Genetically engineered bacterium for producing linear malt oligosaccharide generating enzyme and application of genetically engineered bacterium
A malto-oligosaccharide and genetically engineered bacteria technology, applied in the field of microbial engineering, can solve problems such as unfavorable enzyme separation and purification applications, and achieve the effects of industrial application value, high starch conversion rate and product purity, and reduced production and processing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0023] Example 1 Construction of Bacillus subtilis secretion expression system
[0024] Design the upstream primer (including EcoR I restriction site) according to the gene of linear maltooligosaccharide producing enzyme: 5'-GTATAACGAATTCCAACCGCGAACCG-3'; the downstream primer (including BamH I restriction site): 5'-CCTTAGGATCCAAAGCTTCCCGTTGGG-3 '.
[0025] The target gene SEQ ID NO.1 containing the coding signal peptide sequence was cloned, and the PCR system was: 10×Ex Taq buffer (Mg 2+ Plus) 5 μL, dNTPs (2.5 mM each) 5 μL, forward primer (10 μM) 1 μL, reverse primer (10 μM) 1 μL, template DNA 1 μL, Ex Taq HS (5U / μL) 0.25 μL, add double distilled water to 50 μL. PCR amplification conditions were: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 4 minutes; further 35 cycles (94°C for 30s, 55°C for 30s, 72°C for 2min); and finally, incubation at 72°C for 10 minutes.
[0026] The PCR product and plasmid pMD 18-T simple were subjected to double enzyme digestion and then gel-cut to recover, ligate...
Embodiment 2
[0029] Embodiment 2 Fermentative production of recombinant linear maltooligosaccharide generating enzyme
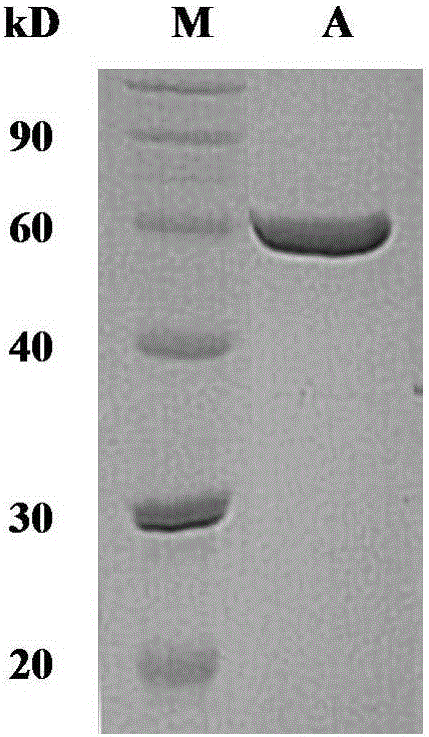
[0030] Pick a single colony of Bacillus subtilis containing the expression vector mfa / pST from the preservation plate and inoculate it into 50 mL of LB medium containing 5 μg / mL kanamycin and gibberellin (1% tryptone, 0.5% yeast extract, 1% Sodium chloride, pH 7.0), culture overnight at 37°C and 200rpm in shake flasks; transfer to 50mL TB medium containing 5μg / mL kanamycin and gibberellin (1.2% tryptone , 2.4% yeast extract, 0.4% glycerol, 17mM KH 2 PO 4 , 72mM K 2 HPO 4 , pH 6.0), 25°C, 200rpm shake flask culture for 60h; the obtained fermentation broth was centrifuged at 10000rpm for 10min to remove bacteria, and the obtained fermentation supernatant was the crude enzyme solution. The hydrolytic activity of the crude enzyme solution was determined to reach 36.6U / mL.
Embodiment 3
[0031] Example 3 Determination of Hydrolytic Activity of Recombinant Linear Maltooligosaccharide Generating Enzyme
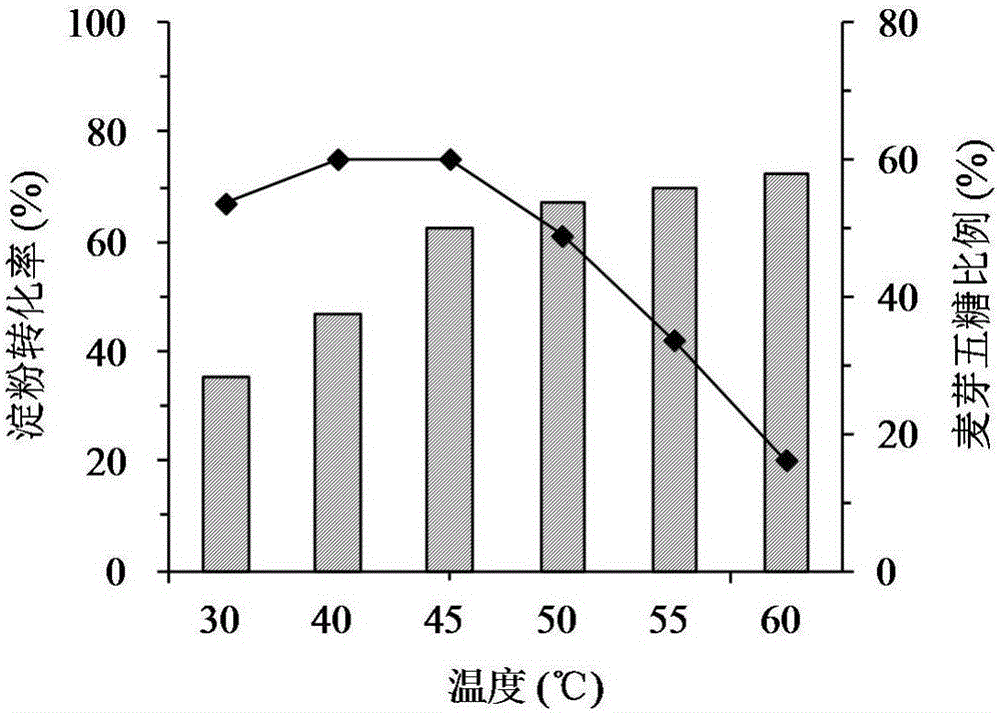
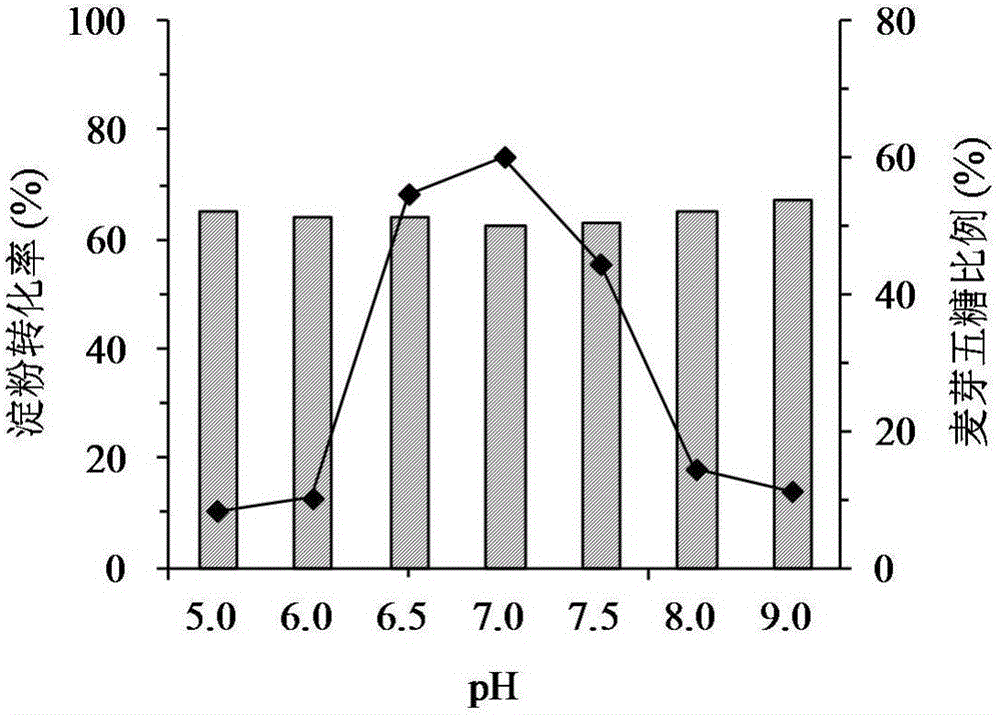
[0032]Prepare a 1% (w / v) soluble starch solution with citric acid-disodium hydrogen phosphate buffer (20mM, pH 6.5) as the substrate, add 0.2mL of appropriately diluted enzyme solution to 1.8mL of the substrate, and set the temperature at 45°C After reacting for 15 minutes, 2 mL of 3,5-dinitrosalicylic acid (DNS) solution was added to terminate the enzymatic reaction. After boiling in water for 5 minutes, the mixture was cooled in an ice bath. The absorbance was measured at 540 nm and compared with the glucose standard curve. Define the amount of enzyme needed to generate 1 μmol of reducing sugar (calculated as glucose) per minute as 1 enzyme activity unit (U).
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com