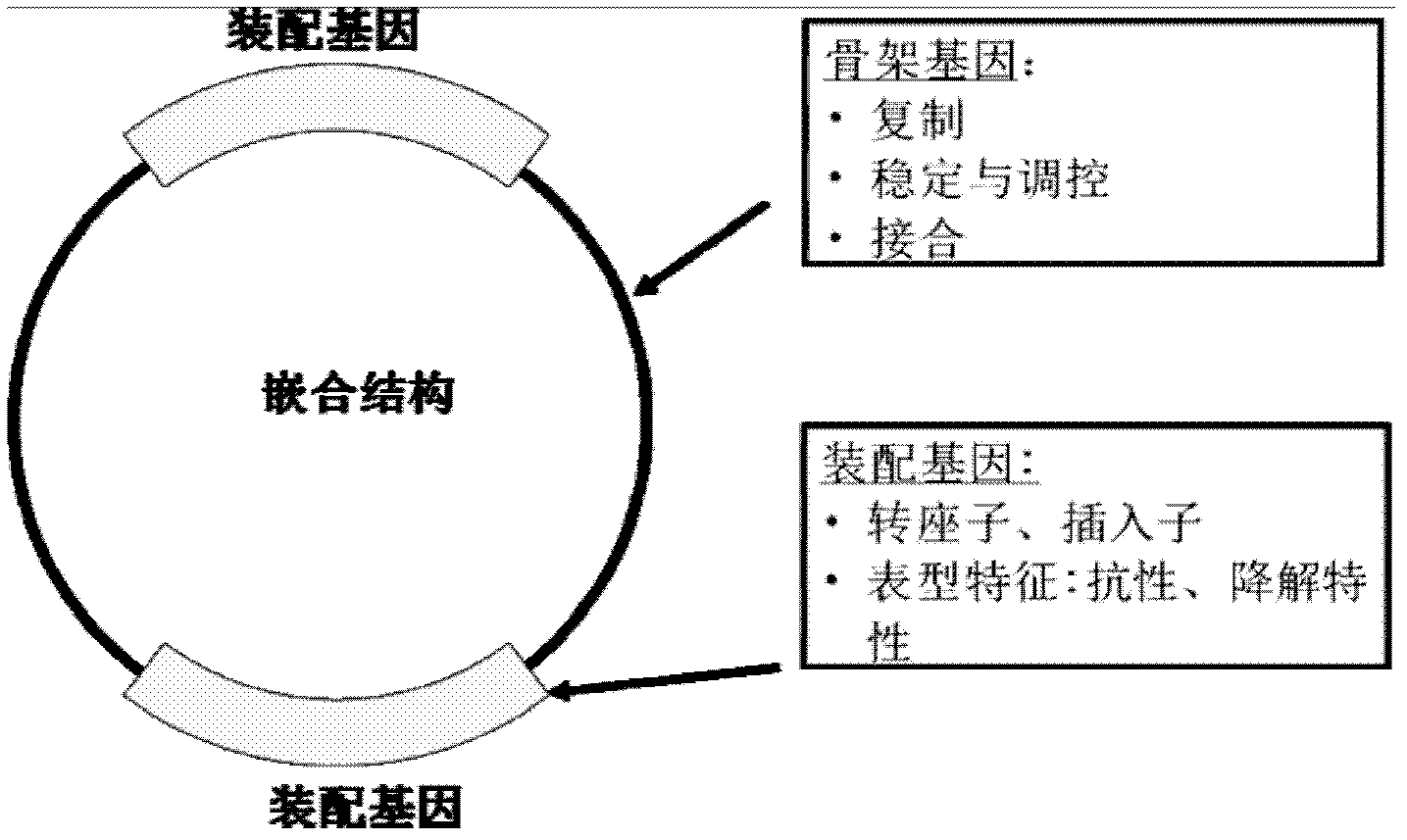
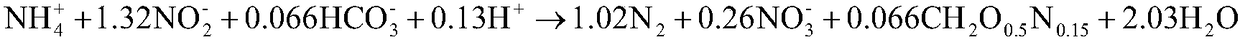Patents
Literature
39 results about "Phylum Proteobacteria" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
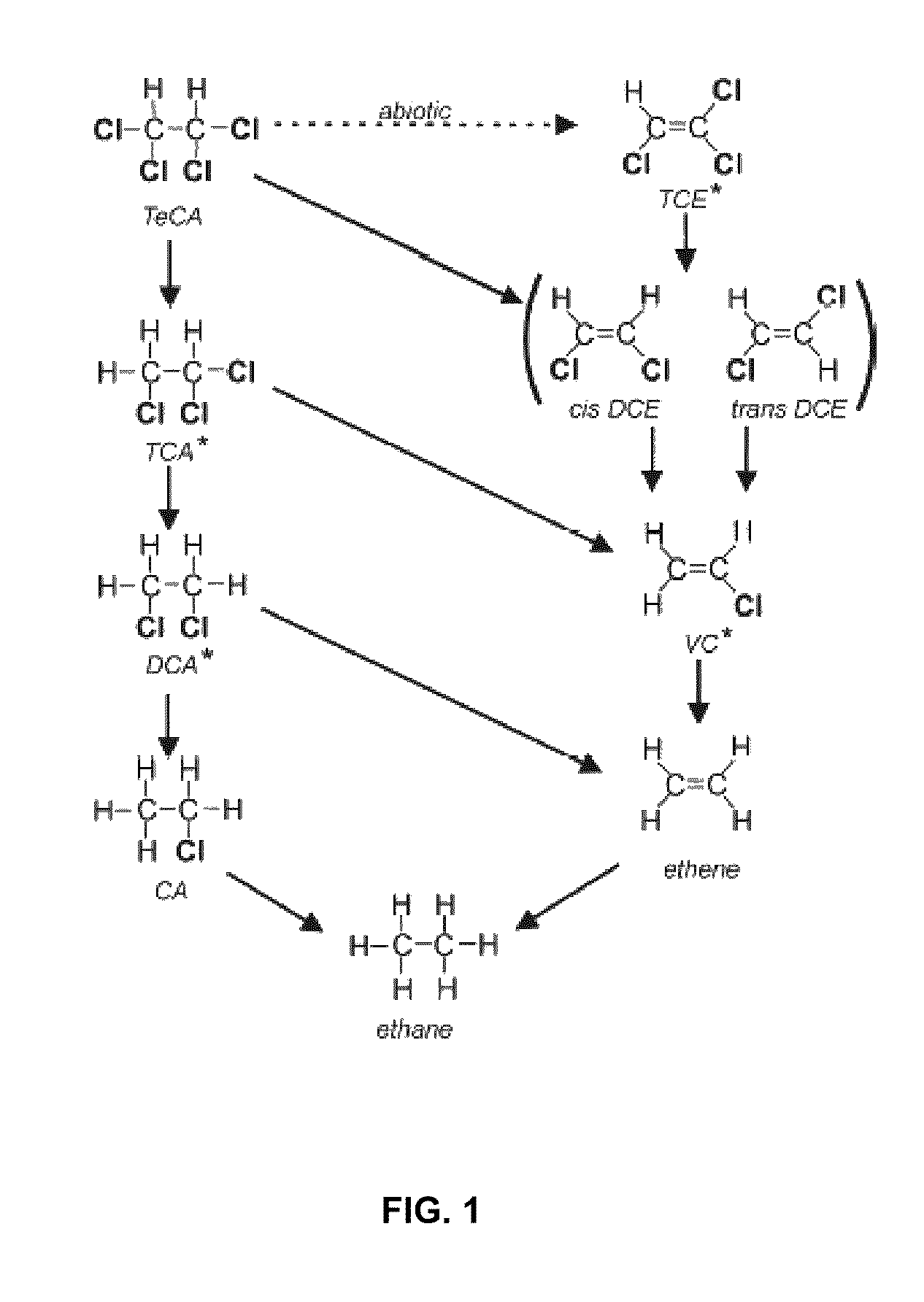
Proteobacteria is a major phylum of gram-negative bacteria. They include a wide variety of pathogens, such as Escherichia, Salmonella, Vibrio, Helicobacter, Yersinia, Legionellales, and many other notable genera.
Compositions of microbiota and methods related thereto
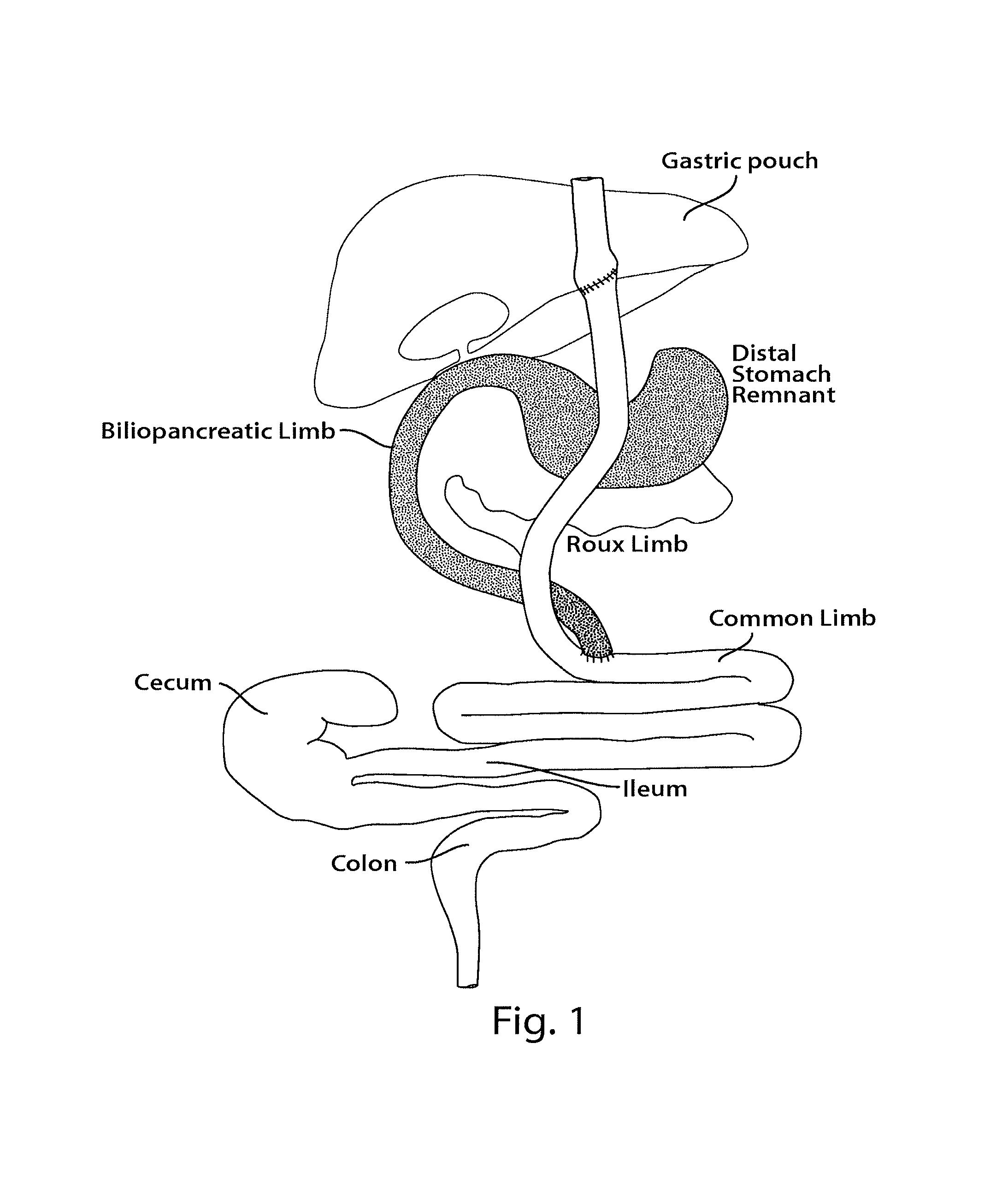
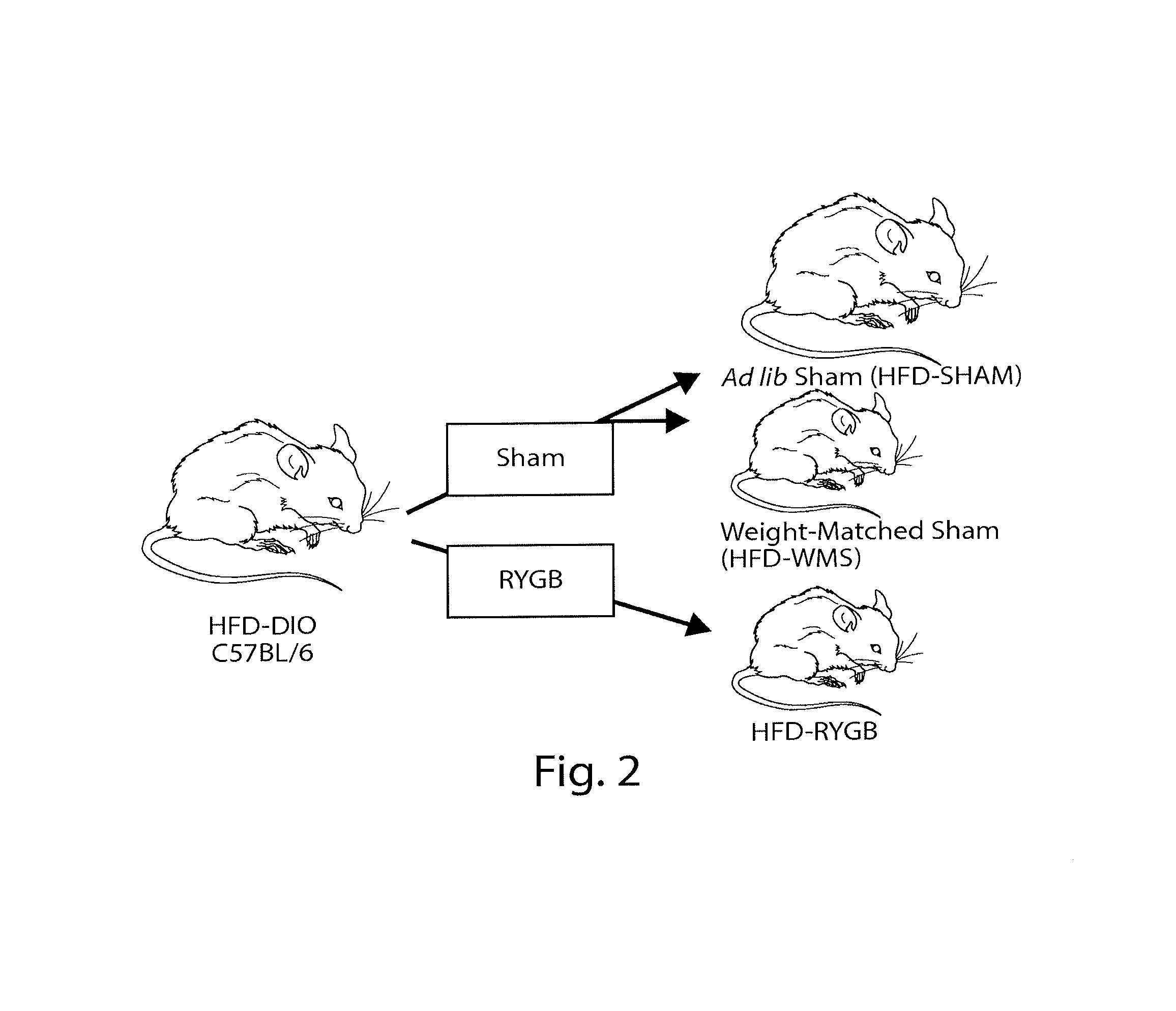
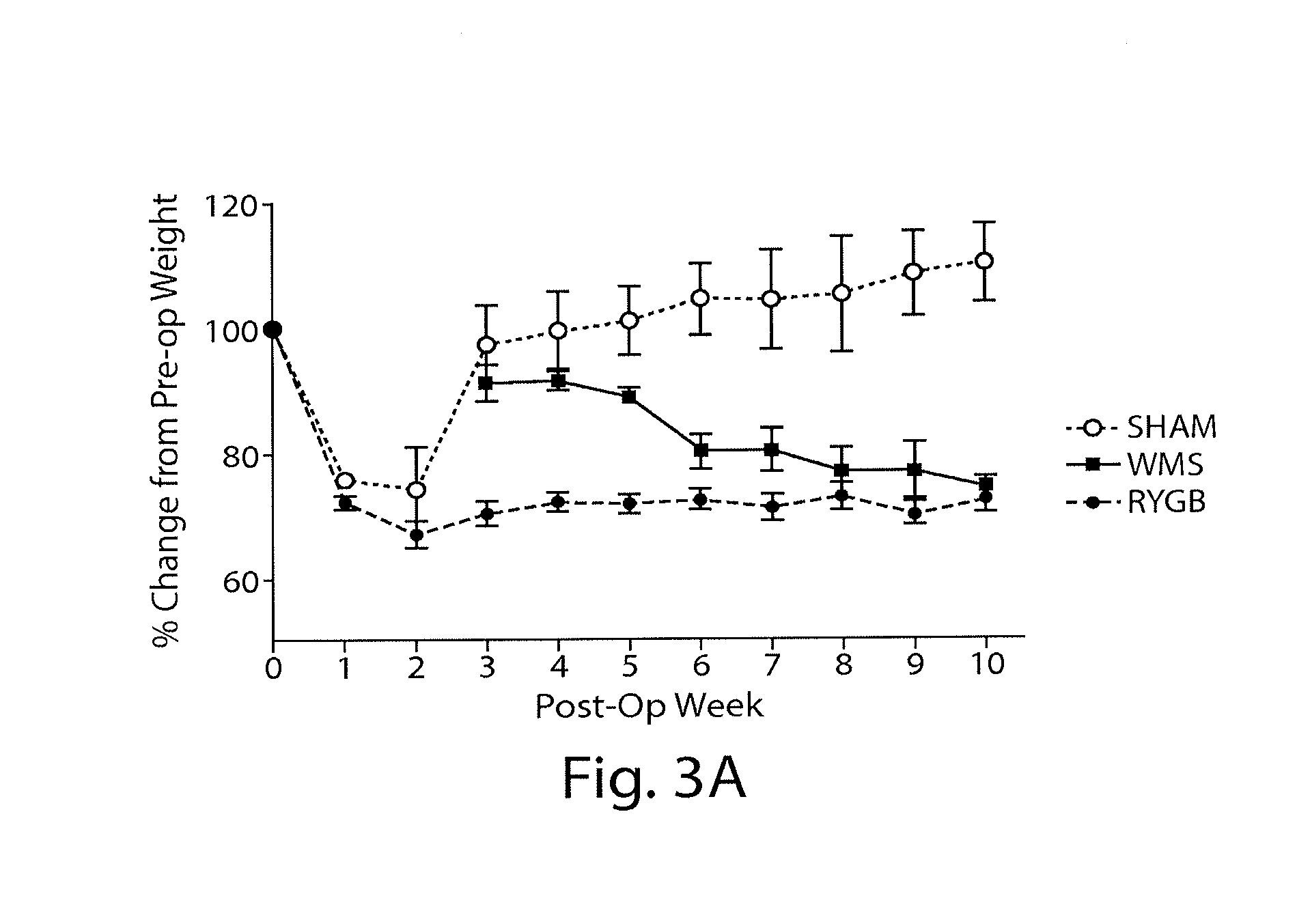
Methods and compositions are provided for treating weight related conditions and metabolic disorders by altering microbiota in a subject. One aspect provides methods and compositions to alter microbiota in a subject by administering to the subject a composition that includes a substantially purified microbiota from phyla such as Bacteroidetes, Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and Verrucomicrobia or orders such as Bacteroidales, Verrucomicrobiales, Clostridiales and Enterobacteriales or genera such as Alistipes, Clostridium, Escherichia, and Akkermansia. Another aspect includes a pharmaceutical composition for altering microbiota that includes a therapeutically effective amount of substantially purified microbiota and a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier. Yet another aspect includes methods for treating a disorder, such as obesity, in a subject in need of such treatment by changing relative abundance of microbiota in a gastrointestinal tract of the subject without or in addition to a surgical procedure.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
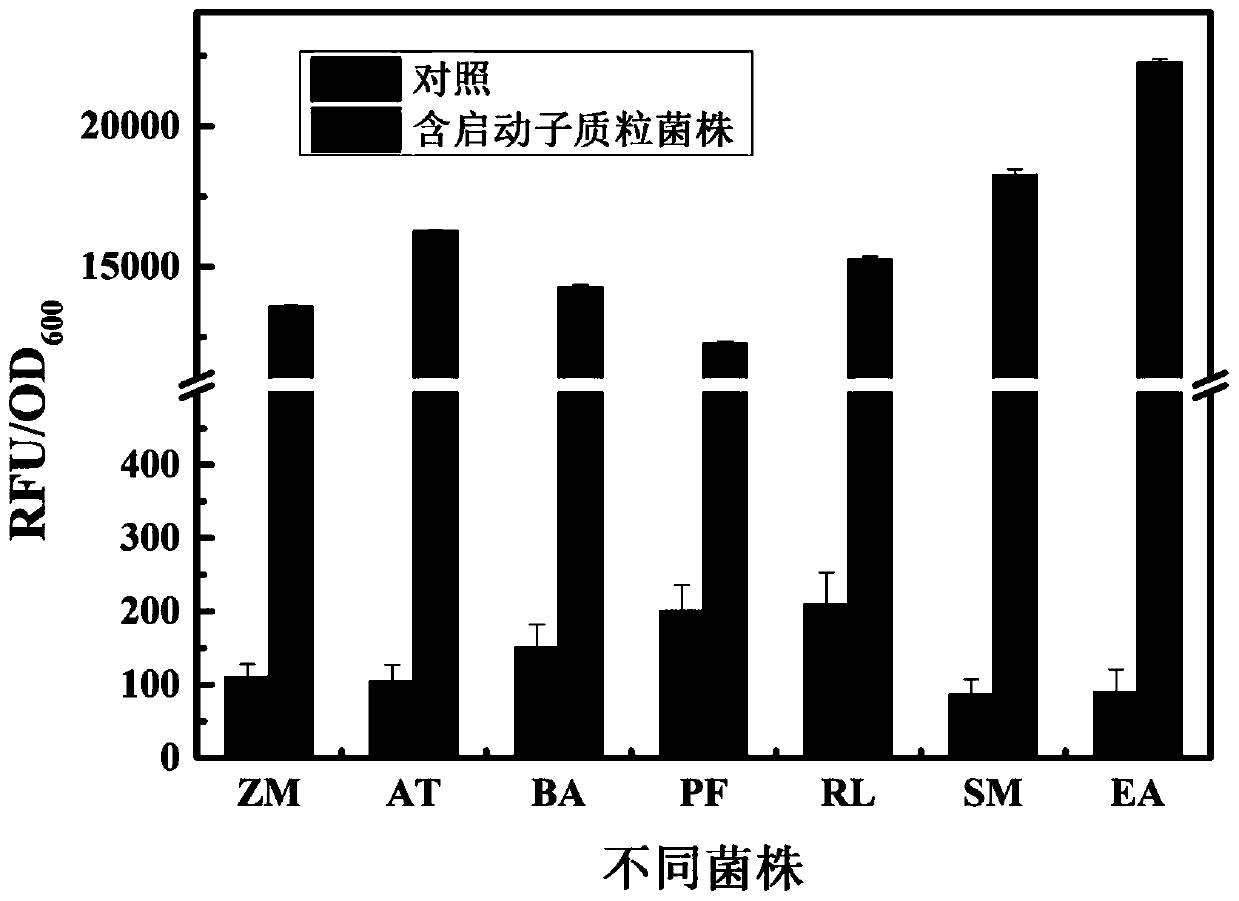
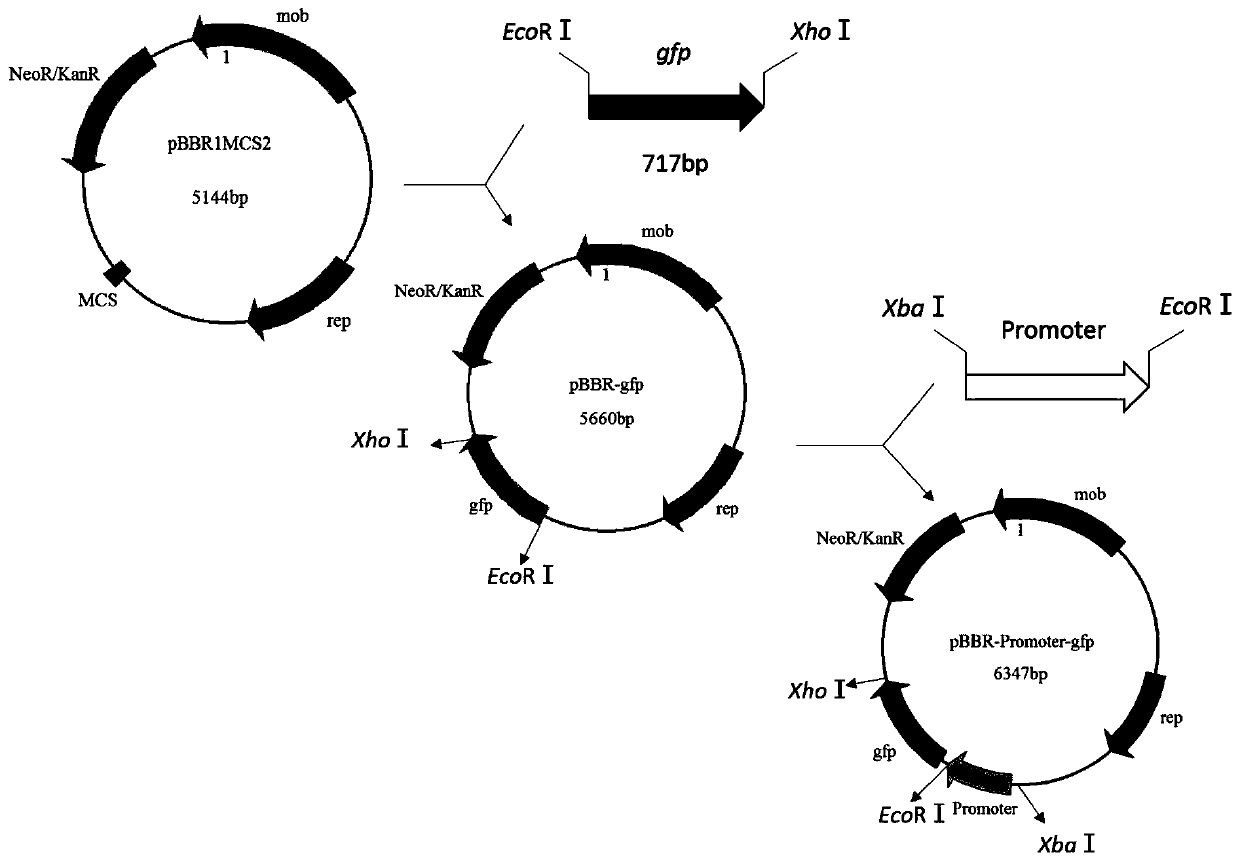
Strong promoter and plasmid vector containing strong promoter and application of strong promoter and plasmid vector
According to the invention, through amplifying a strong promoter in Ensifer adhaerens and carrying out bioinformatics analysis and functional verification, a strong promoter is obtained, and the strong promoter can be widely used for gene expression, genetic manipulation and strain improvement in Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum, Ensifer adhaerens and other alpha-proteobacteria and has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO: 1. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using the strong promoter, and an application of the corresponding strain and ahost cell in starting expression of a target gene.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
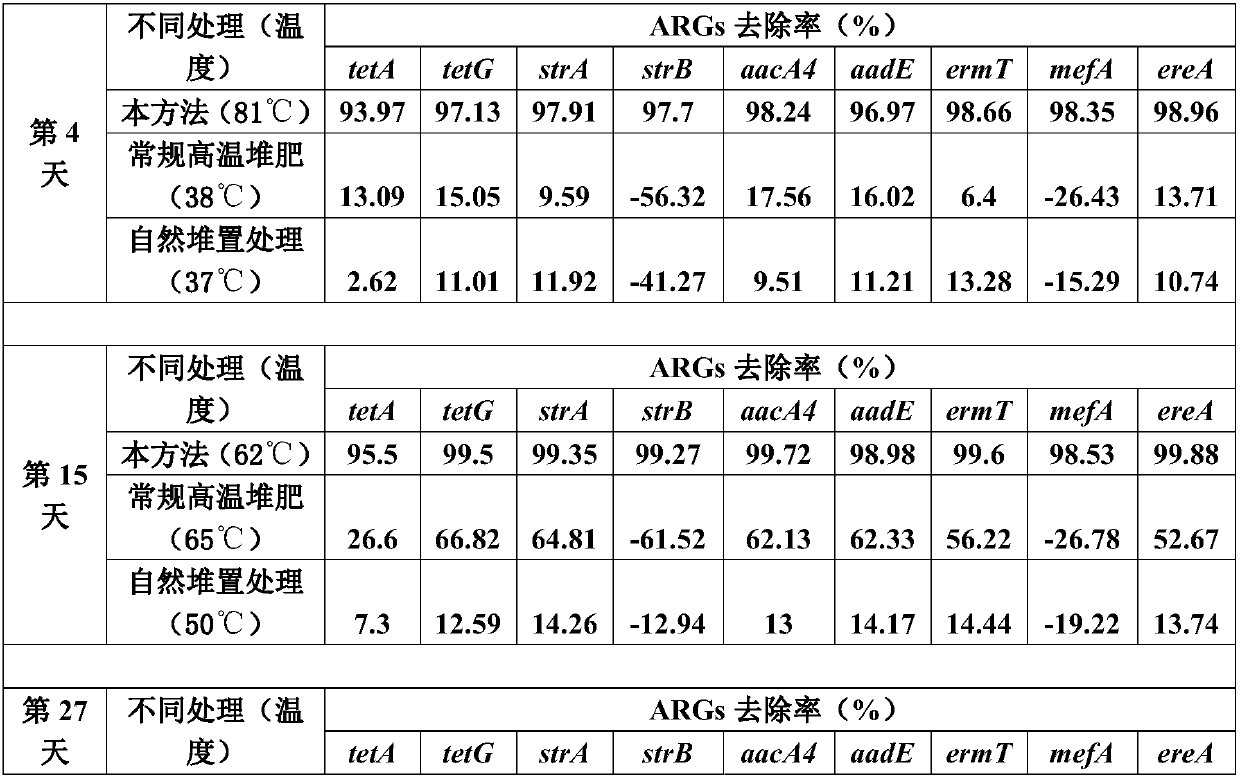
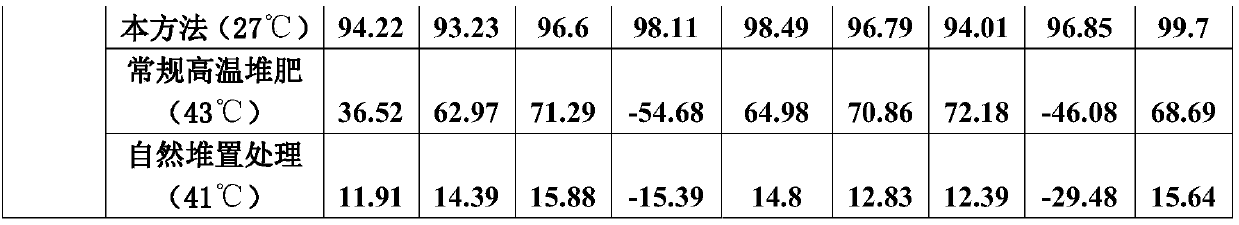
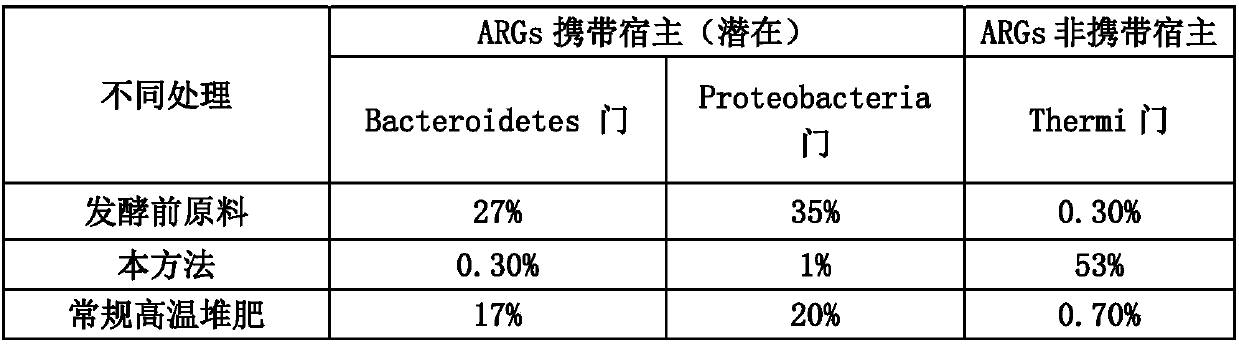
Method for quickly reducing antibiotics and resistance genes in organic solid waste
ActiveCN108033817AReduce the risk of gene transferNo reboundBio-organic fraction processingBacteriaGene transferBacteroidetes
The invention discloses a method for quickly reducing antibiotics and resistance genes in organic solid waste, and belongs to the field of organic solid waste treatment. The method has the advantagesthat ultrahigh-temperature aerobic fermentation is carried out on the organic solid waste by the aid of aerobic zymocyte capable of tolerating the temperatures of at least 80 DEG C under the conditionthat pile temperatures are not lower than 80 DEG C under the control for at least 5-7 days, and accordingly effects of quickly and stably reducing the antibiotics and the resistance genes in the organic solid waste can be realized; the antibiotics and the ARGs (antibiotic resistance genes) can be quickly degraded by means of ultrahigh-temperature aerobic fermentation, integral microbial communitystructures in piles further can be changed, 90% of microorganisms (mainly including Proteobacteria and Bacteroidetes) which carry the ARGs can be killed, risks of gene transfer of the ARGs can be reduced, diffusion of the ARGs can be controlled from the source, and the ARGs can be guaranteed against rebounding; the organic solid waste can be treated, and double effects of efficiently removing antibiotic residues and resistance gene pollution can be realized; exogenous heating can be omitted, energy can be produced only by the aid of metabolism of thermophilic microorganisms to reach the highfermentation temperatures, and accordingly the method is low in energy consumption and is environmentally friendly.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
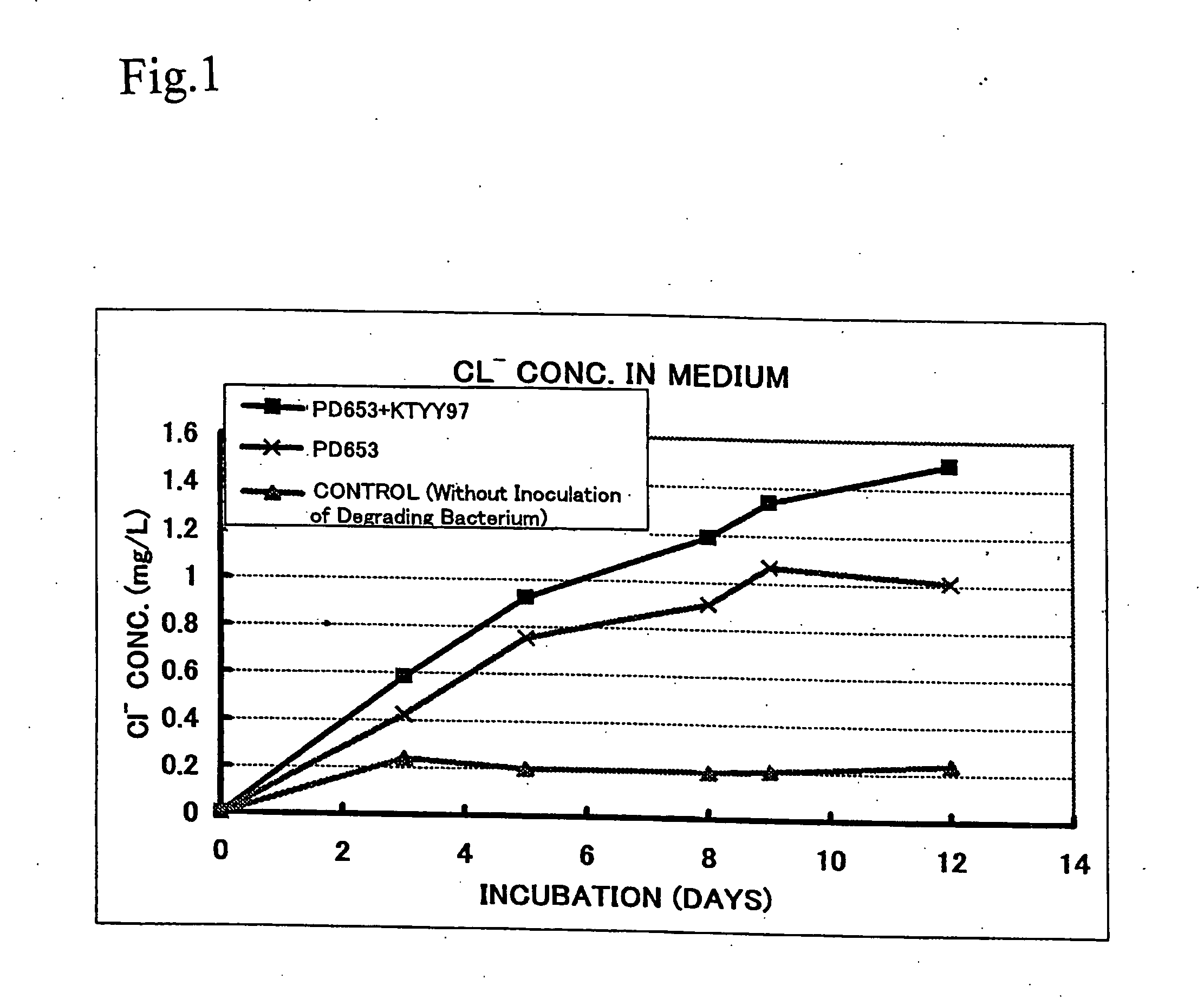
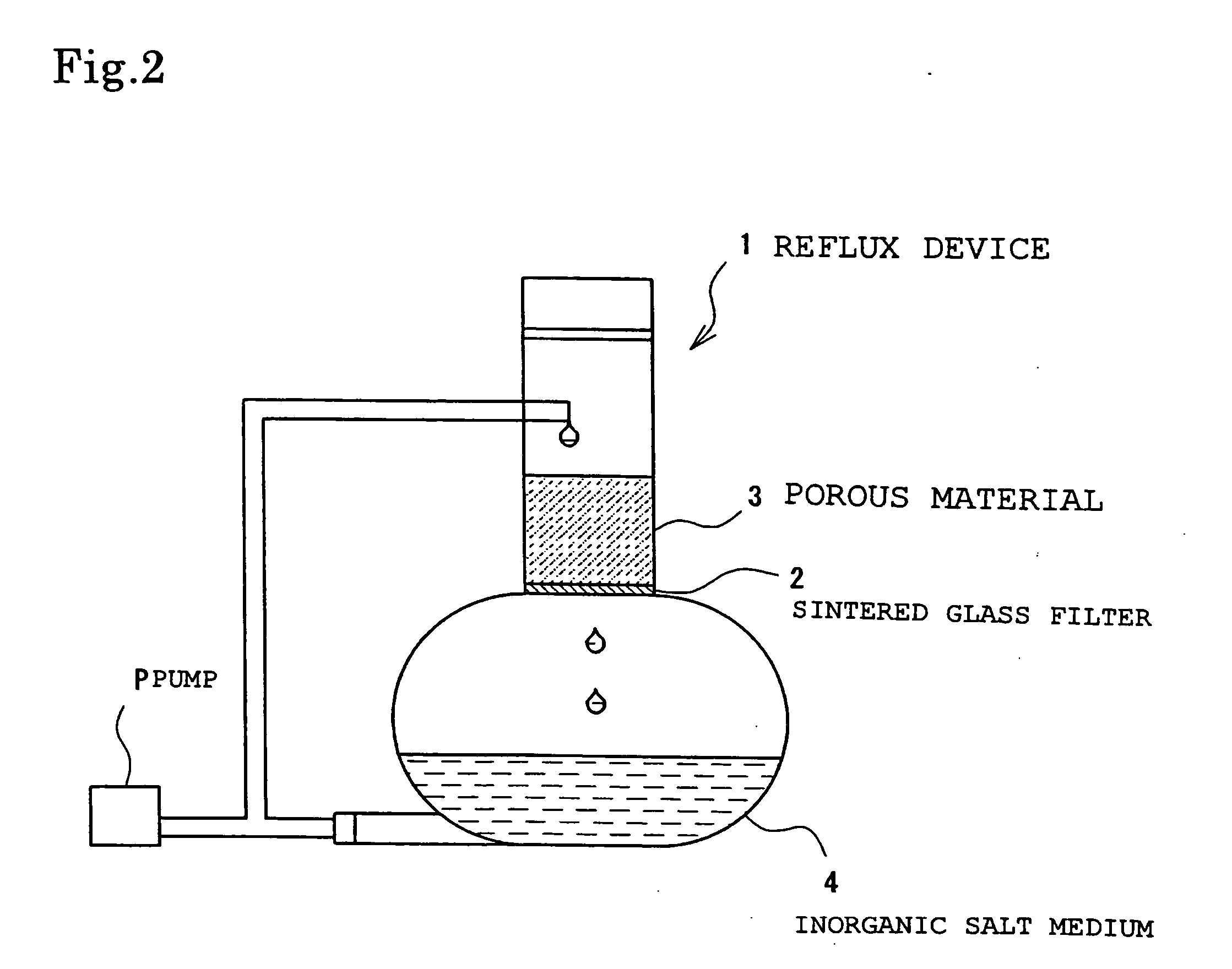
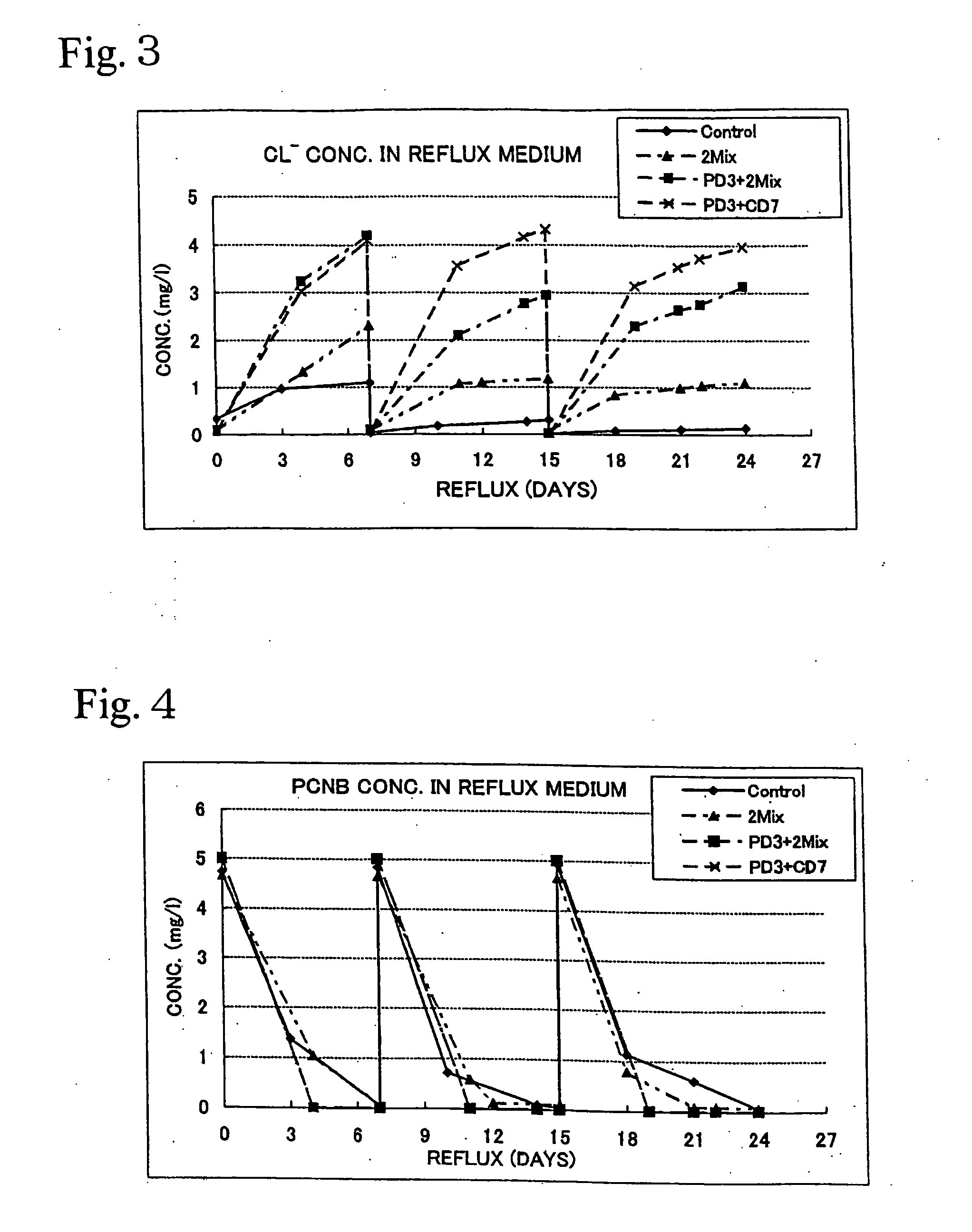
Support for holding a complexed enrichment of degrading bacteria and manufacturing method thereof, novel bacteria, and method of cleaning pollution environment and device thereof
InactiveUS20060166346A1Stability of complexEfficient decompositionBacteriaUnicellular algaeBacteroidesMicroorganism
The present invention provides a stable complex microbial system, which simultaneously decomposes a plurality of organic contaminants even under a polluted environment with these contaminants and permits more effective decomposition of persistent organic contaminants such as PCNB and simazine. A support for holding a complexed enrichment of degrading bacteria, which contains a porous material provided as a support on which degrading bacteria A capable of degrading at least one organic contaminant and degrading bacteria B capable of degrading another organic contaminant are enriched, is produced. The degrading bacteria A may be a PCNB-degrading bacteria, particularly degrading bacteria containing degrading bacteria having part or all of the bacteriological characteristics of Nocardioides sp. PD653 and the degrading bacteria B may be degrading bacteria containing degrading bacteria having part or all of the bacteriological characteristics of β-Proteobacteria CDB21.
Owner:NAT INST FOR AGRO ENVIRONMENTAL SCI INDEPENDENT ADMINISTRATIVE INST +2
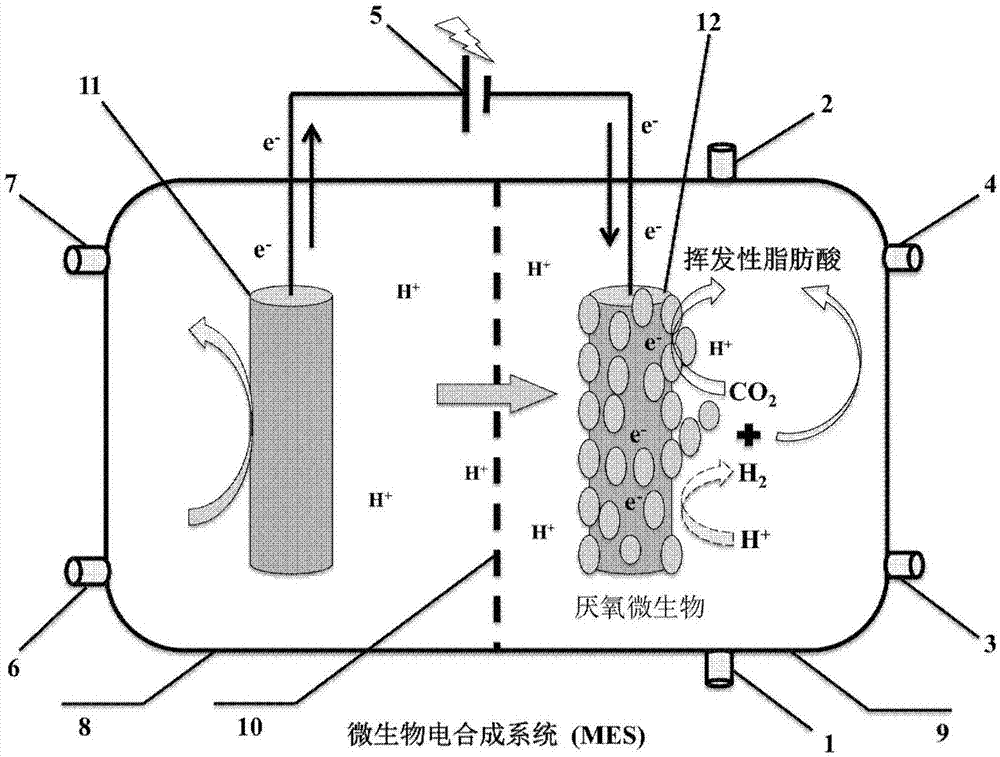
Method for achieving recycling of carbon dioxide through microbial electro-synthesis system
InactiveCN107354478AIncrease productionCellsElectrolytic organic productionElectricityMicrobial electrosynthesis
The invention provides a method for achieving recycling of carbon dioxide through a microbial electro-synthesis system. According to the method for achieving recycling of the carbon dioxide through the microbial electro-synthesis system, a mixed anaerobe serves as a cathode, the mixed anaerobe comprises Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes. The invention further provides a microbial electro-synthesis system device. The microbial electro-synthesis system device comprises at least an anode and at least a cathode, wherein the mixed anaerobe serves as the cathode, the mixed anaerobe comprises Proteobacteria, Firmicutes and Bacteroidetes. The method for achieving recycling of the carbon dioxide through the microbial electro-synthesis system and the microbial electro-synthesis system device can achieve that the carbon dioxide is reduced into volatile fatty acid by taking use of common electrode materials, the cost is saved, and meanwhile, substances with high added values are generated by taking use of and domesticating an enriched mixed bacterial system, so that the good effects are achieved on the three aspects of the environment, the energy and the resources.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Anaerobic Microbial Composition and Methods of Using Same
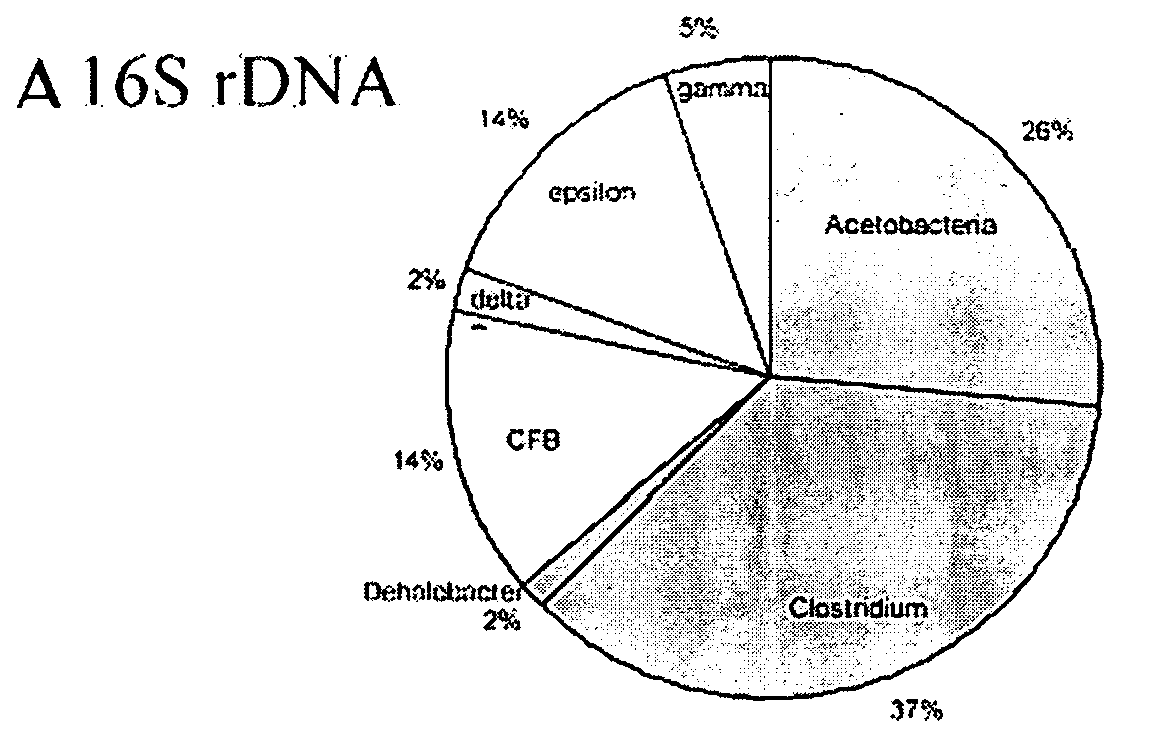
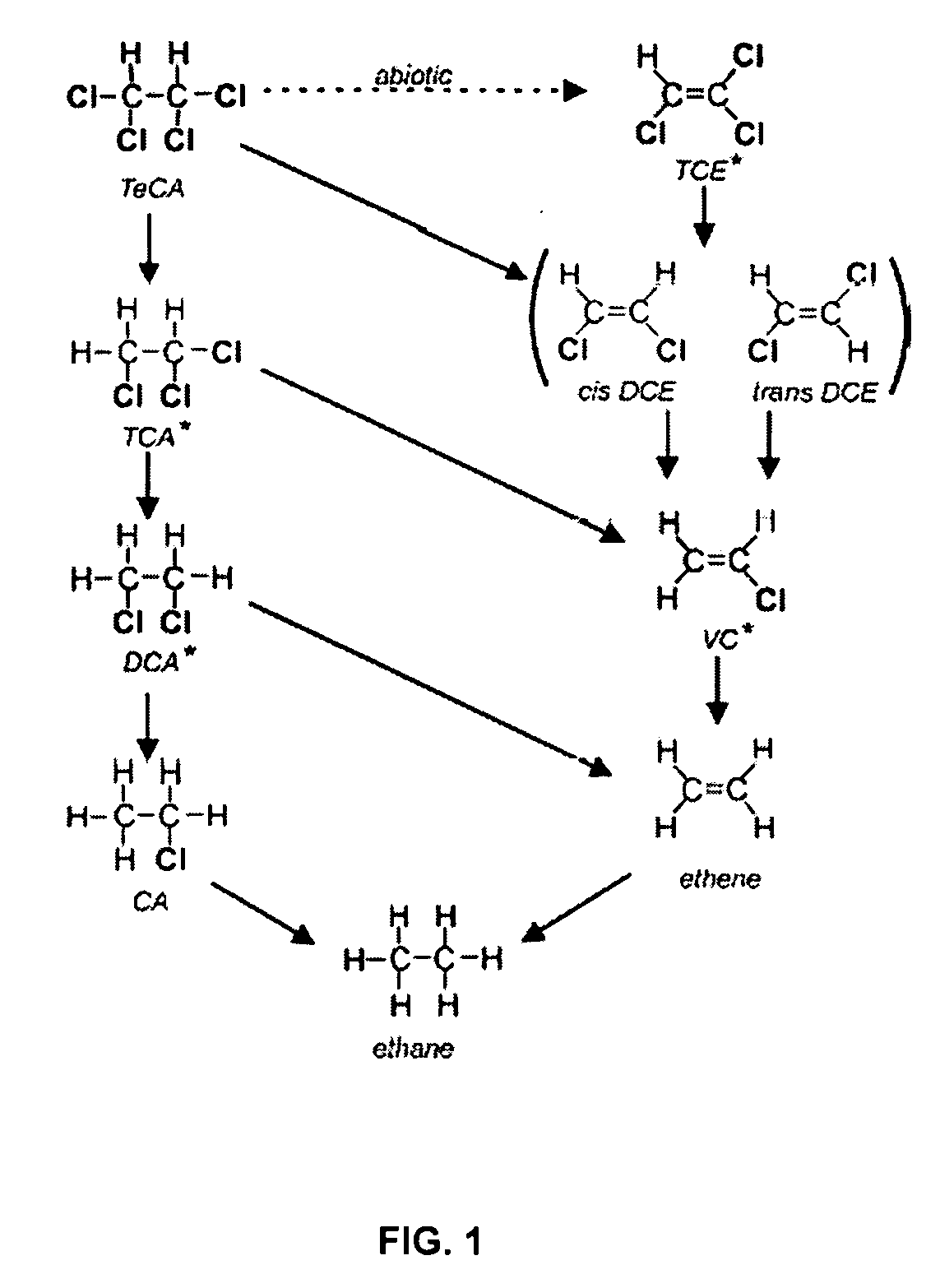
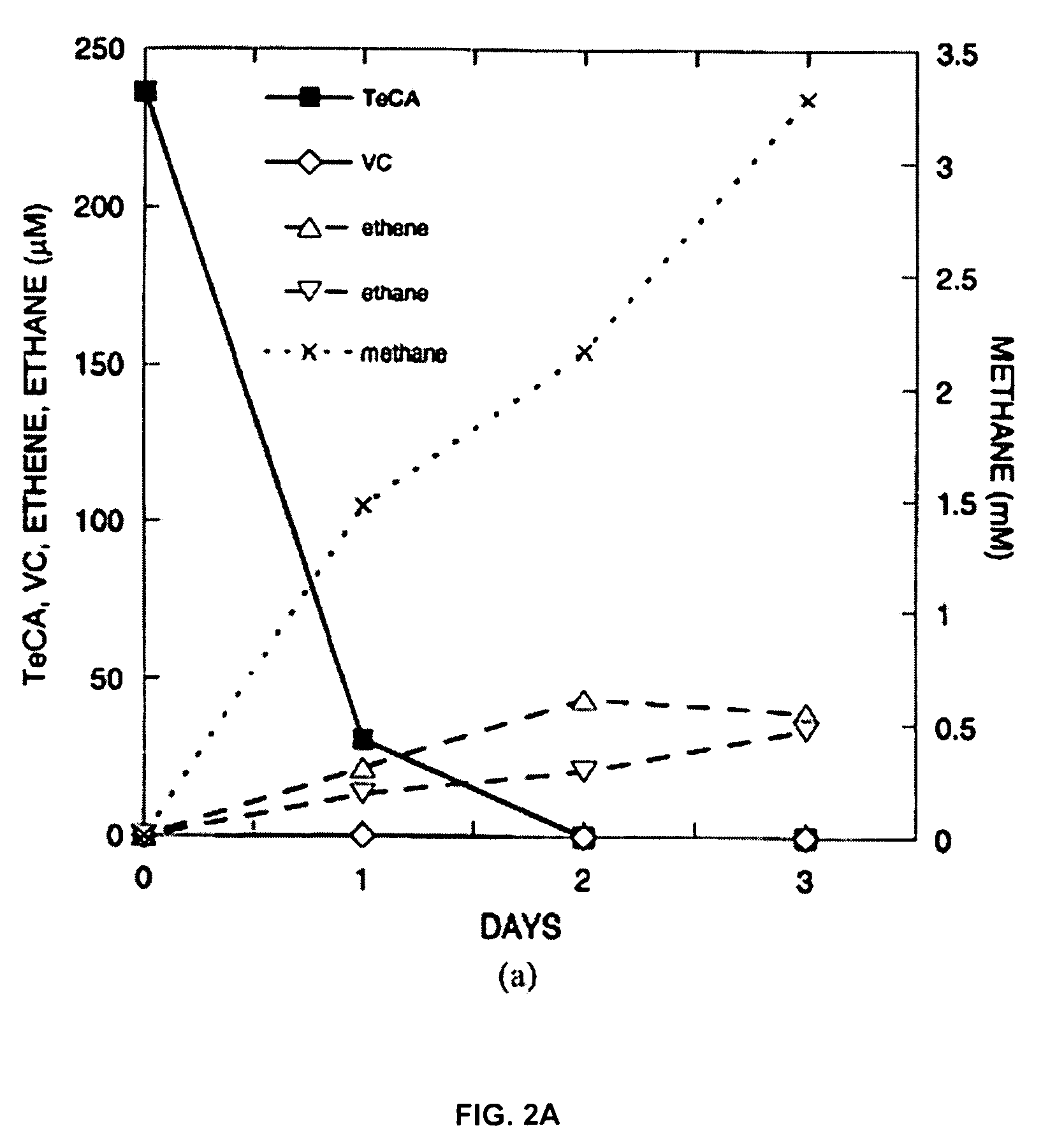
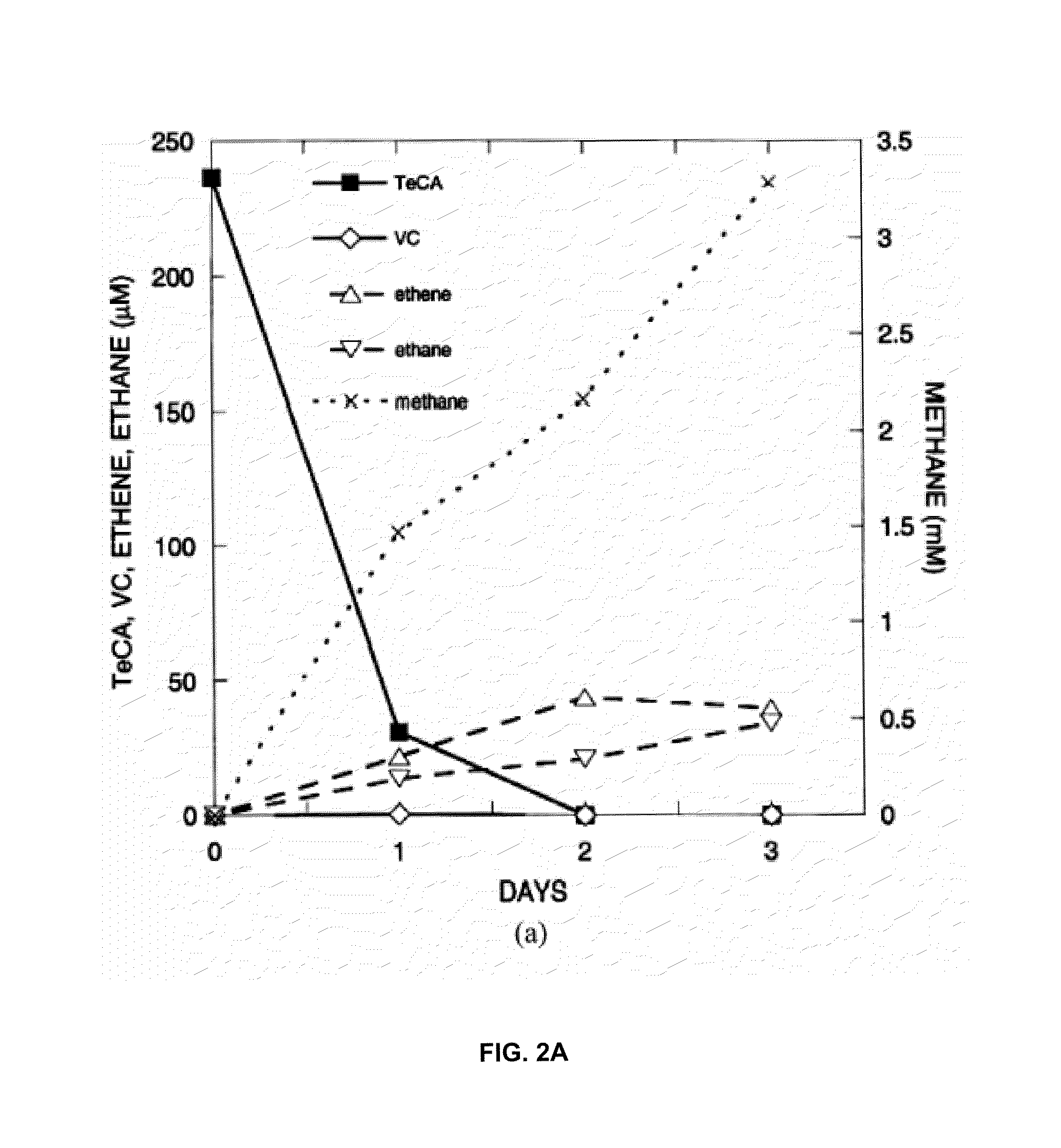
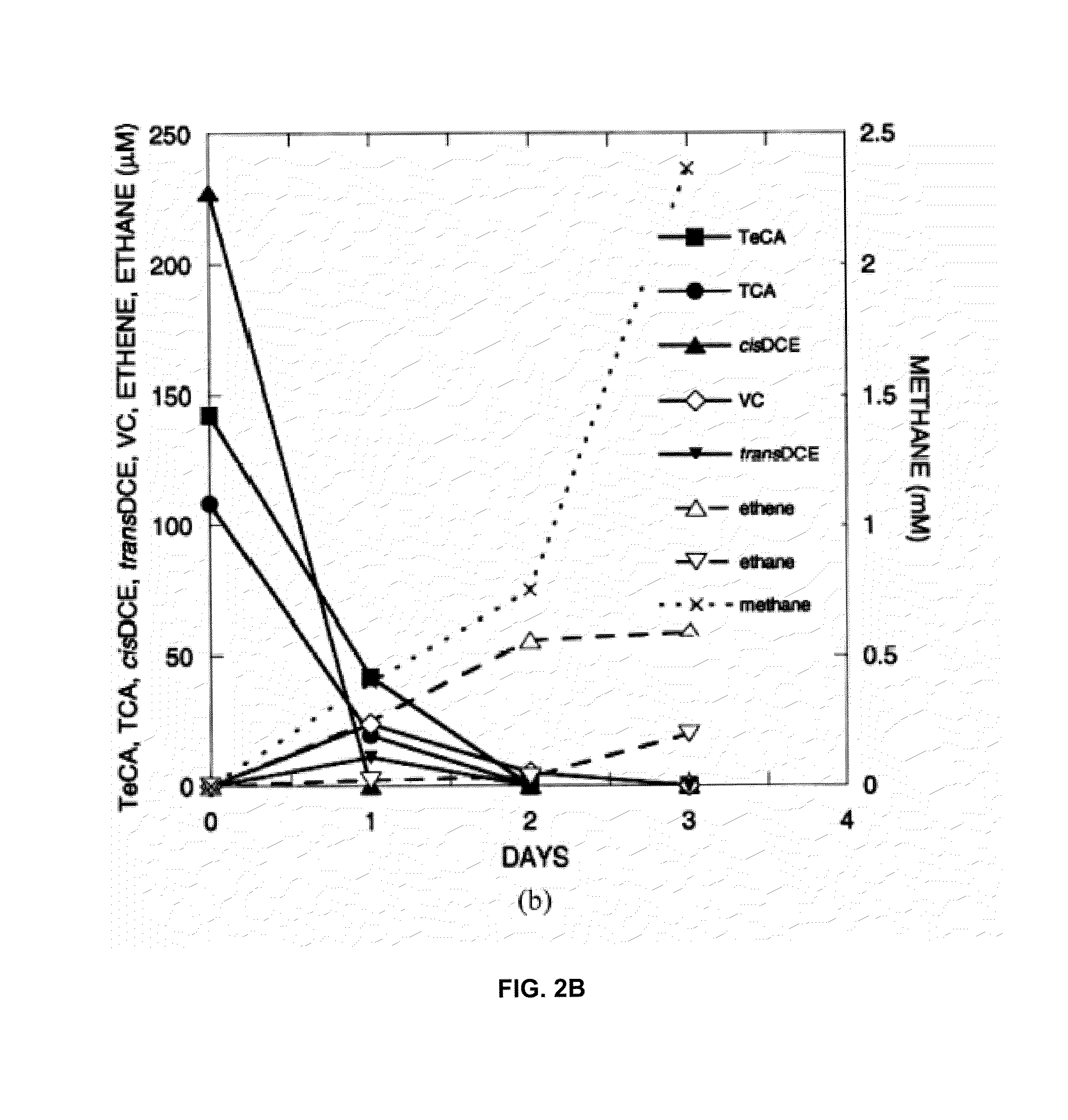
A microbial composition for concurrent dechlorination of a mixture of chlorinated ethanes and chlorinated ethenes includes a isolated consortium of bioremediative microorganisms comprising strains of microorganism comprising Clostridium, Acetobacterium, Dehalobacter, Bacteroides, and Proteobacteria. The composition may also include Methanomicrobia.
Owner:USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE UNITED STATES DEPT OF INTERIOR +1
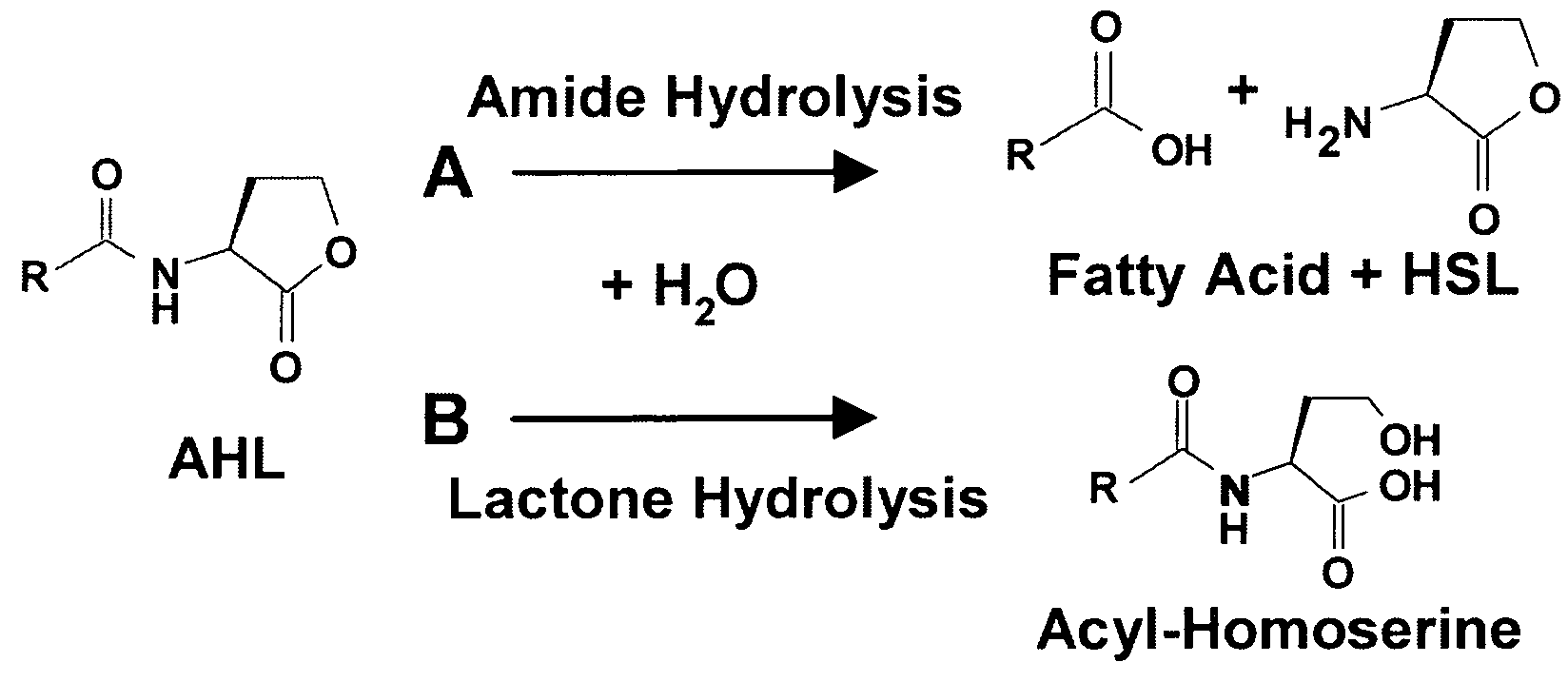
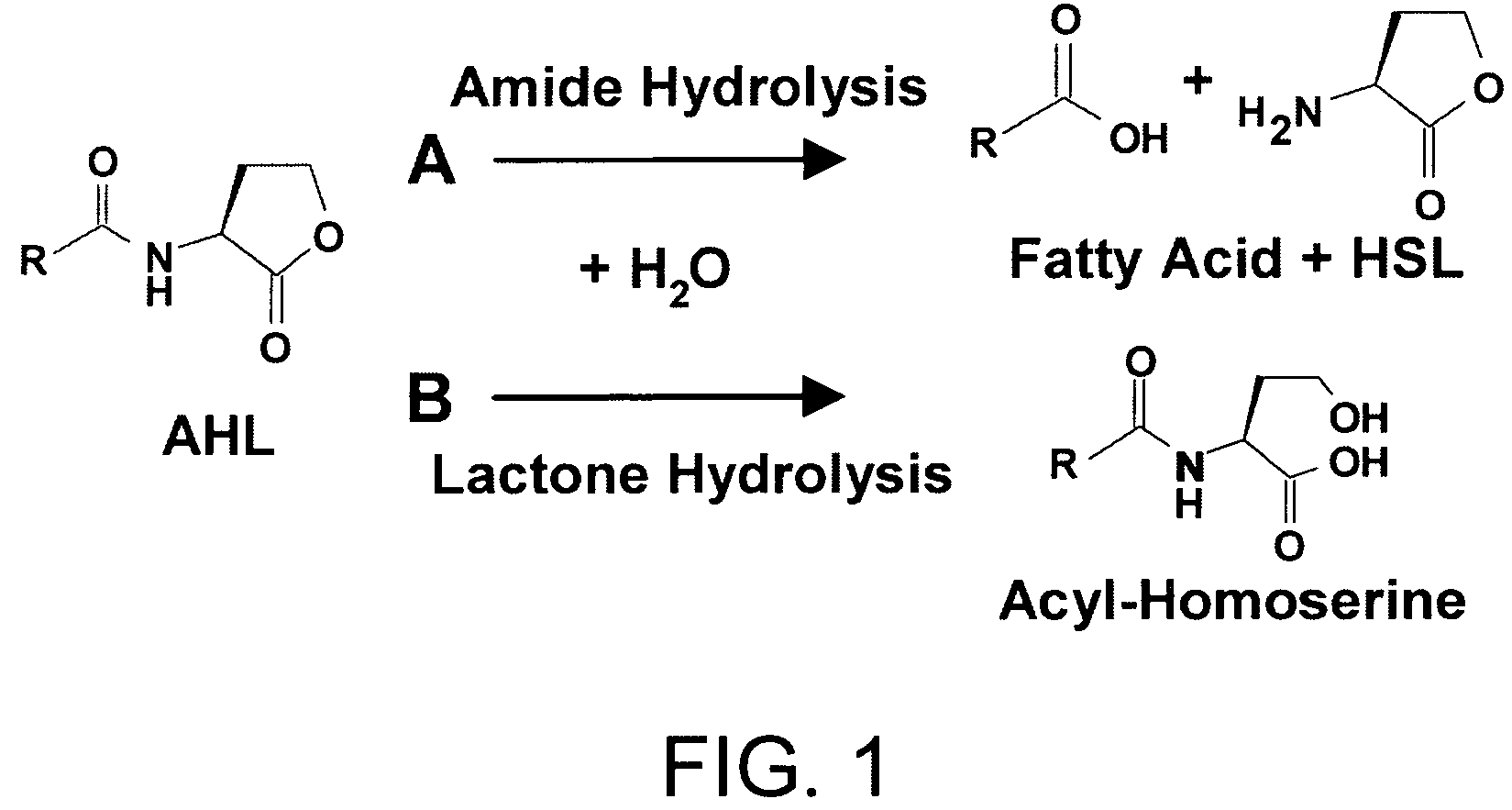
Method of identifying agents that inhibit quorum sensing activity of gamma-proteobacteria
InactiveUS7335352B1High throughput screeningImprove throughputBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesGamma proteobacteria
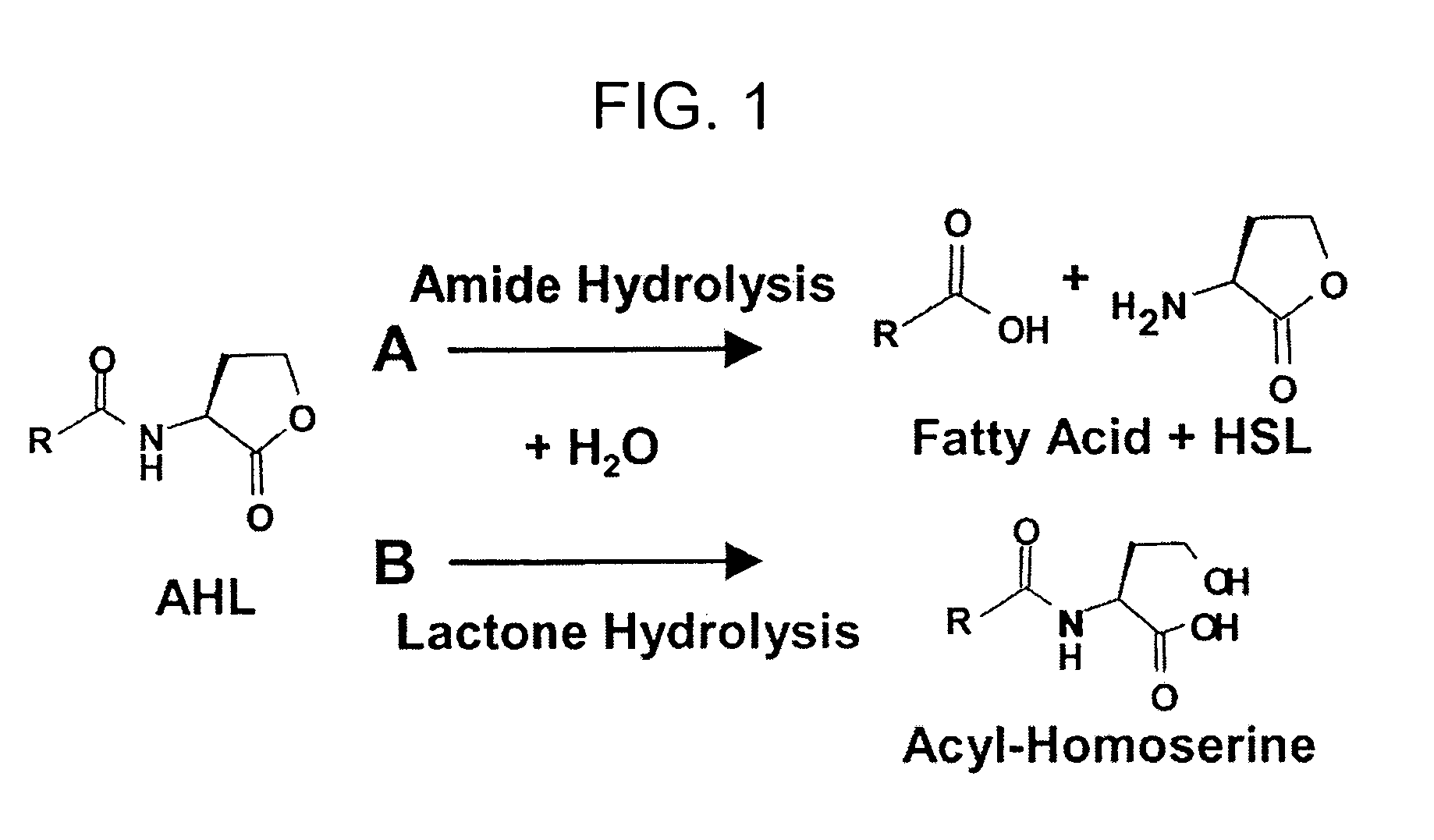
Screening assays that allow for the identification of agents that increase acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) acylase expression and / or AHL acylase activity in γ-proteobacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Such agents are useful, for example, for inhibiting quorum sensing activity of such bacteria by increasing degradation of long chain, but not short chain, AHLs and, therefore, can be useful for treating infections by such bacteria.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Preparation method of controllably degraded O-carboxymethyl cinnamaldehyde-modified chitosan antibacterial film
The invention discloses a preparation method of a controllably degraded O-carboxymethyl cinnamaldehyde-modified chitosan antibacterial film. The preparation method comprises (1) preparation of carboxymethyl chitin, (2) preparation of O-carboxymethyl chitosan through carboxymethyl chitin deacetylation, (3) preparation of O-carboxymethyl cinnamaldehyde-modified chitosan, and (4) preparation of the controllably degraded antimicrobial film. The controllably degraded film has salmonella, escherichia coli, staphylococcus aureus and aspergillus niger inhibition activity better than those of single chitosan and the traditional cinnamaldehyde-modified chitosan antibacterial film, has good physical properties and breathability and a controllable degradation rate, can be widely used in fields of agriculture, medicines and food packaging preservation and antibiosis. The preparation method is simple, is easy to operate and has good practicability.
Owner:南通药享科技有限公司
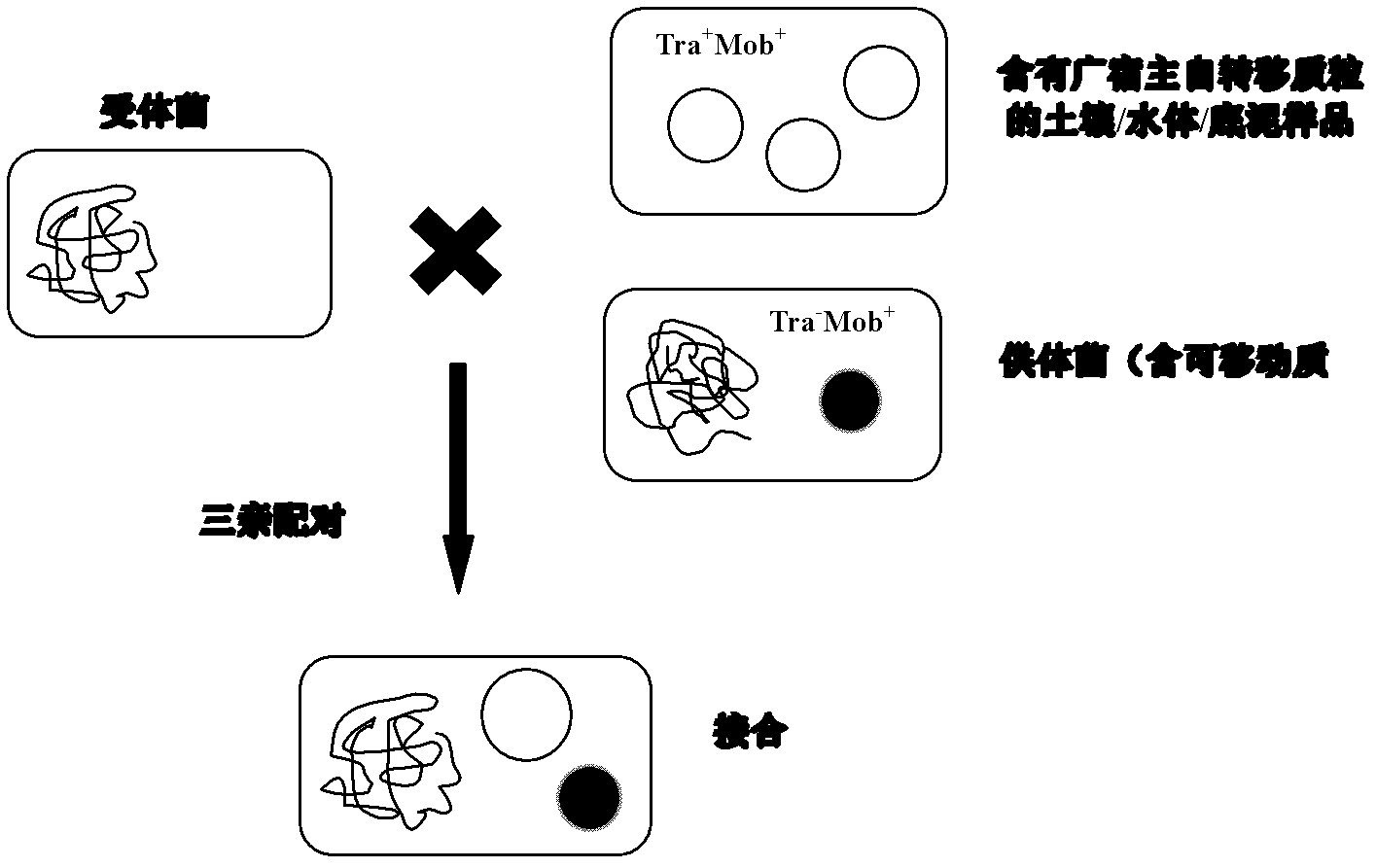
Method for screening self-transmissible broad host range plasmid carrying petroleum hydrocarbon degrading gene by utilizing triparental pairing conjugation and single carbon source of petroleum hydrocarbon
The invention relates to an intersecting field of biotechnology and bioremediation technology of polluted soil and specifically provides a method for screening self-transmissible broad host range plasmids carrying a petroleum hydrocarbon degrading gene by utilizing triparental pairing conjugation and a single carbon source of petroleum hydrocarbon. Different Proteobacteria subclass receptor bacteria with selected marker on chromosome, a donor bacterium carrying non-self-transmissible (Tra-Mob+) plasmid with selected marker and a sample are treated with triparental pairing conjugation; plasmids of the donor bacterium enter receptor bacteria with assistance of self-transmissible (Tra+Mob+) broad host range plasmids in the sample; zygosperms are screened through receptor bacteria and selected markers carried by the donor bacterium plasmids; the screened zygosperms containing self-transmissible broad host range plasmids are cultured in a medium using the single carbon source of petroleum hydrocarbon; and broad host range plasmids capable of degrading petroleum hydrocarbon are screened out. The triparental pairing conjugation provided by the invention can directly separate broad host range plasmids capable of degrading normal octane, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon naphthalene, fluorenes and phenanthrene from petroleum polluted soil, so as to provide heredity material for furtherly employing the plasmids to carry out bioremediation on polluted soil.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
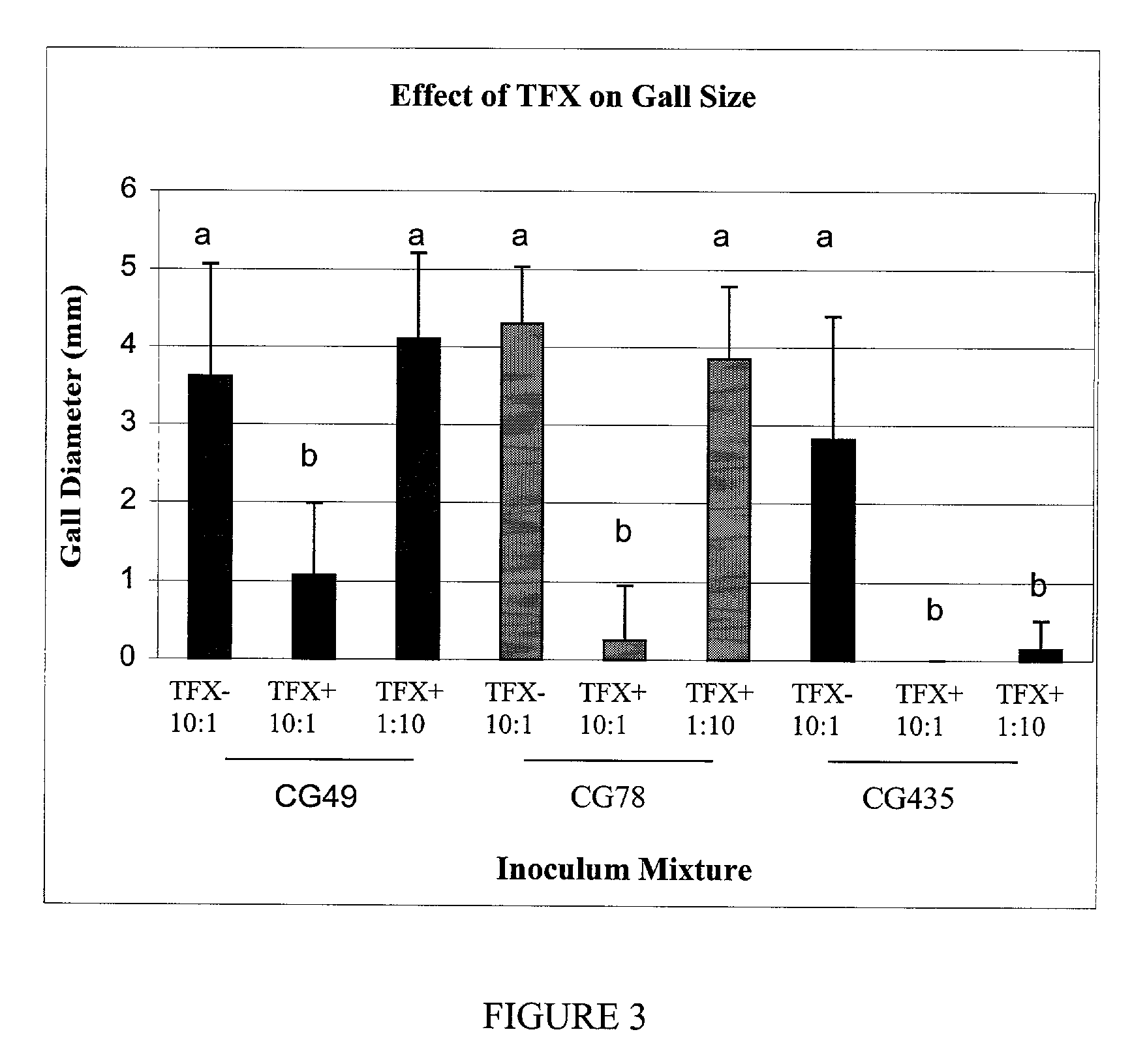
Biological control of crown gall disease
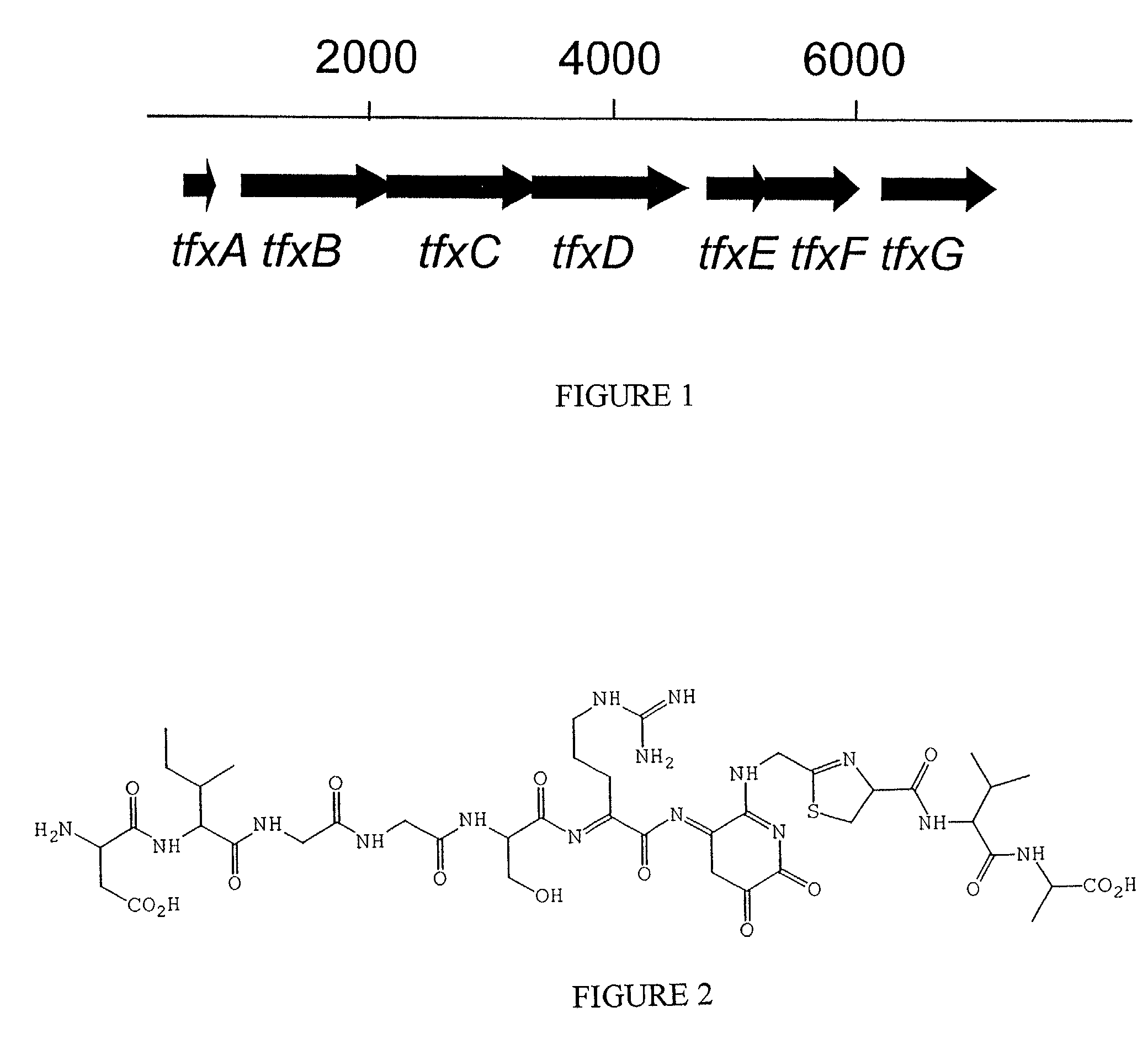
The present invention provides a method for controlling crown gall disease in plants using an effective quantity of α-proteobacteria that produces trifolitoxin (TFX). The present invention also provides a biocontrol agent for use in the above method, and a plant coated with the biological control agent. The biocontrol agent is characterized as a biologically pure culture of an α-proteobacteria strain that produces TFX, or an α-proteobacteria strain genetically engineered to produce TFX. The α-proteobacteria strain employed may include any one of the many strains of Agrobacterium capable of producing crown galls, including Agrobacterium vitis and, in particular, A. vitis F2 / 5. The α-proteobacteria strain employed may be genetically engineered to produce TFX by introducing a genetic construct into the Agrobacterium so as to cause the Agrobacterium to carry and express the tfx operon from Rhizobium. The bacteria may also be genetically engineered to produce TFX by introducing a pT2TFXK plasmid into the Agrobacterium. The biocontrol agent may also be the strain Agrobacterium vitis F2 / 5 (pT2TFXK), ATCC Patent Deposit Designation PTA-2356.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method of Identifying Agents that Inhibit Quorum Sensing Activity of Gamma-Proteobacteria
InactiveUS20080220978A1Improve throughputHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary screeningGamma proteobacteriaBacteroides
Screening assays that allow for the identification of agents that increase acyl homoserine lactone (AHL) acylase expression and / or AHL acylase activity in γ-proteobacteria such as Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Such agents are useful, for example, for inhibiting quorum sensing activity of such bacteria by increasing degradation of long chain, but not short chain, AHLs and, therefore, can be useful for treating infections by such bacteria.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Terephthalic acid producing proteobacteria
InactiveUS6461840B1More cost-effectivelyHarmful wasteBacteriaFermentationBacteroidesBacterial strain
This invention relates to a biocatalytic process to produce terephthalic acid and isophthalic acid from p-xylene and m-xylene, respectively. Terephthalic acid has been prepared by oxidizing p-xylene with bacteria belonging to the genus Burkholderia. Conversion of p-xylene into terephthalic acid is accomplished by a single bacterial strain that produces all of the requisite enzymes. In addition, this invention relates to the preparation of isophthalic acid from a mixture of m- and p-xylene.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Klebsiella pneumoniae, bacterium agent of klebsiella pneumoniae and preparation method and application
InactiveCN106754497AReduce manufacturing costLow production costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGamma proteobacteriaBacteroides dorei
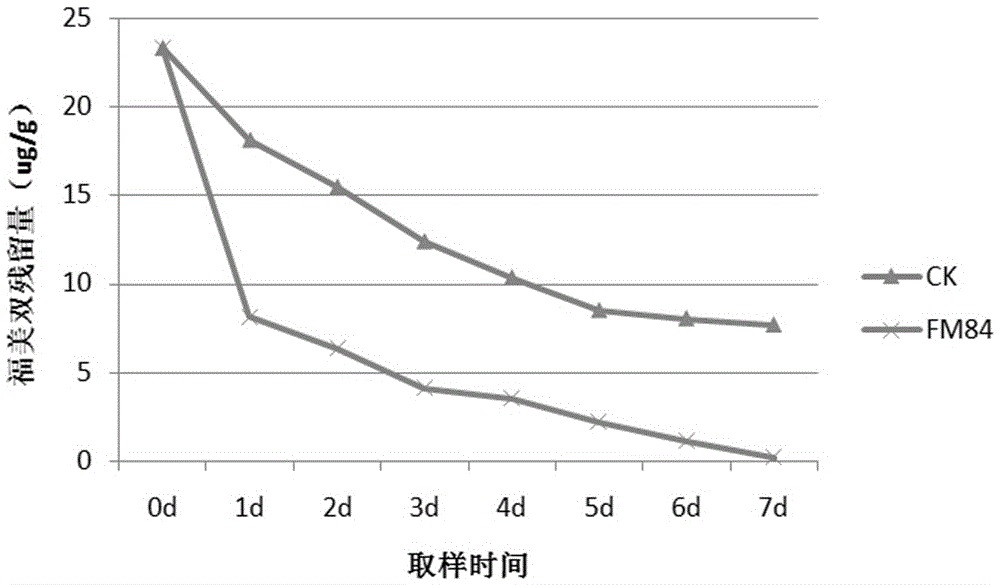
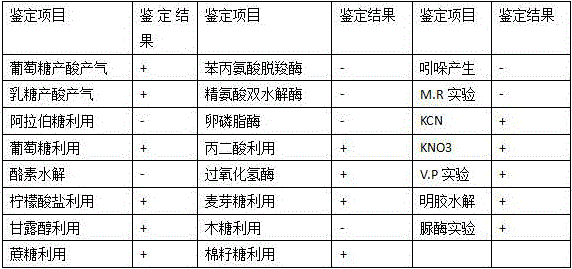
The invention discloses Klebsiella pneumoniae, a bacterium agent of the Klebsiella pneumoniae and a preparation method and application. The Klebsiella pneumoniae FM84 is a thiram degradation bacterium; the preservation unit is China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC); the preservation date is December 15, 2015; the preservation number is CGMCC N0. 11663; the Klebsiella pneumoniae belongs to bacteria, proteobacteria, gamma-proteobacteria, enterobacteriales, enterobacteriaceae and Klebsiella. The bacterium agent with the Klebsiella pneumoniae as an active ingredient is a bacterium agent prepared by activating the Klebsiella pneumoniae FM84 through strains, culturing seeds, producing and culturing and preparing with a preparation. The preparation method comprises an activation culture step and a fermentation culture step; the invention provides application of the bacterium agent to preparation of agricultural plants capable of degrading thiram. The bacterium agent comprising the strains has a simple preparation process, is low in cost and convenient to use, and has very good application prospect.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Use of mussel polysaccharides and degradation products thereof
ActiveCN109090620ARaw materials are easy to getObvious prebiotic effectOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemBacteroidesIntestinal microorganisms
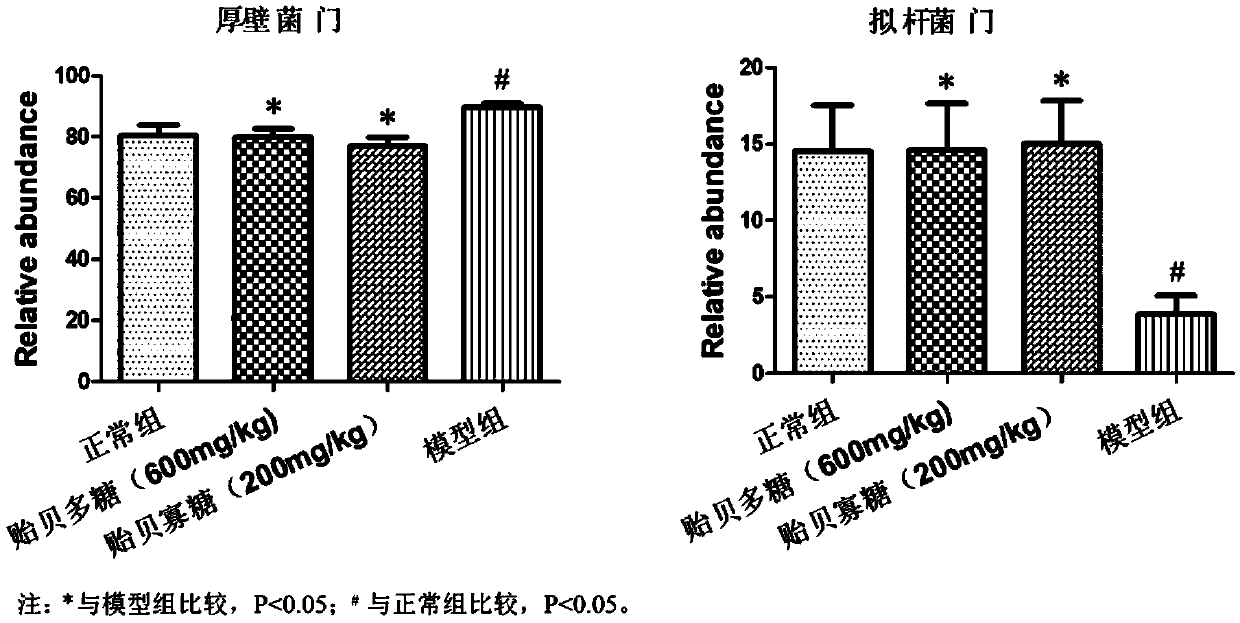
The invention provides use of mussel polysaccharides and degradation products thereof for regulating intestinal microflora, and use of preparation of a food, a health food or a medicine for regulatingintestinal microflora of a human body and feed or a medicine for regulating intestinal microflora of animals. A food, a health food, feed and a medicine containing the mussel polysaccharides and thedegradation products thereof are provided. The mussel polysaccharides have a molecular weight ranging from 2 KDa to 400 KDa. The degradation product is mussel polysaccharides, the molecular weight range is 300 Da to 2 KDa, and the degree of polymerization is 2-10. The mussel polysaccharides serving as a prebiotic raw material are extracted from the marine animal mussel, the source of the raw material is rich, the production and preparation costs are low, the proportion of the phylum firmicutes of obese model rats can be significantly reduced, the proportion of bacteroides is improved, and themussel polysaccharides play a role of improving intestinal microecology and is a novel prebiotic.
Owner:SHANDONG ACADEMY OF PHARMACEUTICAL SCIENCES +1
Method for regulating microbial denitrifying florae on basis of combination of powdered activated carbon and organic matter
PendingCN108178324AAdapt and stabilizeRaise the ratioBacteriaWater contaminantsActivated sludgeCommunity structure
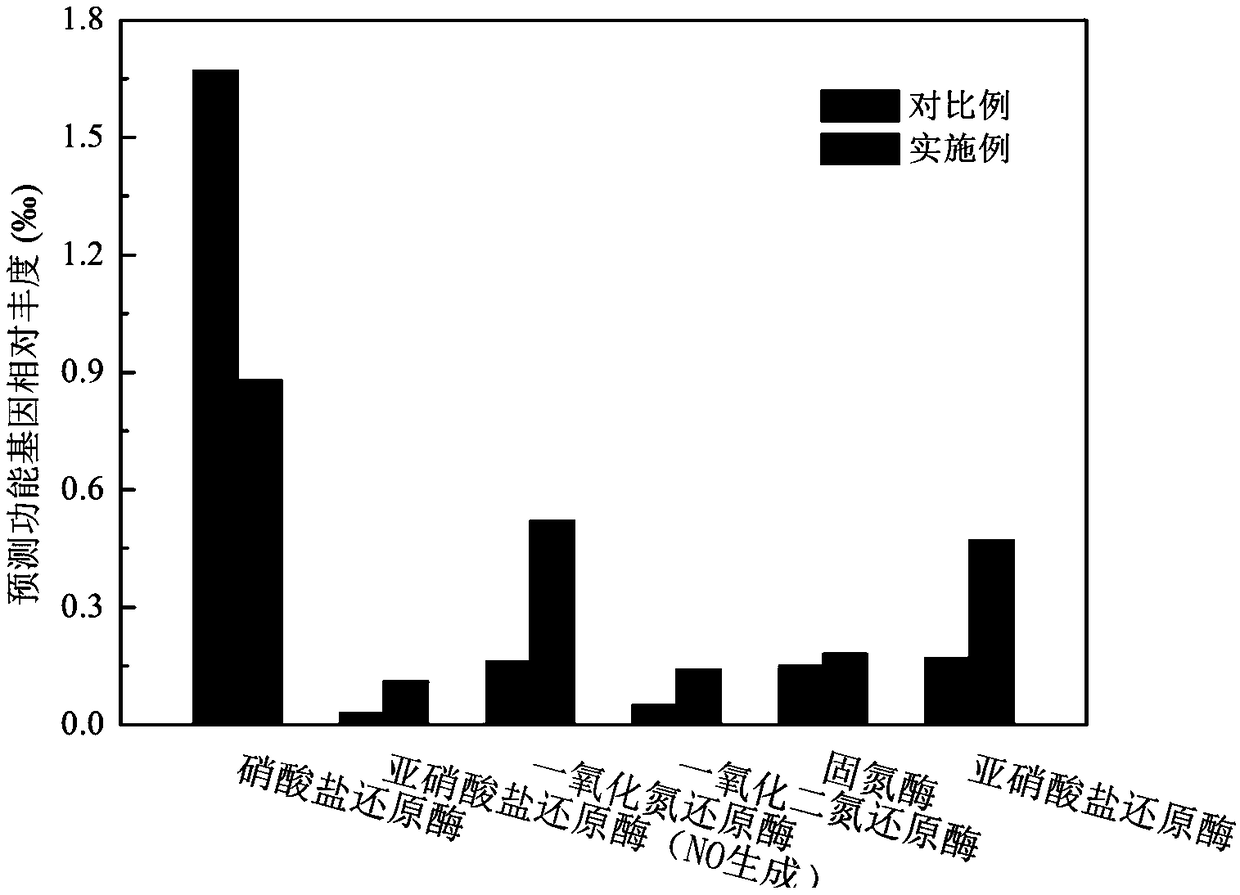
The invention relates to a method for regulating microbial denitrifying florae on the basis of combination of powdered activated carbon and organic matter. According to the method, after activated anammox sludge, anaerobic granular sludge and activated carbon powder are added to an SAMBR, to-be-treated wastewater is introduced, the organic matter is added, and the microbial denitrifying florae areregulated. The method has the following advantages: microbial community structure in the anammox process can be domesticated effectively, and nitrogen-containing wastewater containing the organic matter can be removed from the domesticated activated sludge; proteobacteria becomes dominant phylum, relative content of predicted genes related to nitrite reductase, nitric oxide reductase and other enzymes throughout a denitrification pathway in a nitrogen circulation pathway is increased remarkably, the whole denitrification process is enhanced, and the anammox process can adapt to the wastewatercontaining the organic matter.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Illness state evaluating system and reagent kit for systemic lupus erythematosus
The invention relates to an illness state evaluating system and reagent kit for systemic lupus erythematosus, and belongs to the technical field of biomedicine detection. An evaluating system is provided for conveniently and swiftly evaluating the illness state of the systemic lupus erythematosus. The evaluating system comprises the steps of calculating the ratio of proteobacteria / bacteroidetes (Proteobacteria / Bacteroidetes,P / B) of intestinal tracts of a patient, comparing the ratio with the reference value of healthy crowds (the medical reference value range set based on the early-stage research result is 0.13 to 0.63), when the ratio is higher than the reference value of the healthy crowds, performing effective assistance on SLE disease evaluation; and when the ratio is increased along with increase of an SLE disease activity index (SLE disease activity index, SLEDAI) mark, performing effective evaluation on SLE disease activity according to changes of the ratio. In addition, the invention further provides a corresponding reagent kit.
Owner:THE THIRD AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
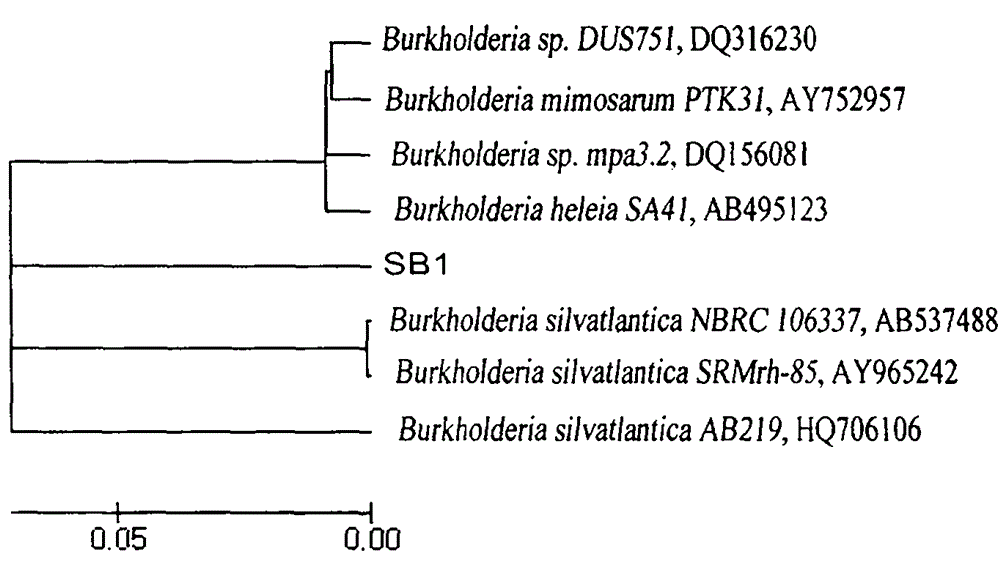
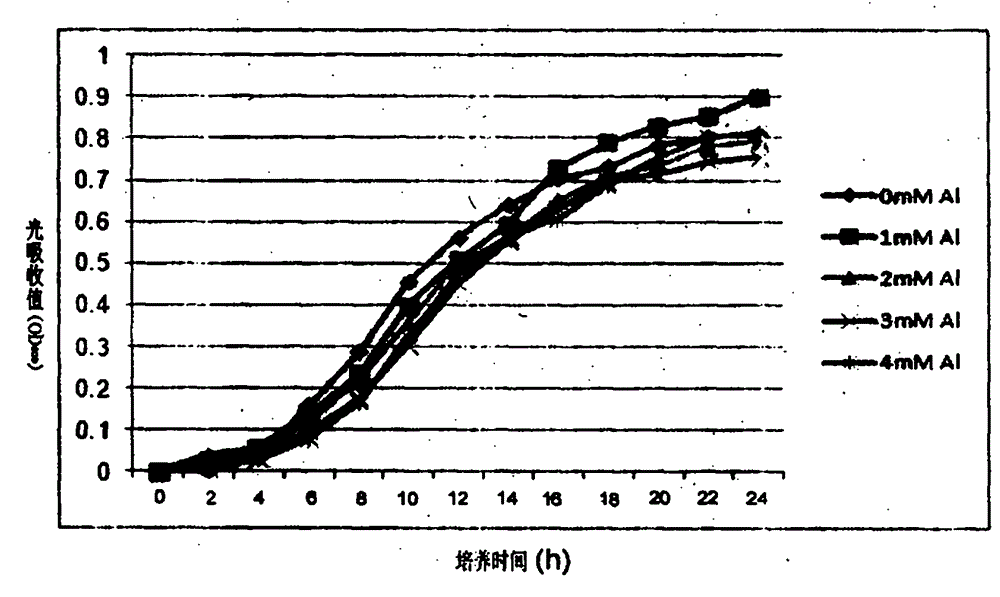
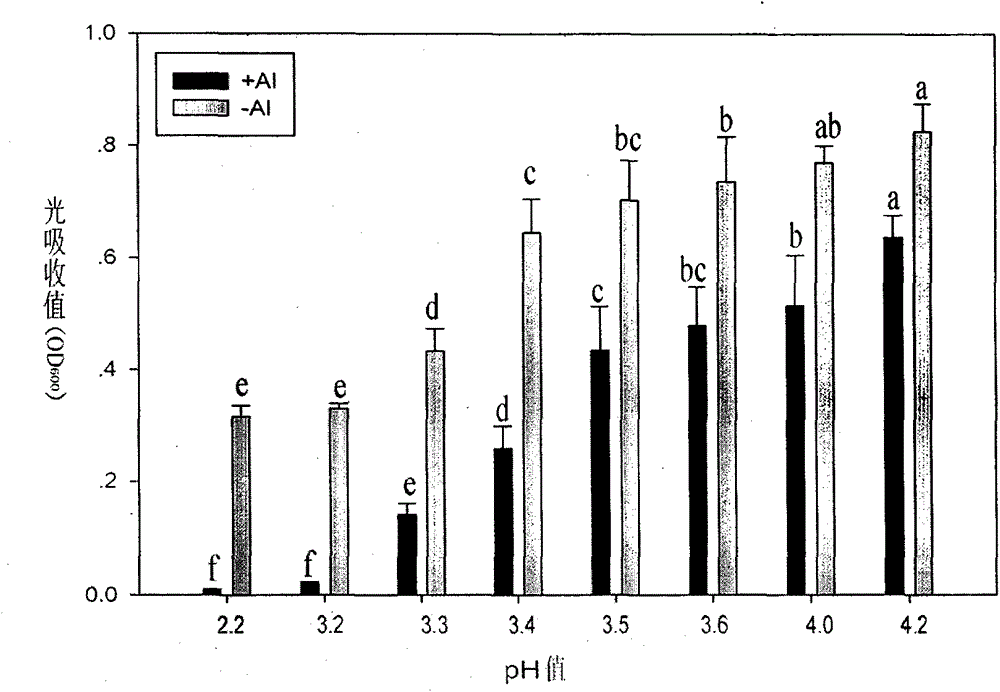
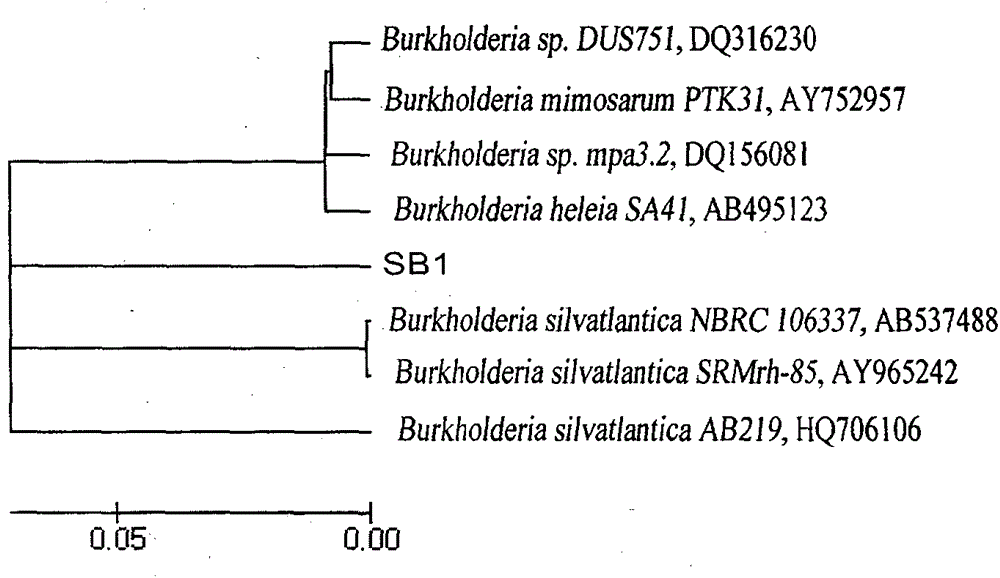
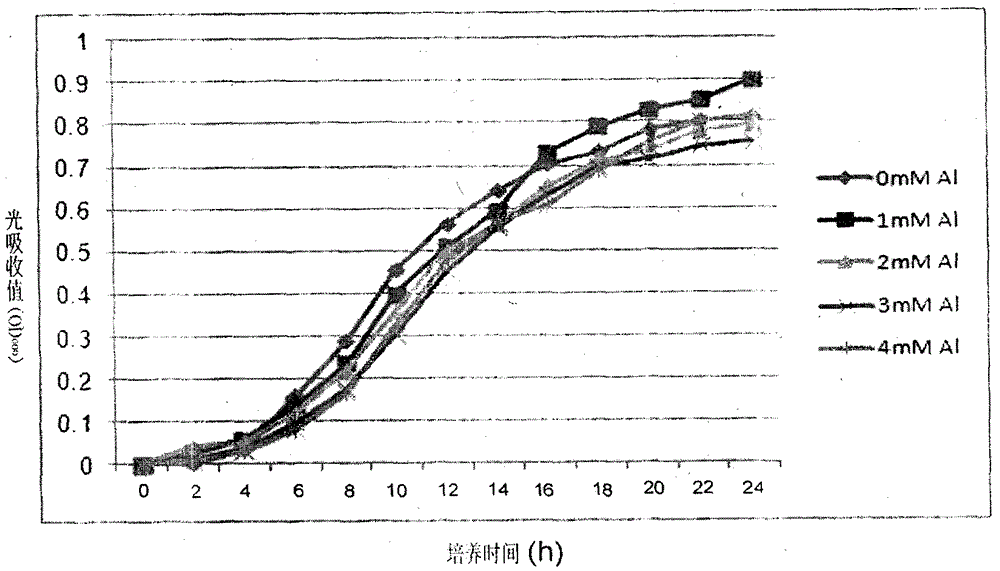
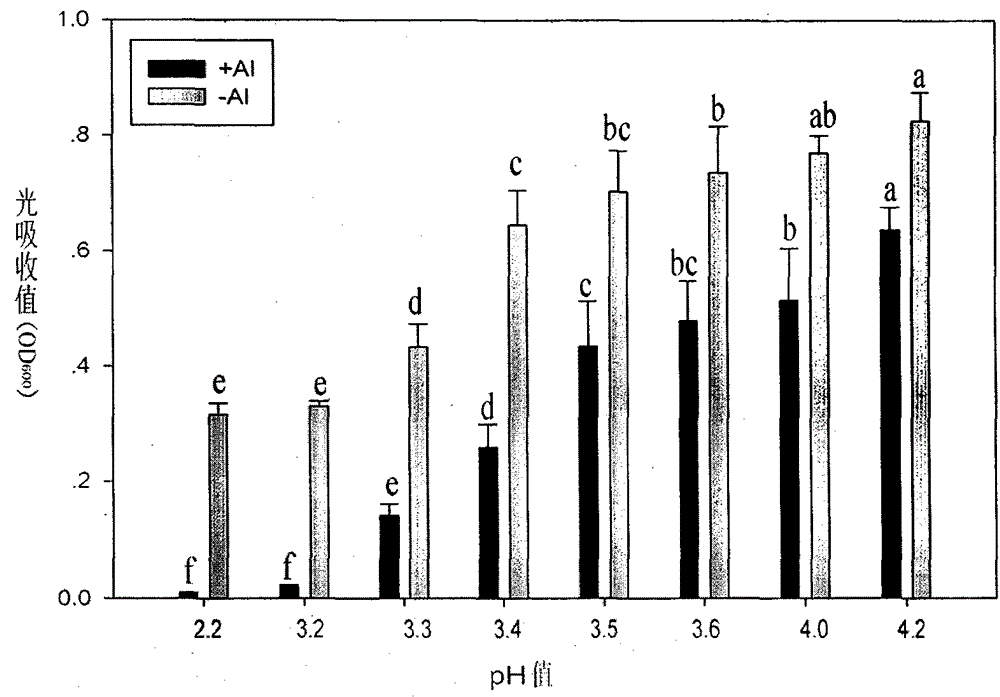
Bacterial strain resistant to acid-aluminum
InactiveCN104017745AStrong acid-resistant aluminum performanceImprove adsorption capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStrong acidsBacterial strain
The invention discloses a bacterial strain resistant to acid-aluminum. The bacterial strain belongs to beta-proteobacteria burkholderia sp., is named as Burkholderia sp.SB1, and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) in September, 2013, with the collection number of CGMCC No. 8396. The bacterial strain has beneficial effects that the bacterial strain shows stronger acid-aluminum resistance performance, and has stronger adsorption effect on aluminum, so that a good microbial material is further provided for improving soil contaminated by aluminum by utilizing the bacterial strain.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
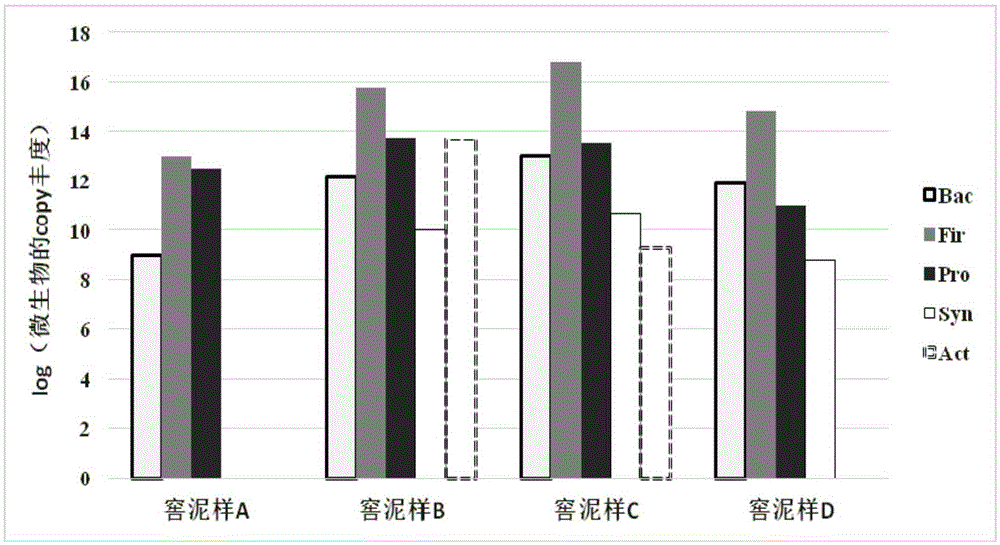
Method for fast and quantitatively measuring microbial community composition in fermentation process of baijiu
ActiveCN105331702AImprove the efficiency of wine productionGuaranteed production efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFermentationPcr dgge
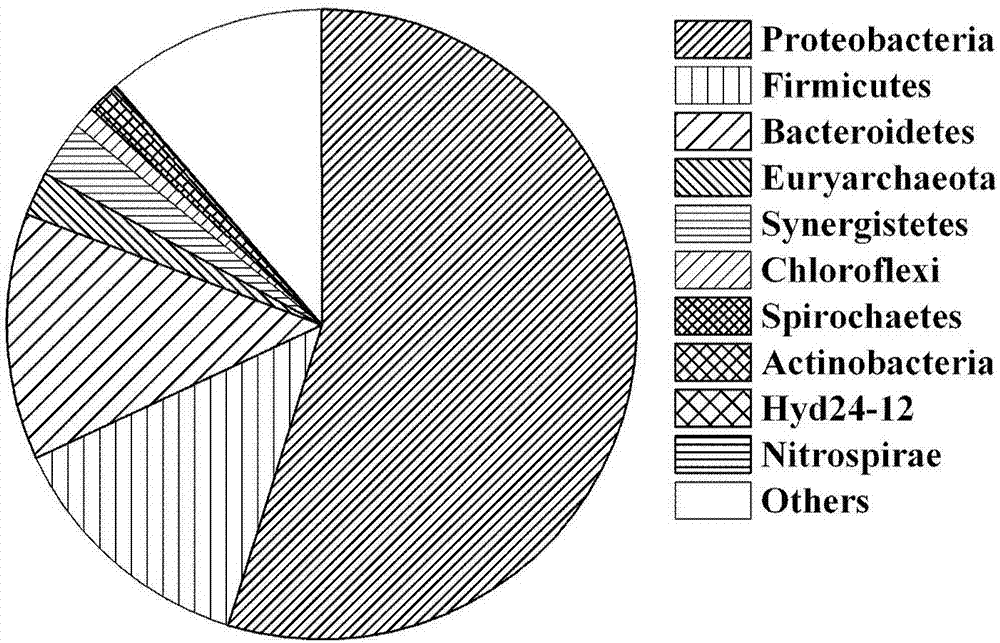
The invention relates to a method for fast and quantitatively measuring the microbial community composition in the fermentation process of baijiu. The method is characterized in that phylum specific primers are used in a PCR system so that special amplification of microbial communities of a certain specific phylum can be performed in the fermentation process of baijiu, quantitative amplification is performed through a qPCR system, and quantitative recognition is achieved. According to the category of known microorganisms, primers of the bacteroidetes, proteobacteria, firmicutes, synergistetes and actinobacteria are respectively designed, and the microstructure change of microbial communities can be fast inspected in the baijiu fermentation process in the level of the phylum on the basis of quantitative amplification of the phylum specific primers.
Owner:ANHUI RUISIWEIER TECH
Biomembrane-alpha proteobacteria quantitative determination method
InactiveCN104152569AAccurate judgmentAvoid interferenceMicrobiological testing/measurementEscherichia coliRestriction factor
The invention belongs to the technical field of molecular biology, and provides a biomembrane-alpha proteobacteria quantitative determination method. The method comprises the following steps: making a sample of alpha-proteobacteria, recovering the sample of alpha-proteobacteria, preparing Escherichia coli competent cell, conversing the alpha-proteobacteria sample to competence bacteria; culturing by selecting bacterium of the sample of alpha-proteobacteria, extracting the plasmid of the sample of alpha-proteobacteria, determining the quantification double chain DNA content of alpha-proteobacteria, pretreating the biomembrane sample to be measured; and performing real-time fluorescence quantification PCR detection. The method has the advantages of fast analysis speed, less restriction factor, high accuracy, and reduced subjective factor influence, and provides support for microbe stability of a drinking water system as well as scientific basis for purifying water quality of a feed pipe net.
Owner:上海浦东威立雅自来水有限公司 +1
Anaerobic microbial composition and methods of using same
A microbial composition for concurrent dechlorination of a mixture of chlorinated ethanes and chlorinated ethenes includes a isolated consortium of bioremediative microorganisms comprising strains of microorganism comprising Clostridium, Acetobacterium, Dehalobacter, Bacteroides, and Proteobacteria. The composition may also include Methanomicrobia.
Owner:USA AS REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE UNITED STATES DEPT OF INTERIOR +1
Separation and identification method for cellulose degradation bacteria in intestinal tracts of monochamus alternatus larvae
ActiveCN108865888APromote degradationSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism separationMolecular identificationLarva currens
The invention discloses a separation and identification method for cellulose degradation bacteria in intestinal tracts of monochamus alternatus larvae and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The separation and identification method comprises the steps: grinding rear intestinal tracts of the monochamus alternatus larvae to obtain original bacteria liquor, performing gradient dilutionon the original bacteria liquor, respectively coating to a No.4 culture medium with sodium carboxymethyl cellulose as a unique carbon source to be subjected to aerobic cultured and performing morphological observation and molecular identification on obtained single colonies. According to the method disclosed by the invention, 154 strains of bacteria with cellulase activity are separated out of rear intestinal tracts of the monochamus alternatus larvae; the 154 strains of bacteria respectively belong to 8 bacterial genus and 10 cultures of proteobacteria, firmicute and bacteroidete bacteria. The separation and identification method provides theoretical basis for interaction between intestinal bacteria and monochamus alternatus.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for quantitatively detecting biofilm beta-proteobacteria
InactiveCN103865994AMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceBacteroidesFluorescence
The invention relates to a method for quantitatively detecting biofilm beta-proteobacteria. The method comprises the following steps: pretreating standard substance beta-proteobacteria; pretreating a biofilm beta-proteobacteria sample to be detected; carrying out real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection on the standard substance beta-proteobacteria and making a standard curve equation y=-ax+b; then carrying out real-time fluorescence quantitative PCR detection on the biofilm beta-proteobacteria to be detected to obtain a cycle threshold and obtaining the concentration of beta-proteobacteria DNA in the sample according to the cycle threshold and a standard curve, wherein y is the cycle threshold and x is the logarithm of the concentration of DNA with 10 as the base number. Compared with the prior art, the method has the effects of effectively solving the problem that traditional pure culture methods have the defects of low analysis speed, more restrictive factors, low microbial diversity, low accuracy, strong subjective factors and the like, more scientifically monitoring the water treatment technology and the information of pathogenic bacteria in the pipe network biofilm, reflecting potential hazards in a drinking water system and providing more scientific bases for water quality purification of water supply networks.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Strong promoter from ensifer adhaerens as well as plasmid vector and application of strong promoter
The invention discloses a strong promoter from ensifer adhaerens as well as a plasmid vector and an application of the strong promoter. Function verification is performed by amplifying one strong promoter in ensifer adhaerens, and the strong promoter which can be widely applied to gene expression, gene operation and strain improvement of alpha-proteobacteria such as sinorhizobium meliloti, zymomonas mobilis, caulobacter crescentus, pseudomonas denitrificans, agrobacterium tumefaciens, brucella abortus, pseudomonas fluorescens, rhizobium leguminosarum and ensifer adhaerens is obtained and has the nucleotide sequence being SEQ ID NO:1. The invention also relates to the plasmid vector containing the strong promoter, a method for constructing a gene engineering strain by use of the promoter, the corresponding strain and an application of a host cell in starting target gene expression.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
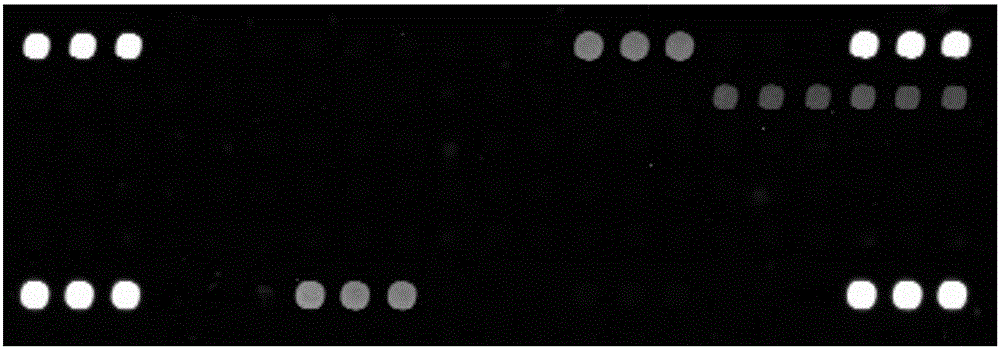
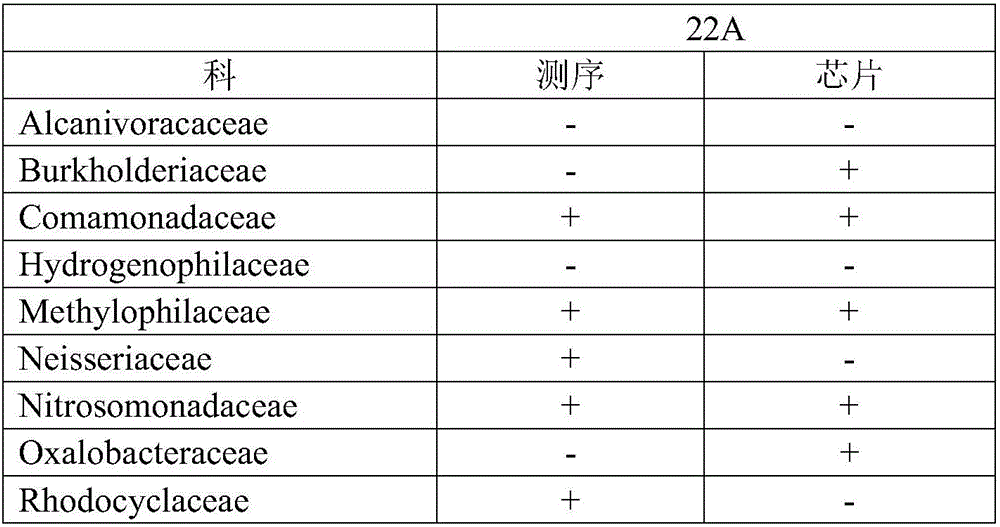
Gene chip for detecting beta-proteobacteria communities in marine environment
InactiveCN106048077AQuick checkDetection parallelNucleotide librariesMicrobiological testing/measurementBurkholderiaceaeSeawater
The invention provides a gene chip for detecting beta-proteobacteria communities in a marine environment. The gene chip comprises a chip carrier and a probe which is fixed on the chip carrier and used for detecting Alcaligenaceae bacteria, Burkholderiaceae bacteria, Comamonadaceae bacteria, Hydrogenophilaceae bacteria, Methylophilaceae bacteria, Neisseriaceae bacteria, Nitrosomonadaceae bacteria, Oxalobacteraceae bacteria and Rhodocyclaceae bacteria in seawater. The probe used for the chip can realize rapid and high-throughput detection of beta-proteobacteria communities in seawater, and can detect up to 9 beta-proteobacteria families' information. Therefore, the invention provides powerful technical support for monitoring bacterial communities in the marine environment and has laid a solid foundation for establishing and improving an offshore and marine environmental quality comprehensive assessment system.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
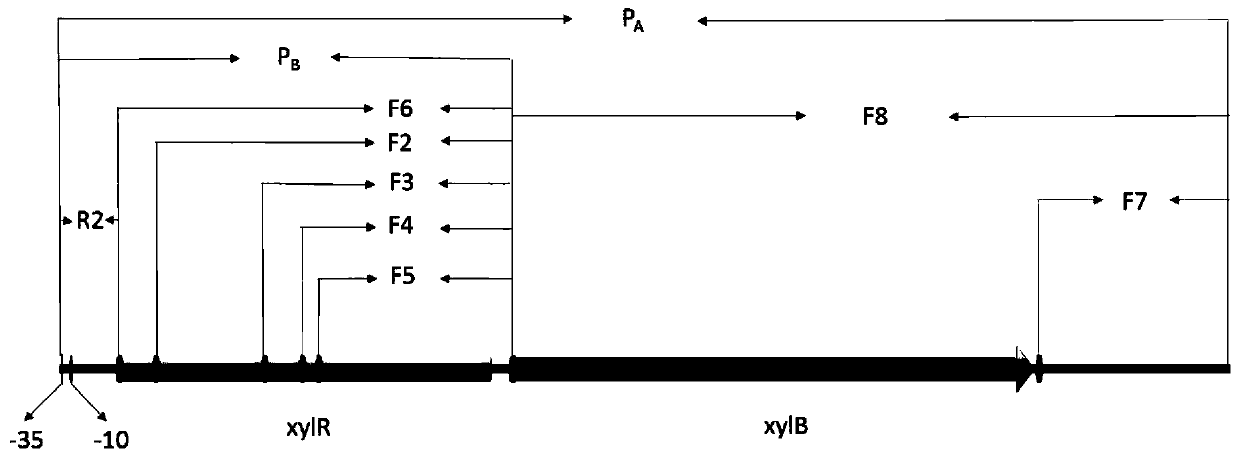
Xylose-induced promoter and plasmid vector and application thereof
The invention discloses a xylose-induced promoter. By amplifying a xylose-induced promoter in sinorhizobium meliloti, bioinformatics analysis and function verification are carried out, the xylose-induced promoter which can be widely applied to gene expression, genetic gene operation and strain improvement in alpha-proteobacteria such as Sinorhizobium meliloti, Zymomonas mobilis, Caulobacter crescentus, Pseudomonas denitrificans, Agrobacterium tumefaciens, Brucella abortus, Pseudomonas fluorescens, Rhizobium leguminosarum and Sinorhizobium adhaerens is obtained, and the nucleotide sequence of the promoter is SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention also relates to a plasmid vector containing the xylose-induced promoter, a method for constructing a genetic engineering strain by using thepromoter, a corresponding strain, and application of a host cell to induction and starting of expression of a target gene under xylose inducible conditions.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
The use of sodium copper chlorophyllin
ActiveCN105250267BRestrict growthReduce in quantityOrganic active ingredientsDigestive systemBacteroidesDisease
The invention discloses a new application of sodium copper chlorophyllin, relates to the field of medicine, and relates to the application of sodium copper chlorophyllin in the preparation of medicines for treating and regulating intestinal flora. The beneficial effects of the present invention are: the sodium copper chlorophyllin is similar to prebiotics, which balances the microbial flora ecology of the intestinal tract, thereby limiting the growth of conditional pathogenic bacteria and the release of bacterial toxins in the intestinal tract, thereby alleviating liver disease. The present invention verifies through experiments that the sodium copper chlorophyllin can be used to regulate intestinal flora, increase the number of Firmicutes bacteria, and inhibit the abundance of α-proteobacteria and γ-proteobacteria. The imbalance of intestinal flora is closely related to various liver diseases, including liver failure and cirrhosis. Therefore, the preparation of sodium copper chlorophyllin can be used to prevent and treat various liver diseases.
Owner:CHENGDU TONGDE PHARMA
Production process of novel chicken soup-stock
PendingCN114532508AAvoid inconvenienceGood workmanship standardMeat/fish preservation by heatingFood ingredientsBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
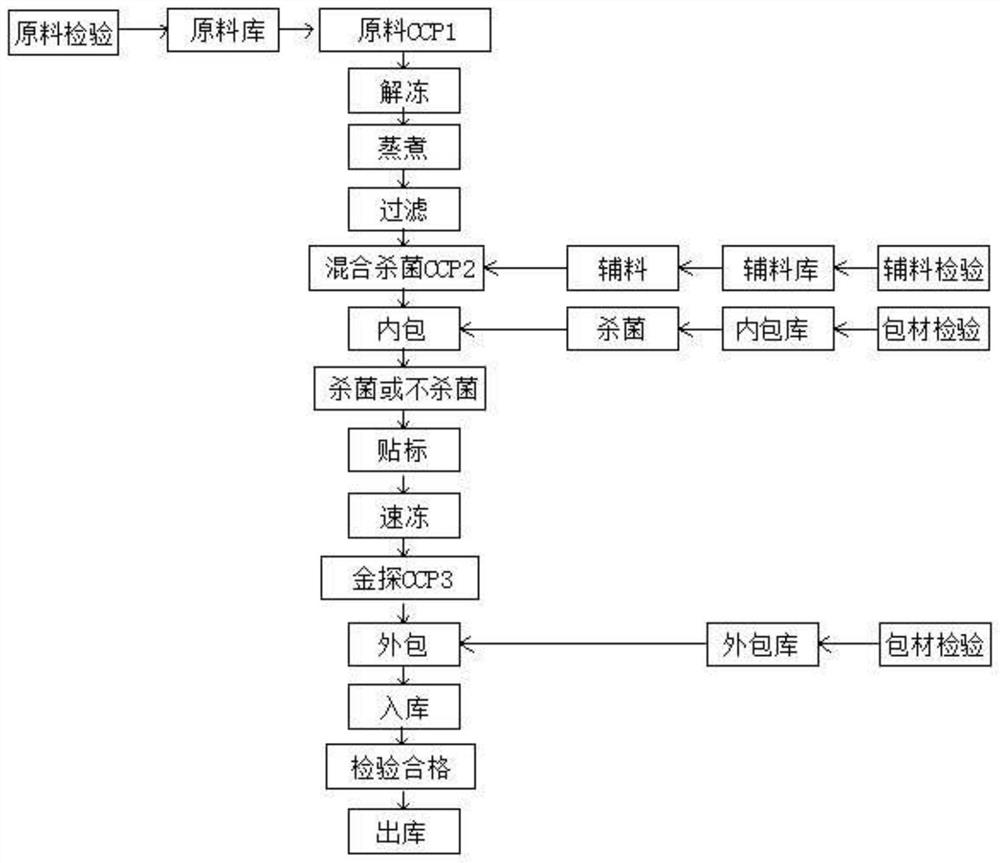
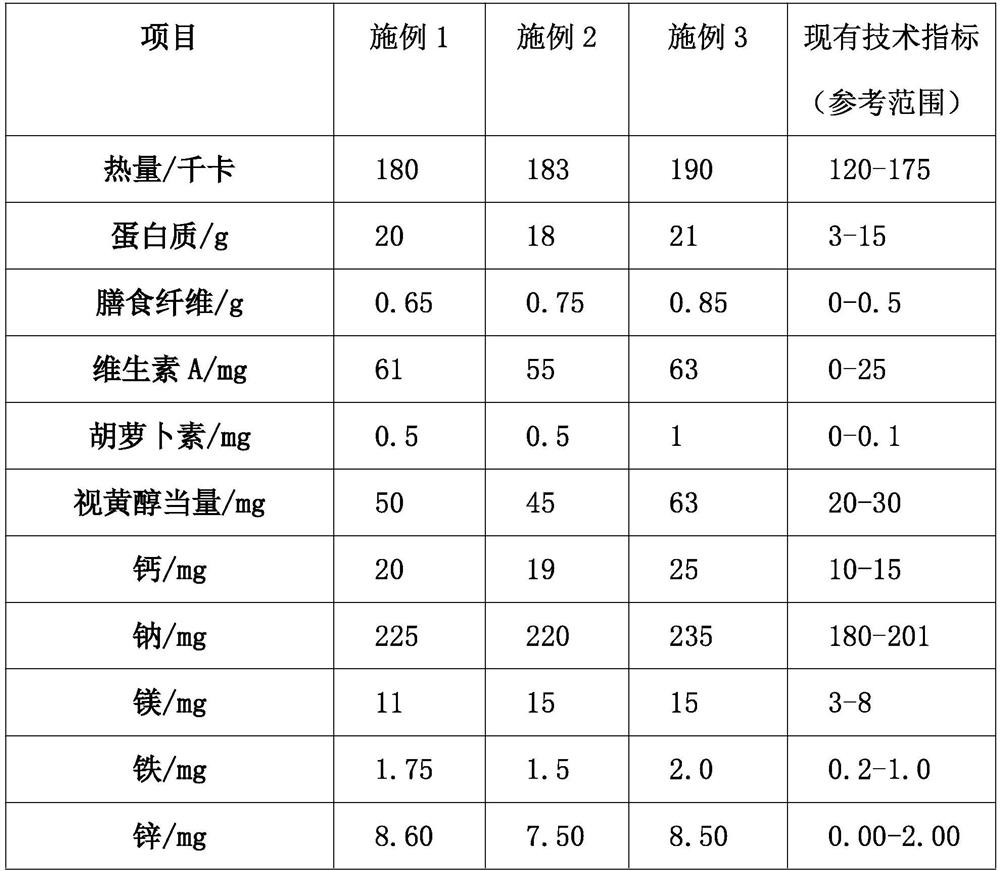
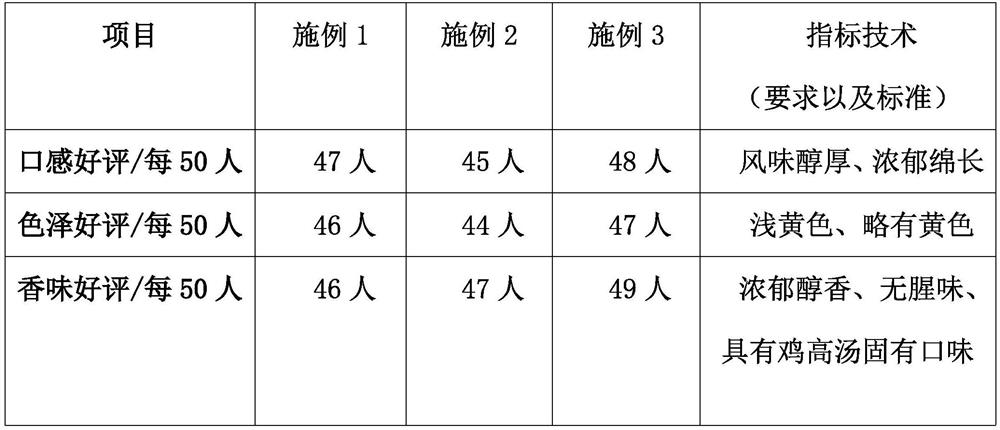
The invention discloses a production process of novel chicken soup-stock. The production process comprises the following steps: raw material inspection, raw material storage, raw material CCP1, unfreezing, cooking, filtering, CCP2 mixed sterilization, inner packaging, sterilization or no sterilization, labeling, quick freezing, CCP3 gold detection, outer packaging, warehousing, qualified inspection and delivery. According to the method, the optimal process is achieved in the indexes such as nutrition, taste, color and fragrance, meanwhile, the indexes of other pathogenic bacteria such as the total number of bacterial colonies, escherichia coli, streptococcus, salmonella, staphylococcus and pseudomonas aeruginosa are remarkably reduced or not detected, and the optimal hygienic index and the process standard of the sterilization effect are achieved; moreover, in the whole chicken soup-stock processing process, workshop standardized production processing is adopted, the taste is stable, the nutritional value is better guaranteed, inconvenience caused by household making of existing traditional clear chicken soup is avoided, the production efficiency is improved, and the wide requirements of existing marketization are greatly met.
Owner:江苏万业食品科技有限公司
A kind of bacterial strain resistant to aluminum
InactiveCN104017745BStrong acid-resistant aluminum performanceImprove adsorption capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesStrong acids
The invention discloses a bacterial strain resistant to acid-aluminum. The bacterial strain belongs to beta-proteobacteria burkholderia sp., is named as Burkholderia sp.SB1, and is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) in September, 2013, with the collection number of CGMCC No. 8396. The bacterial strain has beneficial effects that the bacterial strain shows stronger acid-aluminum resistance performance, and has stronger adsorption effect on aluminum, so that a good microbial material is further provided for improving soil contaminated by aluminum by utilizing the bacterial strain.
Owner:JINGGANGSHAN UNIVERSITY
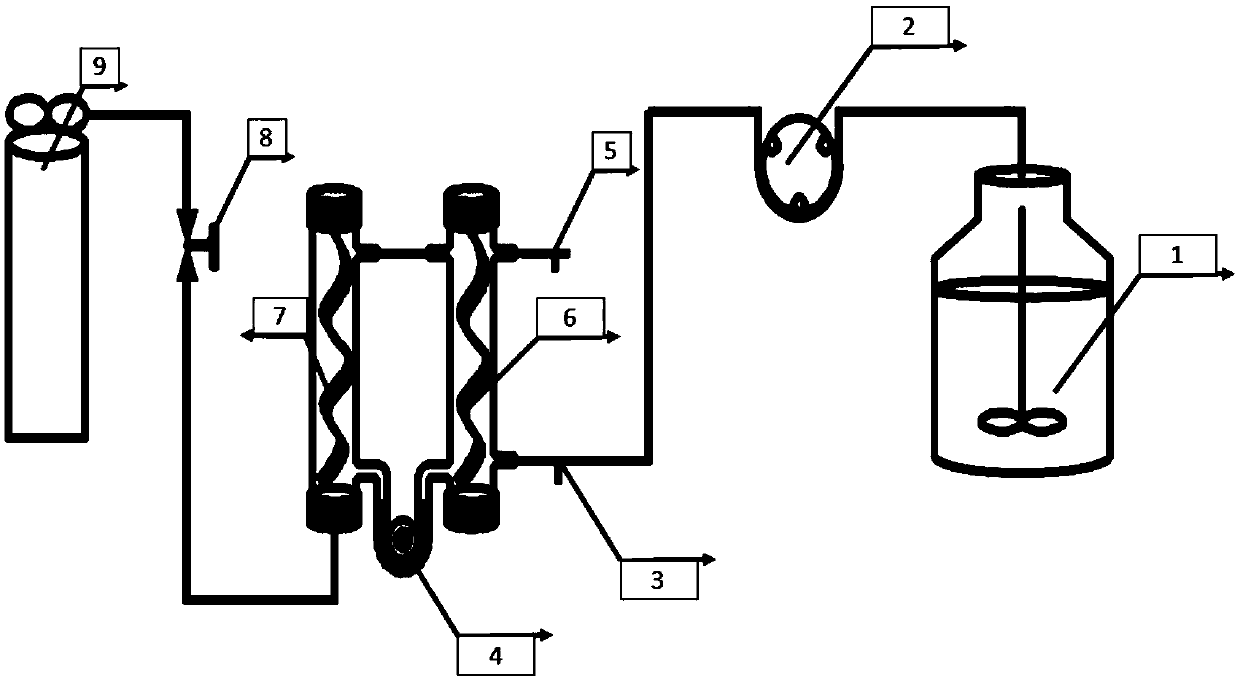
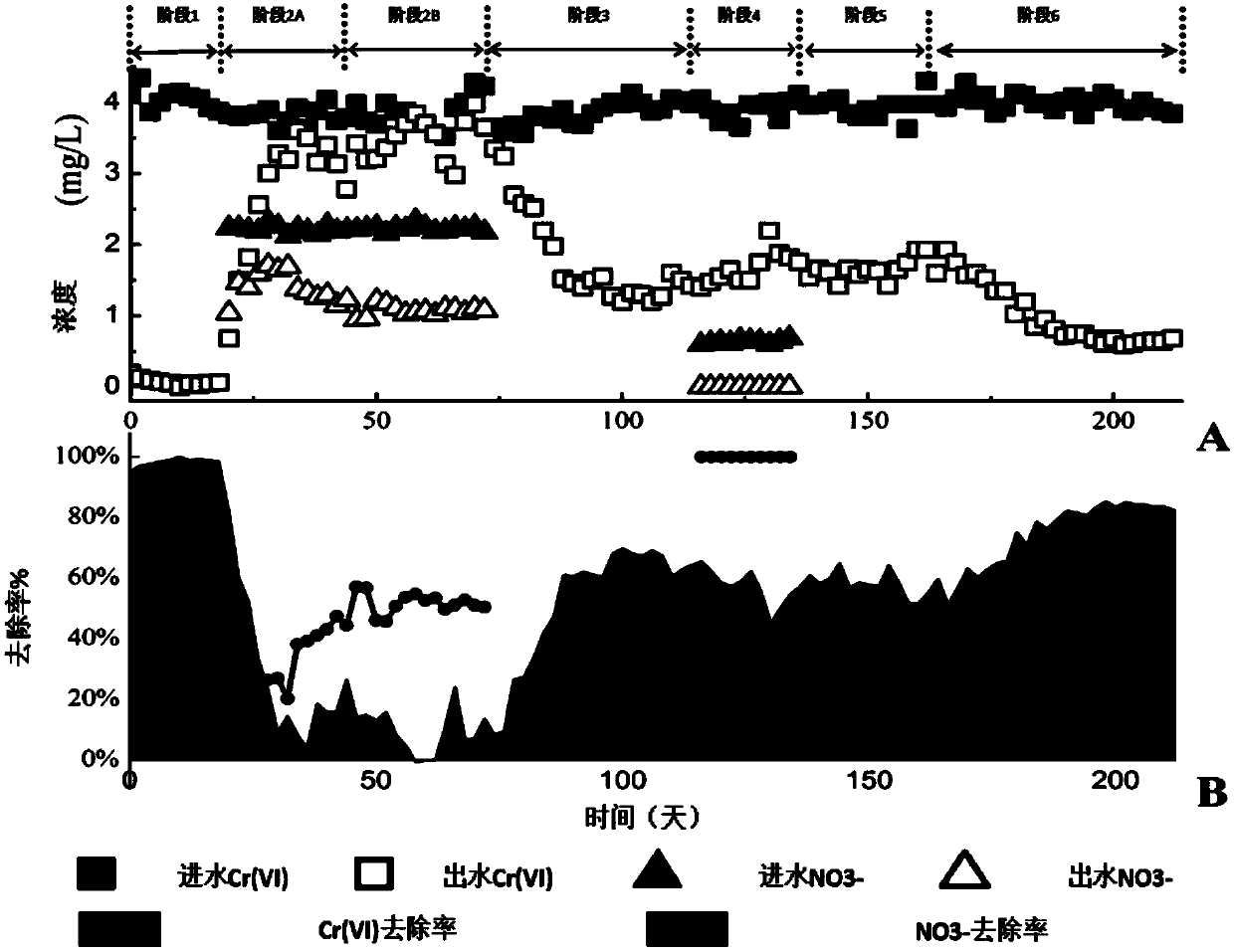
Method for reducing hexavalent chromium in methane matrix biomembrane by NO<3><->
ActiveCN108675445ASignificant inhibitory effectIrreversible inhibitionBiological treatment regulationWater contaminantsActivated sludgeContinuous flow
The invention relates to a biological reduction technology for composite pollutants, and aims to provide a method for reducing hexavalent chromium in a methane matrix biomembrane by NO<3><->. The method includes the following steps: adding Na2CrO4 and NaNO3 to an inorganic medium, and allowing the obtained medium, for later use, to stand under a micro-aerobic condition; introducing simulated wastewater into a methane matrix membrane bioreactor, adding CrO<4><2-> and activated sludge, and carrying out self-circulation to obtain the a bacterial solution; introducing the simulated wastewater andCH4 into the reactor in a continuous flow manner, and controlling the concentration of NO<3><-> in inlet water in stages; and ensuring that the concentrations of the CrO<4><2-> and NO<3><-> in outletwater reach a steady state for at least 10 days in every running stage. Compared with the prior art, the method has the following advantages: the high load of NO<3><-> has a significant irreversible inhibition effect on the reduction of Cr(VI); the introduction of the NO<3><-> deceases Meiothermus originally involved in the reduction of Cr(VI) and makes alpha-proteobacteria enriched; and when theNO<3><-> is removed, beta-proteobacteria become important, so the beta-proteobacteria play a potential role in Cr(VI) reduction.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
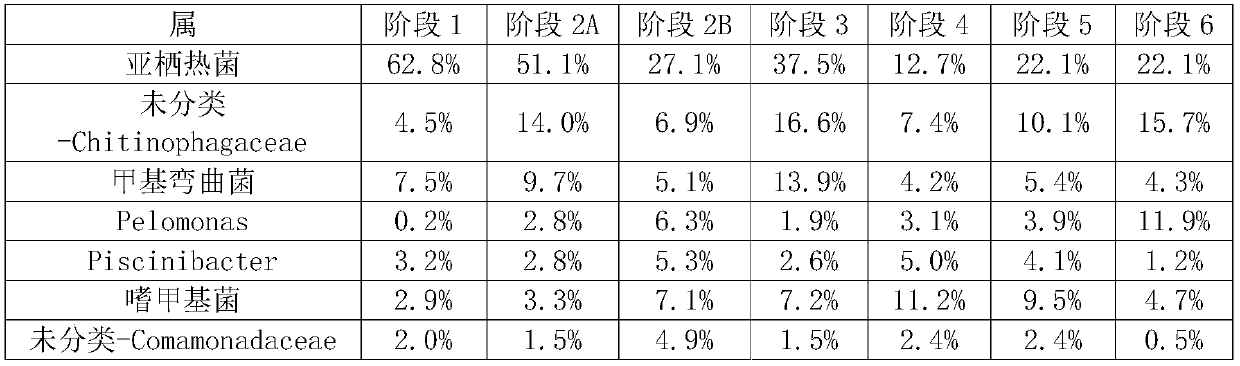
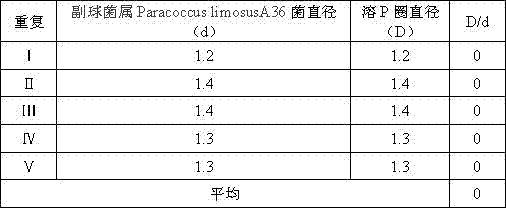
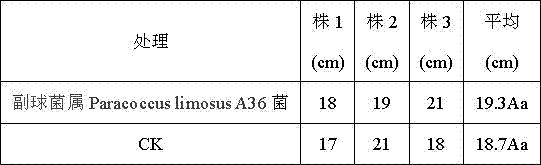
Paracoccus and its bacterial agent, preparation method and application
ActiveCN104877916BIncrease contentPromotes immediate releaseFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyFamily Rhodobacteraceae
The invention discloses a paracoccus and its preparation, preparation method and application. The paracoccus is Paracoccus limosus (Paracoccus limosus) A36. Date: November 21, 2014, deposit number: CGMCC No. 10032; the Paracoccus belongs to the kingdom Bacteria, the phylum Proteobacteria, the class α-Proteobacteria, the order Rhodobacteria, the family Rhodobacteraceae, and the genus Paracoccus. The bacterial agent in which the paracoccus is the active ingredient is a bacterial agent made from the paracoccus actinomycetes through plate culture, seed culture, and fermentation; the preparation method of the bacterial agent in which the bacillus is the active ingredient includes a flat plate Cultivation, seed cultivation, fermentation, and bacterial agent preparation steps; the application of the bacterial agent in preparing phosphorus-dissolving, potassium-relieving, and improving soil quick-acting nitrogen-based fertilizers.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com