Patents
Literature
78 results about "4d imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
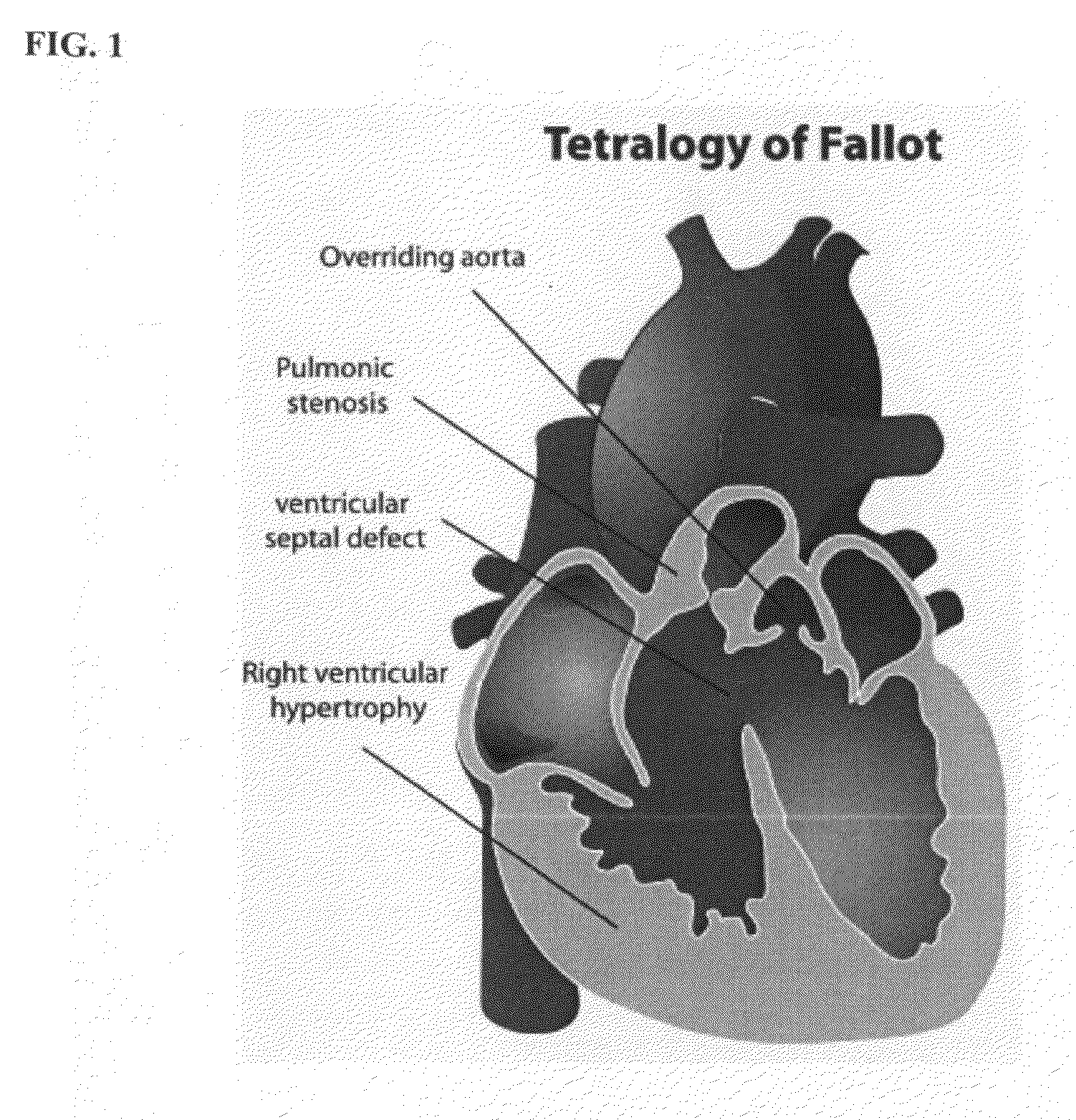
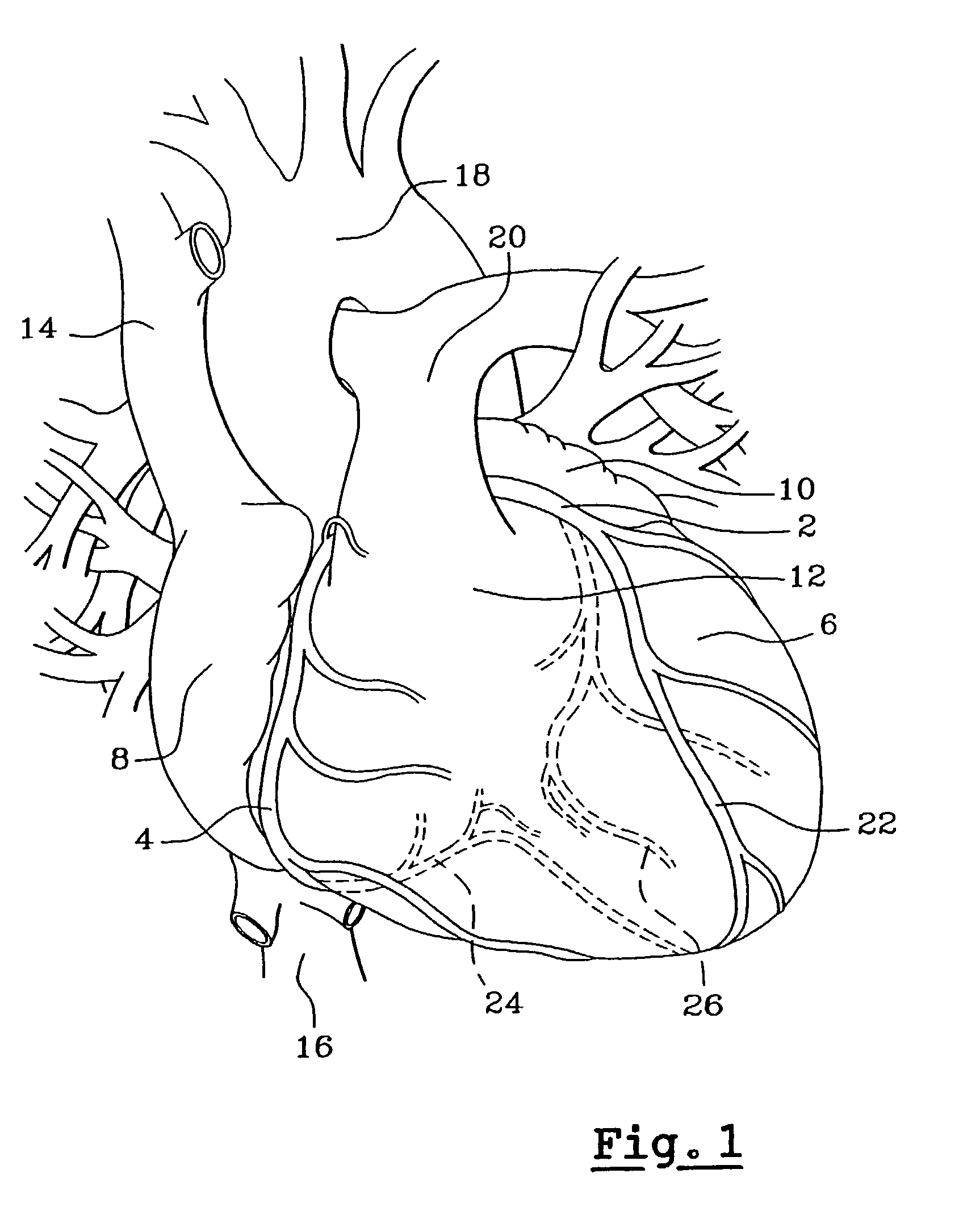
Arrangement for supporting a percutaneous intervention
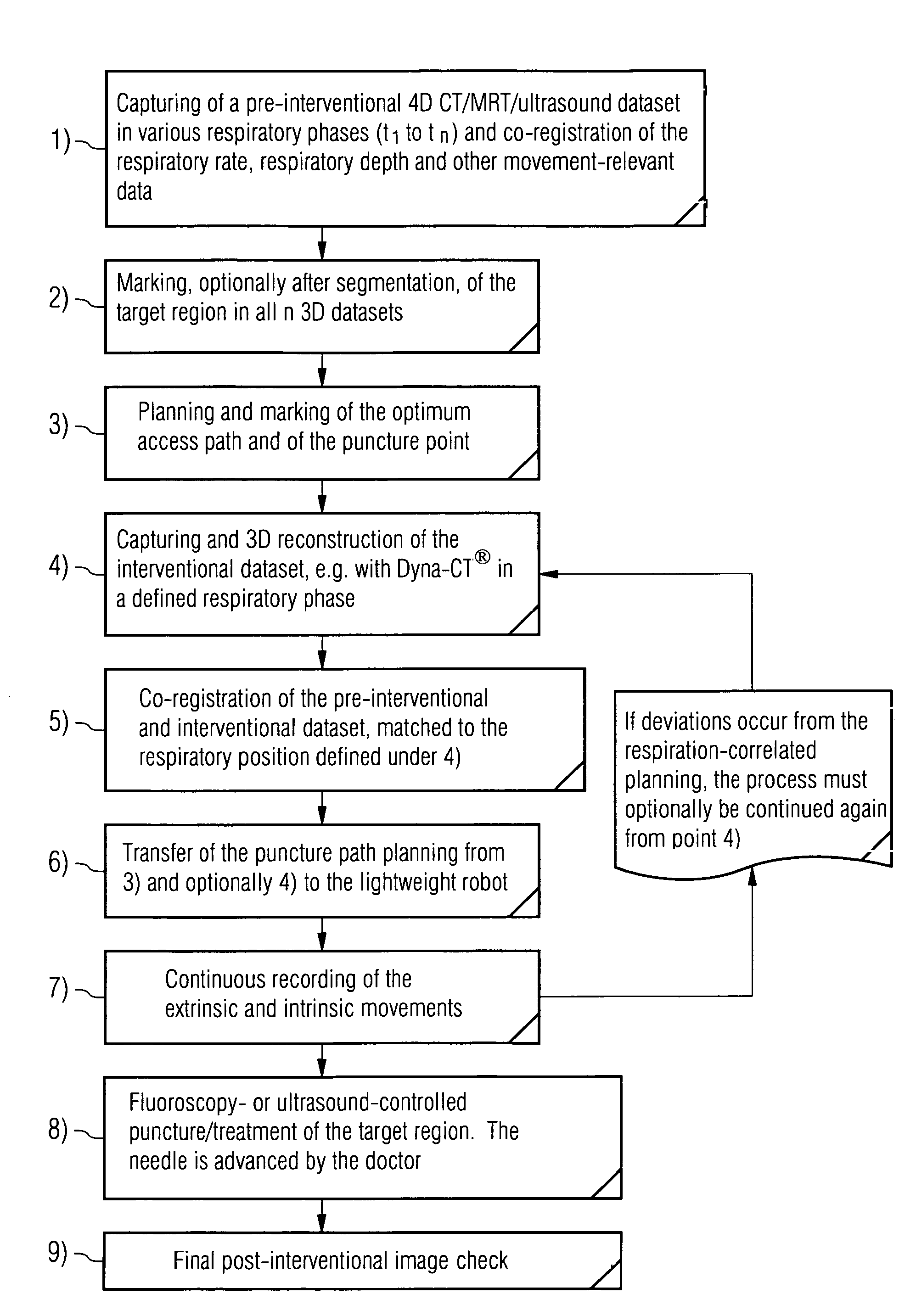
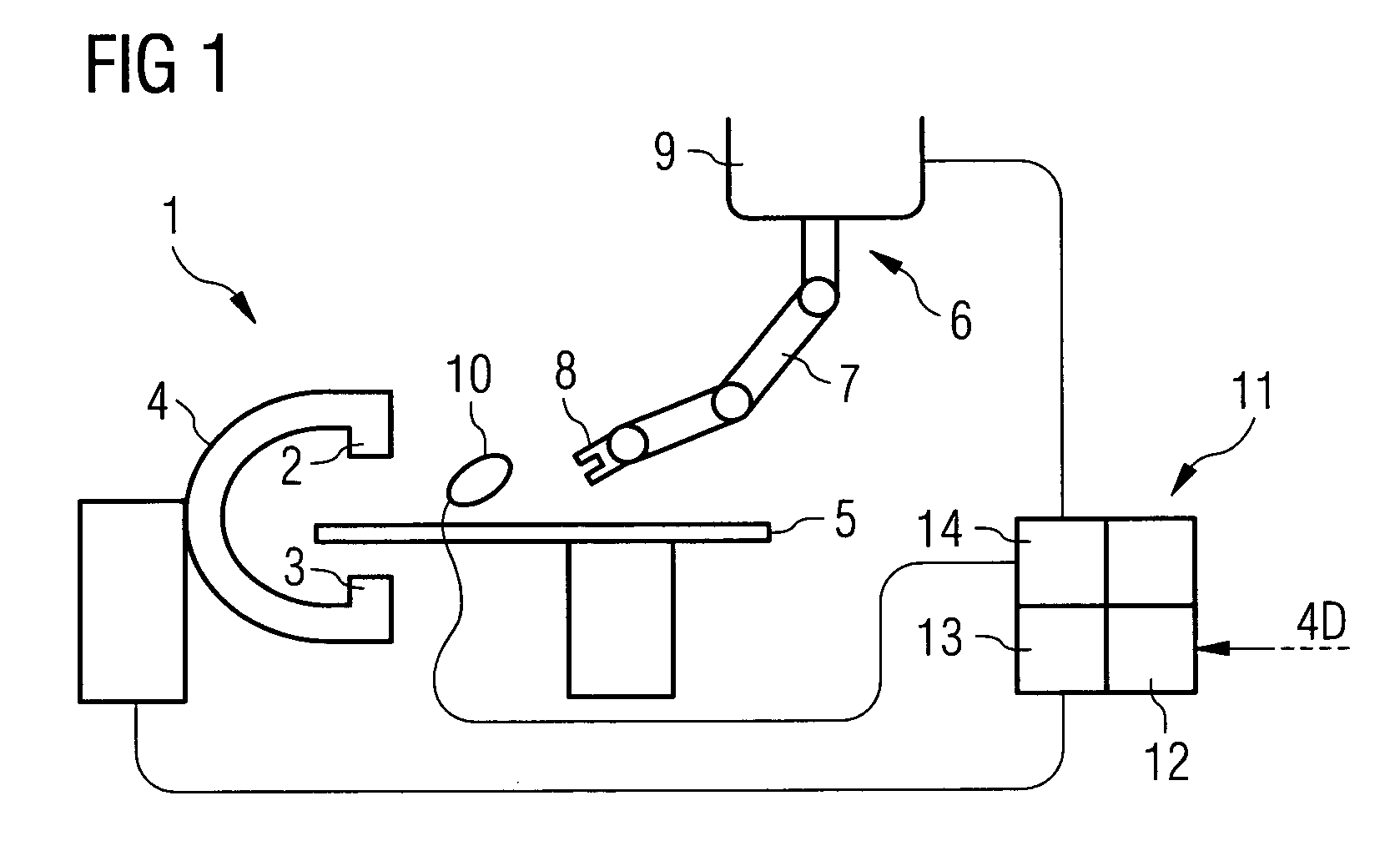
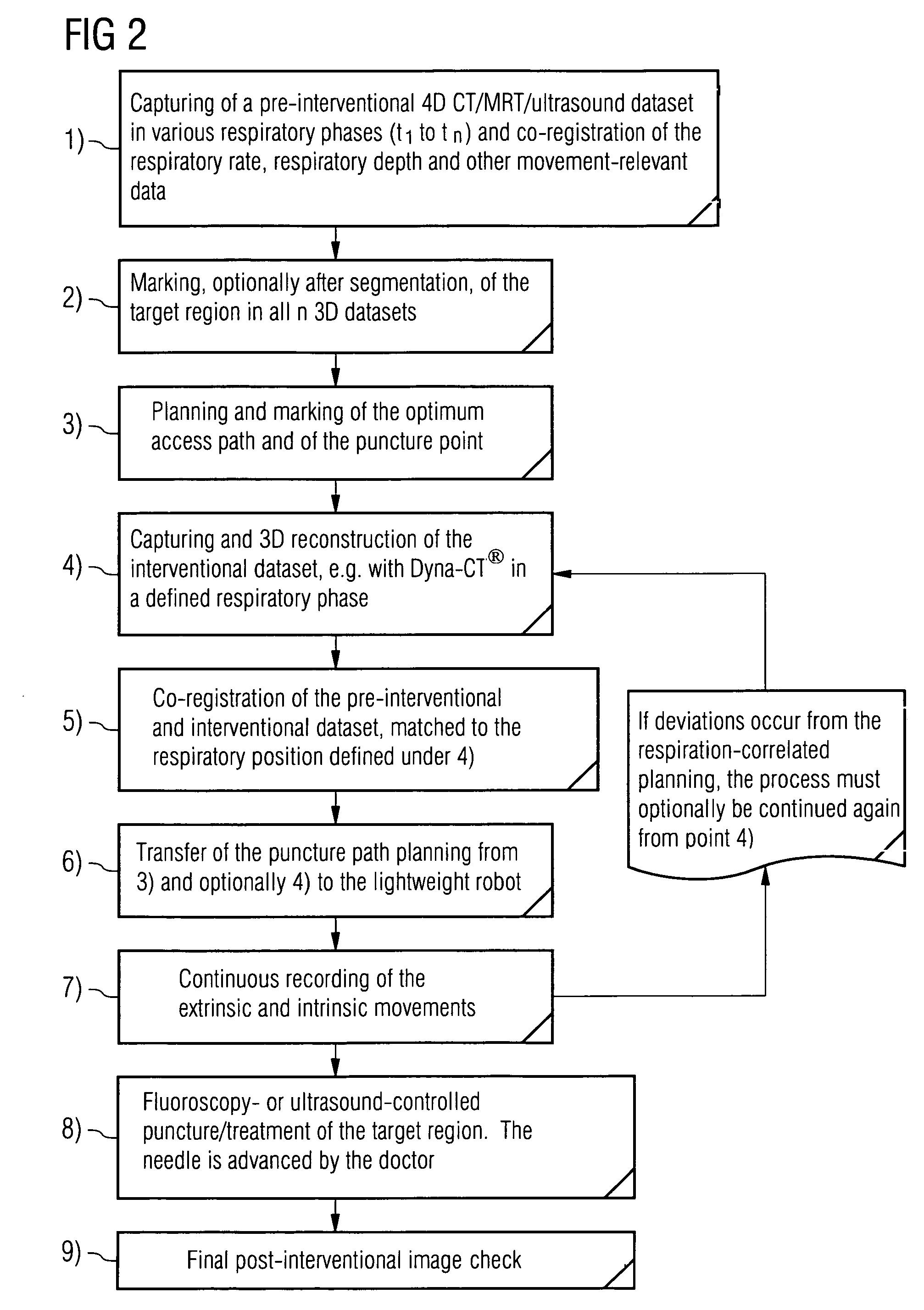
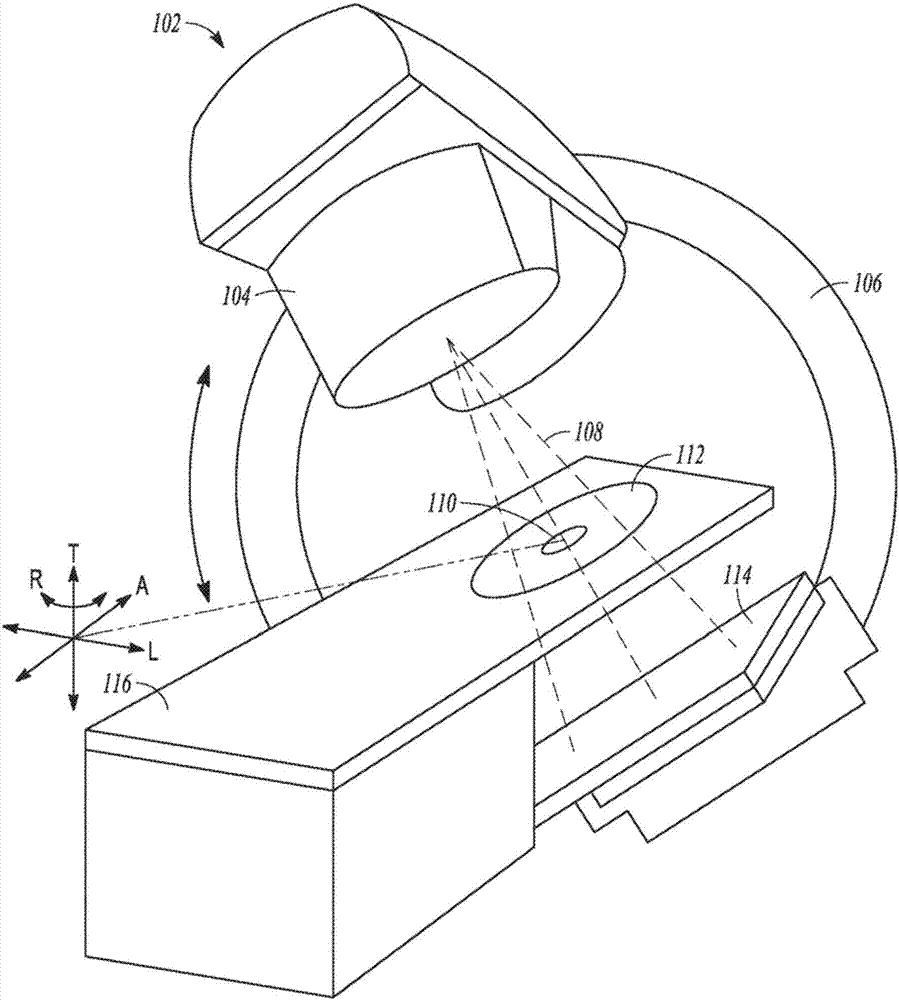
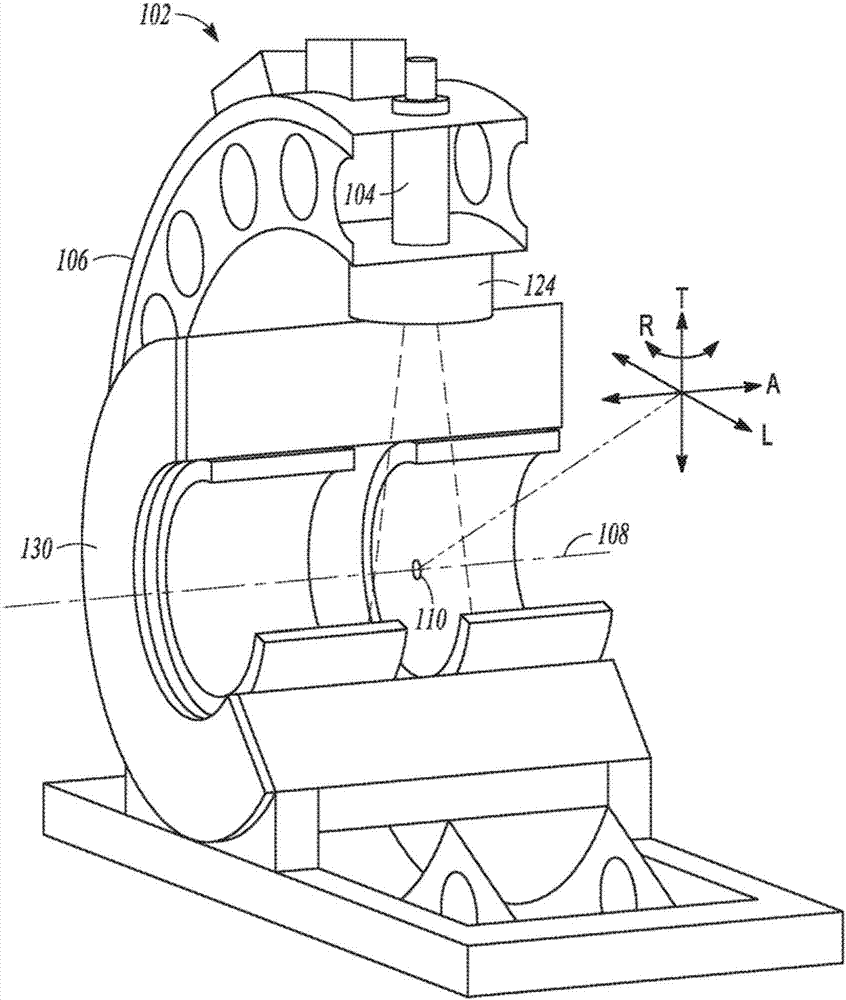
The invention relates to an arrangement for assisting a percutaneous intervention, comprising an imaging system for tomographic imaging, a robot registered therewith and devices for capturing movements of the patient. A processing unit registers a 4D image dataset recorded before the intervention with a 2D or 3D image dataset of the patient which was recorded immediately before the intervention by the imaging system at a defined respiratory position. From this image data, the access path is transmitted to the robot as a function of the movements captured during recording the 4D image dataset and registration, said robot in turn, depending on the instantaneous movement data, holding the instrument on a predetermined target path and preventing the instrument from being advanced by the person if and as long as the instantaneous movement data does not match the previously recorded movement data. The arrangement reduces the risk of puncture errors.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
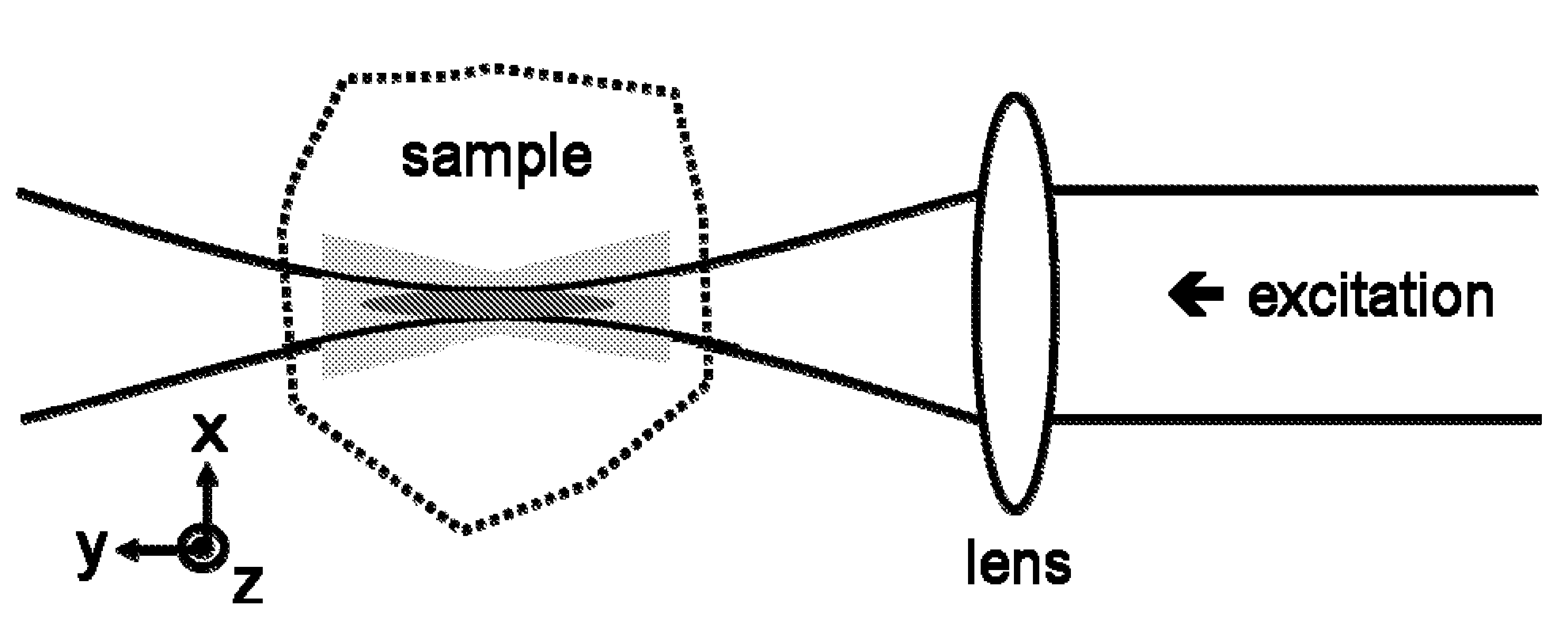
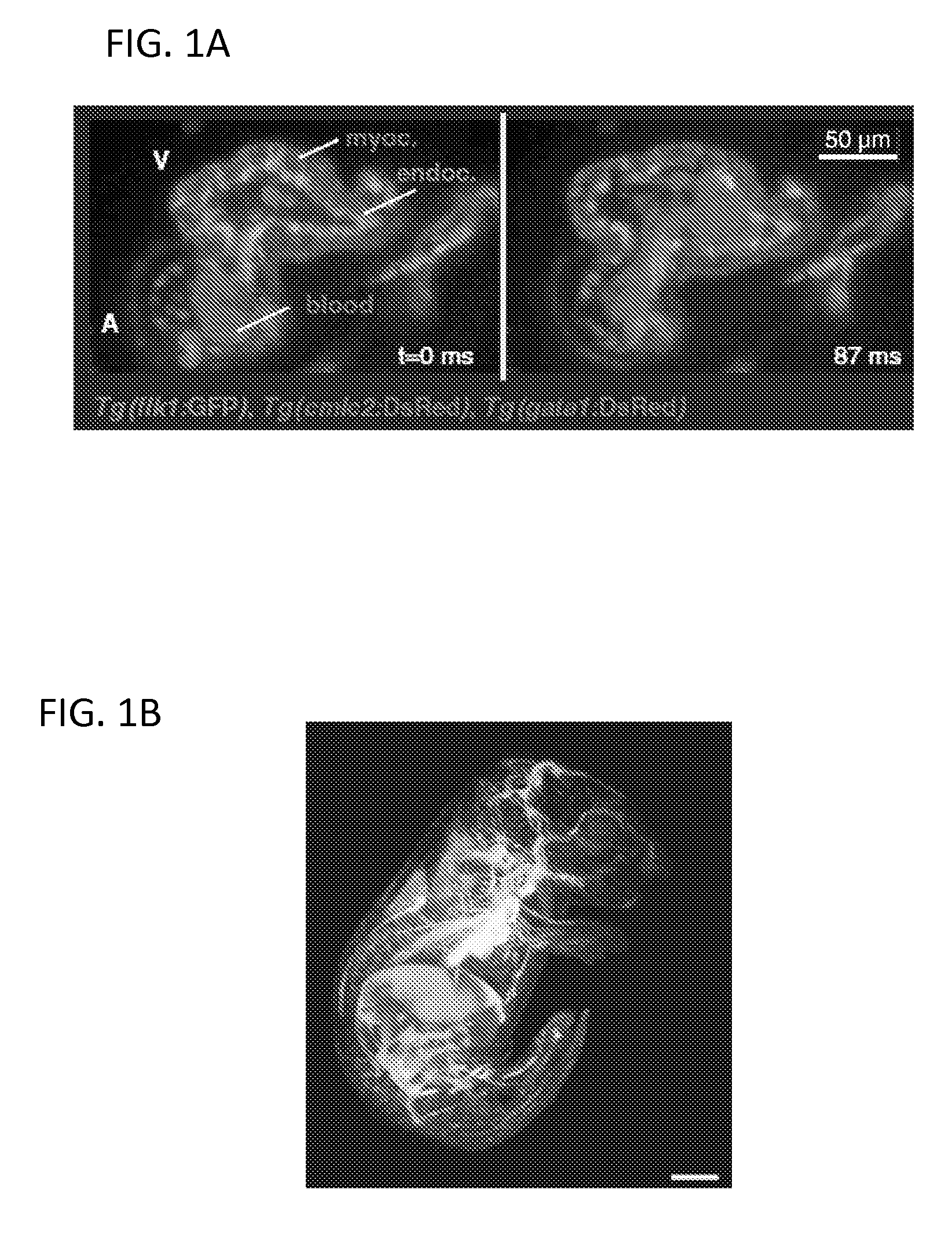
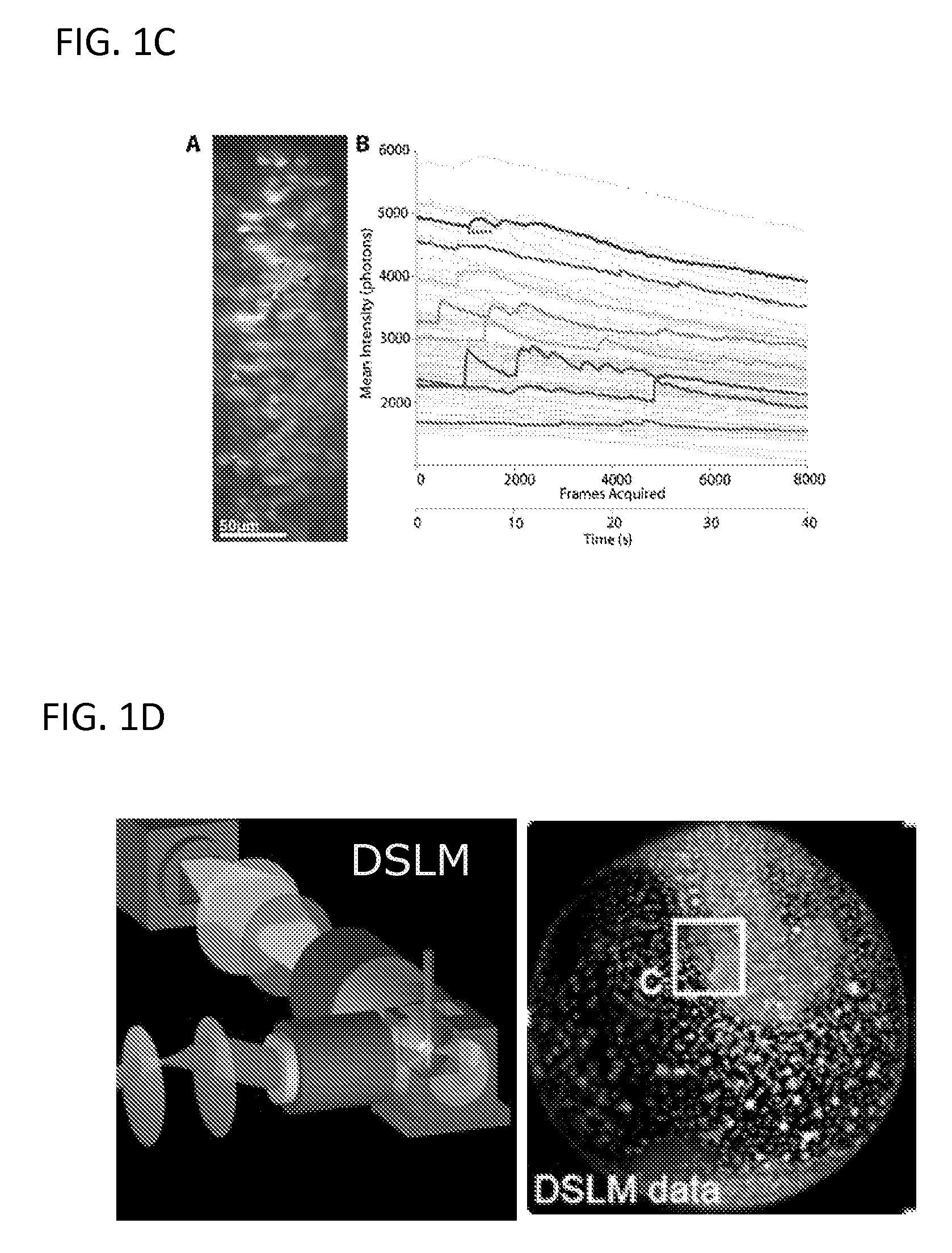
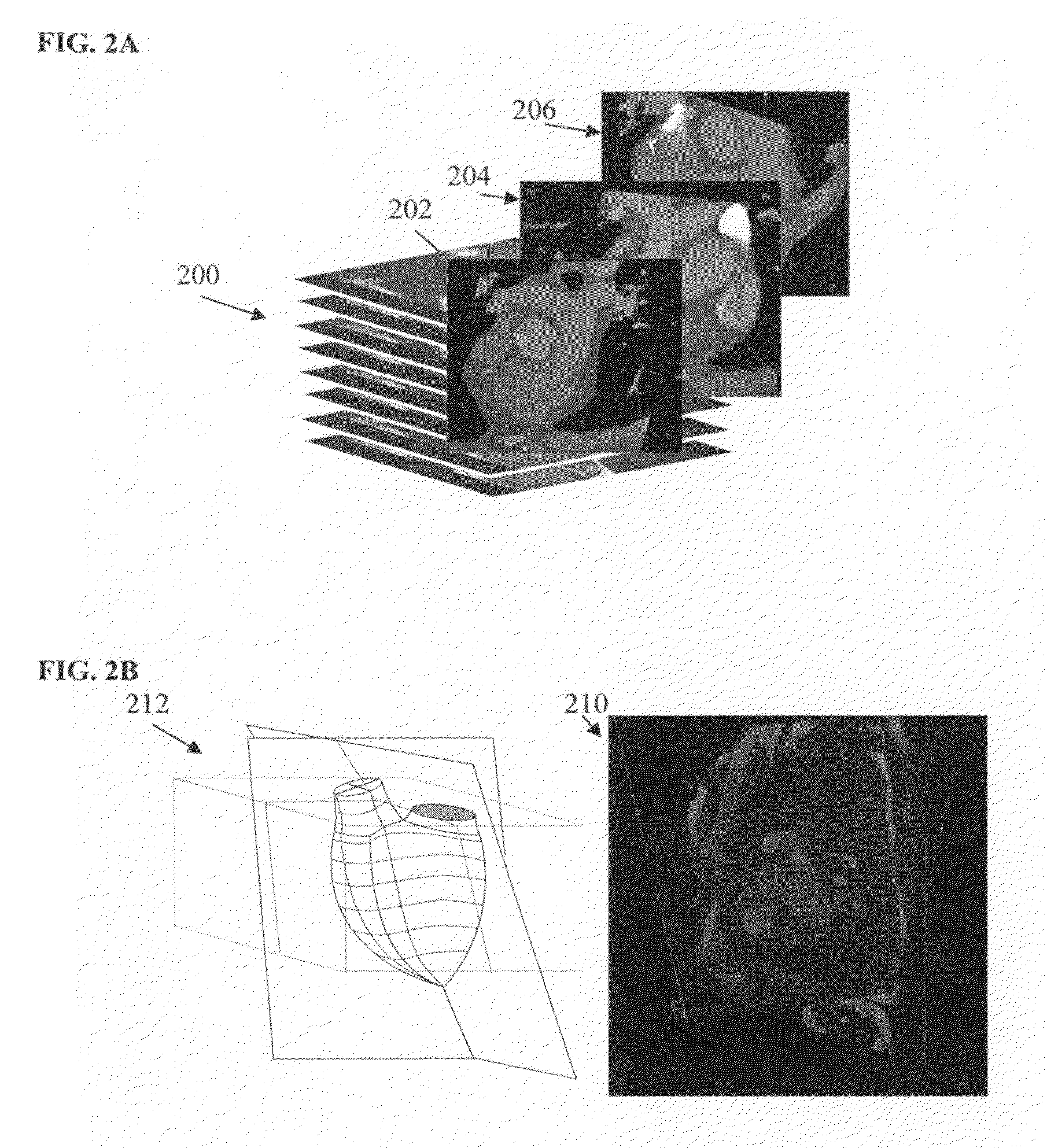
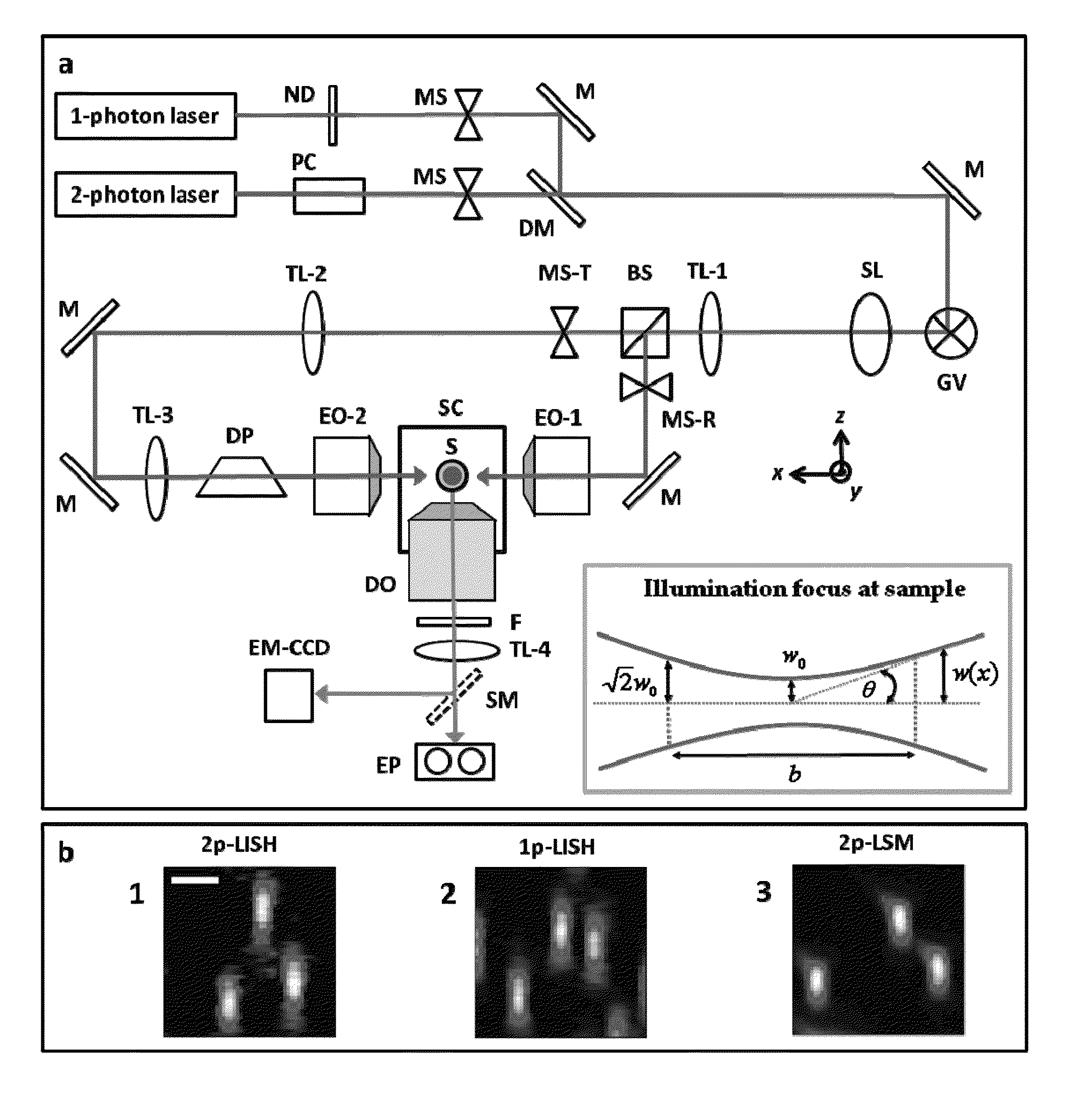
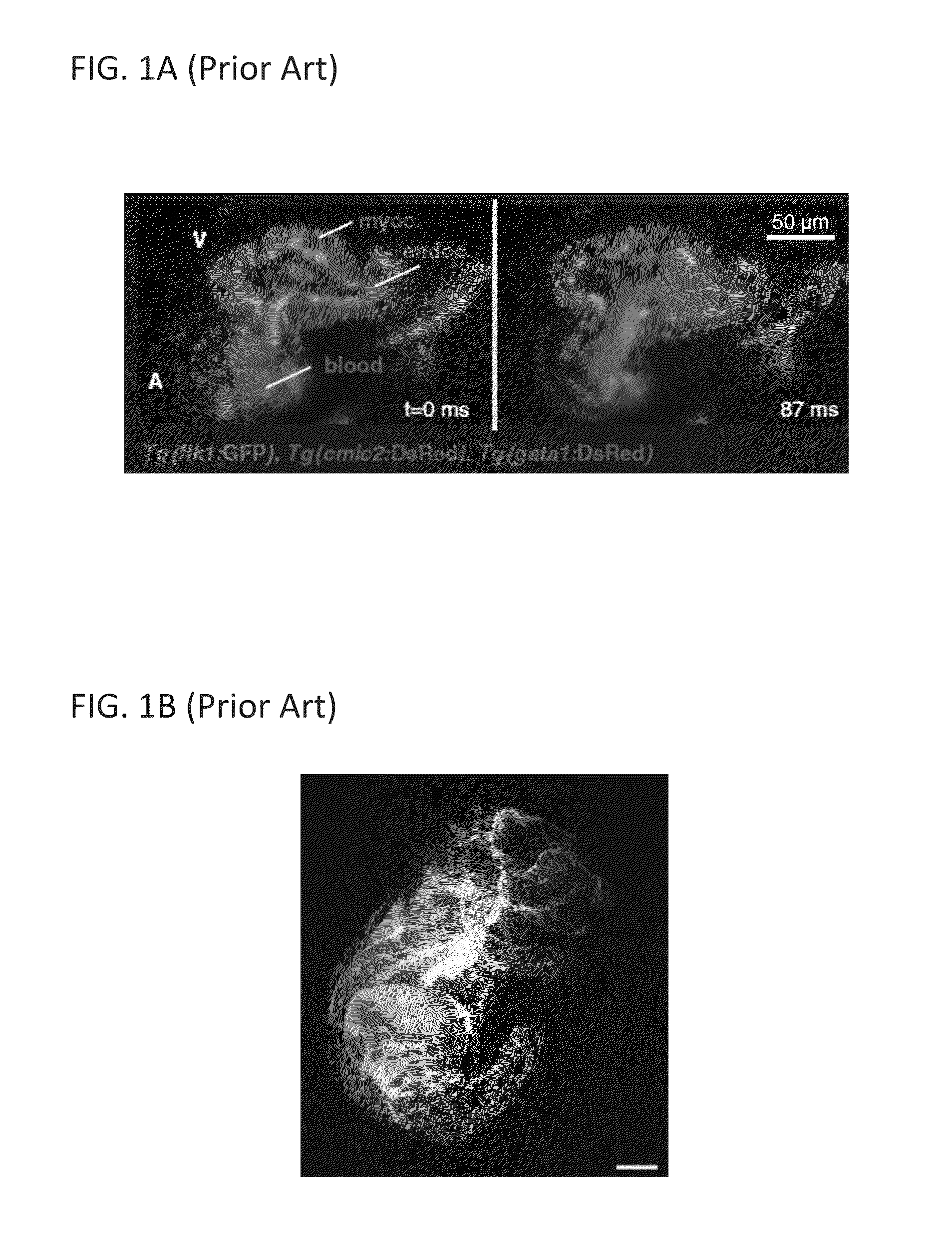
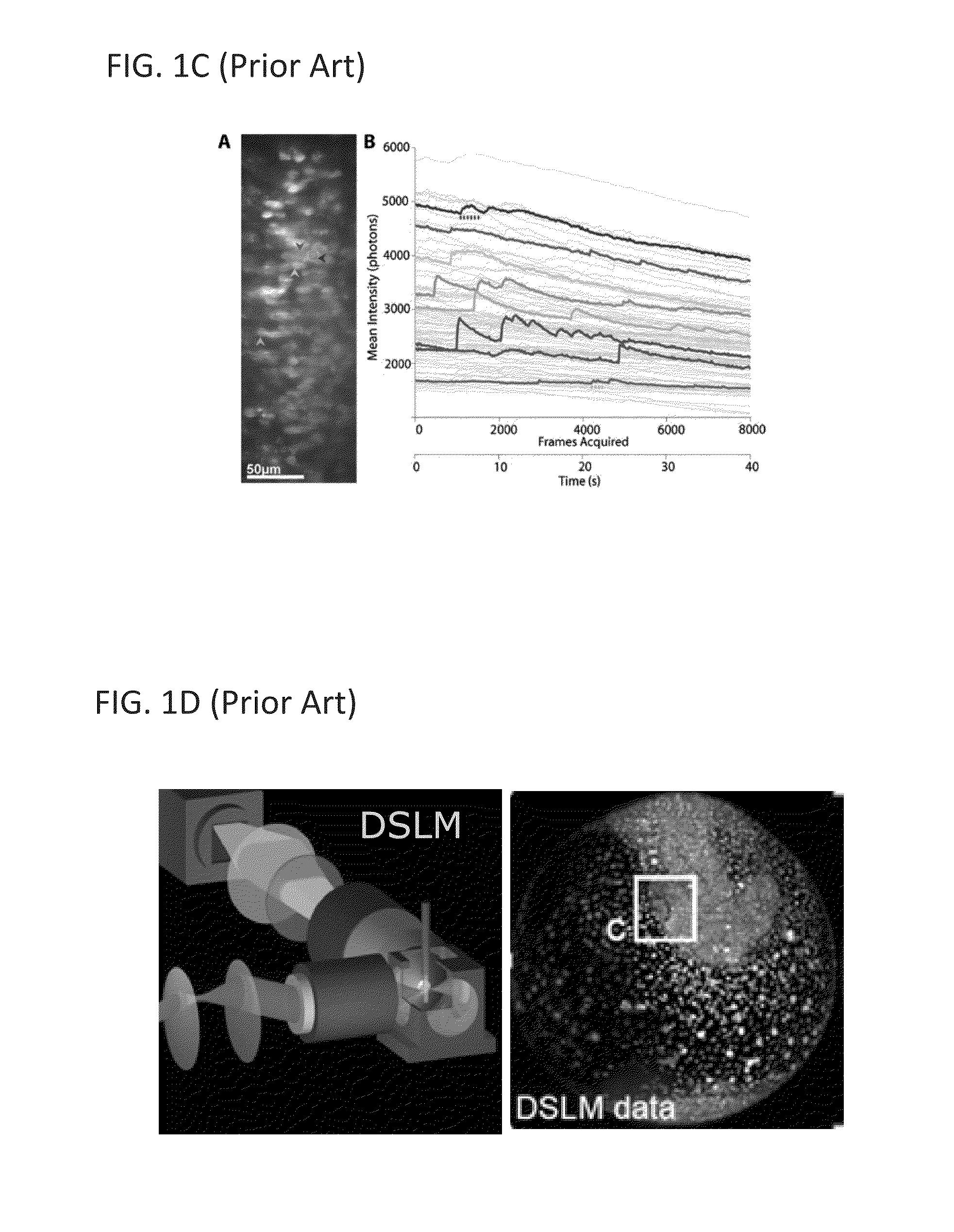
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
ActiveUS20110122488A1Radiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFluorescence
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal. illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
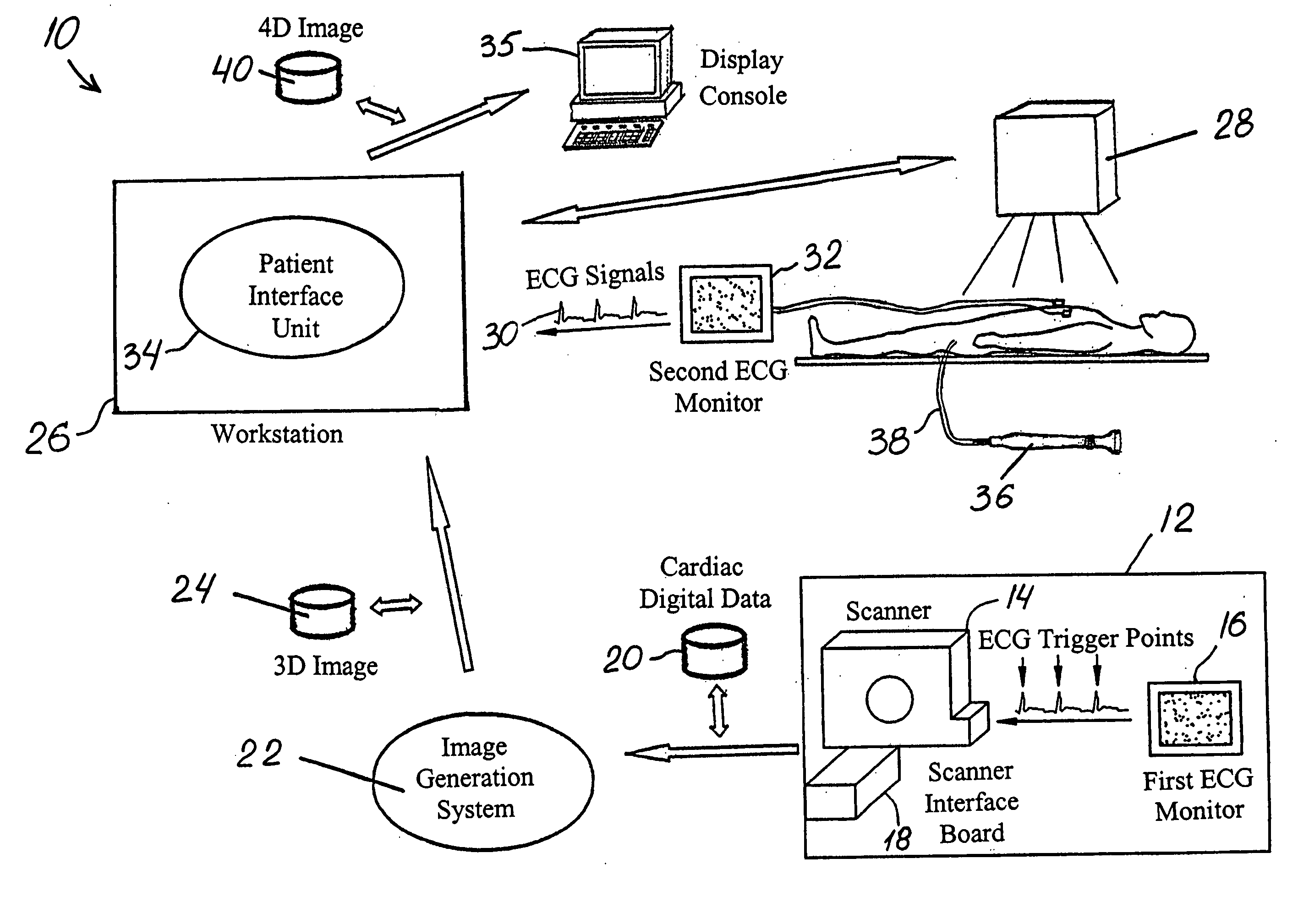
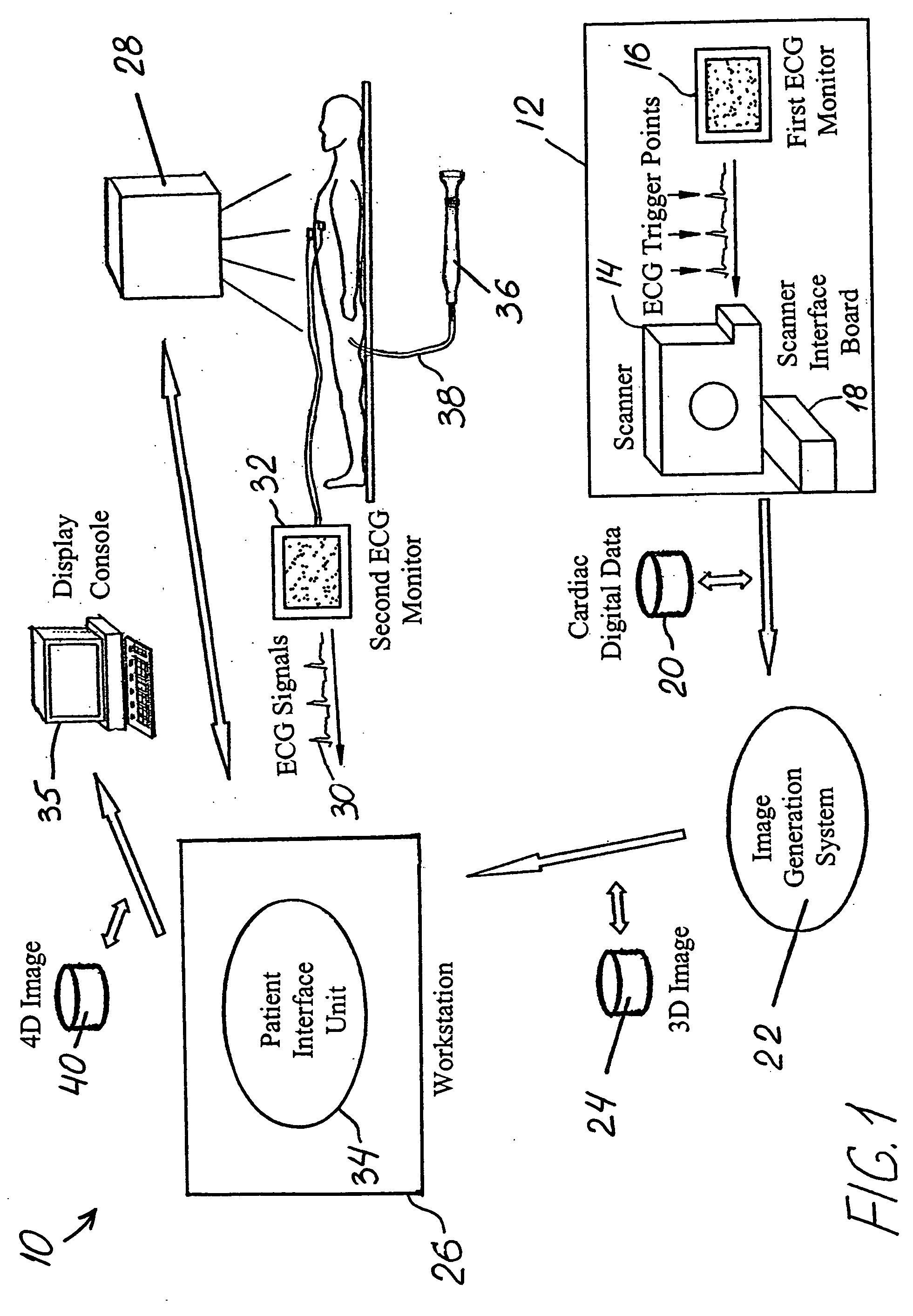
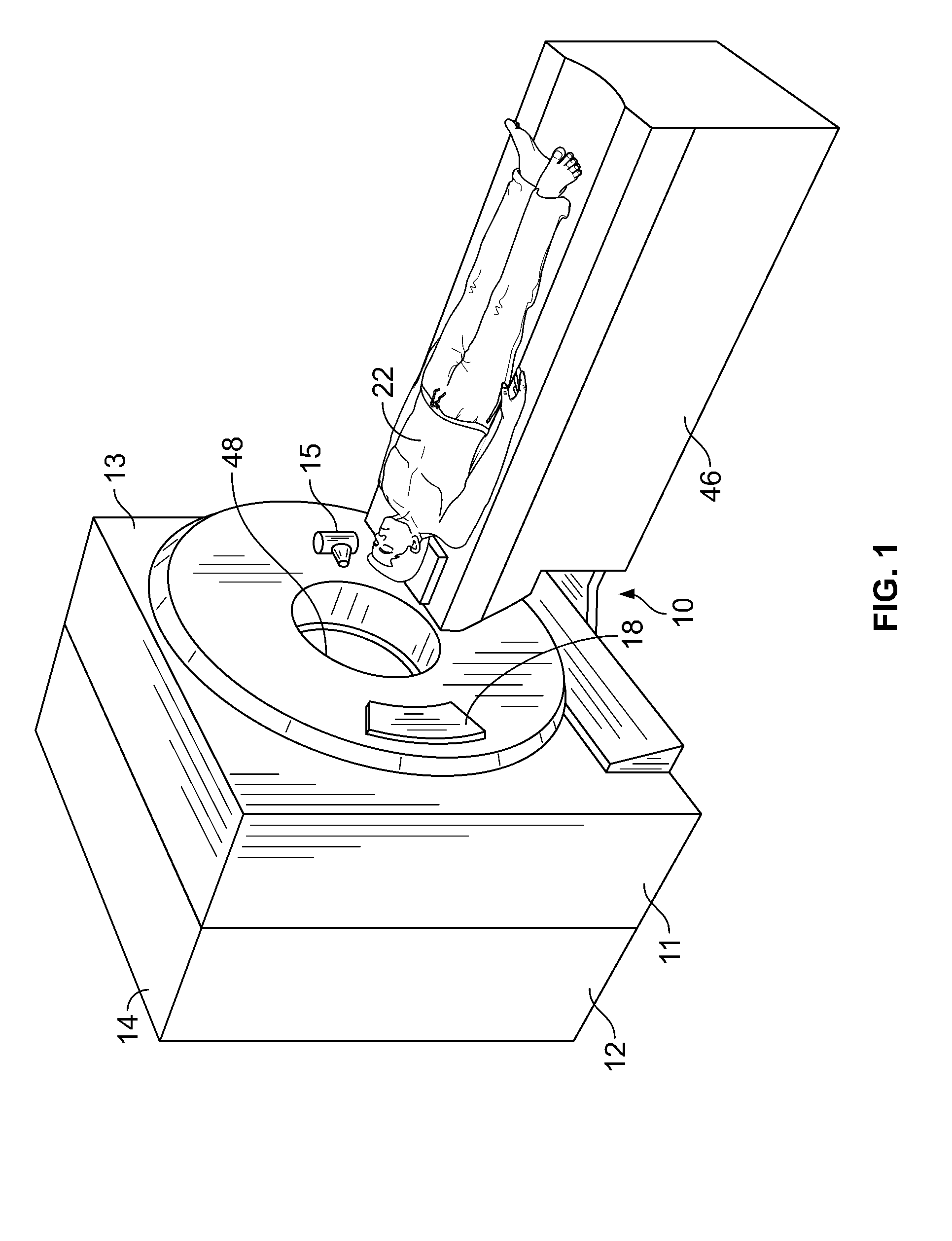
Method and system of treatment of cardiac arrhythmias using 4D imaging
InactiveUS20050137661A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsElectrocardiographyDigital dataEcg signal
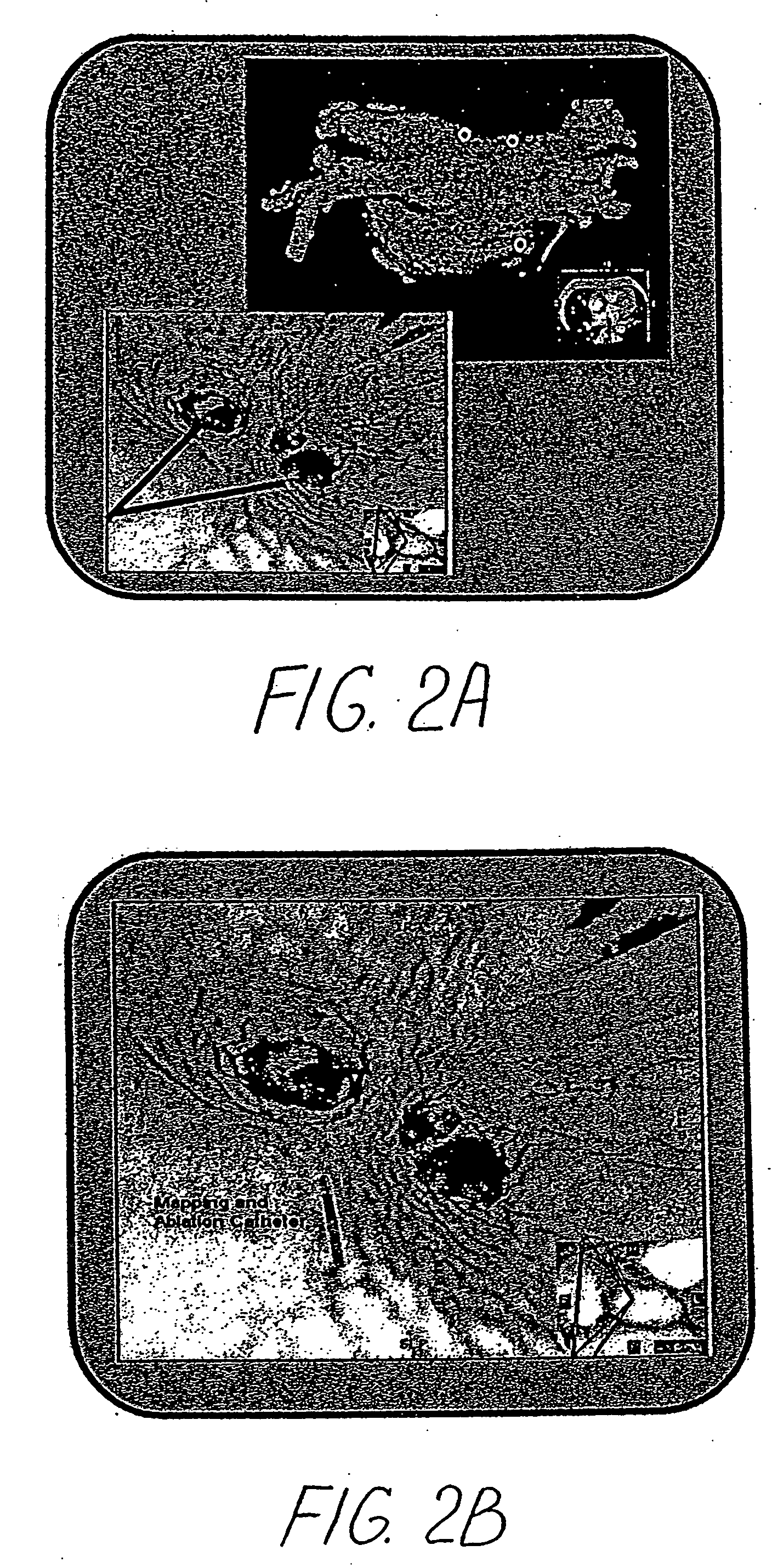
A method is provided for treating a heart arrhythmia having the steps of obtaining cardiac digital data from a medical imaging system utilizing an ECG gated protocol; generating a series of 3D images of a cardiac chamber and its surrounding structures, preferably the left atrium and pulmonary veins, from this cardiac digital data at select ECG trigger points that correspond to different phases of the cardiac cycle; registering these 3D images with an interventional system; acquiring ECG signals from the patient in real-time; transmitting these ECG signals to the interventional system; synchronizing the registered 3D images with trigger points on the transmitted ECG signals to generate a 4D image; visualizing this 4D image upon the interventional system in real-time; visualizing a catheter over the 4D image upon the interventional system; navigating the catheter within the cardiac chamber utilizing the 4D image; and using the catheter to treat the cardiac chamber, preferably with ablation.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
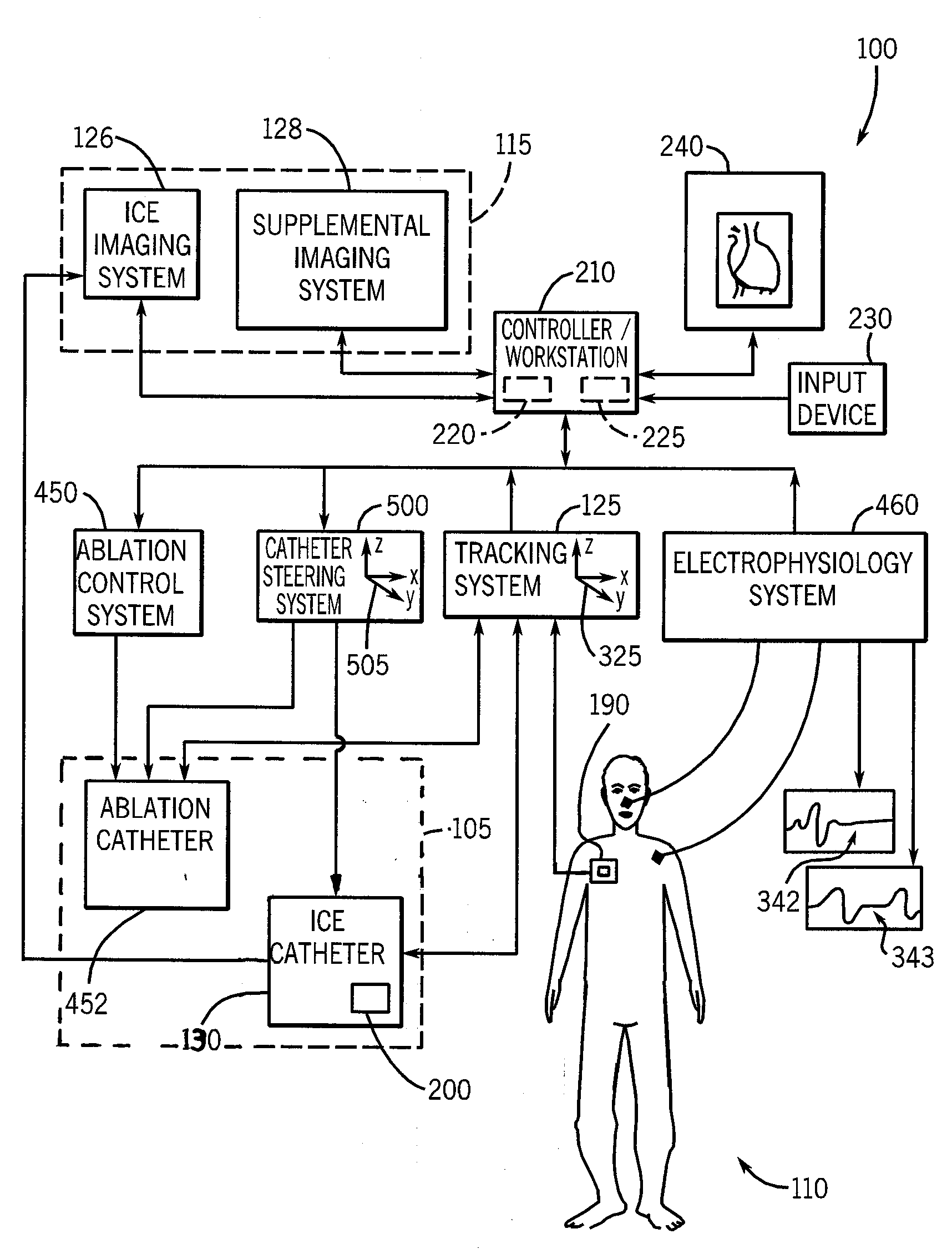
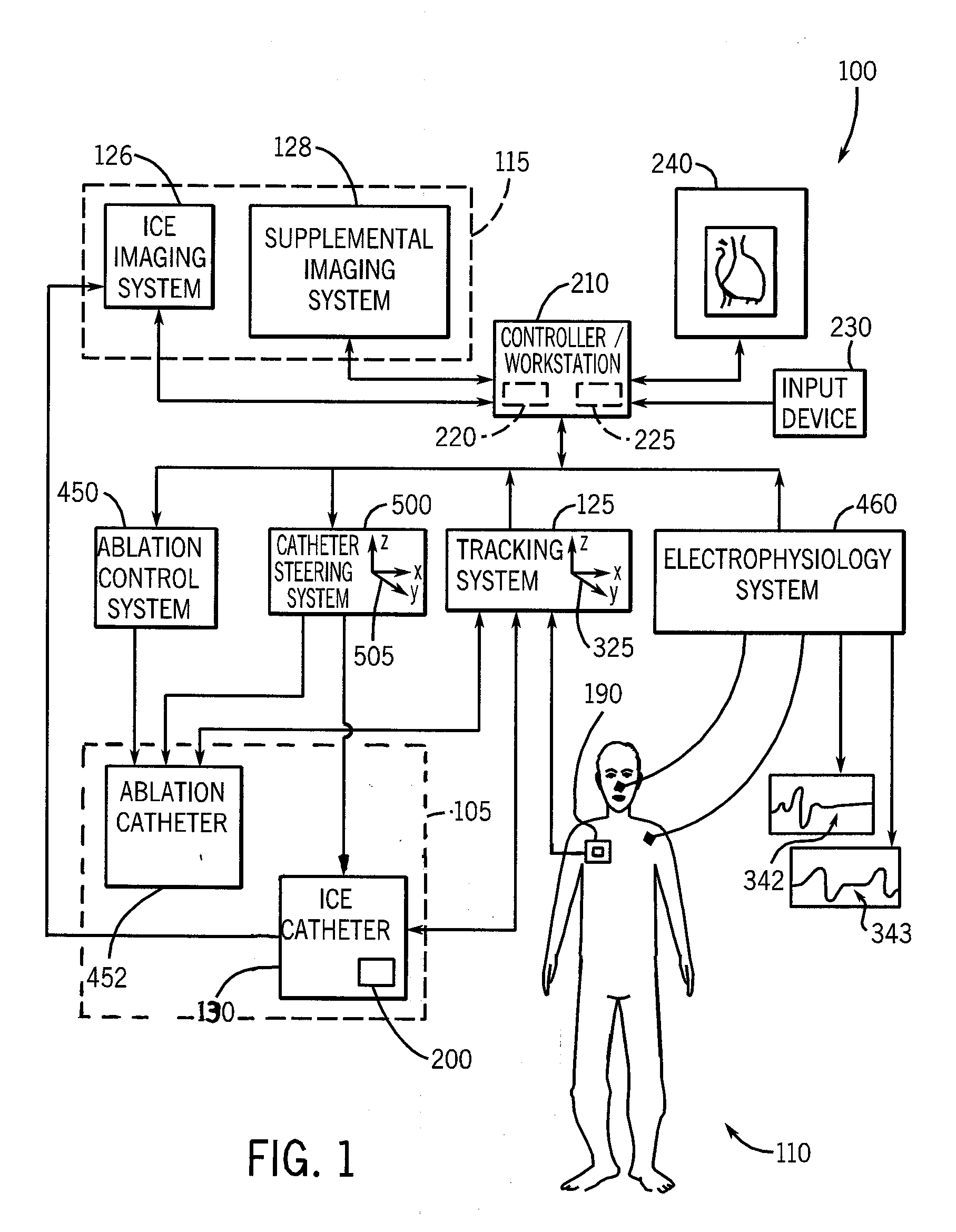
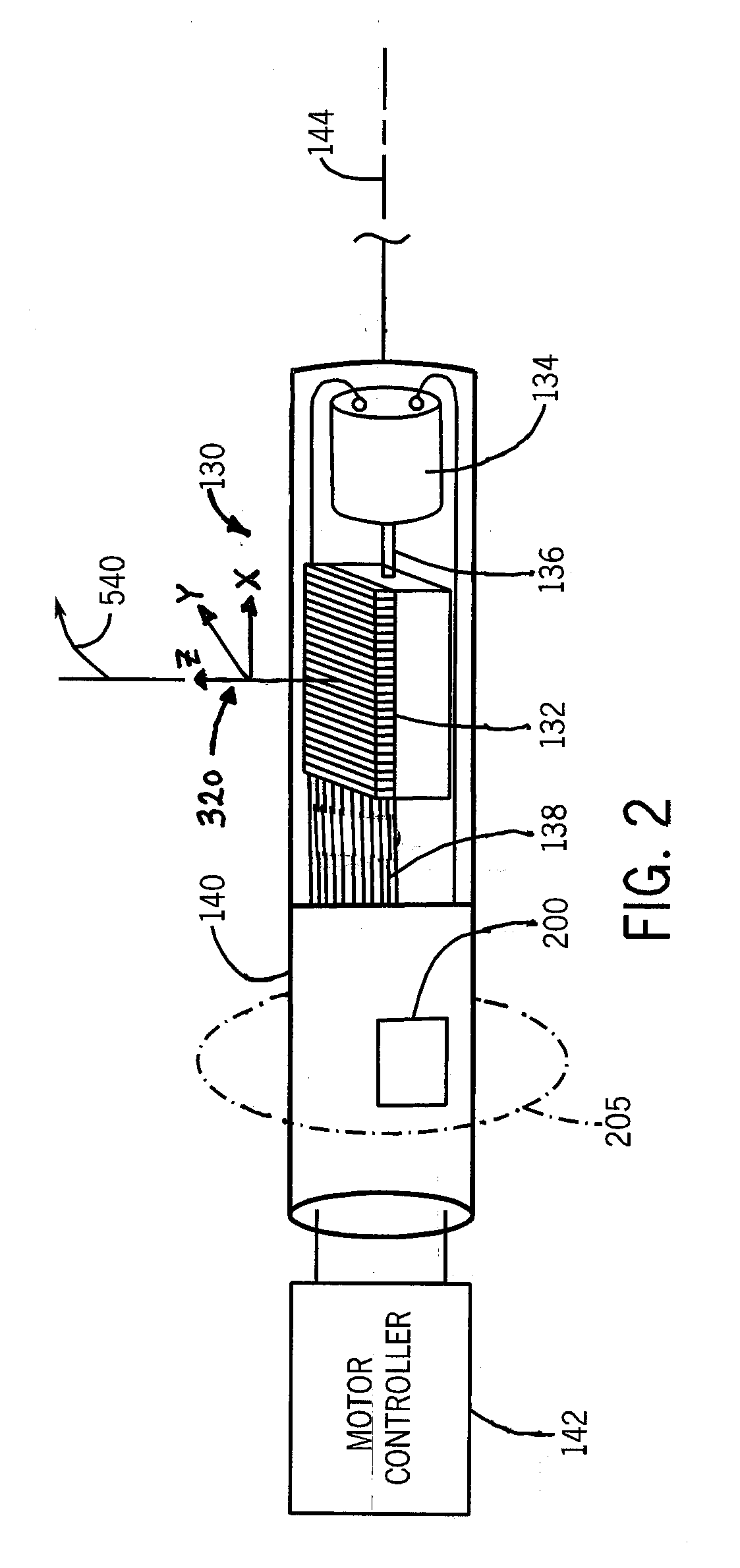
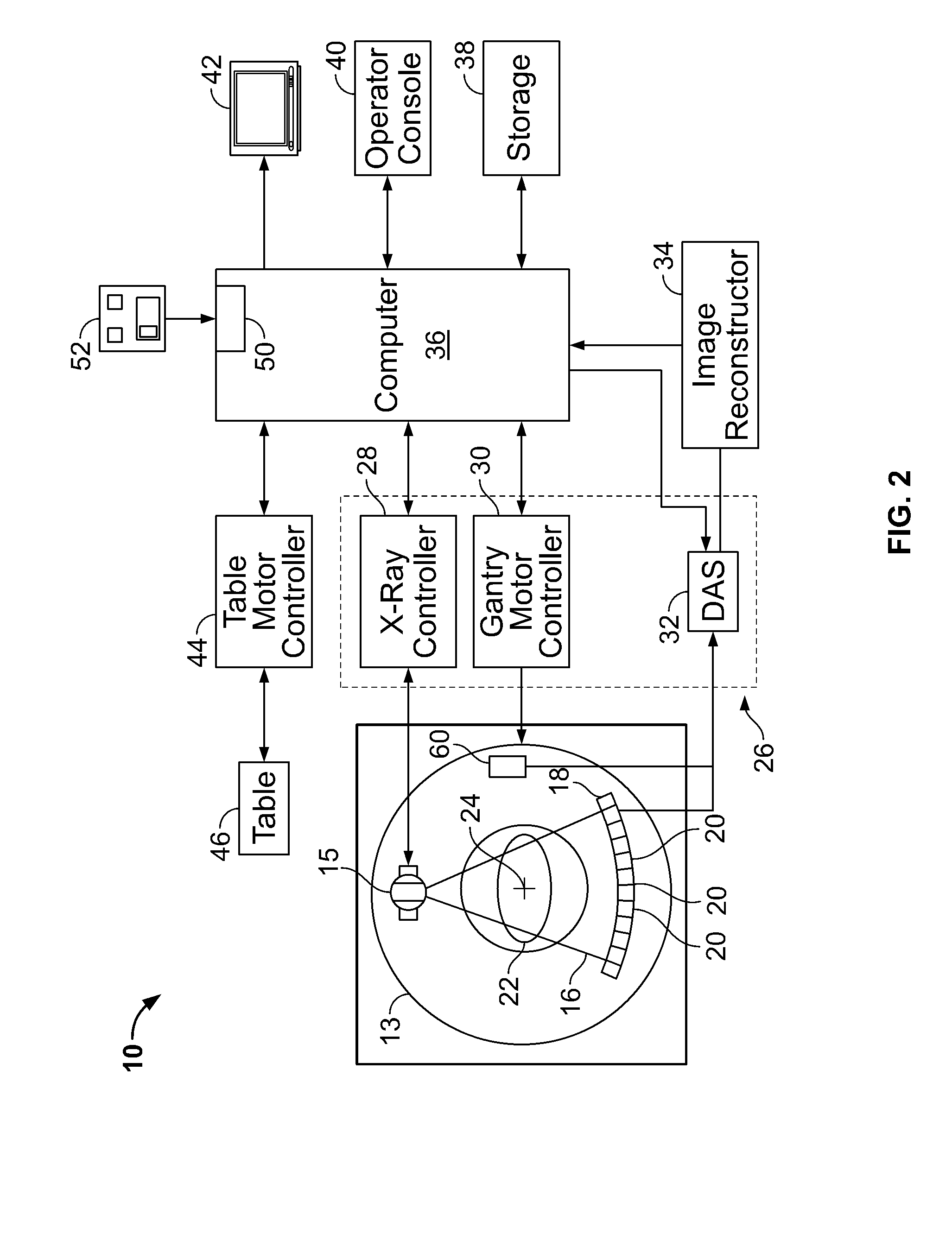
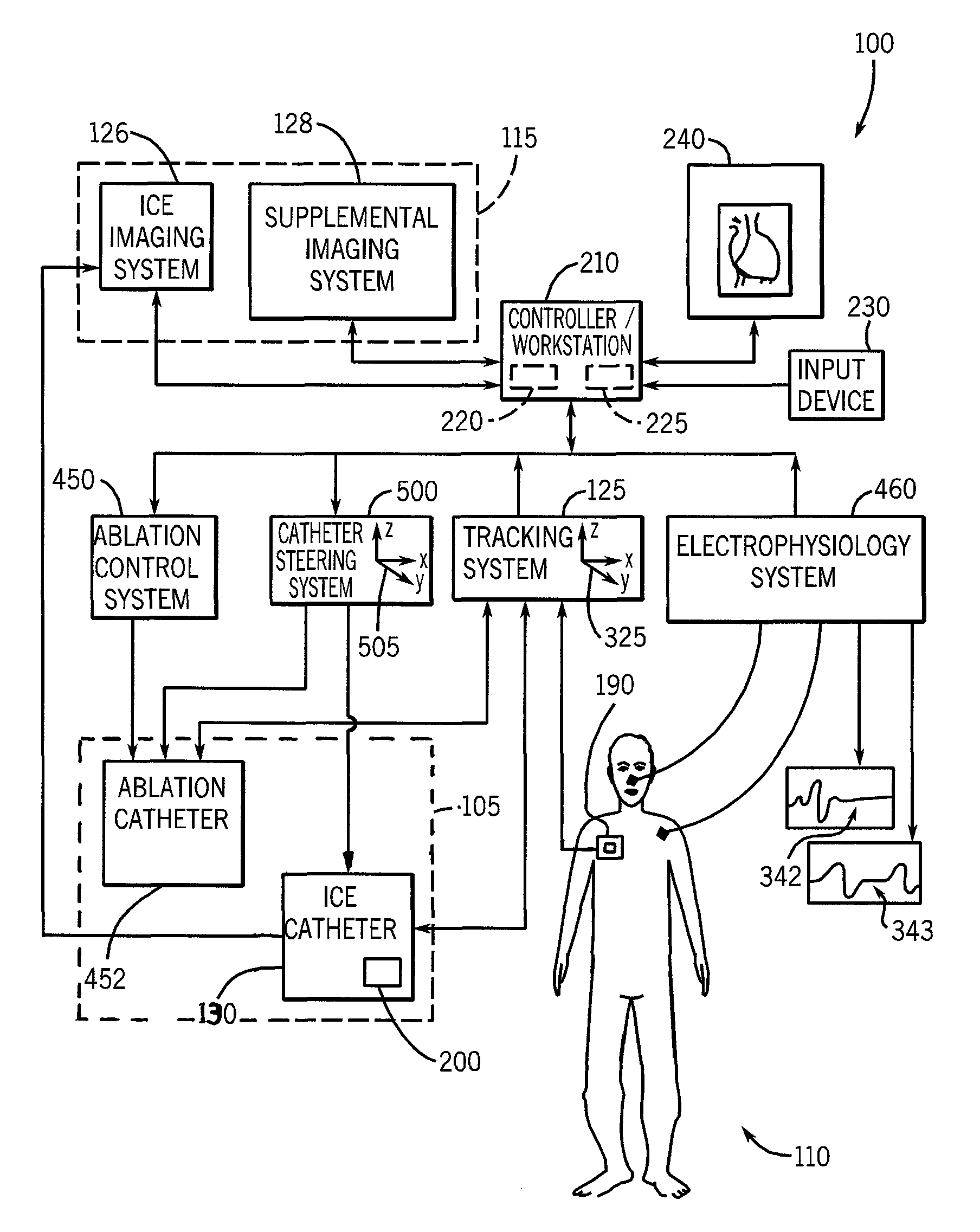
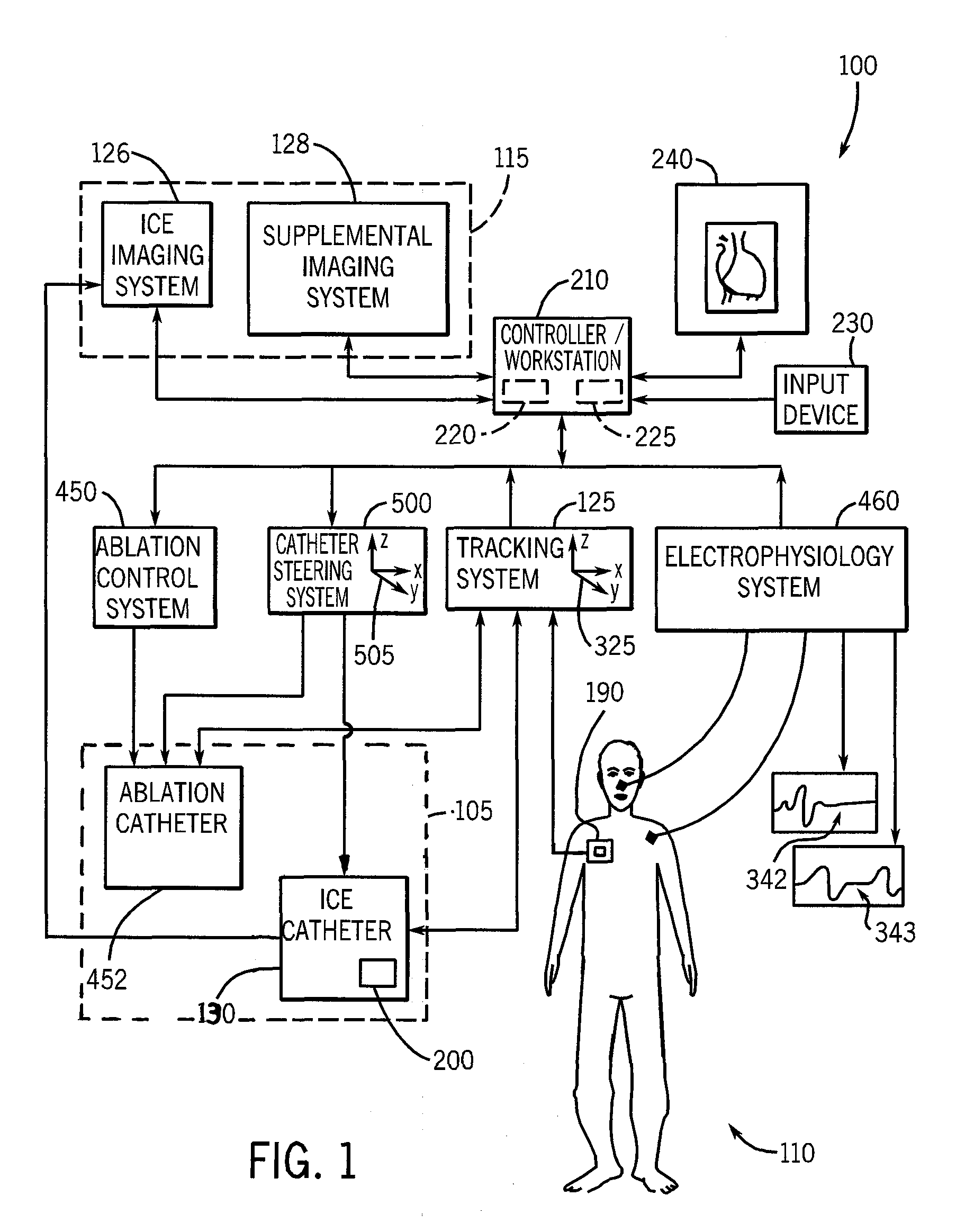
System and method to register a tracking system with an intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) imaging system
ActiveUS20080287777A1Readily spatial relationshipUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgery4d imagingProgram instruction
A system to navigate an object traveling in an imaged subject is provided. The system includes a four-dimensional (4D) imaging system to create a first three-dimensional model of the acquired imaged data correlated relative to a time reference and defined relative to a first image coordinate system. A second imaging system creates a second three-dimensional model of the imaged subject defined relative to a second image coordinate system. A tracking system tracks movement and orientation of the object relative to a tracking coordinate system. A controller includes program instructions in combination with the processor operable to register the first and second image coordinate systems and the tracking coordinate system relative to a world coordinate system, and to combine the three-dimensional model created by the 4D imaging system with the three-dimensional model created by the second imaging system with a tracked location of the object relative to the world coordinate system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and system of treatment of heart failure using 4D imaging
InactiveUS20050143777A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPhysical therapies and activitiesEcg signalDigital data
A method is provided for treatment of heart failure having the steps of obtaining cardiac digital data from a medical imaging system utilizing an ECG gated protocol; generating a series of 3D images of a cardiac chamber and its surrounding structures, preferably the left ventricle and coronary sinus, from this cardiac digital data at select ECG trigger points that correspond to different phases of the cardiac cycle; registering these 3D images with an interventional system; acquiring ECG signals from the patient in real-time; transmitting these ECG signals to the interventional system; synchronizing the registered 3D images with trigger points on the transmitted ECG signals to generate a 4D image; visualizing this 4D image upon the interventional system in real-time; visualizing a pacing / defibrillation lead over the 4D image upon the interventional system; navigating the pacing / defibrillation lead utilizing the 4D image; and placing the pacing / defibrillation lead over the cardiac chamber at an appropriate site to treat the heart failure.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
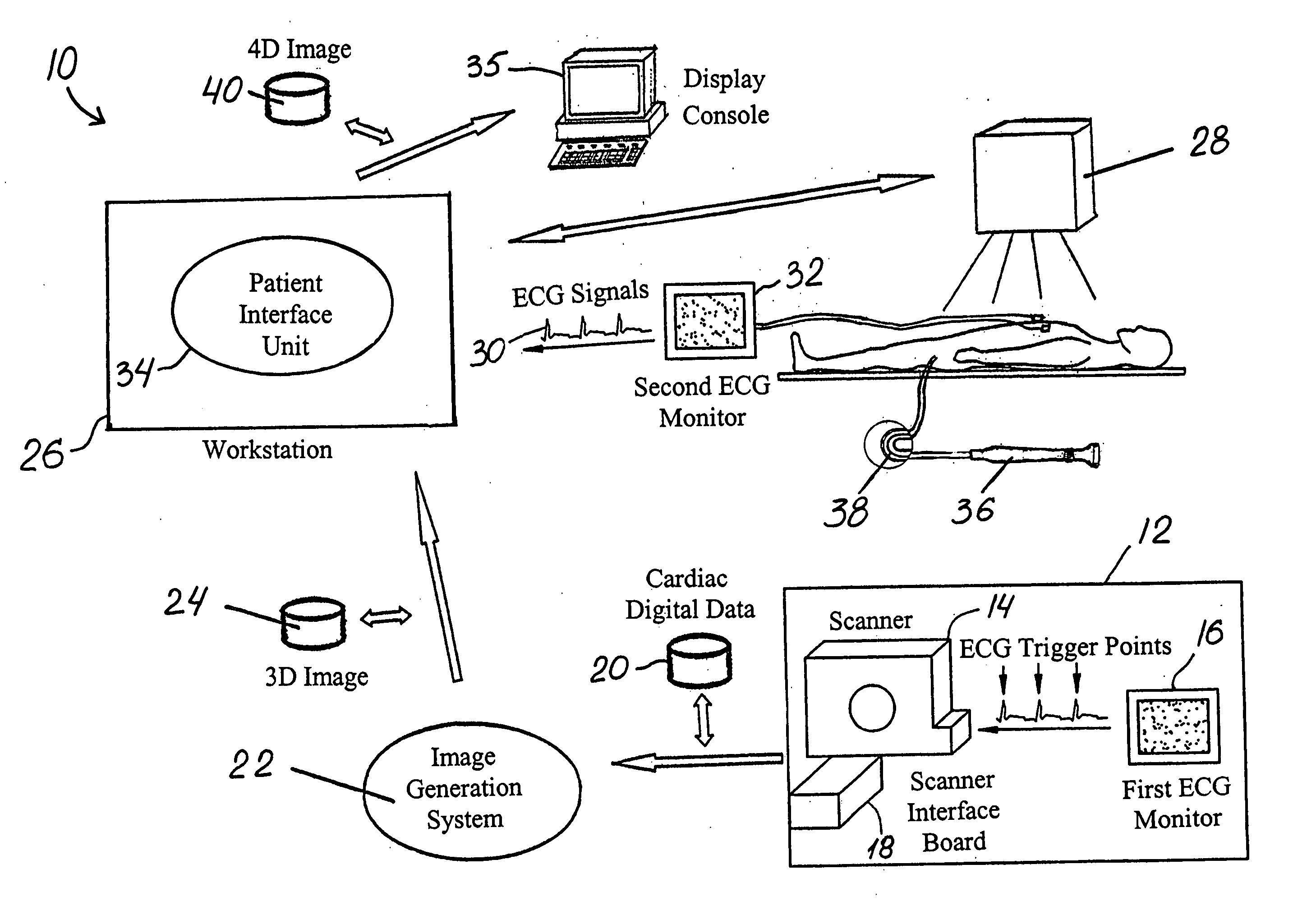
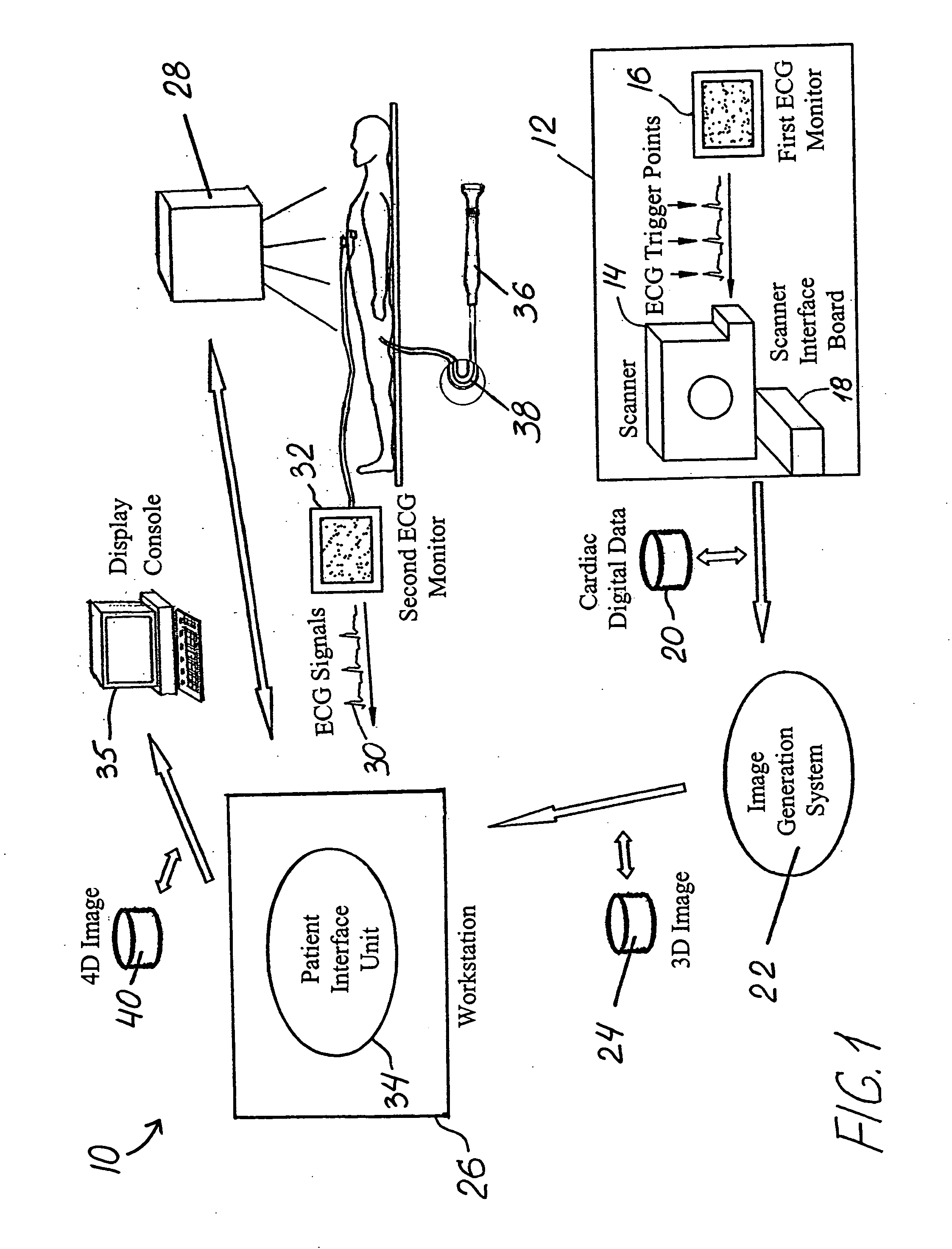
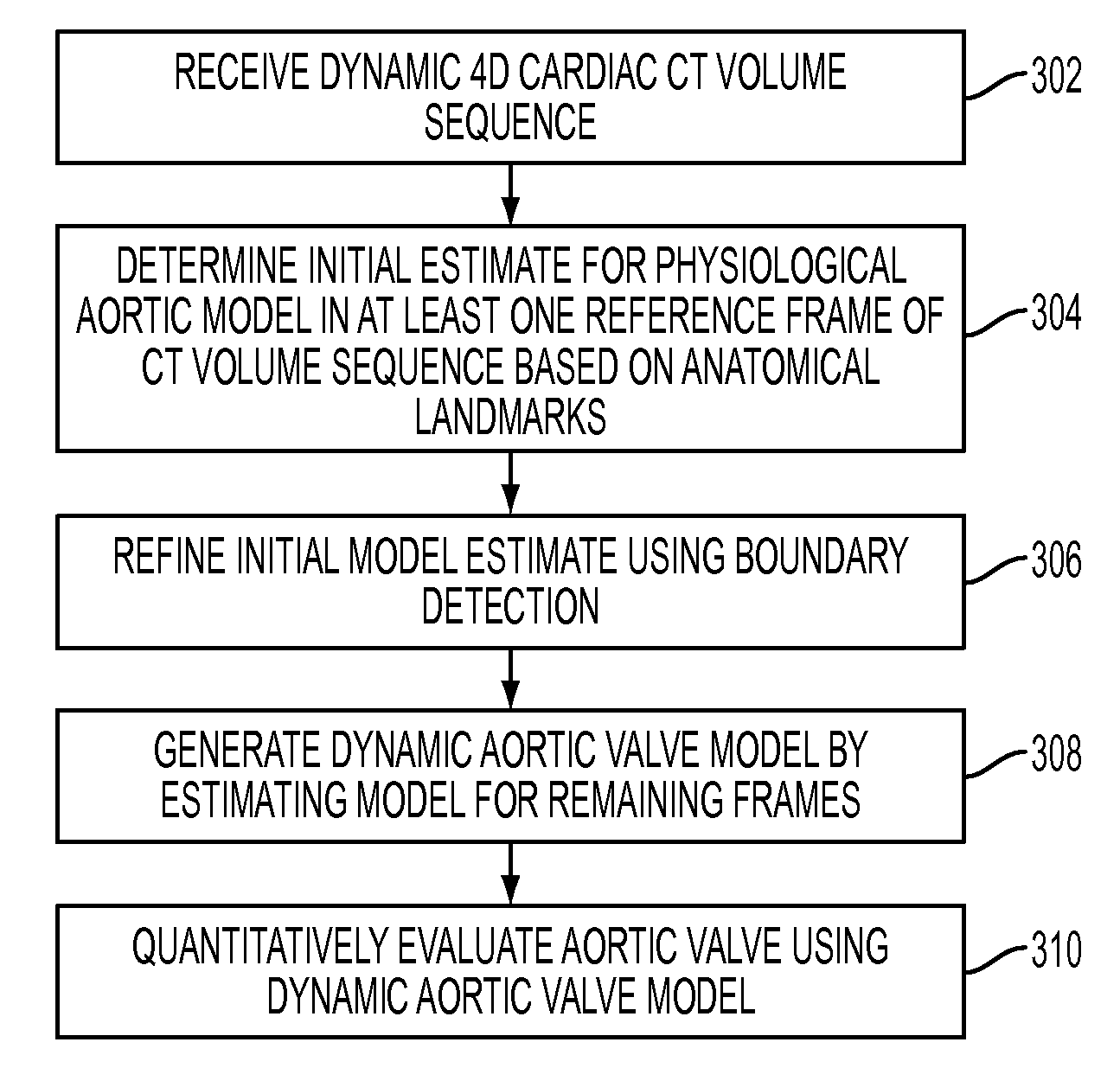
Method and system for automatic quantification of aortic valve function from 4D computed tomography data using a physiological model
A method and system for modeling the aortic valve in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and echocardiography, is disclosed. An initial estimate of a physiological aortic valve model is determined for at least one reference frame of a 4D image sequence based on anatomic features in the reference frame. The initial estimate is refined to generate a final estimate in the reference frame. A dynamic model of the aortic valve is then generated by estimating the physiological aortic valve model for each remaining frame of the 4D image sequence based on the final estimate in the reference frame. The aortic valve can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +2
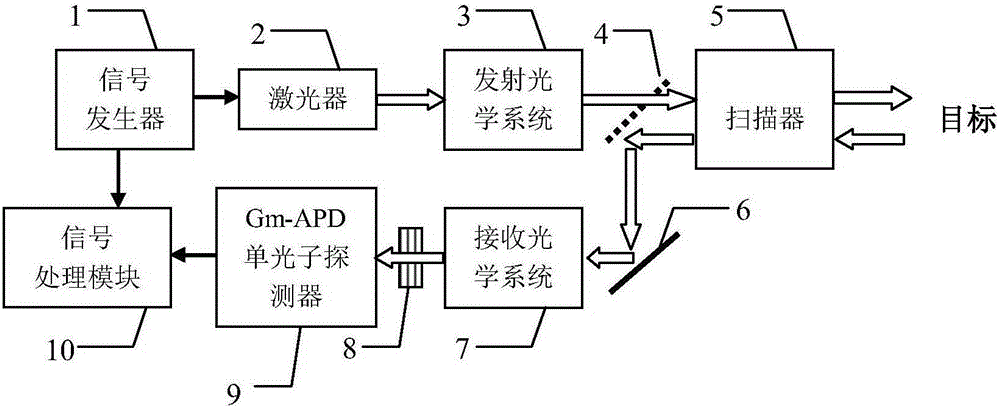
Composite-modulation-pulse-code-based 4D imaging photon counting laser radar
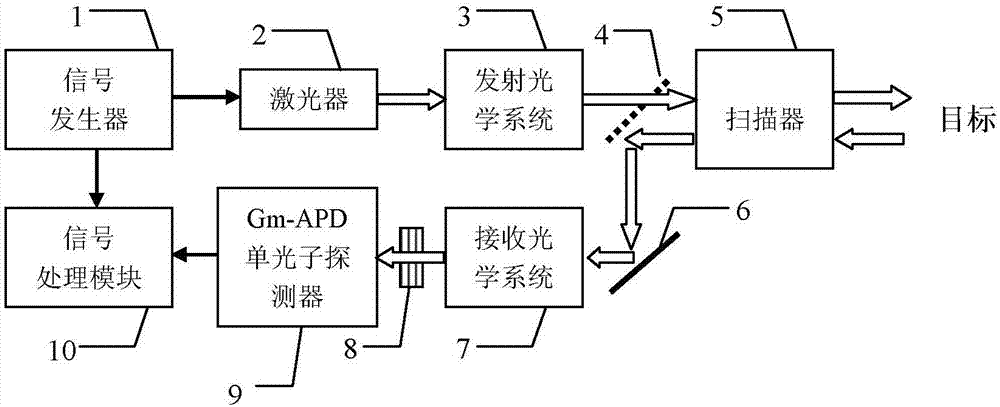
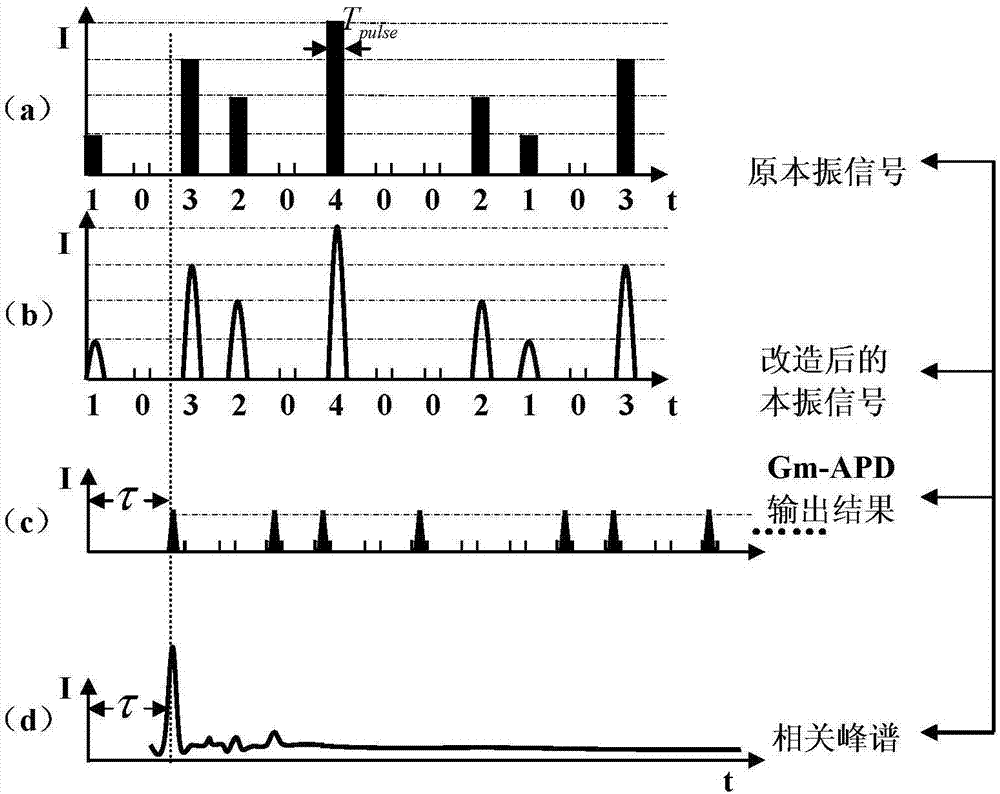
InactiveCN105182361AThe recognition effect is accurateAccurate judgmentElectromagnetic wave reradiation4d imagingRadar
The invention, which belongs to the technical field of the laser radar, provides a composite-modulation-pulse-code-based 4D imaging photon counting laser radar, so that a problem that the existing photon counting laser radar loses target strength information can be solved. The composite-modulation-pulse-code-based 4D imaging photon counting laser radar comprises a signal generator, a laser, a transmitting optical system, a unidirectional reflector, a scanner, a total reflection mirror, a receiving optical system, a narrow-band filter, a Gm-APD single photon detector, and a signal processing module. An optical signal outputted by the transmitting optical system is transmitted by the unidirectional reflector and is sent into the scanner; the scanner outputs an optical detection signal to a target; an echo signal reflected by the target is transmitted into the scanner; the echo signal outputted by the scanner is reflected by the unidirectional reflector and the total reflection mirror and the is transmitted to the transmitting optical system to carry out collection and echoing; the collected echo signal is filtered by the narrow-band filter and the is detected by the Gm-APD single photon detector; and a detection result is inputted into the signal processing module. The composite-modulation-pulse-code-based 4D imaging photon counting laser radar is mainly applied to target detection.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method and system for automatic quantification of aortic valve function from 4D computed tomography data using a physiological model
A method and system for modeling the aortic valve in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and echocardiography, is disclosed. An initial estimate of a physiological aortic valve model is determined for at least one reference frame of a 4D image sequence based on anatomic features in the reference frame. The initial estimate is refined to generate a final estimate in the reference frame. A dynamic model of the aortic valve is then generated by estimating the physiological aortic valve model for each remaining frame of the 4D image sequence based on the final estimate in the reference frame. The aortic valve can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS CORP +2
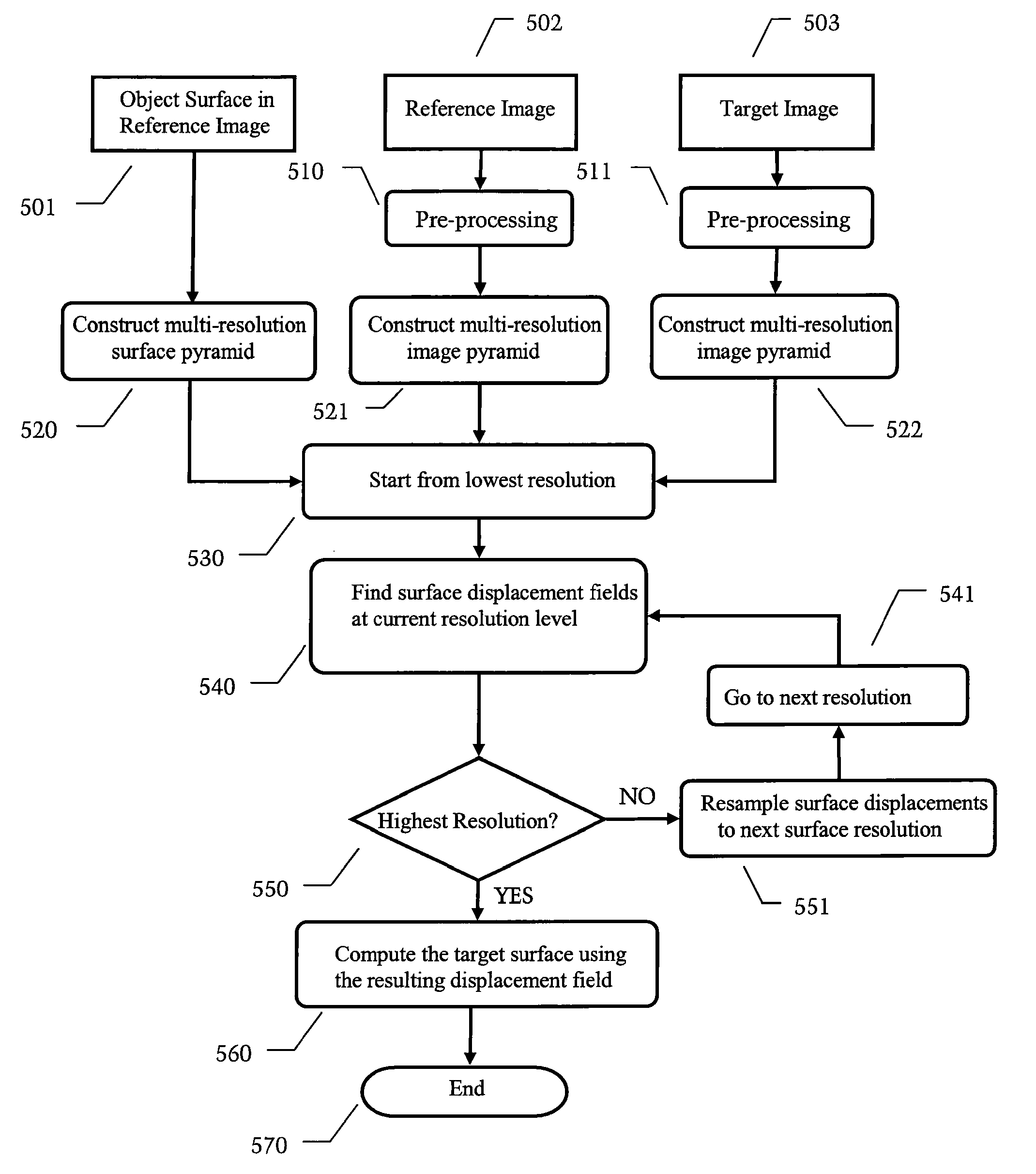
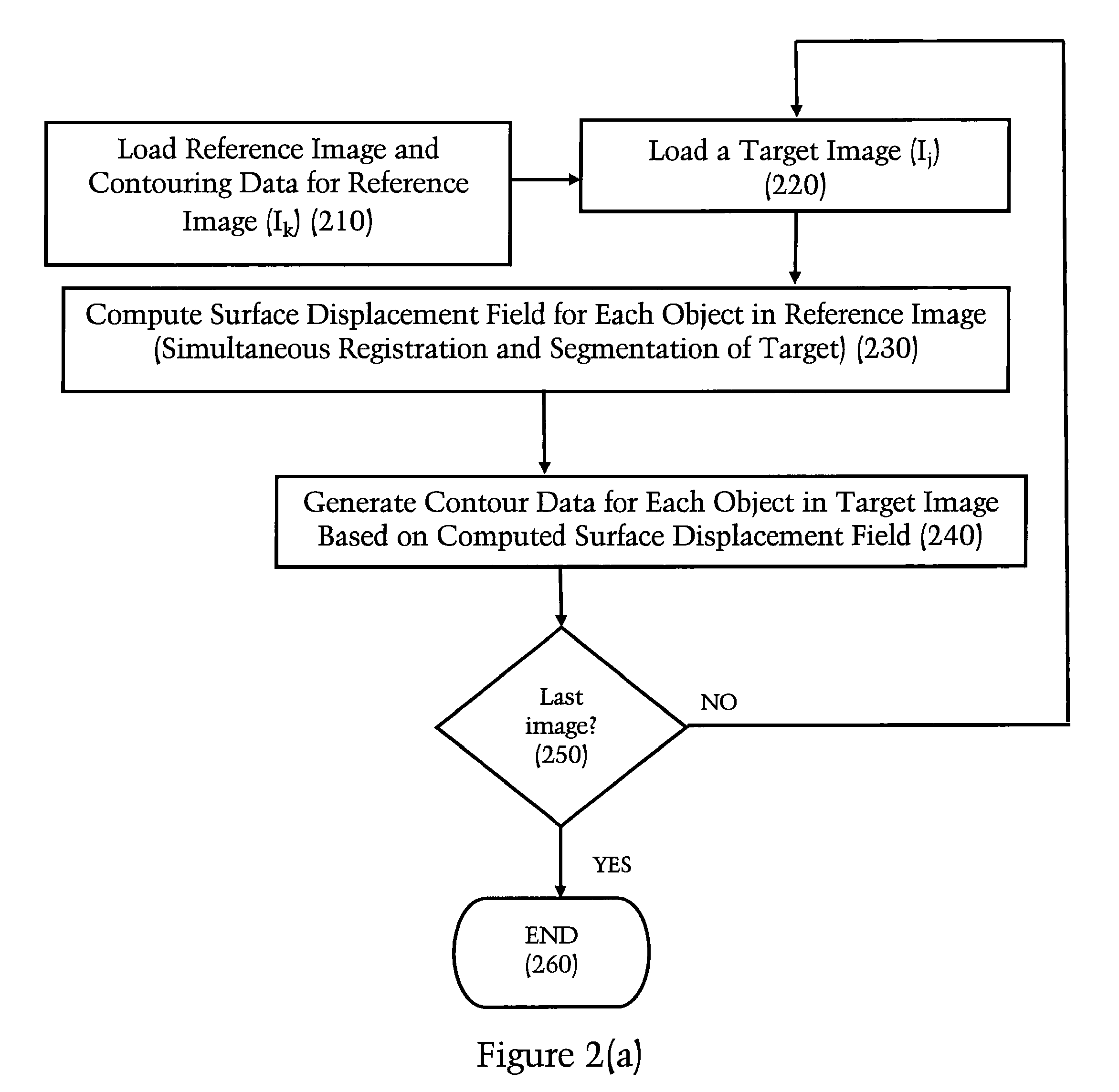
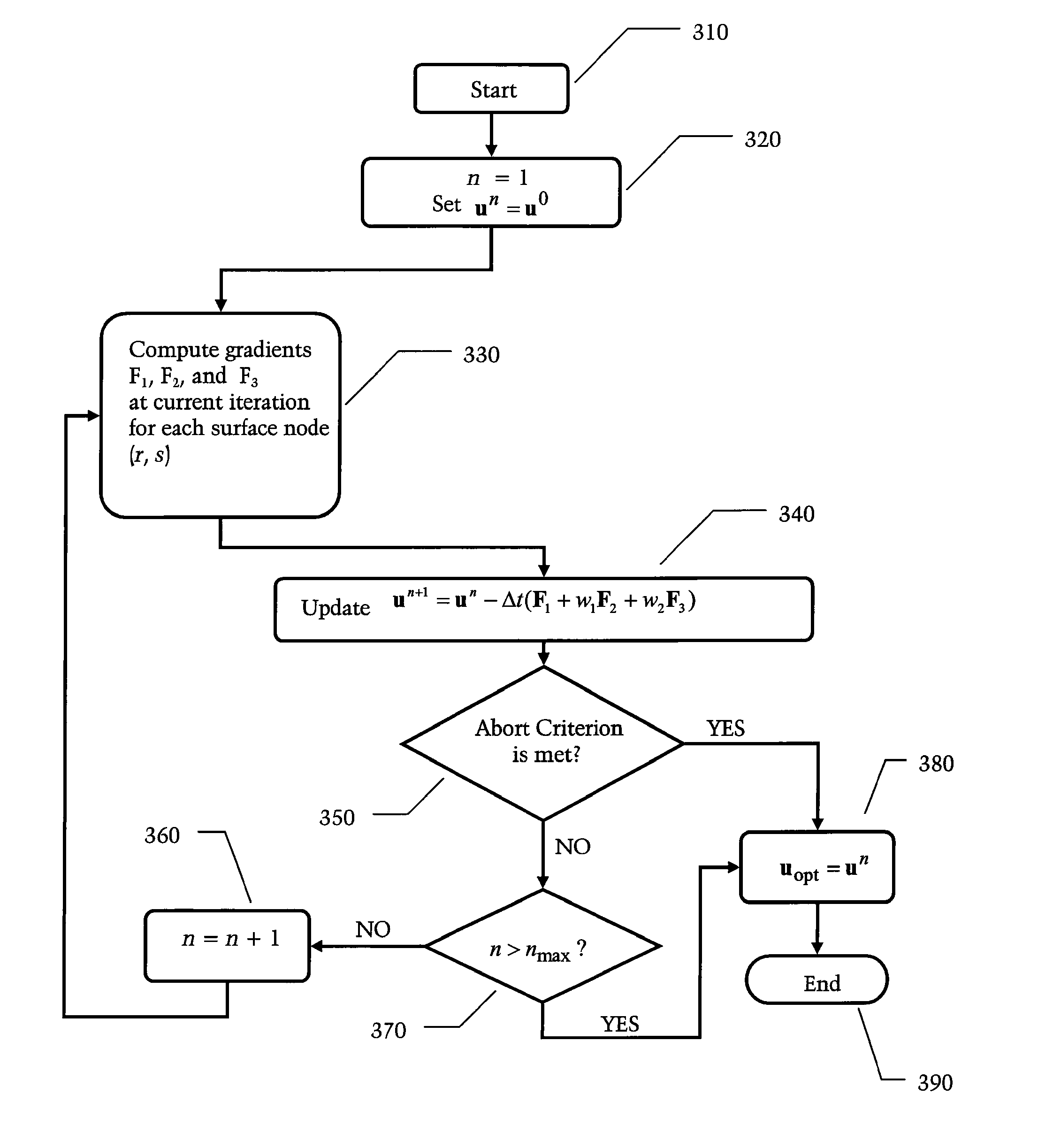
Method and Apparatus for Efficient Automated Re-Contouring of Four-Dimensional Medical Imagery Using Surface Displacement Fields
ActiveUS20090190809A1Improved accuracy in contouring the target imageImprove computing efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognition4d imagingReference image
A technique is disclosed for generating a new contour and / or a 3D surface from contour data using a surface displacement field. The technique is preferably applied to un-contoured target images within a 4D image sequence for which contour data is desired. The technique can be initialized with contour data related to a reference image that has already been contoured, e.g. by a doctor who manually enters contour information into a computer. Image registration (calculation of correspondence between the reference image and target image) can be performed simultaneously with segmentation (identifying regions of interest in the target image). This allows one to make use of segmentation information in a reference image to improve the accuracy of contouring within the target image.
Owner:IMPAC MEDICAL SYST
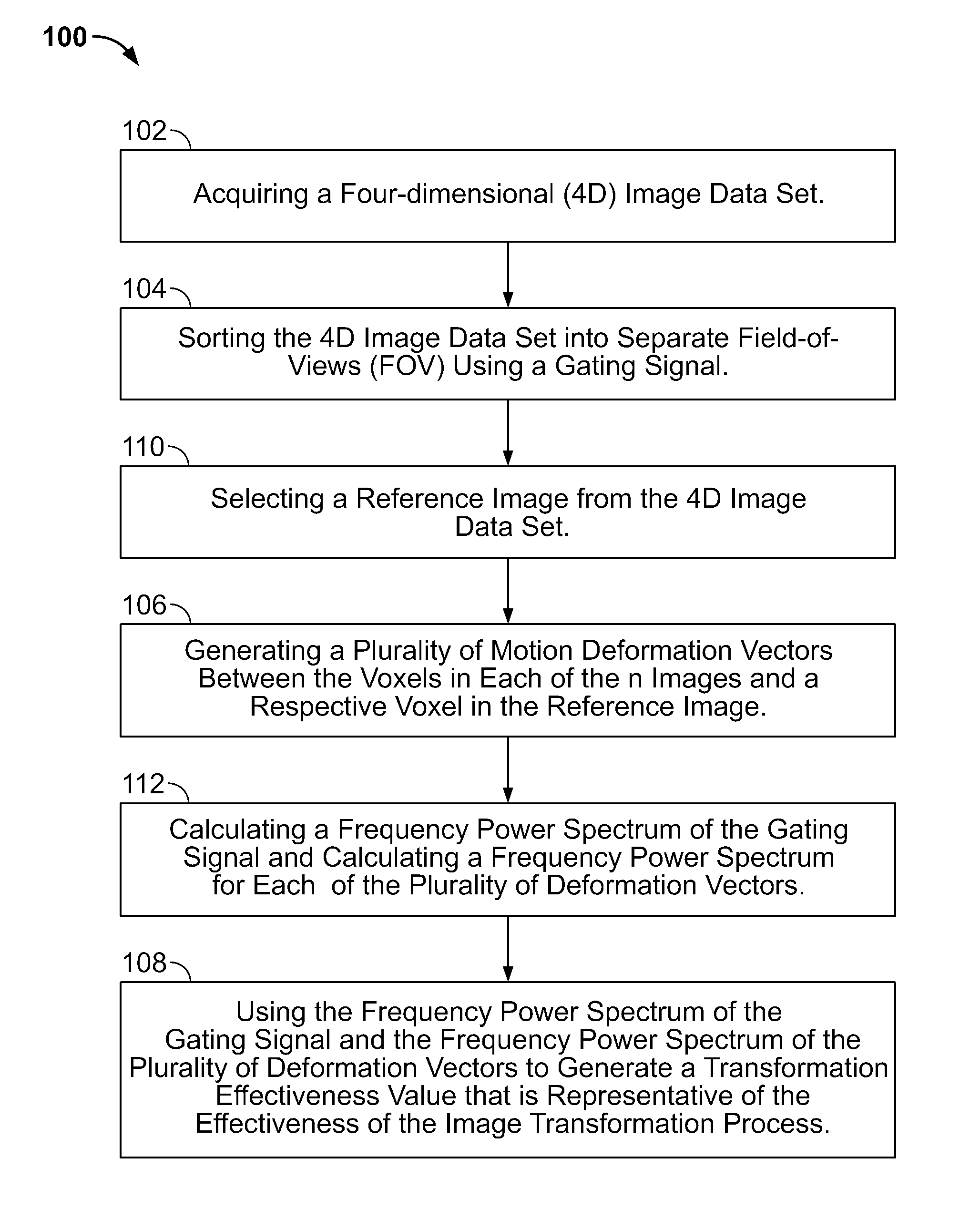
Method and apparatus for determining the effectiveness of an image transformation process
A method for determining the effectiveness of an image transformation process includes acquiring a four-dimensional (4D) image data set, sorting the 4D image data set into separate field-of-view bins using a temporal gating system generating a plurality of deformation vectors using the sorted 4D image data set, and using the plurality of deformation vectors to generate a transformation effectiveness value that is representative of the effectiveness of the image transformation process. The method further includes acquiring a respiratory signal, calculating a power spectrum of the respiratory signal, calculating a power spectrum for each of the plurality of deformation vectors, and comparing the power spectrum of the respiratory signal to the power spectrum of the plurality of deformation vectors to generate the transformation effectiveness value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method to register a tracking system with intracardiac echocardiography (ICE) imaging system
ActiveUS8989842B2Readily spatial relationshipOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgery4d imagingIntracardiac echocardiography
A system to navigate an object traveling in an imaged subject is provided. The system includes a four-dimensional (4D) imaging system to create a first three-dimensional model of the acquired imaged data correlated relative to a time reference and defined relative to a first image coordinate system. A second imaging system creates a second three-dimensional model of the imaged subject defined relative to a second image coordinate system. A tracking system tracks movement and orientation of the object relative to a tracking coordinate system. A controller includes program instructions in combination with the processor operable to register the first and second image coordinate systems and the tracking coordinate system relative to a world coordinate system, and to combine the three-dimensional model created by the 4D imaging system with the three-dimensional model created by the second imaging system with a tracked location of the object relative to the world coordinate system.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
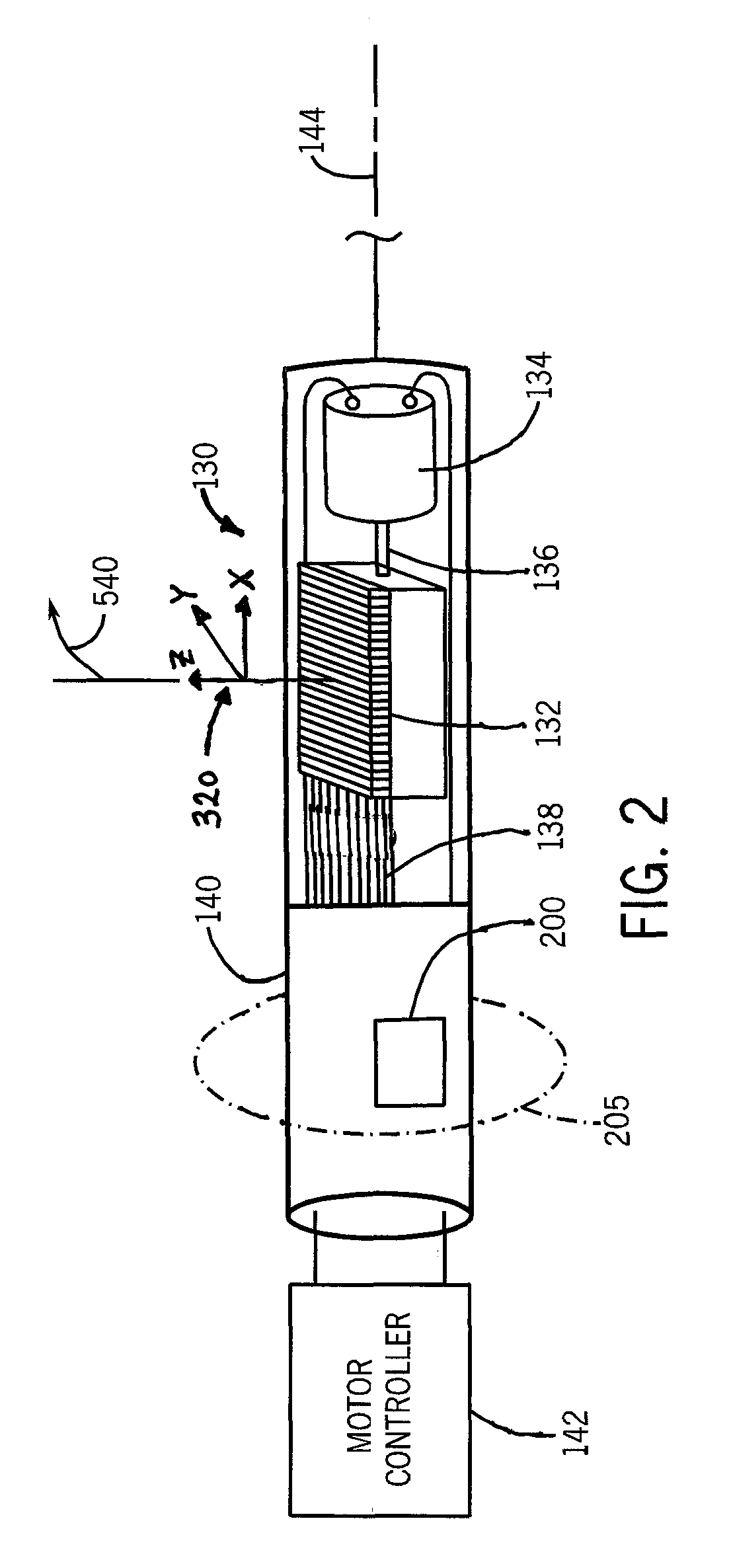
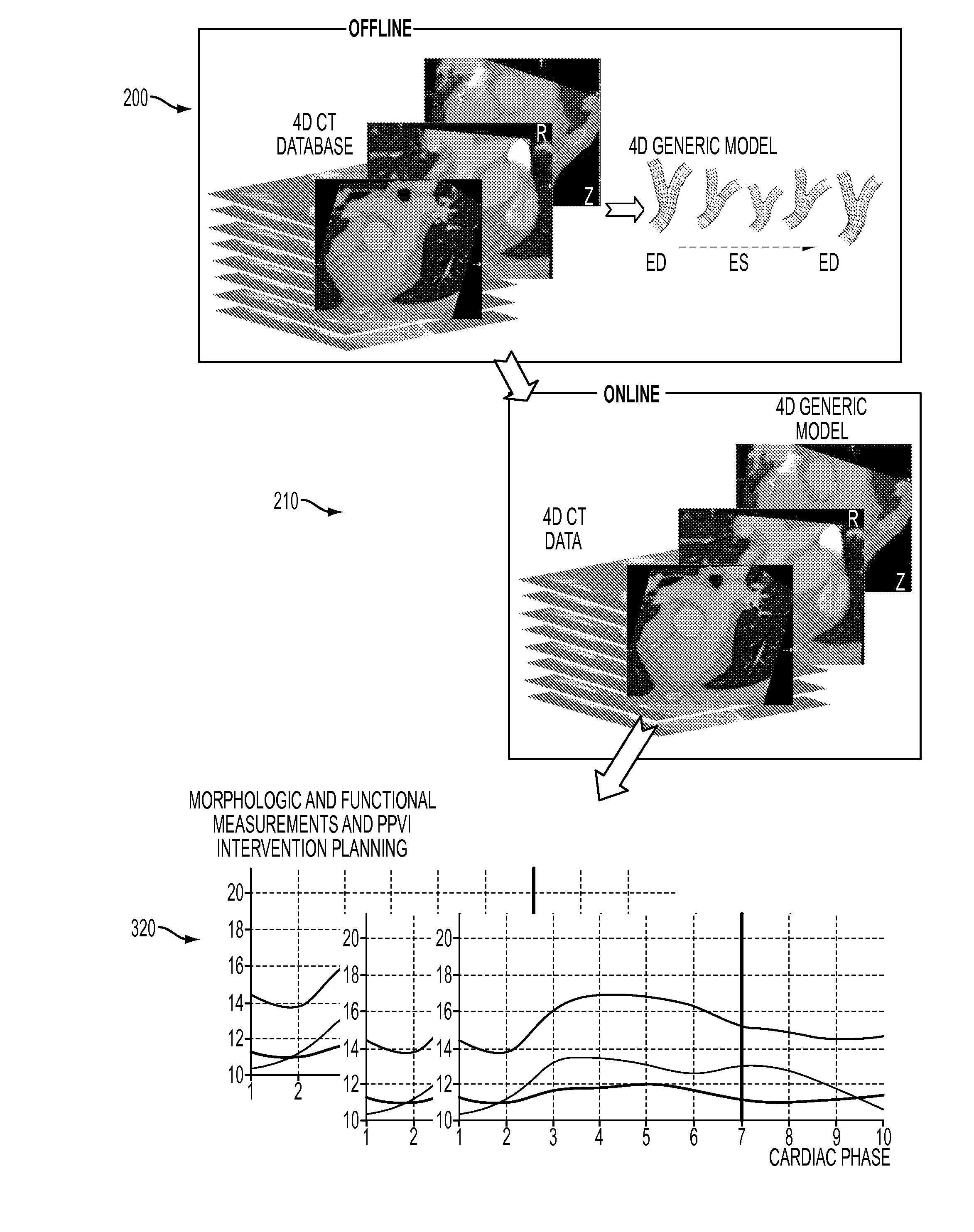
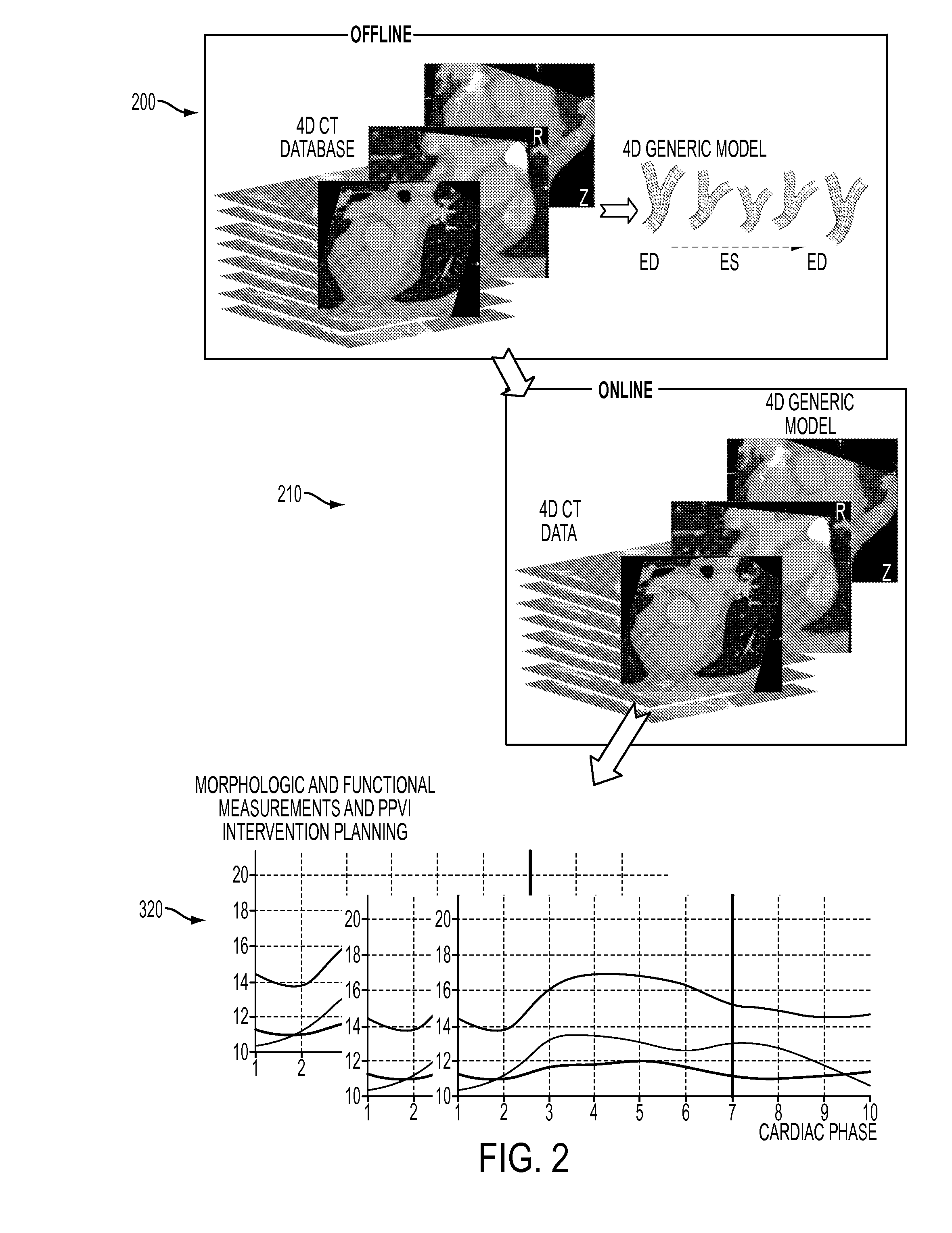
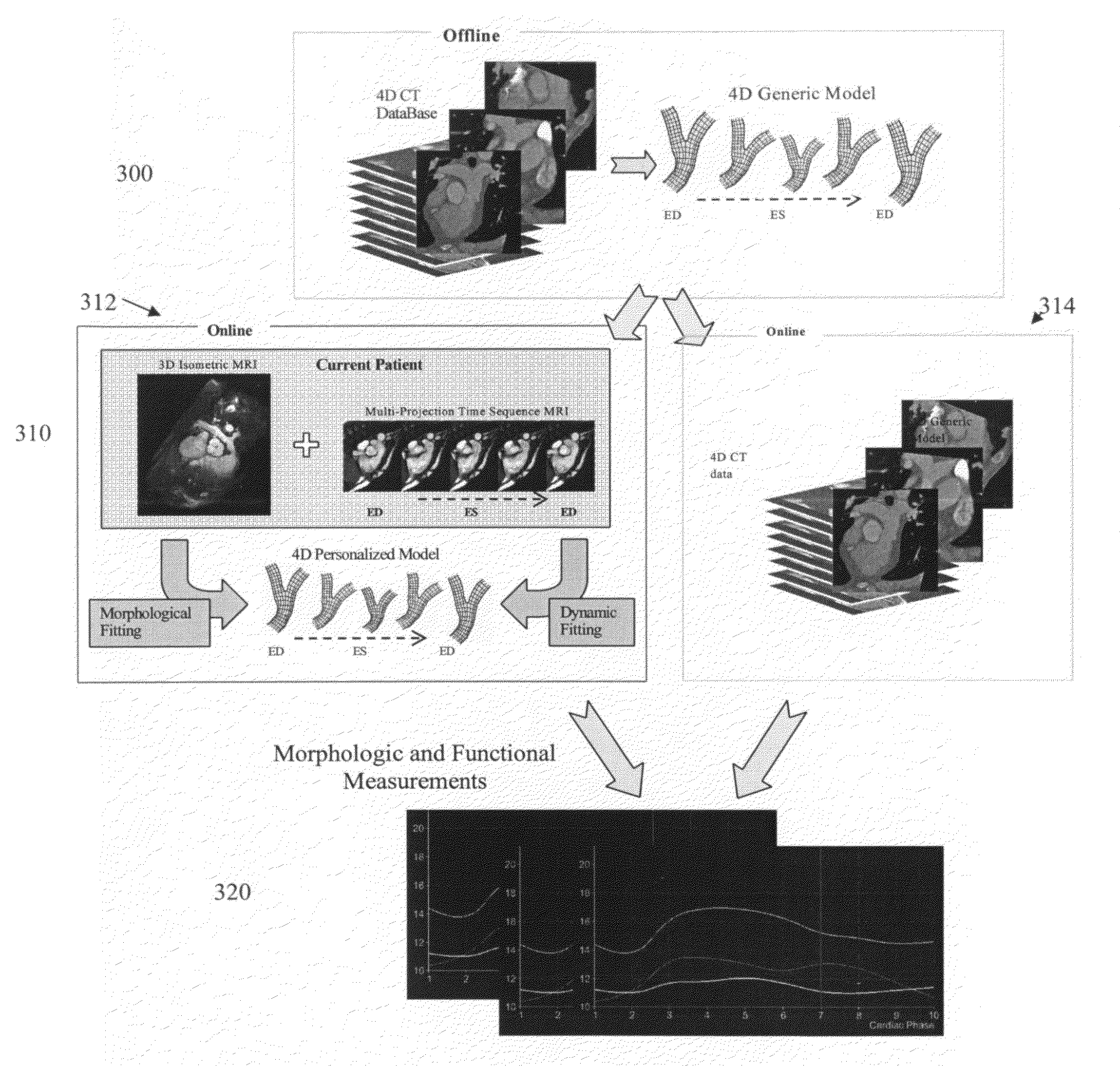
Method and System for Dynamic Pulmonary Trunk Modeling and Intervention Planning
InactiveUS20100239147A1Image enhancementImage analysisPercutaneous pulmonary valve implantation4d imaging
A method and system for modeling the pulmonary trunk in 4D image data, such as 4D CT data, and model-based percutaneous pulmonary valve implantation (PPVI) intervention is disclosed. A patient-specific dynamic pulmonary trunk data is generated from 4D image data of a patient. The patient is automatically classified as suitable for PPVI intervention or not suitable for PPVI intervention based on the generated patient-specific dynamic pulmonary trunk model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
White matter fiber brain map construction method by means of diffusion tensor imaging medical image
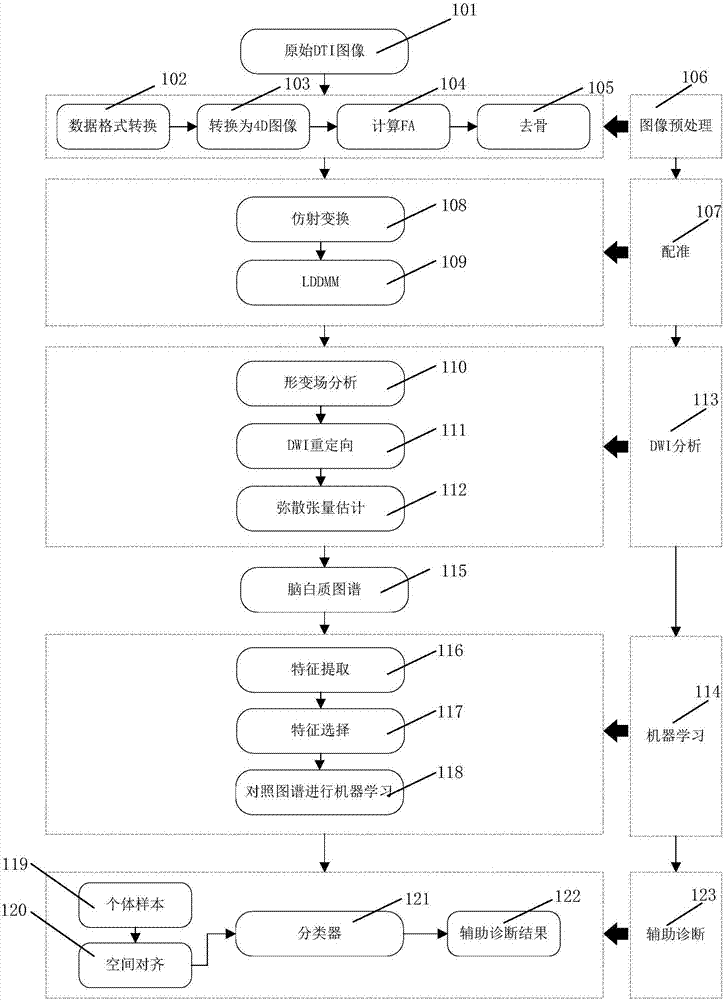
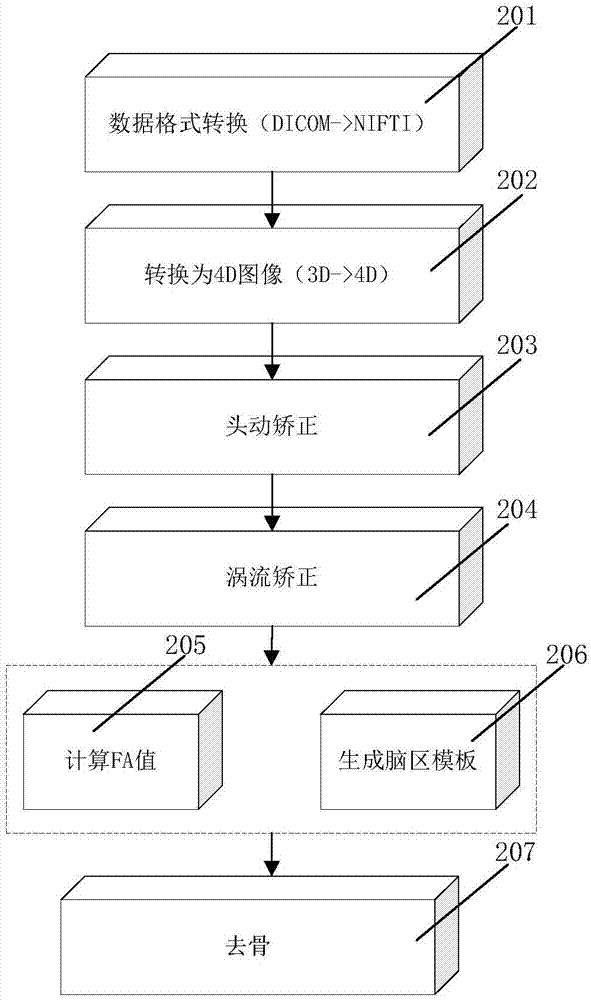
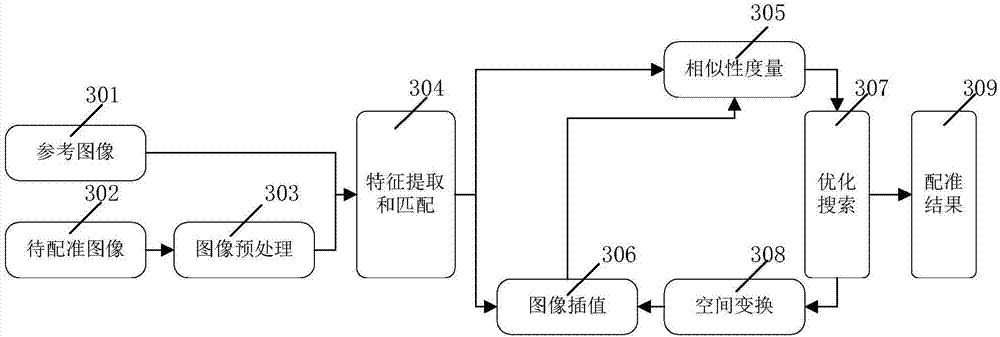
Provided is a white matter fiber brain map construction method by means of a diffusion tensor imaging medical image. The method comprises the steps that an original diffusion tensor imaging image is input (101); image preprocessing is conducted on a diffusion tensor image (106), wherein the substeps of data format conversion (102), 4D image converting (103), anisotropy value computing (104) and bone removing operation (105) are included; a registration technology is utilized (107), reflection transformation (108) and a large-deformation differential homomorphic mapping algorithm (109) are used, and different tested diffusion tensor images are registrated to the same standardized space (107); diffusion weighted imaging analysis is conducted (113), wherein the substeps of analyzing a deformation field by means of a diffusion tensor model (110), conducting diffusion weighted imaging redirection (111) and estimating diffusion tensor (112) are included; two brain white matter maps are constructed for patients and normal people (115); machine learning is conducted (114), wherein feature extraction (116) and feature selection (117) are conducted on tested pictures, data sets are divided into a training set and a test set, machine learning is conducted according to the maps (118), and training is conducted to generate a classifier (121).
Owner:XUANWU HOSPITAL OF CAPITAL UNIV OF MEDICAL SCI
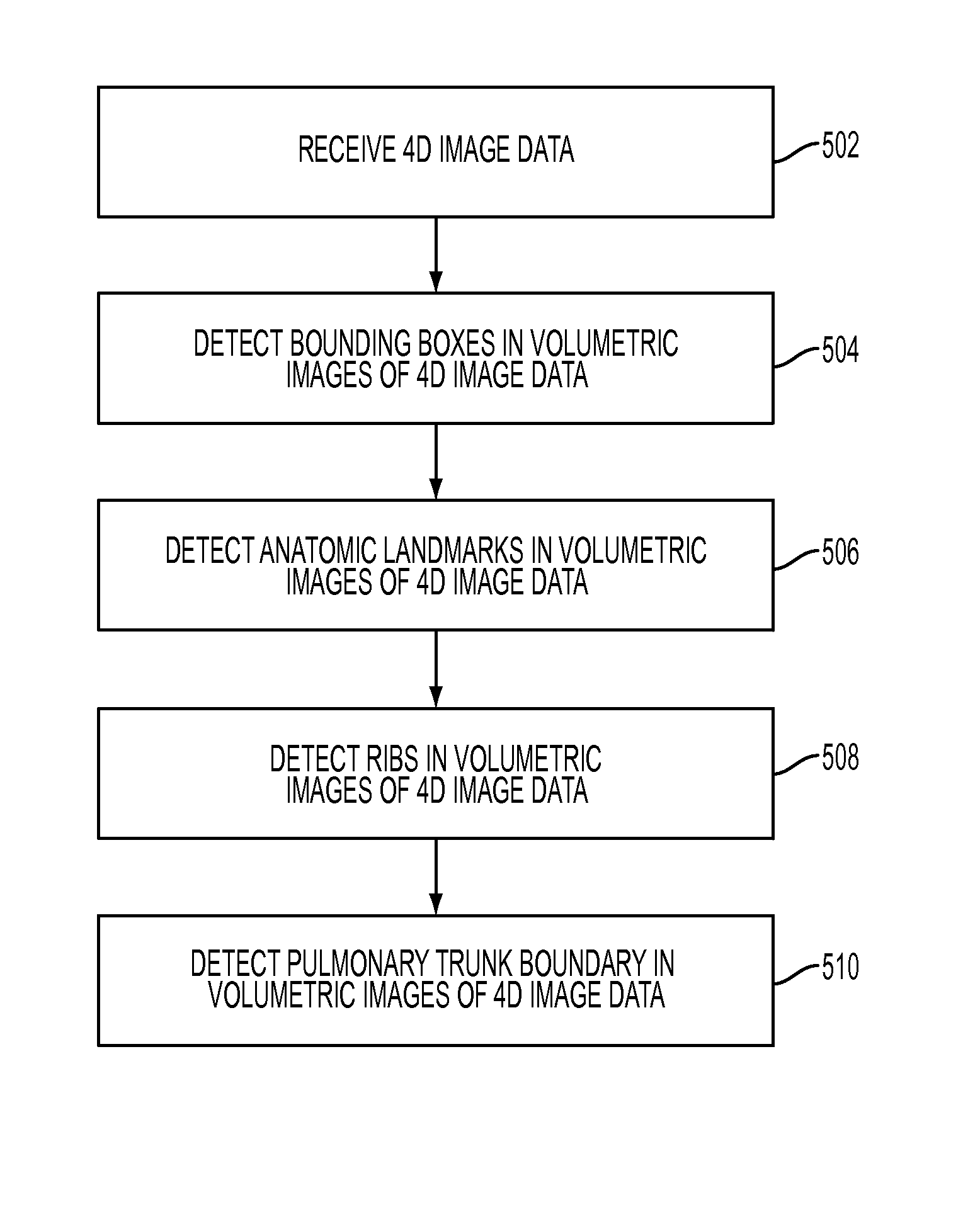
Method and system for dynamic pulmonary trunk modeling in computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging
A method and system for modeling the pulmonary trunk in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and MRI data, is disclosed. Bounding boxes are detected in frames of the 4D image data. Anatomic landmarks are detected in the frames of the 4D image data based on the bounding boxes. Ribs or centerlines of the pulmonary artery are detected in the frames of the 4D image data based on the anatomic landmarks, and a physiological pulmonary trunk model is fit the frames of the 4D image data based on the detected ribs and anatomic landmarks. The boundary of the pulmonary trunk is detected in order to refine the boundary of the pulmonary trunk model in the frames of the 4D image data, resulting in a dynamic model of the pulmonary trunk. The pulmonary trunk can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Multiple-photon excitation light sheet illumination microscope
An apparatus for and method of performing multi-photon light sheet microscopy (MP-LISH), combining multi-photon excited fluorescence with the orthogonal illumination of light sheet microscopy are provided. With live imaging of whole Drosophila and zebrafish embryos, the high performance of MP-LISH compared to current state-of-the-art imaging techniques in maintaining good signal and high spatial resolution deep inside biological tissues (two times deeper than one-photon light sheet microscopy), in acquisition speed (more than one order of magnitude faster than conventional two-photon laser scanning microscopy), and in low phototoxicity are demonstrated. The inherent multi-modality of this new imaging technique is also demonstrated second harmonic generation light sheet microscopy to detect collagen in mouse tail tissue. Together, these properties create the potential for a wide range of applications for MP-LISH in 4D imaging of live biological systems.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
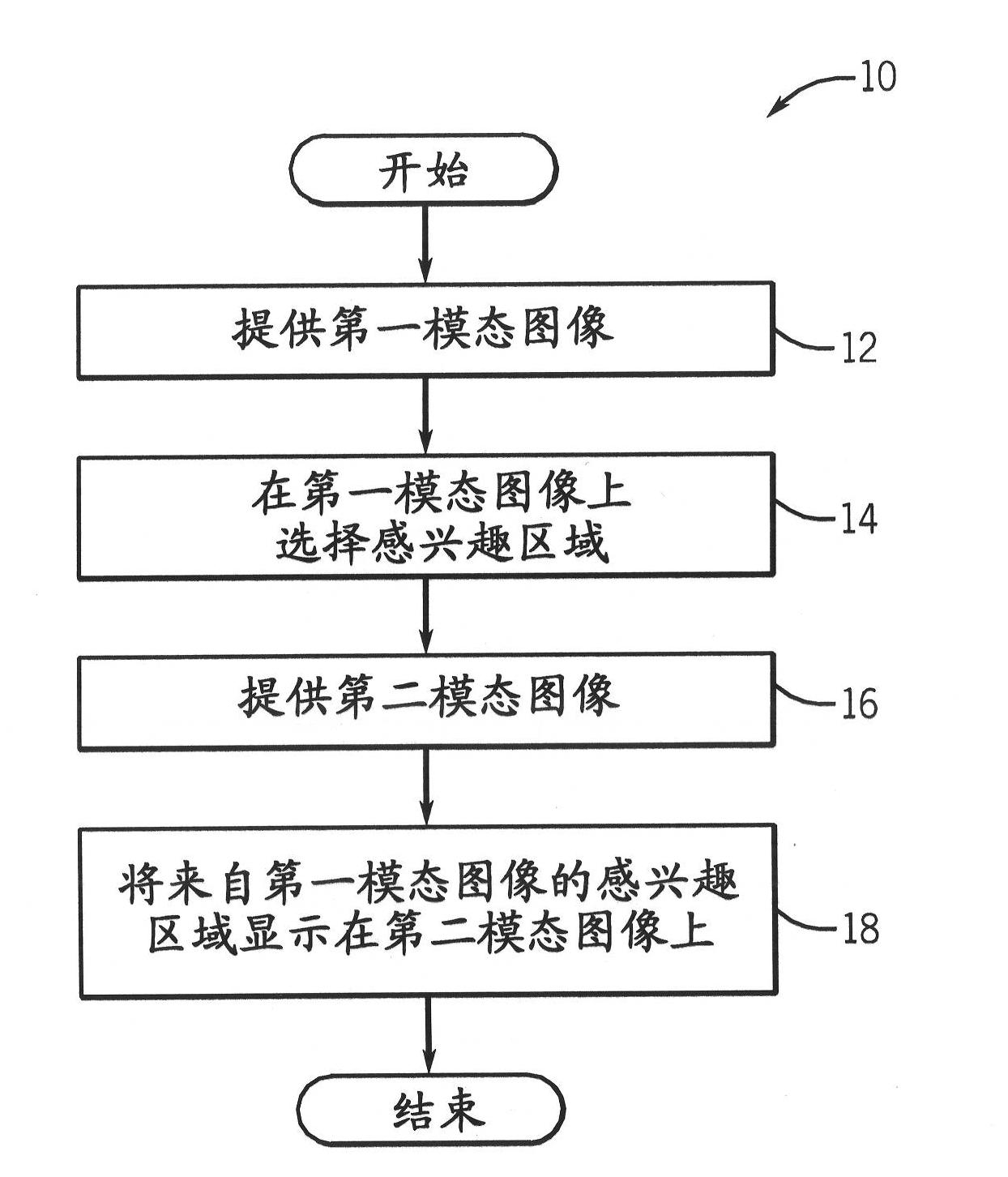
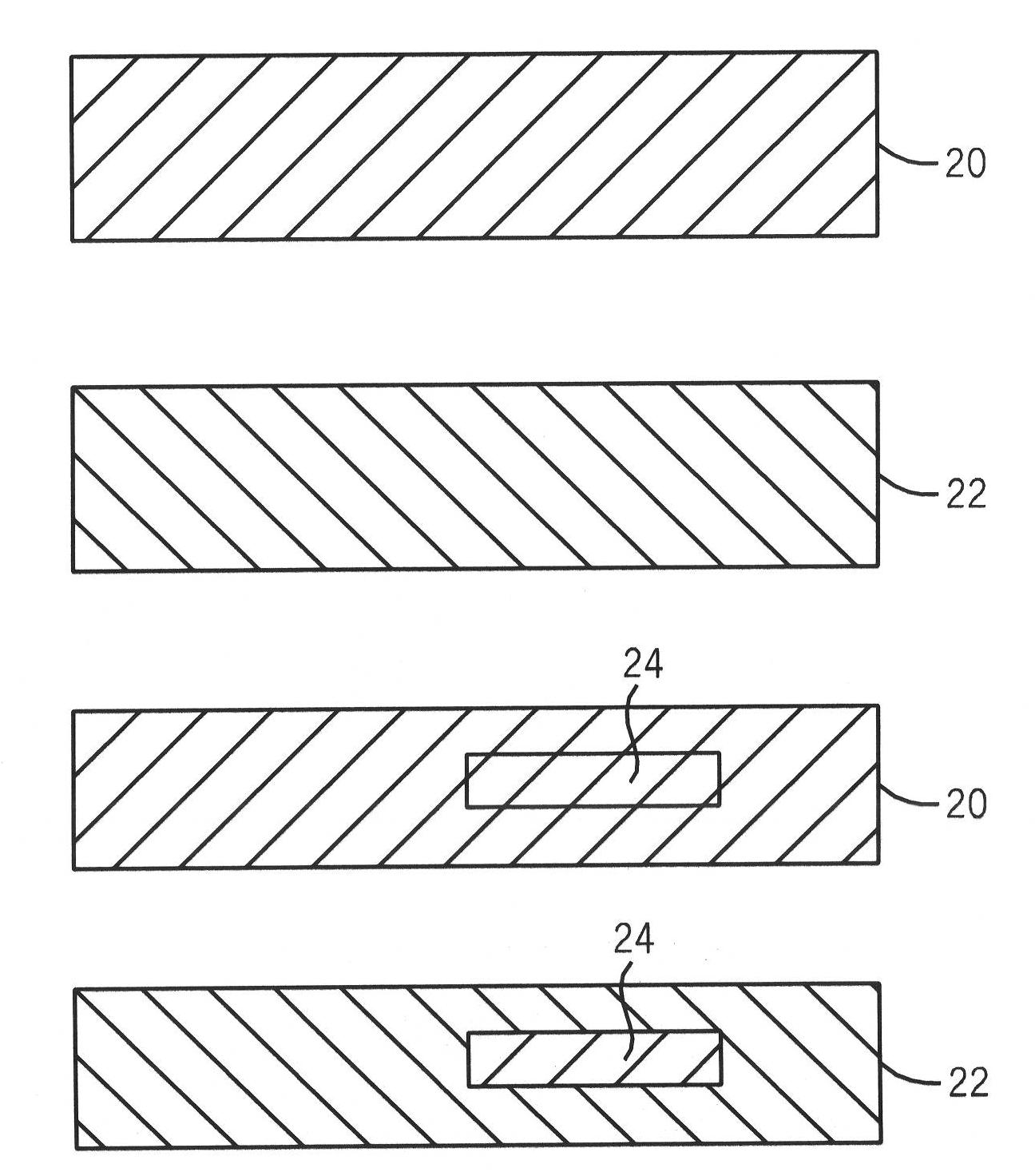
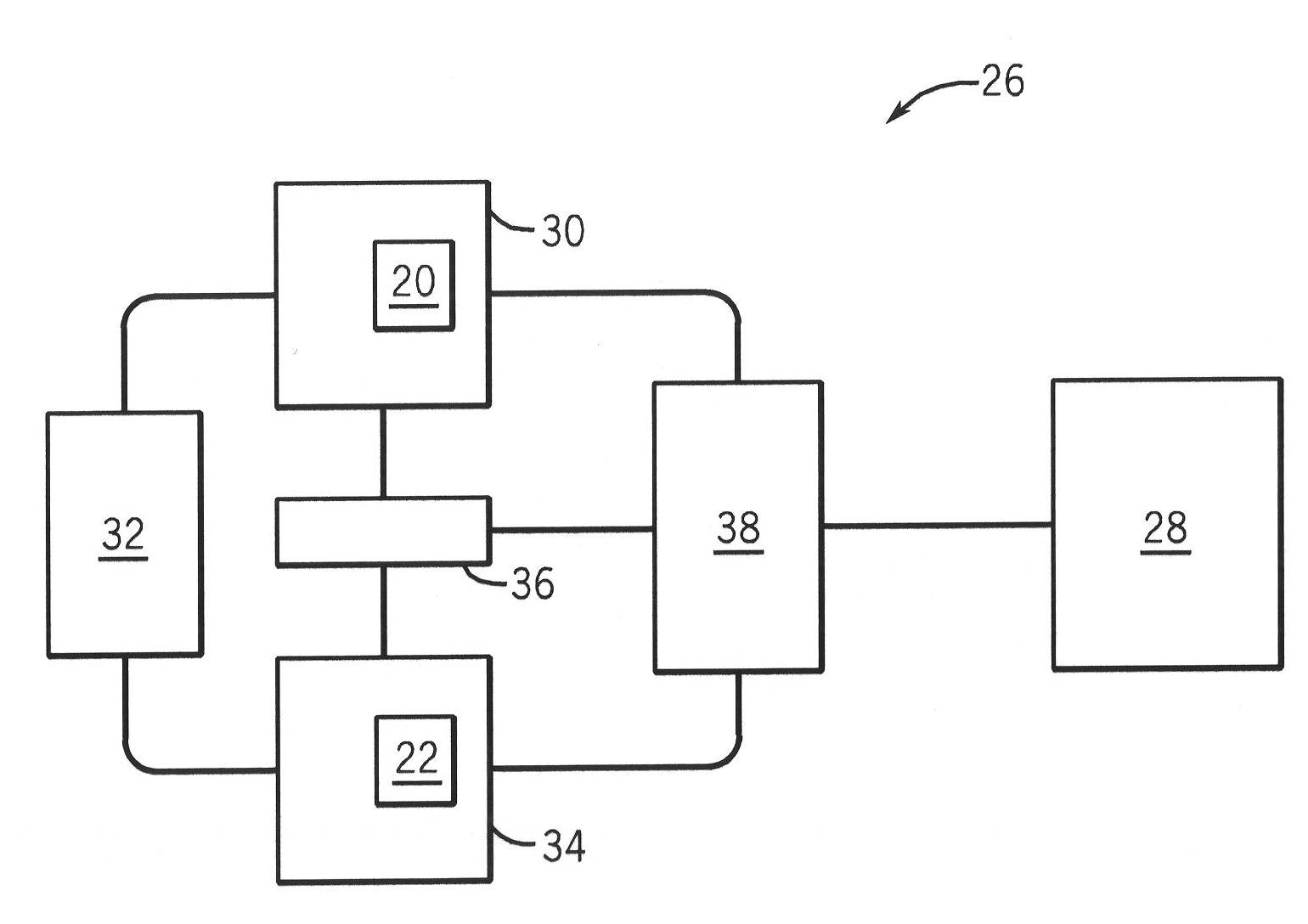
Single screen multi-modality imaging displays
InactiveCN102117180AUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage analysis4d imagingDiagnostic Radiology Modality
Methods (10) and systems (26) provide an integrated display, on a single screen (28), of images (20, 22) obtained from multiple modalities (30, 34) used in screening a subject (32). The methods and systems are usable with 2D, 3D, and 4D imaging, by which a single screen (28) displays a screen image (20) from a first modality (30). A window delineating an area of interest (24) is placed on a first modality image (20) from the first modality (30), and this area of interest (24) is then displayed on a second modality image (22) from a second modality (34), thereby providing a combined image representing the area of interest (24) through both modalities. Preferably, the first modality image (20) corresponds and / or is correlated with the second modality image (22).
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method for 4d x-ray imaging
InactiveUS20180070902A1Reconstruction from projectionRadiation diagnostic device control4d imagingProjection image
A system for reconstructing a 4D image has a surface acquisition system for generating a 3D surface model of an object and an X-ray imaging system for acquiring at least one 2D X-ray projection image of the object. A controller controls the surface acquisition system and the X-ray imaging system. A processor applies a 4D reconstruction algorithm / method to the 3D surface model and the at least one 2D X-ray projection to reconstruct a 4D X-ray volume of the imaged body part in motion.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
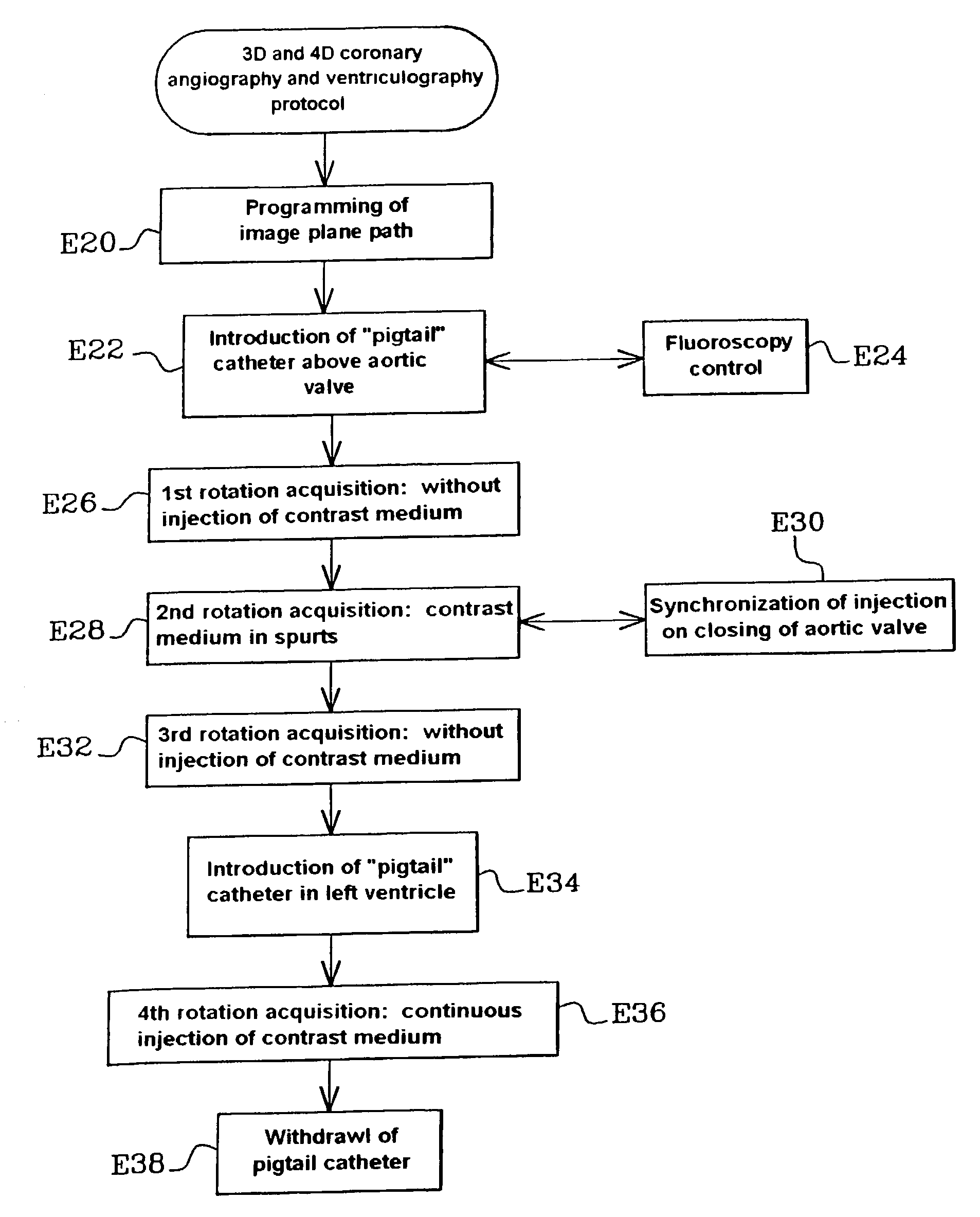
Method and apparatus for cardiac radiological examination in coronary angiography
InactiveUS7065395B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingAortic rootImage plane
A method of cardiac radiological examination for coronarography comprises the steps of:a) introducing contrast medium simultaneously in the left coronary artery and in the right coronary artery from the aortic root and, in parallel,b) acquiring a sequence of dynamic images of the propagation of the contrast medium in the left and right coronary arteries with a displacement of the image plane, during the acquisition of said images, along a determined trajectory (E28). The contrast medium can be introduced in a cyclic manner during the acquisition of dynamic images, each cycle of introduction corresponding to a phase of closure of the aortic valve in the cardiac rhythm. 3D and 4D images with optimal efficiency can be obtained in the use of contrast medium. An injection device for producing the above cycles is synchronized with the introduction of the contrast medium.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
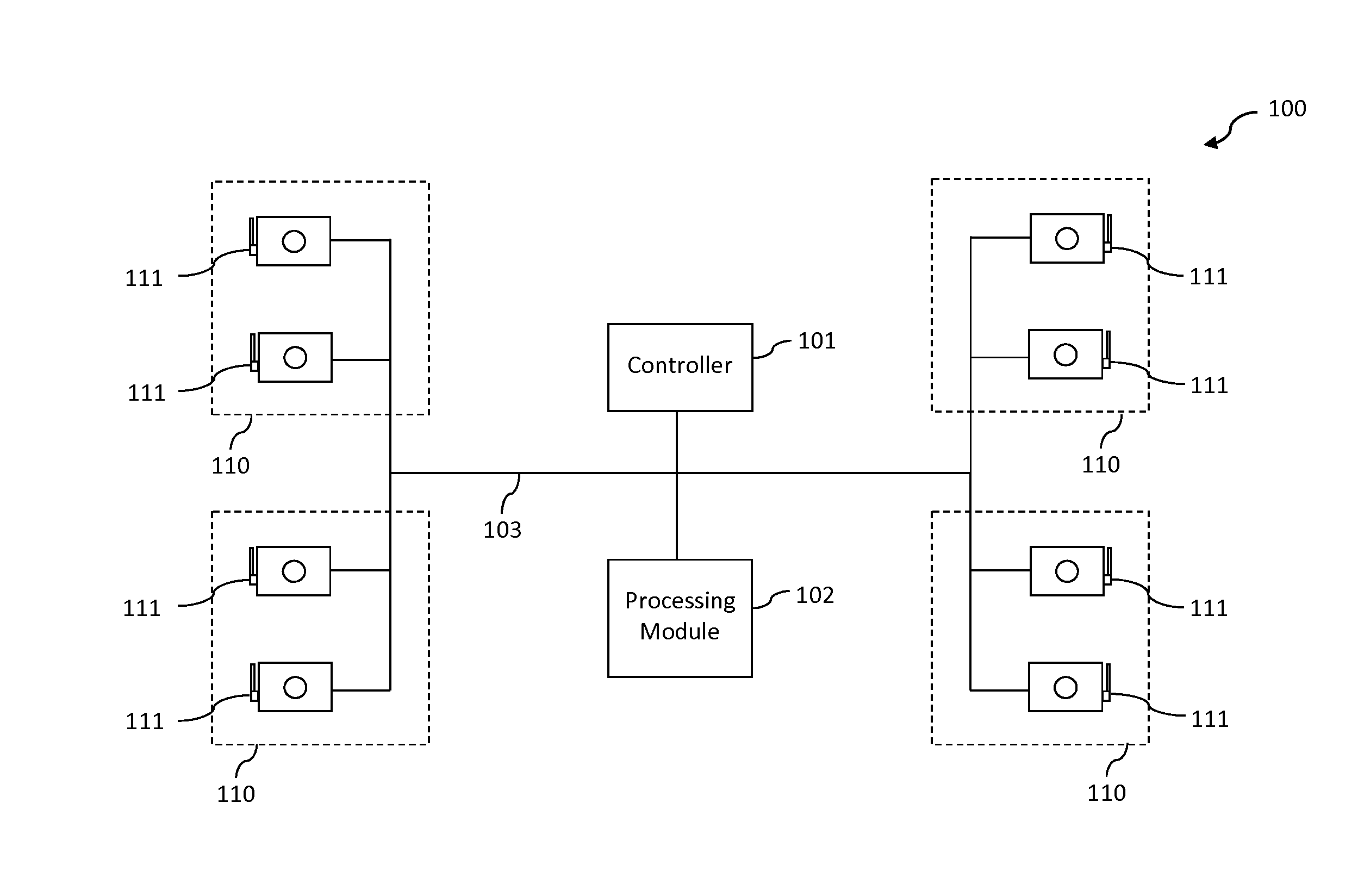
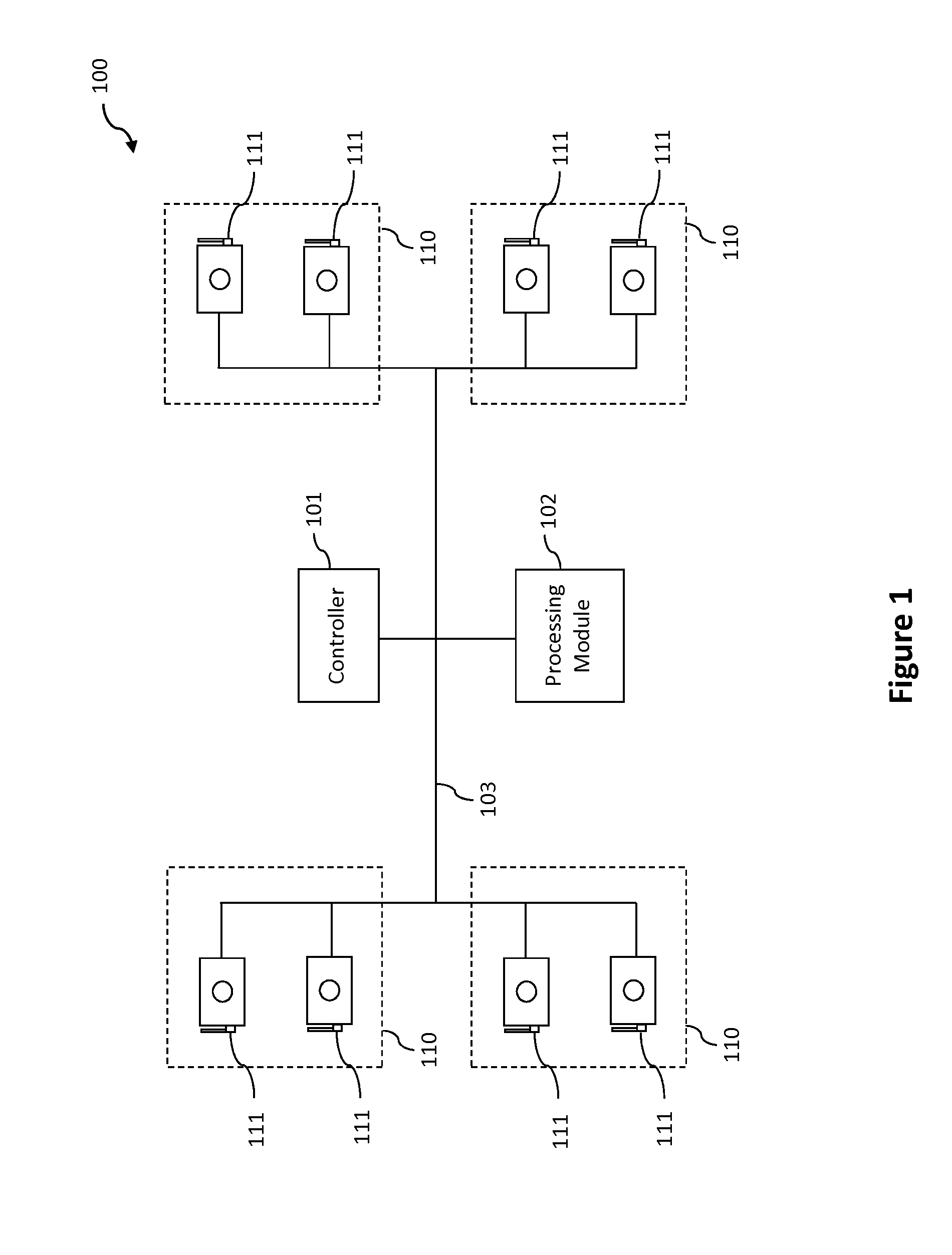
System and method for stereophotogrammetry
InactiveUS20150304629A1Reduce the differenceIncrease catch ratePicture interpretationSteroscopic systems4d imaging3d image
The invention is directed to a stereophotogrammetric system and method for generating 3D images. A stereophotogrammetric unit, having a plurality of cameras, is structured to capture a set of images of an object at different angles. A controller is communicably connected to the stereophotogrammetric unit, and is configured to facilitate the simultaneous triggering of the plurality of cameras through a synchronized trigger signal, such that the cameras will capture respective images of the object at the same time. A processing module is configured to generate 3D image from the set of images captured. The controller may further be configured to facilitate the sequential triggering of a plurality of stereophotogrammetric units, such that the object in motion may be captured at increased frames per second. The processing module may further be configured to link together the plurality of 3D images in sequence to then create a 4D image.
Owner:ZHANG XIUCHUAN +1
Computer-Based Method And System For Imaging-Based Dynamic Function Evaluation Of An Organ
InactiveUS20110098556A1Easy to determineImprove dysfunctionMagnetic measurementsMedical automated diagnosisSingular value decomposition4d imaging
A computer-based method of determining a functional assessment of at least one organ having secretional or excretional functions, such as a liver or kidneys, of a human is disclosed. The method comprises processing a four-dimensional (4D) image data set of said human comprising data for an assessment of said organ function, wherein said 4D image data is acquired by an image modality; and wherein said processing said 4D image data comprises performing a deconvolutional analysis (DA) comprising a matrix inversion using singular value decomposition (SVD) based on said 4D image data.
Owner:BAYER PHARMA AG
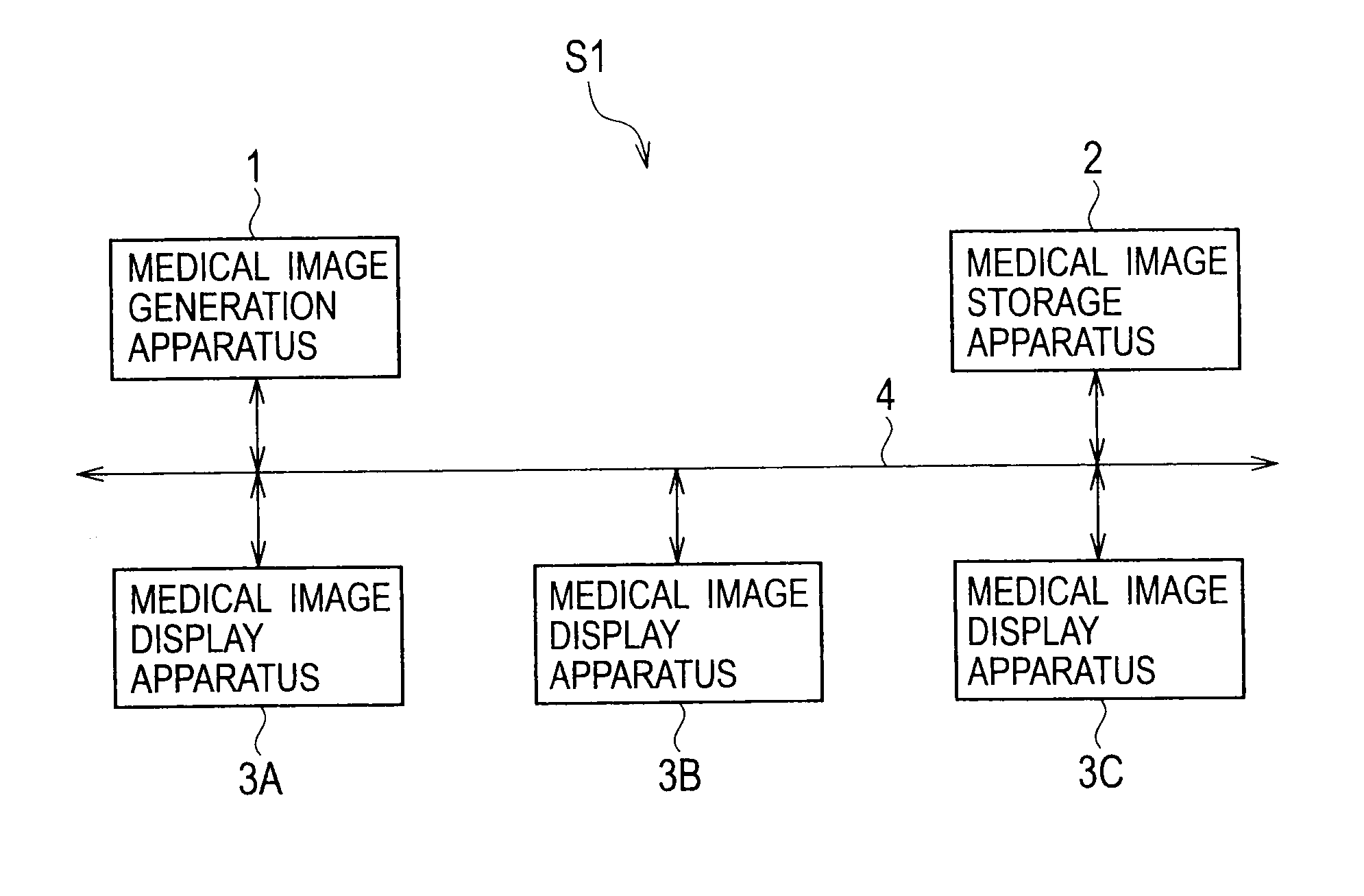
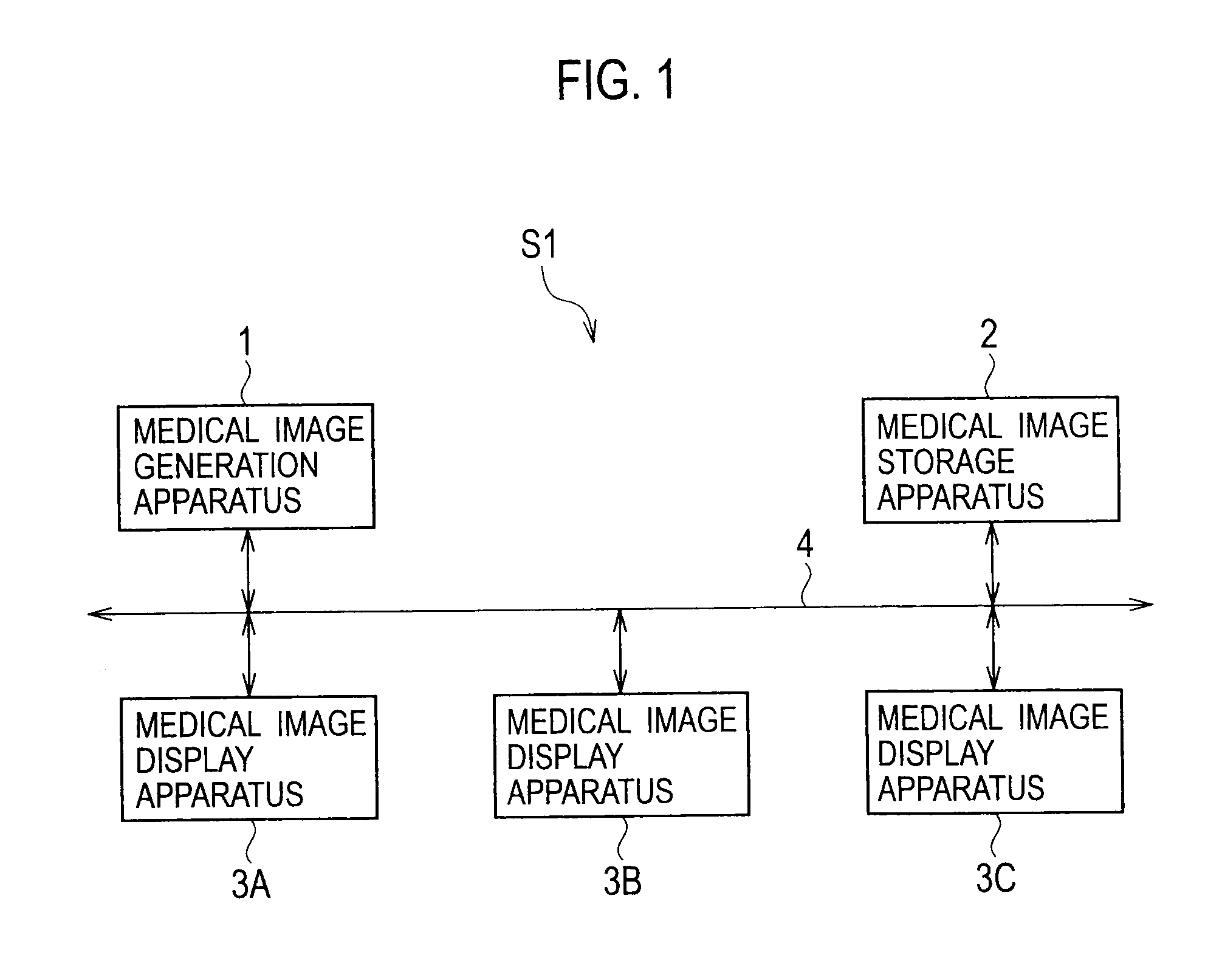
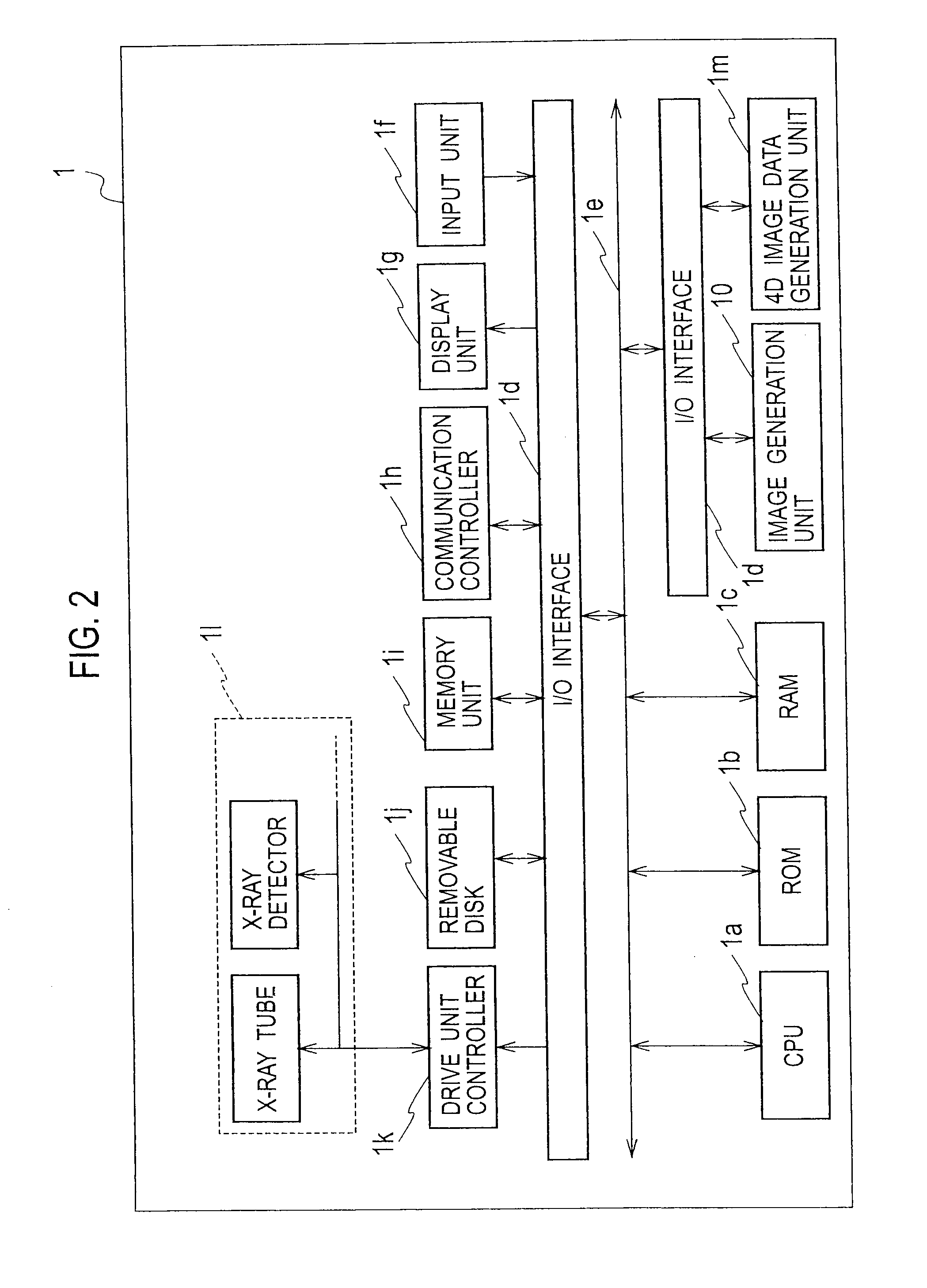
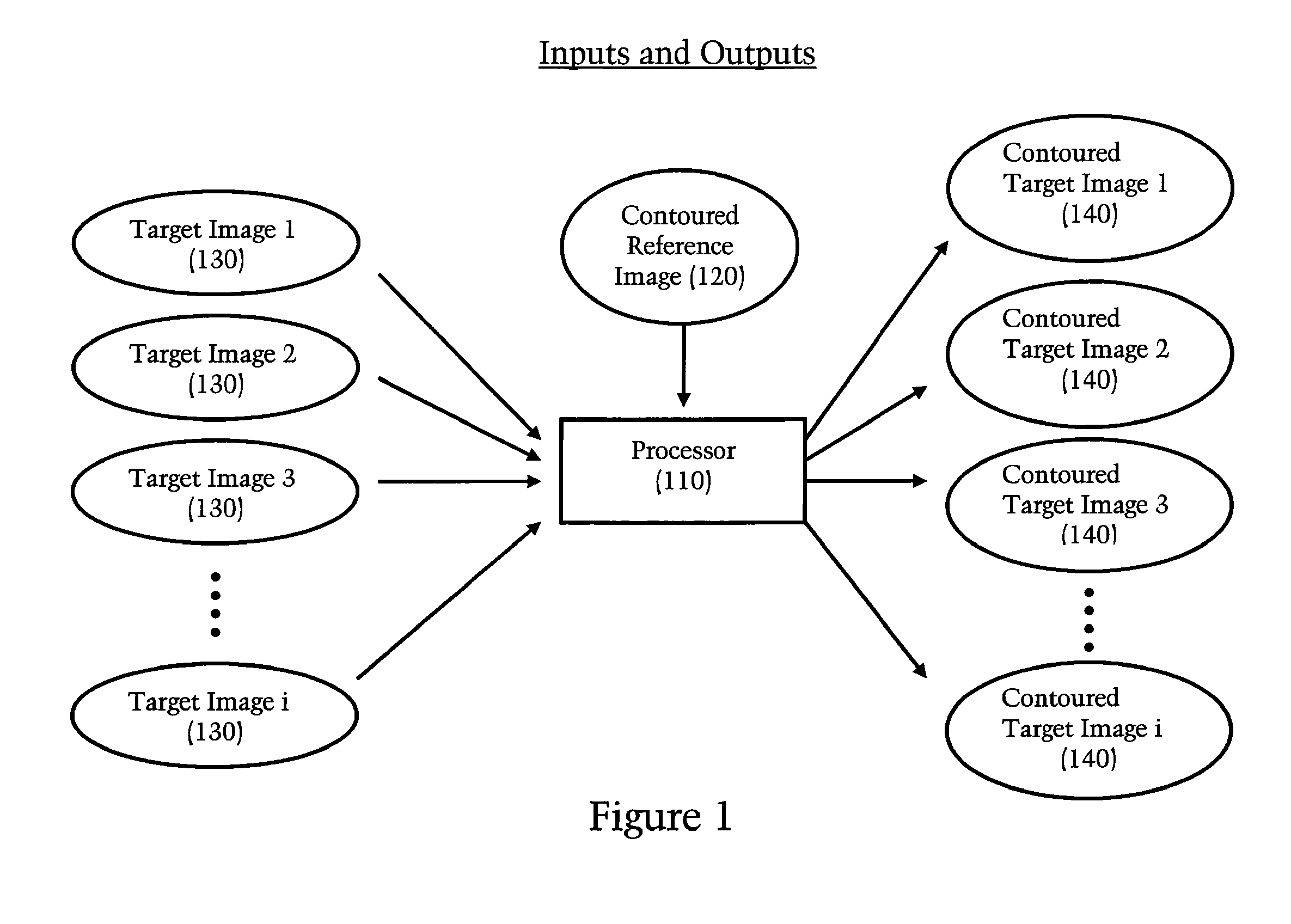
Medical image generation apparatus, medical image storage apparatus, medical image display apparatus, and medical image display system
ActiveUS20100128943A1Displaying large amountEasy to operateSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognition4d imagingRelevant information
A medical image generation apparatus including: a 4D image data generation unit generating 4D image data composed of a plurality of 3D image data blocks each having information indicating a number in chronological order of the 3D image data blocks using image information acquired by taking images of an object; and an image generation unit generating movie data composed of a plurality of 2D image data blocks generated from the plurality of 3D image data blocks constituting the four-dimensional image data and generating relevant information associating each of the two-dimensional image data blocks constituting the movie data with one of the 3D image data blocks which is the source of the 2D image data block.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA +1
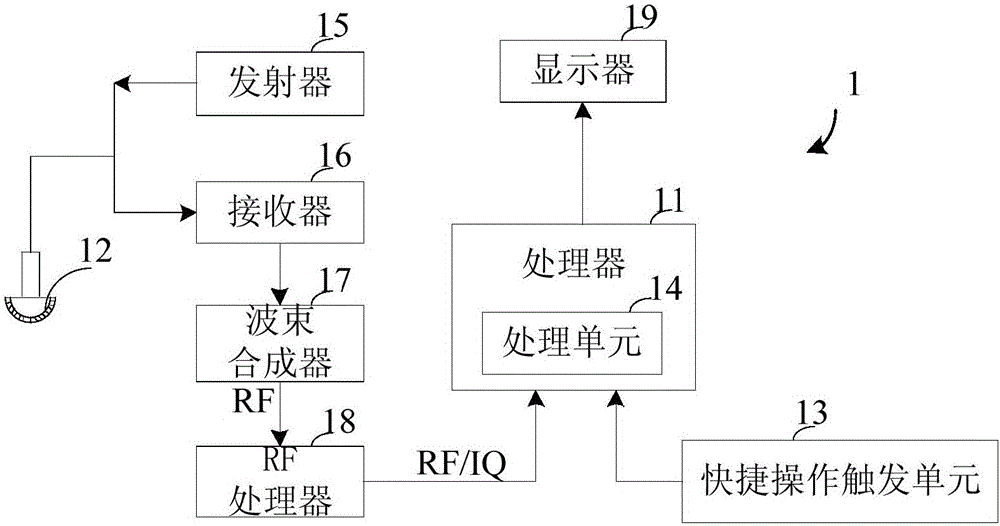
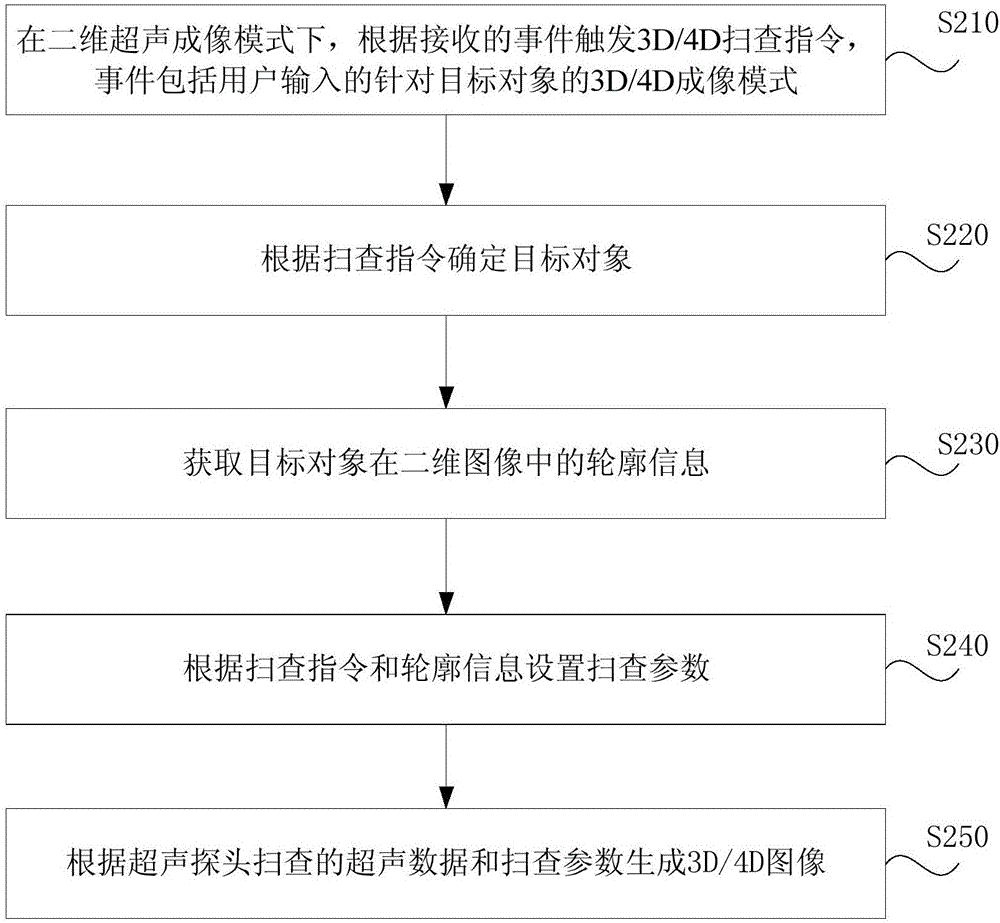
Ultrasonic imaging equipment, method and device
ActiveCN106725614AImprove experienceEasy to operateOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnostics4d imagingDisplay device
The embodiment of the invention discloses ultrasonic imaging equipment, method and device. The ultrasonic imaging equipment comprises a displayer, an ultrasonic probe, an operation panel and an upper computer, and further comprises a fast operation trigger unit and a processing unit, wherein the fast operation trigger unit is used for generating a scanning instruction according to an event, the scanning instruction is used for 3D / 4D imaging on the basis of two-dimensional ultrasonic data, and the event includes a 3D / 4D imaging mode selected by a user according to a target object; the processing unit is used for configuring scanning parameters according to the scanning instruction and generating a 3D / 4D image according to ultrasonic data scanned by the ultrasonic probe and the scanning parameters. The scanning instruction used for 3D / 4D imaging is generated through the fast operation trigger unit, the processing unit automatically configures the scanning parameters according to the scanning instruction and generates the 3D / 4D image automatically according to the ultrasonic data scanned by the ultrasonic probe and the scanning parameters, 3D / 4D imaging can be conveniently achieved through one-key operation on the fast operation trigger unit, operation is easy, the practicality is high, and the user experience is good.
Owner:SONOSCAPE MEDICAL CORP
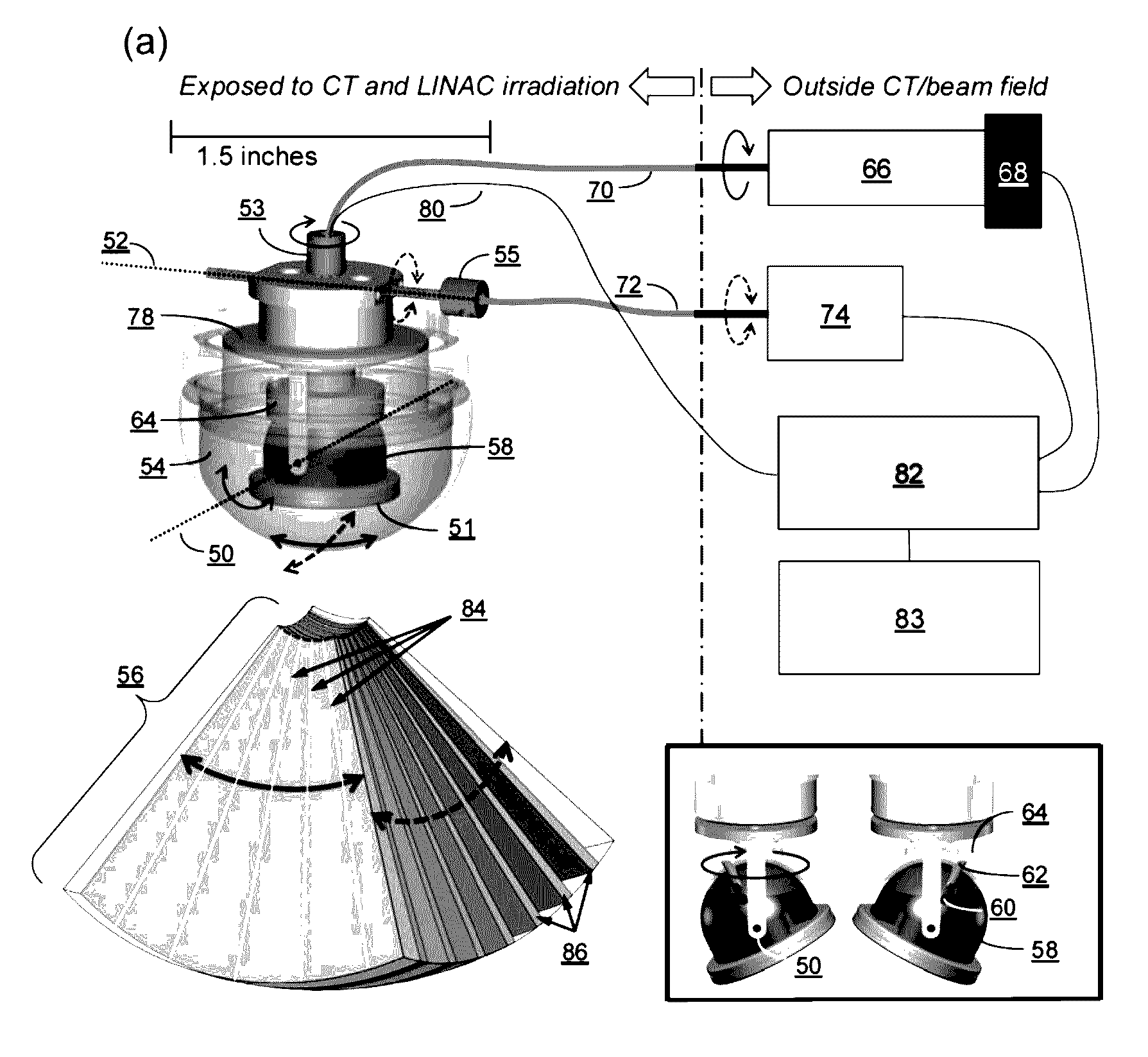
Mechanically driven ultrasound scanning system and method
InactiveUS20160354058A1Improve compatibilityMinimizing radiotherapy discrepancyOrgan movement/changes detectionInfrasonic diagnostics4d imagingSonification
Described herein are radiolucent imaging devices and methods capable of acquiring real-time 2D, 3D, or 4D images. By using remote-actuation techniques to mechanically drive an ultrasound transducer element in multiple directions, the majority of dense metallic components typically present in the ultrasound probe itself are eliminated. Therefore the system herein achieves both CT compatibility and radiation beam compatibility.
Owner:SONITRACK SYST
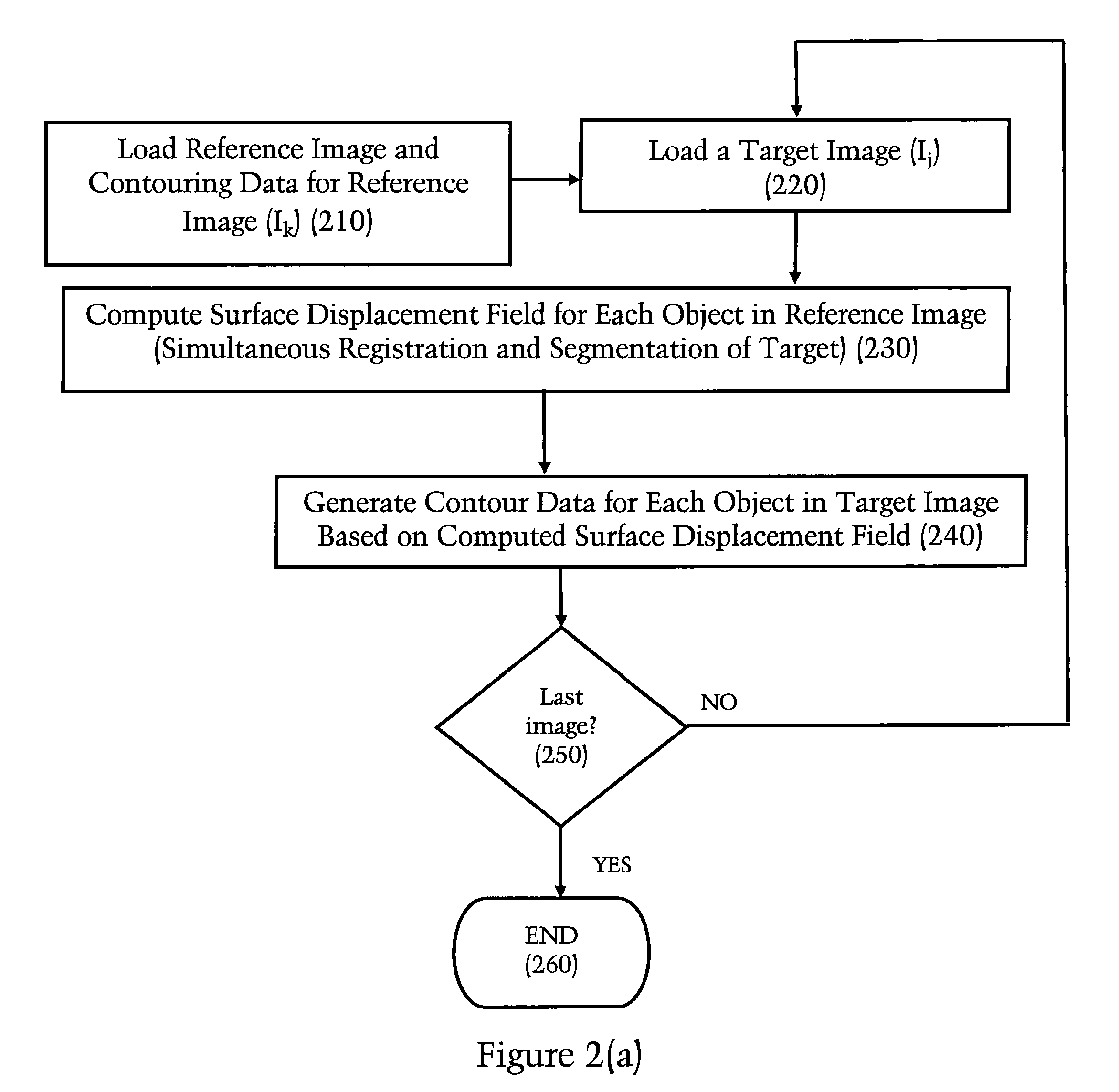
Processing of abdominal images
According to one embodiment there is provided a computer-automated image processing method applied to a four-dimensional (4D) image data set of a patient's abdomen, e.g. by dynamic contrast enhanced computer-assisted tomography (DCE-CT). One of the three-dimensional (3D) scan images is taken to as the reference volume and the others as target volumes. Before registration between the 3D scan images, the image data set is partitioned into an abdominal cavity domain, containing the organs inside the abdominal wall, and an abdominal wall domain including the abdominal wall and externally adjacent skeletal features, such as the spine and ribs. Registration is then carried out separately on the two domains to obtain two warp fields which are then merged into a 4D image data set of the whole volume for further use, which may be to carry out perfusion measurements, to display and to store the registered 4D image data set.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Method and apparatus for determining the effectiveness of an image transformation process
A method for determining the effectiveness of an image transformation process includes acquiring a four-dimensional (4D) image data set, sorting the 4D image data set into separate field-of-view bins using a temporal gating system generating a plurality of deformation vectors using the sorted 4D image data set, and using the plurality of deformation vectors to generate a transformation effectiveness value that is representative of the effectiveness of the image transformation process. The method further includes acquiring a respiratory signal, calculating a power spectrum of the respiratory signal, calculating a power spectrum for each of the plurality of deformation vectors, and comparing the power spectrum of the respiratory signal to the power spectrum of the plurality of deformation vectors to generate the transformation effectiveness value.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
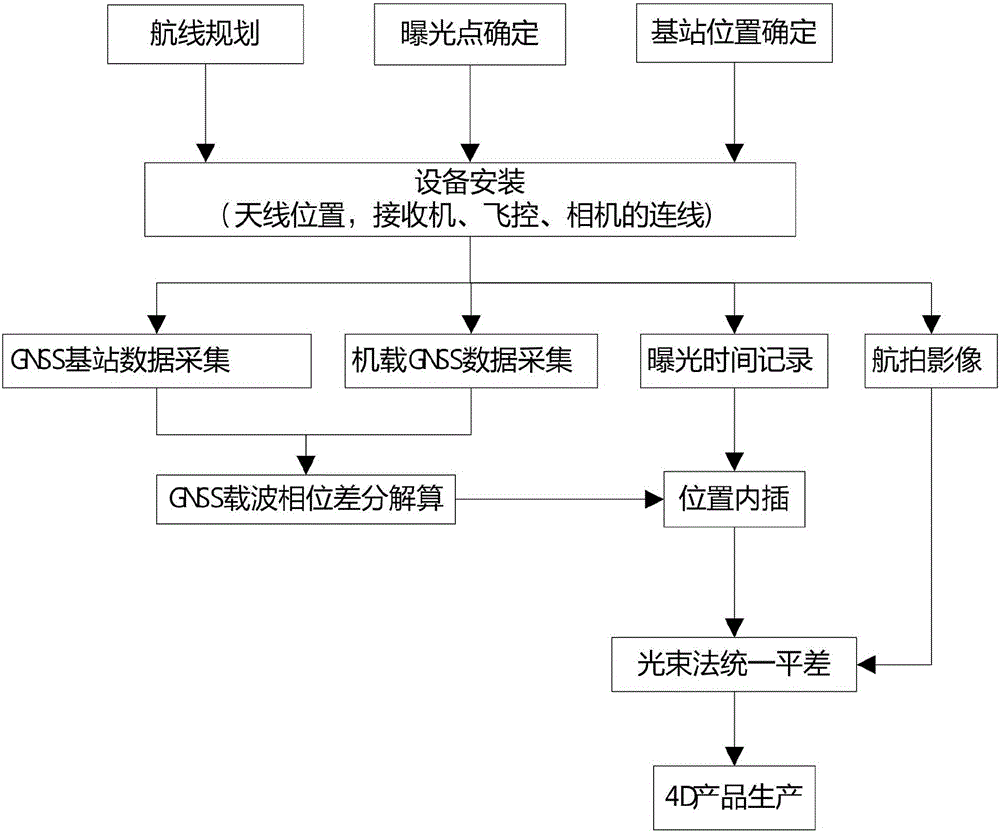
GNSS high precision assisted unmanned plane aerotriangulation method
InactiveCN105823469AImproving the Efficiency of Low Altitude PhotogrammetryReduce field workloadPhotogrammetry/videogrammetryAviation4d imaging
The invention discloses a GNSS high-precision assisted unmanned aerial vehicle three-dimensional measurement method, which uses an airborne GNSS receiver, a GNSS base station receiver, and a camera for synchronous observation, including: the airborne GNSS receiver accurately records the exposure time of the camera, and uses a carrier After the phase difference is decomposed and calculated, the centimeter-level position information of the antenna is obtained, and then the outer bearing line element at the exposure time of the camera is obtained by interpolation, which is used as the starting data. Combined with a small number of ground control points, the aerial triangulation software is used for automatic processing, and each image is obtained. The outer orientation elements of the film, and then produce the required 4D image. The present invention adopts the method of differential positioning, and uses the GNSS differential position information corrected by the eccentricity to replace the position information of the exposure point, so as to obtain the line elements in the outer orientation elements required in aerial photogrammetry, which greatly improves the accuracy of the UAV. The efficiency of low-altitude photogrammetry reduces field workload.
Owner:李德仁
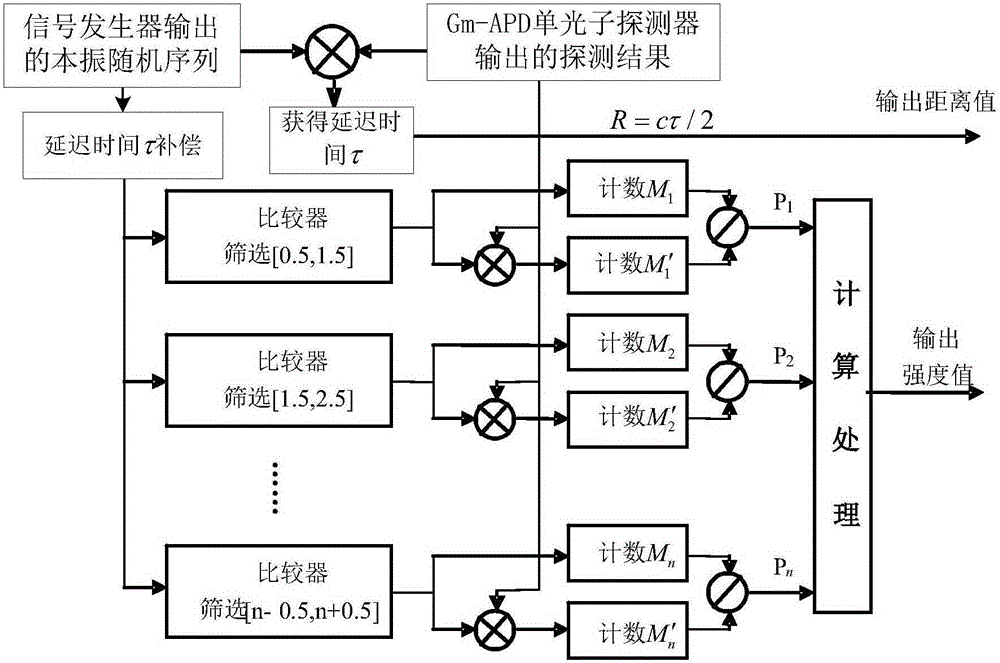
Method for obtaining target distance and target intensity realized on the basis of 4D imaging photon counting laser radar system
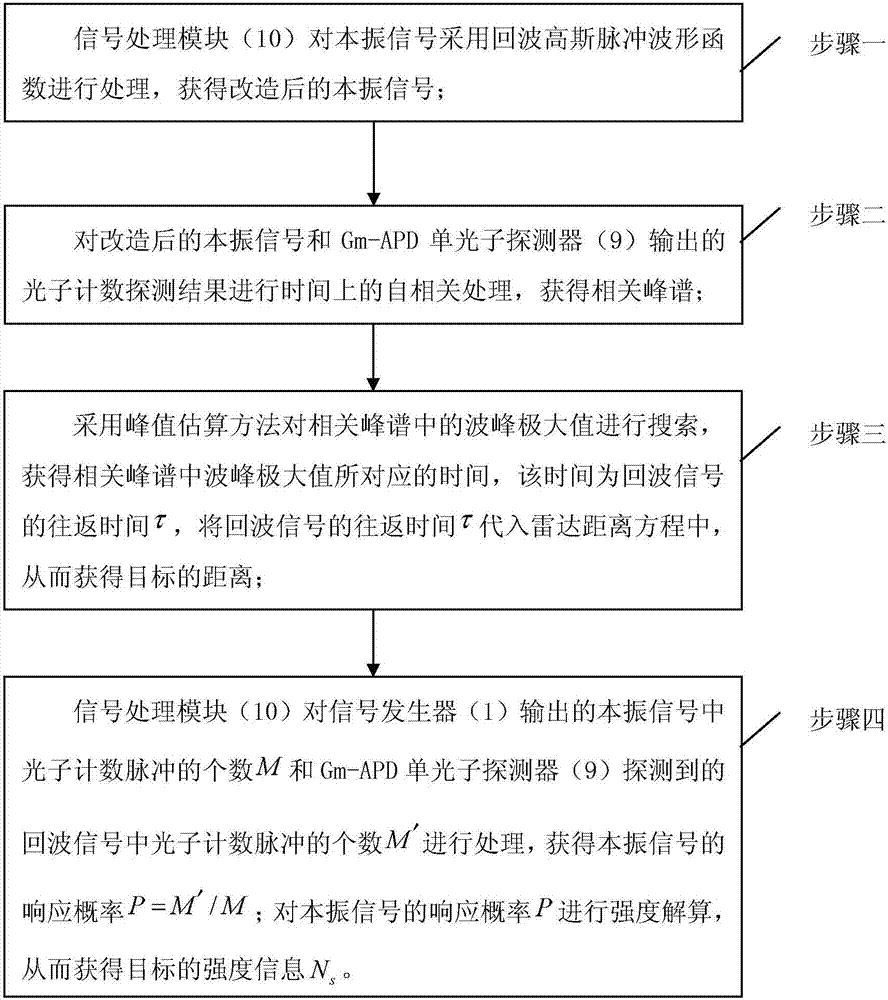
ActiveCN107290755AHigh precisionImprove processing efficiencyElectromagnetic wave reradiation4d imagingLocal oscillator signal
The invention proposes a method for obtaining the target distance and the target intensity realized on the basis of a 4D imaging photon counting laser radar system, which relates to the technical field of a laser radar. The method solves the problems that a currently available method for obtaining the target distance and the target intensity requires a large amount of computation for distance calculation and that the process is time consuming and the computation intensity is low in accuracy. According to the invention, first, a local oscillation signal is transformed so that is possesses the same form as an echo signal, then the reconstructed local oscillation signal and the Gm-APD detection result are subjected to frequency-mixing treatment to obtain a related peak spectrum. On the one hand, the distance information is worked out by searching the position of the peak maximum in the peak spectrum; on the one hand, the intensity information is worked out through processing the number M of photon counting pulses in the local oscillator signal outputted by the signal generator and the number of photon counting pulses M' in the echo signal detected by the Gm-APD single-photon detector. The invention is mainly used to detect the distance and intensity of a target.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Magnetic resonance projection for constructing four-dimensional image information
Apparatus and techniques are described herein for nuclear magnetic resonance (MR) projection imaging. Such projection imaging may be used for generating four-dimensional (4D) imaging information representative of a physiologic cycle of a subject, such as including generating two or more two-dimensional (2D) images, the 2D images comprising projection images representative of different projection angles, and the 2D images generated using imaging information obtained via nuclear magnetic resonance (MR) imaging, assigning the particular 2D images to bins at least in part using information indicative of temporal positions within the physiologic cycle corresponding to the particular 2D images, constructing three-dimensional (3D) images using the binned 2D images, and constructing the 4D imaging information, comprising aggregating the 3D images.
Owner:ELEKTA AB
Method and apparatus for efficient automated re-contouring of four-dimensional medical imagery using surface displacement fields
ActiveUS8265356B2Improved accuracy in contouring the target imageImprove computing efficiencyCharacter and pattern recognition4d imagingReference image
A technique is disclosed for generating a new contour and / or a 3D surface from contour data using a surface displacement field. The technique is preferably applied to un-contoured target images within a 4D image sequence for which contour data is desired. The technique can be initialized with contour data related to a reference image that has already been contoured, e.g. by a doctor who manually enters contour information into a computer. Image registration (calculation of correspondence between the reference image and target image) can be performed simultaneously with segmentation (identifying regions of interest in the target image). This allows one to make use of segmentation information in a reference image to improve the accuracy of contouring within the target image.
Owner:IMPAC MEDICAL SYST
Dynamic pulmonary trunk modeling in computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging based on the detection of bounding boxes, anatomical landmarks, and ribs of a pulmonary artery
A method and system for modeling the pulmonary trunk in 4D image data, such as 4D CT and MRI data, is disclosed. Bounding boxes are detected in frames of the 4D image data. Anatomic landmarks are detected in the frames of the 4D image data based on the bounding boxes. Ribs or centerlines of the pulmonary artery are detected in the frames of the 4D image data based on the anatomic landmarks, and a physiological pulmonary trunk model is fit the frames of the 4D image data based on the detected ribs and anatomic landmarks. The boundary of the pulmonary trunk is detected in order to refine the boundary of the pulmonary trunk model in the frames of the 4D image data, resulting in a dynamic model of the pulmonary trunk. The pulmonary trunk can be quantitatively evaluated using the dynamic model.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com