Method for antibacterial finishing loomage by immobilized lysozyme
A technology of antibacterial finishing and lysozyme, applied in the application field of biotechnology in textiles, can solve the problems of harm, inability to wash, poor heat resistance, etc., and achieve the effect of expanding applications
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0021] Embodiment 1: the present embodiment fabric is got woolen fabric, and concrete process step is as follows:
[0022] a. Wool fabric H 2 o 2 Oxidation pretreatment, process prescription and conditions are as follows: H 2 o 2 40mL / L, Na 2 SiO 3 3.5g / L, JFC 1.0g / L, 50°C, pH8.0-8.5, time 35min, bath ratio 1:50. After oxidation pretreatment, it was fully washed with deionized water and dried for later use.
[0023] b. Glutaraldehyde crosslinking: the H 2 o 2 The wool fabric after oxidation pretreatment is cut into small discs with a diameter of 1 cm, immersed in 0.2% glutaraldehyde solution, shaken at a low speed in a water bath constant temperature oscillator at 25°C for 6 hours, and fully washed with deionized water for 3- 4 times, dry and set aside.
[0024] c. Immobilization of lysozyme: put the above-mentioned wool fabric treated with glutaraldehyde in a lysozyme buffer solution (pH 7.0) with a concentration of 5 g / L, react at 4°C for 6 hours, take it out and w...
Embodiment 2
[0031] Embodiment 2: the present embodiment fabric gets cotton fabric, and concrete process step is as follows:
[0032] a. Vector preparation
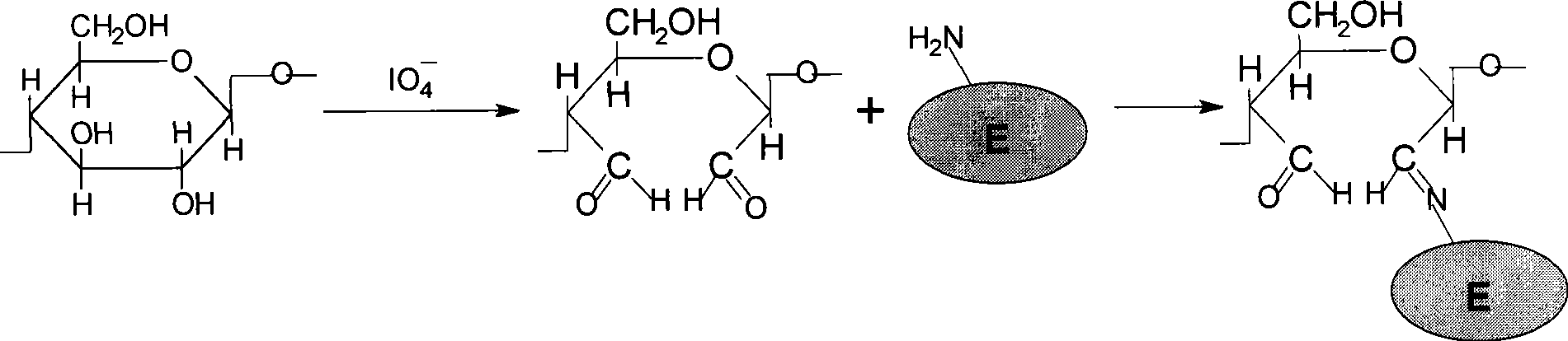
[0033] Soak 1.0g of bleached cotton fabric in 20mL of 0.40mol / L NaIO 4 solution, placed in a fully enclosed water bath constant temperature oscillator, and reacted at 25-50°C in the dark for 20-60 minutes, then washed with 0.10mol / L glycerin solution for 30 minutes to remove residual NaIO 4 , and then fully washed with distilled water to remove the glycerol, and blotted dry with filter paper for later use.
[0034] b. Immobilization of lysozyme
[0035] The above-prepared carrier dialdehyde-based cotton fabric was placed in a lysozyme buffer solution (pH 7.0) with a concentration of 5 g / L, and reacted at 4°C for 6 hours, then taken out, washed fully with deionized water, and air-dried at room temperature for later use.
[0036] In the present invention, the 2,3-dialdehyde-based cellulose produced by the selective oxidation reaction...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com