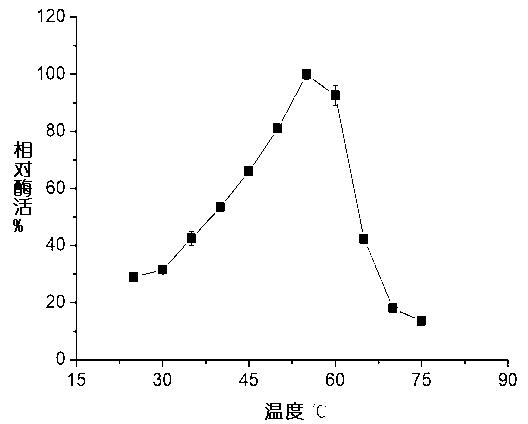
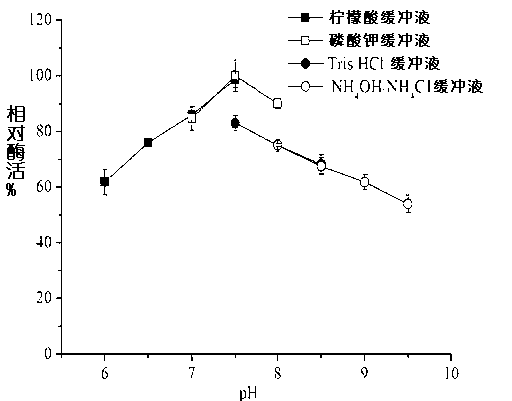
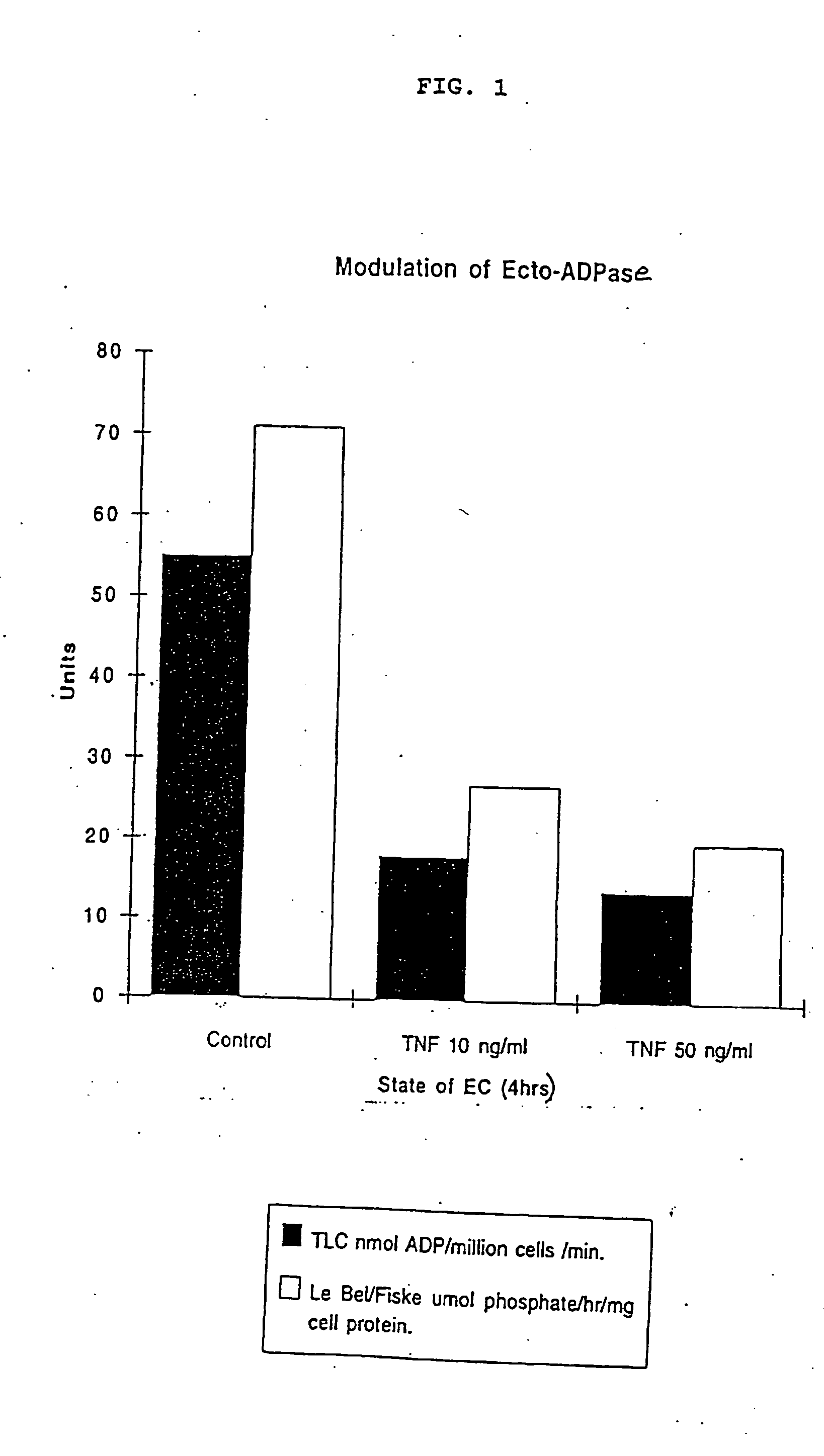
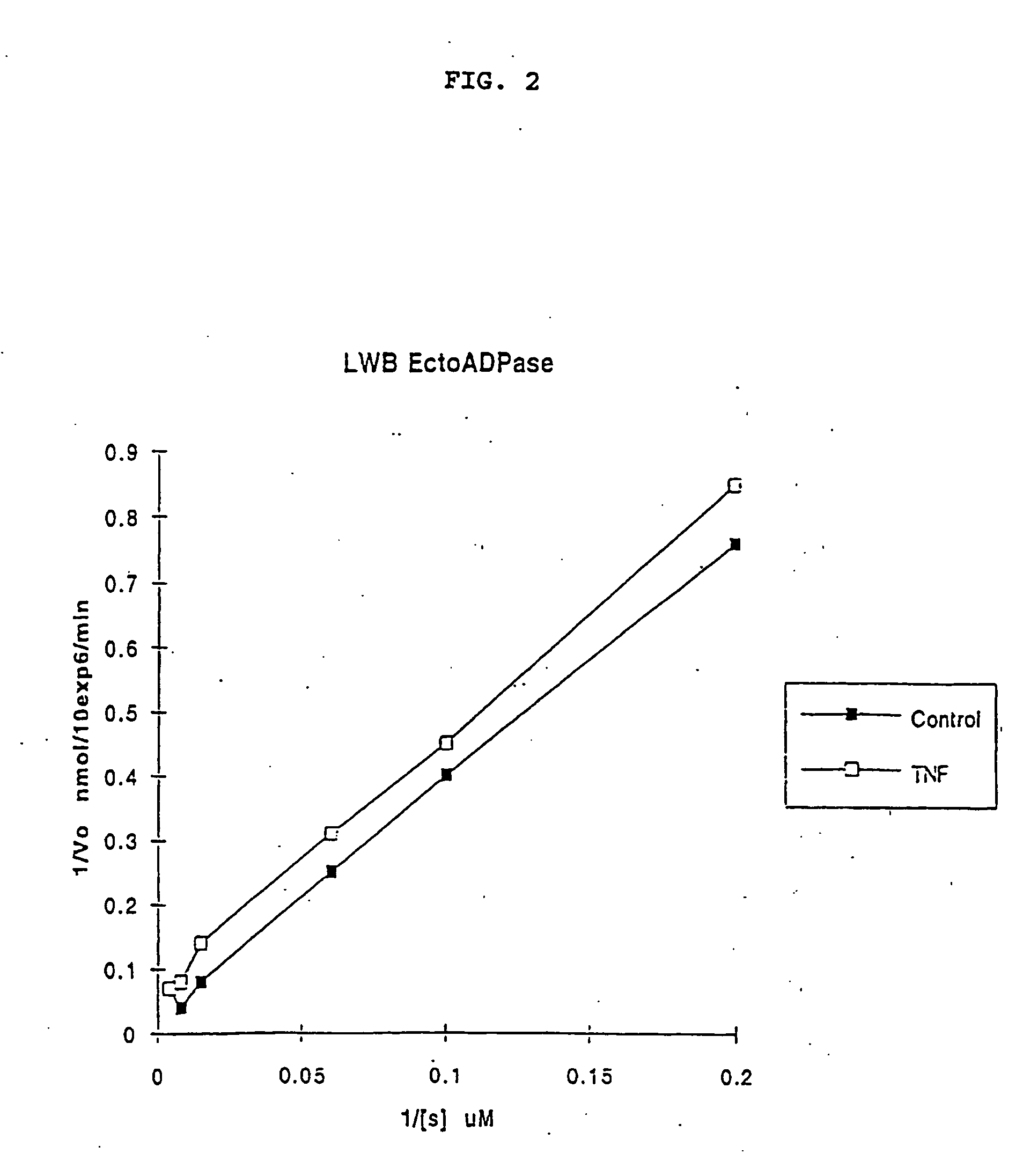
Patents
Literature
128 results about "Hydrolase Gene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A gene that encodes an enzyme capable of catalyzing the hydrolysis of chemical bonds.
Alteration of hydrolase genes and screening of the resulting libraries for the ability to catalyze specific reactions
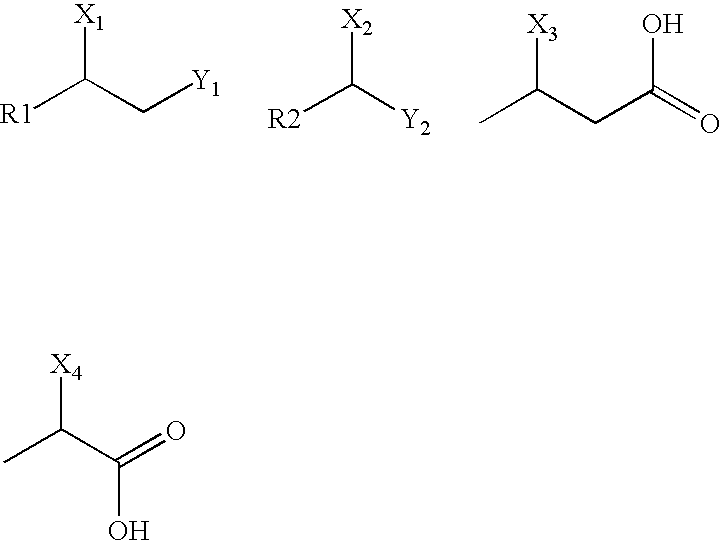
The present invention relates to halocarbon and halohydrocarbon chemistry, including methods of dehalogenating halocarbons and halohydrocarbons to provide, inter alia, alcohols, polyols, and epoxides. In general, the methods involve reaction pathways catalyzed by altered hydrolase enzymes that can provide stereoselective or stereospecific reaction products. The invention also includes methods of providing altered nucleic acids that encode altered dehalogenase or other hydrolase enzymes. Additionally, the invention includes various reaction formats and kits.
Owner:MAXYGEN
Gene engineer strain of Aspergillus niger with high L-malic acid yield, and construction and application thereof
The invention provides a gene engineer strain of Aspergillus niger with high L-malic acid yield and a construction method thereof. The method utilizes gene knockout technique to disrupt the Aspergillus niger oxaloacetic acid hydrolase gene (oahA) so as to obtain the malic acid-producing strain S2. After 7 days of shake flask fermentation, 100 g / L glucose is converted into 120.4 + / - 2. 8 g / L of L-malic acid, the conversion of malic acid and malic acid to glucose is 1.62 mol / mol, which is 81% of the highest conversion in theory. A good strain for the industrialized production of malic acid is provided.
Owner:南京昊禾生物科技有限公司
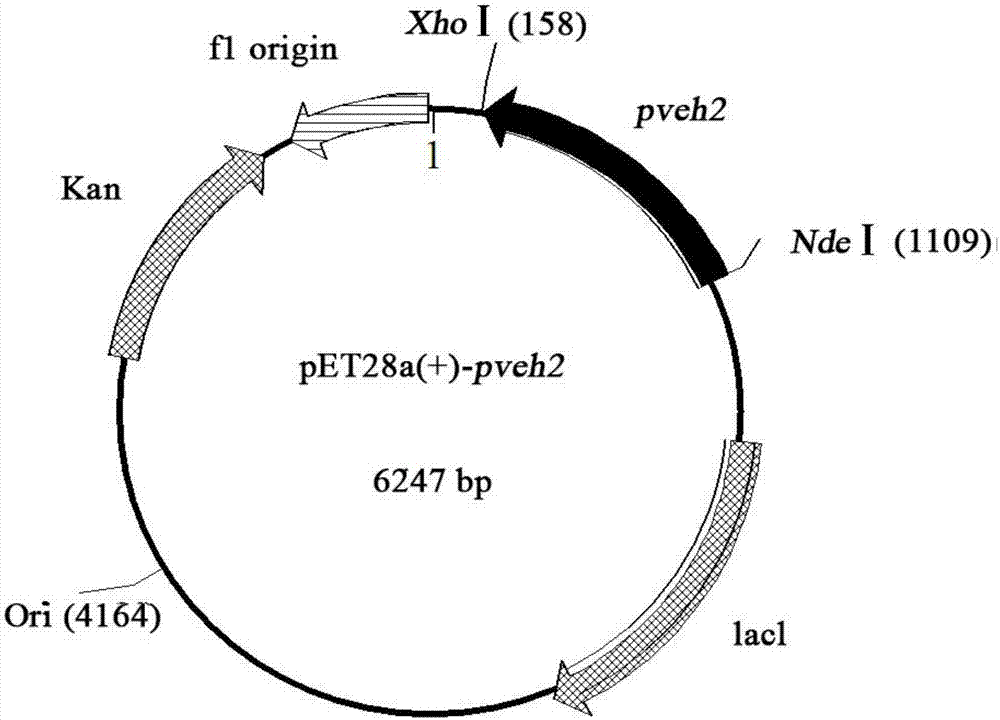
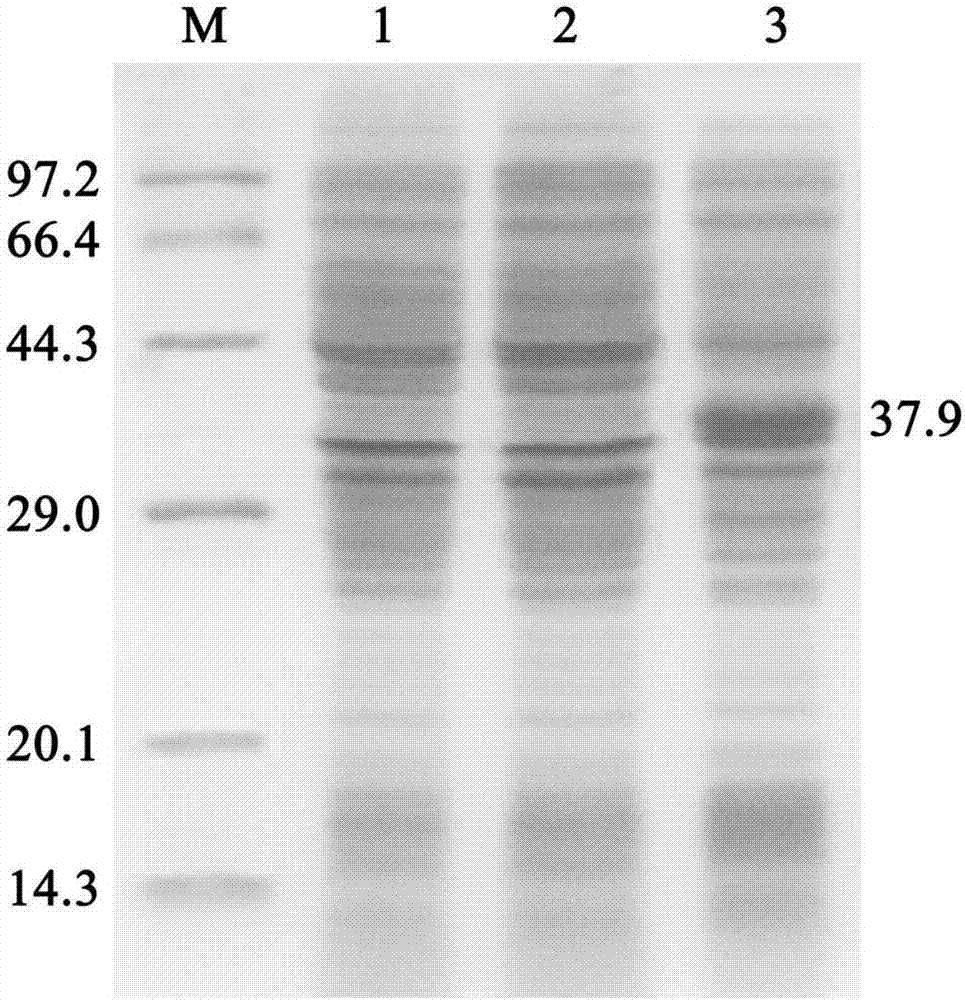
Epoxide hydrolase sourced from Phaseolus vulgaris and application thereof
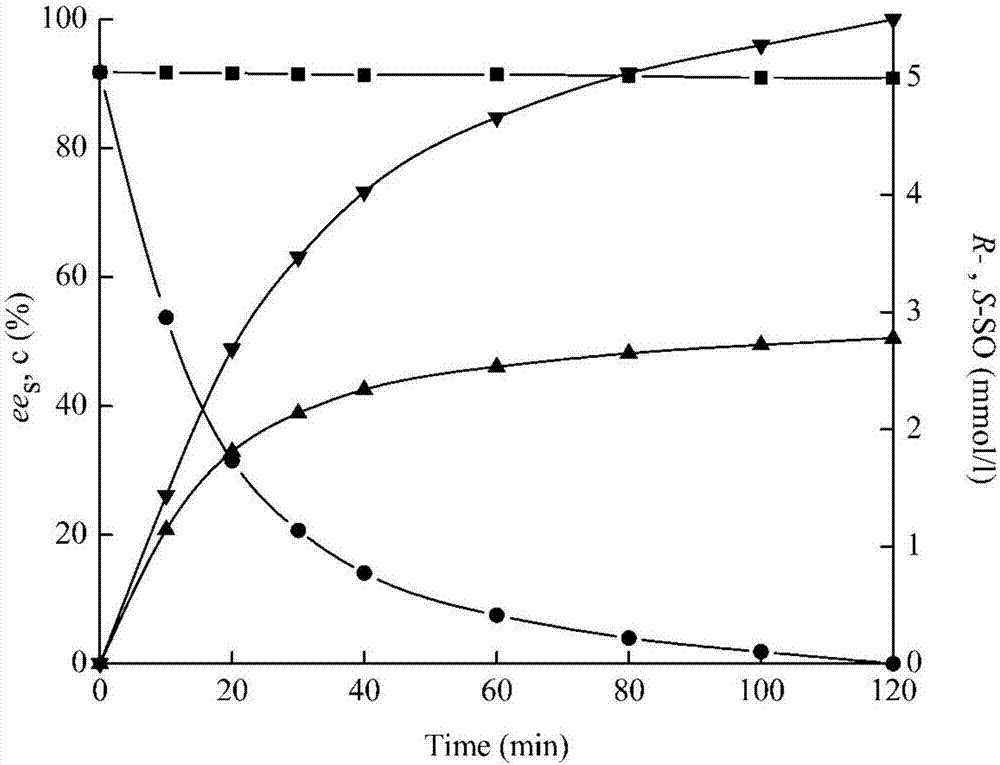
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase sourced from Phaseolus vulgaris and an application thereof and belongs to the technical field of biology. The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase gene (pveh2) sourced from a leguminous plant, Phaseolus vulgaris, as well as a corresponding amino sequence. The invention provides a recombinant plasmid pET28a(+)-pveh2 and a genetic engineering bacteria E.coli BL21(DE3) / pET28a(+)-pveh2, which comprise the gene. A recombinant epoxide hydrolase is prepared through expression by the bacterial strain. The invention provides a method of biocatalysis through fermentation with an enzyme produced by the recombinant bacterial strain constructed in the invention, thus producing enantiomerically pure R-type styrene oxide (ee > 99%); in addition, final yield can reach 49.3%, which is approximate to a theoretical value, 50%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
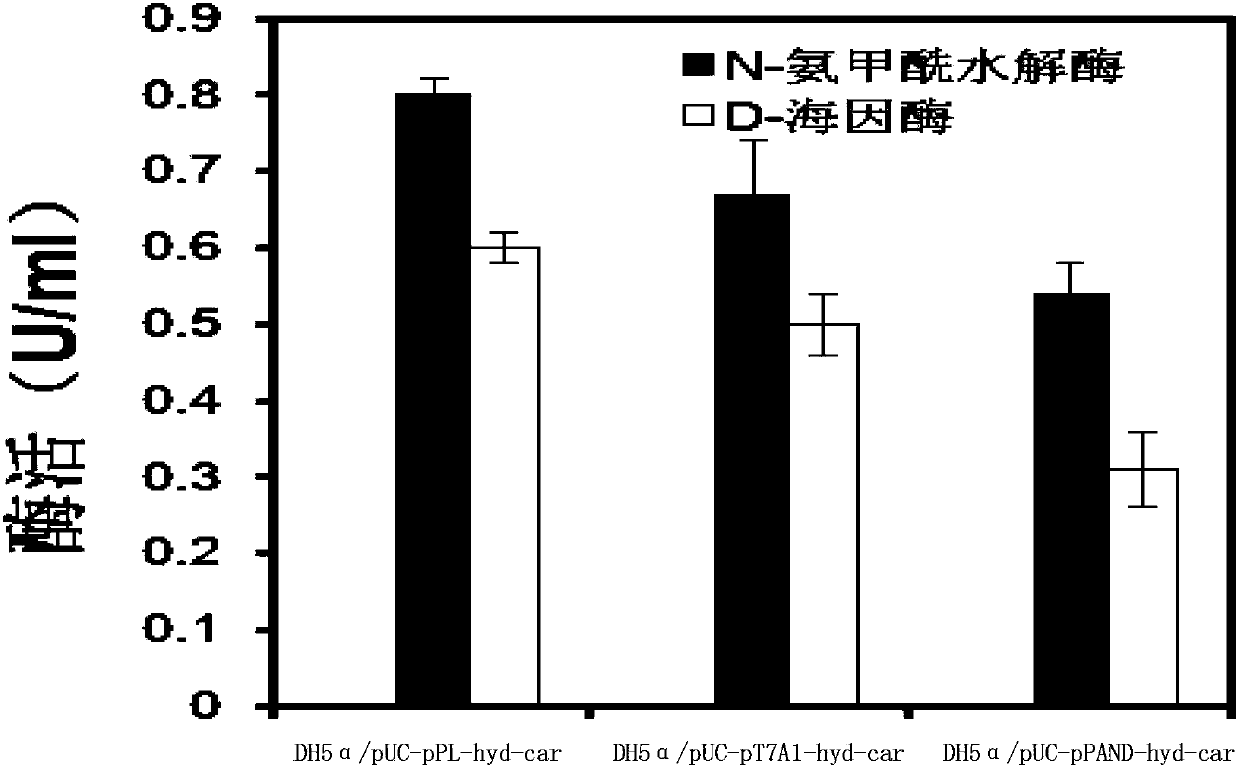
Hydantoinase and carbamoyl hydrolase producing strain, bienzyme gene and application thereof for preparing L-amino acid
InactiveCN101215533AImprove thermal stabilityGood substrate toleranceBacteriaHydrolasesChemical synthesisHydrolase Gene
The invention relates to a new microbe Bacillus fordii MH602 strain which can simultaneously produce hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase, hydantoinase produced by strain, L-N-carbamyl hydrolase gene and an application for preparing serial optical pure L-amino acid through the strain. The hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase that are produced by Bacillus fordii MH602 strain can overcome the defect of worse activity and heat stability of hydantoinase and L-N-carbamyl hydrolase in the L-amino acid procedure prepared by prior biologically inverted DL-5 substitution hydantoin or N-hydantoin amino acid, which is all provided with wide substrate spectrum, can catalyze a plurality of substrates and has better substrate selectivity for aromatic hydantoin. The applying operation for preparing L-amino acid by Bacillus fordii MH602 is simple and stable in operation, good in repeatability, which realizes stable and cheap preparation of L-amino acid and is beneficial to do large-scale preparation.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation method of maltooligosyltrehalose hydrolase gene sequence and recombinant protein thereof
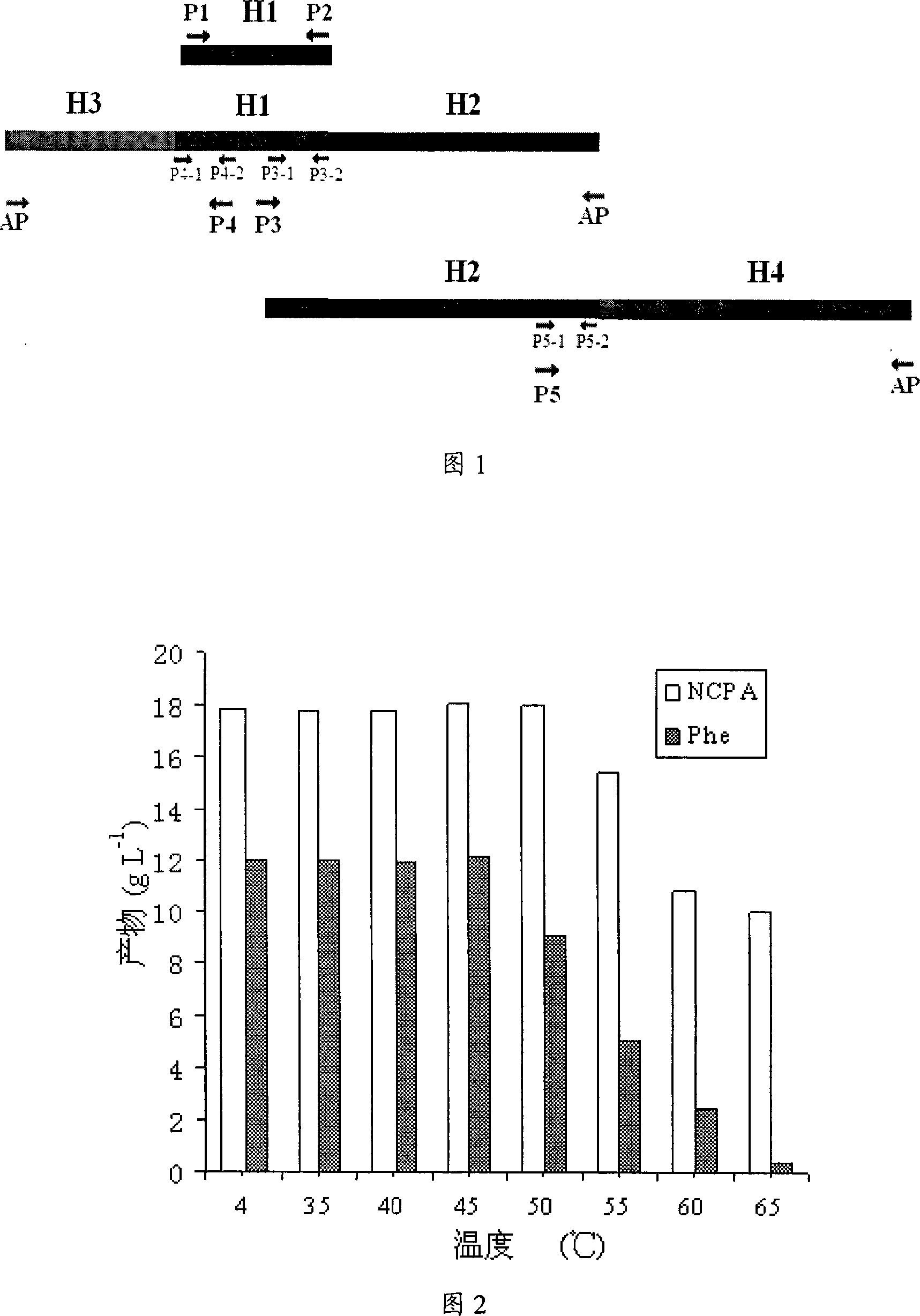
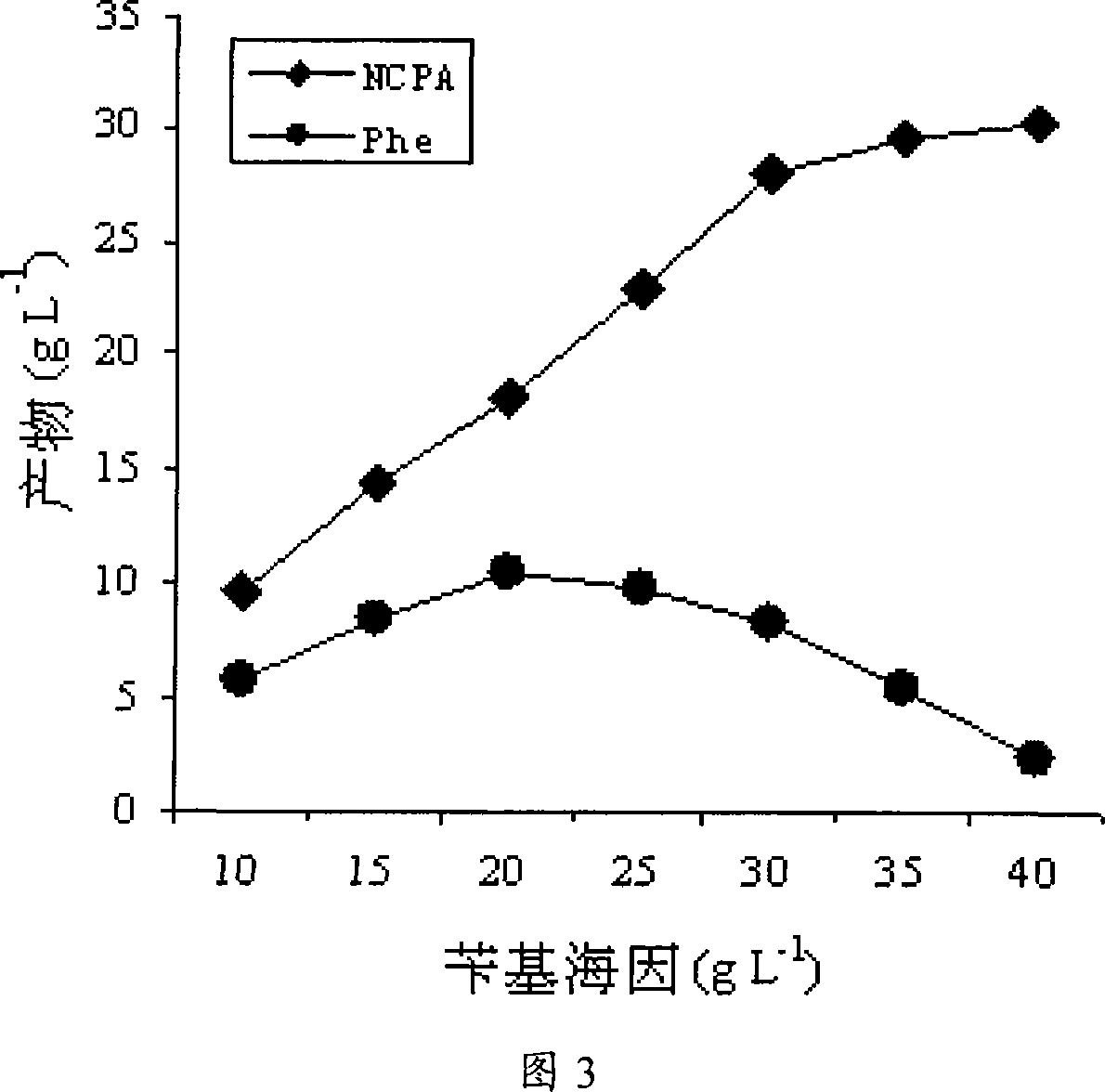
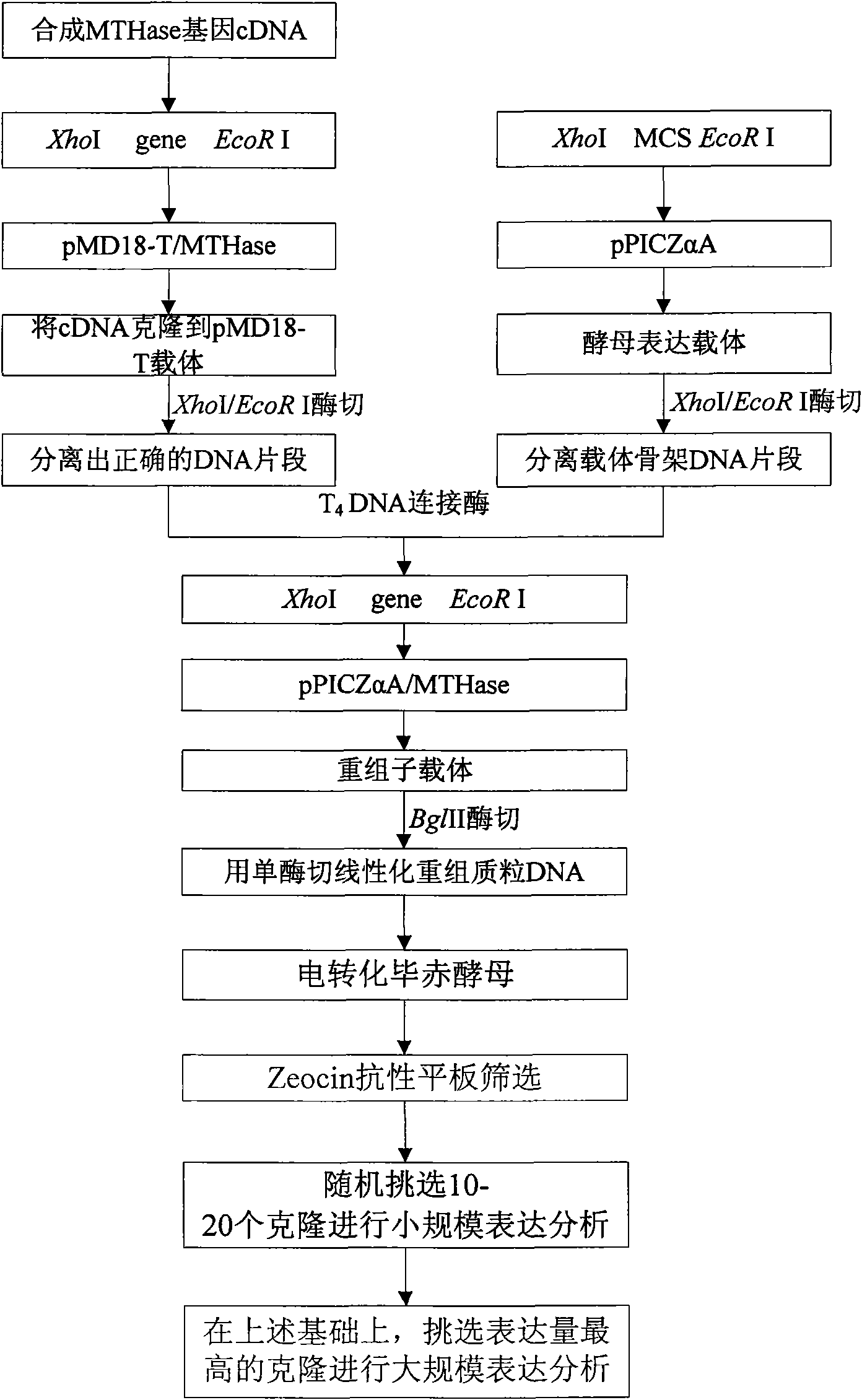
The preparation method of the invention comprises the following steps: the genetic codon of maltooligosyltrehalose hydrolase (MTHase) gene is modified artificially, yeast preferred codon is synthesized and the A / T content of the genetic codon is modified, a MTHase gene sequence of which structure of genetic codon is optimized and A / T content is reduced is obtained; then the complete MTHase gene is cloned to the yeast expression vector pPICZ alpha A, recombinant vector is screened out and introduced in Pichia Pastoris cell to perform recombinant expression; and a yeast strain which can efficiently and stably express MTHase can be obtained. The enzyme activity of MTHase which is secreted by the yeast strain in the supernate of expression culture medium is more than 800mg / L, thus the preparation method of the invention lays a foundation for the industrial production of trehalose which adopts enzyme process and uses starch as raw material.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
Novel phthalate hydrolase EstJ6 as well as coding gene and application thereof
ActiveCN110982803AImprove space utilizationBroad substrate specificityBacteriaHydrolasesEscherichia coliHeterologous
The invention provides a novel phthalate hydrolase gene derived from a soil metagenome library. The nucleotide sequence and an amino acid sequence of the novel phthalate hydrolase gene are shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and SEQ ID NO.2. After the esterase gene is connected to an expression vector pET28a (+), the esterase gene is transformed into escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) to realize heterologous expression. The molecular weight of the purified recombinase (EstJ6) is 33.31 kDa. The EstJ6 has wide substrate specificity on phthalate, and the EstJ6 not only can hydrolyze phthalate with a simple side chain,but also can hydrolyze diethyl hexyl phthalate and monoethyl hexyl phthalate with complex and longer side chains. In addition, site-specific mutagenesis experiments show that the catalytic triad residue of EstJ6 is S146-E240-H270, and mutation of any amino acid in the three causes the EstJ6 to lose the catalytic ability. The novel phthalate hydrolase disclosed by the invention can be applied to the fields of food industry, agriculture, biotechnology and the like due to the specific activity and enzymatic characteristics of the novel phthalate hydrolase.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Bacillus subtilis for high yield of recombinant nitrilase and application of bacillus subtilis
ActiveCN107254429AImprove security levelReduce manufacturing costBacteriaHydrolasesHydrolase GenePseudomonas putida
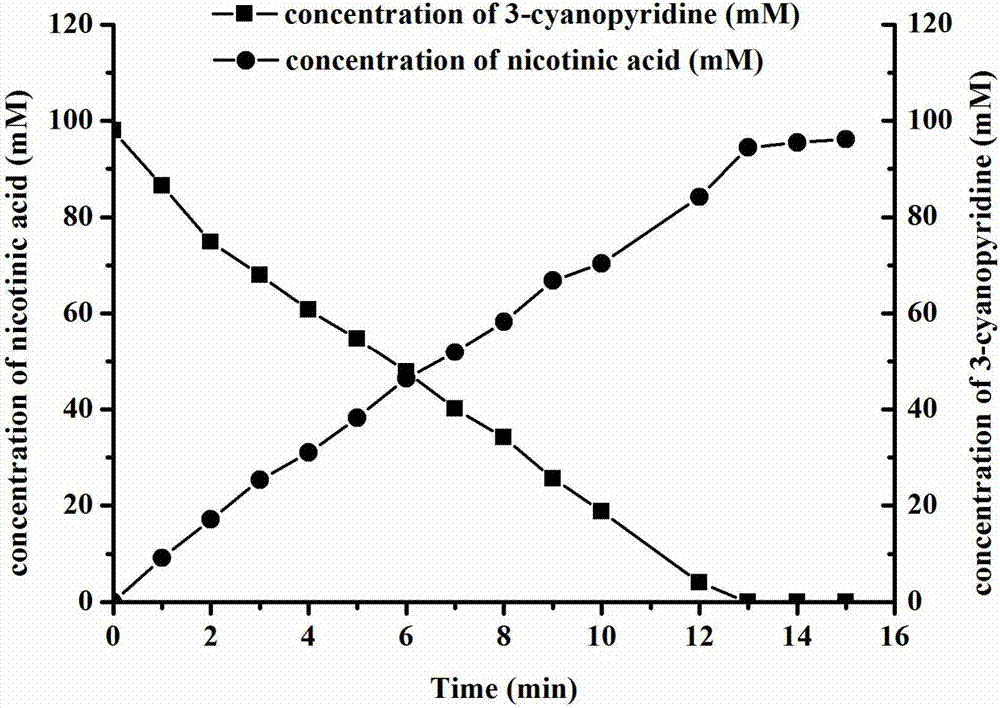
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis for high yield of recombinant nitrilase and application of the bacillus subtilis in nicotinic acid synthesis and belongs to the technical field of biological engineering. A method comprises the following steps: performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification on a Pseudomonas putida CGMCC 3830 nitrilase gene coding sequence, connecting with a pMA5 plasmid, establishing a recombinant plasmid pMat-NIT, and transforming into Bacillus subtilis WB600, thereby obtaining a recombinant bacterium, namely B.subtilis WB600 (pMA5-NIT) which is capable of efficiently expressing nitrilase, wherein the recombinant bacterium is named as Bacillus subtilis NIT-2 and is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the preservation number is CGMCC No.14255. With recombinant bacillus subtilis free cells as a catalyst, 3-cyanopyridine can be completely transformed to generate nicotinic acid. The invention provides a bacillus subtilis strain for high yield of recombinant nitrilase, and the bacillus subtilis strain has outstanding nitrilase activity and is short in recombinant bacterium fermentation period, high in catalysis efficiency and good in application prospect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Construction and application of broad spectrum organic phosphorus pesticide degradation genetic engineering strain
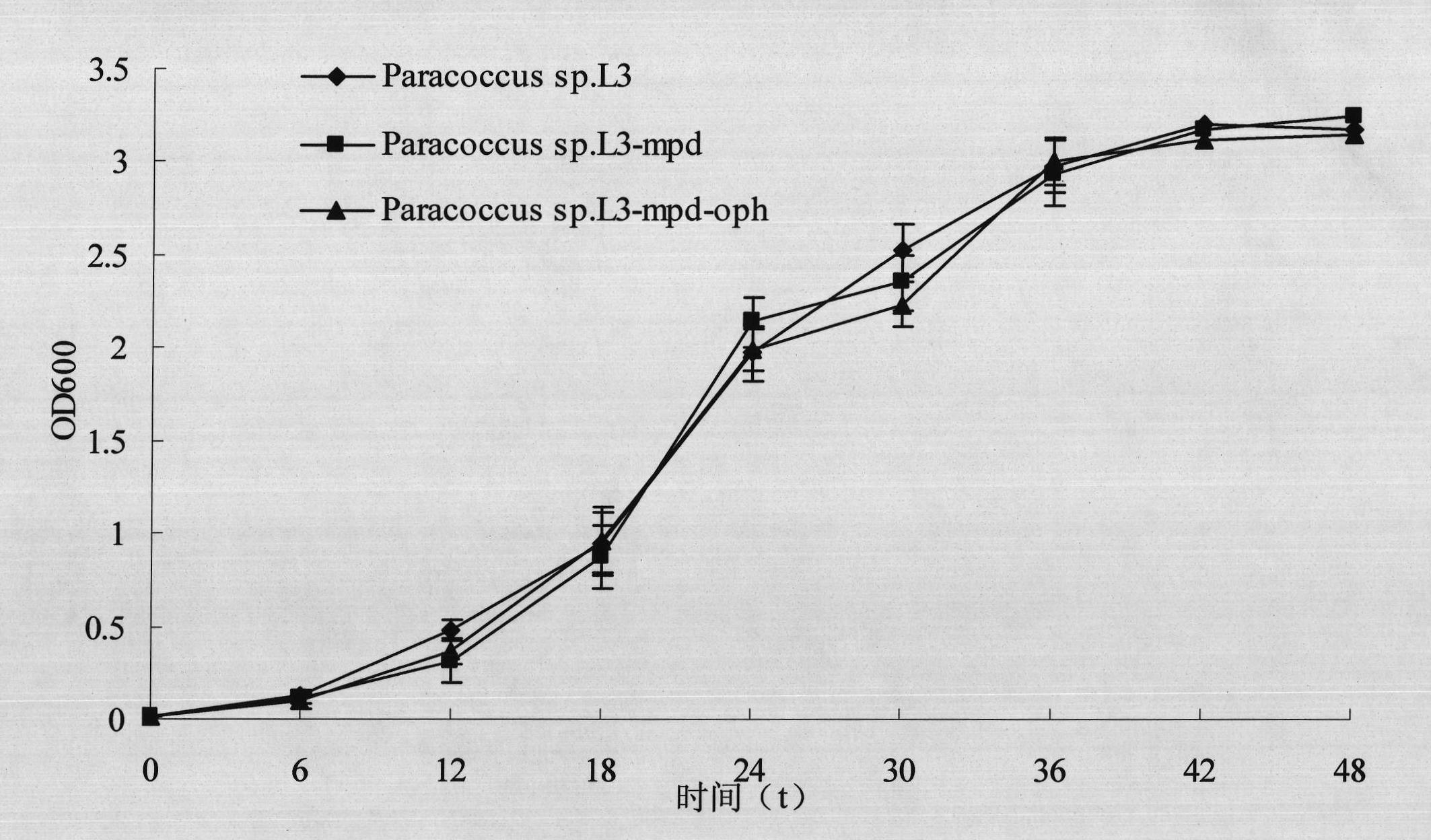
The invention discloses construction and application of a broad spectrum organic phosphorus pesticide degradation genetic engineering strain, and belongs to the field of biological engineering technology. The engineering strain 1gmp is the engineering strain paracoccus sp. 1gmp for degrading the organic phosphorus pesticide in a broad spectrum, which is constructed by sequentially inserting two organic phosphorus hydrolase genes mpd and oph with different substrate degradation spectrums into the chromosome of dimethoate high-efficiency degradation strain paracoccus sp. L3 by using random integration of a serious of vectors pUTTns and deleting a resistant gene by counter-selection marking; and degradation spectrum measurement shows that the engineering strain can efficiently degrade 17 organic phosphorus pesticides generally used in China at present. The engineering strain has the advantages of genetic stability, biological safety and great potential application prospect.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of flavonoids compound and application thereof
ActiveCN107164253AImprove efficacyGood water solubilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydrolase Gene
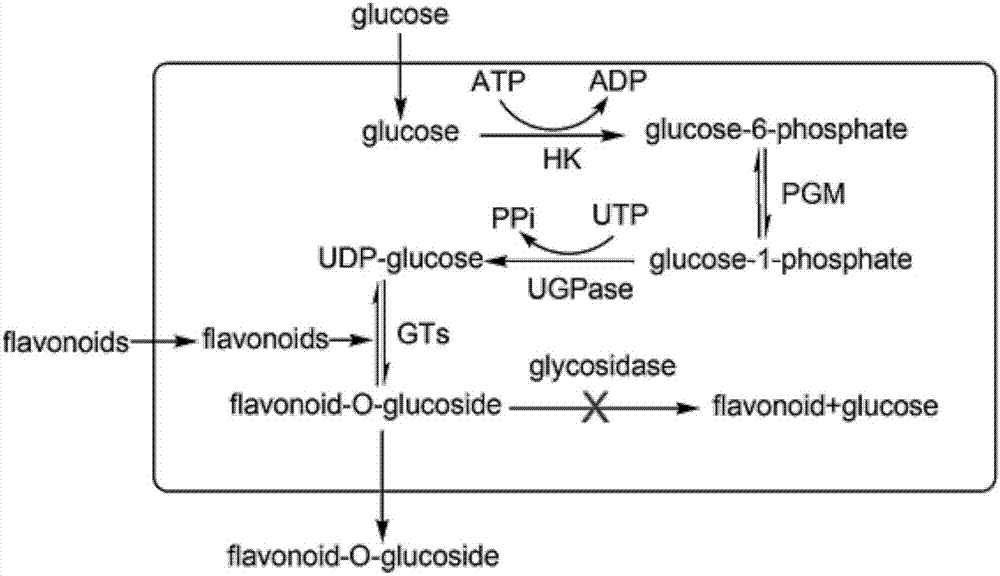
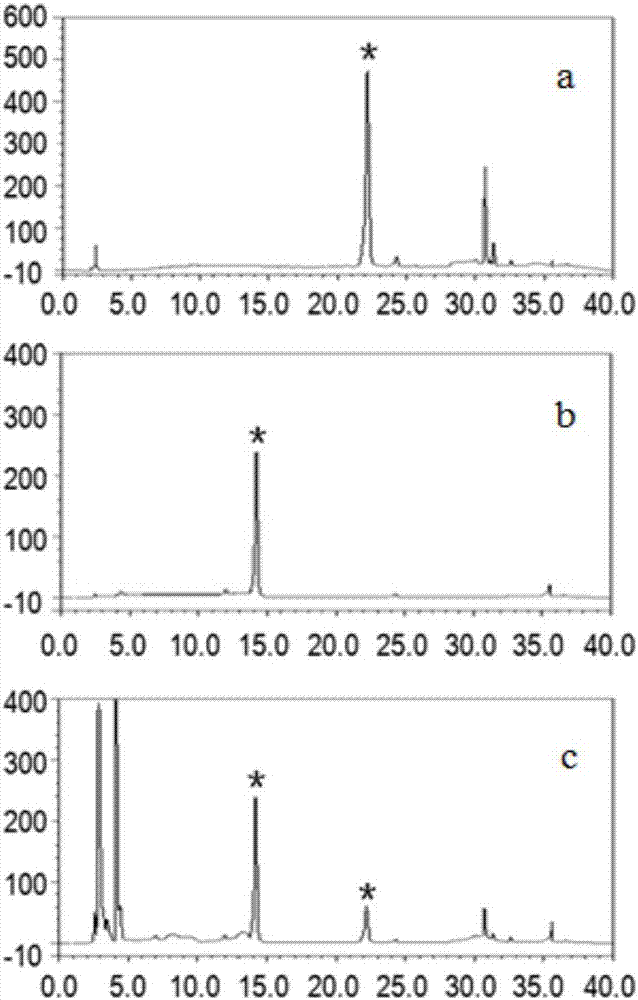
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of a flavonoids compound and an application thereof. Specifically, a Beta-glycoside hydrolases gene of a chassis biological cell is removed according to the genetically engineered bacterium, and endogenous degradation of a glycosylation product is reduced; the high-expression regulation is performed to two key enzymes of glucophosphomutase (PGM) and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGP1) of the chassis biological cell for participating in the synthesis of glycosylated-donor uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-Glu), and a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene for catalyzing the flavonoid aglycones glucose glycosylation is combined so as to obtain a genetically engineered strain for effectively catalyzing the glucose glycosylation of the flavonoids compound, and finally scutellarein is used as a catalytic substrate for fermenting for 54 h in 10 L of a fermentation tank, wherein the yield of scutellarein-7-O-glucose of the glycosylation product is up to 1200 mg / L. The used strategy provides a technology reference for biologically-catalyzing chemical micromolecular glycosylation by using a microbiological method.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Coding gene of cis-form epoxy succinic acid hydrolase, polypeptides coded thereby and related applications
The invention relates to a coding gene of cis-form epoxy succinic acid hydrolase, polypeptides coded thereby and related applications. The coding gene of cis-form epoxy succinic acid hydrolase has a nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The cis-form epoxy succinic acid hydrolase coded by the gene has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:2. Colibacillus is converted by utilization of prokaryotic expression vectors constructed by the cis-form epoxy succinic acid hydrolase gene and genetically engineered bacteria are constructed. After being induced, the genetically engineered bacteria can convert cis-form epoxy succinic acid or salts thereof into L(+)-tartaric acid or salts thereof efficiently. The cis-form epoxy succinic acid hydrolase obtained from the colibacillus has the capability of converting cis-form epoxy succinic acid or salts thereof into L(+)-tartaric acid or salts thereof efficiently.
Owner:HANGZHOU BIOKING BIOCHEM ENG
Marine bacterium derived thermal-stable and salt-tolerant SGNH family hydrolytic enzyme and application
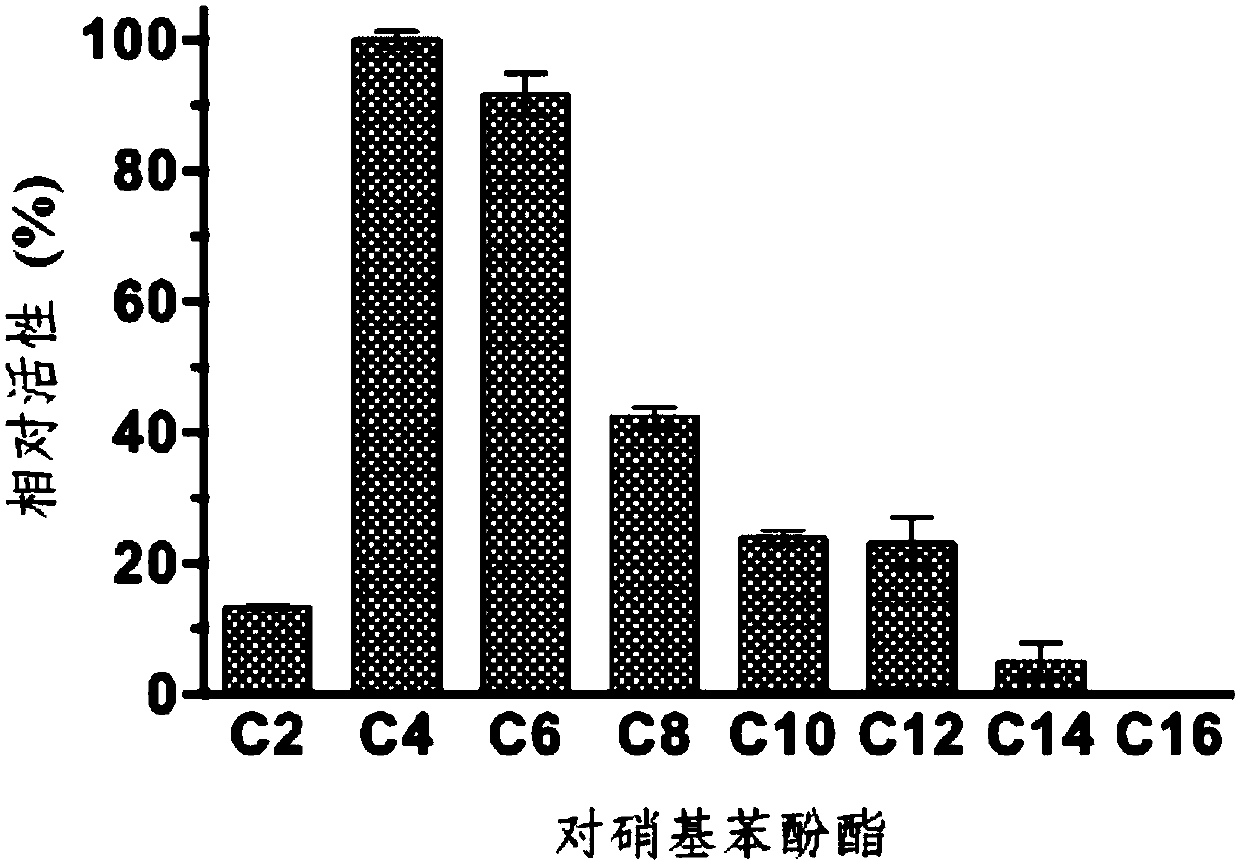
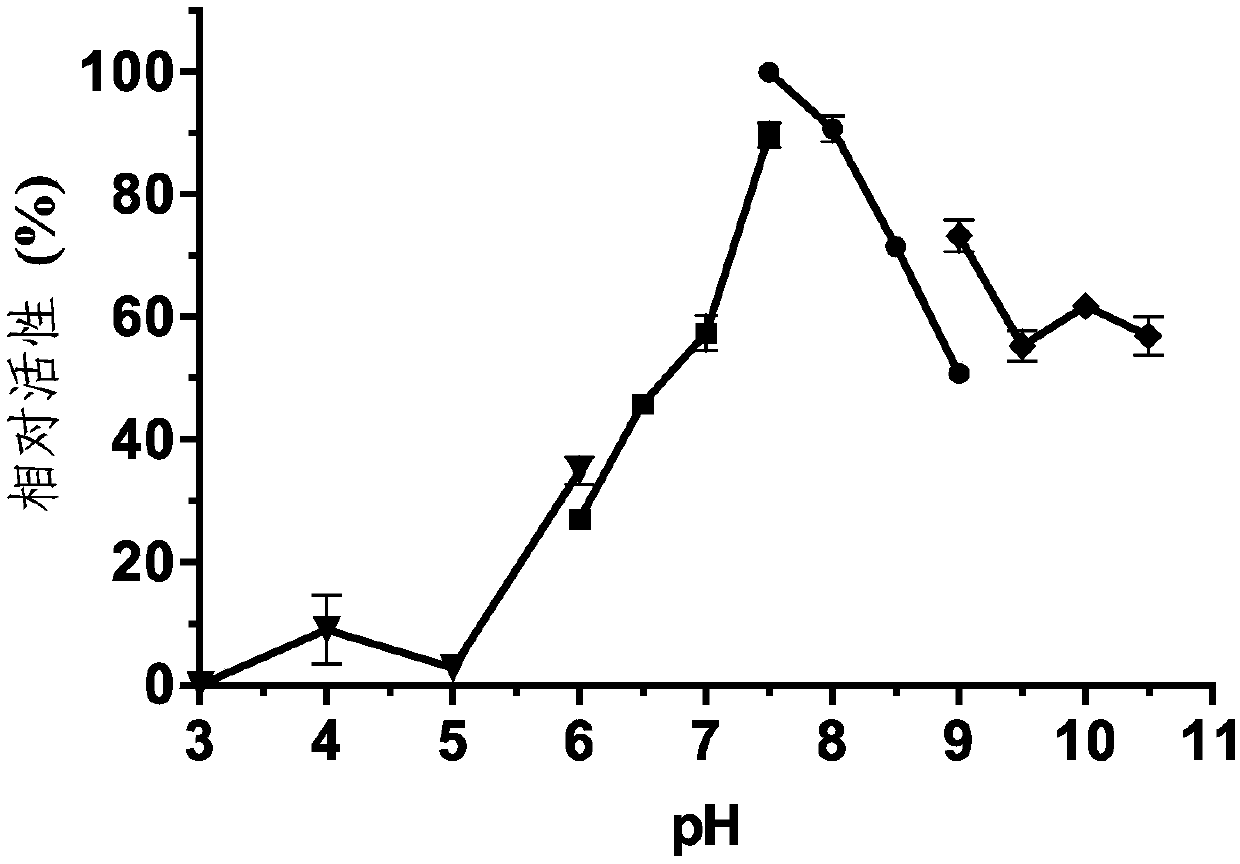
ActiveCN107893060ALow costExcellent enzymatic propertiesHydrolasesGenetic engineeringHeterologousHydrolase Gene
The invention discloses novel marine bacterium derived thermal-stable and salt-tolerant organic solvent SGNH family hydrolytic enzyme AlinE4 as well as a coding gene and an application of the hydrolytic enzyme. The hydrolytic enzyme aline4 provided by the invention comes from Altererythrobacter indicus DSM18604, and a nucleotide sequence of the hydrolytic enzyme aline4 is shown as SEQ ID NO.1. Thehydrolytic enzyme gene provided by the invention, after undergoing heterogeneous expression, has esterase activity, and the maximum catalytic activity, namely 25.8U / mg, is achieved when p-nitrophenolbutyrate (C4) is taken as a substrate. The optimum catalytic hydrolysis pH and temperature of the AlinE4 are 7.5 and 40 DEG C; the AlinE4, when bred at 40 DEG C, 50 DEG C and 60 DEG C for 60min, canstill keep the activity above 50%; and with the presence of an organic solvent and metal ions, relatively high enzymatic activity is kept. The hydrolytic enzyme has the characteristics of being thermal-stable and alkaline; and the hydrolytic enzyme is applicable industrial production in such fields as detergents, wastewater treatment, fine chemical engineering, pharmacy, environmental remediationand the like under the conditions of high temperature and containing salt and organic solvents.
Owner:SECOND INST OF OCEANOGRAPHY MNR
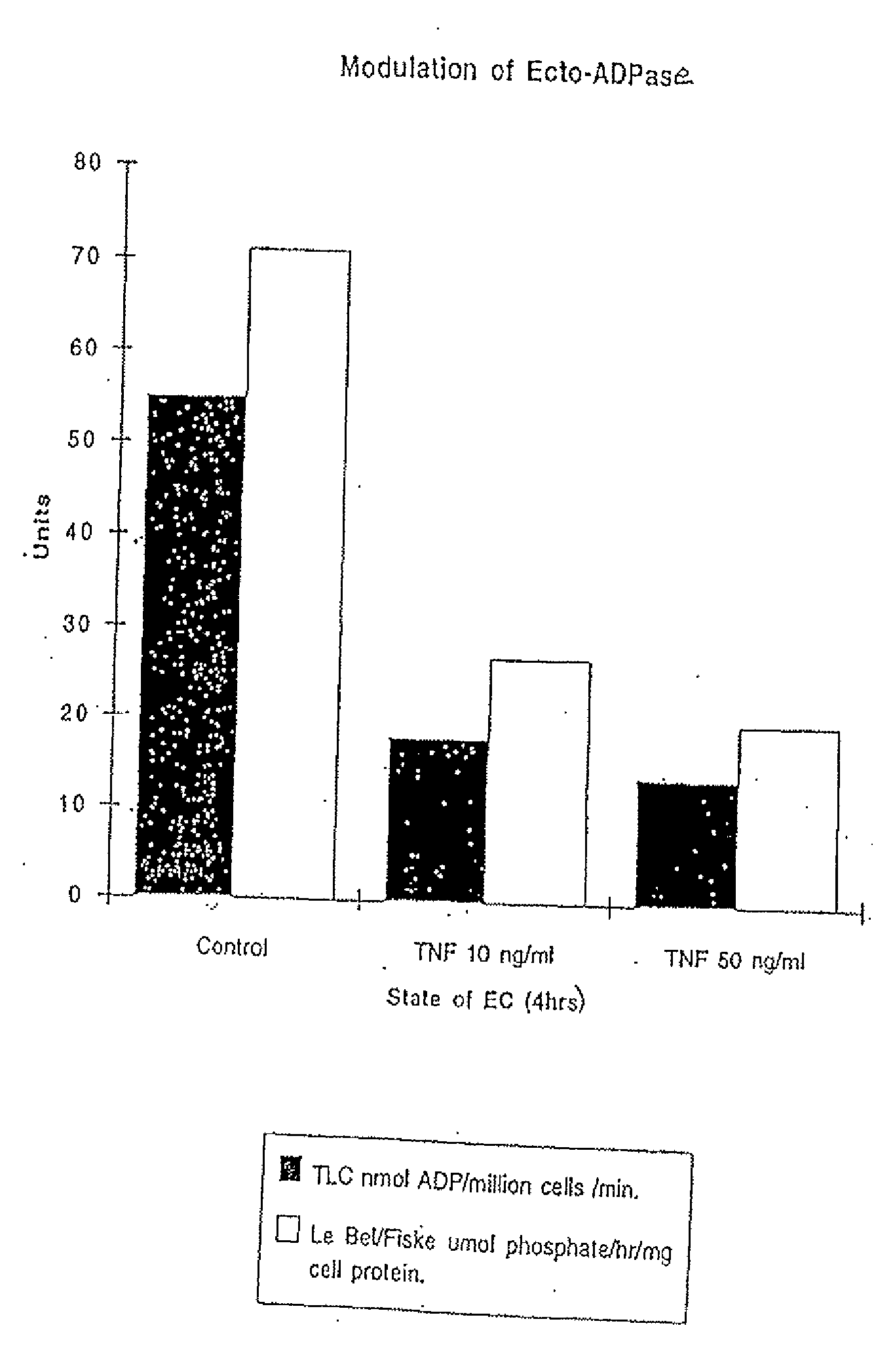
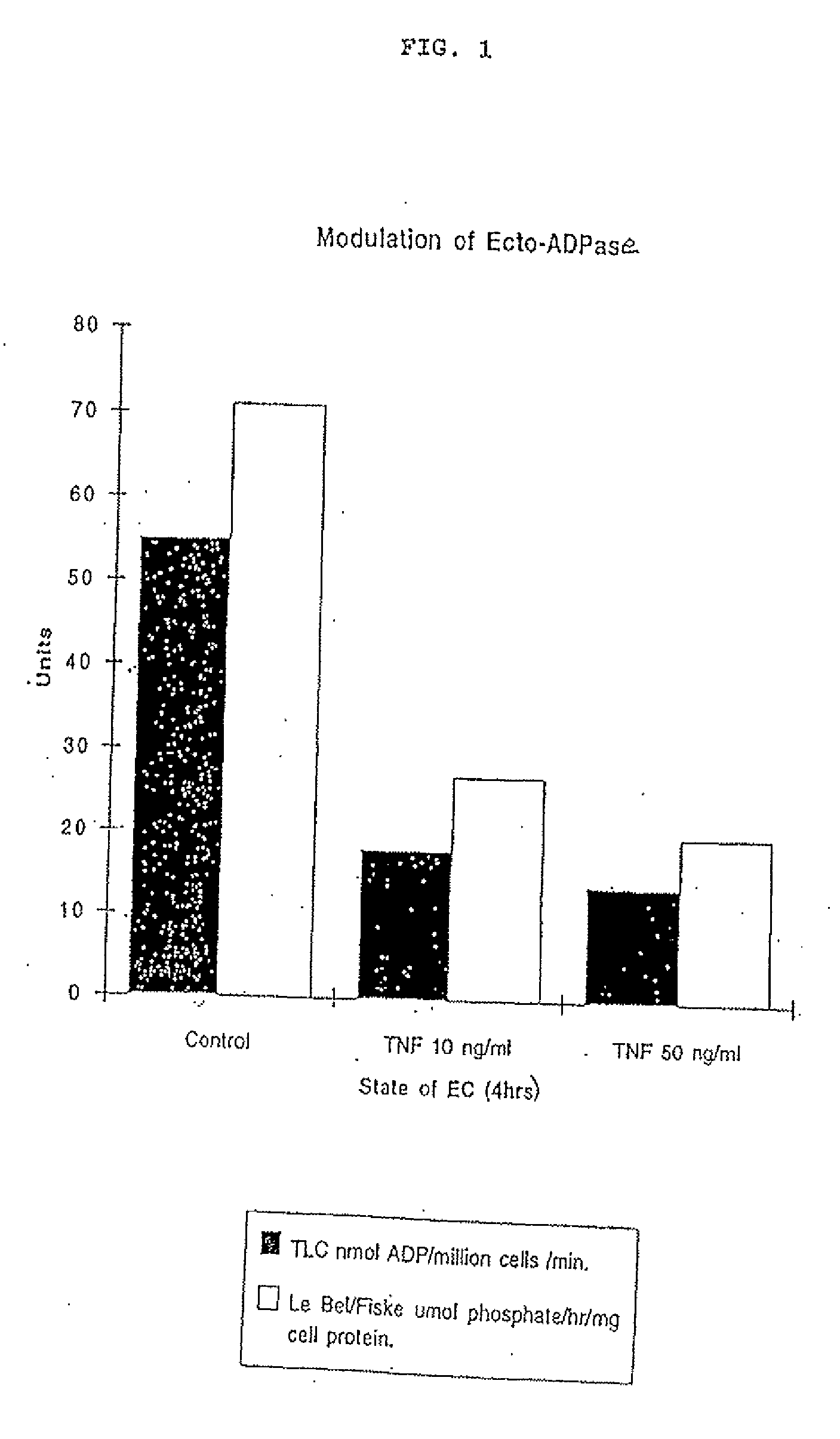
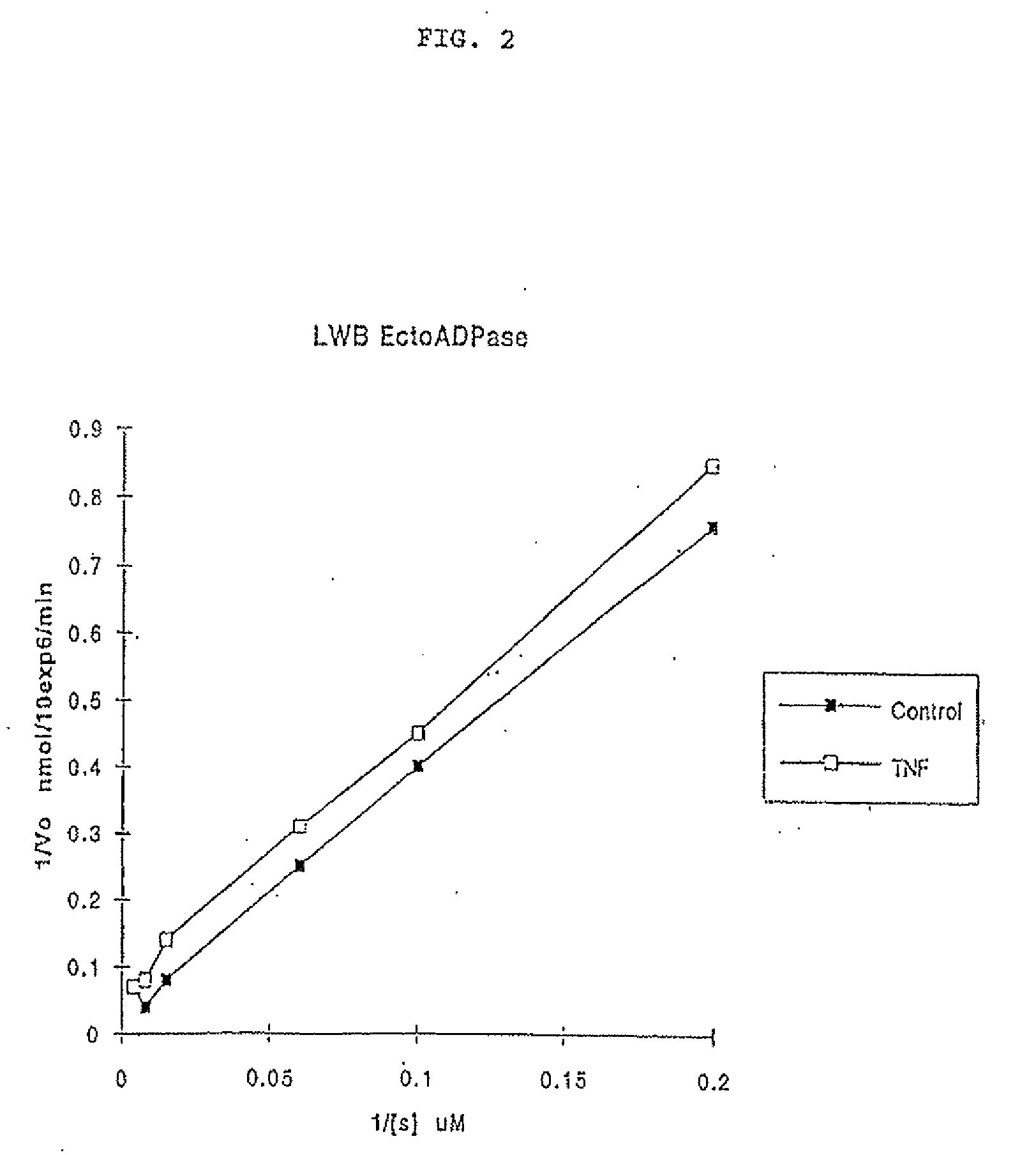
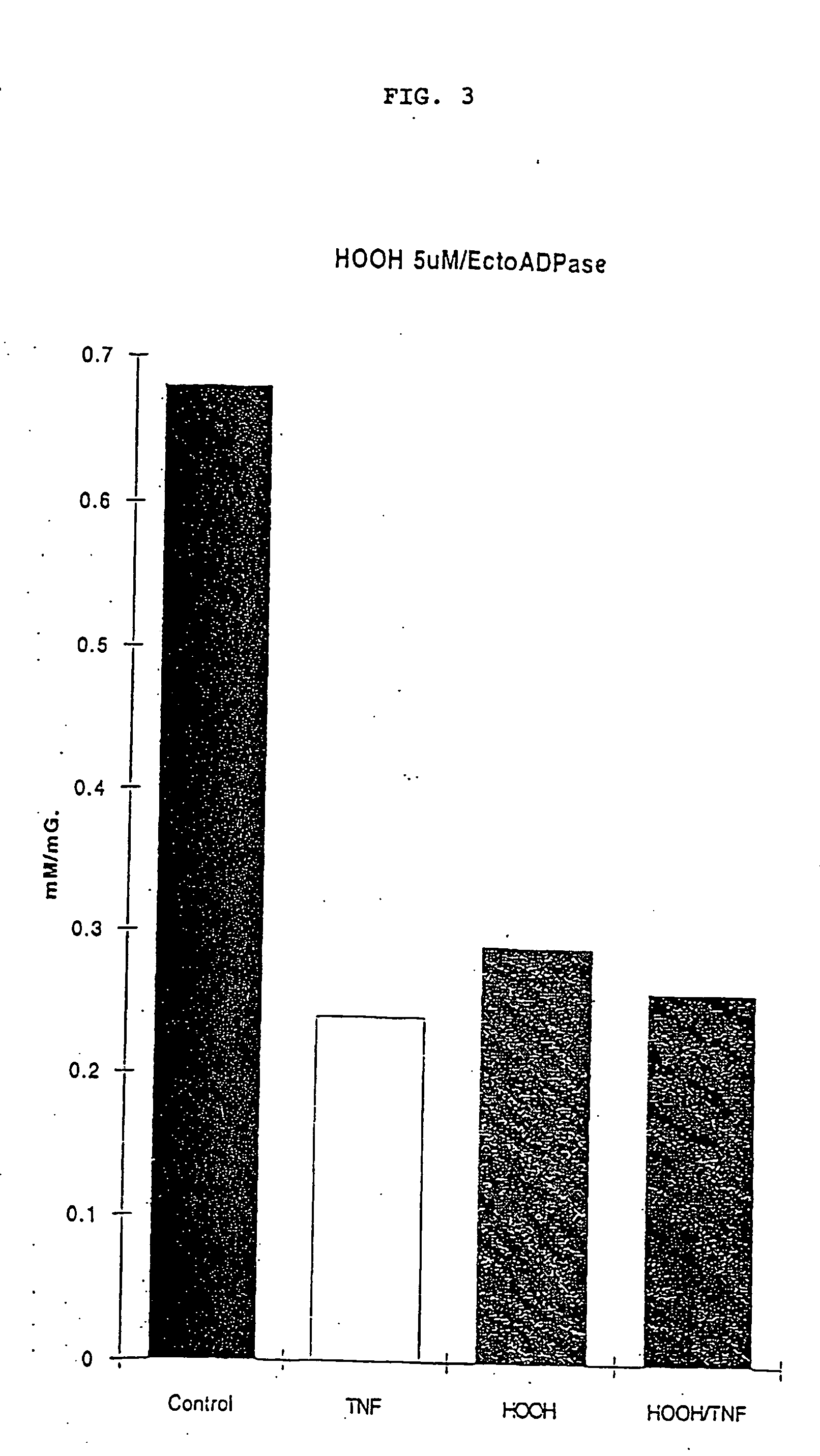
ATP Diphosphohydrolase (CD39) Gene Therapy for Inflammatory or Thrombotic Conditions for Transplantation and Means Therefor
InactiveUS20080003212A1Increased susceptibility to platelet aggregationInhibition of activationPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesHydrolase GeneWhite blood cell
A method render endothelial cells capable of inhibiting platelet and leukocyte-mediated injury and inflammation is described, comprising genetically modifying the cells by inserting DNA encoding ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase or an oxidation-resistant analog thereof, and expressing a protein having functional ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase activity, such as the human CD39 protein, by said cells under cellular activating conditions. The method, which can be carried out in vivo, ex vivo or in vitro, has use in allogeneic or xenogeneic transplantation as well as to treat systemic or local inflammatory conditions characterized by platelet aggregation leading to thrombus formation.
Owner:BACH FRITZ +1
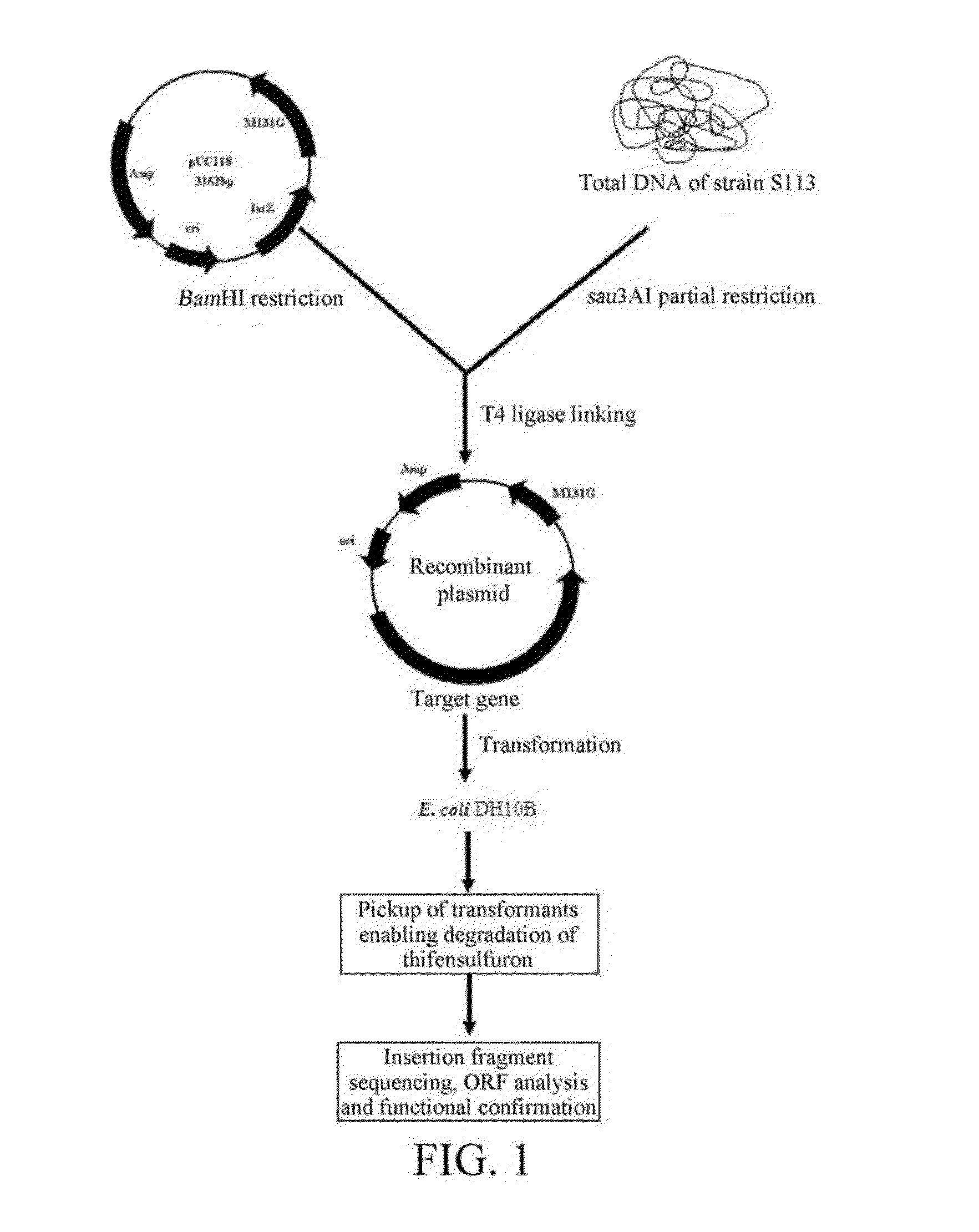
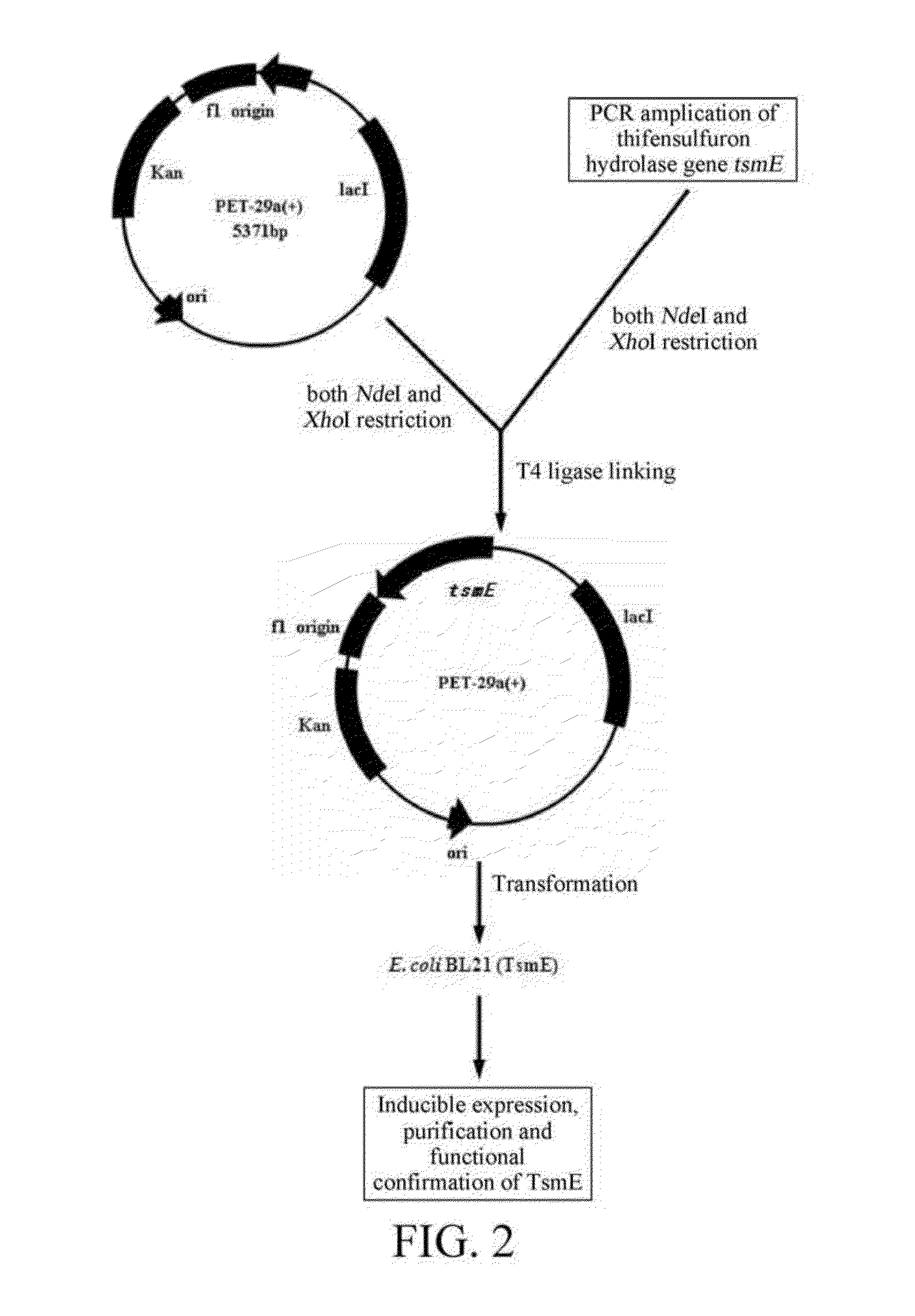
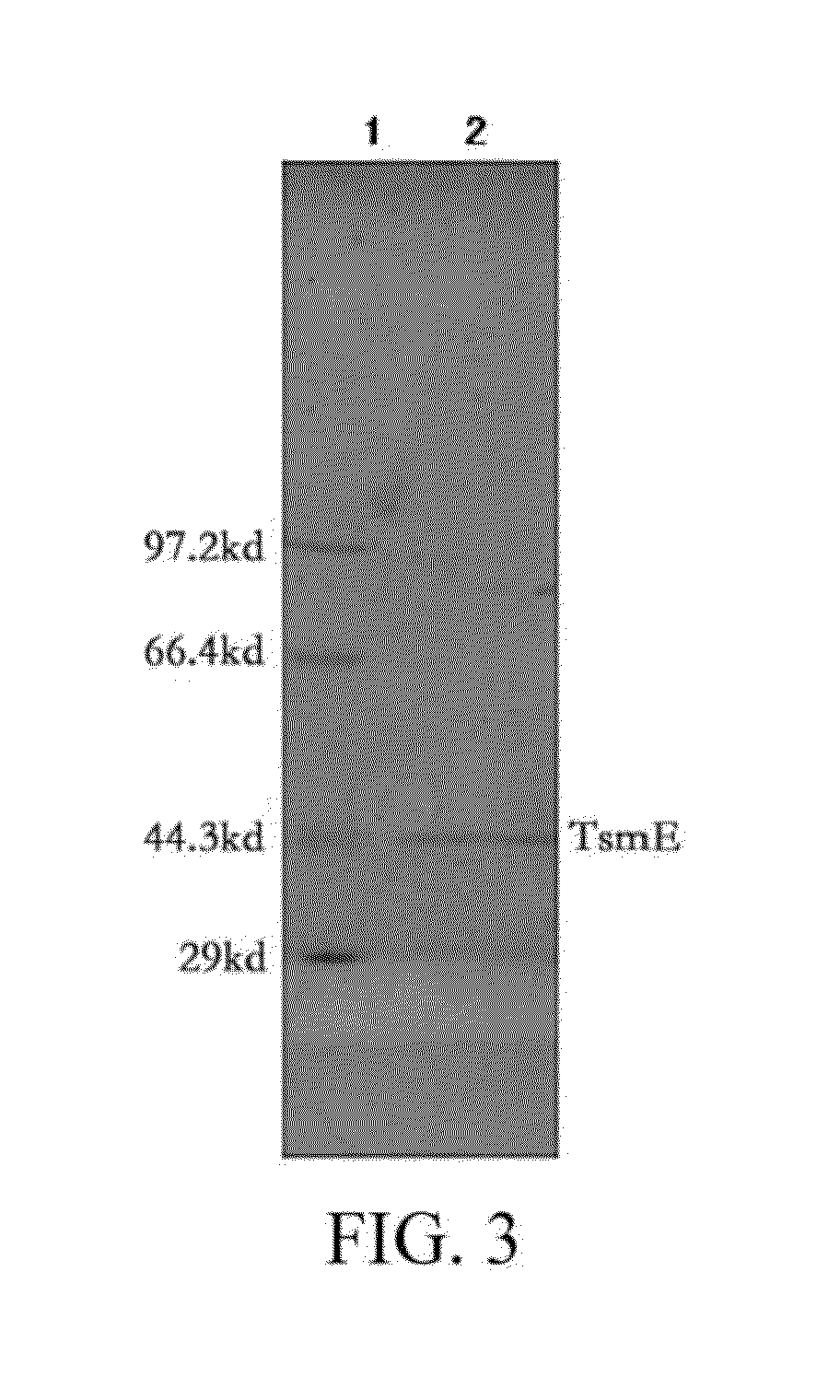
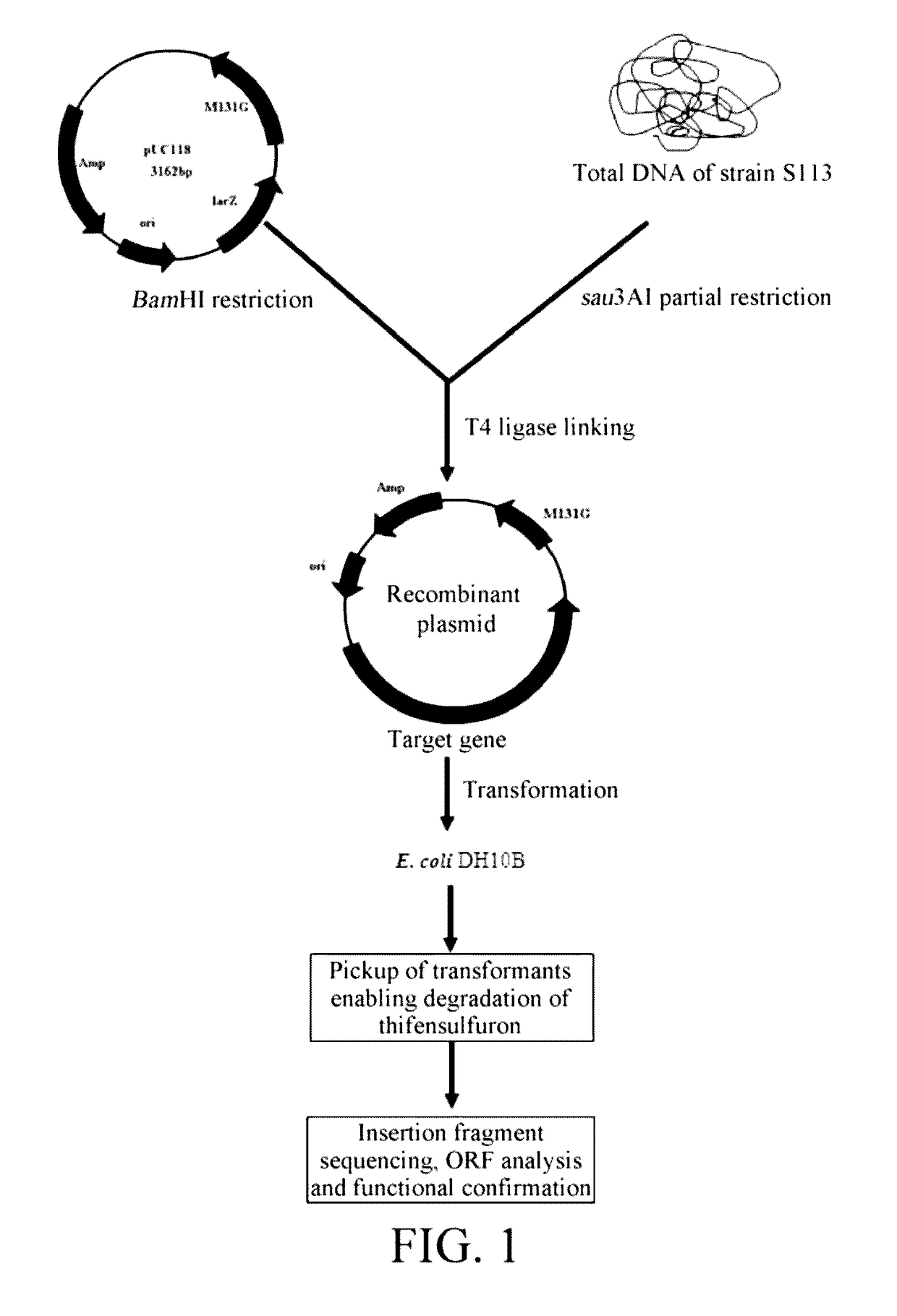
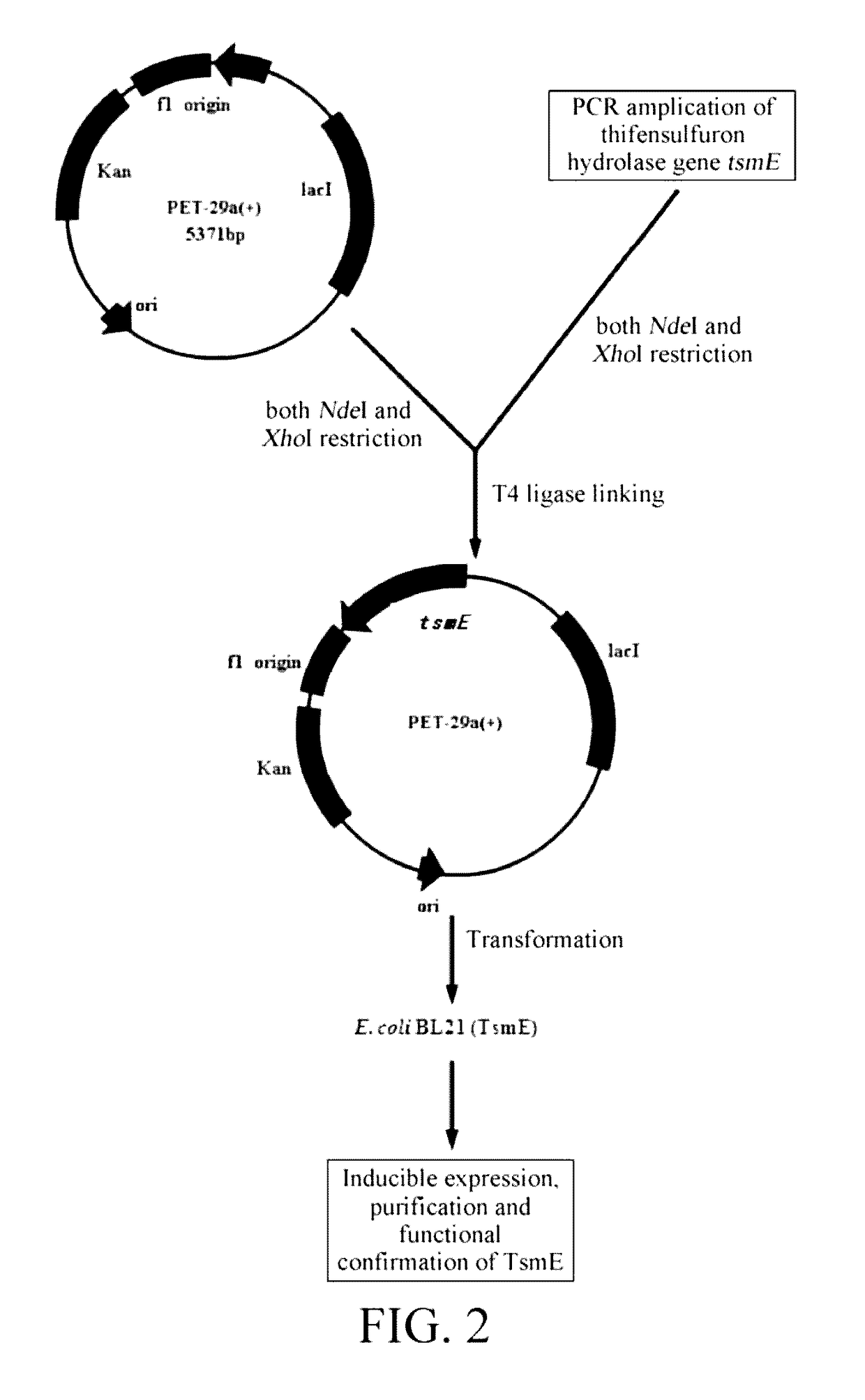
Thifensulfuron hydrolase gene TSME and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the field of applied and environmental microorganism and agriculture. Disclosed are a thifensulfuron hydrolase gene tsmE and uses thereof. The thifensulfuron hydrolase gene tsmE has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO.1, full length of 1194 bp, and G+C content of 51.09%, and encodes 398 amino acids with an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO.2. The thifensulfuron hydrolase TsmE provided by the present invention can degrade completely 100 mg / L thifensulfuron within 1 hour into the herbicidally inactive product thiophenesulfonic acid; in addition, the TsmE also degrade completely 100 mg / L haloxyfop-R-methyl within 1 hour. Therefore, the thifensulfuron hydrolase gene tsmE is useful in construction of thifensulfuron-resistant transgenic crops and bioremediation of thifensulfuron or haloxyfop-R-methyl-contaminated environments.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
GTP cyclohydrolase I gene folE and application
Owner:KUNMING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
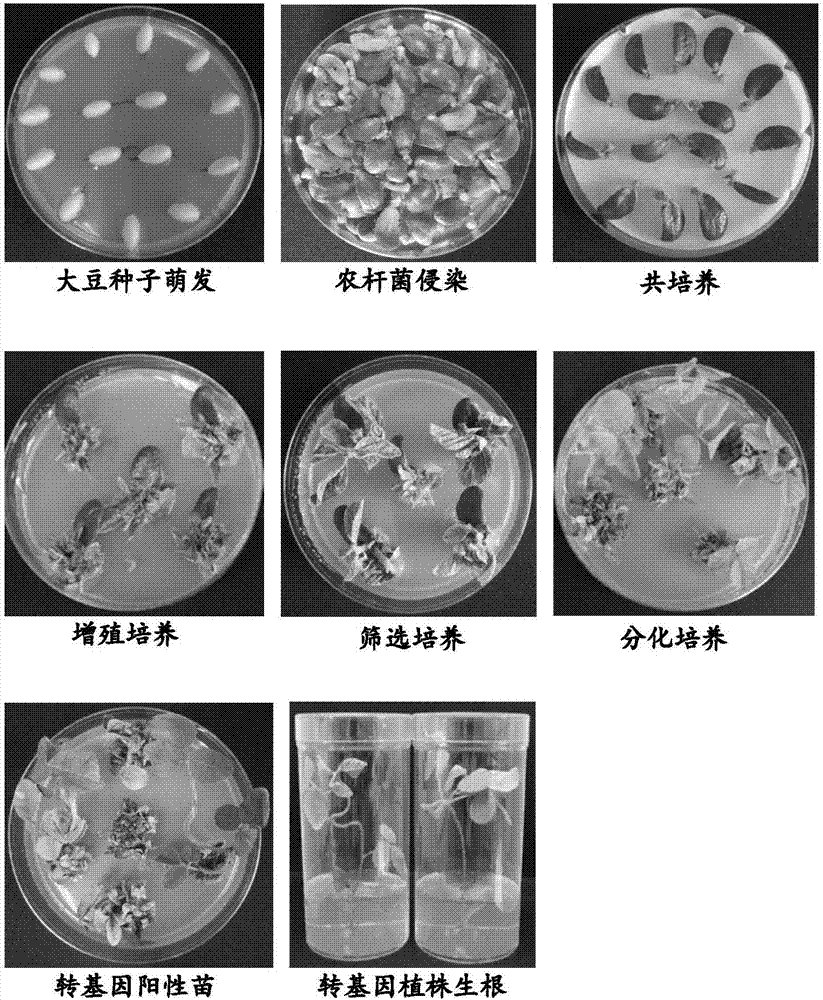
Method for improving transformation efficiency of soybean
ActiveCN107099548AIncreased rate and conversion efficiencyToleratedVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsHydrolase GenePlant cell
The invention relates to a method for improving the transformation efficiency of soybean. A method for selecting transformed plant cells comprises the following steps: transforming the plant cells by using a recombinant carrier of a gene containing a target gene and a gene for encoding sulfonylurea herbicide hydrolase; carrying out screening culture on the transformed plant cells by externally applying an ALS (Acetolactate Synthetase) inhibitor, and using the gene for encoding the sulfonylurea herbicide hydrolase as a selected marker; selecting the plant cells which are not killed and / or not inhibited. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a method of adding a selective agent into an enrichment culture medium and a differential culture medium by an external application mode (in particular to dropping) in the plant transforming process is put forward for the first time, and effective concentration screening range of the selective agent is optimized, and the proportion and the transformation efficiency of positive plants obtained by an offspring are remarkably improved; meanwhile, transgenic plants obtained by transformation using the sulfonylurea herbicide hydrolase as the selected marker have the advantages of high commercial value, good resistance and genetic stability.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Helianthus tuberosus fructan-exohydrolases (Ht-FEH) gene and application thereof
InactiveCN102653769AHas fructan hydrolase activityGood for physical defenseFungiHydrolasesHydrolase GeneAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a helianthus tuberosus fructan-exohydrolases (Ht-FEH) gene and application of the Ht-FEH gene. The gene Ht 1-FEH has a nucleotide sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.1 and is used for coding Ht 1-FEH with an amino acid sequence shown in the SEQ ID NO.2. The gene Ht 1-FEH can be applied to production of fructose substances through hydrolysis of inulin or cultivation of transgenic salt-tolerant plants.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
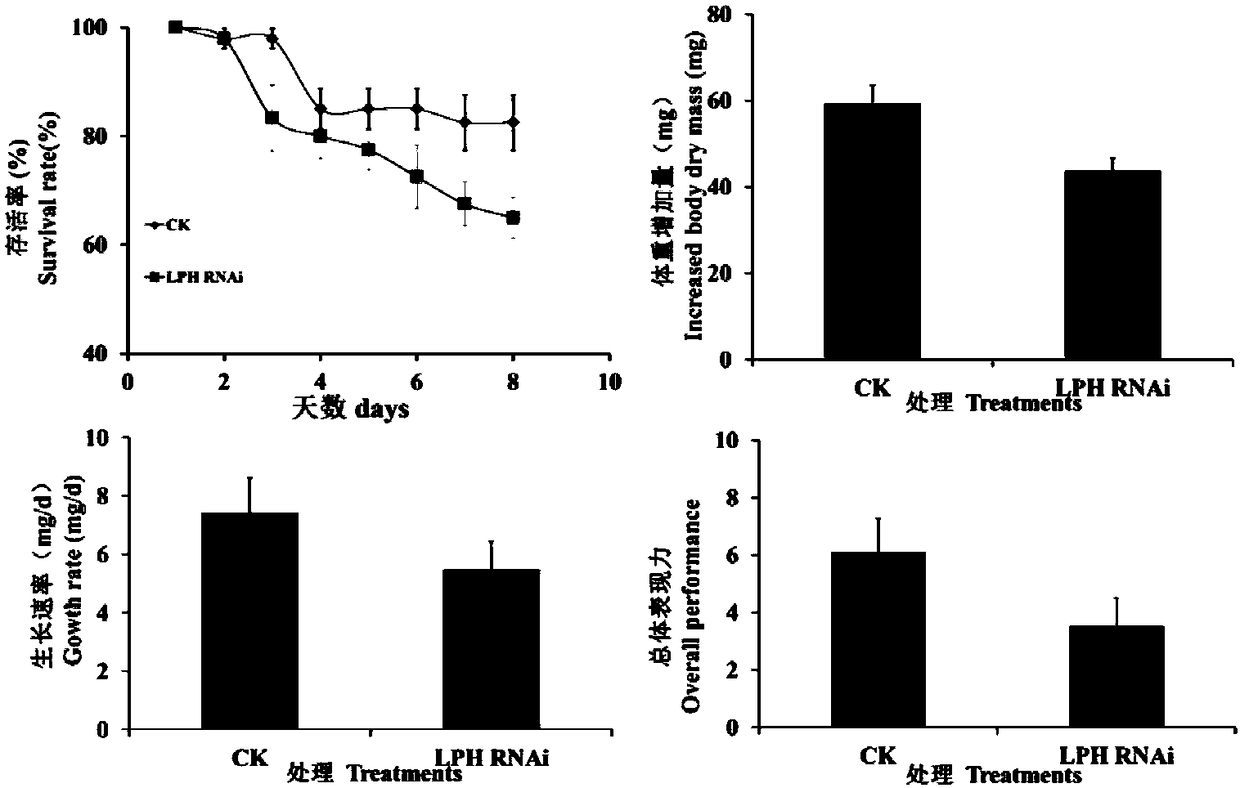
Oedaleus decorus asiaticus lactase-phlorizin hydrolase (LPH) as well as coding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN108611338AReduced survival rateReduced growth rateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiologyLactase-phlorizin hydrolase
The invention discloses oedaleus decorus asiaticus lactase-phlorizin hydrolase (LPH) as well as a coding gene and application thereof. The oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH is cloned from oedaleus decorus asiaticus at first, and a primer is designed for the oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH, so as to synthesize a dsRNA for interfering with an oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH gene; and the dsRNA is introduced into the oedaleus decorus asiaticus through an injection method to perform RNA interfering (RNAi) on the oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH. A result shows that after the dsRNA is injected into the oedaleus decorus asiaticus, the survival rate, the growth rate, the weight and the overall expressiveness are obviously reduced, which indicates that the oedaleus decorus asiaticus LPH plays an important role in an insect growth process. A new method is provided for molecular regulation and control of pests, and a theoretical basis is also provided for deeply understanding an insect growth mechanismand preparing a new biological pesticide preparation.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Recombinant bacterium for expressing glutamine transaminage and application thereof
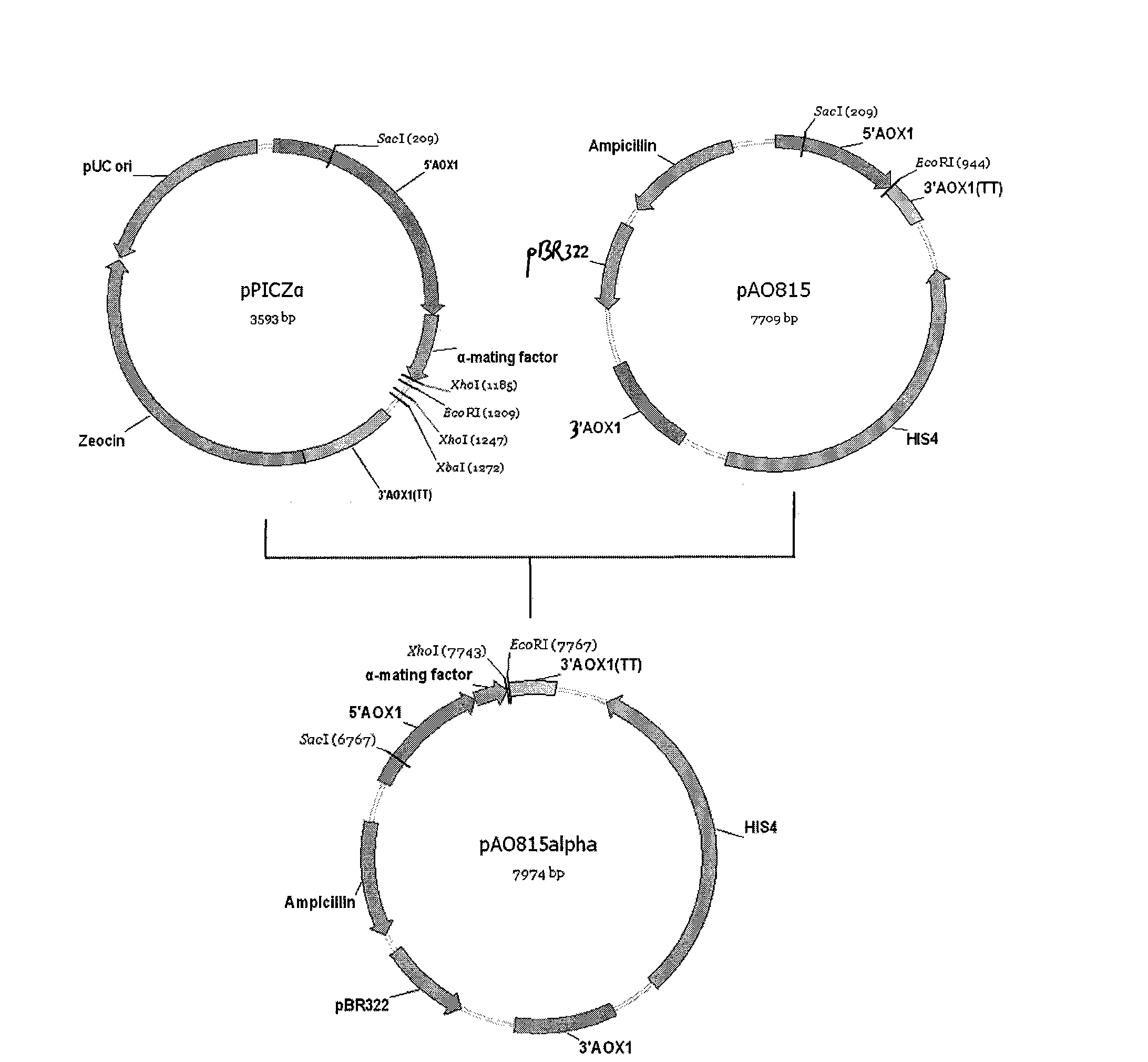
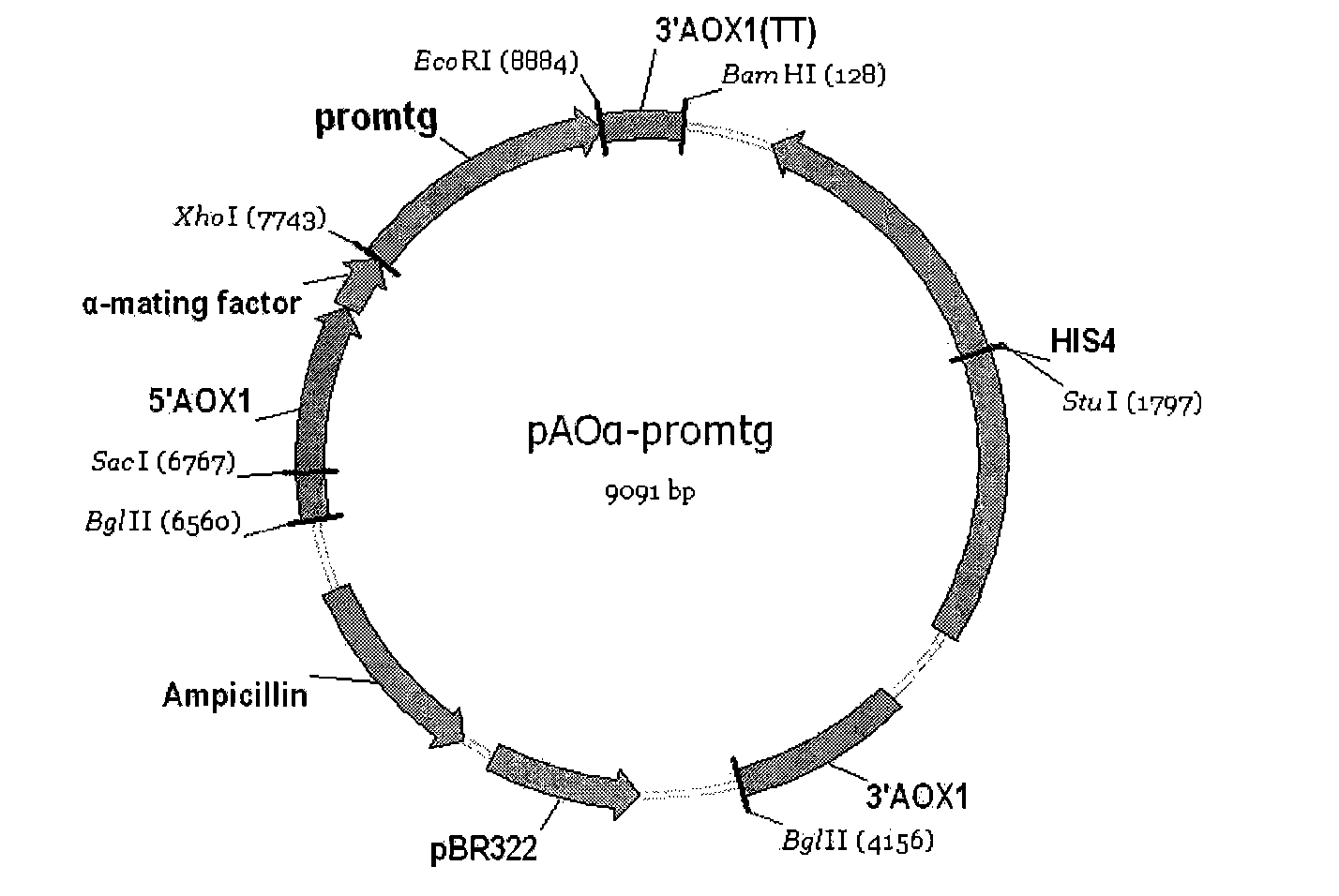
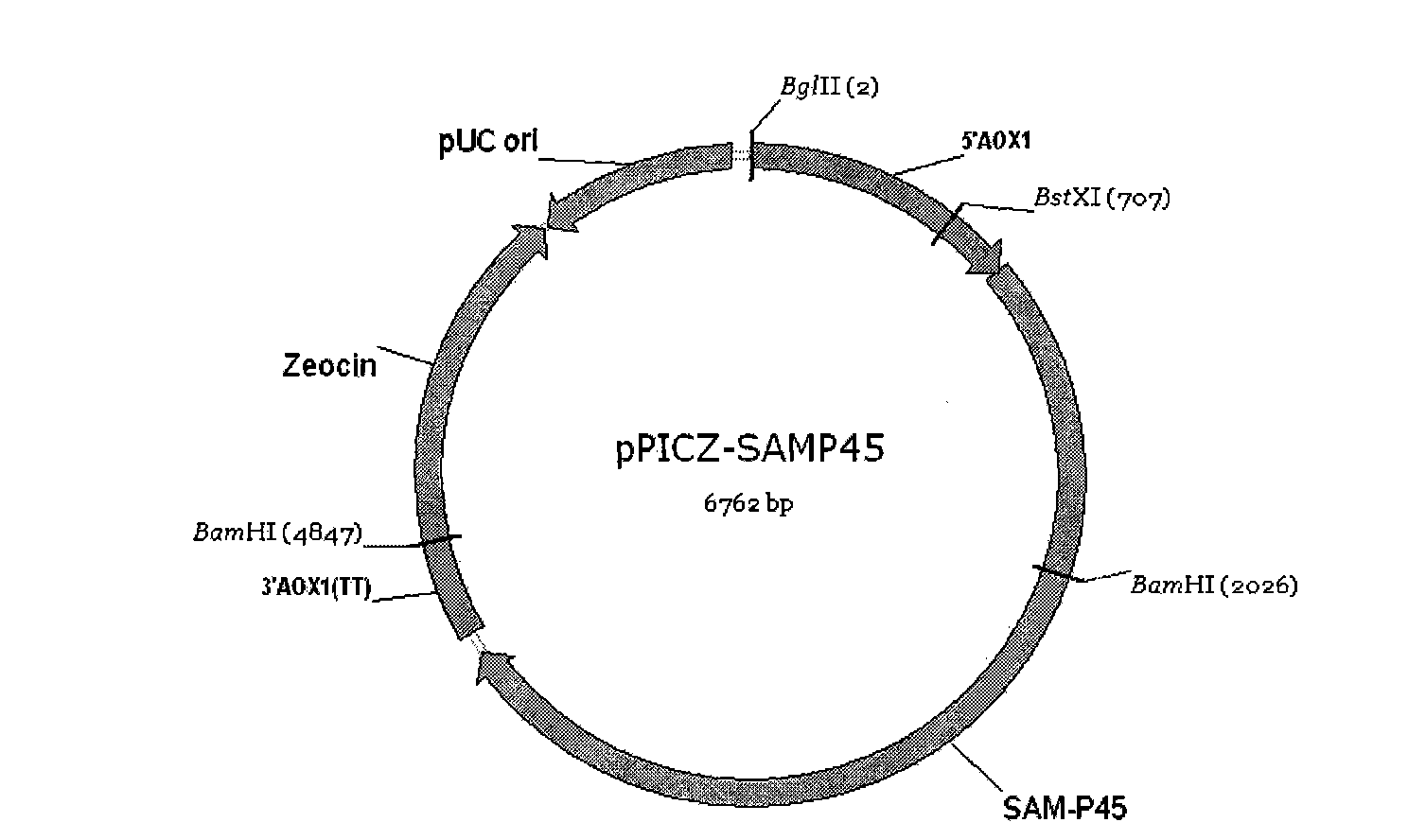
The invention discloses a recombinant bacterium which is a recombinant methanol nutritional type microzyme containing a glutamine transaminage prosoma gene and a subtilisin type hydrolase gene SAM-P45. The invention also protects the recombinant bacterium as Pichia pastoris GSMTGB, the recombinant bacterium is preserved in CGMCC (address: Datun Road, Chaoyang district, Beijing city, China) on August 25th, 2009, the preserving number is CGMCC No.3249, and the enzyme activity of the glutamine transaminage reaches 0.43u / ml when the recombinant bacterium is induced and fermented for 72 hours.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Ethyl carbamate hydrolase gene, protein coded thereby and application
The invention discloses an ethyl carbamate hydrolase gene UH, a protein coded thereby and an application. The ethyl carbamate hydrolase gene UH has a nucleotide sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.1 and an amino acid sequence shown as SEQ ID NO.2. A gene engineering strain constructed by the UH gene provided by the invention has the enzyme activity of 83.5U / g of wet cell; and a wide application foundation is brought.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Nitrilase, gene sequence and application method thereof
ActiveCN102936590AShort fermentation cycleHigh nitrilase activityHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesHydrolase GenePseudomonas putida
The invention relates to novel nitrilase, and a gene cloning and expressing method thereof. A nitrilase gene SEQ ID NO: 1 is acquired from total deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) of pseudomonas putida XY 4 (serial number CGMCC 3830), the total length of the gene is total length of 1113 nucleotides, and the nitrilase is encoded by 370 amino acid with sequences represented as SEQ ID NO: 2. The invention further discloses a method for structuring, efficiently expressing and purifying restructuring nitrilase, an optimum operation temperature and an optimum operation potential of hydrogen (PH) value of purifying the restructuring nitrilase. A plasmid pET28a (+) is used as an expression vector, and E. coli Rosetta-gami (DE3) is used as an expression host to achieve efficient expression of the nitrilase gene. The optimum operation temperature of the restructuring nitrilase is 55 DEG C, the optimum operation PH value is 7.5, the restructuring nitrilase can efficiently convert 3-cyanopyridine into nicotinic acid, and the restructuring nitrilase has large industrial production potential and economic values.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
ATP diphosphohydrolase (CD39) gene therapy for inflammatory or thrombotic conditions and transplantation and means there for
InactiveUS20060182733A1Increased susceptibility to platelet aggregationInhibition of activationHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolase GeneWhite blood cell
A method to render endothelial cells capable of inhibiting platelet and leukocyte-mediated injury and inflammation is described, comprising genetically modifying the cells by inserting DNA encoding ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase or an oxidation-resistant analog thereof, and expressing a protein having functional ecto-ATP diphosphohydrolase activity, such as the human CD39 protein, by said cells under cellular activating conditions. The method, which can be carried out in vivo, ex vivo or in vitro, has use in allogeneic or xenogeneic transplantation as well as to treat systemic or local inflammatory conditions characterized by platelet aggregation leading to thrombus formation.
Owner:BACH FRITZ H +3
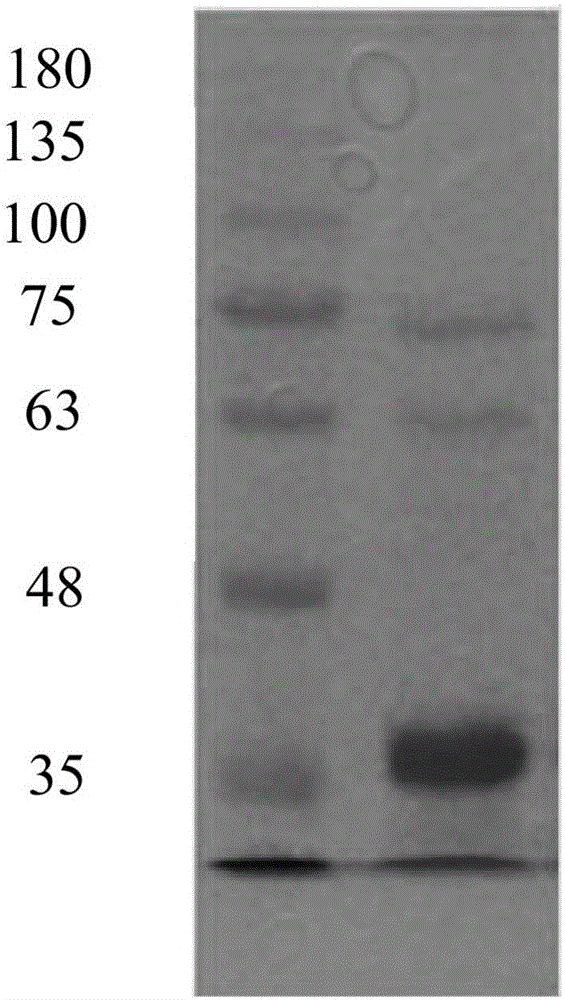
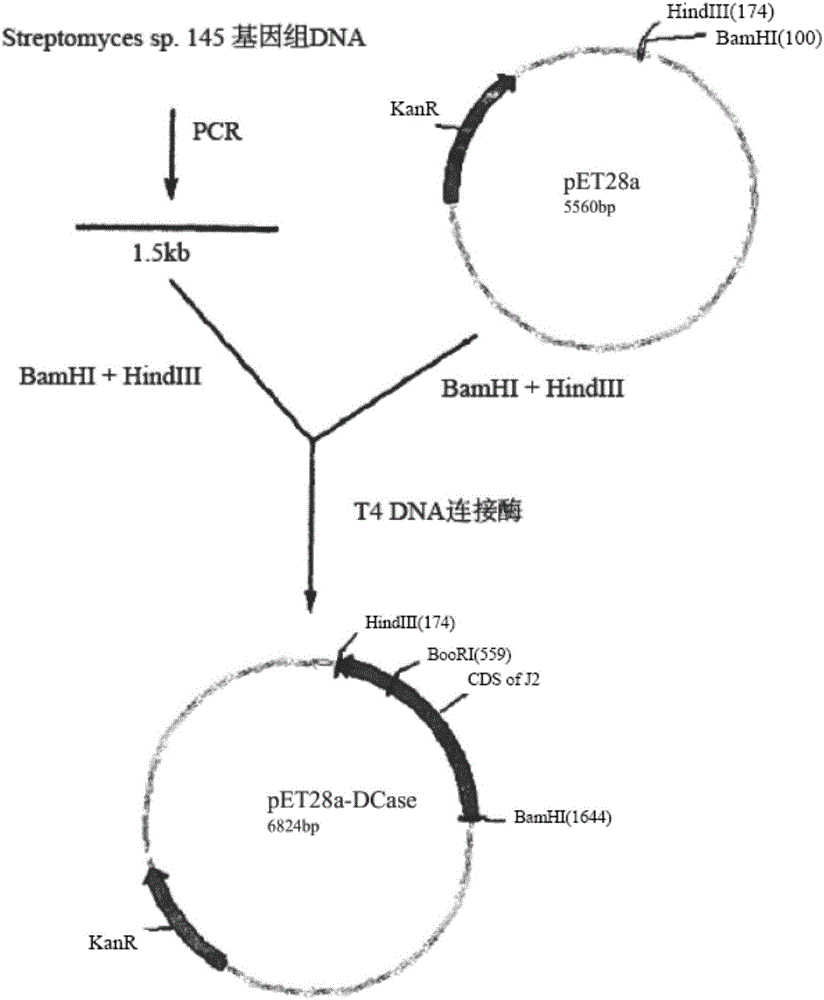
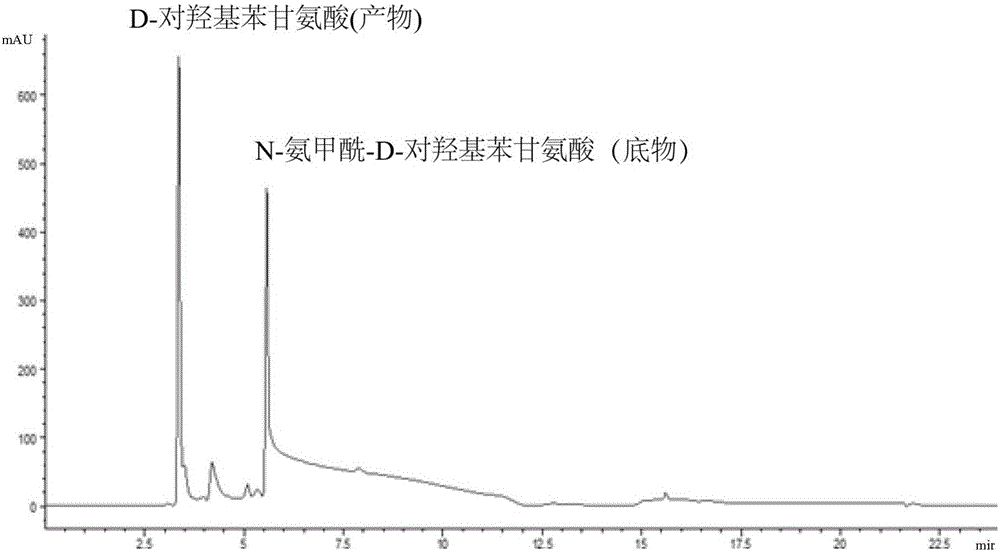
DNA molecule, recombinant plasmid and recombinant bacterium for production of D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine
InactiveCN103993010AImprove conversion rateMild conditionsBacteriaMicroorganism based processesN-carbamoylaseHydrolase Gene
The invention discloses a DNA molecule, a recombinant plasmid and a recombinant bacterium for production of D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine. The DNA molecule provided by the invention comprises a PL promoter, a D-hydantoinase gene and an N-carbamoylase gene, and expression of the D-hydantoinase gene and the N-carbamoylase gene is initiated by the PL promoter. The invention provides the DNA molecule able to stably and massively express D-hydantoinase and N-carbamoylase, and the recombinant plasmid and the recombinant bacterium based on the DNA molecule. At the same time, the invention also provides a method for converting DL-p-hydroxyphenylhydantoin into D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine by the recombinant bacterium or fermented recombinant bacterium. The method only generates D-p-Hydroxyphenylglycine, has no need of splitting and separating an enantiomer, and the conversion rate is high. The whole production process has the advantages of mild conditions, simple operation, and environmental friendliness.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
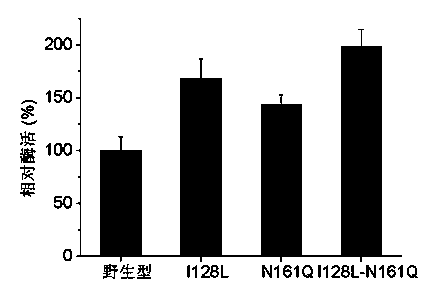
Fungus nitrilase mutants with improved catalytic activity and heat stability and construction method thereof
ActiveCN103667228AHigh activityImprove thermal stabilityHydrolasesFermentationBiotechnologyHydrolase Gene
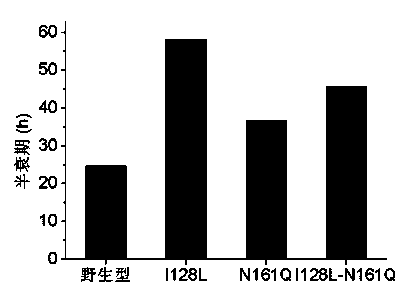
The invention provides fungus nitrilase mutants with improved catalytic activity and heat stability and a construction method thereof. The mutants are obtained by adopting multiple site-saturation mutagenesis, constructing a mutual library and screening based on gibberellaintermedia CA3-1 fungus nitrilase genes. A semi-rational design method is used for obtaining the fungus nitrilase mutants and is characterized in that Ile at the site 128th and Asn at the site 161th nearby the active center of fungus nitrilase are transformed, and the obtained mutants are respectively Ile128Leu, Asn161Gln and Ile128Leu-Asn161Gln. The catalytic activity and the heat stability of the mutants provided by the invention are remarkably improved. The transformed fungus nitrilase mutants can be used for reducing the production cost and improving the production efficiency, and have relatively high application values.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV +1
Toxoplasma gondii rapid detection kit and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101974634AIncreased sensitivityResolution timeMicrobiological testing/measurementHydrolase GeneGondii toxoplasma
The invention relates to a Toxoplasma gondii rapid detection kit and a preparation method thereof. The kit is based on the molecular biology and the nucleoside triphosphate hydrolase (NTPase) gene with high conservation of Toxoplasma gondii to adopt the loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) method to perform the rapid detection of Toxoplasma gondii. The kit contains LAMP reaction solution, primer, Bst DNA polymerase, color reagent, standard positive template and dd H2O. The kit of the invention is characterized by high sensitivity and specificity, rapid reaction, simple operation and the like, does not require special instrument and equipment and solves the defects of the prior art such as long detection time of toxoplasmosis, large workload and complicated operation. The kit of the invention can be used to detect whether a clinical sample contains Toxoplasma gondii and used in the early diagnosis and the molecular epidemiological study of toxoplasmosis.
Owner:LANZHOU INST OF VETERINARY SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Thifensulfuron hydrolase gene tsmE and uses thereof
The present invention relates to the field of applied and environmental microorganism and agriculture. Disclosed are a thifensulfuron hydrolase gene tsmE and uses thereof. The thifensulfuron hydrolase gene tsmE has a nucleotide sequence of SEQ ID NO. 1, full length of 1194 bp, and G+C content of 51.09%, and encodes 398 amino acids with an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO. 2. The thifensulfuron hydrolase TsmE provided by the present invention can degrade completely 100 mg / L thifensulfuron within 1 hour into the herbicidally inactive product thiophenesulfonic acid; in addition, the TsmE also degrade completely 100 mg / L haloxyfop-R-methyl within 1 hour. Therefore, the thifensulfuron hydrolase gene tsmE is useful in construction of thifensulfuron-resistant transgenic crops and bioremediation of thifensulfuron or haloxyfop-R-methyl-contaminated environments.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Construction of N-carbamoylase expression genes and engineering bacteria of N-carbamoylase expression genes
The invention provides construction of N-carbamoylase expression genes and engineering bacteria of the N-carbamoylase expression genes. A preparation method of N-carbamoylase comprises following steps: 1, screening of target bacteria is carried out; 2, extraction of bacteria total DNA is carried out; 3, amplification of the bacteria total DNA is carried out so as to obtain N-carbamoylase genes; 4, DNA segments of the N-carbamoylase genes are connected with expression vectors so as to obtain N-carbamoylase recombinant plasmids; 5, the N-carbamoylase recombinant plasmids are transferred into expression hosts, and fermental cultivation is carried out. According to the invention, amino acid sequences coded by the N-carbamoylase genes possess relatively high enzymatic activity when N-carbamoyl-D-p-hydroxyphenylglycine is taken as a substrate.
Owner:CHONGQING HONOROAD ANIMAL HEALTH
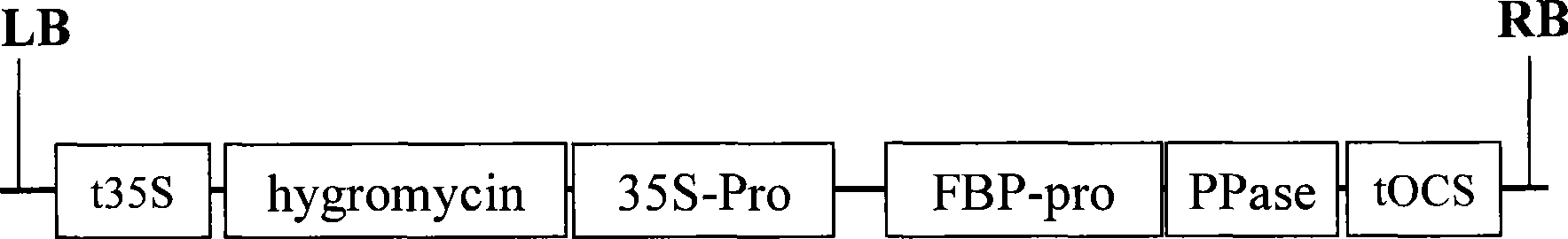
Method for improving plant products and expression box thereof
InactiveCN101457234AIncrease productionIncrease production levelsFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyHydrolase Gene
The invention discloses a method for improving plant yield and its special expression cassette. The method of the invention comprises inducing the expression cassette capable of specifically expressing a pyrophosphoric acid hydrolase in plant mesophyll cells into plants, screening and obtaining plants capable of expressing the pyrophosphoric acid hydrolase, that is the plant with improved yield. The expression cassette capable of specifically expressing the pyrophosphoric acid hydrolase in plant mesophyll cells comprises a series cyFBPase promtor, a pyrophosphoric acid hydrolase gene and an OCS terminator in sequence. The method of the invention can greatly improve the yield level of the transgene plants, especially the transgene crops.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Epoxide hydrolase from rhodosporidium paludigenum and application of epoxide hydrolase
ActiveCN109355271AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic selectivityHydrolasesGenetic engineeringEpoxide hydrolase 3Phenyl glycol
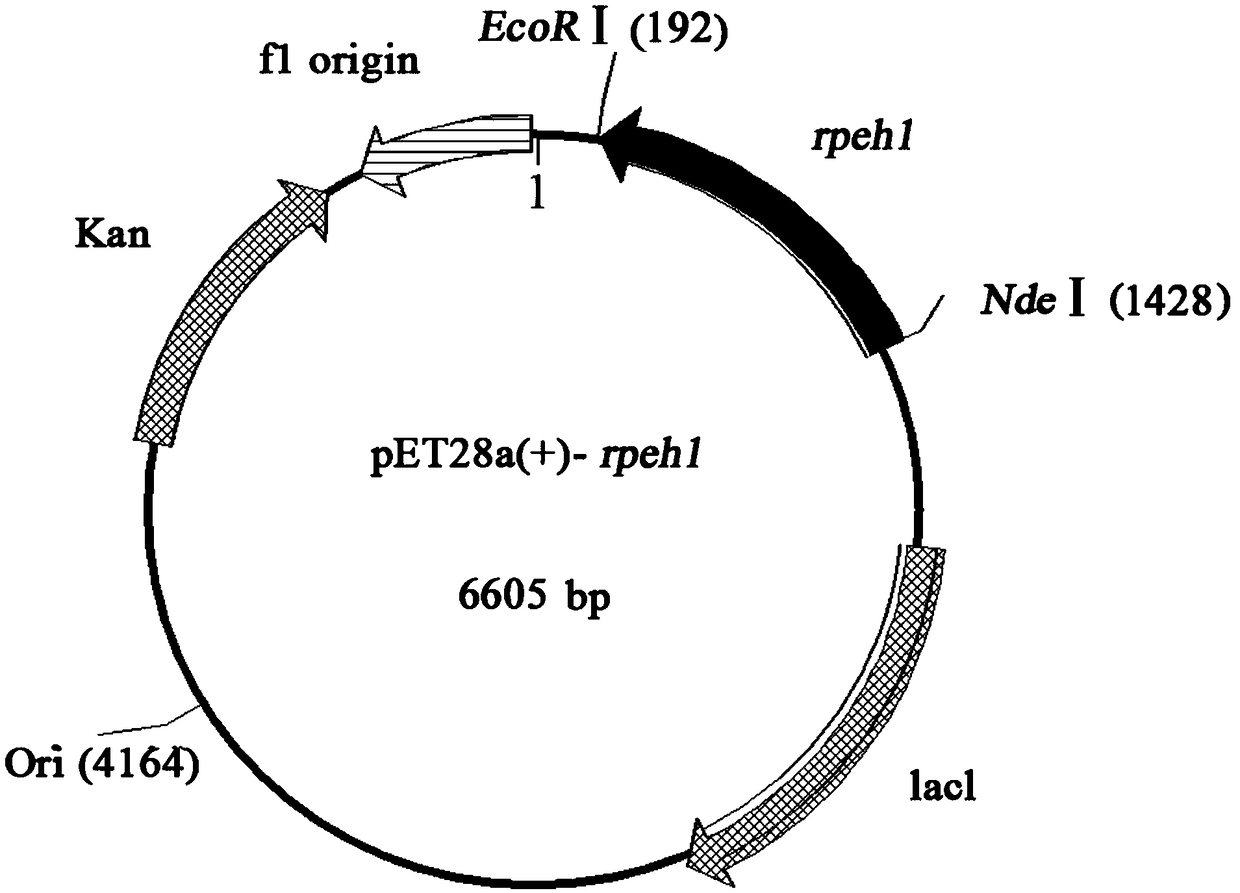
The invention discloses an epoxide hydrolase from rhodosporidium paludigenum and application of the epoxide hydrolase, and belongs to the technical field of biology. The epoxide hydrolase and the application have the advantages that epoxide hydrolase genes (rpeh1) from the rhodosporidium paludigenum R. paludigenum and corresponding amino acid sequences are provided; recombinant plasmids pET28a(+)-rpe1 with the genes and genetically engineered bacteria E. coli BL21 (DE3) / pET28a(+)-rpeh1 are constructed, and recombinant epoxide hydrolases are prepared by the aid of bacterial strains; biologicalcatalysis can be carried out by the constructed genetically engineered bacteria, and accordingly the ee of enantiomerically pure R-type phenyl glycol obtained by means of preparation is higher than 73%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for constructing recombinant bacillus subtilis with high-yield hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide
ActiveCN110055201AIncrease production intensityGreat application advantageBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydrolase GeneMicroorganism
The invention discloses a method for constructing recombinant bacillus subtilis with high-yield hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide, and belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method includes selecting yoyJ-yoyA, lytH, lytD, lytG and lytC as integration loci, and integrating pathway genes glmM, glmS, glum and tuaD and a leech-derived hyaluronan hydrolase gene H6LHyal into a bacillus subtilis genome, which not only improves the yield of hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide but also increases the biomass and facilitates separation and purification of the hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide inthe later stage. The yield of the hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide reaches 36.04g / L when fermented in a 3L fermentation tank for 40h. The hyaluronic acid at the 3L fermentation tank level has the average molecular weight HA Mw of about 3.3*104 Da. The method lays a foundation for high-efficiency fermentation of a microbial system to prepare the hyaluronic acid oligosaccharide, and is suitable for industrial production application.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
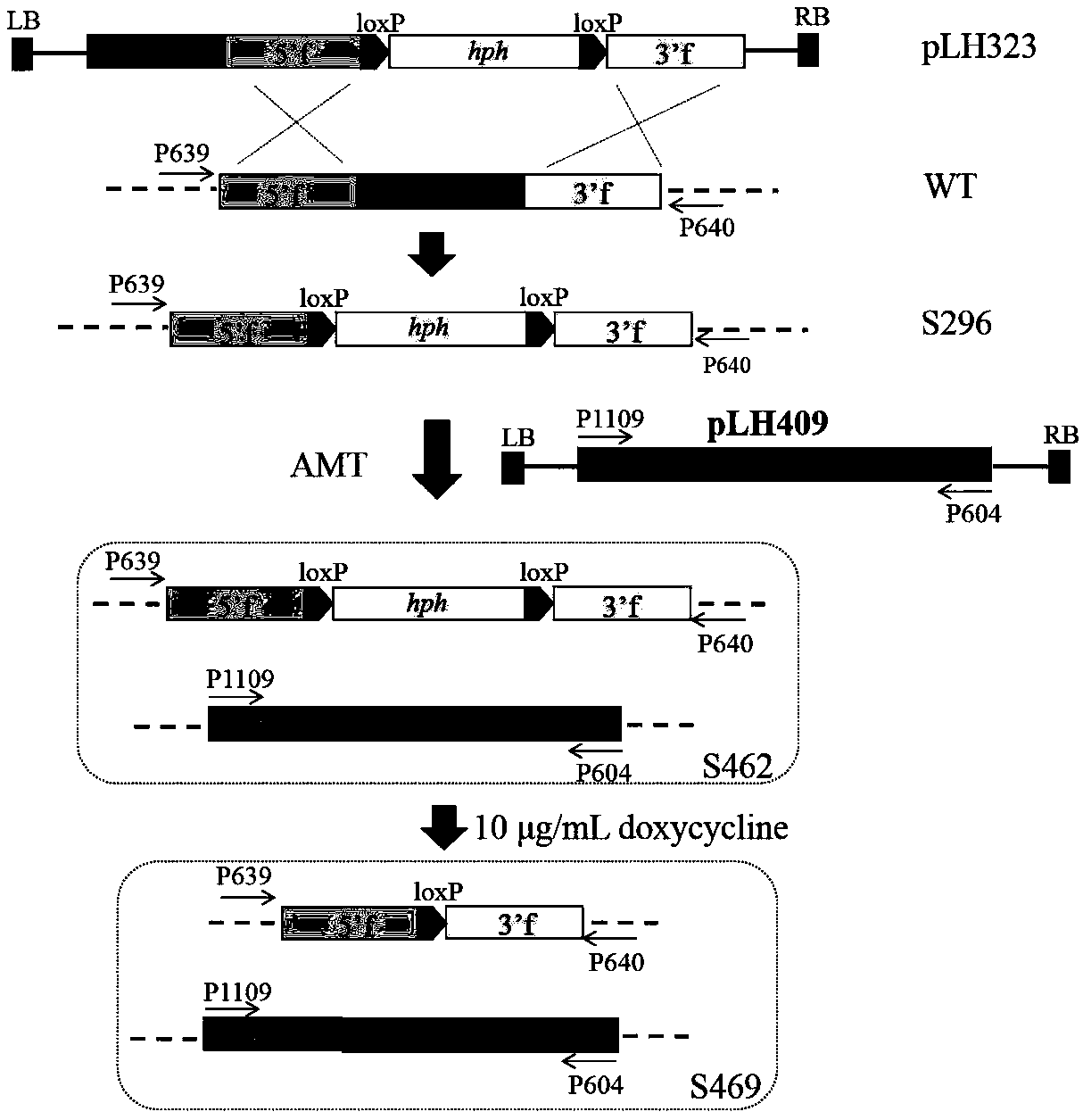
Method for degrading 1,2,3-TCP (trichloropropane) by engineered strain bacillus subtilis
The invention discloses a method for degrading 1,2,3-TCP (trichloropropane) by engineered strain bacillus subtilis. According to the method, firstly, alkyl halide dehalogenase genes, halogenohydrin dehalogenase genes and epoxide hydrolase genes which can degrade 1,2,3-TCP and intermediate products of the 1,2,3-TCP are synthesized; the gene sequence and the codase amino acid sequence are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to 6; then, the bacillus subtilis integrating carrier containing the gene is built; the carrier converts the bacillus subtilis; by a gene ectopic integration and resistance gene knock-out method, the gene is integrated into the bacillus subtilis genome; the engineered strain bacillus subtilis capable of secreting and expressing alkyl halide dehalogenase, halogenohydrin dehalogenase and epoxide hydrolase is obtained. The engineered strain bacillus subtilis has a good degradation effect on TCP and TCP intermediate products; the complete TCP degradation can be realized; the characteristics of high degradation efficiency, high TCP tolerance, stable inheritance and the like are realized; the application prospects are good.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com