Novel phthalate hydrolase EstJ6 as well as coding gene and application thereof
A phthalate ester and hydrolase technology, applied in the fields of hydrolase, application, genetic engineering, etc., can solve the problems of low efficiency of new esterases, non-cultivation, and restrictions on the development and utilization of new enzymes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Embodiment 1: the screening of phthalate hydrolase gene in the soil metagenomic library
[0072] 1. Primary screening of positive clones by substrate plate method
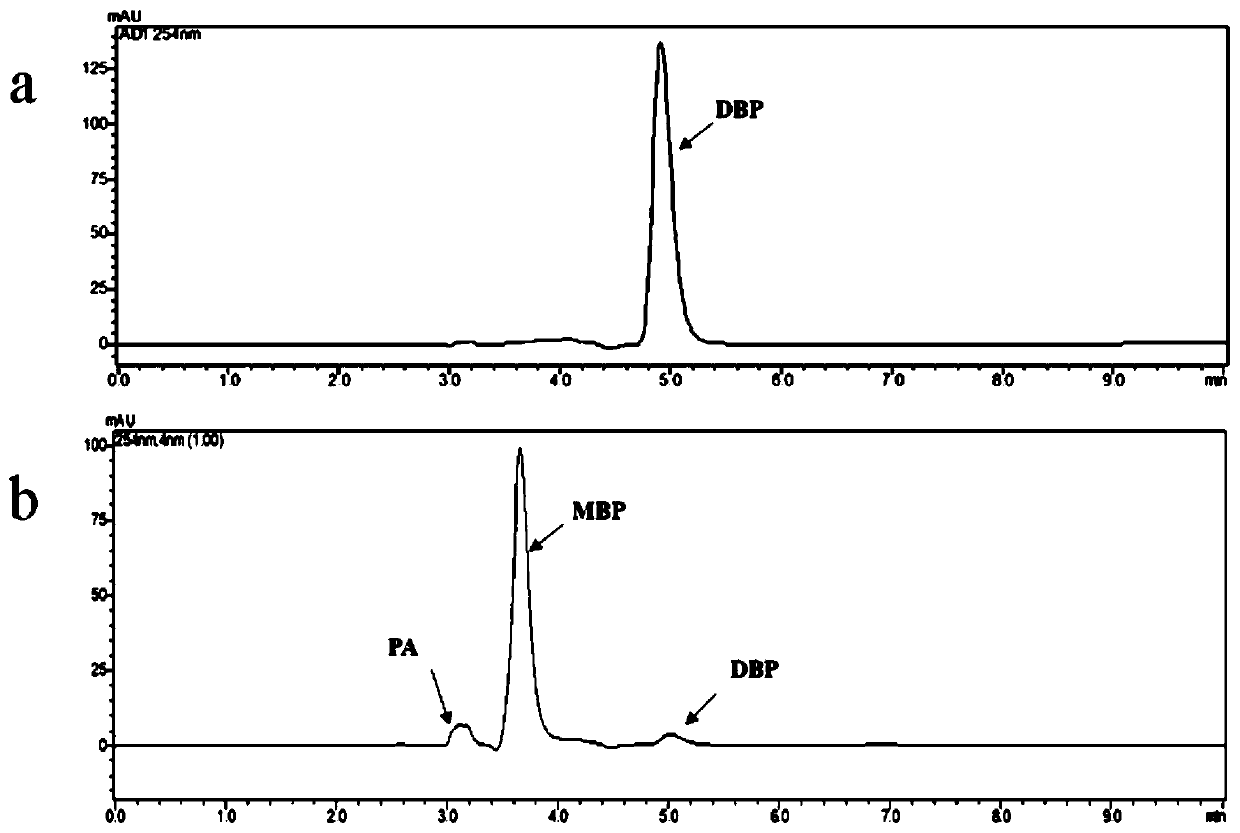
[0073] Prepare the primary screening medium. After the LB solid medium is sterilized by high temperature and high pressure, it is cooled to an appropriate temperature (60°C) and the substrate 1mM dibutyl phthalate (dissolved in DMSO) and 100μg / mL ampicillin, shake well and pour plate. Appropriately dilute the cosmid library bacteria liquid on the screening plate, incubate at 37°C for 1-2 days, observe the formation of transparent circles around the colonies, which are positive clones ( figure 1 ).
[0074] 2. Re-screening, HPLC verification of the enzyme activity of its phthalate hydrolase
[0075] Inoculate the monoclonal obtained from primary screening in liquid LB (containing 100 μg / mL ampicillin) medium, culture at 37°C overnight (12h), centrifuge at 12,000×g at room temperature for 8min, discard the...
Embodiment 2
[0081] Embodiment 2: the cloning of phthalate hydrolase
[0082] 1. PCR amplification
[0083] Using primers:
[0084] Upstream primer: 5'-CATG CCATGG GCATGGCAAGTCCGCAACTA-3' (SEQ ID No. 3); and
[0085] Downstream primer: 5'-CCC AAGCTT CGCGGTGATCTGCCGGAC-3' (SEQ ID No.4) amplifies the phthalate hydrolase gene estj6, and the underlines of the upstream and downstream primers indicate the restriction sites of NcoI and HindIII, respectively.
[0086] PCR reaction system (25 μL): 9.5 μL of ultrapure water, 12.5 μL of 2×Taq Master Mix, 1 μL of upstream and downstream primers, and 1 μL of positive subcloning plasmid DNA. PCR reaction conditions: 94°C for 3min; 35 cycles of 94°C for 30s, 63°C for 45s, and 72°C for 1min; 72°C for 10min. The PCR product was electrophoresed and recovered by tapping the gel to obtain a purified PCR product.
[0087] 2. Digestion
[0088] The purified and recovered PCR product was subjected to double enzyme digestion for 3-4 hours. The enzyme dig...
Embodiment 3
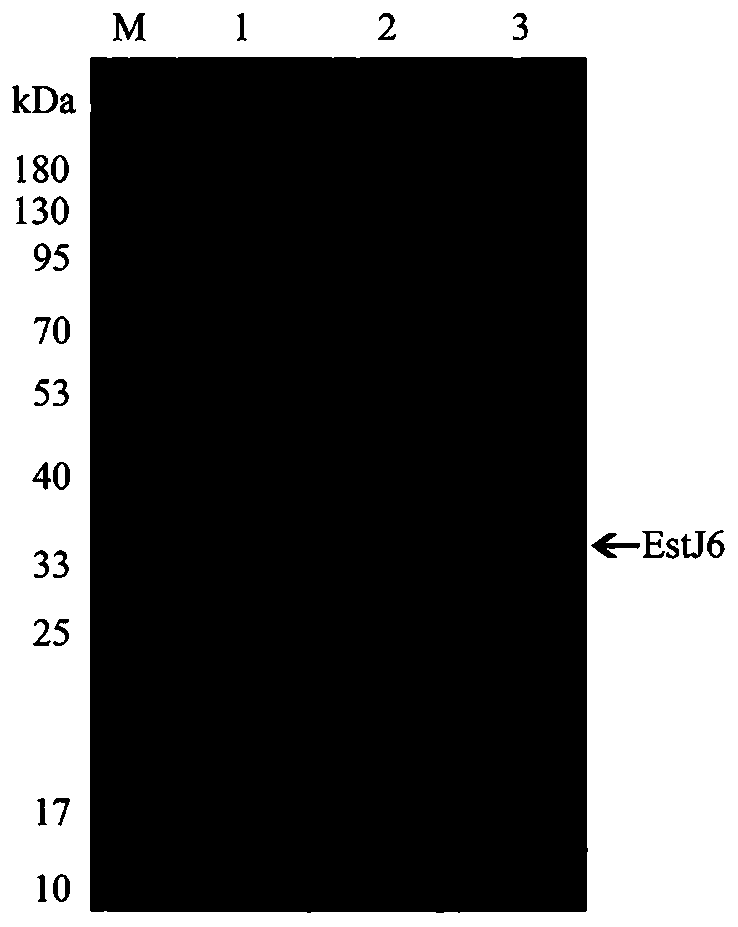
[0094] Example 3: Heterologous expression and purification of phthalate hydrolyzing esterase EstJ6
[0095] 1. Conversion
[0096] Take 10uL of the pET28a-esjt6 plasmid obtained in Example 2 and add it to 100uL Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) competent cells, incubate on ice for 30min, heat shock in a water bath at 42°C for 90s, and add 900uL LB liquid medium after ice bathing for 2min. 180rpm, shaking at 37°C for 1h. The bacteria were resuspended and spread on LB plates containing kanamycin, cultured overnight at 37°C and single colonies were picked.
[0097] 2. Induced expression
[0098] The recombinant bacteria were inoculated into 5 ml of LB liquid medium containing kanamycin, and cultured at 37° C. and 180 rpm for 12 hours. Take 1ml of bacterial liquid and inoculate into 100ml of fresh LB medium, cultivate at 37°C and 200rpm until the OD600nm is about 0.6, add IPTG to the final concentration of 0.5mM, and continue to cultivate at 16°C and 180rpm for 20h.
[0099] 3. Puri...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com