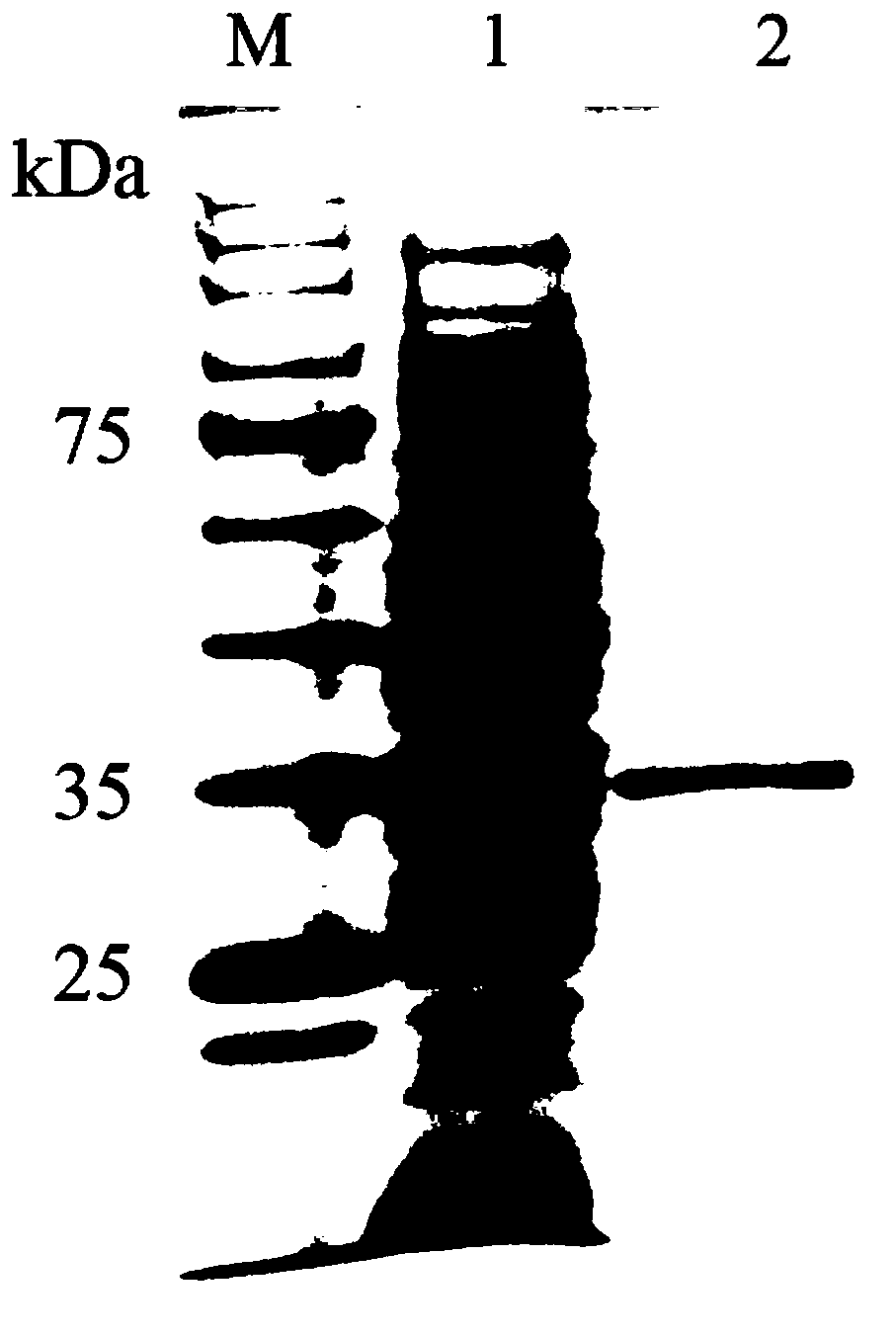
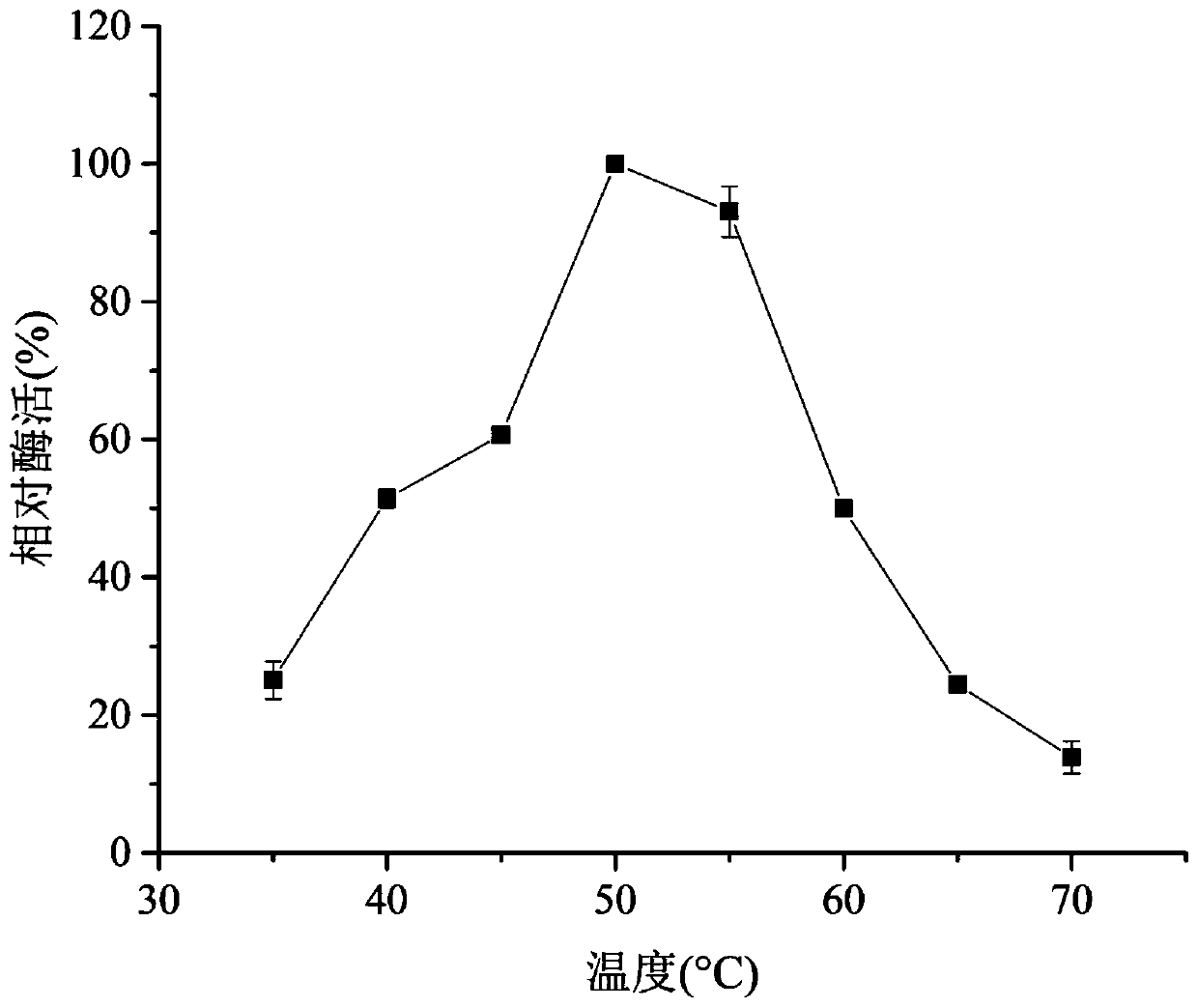
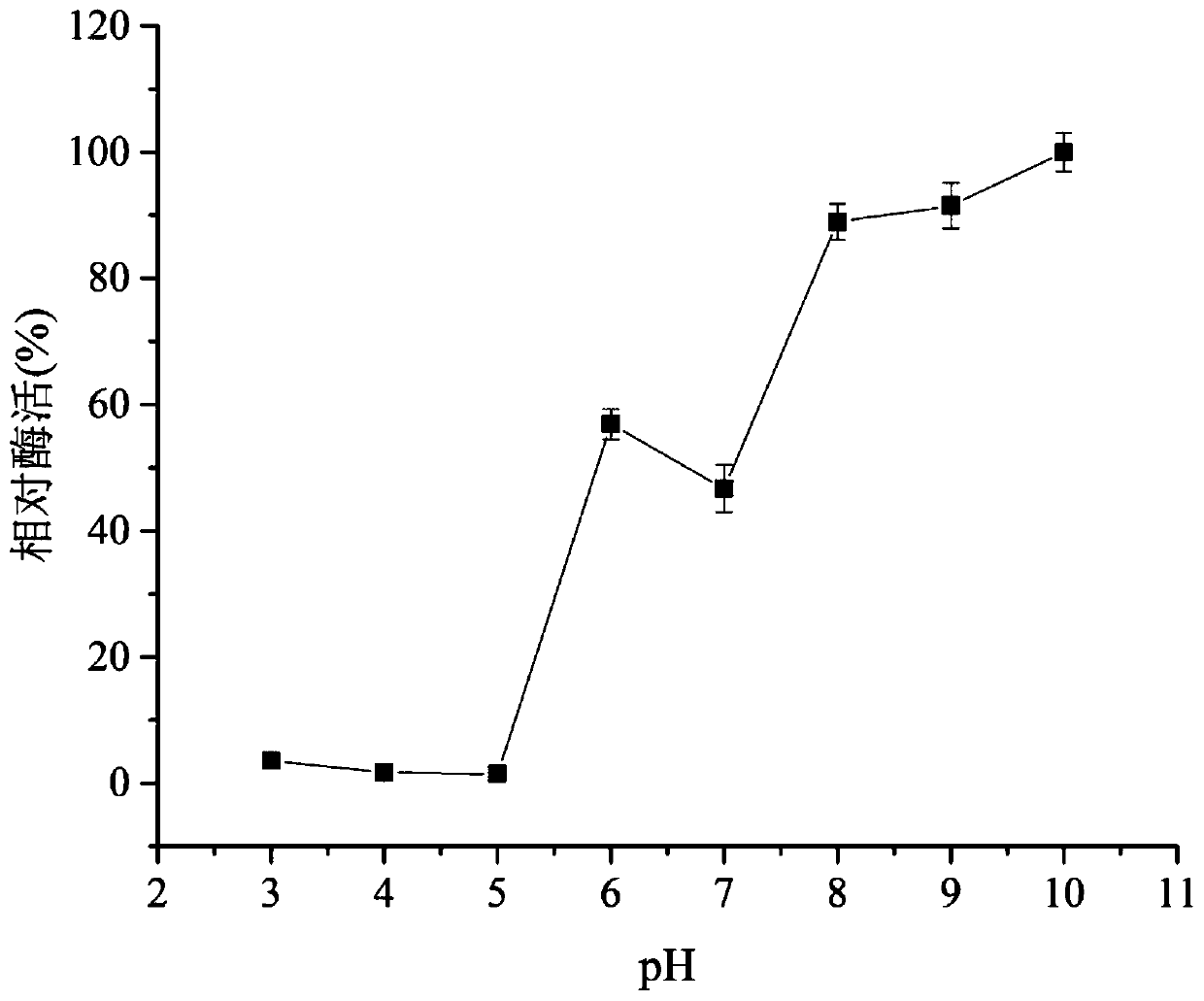
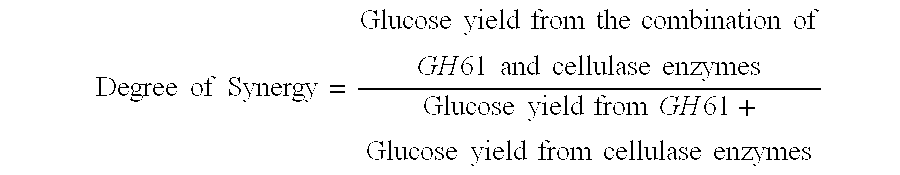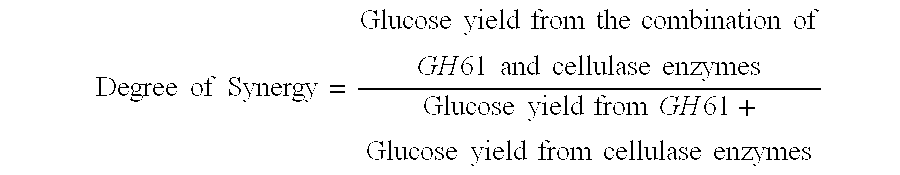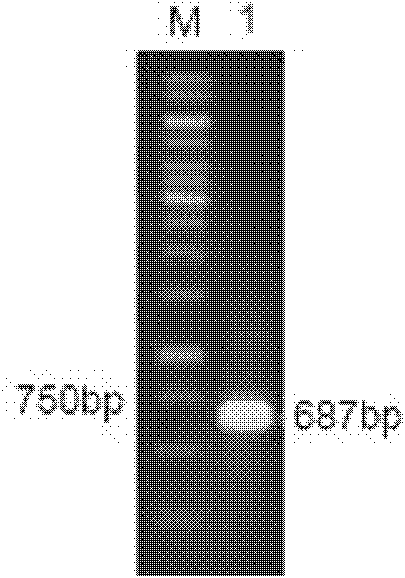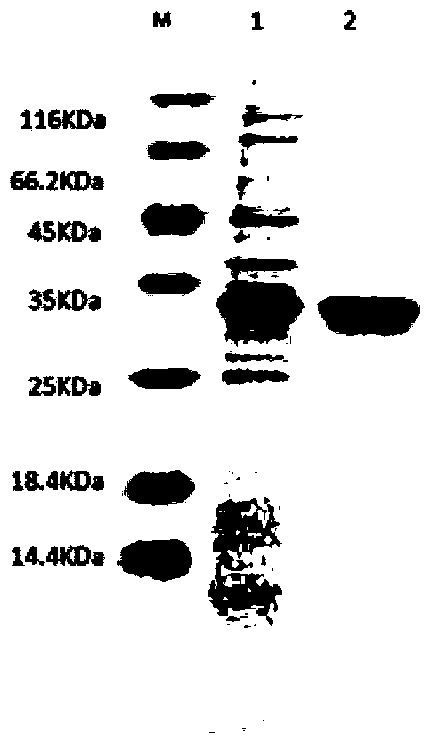Patents
Literature
169 results about "Glycoside hydrolase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Glycoside hydrolases (also called glycosidases or glycosyl hydrolases) catalyze the hydrolysis of glycosidic bonds in complex sugars. They are extremely common enzymes with roles in nature including degradation of biomass such as cellulose (cellulase), hemicellulose, and starch (amylase), in anti-bacterial defense strategies (e.g., lysozyme), in pathogenesis mechanisms (e.g., viral neuraminidases) and in normal cellular function (e.g., trimming mannosidases involved in N-linked glycoprotein biosynthesis). Together with glycosyltransferases, glycosidases form the major catalytic machinery for the synthesis and breakage of glycosidic bonds.
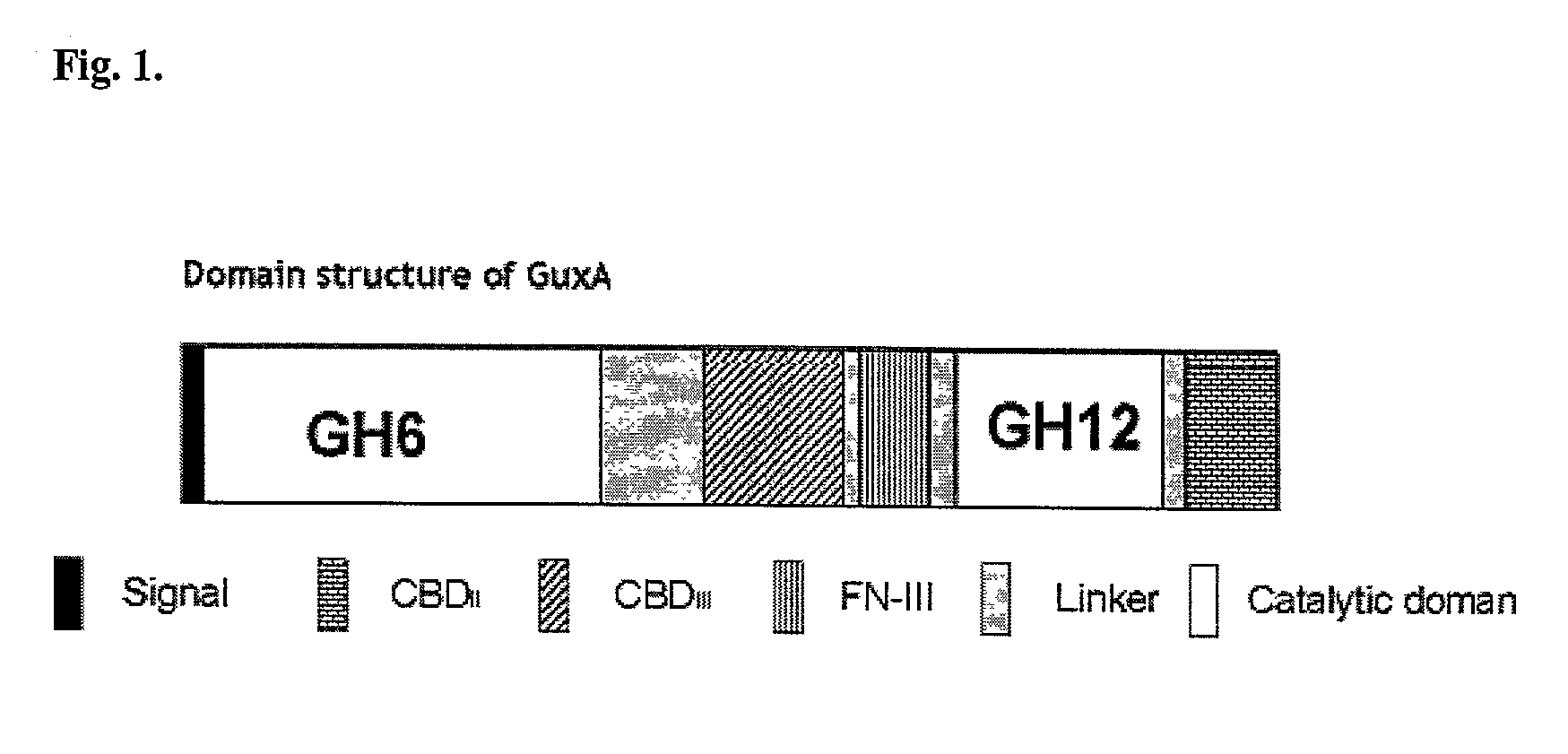
Thermal tolerant cellulase from Acidothermus cellulolyticus
InactiveUS7059993B2Easy to purifyHigh activityBacteriaSugar derivativesGlycosideThermoplasma acidophilum
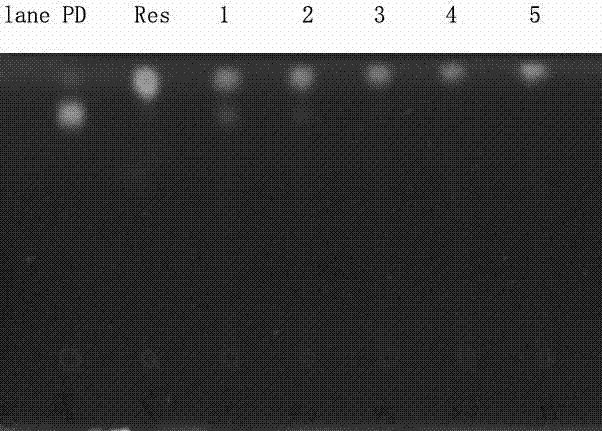
The invention provides a thermal tolerant cellulase that is a member of the glycoside hydrolase family. The invention further discloses this cellulase as GuxA. GuxA has been isolated and characterized from Acidothermus cellulolyticus. The invention further provides recombinant forms of the identified GuxA. Methods of making and using GuxA polypeptides, including fusions, variants, and derivatives, are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Rice wine vinasse extractive as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103757084AMeet the use requirementsHigh economic valueCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsEnzymatic hydrolysisVinasse
The invention discloses a preparation method of a rice wine vinasse extractive, the prepared extractive and an application of the extractive. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) secondary fermentation of rice wine vinasse, to be specific, adding water to the rice wine vinasse, and fermenting to obtain feed liquid 1; (2) enzymatic hydrolysis, to be specific, adding protease and glucoside hydrolase to the feed liquid 1 obtained in the step (1), carrying out enzymatic hydrolysis, and filtering to obtain feed liquid 2; (3) purification and concentration, to be specific, decoloring and deodorizing the feed liquid 2 obtained in the step (2), then filtering to obtain feed liquid 3, and concentrating the feed liquid 3, thus obtaining the rice wine vinasse extractive. When the preparation method can also comprise a step (4) or a step (4'), dry powder of the rice wine vinasse extractive or liquid preparation of the rice wine vinasse extractive can be correspondingly prepared. According to the preparation method, the rice wine vinasse is comprehensively and synthetically is utilized, and the economic value of the rice wine vinasse is greatly increased.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUIWEN BIO TECH
Biological complex enzyme toothpaste and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN101721324AAvoid drug resistanceKill completelyAntibacterial agentsCosmetic preparationsCelluloseTriclosan
The invention relates to biological complex enzyme toothpaste and a preparation method thereof. The toothpaste is prepared from the following components by weight percentage: 5-10% of sorbierite, 15-20% of hydrous silica, 10-20% of aluminum hydroxide, 10-20% of glycerin, 2-3% of sodium lauroyl sarcosine, 1-1.3% of flavor, 0.8-1.2% of cellulose gum, 0.3-0.6% of carrageenin, 0.3-0.5% of droxyethylcellulose, 0.5-1.2% of sodium phytate, 0.15-0.3% of saccharin sodium, 0.3-0.5% of strontium chloride, 0.1-0.3% of trisodium phosphate, 0.00003-0.00008% of staphylococcus lysozyme, 0.00005-0.00015% of muramidase, 0.00001-0.00004% of proteolytic enzyme, 0.00002-0.00005% of glycosidic hydrolase, 0.00002-0.00005% of peroxydase, 0.08-0.15% of borneol, 0.1-0.15% of borax, 0.08-0.1% of vermilion, 0.1-0.15% of natrii sulfas exsiccatus, 0.05-0.1% of triclosan, 0.1-0.4% of allantoin, and the balance of water. The total weight percentage of the components is 100%. The biological complex enzyme toothpaste has complete function.
Owner:JIANGSU XUE BAO DAILY CHEM CO
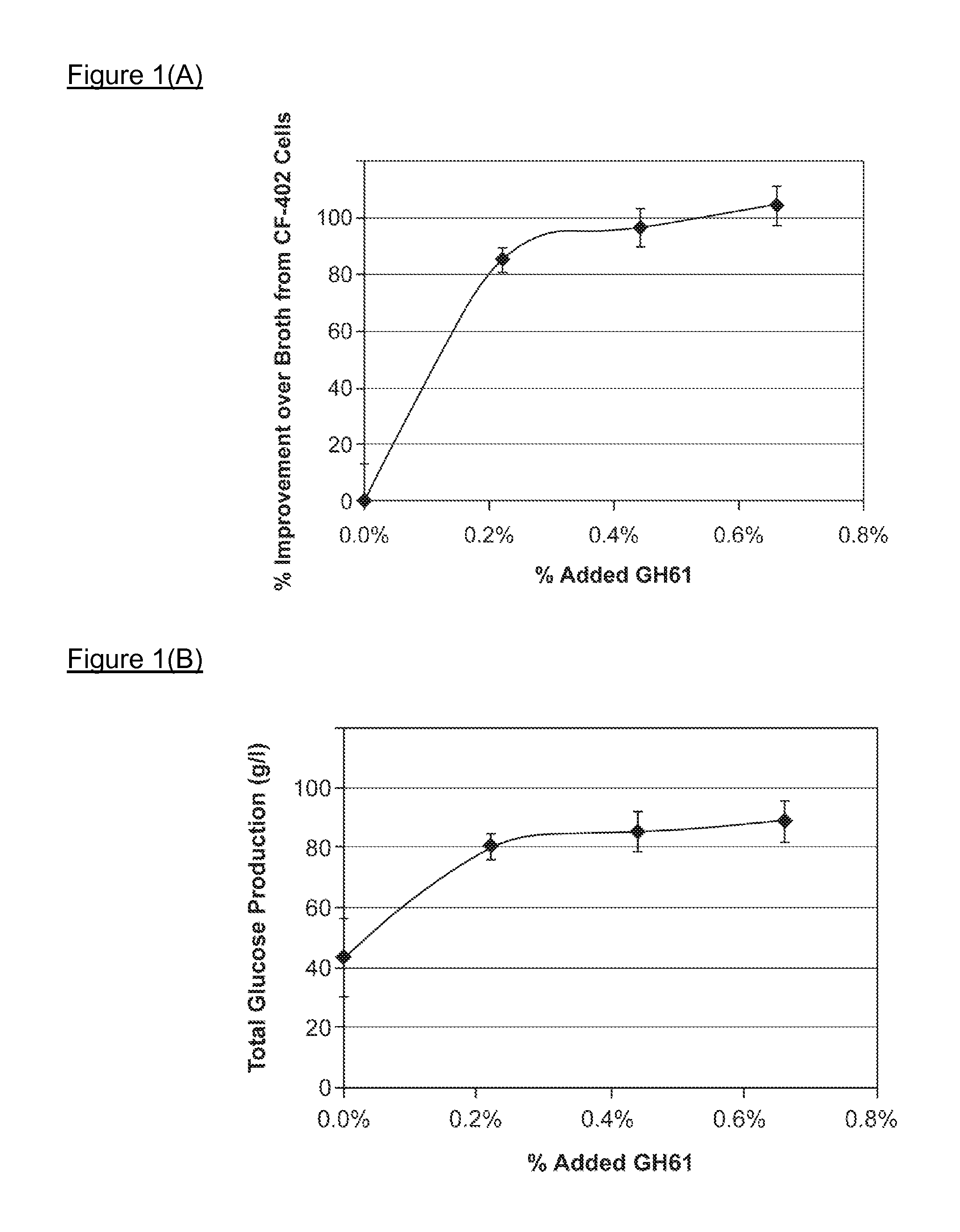
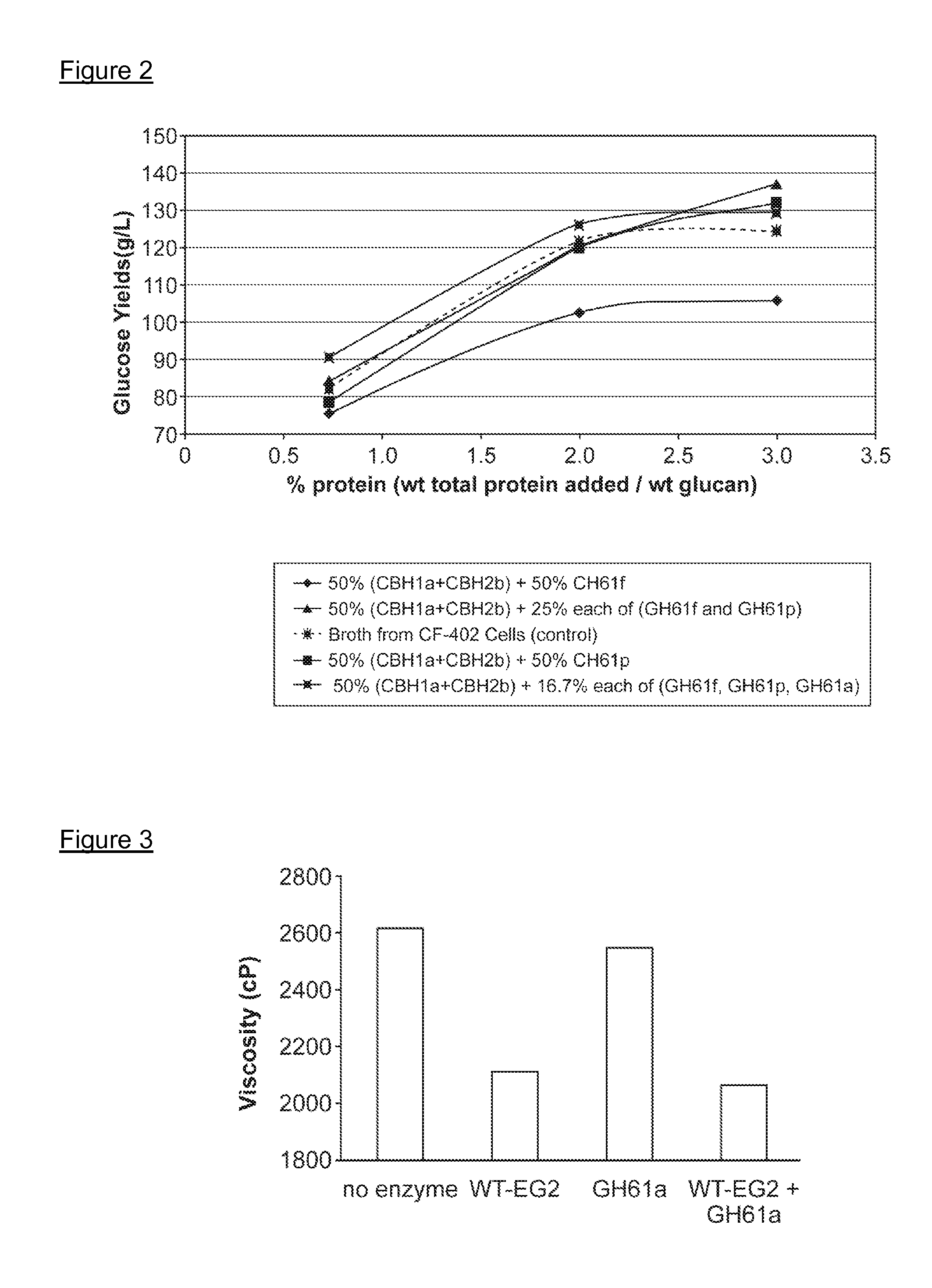
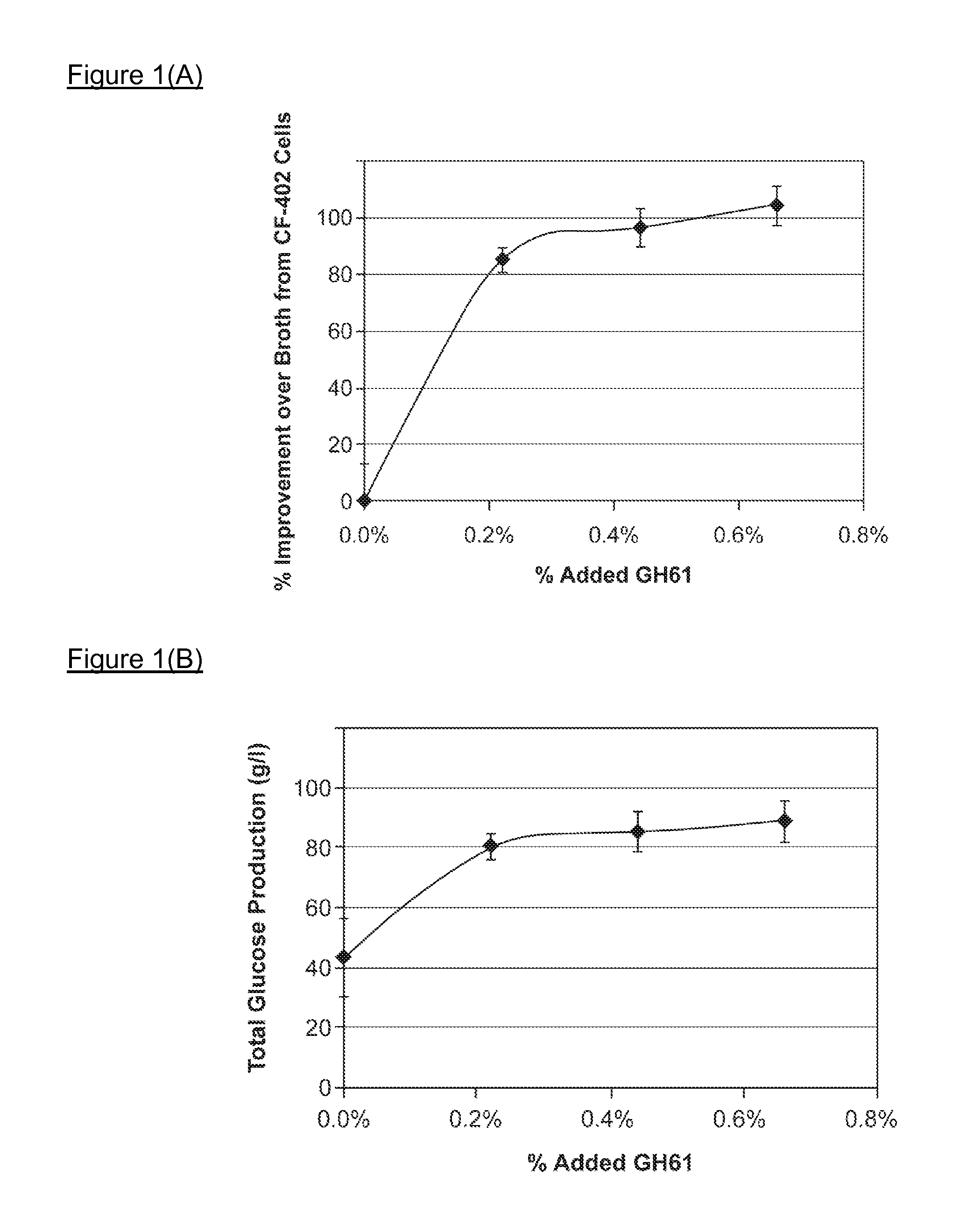
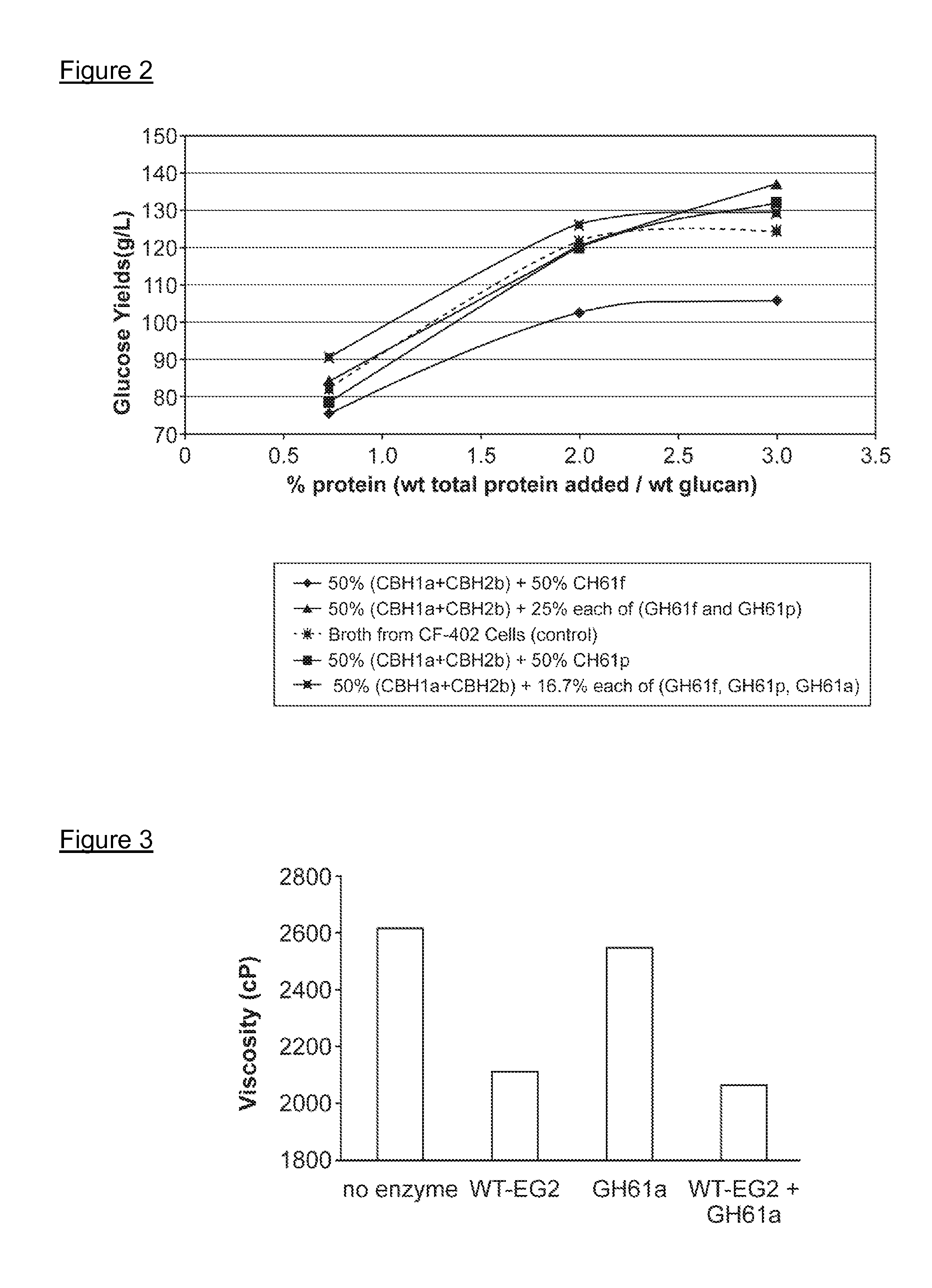
Use of Glycoside Hydrolase 61 Family Proteins in Processing of Cellulose
ActiveUS20120083019A1Increase productionImprove production yieldBiofuelsPeptide preparation methodsFermentable sugarCellulase
The invention provides recombinant GH61 proteins obtained from Myceliophtora thermophila, and nucleic acids that encode such proteins. The invention also provides protein fractions isolated from M. thermophila supernatant that have GH61 protein activity. These preparations can be used to increase yield of products from reactions in which a cellulose-containing substrate undergoes saccharification by one or more cellulase enzymes, such as endoglucanase, β-glucosidase, or cellobiohydrolase. Combinations of GH61 protein and cellulases can be used to break down cellulosic biomass into fermentable sugars in the production of ethanol.
Owner:CODEXIS INC
Method for preparing konjac glucomannan and oligo-glucomannan with different molecular weights
The invention relates to a method for preparing konjac glucomannan and oligo-glucomannan with different molecular weights. The method comprises the following steps of: rapidly adding0.1-30 parts of purified konjac glucomannan into a solution prepared by 0.001-0.01 part of glycoside hydrolase and 10-100 parts of distilled waterunder the stirring condition; reacting for 0.5-72 hours under the condition of the temperature of 30-60 DEG C and the pH of 2.0-10.0; and deactivating enzyme for 15 minutes in a boiling water bath to obtain konjac glucomannan and oligo-glucomannan aqueous solutions with different molecular weights; adding 1-30 parts of peptizing agent for stirring for 0.5-5 hours; depositing konjac glucomannan and oligo-glucomannan molecules with different molecular weights with 10-100 parts of anhydrous ethanol; after centrifugally separating sediments, adding 10-100 parts of anhydrous ethanol for strongly stirring for 0.5-5 hours; repeatedly depositing, centrifuging and stirring for 3-5 times, drying the sediment obtained by last centrifugation in a double-conic vacuum rotary drier; and grinding and screening the sediment to obtain the konjac glucomannan and the oligo-glucomannan. The method disclosed by the invention has the advantages of simplicity, low cost and wide product application.
Owner:SOUTHWEAT UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Recombinant escherichia coli expressing alpha-L-rhamnosidase and application of recombinant escherichia coli
ActiveCN110066760AIncrease enzyme activityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
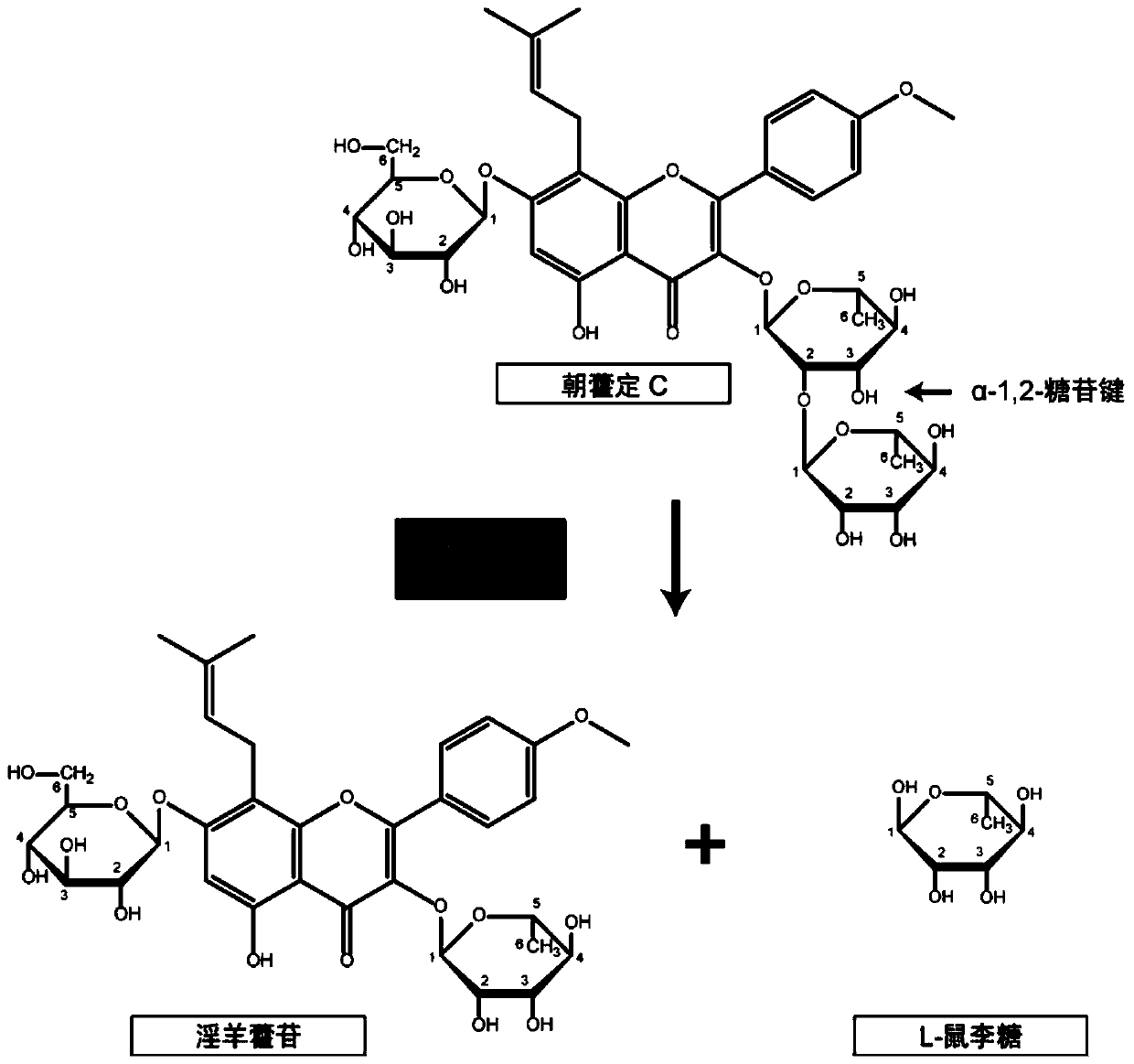
The invention discloses a recombinant escherichia coli expressing alpha-L-rhamnosidase and application of the recombinant escherichia coli, and belongs to the field of genetic engineering technology and biological medicine. A sequence with the coding sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.2 is subjected to heterologous expression in escherichia coli BL21(DE3), induction is carried out with 0.5 micromole / L IPTG, and recombinant rhamnoside hydrolase with vitality of 5.6 U / L is obtained. The recombinase has the specific activity of hydrolyzed rutin, hesperidin, naringin, neohesperidin and epimedin C rhamnoside. When the additive amount of the recombinase is 460 U / L, complete catalytic hydrolysis is carried out on 1 g / L epimedin C within 90 minutes to generate unique product icariin.
Owner:陕西量维生物工程有限公司
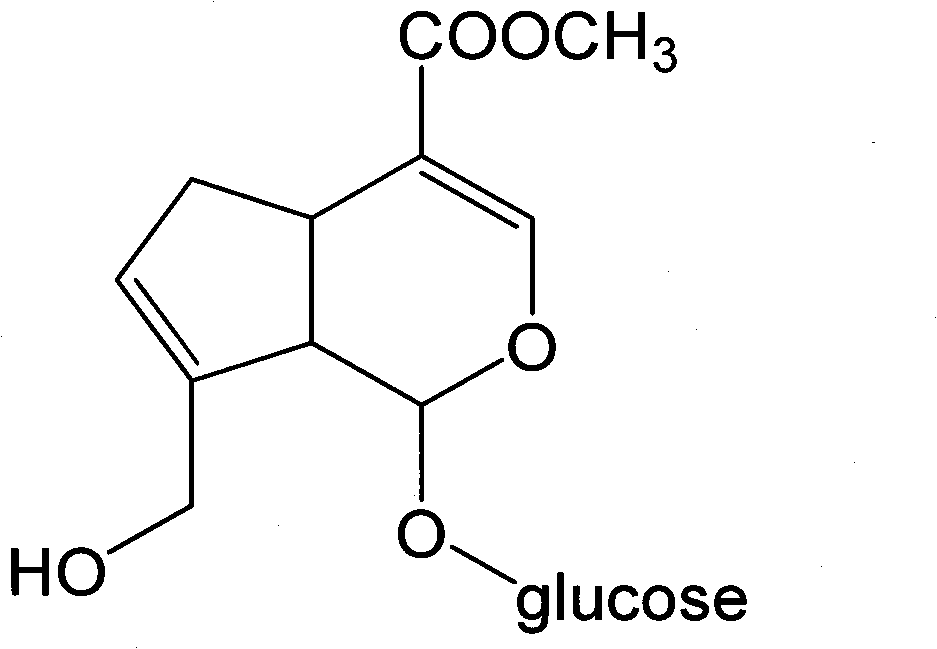
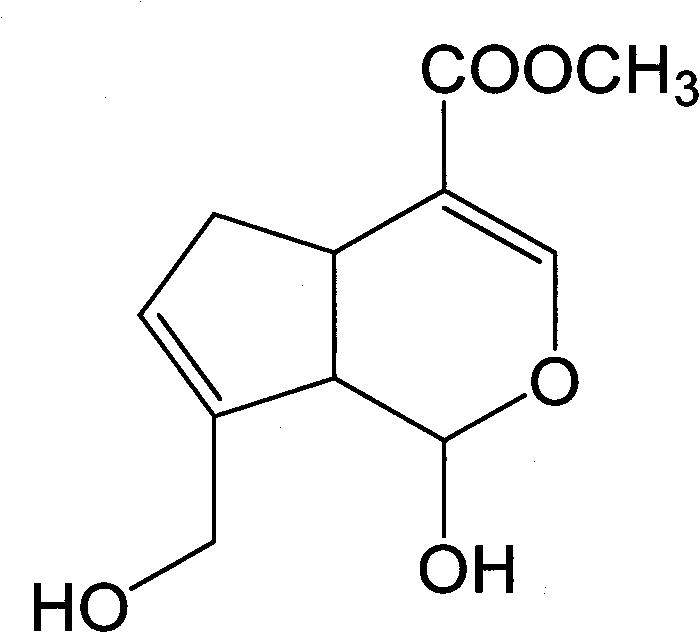
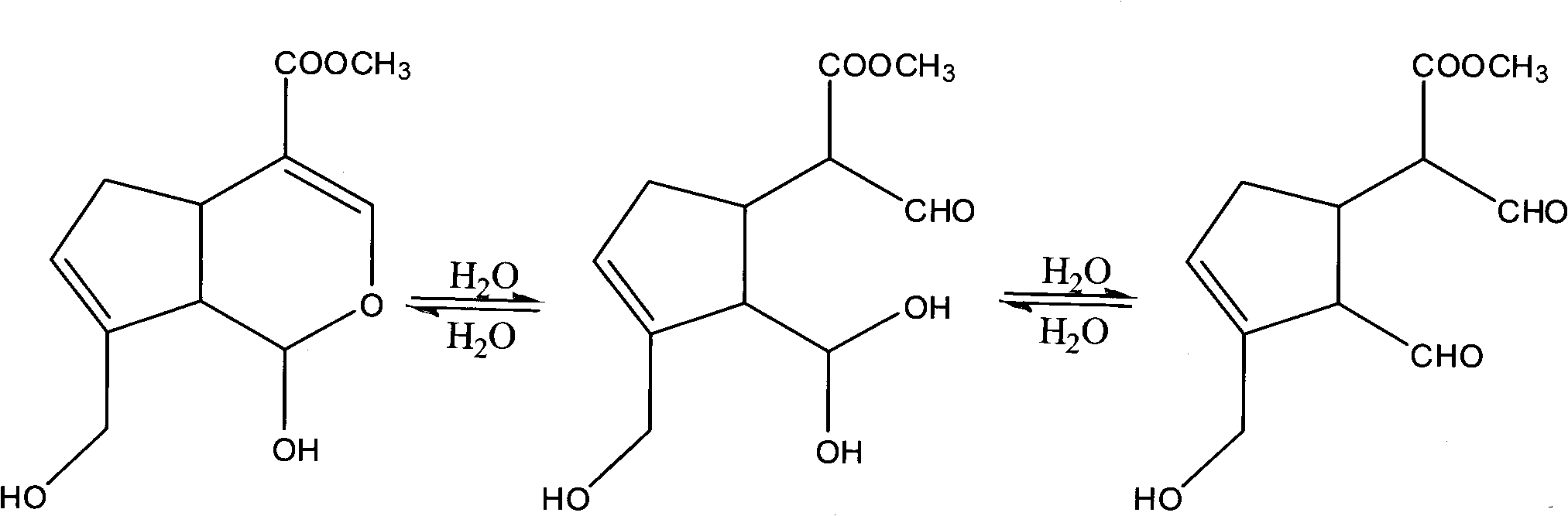
Method for preparing genipin
InactiveCN102146423AReduce supplyEasy to getChemical industryOn/in organic carrierSodium acetateDouble phase
The invention discloses a method for preparing genipin. In the invention, sodium alginate serving as a carrier and glutaraldehyde serving as a crosslinking agent to immobilize glycoside hydrolase, the immobilized glycoside hydrolase catalyzes the hydrolysis geniposide in a double-phase system consisting of acetic acid-sodium acetate buffer solution and ethyl acetate to convert the geniposide into the genipin, the ethyl acetate in the reaction solution is separated out, and white genipin crystalsare obtained by concentration and crystallization. In the invention, the glycoside hydrolase is immobilized before an enzymatic reaction, so the side reactions of the enzymatic reaction glycoside hydrolase and the genipin are reduced, the glycoside hydrolase can be recycled repeatedly, and the production cost is reduced; and the double-phase system used in the invention can extract the genipin to the ethyl acetate phase from a water phase in reaction, so the hydrolysis reaction of the genipin and the side reactions of the glycoside hydrolase and the genipin can be reduced, the yield of the genipin can be improved, the reaction is accelerated, and the separation and purification of the product is more easy.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV OF T C M
Preparation for increasing medicinal value of Parasitism in Cistanche decoction pieces
The invention provides a production method, which can enable the content of Phenylethanoid Glycoside combination before and after the processing to keep stable through improving the processing treatment technology of a broomrape decoction piece, wherein, the Phenylethanoid Glycoside combination is the active ingredient abundant in broomrape. Through a high-frequency microwave electrical field, the invention leads a polar molecule in a succulent stem cell of a waterrich fresh broomrape to perform high-frequency swing, vibration, and intermolecular friction and extrusion to cause the inner and surface temperature of a broomrape cell to rise rapidly; the pyrometric effect for inactivating the enzyme activity, so as to effectively block and restrain the degradation loss of the Phenylethanoid Glycoside combination caused by the enzymatic reaction induced by enzyme systems such as hydrolytic ferment, glucoside hydrolase, etc., abundant in a fresh broomrape cell; at the same time, the broomrape decoction piece is dried through the technology for microwave drying or other drying methods. The analysis determination shows that the content of echinacoside and a verbascoside monomer compound which are the main index components for weighing the quality of the broomrape decoction piece in the acquired broomrape decoction piece can reach 13 percent to 24 percent (by dry matters), and the water content is 1.3 percent to 4.1 percent.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Method for hydrolyzing soybean isoflavone by enzyme
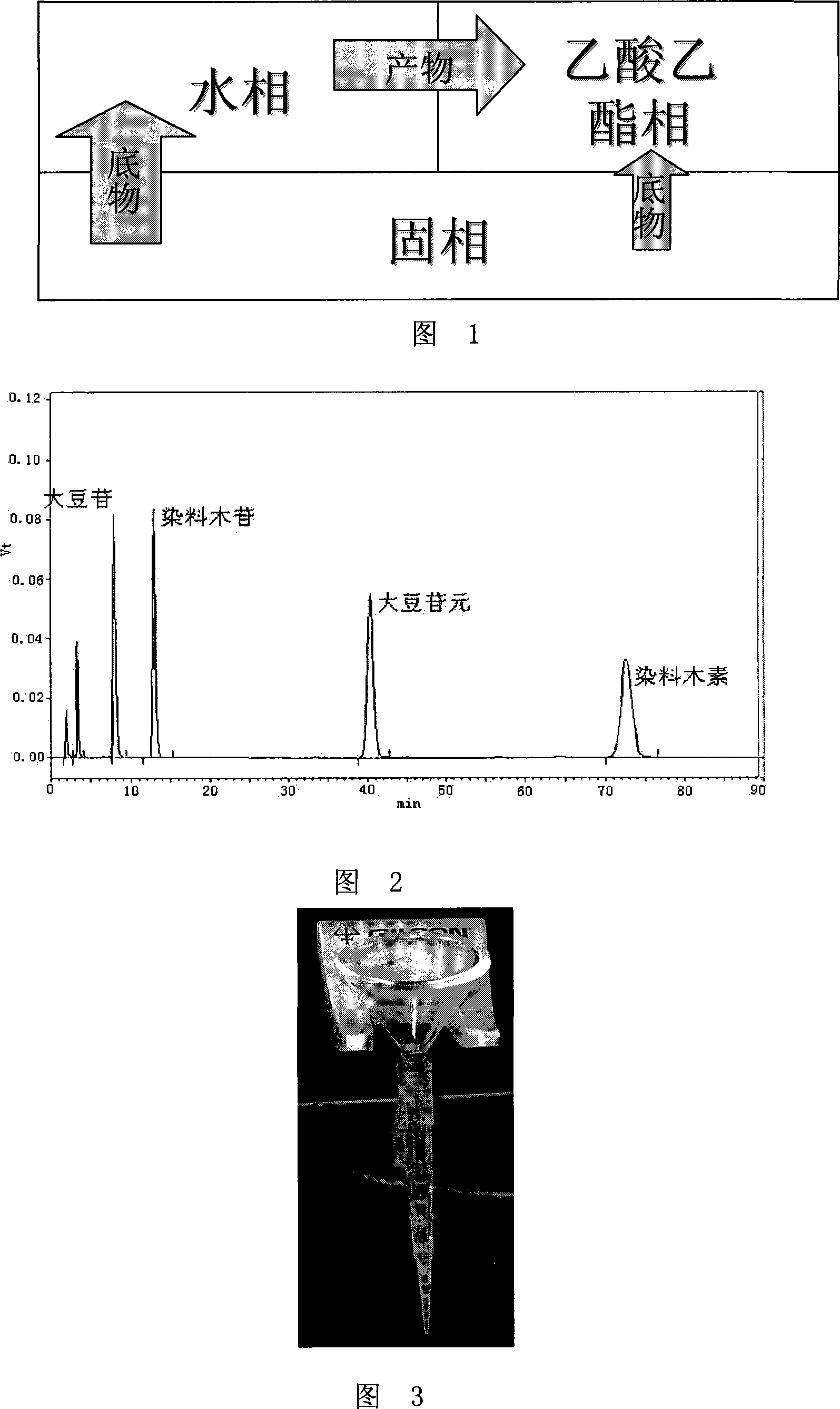
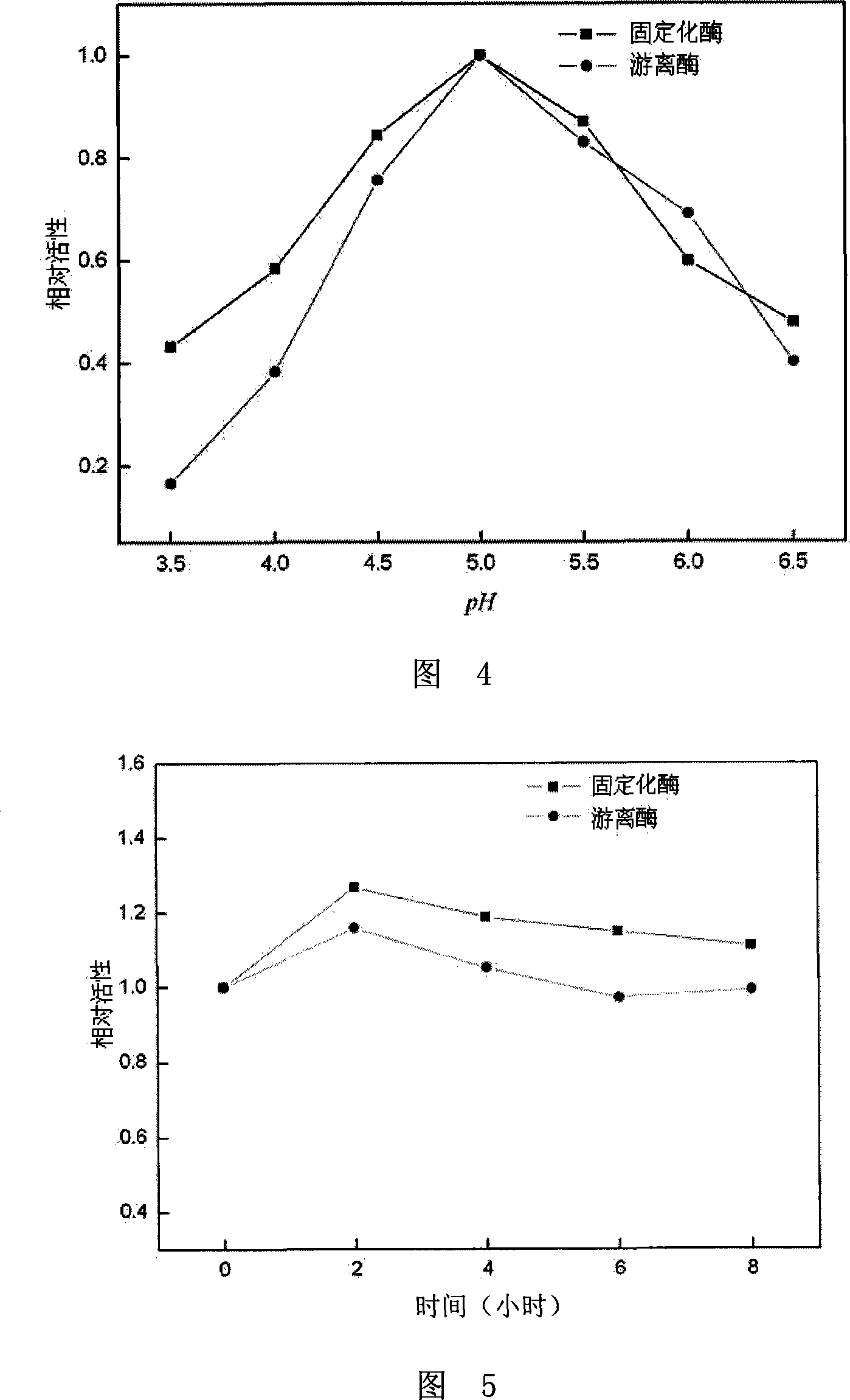
The invention discloses a method for hydrolyzing soybean isoflavone with biphase biological method. It is to hydrolyze glycoside soybean isoflavone by using immobilized soybean isoflavone glycoside hydrolase in biphase system that is composed of organic solvent and buffering solution, and get aglycone soybean isoflavone. The solubility of said organic solvent in said soybean isoflavone is better than that in water. The invention is characterized by effective hydrolysis of soybean isoflavone, no speical smell of product, and simple device and process.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Preparation method and application of fruit flavor extract
InactiveCN106753796APromote conversionHigh purityTobacco preparationTobacco smoke filtersMacromolecular SubstancesSlurry
The invention relates to the field of tobacco additives, in particular to a preparation method and an application of a fruit flavor extract. The preparation method includes the steps: crushing fresh plant fruits to prepare into slurry; adding compound enzyme into the slurry to hydrolyze, and performing purification and concentration for hydrolysis products to obtain the fruit flavor extract. The compound enzyme comprises protease and glycoside hydrolase, and the weight ratio of the protease to the glycoside hydrolase is 1: (15-60). According to the preparation method, enzymolysis is performed for fresh fruits by the aid of specific biological enzyme, walls are effectively and rapidly broken, macromolecular substances are transformed, and impurities are removed. When the obtained fruit flavor extract is used for cigarettes, cigarette flavors can be richened, sweet feeling is increased, moisture retention of cigarette senses is achieved, comprehensive evaluation indexes are good, and the preparation method is simple in preparation process, wide in application range and applicable to large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:YUNNAN YUXI YUNXI ESSENCE & SPICERY +1
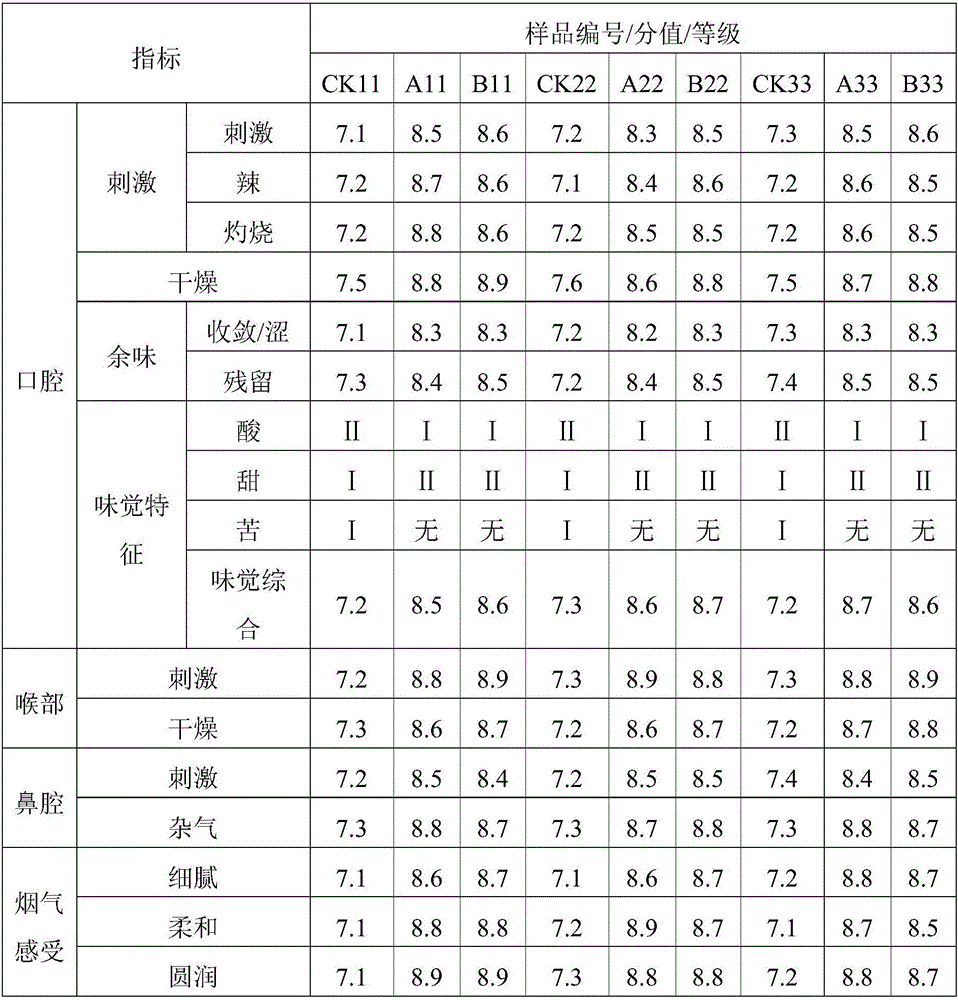
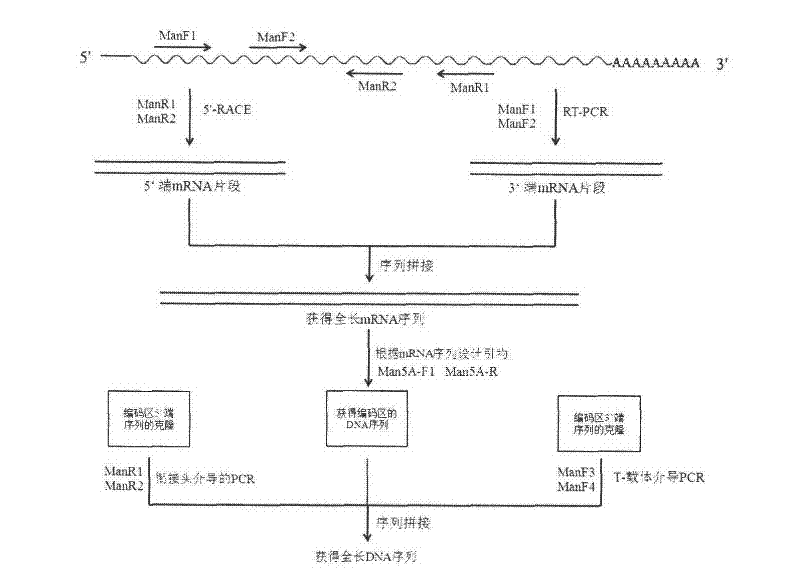
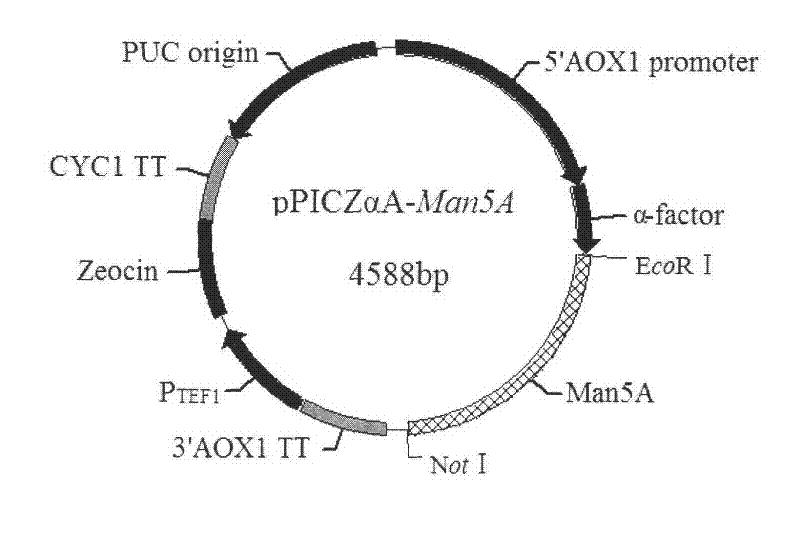
Cloning and expression of beta-1, 4-endo-mannanase (An Man5A) gene
InactiveCN102392037AImprove activity stabilityImprove thermal stabilityFungiMicroorganism based processesNucleotideXylanase
The invention puts forward a cloning method for complete mRNA and DNA sequences of a novel acidic beta-mannanase gene deriving from the Aspergillus niger LW-1 strain. Nucleotide sequences of the gene are respectively SEQ ID NO:1 and SEQ ID NO:2. Bioinformatics analyses show that the xylanase belongs to the 5th family of glycoside hydrolases and is named as An Man5A, with an amino acid sequence of SEQ ID NO:3 and a corresponding gene named as An man5A. The invention also discloses a method for An Man5A construction as well as high expression and purification of recombinant GS115 / man5A. The optimal temperature and pH of the prepared recombinant Man5A are respectively 70DEG C and 4.0, and the recombinant Man5A can be stable under pH of 2.5-7.5 and a temperature lower than 60DEG C, thus boasting great industrial production potential and economic value.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Alkalic xylanase gene and engineering bacterium containing same
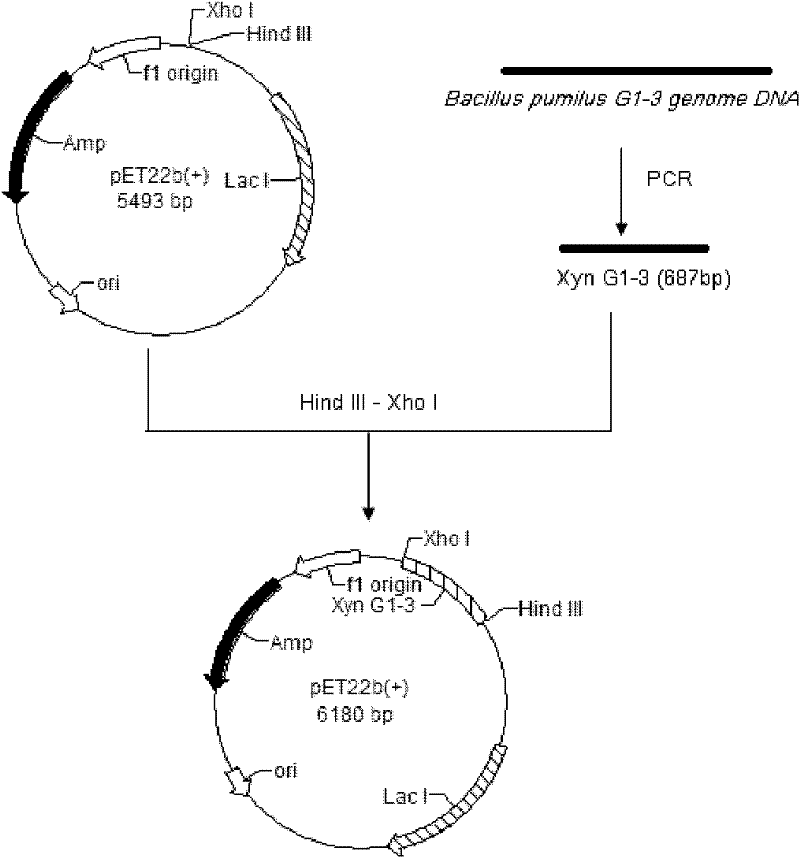
The invention relates to an alkalic xylanase gene and an engineering bacterium containing the same. The alkalic xylanase gene has the overall length of 687 bp, is called XynG1-3, encodes 228 amino acids and predicts that the molecular weight of the amino acids is 25444Da, wherein the first 27 amino acids are signal peptides of the alkalic xylanase gene, and 38th-221st amino acids are conserved sequences of a glycoside hydrolase GH11 family. Compared with a reported xylanase gene sequence, individual nucleotides of the obtained and expressed alkalic xylanase gene are different; the optimal operative temperature and the optimal pH of the recombinase are respectively 55 DEG C and 8.0, relative enzyme activity is more than 50 percent after preserving heat at the pH of 9.0 and 60 DEG C for 1 hour, and the relative enzyme activity is more than 70 percent after preserving the heat under the conditions of the pH of 6-9 and the temperature of 55 DEG C for 1 hour.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for converting polydatin to resveratrol by microbial enzyme method
InactiveCN102408999APromote the application of production practiceFungiHydrolasesBiotechnologyGlycoside hydrolase
The invention provides a microbial strain aspergillus.aculeatus (CGMCCNo.3876) used for efficiently extracting polydatin and analogues thereof from plant materials such as polygonum cuspidatum, peanut shells, grape skins and the like, and a complex enzyme prepared by fermenting the microbial strain. The complex enzyme of the strain is used for extracting polydatin and analogues thereof by an enzyme method, and the extraction ratio is 2.3%. The extraction ratio of the complex enzyme is improved by 91.7% through treatment compared with the exoenzyme (control) to which the strain aspergillus.aculeatus is not added. The ratio of conversion from polydatin to resveratrol by using the complex enzyme of the strain is above 99.5%. The polygonum cuspidatum glycoside hydrolase purified from the complex enzyme of the strain is used for converting 98% of polydatin to resveratrol, and the conversion ratio is 99.7%. The purity of resveratrol is 98.5%. By the invention, a novel complex enzyme preparation is actually provided for production, the problems of low catalytic activity of enzymes, low conversion ratio, overlong time and high cost in current production upgrading are fundamentally solved, and the production practice application is promoted.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
Method for extracting oxidized resveratrol
InactiveCN101591680ASimple processEasy to operateOrganic chemistryOrganic compound preparationGradient elutionSolvent
The invention relates to a method for extracting oxidized resveratrol. The oxidized resveratrol is directly extracted from mulberry barks (mulberry branch barks or mulberry root barks) through enzymolysis. The method comprises the following steps: peeling off barks of fresh mulberry branches or mulberry roots first; drying the barks, and smashing the barks; performing enzymolysis on the smashed barks by using ethanol solution added with glucoside hydrolase; filtering and concentrating the mixture; putting the mixture on a polyamide chromatographic column to perform gradient elution with ethanol; and recovering the eluant to obtain a product. The method breaks through the conventional pure alcohol extraction or pure water extraction, combines enzymatic conversion with extraction and has simple process and convenient operation; the technical process has no solvent which are poisonous to human bodies; and the obtained product is safe and is suitable for industrialized production. The content of the product of the oxidized resveratrol extracted by the method is between 95 and 98 percent, and the recovery percent of the ethanol is between 60 and 80 percent.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Non-dairy contanining milk substitute products
Efficient, selective, and economical methods for producing non-dairy ready-to-use milk substitute cereal dispersions having intact beta-glucans, proteins, and natural sugars, while retaining the aroma and flavor of natural cereal. The methods include treating a cereal substrate suspension with an enzyme preparation that comprises at least one hydrolase having the ability to hydrolyze alpha-glycosidic bonds and having no glucanase and proteinase effect. The hydrolase may be selected from the group consisting of beta-amylase, alpha-amylase, amyloglucosidase and pullulanase, with the proviso that when the enzyme preparation comprises alpha-amylase or beta-amylase, there is always a mixture of at least one other of the alpha-glycosidic hydrolases. When beta-amylase and alpha-amylase are selected, they are used as a mixture, i.e., introduced simultaneously, to provide for accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis and for reduced amounts of the enzymes than otherwise needed if the enzymes were used separately. In addition to the above-identified hydrolases, the enzyme preparations of the present invention may further comprise an isomerase, such as glucose isomerase.
Owner:OATLY AB
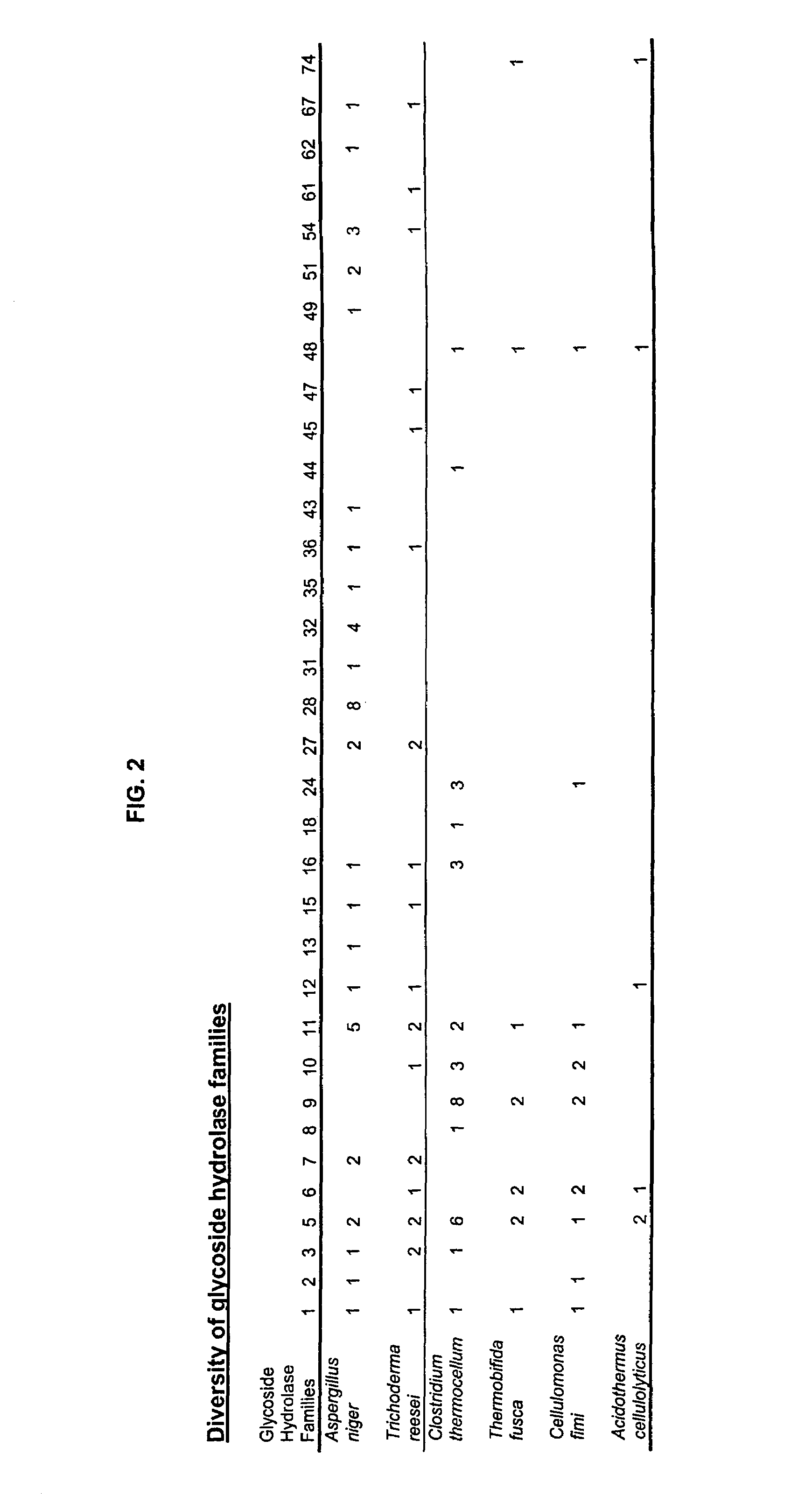
Glycoside hydrolases from thermophilic fungi
The present invention relates to isolated polypeptides having cellulolytic activity or hemicellulolytic activity and polynucleotides encoding the polypeptides. The invention also relates to nucleic acid constructs, vectors, and host cells comprising the polynucleotides as well as methods of producing and using the polypeptides.
Owner:NOVOZYMES AS
Magnetic nano immobilized enzyme catalysis production method of soya isoflavone
InactiveCN101532039AEasy to prepareHigh extraction rateFermentationOn/in inorganic carrierDrug biological activityGlycoside hydrolase
The invention relates to a magnetic nano immobilized enzyme catalysis production method of soya isoflavone, comprising the following steps: (1) concentrating glycoside type soya isoflavone raw material using supercritical fluid extraction; (2) extracting soya isoflavone glycoside hydrolase; (3) preparing the magnetic nano immobilized enzyme; (4) catalyzing the glycoside type soya isoflavone raw material using magnetic nano immobilized enzyme; (5) extracting soya isoflavone aglycone. The preparation method has features of simple and easily-operable supercritical extraction technology, innocuity and no-residue of carbon dioxide in operation process, high glycoside extraction ratio; simple preparation method of magnetic nano immobilized enzyme, simple recovery and repeat use of the enzyme using the external magnetic field; no destruction of the soya isoflavone aglycone and biological activity, high content of the soya isoflavone aglycone. The sum of the soya isoflavone aglycone concentration is 82.7% in the soya isoflavone aglycone product and the content of genistein is 90.3%.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
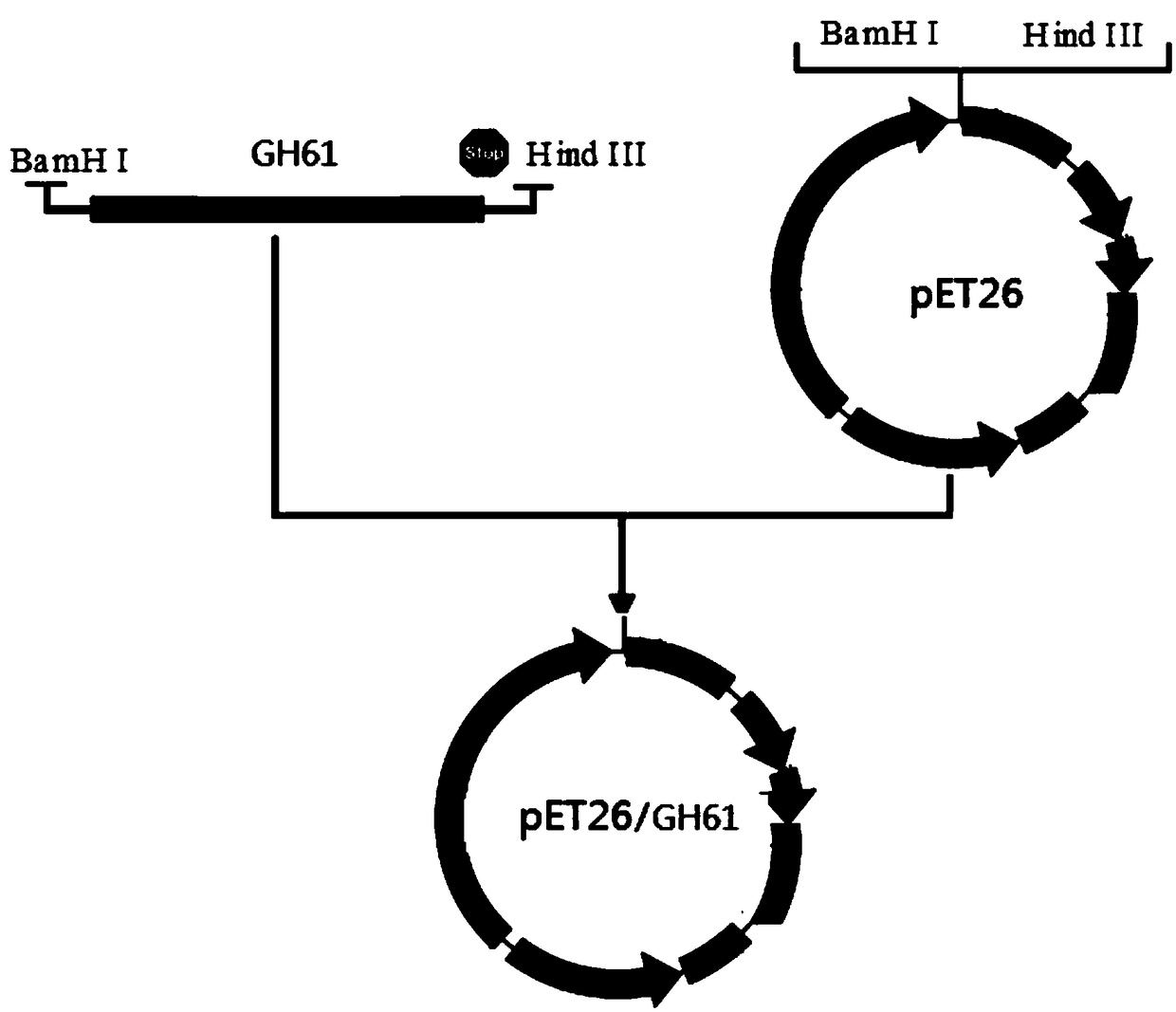
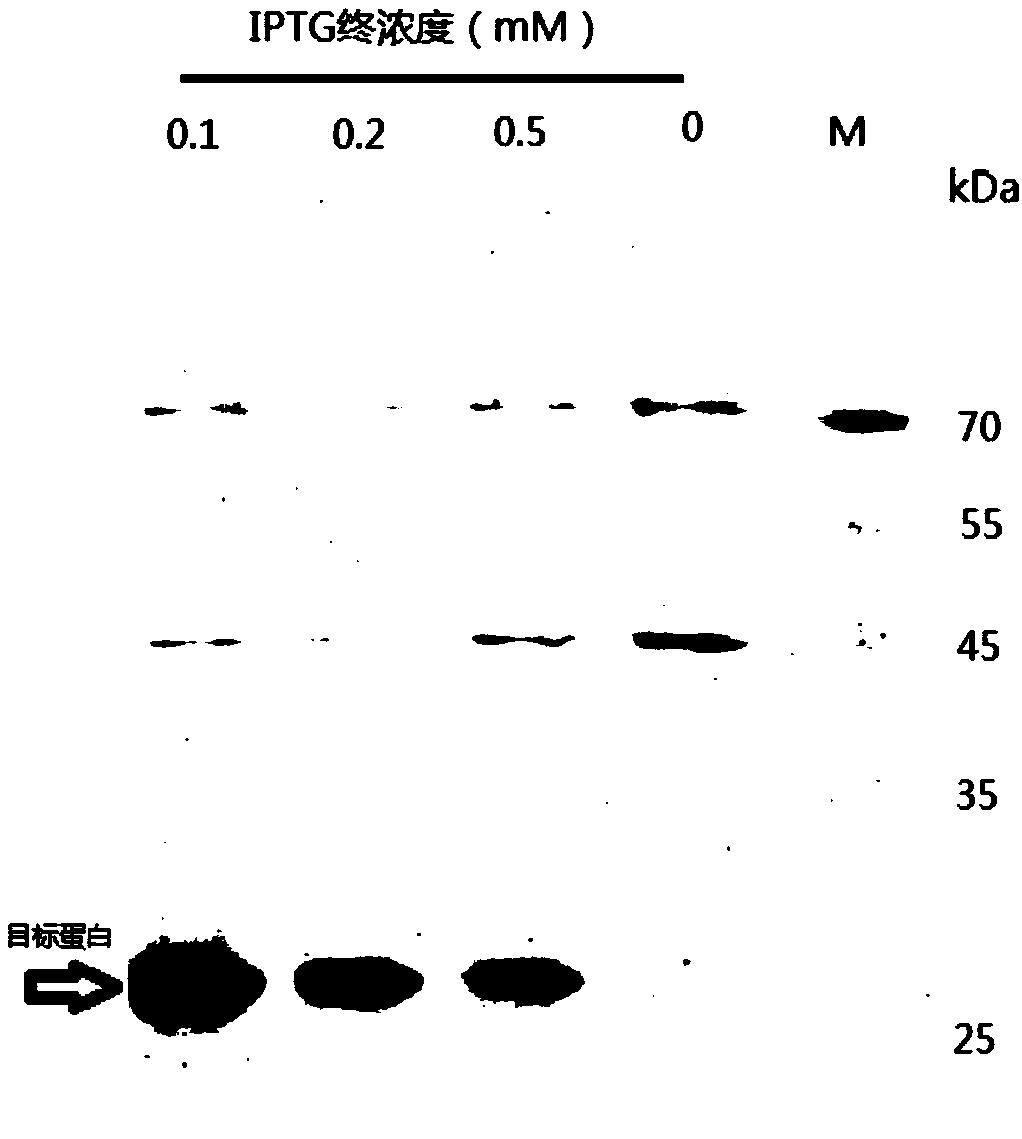
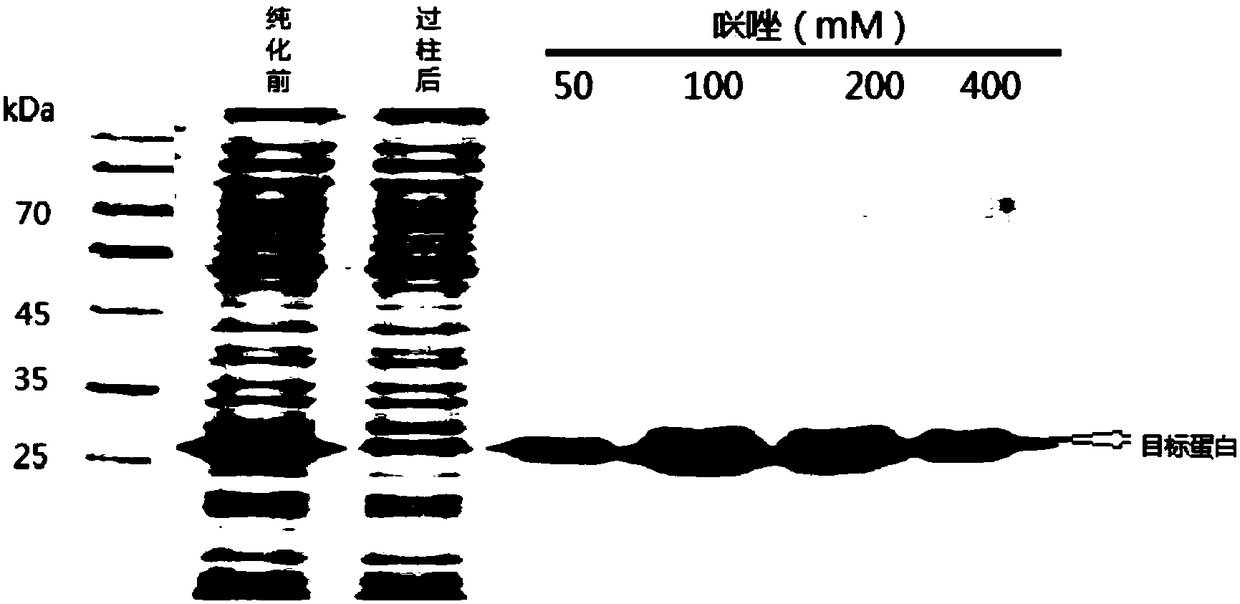
Glucoside hydrolase family 61 protein gene, protein thereof and preparation method of protein
ActiveCN109439642AIncrease concentrationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPurification methods
The invention relates to a glucoside hydrolase family 61 protein gene. The nucleotide sequence of the glucoside hydrolase family 61 protein gene is shown as SEQ ID No. 1. The invention relates to a protein of the glucoside hydrolase family 61 protein gene, and the amino acid sequence of the protein is shown as SEQ ID NO. 2. The glucoside hydrolase family 61 protein gene can further utilize pET26 plasmids to structure recombinant plasmids and converts the recombinants plasmids into Escherichia coli expression strains, thereby achieving soluble expression of expression products. The invention also provides preparation and purification methods of the protein. The preparation and purification methods can help obtain recombinant glucoside hydrolase family 61 proteins with a degree of purity upto higher than 95%; the prepared recombinant glucoside hydrolase family 61 proteins have enzymatic activity for hydrolyzing sodium carboxymethylcellulose to produce glucose, belong to glucoside hydrolase family 61 enzymes and can be matched with other types of cellulases during different types of application, preferably, be combined with one or more beta-glucosidases or endoglucanases.
Owner:HUNAN BUTIAN PHARMA
Production method of sweet osmanthus Longjing tea
InactiveCN104430973AKeep the fragranceImprove flavor qualityPre-extraction tea treatmentTea flavoringCooking & bakingHigh humidity
The invention discloses a production method of sweet osmanthus Longjing tea. The production method comprises the following production steps: producing a tea billet, pre-treating the tea billet, blending and scenting, compositely re-firing by a microwave and a far-infrared ray, extracting flowers and the like. According to the production method disclosed by the invention, the purposes of treating lots of fresh sweet osmanthus in a short time and preventing the fresh sweet osmanthus from being oxidized and browned are effectively solved by virtue of a microwave green-removing technology, the hydrolysis of a fragrance precursor is promoted by spraying glycoside hydrolase to generate fragrance flavour substances, and thus the fragrance of the sweet osmanthus is improved, and the scenting efficiency is greatly increased; the microwave and the far-infrared ray are combined for composite baking in a wet billet re-firing process, thus the problems of yellow colour and fragrance loss of the Longjing green tea due to high temperature and high humidity in the traditional oven-type re-firing process are solved, the fragrance freshness and liveliness, and the taste freshness and mellowness of the sweet osmanthus Longjing tea are effectively improved, bitterness is removed and converted to sweetness, and the quality of the sweet osmanthus Longjing tea is improved.
Owner:HANGZHOU JU FANG YONG HLDG
Chitosanase and application thereof
ActiveCN111235131AEfficient degradationGood biocatalytic activityFermentationGlycosylasesNucleotideGlucoside
The invention discloses chitosanase having an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.1. A gene encoding the chitosanase has a nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The chitosanase is derivedfrom the GH5 family of glucoside hydrolase, can degrade chitosan to generate GlcN-(GlcN)4 and can be used for preparing an enzymatic COS mixture of a new component. The chitosanase has excellent biocatalytic activity, can hydrolyze chitosan to generate glucosamine, chitobiose, chitotriose and chitotetraose hydrochloride, and is relatively high in product purity; and when the pH is 10 and temperature is 50 DEG C, the chitosanase has relatively enzymatic activity of 898.6U / mg which is higher than those of most other known chitosanase, can effectively degrade chitosan, has mild reaction condition, easy control, high efficiency, environmental friendliness. The chitosanase has an industrial application value for producing novel chitosanase mixture.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Chitosanase gene derived from soil metagenome library and obtaining method and application of chitosanase gene
InactiveCN103361374AHigh catalytic activityImprove thermal stabilityBacteriaEnzymesEscherichia coliGenomic library
The invention provides chitosanase gene derived from soil metagenome library, and the DNA sequence of the chitosanase gene is shown in SEQID NO:1. The invention also provides chitosanase obtained by encoding of the chitosanase gene and recombinant plasmid including the chitosanase gene, and further provides escherichia coli engineering bacteria containing the chitosanase gene and an obtaining method thereof. The obtaining method of the chitosanase gene is simple, and the escherichia coli engineering bacteria containing the chitosanase gene is provided. The chitosanase can be obtained through high-efficiency expressionof the escherichia coli engineering bacteria. The bioinformatics analysis shows that the obtained chitosanase gene belongs to the forty-sixth family of glycoside hydrolase. The chitosanase gene has high catalytic activity and good thermal stability, with optimal action temperature being 55 DEG C and pH being 6.0, and has great industrial value and economic value.
Owner:YANGZHOU RIXING BIO TECH
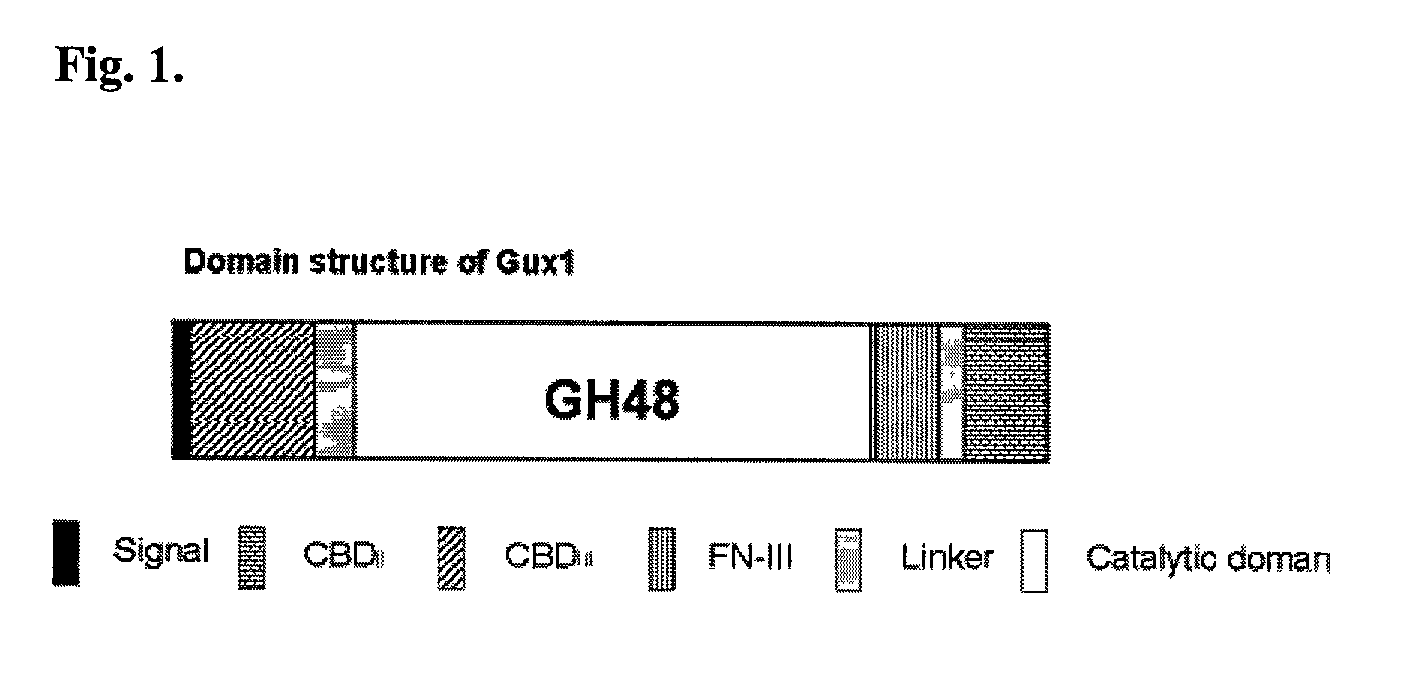
Thermal tolerant exoglucanase from Acidothermus cellulolyticus
InactiveUS7393673B2Easy to purifyHigh activitySugar derivativesBacteriaCellulose breakdownAcidothermus cellulolyticus
The invention provides a thermal tolerant cellulase that is a member of the glycoside hydrolase family. The invention further discloses this cellulase as Gux1. Gux1 has been isolated and characterized from Acidothermus cellulolyticus. The invention further provides recombinant forms of the identified Gux1. Methods of making and using Gux1 polypeptides, including fusions, variants, and derivatives, are also disclosed.
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY
Preparation method and application of fruit flavor extract
InactiveCN106753797APromote conversionHigh purityTobacco preparationTobacco treatmentMacromolecular SubstancesImpurity
The invention relates to the field of tobacco additives, in particular to a preparation method and an application of a fruit flavor extract. The preparation method includes the steps: crushing fruit raw materials, extracting in an ethanol refluxing manner, filtering mixture, and taking filter residues; adding compound enzyme to hydrolyze, and performing purification and concentration for hydrolysis products to obtain the fruit flavor extract. The compound enzyme comprises protease and glycoside hydrolase, and the weight ratio of the protease to the glycoside hydrolase is 1: (15-60). According to the preparation method, refluxing and extracting are firstly performed, enzymolysis is secondly performed, lipid materials releasing irritating odor are removed, walls are effectively and rapidly broken, macromolecular substances are transformed, and impurities are removed. When the obtained fruit flavor extract is used for cigarettes, cigarette flavors can be richened, sweet feeling is increased, moisture retention of cigarette senses is achieved, comprehensive evaluation indexes are good, and the preparation method is simple in preparation process, wide in application range and applicable to large-scale popularization and application.
Owner:YUNNAN YUXI YUNXI ESSENCE & SPICERY +1
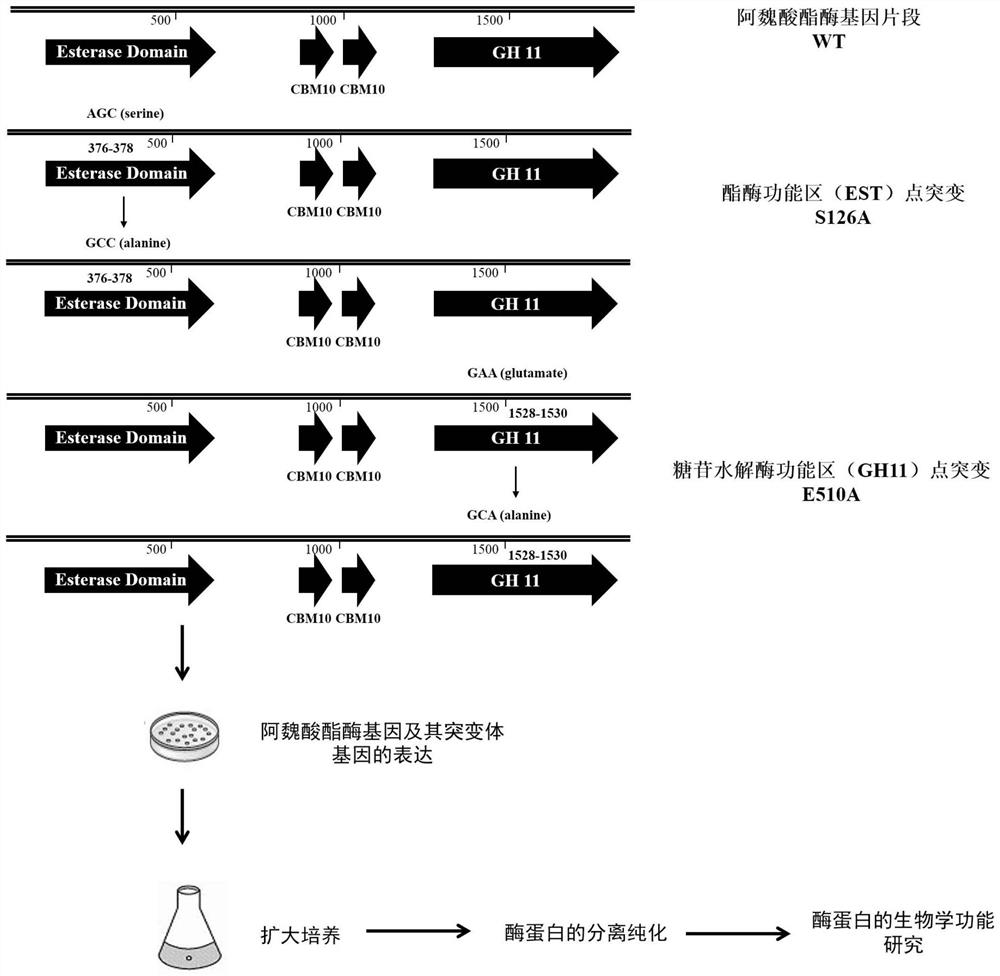
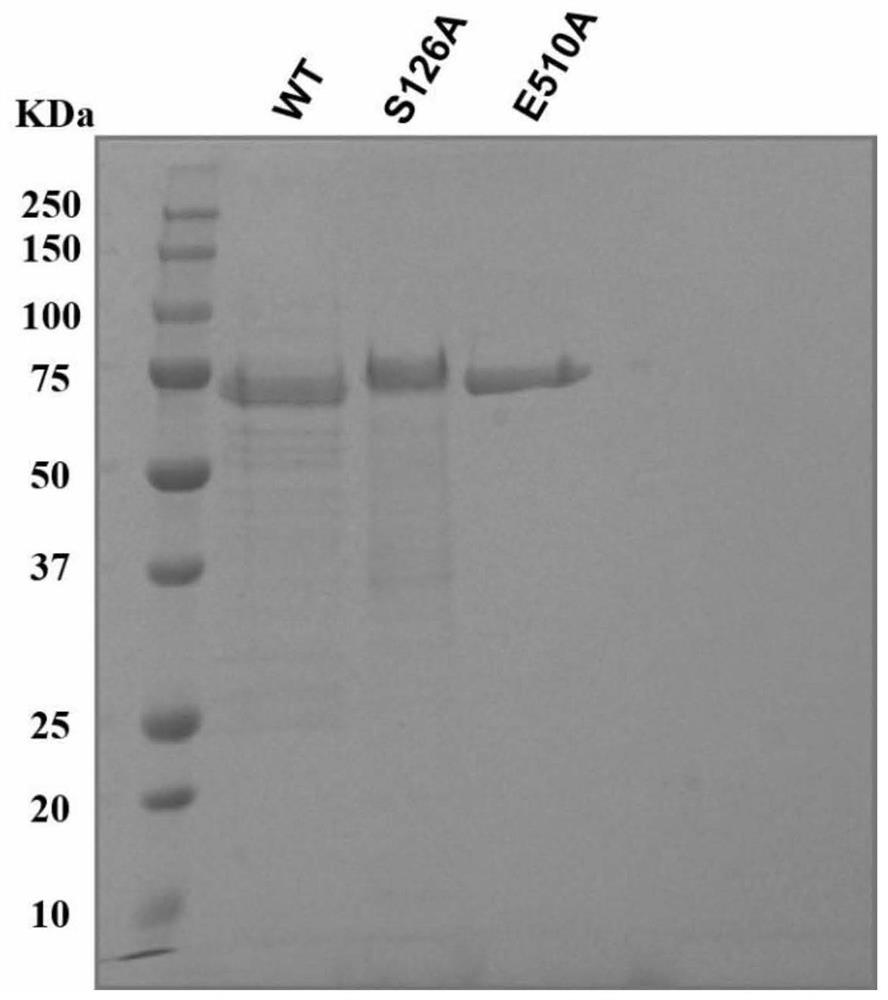
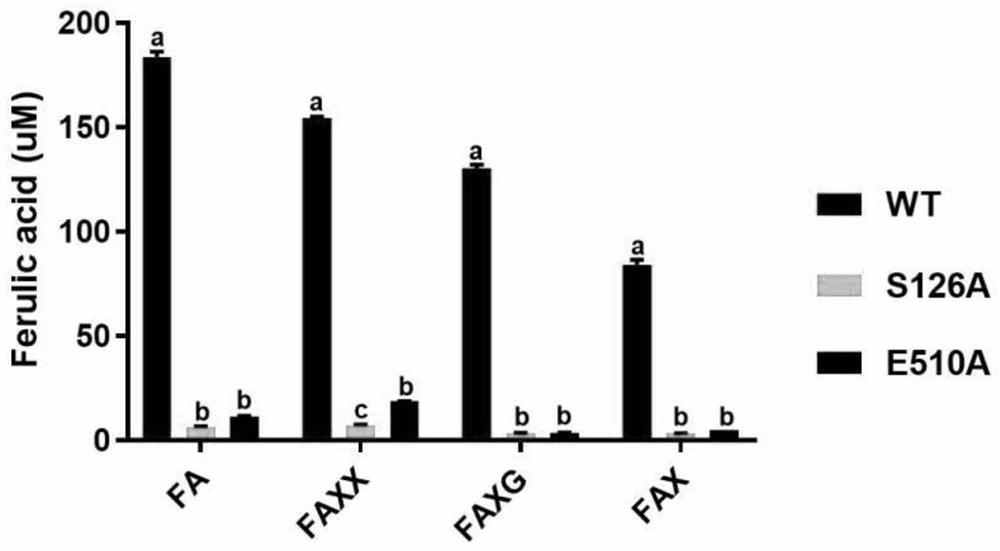
Novel feruloyl esterase, mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN111748538ARich sources of bacteriaRich sourcesHydrolasesFood processingEscherichia coliGenetics genomics
The invention discloses novel feruloyl esterase, a mutant and an application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, successfully screening out a feruloyl esterase gene from anaerobic fungi Neocallimatix sp. by utilizing a genomics technology; according to the preference of a prokaryotic system codon, the GC content of a feruloyl esterase gene and the secondary structure of mRNA, and codon optimization is carried out on the feruloyl esterase gene to obtain a novel feruloyl esterase gene sequence. The enzyme has an esterase regionand a glucoside hydrolase 11 region, site-specific mutagenesis is carried out on the two regions; the obtained mutant gene is also expressed in escherichia coli; separation and purification results show that the novel feruloyl esterase and the mutant thereof are successfully expressed in escherichia coli, and the esterase activity of the mutant is far lower than that of a non-mutant, so that the strain source of the feruloyl esterase is enriched, and the feruloyl esterase has theoretical guiding significance in the aspects of improving the digestibility of feed fibers and improving the production performance of animals.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
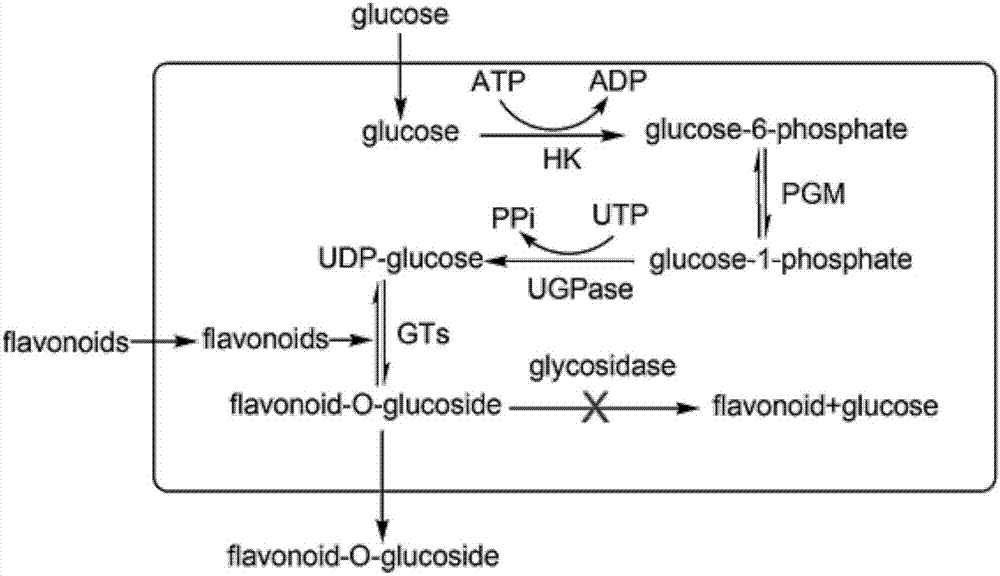
Genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of flavonoids compound and application thereof
ActiveCN107164253AImprove efficacyGood water solubilityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHydrolase Gene
The invention discloses a genetically engineered bacterium for catalyzing glucose glycosylation of a flavonoids compound and an application thereof. Specifically, a Beta-glycoside hydrolases gene of a chassis biological cell is removed according to the genetically engineered bacterium, and endogenous degradation of a glycosylation product is reduced; the high-expression regulation is performed to two key enzymes of glucophosphomutase (PGM) and uridine diphosphate glucose pyrophosphorylase (UGP1) of the chassis biological cell for participating in the synthesis of glycosylated-donor uridine diphosphate glucose (UDP-Glu), and a UDP-glucuronosyltransferase gene for catalyzing the flavonoid aglycones glucose glycosylation is combined so as to obtain a genetically engineered strain for effectively catalyzing the glucose glycosylation of the flavonoids compound, and finally scutellarein is used as a catalytic substrate for fermenting for 54 h in 10 L of a fermentation tank, wherein the yield of scutellarein-7-O-glucose of the glycosylation product is up to 1200 mg / L. The used strategy provides a technology reference for biologically-catalyzing chemical micromolecular glycosylation by using a microbiological method.
Owner:INST OF MATERIA MEDICA AN INST OF THE CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Nucleotide sequence of encoded fucoidin glucoside hydrolase and application thereof
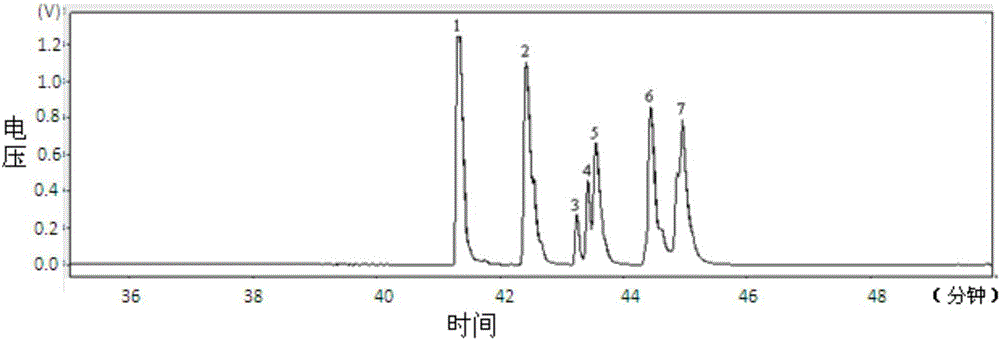
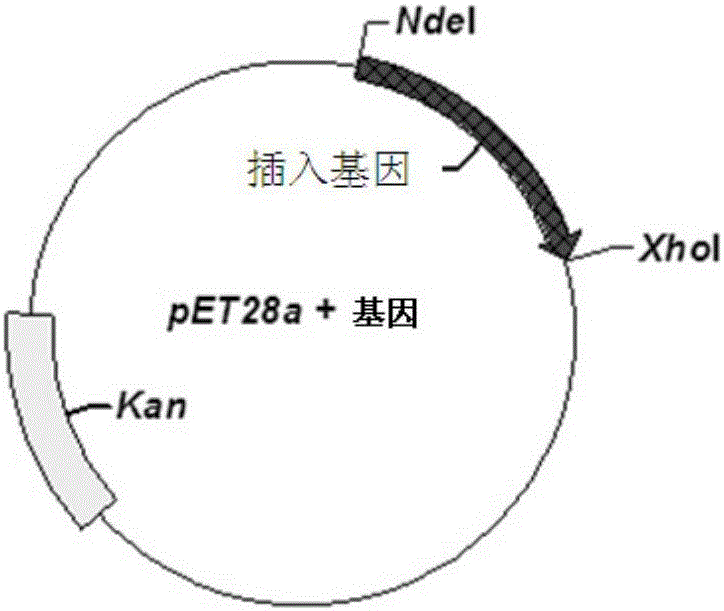
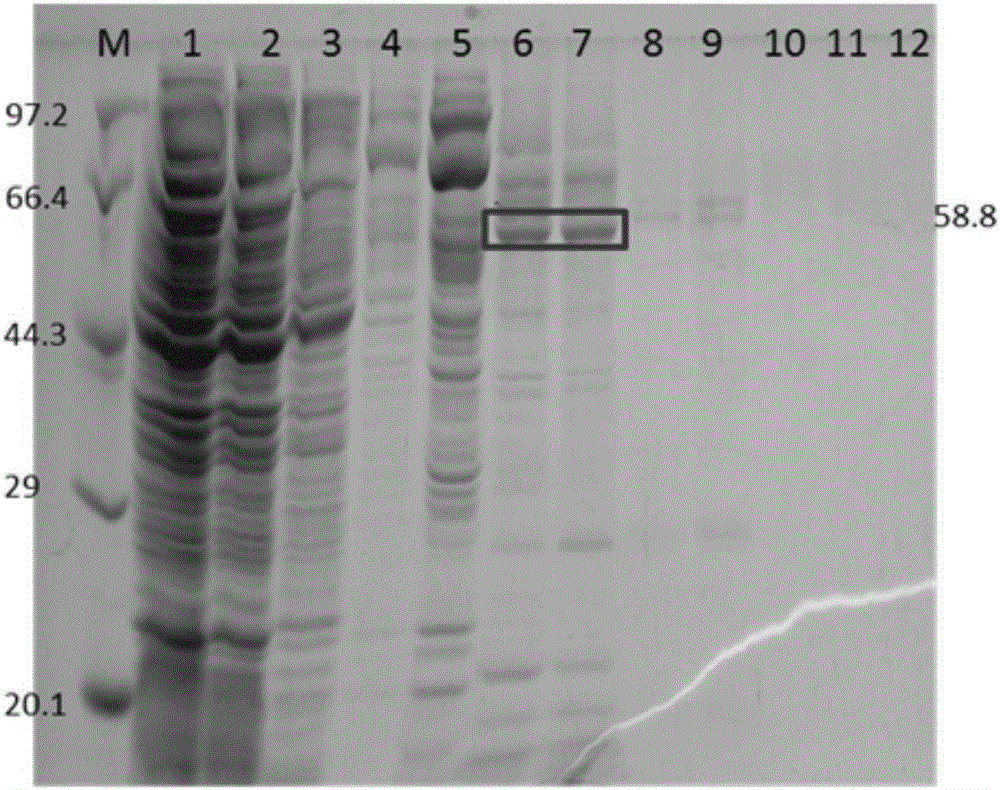
The invention relates to a nucleotide sequence of encoded fucoidin glucoside hydrolase and an application thereof. The nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO.1, encoded protein contains 529 amino acids, the nucleotide sequence is SEQ ID NO.2, and the predicted molecular mass of protein is 58.8 kDa. According to the nucleotide sequence and the application thereof, the gene GenBank No:AJ877239 of the encoded fucoidin hydrolase is subjected to codon optimization, 1599bp basic groups exist after optimization, and are loaded into a cloning vector pET28a, genes of the optimized fucoidin hydrolase can be expressed in escherichia coli BL21, glucoside hydrolase capable of efficiently and exclusively hydrolyzing fucoidin is obtained, and a biological degrading enzyme is provided for fucoidin hydrolysis.
Owner:SHANDONG JIEJING GROUP CORP
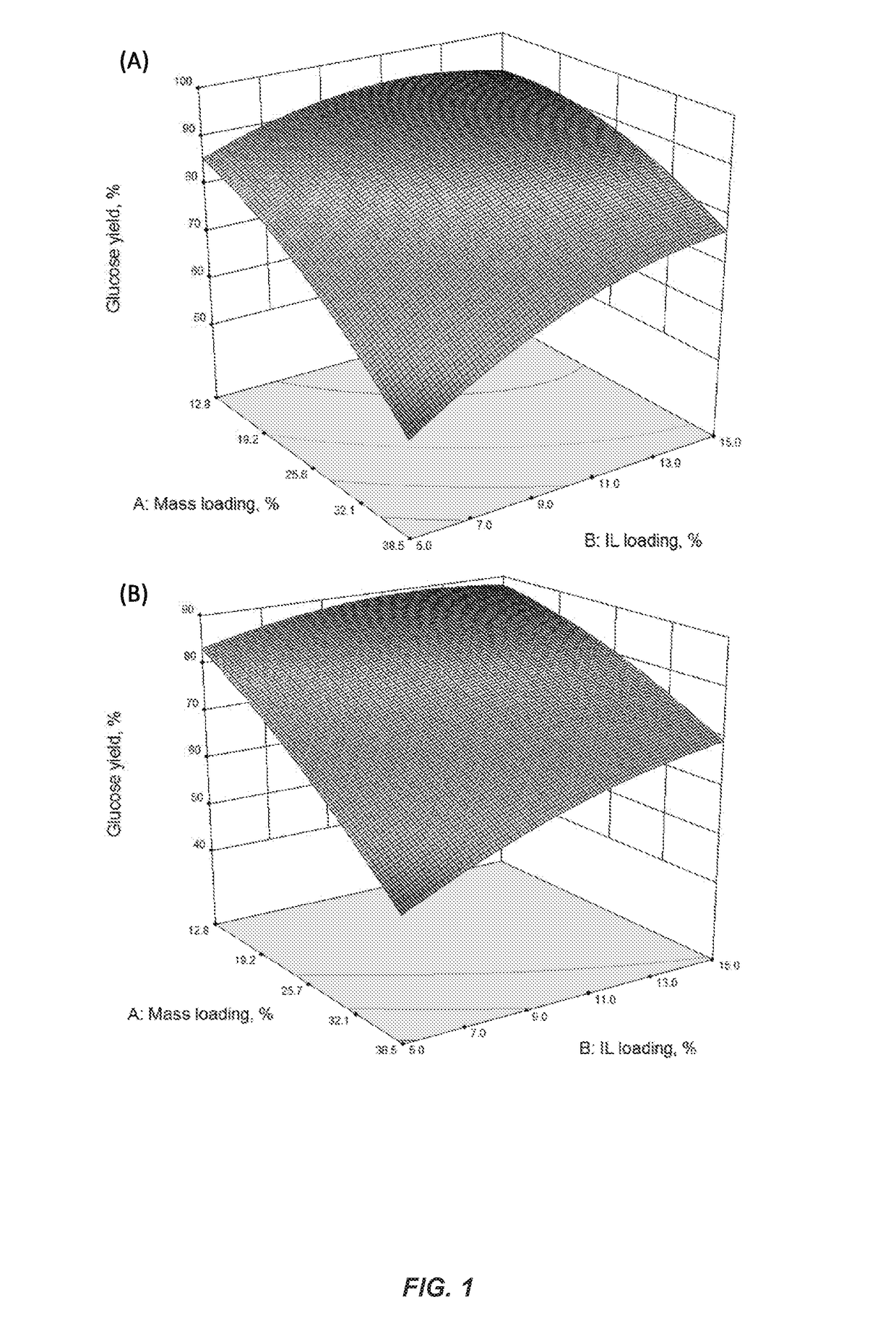
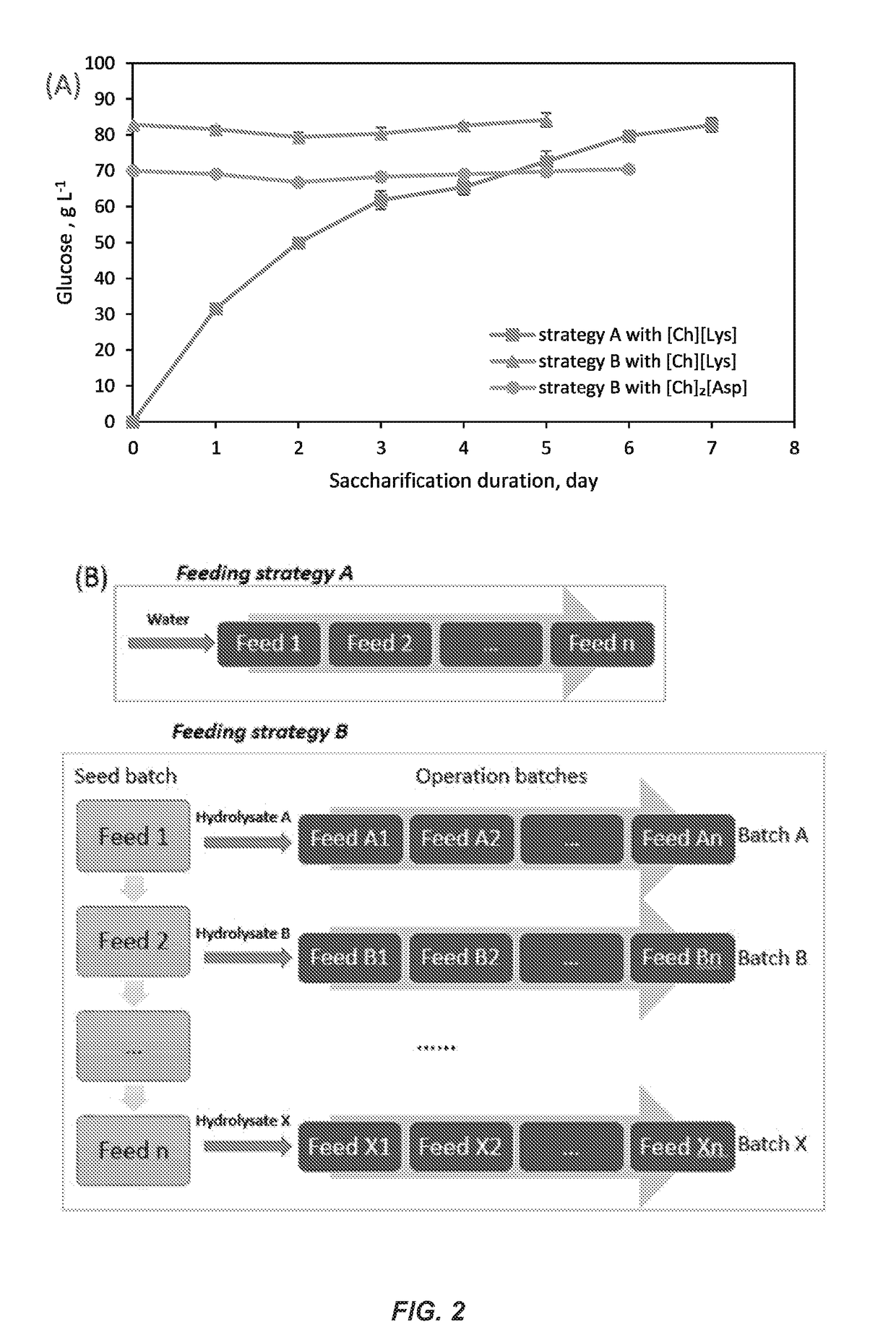
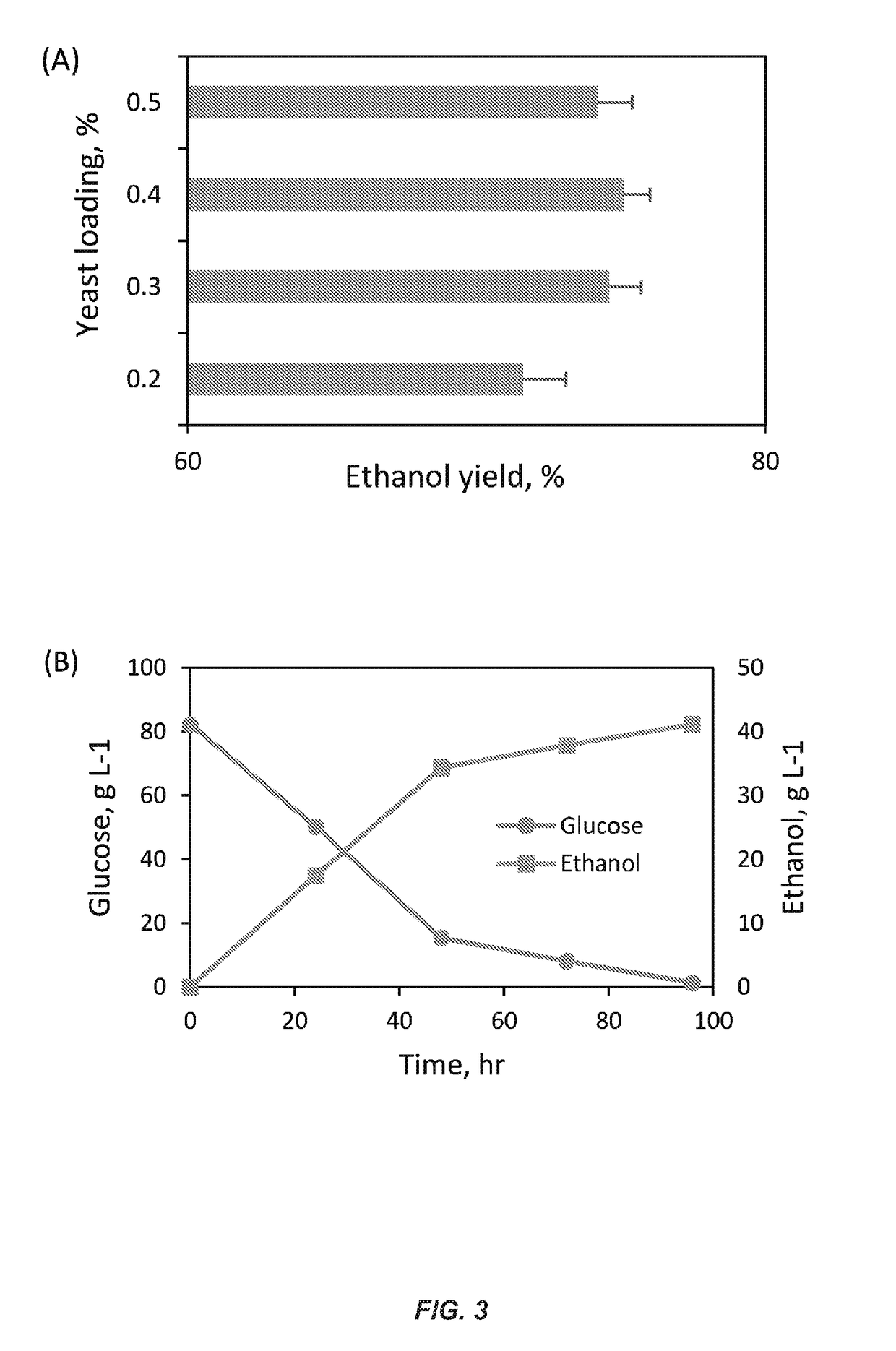
High gravity, fed-batch ionic liquid based process for deconstructing biomass
In one aspect, the present invention provides methods for preparing a fermentation product. The methods include pre-treating a mixture of biomass and ionic liquid, wherein the ionic liquid comprises a choline cation and the biomass comprises polysaccharide and lignin. The methods further include forming hydrolysates from the introduction of glycoside hydrolase to the pre-treated mixture at conditions sufficient to produce a sugar composition mixture for fermentation steps. The present invention provides methods for loading biomass mixtures in a batch-fed process, wherein the biomass slurries can be loaded into water or a concentrated sugar composition for hydrolysate production. The methods can be performed in a one-pot process, wherein the ionic liquids are present in the mixtures throughout each step. Aspects of the invention provide compositions of sugar composition mixtures and fermentation product mixtures.
Owner:NAT TECH & ENG SOLUTIONS OF SANDIA LLC
Enzyme-modified cereal suspensions
Efficient, selective, and economical methods for producing non-dairy ready-to-use milk substitute cereal dispersions having intact beta-glucans, proteins, and natural sugars, while retaining the aroma and flavor of natural cereal. The methods include treating a cereal substrate suspension with an enzyme preparation that comprises at least one hydrolase having the ability to hydrolyze alpha-glycosidic bonds and having no glucanase and proteinase effect. The hydrolase may be selected from the group consisting of beta-amylase, alpha-amylase, amyloglucosidase and pullulanase, with the proviso that when the enzyme preparation comprises alpha-amylase or beta-amylase, there is always a mixture of at least one other of the alpha-glycosidic hydrolases. When beta-amylase and alpha-amylase are selected, they are used as a mixture, i.e., introduced simultaneously, to provide for accelerated enzymatic hydrolysis and for reduced amounts of the enzymes than otherwise needed if the enzymes were used separately. In addition to the above-identified hydrolases, the enzyme preparations of the present invention may further comprise an isomerase, such as glucose isomerase.
Owner:OATLY AB
Novel beta-1,6-glucanase, encoding gene thereof, and applications of encoding gene
ActiveCN105524934AAchieve prokaryotic expressionHas hydrolytic activityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention discloses a novel beta-1,6-glucanase, an encoding gene thereof, and applications of the encoding gene. The invention provides the beta-1,6-glucanase gene belonging to the glucoside hydrolase system, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the beta-1,6-glucanase gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1, and the protein (amino acid) sequence of the encoded outer membrane glucoside hydrolase is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The beta-1,6-glucanase can effectively prevent the infection of plant pathogenic fungi to plants. An engineered strain established by the gene realizes the prokaryotic expression of the beta-1,6-glucanase gene, and verifies the function of the glucoside hydrolase of the beta-1,6-glucanase gene, the result shows that GluM can effectively inhibit the germination of rice blast spores, and decompose the rice blast spores. After the beta-1,6-glucanase gene is transplanted into the dicotyledonous model plant arabidopsis thaliana and the monocotyledonous model plant rice, the result shows that the obtained transgenic plants have good anti-infection effects for grey mould and rice blast.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com