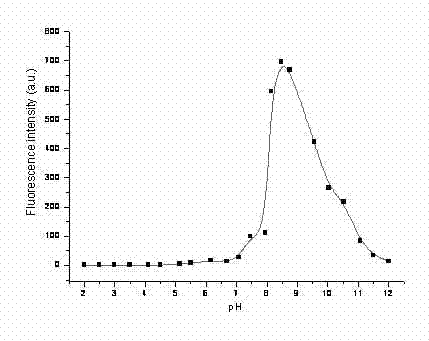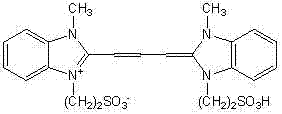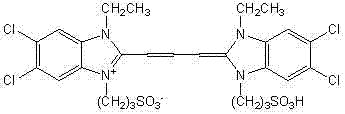Patents
Literature
46 results about "Laser Scanning Microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Confocal microscopy, most frequently confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) or laser confocal scanning microscopy (LCSM), is an optical imaging technique for increasing optical resolution and contrast of a micrograph by means of using a spatial pinhole to block out-of-focus light in image formation.
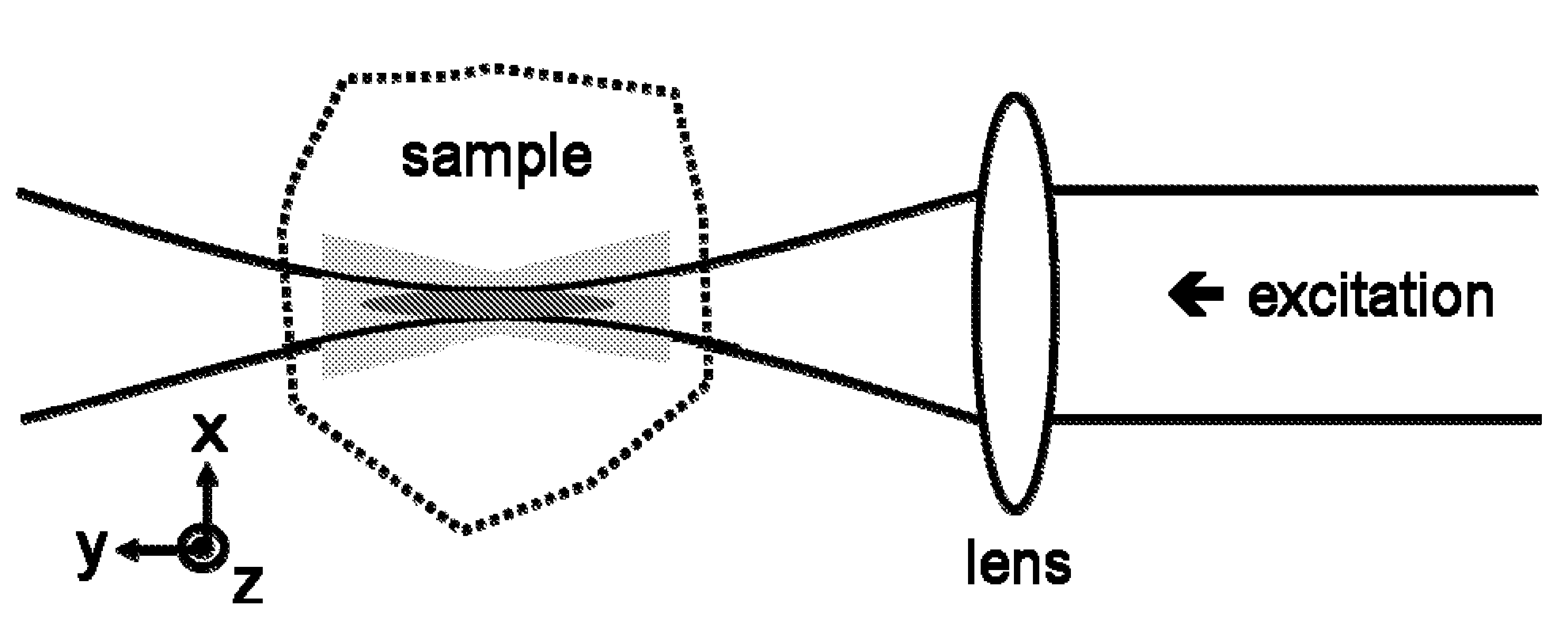
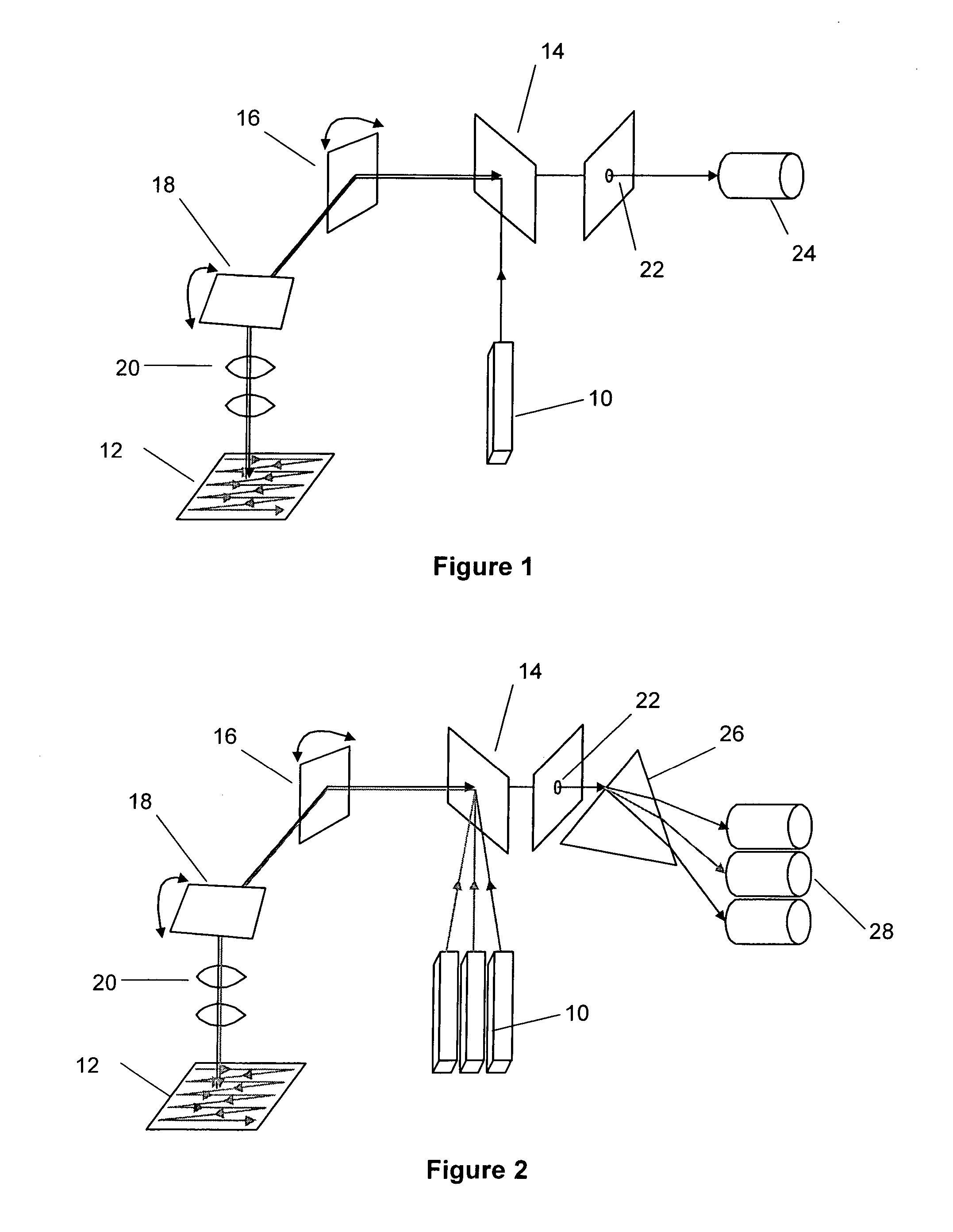
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
ActiveUS20110122488A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFluorescence
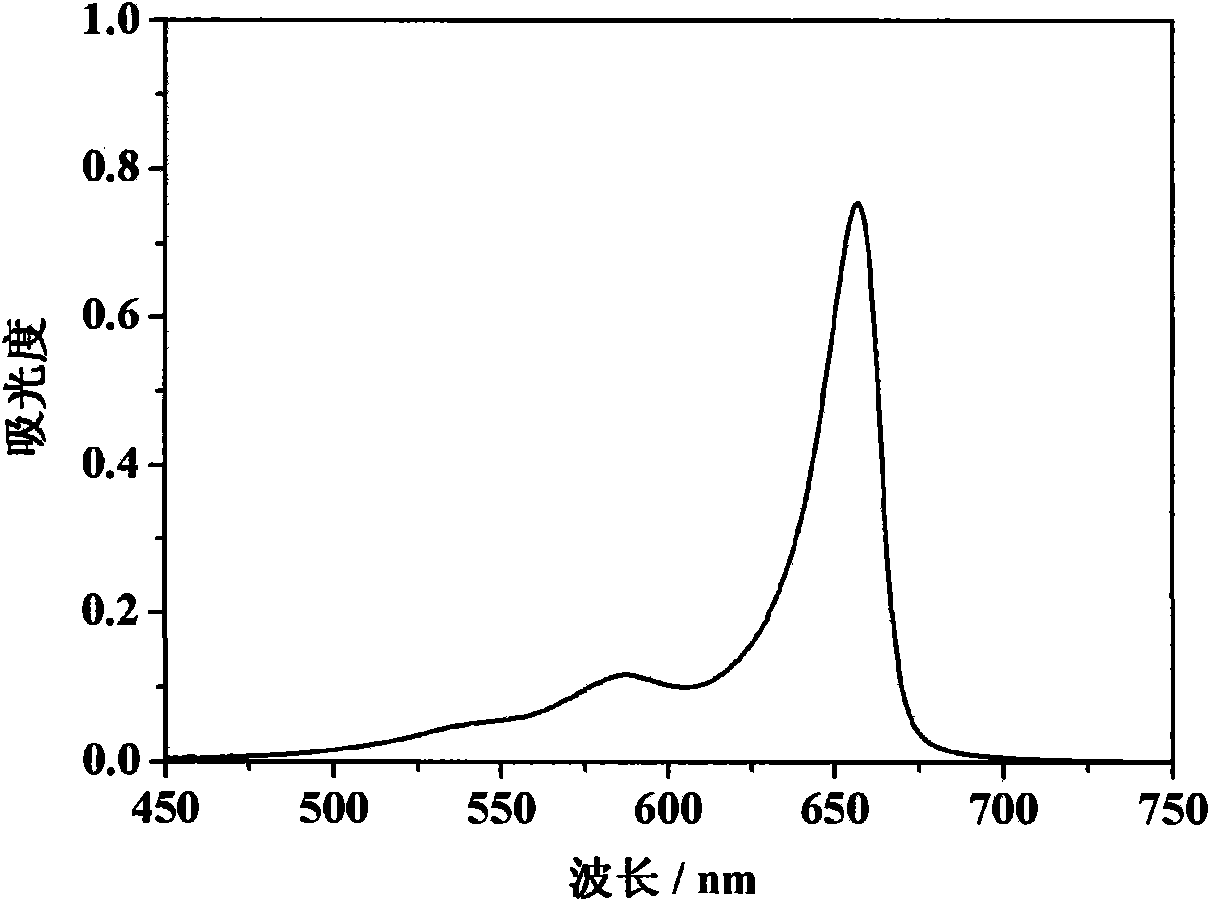
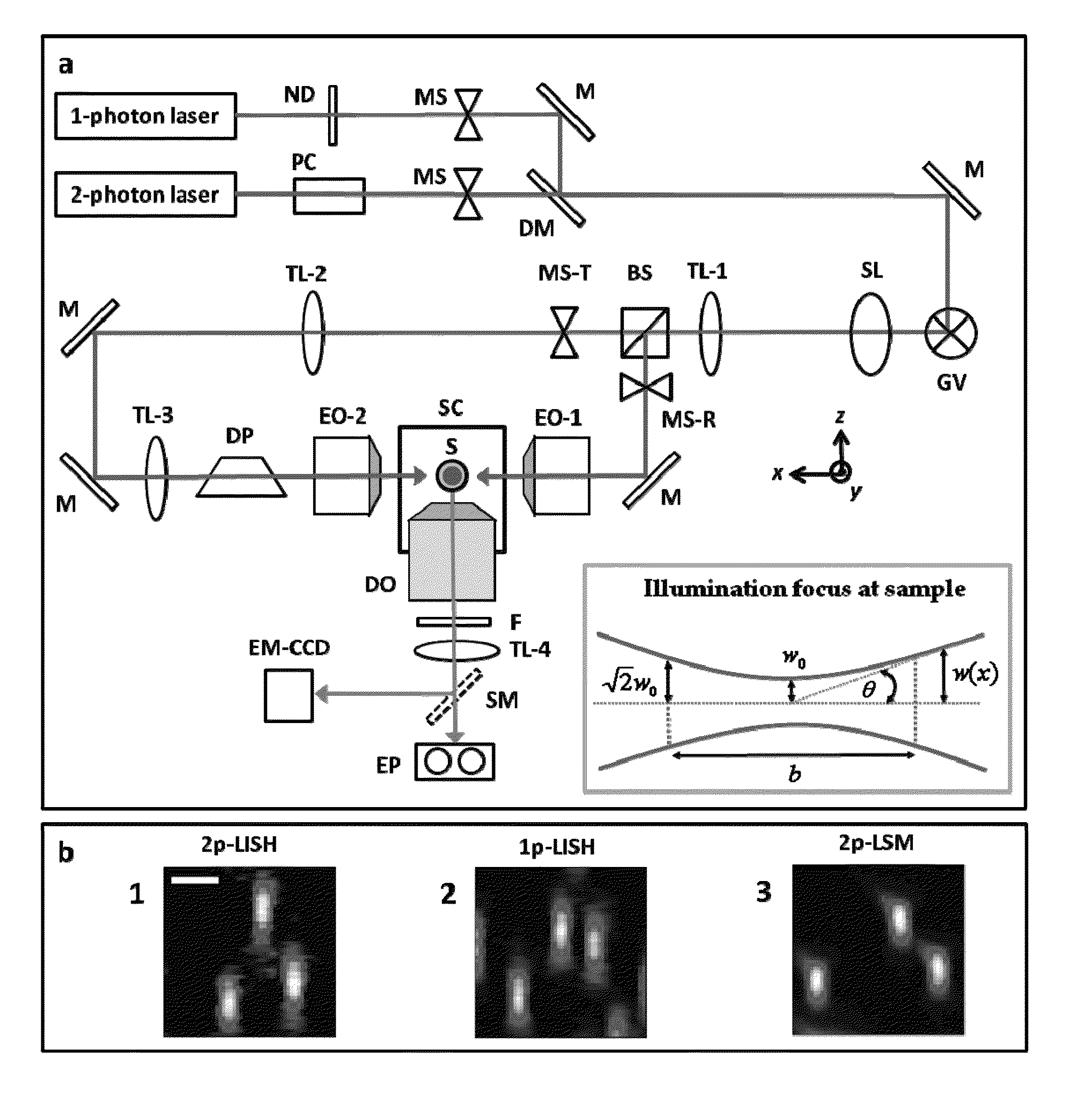
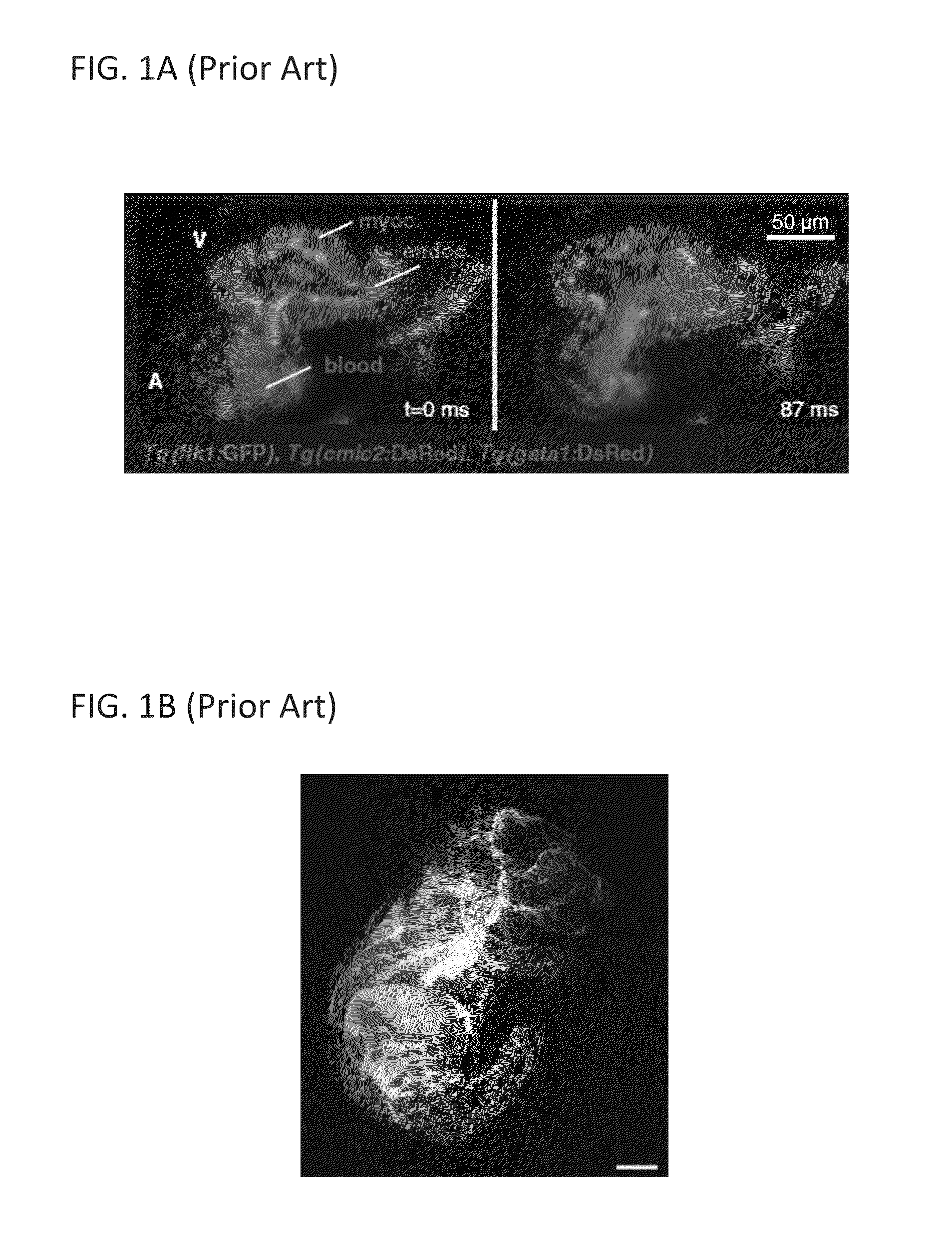
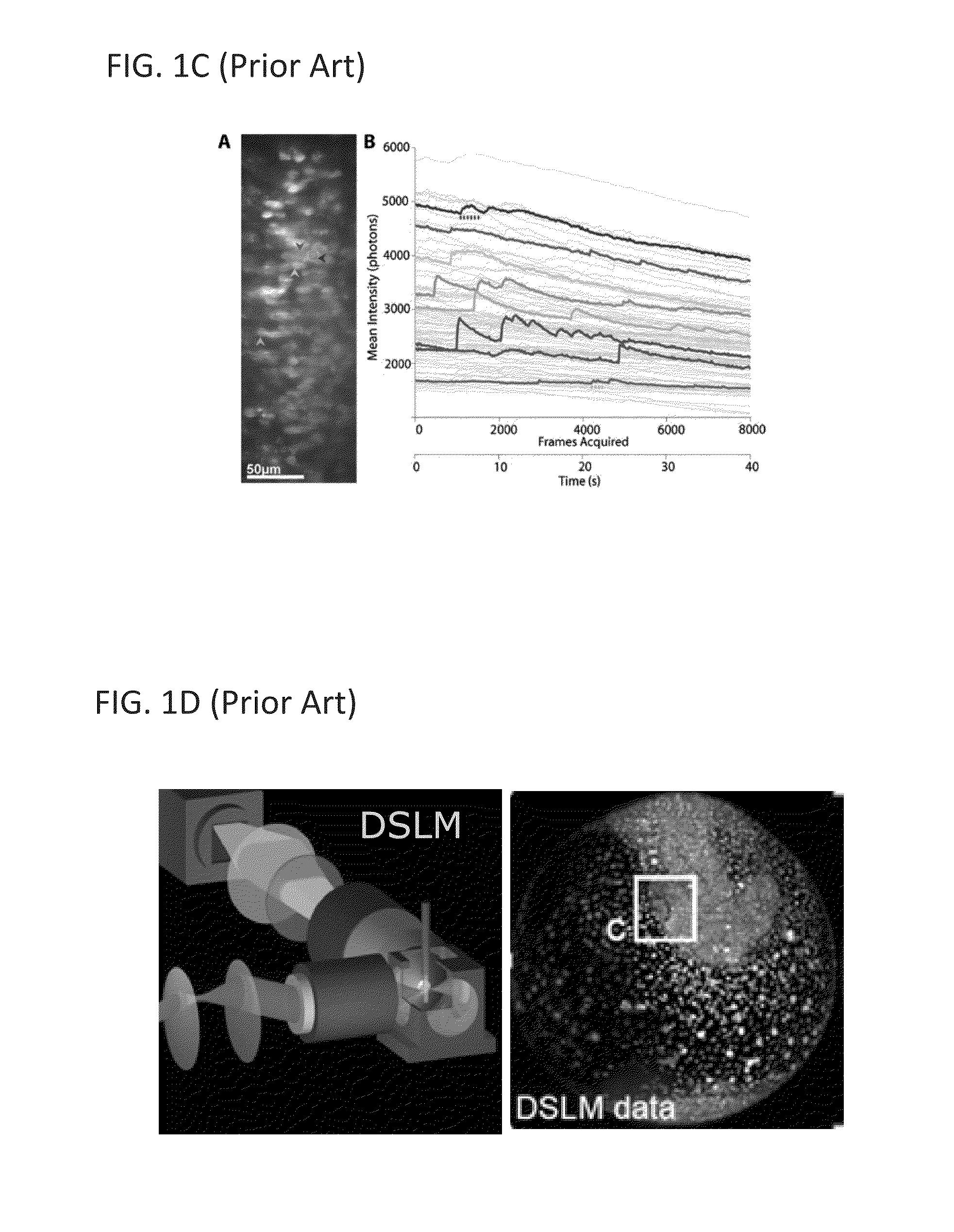
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal. illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Confocal laser scanning microscopy apparatus
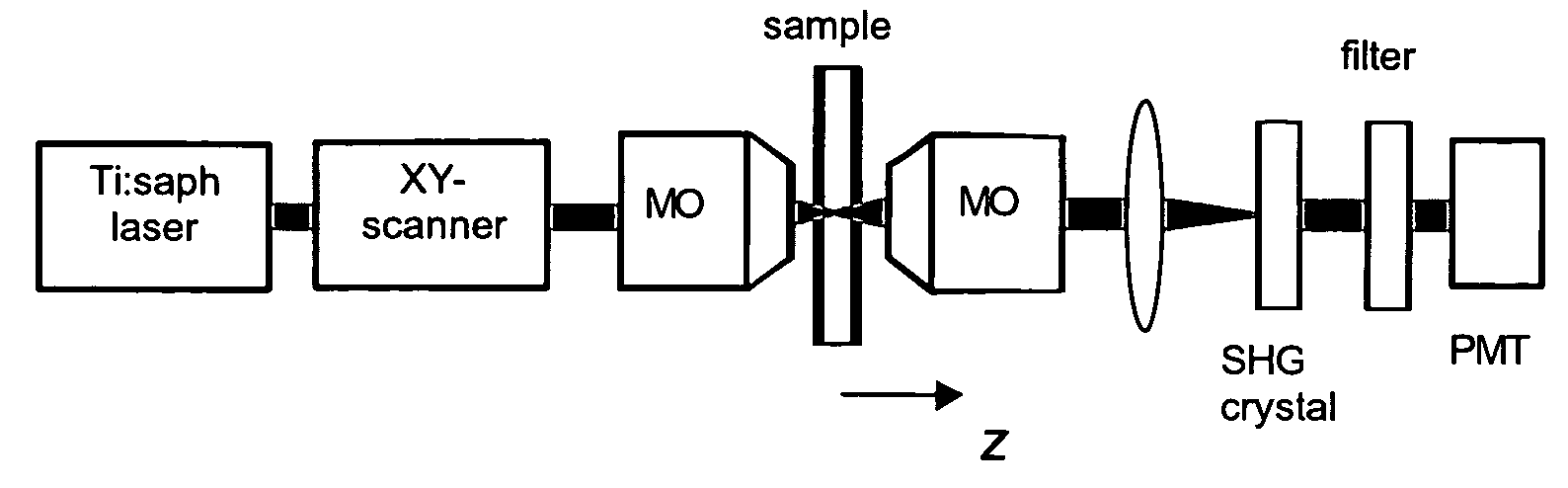
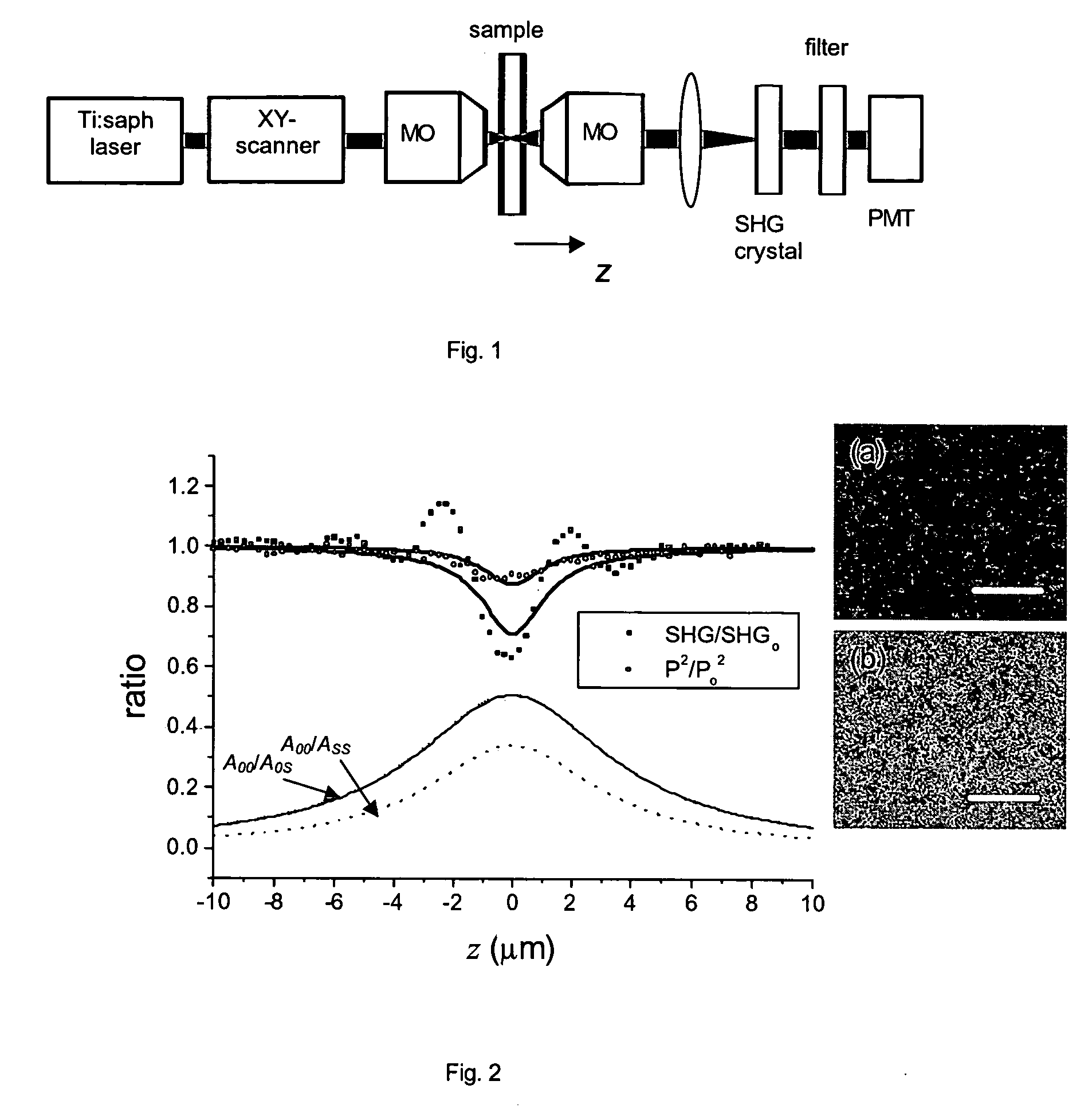
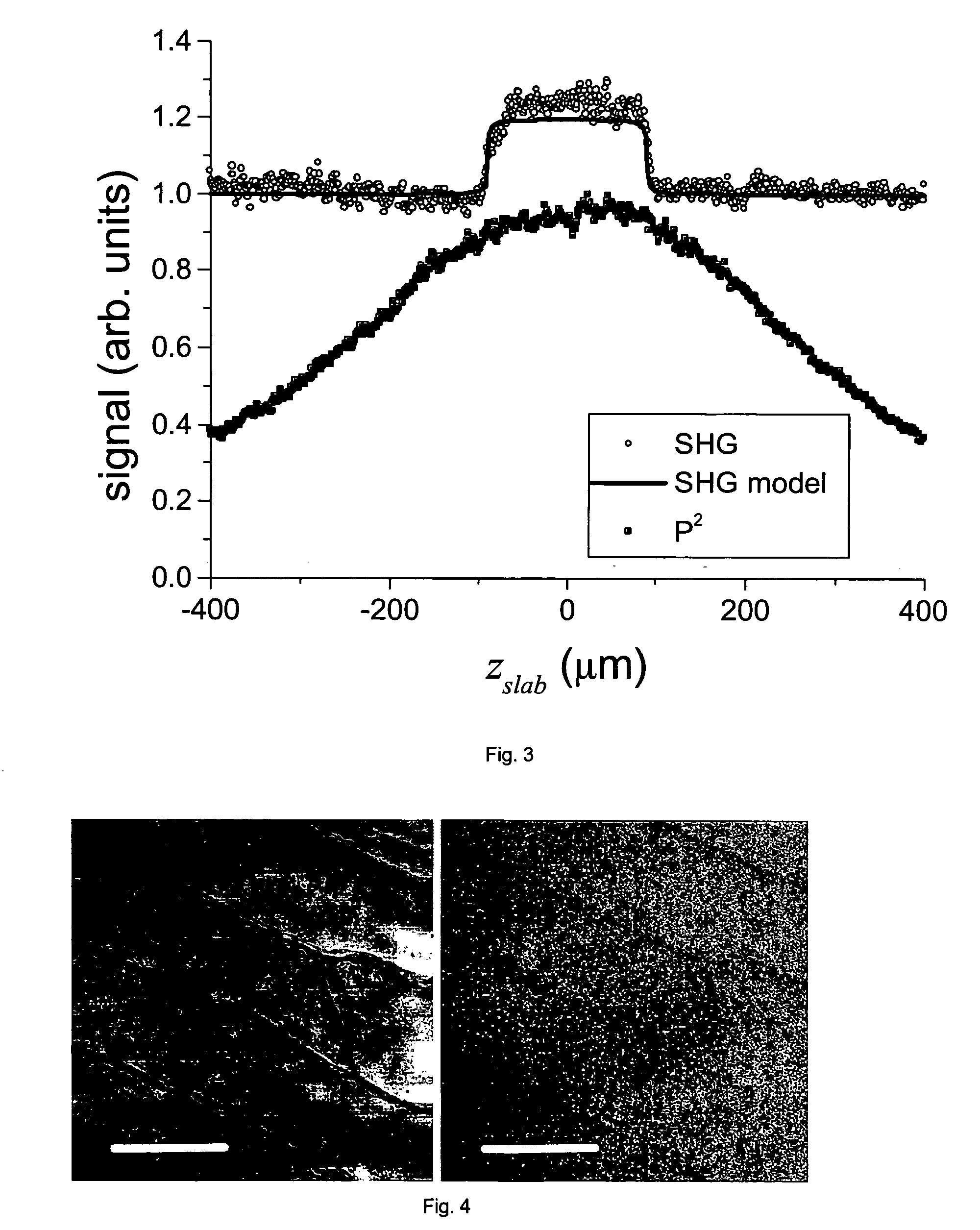
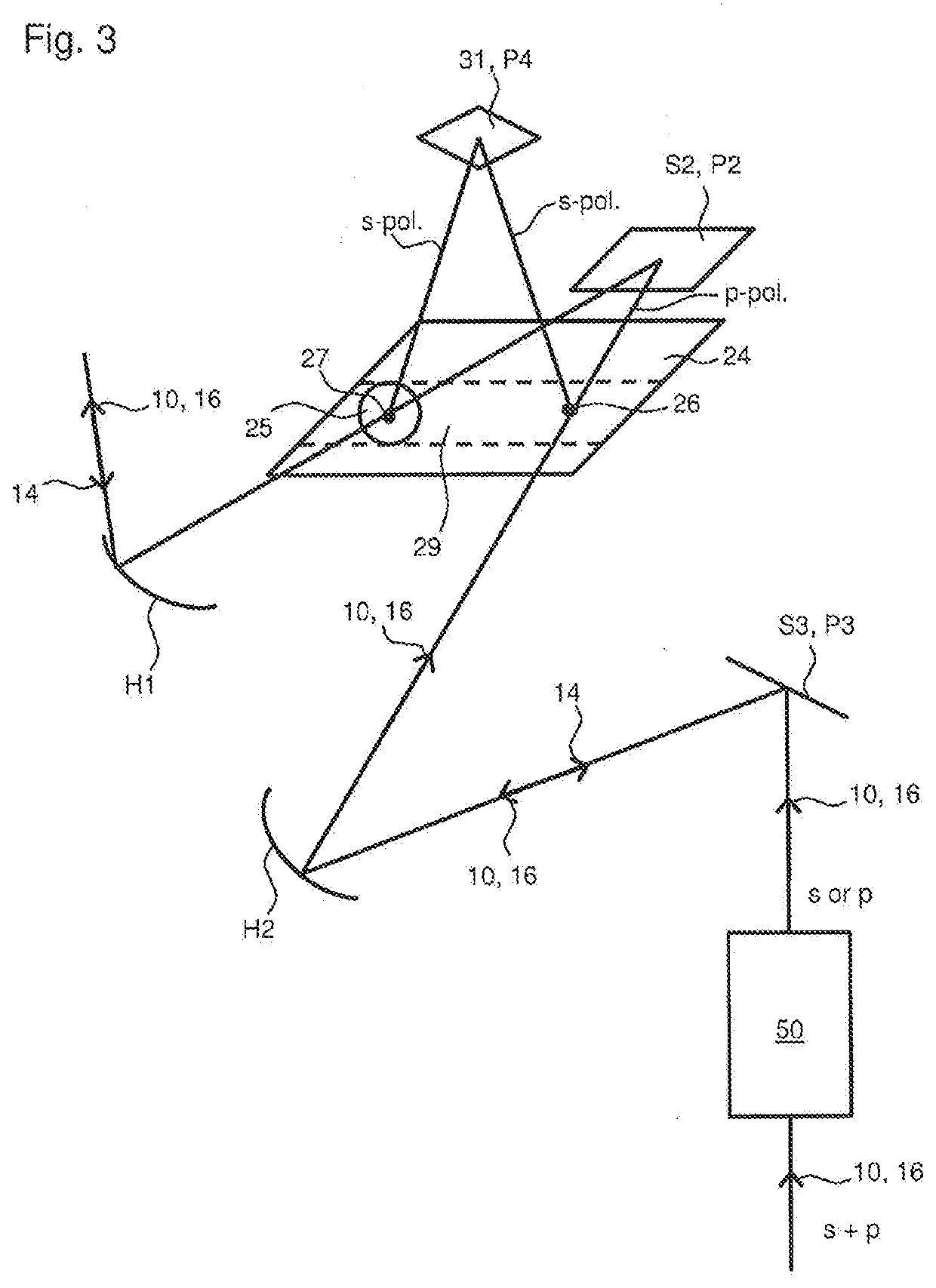
The present invention concerns a confocal laser scanning microscopy apparatus, comprising: means for emitting a laser beam; means for scanning this laser beam in at least two directions onto an observed sample; means for generating a non linear light signal from the transmitted laser light, these non linear light signal generating means being disposed in the light path between the observed sample and detecting means which are adapted for detecting said non linear light signal.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM)
Novel use of cyanine dye in detection of G-quadruplex DNA
InactiveCN101587066AOvercoming demandsEfficient identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsCyanineUv vis absorbance
The invention provides novel use of a cyanine dye in the detection of a G-quadruplex DNA. The detection of the G-quadruplex DNA by using the cyanine dye has the advantages of simplicity, quickness and relatively low prices and overcomes the drawbacks of the prior detection technology such as long period, high price and high technical and equipment requirements. The use of the cyanine dye in the detection of the G-quadruplex DNA makes whether a DNA sample in solution has a G-quadruplex structure or a linear double helical structure determined quickly by a UV-visible absorption spectrum, fluorescence spectrum or confocal laser scanning microscopy. By using confocal laser scanning microscopy, the DNA sample assembled on the surface of Au can be marked visually, so the structure of the DNA sample can be recognized and the specific assembly position of the DNA sample on the surface of the Au can be marked at the same time.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
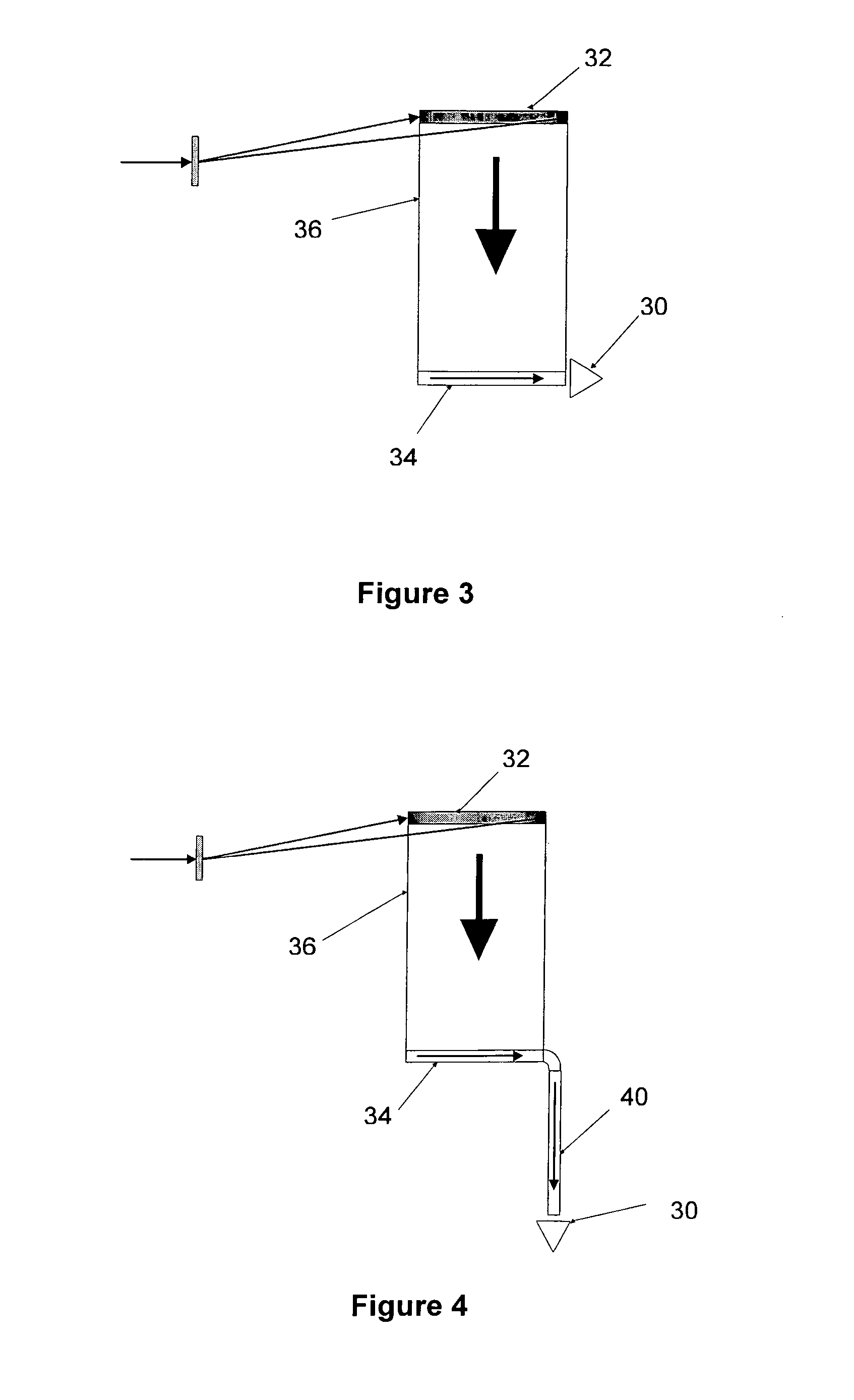
Method for differentiated investigation of diverse structures in preferably biological preparations
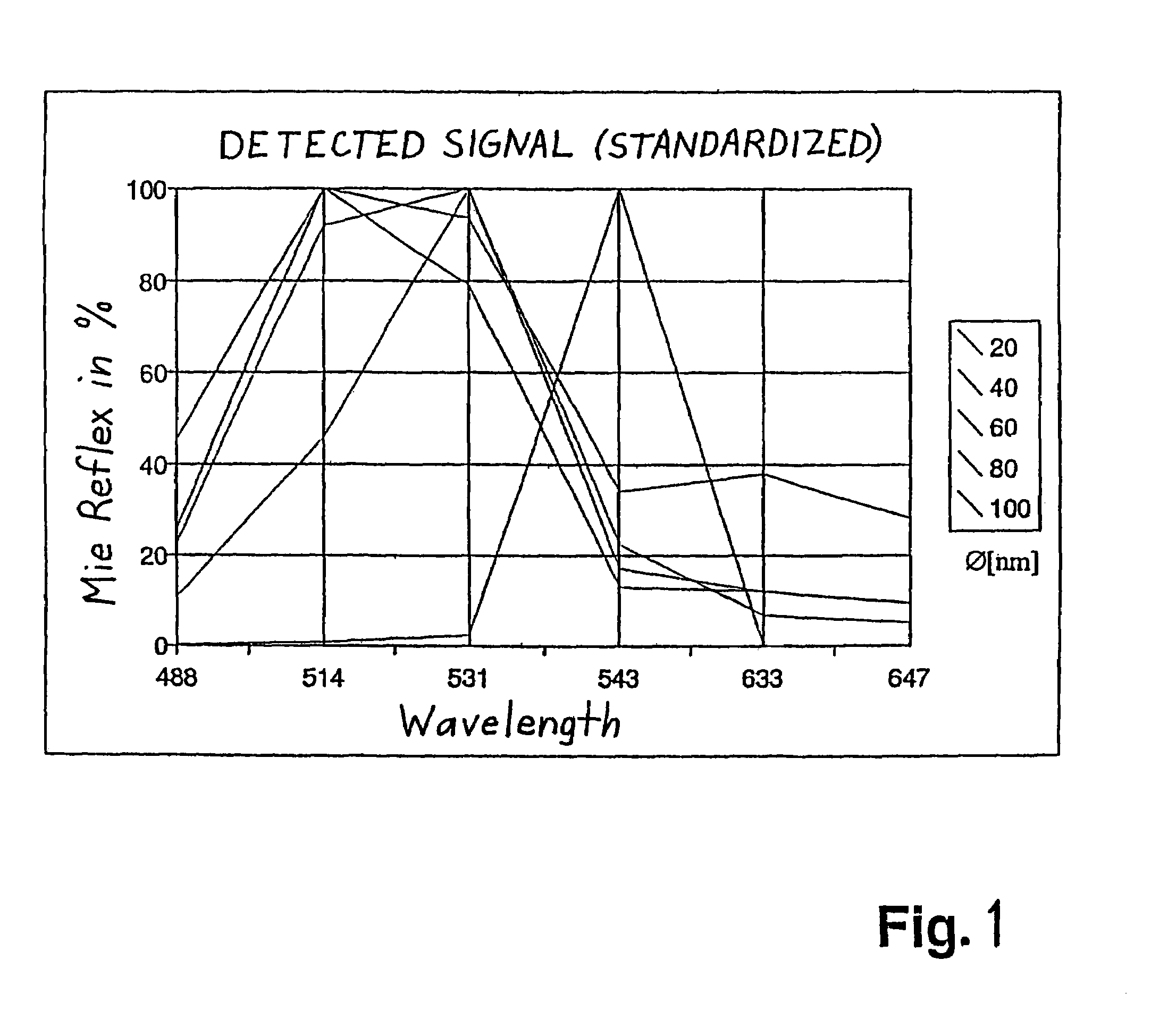
The invention relates to a method for examining different structures in preferably biological preparations in a differential manner, especially by means of confocal laser scanning microscopy. The method is characterized in that particles having a specific diameter and specific characteristics are assigned to the structures and in that said structures are detected by detecting the particles which have specifically bonded in or to the preparations. The detection process is carried out in an advantageous manner by marking the structures with metal particles with diameters of 10 nm to 1,500 nm and detecting Mie scattering or a plasmon signal.
Owner:LEICA MICROSYSTEMS CMS GMBH
Evaluation of signals of fluorescence scanning microscopy using a confocal laser scanning microscope
ActiveUS20180113292A1High resolutionEasy to adjustMicroscopesFluorescence/phosphorescenceDiffraction orderMicroscopic observation
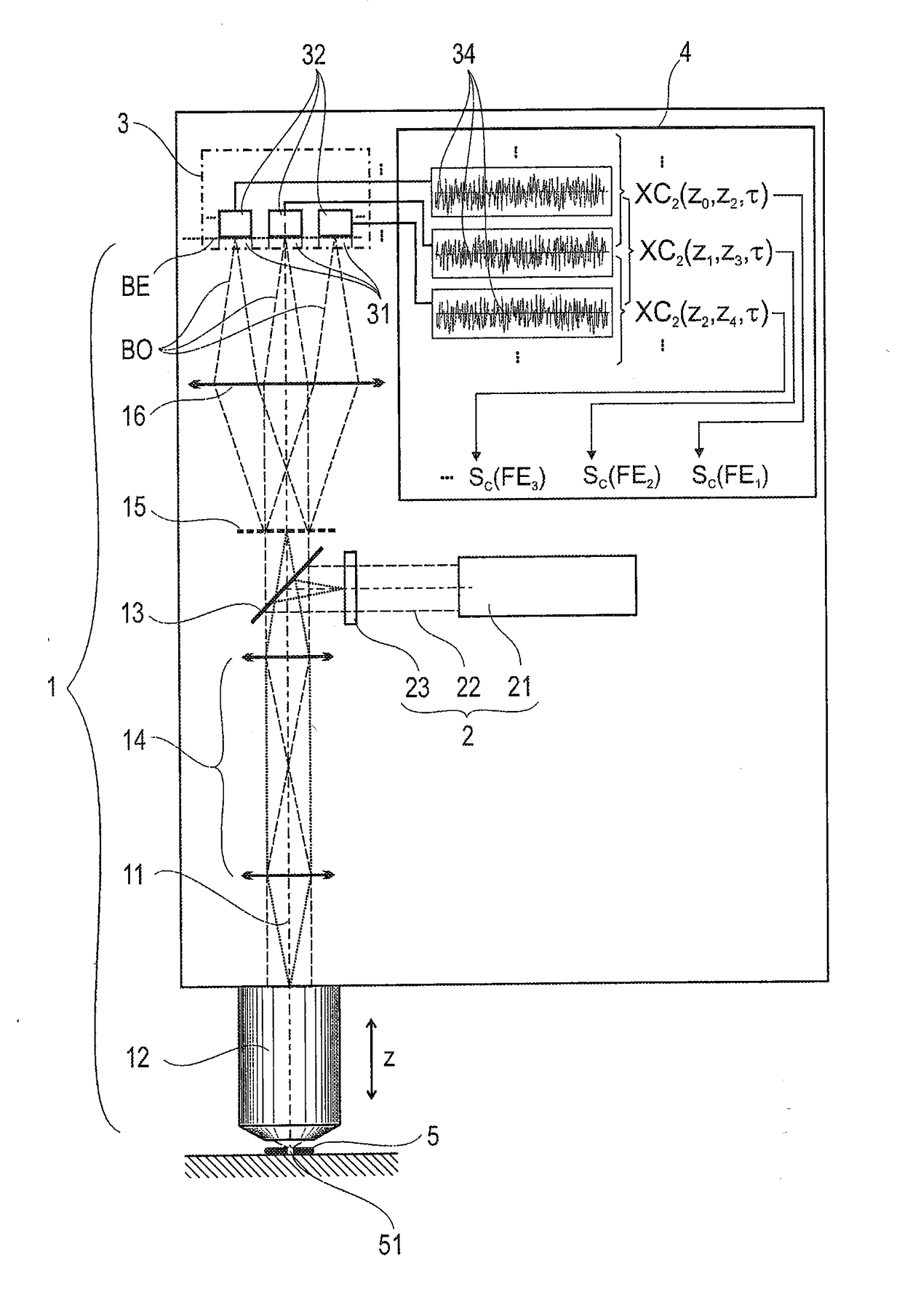
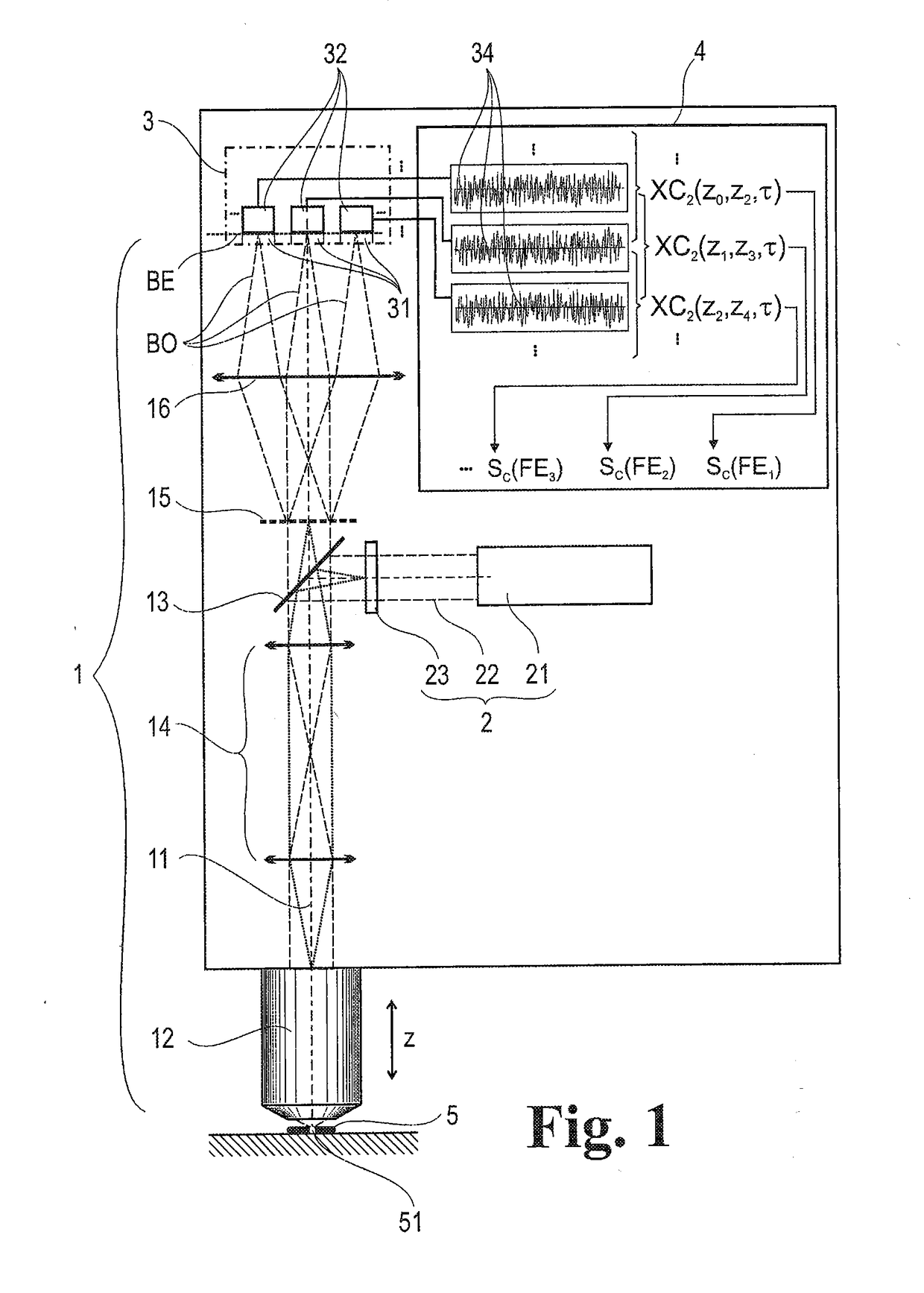
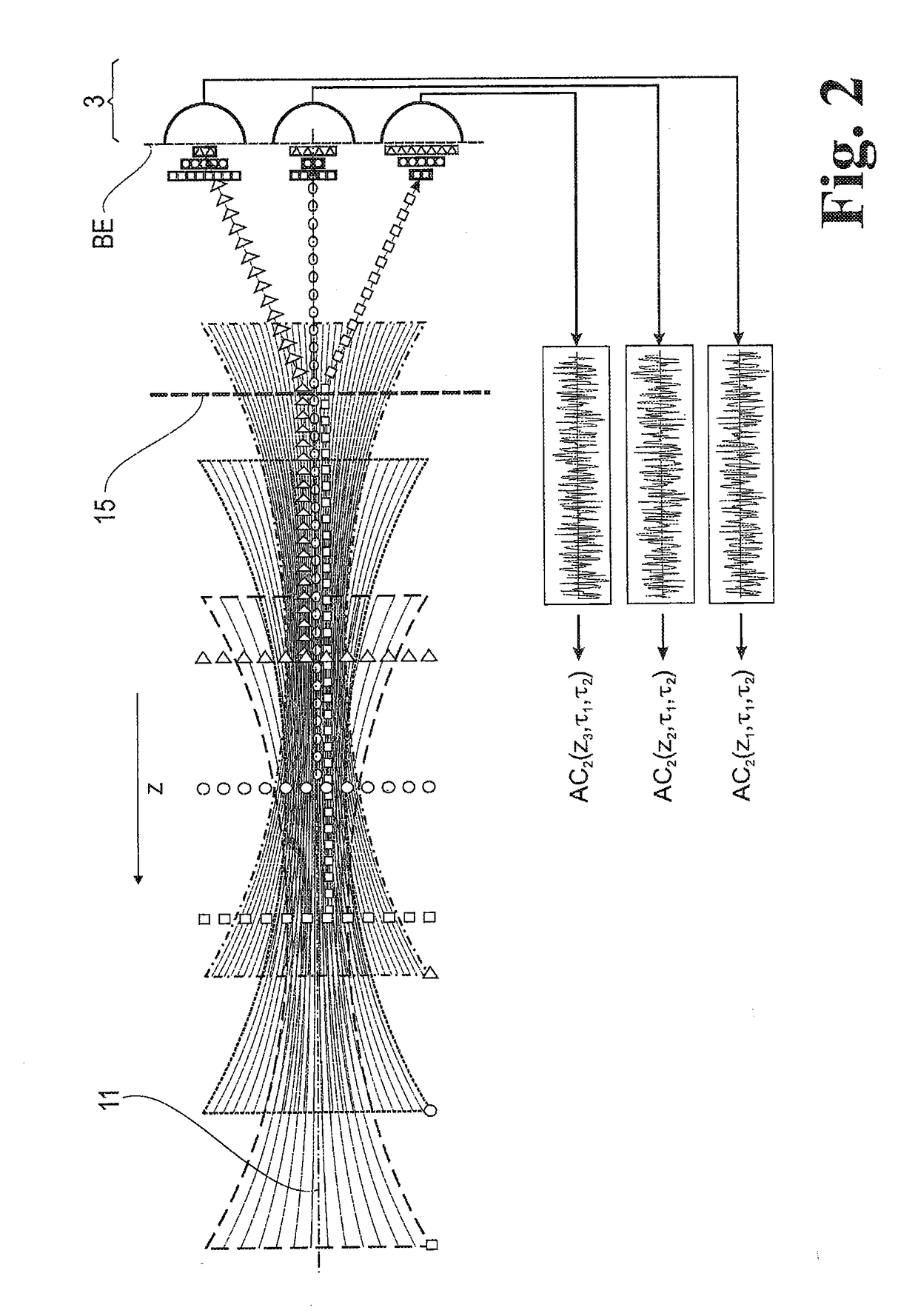
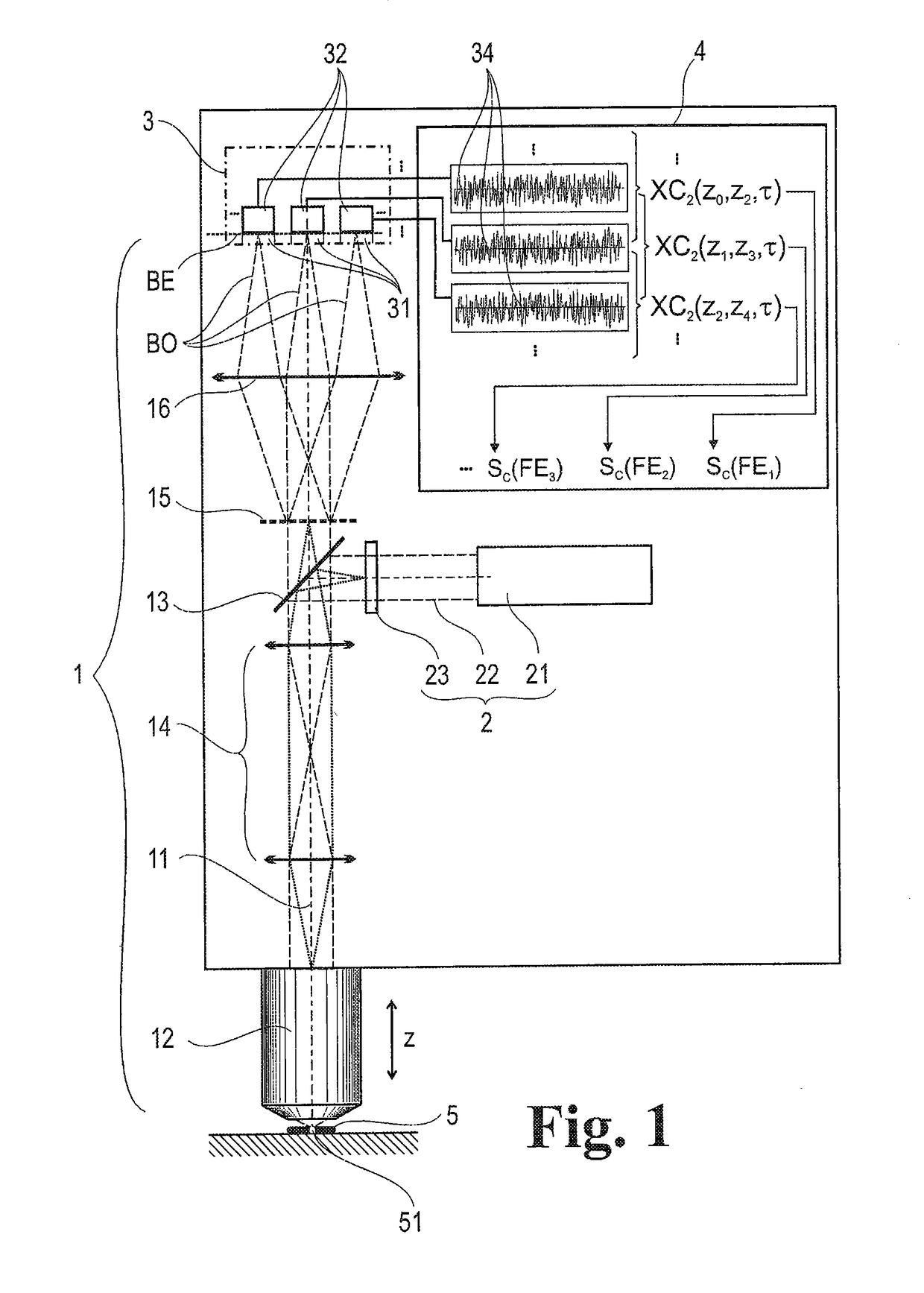
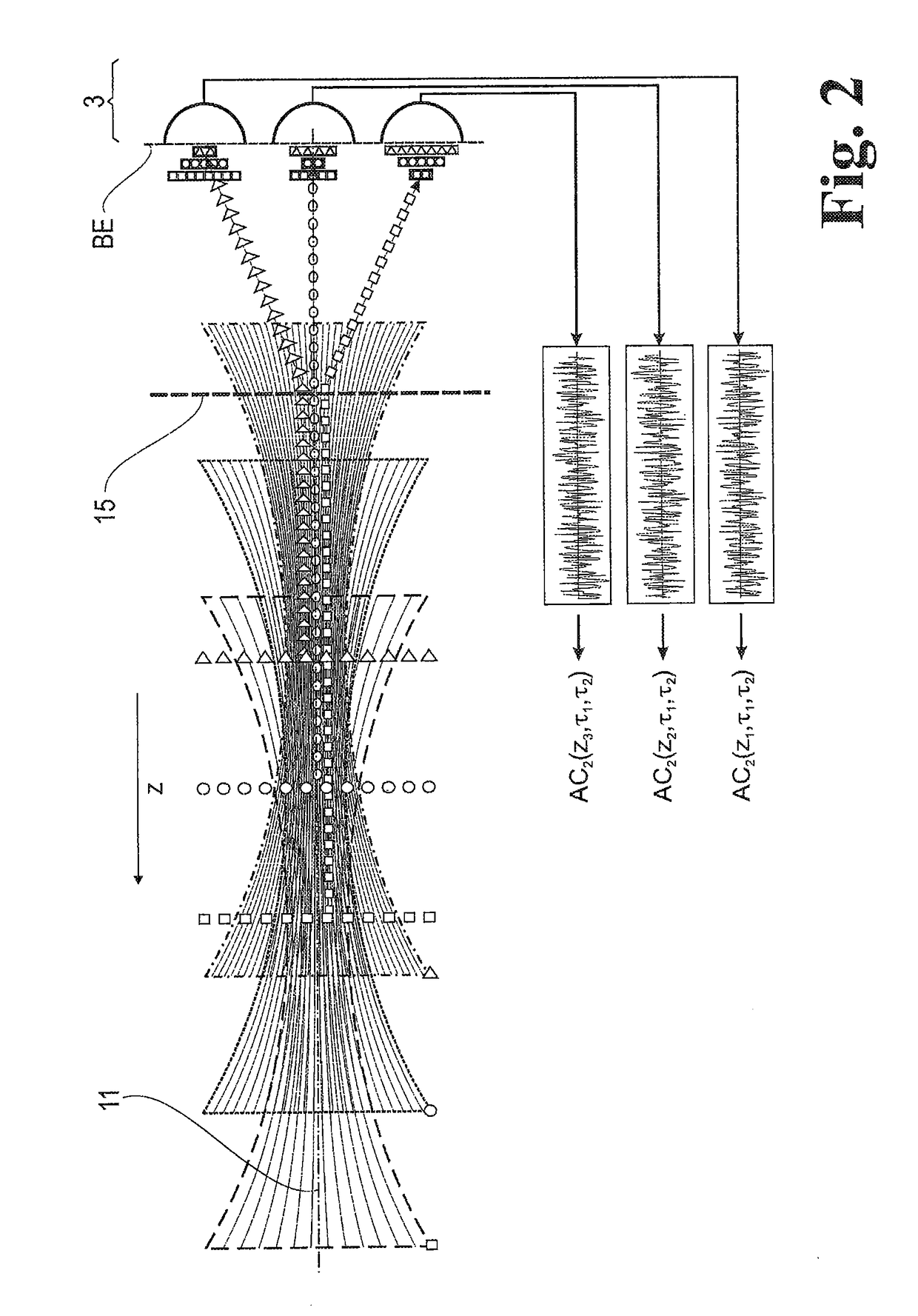
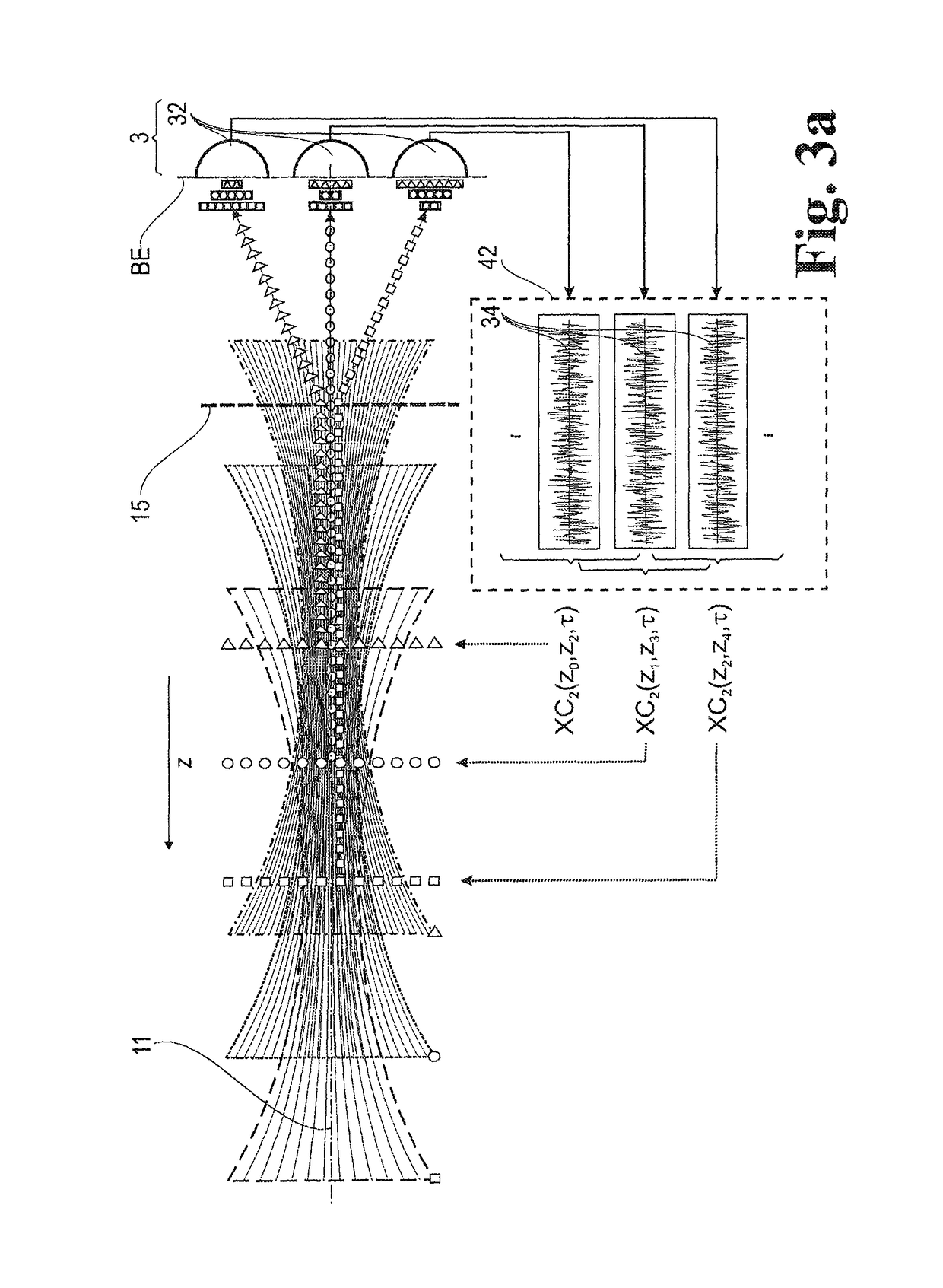
A method for evaluating signals of fluorescence scanning microscopy with simultaneous excitation and detection of fluorescence in different focal planes of a sample by means of confocal laser scanning microscopy. The invention evaluates signals of fluorescence scanning microscopy without the signal losses usually taking place with a confocal aperture, by coupling an illumination beam into a microscope observation beam path which images a measuring volume on a detector array arranged in the image plane, focusing the illumination beam which passes through a beam-forming phase mask for generating an elongated focus in the measuring volume, collecting and collimating fluorescent light generated in the measuring volume and routing it to diffractive optics which split the light beams into different diffraction orders and impress a different spherical phase on the light beams, imaging the different diffraction orders on detector regions of the detector array so that fluorescent light from focal planes at different depths of the measuring volume are associated with different diffraction orders, and associating the fluorescence signals on which crosstalk is superposed from different focal planes of the measuring volume with defined focal planes by means of correlation-based association based on distinguishable blinking behavior of fluorescing dyes.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH +1
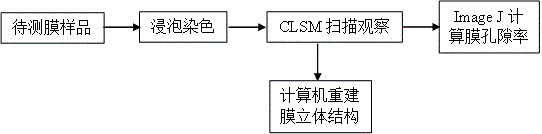
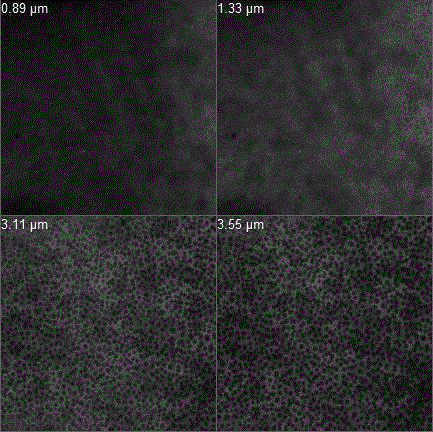
Membrane pore structure and porosity testing method based on confocal laser scanning microscopy
InactiveCN106353234AUniform dyeingSimple and fast manufacturing methodPermeability/surface area analysisPorosityFluorescence
The invention provides a membrane pore structure and a porosity testing method based on CLSM (confocal laser scanning microscopy), comprising: preparing a sample, observing the sample, processing data and the other steps. Traditional testing methods include scanning electron microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, mercury intrusion method, nitrogen adsorption method and other methods and have their respective disadvantages; for example, high pressure required in the testing process of the mercury intrusion method may deform membrane structure; sample preparation in the transmission electron microscopy and scanning electron microscopy is high in time consumption and results in big damage to samples. Membrane pore structure and porosity are tested by means of confocal laser scanning microscopy, it is only required to perform single dyeing on a sample under test with fluorescent dye, information in the sample can be acquired without destroying the sample, operating is simple, and little damage is caused to the sample; in addition, sample testing herein has no need for drying, namely, a sample can be tested in an environment similar to a membrane when a liquid separation membrane is under test, and the results are more accurate and reliable.
Owner:王凯军 +2
Fluorescence labeling method for free calcium ions of cotton pollen tube
InactiveCN101806736AEasy to importAvoid damagePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceZoology
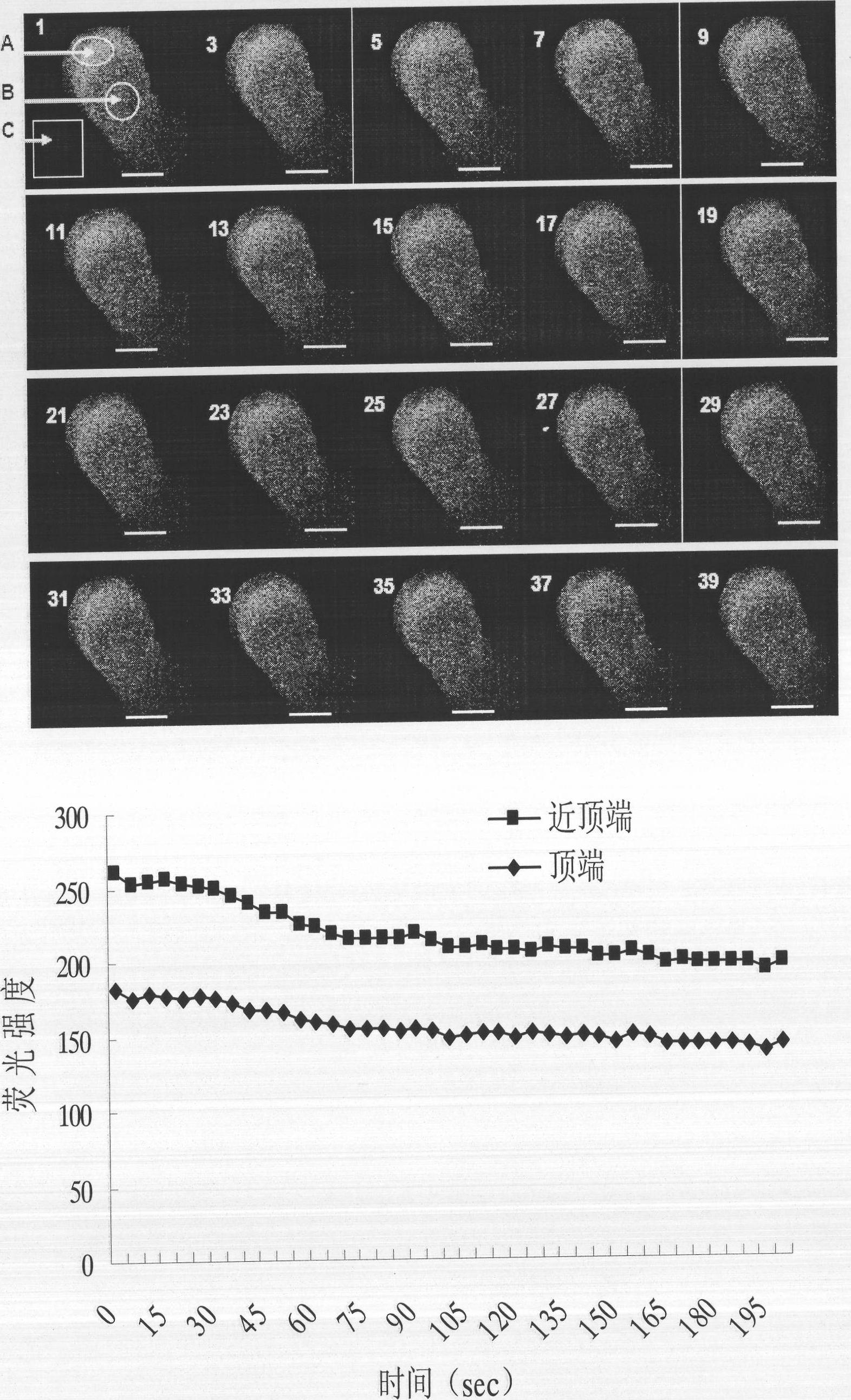
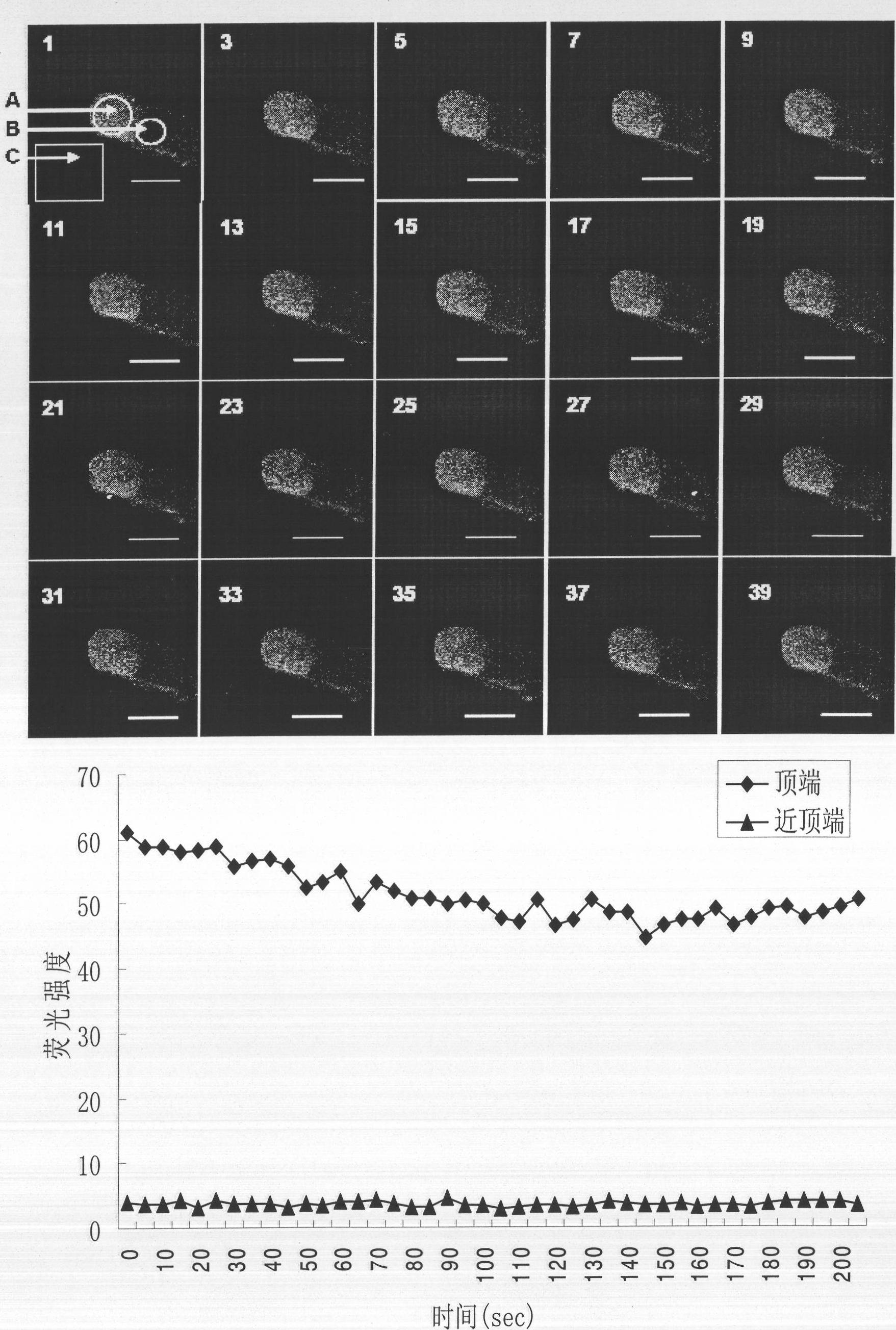
The invention discloses a fluorescence labeling method for free calcium ions of a cotton pollen tube, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The fluorescence labeling method comprises the following steps: perforating glass slide to make a small chamber for culturing the pollen tube; culturing pollen in the small chamber, and sprouting the pollen tube; loading Fluo-3AM into the cultured pollen tube by a low temperature incubation method; and observing dynamic variation of Ca2+ in the pollen tube under a confocal laser scanning microscopy. The invention establishes a method for researching the concentration change of the Ca2+ in the cotton pollen tube by using the confocal laser microtechnique, has simple operation and good labeling effect, plays an important role in the growth of the cotton pollen tube and fertilization reproduction research, and has important practical application value.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
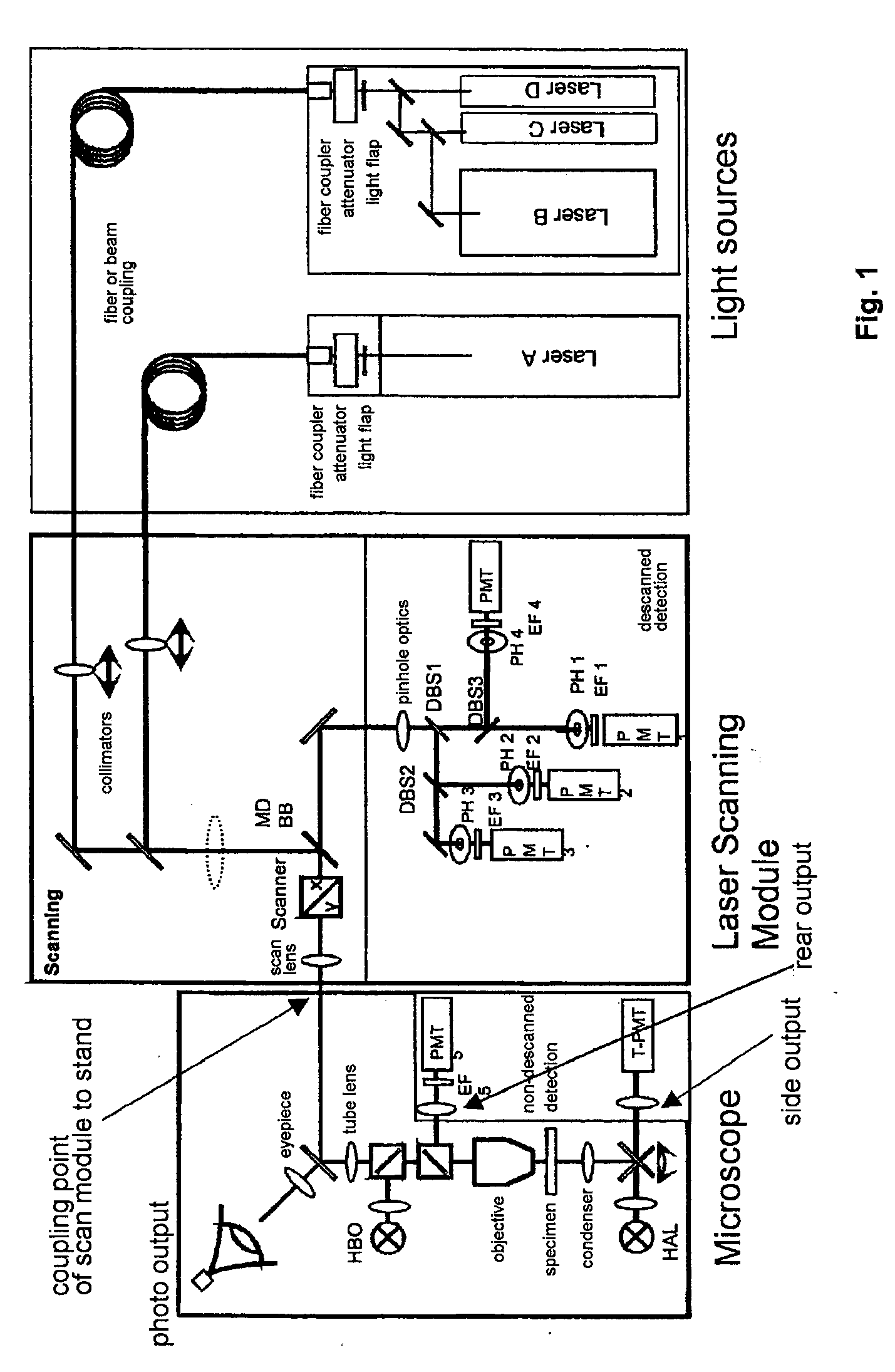
Microscope having internal focusing
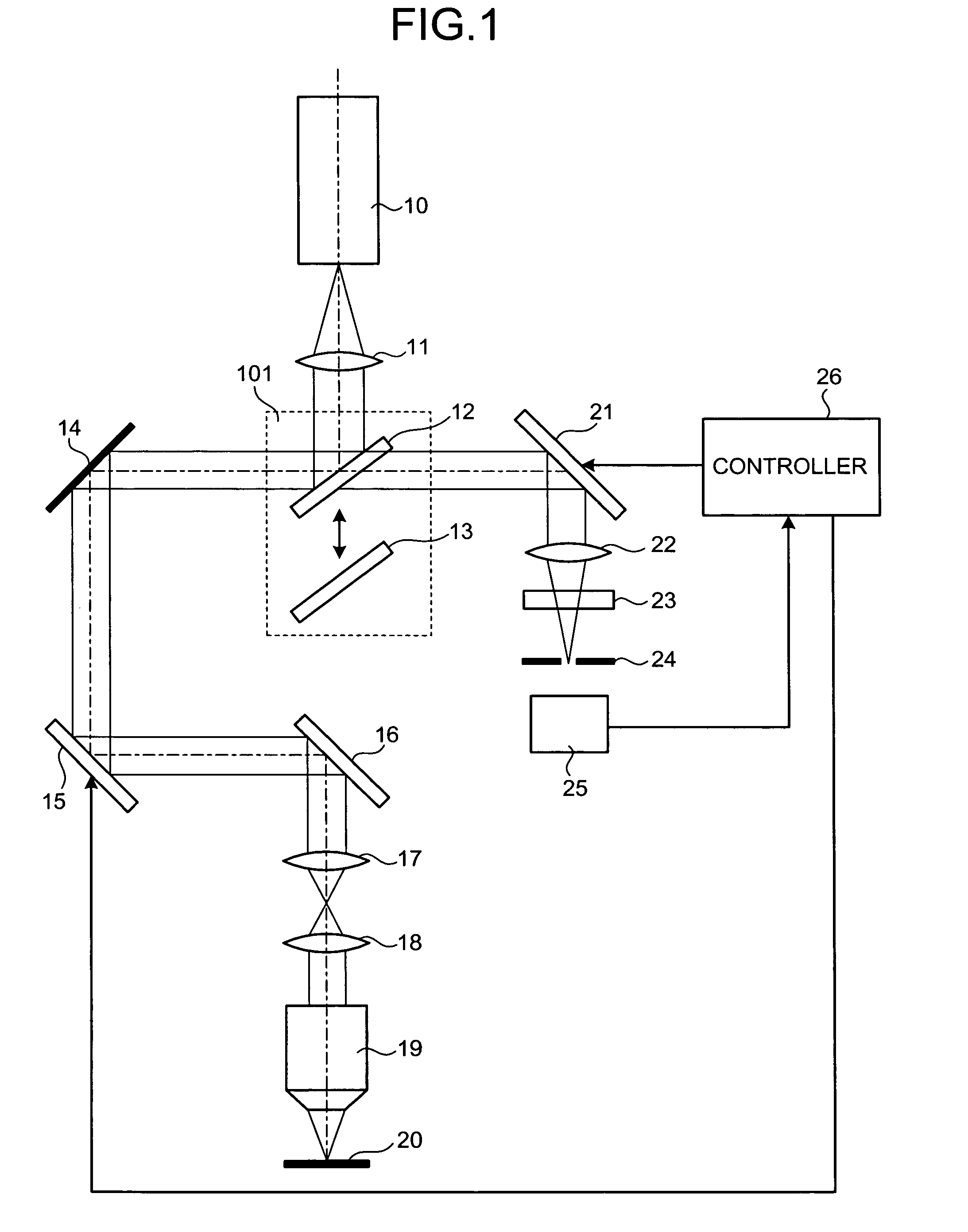
The invention relates to a laser scanning microscope with a scanner and a microscope objective, and to a control method for such a microscope. In order to obtain sharp imaging of the sample in a laser scanning microscope, the distance between the microscope objective and the sample is usually varied for adjusting the focus position. However, relative movements between the objective and the sample can be problematic. In view of the costly special objective, internal focusing of the objective is a disadvantageous solution. An improved laser scanning microscope should make it possible to sharply image a sample with standard objectives without relative movement between the microscope objective and sample. According to the invention, a tube lens is provided which is displaceable along the optical axis, and the focus position is adjustable relative to a front optical element of the microscope objective by adjusting the tube lens.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Laser scanning microscope and method for operation thereof
ActiveUS20120229815A1Increase speedMinimum errorImage enhancementImage analysisLaser scanning microscopeOptoelectronics
Laser scanning microscope and method for the operation thereof having at least two detection channels which has at least one beamsplitter with a splitting of the sample light deviating from the 50:50 split and / or, with 50:50 split in the detection channels, has detectors with differently adjusted gain, or in at least one detection channel with equal light splitting has an additional light attenuator.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Methods of enucleating an avian oocyte or zygote using two-photon laser scanning microscopy
Owner:SYNAGEVA BIOPHARMA CORP
System and method for time resolved spectroscopy
InactiveUS20070041017A1High sensitivityRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryTime-resolved spectroscopyAtomic physics
A system for time resolved spectroscopy comprises a CCD device arranged to receive a time varying spectrum. Time resolved spectroscopy is the analysis of a spectrum that varies with time due to any cause. The variation with time of the spectrum may be due, for example, to (i) changes of the spectrum from a given sample space with time (such as due to emission decay); and (ii) changes in the spectrum as successive portions of a sample space are sampled (such as laser scanning microscopy). The CCD device comprises an array of photosites arranged to detect the time varying spectrum and to produce signal charge representative of the spectrum, and one or more CCD multiplication registers arranged to receive the signal charge and to provide charge multiplication. An enhancement of speed and sensitivity is given by a storage area which receives the signal charge in parallel from the array of photosites to provide the charge in serial to the one or more multiplication registers.
Owner:E2V TECH (UK) LTD
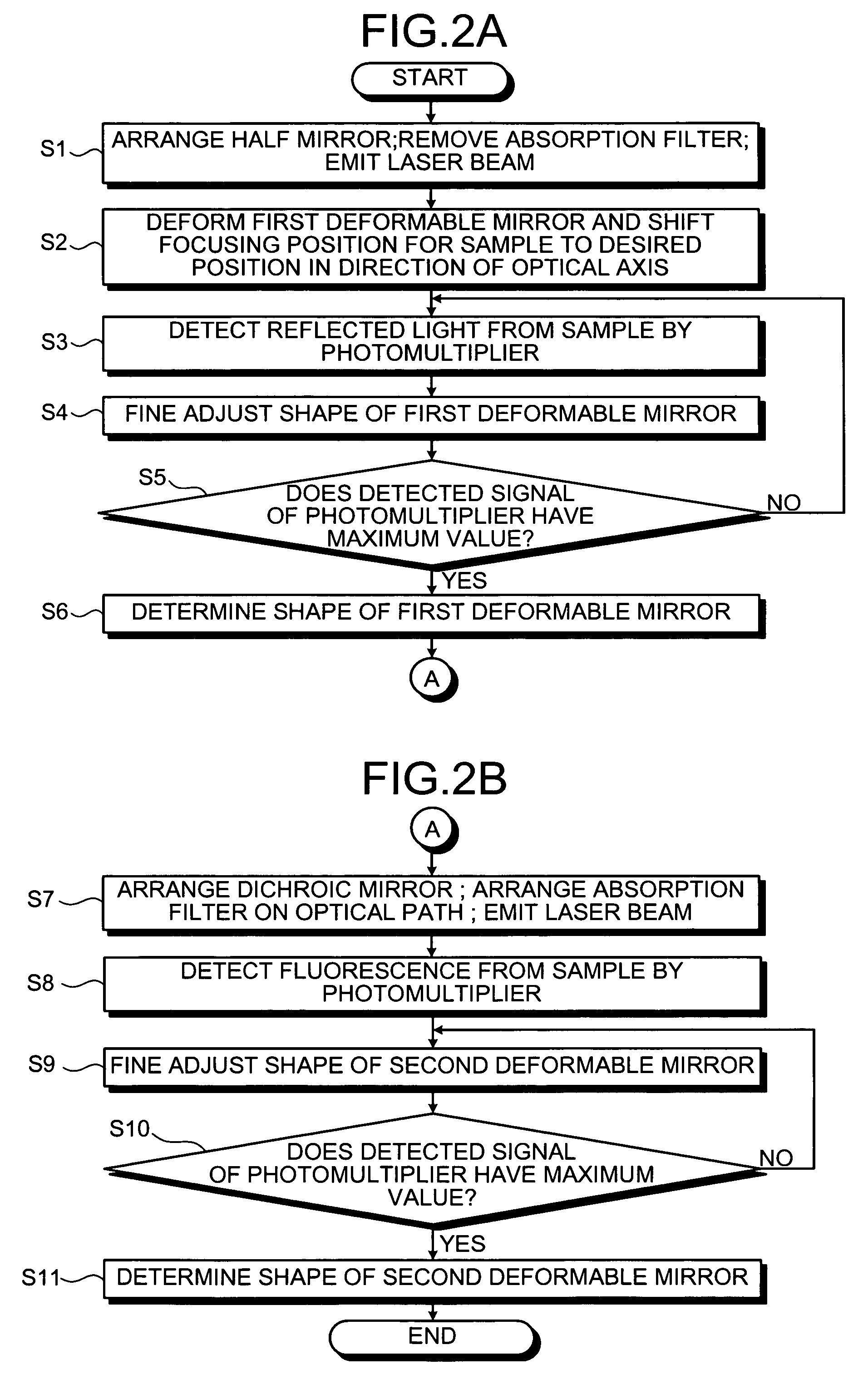
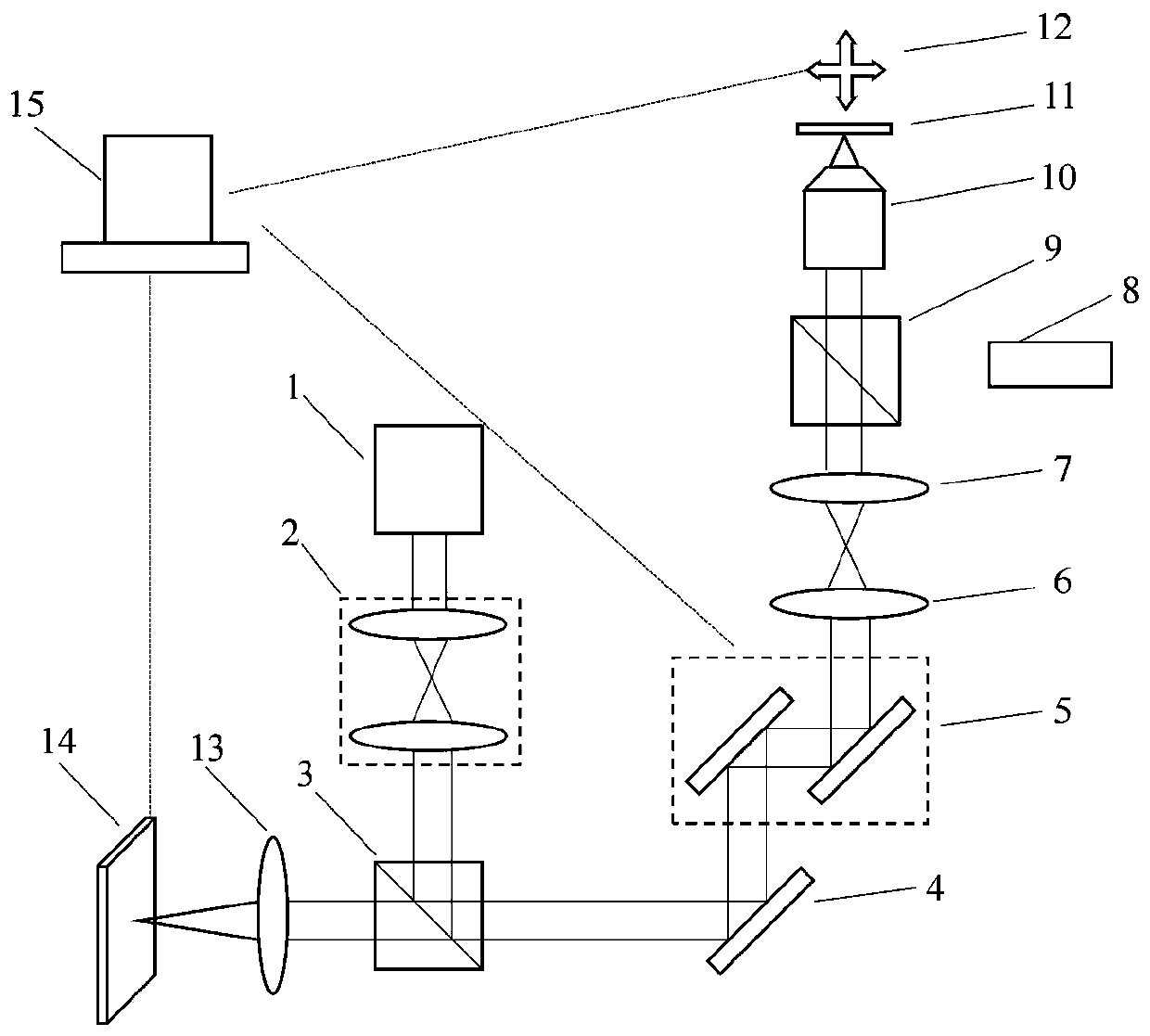
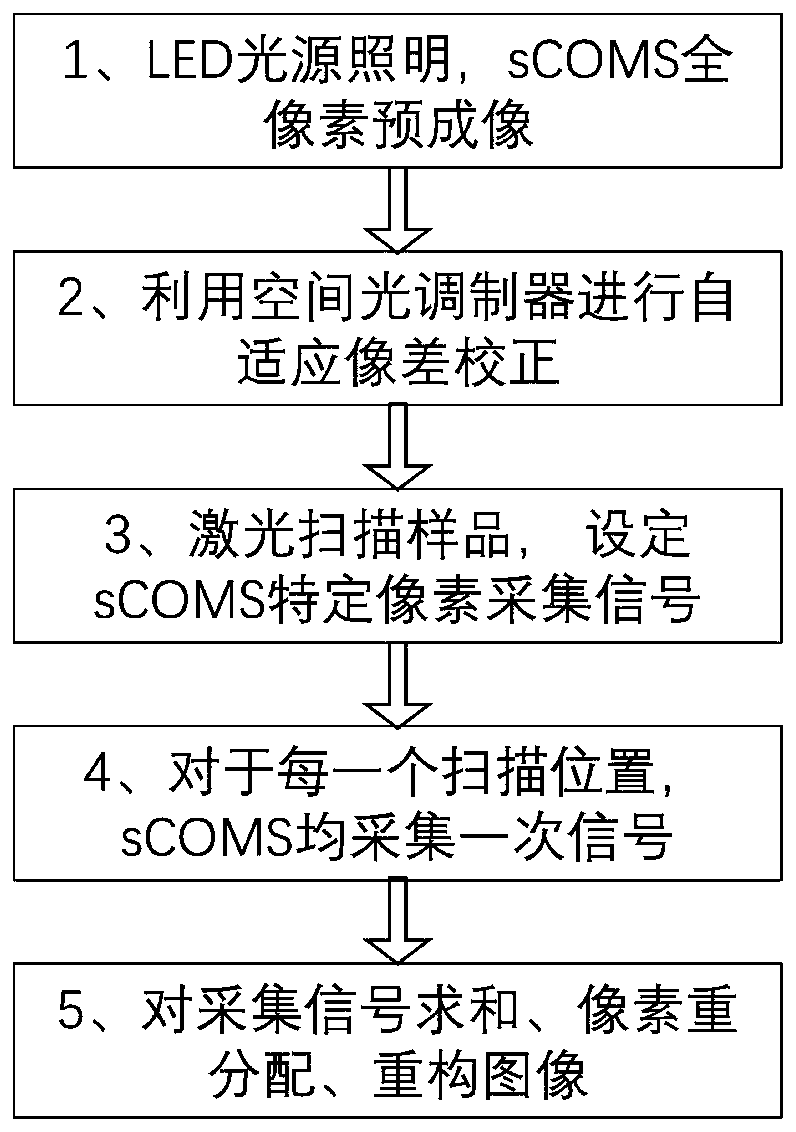
Self-adaptive aberration correction image scanning microscopic imaging method and device
ActiveCN110567959AReal-time correctionIncrease contrastMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesImage resolutionImage evaluation
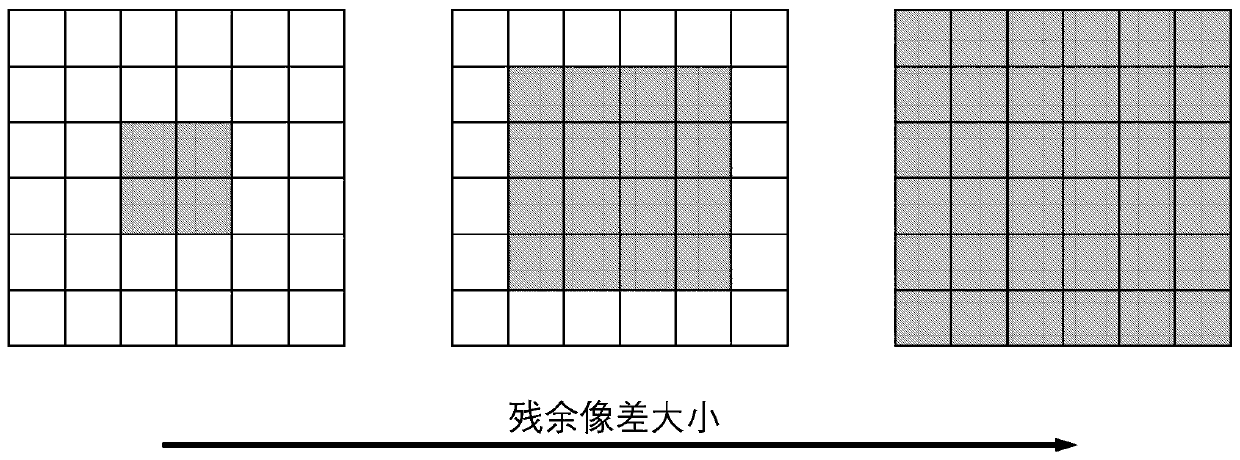
The invention relates to a self-adaptive aberration correction image scanning microscopic imaging method and device and belongs to the field of optical microscopic measurement. According to the self-adaptive aberration correction image scanning microscopic imaging method and device of the invention, an aberration correction system is introduced into an image scanning microscopic imaging method soas to carry out adaptive aberration correction. Before correction, a sCOMS is directly utilized to perform full-pixel pre-imaging, and a full-pixel image is utilized to form an adaptive aberration correction evaluation function. An image evaluation function is tested in real time in a correction process, and a computer is used for controlling the aberration correction system to carry out self-adaptive aberration correction. This process does not need scanning, and is quick and simple. And parameters of a pixel redistribution process are reset on the basis of the change of the evaluation function in an aberration correction process, so that the pixel redistribution process is optimized. The number of the effective pixels of the sCMOS camera in a laser scanning microscopy process is set according to residual aberration. With the method adopted, the aberration of the image scanning microscopic imaging system can be effectively corrected, the effectiveness of the pixel redistribution process can be improved, and the improvement of image scanning imaging resolution can be achieved to the greatest extent.
Owner:哈工大机器人(中山)无人装备与人工智能研究院
Integrative con-focal laparoscopic system for diagnosis and treatment
InactiveCN102599878AImprove accuracyImprove securityEndoscopesLaproscopesLaser scanningOperative time
The invention belongs to the field of medical instruments, and specifically relates to an integrative con-focal laparoscopic system for diagnosis and treatment. A treatment device is arranged at the end of a hard endoscope of a hard laparoscope; and a treatment system host matched with the treatment device is connected on the hard laparoscope. The integrative con-focal laparoscope, the con-focal laser-scanning microscopy and laser knife system are organically combined by the invention, or the laparoscope, the con-focal laser-scanning microscopy and microwave knife system are organically combined by the invention. By the integrative con-focal laparoscopic system for diagnosis and treatment, the diagnosis and the treatment are performed synchronously; the diseased tissue of intra-abdominal organ is subjected to biopsy without exchanging the endoscope according to the invention in order to determine a diagnosis. By adoption of the integrative con-focal laparoscopic system for diagnosis and treatment to carry out the laparoscopic surgery, the two problems of diagnosis and treatment of a patient are solved by one endoscope, the trouble of continually exchanging endoscopes is avoided, the operation time is saved, the suffering of the patient is reduced, and the accuracy and the safety of the operation are further enhanced.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAODAN MEDICAL INSTR TECH
Pyrene-based ratiometric fluorescent probe as well as preparation method and biological application thereof
InactiveCN108191818AThe synthesis steps are simpleLow costOrganic chemistryChemical analysis using titrationFluorescencePyrene
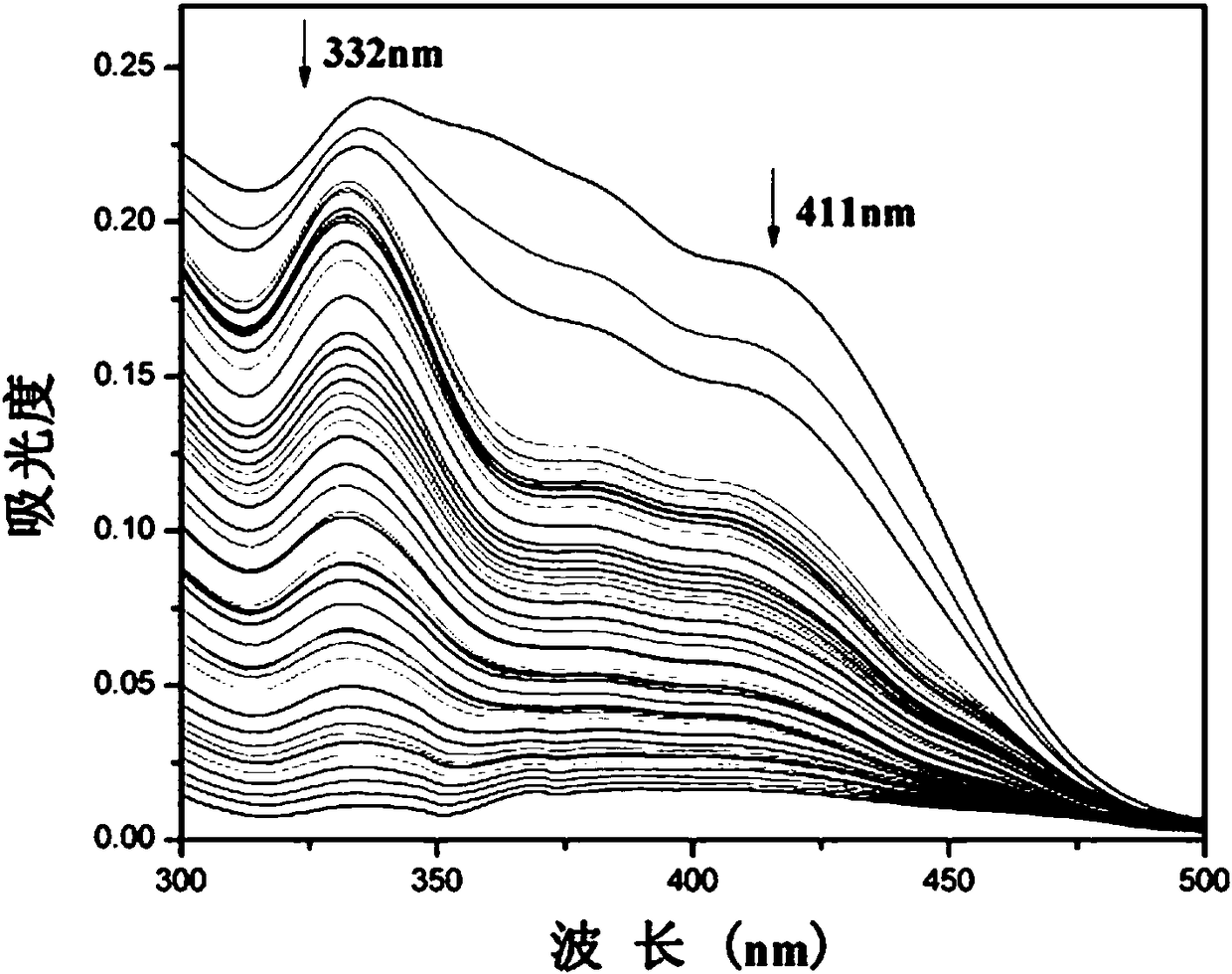
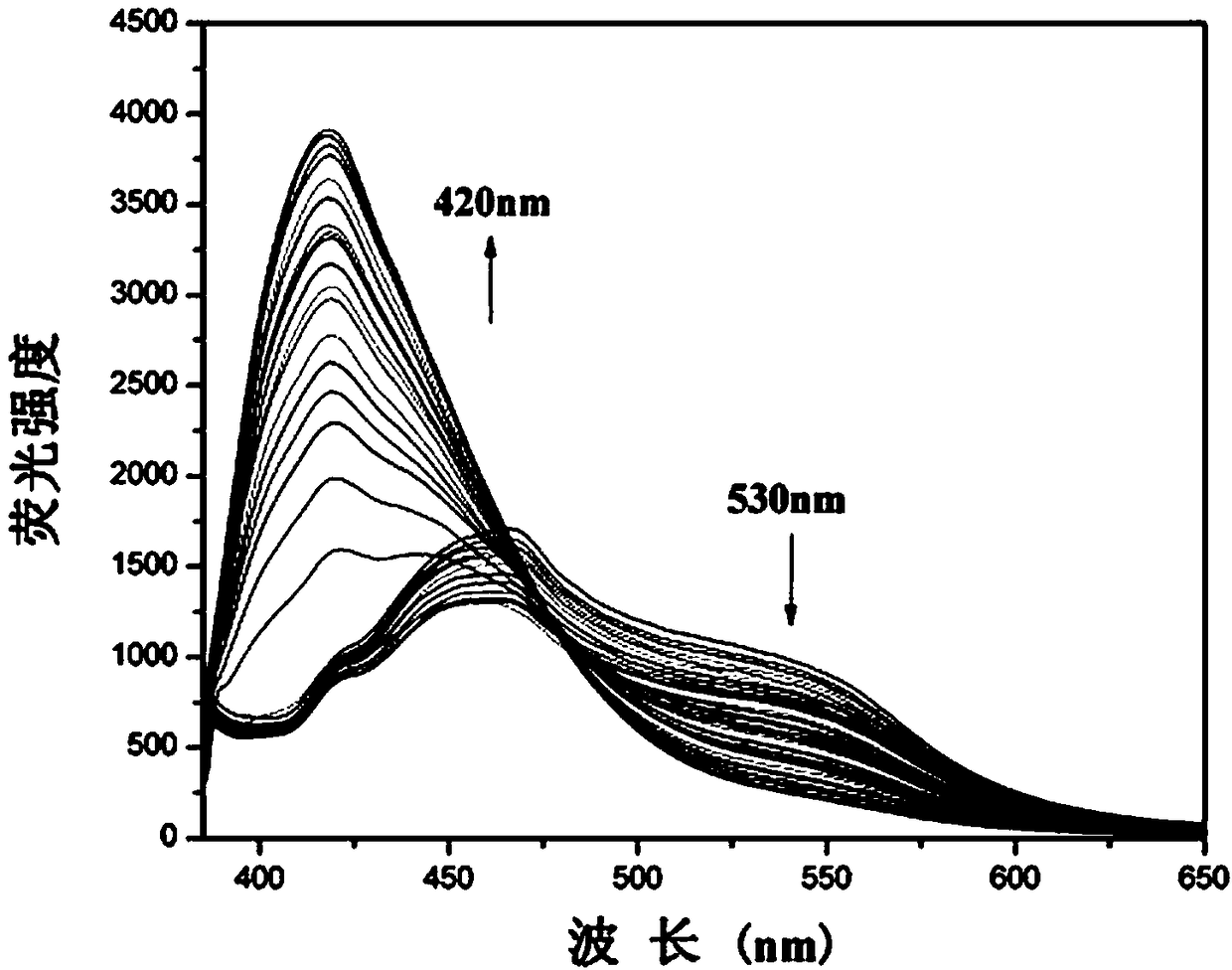
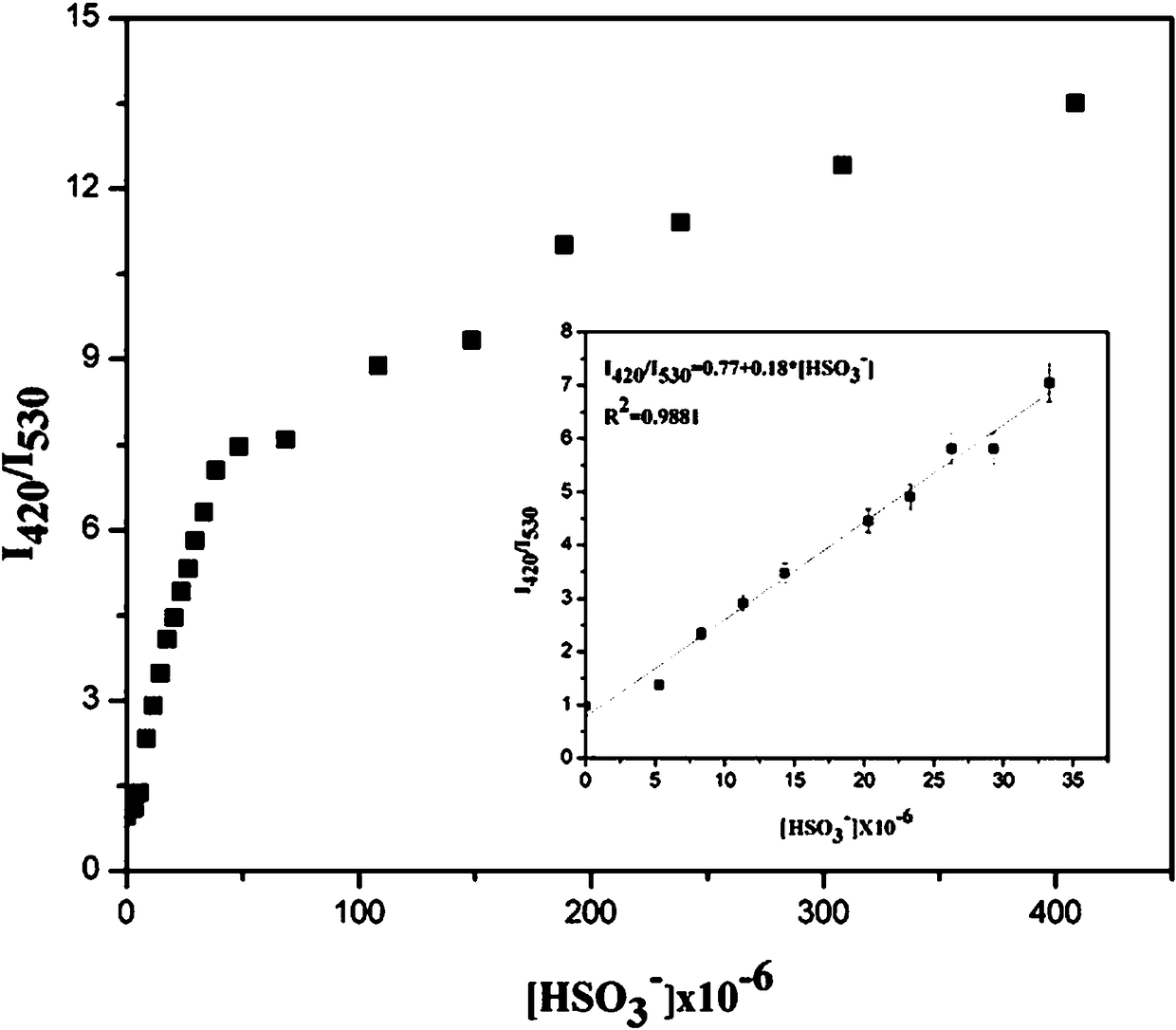
The invention belongs to the technical field of synthesis of fluorescent probes, and provides a pyrene-based ratiometric fluorescent probe as well as a preparation method and a biological applicationthereof to solve the problems that the conventional fluorescent probes are high in detection limit, poor in light stability and the like. The pyrene-based ratiometric fluorescent probe is used for detection of HSO3<-> and imaging in a biological body, is 1-(pyrene-1-yl)-3-(4,5-dibromothiophene-2-yl)acrylketone, and is prepared through the following steps: pyrene taken as a starting material is subjected to a reaction with anhydrous aluminium trichloride and acetyl chloride in the mole ratio of 4:5:7, 1-acetylpyrene is obtained and is mixed and dissolved with 4,5-dibromothiophene-2-formaldehydein the mole ratio of 3:4, 10% NaOH solution is added, stirring reaction is performed at room temperature, and the fluorescent probe is obtained. Detection of HSO3<-> by the fluorescent probe is ratiometric, reaction is quick, selectivity and sensitivity are high, and the fluorescent probe can be used for detecting HSO3<-> in the biological body through combination with confocal laser scanning microscopy.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
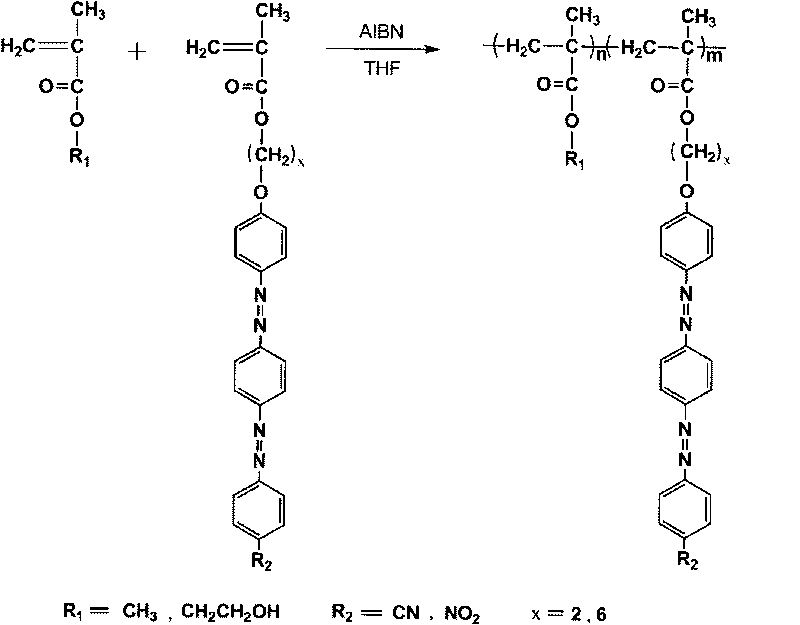
Use and structure of bisazo benzene polymer as two-photon optical storage medium
InactiveCN101763868AIncrease concentrationWon't gatherRecord information storageRecord carrier materialsPolyvinyl alcoholBright spot
The invention relates to an erasable two-photon polarized multivariate, multistage and multilayer optical storage technology based on a bisazo benzene polymer. The prepared bisazo benzene polymer is used as the two-photon optical storage medium. Linearly polarized titanium: sapphire laser (wavelength: 800mm, pulse cycle: 80fs and repetition frequency: 80MHz) two photons are used to write data and a reflective confocal laser scanning microscopy is used to read the data. When the bisazo benzene polymer is used for two-photon storage, if light polarization direction is read that the light polarization direction is changed from the direction in parallel with writing light to the direction forming an angle of 45 degrees with the writing light and then to the direction perpendicular to the writing light, the data undergoes a change from 'dark spot' to 'disappearance' and then to 'bright spot'. Based on the characteristic, polarized multivariate and multistage optical storage can be realized. The written data is erasable. Data can be rewritten after being erased. A composite multilayer film which takes a bisazo benzene polymer layer as a storage layer and takes a polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) layer as a spacing layer is prepared, so multilayer storage can be realized on the basis of polarized multivariate and multistage optical storage. Thereby, a new way is provided for the realization of high-density optical storage.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Novel pH response fluorescent molecular probe and application thereof
ActiveCN103396788ADetection wavelength widthEasy to prepareOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceBromineFluorescent imaging
The invention discloses a novel pH response fluorescent molecular probe, which has a general formula of the structure as shown in the specification, wherein, n is equal to 1 to 5; R1 is an alkyl chain with 1 to 8 carbon atoms; and R2 is hydrogen, fluorine, chlorine, bromine, iodine, methoxy, ethoxy or nitro connected to the 4th, 5th, 6th, 7th, 4'th, 5'th, 6'th or 7'th site of a benzimidazole ring. The invention also discloses an application of the novel fluorescent molecular probe in the field of pH response fluorescent detection. The novel pH response fluorescent molecular probe has very wide detection wavelength, and can be excited from ultraviolet to visible light (less than 520nm). Fluorescent images of the novel fluorescent molecular probe in different areas of a life system can also be acquired in combination with confocal laser scanning microscopy. Compared with the existing pH response fluorescent molecular probe, the novel pH response fluorescent molecular probe has the advantages that the preparation method is simple and the displacement value with exciting light is large.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
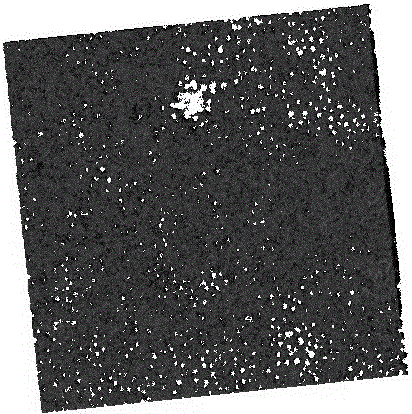
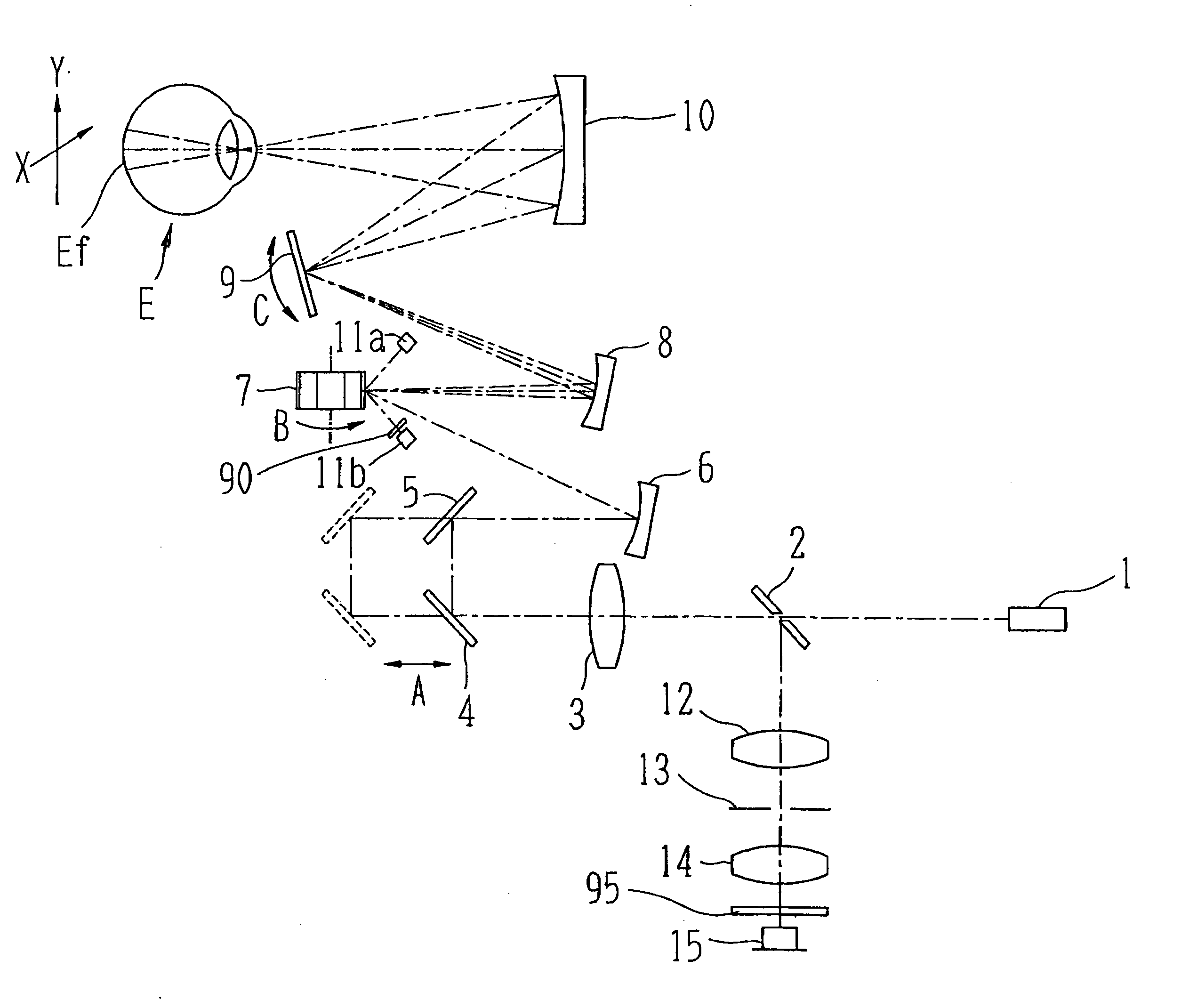
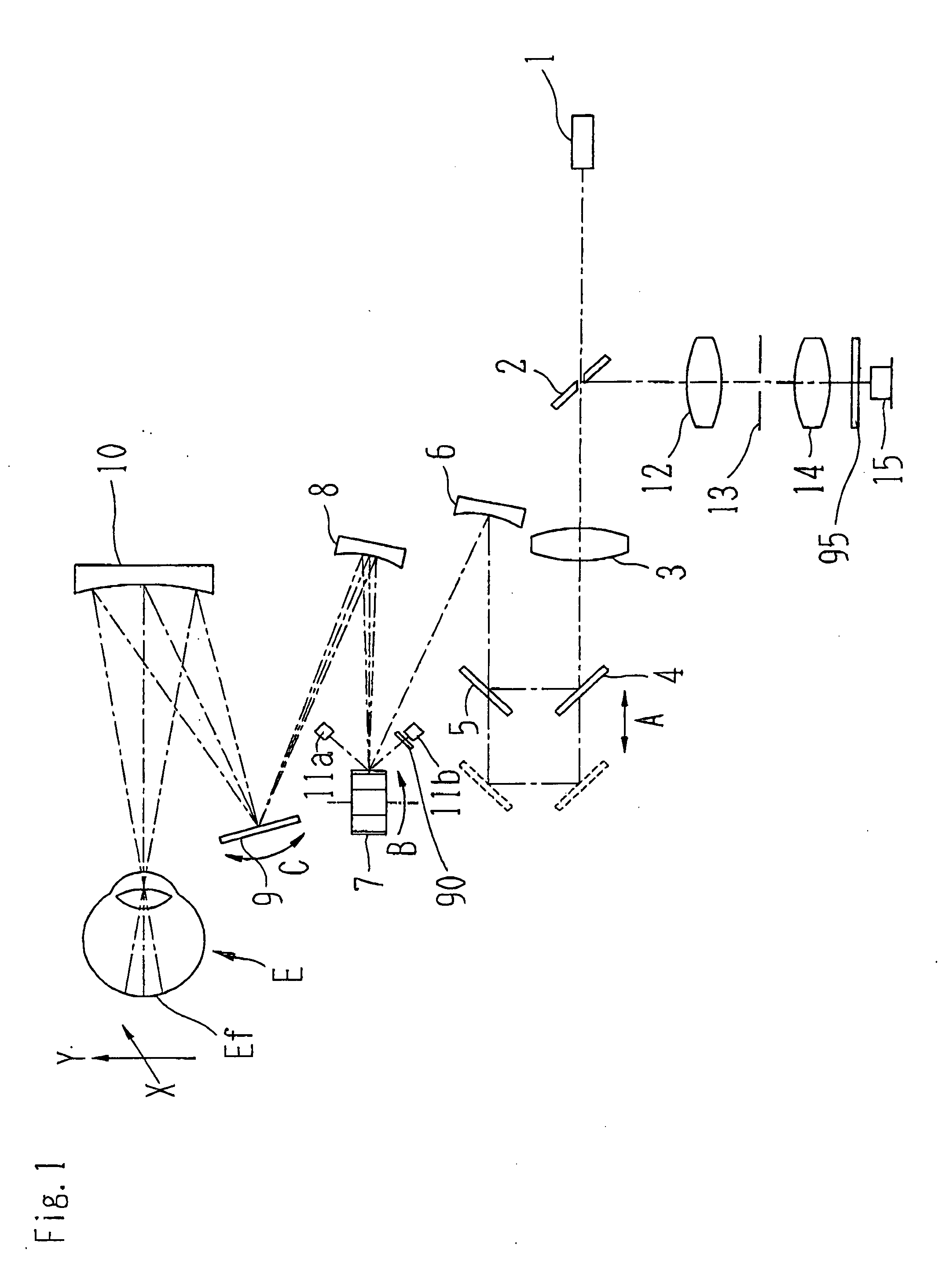
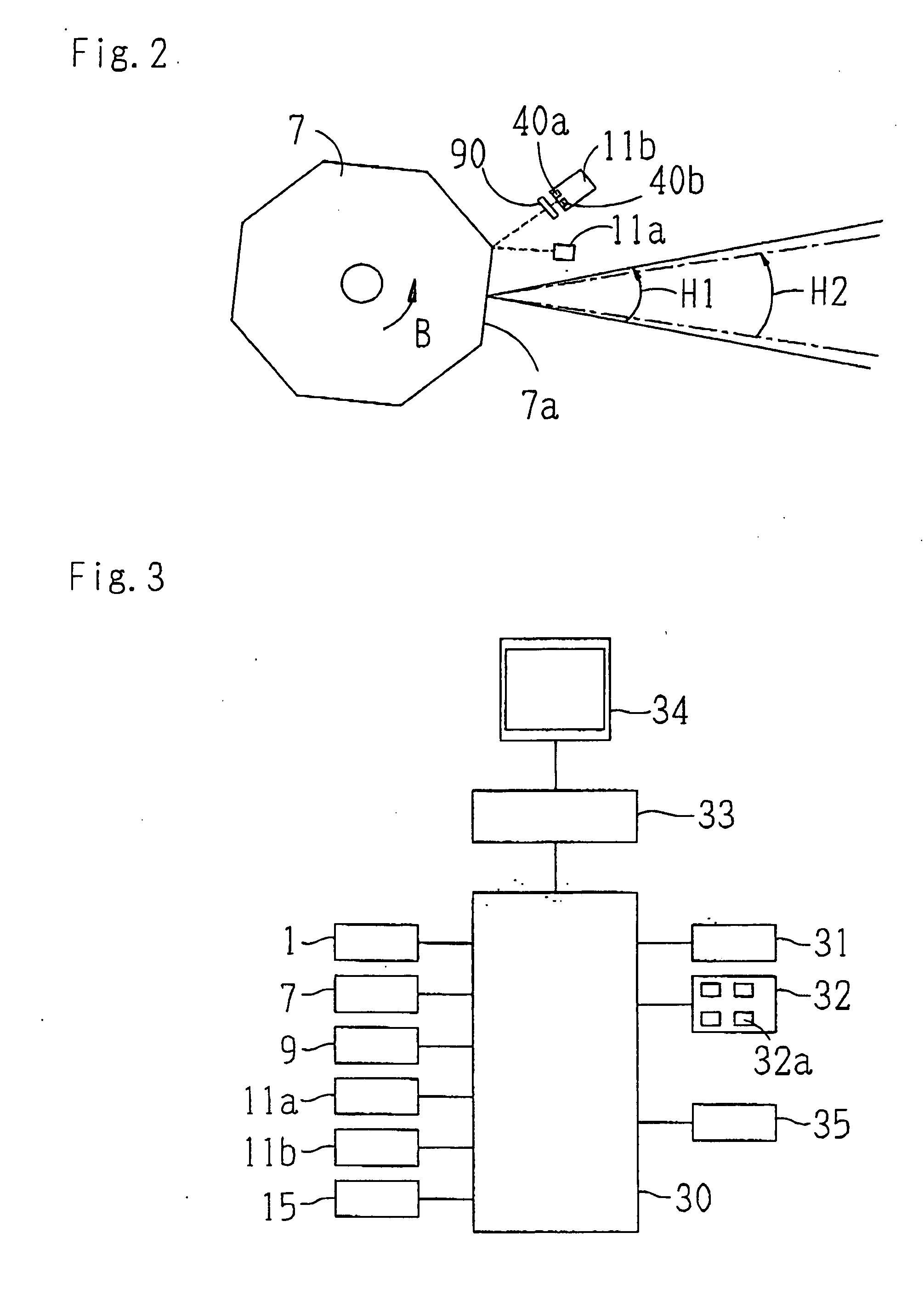
Ophthalmologic observation apparatus
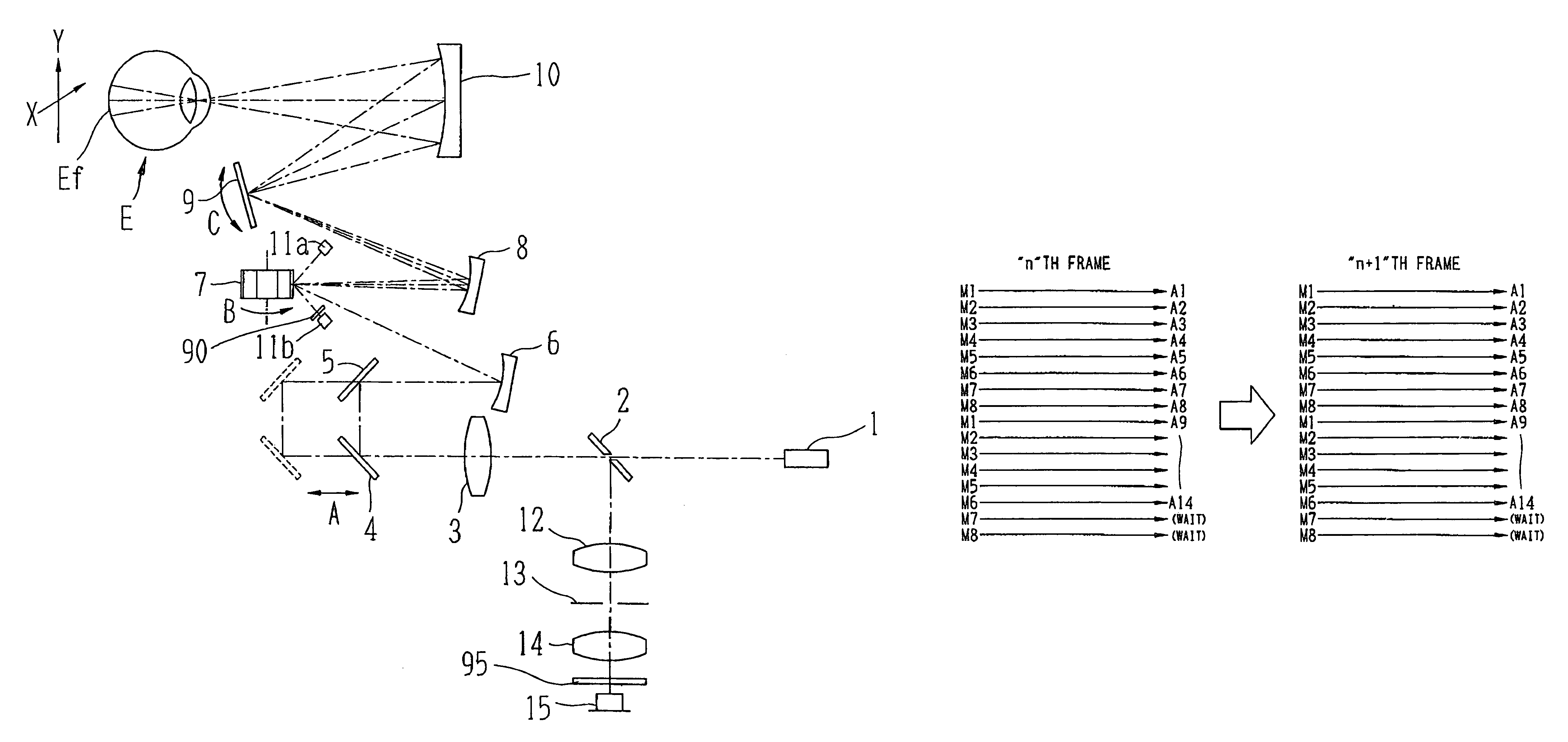
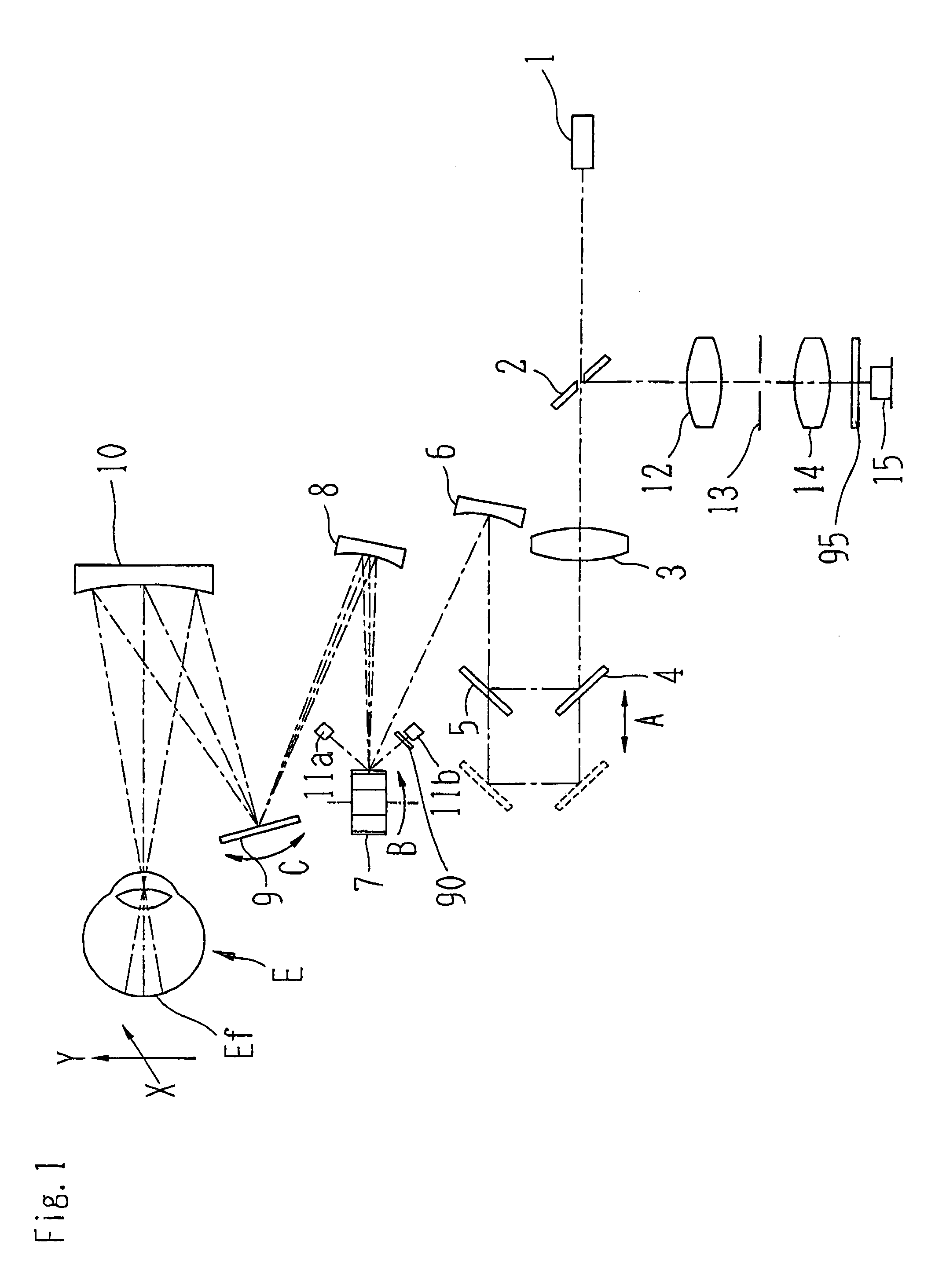
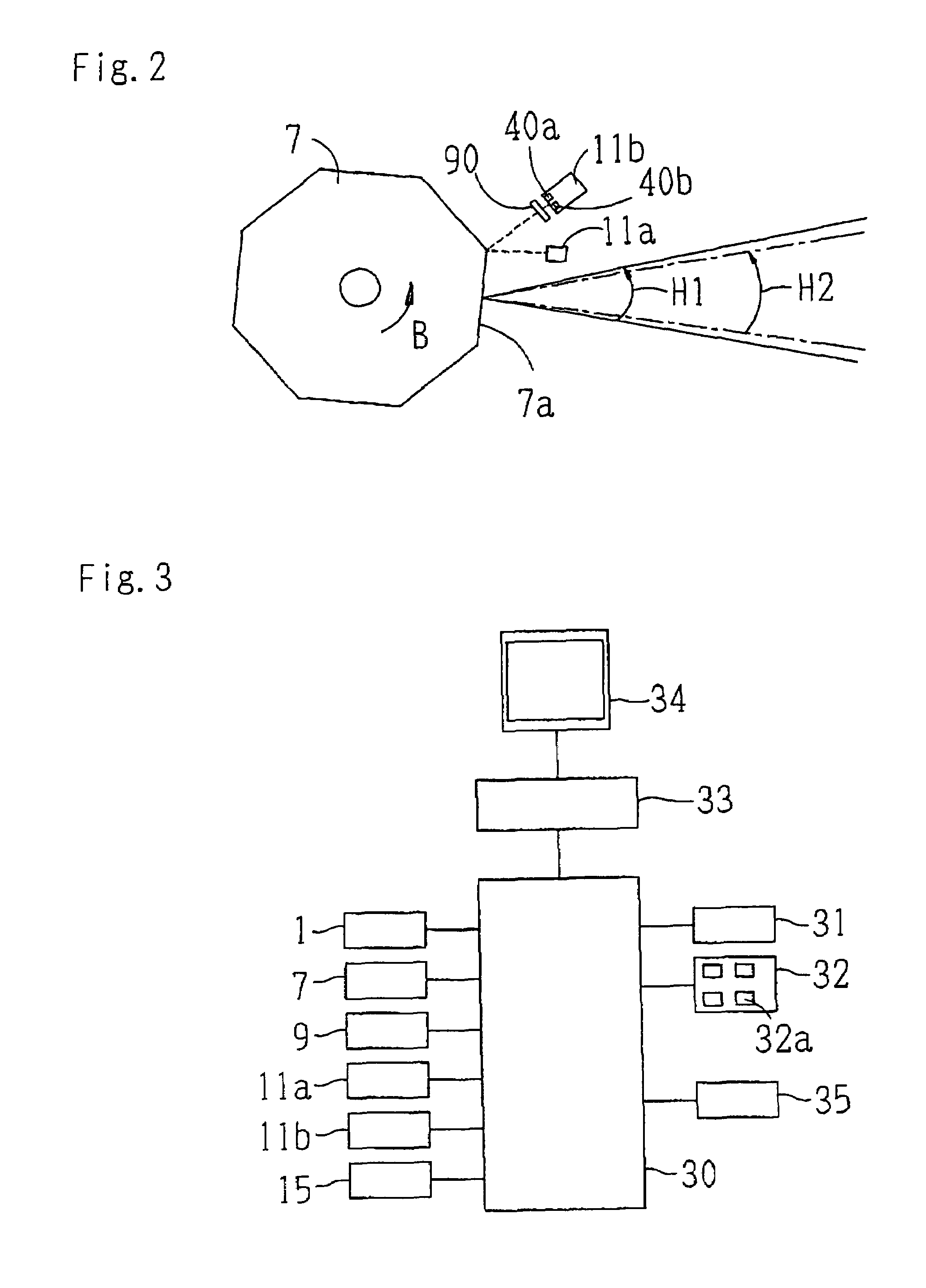
An ophthalmologic observation apparatus of a confocal laser scanning microscopy system for photographing and observing a target site of an eye of an examinee, includes a controller that, based on a number of image lines of one frame of a motion image to be displayed, a number of reflection faces of a polygon mirror, and a detection result of a photo sensor, controls a galvano mirror and an image forming unit so as to form each image line of each frame of the motion image based on the photo-receiving signals of a laser beam reflected on same reflection face of the polygon mirror.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
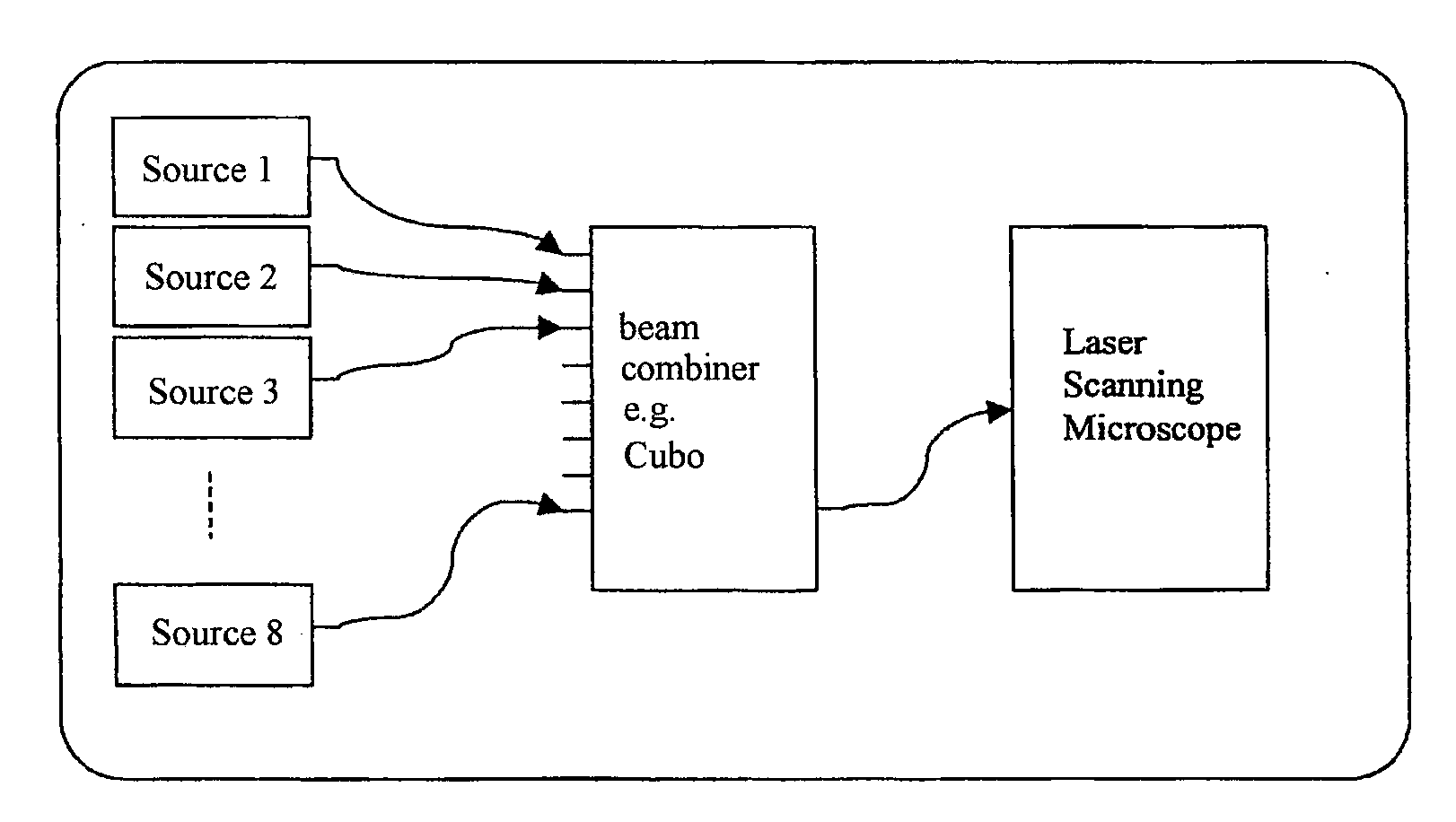
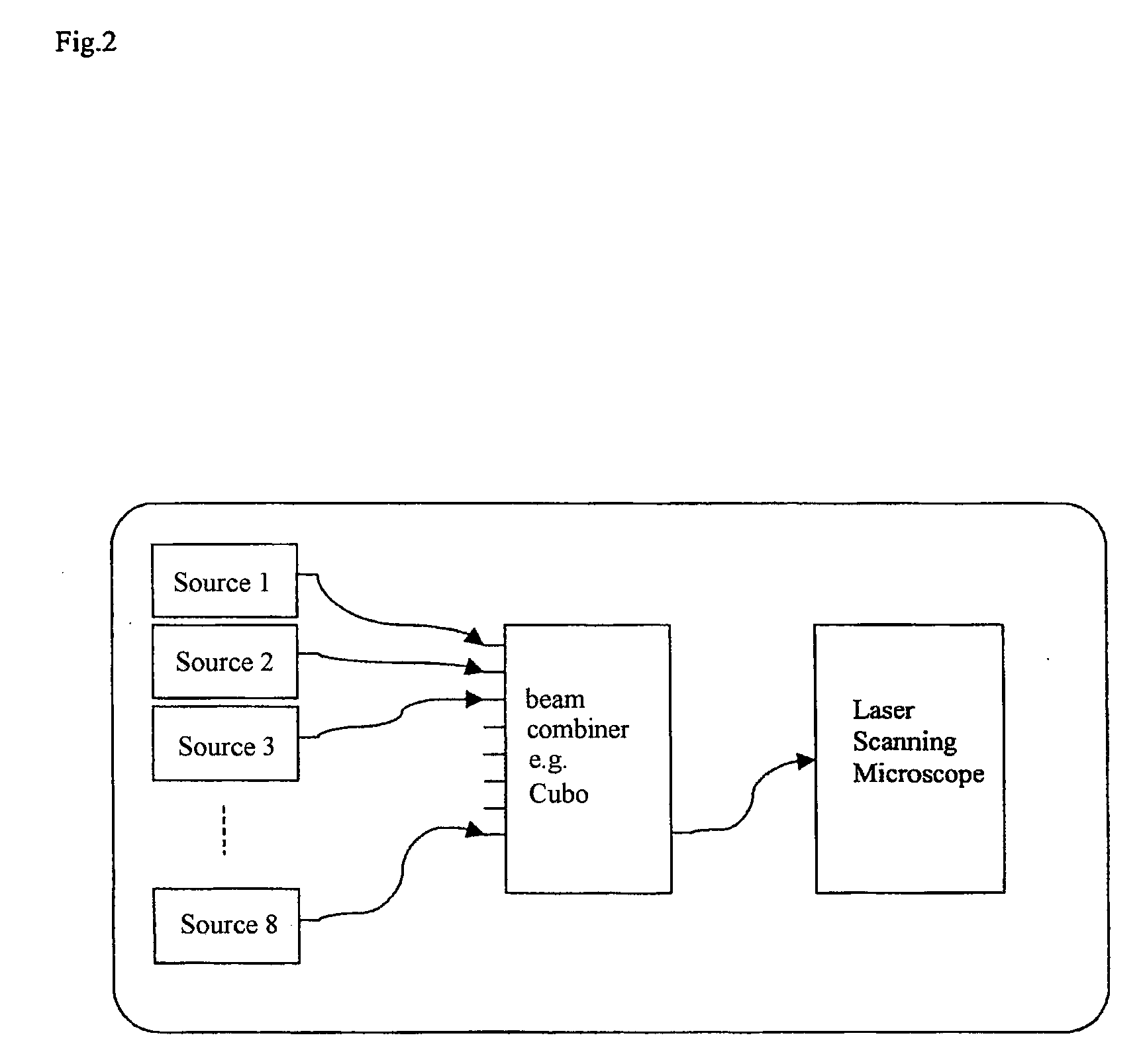
Method for laser scanning microscopy and beam combiner
InactiveUS20090303584A1Improve reliabilityReduce weightMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopesLaser scanning microscopeElectrical conductor
A method for laser scanning microscopy is characterized by the use of encapsulated fiber multiplexers from the telecommunications field for combining the beams of a plurality of lasers of different wavelengths and coupling them together into a laser scanning microscope and by corresponding beam combiners. Light-conducting guides to which different lasers can be coupled, preferably by light guides, are advantageously guided out of an encapsulated component.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MIKROLMAGING
Novel use of cyanine dye in detection of G-quadruplex DNA
InactiveCN101587066BEfficient identificationRealize identificationMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsCyanineUv vis absorbance
The invention provides novel use of a cyanine dye in the detection of a G-quadruplex DNA. The detection of the G-quadruplex DNA by using the cyanine dye has the advantages of simplicity, quickness andrelatively low prices and overcomes the drawbacks of the prior detection technology such as long period, high price and high technical and equipment requirements. The use of the cyanine dye in the detection of the G-quadruplex DNA makes whether a DNA sample in solution has a G-quadruplex structure or a linear double helical structure determined quickly by a UV-visible absorption spectrum, fluorescence spectrum or confocal laser scanning microscopy. By using confocal laser scanning microscopy, the DNA sample assembled on the surface of Au can be marked visually, so the structure of the DNA sample can be recognized and the specific assembly position of the DNA sample on the surface of the Au can be marked at the same time.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Novel fluorescent molecular probe and application thereof in field of Al (III) detection
InactiveCN102766086AHigh selectivityHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceHydrogenMolecular probe
The invention discloses a novel fluorescent molecular probe, which has a general formula with the following structure, wherein R1 is an alkyl chain having 1-8 carbon atoms, and R2 is hydrogen, a sulfonic acid group, a sulfonic acid ion group or a 3-15 carbon atom-containing quaternary ammonium group which is connected to a position 2,3,5 or 6 of an intermediate benzene ring. The invention also discloses application of the novel fluorescent molecular probe in the field of Al (III) detection. The novel fluorescent molecular probe provided by the invention has higher selectivity and sensitivity on Al (III). Through combining confocal laser scanning microscopy, fluorescence imaging of the fluorescent molecular probe after Al (III) is captured in cells can also be obtained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Laser scanning microscope apparatus and laser scanning method
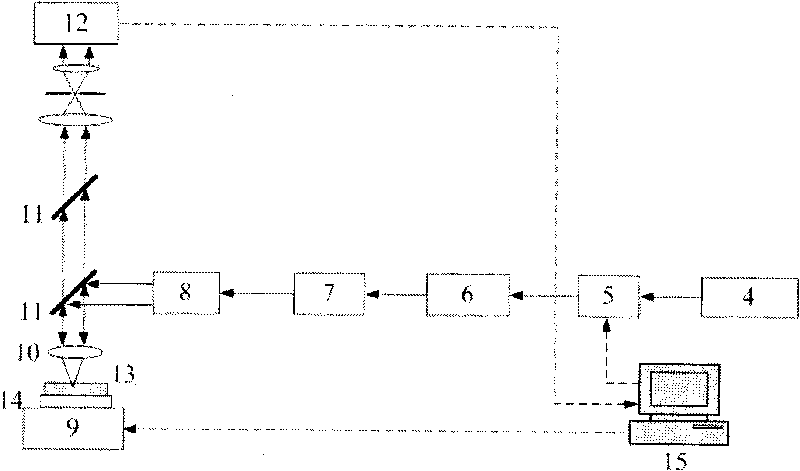
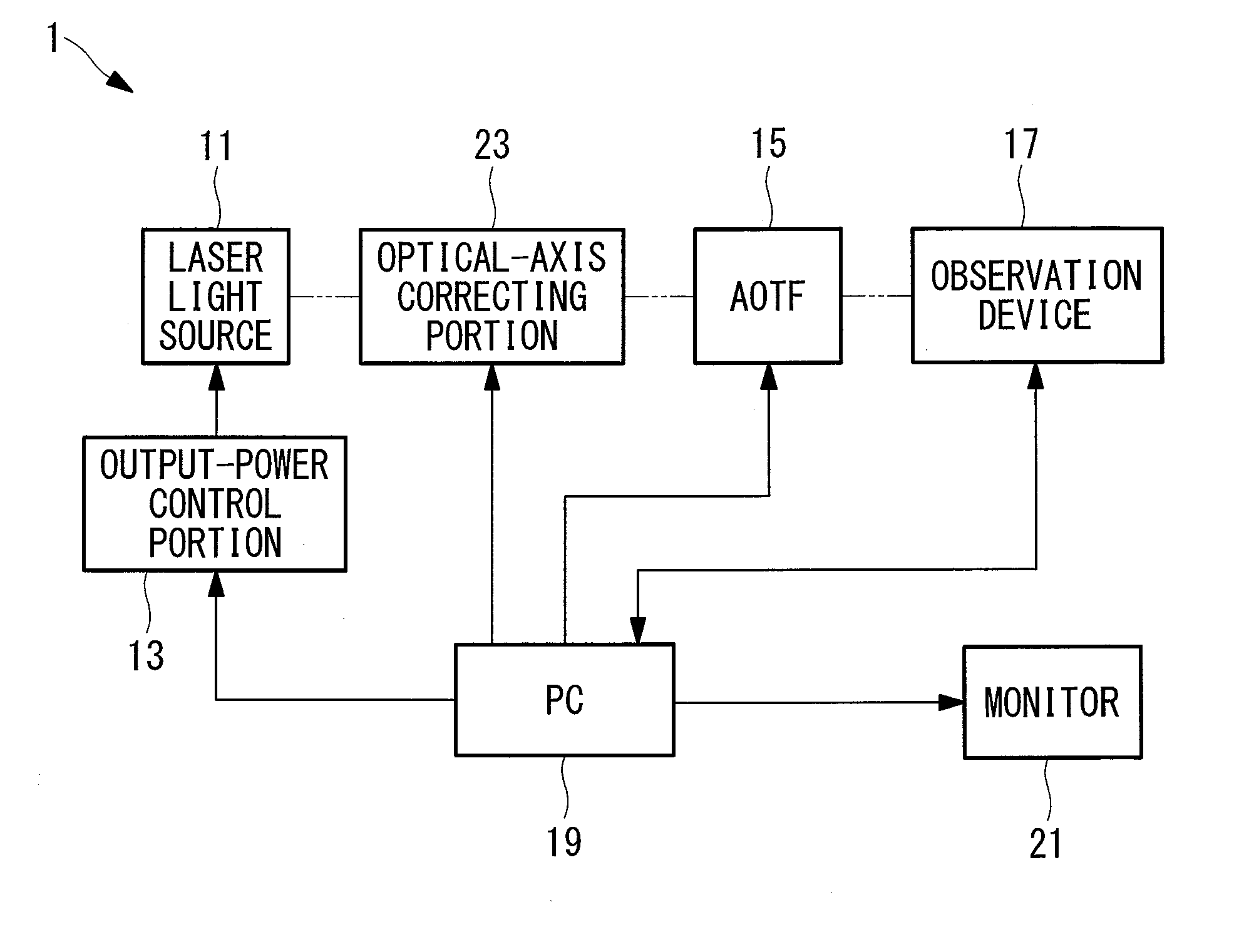
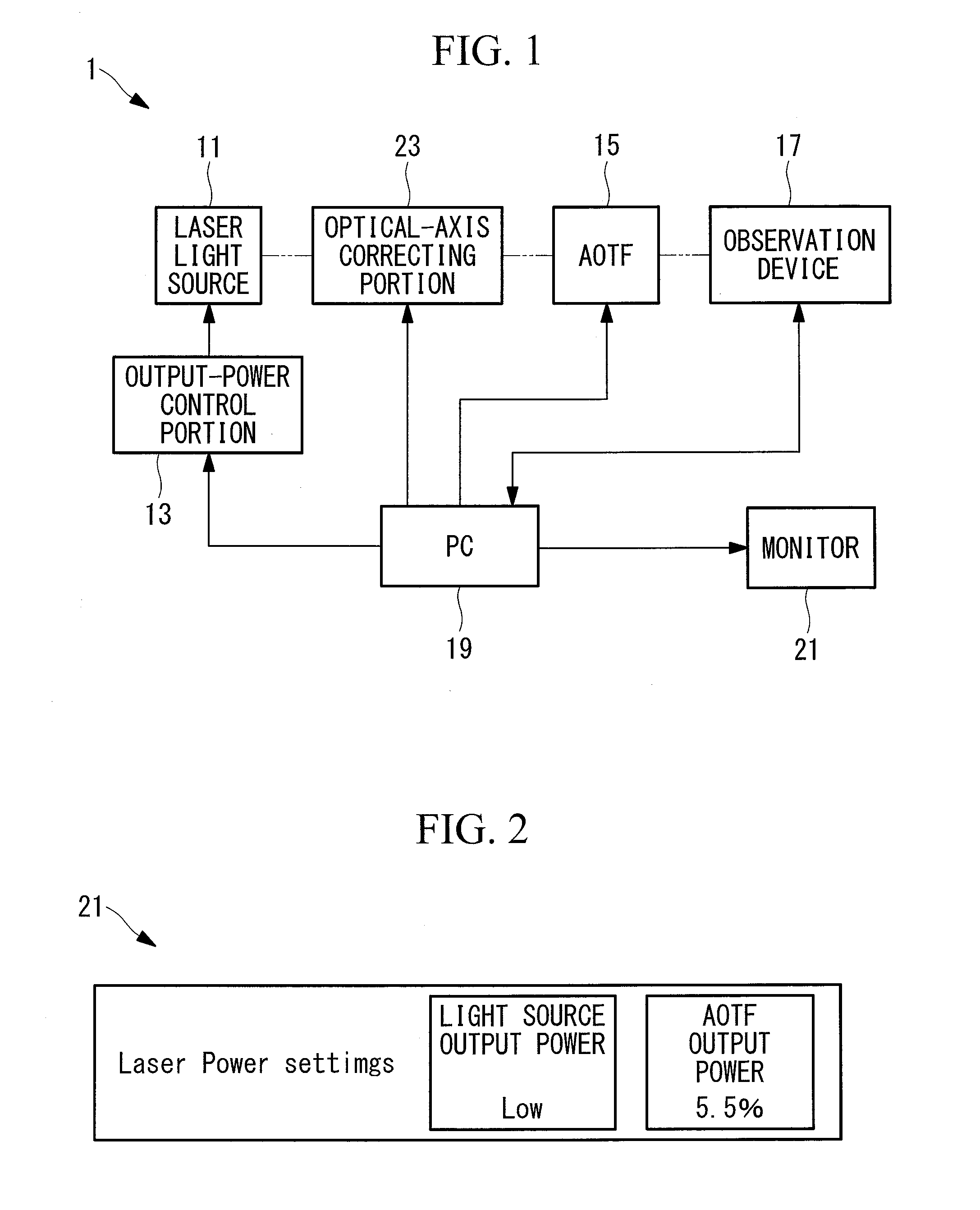
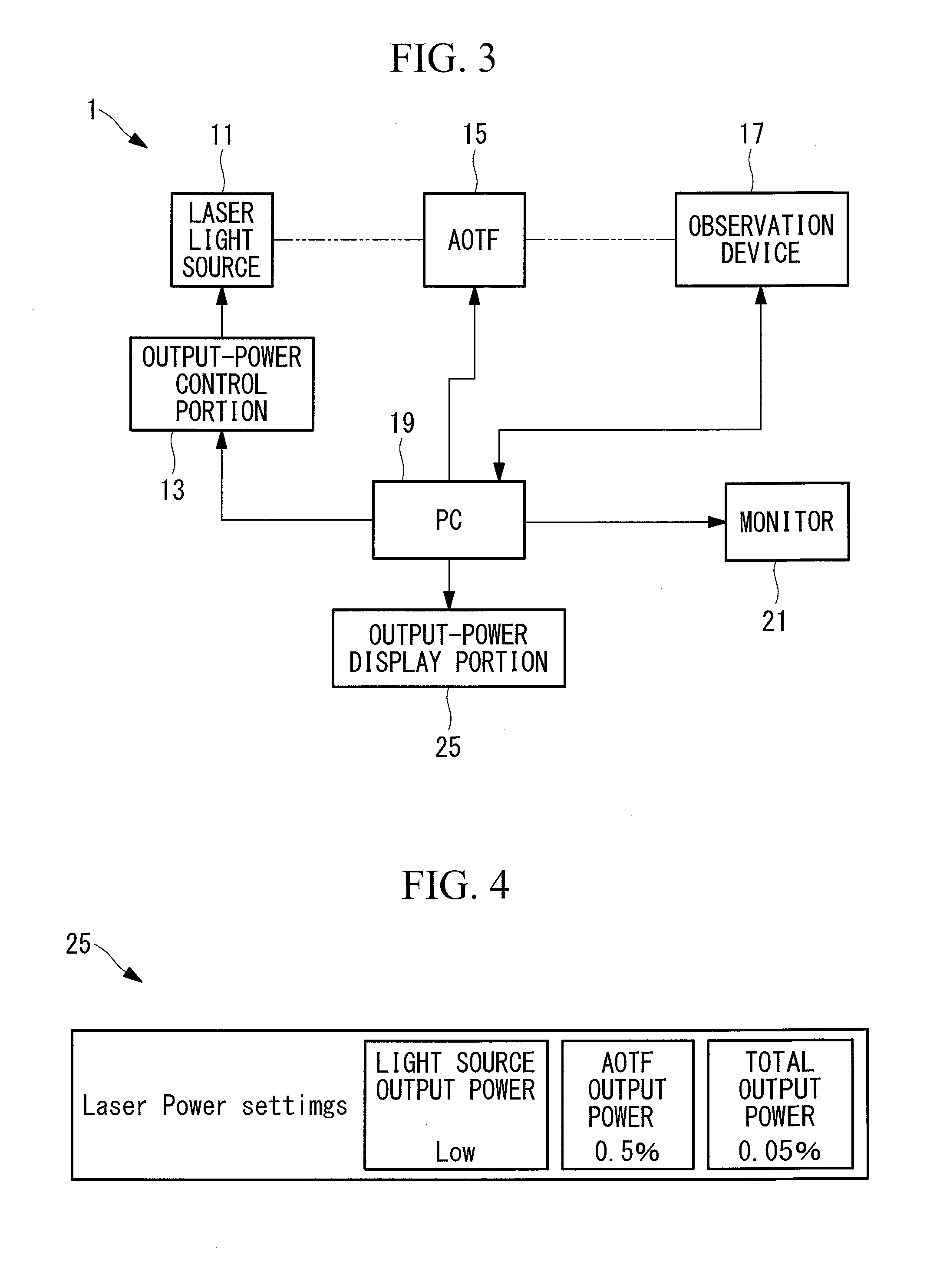
Both light stimulation of a specimen at a high intensity and detailed fluorescence observation at a low intensity are realized by using a single laser light source. Provided is a laser scanning microscope apparatus (1) including a laser light source (11) that generates laser light; output-power control portion (13) that can set an output power of the laser light source (11) by changing the output power in a step-wise manner; an AOTF (15) that can adjust a light level of the laser light emitted from the laser light source (11) in a step-wise manner at a resolution that is finer than a resolution at which the output-power control portion (13) changes the output power of the laser light source (11); and an observation device (17) that scans the laser light whose light level has been adjusted by the AOTF (15) on a specimen and that detects fluorescence generated at the specimen.
Owner:EVIDENT CORP
Ophthalmologic observation apparatus
An ophthalmologic observation apparatus of a confocal laser scanning microscopy system for photographing and observing a target site of an eye of an examinee, includes a controller that, based on a number of image lines of one frame of a motion image to be displayed, a number of reflection faces of a polygon mirror, and a detection result of a photo sensor, controls a galvano mirror and an image forming unit so as to form each image line of each frame of the motion image based on the photo-receiving signals of a laser beam reflected on same reflection face of the polygon mirror.
Owner:NIDEK CO LTD
Fluorescence labeling method for free calcium ions of cotton pollen tube
InactiveCN101806736BEasy to importAvoid damagePreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceZoology
The invention discloses a fluorescence labeling method for free calcium ions of a cotton pollen tube, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The fluorescence labeling method comprises the following steps: perforating glass slide to make a small chamber for culturing the pollen tube; culturing pollen in the small chamber, and sprouting the pollen tube; loading Fluo-3AM into the cultured pollen tube by a low temperature incubation method; and observing dynamic variation of Ca2+ in the pollen tube under a confocal laser scanning microscopy. The invention establishes a method for researching the concentration change of the Ca2+ in the cotton pollen tube by using the confocal laser microtechnique, has simple operation and good labeling effect, plays an important role in the growth of the cotton pollen tube and fertilization reproduction research, and has important practical application value.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Optical assembly for scanning excitation radiation and/or manipulation radiation in a laser scaning microscope, and laser scanning microscope
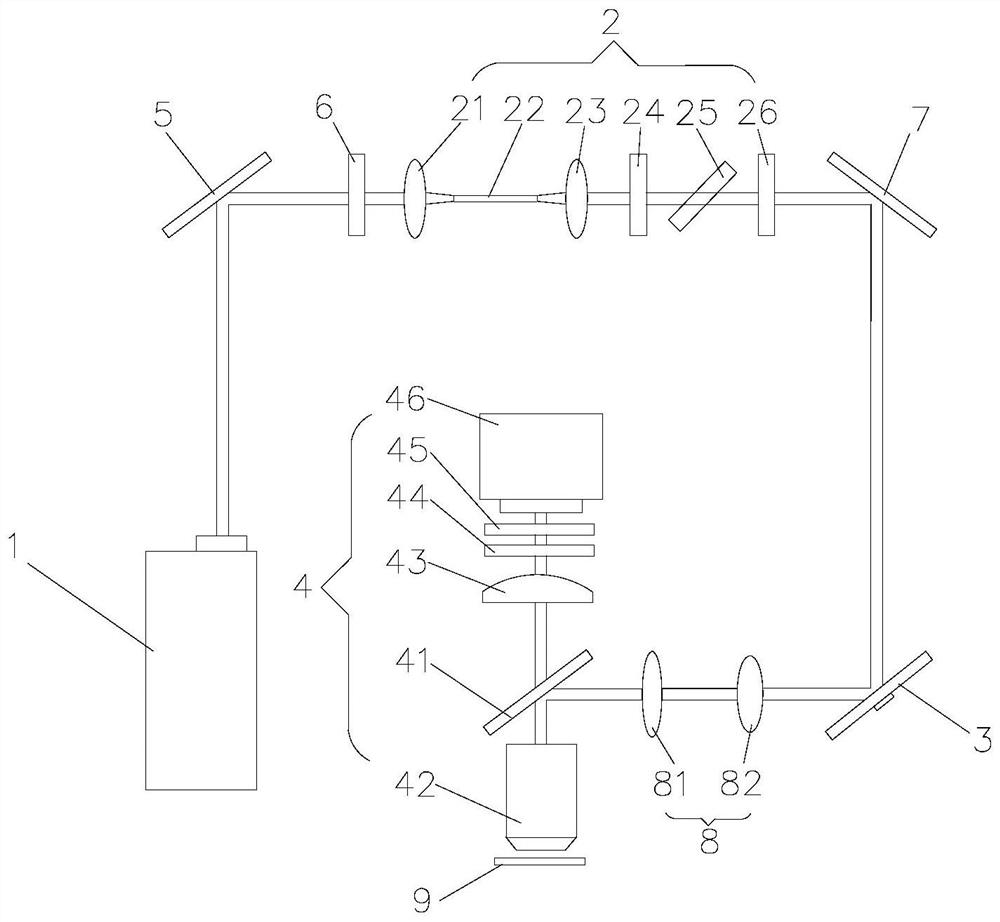
An optical assembly for scanning excitation radiation and / or manipulation radiation in a laser scanning microscope, having an optical scanning unit for providing a first pupil plane, a first beam deflecting device, which is made of a first scanner arranged on the first pupil plane, for scanning the excitation radiation and / or manipulation radiation in a first coordinate direction, a first focusing device for generating a second pupil plane, which is optically conjugated to the first pupil plane, and a second beam deflecting device for deflecting the excitation radiation and / or manipulation radiation, said second deflecting device being arranged on the second pupil plane, a second focusing device in order to generate a third pupil plane, which is optically conjugated to the first pupil plane and the second pupil plane, a third beam deflecting device is arranged on the third pupil plane for deflecting the excitation radiation and / or manipulation radiation, and a variable beam deflecting means is provided between the first focusing device and the second pupil plane and the second pupil plane and the second focusing device in order to switch an optical beam path between a first beam path and a second beam path.
Owner:CARL ZEISS MICROSCOPY GMBH
Diagnosis and treatment integral confocal anorectal enteroscope system
InactiveCN102697465AImprove accuracyImprove securityEndoscopesSurgical instrument detailsLaser scanningOperative time
The invention belongs to the field of medical appliances and particularly relates to a diagnosis and treatment integral confocal anorectal enteroscope system, which comprises a hard anorectal enteroscope, wherein the end part of a hard endoscope of the hard anorectal enteroscope is provided with a treatment device, and a treatment system host machine matched with the treatment device to be used is connected onto the hard anorectal enteroscope. The diagnosis and treatment integral confocal anorectal enteroscope system is concretely and organically combined with a laser cutter system or a microwave coagulator system through the hard anorectal enteroscope and a confocal laser scanning microscopy system. The diagnosis and treatment integral confocal anorectal enteroscope system can realize the effect that the diagnosis and the treatment are simultaneously carried out during the clinic application, an optical system and the confocal laser scanning microscopy system can be respectively used for observing the macroscopical conditions in the anorectum and the microscopic structures of the anorectal wall and the pathological changes to make accurate diagnosis, the laser cutter system or the microwave coagulator system can be used for carrying out laser treatment or microwave treatment on the pathological changes under the direct viewing condition through a monitor. When the diagnosis and treatment integral confocal anorectal enteroscope system is used for operation, the goal of simultaneously solving the problems in the diagnosis aspect and in the treatment aspect by one enteroscope can be realized, the frequent endoscope replacement is avoided, the operation time is greatly saved, the pain of patients is relieved, the accuracy and the safety of the operation are further improved, and effects beyond the imagination can be reached.
Owner:GUANGZHOU BAODAN MEDICAL INSTR TECH
Microscopic imaging device
The invention provides a microscopic imaging device. The microscopic imaging device comprises a laser generator for generating laser, and frequency modulation equipment, scanning galvanometer equipment and microscopic equipment which are sequentially arranged along a light path of the laser, the frequency modulation device comprises a coupling lens, an optical fiber, a decoupling lens, a first optical filter, a germanium sheet and a medium-density attenuation sheet which are sequentially arranged along the optical path of the laser. The soliton self-frequency-shift effect of the laser in the optical fiber is utilized, after the laser generates frequency shift in the polarization-maintaining large-mode-field optical fiber, the first optical filter is used for selecting the frequency of the laser, and then the laser with the corresponding frequency and wavelength is obtained and used for laser scanning microscopy.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
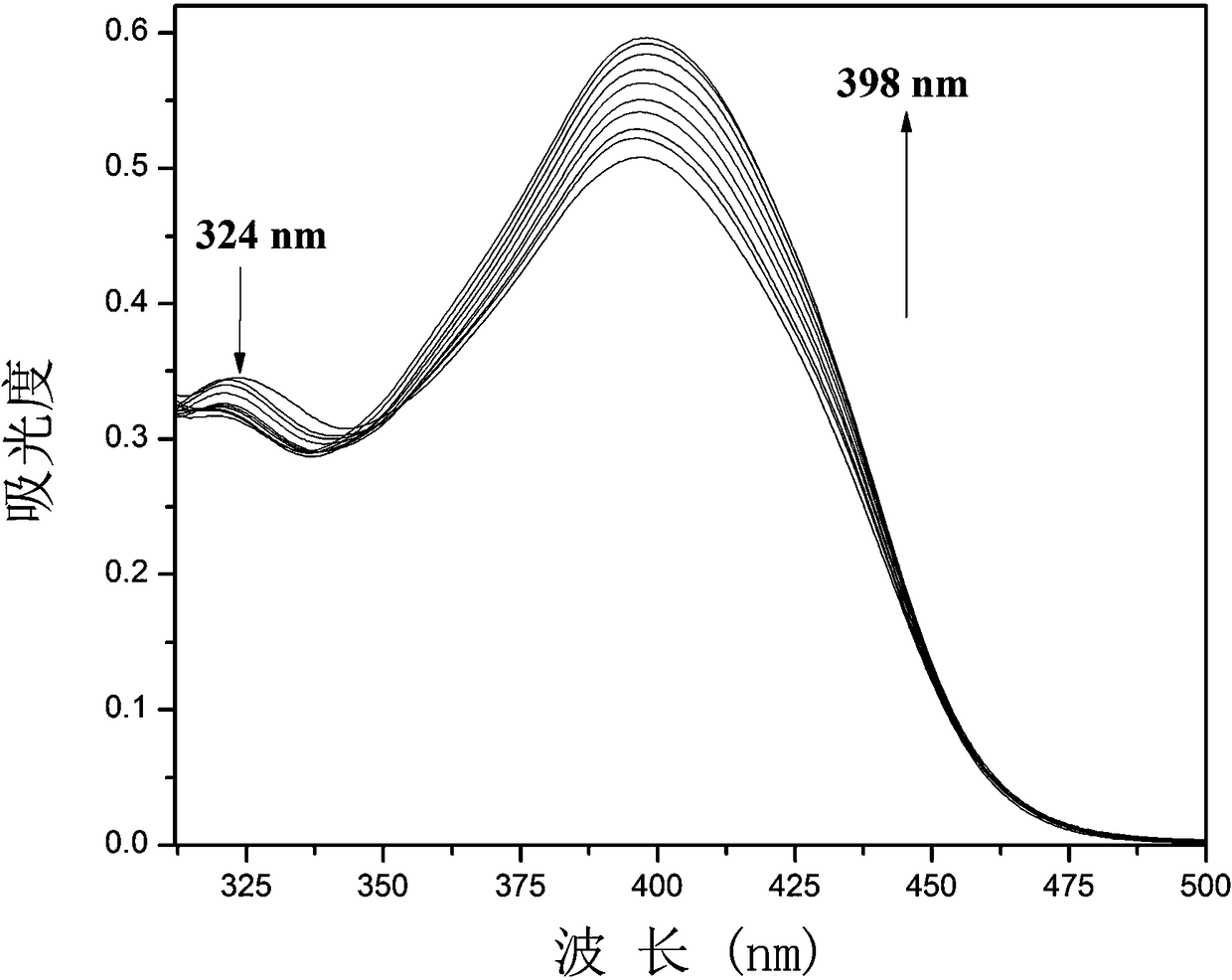
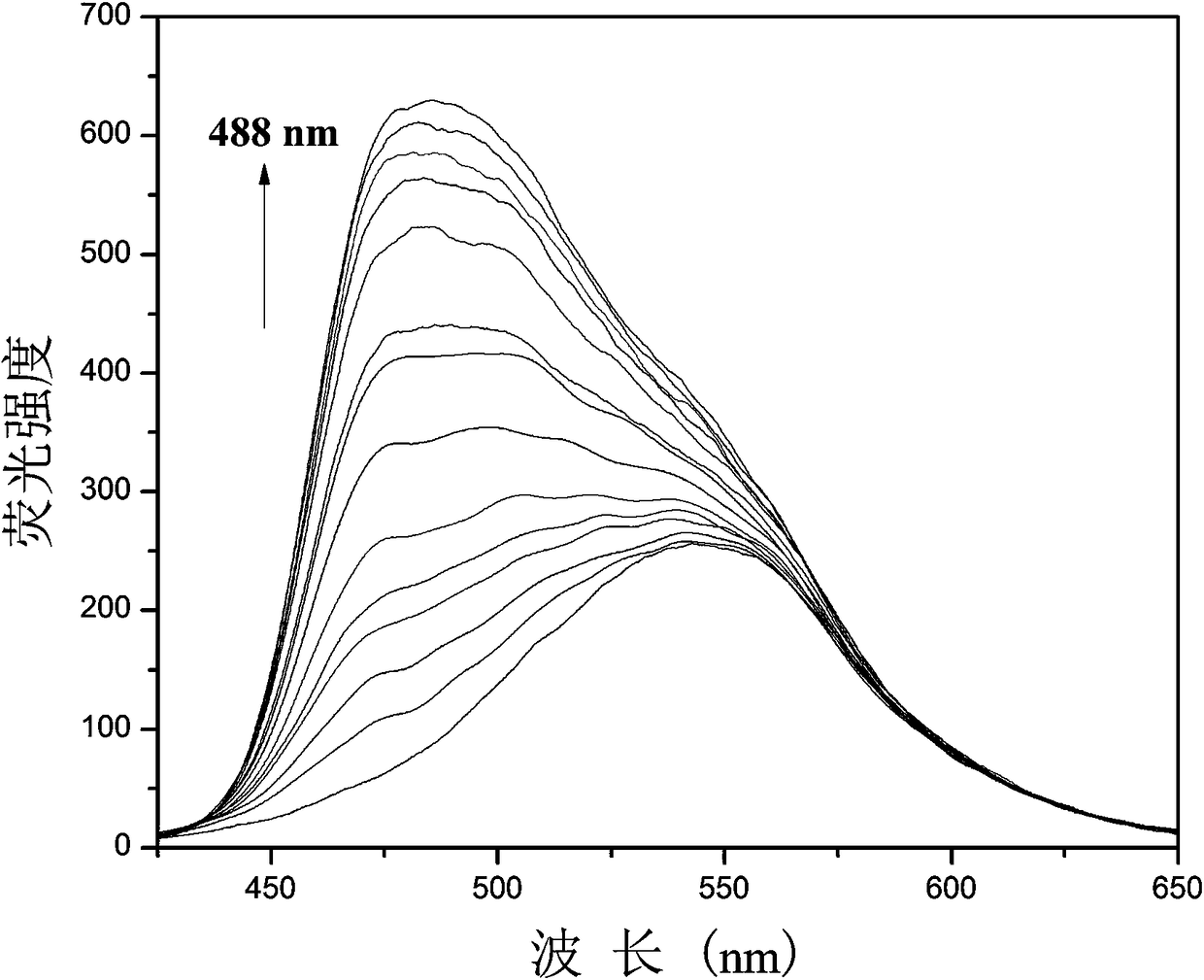
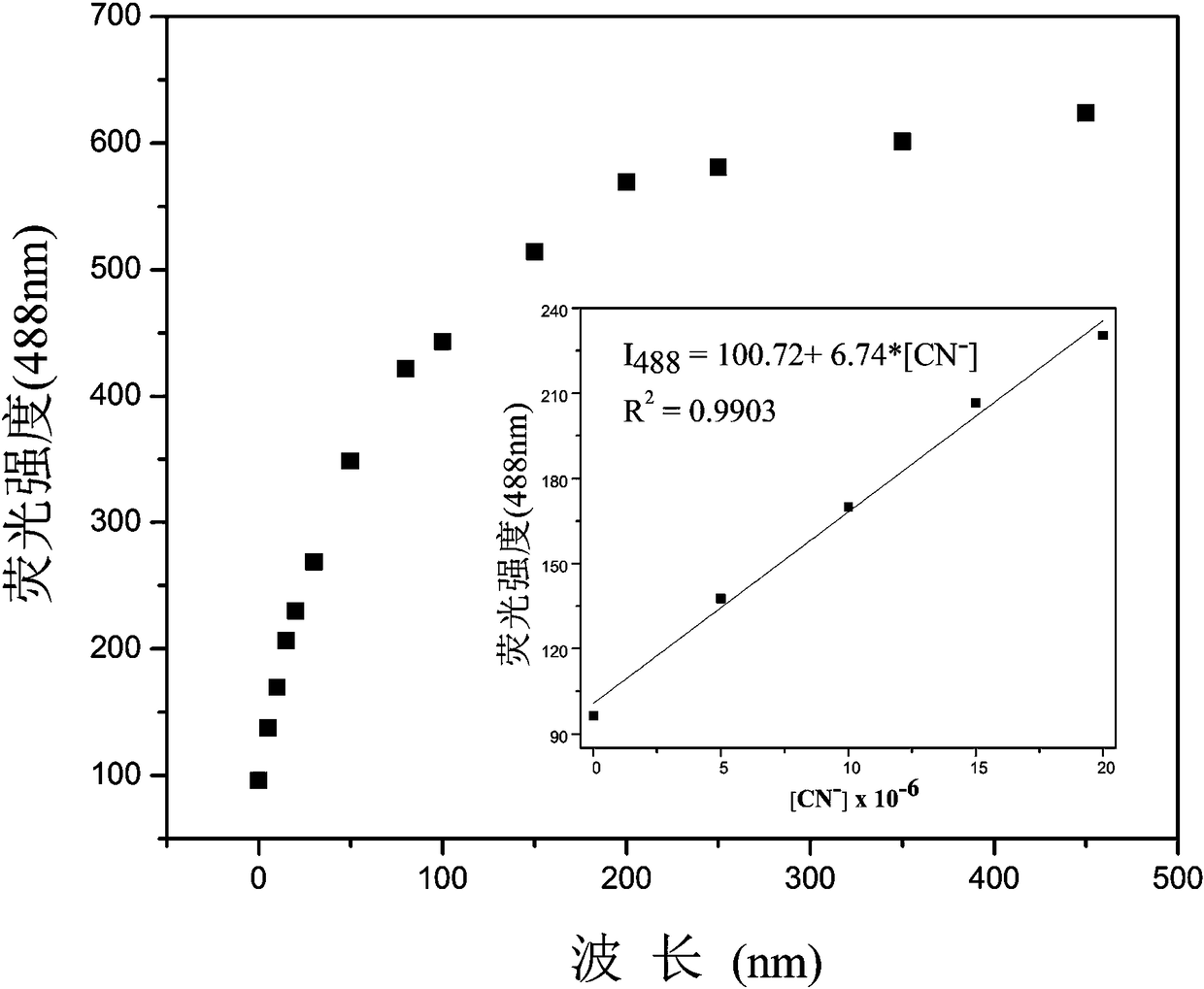
Enhanced fluorescent probe for detection CN-(Cyanogen), preparation method and biological application thereof
ActiveCN109232379AThe synthesis steps are simpleLow costOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFiltrationFluorescence
The invention belongs to the technical field of synthesis of a fluorescent probe. In order to solve the problems that an existing fluorescent probe is high in detection limit and poor in photostability, the invention provides an enhanced fluorescent probe for detecting CN- (Cyanogens), a preparation method and a biological application thereof. The fluorescent probe is 1-(pyren-1-yl)-3-(N-ethyl carbazole-3-yl)acrylketone. The preparation method comprises the steps of dissolving 1-acetylpyrene and N-ethyl carbazole-3-formaldehyde in anhydrous ethanol, then adding sodium hydroxide, continuously stirring the mixture at room temperature for 4 h, precipitating a yellow solid, tracking the reaction with a TLC (Thin-Layer Chromatography), performing suction filtration after the reaction is completed, washing with anhydrous ethanol and water (1 / 1, v / v), and drying in vacuum to obtain yellow powder. The detection of the fluorescent probe for CN- is enhanced, the reaction is rapid, the selectivity and sensitivity are high, and the fluorescent probe can be used for detection of CN- in an organism in combination with a confocal laser scanning microscopy.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com