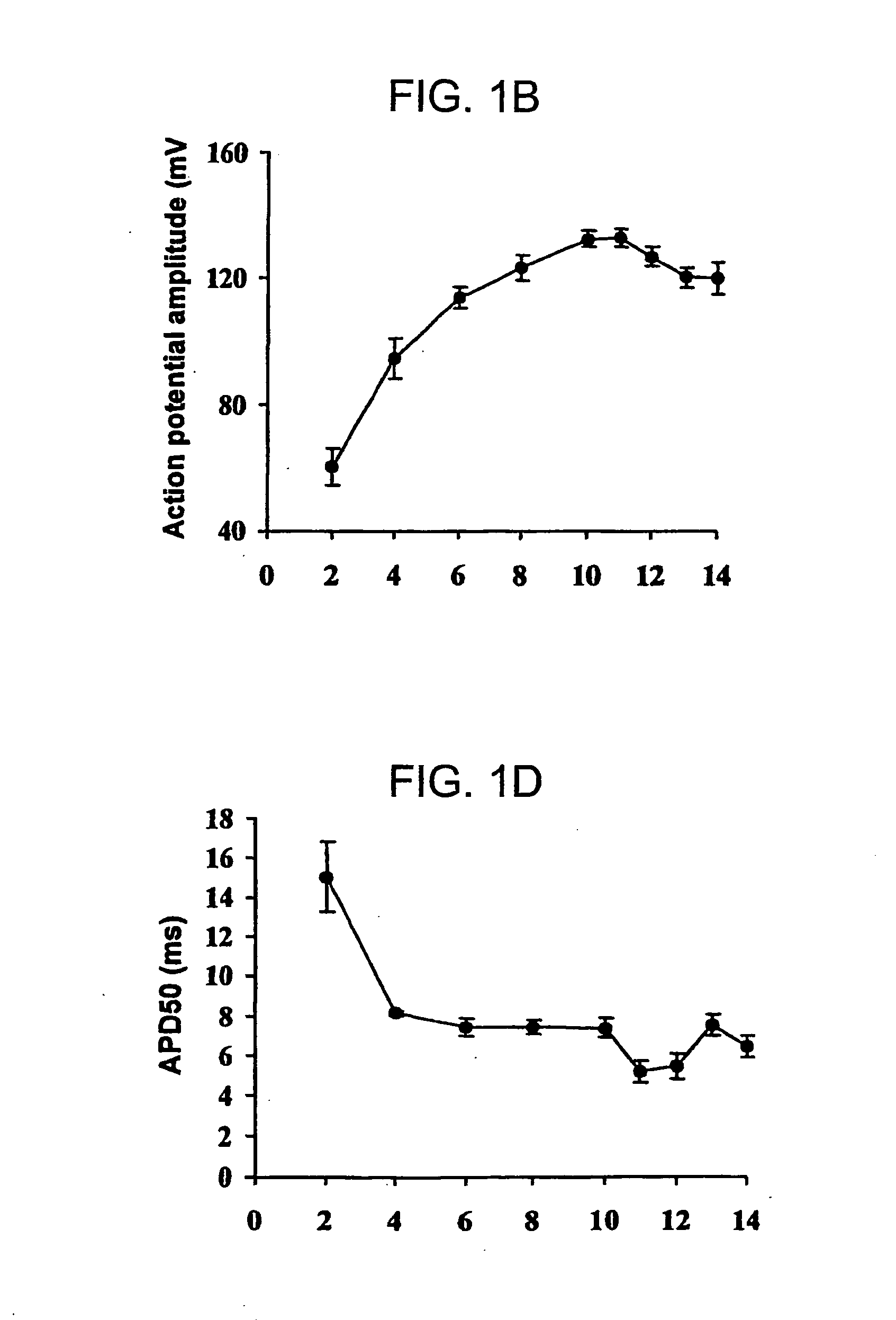
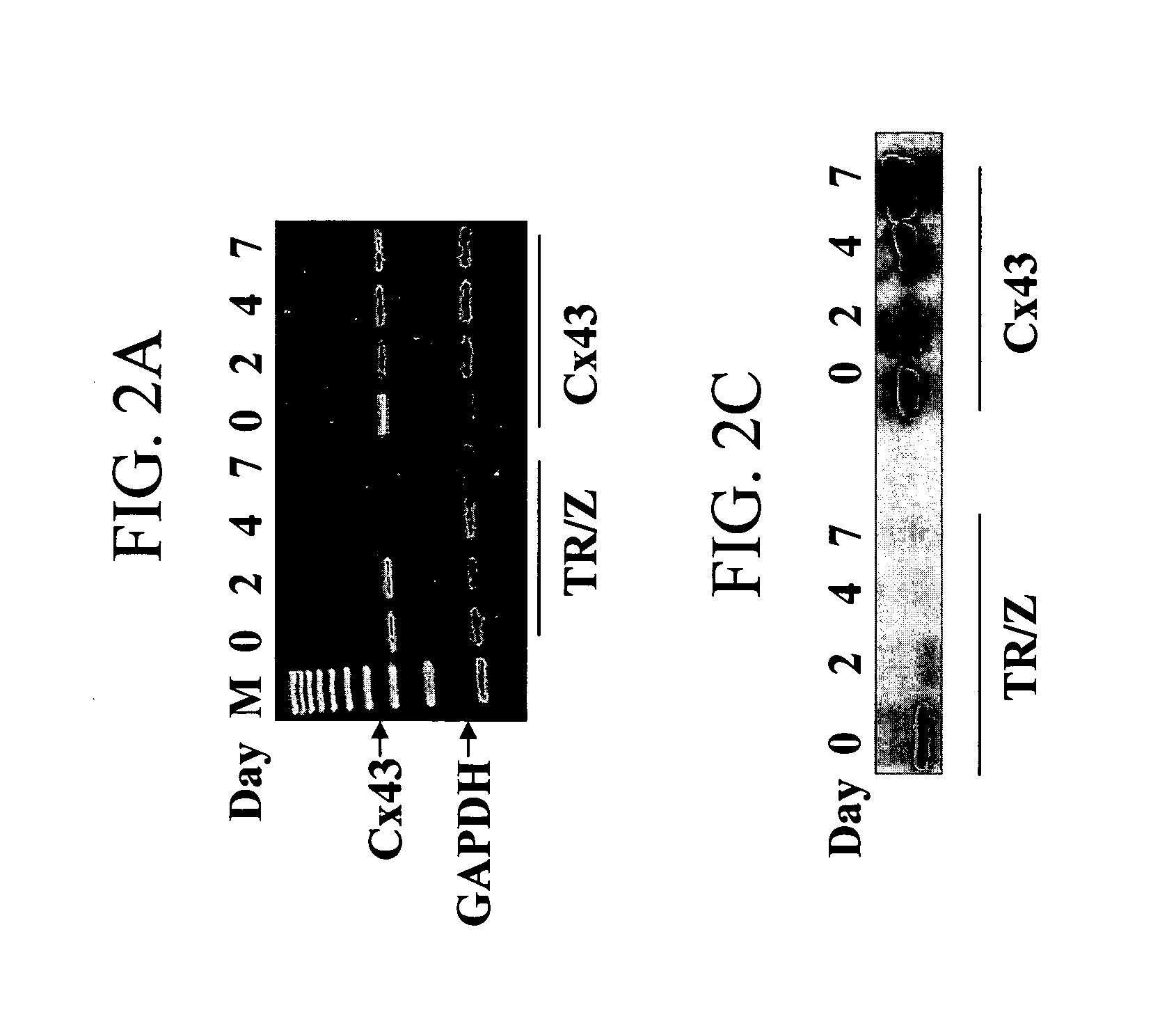
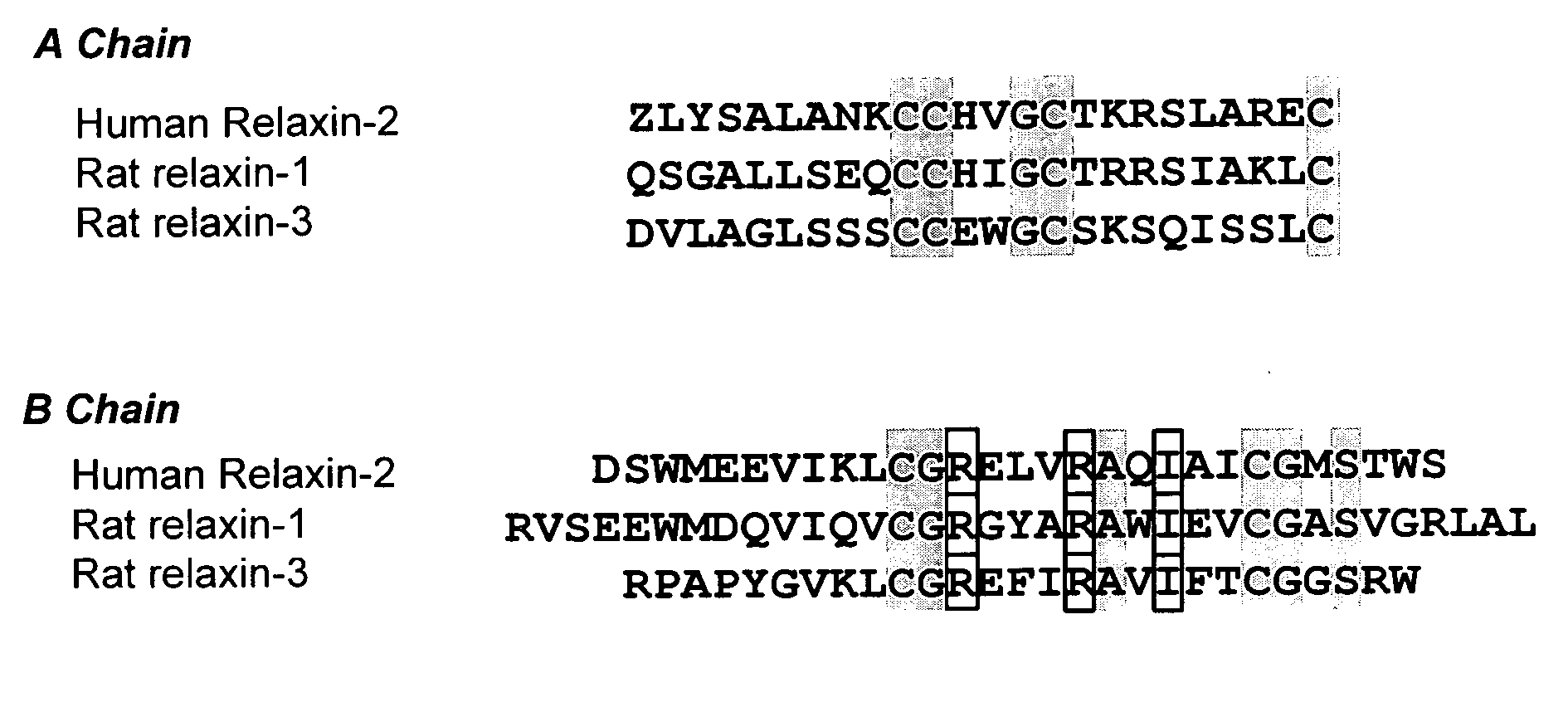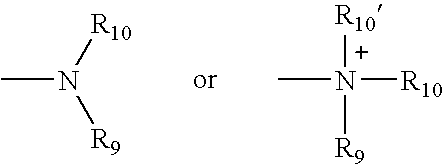Patents
Literature
111 results about "Cardiac cell" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for low-voltage termination of cardiac arrhythmias by effectively unpinning anatomical reentries
ActiveUS20060161206A1Difficulties terminating anatomical reentryEfficient managementElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsLower limitLow voltage
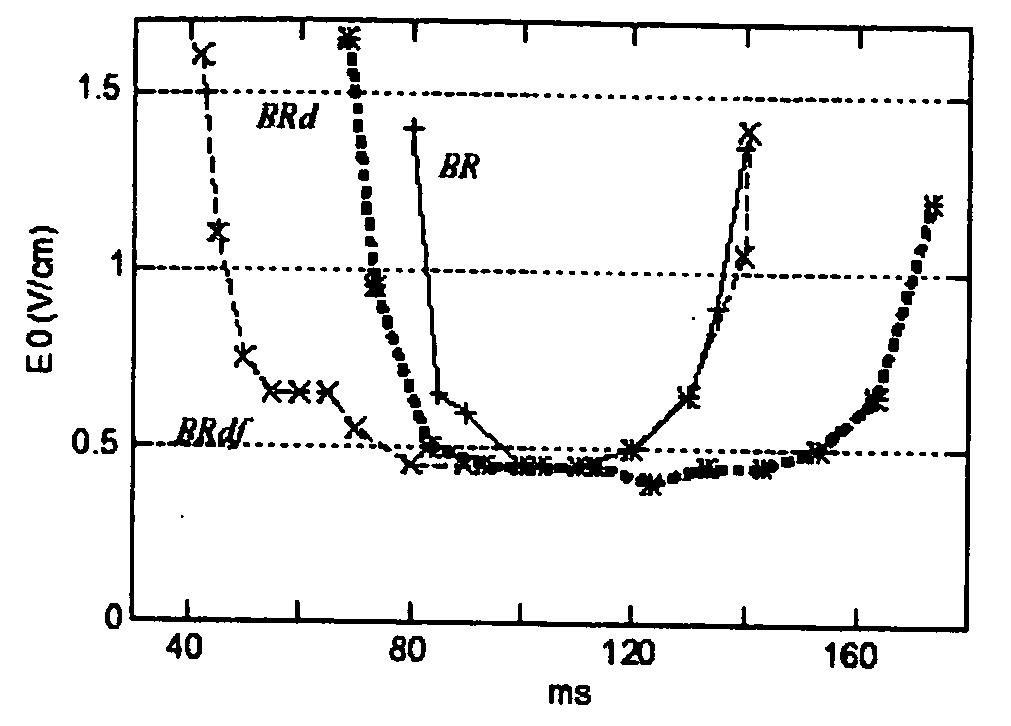
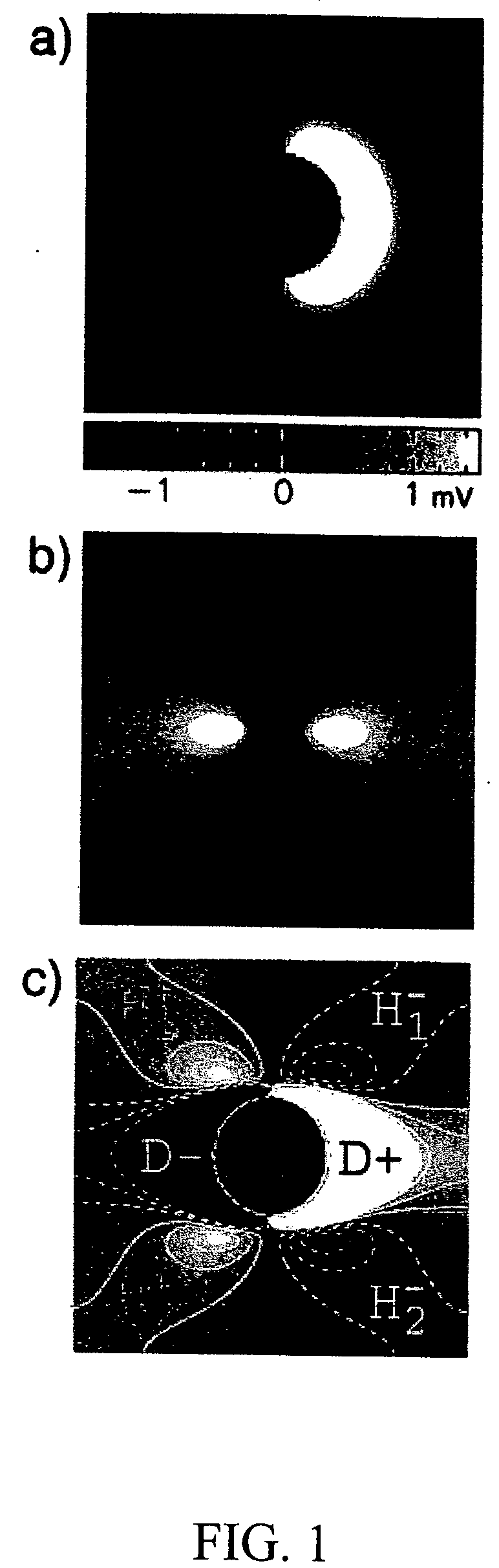
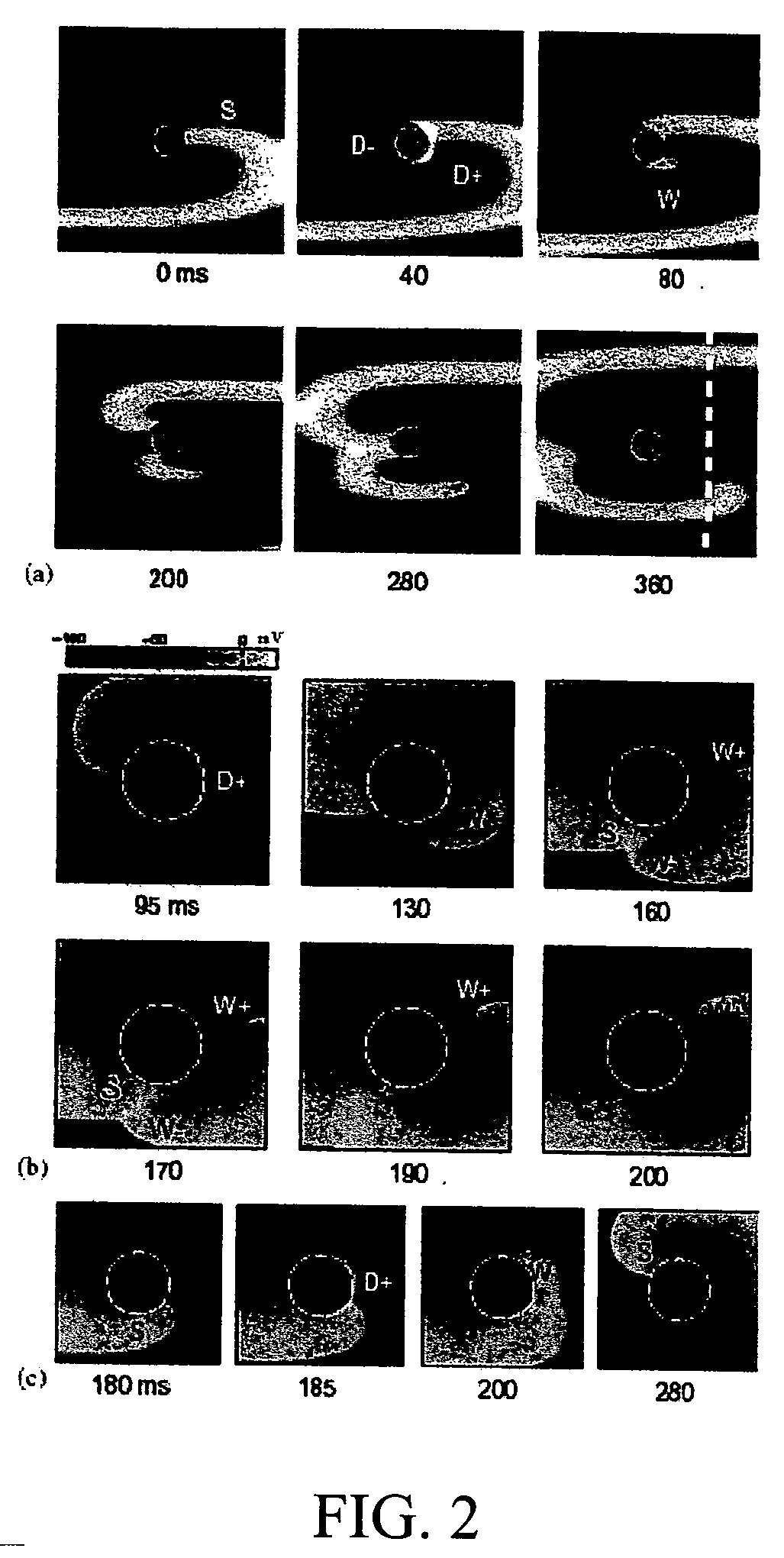
A method for extinguishing a cardiac arrhythmia utilizes destructive interference of the passing of the reentry wave tip of an anatomical reentry through a depolarized region created by a relatively low voltage electric field in such a way as to effectively unpin the anatomical reentry. Preferably, the relatively low voltage electric field is defined by at least one unpinning shock(s) that are lower than an expected lower limit of vulnerability as established, for example, by a defibrillation threshold test. By understanding the physics of the electric field distribution between cardiac cells, the method permits the delivery of an electric field sufficient to unpin the core of the anatomical reentry, whether the precise or estimated location of the reentry is known or unknown and without the risk of inducting ventricular fibrillation. A number of embodiments for performing the method are disclosed.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Method for low-voltage termination of cardiac arrhythmias by effectively unpinning anatomical reentries
ActiveUS8175702B2Difficulties terminating anatomical reentryEfficient managementElectrocardiographyHeart defibrillatorsLower limitLow voltage
A method for extinguishing a cardiac arrhythmia utilizes destructive interference of the passing of the reentry wave tip of an anatomical reentry through a depolarized region created by a relatively low voltage electric field in such a way as to effectively unpin the anatomical reentry. Preferably, the relatively low voltage electric field is defined by at least one unpinning shock(s) that are lower than an expected lower limit of vulnerability as established, for example, by a defibrillation threshold test. By understanding the physics of the electric field distribution between cardiac cells, the method permits the delivery of an electric field sufficient to unpin the core of the anatomical reentry, whether the precise or estimated location of the reentry is known or unknown and without the risk of inducting ventricular fibrillation. A number of embodiments for performing the method are disclosed.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Biological pacemaker
Disclosed are methods and systems for modulating electrical behavior of cardiac cells. Preferred methods include administering a polynucleotide or cell-based composition that can modulate cardiac contraction to desired levels, i.e., the administered composition functions as a biological pacemaker.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Methods of generating human cardiac cells and tissues and uses thereof
A method of generating cells predominantly displaying at least one characteristic associated with a cardiac phenotype is disclosed. The method comprises (a) partially dispersing a confluent cultured population of human stem cells, thereby generating a cell population including cell aggregates; (b) subjecting said cell aggregates to culturing conditions suitable for generating embryoid bodies; (c) subjecting said embryoid bodies to culturing conditions suitable for inducing cardiac lineage differentiation in at least a portion of the cells of said embryoid bodies, said culturing conditions suitable for inducing cardiac lineage differentiation including adherence of said embryoid bodies to a surface, and culture, medium supplemented with serum, thereby generating cells predominantly displaying at least one characteristic associated with a cardiac phenotype.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
Method of providing a dynamic cellular cardiac support
The present invention provides a method for repairing damaged myocardium. The method comprises using a combination of cellular cardiomyoplasty and electrostimulation for myogenic predifferentiation of stem cells and to synchronize the contractions of the transplanted cells with the cardiac cells. The method comprises the steps of obtaining stem or myogenic cells from a donor, culturing and electrostimulating the isolated cells in vitro, and implanting the cells into the damaged myocardium.
Owner:BIOHEART
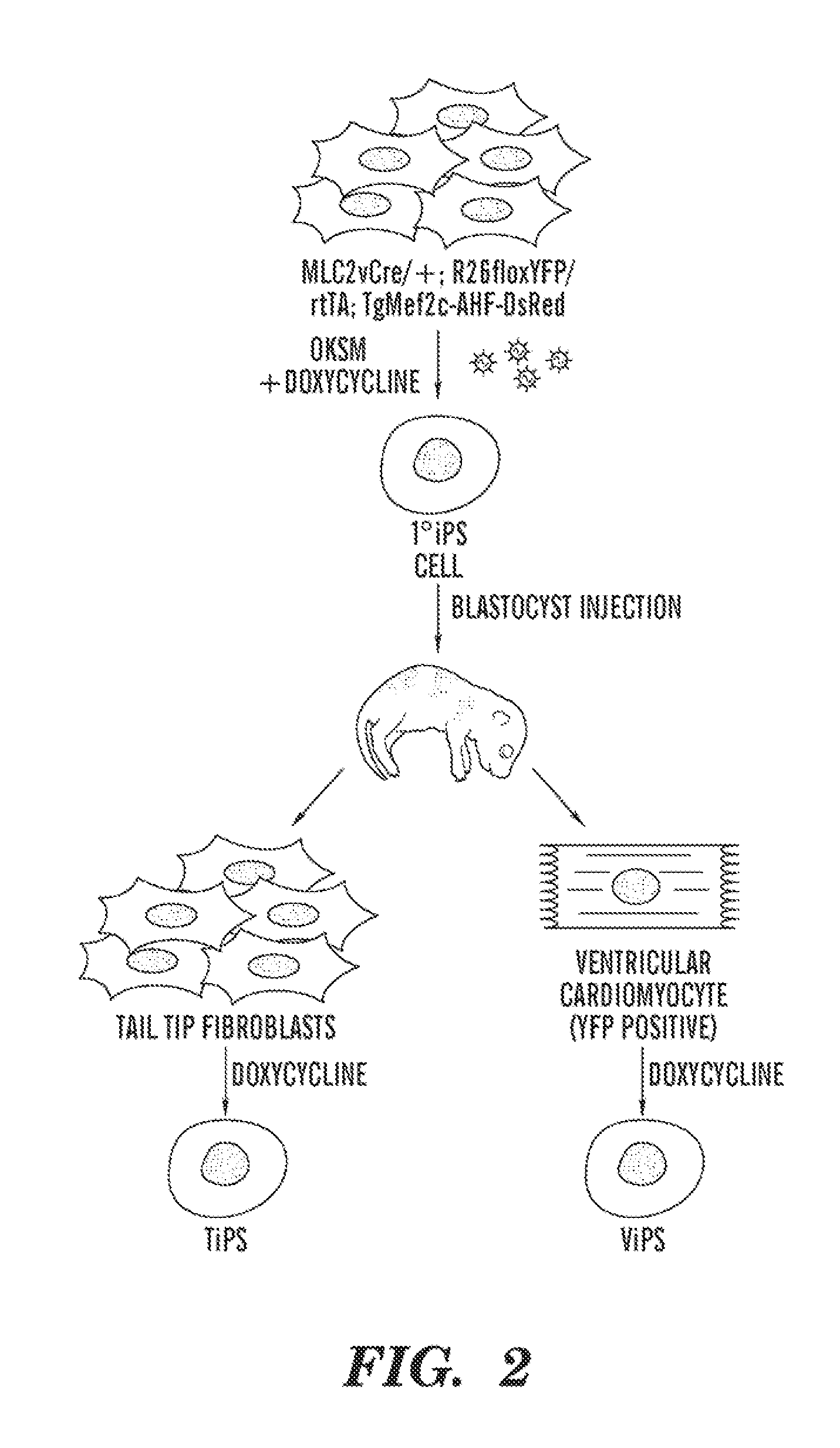
VENTRICULAR INDUCED PLURIPOTENT STEM (ViPS) CELLS FOR GENERATION OF AUTOLOGOUS VENTRICULAR CARDIOMYOCYTES AND USES THEREOF
InactiveUS20120009158A1More cardiomyogenicYieldBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsDiseaseCells heart
The present invention generally relates to methods and compositions to generate a secondary iPS (2iPS) cell to produce somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate. In some embodiments, the method relates to an increase in efficiency of differentiation and production of high yields of somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate produced from secondary iPS (2iPS) cells as compared to their differentiation from other pluripotent stem cell sources such as ES cells or primary iPS cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems for reprogramming a first somatic cell into a primary iPS cell, where the primary iPS cell is then differentiated along a selected linage to produce a second somatic cell, which is then reprogrammed to a secondary iPS cell (2iPS) cell. The 2iPS cell has a high efficiency of differentiating into a cell of the same cell type as the second somatic cell, e.g., a somatic cells of a rare differentiation cell type fate such as but not limited to a ventricular cardiomyocyte, a pancreatic β-cell or a hepatic cell. In some embodiments, the first somatic cell is a fibroblast, or a cardiac cell, but is not limited to cardiac fibroblast cells. In some embodiments, the present invention relates to compositions, methods and systems to produce ventricular cardiomyocytes from secondary induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSC), where the iPSC are themselves generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes. The secondary iPS (2iPS) cell generated from ventricular cardiomyocytes have a higher cardiomyogenic potential and high cardiomyogenic yield as compared to primary iPSC, and are useful in drug discovery, disease modeling and cell-based therapy.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Method of providing a dynamic cellular cardiac support
The present invention provides a method for repairing damaged myocardium. The method comprises using a combination of cellular cardiomyoplasty and electrostimulation for myogenic predifferentiation of stem cells and to synchronize the contractions of the transplanted cells with the cardiac cells. The method comprises the steps of obtaining stem or myogenic cells from a donor, culturing and electrostimulating the isolated cells in vitro, and implanting the cells into the damaged myocardium.
Owner:BIOHEART
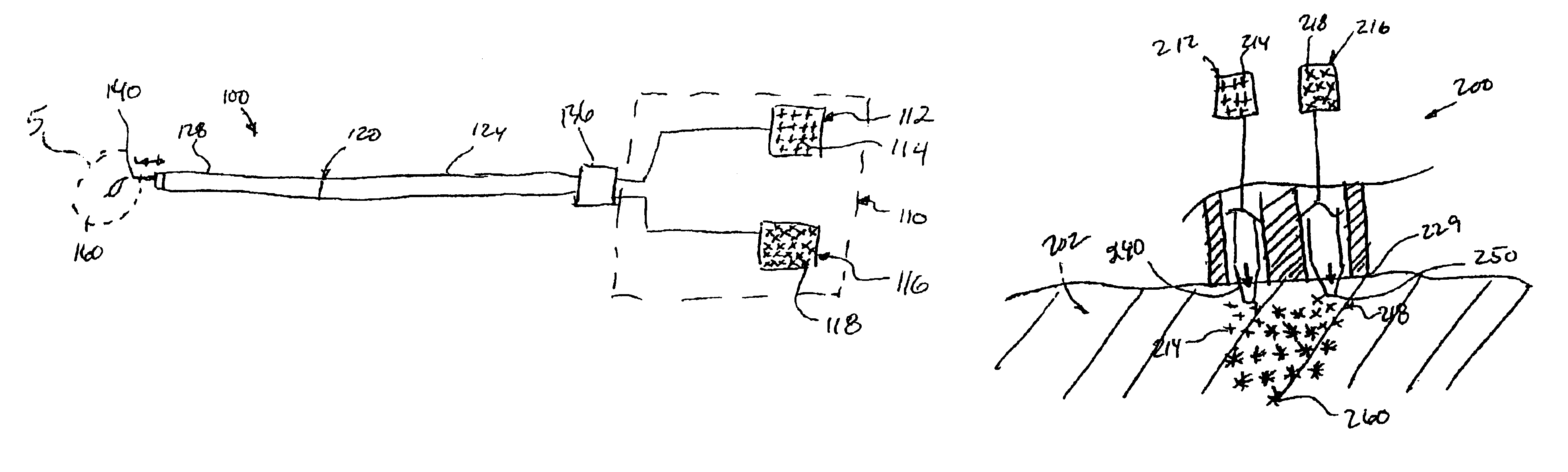
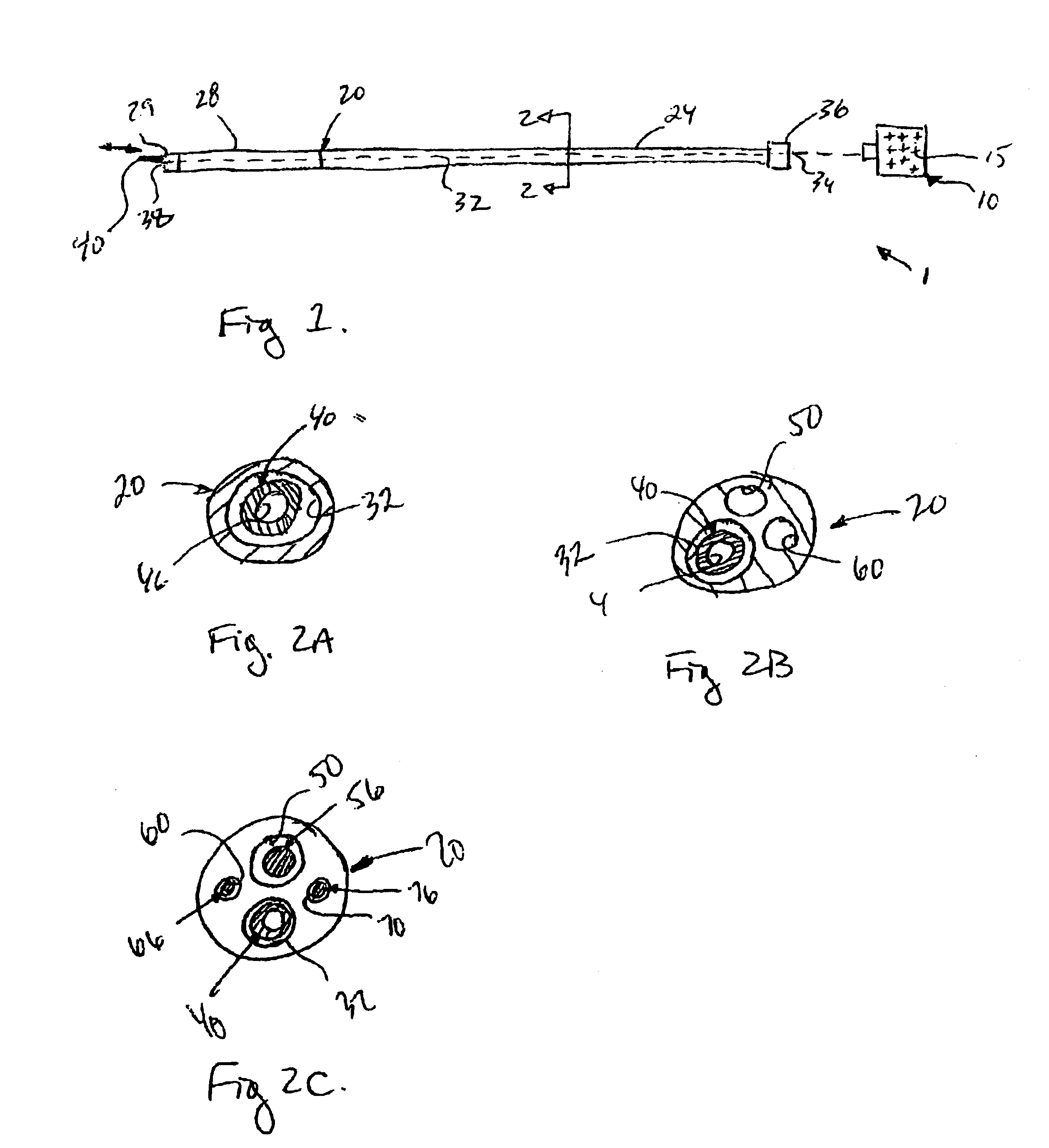
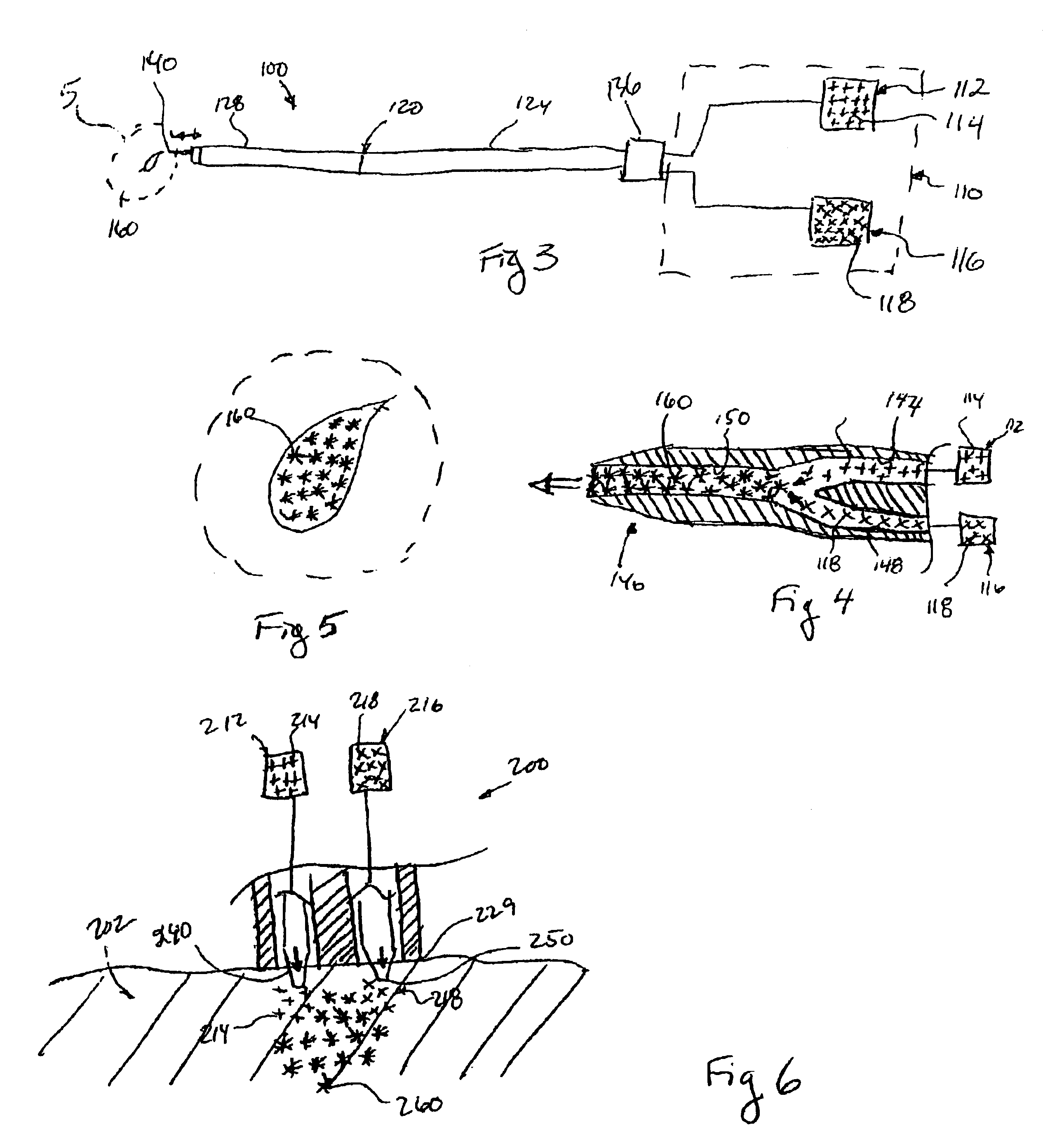
System and method for forming a non-ablative cardiac conduction block
A system forms a cardiac conduction block at a location in a heart of a patient without substantially ablating cardiac tissue. The system includes a delivery system coupled to a source of material that is substantially non-ablative with respect to cardiac tissue. The delivery system delivers the material to the location, and the material at the location forms a conduction block without ablating the cardiac cells there. The material may include living cells, such as for example skeletal myocytes, and / or may include a non-living matter such as biopolymers such as a fibrin glue agent, or collagen agents. An expandable member with needle assembly is used to deliver the material so as to form a non-ablative circumferential conduction block at a location where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and method for forming a non-ablative cardiac conduction block
InactiveUS20060083717A1High retention rateIncreased formationPowder deliveryPeptide/protein ingredientsVeinHeart block
A system forms a cardiac conduction block at a location in a heart of a patient, generally without substantially ablating cardiac tissue. The system includes a delivery system coupled to a source of material that is substantially non-ablative with respect to cardiac tissue but that substantially interrupts and thus blocks cardiac conduction. The delivery system delivers the material to the location, and the material at the location forms a conduction block without substantially ablating the cardiac cells there. The material includes a synthetic polymer, a polysaccharide (e.g. block polysaccharide, alginate, etc.), or a protein, or an analog, derivative, precursor, or agent thereof, or a combination or blend thereof. The material may include living cells. The delivery assembly may include a needle for injecting the material. An expandable member is provided with a needle assembly to deliver the material and form a non-ablative circumferential conduction block where a pulmonary vein extends from an atrium.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
pDJA1, a cardiac specific gene, corresponding proteins, and uses thereof
InactiveUS7009038B2Avoid irreversible damageAugment existing diagnostic methodologiesSugar derivativesHydrolasesAnginaCoronary event
The present invention provides novel nucleic acid and protein sequences for methods and compositions for treating, screening, and diagnosing cardiovascular disease and methods for using these genes and gene products for prevention of cardiac cell death and prevention of cardiac tissue damage resulting from ischemic events in cardiac tissue, as well as other tissue that is subject to damage resulting from an ischemic event. The genes, gene products and agents of the invention are also useful for treating other related clinical or coronary events such as angina, myocardial infarct (MI), and stroke, for monitoring the effectiveness of their treatment, and for drug development. The genes, gene products and agents of the present invention are also provided as pharmaceutical compositions for treatment of cardiovascular disease, ischemic heart disease, myocardial infarct and related conditions. Kits are also provided for the diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of cardiac diseases and related conditions.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
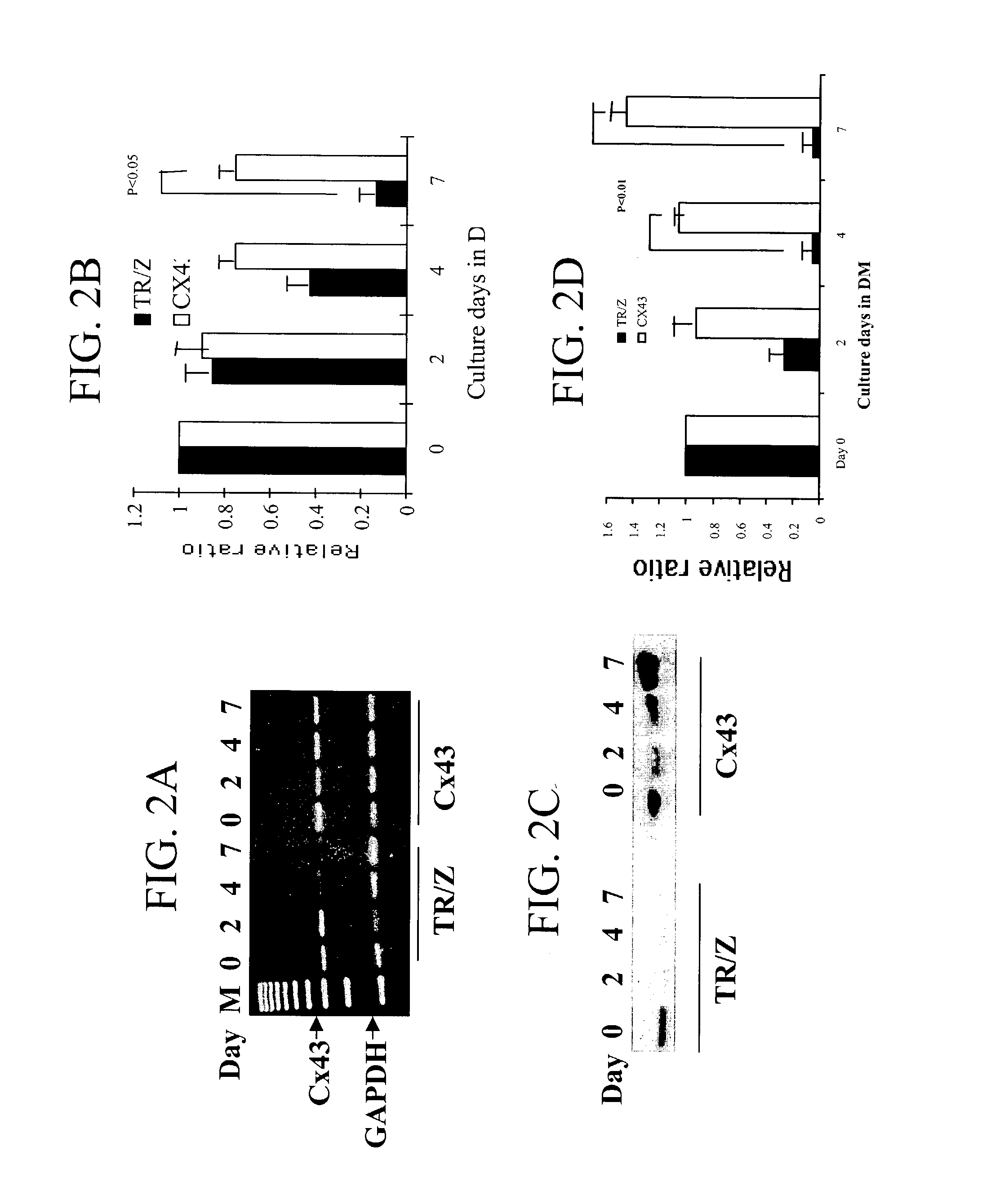
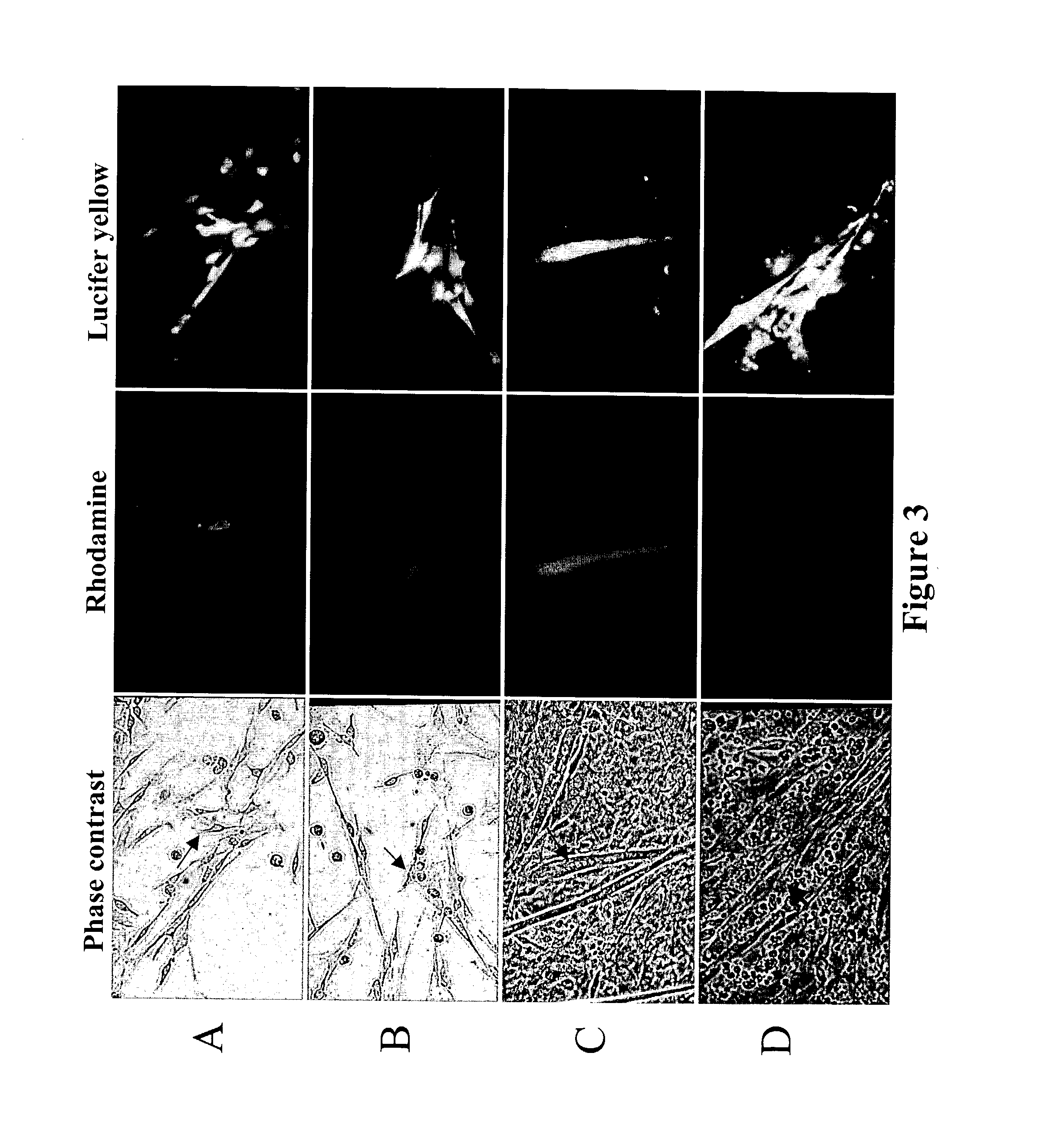
Methods and compositions for correction of cardiac conduction disturbances
The invention provides methods for establishing electrical coupling between cardionyocytes and recombinant cells which have been genetically engineered to express a gap junction protein, eg., Connexin protein such as Connexin 43 (CX43) protein, n invention is based on the discovery that genetic modification of skeletal muscle cells to express a recombinant connexin, enables the genetically modified cells to establish electrocommunication with cardiac cells via gap junctions. The recombinant connexin-expressing cells can be used for repair of cardiac issue and for treatment of cardiac disease by transplantation into cardiac tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Prevention of fibrosis following cardiac injury
InactiveUS20060264367A1Reduce fibrosisReduce activationHormone peptidesPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac fibrosisRelaxin
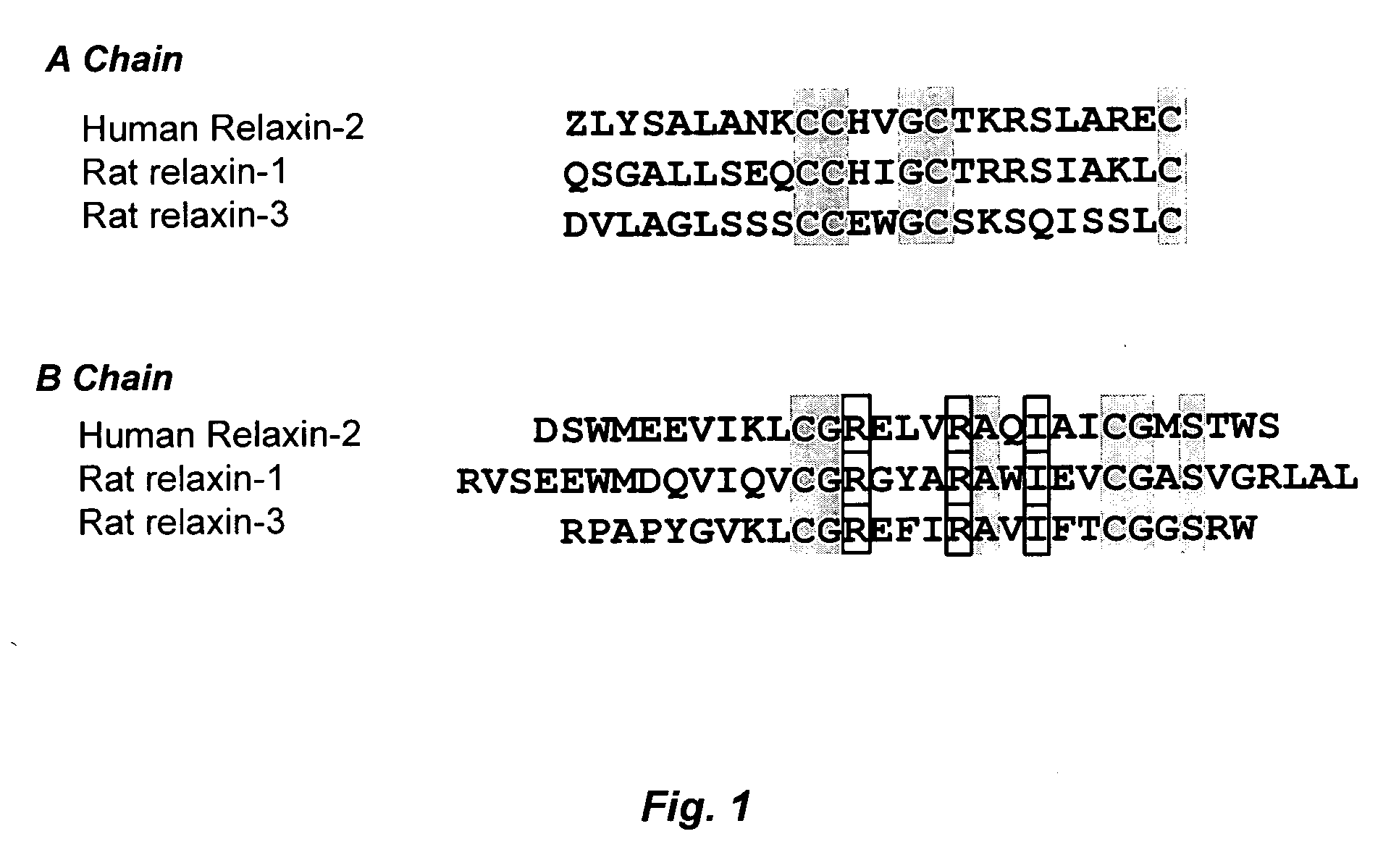
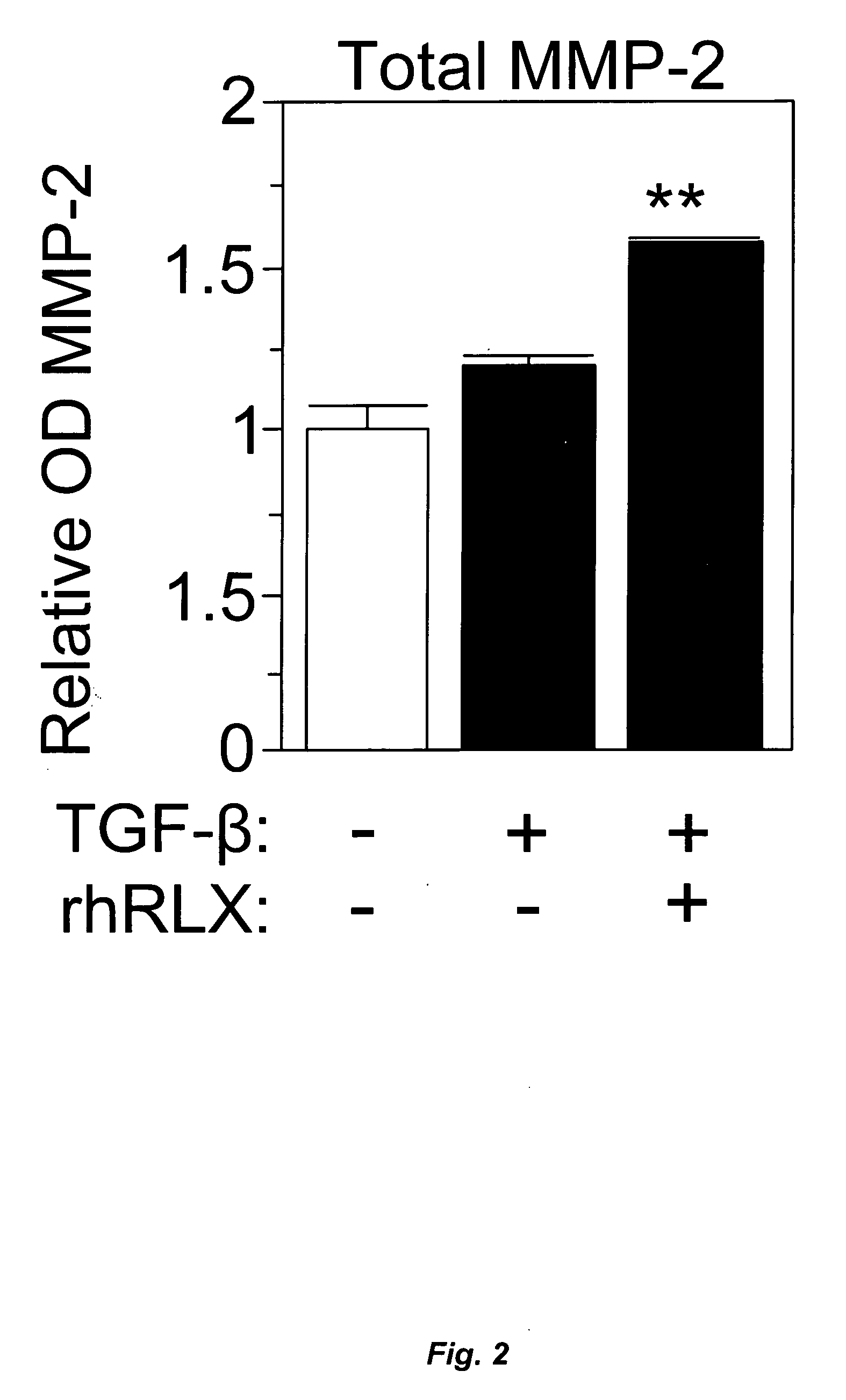
A method for treating cardiac fibrosis resulting from injury of a mammalian heart is described comprising the step of contacting a therapeutically effective amount of relaxin and / or an LGR7 activating agent with cardiac cells following the injury in an amount sufficient to reduce the fibrosis. Also described are methods for protecting the heart following an ischemic event, inhibiting the proliferation of activated fibroblasts and antagonising collagen secretion or deposition in a mammalian heart.
Owner:BAKER MEDICAL RES INST +1
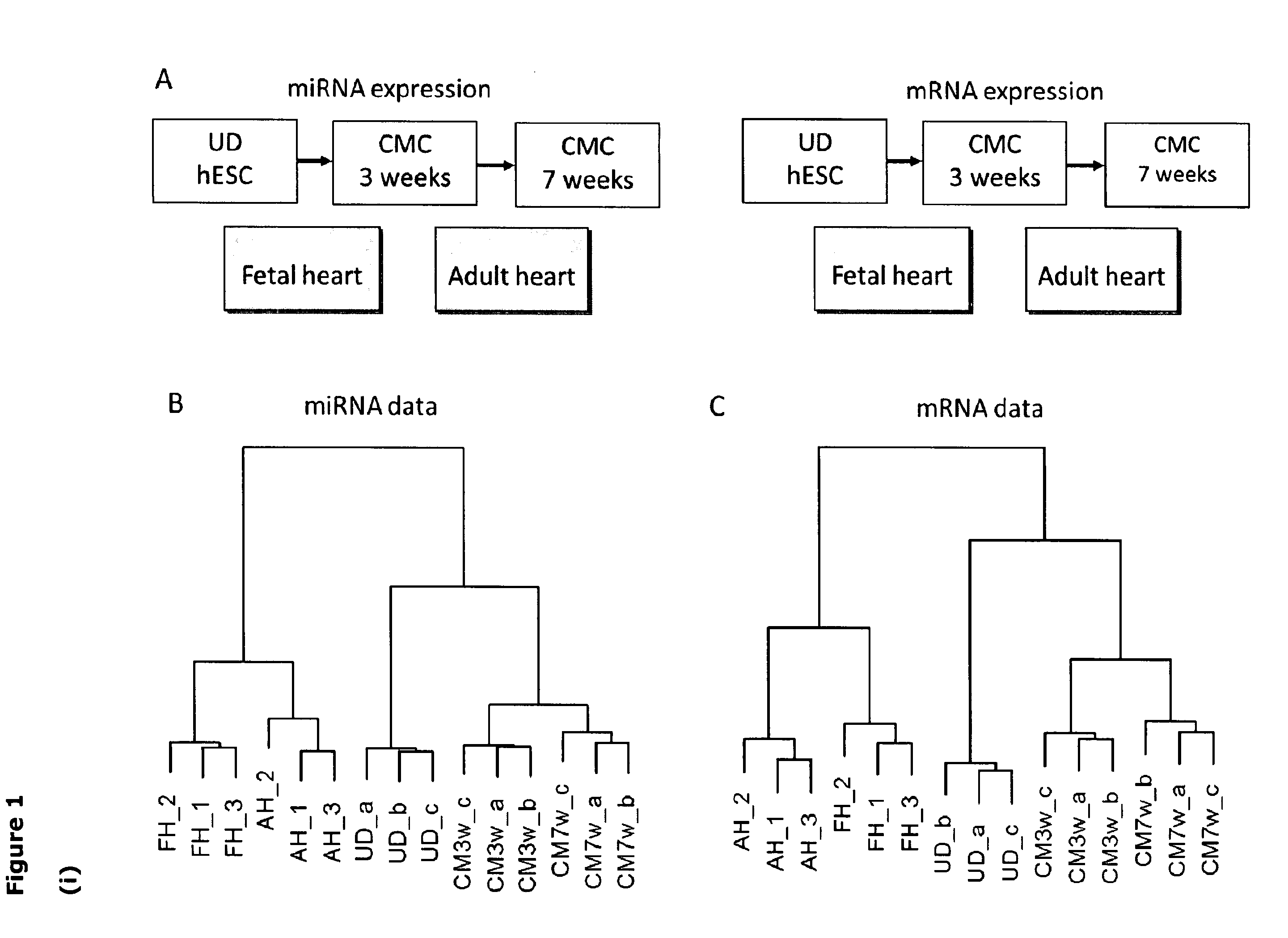
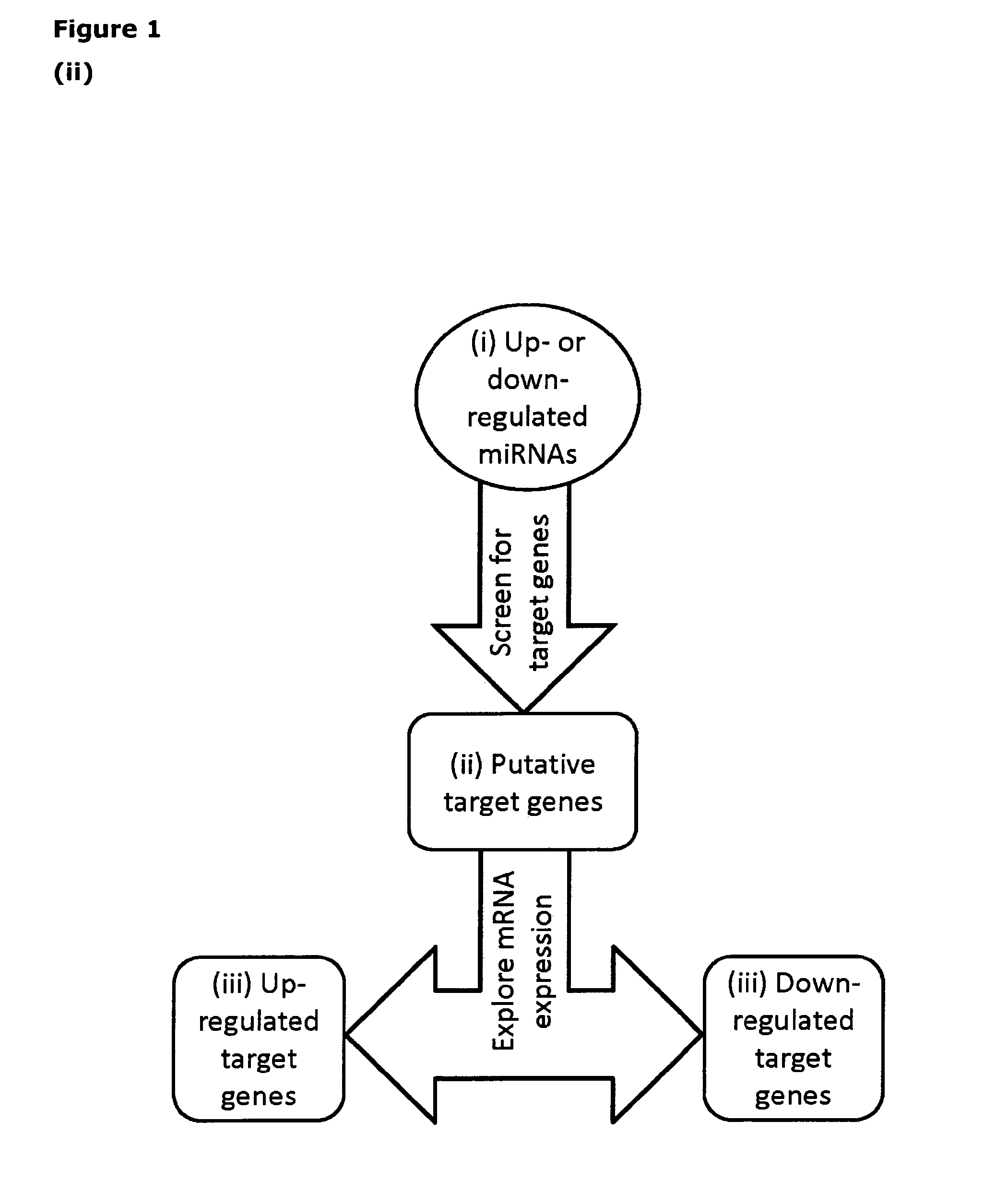
Novel micrornas for the detection and isolation of human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiac cell types
InactiveUS20130150256A1Simple and cheap to manufactureStable storageSugar derivativesLibrary screeningCardiac differentiationCardiac cell
Owner:TAKARA BIO EURO
System and method for enhancing cardiac signal sensing by cardiac pacemakers through genetic treatment
InactiveUS7337011B2Enhancing cardiac pacemaker signal sensingImprove and correct signal to noise ratioTransvascular endocardial electrodesGenetic material ingredientsIon Channel ProteinCardiac pacemaker
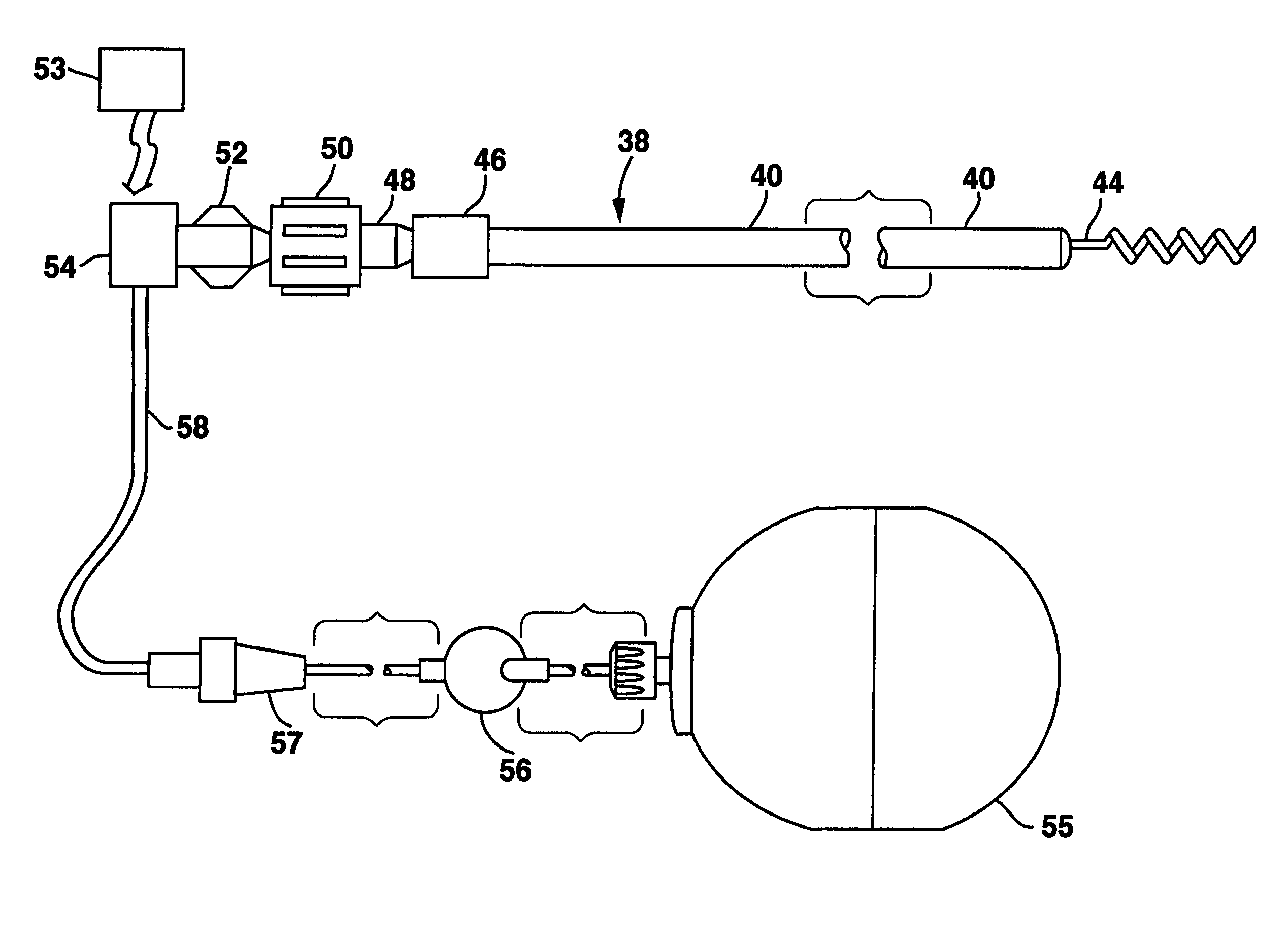
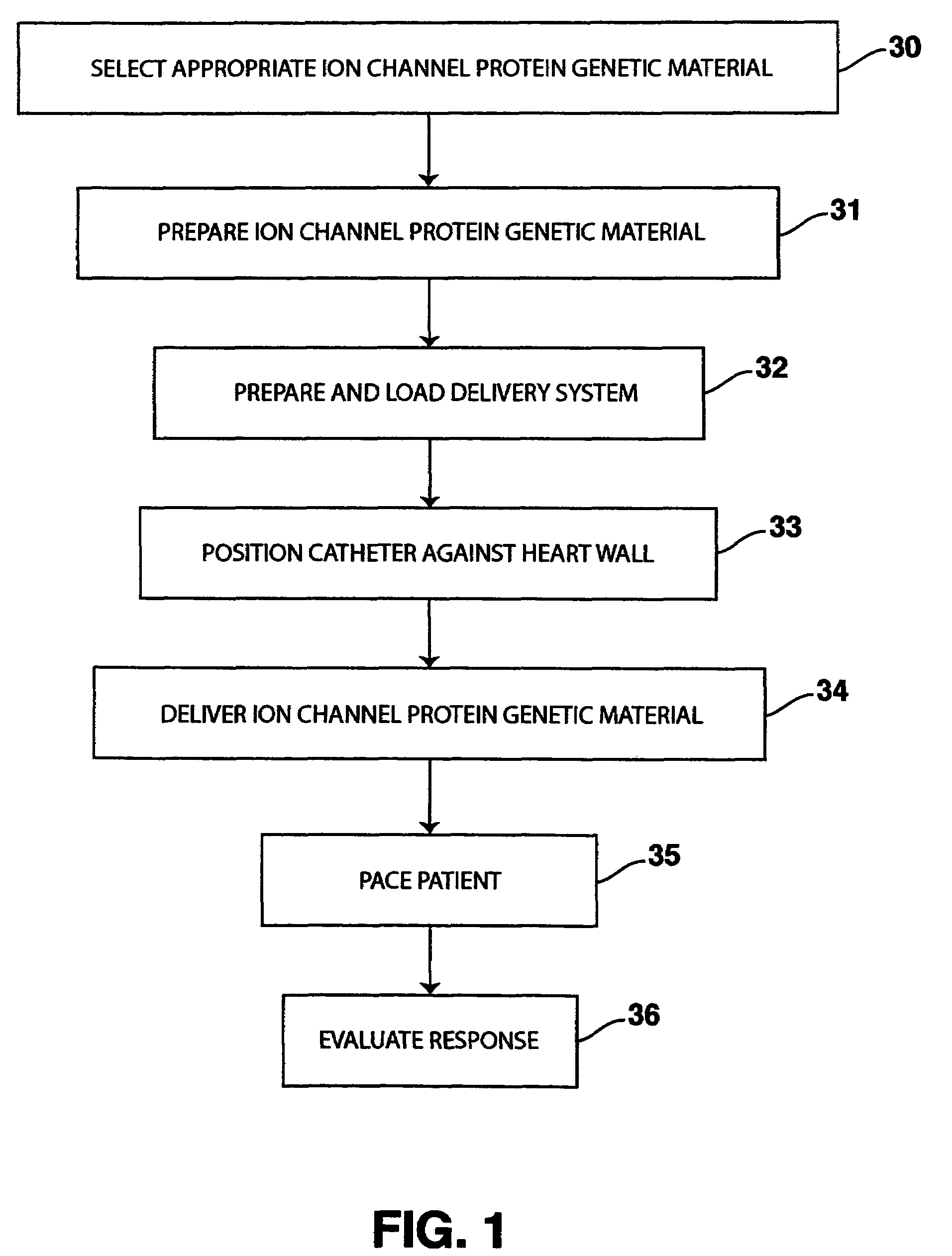
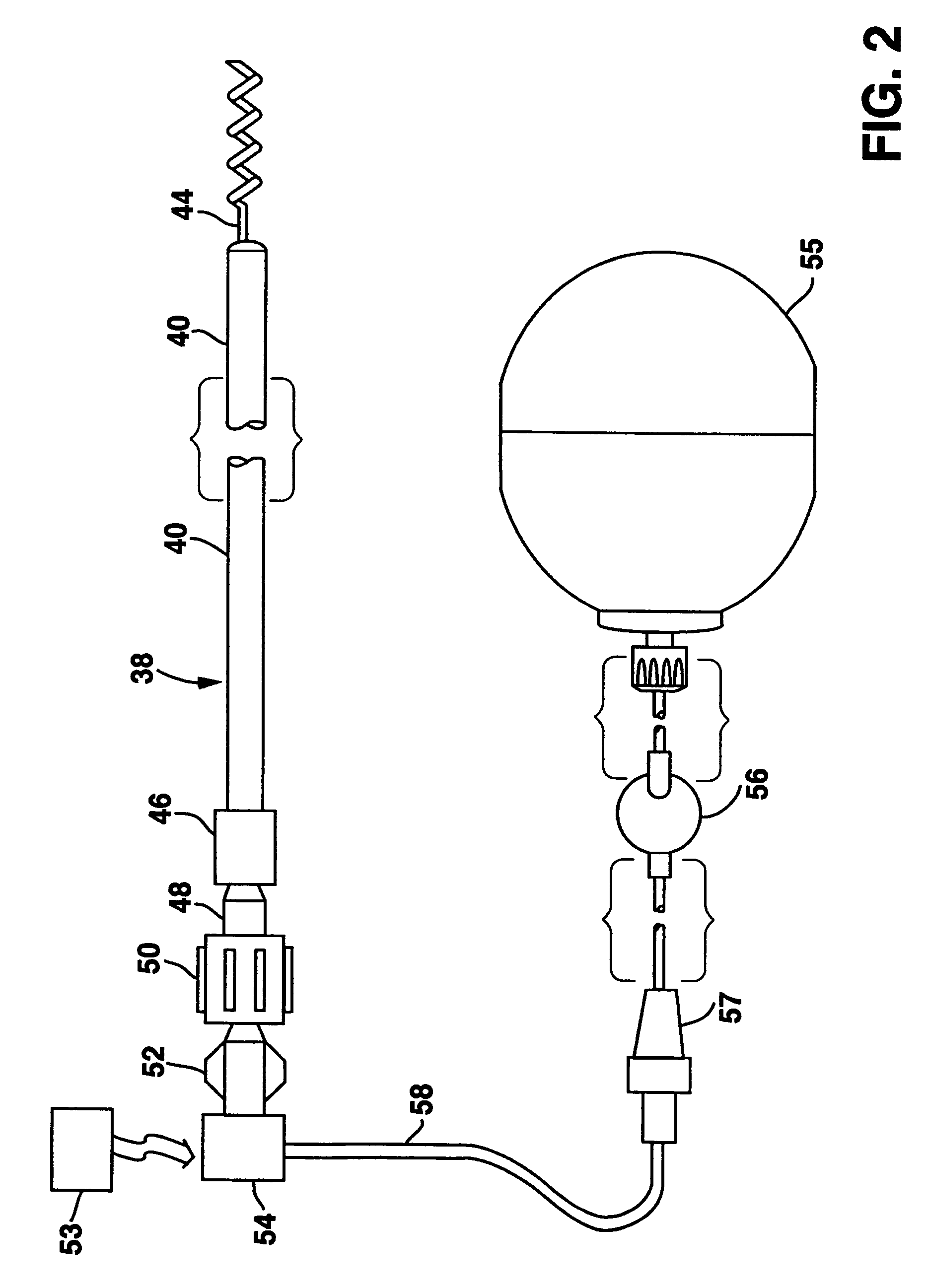
The present invention provides delivery systems for and methods of delivering ion channel protein genetic material to cardiac cells in areas adjacent to where an electrode is to be positioned in a patient's heart to improve or correct the signal to noise ratio of cardiac signals, such as the P-wave. More specifically, there is provided a system and method for delivering sodium ion channel proteins or nucleic acid molecules encoding sodium ion channel proteins to a site in the heart adjacent to an electrode to increase the expression of the same, thereby enhancing the cardiac signal amplitude and enabling improved sensing of cardiac signals by an implanted pacemaker.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Methods of promoting cardiac cell proliferation
InactiveUS20050261189A1Enhance cell viabilityEnhanced signalAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsCardiac muscleCardiac cell
Owner:HYDRA BIOSCIENCES LLC
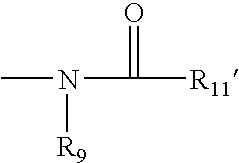
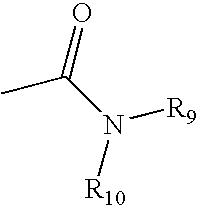
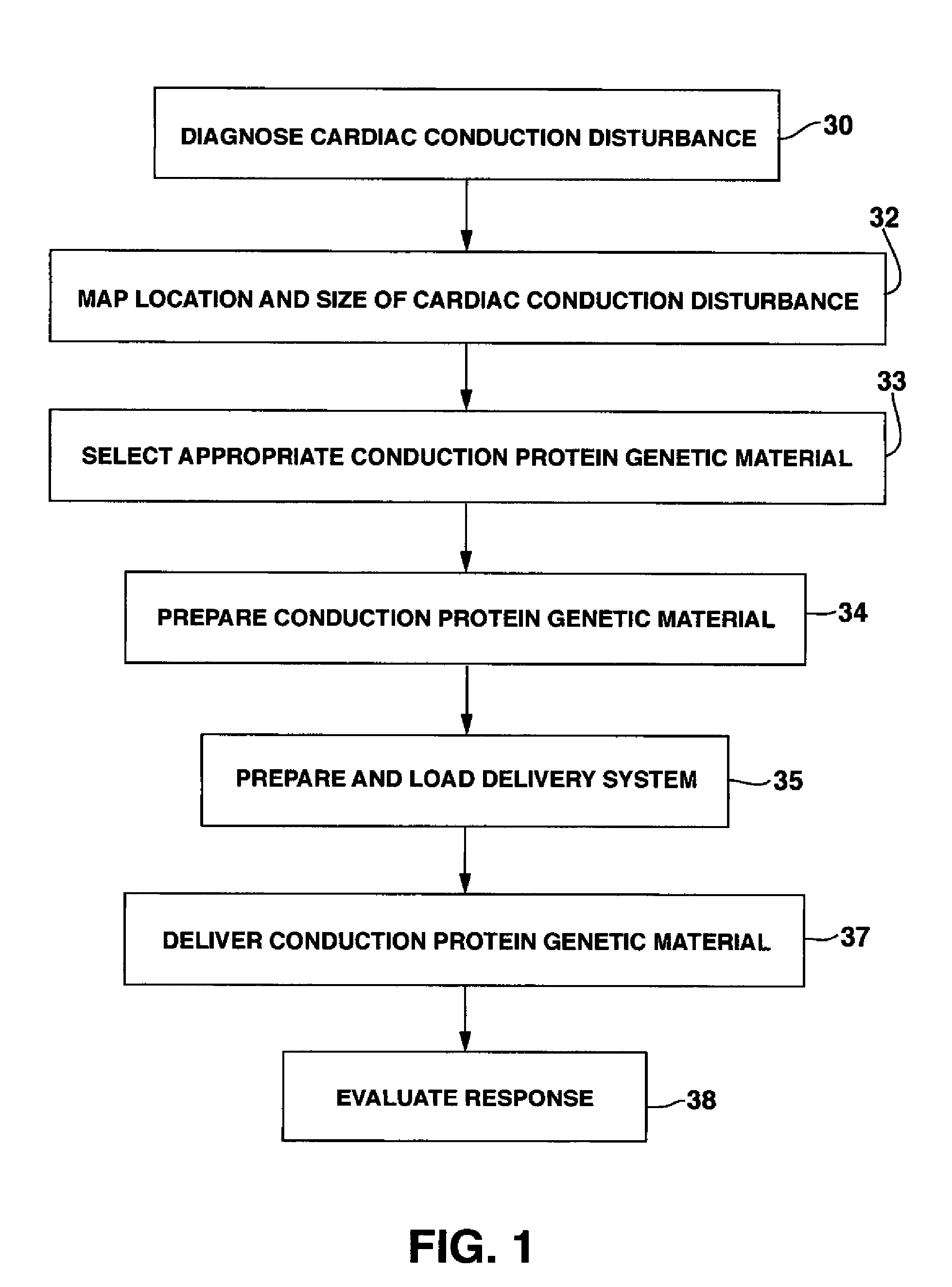
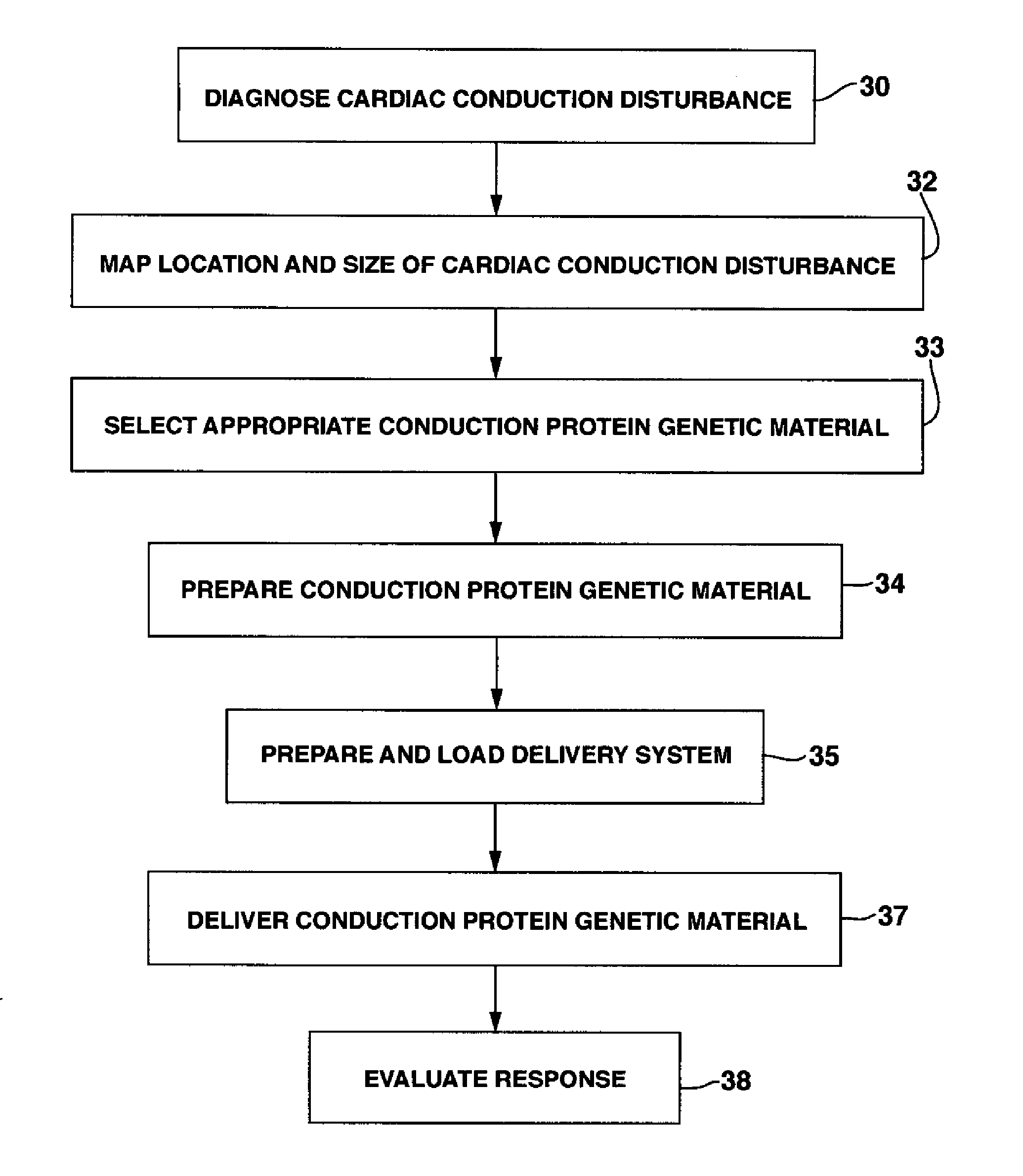
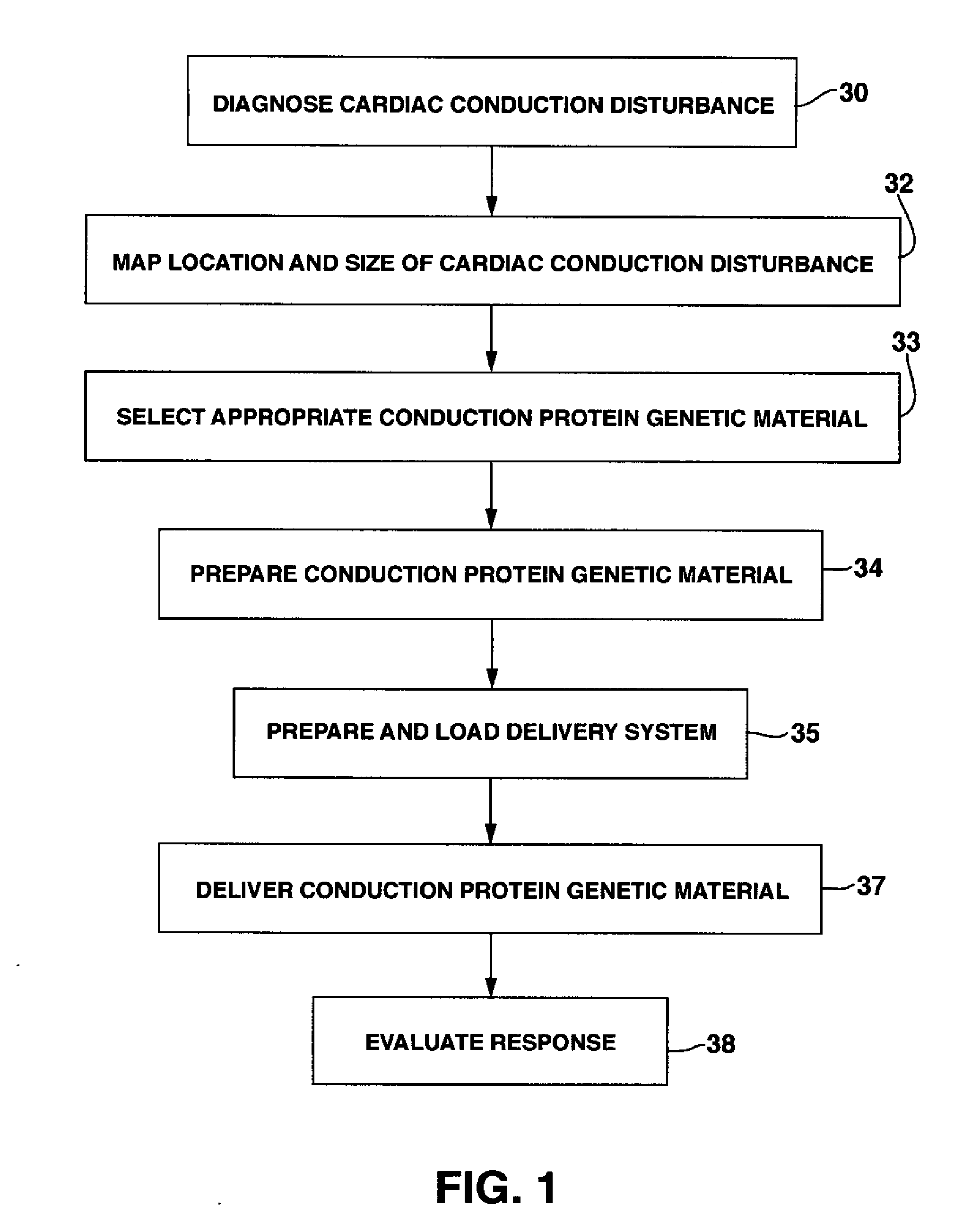
System and method for genetically treating cardiac conduction disturbances
InactiveUS7094201B1Improve cardiac conductionCorrects and improves cardiac conductionPeptide/protein ingredientsInternal electrodesGenetic MaterialsCardiac cell
The present invention provides delivery systems for and methods of delivering conduction protein genetic material to cardiac cells in localized areas of the heart to improve the conductance therein. More specifically, there is provided a system and method for delivering connexin proteins or nucleic acid molecules encoding connexin proteins to a site in the heart which has been determined by mapping procedures to have a conduction disturbance. For cases where conduction is impaired, selected genetic material is delivered to cells around the disturbance area, in order to enhance overall conductivity patterns; in other cases, genetic material is selected to slow conduction in affected areas, so as to prevent, e.g., brady-tachy syndrome.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
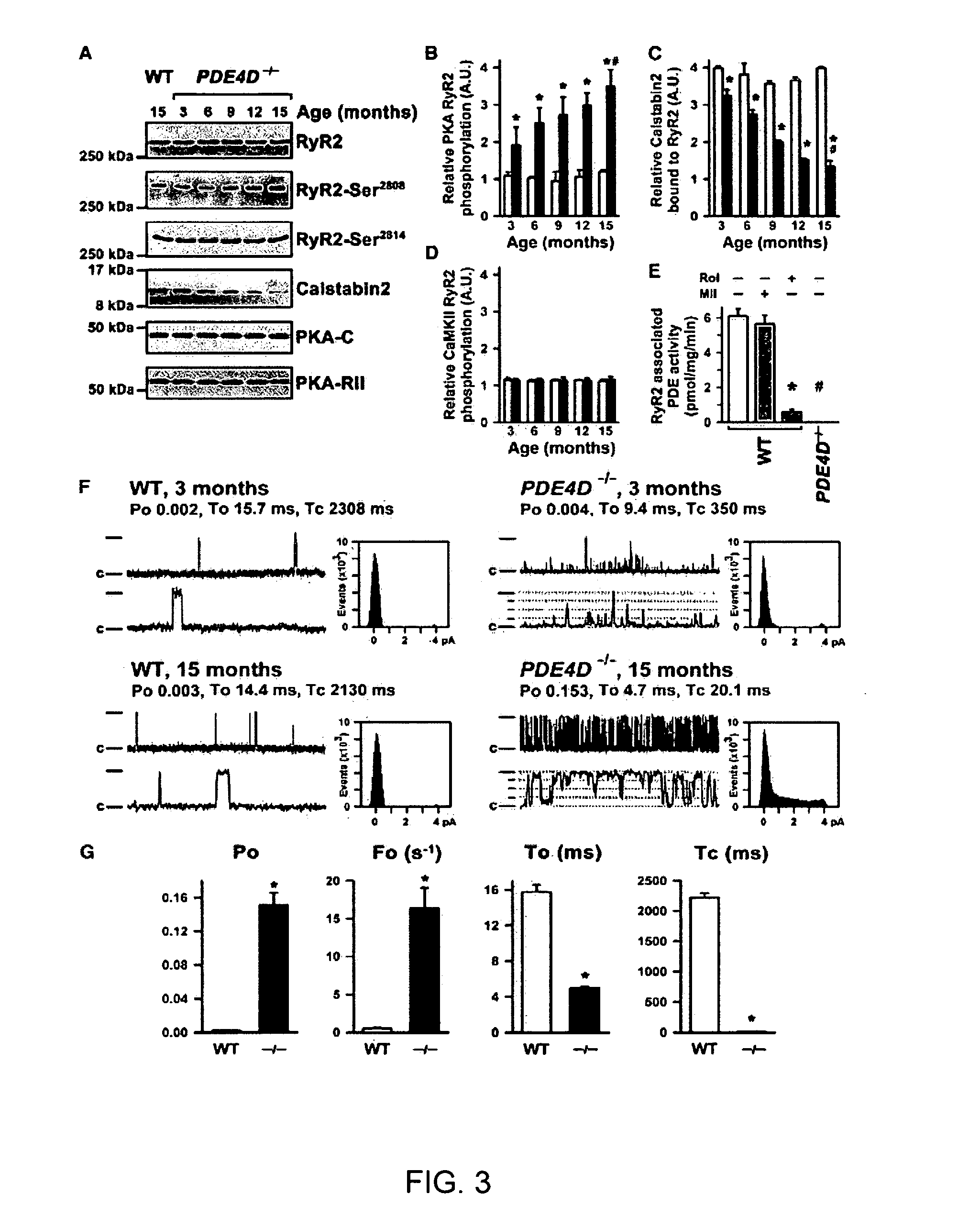
Phosphodiesterase 4D in the ryanodine receptor complex protects against heart failure
InactiveUS20060293266A1Effective treatmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsPhosphodiesteraseRyanodine receptor complex
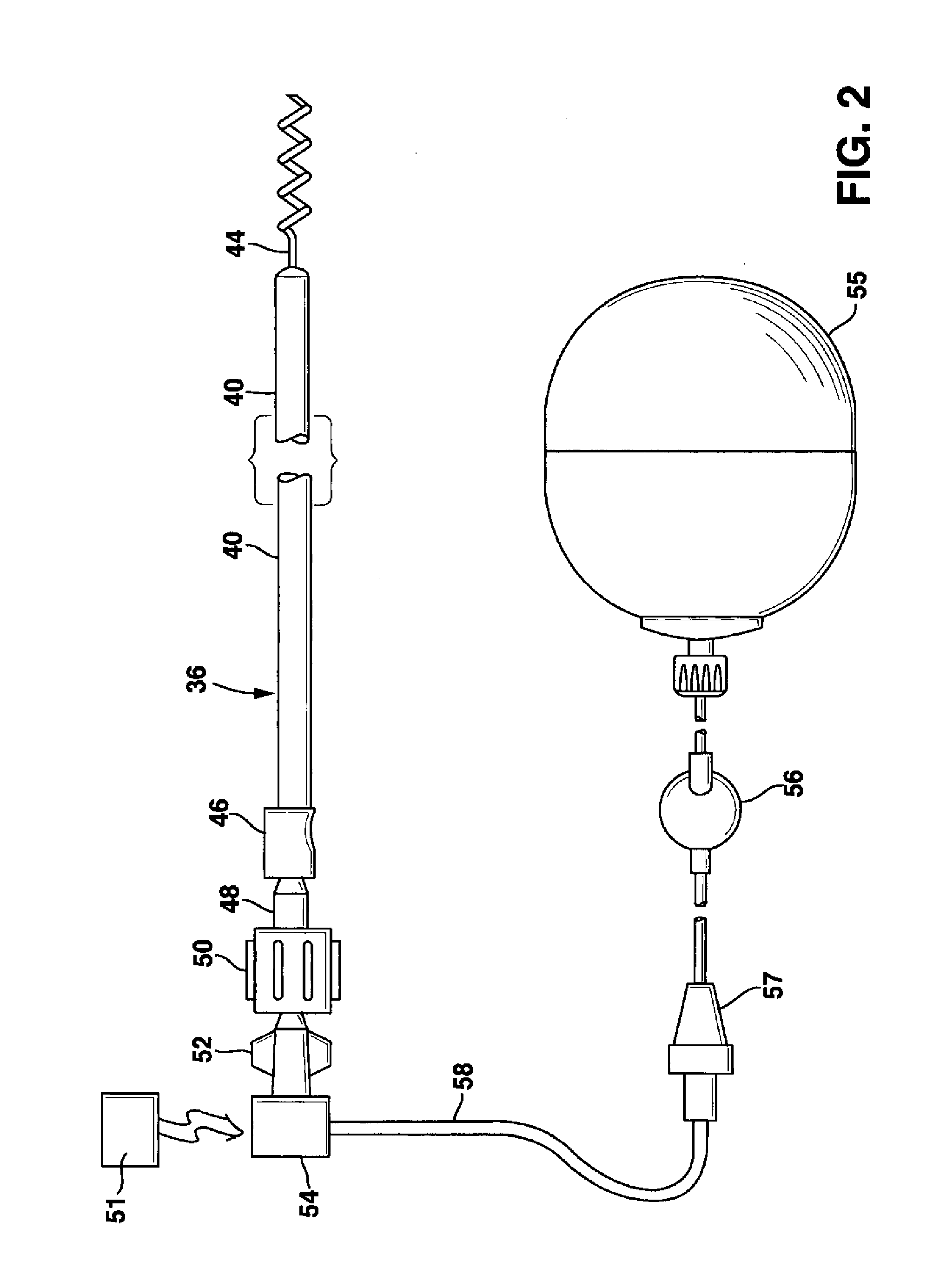
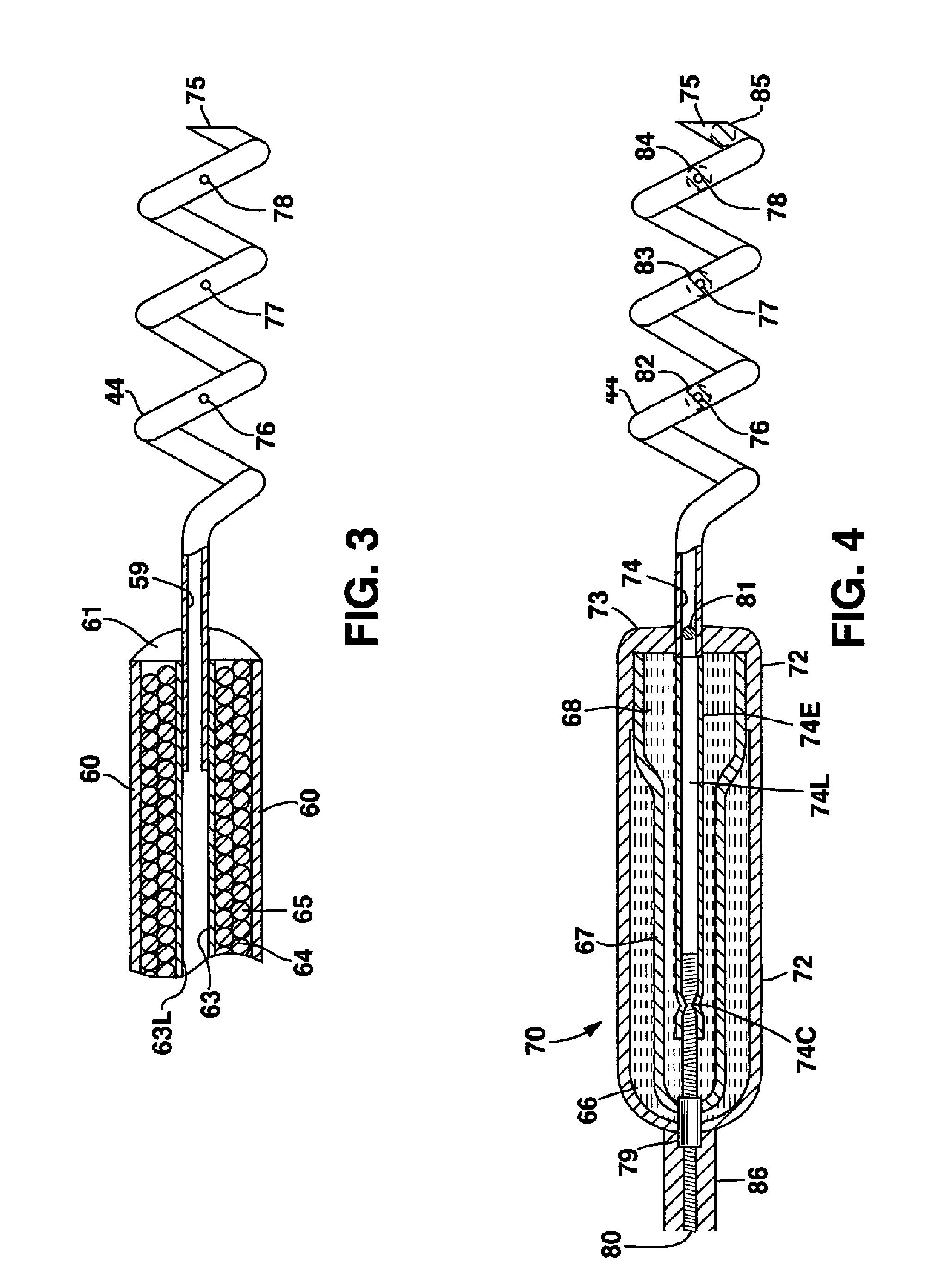
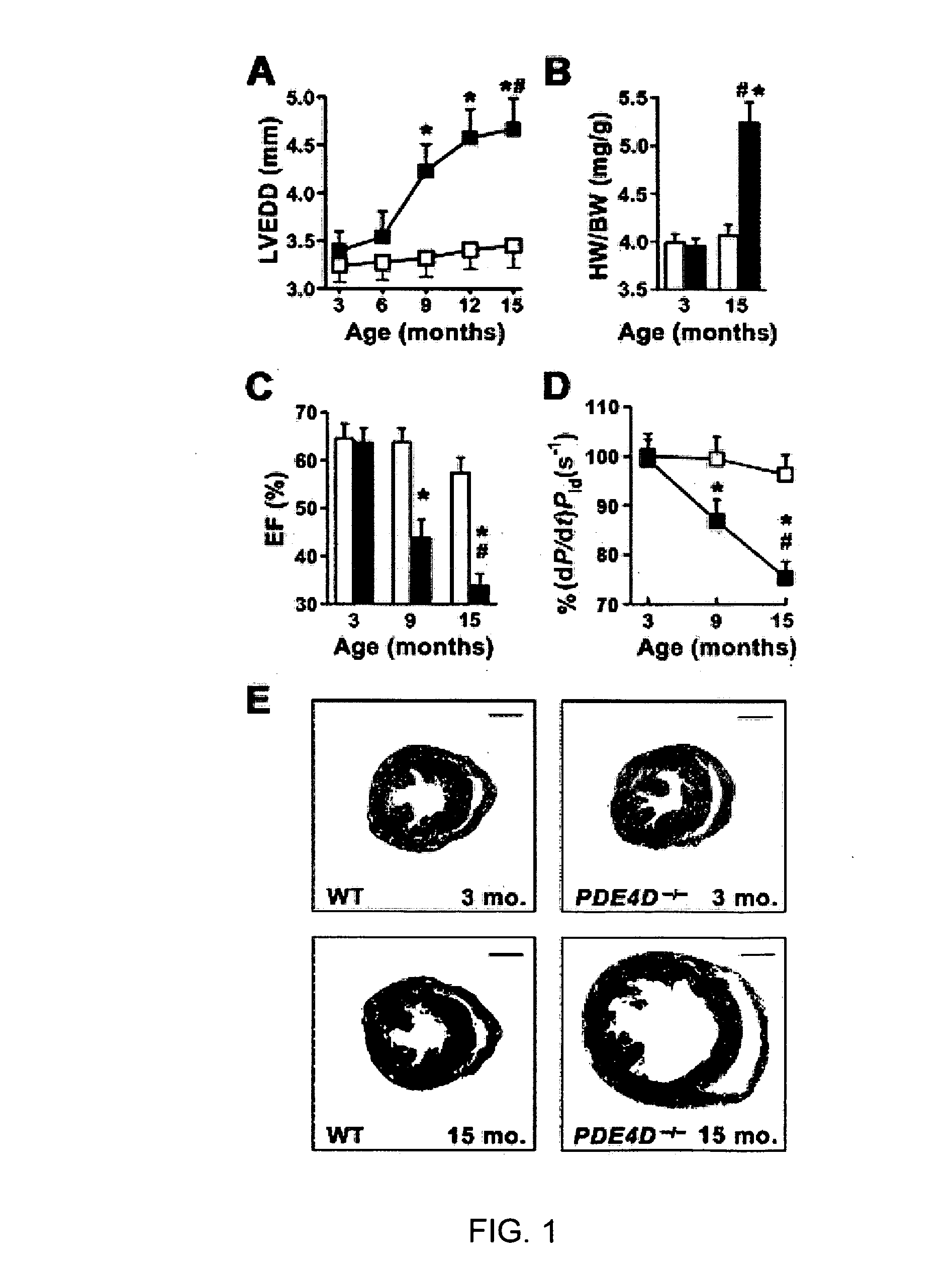
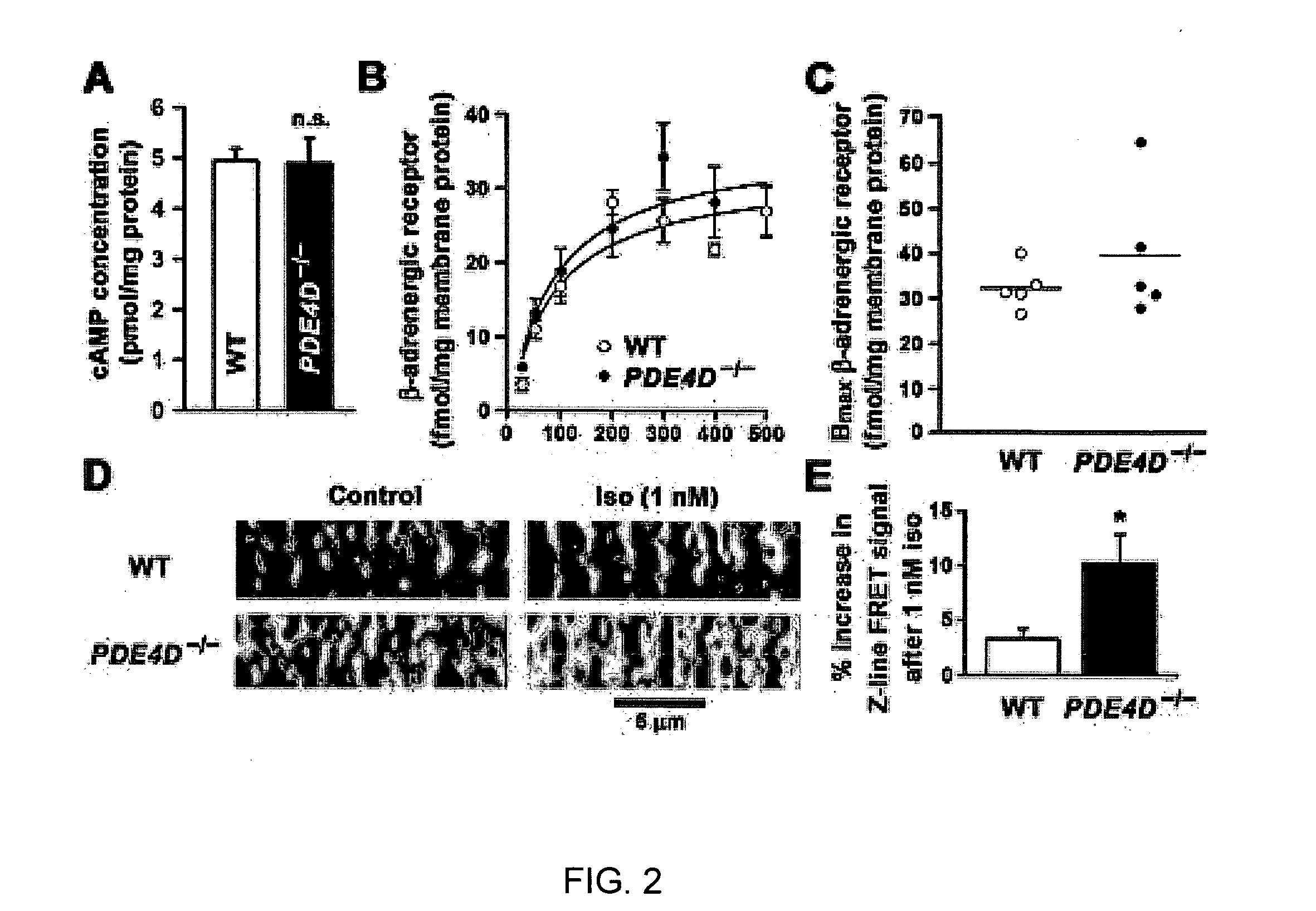
The present invention provides compositions useful for treating and preventing ryanodine receptor associated disorders comprising a PDE-associated agent and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. The present invention also provides methods for treating or preventing ryanodine receptor associated disorders including cardiac disorders and diseases, skeletal muscular disorders and diseases, cognitive disorders and diseases malignant hyperthermia, diabetes and sudden infant death syndrome. The present invention further provides methods for regulating PKA phosphorylation of a ryanodine receptor as well as methods for regulating Ca+2 release and reuptake in cells. Also provided are kits for use in delivering a PDE-associated agent to cardiac cells in a subject, comprising the composition of the present invention and a catheter.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
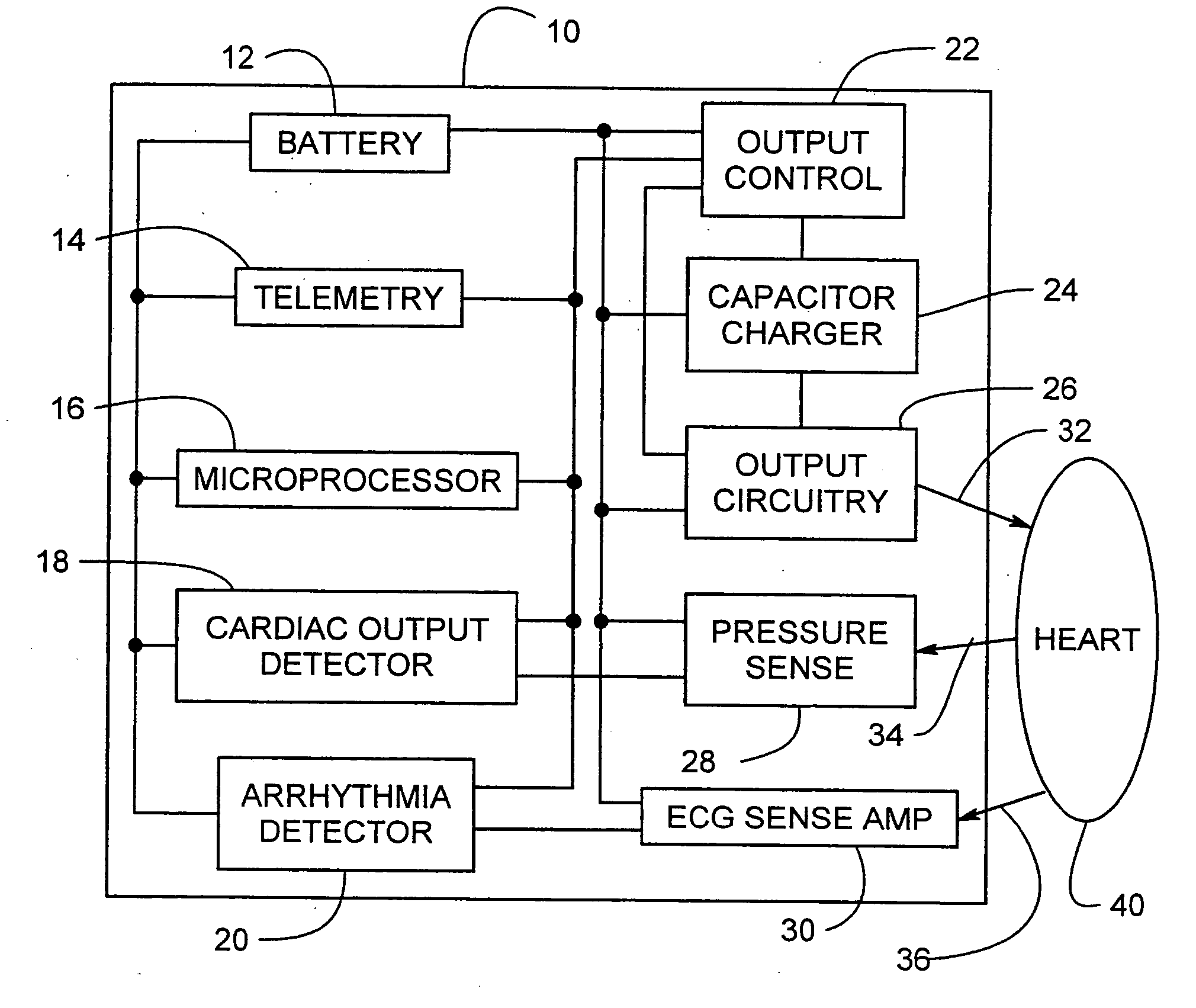
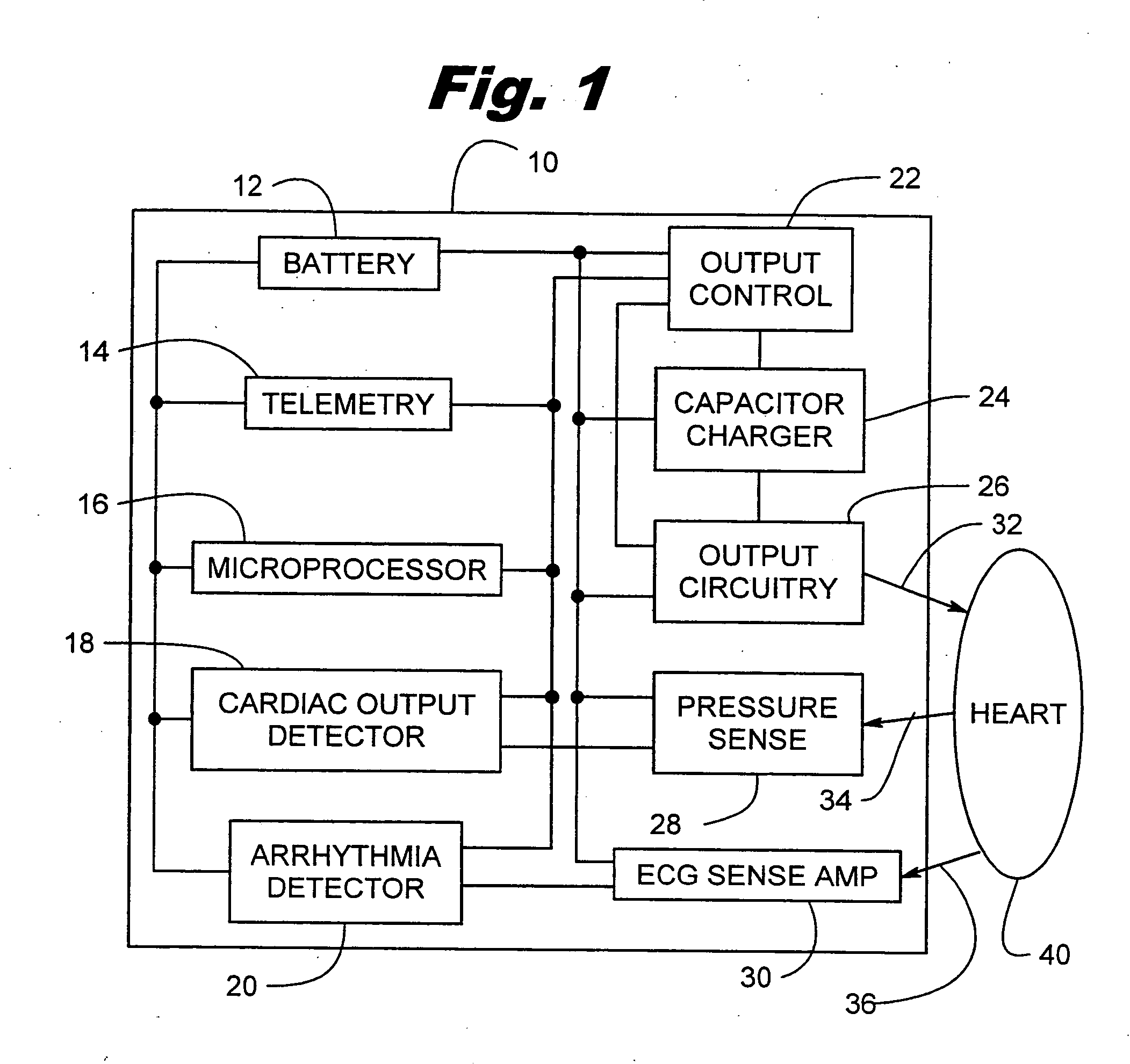
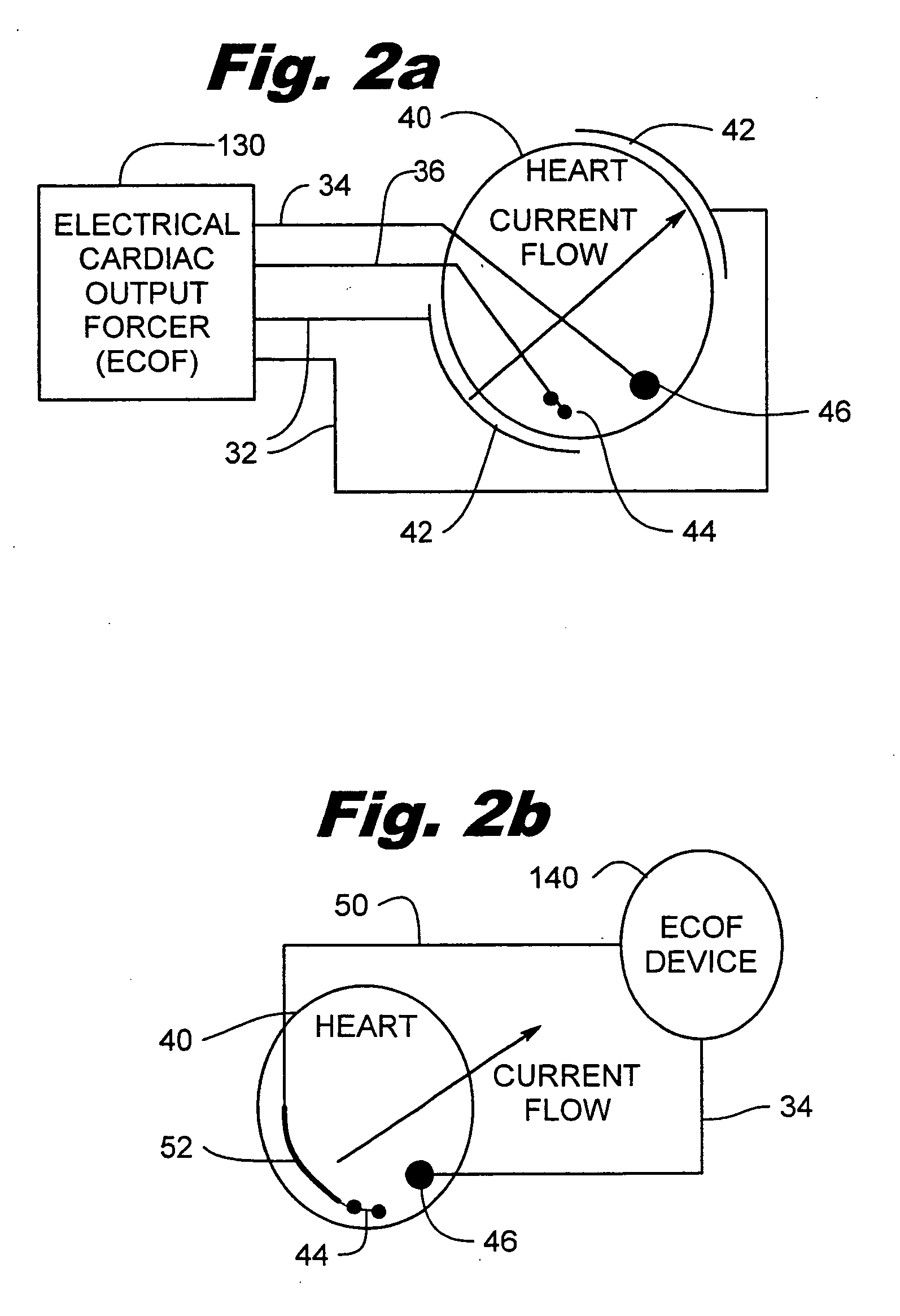
Electrical cardiac output forcer
InactiveUS20050197676A1Maintain consciousnessLife maintenanceHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeCardiac cell
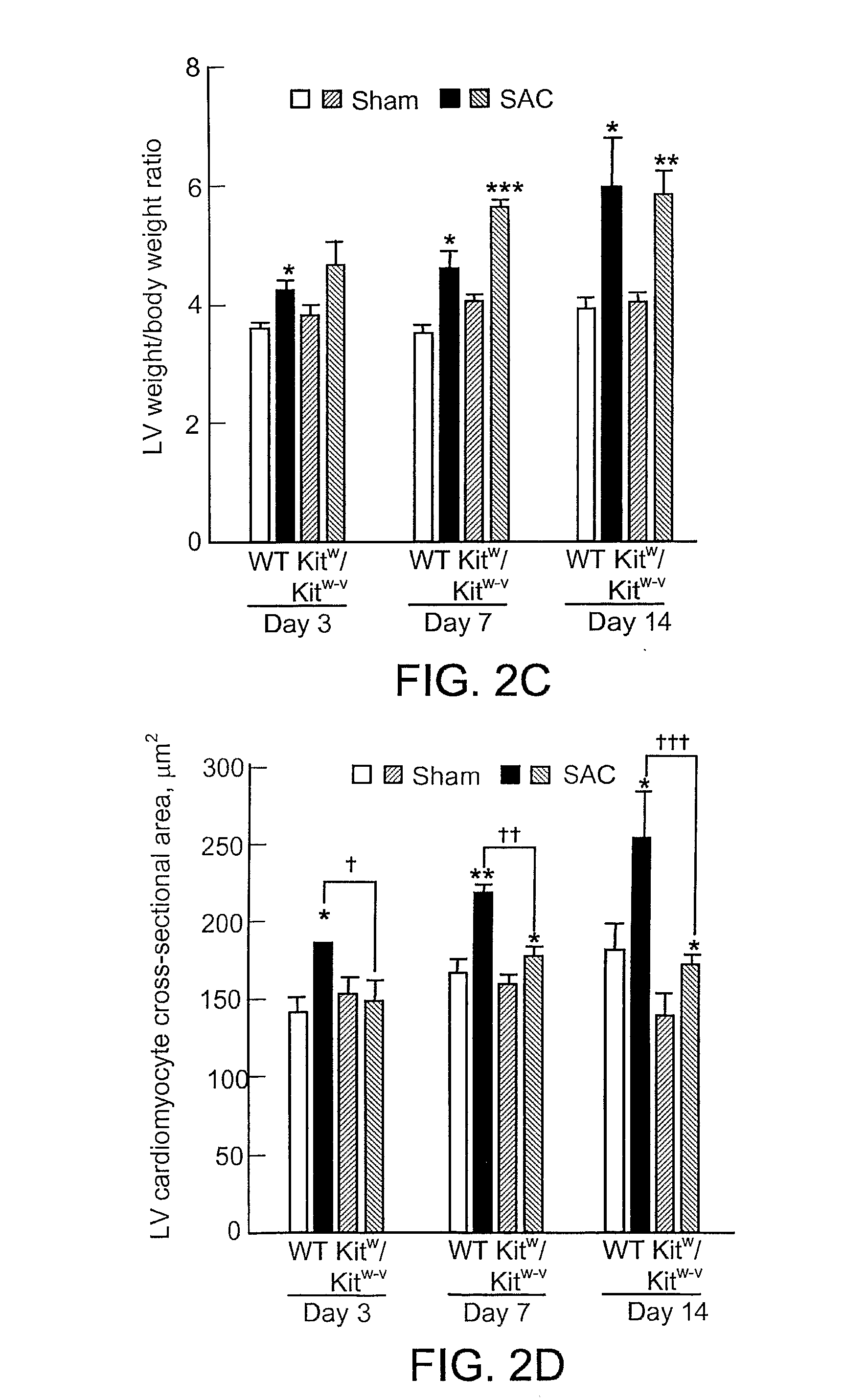
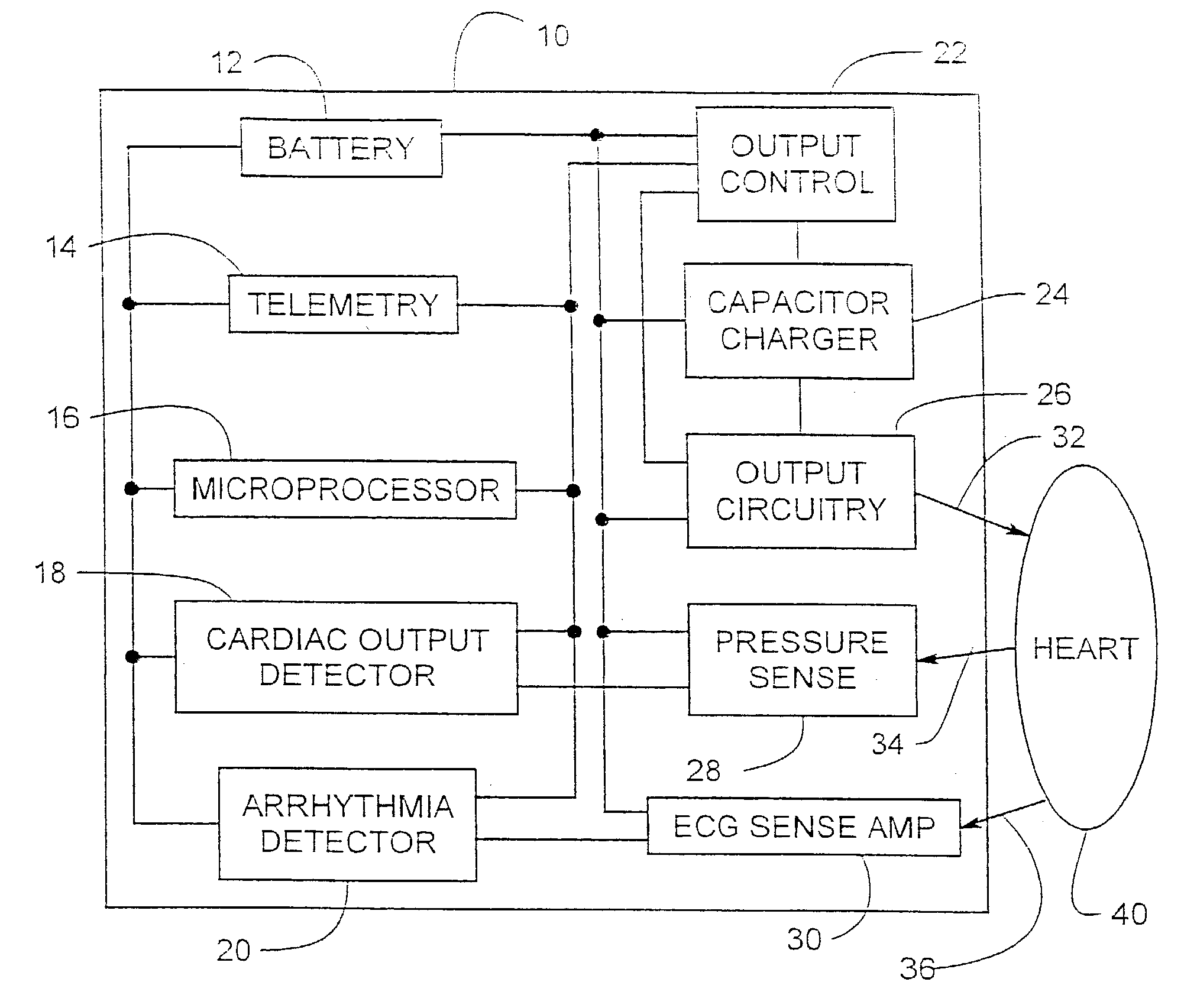
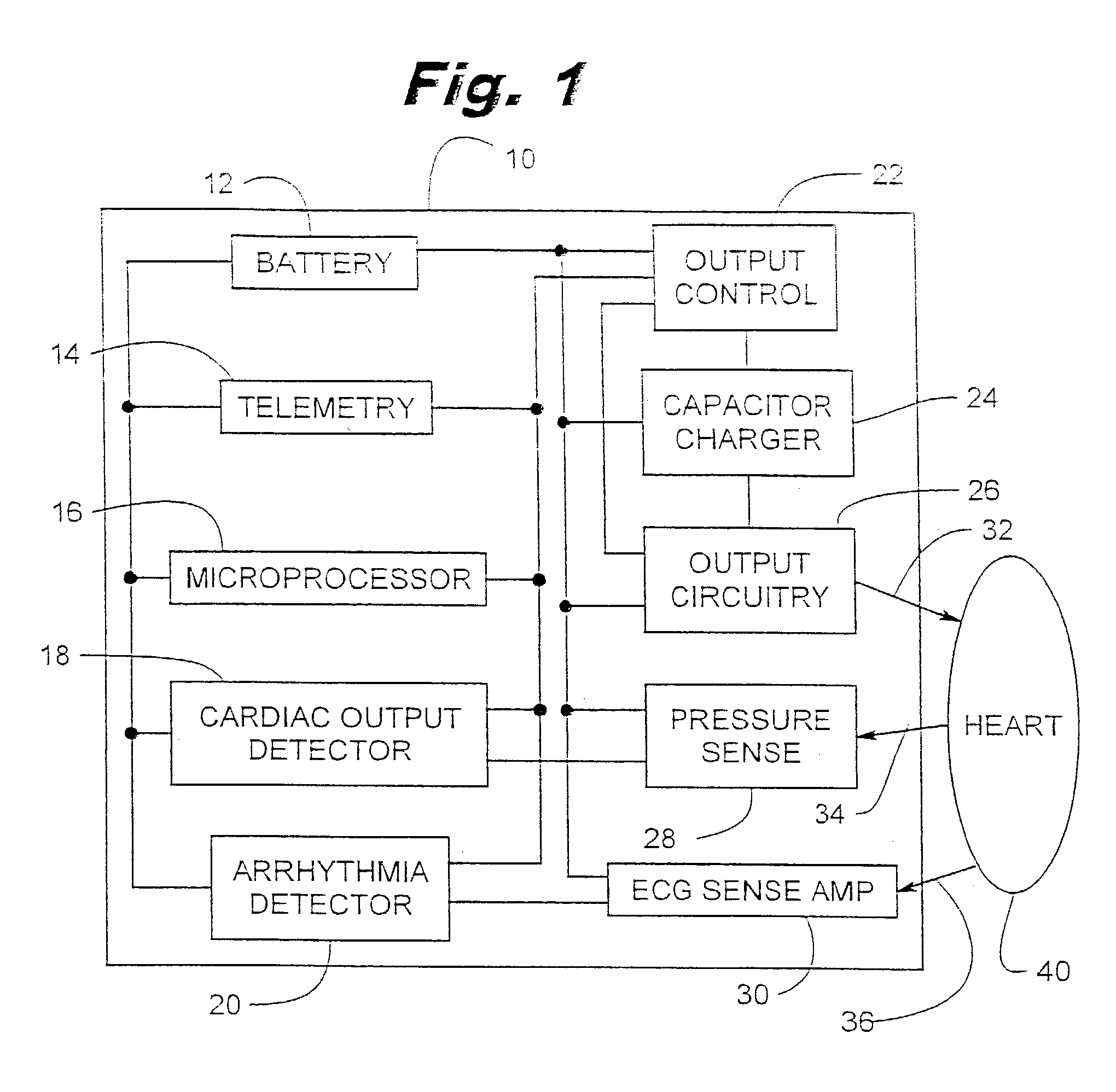
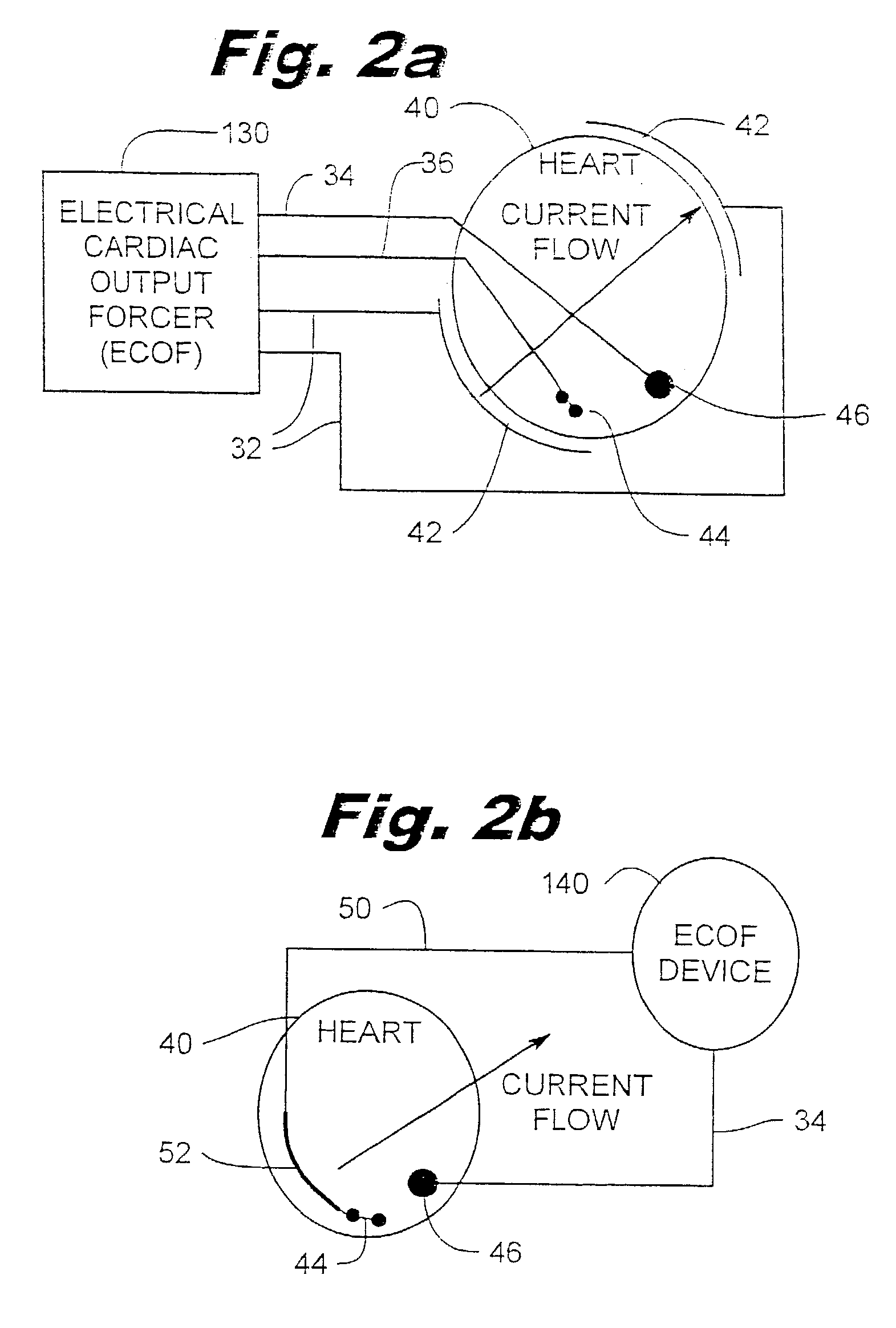
An electrical method and apparatus for stimulating cardiac cells causing contraction to force hemodynamic output during fibrillation, hemodynamically compromising tachycardia, or asystole. Forcing fields are applied to the heart to give cardiac output on an emergency basis until the arrhythmia ceases or other intervention takes place. The device is used as a stand alone external or internal device, or as a backup to an ICD, atrial defibrillator, or an anti-tachycardia pacemaker. The method and apparatus maintain some cardiac output and not necessarily defibrillation.
Owner:GALVANI
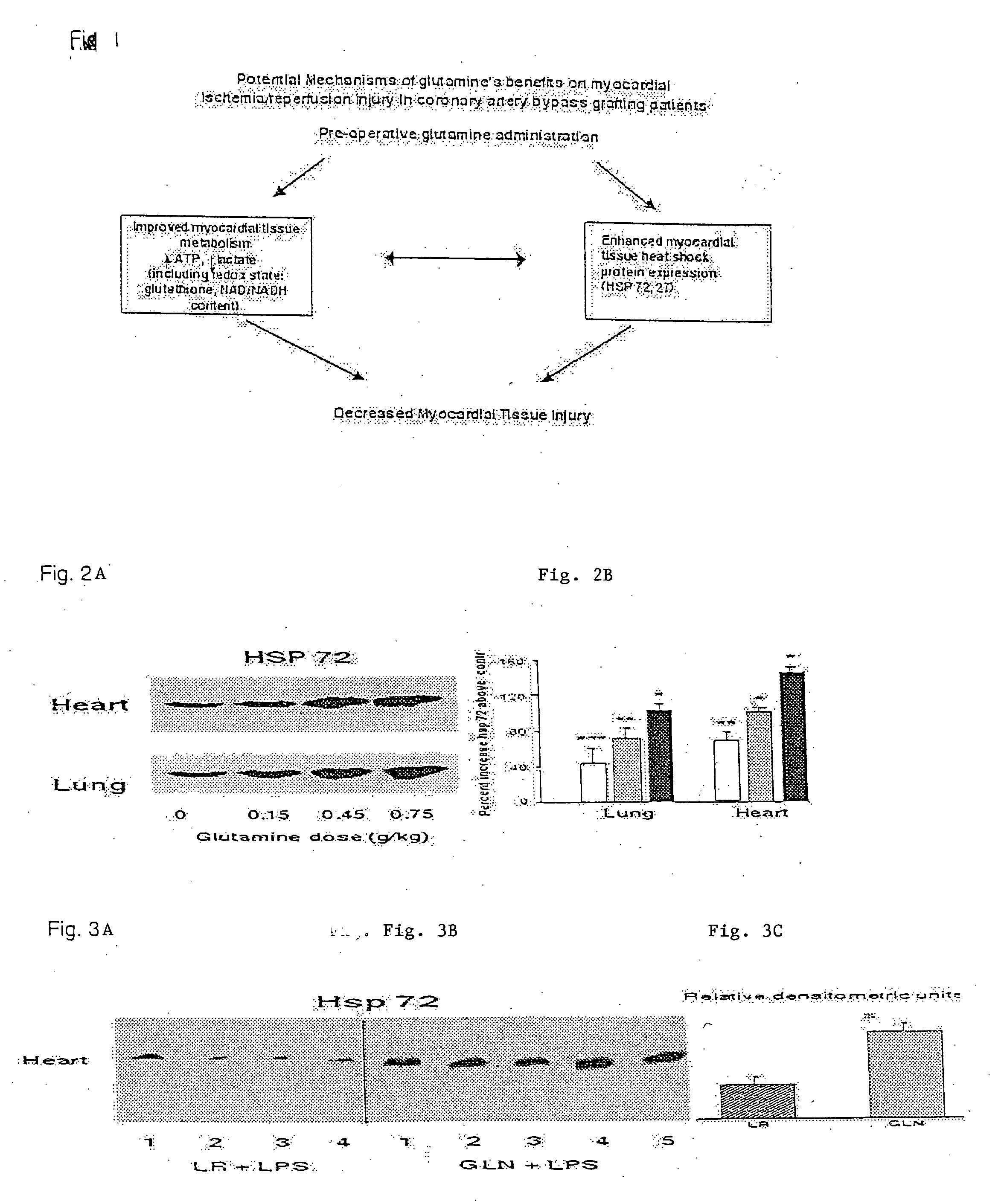
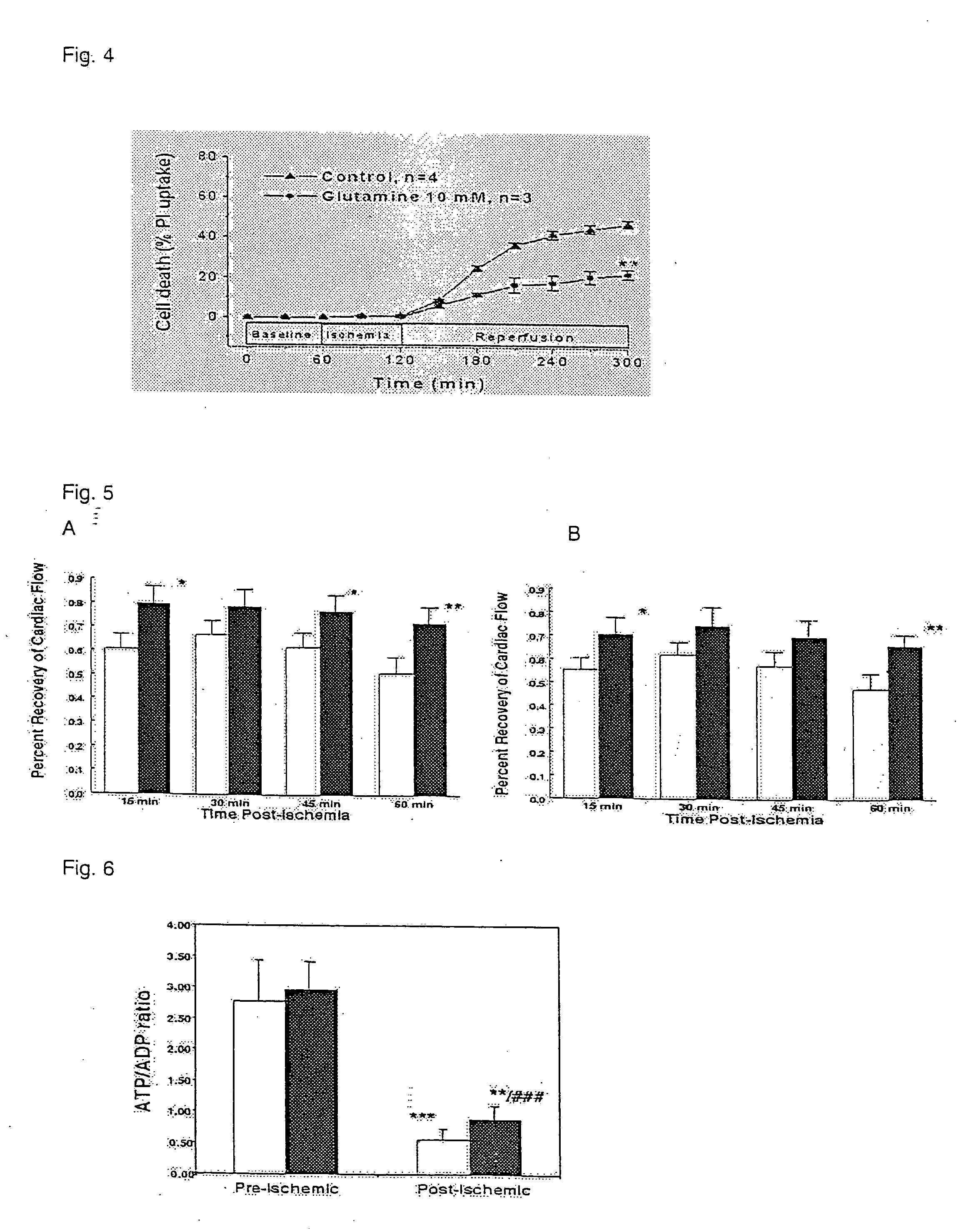
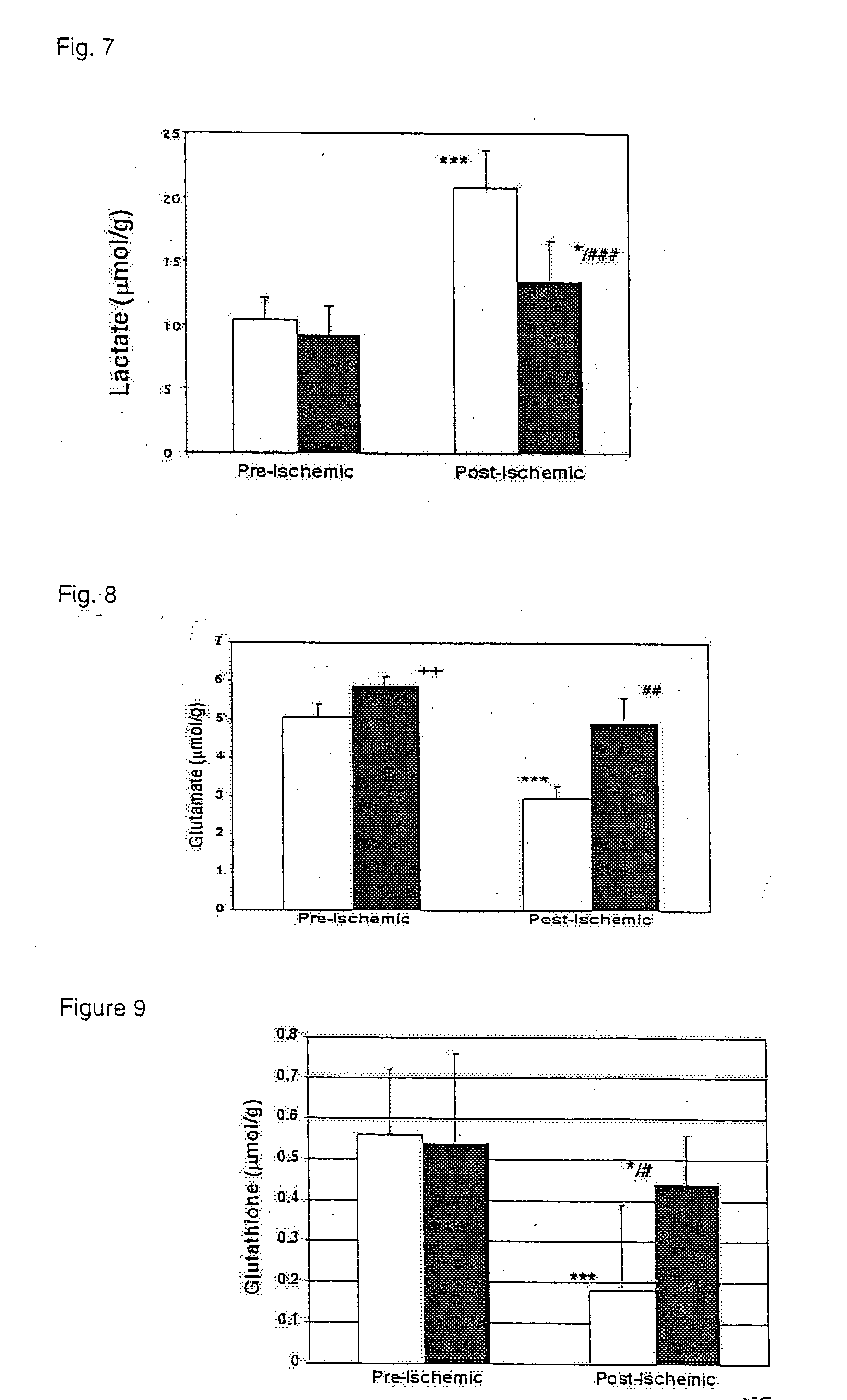
Glutamine for use in treating injury
InactiveUS20050059610A1Increase productionHigh expressionBiocideOrganic active ingredientsHeat shockMedicine
A method of treating a problem relating to tissue metabolism by administering to a patient in need a single dose of glutamine in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Also provided is glutamine for the treatment of an injury relating to tissue metabolism and for preventing cardiac cell damage. A therapeutic composition for treating and preventing cellular metabolic injury, preventing cardiac cell damage, and increasing heat shock protein expression where in the therapeutic includes a single dose of glutamine in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier is also provided. A method of increasing the expression of heat shock proteins by administering a single dose of glutamine in a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier to a location in need is further provided.
Owner:UNIV OF COLORADO THE REGENTS OF
Methods and compositions for correction of cardiac conduction disturbances
The invention provides methods for establishing electrical coupling between cardiomyocytes and recombinant cells which have been genetically engineered to express a connexin protein such as connexin 43 (Cx43) protein. The invention is based on the discovery that genetic modification of skeletal muscle cells to express a recombinant connexin, enables the genetically modified cells to establish electrocommunication with cardiac cells via gap junctions. The recombinant connexin-expressing cells can be used for repair of cardiac tissue and for treatment of cardiac disease by transplantation into cardiac tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
System and Method for Genetically Treating Cardiac Conduction Disturbances
InactiveUS20080008688A1Improve cardiac conductionCorrects and improves cardiac conductionBiocideElectrotherapyGenetic MaterialsCardiac cell
The present invention provides delivery systems for and methods of delivering conduction protein genetic material to cardiac cells in localized areas of the heart to improve the conductance therein. More specifically, there is provided a system and method for delivering connexin proteins or nucleic acid molecules encoding connexin proteins to a site in the heart which has been determined by mapping procedures to have a conduction disturbance. For cases where conduction is impaired, selected genetic material is delivered to cells around the disturbance area, in order to enhance overall conductivity patterns; in other cases, genetic material is selected to slow conduction in affected areas, so as to prevent, e.g., brady-tachy syndrome.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Method and apparatus for delivering a biphasic defibrillation pulse with variable energy
Owner:ZOLL MEDICAL CORPORATION
Method and system for generating spatially and temporally controllable concentration gradients
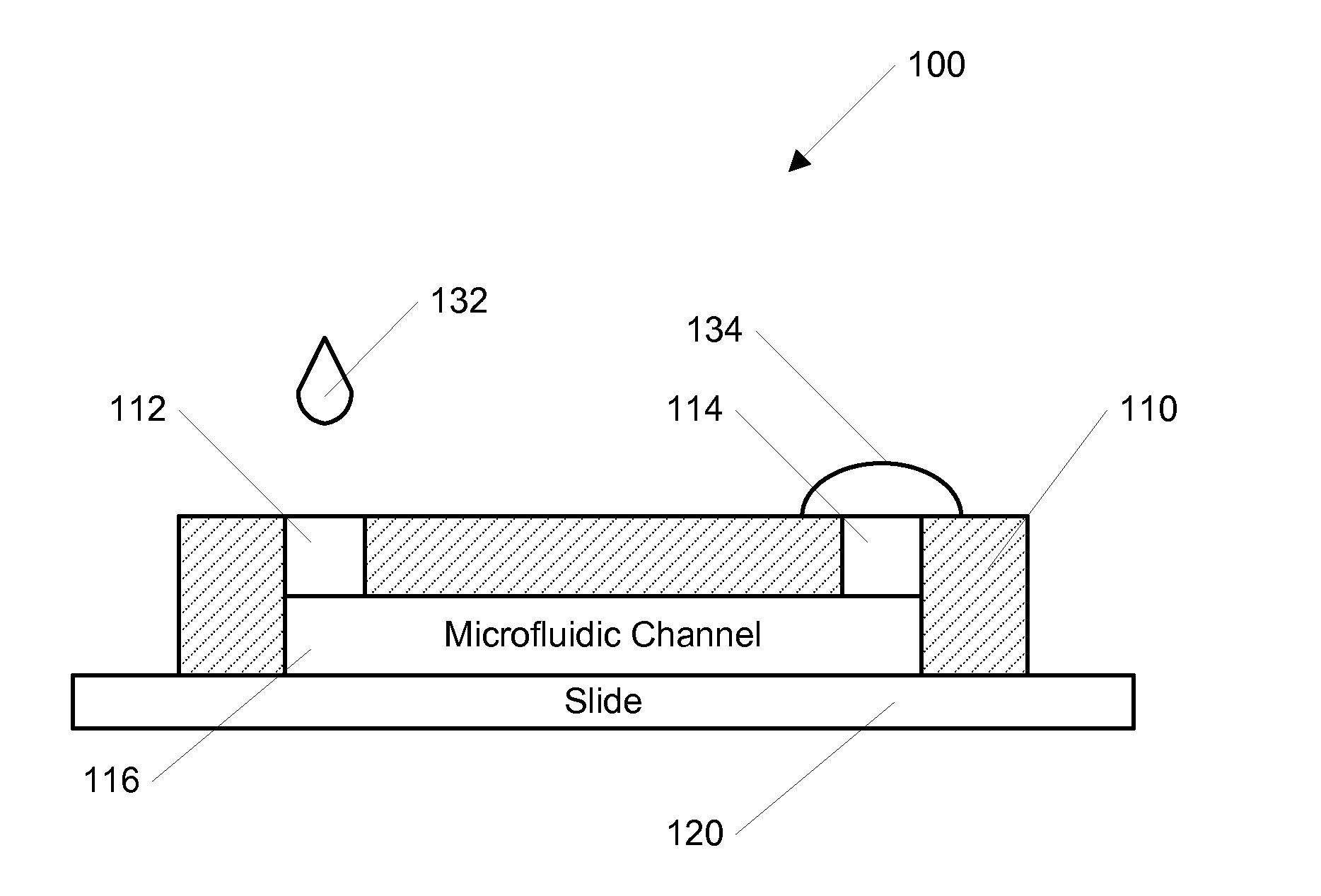
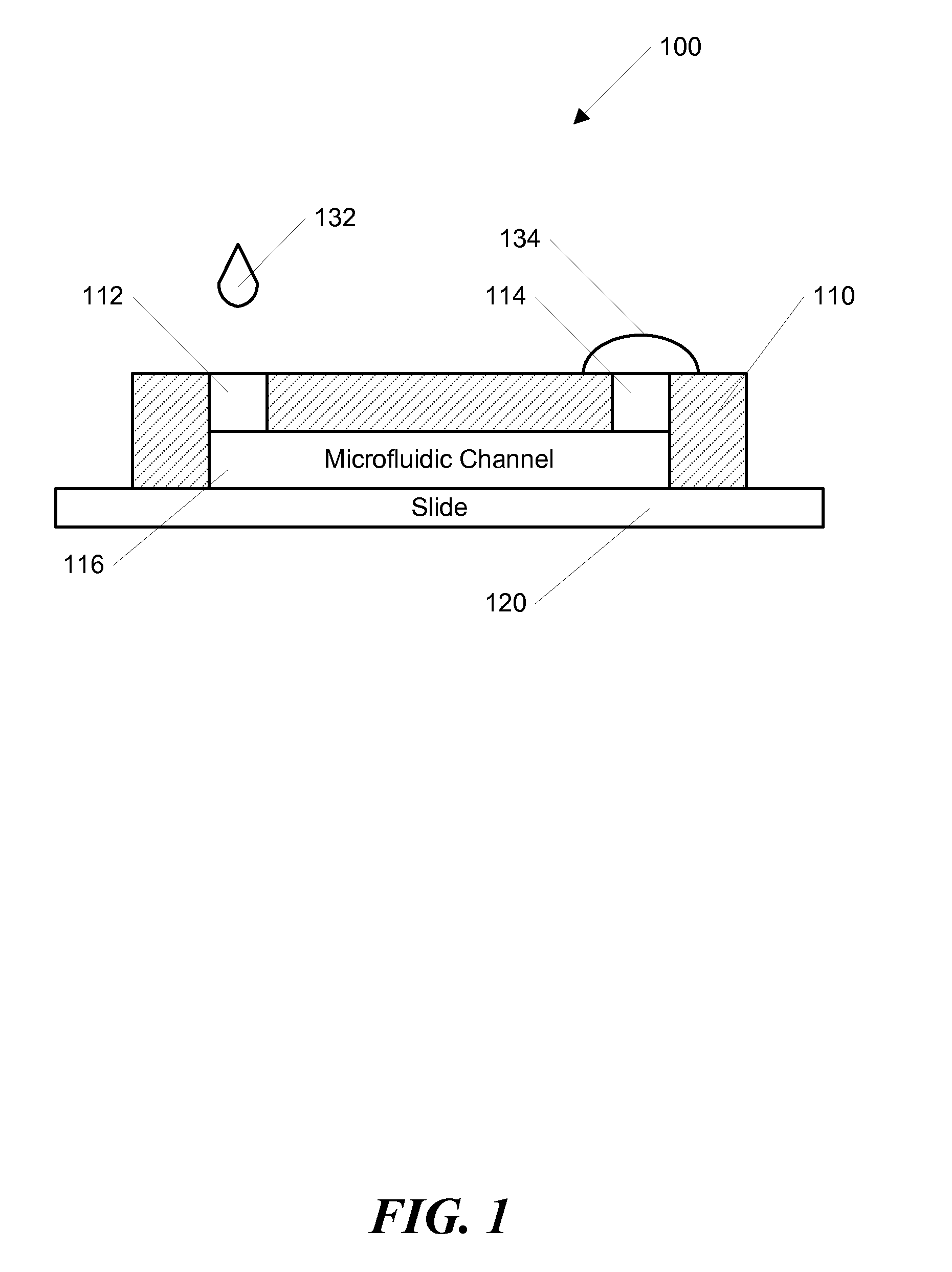
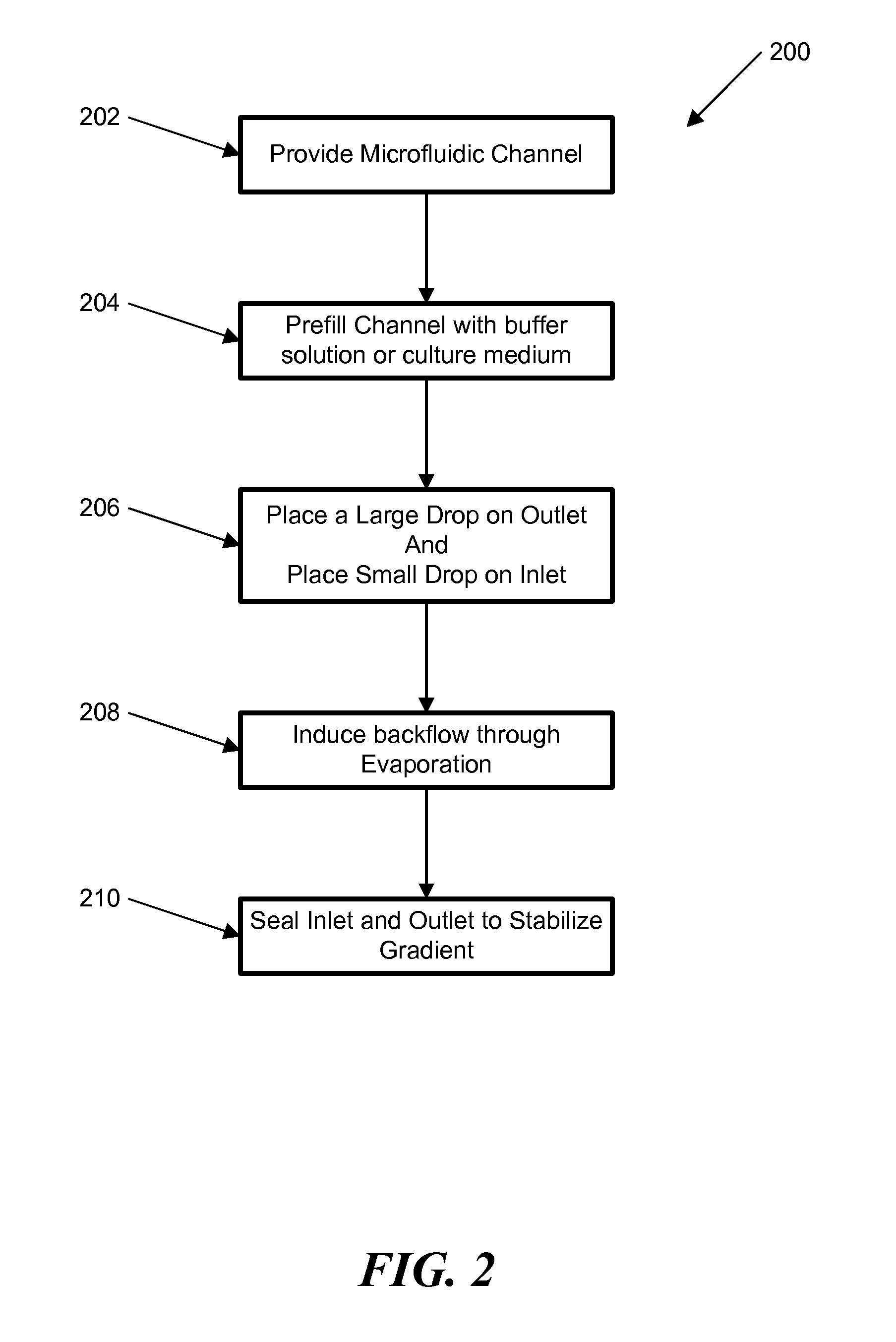
InactiveUS20110300570A1Regulate cellular responseProfile can be stabilizedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsBiological studiesCardiac cell
The ability to rapidly generate concentration gradients of diffusible molecules has important applications in many chemical and biological studies. The present invention is directed to methods and systems for generating spatially and temporally controllable concentration gradients of molecules (i.e. proteins or toxins) in a portable microfluidic device. The formation of the concentration gradients can be initiated by an induced forward flow and further optimized during an induced backward flow. The forward and backward flows can be either passively induced and / or actively pumped. The centimeter-length gradients along the microfluidic channel can be spatially and temporally controlled by the backward flow. The gradient profile was stabilized by stopping the flow. In one example, a stabilized concentration gradient of a cardiac toxin, Alpha-cypermethrin, generated according to the invention was used to test the response of HL-1 cardiac cells in the microfluidic device, which correlated with toxicity data obtained from multi-well plates. The invention can be useful for bio-logical and chemical processes that require rapid generation of concentration gradients in a portable microfluidic device.
Owner:THE BRIGHAM & WOMEN S HOSPITAL INC
Manufacturing method of bracket material for applying in myocardial tissue engineering
InactiveCN1565649AImprove developmentFunction increaseSurgerySkeletal/connective tissue cellsEmbryoCells heart
The invention belongs to the tissue engineering field, more specifically relates to a manufacturing method of stent material for cardiac muscle tissue enginerering. The stent simulates extracellular matrix component. Its original form is a liquid hydrogel. It mainly comprises liquid collagen(I type and III type), elastin, laminin, chicken embryo extractive, 2xDMEM and cow embryo serum. Blending these constituents in proper ratio to obtain natural cardiac muscle analog stent materials and blending them with cardiac cell can generate cardiac cell-bracket materials in various shape, by which a tissue engineered cardiac muscle tissue capable of beating synchronistically can be generated.
Owner:INST OF BASIC MEDICAL SCI ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF PLA
Compositions and Methods for Treating Cardiac Conditions
InactiveUS20090018061A1Avoid undesirable systemic side effectPeptide/protein ingredientsPharmaceutical delivery mechanismEpiregulinCardiac cell
Pharmaceutical polypeptide compositions promote the survival of cardiac cells, recruit cardiac cells to the cardiac area, stimulate the differentiation of cardiac cells, stimulate the proliferation of cardiac cells, and promote the activity of cardiac cells, thereby treating cardiac conditions. Methods of providing these compositions to the cardiac area include catheterization and direct injection. In preferred embodiments, the compositions comprise one of more of the following growth factors: EGF, hFGF, cardiotrophin-1, thrombin, PDGF-BB, amphiregulin, epiregulin, HB-EGF, TGFalpha, betacellulin, heregulin alpha, NRG-1-beta1-HRG-beta1, FGF 9.
Owner:FIVE PRIME THERAPEUTICS
Modulators of cardiac cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia
InactiveUS20090304625A1Inhibiting hypertension-induced hypertrophyAvoid problemsOrganic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsEccentric hypertrophyMedicine
Provided are compositions and methods for modulating cardiac cell hypertrophy and hyperplasia using inhibitors of c-Kit activity.
Owner:VICTOR CHANG CARIDAC RES INST LTD +1
Method and apparatus for electrically forcing cardiac output in an arrhythmia patient
InactiveUS7706864B2Maintain consciousnessLife maintenanceHeart defibrillatorsHeart stimulatorsCardiac pacemaker electrodeFibrillation
An electrical method and apparatus for stimulating cardiac cells causing contraction to force hemodynamic output during fibrillation, hemodynamically compromising tachycardia, or asystole. Forcing fields are applied to the heart to give cardiac output on an emergency basis until the arrhythmia ceases or other intervention takes place. The device is used as a stand alone external or internal device, or as a backup to an ICD, atrial defibrillator, or an anti-tachycardia pacemaker. The method and apparatus maintain some cardiac output and not necessarily defibrillation.
Owner:GALVANI
Methods and compositions for correction of cardiac conduction disturbances
The invention provides methods for establishing electrical coupling between cardiomyocytes and recombinant cells which have been genetically engineered to express a gap junction protein, e.g., a connexin protein such as connexin 43 (Cx43) protein. The invention is based on the discovery that genetic modification of skeletal muscle cells to express a recombinant connexin, enables the genetically modified cells to establish electrocommunication with cardiac cells via gap junctions. The recombinant connexin expressing cells can be used for repair of cardiac tissue and for treatment of cardiac disease by transplantation into cardiac tissue.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method for enhanced uptake of viral vectors in the myocardium
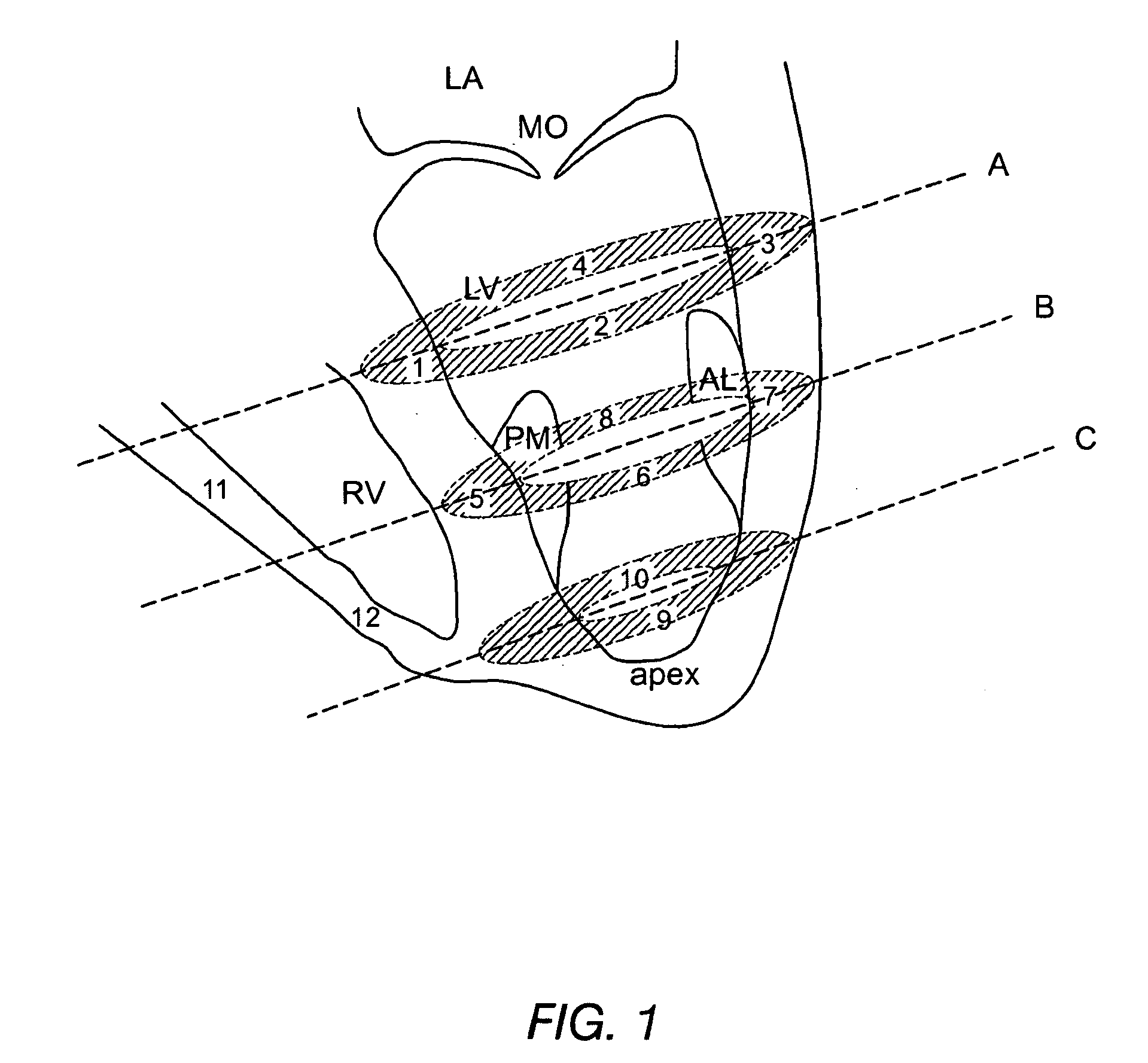
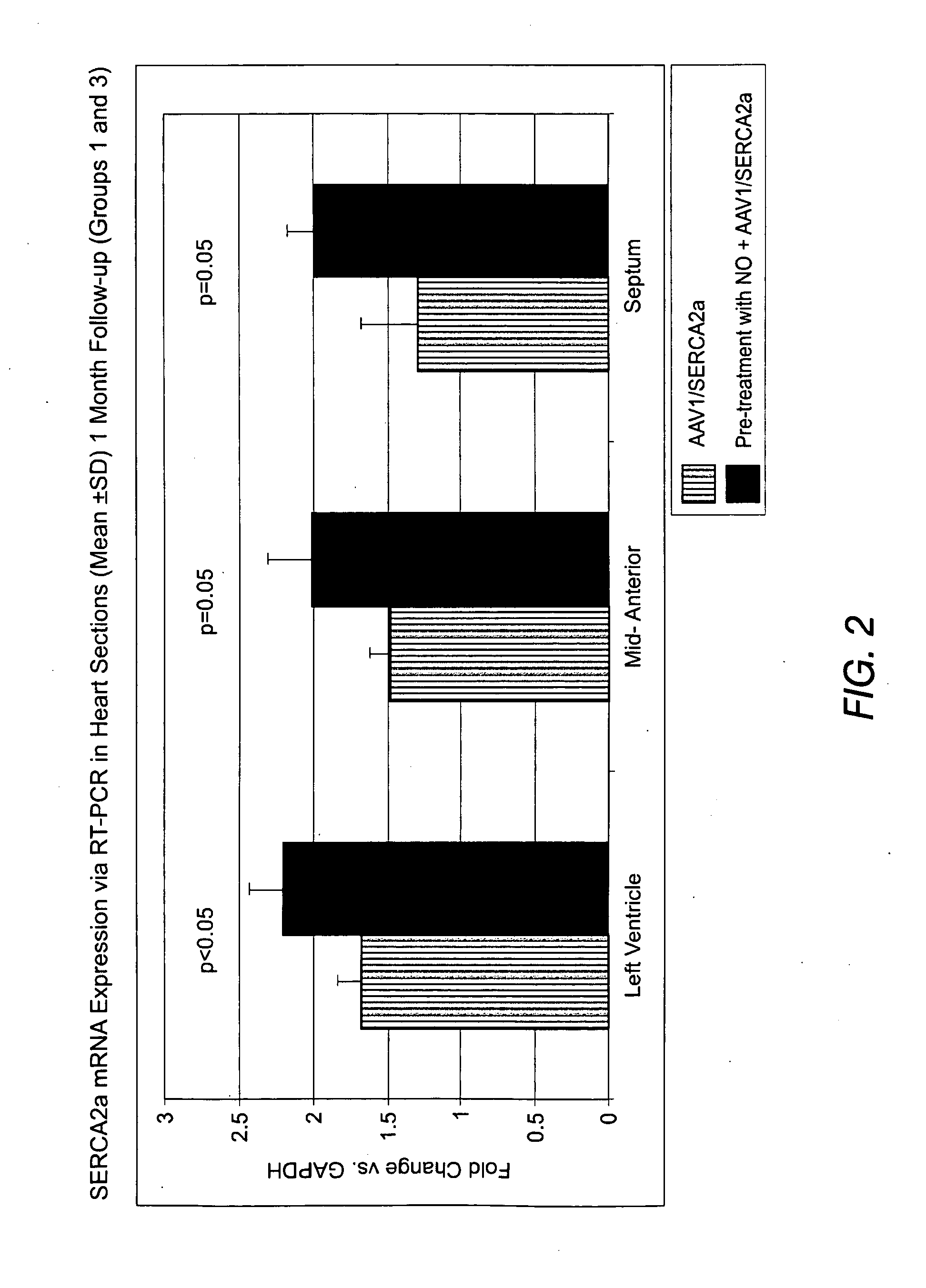
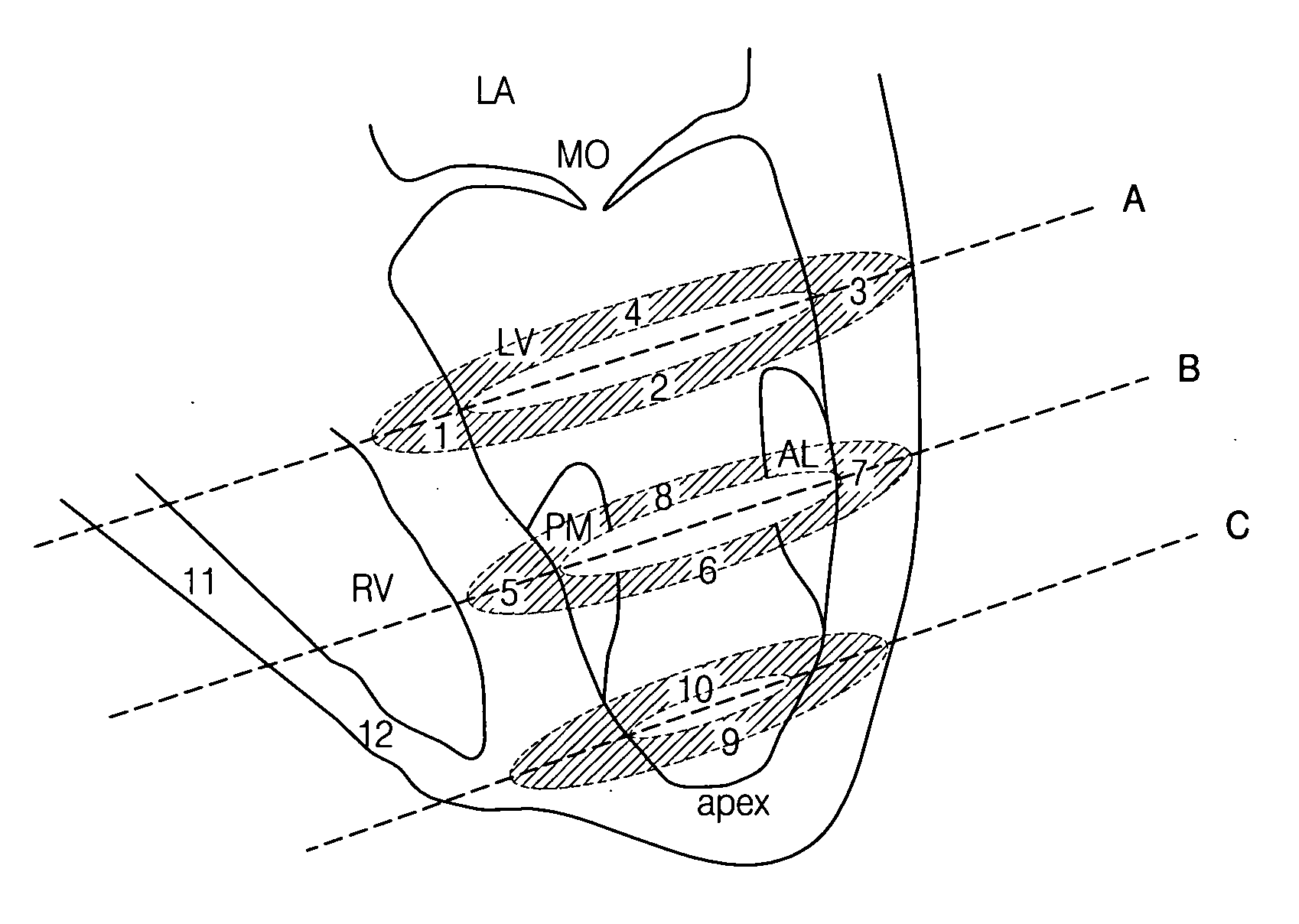
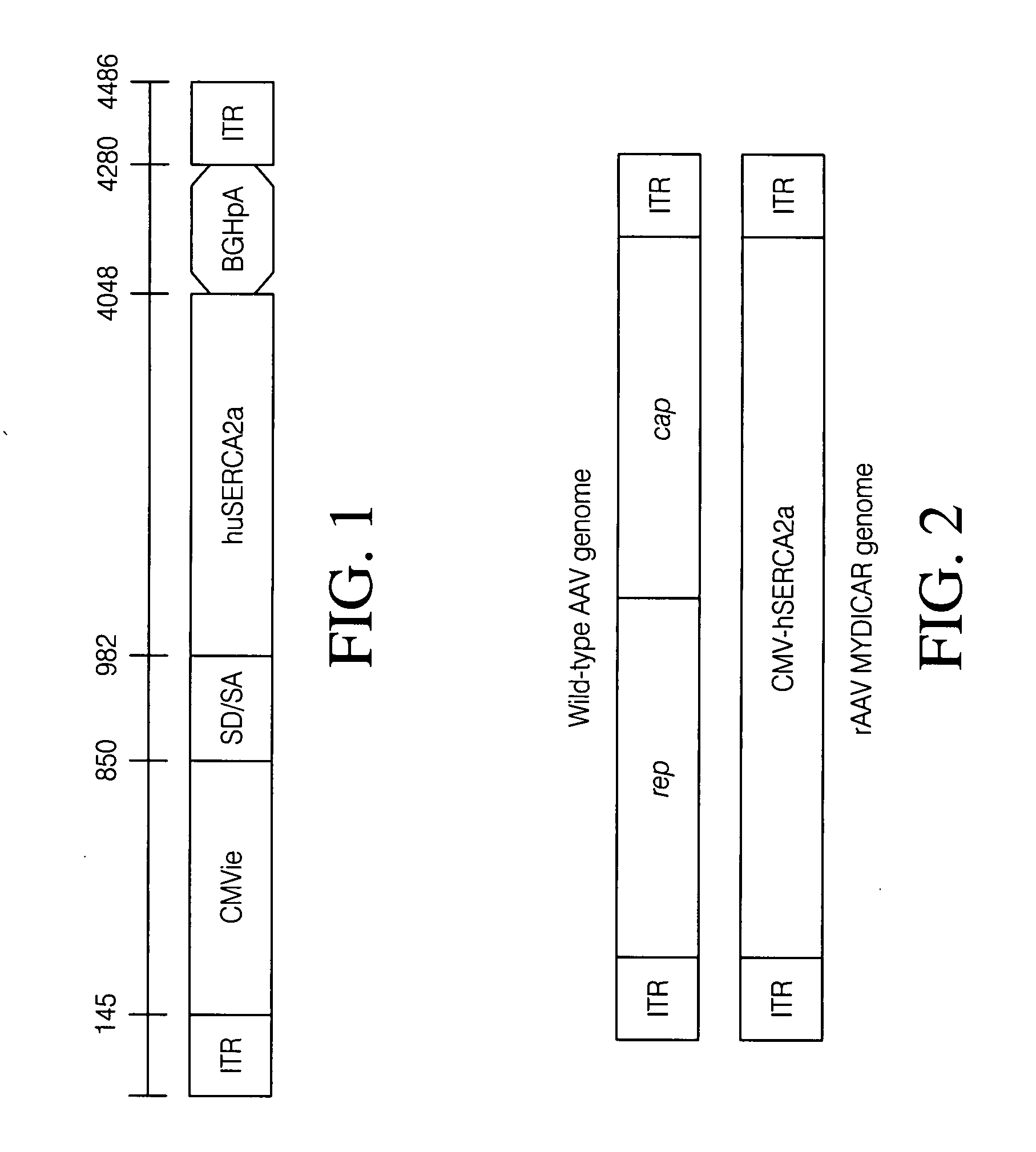
The present invention relates to improved therapies for the treatment of heart disease, particularly the improved delivery of therapeutic agents to heart tissue by direct infusion into the coronary circulation. A preferred embodiment of the invention is a method of treating or preventing a cardiovascular disease by transfecting cardiac cells of a large mammal, the method comprising, identifying a mammal in need of treatment or prevention of heart disease, supplying NO to the coronary circulation prior to, and / or during the infusion of a therapeutic polynucleotide into a blood vessel of the coronary circulation in vivo, where the therapeutic polynucleotide is infused into the blood vessel over a period of at least about three minutes, where the coronary circulation is not isolated or substantially isolated from the systemic circulation of the mammal; and where the therapeutic polynucleotide transfects cardiac cells of the animal resulting in the treatment or prevention of the heart disease.
Owner:SARDOCOR CORP
Extended antegrade epicardial coronary infusion of adeno-associated viral vectors for gene therapy
The present invention relates to therapies for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases, particularly the delivery of therapeutic agents to heart tissue by direct infusion into the coronary circulation. A preferred embodiment of the invention is a method of treating or preventing a cardiovascular disease by transfecting cardiac cells of a large mammal, the method comprising, identifying an mammal in need of treatment or prevention of a cardiovascular disease, infusing a therapeutic polynucleotide into a blood vessel of the coronary circulation in vivo, where the therapeutic polynucleotide is infused into the blood vessel over a period of at least about three minutes, where the coronary circulation is not isolated or substantially isolated from the systemic circulation of the mammal; and where the therapeutic polynucleotide transfects cardiac cells of the animal resulting in the treatment or prevention of the cardiovascular disease.
Owner:CELLADON CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com