Paracoccus with denitrification and phosphorus removal functions and application thereof
A paracoccus and denitrification technology, applied in the field of environmental microorganisms, to achieve the effect of reducing the total phosphorus content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0026] Example 1. Isolation and Screening of Bacterial Strains
[0027] 1. Enrichment
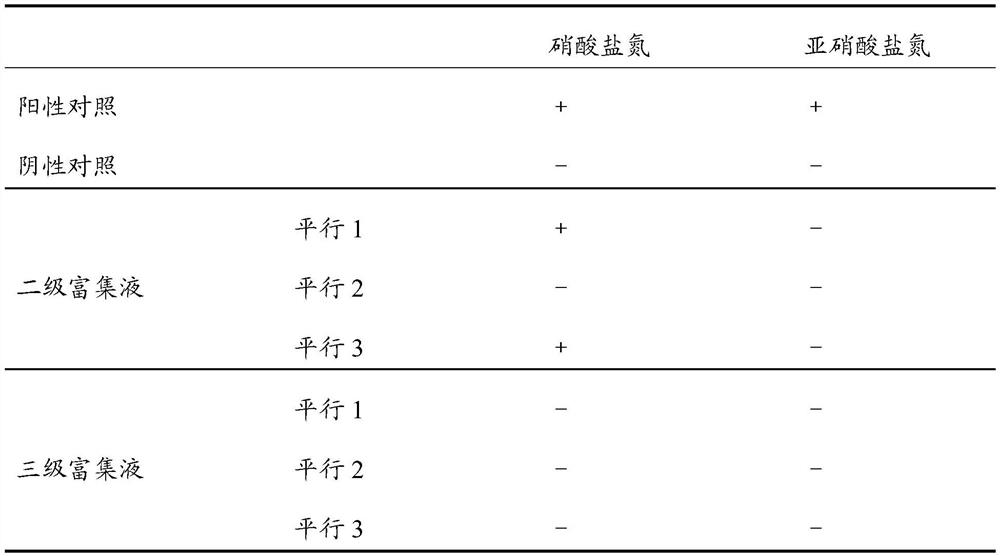
[0028] Collect the mud-water mixture of the anoxic section of a biological factory sewage treatment station in Gaomi City, Weifang City, Shandong Province, and inoculate it into the enrichment medium (potassium nitrate 2.0g, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2 g, potassium sodium tartrate 20.0g, water 1000mL, pH=7.2±0.1), and cultured in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C for 120 hours to obtain a first-level enrichment solution; the first-level enrichment solution was inoculated at an inoculum size of 10vol%. Into a fresh enrichment medium, culture in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C for 120 hours to obtain a secondary enrichment solution; inoculate the secondary enrichment solution into a fresh enrichment medium at a 10vol% inoculum size, and keep the temperature at 30°C The incubator was left to culture for 120 hours to obtain three leve...
Embodiment 2
[0048] Example 2. Identification of bacterial strain DB133C
[0049] The strain DB133C was sent to the Institute of Microbiology, Chinese Academy of Sciences for strain identification. According to the cell morphology, physiological and biochemical characteristics of the strain, 16SrRNA gene sequence, tauY gene sequence, etc., referring to "Bergey's Handbook of Systematic Bacteriology" and related research papers, DB133C was identified For Paracoccus. The 16S rDNA sequence of the strain is shown in SEQ ID No: 1, the tauY DNA sequence is shown in SEQ ID No: 2, and the cell morphology and physicochemical experiment results of the strain are shown in Table 3.
[0050] Table 3. DB133C cell morphology and physicochemical experiment results
[0051]
[0052]
Embodiment 3
[0053] Example 3. Evaluation experiment of aerobic denitrification ability of Paracoccus strain DB133C
[0054] 3.1 Preparation of bacteria solution
[0055] Activate the Paracoccus strain DB133C, use a sterile inoculation loop to pick up a lawn on the slant of the test tube and inoculate it into 100mL liquid nutrient broth medium (peptone 10g, beef powder 3g, sodium chloride 5g, water 1000mL, pH natural ) at 30°C and 220rpm on a shaker for 24 hours to obtain an activated bacterial liquid, which can be inserted into the evaluation medium.
[0056] 3.2 Effect evaluation experiment of aerobic denitrification capacity
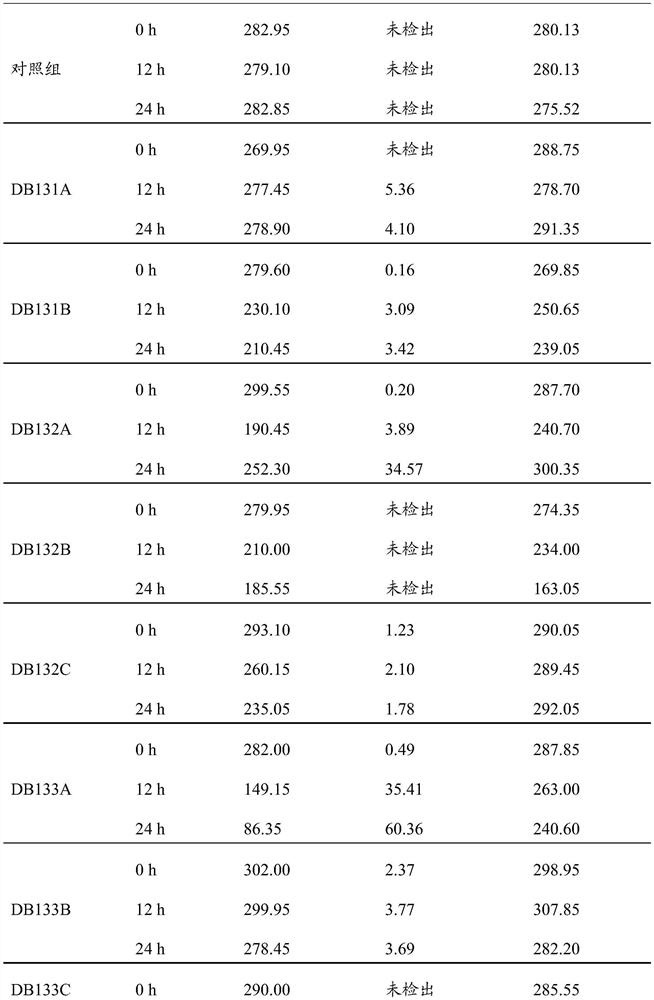
[0057] The activated bacterial solution was inoculated into 100mL denitrification evaluation medium (KNO 3 2.0g, K 2 HPO 4 0.5g, MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O 0.2g, potassium sodium tartrate 20.0g, tap water 1000mL, pH = 7.2 ± 0.1), after inoculation, place in 30 ℃, 220rpm shaking table for aerobic culture, detect the total nitrogen content in the medium every 24 hours, th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com