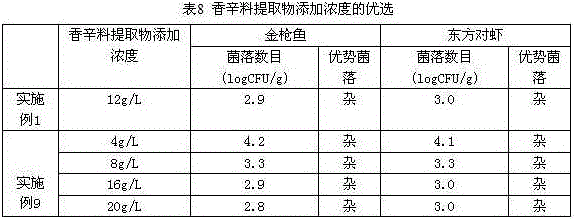
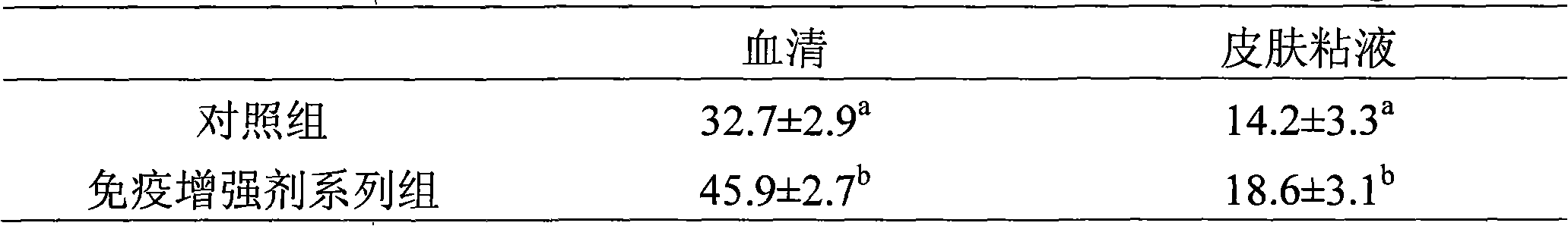
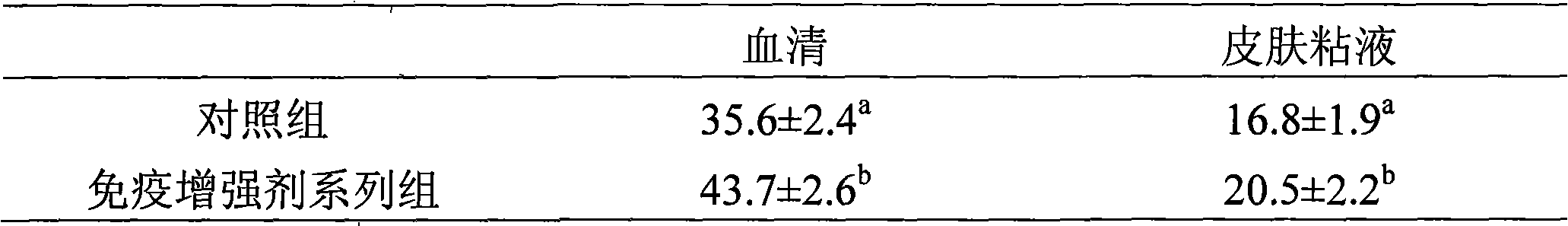
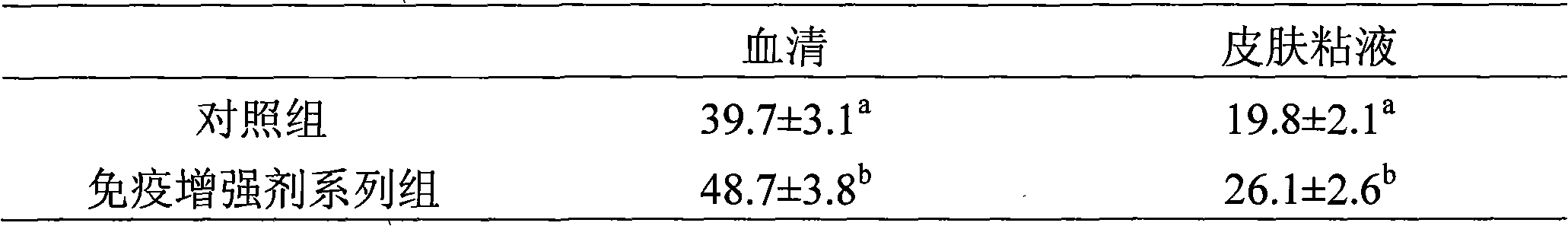
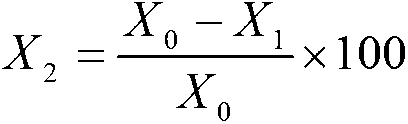Patents
Literature
64 results about "Muramidase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A basic enzyme that is present in saliva, tears, egg white, and many animal fluids. It functions as an antibacterial agent. The enzyme catalyzes the hydrolysis of 1,4-beta-linkages between N-acetylmuramic acid and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in peptidoglycan and between N-acetyl-D-glucosamine residues in chitodextrin. EC 3.2.1.17.
Method for preparing protein magnetic blotting nanospheres
InactiveCN101347721AAvoid complicated centrifugationSimplified centrifugation processOther chemical processesPolymerSerum protein
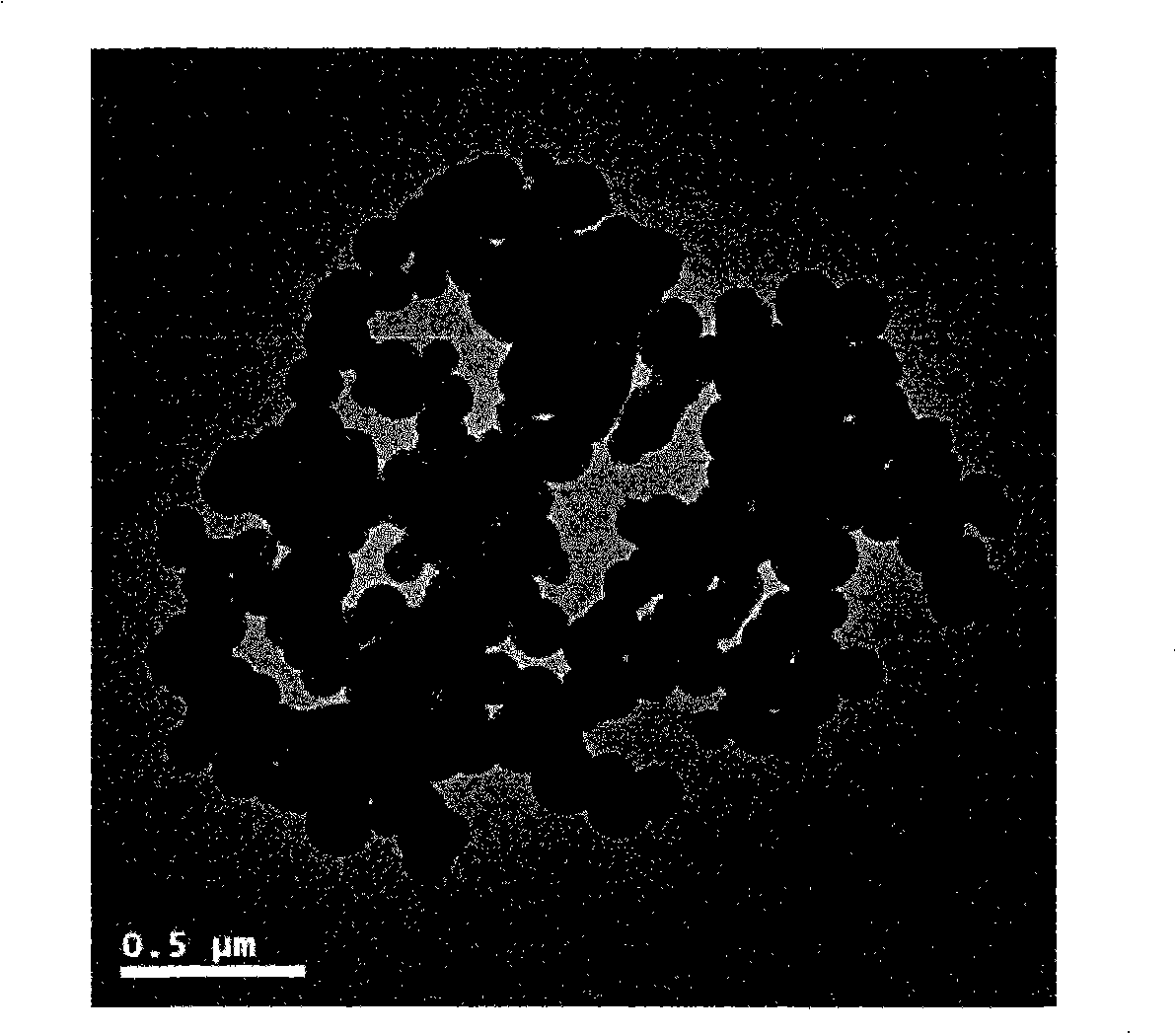
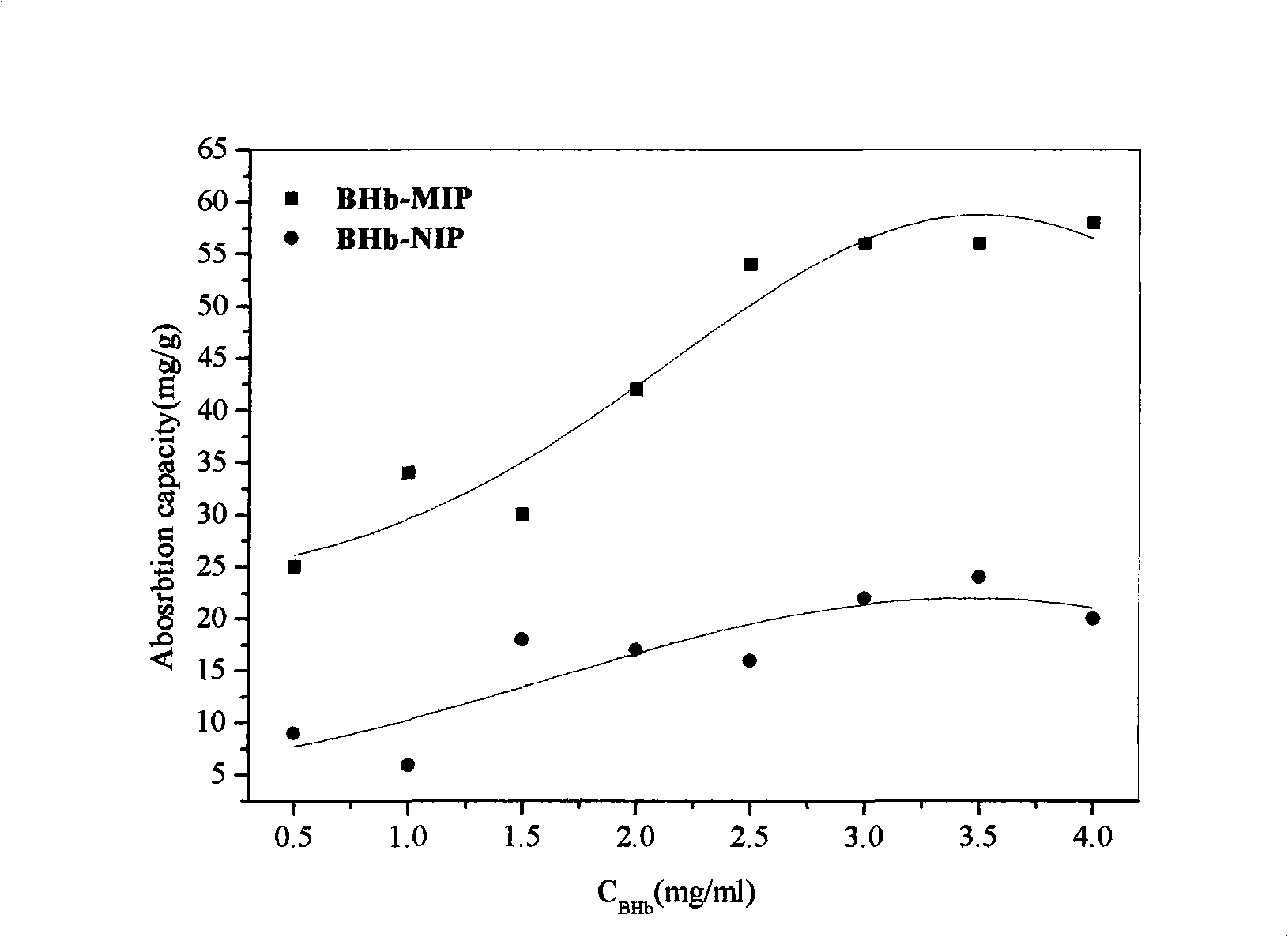
The invention relates to a preparation method of a protein magnetic imprinting nano sphere, in particular to a preparation method of a protein magnetic imprinting nano sphere which takes one of hemoglobin, muramidase or serum protein as template molecules; the preparation method includes the following steps: synthesizing magnetic nano particles which are Fe3O4 nano particles covered with silicon dioxide on the surfaces; carrying out silanization to the amino-groups on the surface of the magnetic sphere; using glutaric dialdehyde to connect protein; using silylation agent to fix the space structure of template protein; alkaline eluting the protein on the surface of the magnetic sphere to form imprinting sites. The hemoglobin, muramidase or serum protein magnetic nano imprinting polymer sphere prepared by the invention combines the precise and specific identification property of molecular imprinting and the quick separation property of the magnetic nano sphere under the action of an external magnetic field, integrates the advantages of molecular imprinting and the magnetic nano sphere, avoids complex centrifugation operation, plays vital roles in the separation of cells, protein and nucleic acid, the detection of biomolecules, tumor diagnosis and medicine targeting therapy and has promising application prospect in the field of isolation analysis.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Formula of aquatic product composite preservative
InactiveCN106259830AStrong Broad Spectrum ResistanceEnhanced inhibitory effectNatural extract food ingredientsMeat/fish preservation using chemicalsPropolisAllium sativum
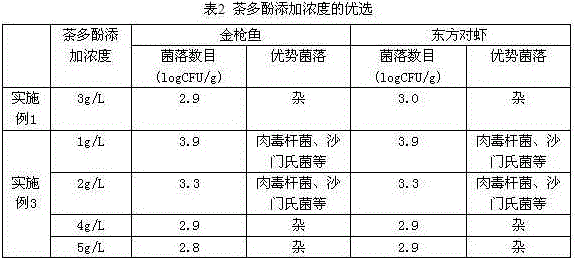
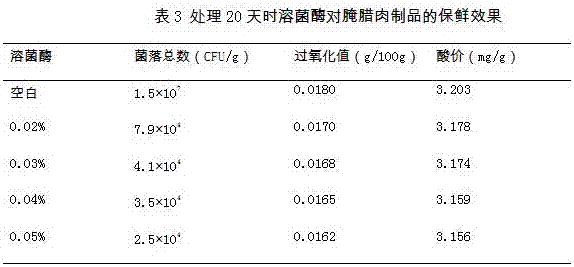
The invention relates to a formula of an aquatic product composite preservative. The formula of the aquatic product composite preservative is characterized in that the aquatic product composite preservative in each liter of distilled water comprises the following components: 0.4 to 0.6 g of muramidase, 2.5 to 3.5 g of tea polyphenol, 16 to 20 g of carboxymethyl chitosan, 10 to 14 g of nisin, 25 to 35 g of potassium sorbate, 17 to 23 g of sodium alginate, 20 to 30 g of lactobacillus, 1.5 to 2.5 g of propolis extracts and 10 to 14 g of spice extracts; and the spice extracting liquid comprises the raw materials: galangal, garlic, onion, cinnamon, clove and rosemary. The aquatic product composite preservative provided by the invention is prepared by compounding biological preservatives, is safe and non-toxic, has simple preparation and application methods, prominent microbial inhibition effect and good preservation effect, can greatly prolong the shelf life of frozen aquatic products, and has important industrial value.
Owner:黎建波
Feedstuff additive for reinforcing immunity of sea water fish
InactiveCN101326964AImprove immune functionRaise the level of immune responseAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsDiseaseWeight gaining
The invention discloses feed additive which improves the immunity of seawater fish. The feed additive consists of three or more than three types in clostridium butyricum, mannan oligosaccharide, xylo-oligosaccharide and fructooligosaccharide by proportion. 0.1 percent to 1 percent of seawater fish immunity intensifier of the invention is added into seawater fish feed, which can obviously improve the level of the muramidase in serum and skin mucus, obviously improve the level of IgM in the serum and the skin mucus, improve the fish immunity response capability, thereby improving the disease resistance of the cultivated fish. 1 percent of the immunity intensifier of the invention is added into the seawater fish feed, which can obviously improve the daily weight gain of the fish and reduce the food coefficient. The feed additive which improves the immunity of the seawater cultivating fish of the invention can obviously improve the immunity response level of the seawater cultivating fish, improve the disease resistance, and is safe without public harm and residue; the seawater fish cultivated by the additive meet the green food sanitation requirements.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV +2
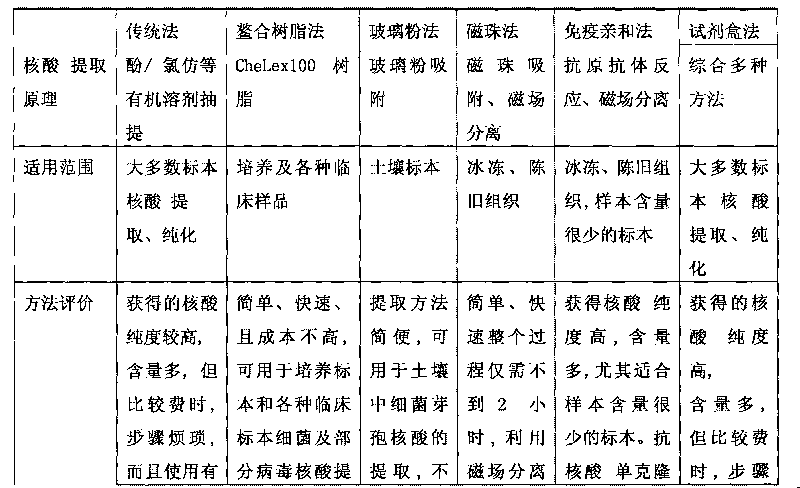
DNA extraction method suitable for structural analysis of microbial community in sediment
InactiveCN101696410AEfficient removalSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationTE bufferA-DNA
The invention discloses a DNA extraction method suitable for structural analysis of microbial community in sediment, which comprises the following steps: washing a sediment sample with TENPbuffer, and suspending the washed sediment sample in PBS buffer; repeatedly freezing and melting the pretreated sediment sample, adding muramidase, adding proteinase K and sodium dodecyl sulfate into the sediment sample, centrifuging the sample at room temperature, taking supernate, adding mixed solution of phenol, chloroform and isoamylol in equal volume into the supernate, mixing evenly by oscillation, centrifuging the obtained sample at room temperature, taking a liquid phase, adding mixed solution of chloroform and isoamylol in equal volume into the liquid phase, centrifuging the obtained sample at room temperature, taking a liquid phase, and adding precooled isopropanol into the liquid phase; centrifuging the obtained sample to remove supernate, adding precooled ethanol into the sediment, washing the sediment for three times, and centrifuging to remove the ethanol; and naturally air-drying the sample, and dissolving DNA with TE buffer solution for preservation.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV
Pet staple food capable of enhancing dog disease resistance and regulating stomachic and intestinal microflora
InactiveCN106490373ANutritiousImprove immunityFood processingAnimal feeding stuffDiseaseAnimal science
The invention relates to a pet staple food capable of enhancing dog disease resistance and regulating stomachic and intestinal microflora, and belongs to the technical field of pet foods. The pet staple food is prepared from dewatered chicken meal, dewatered fish meal, polished rice, bean pulp, wheatmeal, corn flour, monocalcium phosphate, table salt, vitamins, mineral substances, potassium sorbate, lactoferrin, muramidase, whey protein, fructo-oligosaccharide, yeast extracts, glucosamine and attapulgite powder. The pet dog fodder can meet the basic nutritional requirements of dogs, and meanwhile, a proper amount of lactoferrin, muramidase, whey protein and the like are added, so the antioxidant ability and the immunologic function of an organism can be obviously improved; the dog anorexia and apastia phenomena caused by eating a common fodder are improved, and the stomachic and intestinal microflora of the pet dogs can be regulated, so that the pet dogs are healthy in skeleton, bright in hair and healthy in intestinal tract; colon bacillus and intestinal tract toxins of animals can be effectively adsorbed and removed, so the pet staple food achieves the effects of preventing plague, curing diseases, eliminating insects and killing bacteria, enhances the disease resistance of pets, and has a very good overall health care function.
Owner:WUXI KINGENEW BIOTECHNOLOGY LIMITED COMPANY
Method for antibacterial finishing loomage by immobilized lysozyme
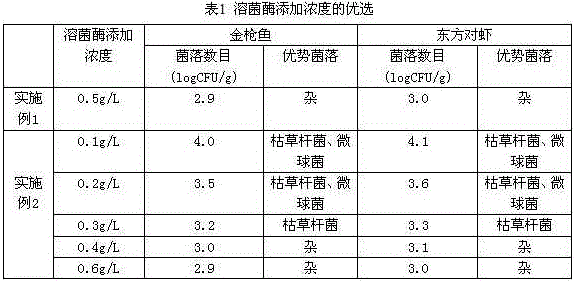
The invention relates to a method for performing antibacterial finish to a fabric by immobilizing muramidase, which belongs to the technical field of application of biotechnology to textile. The method comprises the following process steps: (1) the fabric is pretreated, wherein different fabrics adopt different pretreatment methods; and (2) the immobilization of the muramidase is performed, wherein the pretreated fabric is placed in a 5-25g / L muramidase buffer solution (pH7.0) to react for 4 to 16 hours at a temperature of between 0 and 10 DEG C, is taken out to be fully washed by deionized water, and is dried at room temperature for standby. The method is a novel fabric antibacterial finish method, immobilizes the muramidase on textiles through a biological enzyme immobilization technology, and endows the fabric with good antibacterial effect.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
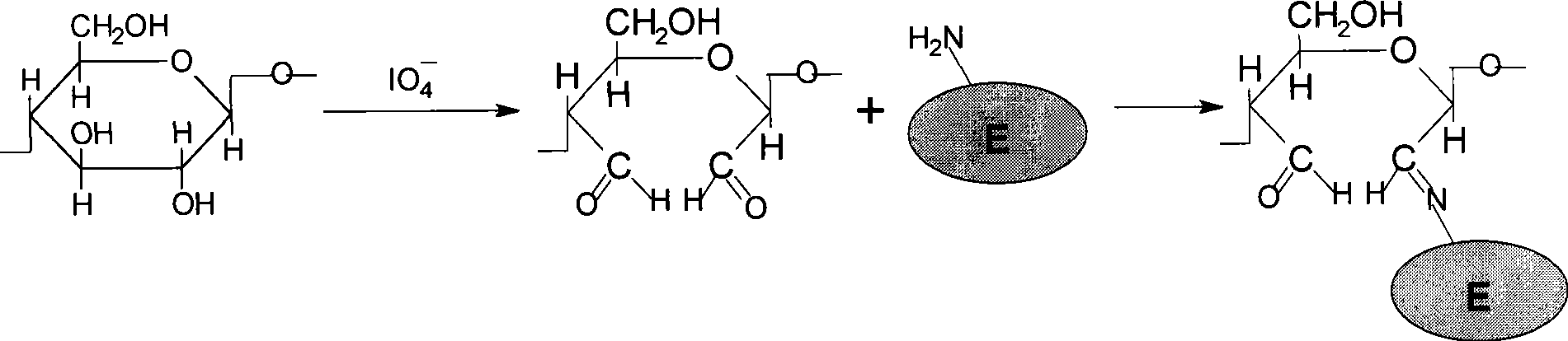
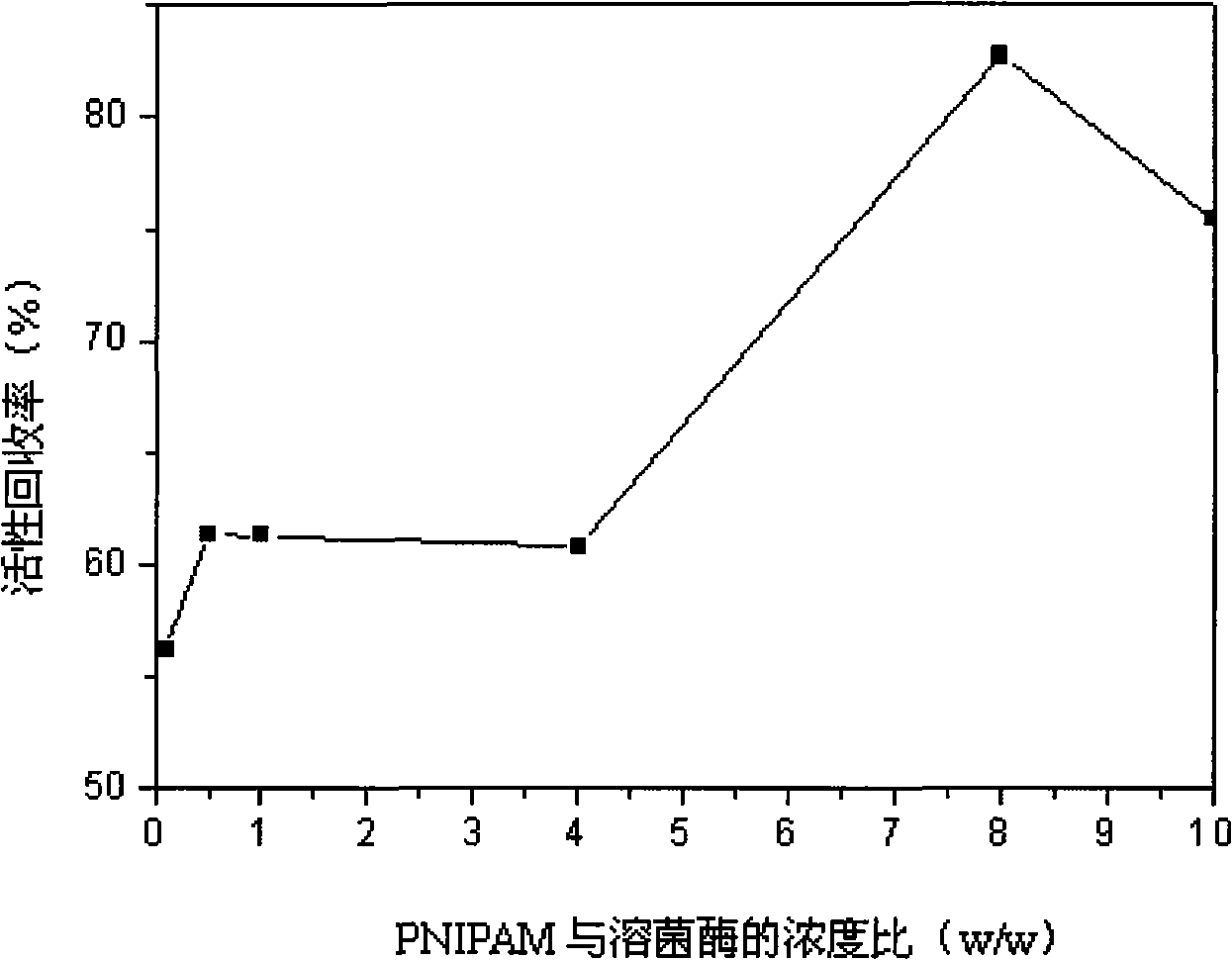
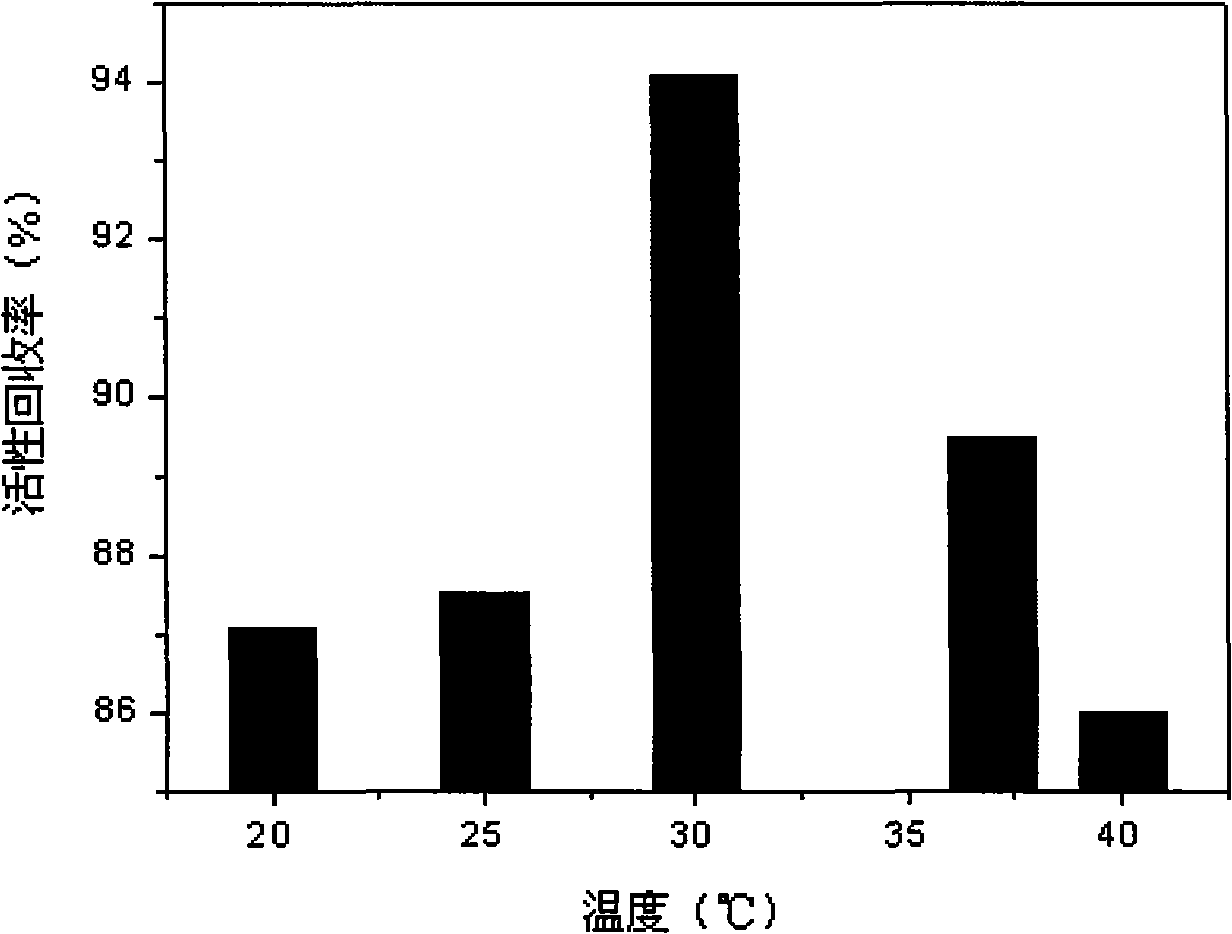
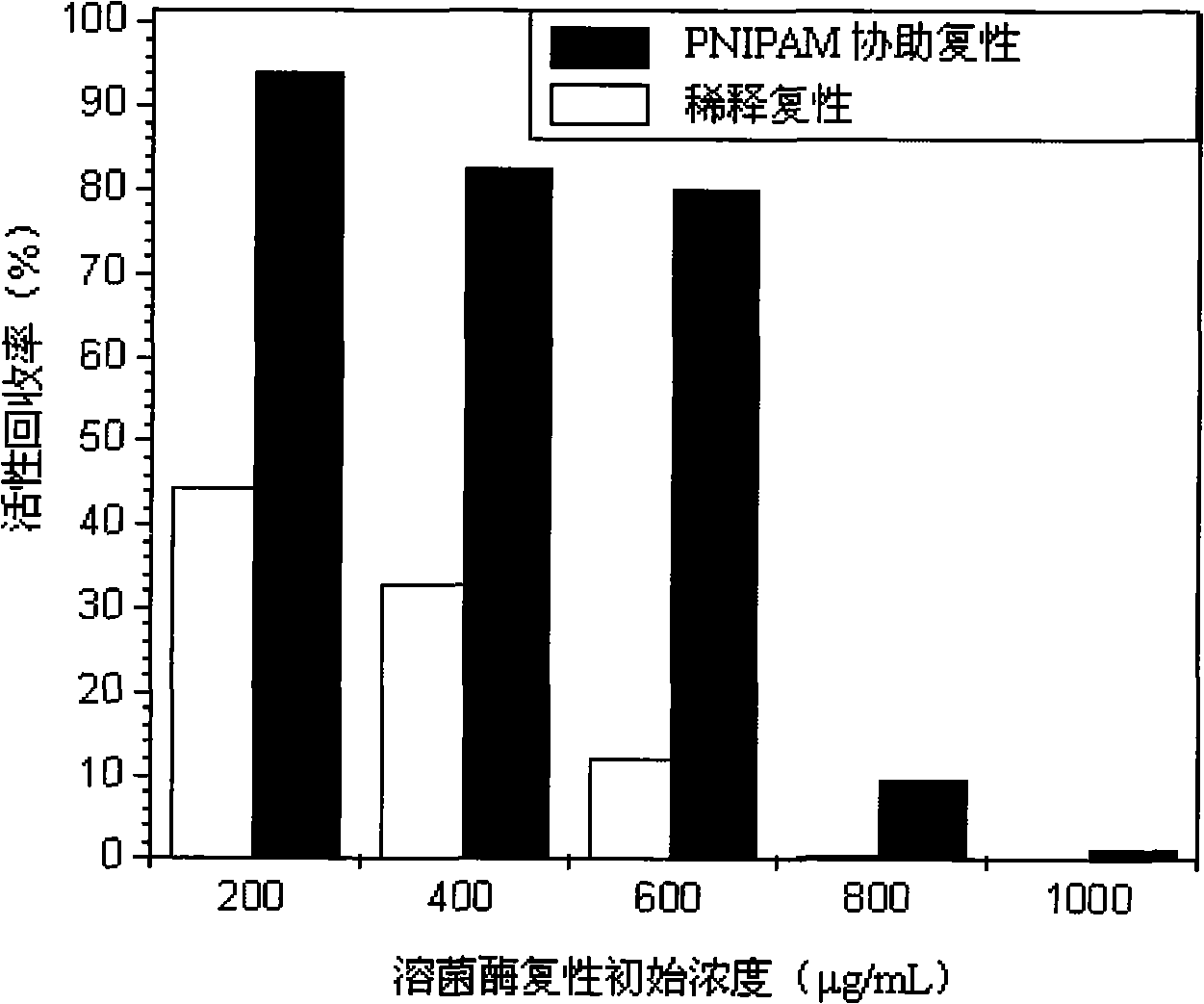
Method for assisting lysozyme in vitro refolding by means of linear poly N-isopropyl acrylamide
The invention discloses a method adopting linear poly N-isopropyl acrylamide adhesive to assist the renaturation of muramidase in vitro, comprising the following steps that: 1) the linear N-isopropyl acrylamide is prepared by a free radical polymerization method; 2) the linear poly N-isopropyl acrylamide is used to assist the renaturation of muramidase in vitro. The linear poly N-isopropyl acrylamide is taken as a novel protein in vitro additive which can increase the processing concentration of the renaturation muramidase, lower the production cost, and improve the activity recovery rate of the muramidase up to about 80 percent when the processing concentration is 600 Mug / mL; while the activity recovery rate of the dilution renaturation on the same condition is only 10 percent. The gel has the advantages of high efficiency, convenient operation and simple technique, etc., thereby having good potential application in the protein in vitro renaturation field.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Embroidery artware antibiosis and mildew-proof care solution
InactiveCN103147307ANon-irritatingPrevent mildewBiochemical fibre treatmentAnimal fibresBiotechnologyAntibiosis
The invention relates to embroidery artware antibiosis and mildew-proof care solution and a preparation method of the embroidery artware antibiosis and mildew-proof care solution. The embroidery artware antibiosis and mildew-proof care solution and the preparation method of the embroidery artware antibiosis and mildew-proof care solution are used for mildew-proof processing for embroidery threads and embroidery pieces in an embroidery artware manufacturing process and before the embroidery threads and the embroidery pieces are stored. The embroidery artware antibiosis and mildew-proof care solution and the preparation method of the embroidery artware antibiosis and mildew-proof care solution overcome shortcomings of the prior art, and have the advantages of being colorless, tasteless, free of corrosivity for real silk, non-irritant for skin, significant in antibiosis performance, free of decoloration phenomenon after being used, capable of preventing generation of germs and mildew, easy and convenient to use, simple in process, and the like. The technical scheme includes that the solution comprises the following ingredients by weight: 2.0-4.0% of carboxymethyl chitosan, 2.0-3.0% of algal polysaccharides, 6.0-8.0% of marine organism muramidase and 100% of purified water. The preparation method includes culturing the marine organism muramidase for backup use according to a culturing method disclosed in a Chinese patent CN200410097081, and then performing an emulsifying mixing process which includes adding the purified water required in the ingredient into an emulsifying tank and heating the purified water to be at 40 DEG C, adding the carboxymethyl chitosan and the algal polysaccharides into the emulsifying tank according to the proportion in the ingredient to be mixed for 45 minutes, adding the marine organism muramidase into the tank to be mixed for 15 minutes when the temperature of the solution declines to be at 30 DEG C, and canning and packaging the solution after the solution is cooled.
Owner:QINGDAO HIFUN MARINE BIOLOGICAL TECH
Preparation method of polydopamine/graphene oxide composite film with muramidase immobilized
InactiveCN105734039AHas antibacterial propertiesImprove antibacterial propertiesOn/in inorganic carrierOxide compositePhysical chemistry
The invention discloses a preparation method of a polydopamine / graphene oxide composite film with muramidase immobilized.The method includes the steps that firstly, autopolymerization of dopamine is carried out on the surface of a substrate like glass, an incomplete graphene oxide film layer is introduced onto a polydopamine film layer, part of the zone of the polydopamine film layer is covered with graphene oxide by controlling the concentration of graphene oxide and the temperature of the soaking process, the oxygen-containing functional group part of graphene oxide is reduced by polydopamine at the same time in the process, and a partially-reduced graphene oxide film layer is formed; finally, muramidase is immobilized to the incomplete partially-reduced graphene oxide film layer, and the polydopamine / graphene oxide composite film with muramidase immobilized is obtained.The method is simple and easy to implement; by inserting the incomplete graphene oxide film layer, the enzyme loading capacity of the composite film is obviously increased, the antimicrobial property is remarkably improved, and long-term high-efficiency bacteriostasis can be achieved; the composite film has good application prospects in the fields of food safety, medical treatment and public health and the like.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
Muramidase hydrolase external sterile cream for treating skin ulcer and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a muramidase hydrolase external sterile cream for treating skin ulcer and a preparation method thereof. The muramidase hydrolase external sterile cream is prepared from the following raw materials of: muramidase hydrolase, Span, poloxamer, Tween, sorbierite, sodium dihydrogen phosphate, ethylparaben, liquid paraffin, glycerin monostearate, cetyl alcohol, stearyl alcohol, albolene and sterile water. The invention also provides a preparation method for the muramidase hydrolase external sterile cream. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: dissolving; performing high temperature sterilization; filtering and removing bacteria by using a filter membrane; homogenizing at a low speed; homogenizing at a high speed; stirring; reducing temperature; and performing sterile filling. The muramidase hydrolase external sterile cream is used for treating the skin ulcer including bedsore, burn ulcer, calf ulcer, post-zoster ulcer, diabetic ulcer and postoperative ulcer in a transdermal administration form.
Owner:SHANDONG SBOND PHARMA
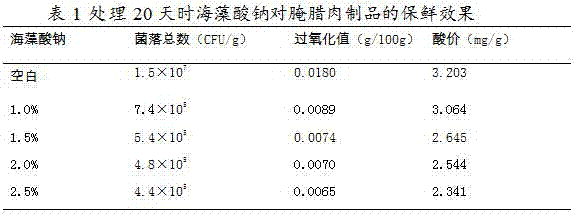
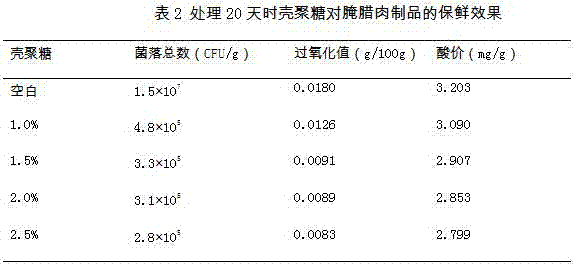
A pickled bacon fresh-keeping method utilizing a natural coating liquid
InactiveCN107094858AHave contactReduce exposureMeat/fish preservation by coatingMeat/fish preservation by freezing/coolingGlycerolDissolution
A pickled bacon fresh-keeping method utilizing a natural coating liquid is disclosed. The method includes a step of heating 1-10% of sodium alginate and 0.2-0.4% of glycerin under stirring until complete dissolution, performing ultrasonic treatment for 10-60 min to remove bubbles, and keeping the sodium alginate solution for later use; a step of adding 0.1-4% of an acetic acid solution in a chitosan treatment process with the adding amount of the chitosan being 1-8%, performing ultrasonic treatment for 10-60 min to remove bubbles, and keeping the chitosan solution for later use; a step of fully mixing the cooled sodium alginate solution and the chitosan solution, adding 0.01-0.20% of muramidase, and allowing the mixture to stand to obtain the natural coating liquid; and a step of adding preserved bacon slices into the natural coating liquid, soaking the slices for 0.5-5 min, draining the slices off, packaging the slices in vacuum, and preserving the slices at a low temperature, wherein the slices after being packaged in vacuum is preserved at a low temperature that is 8-16 DEG C. The method can achieve a deep-layer fresh-keeping effect, prolongs the shelf life of a pickled bacon product and improves quality of the pickled bacon product.
Owner:GUIZHOU UNIV
High-efficiency extracting method of food-borne pathogen nucleic acid
The present invention provides a high-efficiency extracting method of food-borne pathogen nucleic acid. A PCR technology has been widely used for the detection of pathogenic microorganisms currently. A first step of the PCR detecting technology is the preparation of template nucleic acid, that is, the extraction of nucleic acid in a sample, which directly affects the result of PCR reaction. For a long time, the processes of extraction and purification of the nucleic acid in a sample consume time, and are fussy all the time, so detection speed is seriously slowed down. Thus, a plurality of scholars searches after the extracting method of various nucleic acids. The high-efficiency extracting method of food-borne pathogen nucleic acid comprises the following steps: bacterial culture solution is centrifuged; buffer solution A is added into centrifugal sediment to be vibrated, and muramidase is added; prolease K is added after incubation; buffer solution B is added to be incubated at the temperature of 65 DEG C for 10 minutes after being vibrated violently to be prepared into cracking solution; and high-quality nucleic acid is collected by an adsorption film of silicon matrix SiO2 material is used for extracting nucleic acid solution. The present invention is applied to the detection of the pathogenic microorganisms.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF HEILONGJIANG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU OF P R C
Human-derived muramidase protein fermentation method
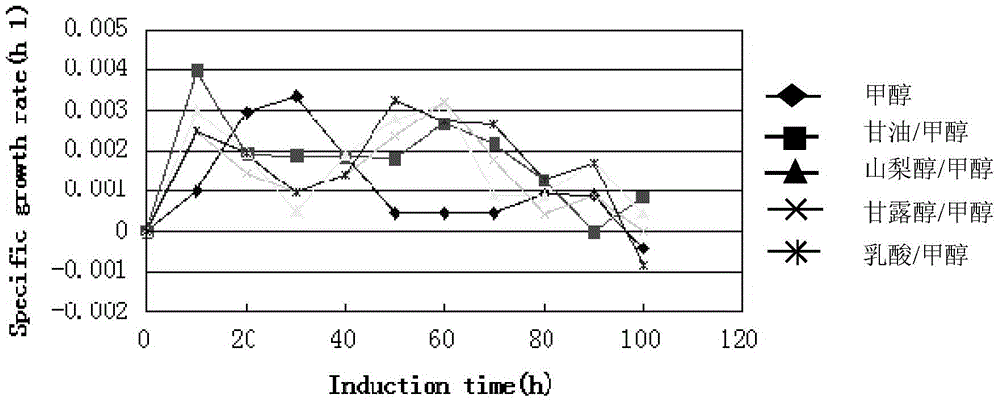
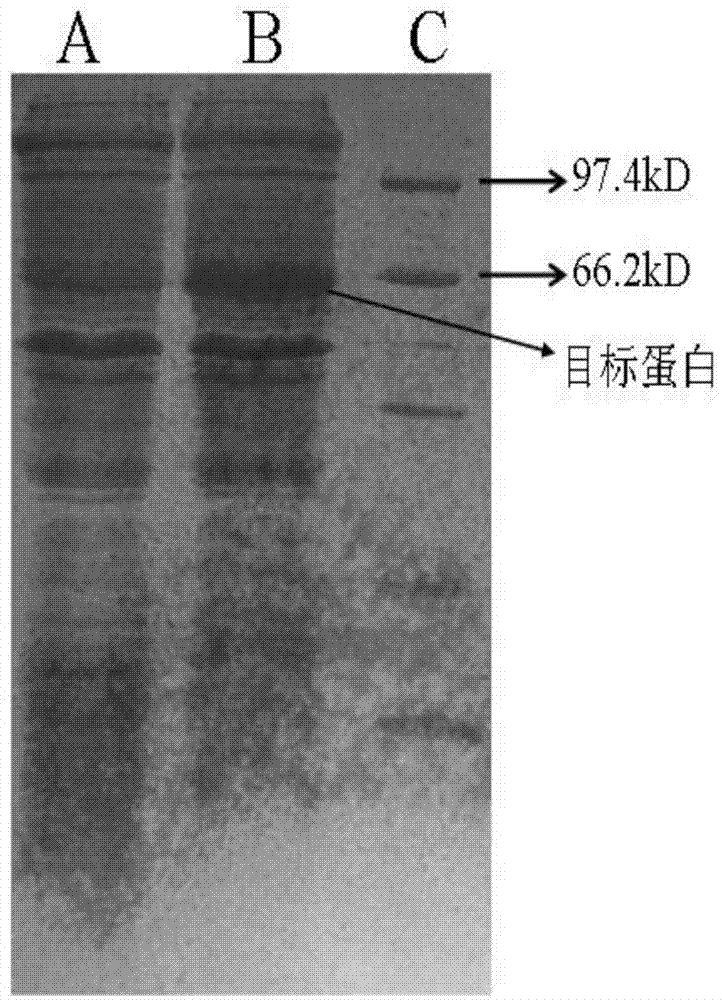
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering, and provides a human-derived muramidase protein fermentation method. Seed fermentation liquor of human-derived muramidase is added into a fermentation tank for high-density fermentation; high-cell-density fermentation includes methyl alcohol induction, tryptone addition and glycerinum supplement; a BSM fermentation medium is adopted in high-density fermentation of the fermentation tank and is inoculated with seed culture liquor of 5%. The highest activity of human-derived muramidase obtained through the method is 151600 U / ml and 127300 U / ml, the highest protein expression quantity reaches 1.65 g / L, and the batch has high stability. The amplification result is ideal, and practical reference base is provided for industrial production.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Method for preparing protoplast of white rot fungi
InactiveCN101712932ASimple preparation processEasy to operateFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyLiquid medium
The invention provides a method for preparing protoplast of white rot fungi. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating strong mycelium on a PDA solid medium to a liquid medium and culturing for 240 to 290 hours; pretreating the mycelium by 0.1 to 0.3 percent beta-mercaptoethanol; performing enzymolysis on the mycelium at the temperature of between 26 and 32 DEG C for 1 to 4 hours by adopting mixed enzyme of muramidase, cellulase and helicase with the pH of between 4 and 7; and ensuring that the number of the protoplast reaches 5-8*10<6> per milliliter when 0.6mol / L MgSO4 is used as an osmotic pressure stabilizer. The method for preparing the protoplast of the white rot fungi has the advantages of simple preparation process and easy operation. The preparation yield of the protoplast reaches 5-8*10<6> per milliliter.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY & VETERINARY
Food fresh-keeping method by using biological bacteriostatic agent in combination with ultra high pressure-assisted thermal treatment
ActiveCN103750497AInhibition of germinationEffective passivationFood preservationSpore germinationUltra high pressure
The invention belongs to the field of food preservation and fresh keeping and in particular relates to a food fresh-keeping method by using a biological bacteriostatic agent in combination with ultra high pressure-assisted thermal treatment. The food fresh-keeping method comprises the following steps: (1) carrying out thermal treatment on low acid food; (2) adding the biological bacteriostatic agent to the low acid food subjected to thermal treatment, wherein the biological bacteriostatic agent comprises the following components of 0.1-0.5g / kg of nisin, 0.1-0.5g / kg of chitosan, 0.1-0.5g / kg of muramidase, 0.1-0.4g / kg of epsilon-polylysine, 0.2-1g / kg of allicin and 20-250g / kg of sodium chloride; and (3) carrying out temperature and ultrahigh pressure treatment. By using the food fresh-keeping method, bacterial spores in the low acid food can be effectively passivated and spore germination can be inhibited at 4 DEG C when the low acid food is stored within a shelf life of 20 days, and meanwhile, the losses of textures, flavor, nutrition and color caused by a conventional high temperature and high pressure food sterilization method can be avoided; and the food fresh-keeping method is especially advantageous to the low acid food with pH not less than 4.5.
Owner:INST AGRO PROD PROCESSING ANHUI ACADEMY AGRI SCI
Polymorphism mark screening of chlamys ferrari G-type lysozyme gene and auxiliary breeding means
InactiveCN101255477AEasy to operateImprove breeding efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal husbandryDiseaseLysobacter enzymogenes
The invention relates to a method for screening of chlamys farreri G-type muramidase gene polymorphism markers and the assistant breeding method thereof, belonging to shellfish molecular marker assistant breeding technology in the filed of aquatic organism technology, mainly comprising the steps of: cloning partial sequence of promoter region of a chlamys farreri G-type muramidase gene, preparing disease-resistance population and sensitive population, screening of disease-resistance G-type muramidase gene markers, quickly screening the disease-resistance population and building gene marker assistant breeding technology. According to the invention, promoter region sequence of the chlamys farreri G-type muramidase gene is cloned, and its polymorphism sites are screened. The occurrence frequency of -391 AG individual in disease-resistance population is obviously higher than that in sensitive population, therefore, resistance-related gene marker assistance breeding method is built with -391 AG as chlamys farreri resistance-related G-type muramidase gene marker. The invention has the characteristics of strong pertinence, high breeding efficiency, simple and quick operation, etc., and is suitable for screening of shellfish resistance-related markers and breeding of disease-resistance fine varieties.
Owner:INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Enzyme supplementation gum
The invention discloses enzyme supplementation gum which is composed of 0.1%-0.3% of muramidase, 18%-22% of aluminium hydroxide, 2%-3% of vitamin C, 0.6%-1% of citric acid, 2%-3% of glycerinum, 20%-30% of gum base, 40%-45% of sorbitol, 4%-6% of mannitol, 0.5%-1% of essence and 6%-10% of water. According to the enzyme supplementation gum, the biological muramidase and the citric acid are added, the pH value of the gum can keep the activity of the muramidase to the maximum degree, and bacteria resistance and bacteriostasis, dental calculus prevention, caries prevention, ozostomia relieving, dental plaque inhibition and remarkable improvement of gingival bleeding are conducted on the aspect of biology; the aluminium hydroxide and the vitamin C can assist the muramidase in removing dental plaque and stain, the effect is more remarkable, gingival bleeding is inhibited, and the gum can taste sour and sweet and delicious; the teeth can be healthy and white and breath can be fresh through long-term use of the enzyme supplementation gum.
Owner:JIESHOU ZHAOLONG FOOD
Preparation of antimicrobial nanofiber complex film with biological activity and application thereof
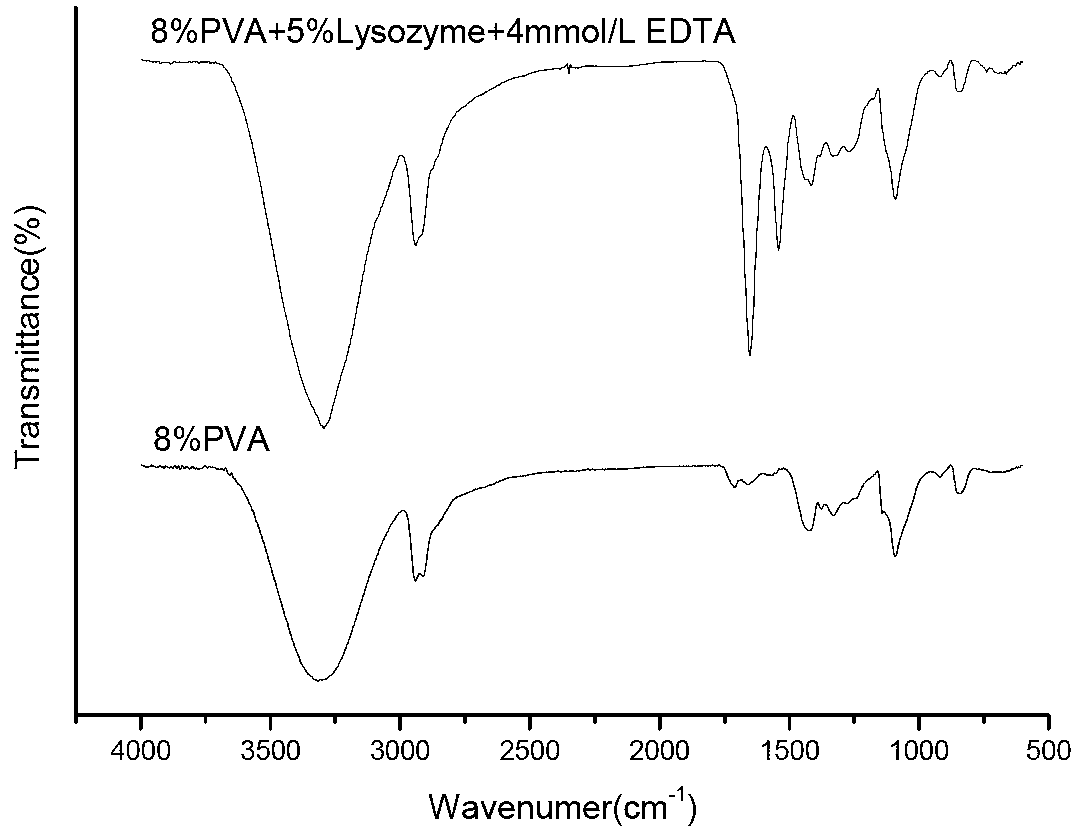
InactiveCN103103696AGood water solubilityGood biocompatibilityMonocomponent synthetic polymer artificial filamentNon-woven fabricsPolyvinyl alcoholStaphyloccocus aureus
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano material preparation, and discloses a method of preparing antimicrobial nanofiber complex film of polyvinyl alcohol / muramidase / ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA) from electrostatic spinning and the application of the antimicrobial nanofiber complex film of the polyvinyl alcohol / muramidase / EDTA. The preparation comprises the following steps: solving the polyvinyl alcohol in distilled water, carrying out magnetic stirring and obtaining polyvinyl alcohol solution; cooling the obtained polyvinyl alcohol solution to room temperature, and adding the muramidase and the EDTA to the polyvinyl alcohol solution; carrying out magnetic stirring to obtain spinning solution; and sucking the spinning solution into an injection syringe, controlling the flow speed of the injection syringe, spinning, drying in vacuum, and obtaining the antimicrobial nanofiber complex film with the biological activity. The antimicrobial nanofiber complex film with the biological activity has obvious bacteriostasis to escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. The staphylococcus aureus has good toughness and low toxicity features, and has wide application prospect in the field of food packaging materials and biological materials.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
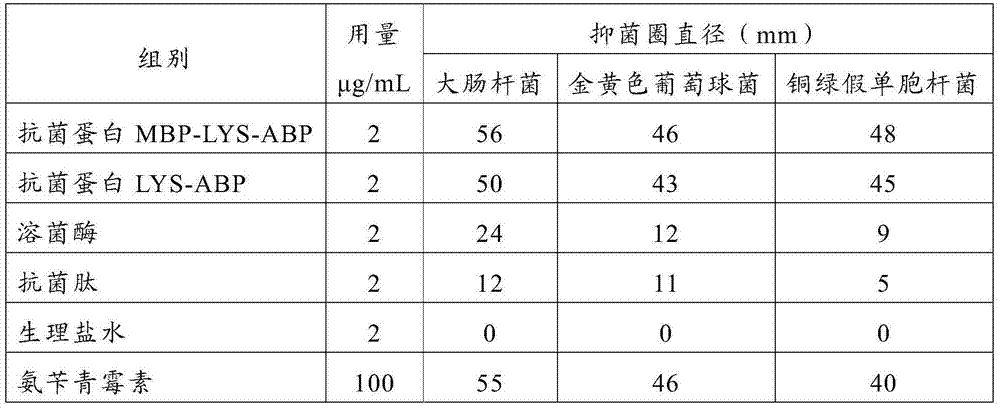
Antibacterial proteins
ActiveCN104761621ANon-irritatingGood antibacterial effectPeptide preparation methodsDepsipeptidesLysobacter soliEnzyme digestion
The invention belongs to the field of biochemistry, and discloses an antibacterial protein LYS-ABP and an antibacterial protein MBP-LYS-ABP having an LYS-ABP protein N terminal added with MBP, and preparation methods thereof, wherein the antibacterial protein LYS-ABP and the antibacterial protein MBP-LYS-ABP have no stimulation to human bodies and have good antibacterial effect. The antibacterial protein LYS-ABP and the antibacterial protein MBP-LYS-ABP have no stimulation to the human bodies and have good antibacterial effect, the antibacterial effect is better than single muramidases and antibacterial peptide proteins, and the biological activity stability is good. The antibacterial protein MBP-LYS-ABP is obtained by in-vitro recombinant expression, and is easy to prepare and relatively low in cost; and the antibacterial protein MBP-LYS-ABP has high soluble expression yield and is suitable for large-scale preparation. The antibacterial protein LYS-ABP is obtained by enzyme digestion of a recombinant expression-prepared MBP-LYS-ABP fusion protein with thrombin, and is easy to prepare and relatively low in cost.
Owner:CHANGCHUN XINYUERAN SCI & TECH CO LTD
Mouth wash and preparation method thereof
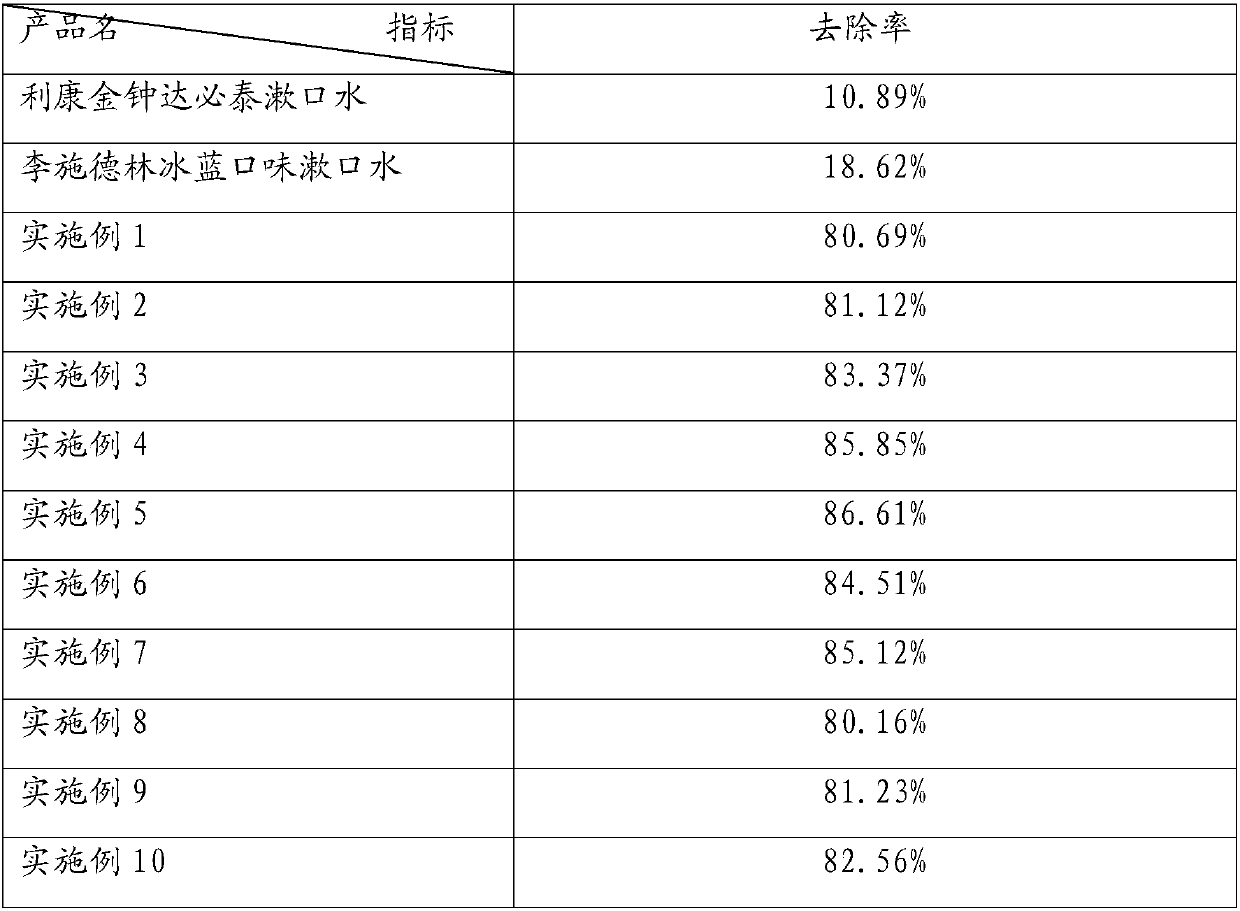
InactiveCN108186384AImproves natural defensesEfficient removalCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsBleeding gumActive agent
The invention is applicable to the technical field of an oral cavity health care product, and provides mouth wash and a preparation method thereof. The mouth wash is prepared from the following ingredients in percentage by weight: 0.45 to 0.6 percent of nonionic surfactants, 0.5 to 1.5 percent of enzyme preparations, 0.1 to 0.15 percent of preservatives, 0.1 to 0.2 percent of pH conditioning agents and the balance of deionized water, wherein the enzyme preparations are mixtures of at least three kinds of materials from glucanase, glucose oxidase, polyphenol oxidase, muramidase, coenzyme Q10, amylase, trypsin, catalase, bromelin or protease. The mouth wash is weakly acidic; stimulating ingredients such as ethyl alcohol are not contained; the mouth wash is mild and inirritative on the oral cavity; food-grade raw materials are used; safety and nontoxicity are realized; meanwhile, various kinds of enzymes are compounded; various enzymes can maintain higher enzyme activity in the recipe; teeth stain can be effectively removed; the growth of dental plaque can be inhibited; the effects of obviously relieving gingival bleeding, reliving gingivitis, improving oral cavity natural defense capability and creating good oral environment can be achieved.
Owner:深圳市芭格美生物科技有限公司
Earthworm composite multienzyme and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a composite multienzyme prepared from earthworms and a preparation method thereof. The composite multienzyme comprises various proteolytic enzymes, nuclease, lipoidase, muramidase, phytase, amylase, superoxide dismutase, catalase, cellulose, and the like. The preparation method comprises the following steps: using the earthworms as materials; protecting homogenate at low temperature by a buffer solution; centrifugally separating; washing; precipitating and separating by adding ammonium sulphate; dialyzing to remove SO4; carrying out chromatography by a molecular sieve; and ultrafiltering, concentrating and drying in vacuum at low temperature. The composite multienzyme prepared by purification has the characteristics of high efficiency and multifunction in the aspects of biomacromolecule decomposition and substrate utilization. The preparation method has low cost, and the composite multienzyme has high activity. The functions of all enzymes or partial enzymes of the composite multienzyme can be utilized to achieve a corresponding use aim, thus the composite multienzyme has wide application range.
Owner:珠海博康药业有限公司
Anionic framework polymer for extracting muramidase, preparation method of anionic framework polymer
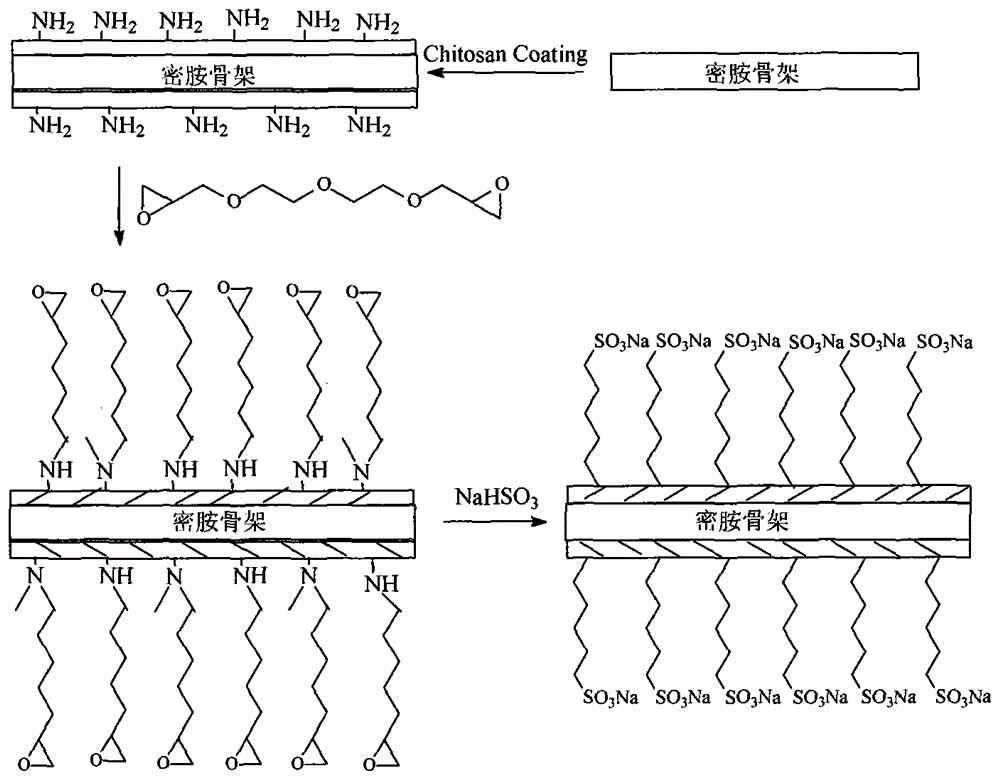
ActiveCN105013453ALarge apertureLarge freenessOther chemical processesIon exchangeSodium hydrogen sulphite
The invention discloses an anionic framework polymer for extracting muramidase, a preparation method of the anionic framework polymer, and an application of the anionic framework polymer in the muramidase extraction. A special three-dimensional framework structure of existing melamine sponge is used; a framework is wrapped with a chitosan coating; diethylene glycol diglycidyl ether reacts with the chitosan coating, so that the chitosan coating is crosslinked, and the surface of the chitosan coating is provided with suspended epoxy groups; the epoxy groups react with sodium hydrogen sulfite to obtain sulfonate anions; in an ion exchange step in the muramidase extraction, the purification operation is carried out by taking the anionic framework polymer as an integral column, so that the surface of a material and muramidase are subjected to electrostatic interaction, the defect of poor diffusivity of muramidase macromolecules is overcome, the adsorption capacity of the material is improved, and the production efficiency of the muramidase is improved. A framework material has the advantages that the operation is easy and convenient, the repeated use is realized, the cost is low and the efficiency is high.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Nutrient conditioner specially used for root-promoting disease-preventing tobacco and preparation method of nutrient conditioner
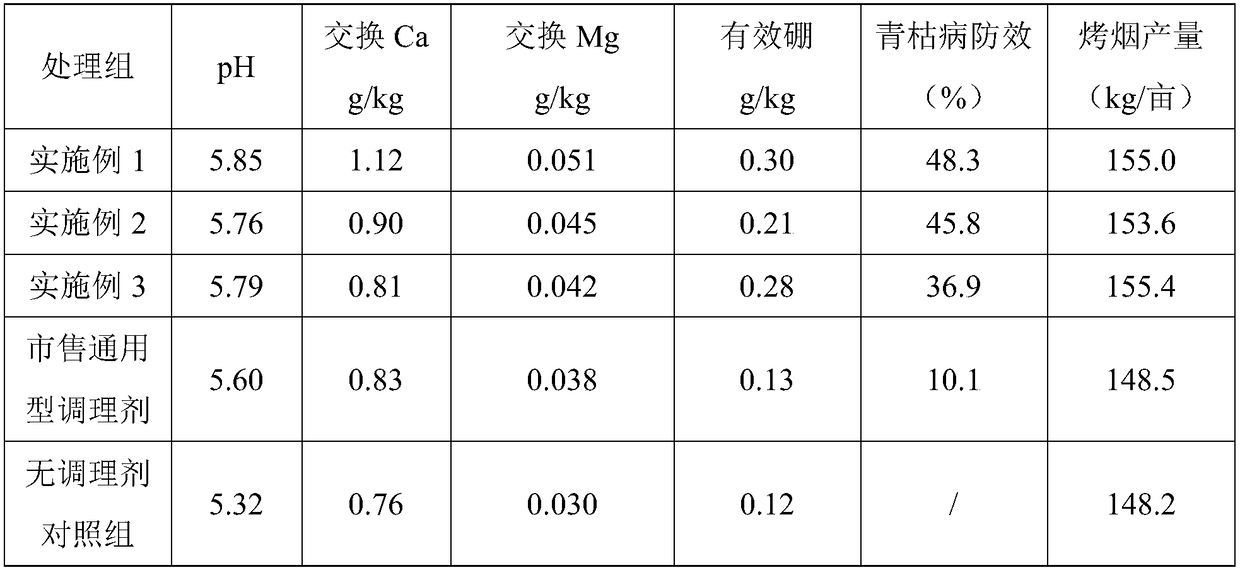
InactiveCN108341717AImprove resilience to adversityRaise the pHOrganic fertilisersPotassium fertilisersMicrobial agentAdditive ingredient
The invention discloses a nutrient conditioner specially used for a root-promoting disease-preventing tobacco and a preparation method of the nutrient conditioner. The conditioner is prepared from organic ingredients and inorganic ingredients, wherein the organic ingredients are prepared from an organic fertilizer, biochar, fulvic acid, chitosan, a compound microbial agent, egg white muramidase and polyaspartic acid; the inorganic ingredients are prepared from potassium feldspar, phosphorus slag, montmorillonite and borax. Specific to the characteristics of the tobacco, the compound microbialagent, the chitosan and the egg white muramidase are compounded, the obtained nutrient conditioner not only is conducive to activating soil nutrient, ameliorating soil and increasing pH value, but also has very good anti-bacterial and antiviral effects, the occurrence of tobacco bacterial wilt is reduced, the tobacco planting soil micro-ecotope system is improved, the disease-resistant property isenhanced, the occurrence of diseases is reduced, and the yield of the tobacco is increased.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI +2
Antimicrobial muramidase
InactiveUS20160030528A1BacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsAciduliprofundum booneiAntibacterial activity
Aciduliprofundum boonei glycosyl hydrolase 25 (GH25) muramidase is shown here to exhibit antibacterial activity against several distinct bacterial families. Formulations and methods of use for this GH25 are provided.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Industrial preparation of radish dual-function enzyme with chitinase and antalzyme activity
InactiveCN101434936AIncreased enzyme contentWide variety of sourcesEnzymesCentrifugationRoom temperature
The invention discloses an industrial preparation method of a dual-functional radish enzyme that is provided with the activity of both chitinase and muramidase and comprises the following steps: firstly raw material is washed and cut, low-temperature induction is implemented to produce the enzyme, homogenate is agitated with a homogenate liquid, a concentrated solution of the dual-functional radish enzyme is obtained through steps of centrifugation, filtering and hyperfiltration and the like, and a protecting agent and a stabilizing agent are respectively added into the concentrated solution, thus obtaining the liquid dual-functional radish enzyme or the dry dual-functional radish enzyme powder. The industrial preparation method of the dual-functional radish enzyme has the following advantages: 1. low-temperature lighting induction technique is adopted, thus raising the raw enzyme content by 2 to 3 times; 2. specific activity stabilizing agent and protecting agent of the dual-functional radish enzyme are developed, thus keeping the activity of the dual-functional radish enzyme basically unchanged in two years at room temperature and reaching the activity of over 97 percent of the raw enzyme; 3. the raw material has wide source and low price, is not affected by factors including season and weather and the like, and can be planted in all seasons; 4. the preparation method has simple technique and low price.
Owner:宋秋兰
Bio-enzyme corrosion inhibitor for circulating water system and application method thereof
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF PETROLEUM (EAST CHINA)
Muramidase detction reagent and its preparing method
InactiveCN1587994AImprove performanceRealize automated detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementColor/spectral properties measurementsThallusAbsorbance
The invention of biochemical analysis field relates to a lysozyme testing agent and its manufacture method. The lysozyme testing agent contains killing Micrococcus and gelatin, which is bacteria suspension with high stability, created by new method of killing Micrococcus and using gelatin as medium and stabilizer of disperse thallus. After more than four hours of standing, if absorbance of bacteria suspension does not change notably, agent abtained is proved to have excellent stability and can satisfy various testing requirement, be used in automatic biochemical analysis and realize automatic and quantitive detection of lysozyme activity.
Owner:SHANGHAI CHEST HOSPITAL
Microbiological feed additive and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105104712AReduce or substituteIncrease production capacityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSerum lysozymeBacillus perfringens
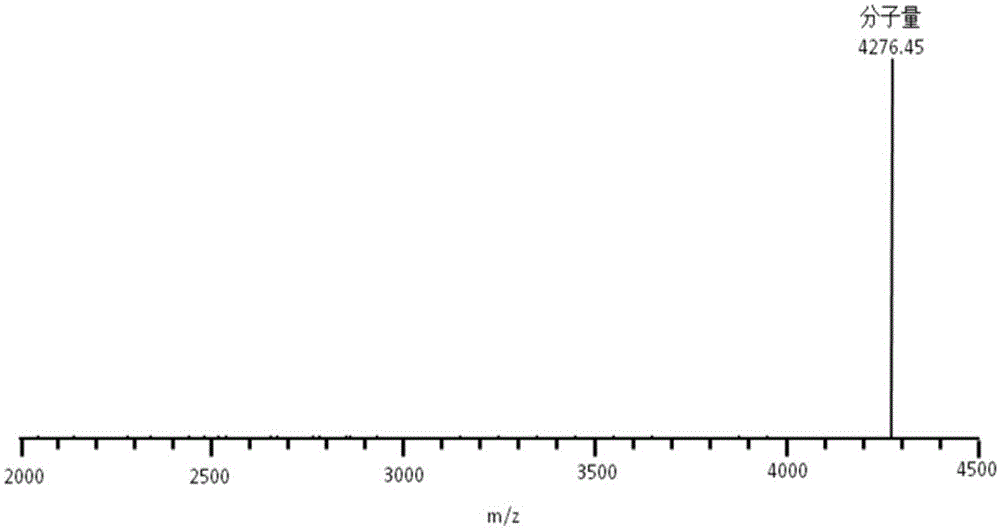
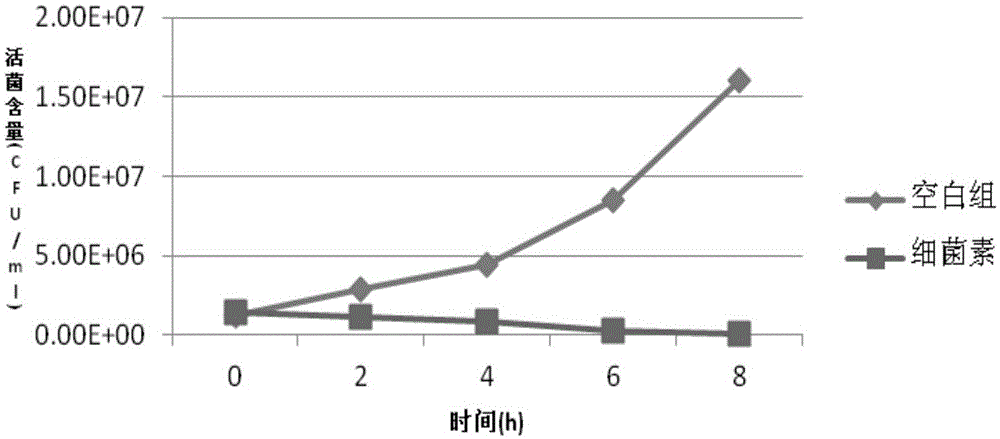
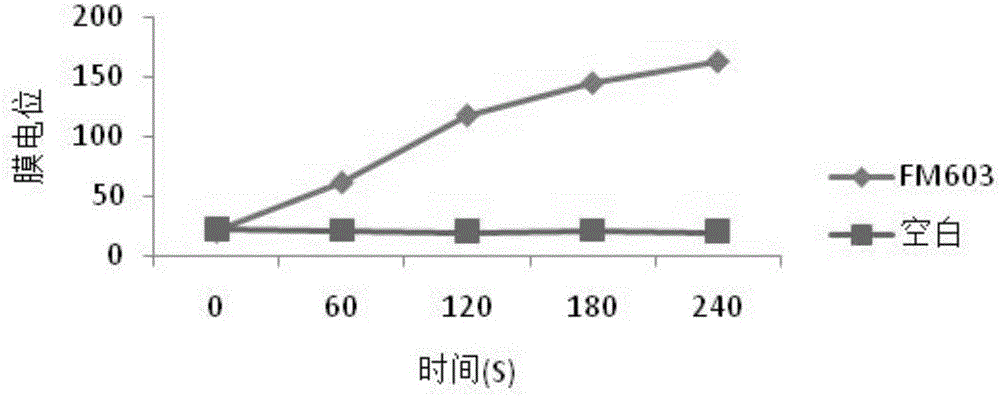
The invention provides a microbiological feed additive. The feed additive contains bacillus coagulans FM603 or a fermentative substance of the bacillus coagulans FM603; the fermentative substance of the bacillus coagulans FM603 contains bacteriocin and has antibacterial activity on gram-positive pathogenic bacteria such as Listeria monocytogenes, staphylococcus aureus, methicillin resistant staphylococcus aureus, clostridium perfringens, clostridium firmus and the like. The molecular weight of the bacteriocin is 4276.45 Da, a partial amino acid sequence is Ala-Gly-His-Dhb-Phe-Val-Dhb-Gly-Pro, and the bacteriocin is more stable under the processing of heat, acid, pepsin or trypsin, is likely to be degraded by pronase and loses activity. With the adoption of the feed additive, the egg laying rate of laying hens can be increased, the feed-egg ratio is reduced, and the egg quality is improved; the feed intake and the daily gain of piglets are increased, and the feed-meat ratio is decreased; the daily gain and the serum muramidase content of broilers are increased, and the feed-meat ratio and the death rate are decreased.
Owner:LIAONING WELLHOPE AGRI TECH
Composition with nutritional and moisturizing efficacies as well as preparation method and application of composition
ActiveCN105106075ASimple processLow costCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsPectinaseHydrolysate
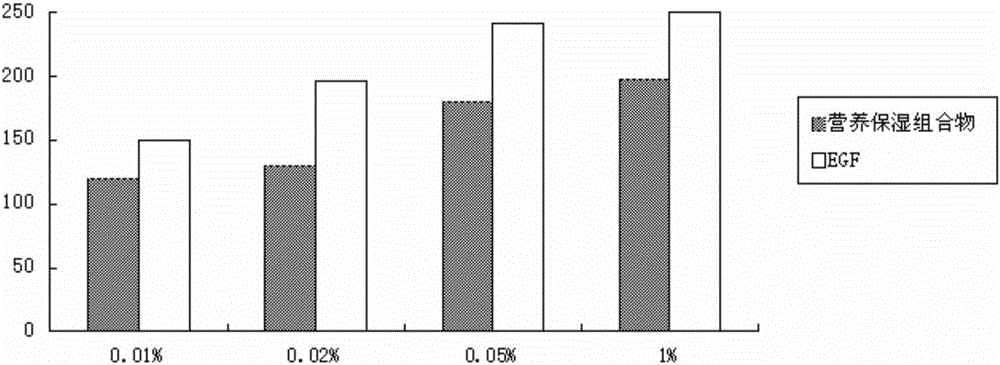
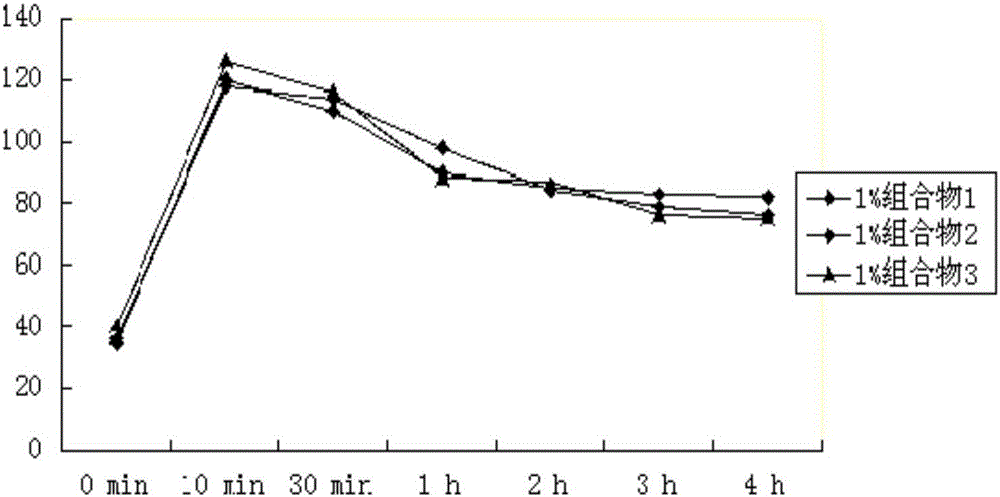
The invention discloses a composition with nutritional and moisturizing efficacies as well as a preparation method and application of the composition. The preparation method comprises the following steps: conducting ultrasonic treatment on chitosan, utilizing muramidase and cellulase for first-stage enzymolysis, and then utilizing chitosanase and pectinase for second-stage enzymolysis; after the enzymolysis reactions are finished, conducting inactivation, decolorization, solid-liquid separation and liquid taking on an enzymatic hydrolysate to obtain a chitooligosaccharides aqueous solution; uniformly mixing a beetroot extract, the chitooligosaccharides aqueous solution, methylisothiazolinone and phenoxyethanol to obtain the composition. The composition has a remarkable effect of nourishing skin and the remarkable capability of promoting the growth of fibroblasts affecting skin aging in the dermis layer; the composition can be utilized for preparation of daily cosmetics, and the market potential of the prepared daily cosmetics is great.
Owner:广州增城潮徽生物技术有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com