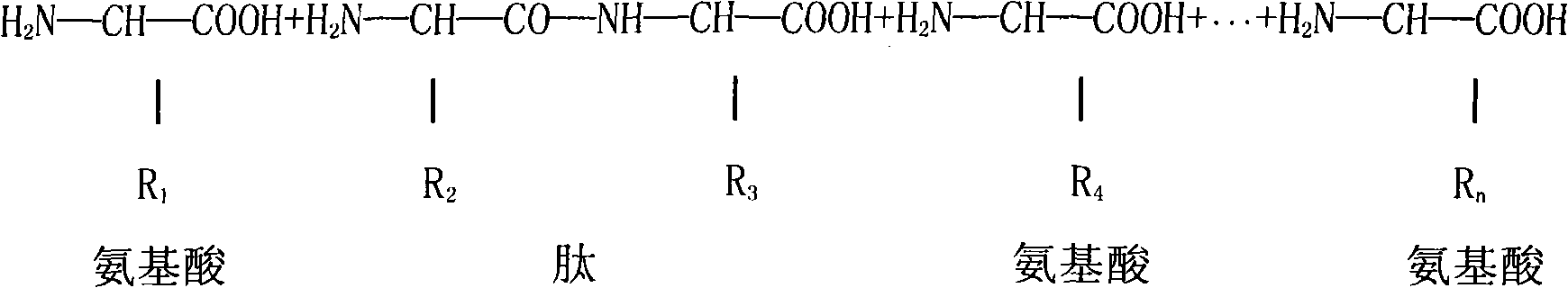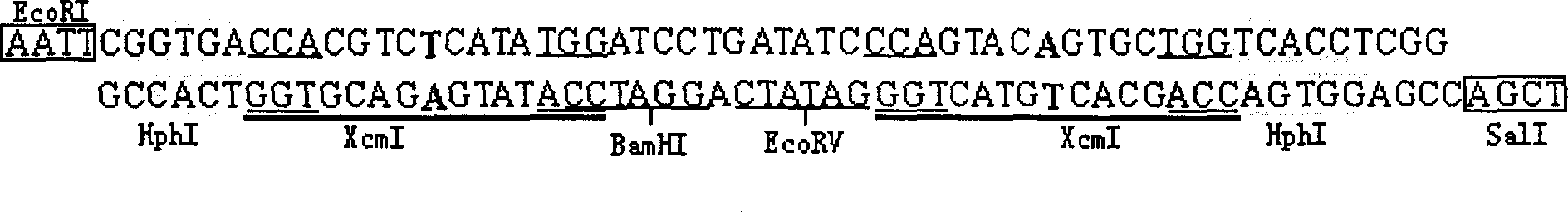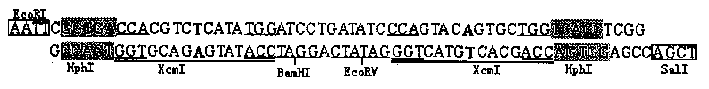Patents
Literature
174 results about "Exoenzyme" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
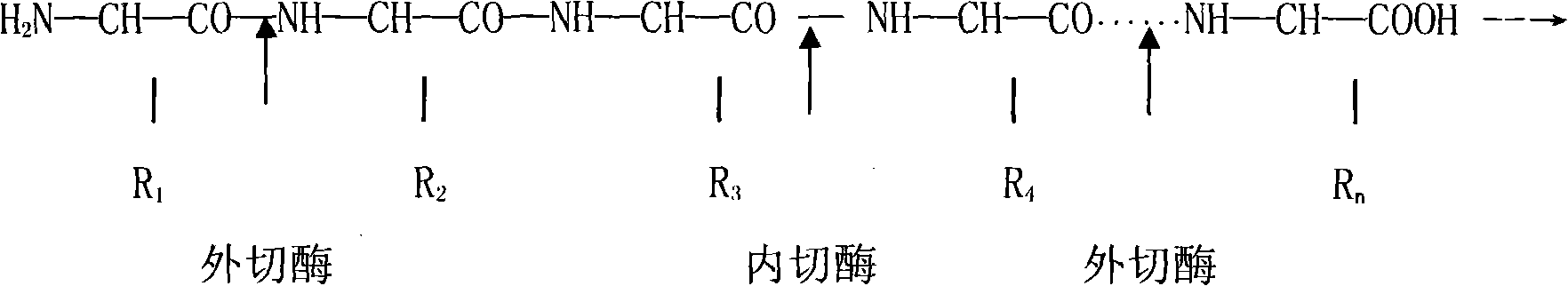
An exoenzyme, or extracellular enzyme, is an enzyme that is secreted by a cell and functions outside of that cell. Exoenzymes are produced by both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and have been shown to be a crucial component of many biological processes. Most often these enzymes are involved in the breakdown of larger macromolecules. The breakdown of these larger macromolecules is critical for allowing their constituents to pass through the cell membrane and enter into the cell. For humans and other complex organisms, this process is best characterized by the digestive system which breaks down solid food via exoenzymes. The small molecules, generated by the exoenzyme activity, enter into cells and are utilized for various cellular functions. Bacteria and fungi also produce exoenzymes to digest nutrients in their environment, and these organisms can be used to conduct laboratory assays to identify the presence and function of such exoenzymes. Some pathogenic species also use exoenzymes as virulence factors to assist in the spread of these disease causing microorganisms. In addition to the integral roles in biological systems, different classes of microbial exoenzymes have been used by humans since pre-historic times for such diverse purposes as food production, biofuels, textile production and in the paper industry. Another important role that microbial exoenzymes serve is in the natural ecology and bioremediation of terrestrial and marine environments.
Fungal fibrinolytic enzyme and cultivating method thereof
ActiveCN101503682AThrombolytic effect is goodNo obvious acute toxicityMicroorganism based processesEnzymesBiotechnologyCordyceps
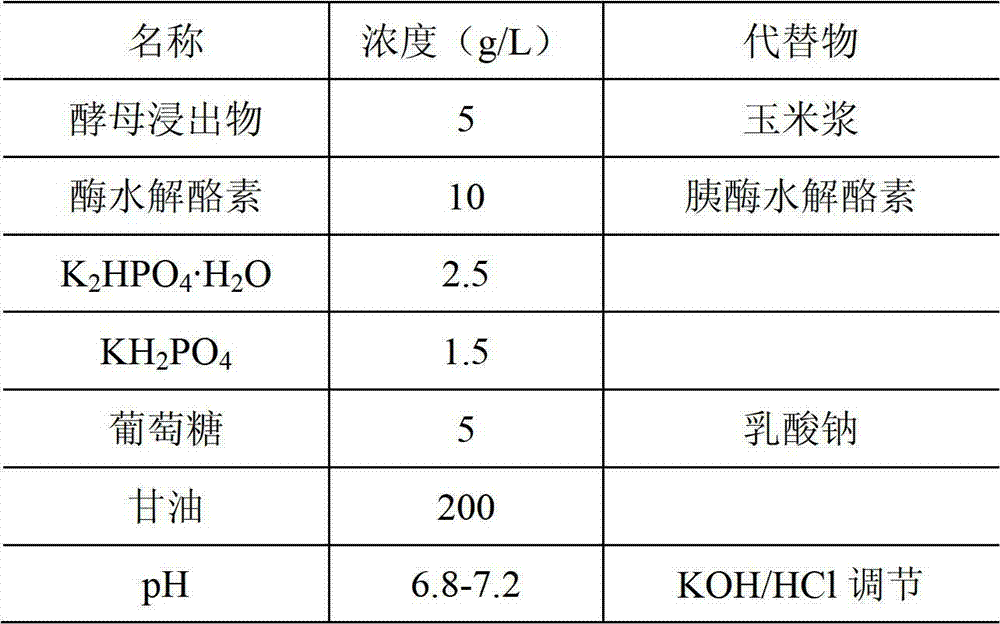
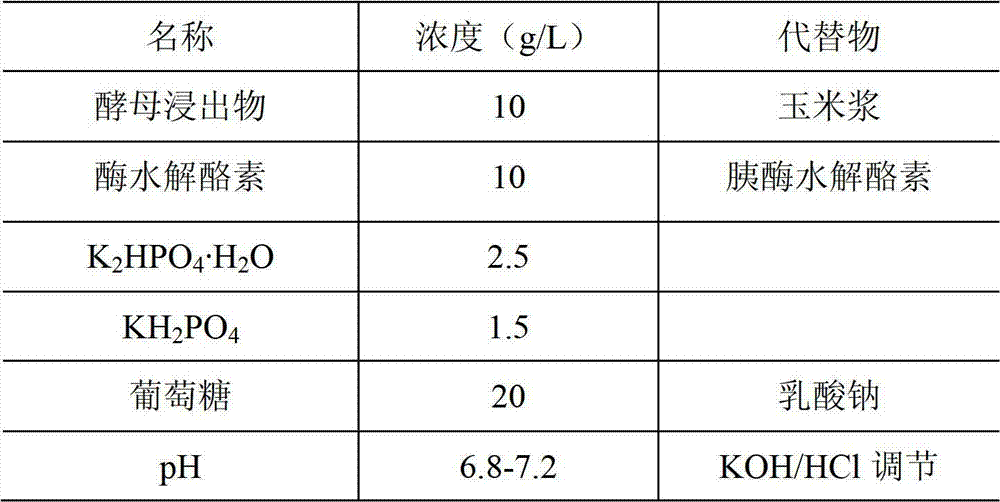
The invention discloses a fungal fibrinolytic enzyme and a preparation method thereof. The fungal fibrinolytic enzyme is prepared by taking a Cordyceps militaris strain as a strain and performing liquid fermentation culture, separation and purification. The relative molecular weight of the fibrinolytic enzyme is about 21,000. The Cordyceps militaris fibrinolytic enzyme has good thrombolytic performance, is free from obvious acute toxicity, has prospects for clinical trial, development and application, and adds a new member to a rare fibrinolytic enzyme family. Particularly, a preferable fibrinolytic-enzyme Cordyceps militaris strain C.LSG-1 obtained through severe screening is rough in growth conditions, short in enzyme production cycle and capable of harvesting a large amount of Cordyceps militaris mycelium during enzyme production, and is the strain excellent in production performance. The Cordyceps militaris fibrinolytic enzyme is an extracellular enzyme which is particularly beneficial to subsequent separation and purification during preparation. The fungal fibrinolytic enzyme takes corn protein with extensive sources as a main culture medium, thereby having low cost for raw materials and providing a novel way for developing and utilizing the prior resources.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
Preparation method for k-carrageenan oligosaccharide with low polymerization degree
The invention discloses a preparation method for k-carrageenan oligosaccharide with a low-polymerization degree. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: carrying out enzymolysis preparation on the k-carrageenan; and separating and purifying the degradation products to obtain pure k-carrageenan oligosaccharide mixing component. The preparation method is characterized in that carrageenan degradative enzyme is obtained from a marine microorganism Cellulophaga lytica strain: N5-2(NCBI (National Center of Biotechnology Information), GENBANKD registry number being GU129978) and used for degrading the k-carrageenan to obtain the k-carrageenan oligosaccharide mixture with the low polymerization degree. The enzyme is an extracellular enzyme, can be acted to beta-1,4 glucosidic bond of the k-carrageenan, wherein the acting sites are respectively octasaccharide and hexaose; and the product is low-polymerization degree oligosaccharide consisting of disaccharide repeating units. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is low in cost and simple. Compared with the methods such as chemical method and a physical method, the obtained product is single, the side products are less and the large-scale production is convenient.
Owner:WEIHAI KANGBOER BIOLOGICAL PHARMA
Aminopeptidase for catalytic synthesis of carnosine, and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN107217048ALow cost of industrializationHigh reaction rateHydrolasesGenetic engineeringEnzyme GeneUltrafiltration
The invention provides aminopeptidase for catalytic synthesis of carnosine, and a preparation method and application thereof. The aminopeptidase has the amino acid sequence shown by SEQ ID NO:2. For the preparation of biological enzymes, firstly, a gene engineering strain of the biological enzymes is built; the biological enzyme gene fragment obtained through full gene synthesis is subjected to linearized plasmid recombination by using restriction enzymes SalI. The built gene-engineered strain is suitable for high-density culture; the exoenzyme is biologically synthesized; solid-liquid separation is performed; ultrafiltration concentration is performed to obtain enzyme liquid; histidine and beta-alanine can be catalyzed in normal-temperature and normal-pressure water solution to efficiently synthesize carnosine; the reaction environment is friendly; the production cost is low; the conversion time is short; the process operation is simple; the reaction system impurity content is low; the post treatment is easy; the wide prospects of large-scale industrial application are realized.
Owner:JIANGSU CHENGXIN PHARMA
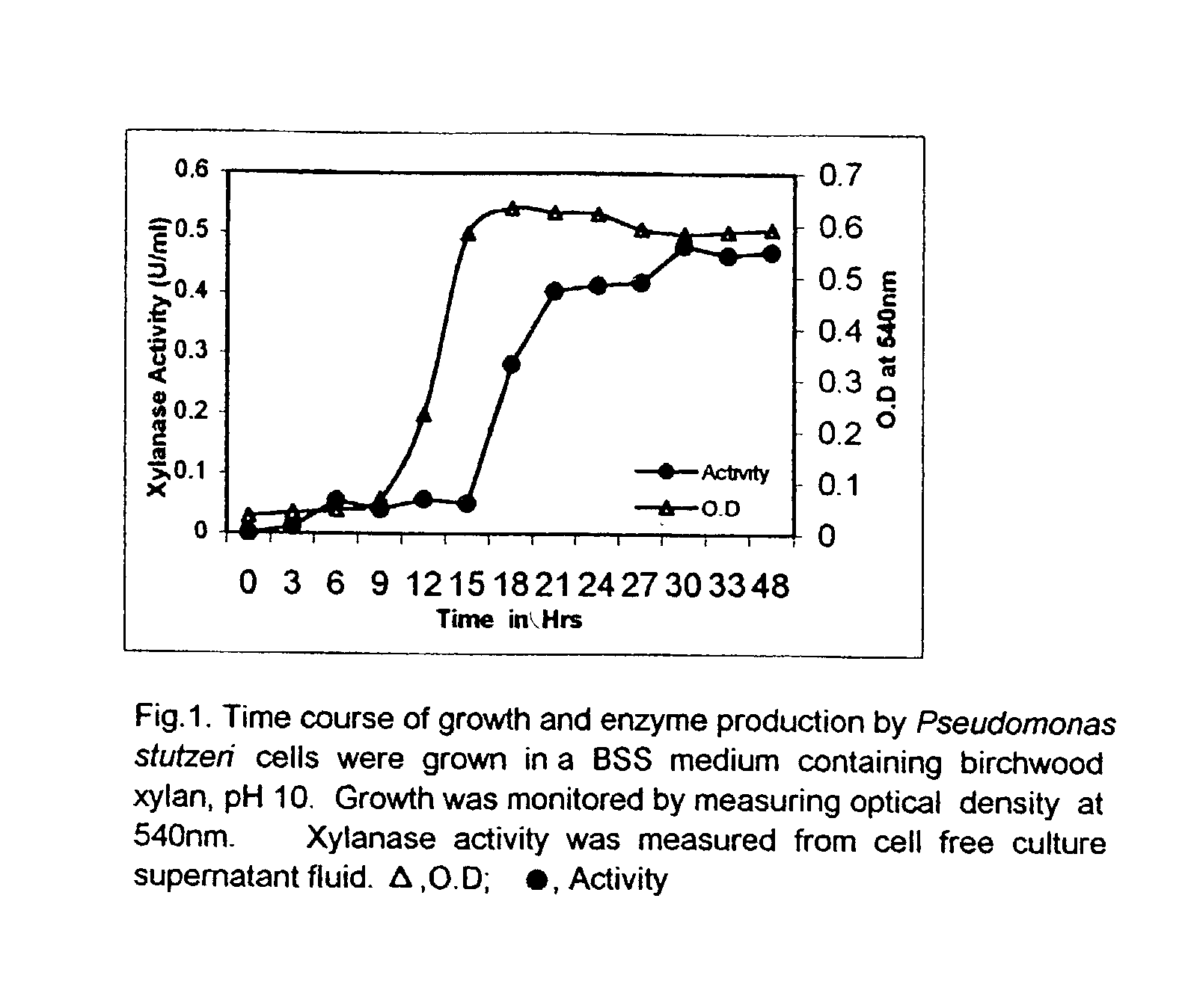
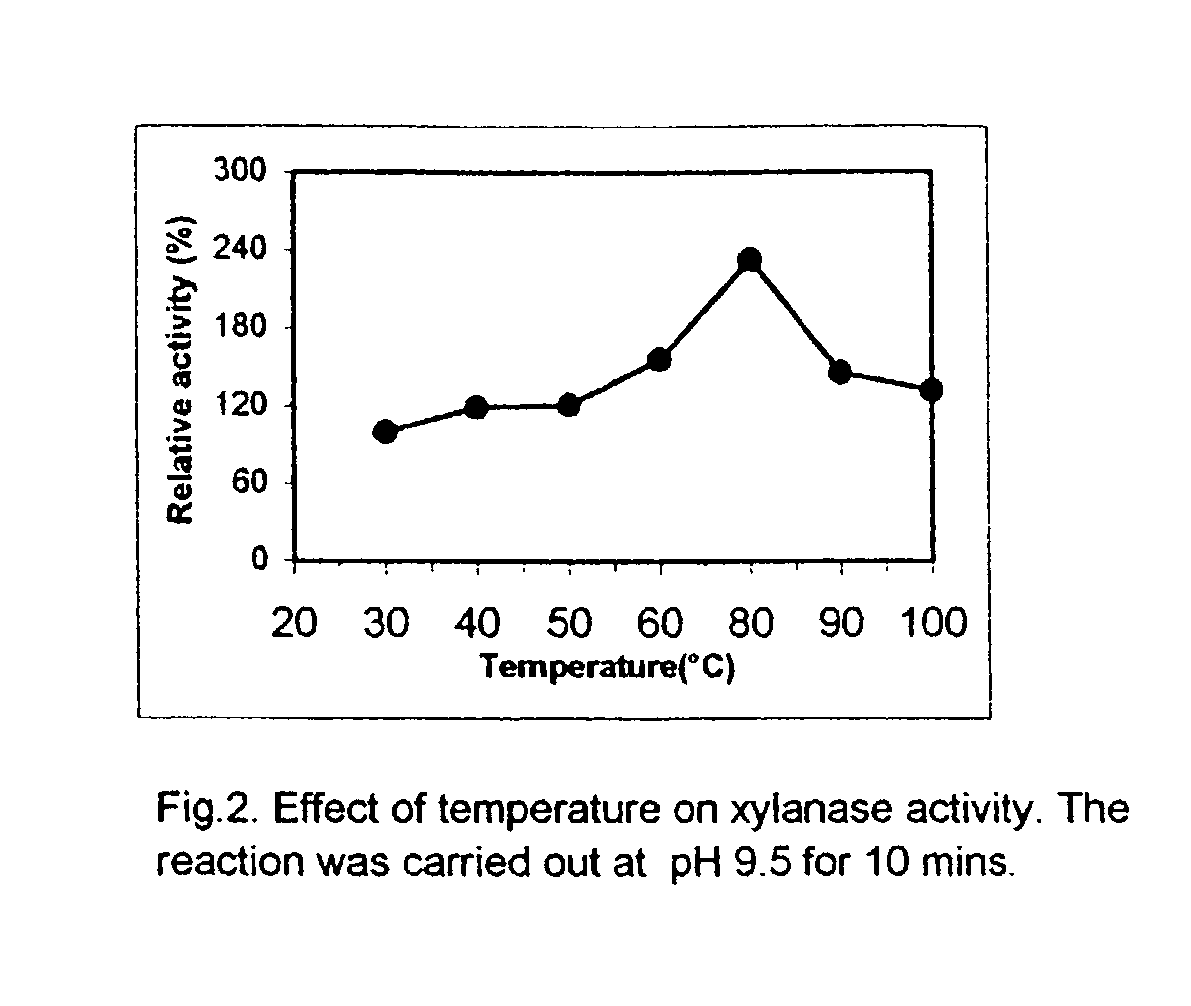
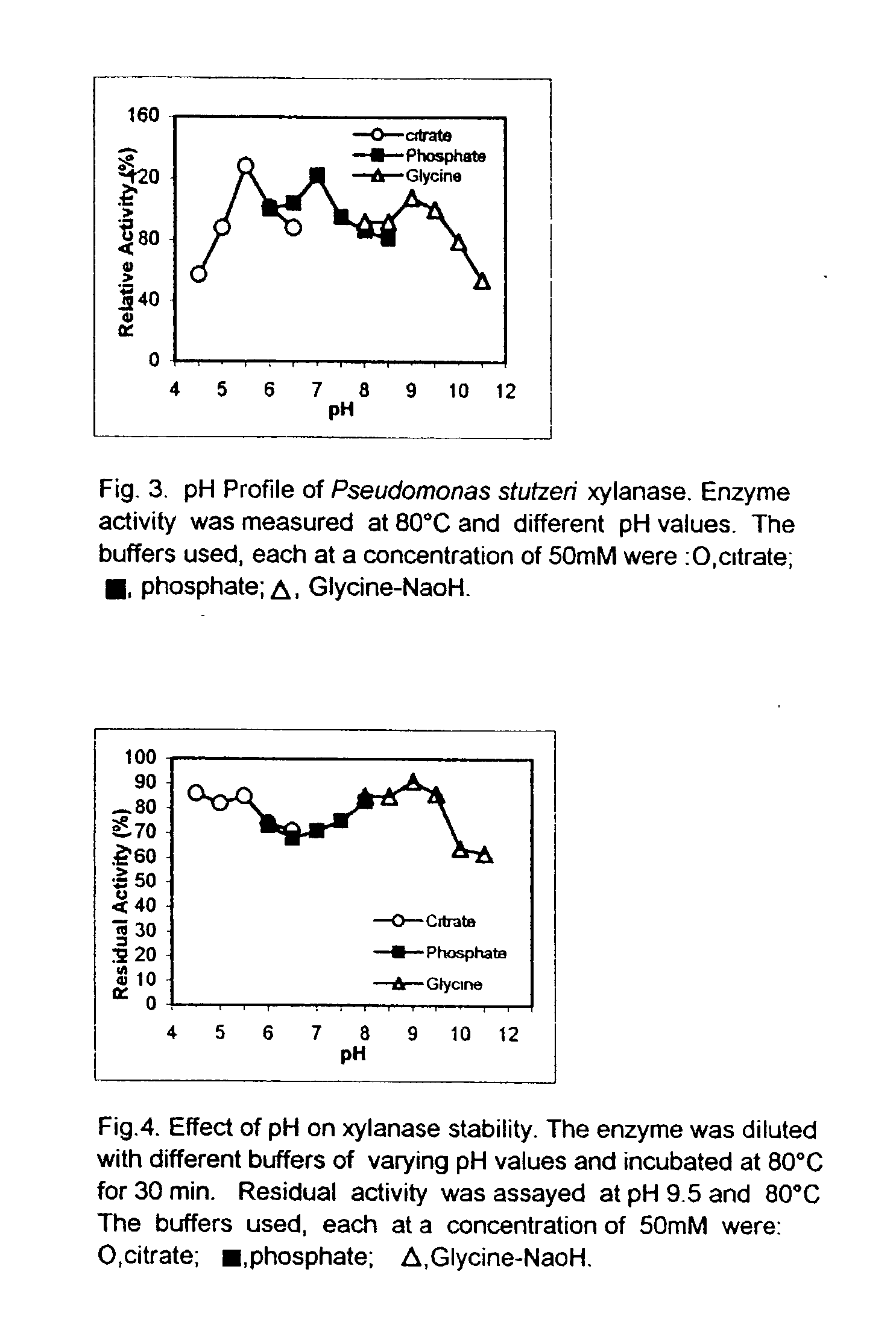
Novel 'pseudomonas stutzeri' strain and process for preparation of xylanase
The present invention relates to a novel xylanase producing bacteria, Pseudomonas stutzeri deposited at the MCMRD, National Institute of Oceanography, Dona Paula, Goa 403004, India and having the assession number MCMRD-AB-001 and also deposited at ______ having accession No. ______, and a process for production of thermophilic and alkalophilic extracellular enzyme xylanase using the said bacteria.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
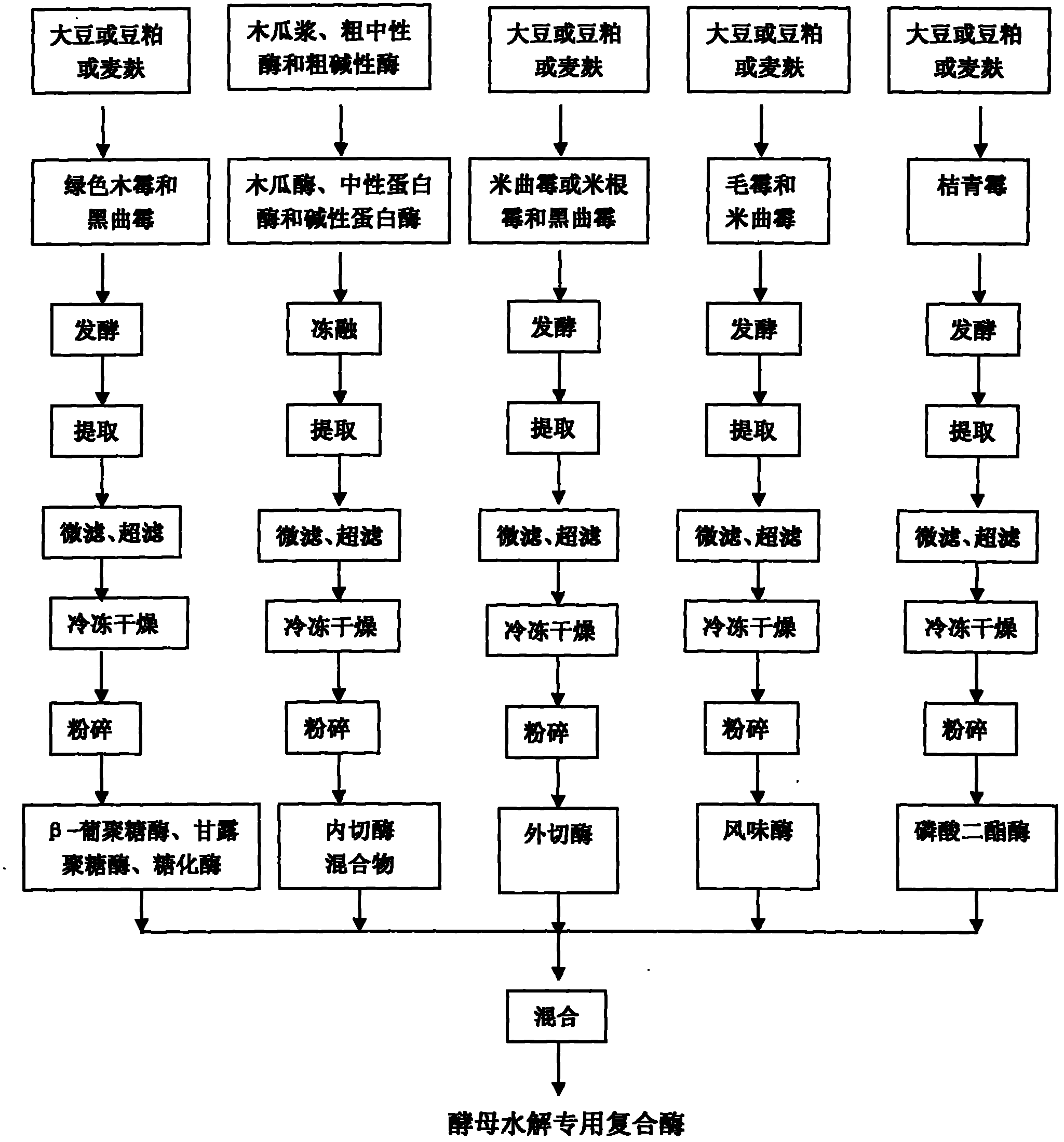
Special compound enzyme for yeast hydrolysis and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102115734AEfficient releaseEffective structureEnzymesFood preparationPhosphodiesteraseGeneration rate
Owner:南宁庞博生物工程有限公司
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase and applications thereof
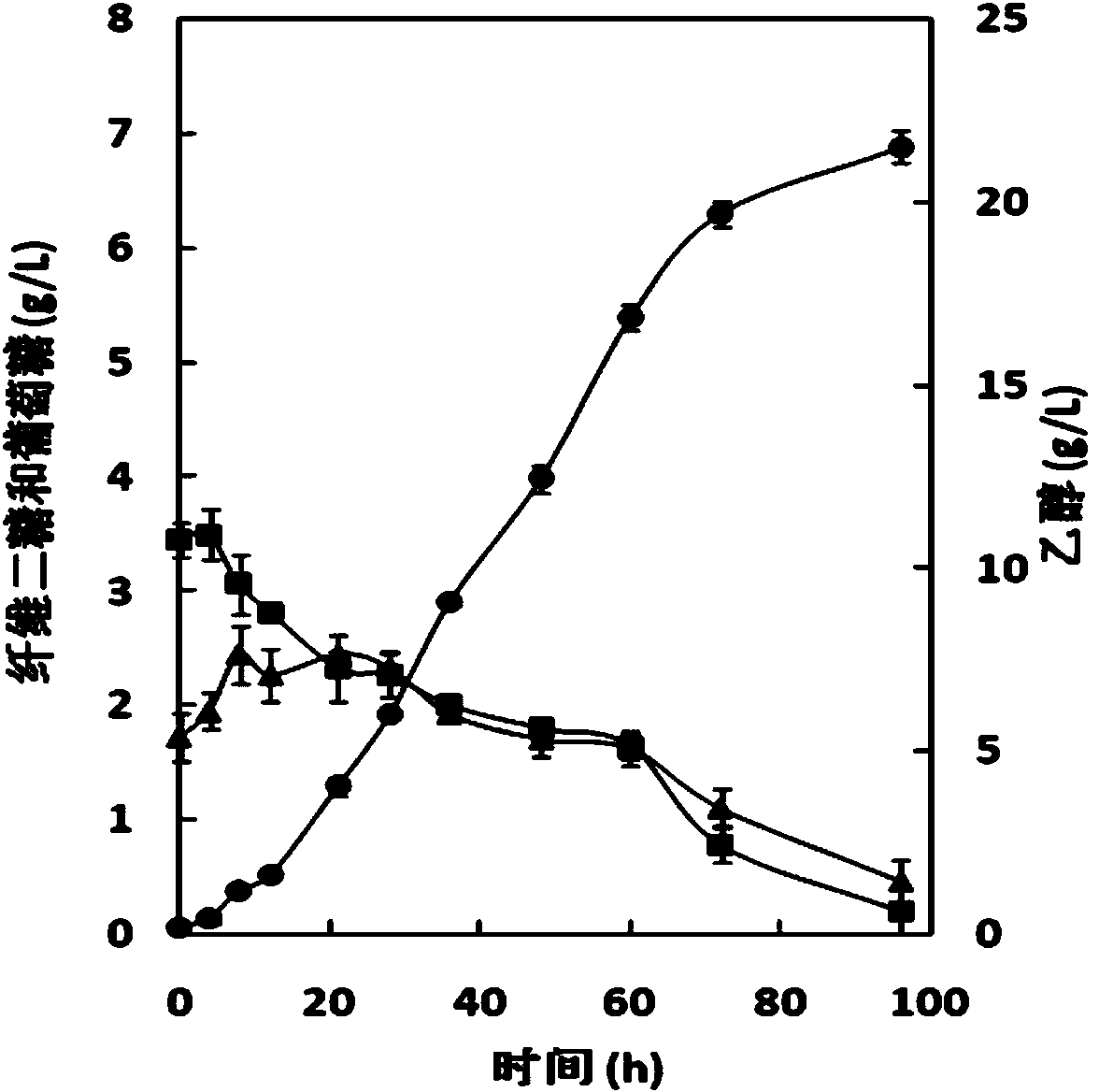
The invention provides a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for continuously and efficiently secreting beta-glucosidase, which is named Saccharomyces cerevisiae 102SB, and preserved with a Preservation No. of CGMCC No. 7450 in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on April 11, 2013. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae disclosed by the invention can continuously and efficiently secrete beta-glucosidase in a complex non-selective medium, and the extracellular enzyme activity can reach 1005.3 U / g (dry weight). By using a characteristic that the maximum specific growth rate of cellobiose is consistent with that of glucose, the strain reaches 0.29 h<-1> under the condition of limited oxygen. In SSF taking a cellulose material as a substrate, the yield of ethanol taking microcrystalline cellulose as a substrate is increased by 110%, and the yield of ethanol taking acid-hydrolyzed corncobs as a substrate is increased by 89%. The recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain disclosed by the invention is of great importance in reducing the production cost of simultaneous saccharification and fermentation in the process of cellulosic ethanol production, and simplifying the production process.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Pullulanase with high secretion capacity and application thereof
ActiveCN109628433AHigh extracellular secretion capacityEasy Fermentation PreparationFungiBacteriaEscherichia coliMicroorganism
The invention discloses pullulanase with high secretion capacity and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering and microbial engineering. The pullulanase has high extracellular secretion capacity, and escherichia coli carrying the pullulanase is fermented in a shake flask for 48 hours, the total enzyme activity in the fermentation liquor can reach 212.0 U mL<-1>, wherein the extracellular enzyme activity reaches 200.5 U mL<-1>, which accounts for 94.5% of the total enzyme activity; therefore, the pullulanase is easy to prepare through fermentation, and the control difficulty and cost of the fermentation process can be obviously reduced; the pullulanase has mild action condition, and can hydrolyze alpha-1, 6-glucosidic linkage at a condition with a temperature of 40-60 DEG C and a pH value of 6.0-7.5, therefore, the pullulanase can reduce the cost in industrial transformation, and has potential utilization value in industries such as food, starch sugar and the like.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method for increasing lipase expression through glycosylation modification as well as mutant enzyme and application thereof
ActiveCN104762277ADoes not affect growthIncrease enzyme activityFungiHydrolasesExtracellular proteinsPeptide sequence
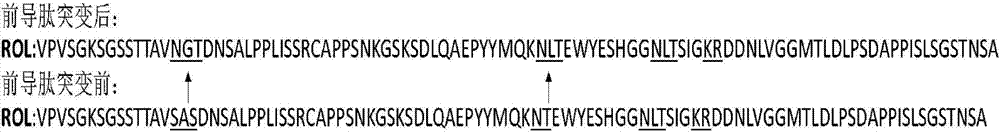
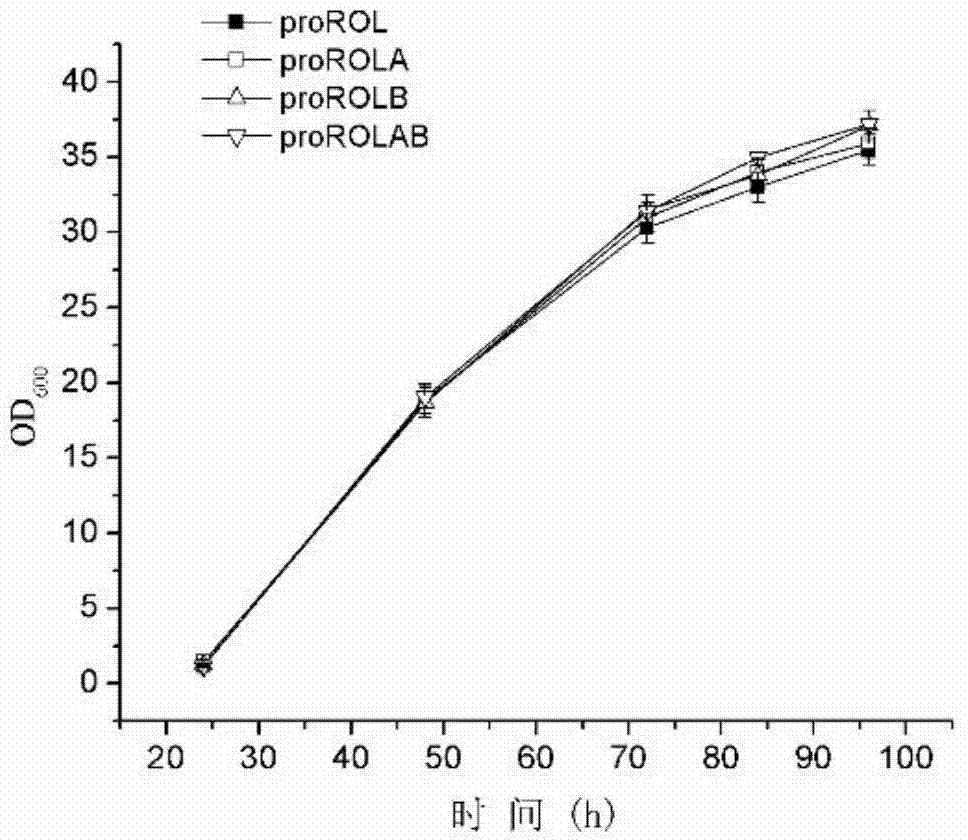
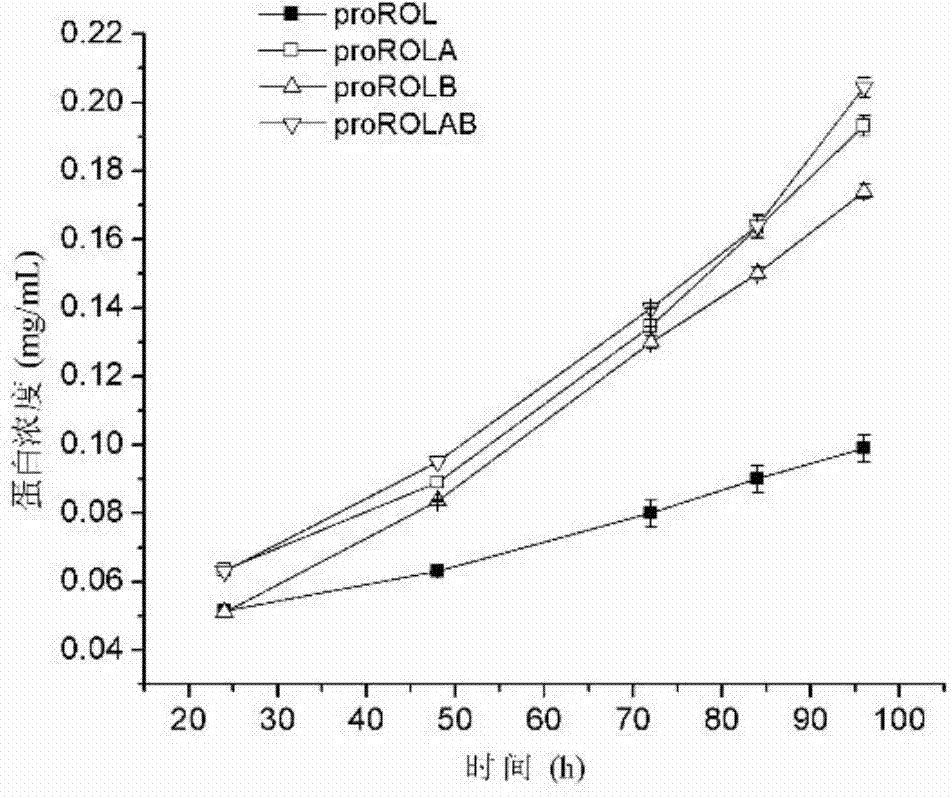
The invention discloses a method for increasing lipase expression through glycosylation modification as well as a mutant enzyme and an application thereof and belongs to the field of enzyme engineering. The N-glycosylation mutation is performed on a leading peptide sequence of rhizopus oryzae lipase, the SAS and / or NT amino acid are / is respectively modified to an N-glycosylation site NGT and / or NLT, the extracellular protein concentrations of the obtained mutant enzyme proROLA, proROLB and proROLAB are increased by 211%, 188% and 233% compared with those of the un-glycosylated proROL, the enzyme activities when culturing in a fermentation tank are respectively 8210 U.mL<-1>, 8457 U.ml<-1> and 9366 U.mL<-1>, and the un-mutated proROL extracellular enzyme activity is almost zero. The rhizopus oryzae lipase provided by the invention has obviously increased lipase enzyme activity and can be used in the fields such as food, chemical engineering and biological energy source.
Owner:TAIXING YIMING BIOLOGICAL PRODS
Preparation method of hybrid hydrolase formulation for promoting methane yield from fermentation
InactiveCN1884509AIncrease fermentation gas productionPromote degradationHydrolasesMicroorganismsBiotechnologyMethane yield
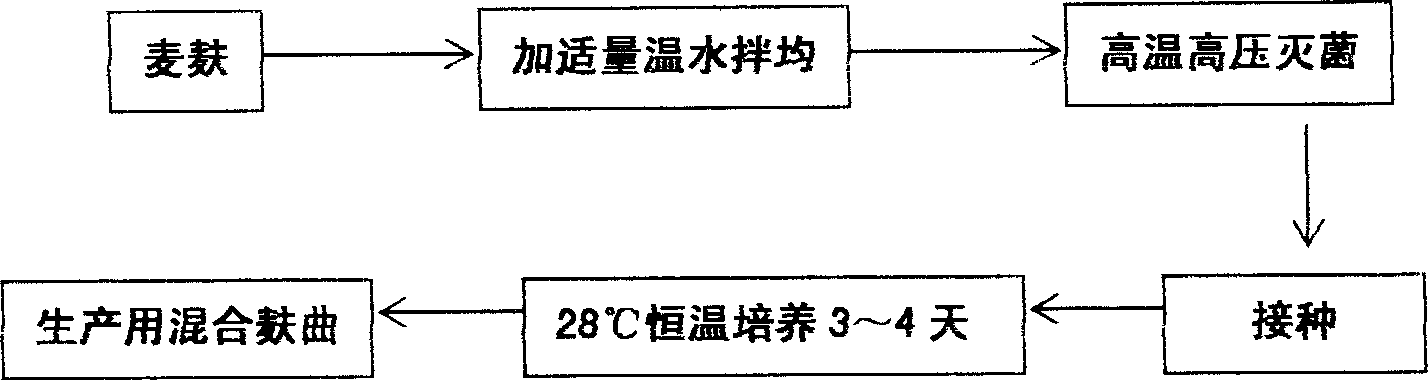
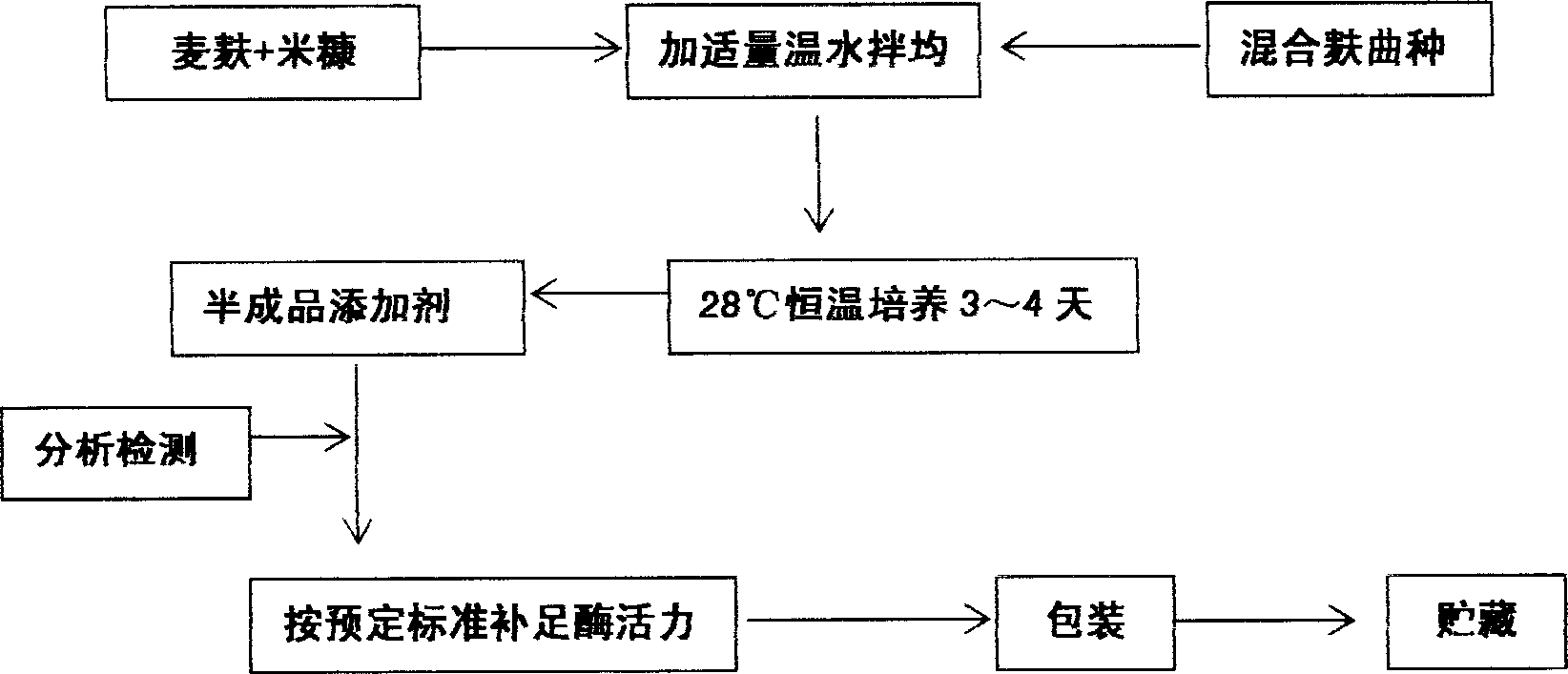
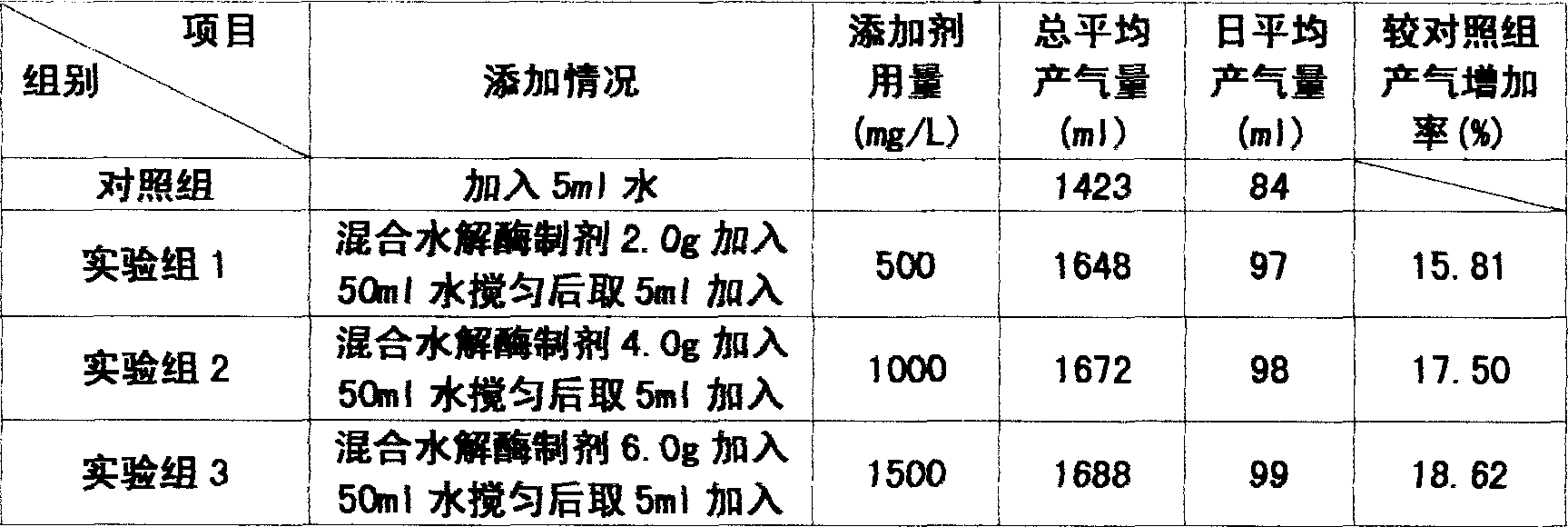
The method for preparation of hydrolytic enzyme preparation used for improving gas-producing rate of marsh gas fermentation belongs to preparation of supplementary exoenzyme used for marsh gas fermentation. The invention is to provide a method for preparation of hydrolytic enzyme preparation used for improving gas-producing rate of marsh gas fermentation, which has the production bacteria with the following enzymatic vitality index: selecting wheat bran and rice bran as mixed culture medium, obtaining mixed bran seeds by pedigree breed two-stage enlargement culture of the bacteria with solid method, fermenting for 3-4 days at 28 DEG after evenly mixed, sampling and analyzing every enzymatic vitality index, adding commodity enzyme preparation to reach enzymatic vitality index, and airing until the humidity is lower than 5%. The enzymatic vitality index of the prolease in the said mixed bran seeds is not more than 2000+-5% mug tyrosine / g / min. The bacteria can be obtained by bacteria and fungus separated from different environment. The test proves that when hydrolytic enzyme preparation is input into the methane tank fermentation raw materials, the rate of dissolution and degradation of the marsh gas fermentation raw materials can be improve, and the gas-producing rate of marsh gas fermentation, TS and VS gas-production potential and methane content in marsh gas can be increased.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
Method for converting polydatin to resveratrol by microbial enzyme method
InactiveCN102408999APromote the application of production practiceFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyGlycoside hydrolase
The invention provides a microbial strain aspergillus.aculeatus (CGMCCNo.3876) used for efficiently extracting polydatin and analogues thereof from plant materials such as polygonum cuspidatum, peanut shells, grape skins and the like, and a complex enzyme prepared by fermenting the microbial strain. The complex enzyme of the strain is used for extracting polydatin and analogues thereof by an enzyme method, and the extraction ratio is 2.3%. The extraction ratio of the complex enzyme is improved by 91.7% through treatment compared with the exoenzyme (control) to which the strain aspergillus.aculeatus is not added. The ratio of conversion from polydatin to resveratrol by using the complex enzyme of the strain is above 99.5%. The polygonum cuspidatum glycoside hydrolase purified from the complex enzyme of the strain is used for converting 98% of polydatin to resveratrol, and the conversion ratio is 99.7%. The purity of resveratrol is 98.5%. By the invention, a novel complex enzyme preparation is actually provided for production, the problems of low catalytic activity of enzymes, low conversion ratio, overlong time and high cost in current production upgrading are fundamentally solved, and the production practice application is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
PelB signal peptide mutant capable of improving protein secretion efficiency and application of pelB signal peptide mutant
The invention discloses a pelB signal peptide mutant capable of improving the protein secretion efficiency and an application of the pelB signal peptide mutant and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. A sequence of a pelB mutant secretive expression signal peptide is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. The signal peptide is capable of improving the extracellular enzyme activity of objective protein cyclodextrin glycosyltransferase by 1.6 times. The extracellular protein production capability of recombinant escherichia coli transformed by using the signal peptide is strengthened, and industrialized production is facilitated.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
DNA sequence for constituting T carrier and the T carrier constituting process
InactiveCN1344795ASimple and fast operationEasy to operateVector-based foreign material introductionDNA preparationDNA fragmentationEndoenzyme
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
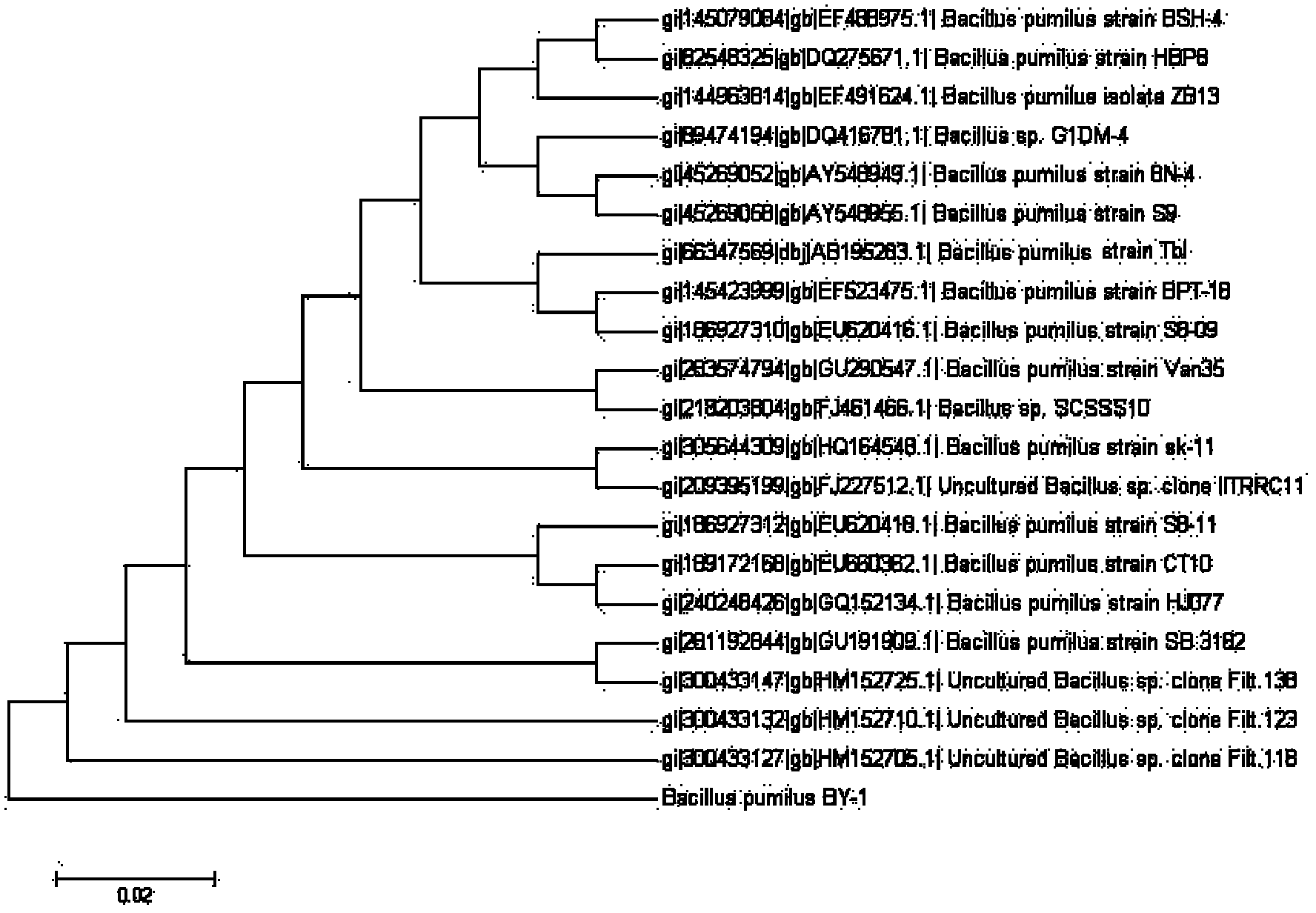
Bacillus and application thereof
InactiveCN102433269AIncrease enzyme activityHigh activityBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsTibetan pigFeces
The invention relates to a new bacillus, which is classified and designated as Bacillus pumilus BY-1. The bacillus pumilus is separated from fresh excrement of a Tibetan pig; the bacillus pumilus is capable of generating cellulase and has the ability of degrading sodium carboxymethylcellulose; after 96 h of culture at 37 DEG C and 220 rpm, the activity of the carboxymethylcellulase is 0.92 mu mol / ml.min. With the gene sequence of the endonuclease gene bglC of Bacillus pumilus SAFR-032 as reference, a designed primer is successful in amplifying the endo-beta-1,4-glucanase gene of the Bacillus pumilus BY-1, which is designated as bglC-BY; and through NCBI blast (National Center for Biotechnology Information, Basic Local Alignment Search Tool), the similarity of the gene to the bglC is 88%, and the similarity thereof to the gene of Bacillus pumilus endoglucanase A precursor(EglA) is higher, up to 96%; therefore, the expression of pET expression system is realized and induction is started when the absorbance A595 of the bacterial fluid is 0.7534 at a culture temperature of 30 DEG C and 220 rpm; the activity is highest in 42 hours after the induction; and the highest activity of the extracellular enzyme is measured to be 0.5434 mu mol / ml.min.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
A preparation method of yeast-derived active polypeptide
The invention discloses a preparation method of active polypeptide derived from yeast. Mix yeast powder and water, add a mixed enzyme consisting of endoenzyme, exoenzyme, and flavor enzyme, and separate solid and liquid after enzymatic hydrolysis. The polysaccharide and nucleic acid impurities in the liquid phase components were removed by ethanol precipitation. The supernatant is filtered and separated by an ultrafiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 5kDa to 10kDa, and the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure and vacuum freeze-dried to obtain the active polypeptide. Through in vitro activity determination, the yeast-derived active polypeptide has blood pressure-lowering, anti-oxidation and blood-sugar-lowering activities.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH +1
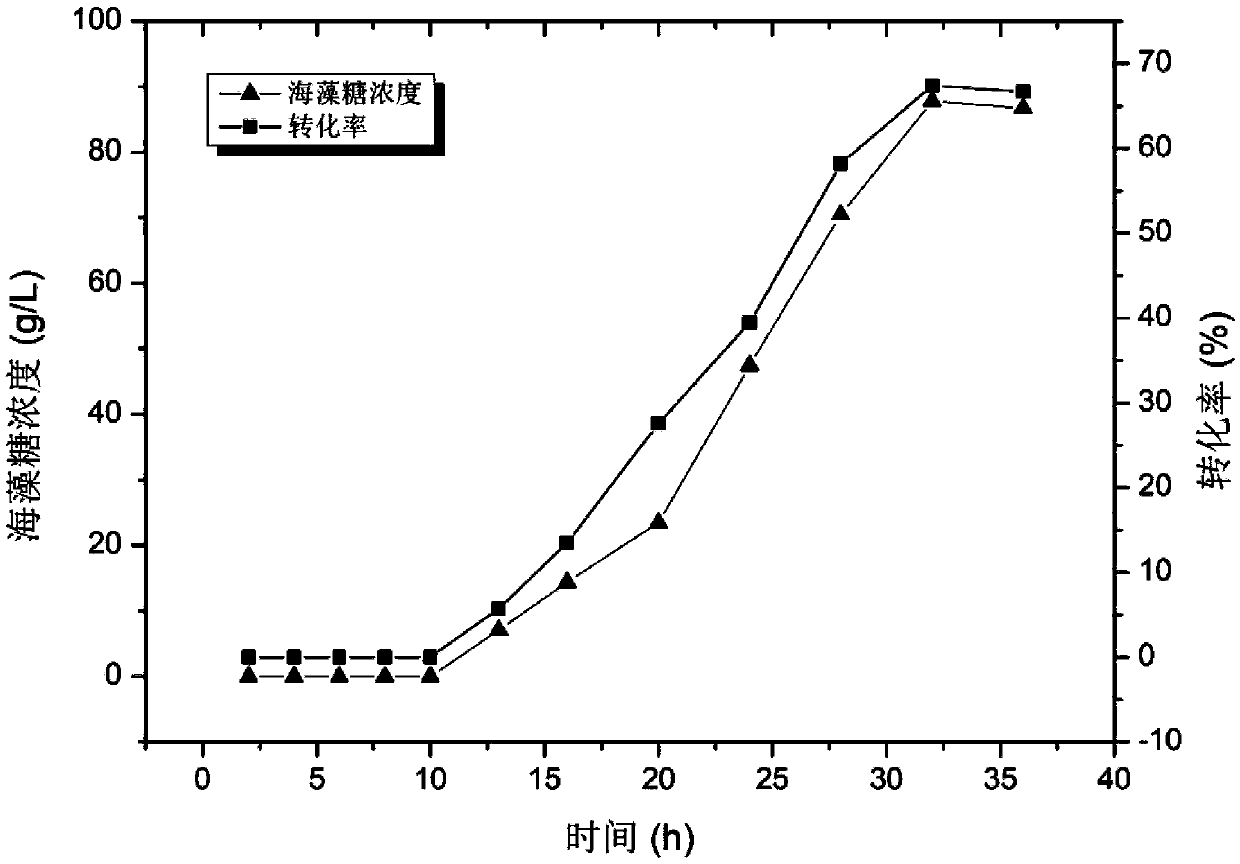
Method for producing trehalose by coupling fermentation on double enzyme fusion enzyme expressed by efficient secretion
ActiveCN109679887ARealize functional expressionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSecretionSecreted substance
The invention relates to a method for producing trehalose by coupling fermentation on double enzyme fusion enzyme expressed by efficient secretion. The method is characterized in that a promoter P43,a signal peptide PhoD, maltooligosyl trehalose synthase (MTSase) and maltooligosyl trehalose trehalohydrolase (MTHase) are inserted into bacillus subtilis for the first time; meanwhile, after lytic genes Xpf, SkfA, LytC and SdpC are knocked out, construction is carried out to obtain recombinant bacteria pHT01-P43-PhoD-MTSase-MTHase(LM1234), and the rigid connection of a special sequence is adoptedto realize the function expression of a target enzyme; after the trehalose is produced by practical fermentation, an amazing discovery shows that the reformed recombinant bacteria exoenzyme activitycan occupy 70% of total enzyme activity, exoenzyme production and conversion are synchronously carried out, so that a process that trehalose production is carried out after enzyme separation is carried out in traditional fermentation liquor is omitted, and the fermentation of the recombinant bacteria and the production of the trehalose are similar to coupling.
Owner:烟台兆易生物科技有限公司
Phosphate solubilizing bacterium and extraction method thereof
InactiveCN110669696AAbundant resourcesPhosphorus dissolving ability is strongBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologySucrose
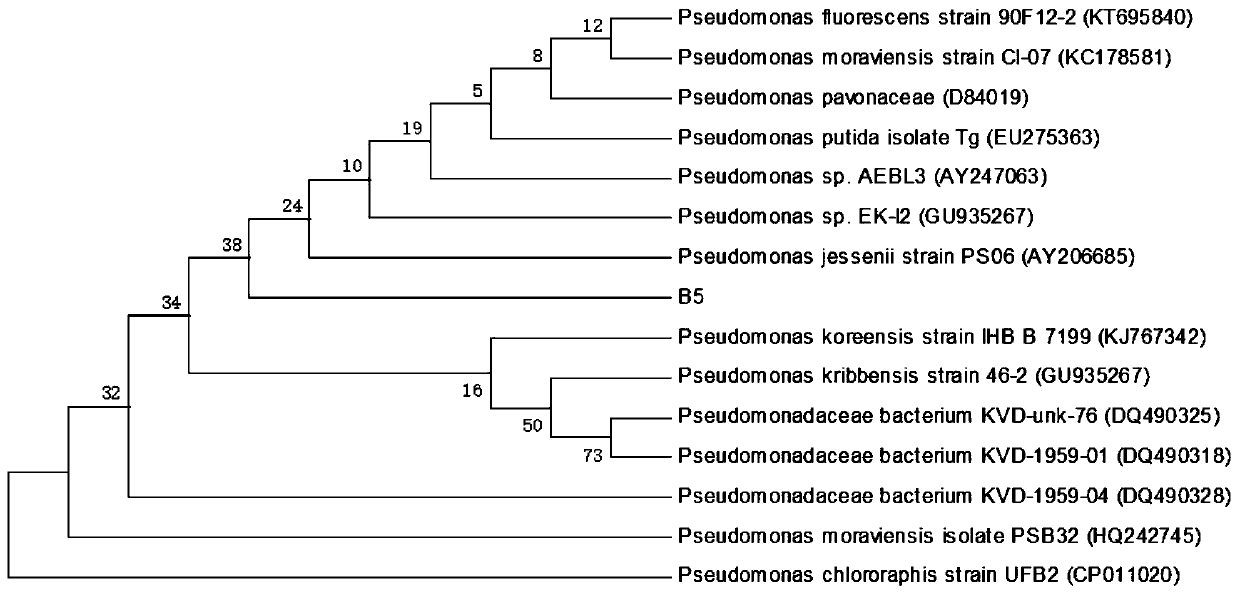
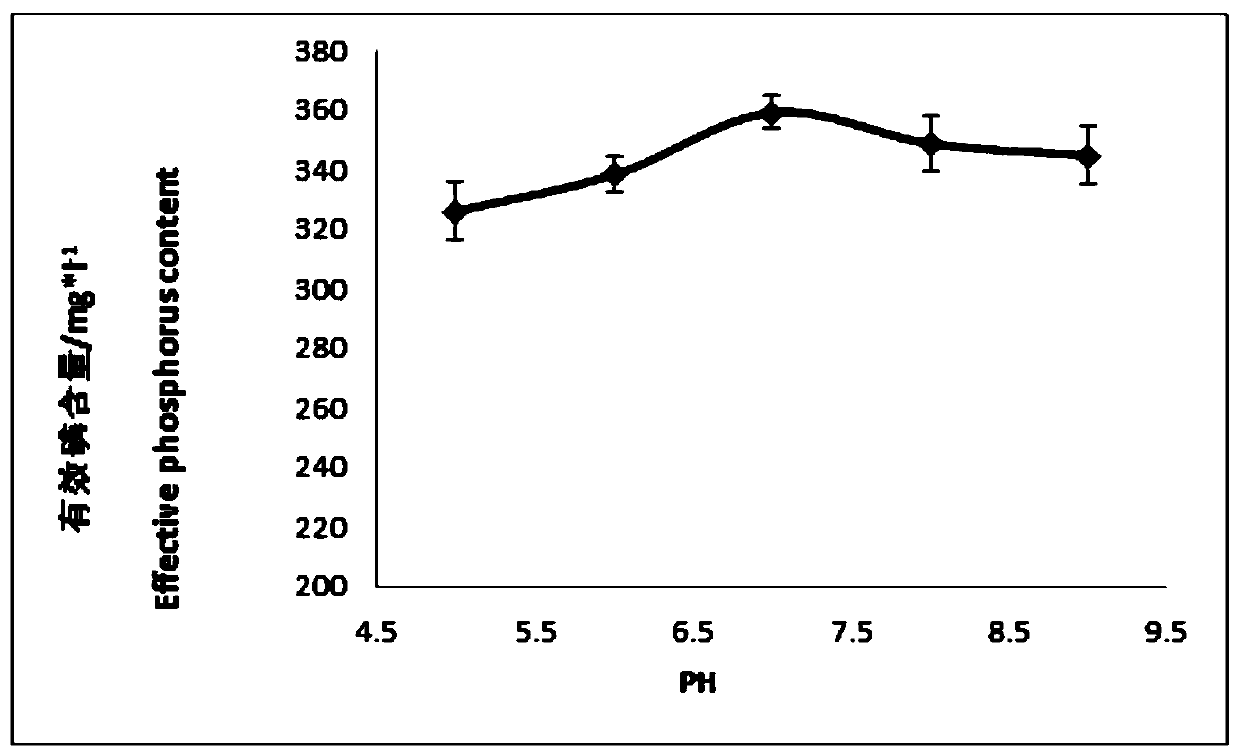
The invention discloses a phosphate solubilizing bacterium and an extraction method thereof. The phosphate solubilizing bacterium is named a strain B5, the strain B5 is a pseudomonas bacterium, determination results of biochemical criterion are gram staining is negative, a methyl red test is negative, a V-P reaction is negative, an indole test is negative, an oxidase test is negative, the strain B5 can use citrate as a carbon source to produce extracellular enzyme-gelatinase liquidation gelatin, catalase and indole are produced, and H2S is generated; the order of the phosphate solubilizing ability of the strain B5 from high to low under different carbon sources is that glucose is greater than galactose, the galactose is greater than lactose, the lactose is greater than sucrose, and the sucrose is greater than soluble phosphate starch, and the order of the phosphate solubilizing ability under different nitrogen sources is that ammonium sulfate is greater than ammonium chloride, the ammonium chloride is greater than urea, and the urea is greater than potassium nitrate; and the optimum growth temperature of the strain B5 is 28-32 DEG C, and the optimum growth pH of the strain B5 is 7-9.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Plasminogen and cultivation method therefor
The present invention relates to one kind of and its culturing and preparing process. The plasmin is prepared with N. sitophila strain No. 17 in the preservation number of CGMCC No. 1836, and through fermentation, separation and purification. It consists of two subunits of molecular weight 30000 and 15500 separately and isoelectric point of 7.9+ / -0.2. The plasmin has high thrombolysis performance, no bleeding activity, no blood coagulating activity and no obvious acute toxicity, and thus possesses clinical test, development and application foreground. The plasmin of the present invention is one kind of extracellular enzyme, and is favorable to post separation and purification. Its preparation adopts wheat bran and soybean residue as main culture medium material, and thus has low material cost.
Owner:QIQIHAR UNIVERSITY
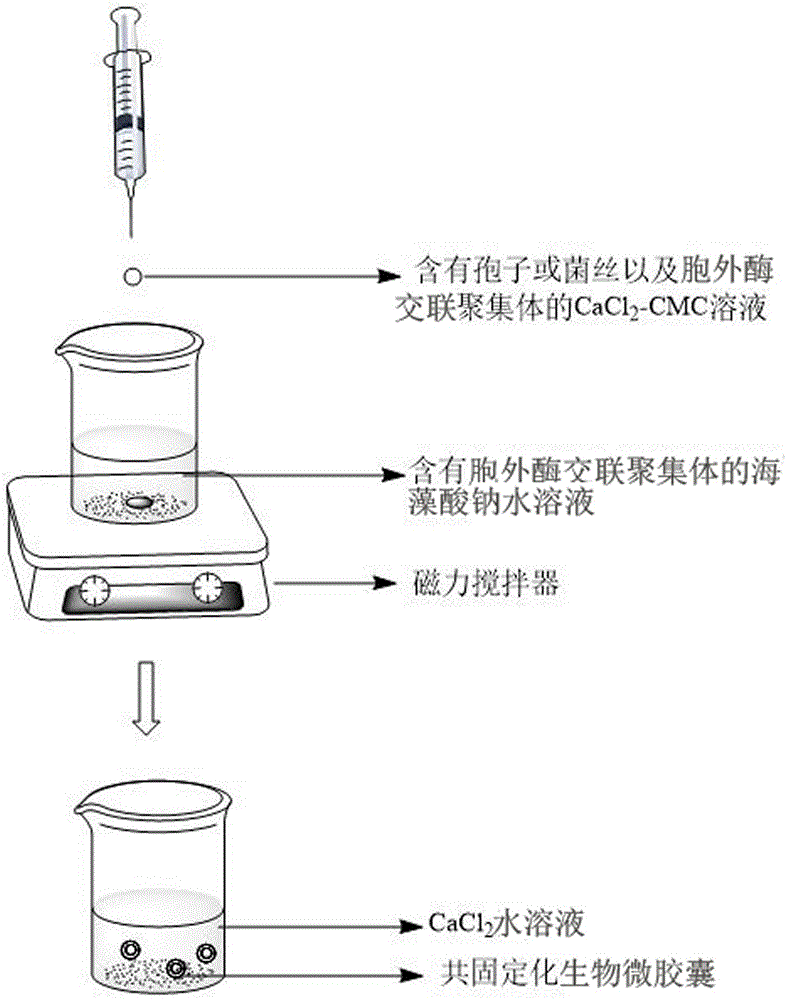
Calcium alginate-sodium carboxymethyl cellulose co-immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium strain and biological microcapsule of exoenzyme thereof, and preparation method of strain
ActiveCN105176963AEliminate the purification stepReduce manufacturing costMicroorganism based processesOn/in organic carrierCarboxymethyl celluloseCross-linked enzyme aggregate
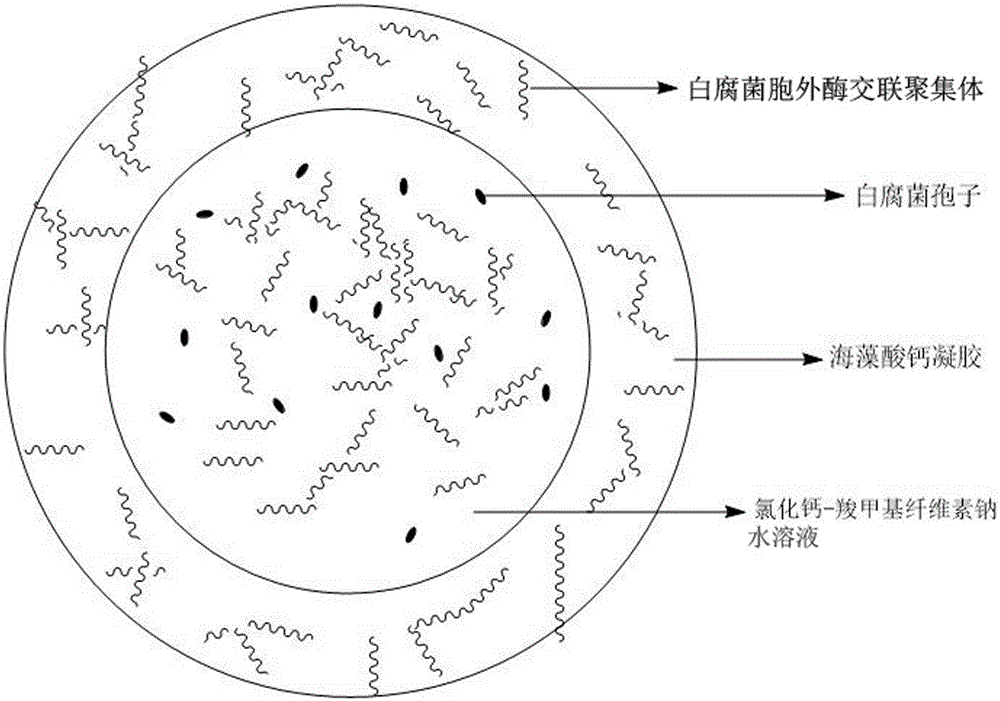
The invention relates to a calcium alginate-sodium carboxymethyl cellulose co-immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium strain and a biological microcapsule of exoenzyme thereof, and a preparation method of the strain. The biological microcapsule comprises a shell and a shell inside core, wherein the shell material is a calcium alginate gel, and a Phanerochaete chrysosporium exoenzyme crosslinking aggregate is embedded inside the calcium alginate gel; and the shell inside core is a calcium chloride-sodium carboxymethyl cellulose water solution, and Phanerochaete chrysosporium cells and an extracellular crosslinking enzyme aggregate are dispersed inside the calcium chloride-sodium carboxymethyl cellulose water solution. In the biological microcapsule preparation process, the Phanerochaete chrysosporium exoenzyme is directly prepared into the crosslinking enzyme aggregate, thereby omitting the step of purification of the lignin degrading enzyme, effectively lowering the production cost and enhancing the degradation efficiency since the crosslinking enzyme aggregate and Phanerochaete chrysosporium form a close relation.
Owner:山东济清科技服务有限公司
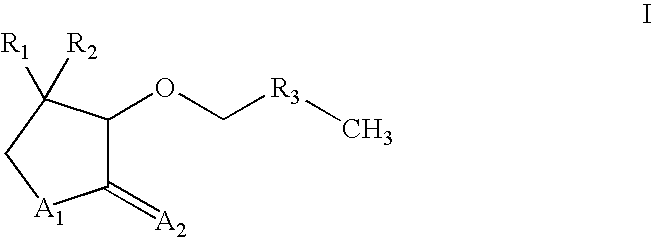
Alkoxylactones, alkoxylactams and alkoxythiolactams for controlling processes based on microbial interaction
Compounds of the Formula I,wherein A1 is O or NH; A2 is O or S; each of R1 and R2 is independently hydrogen, a methyl or C2-C8-saturated or mono- or doubly unsaturated, branched or linear hydrocarbon group; and R3 is a C1-C18-saturated or mono- or doubly unsaturated, branched or linear hydrocarbon group wherein, each of R1, R2 and R3 comprises a heteroatom selected from the group consisting of O and S in the chain and / or is mono- or multiply-substituted by a substituent selected from the group consisting of halogen, hydroxy, C1-C6-alkyl, trifluoromethyl, C1-C6-alkoxy, C6-C10-aryl, and C1-C6-alkyl-C6-C10-aryl are useful for controlling the interaction process between microorganisms such as in the development and / or maturation of biofilms; multicellular swarm behavior; the concerted development of antibiotic resistances; the concerted synthesis of antibiotics; the concerted synthesis of pigments; the concerted production of extracellular enzymes; or the concerted production of virulence factors.
Owner:HENKEL KGAA
Recombinant bacillus subtilis for producing pullulanase and construction thereof
InactiveCN106190934AResolve dependenciesGood acid and heat resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesShuttle vectorEnzyme Gene
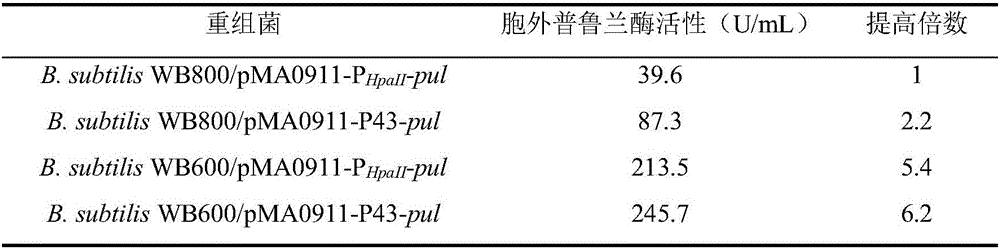
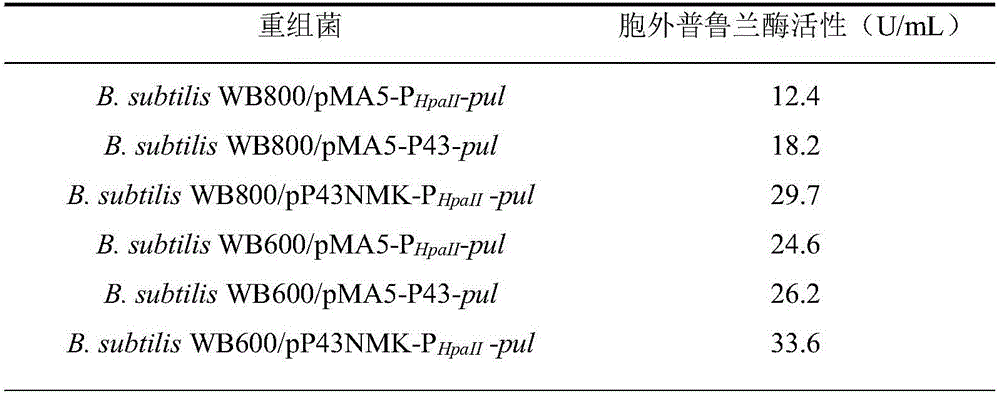
The invention discloses recombinant bacillus subtilis for producing pullulanase and construction thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microbial fermentation production of pullulanase. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis for producing the pullulanase and the construction thereof, a bacillus naganoensis CCTCC NO:M 2012388 pullulanase gene pul is inserted into a shuttle vector pMA0911, the obtained recombinant plasmid pMA0911-PHpaII-pul is electrically converted into B.subtilis WB800 to construct a recombinant bacterium B.subtilis WB800 / pMA0911-PHpaII-pul, and the extracellular pullulanase activity is 39.6 U / mL. An original promoter PHpaII is replaced with a strong promoter, and the extracellular enzyme activity of recombinant bacterium B.subtilis WB800 / pMA0911-P43-pul is improved to be 87.3 U / mL; the constructed recombinant plasmid pMA0911-PHpaII-pul and the pMA0911-P43-pul are converted into a host bacterium B.subtilis WB600, and the extracellular enzyme activity of the obtained recombinant bacterium B.subtilis WB600 / pMA0911-PHpaII-pul and the extracellular enzyme activity of the obtained recombinant bacterium WB600 / pMA0911-P43-pul are up to 213.5 U / mL and 245.7 U / mL respectively.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Genetically engineered bacterium for producing linear malt oligosaccharide generating enzyme and application of genetically engineered bacterium
ActiveCN105950528AMethod securityHigh starch conversion rate and product purityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesOligosaccharideBiotechnology
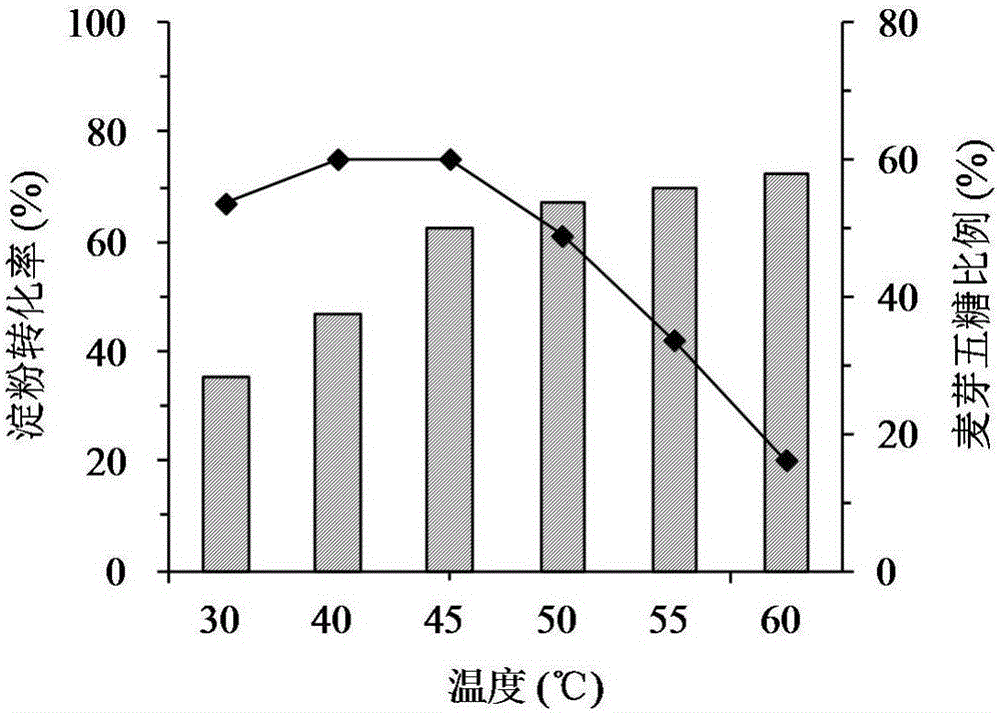
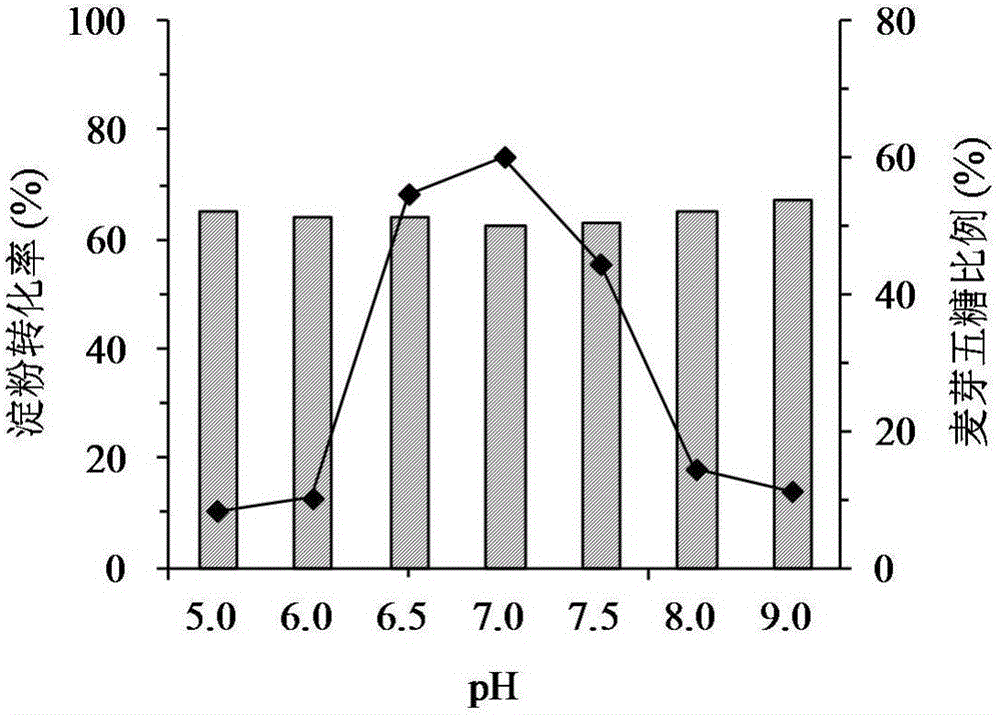
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for producing a linear malt oligosaccharide generating enzyme and application of the genetically engineered bacterium, and belongs to the technical field of microbial engineering. According to the genetically engineered bacterium, secretory expression of the linear malt oligosaccharide generating enzyme in bacillus subtilis is achieved, a method is safe and efficient, the hydrolytic activity reaches 36.6 U / mL, and the enzyme producing capacity is 10 times or above of that of an original bacterium; the obtained recombinant enzyme is an extracellular enzyme, convenience is brought for extraction and purification of large-scale production in the later period, and the product meets the food requirement. Starch is hydrolyzed by the purified recombinant linear malt oligosaccharide generating enzyme to generate linear malt oligosaccharide syrup which does not contain glucose and contains a high proportion of maltopentaose, and the linear malt oligosaccharide syrup can be directly used for producing functional food and also can be used for producing products such as high-purity linear malt oligosaccharides.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Beta-xylosidase and encoding gene and application thereof
InactiveCN101724615AEasy to purifyHigh recovery rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliBiology
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Method for efficiently synthesizing L-theanine through recombined corynebacterium crenatum
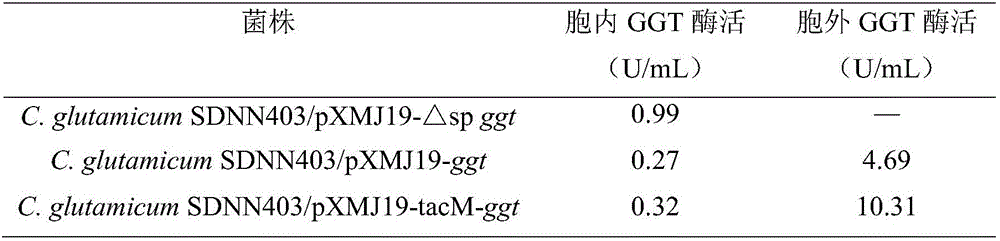
The invention discloses a method for efficiently synthesizing L-theanine through recombined corynebacterium crenatum, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the method, it is firstly verified that GGT signal peptide of a bacillus subtilis source can achieve secretory expression in a C.glutamicum system. Meanwhile, extracellular enzyme activity of recombinant bacteria C.glutamicum SDNN403 / pXMJ19-tacM-ggt is about two times that of C.glutamicum SDNN403 / pXMJ19-ggt, and it indicates that a tac Mpromoter is more beneficial for synthesis of GGT enzyme activity. Substrate flow and strategic high-yield L-theanine are adopted, a conversion system contains GGT with the concentration of 0.8 u / mL, the pH is 10, the temperature is 37 DEG C, and 22 mmol / L L-theanine and 66 mmol / L ethylamine are supplemented every other two hours from 0 h. The maximum theanine yield of 118 mmol is achieved when batch flow is added for 12 h, and the conversion rate is 92.8%. The secretory expression of gamma-glutamyltranspeptidase genes (ggt) of the B.subtilis source in C.glutamicum SDNN403 is achieved for the first time, and the highest yield of L-theanine reported currently and synthesized through recombined C.glutamicum is obtained by adding the substrate in batch flow.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for preparing T vector
InactiveCN1142279CQuality improvementImprove cloning efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionEndoenzymeT vector
A process for preparing T vector by using endoenzyme to digest the pre-T vector features that the single- or dual-chain oligo-DNA as the competitive substrate of exoenzyme, whose mole concentration is at least 10 times higher than that of pre-T vector, is added to the over-digestive system used to prepare said T vector in the condition of no excessive increasement of total DNA concentration to suppress the influence of exoenzyme activity on T vector, so obtaining excellent T vector with stable quality.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
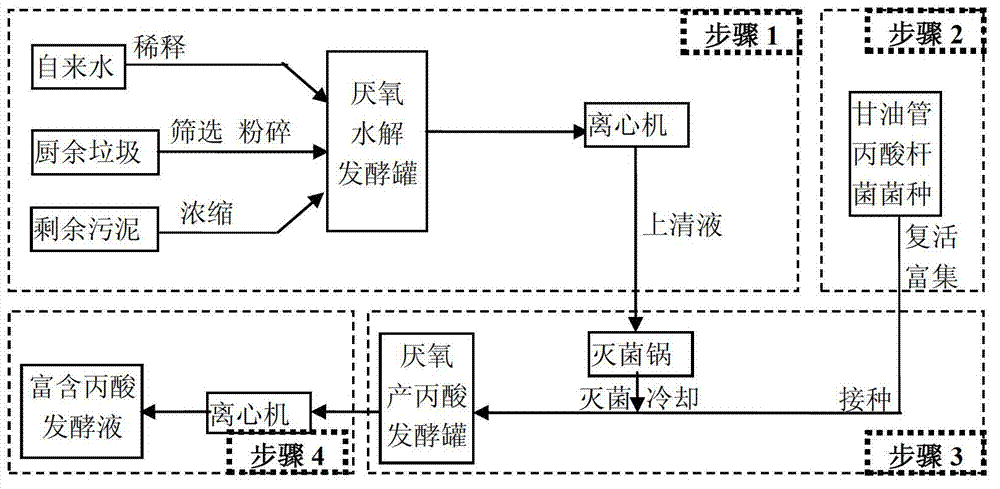
Method for increasing content of propionic acid in batch fermentation acid-producing liquid
ActiveCN102776247APropionic acid content enhancedFacilitate the hydrolysis of sugarMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismExtracellular
The invention belongs to the technical field of environmental protection and relates to a method for increasing content of propionic acid in batch fermentation acid-producing liquid. The method includes the steps of firstly, mixing kitchen waste and thickened sludge, adding mixture into an anaerobic hydrolysis fermenter for anaerobic fermentation, centrifugally separating mixture, and taking supernate for standby; secondly, activating and enriching propionibacterium seed broth; thirdly, sterilizing the supernate obtained in the step 1, inoculating the propionibacterium seed broth obtained in the step 2 to the supernate, and fermenting in an anaerobic fermenter to generate propionic acid; and fourthly, centrifuging the fermented mixture to obtain the fermented supernate rich in propionic acid after fermentation. The sludge and the kitchen waste are subjected to primary fermentation under the weak alkaline condition, and microorganism extracellular enzyme hydrolysis of macromolecular organic matters such as microorganism exoenzyme hydrolysate, protein and fat is facilitated. The content of the propionic acid in the fermented supernate is 3.56-9.95g COD per L of total acid in the supernate.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Method for preparing hyperoxide dismutase by fermenting shiraia bambusicola
InactiveCN101638639AOutput stimulusEasy accessMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesDismutaseAlkane
A method for preparing hyperoxide dismutase (SOD) by fermenting shiraia bambusicola belongs to the technical field of bioengineering. The method adopts shiraia bambusicola strain for preparing the SODwhich is mainly exoenzyme under the condition of liquid state fermentation. During the fermentation, the SOD yield can be improved by adding H2O2, surfactant or alkane or by illumination. The maximumSOD yield can be 800 U / mL. During the fermentation, the strain can simultaneously generate quinochromes which can have a yield as high as 1.1 g / L, wherein hypocrellin A accounts for 90 percent and hypocrellin B accounts for 5 percent. Tabasheer is an officinal fungus and mainly generates hypocrellins and other quinochromes by means of fermentation, thereby having high officinal value and healthcare function. The fermentation of the tabasheer to prepare the SOD has the advantage of short fermentation period, the activity of the SOD in fermentation liquid is relatively high, and the quinochromes can be simultaneously generated. The method has a good prospect for industrial application.
Owner:江苏竹红生物科技有限公司
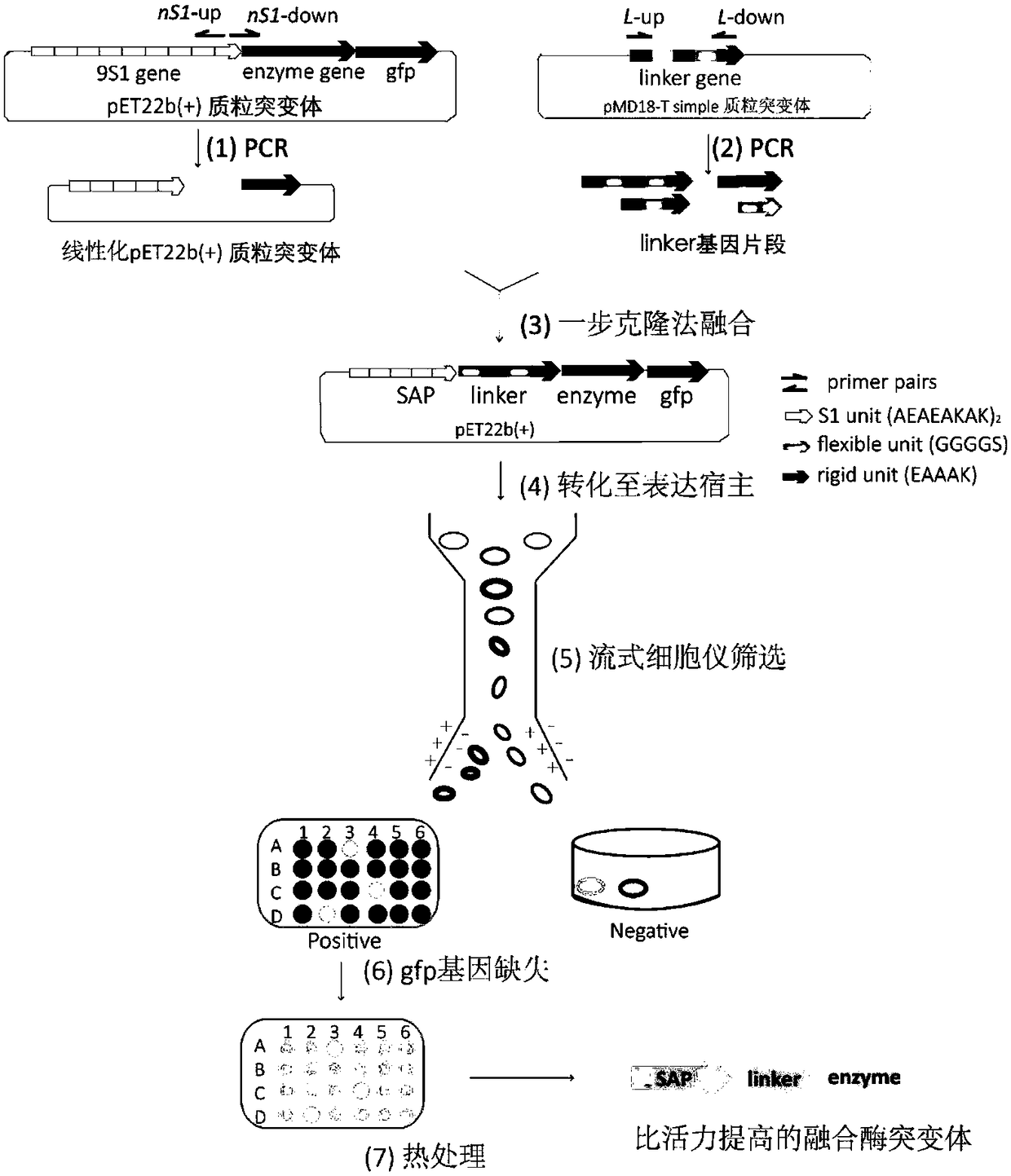
Method for obtaining enzyme mutant with high expression, high activity and high stability
InactiveCN108342407AMutant class balanceSimple screening methodBacteriaHydrolasesGenetic engineeringPectinase
The invention discloses a method for obtaining an enzyme mutant with high expression, a high activity and high stability, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. By means of a functional polypeptide library which is constructed on the basis of SAPs, the whole process of obtaining the enzyme mutant is quick, efficient and convenient; meanwhile, compared with wild-type alkaline pectinase, the activity of extracellular amylase of the fused enzyme mutant of alkaline pectinase is maximally improved by 15.32 times, the stability is maximally improved by 3.86 times, and the specific enzyme activity is improved by 2.55 times; the activity of intracellular amylase of the fused enzyme mutant of lipoxygenase is maximally improved by 2.49 times, the stability is maximally improved by 3.13 times, and the specific enzyme activity is improved by 0.9 time; the activity of extracellular amylase of the fused enzyme mutant of asparaginase is maximally improved by 2.25 times, the stability is maximally improved by 3.56 times, and the specific enzyme activity is maximally improved by 1.34 times.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Penicillium pinophilum strain and method for preparation of dextranase from the same
ActiveCN104911106APromote degradationIncrease contactFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBiotechnology
The invention provides a dextranase producing strain with high enzyme activity and a method for preparation of dextranase from the strain. The strain is characterized in that it is Penicillium pinophilum H6 separated from soil, the strain is preserved by China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with a preservation number of CGMCC No.9260. The invention successfully utilizes Penicillium pinophilum H6 fermentation to prepare dextranase, also can produce dextranase with high enzyme activity, and the produced dextranase is extracellular enzyme. Preparation of dextranase by Penicillium pinophilum H6 fermentation process is characterized in that the most suitable action temperature is 40DEG-50DEG C, the most suitable pH is 5.0-6.0, and the stable pH is 3.0-10.0. The level of Penicillium pinophilum H6 fermentation for production of dextranase is 345U / ml.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAMAO PHARMA
Heat-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant and application thereof
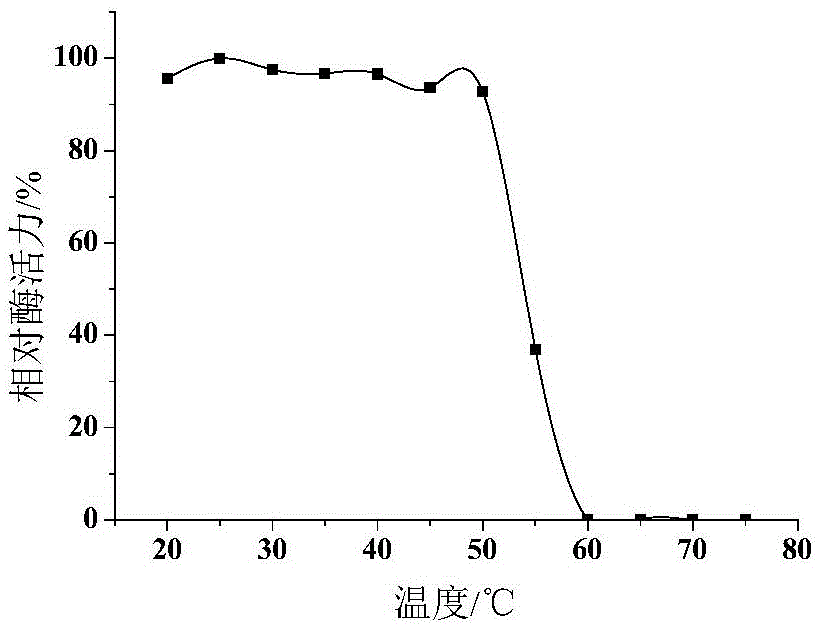
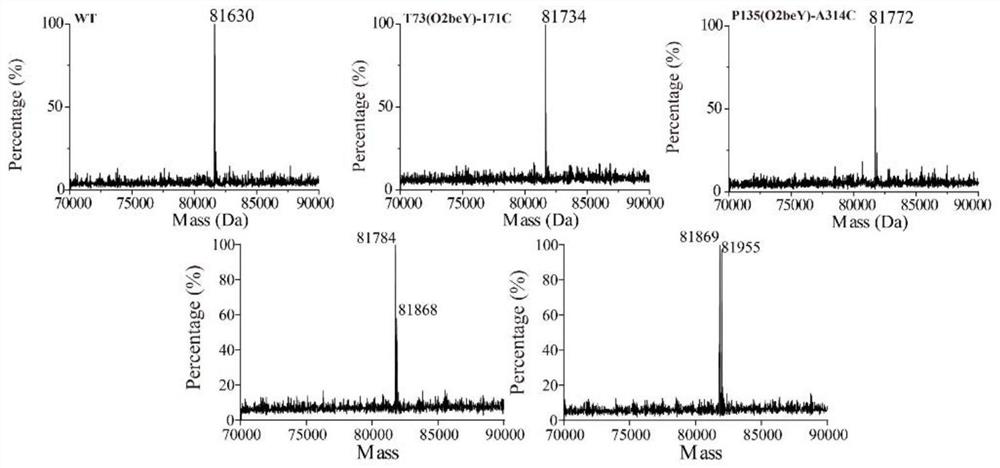
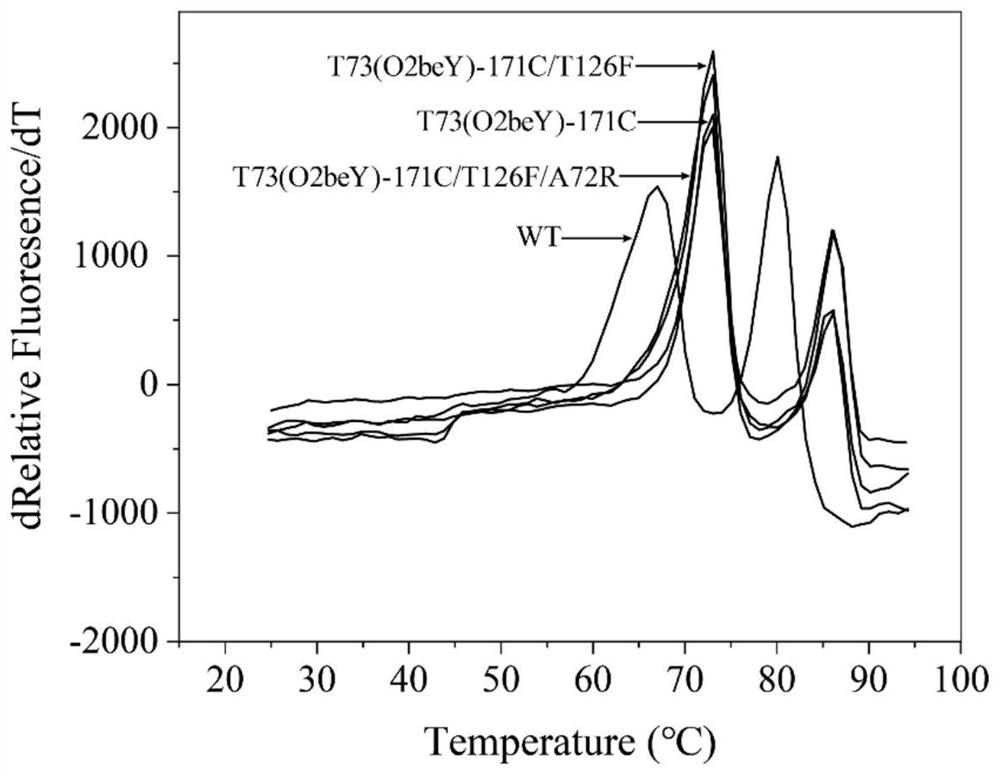
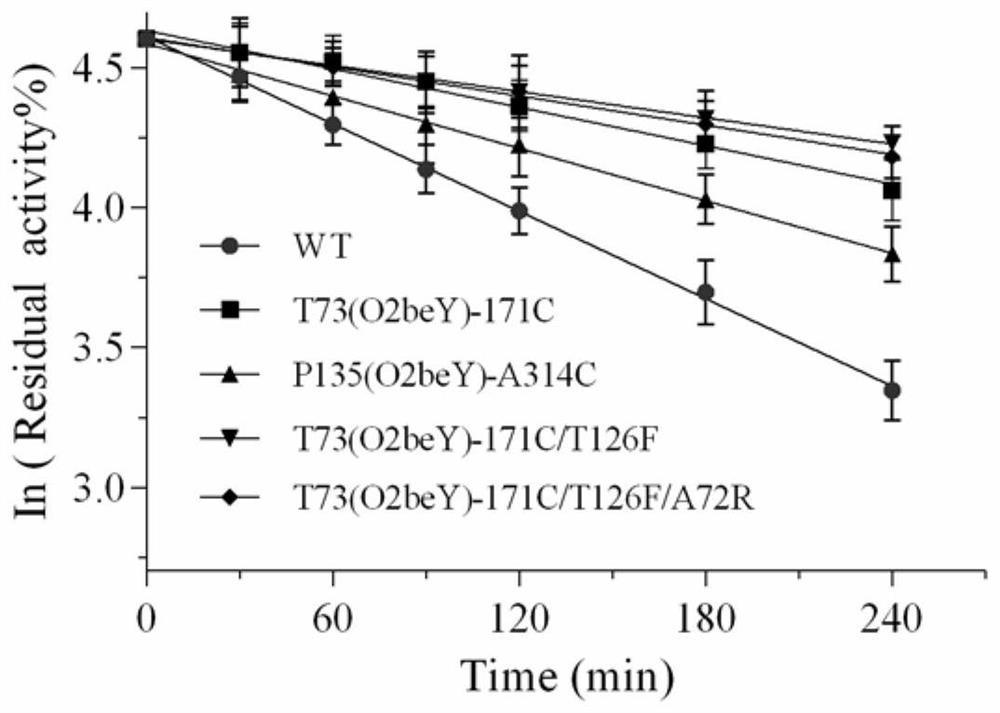
ActiveCN113265386AImprove thermal stabilityImprove secretion efficiencyPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFungiExtracellularSecretion expression
The invention discloses a heat-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant and application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering and enzyme engineering. According to the invention, amino acids at the 73th site, the 135th / 314th site, the 135th / 314th / 126th site and the 135th / 314th / 126th / 72nd site of pullulanase are respectively mutated, so that four pullulanase mutants with improved thermal stability and unchanged or improved catalytic efficiency are obtained. At the temperature of 70 DEG C, the half-life periods of the four mutants are respectively 2.6, 1.9, 3.3 and 3.1 times that of a wild type; and the Tm values are respectively increased by 7.0 DEG C, 6.5 DEG C, 6.7 DEG C and 6.9 DEG C. The extracellular enzyme activity of pullulanase reaches 9.7 U / mL by fusing OptPelB at the N terminal of the high-temperature-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant, and is 4.9 times that of a wild type. The heat-resistant neutral pullulanase mutant capable of secreting and expressing has the application potential of high-value utilization of starch raw materials.
Owner:宿迁市江南大学产业技术研究院
Alkaline pectinase mutant with improved secretion property
ActiveCN106636049AImprove secretion efficiencyHigh thermodynamic stabilityBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsPectinasePentagalacturonic acid
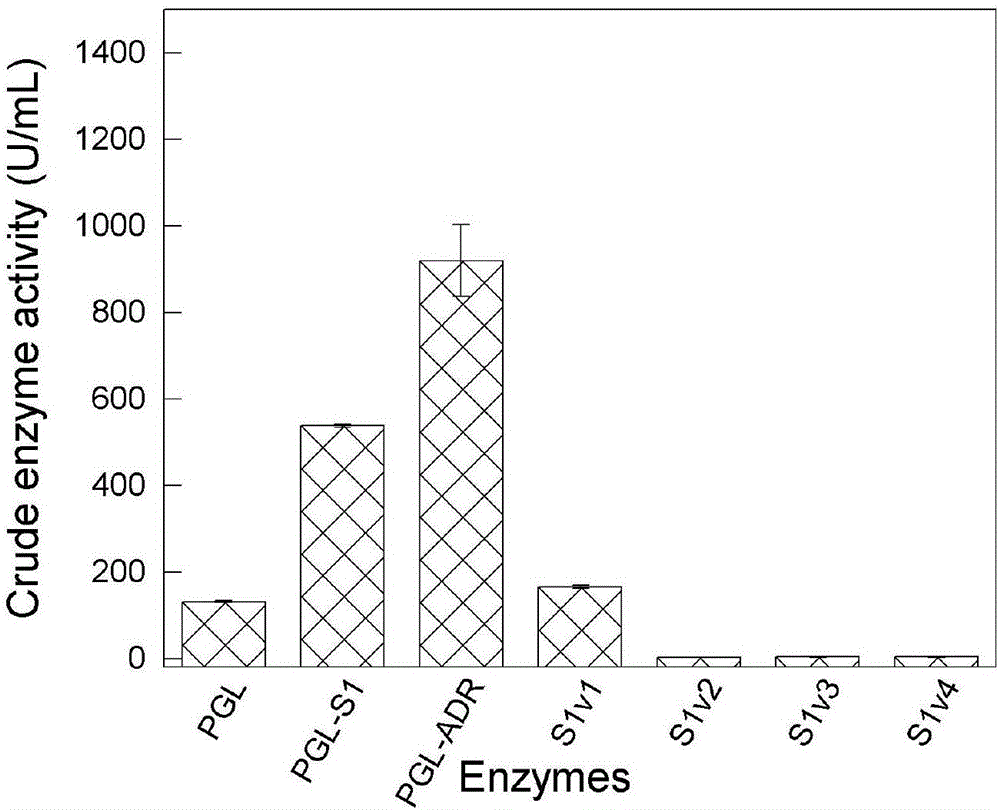
The invention discloses an alkaline pectinase mutant with an improved secretion property, and belongs to the technical field of enzyme engineering. The sequence of the provided alkaline pectinase mutant is shown as in SEQ ID NO.1. Compared with the existing alkaline pectinase or the alkaline pectinase mutant PGL-S1, the activity of an extracellular enzyme of the mutant PGL-ADR is up to 919.88 plus or minus 82.64 U / mL and is 1.7 times higher than that of the PGL-S1 (the average value of three repeated experiments), the specific enzyme activity of the purified PGL-ADR is 448.36 U / mL, the melting temperature is increased by 4.11 DEG C, and the data prove that the thermodynamic stability is remarkably improved. The alkaline pectinase can catalyze the splitting decomposition of glucosidic bond alpha-1,4 of polygalacturonic acid through trans-elimination under the alkaline conditions, and is widely used in the industries of foods, textiles and papermaking, etc.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com