Patents
Literature
152 results about "Zebrafish embryo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
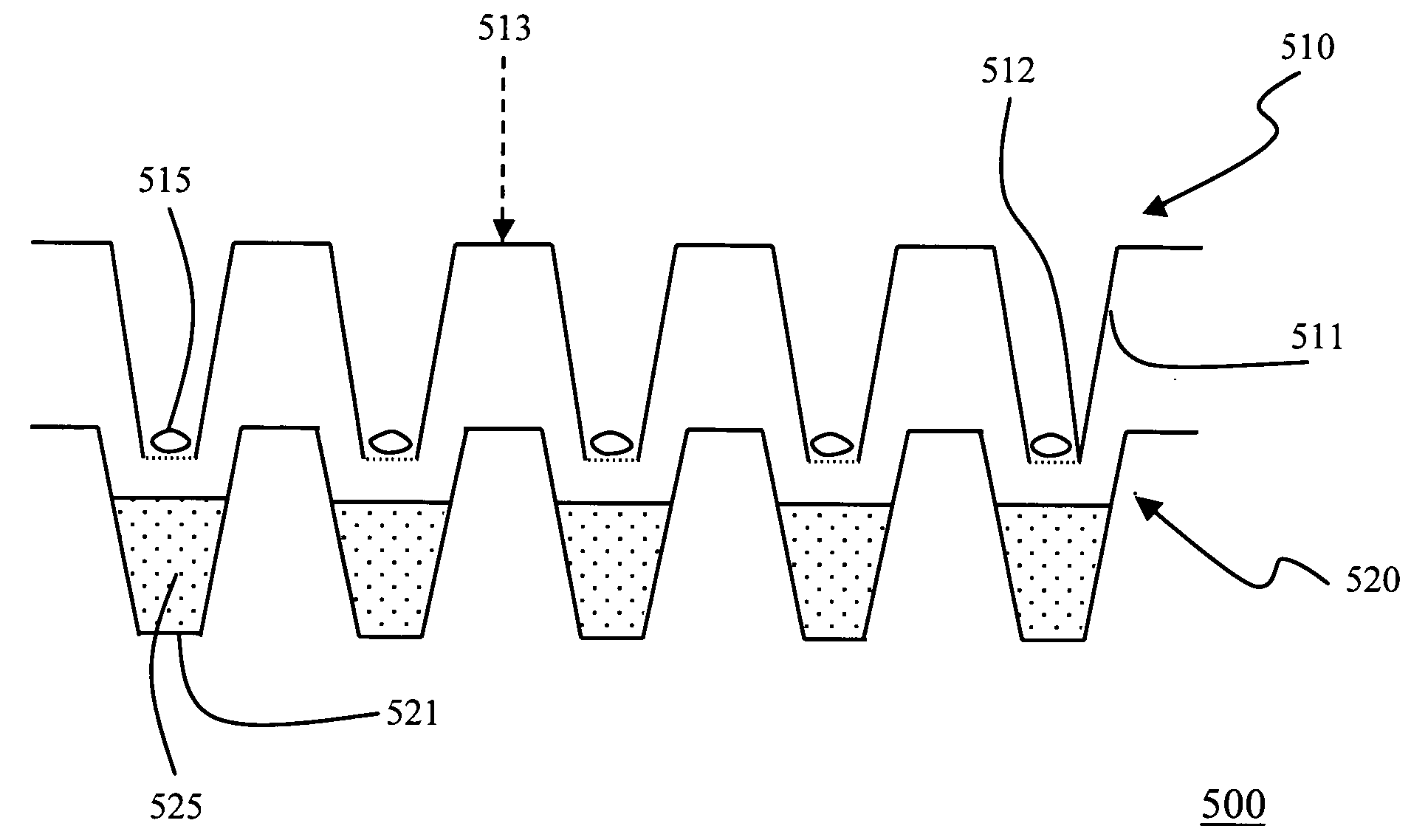
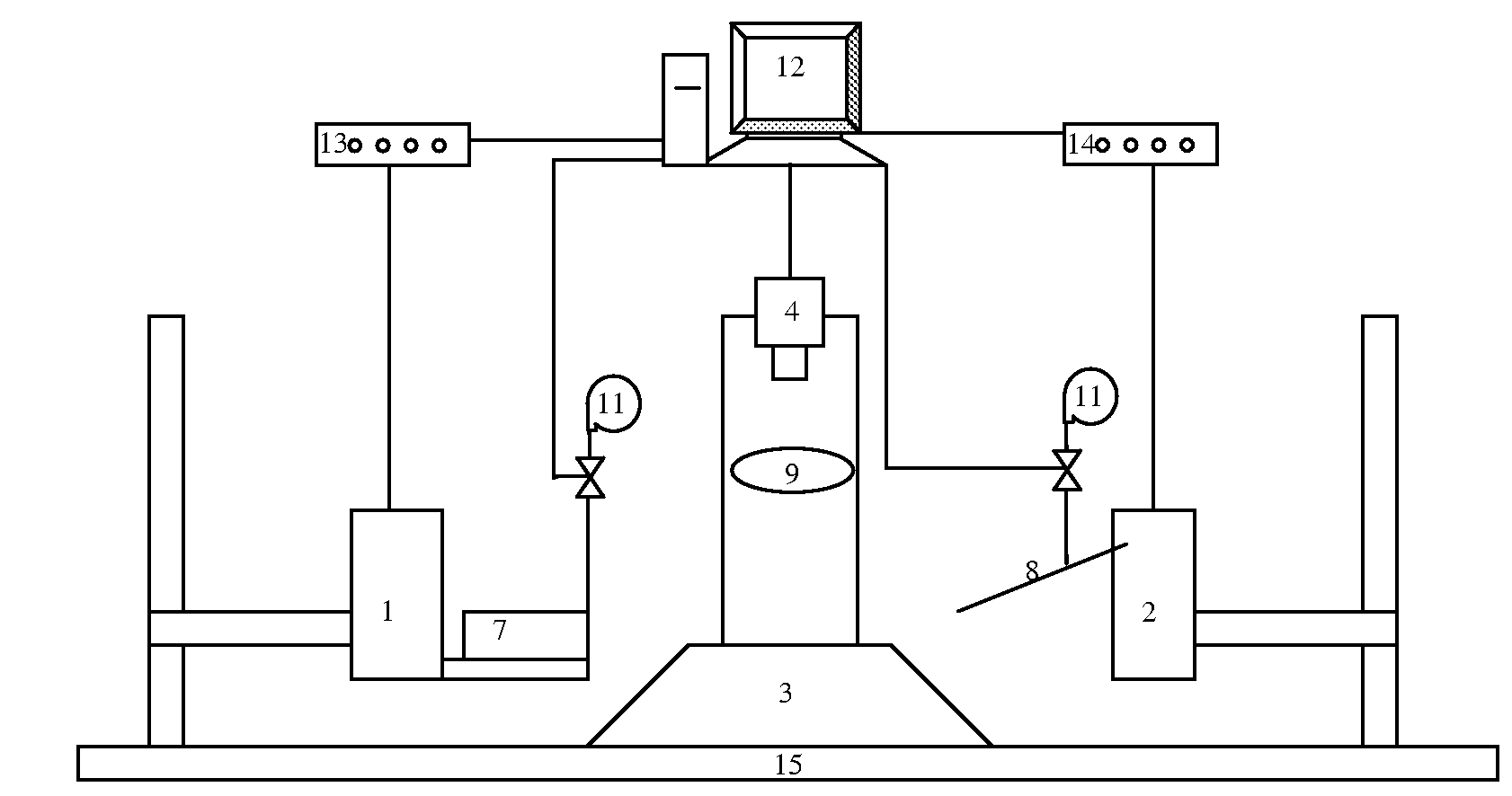
Meshwell plates
InactiveUS20050112030A1Rapid and highly reproducible high-throughput processingDrain fastAnalysis using chemical indicatorsLaboratory glasswaresTissue sampleEngineering
A versatile mesh-bottom Meshwell plate enables simultaneous rapid and highly reproducible high-throughput processing of small tissue samples or organisms. In an embodiment, the Meshwell plate consists of 96 meshwells and is particularly useful in assaying zebrafish embryos. The bottom tips of standard 96-well PCR plates are removed and replaced by a mesh with openings of about 75-300 μm, preferably 150 μm, in size. The Meshwell plate is optimized to allow fast draining of solutions and to prevent “wicking” of solution between wells. Quick and clean changes of solution can be done either by hand or a robot. With the Meshwell plate, waste of reagent solution and handling hazards, which may cause damage to and / or loss of samples, are substantially minimized and / or essentially eliminated. The Meshwell plate can be easily customized according to number of meshwells desired and can be economically mass-produced.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
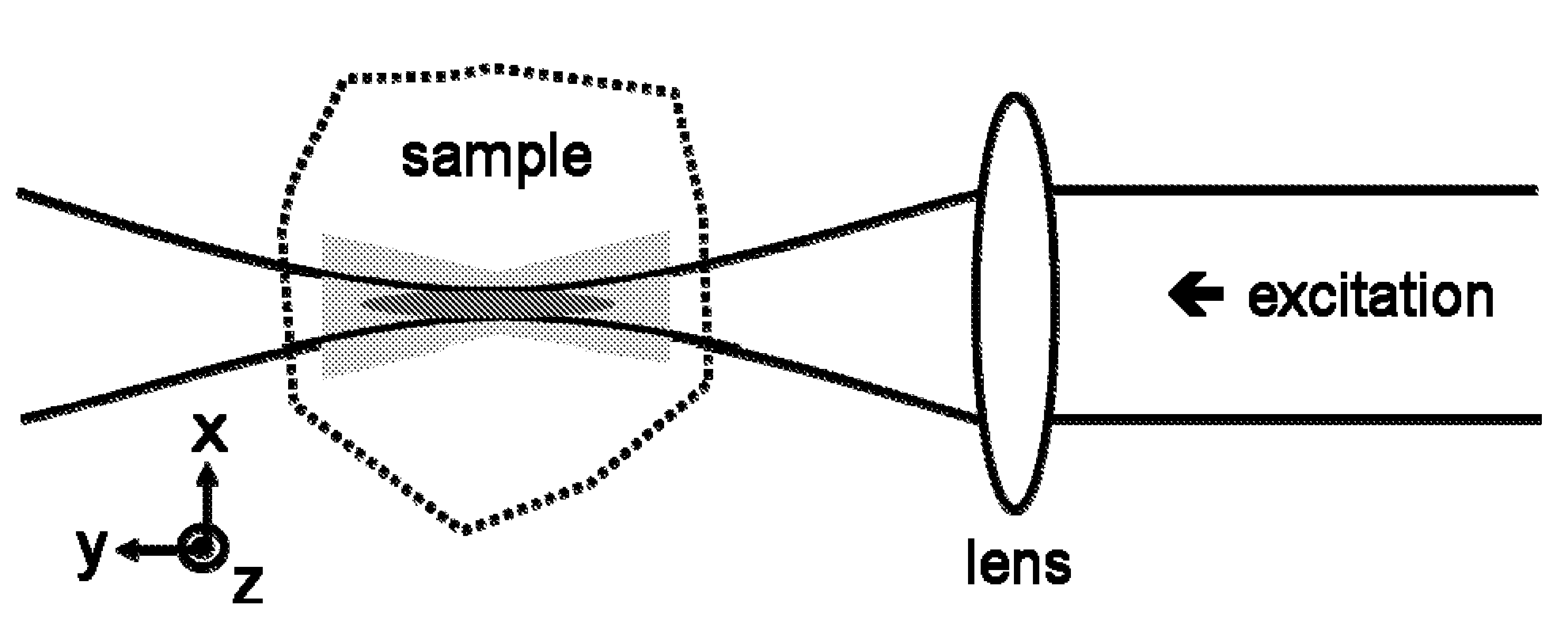
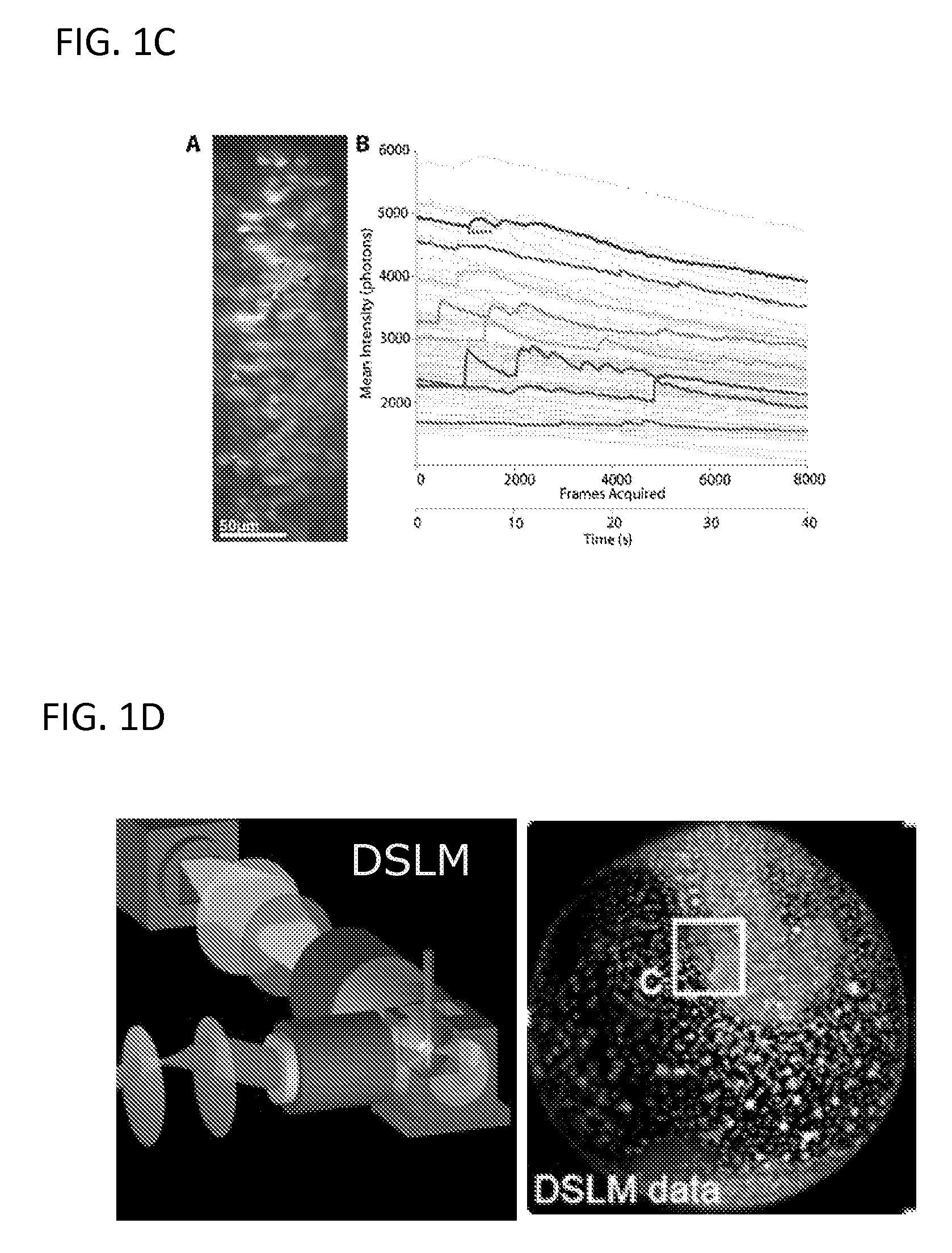
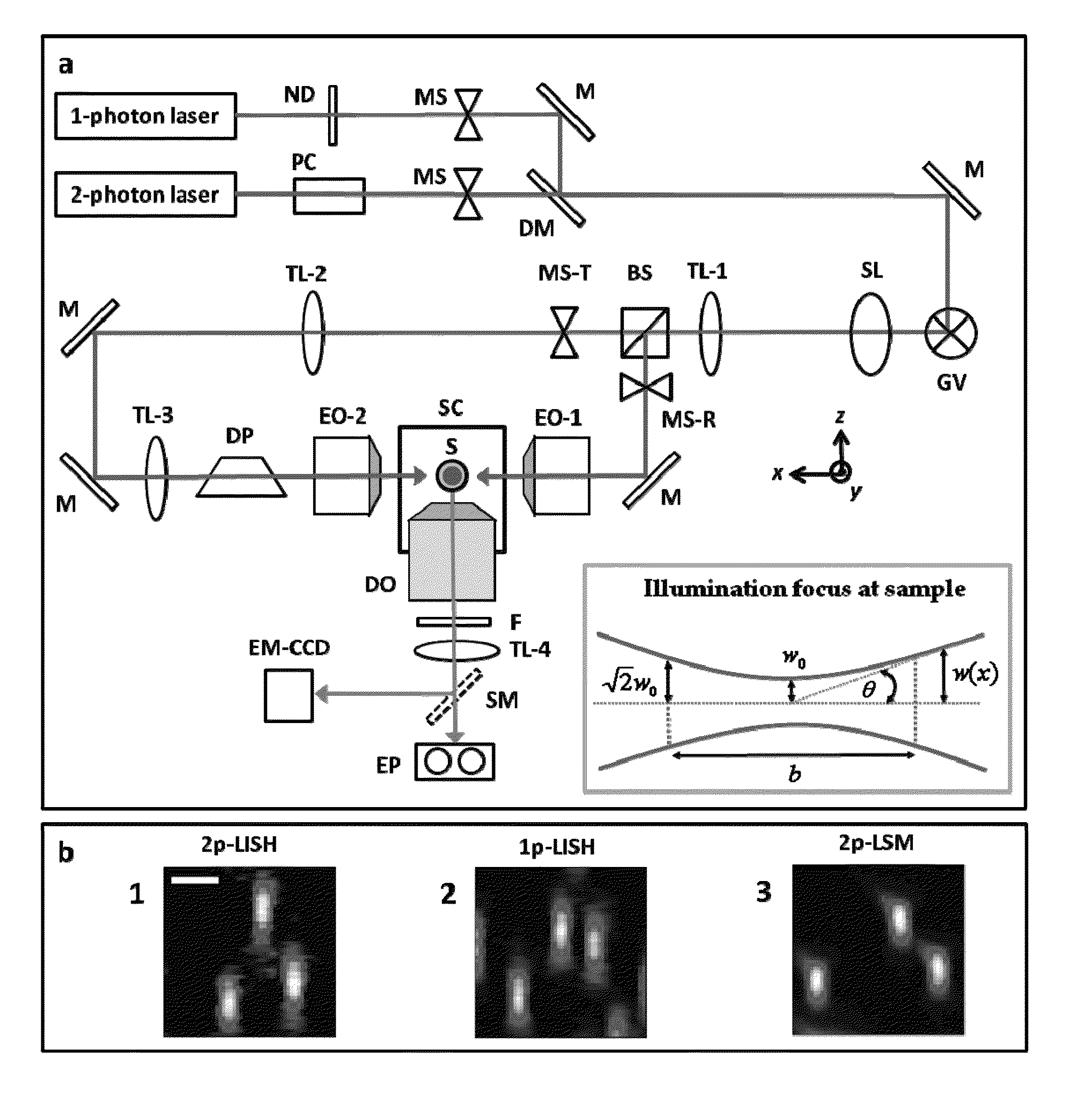
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
ActiveUS20110122488A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFluorescence
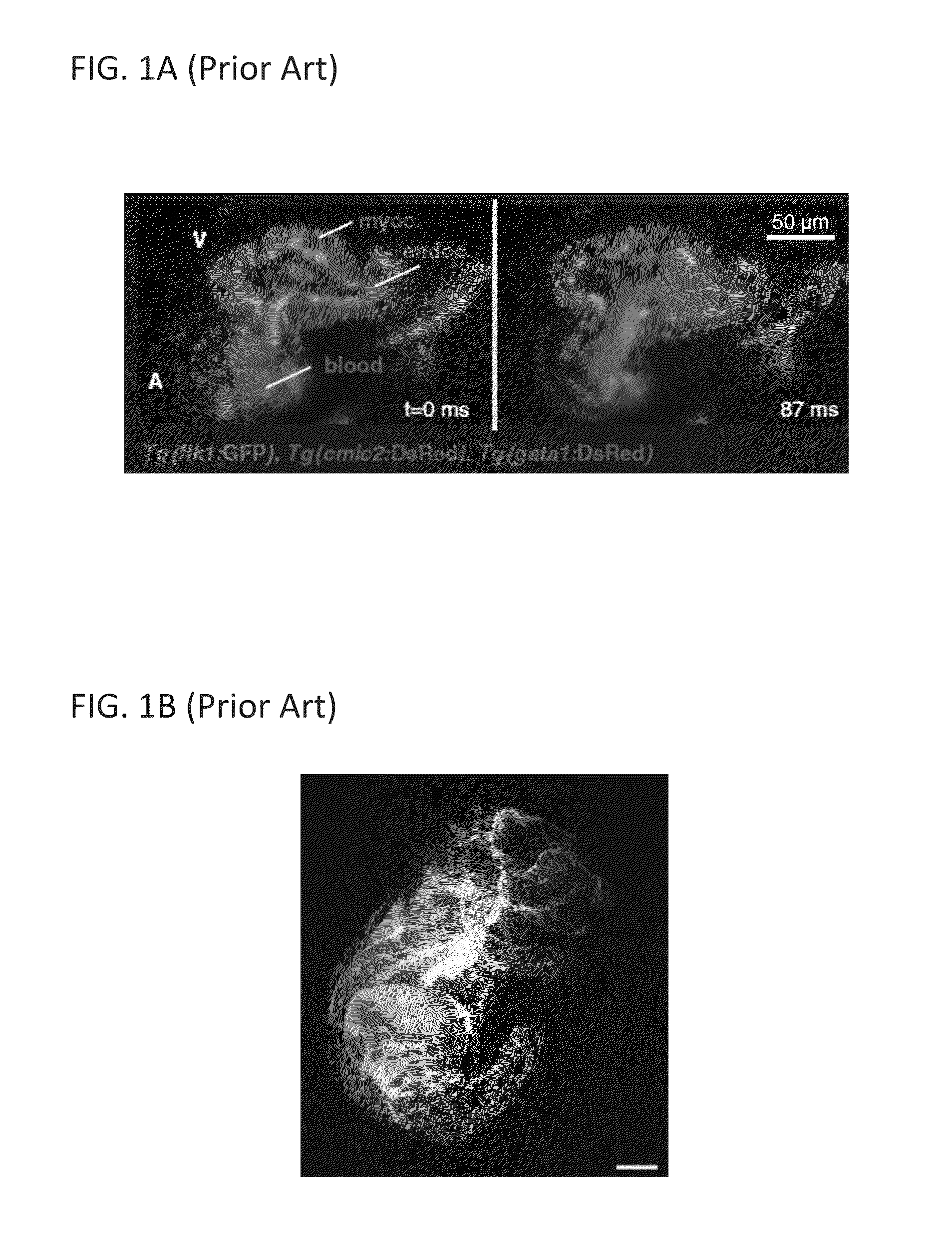
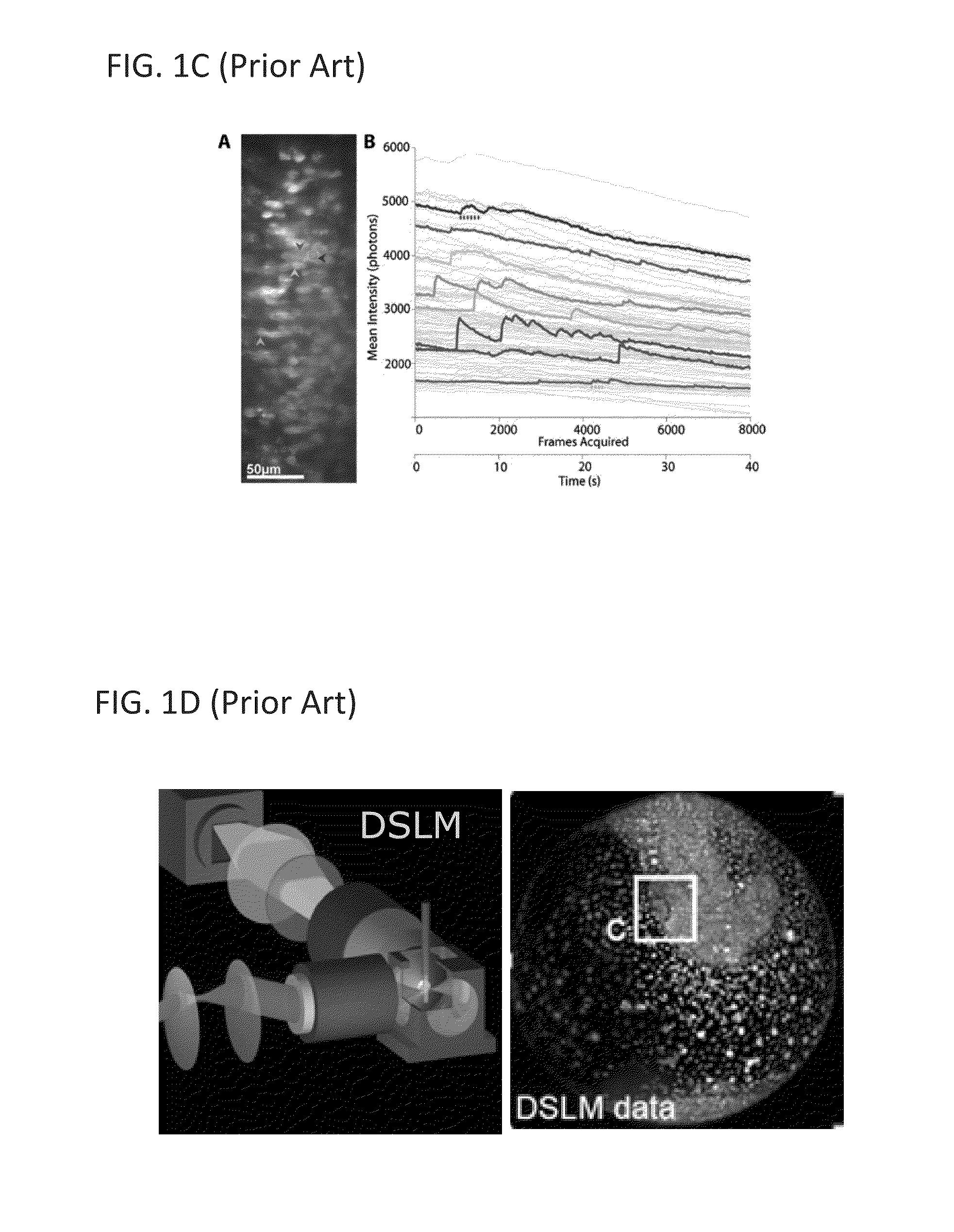
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal. illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
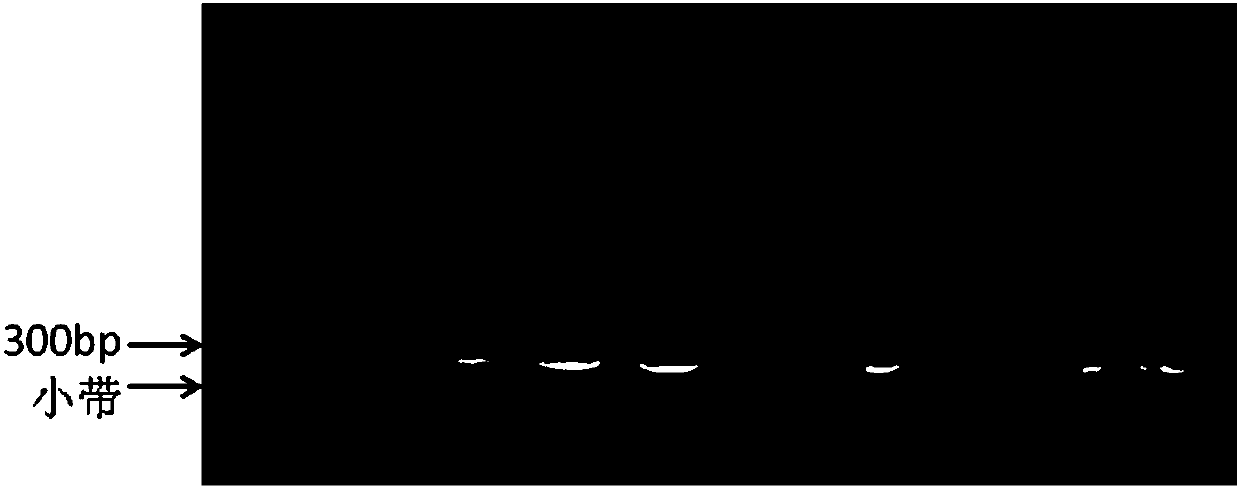
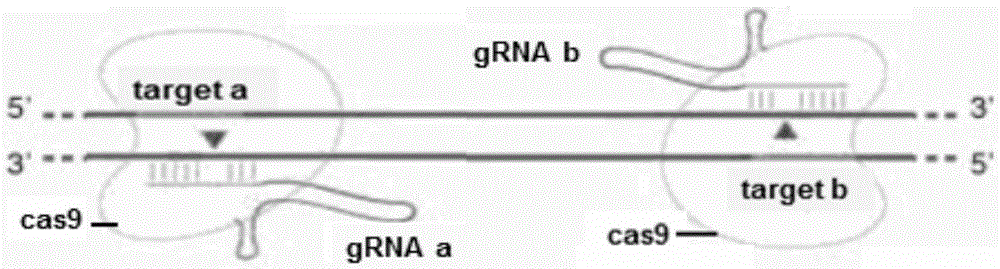
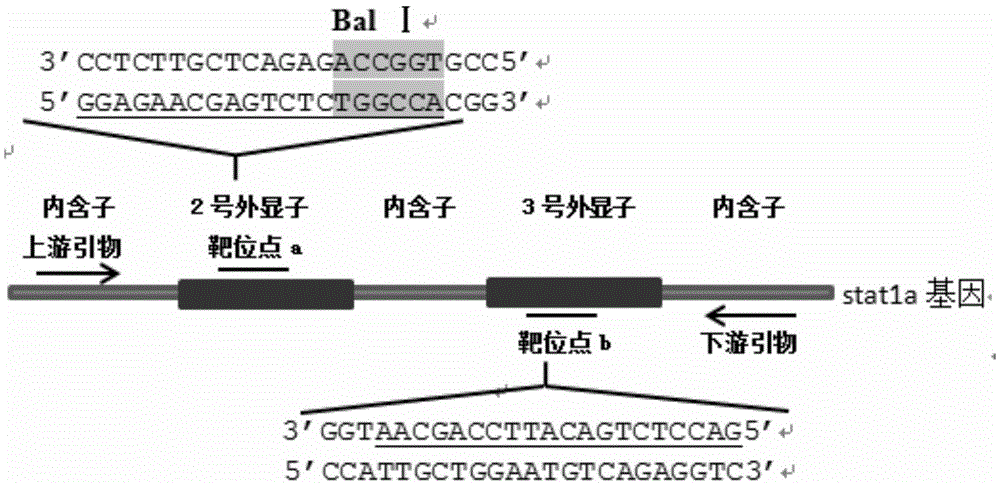
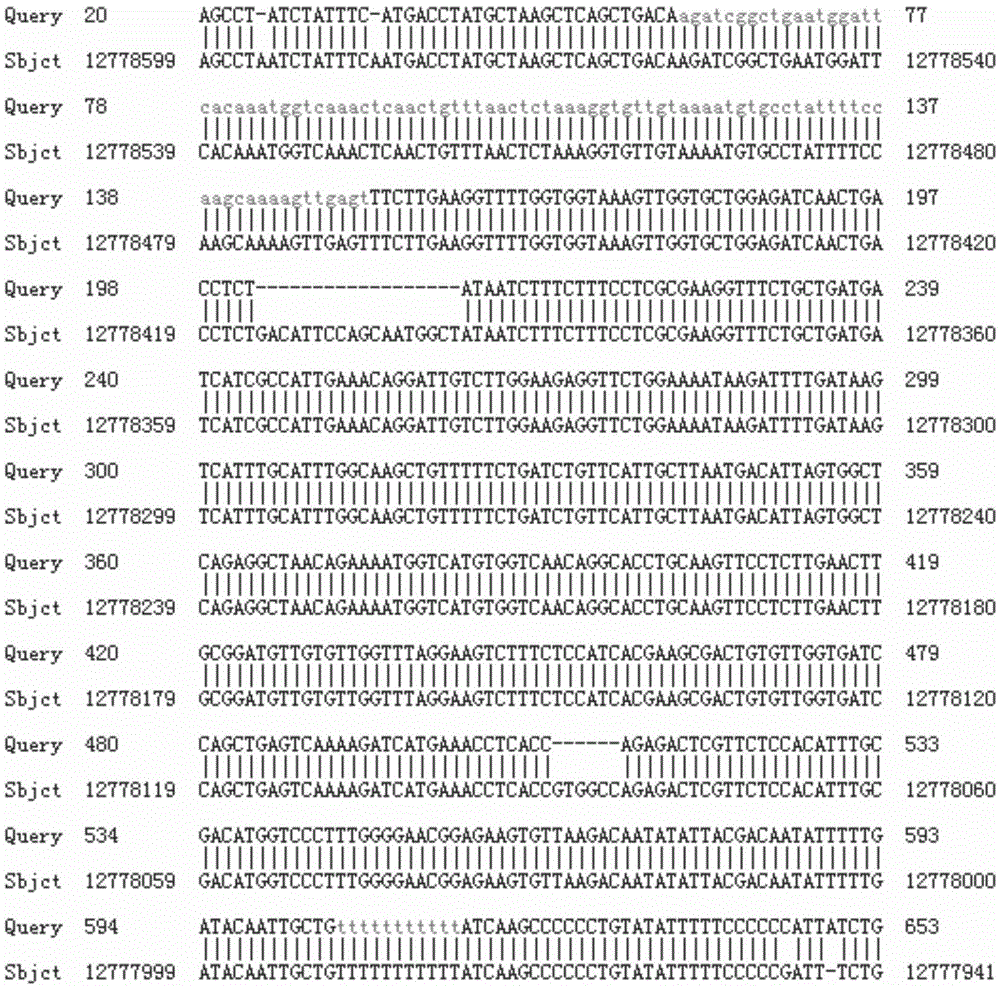
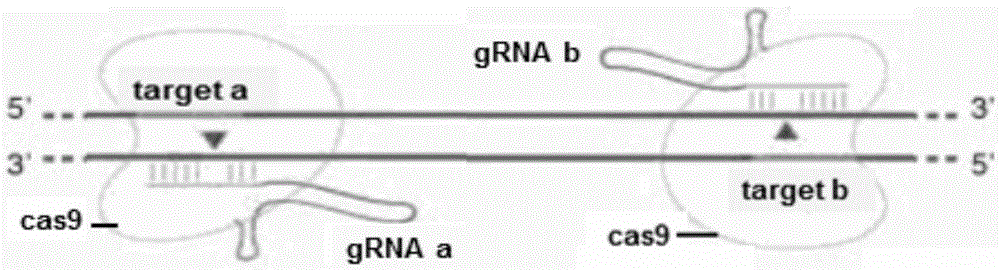
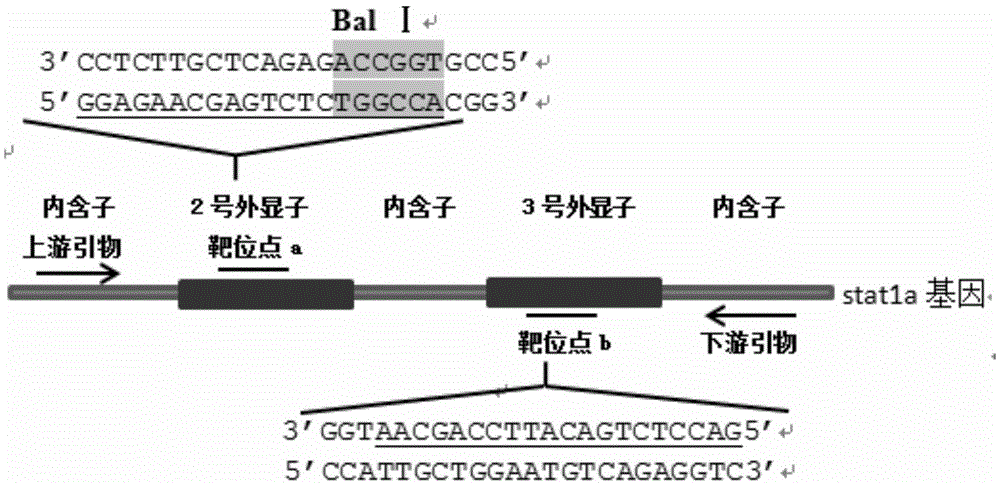
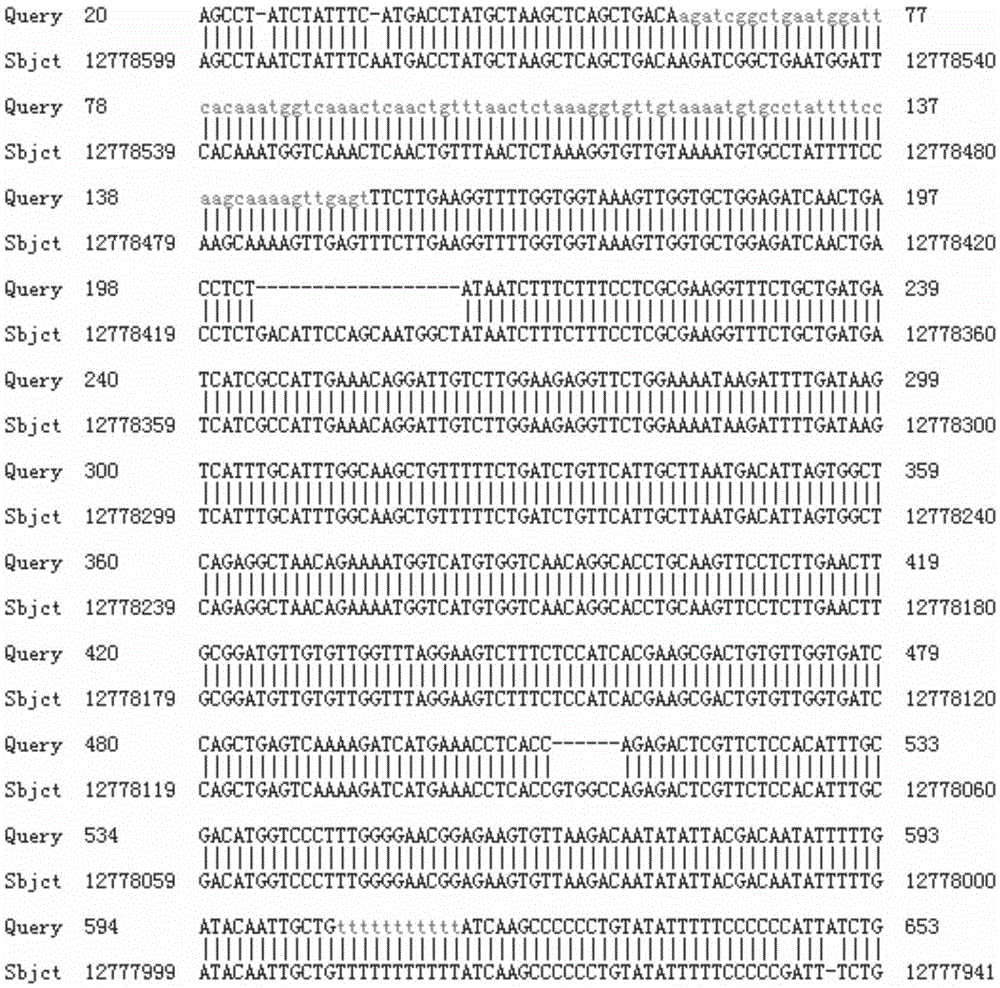
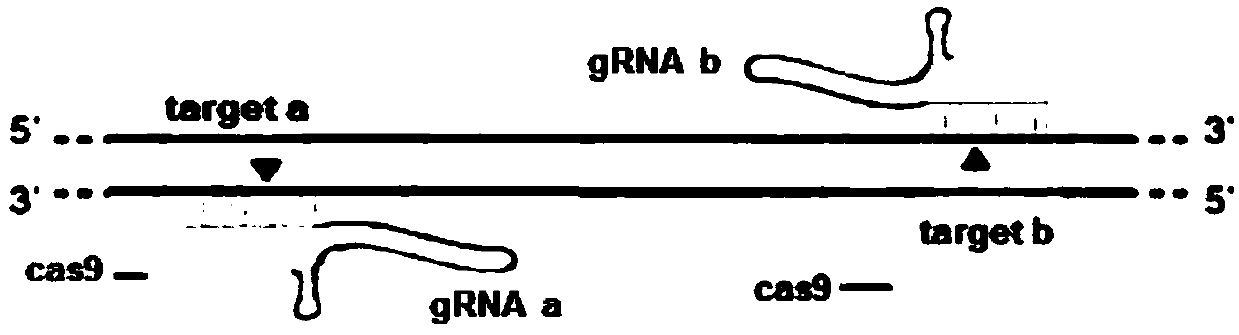
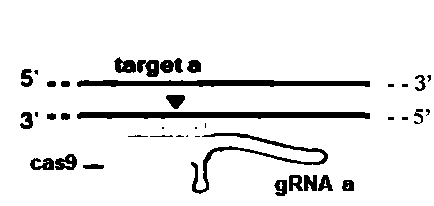
Method for breeding stat1a (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) gene-deleted zebra fish through gene knockout
InactiveCN105647969AInefficient shooting techniqueLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesFish embryoEmbryo
A method for breeding stat1a (signal transducer and activator of transcription 1) gene-deleted zebra fish through gene knockout comprises steps as follows: design of a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout target site: a gRNA expression carrier is established and gRNA is synthesized in vitro; micro-injection of a zebra fish embryo; detection of effectiveness of the target site with a T7E1 method through Sanger sequencing; tail cutting identification according to the identification steps after two months of injection; TA cloning of a target sequence; Sanger sequencing of plasmids; obtaining of heritable F1 generation of a zebra fish mutant; obtaining of F2 generation homozygote of the zebra fish mutant, F3 generation pure line inheritance of the gene-deleted zebra fish with the above method, and obtaining of a new zebra fish strain.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Statla gene deletion type zebra fish
InactiveCN105594664AInefficient shooting techniqueLow costMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesFish embryoEmbryo
The invention provides statla gene deletion type zebra fish. After an experiment design region is knocked out, the sequence is represented as SEQ ID No.1; an experiment comprises the following steps: designing a CRISPR / Cas9 gene knockout target point: constructing a gRNA expression vector and synthesizing gRNA in vitro; carrying out micro-injection of zebra fish embryos; detecting the effectiveness of the target point by a T7E1 method and Sanger sequencing; two months after injection, carrying out tail shearing and identification and carrying out identification steps above; carrying out TA cloning of a target sequence; carrying out Sanger sequencing of plasmids; obtaining an F1 generation of descendible zebra fish mutants; obtaining F2 generation homozygotes of the zebra fish mutants; and carrying out F3 generation homozygous heredity of the gene deletion type zebra fish according to the method above to obtain a new zebra fish line.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
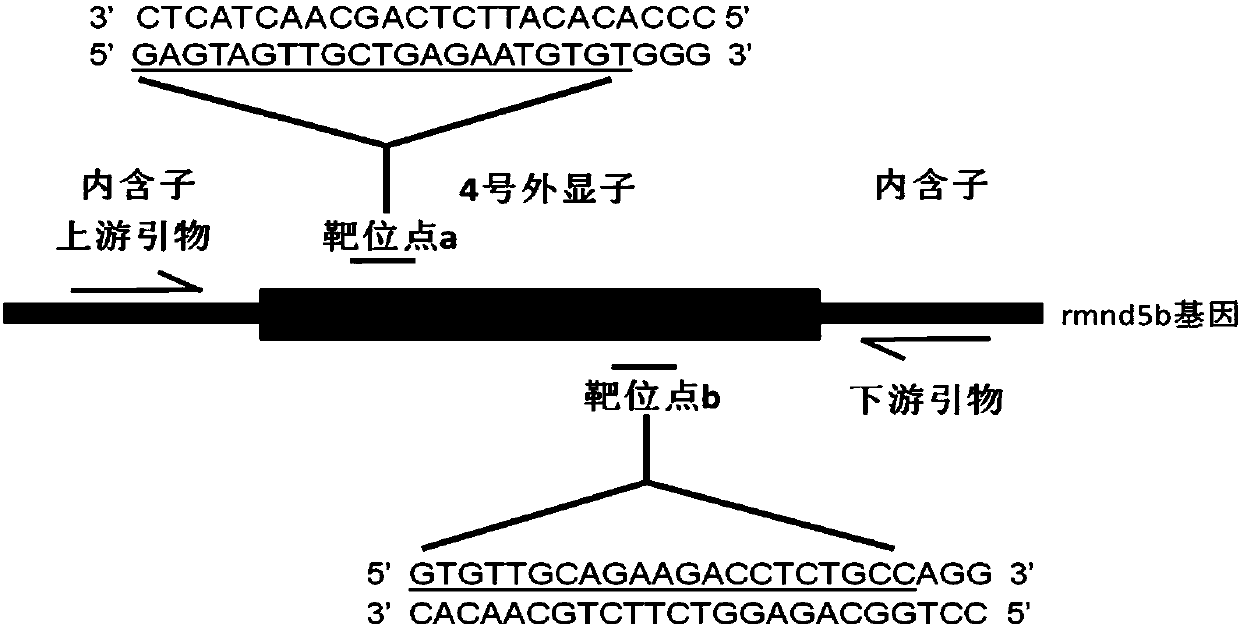
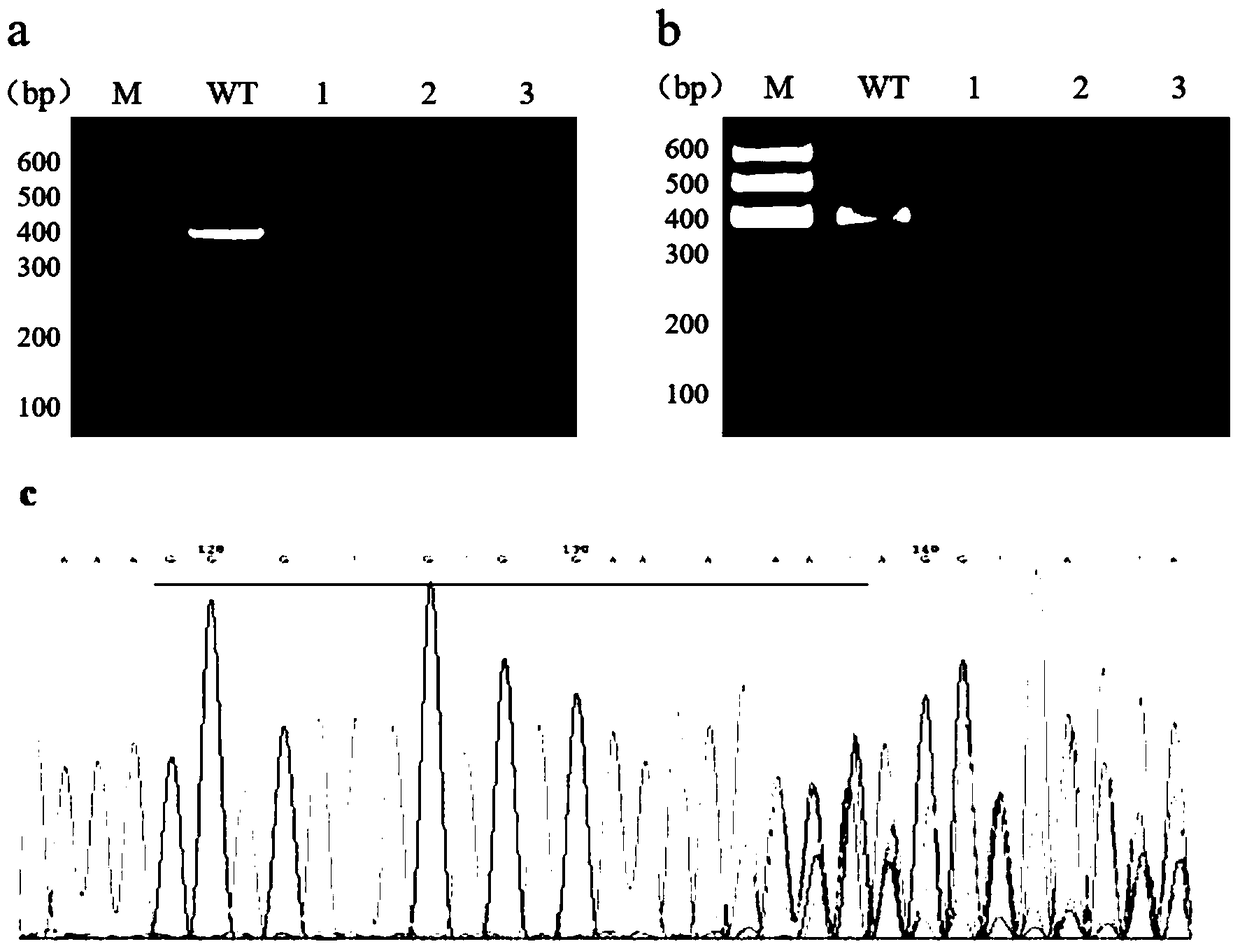
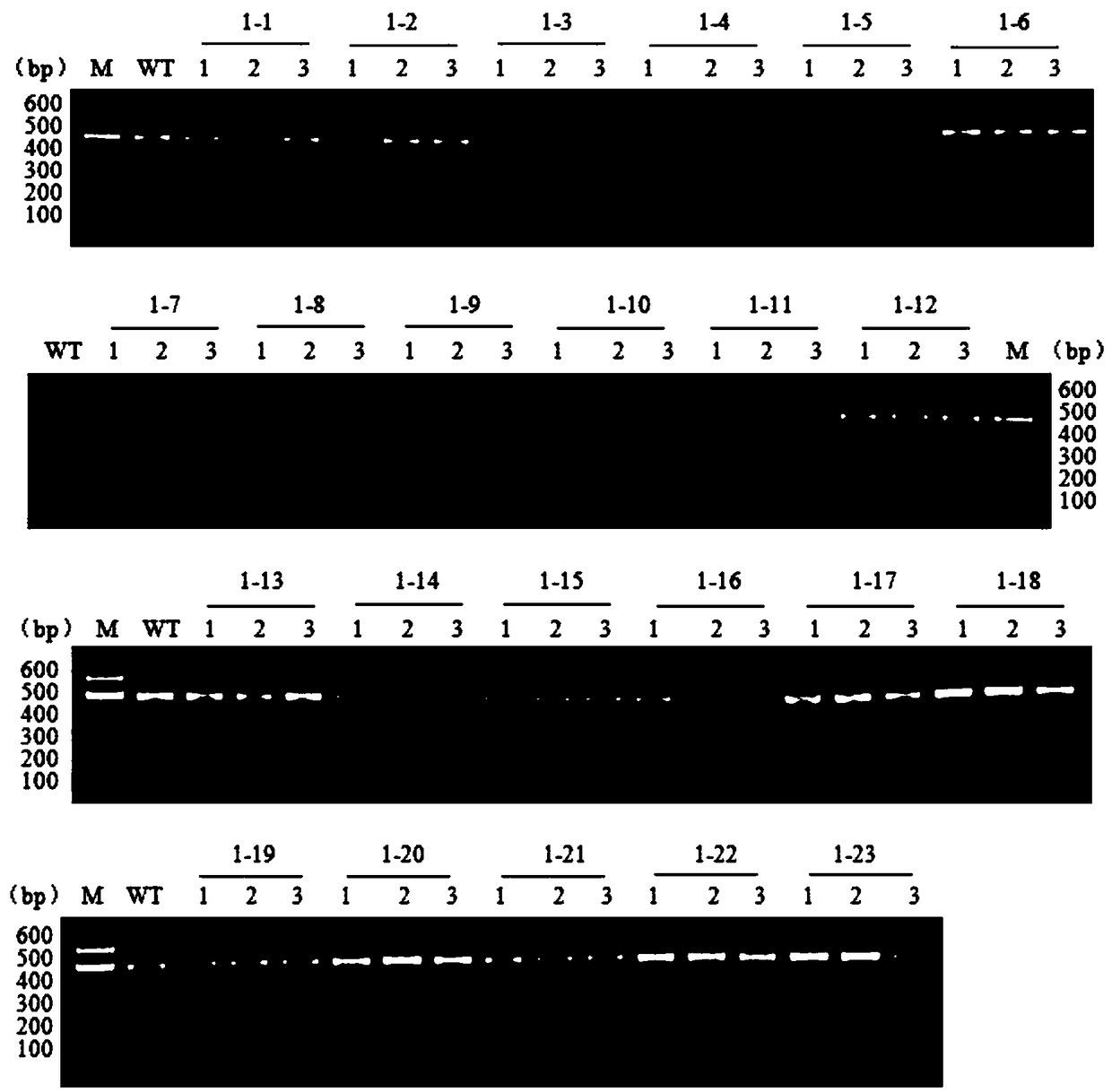
Method for breeding rmnd5b (required for meiotic nuclear division 5homolog B) gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout
InactiveCN108018316AEasy to makeLow miss rateHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAMeiotic nuclear divisionEmbryo
The invention discloses a method for breeding rmnd5b (required for meiotic nuclear division 5homolog B) gene deletion type zebra fish through gene knockout and belongs to the field of gene knockout. According to the method, construction of a gRNA expression vector and gRNA in-vitro synthesis are performed through design of a CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeats / CRISPR-associated 9) gene knockout target site, micro-injection is performed on an embryo of the zebra fish, the effectiveness of the target site is detected, tail cutting identification is performed, TA cloning is performed on a target sequence, plasmids are subjected to Sanger sequencing, an F1 generation of heritable zebra fish mutants is obtained, the same mutant female fish and male fish are picked from mutants of the F1 generation, hybridization is performed, an F2 generation of the zebra fish mutants is obtained, F2 generation homozygote is picked from the F2 generation of the zebra fishmutants, F3 generation pure-line inheritance is performed, and an rmnd5b gene deletion type zebra fish strain is obtained. The method is lower in off-target rate and has good medical research value inresearch of the correlation between rmnd5b gene deletion and development of other organs.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
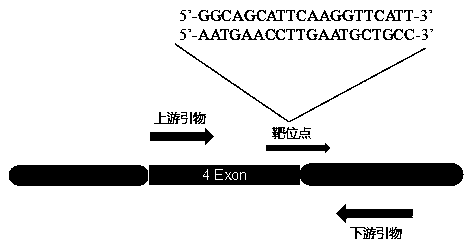
Preparation method of zebrafish notch2 gene mutant
ActiveCN108707628AGenetic stabilityFacilitate in-depth researchHydrolasesStable introduction of DNAPUC19Embryo
The invention discloses a preparation method of a zebrafish notch2 gene mutant. The preparation method includes: determining positions of knock-out target spots of the notch2 gene; utilizing pUC19-gRNA scaffold plasmid as a template, and performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification with primers T7-notch2-sfd and tracr rev; subjecting a PCR product to purification and in-vitro transcription to obtain gRNA (guide ribose nucleic acid); introducing the gRNA and Cas9 protein into a cell-stage embryo of zebrafish through micro-injection, and screening to obtain the notch2 gene mutant stable in inheritance. The preparation method has the advantages that by the aid of the CRISPR / Cas9 (clustered regularly interspersed short palindromic repeats, CRISPR / CRISPR-associated genes, cas gene)technology, and by means of selecting a specific section of targeting domain, the notch2 gene in the zebrafish is knocked out, other genes are protected from being 'injured accidentally', the zebrafish without the Notch2 gene is formed, experimental materials are provided for in-depth study on follow-up gene functions, and great significance is achieved on study of Notch signal channels.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
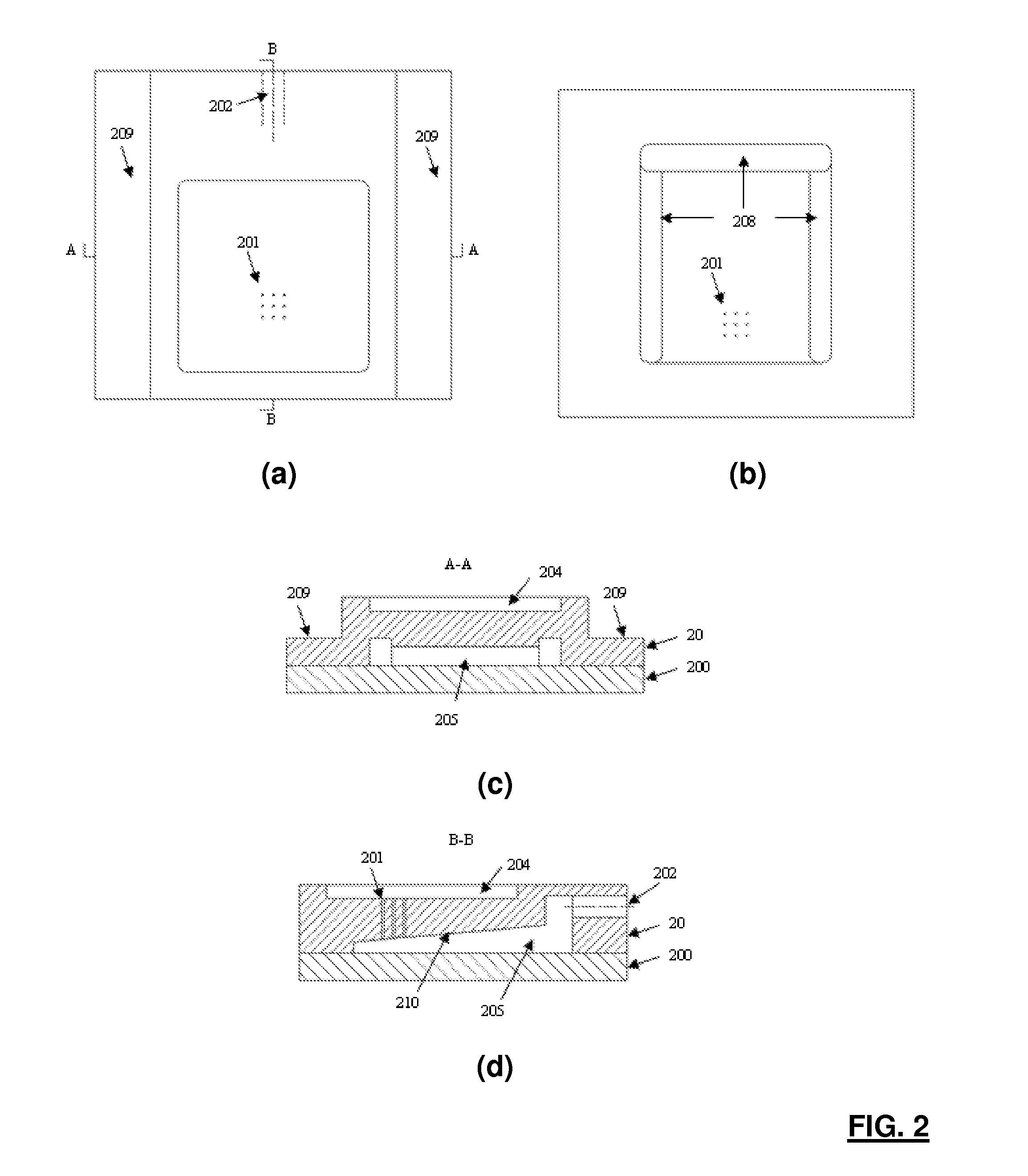
PiggyBac constructs in vertebrates
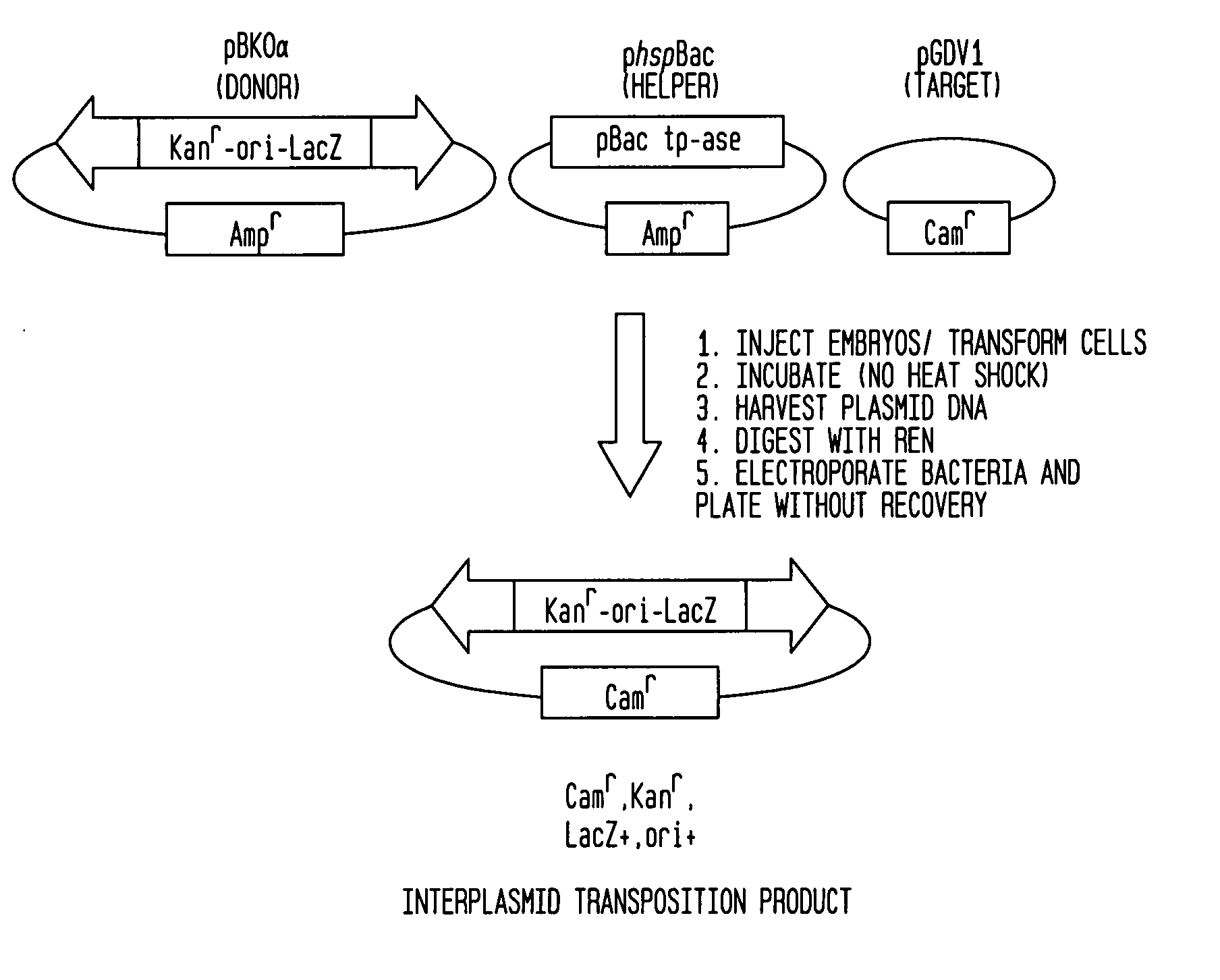
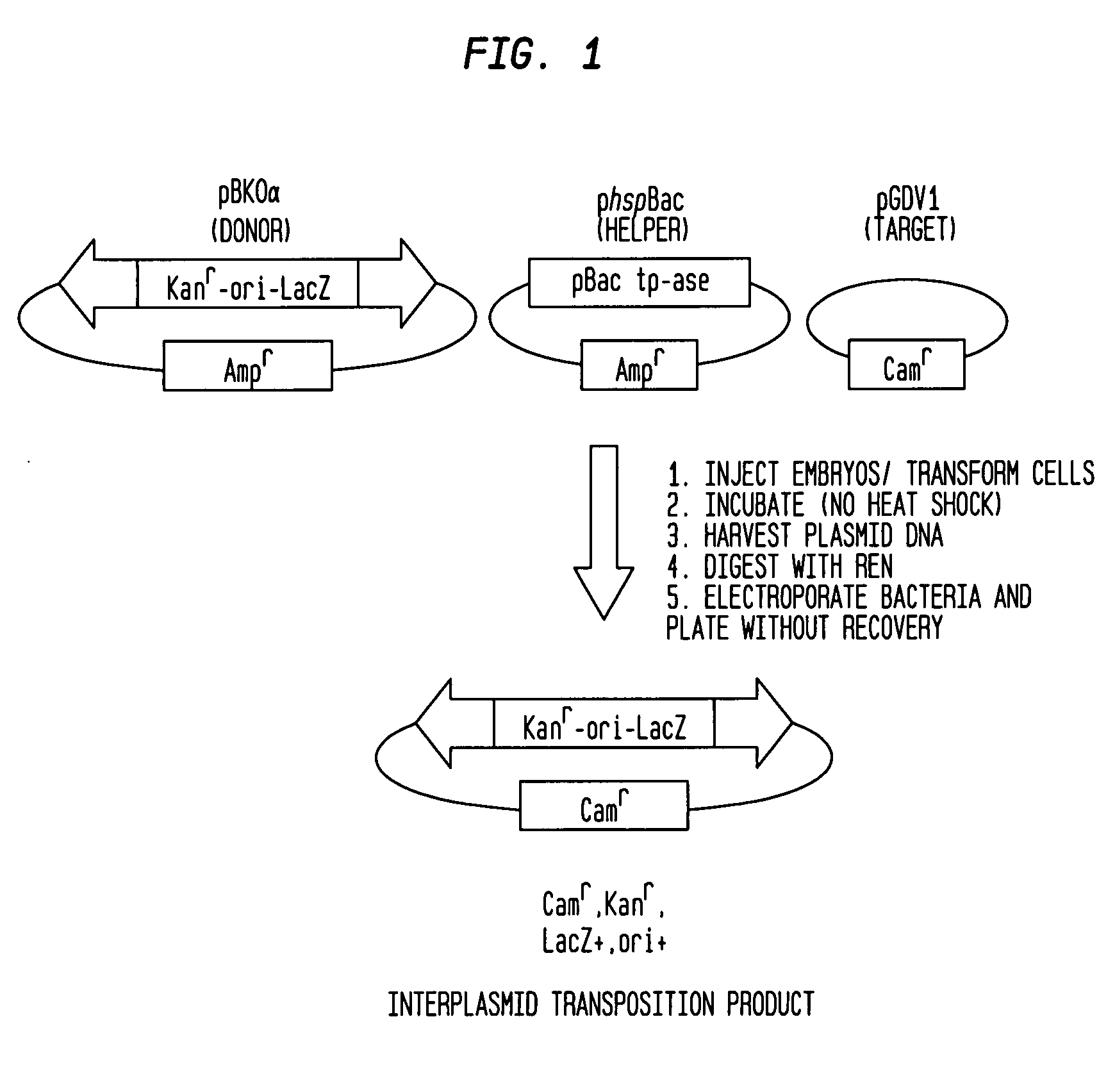
The piggyBac transposon is disclosed herein as an extremely versatile helper-dependent vector for gene transfer and germ line transformation in a wide range of vertebrate species. Presented are methods wherein genome sequencing databases may be examined using piggyBac, as homologues of piggyBac have been found among several sequenced animal genomes, including the human genome. This transposon is demonstrated to provide transposition in primate cells and embryos of the zebra fish, Danio rerio. PiggyBac mobility is demonstrated using an interplasmid transposition assay that consistently predicts the germ line transformation capabilities of this mobile element in several species. Both transfected COS-7 primate cells and injected zebrafish embryos supported the helper-dependent movement of tagged piggyBac element between plasmids in a cut-and-paste, TTAA target-site specific manner. The present invention discloses the use of piggyBac as a tool for genetic analysis of vertebrates.
Owner:UNIV OF NOTRE DAME DU LAC
High-throughput automated cellular injection system and method
ActiveUS20080077329A1Easy to adaptReduce throughputBiological testingSpecial data processing applicationsHigh fluxGenetic Materials
An automated cell injection system and method are described, which can perform automatic, reliable, and high-throughput cell injection of foreign genetic materials, proteins, and other compounds. The system and method overcome the problems inherent in traditional manual injection that is characterized by poor reproducibility, human fatigue, and low throughput. The present invention is particularly suited for zebrafish embryo injection but can be readily extended to other biological injection applications such as mouse embryo, drosophila embryo, and C. elegans injections, capable of facilitating high-throughput genetic research at both academic and industry levels. A novel vacuum based cell-holding device is also provided.
Owner:SUZHOU BOUNDLESS MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting activity of anti-angiogenesis protein factor or pro-angiogenesis protein factor via zebra fish embryo model and application method thereof
InactiveCN1866025AMaterials are readily availableReproduce fastBiological testingIn-vivo testing preparationsProtein insertionFish embryo
The invention relates to the activity detection method for the new-type anti or promote angiogenic factor by zebra fish embryo model. Wherein, after hatching, adding former protein constituent to culture for some time at constant temperature; observing its development; then, dyeing blood vessel, observing with cubic microscope, sampling and storing image. This invention is simple and fit to wide application with low cost.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos
InactiveCN105463089AHigh degree of enrichmentSimple stepsMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationWater bathsFluorescence
The invention relates to an assay for transposase accessible chromatin using sequencing (ATAC-seq) method applied to zebrafish embryos. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing zebrafish embryo sample pretreatment; adding lysis buffer into the embryos; cracking the embryos in a water bath by using a wild-neck spearhead; performing a transposition reaction immediately and purifying DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid); determining a cycle number for library establishment by using a real-time fluorescence quantification method; directly performing library establishment and sequencing by using a further PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) method. A regulatory sequence on genome chromatin can be located and decoded by the ATAC-seq method and a DNase-seq (DNase I hypersensitive sites sequencing) method, but the steps in ATAC-seq are simpler, a required cell quantity is smaller, the ATAC-seq is more helpful under the situation that a large quantity of cells cannot be obtained, and the data enriching degree of the ATAC-seq is higher according to an assay result. The ATAC-seq method is further applied to zebrafish embryo cells. Thus, an effective and simple method is provided for the researches of changes of chromatin structures in early developing processes of living organisms and corresponding gene expression regulation and control researches.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for evaluating influence of pollutants on zebra fish biotoxicity
The invention provides a method for evaluating the influence of pollutants on zebra fish biotoxicity. The method comprises the following steps of: respectively carrying out toxicity tests on zebra fish embryos, larva zebra fish and adult zebra fish to respectively obtain LC50 values and / or sub-lethal doses of zebra fish in different growth stages; selecting the zebra fish at a growth stage with the lowest LC50 value and / or sub-lethal dose as the most sensitive stage zebra fish; evaluating the toxicity strength of pollutants by adopting the LC50 value and / or the sub-lethal dose of the most sensitive stage zebra fish; according to the evaluation method, toxicity tests are carried out on zebra fish at different growth stages respectively, the most sensitive stage zebra fish can be determinedaccording to the biotoxicity difference of pollutants to zebra fish at different stages, and important guiding significance is achieved on zebra fish protection work by determining the most sensitivestage of zebra fish; in addition, the toxicity strength of pollutants is evaluated by the biotoxicity of zebra fish at the most sensitive stage, and the accuracy of pollutant toxicity evaluation is improved.
Owner:CHINESE ACAD OF FISHERY SCI
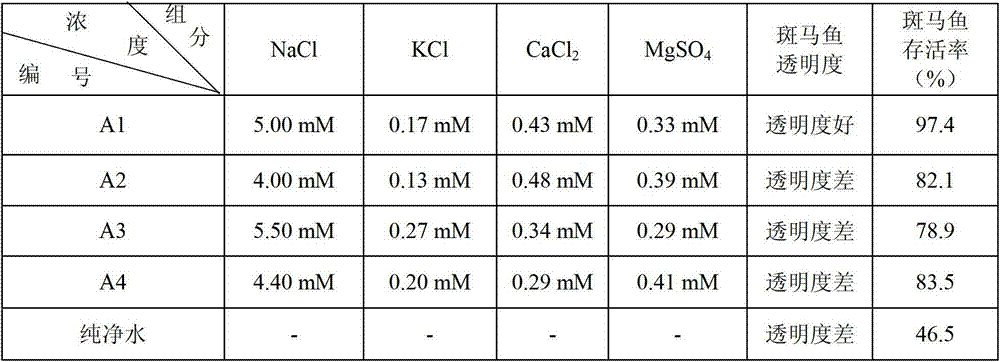
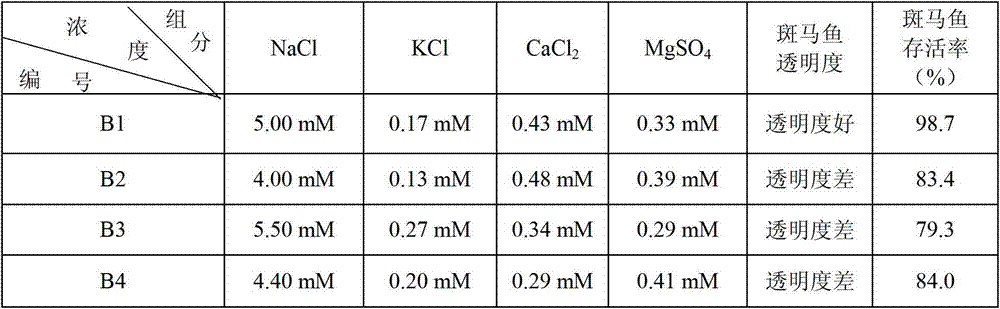
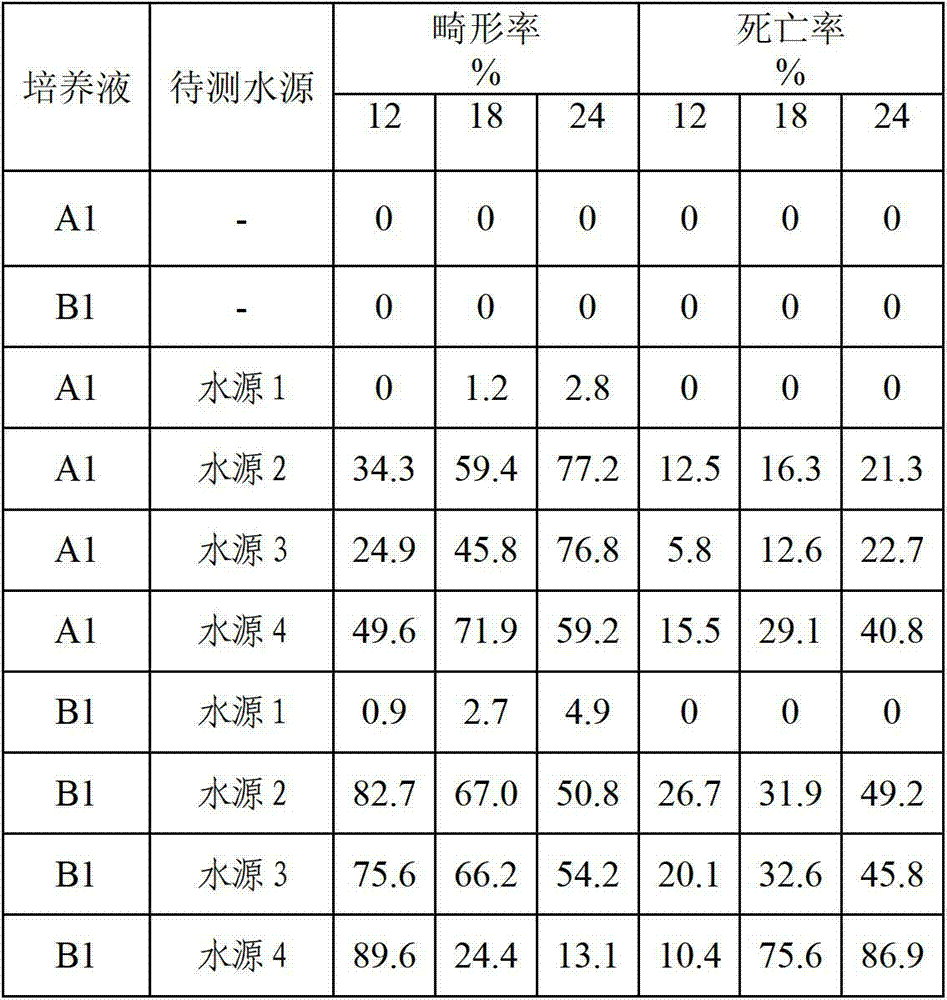
Application of zebra fish to testing water quality and toxicity and method for applying zebra fish to test water quality and toxicity
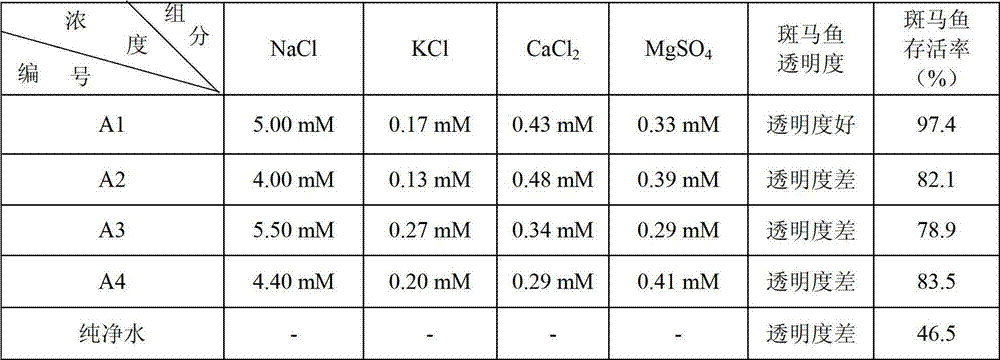
ActiveCN102899383ARapid Test Synthetic ToxicityShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementWater sourceFish embryo
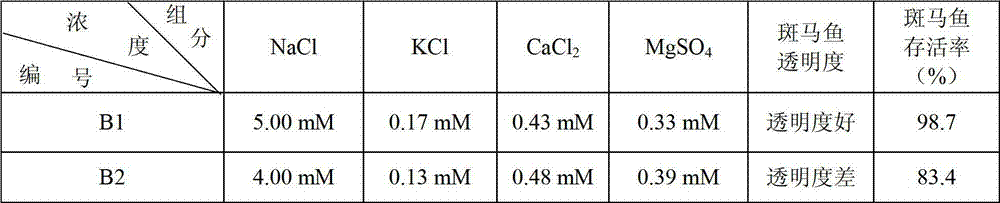
The invention relates to an application of zebra fish to testing water quality and toxicity and a method for applying zebra fish to test water quality and toxicity. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing an embryo culture solution, then adding a water source to be tested to the embryo culture solution, using the embryo culture solution to which the water source to be tested is added to culture zebra fish embryos and then observing and recording the developmental aberration rates and mortality of the zebra fish embryos in 12-24 hours to judge the toxicity of the water source to be tested toward the embryos, wherein the ratio of the volume of the added water source to be tested to the volume of the embryo culture solution is 1:3; the embryo culture solution is directly prepared from alkalescent water with pH value being 6.7-8.5; and the embryo culture solution contains 5mM of NaCl, 0.17mM of KCl, 0.43mM of CaCl2 and 0.33mM of MgSO4. The method has the following beneficial effect that the embryo culture solution prepared from the alkalescent water ensures that the zebra fish embryos can quickly test the comprehensive toxicity of the water source to be tested, thus shortening the detection period.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
Method for applying zebra fish to test toxicity of organic solvent
InactiveCN102899384AQuick testShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementOrganic solventFish embryo
The invention relates to a method for applying zebra fish to test toxicity of an organic solvent. The method comprises the following main steps of: preparing an embryo culture solution, then adding the organic solvent to the embryo culture solution, ensuring that the concentration of the organic solvent in the embryo culture solution reaches the concentration needed by measuring, using the embryo culture solution to which the organic solvent is added to culture zebra fish embryos and then observing and recording the developmental aberration rates and mortality of the zebra fish embryos in 6-12 hours to judge the toxicity of the organic solvent toward the embryos, wherein the embryo culture solution is directly prepared from alkalescent water with pH value being 6.7-8.5; and the embryo culture solution contains 5mM of NaCl, 0.17mM of KCl, 0.43mM of CaCl2 and 0.33mM of MgSO4. The method has the following beneficial effect that the embryo culture solution prepared from the alkalescent water ensures that the zebra fish embryos can quickly test the toxicity of the organic solvent, thus shortening the detection period.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Modified zebra fish drug metabolism modeling method
InactiveCN103623433AEasy to administerEfficient enrichmentComponent separationPreparing sample for investigationBiotechnologyMetabolite
The invention relates to a modified zebra fish drug metabolism modeling method, which specifically comprises the steps of (1) enriching metabolites by virtue of a zebra fish metabolism model; (2) separating and analyzing the enriched metabolic components of the zebra fish in the last step by using modern chromatography or the hyphenated technique thereof, capturing or knocking out target components or metabolites; (3) collecting zebra fish germ cells; (4) putting zebra fish embryos in three days after fertilization in a culture plate which holds an embryo culture medium and administrating a drug; (5) dyeing the bones of the zebra fish; and (6) detecting and analyzing the dyed bones of the zebra fish. According to the invention, an adolescent zebra fish osteoporosis model is applicable to in-vivo effective evaluation of anti-osteoporosis activity of Chinese herbal medicinal ingredients such as trace ingredients; an adult zebra fish metabolism model is simple in metabolites and efficient in enrichment; the modern chromatography or the hyphenated technique thereof provide powerful guarantee for the separation and analysis of the complex Chinese herbal medicinal system and the metabolic components. The model obtained by the method has the outstanding advantage that the separation and analysis of Chinese herbal medicinal original-form ingredients and the metabolic components are integrated with the in-vivo anti-osteoporosis activity evaluation, and simple and efficient.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE INST OF TRADITIONAL CHINESE MEDICINE
Index-first chromatin immunoprecipitation (iChIP) high-throughput sequencing experimental method applied to zebrafish embryos
InactiveCN105463090AReduce experimental biasMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationAntigenEnzyme digestion
The invention relates to an index-first chromatin immunoprecipitation (iChIP) high-throughput sequencing (iChIP-seq) experimental method applied to zebrafish embryos. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, performing formaldehyde crosslinking on zebrafish embryo samples; secondly, acquiring mononucleosome through MNase (Micrococcal Nuclease) enzyme digestion; fixing chromatin on magnetic beads through H3 antigens; labeling various different samples on the magnetic beads with index joints; releasing the chromatin from the magnetic beads, concentrating, mixing the samples together, performing a chromatin immunoprecipitation reaction on various antigens to obtain DNA (Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid) sample, and purifying the DNA sample to perform library establishment and sequencing. The iChIP is an improvement on conventional ChIP (Chromatin Immunoprecipitation). According to the method, each sample is marked before ChIP, and then all the samples are mixed together to perform an experiment, so that a dynamical change decorated by the chromatin in a developing process can be observed, experimental deviations possibly caused by a small quantity of early-period cells are reduced, and the chromatin-modified dynamical change in the whole developing process can be quantitatively observed through the quantity of cells.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for predicating embryotoxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants on early-phase life stage of zebra fish
ActiveCN105044317AAddressing non-reflective typical NSAID sewage biotoxicityBiological testingLife stageFish embryo
The invention discloses a method for predicating the embryotoxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants on an early-phase life stage of zebra fish. The method comprises the following steps: exposing zebra fish embryos in the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants which have equal logarithm space concentrations; recording the death rate and the aberration rate of the zebra fish embryos 7 days after exposing; and calculating by using SPSS software to obtain corresponding LC50 and teratogenetic EC50, which are used for evaluating the toxicity of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants. With the adoption of the method, the toxicity feature and the toxicity level of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug type novel pollutants are subjected to an analytical test and quantitative description; and meanwhile, the method also can be used as an index for monitoring and evaluating the wastewater biological toxicity of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, and reference is provided for risk predication and evaluation of the potential biological toxicity of the pollutants in a water body.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROBIOLOGY GUANGDONG DETECTION CENT OF MICROBIOLOGY
Monitoring and identifying evaluation method for group biotoxicity in printing and dyeing wastewater
InactiveCN108120812ASolve unrepresentative problemsImprove securityChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceTesting waterToxicity reductionResearch Object
The invention discloses a monitoring and identifying evaluation method for group biotoxicity in printing and dyeing wastewater and belongs to the field of biotoxicity identification. The method comprises the following steps: screening photogenic bacteria, zebrafish larvae, zebrafish embryos and chlorella as test organisms; and performing risk and toxicity reduction evaluation on the printing and dyeing wastewater by adopting group biotoxicity tests and combining with a toxicity evaluation method, and constructing a toxicity identification evaluation system by combining with a TIE technology according to the wastewater contamination characteristics and results. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the group biotoxicity tests comprising three trophic levels such as decomposer,producer and consumer are performed for characterizing toxicities of the printing and dyeing wastewater, and the problem that a single biotoxicity test does not have representativeness is solved. Themethod has the advantages of being comprehensive, simple, high-efficiency, capable of controlling from the source, high in safety and the like, can be widely applied to researching and evaluating influences of toxic pollutants on the ecological environment, and provides a certain basis for ecological risk assessment.
Owner:CHANGZHOU UNIV
Microfluidic chip applicable to medicine screening of zebra fish embryos
InactiveCN102757885ASave human effortSimple and cheap to manufactureBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsElastomerControl layer
The invention relates to a microfluidic chip applicable to medicine screening of zebra fish embryos. The microfluidic chip is low in price, easy to prepare and suitable for large scale, high flux and automation. The microfluidic chip comprises at least one microfluidic layer, at least one control layer, a connecting layer and at least one micro cell, wherein the control layer is adjacent to the microfluidic layer; the connecting layer is used for connecting the adjacent microfluidic layer and the control layer; the micro cell is used for accommodating the zebra fish embryos and providing the growth environment for the zebra fish embryos; the microfluidic layer is provided with a microfluidic channel; the microfluidic channel is communicated with the internal space of the micro cell; the control layer is provided with at least one control channel; the microfluidic channel and the control channel are provided with at least one intersected point; and the connecting layer at the position of the at least one intersected point consists of an elastomer material and forms an elastomer valve. The communication state of the microfluidic channel can be controlled convenient through the elastomer valve, so that fully-automatic operation of medicine screening of the zebra fish embryos can be realized through an electromagnetic valve controlled by an external computer.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Cell microinjection system with force feedback
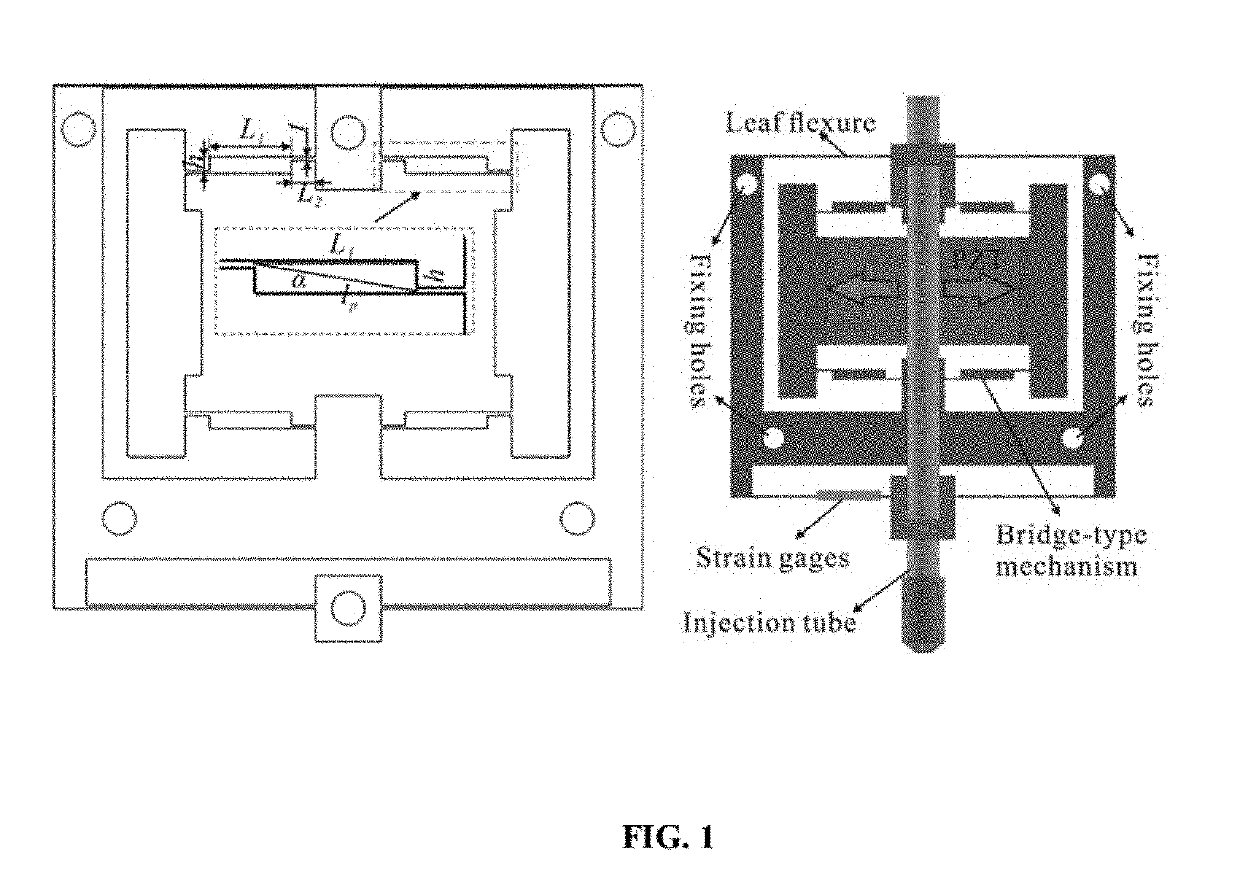
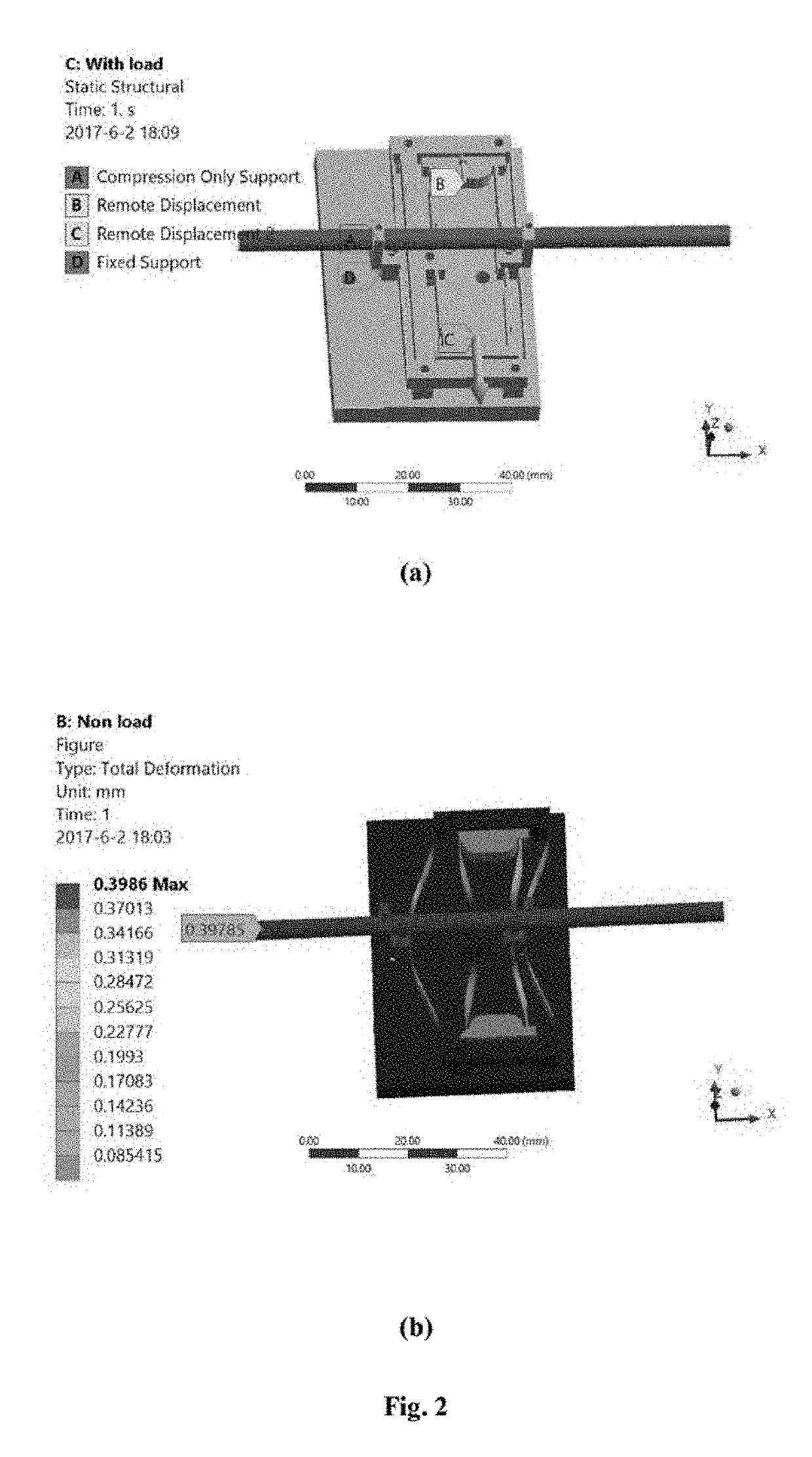
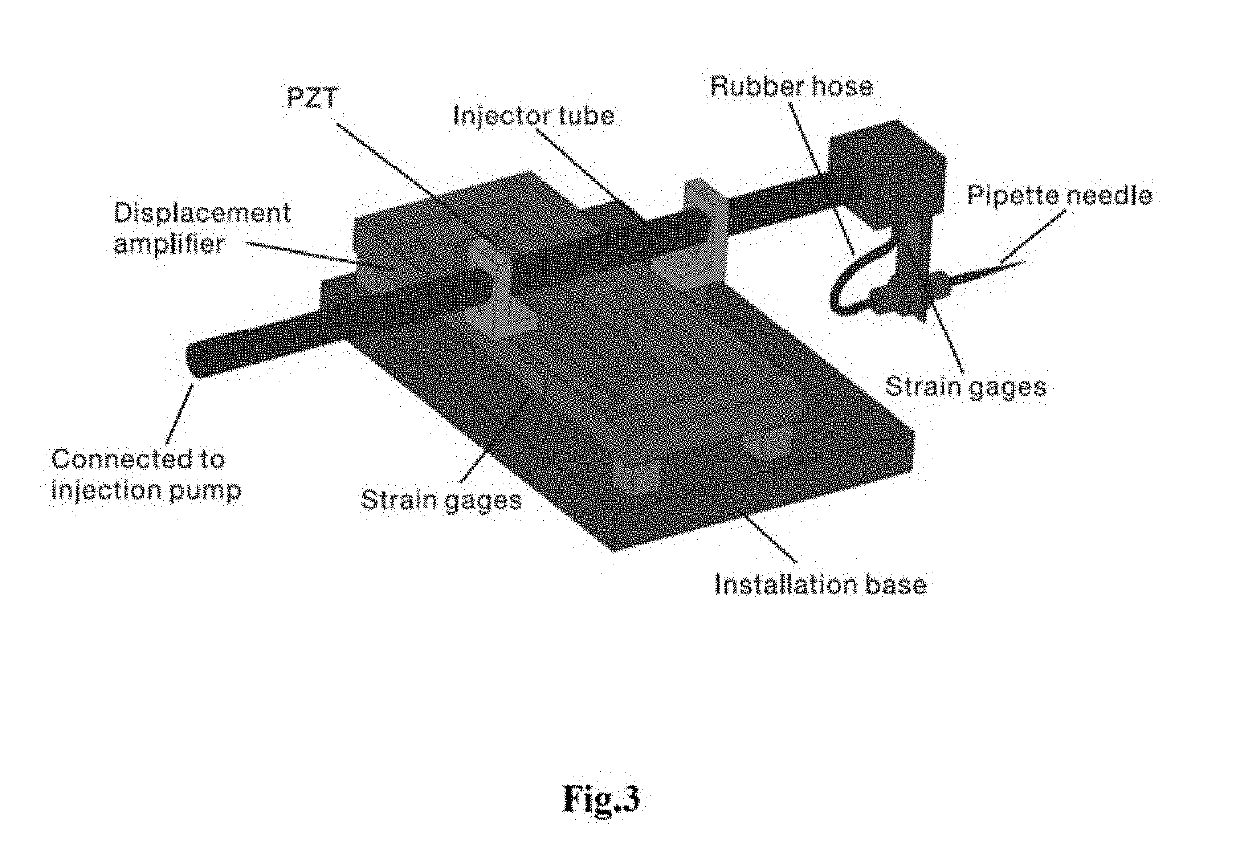
ActiveUS20190292567A1Low costEasy to installAnimal reproductionProgramme-controlled manipulatorElectricityEmbryo
A novel piezo-driven cell injection system with force feedback overcomes the unsatisfied force interaction between the pipette needle and embryos in conventional position control. By integrating semiconductor strain-gage sensors for detecting the cell penetration force and the micropipette relative position in real time, the developed cell microinjection system features high operation speed, confident success rate, and high survival rate. The effectiveness of the developed cell injection system is experimentally verified by penetrating zebrafish embryos. The injection of 100 embryos are conducted with separate position control and force control. Results indicate that the force control enables a survival rate of 86%, which is higher than the survival rate of 82% produced by the position control in the same control environment. The experimental results quantitatively demonstrate the superiority of force control over conventional position control for the first time.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF MACAU
Application of zebra fish to testing safety of safe substance and method for applying zebra fish to test safety of safe substance
InactiveCN102899385AShort detection cycleMicrobiological testing/measurementFish embryoMortality rate
The invention relates to an application of zebra fish to testing safety of a safe substance and a method for applying zebra fish to test safety of the safe substance. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: preparing an embryo culture solution, then adding the safe substance to be tested to the embryo culture solution, using the embryo culture solution to which the safe substance to be tested is added to culture zebra fish embryos and then observing and recording the developmental aberration rates and mortality of the zebra fish embryos in 4-72 hours to judge the toxicity of the safe substance to be tested toward development of the zebra fish embryos, wherein the addition of the safe substance to be tested ensures that the concentration of the substance to be tested in the culture solution is distributed in echelon; the embryo culture solution is directly prepared from alkalescent water with pH value being 6.7-8.5; and the embryo culture solution contains 5mM of NaCl, 0.17mM of KCl, 0.43mM of CaCl2 and 0.33mM of MgSO4. The method has the following beneficial effect that the embryo culture solution prepared from the alkalescent water ensures that the zebra fish embryos can quickly test the comprehensive toxicity of the safe substance to be tested, thus shortening the detection period.
Owner:INST OF MEDICINAL PLANT DEV CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI +1
Method for evaluating kidney toxicity of compounds through detecting contents of creatinine in zebra fish tissues
ActiveCN104122355ARealize quantitative evaluationRepresentativeComponent separationCreatinine riseFish embryo
The invention relates to a method for evaluating kidney toxicity of compounds through detecting the contents of creatinine in zebra fish tissues. The method is applied to kidney toxicity researches. In the researches that utilize a zebra fish embryo model to study the toxic effect of compounds on the kidney, the creatinine component in embryo tissues is extracted, then the creatinine content is measured through a LC-MS (liquid chromatography-mass spectrum) method, the creatinine content can be taken as a detection index for evaluating the embryo kidney functions, and thus a rapid and precise compound kidney toxicity evaluation system with strong specificity is built.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Preparation method of transgenetic zebrafish used for detecting environment pollutants
ActiveCN103667327AVector-based foreign material introductionAnimal husbandryWild typeFluorescence microscope
A disclosed preparation method of transgenetic zebrafish used for detecting environment pollutants comprises: (1) cloning the promoter regulatory sequence of Mdr1 protein from zebrafish genome; (2) fusing the DNA fragment obtained by cloning into the upstream of GFP coding sequence for constructing an expression vector; (3) performing zebrafish embryo microinjection on the expression vector; (4) culturing the embryo subjected to injection to sexual maturity, and enabling cultured zebrafish and wide zebrafish to copulate and oviposit; and (5) screening positive F1 generation under a fluorescence microscope, and performing inbreeding to obtain F2 generation and further to obtain a transgenic line with stable inheritance. Because the expression level of fluorescin can be induced in a concentration dependent way by multiple environment pollutants such as heavy metals, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and the like, the transgenic zebrafish prepared by employing the preparation method can be used to detecting the existence and the concentration of the above chemical pollutants in environment; and the preparation method has the advantages of being economic, rapid, convenient and accurate.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
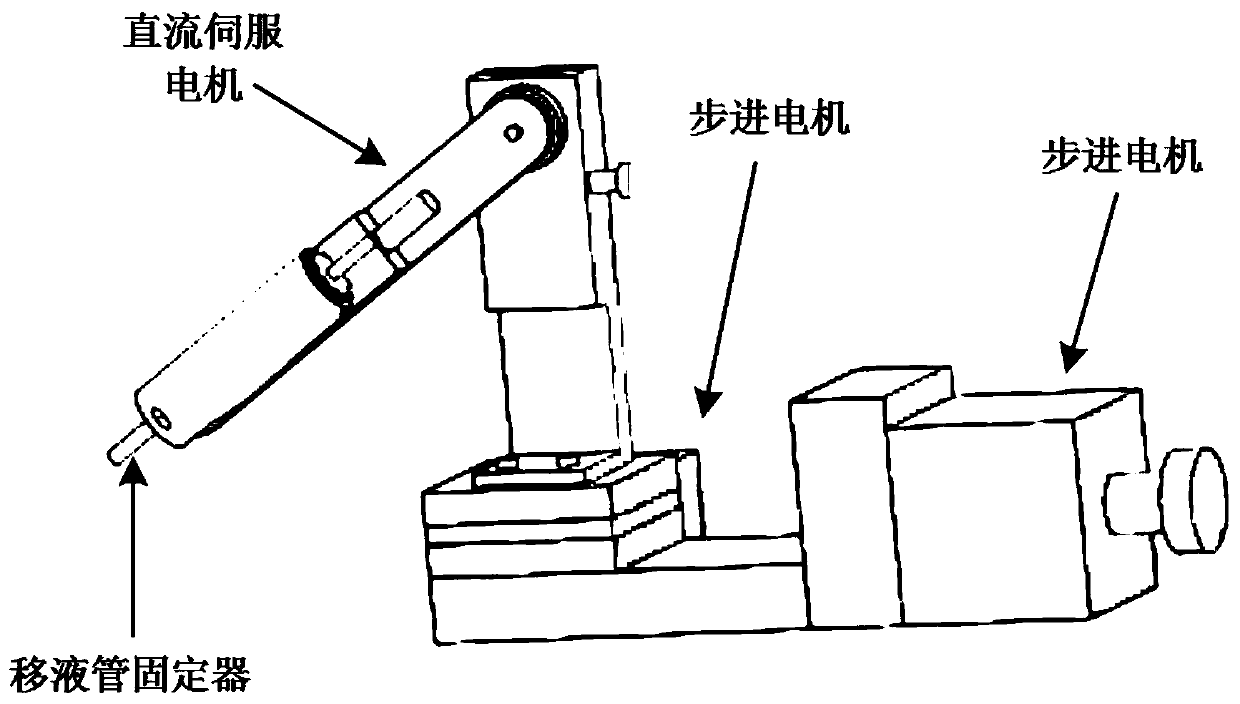
Zebrafish embryo heart injecting system and method based on vision servo three-dimensional rotation
ActiveCN110016431AFix inaccurate positioningLow costBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsControl signalEmbryo
The invention discloses a zebrafish embryo heart injecting system and method based on vision servo three-dimensional rotation, and relates to the field of micro-injection. The zebrafish embryo heart injecting system comprises a stereomicroscope, a CCD camera, a supervisory computer, a triaxial mechanical hand, a rotating manipulator, a micropipet and a pump, wherein the CCD camera is located abovethe stereomicroscope, and is used for collecting images and transmitting the collected images to the supervisory computer for treatment; the supervisory computer is connected with the triaxial mechanical hand and the rotating manipulator, and is used for analyzing the real-time position and the gesture of a zebrafish embryo as well as the point position of the micropipet according to the collected images, and transmitting a control signal to the triaxial mechanical hand and the rotating manipulator to control the direction and the speed of the triaxial mechanical hand and the rotating angle of the rotating manipulator; the triaxial mechanical hand is used for clamping the corresponding micropipet to move the point of the corresponding micropipet to a target position; the rotating manipulator is used for clamping the corresponding micropipet to rotate the zebrafish embryo; and the pump is used for providing sucking force for sucking and holding the zebrafish embryo and thrust for pushing out foreign substances. The system is simple in structure, high in precision and good in stability.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
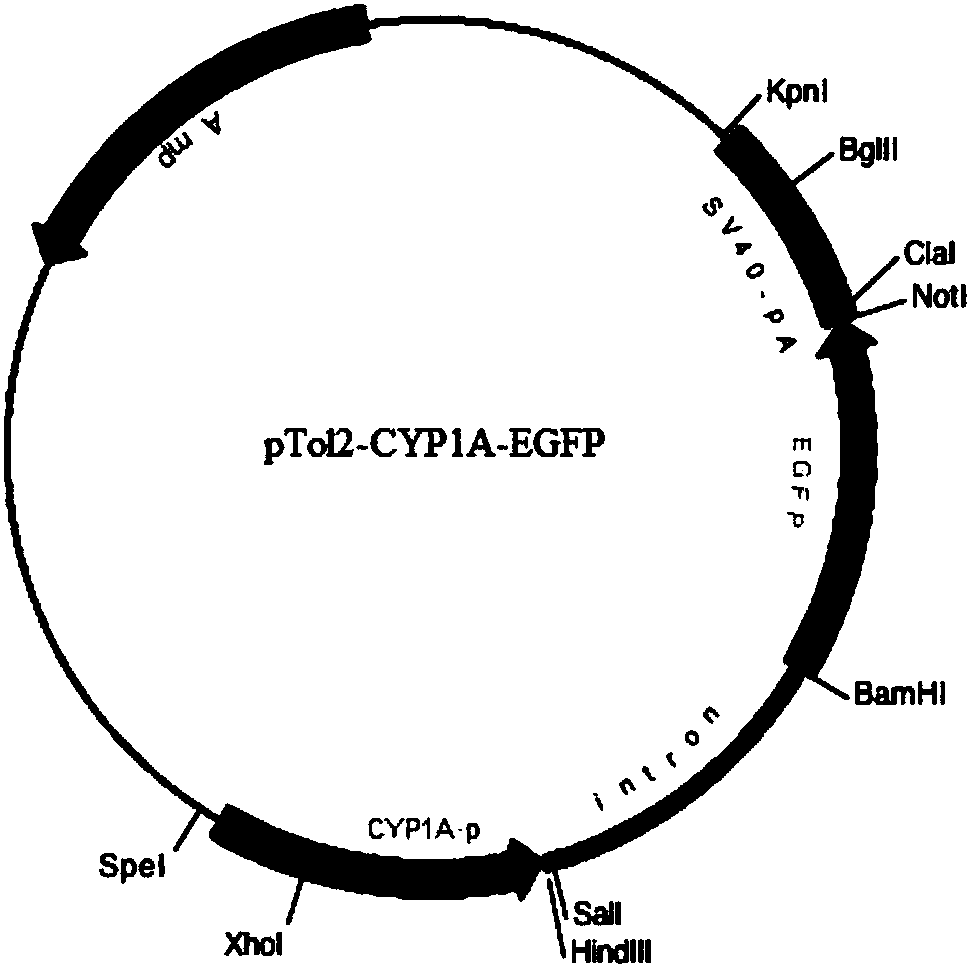
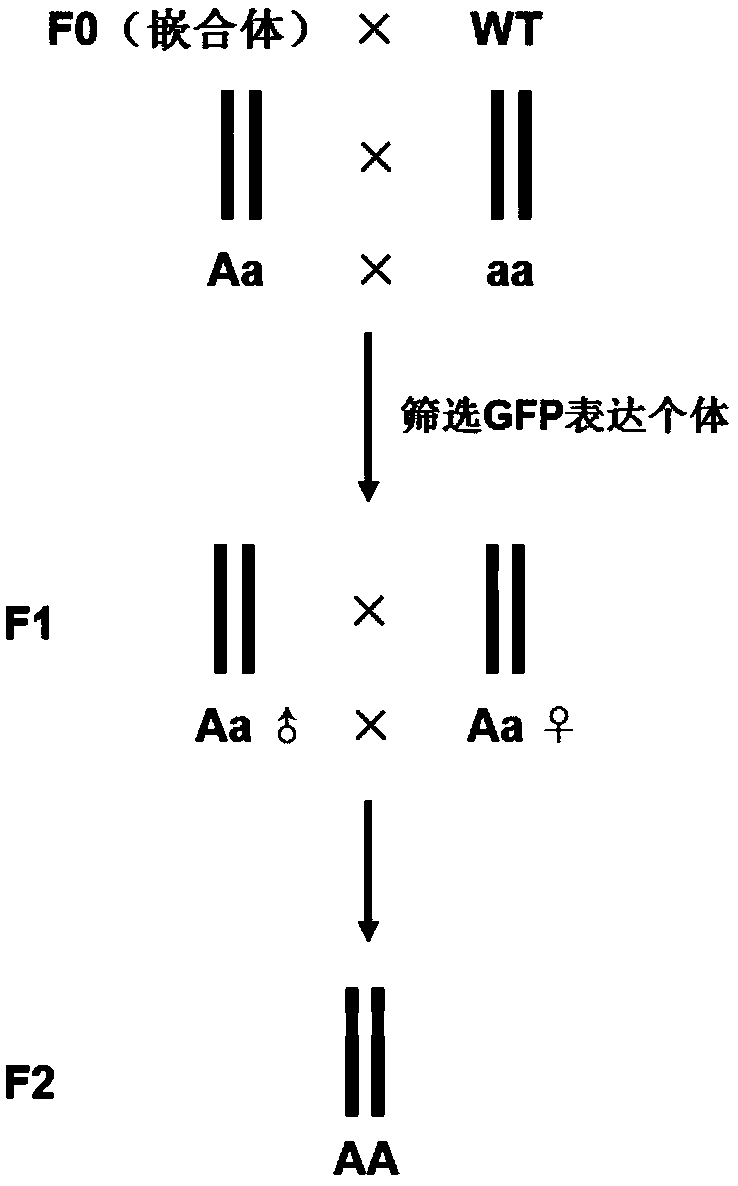
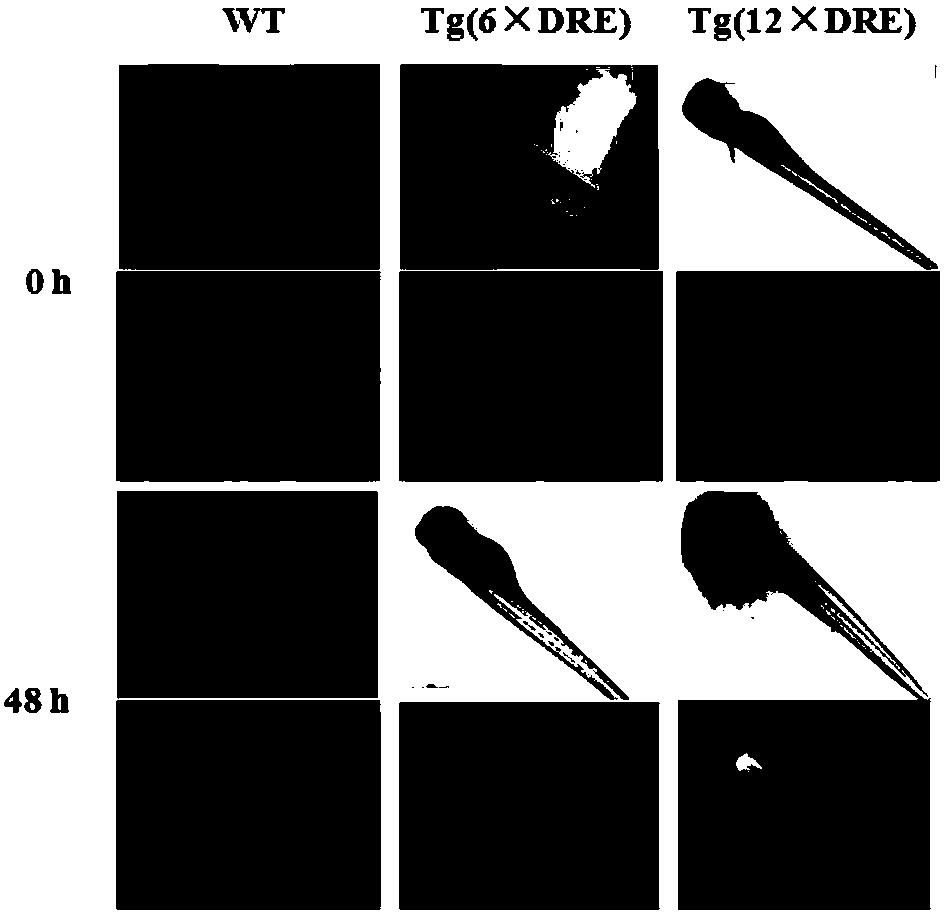
Preparation method of transgenic zebrafish
InactiveCN107058386AHigh activityImprove efficiencyNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionFluorescenceEmbryo
The invention relates to a preparation method of transgenic zebrafish, and relates to gene engineering. The preparation method comprises the following steps of (1) modifying a CYPIA starter sequence; (2) establishing a Tol2 transposon system knocking plasmid, and preparing a microinjection sample; (3) performing microinjection and subculture on zebrafish embryos. The invention provides an establishing method of a CYP1A starter containing twelve DREs (dehydration-responsive element), and a recombination Tol2 transposon knocking plasmid which contains the starter and is connected with a green fluorescent protein gene, a plasmid linear purifying method, and a microinjection sample method. The Tg(pCYP1A-6*DRE-EGFP) and Tg(pCYP1A-12*DRE-EGFP) transgenic zebrafish prepared by the microinjection technique can be used for comparing the activities of the starters respectively containing six DREs and twelve DREs.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Gene knockout breeding method for tnni3k gene deletion zebrafish
PendingCN109266687AEfficient and More Precise SilenceEasy to makeHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementGenotype AnalysisEmbryo
The invention relates to the technical field of gene knockout, in particular, the invention discloses a gene knockout breeding method for tnni3k gene deletion zebrafish, which adopts CRISPR / Cas9 geneediting technology to design a suitable target site on the tnni3k gene of zebrafish, and synthesizes specific gRNA and Cas9-protein was co-injected into zebrafish cells. After 48 hours of embryo culture, the embryos were selected for genotypic analysis, which confirmed the validity of the selected sites. The invention can more efficiently and more accurately silence a specific gene in the genome of an organism, and has the advantages of simple production, low cost, and can simultaneously cut a plurality of loci on a target gene and silence any number of single genes. At that same time, zebrafish embryo interfered with the tnni3k gene appear obvious developmental abnormalities.
Owner:HUNAN NORMAL UNIVERSITY
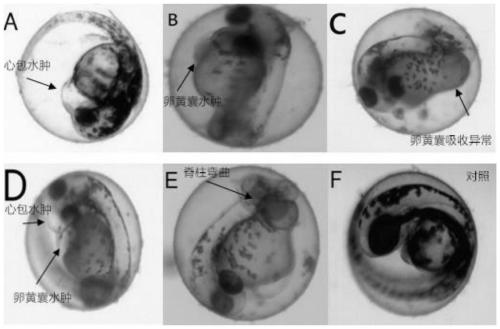
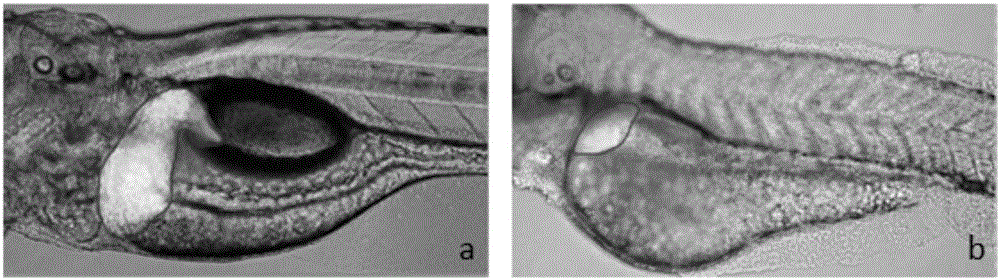
Method for rapidly evaluating damage effect on hepatic function of zebra fishes by compounds
The invention relates to a method for rapidly evaluating the damage effect on the hepatic function of zebra fishes by compounds. The method includes the steps that 1, fertilized normal zebra fish embryos are moved into breeding holes; 2, continuous chemical hatching is performed on the zebra fish embryos in the breeding holes, and the zebra fish embryos are marked to be a compound set to be detected; 3, livers of the zebra fish embryos are observed, and the liver area of the zebra fish embryos and the area of zebra fish embryo bodies are recorded and calculated; 4, according to the range relation between the index of the liver area of the zebra fish embryos of the compound set to be detected and the index of the liver area of normal zebra fish embryos, whether the compound set to be detected has liver toxicity is judged. The index of the liver area is used as a detection index for evaluating the hepatic function of the zebra fishes for the first time, and therefore the method is more scientific and objective and improves the accuracy of results. An established model for evaluating the damage effect on the hepatic function of the zebra fishes by the compounds has the advantages of being easy to manufacture, rapid to use, stable, reliable and good in repeatability.
Owner:BIOLOGY INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Method for incubating transgenic zebrafishes with intestinal-specific expression of red fluorescence
InactiveCN111621522AThe implementation process is simple and easy to controlNucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionWild typeEmbryo
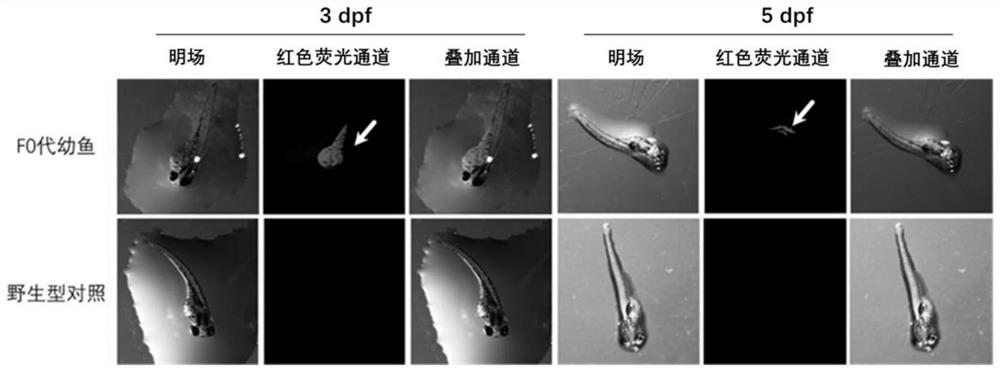
The invention relates to an incubation method for transgenic zebrafishes, and aims to provide a method for incubating transgenic zebrafishes with intestinal-specific expression of red fluorescence. According to the invention, by observing the expression of embryonic red fluorescent protein gene, zebrafish embryos with intestinal-specific fluorescence are selected, and hybrid offsprings are obtained by artificial feeding. The stably genetic zebrafishes with intestinal expression of red fluorescent protein are obtained by selfing of the hybrid offsprings, and then parent zebrafishes corresponding to embryos with 100% intestinal expression of red fluorescent protein are screened as double integration pure lines for seeding and preservation after test cross with wild type zebrafishes. The method of the present invention is simple and easy-to-control in implementation process, and can obtain a promoter with intestinal-specific expression and zebrafish strains with red fluorescent protein highly expressed in the intestine. The obtained zebrafish strains are used for the study of zebrafish intestinal function and can be observed for expression characteristics of intestinal red fluorescentprotein at any time, thereby meeting the integrity and completeness requirements on study of zebrafish intestinal function.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Zebra fish embryo incubation device for experiment
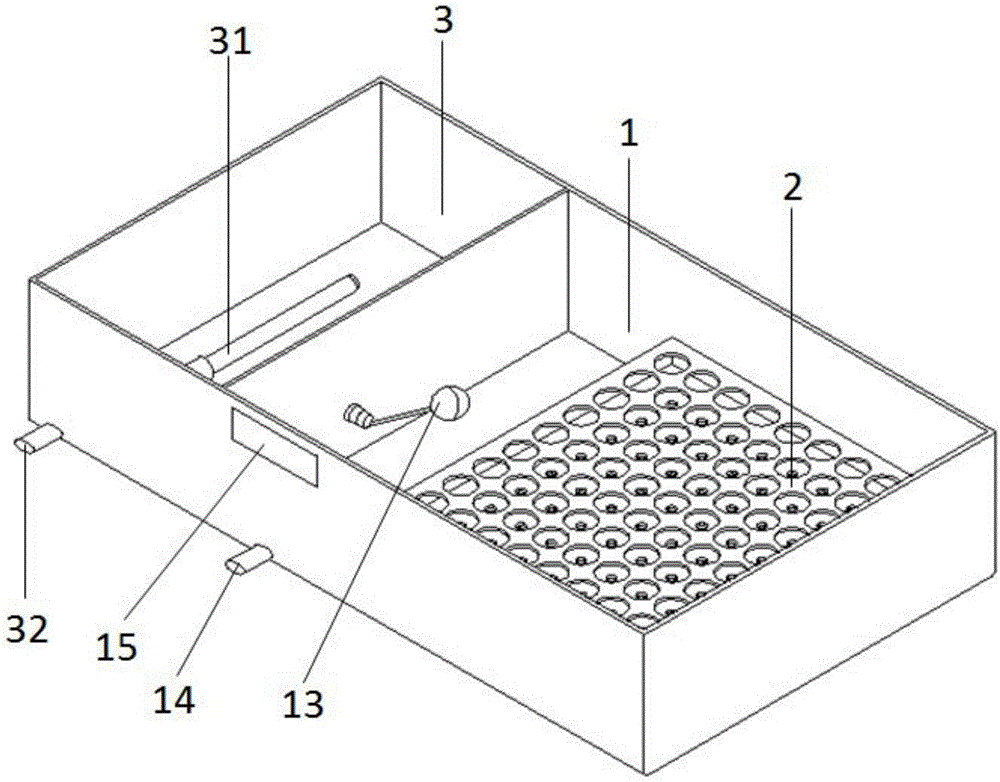
PendingCN106719172AImprove lighting conditionsSame lighting conditionsClimate change adaptationPisciculture and aquariaWater bathsDiameter ratio
The invention provides a zebra fish embryo incubation device for an experiment. The device comprises an incubation box and a supporting frame arranged in the incubation box. A first heater for heating a water bath is arranged at the bottom in the incubation box, a first cover body is arranged on the top of the incubation box, and a light source is arranged at the bottom of the first cover body. The supporting frame comprises a first installing plate, and a second installing plate parallel to the first installing plate. The edge of the first installing plate and the edge of the second installing plate are connected through a side plate to form a culture dish heating cavity, multiple arrayed installing holes are formed in the first installing plate, multiple water inlets are formed in the first installing plate, and the diameter ratio of the installing holes to the water inlets is 5:1 to 4:1. Due to the adoption of water bath heating, temperature is more constant than temperature of hot air heating adopted, in an illumination incubator, meanwhile, the diameter ratio of the installing holes to the water inlets is 5:1 to 4:1, fluctuation of heat exchange of water in the culture dish heating cavity and a culture solution in a culture dish is small, therefore, the experimental temperature is more constant, and the experimental result is more reliable.
Owner:ZHEJIANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
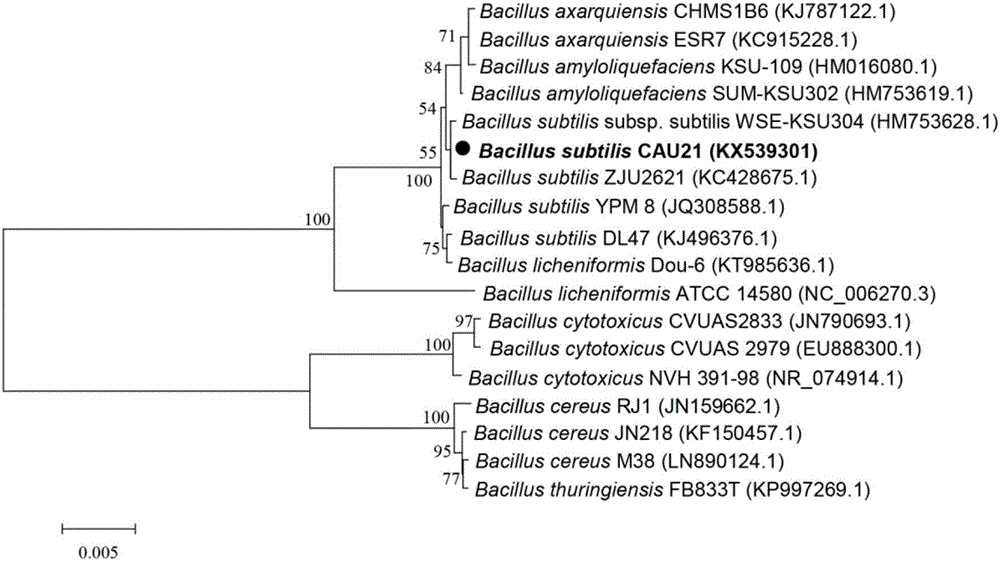
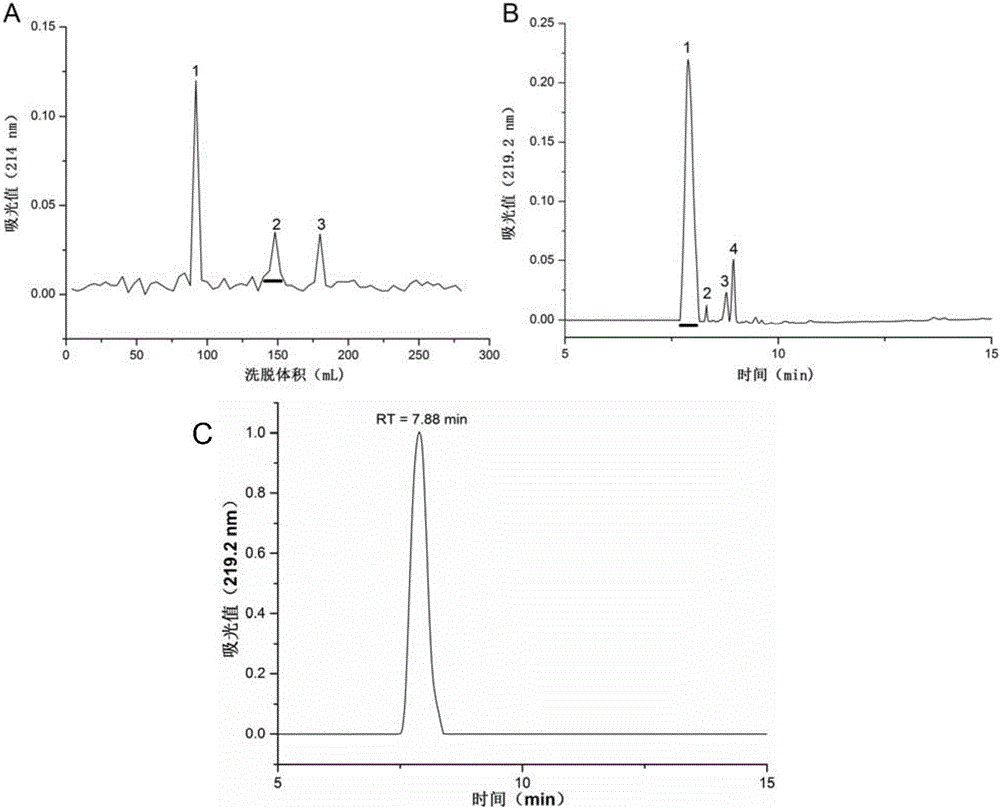
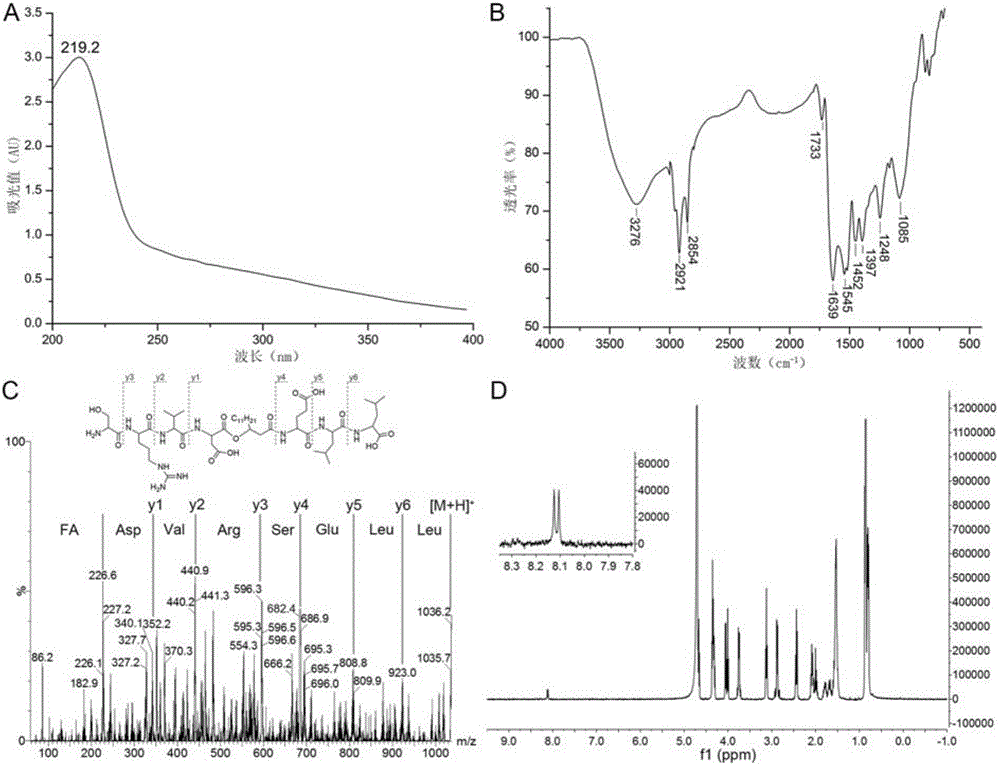
Antimicrobial lipopeptide bacaucin derivatives and application thereof in bacterial infection inhibition
The invention discloses antimicrobial lipopeptide bacaucin derivatives and application thereof in bacterial infection inhibition. The antimicrobial lipopeptide bacaucin derivatives disclosed by the invention are polypeptides shown as SEQ ID No. 4 and SEQ ID No. 9-18 or derivatives thereof. The experiment proves that the bacaucin derivatives disclosed by the invention have effects of inhibiting bacteria, particularly bacaucin-1 has a specific effect on inhibiting staphylococcus aureus, and the minimum inhibitory concentration is 4mu g / mL; and moreover, the derivatives do not have any cytotoxic effect on Vero, Hep-2 and A549, are not hemolytic, have excellent histocompatibility and do not have any toxic effect on zebrafish embryos. The bacaucin derivatives have effects on inhibiting Gram positive bacteria and Gram negative bacteria and can be used for inhibiting bacteria.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com