Patents
Literature
243 results about "Operative temperature" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Operative temperature (tₒ), also known as Dry resultant temperature, or Resultant temperature, is defined as a uniform temperature of an imaginary black enclosure in which an occupant would exchange the same amount of heat by radiation plus convection as in the actual nonuniform environment. Some references also use the terms 'equivalent temperature" or 'effective temperature' to describe combined effects of convective and radiant heat transfer.
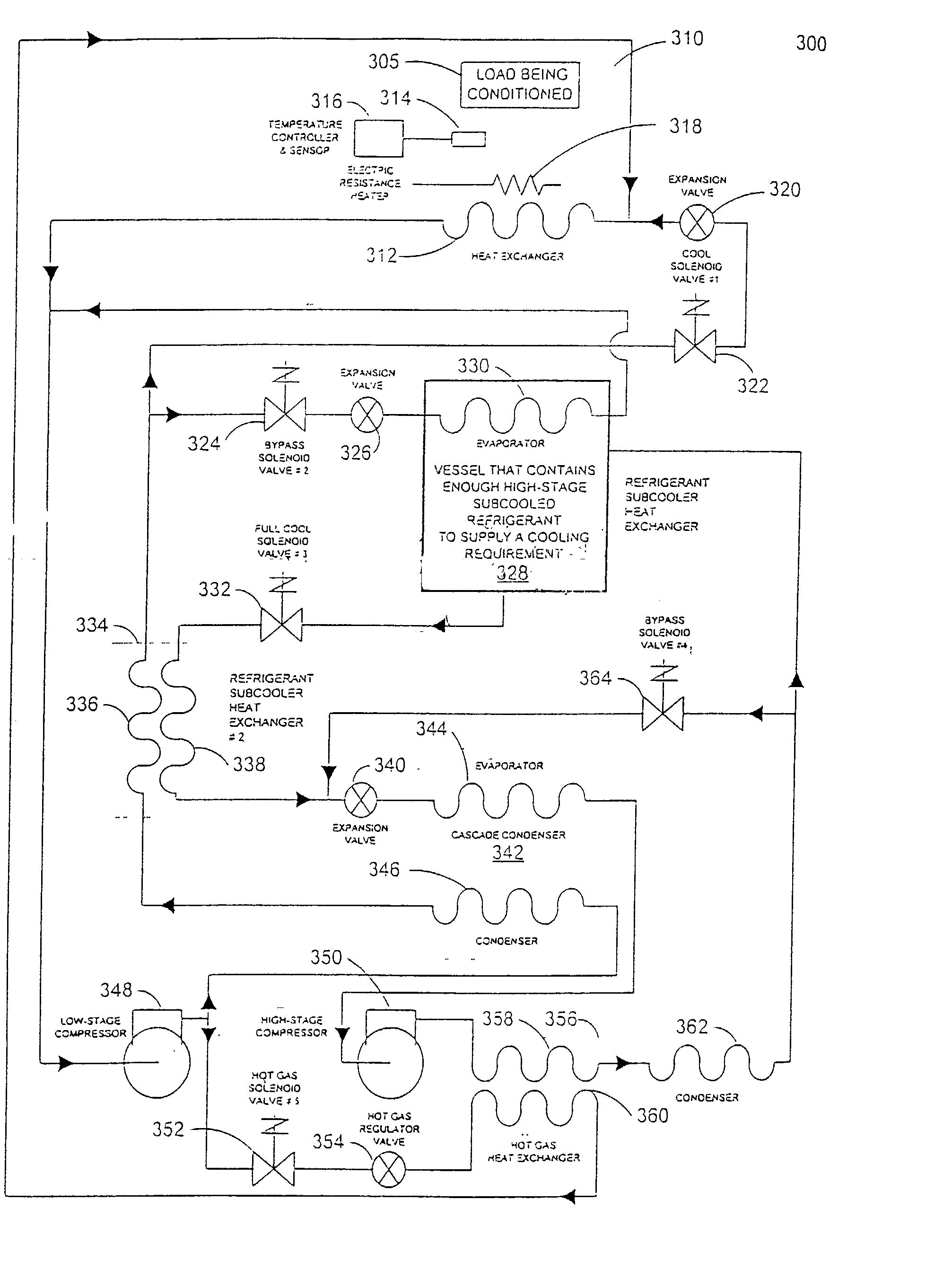
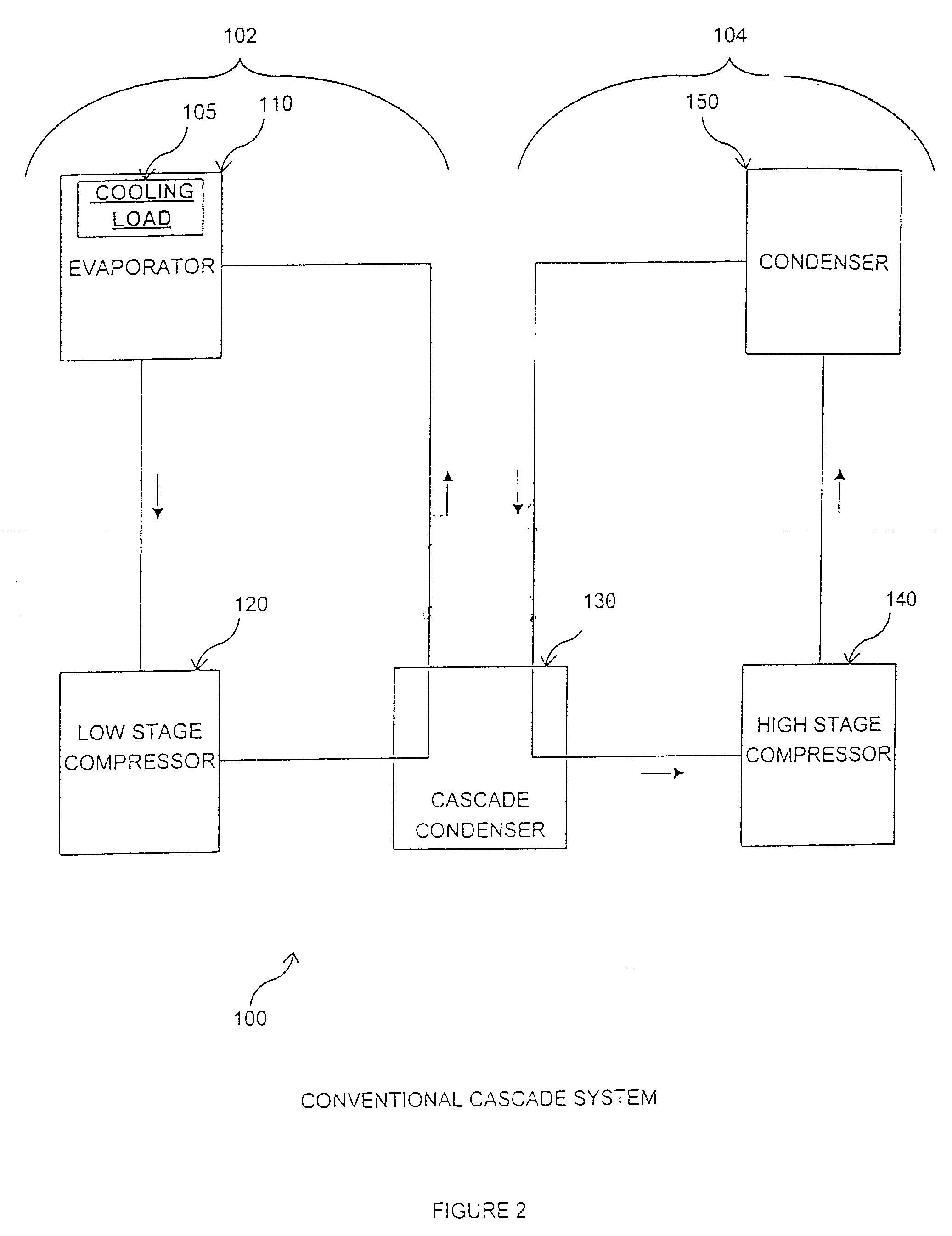
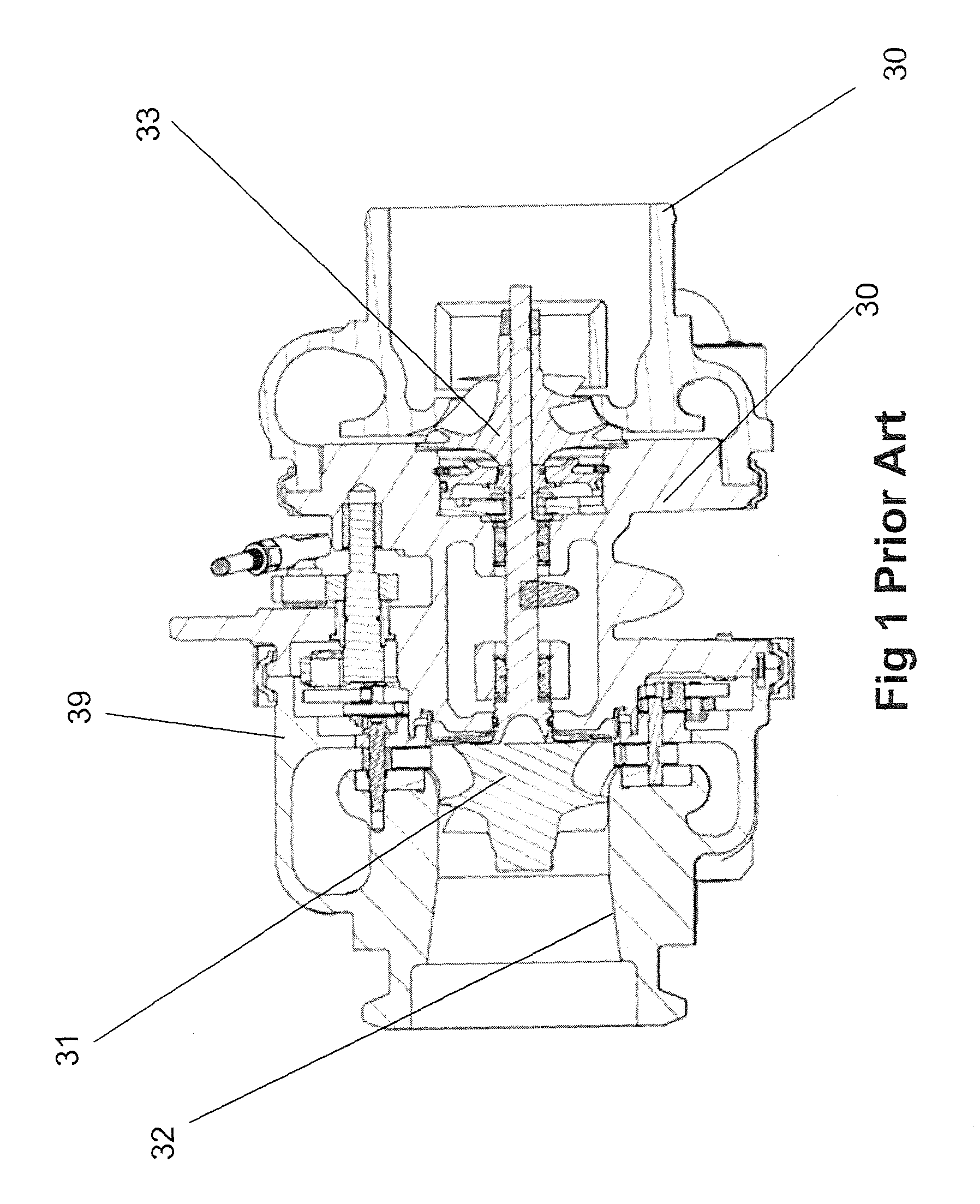
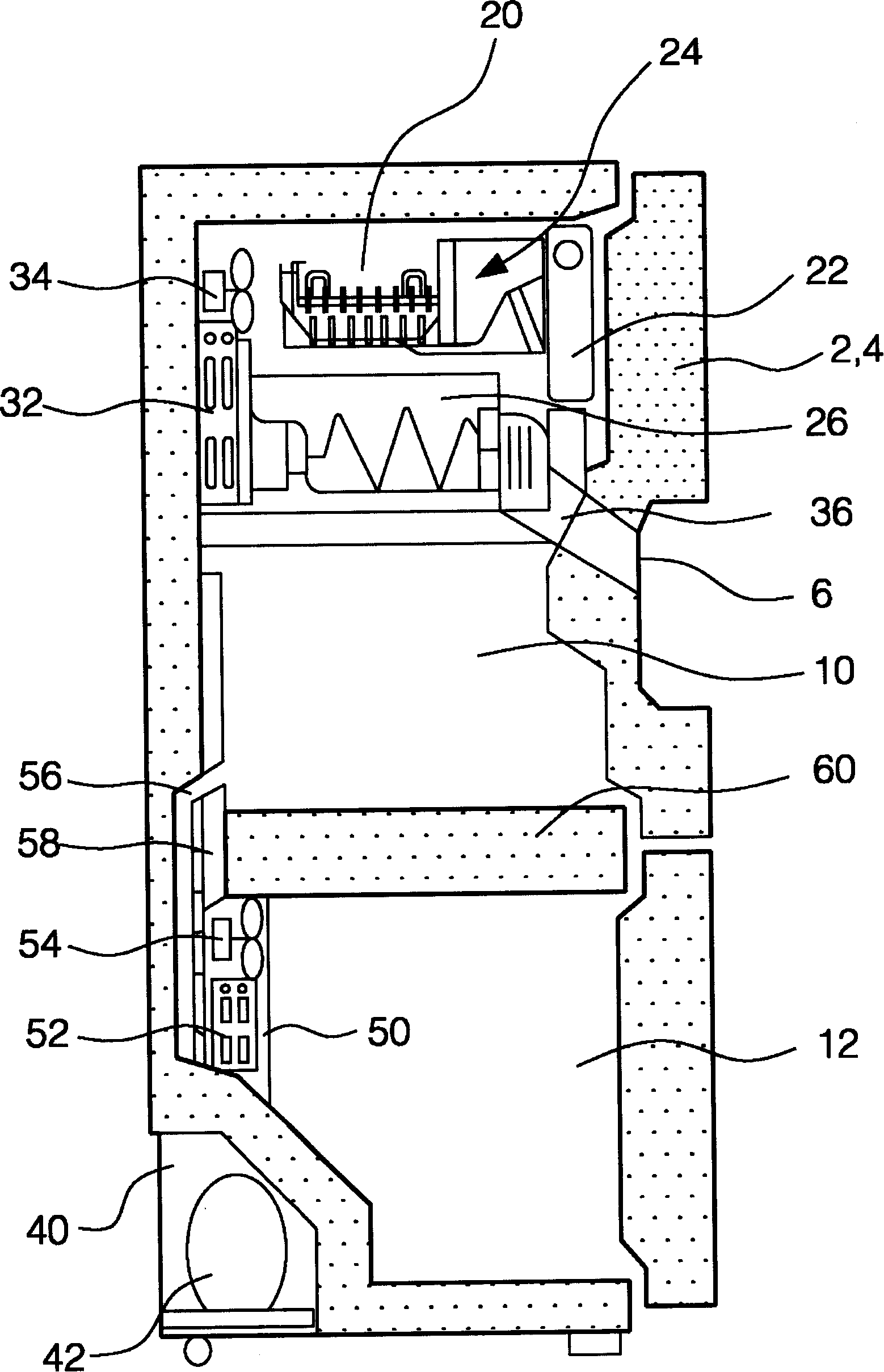
Refrigeration system for an environmental test chamber
InactiveUS20020148239A1Weather/light/corrosion resistanceCompression machines with several evaporatorsEngineeringSecondary stage
An environmental test chamber fast cool down and heat up system. The environmental test chamber fast cool down and heat up system comprises: an environmental test chamber having a fast cool down evaporator and fast heat up condenser coil, wherein the coil is selectively coupled either to receive a hot refrigerant gas flow or to receive a sub-cooled refrigerant flow; a cascade condenser coupled to the environmental test chamber; a primary stage sub-system coupled to the cascade condenser; a secondary stage sub-system coupled to the cascade condenser; and a thermal storage unit coupled to the primary stage sub-system and to the secondary stage sub-system. Wherein the environmental test chamber has an operational temperature down to about -125° F.
Owner:TRIESKEY GUY T
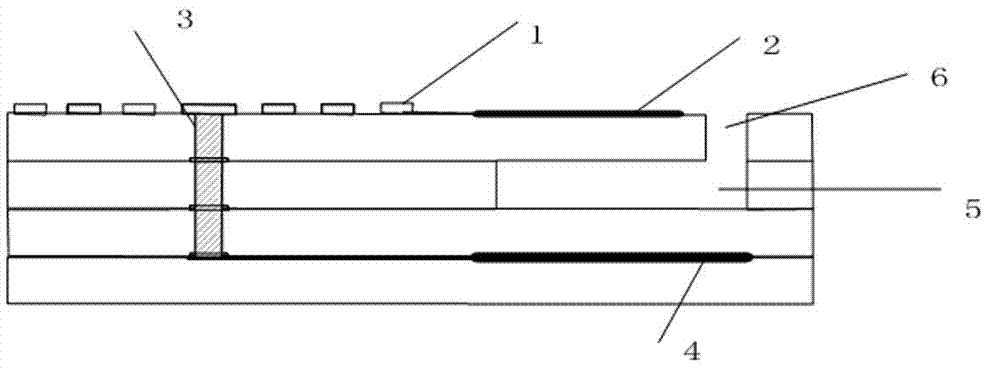
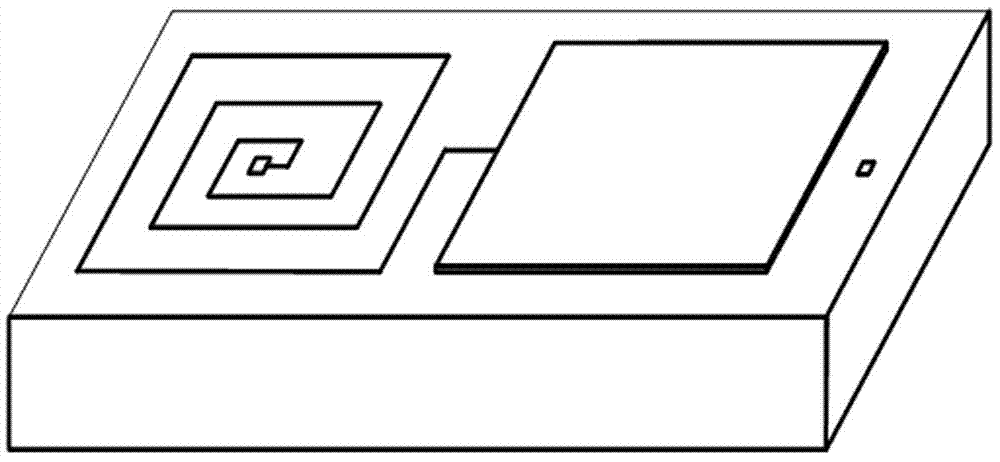
High-temperature pressure sensor and production method thereof
ActiveCN103115704AAvoid it happening againHigh sensitivityPrecision positioning equipmentLamination ancillary operationsCapacitanceSpiral inductor
The invention belongs to the technical field of pressure sensors, particularly relates to a high-temperature pressure sensor and a production method thereof and solves the problem that the existing pressure sensor fails to operate normally in environments of high temperature, moistness and the like due to the insufficiently reasonable design. The high-temperature pressure sensor comprises four layers. A planar square spiral inductor and a capacitor upper electrode are made on the first layer by pasting; a sealed pressure cavity is arranged on the second layer; a capacitor electrode is made on the fourth layer by pasting and is connected with an inner circular core of the top planar square spiral inductor. The production method includes filling the pressure cavity with carbon paste; subjecting the laminated structure to high-temperature sintering to volatilize carbon from air holes so as to form a complete cavity; and after sintering, placing glass beads at the air holes to allow for secondary sintering sealing. The high-temperature pressure sensor is capable of operating at normal temperature and high temperature more than 400 DEG C, and is simple in structure, small in size, simple in manufacture process and easy for industrial production.
Owner:ZHONGBEI UNIV
Thermatically operated bypass valve for passive warmup control of aftertreatment device
InactiveUS8234865B2Minimize timeMore energyOperating means/releasing devices for valvesInternal combustion piston enginesImpellerAfter treatment
In order for automobile exhaust catalysts to function they must be at operational temperatures. When an engine starts from cold the vehicle, including the exhaust system and any after-treatment device located therein, is at ambient temperature. Since 60% to 80% of the total emissions emitted occur at engine cold start and idle up to 120 seconds, it is imperative that the catalyst function as fast as possible. This invention provides a passive thermatically controlled bypass valve to enable the exhaust flow to bypass the enthalpy loss incurred by driving the turbine wheel of a turbocharger, and thus more rapidly deliver heat to the catalyst or after-treatment.
Owner:BORGWARNER INC
Liquid metal electromagnetic pump
InactiveCN101582627AEasily oxidizedAre more importantDynamo-electric machinesInsulation layerLiquid metal
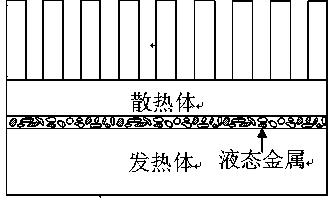
The invention discloses a liquid metal electromagnetic pump which comprises a pump ditch, an electromagnetic drive unit, a control system and the like. The pump ditch of the electromagnetic pump vertically passes through the electromagnetic drive unit and can freely move out of the electromagnetic drive unit, thus bringing convenience for maintenance. Variable diameter shrinkage ports at the two ends of the pump ditch are welded with interfaces of peripheral equipment; a progressive wave magnetic field generated by a magnetic coil drives a high-temperature liquid metal medium to flow in the pump ditch, and the flow rate of the liquid metal is adjusted by changing the current intensity in the magnetic coil. An insulation layer between the magnetic coil and the pump ditch isolates the high-temperature radiation of the liquid metal, circulating cooling water is led into the hollow magnetic coil to reduce the temperature of the coil, and the comprehensive effect of the two causes the electromagnetic pump to be capable of working in the liquid metal environment with higher temperature. The liquid metal electromagnetic pump is applicable to the transmission and application of liquid metal with the characteristics of high working temperature, strong corrosiveness, easy oxidization, or large specific gravity and the like, and has the advantages of simple and convenient operation, high efficiency, long service life and the like.
Owner:INST OF PLASMA PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Zinc-containing multiphase liquid metal thermal interface material and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a zinc-containing multiphase liquid metal thermal interface material and a preparation method thereof. The zinc-containing multiphase liquid metal thermal interface material comprises the following components: by weight, 30-40% of bismuth, 10-20% of tin, 10-20% of zinc, and the balance of indium. The multiphase structure liquid metal thermal interface material designed by the invention is a quaternary alloy, is completely in a solid structure at room temperature and rolling temperature, and in a liquid-solid state at working temperature. In the working status, the solid content is about 60%. The multiphase structure liquid metal thermal interface material can maintain the liquid-solid state in a large range of working temperature, can fully inhibit the heated melting fluidity of a low melting point alloy foil, and can eliminate the liquid droplet leak problem. In addition, the thermal interface material thickness remains in the vicinity of 0.04mm, and the liquid phase surface tension can be further used to achieve the anti leakage effect..
Owner:NINGBO SYRNMA METAL MATERIALS CO LTD
Devices and methods for controlling patient temperature
Relatively non-invasive devices and methods for heating or cooling a patient's body are disclosed. Devices and methods for treating ischemic conditions by inducing therapeutic hypothermia are disclosed. Devices and methods for inducing therapeutic hypothermia through esophageal cooling are disclosed. Devices and methods for operative temperature management are disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED COOLING THERAPY INC
Inherent safety pool case combination low-temperature stack nuclear heating station apparatus and operational procedure thereof
InactiveCN101441902AIncreased average volume specific powerReduce initial loadIntegral reactorsNuclear energy generationInherent safetyPressurized water reactor
The present invention provides an inherent security pool-shell combination low temperature nuclear heating device and an operation program thereof, which belongs to nuclear energy centralized heat-supply field. The invention mainly comprises the following procedures: adopting separated layout, forced circulation and high effective small temperature difference heat exchange in primary loop of reactor; under the precondition that parameter requirements of centralized heat-supply by big cities heat supply network satisfied, reducing work temperature of shell-type heating reactor as far as possible; meanwhile optimized layout of equipment, and organic combination of normal pressure pool in large volume (47) and shell-style heating reactor(29) remove accident possibility of water loss and coldness loss of reactor core (1). Complete inherent safety principle is carried out in the invention. Thus, absolute security of nuclear heating can be guaranteed by using mature pressurized water reactor technology, and enterprises have develop nuclear station pressurized water reactor experience can possibly jump over research and develop stage and enter into nuclear heating market directly, and make a real contribution for energy-saving and emission-reduction and improving country energy structure.
Owner:肖宏才
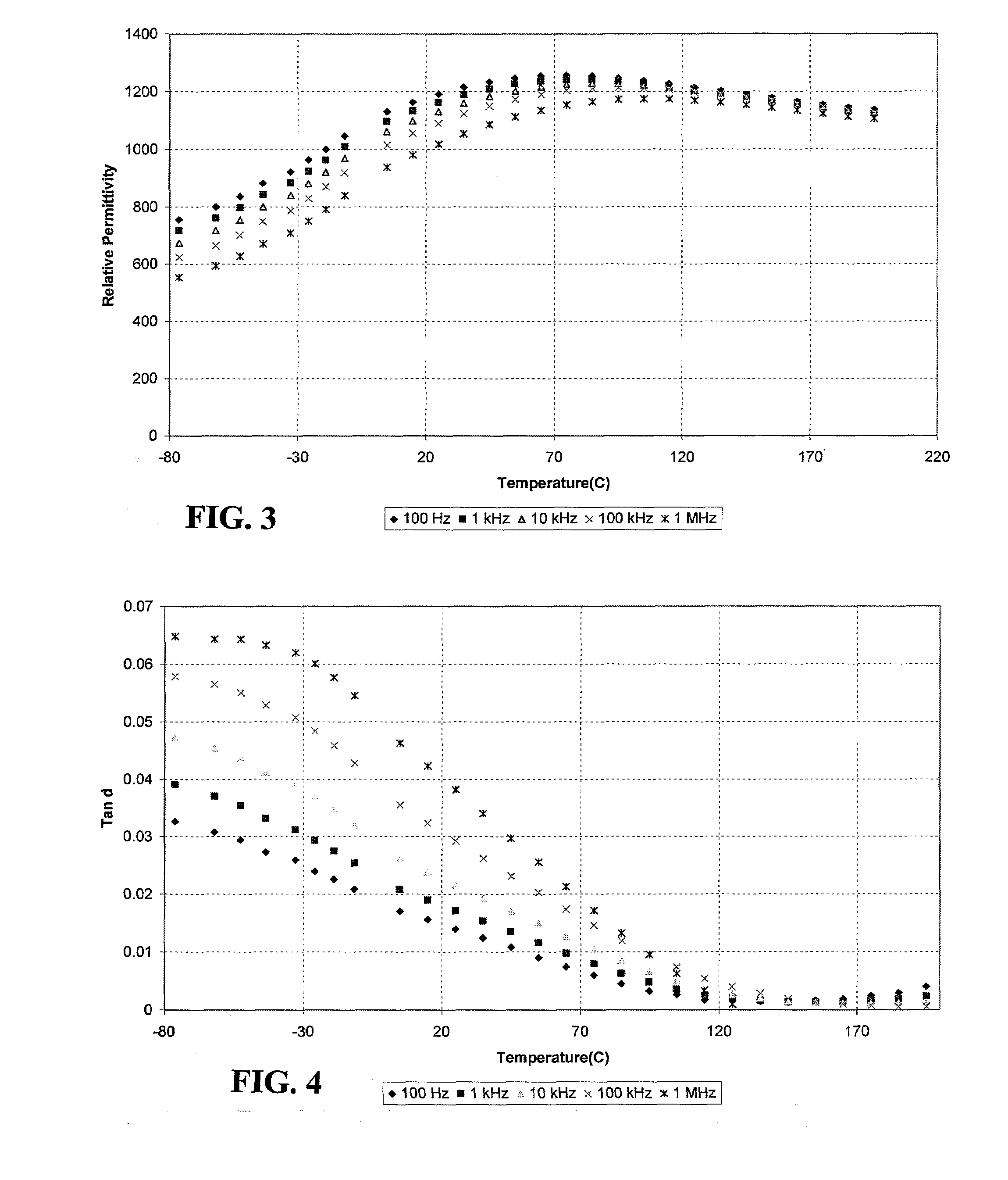
High-Temperature Dielectric Materials and Capacitors Made Therefrom
InactiveUS20080239627A1Reduce lossHigh dielectric constantFixed capacitor dielectricFixed capacitor terminalsCapacitanceLow voltage
A ceramic dielectric composition suitable for preparing capacitors for use in high-temperature service conditions is disclosed. The ceramic material and capacitors made from it exhibit unique and heretofore unrealizable properties including low variation in capacitance with voltage up to high fields, low variation in capacitance with temperature over a broad temperature range, retained high permittivity at temperatures up to 200° C. and beyond, low loss, low field-induced strain and adequate capacitance to retain performance at very low service temperatures. The material is based on sodium bismuth titanate (NBT) with selected additions of substituents and dopants to broaden and flatten its dielectric response, lower loss, lower strain, lower voltage coefficient and increase resistivity.
Owner:ALFRED UNIVERSITY +1
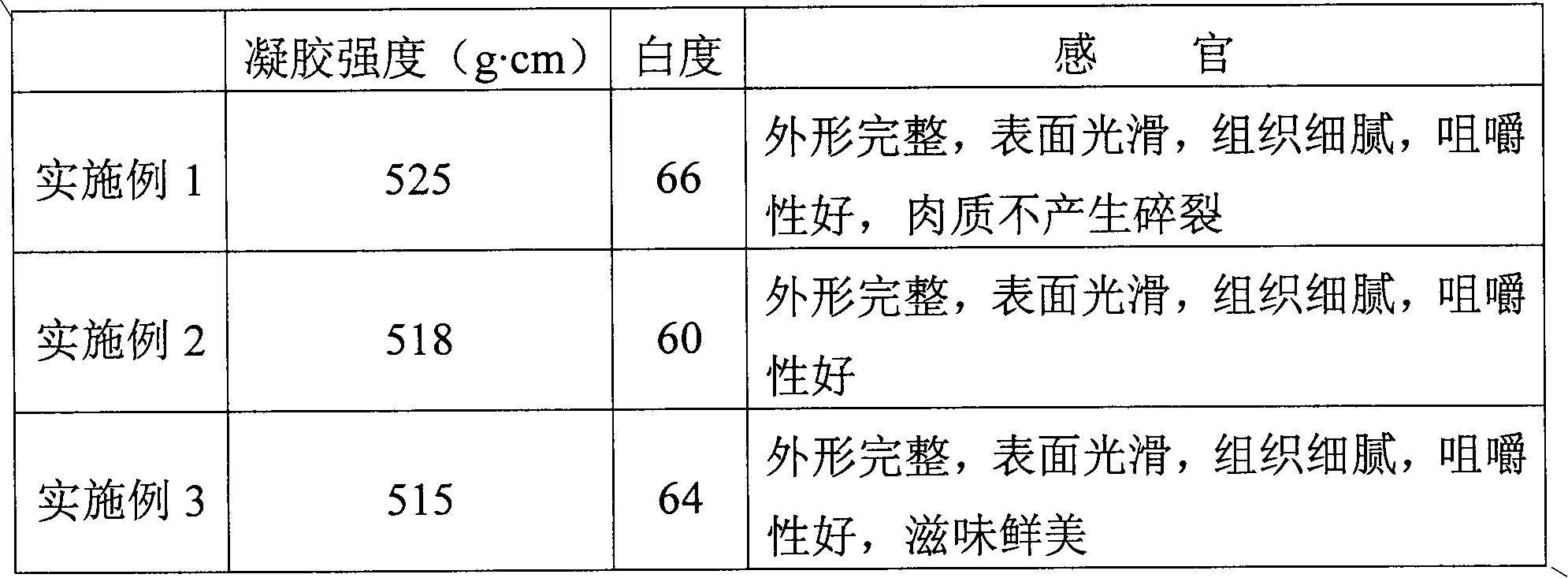
Method for preparing squid surimi
Owner:福州百洋海味食品有限公司
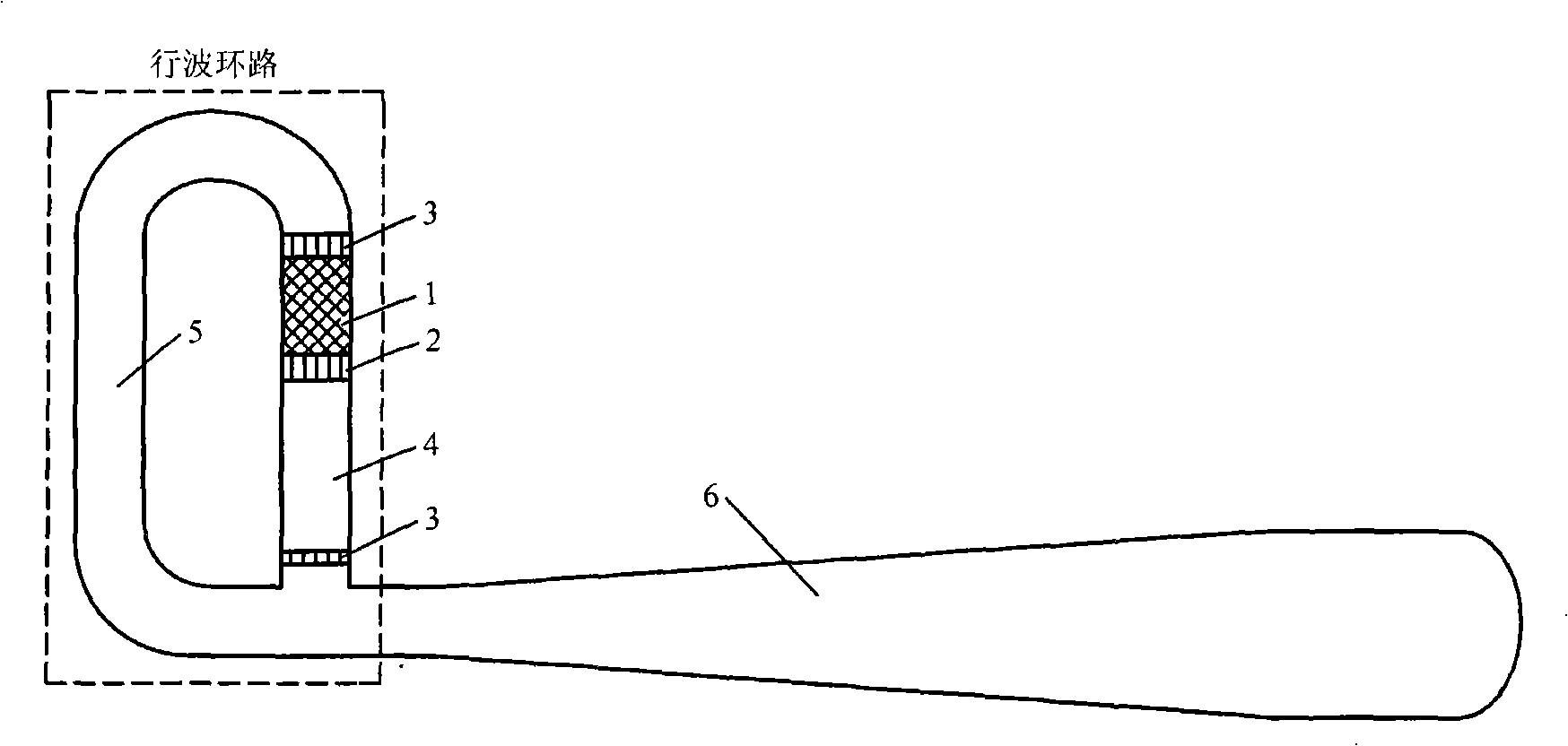
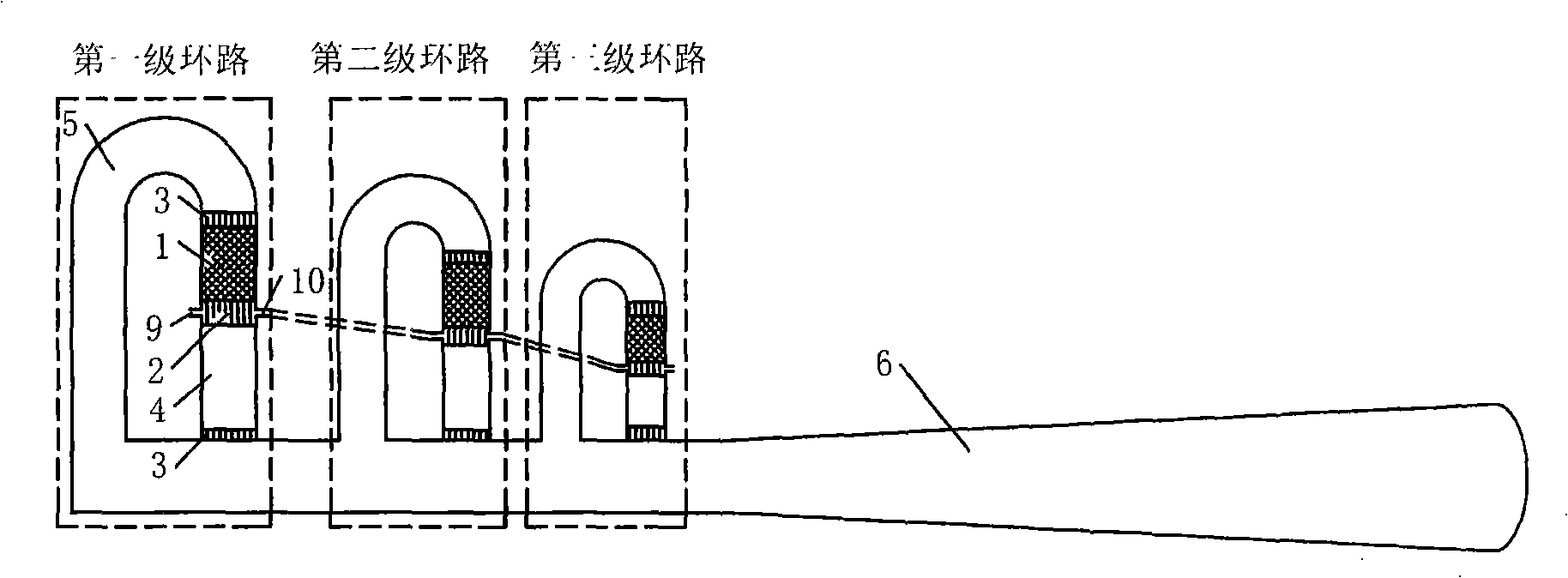
Thermo-acoustic engine system using temperature-variable heat source
InactiveCN101294554AImprove conversion efficiencyCompact structureStirling type enginesCompression machinesThermoacousticsMechanical energy
The invention provides a thermo-acoustic engine system by adopting variable-temperature heat source. The system comprises a resonant tube. The resonant tube is provided with a mechanical energy output device and at least two stages of traveling wave loops; all the traveling wave loops share the resonant tube; each traveling wave loop is provided with a high-temperature heat exchanger; the high-temperature heat exchanger is provided with an input port and an output port used as the input and output medium; the output port of the high-temperature heat exchanger of the previous traveling wave loop communicates with the input port of the high-temperature heat exchanger of the next traveling wave loop, and the working temperature of the high-temperature heat exchangers of the at least two stages of traveling wave loops gradually reduce from the previous traveling wave loop to the next traveling wave loop. The system improves the heat conversion efficiency and has compact structure.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
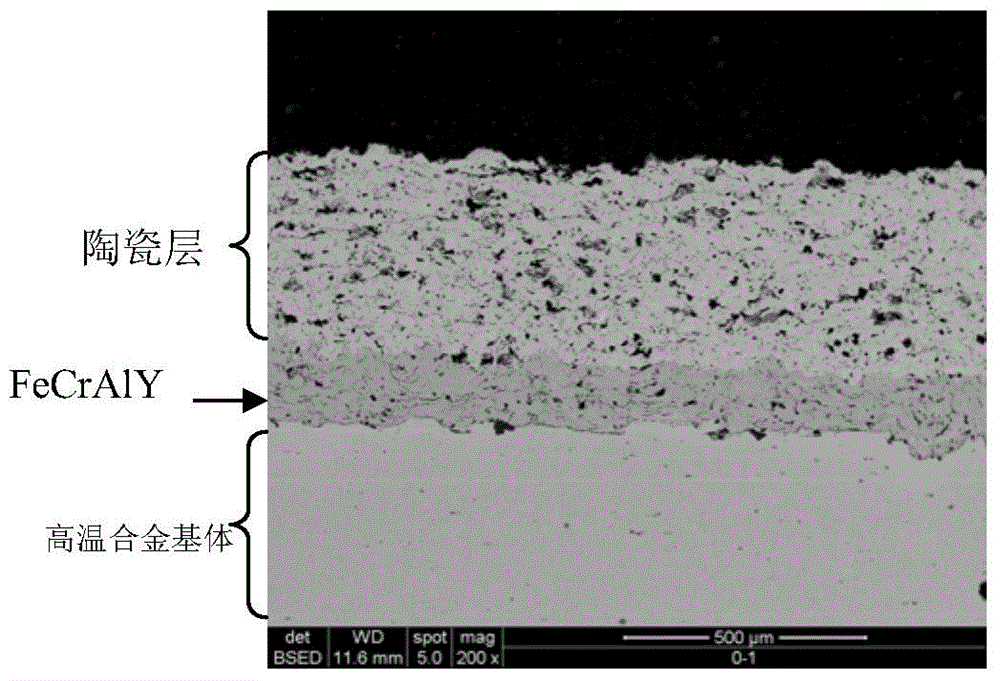
Preparation method of thermal barrier coating containing long-service-life antioxidant bonding layer
InactiveCN104630686APromote growthImprove antioxidant capacityMolten spray coatingVacuum evaporation coatingElectron beam physical vapor depositionGas phase
The invention relates to a preparation method of a thermal barrier coating containing a long-service-life antioxidant bonding layer. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) sequentially performing deoiling and sand blasting treatment on a high-temperature alloy matrix; (2) preparing a metal bonding layer on the high-temperature alloy matrix by virtue of atmosphere plasma spraying, low-pressure plasma spraying, high-speed oxygen flame spraying or high-speed compressed air flame spraying; and (3) then depositing a ceramic layer on the metal bonding layer by virtue of atmosphere plasma spraying, high-speed oxygen flame spraying, supersonic plasma spraying, solution plasma spraying or electron beam physical vapor deposition. Compared with the prior art, the thermal barrier coating prepared by using an FeCrAlY bonding layer, disclosed by the invention, has higher working temperature and slower oxidation layer growth rate compared with that of a conventional MCrAlY thermal barrier coating (M refers to Ni and Co) so as to avoid the interfacial properties of the bonding layer and the ceramic layer from forming a brittle Ni2Al2O4 phase; and the thermal barrier coating has excellent high-temperature oxidation resistance and longer service life.
Owner:HENAN PULAIMU COATING TECH +1
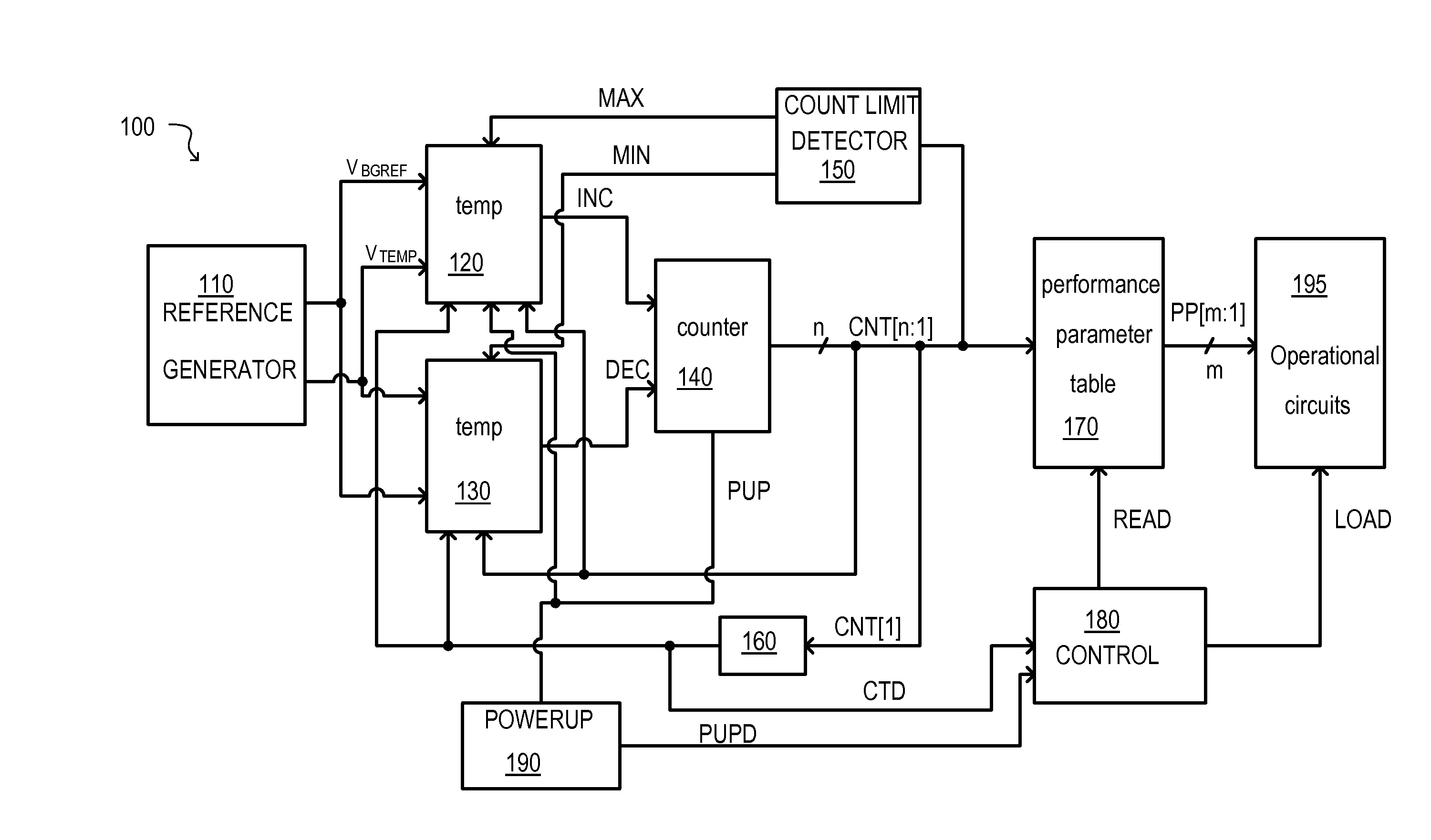
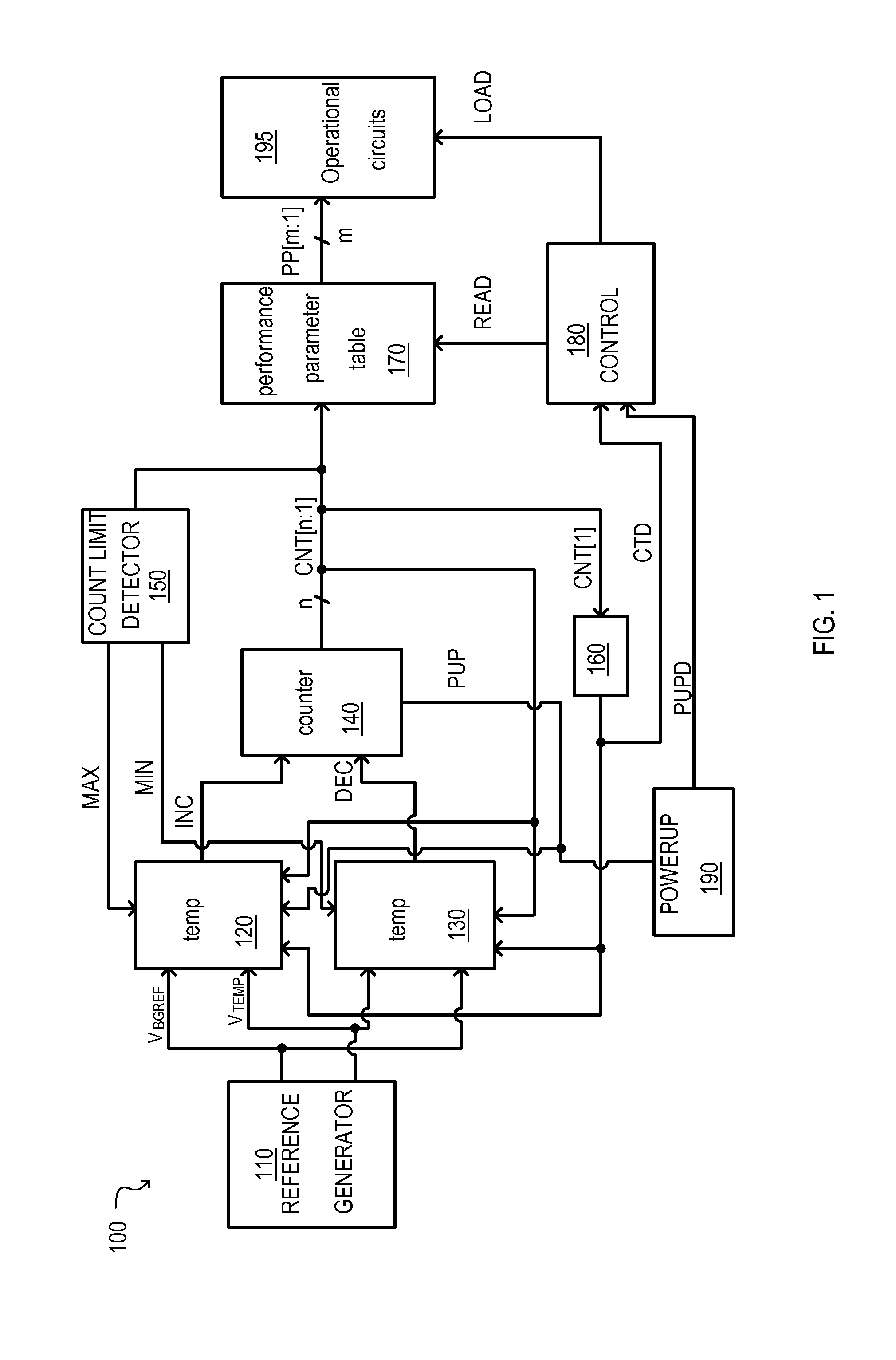
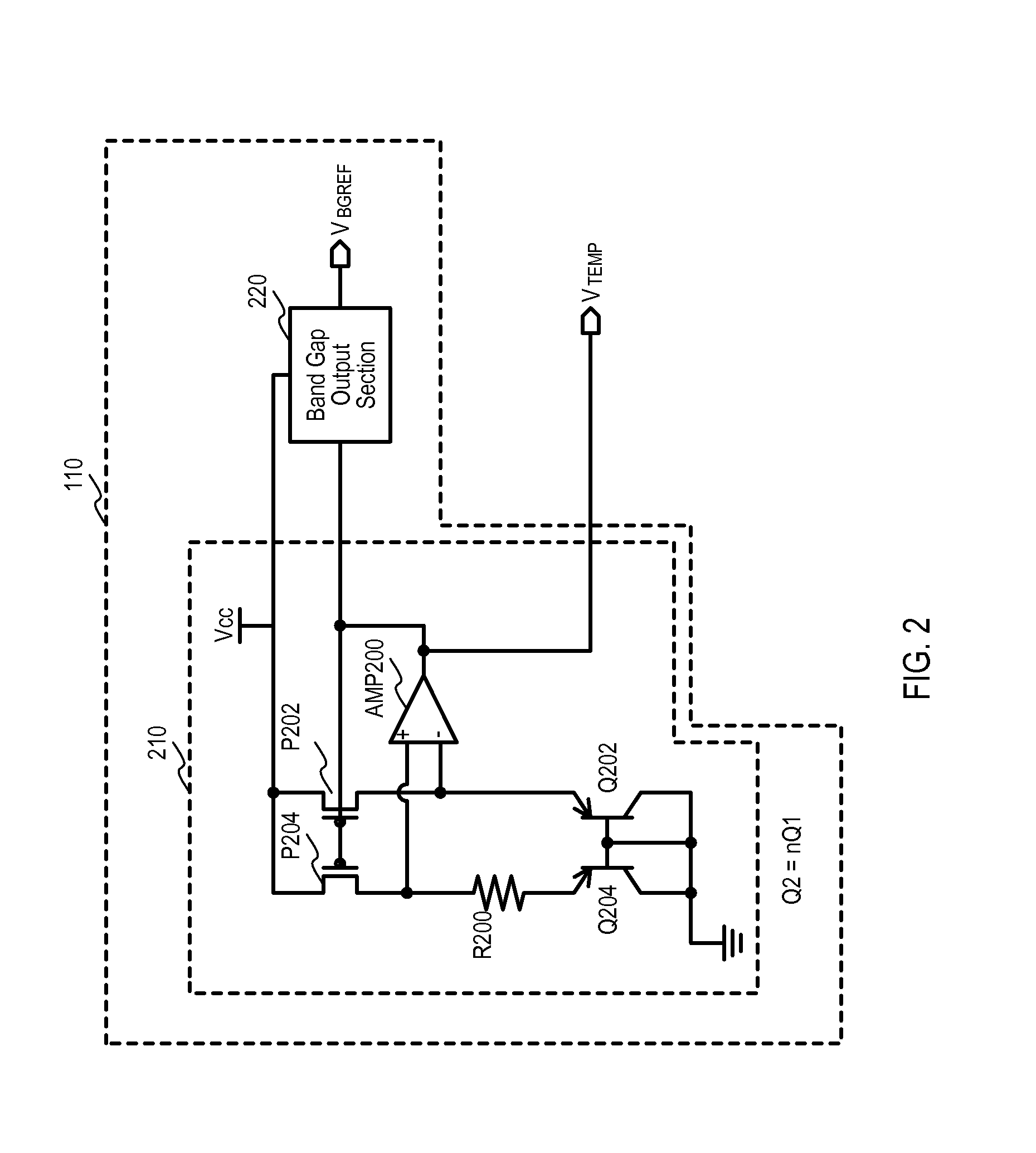
Semiconductor device having temperature sensor circuit that detects a temperature range upper limit value and a temperature range lower limit value
ActiveUS20150276500A1Boards/switchyards circuit arrangementsThermometers using electric/magnetic elementsLower limitEngineering
A semiconductor device that may include at least one temperature sensing circuit is disclosed. The temperature sensing circuits may be used to control various operating parameters to improve the operation of the semiconductor device over a wide temperature range. In this way, operating specifications of a semiconductor device at worst case temperatures may be met without compromising performance at other operating temperatures. The temperature sensing circuit may provide a plurality of temperature ranges for setting the operational parameters. Each temperature range can include a temperature range upper limit value and a temperature range lower limit value and adjacent temperature ranges may overlap. The temperature ranges may be set in accordance with a count value that can incrementally change in response to the at least one temperature sensing circuit.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
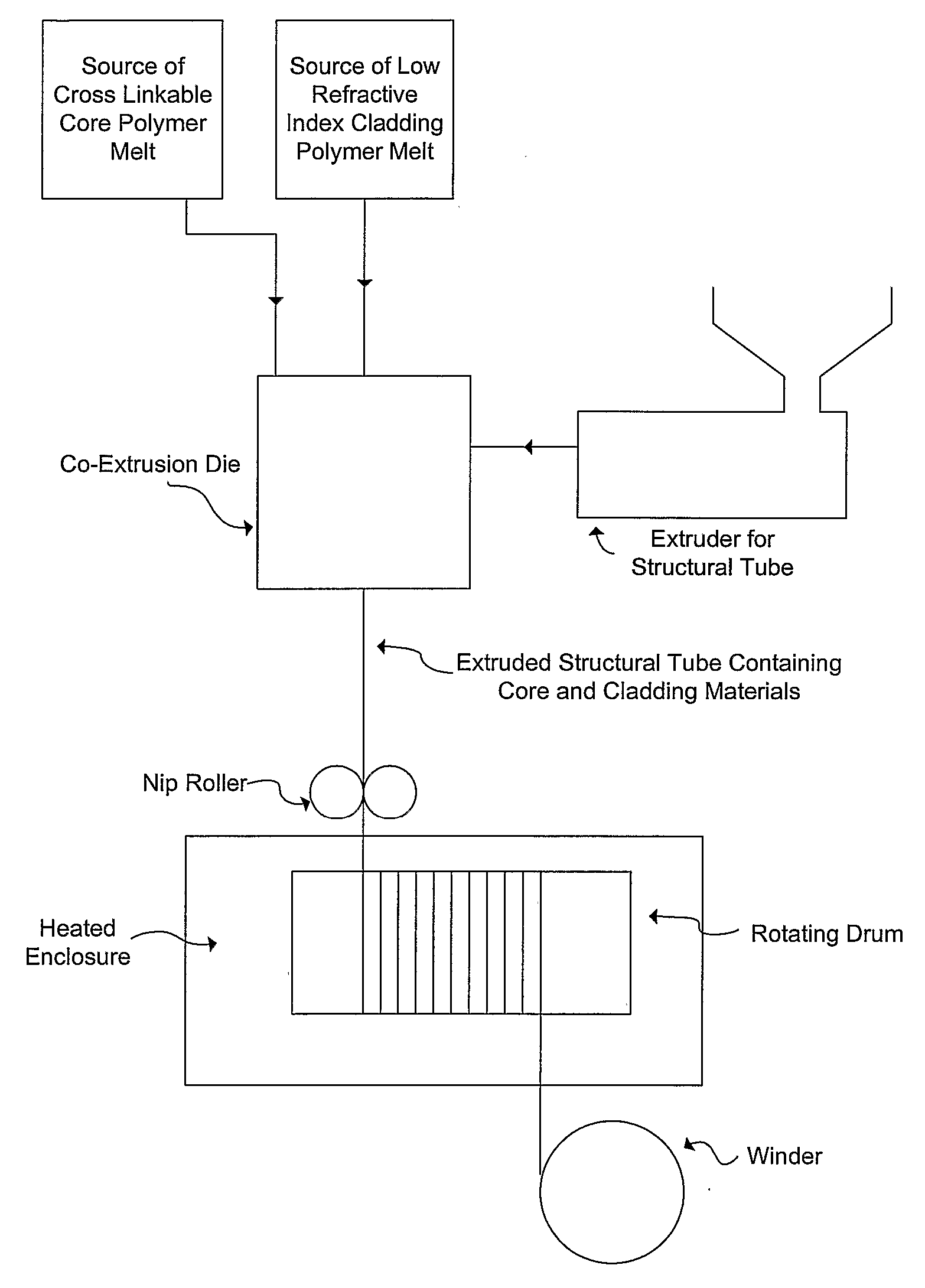
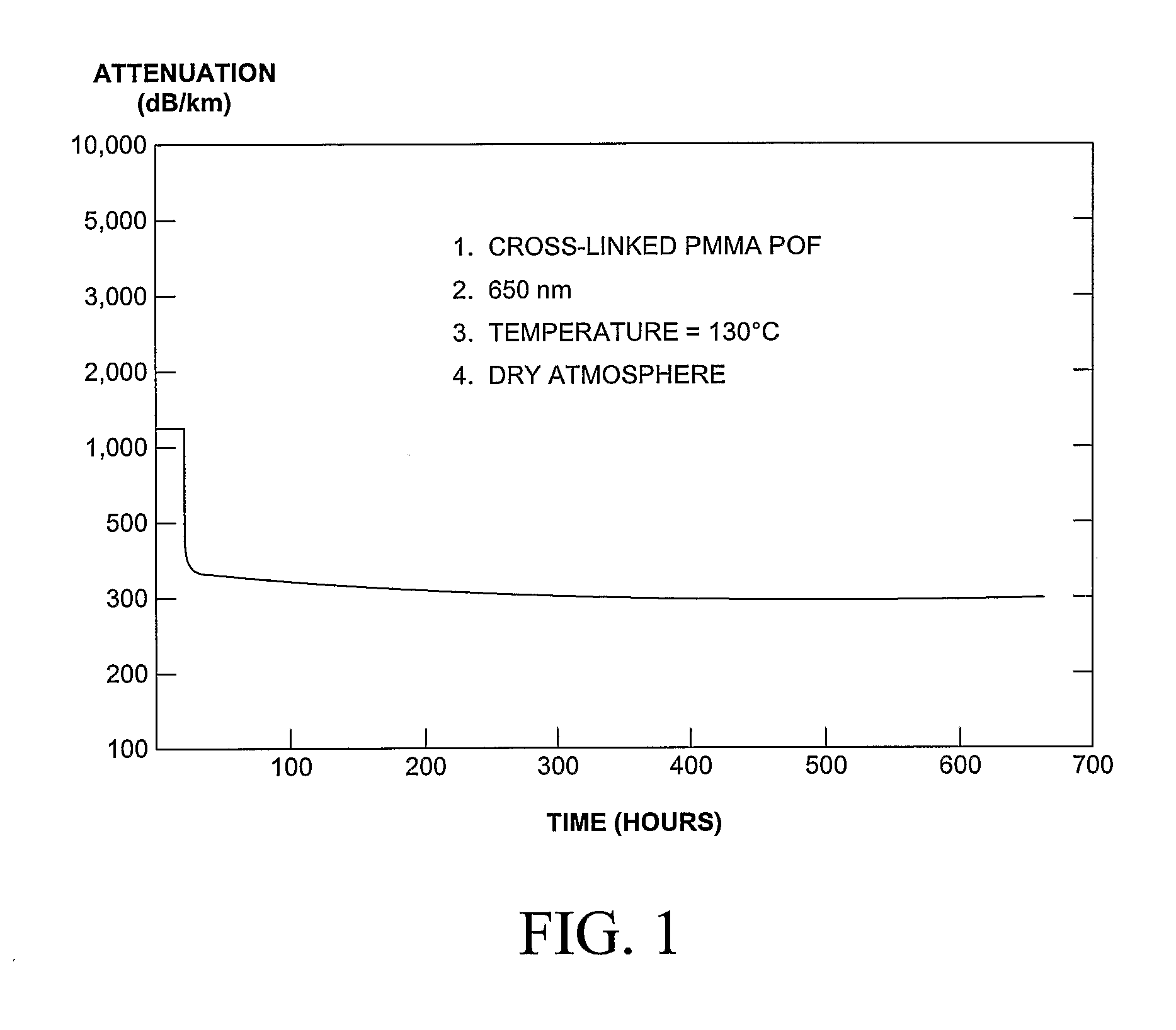
Manufacturing Method of Acrylic Optical Fiber with Improved Environmental Stability
InactiveUS20080061457A1Improve heat resistanceOptical articlesMulticore optical fibreChemical structureFiber
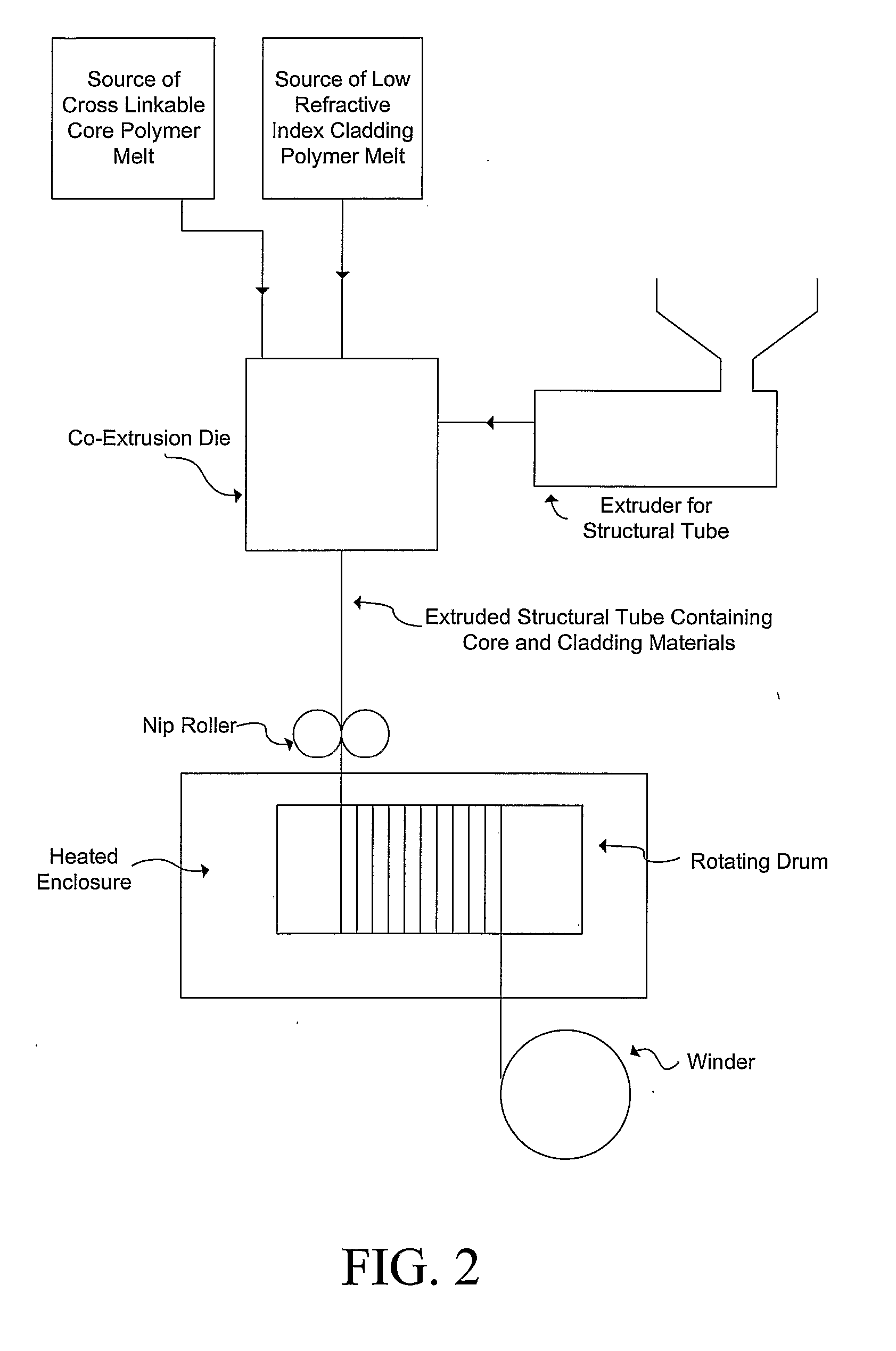
The subject invention pertains to a method and apparatus for manufacturing a plastic optical transmission medium. The subject invention also relates to materials for use in producing plastic optical transmission medium. The subject method can allow continuous high-speed production while controlling the refractive index profile, step or graded, of the optical transmission medium. In a specific embodiment, the medium POTM can have high optical transmission, and be able to operate in conditions up to 125° C. at 95% R.H. In a specific embodiment of the subject invention, two or more concentric cylinders of transparent polymer melts, of which at least one is a cross-linkable material, can be utilized to produce a plastic optical transmission medium. In addition, zero, one, or more transparent, nonreactive, low molecular weight diffusible additive(s) can be added to zero, one, or more of the transparent polymer melts to provide a graded refractive index profile. The molecular weights and chemical structures of the index modifying additives can be chosen to ensure their diffusion constants are low enough to provide a stable refractive index profile at the desired operating temperature of the fiber. The cylinders of melt can be extruded into a solidified polymeric tube via, for example, a cross-head type of die. The tube containing the melt materials can be maintained at high temperature for a specific time period, such that the cross-linking can occur and, optionally, the additives can diffuse within the polymeric tube.
Owner:NANOPTICS
High-stability light source system and method
InactiveUS20150146751A1Stable outputMinimize control errorLaser detailsElectroluminescent light sourcesDriver circuitControl signal
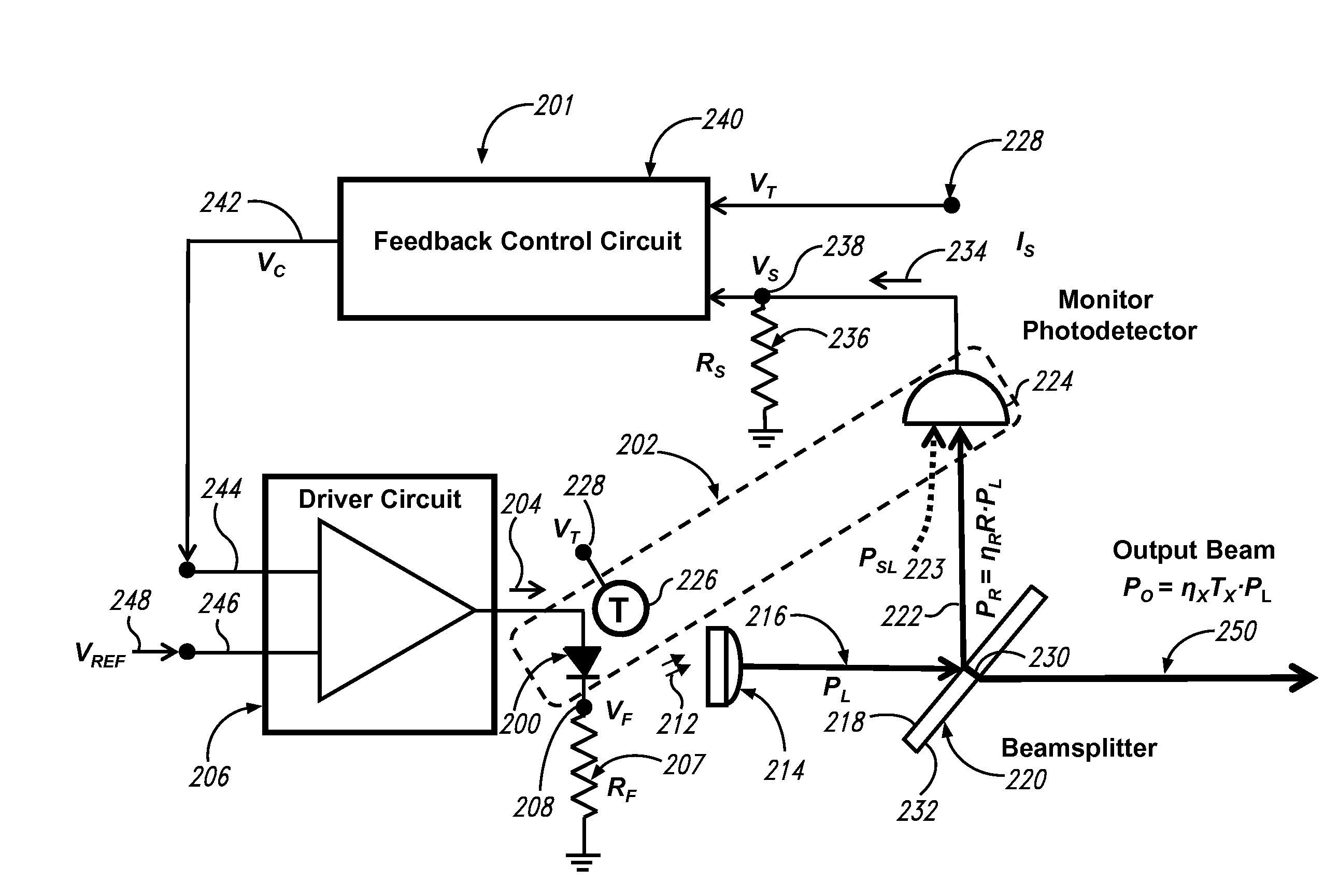
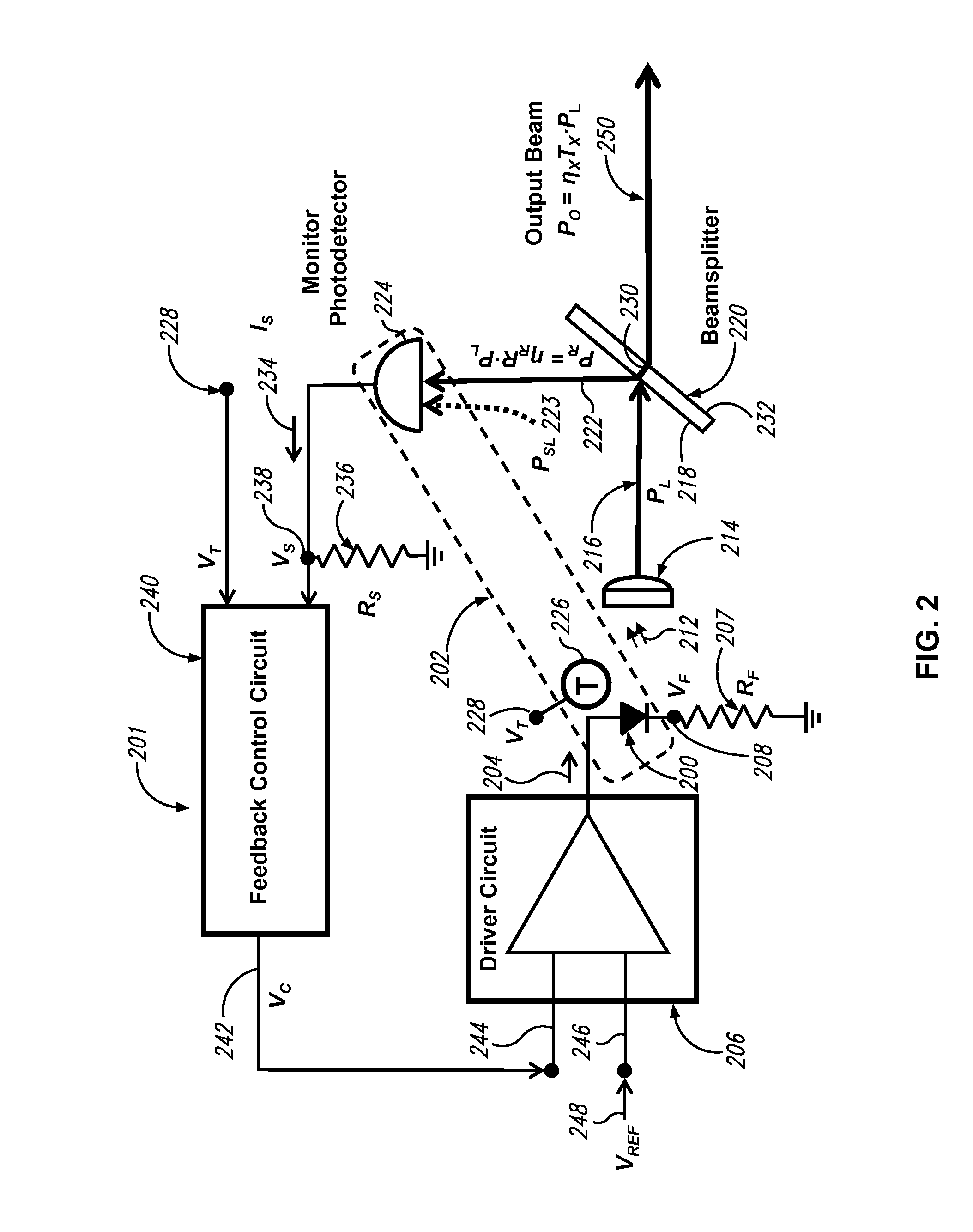
A light source system that generates stable optical power over time and temperature in which a feedback control circuit is operative to receive a temperature signal and a sample signal and in response thereto generate a control signal to a driver circuit to maintain a power level of the light output substantially constant over an operative temperature range defined by Tmin and Tmax.
Owner:USL TECH
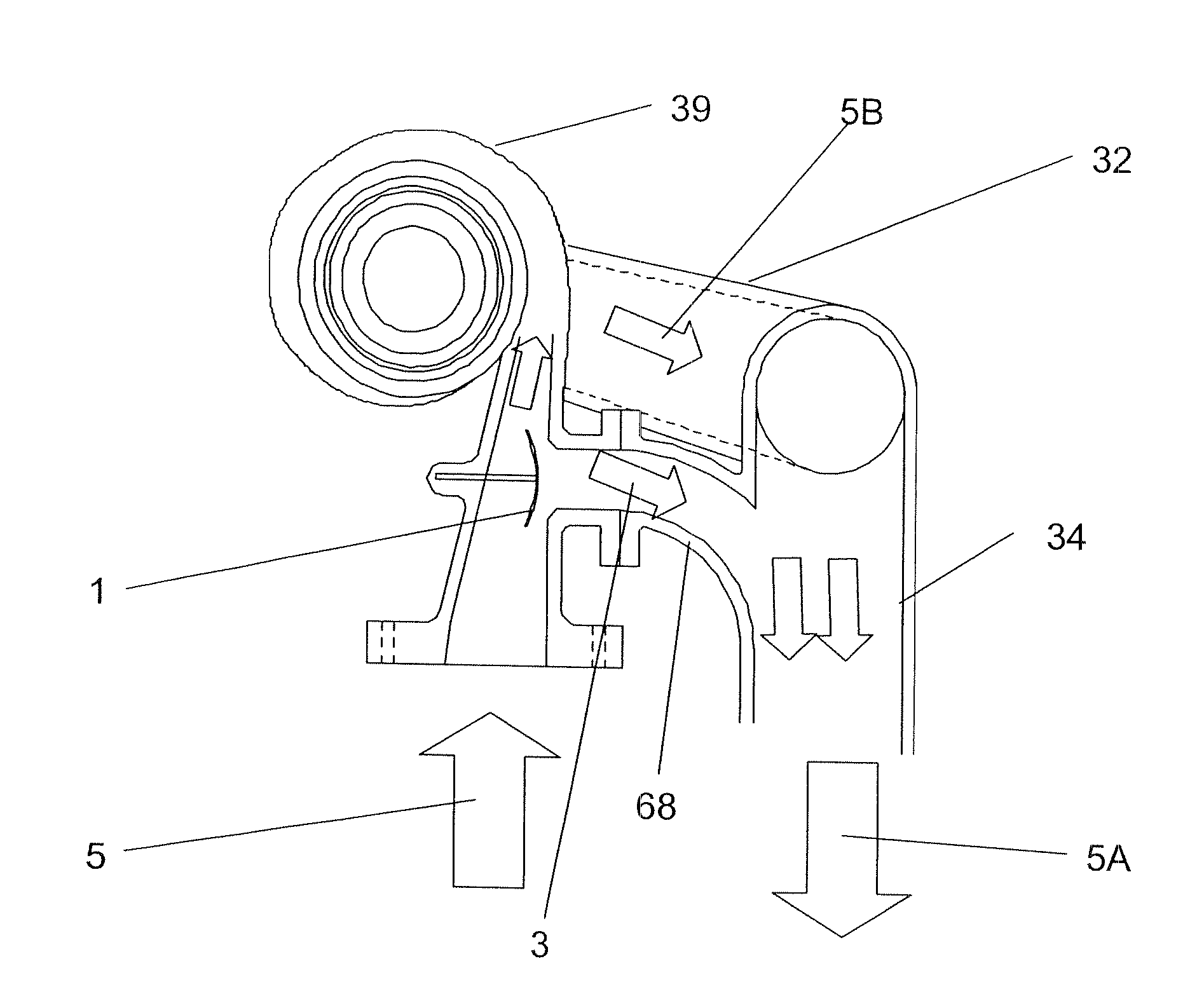
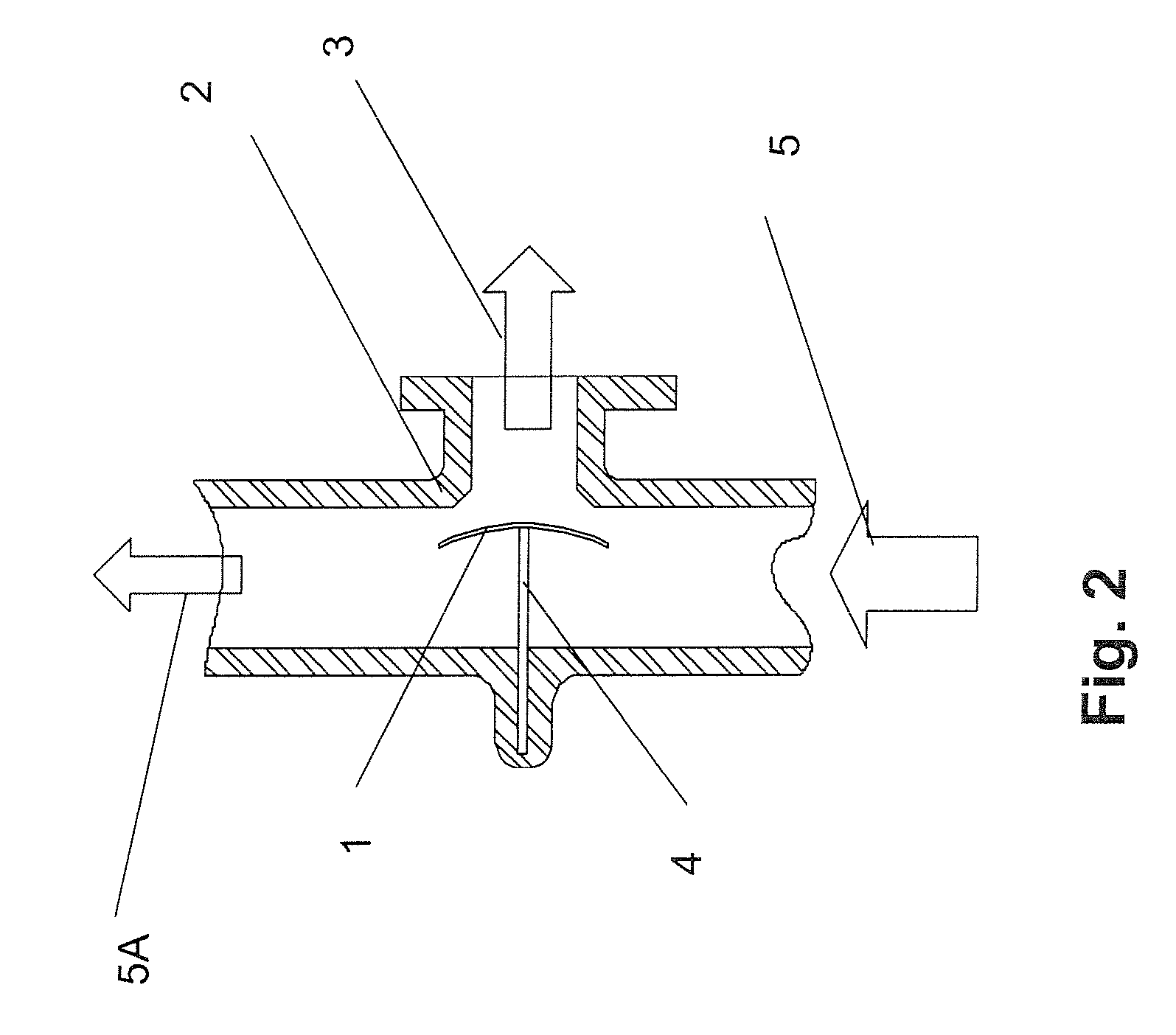
Devices and methods for controlling patient temperature
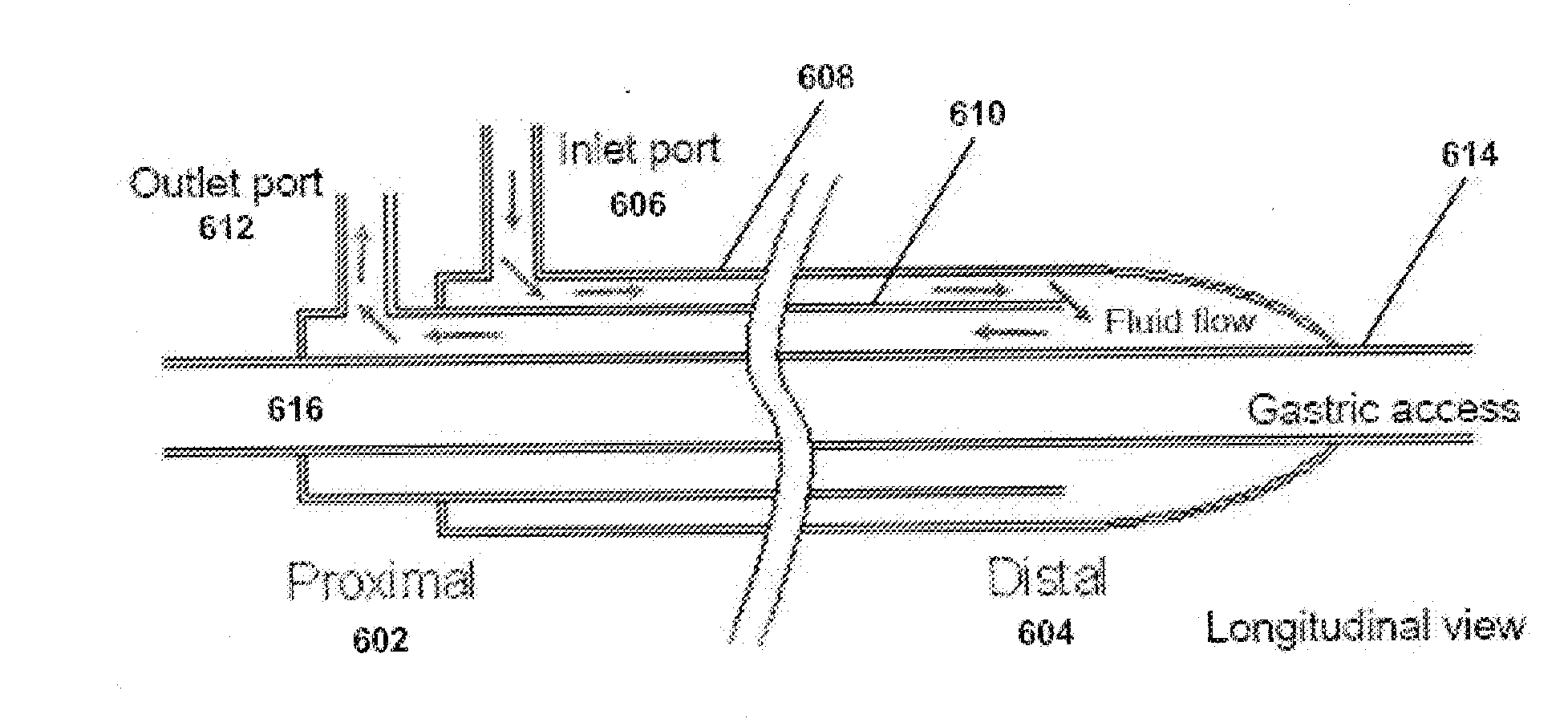
ActiveUS20140155965A1Restricts gastric ventilationReduce pressure buildupDiagnosticsSurgeryNon invasiveBiomedical engineering
Relatively non-invasive devices and methods for heating or cooling a patient's body are disclosed. Devices and methods for treating ischemic conditions by inducing therapeutic hypothermia are disclosed. Devices and methods for inducing therapeutic hypothermia through esophageal cooling are disclosed. Devices and methods for operative temperature management are disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED COOLING THERAPY INC
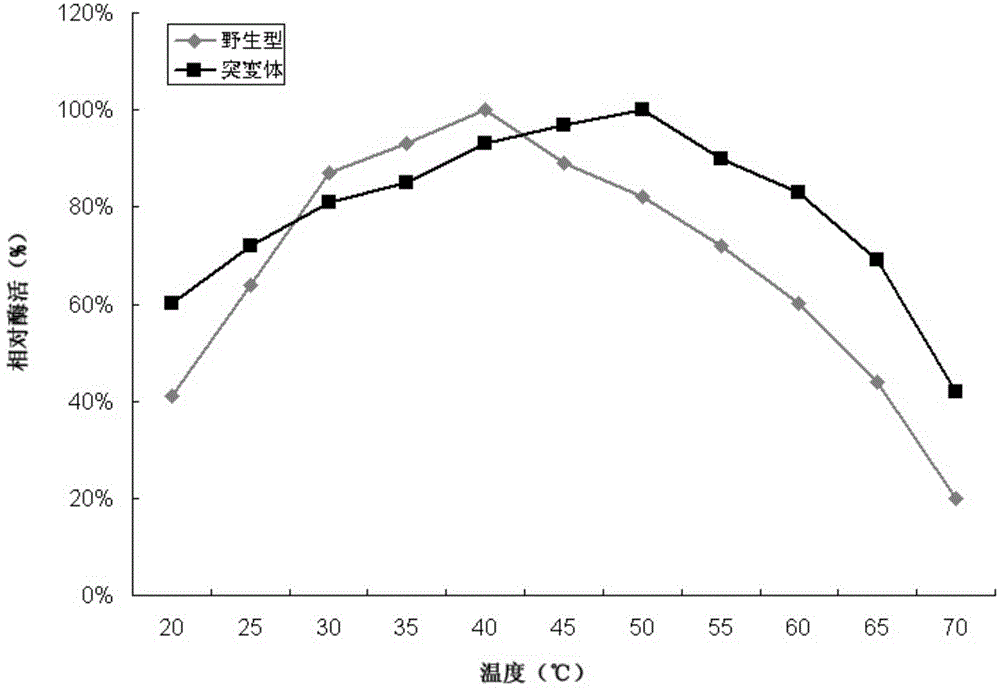
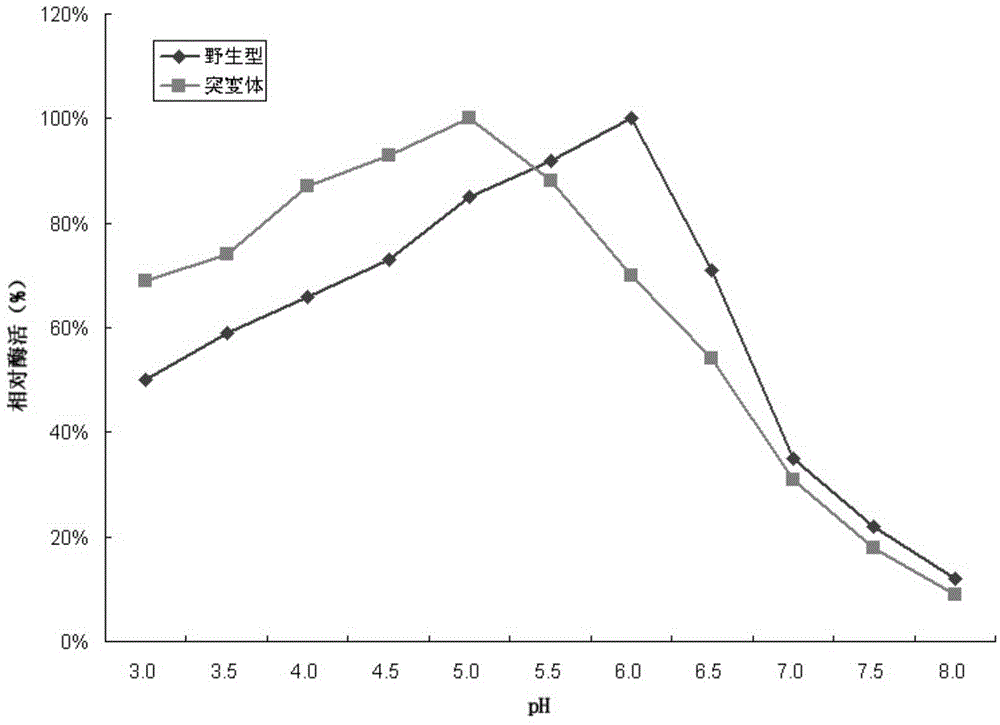
Beta-glucosidase mutant and application thereof
The invention aims at providing a beta-glucosidase mutant and application thereof. The amino acid sequence of the beta-glucosidase mutant is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 3, a nucleotide sequence of a coding gene is as shown in SEQ ID NO: 4, the optimum operative temperature is 50 DEG C and enzyme activity can be kept above 80% within 30-60 DEG C, and the mutant is stronger than a wild type in heat resistance; the optimum operative pH is 5.0 and the enzyme activity can be kept above 70% within 3.0-6.0, and the mutant is wider than the wild type in application scope under an acid condition; therefore, the beta-glucosidase mutant is conducive to the application in a cellulose raw material degrading process.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP +1
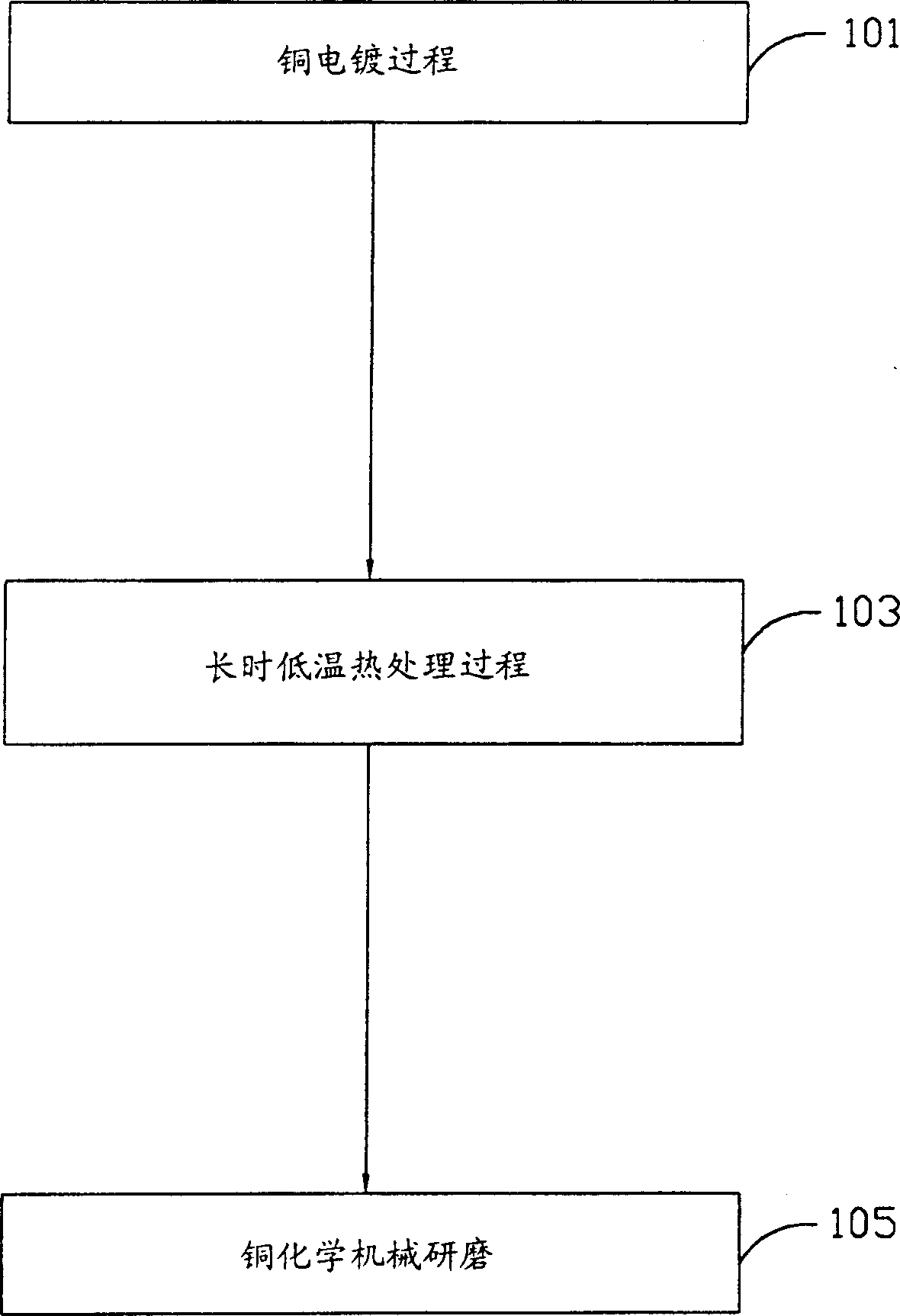
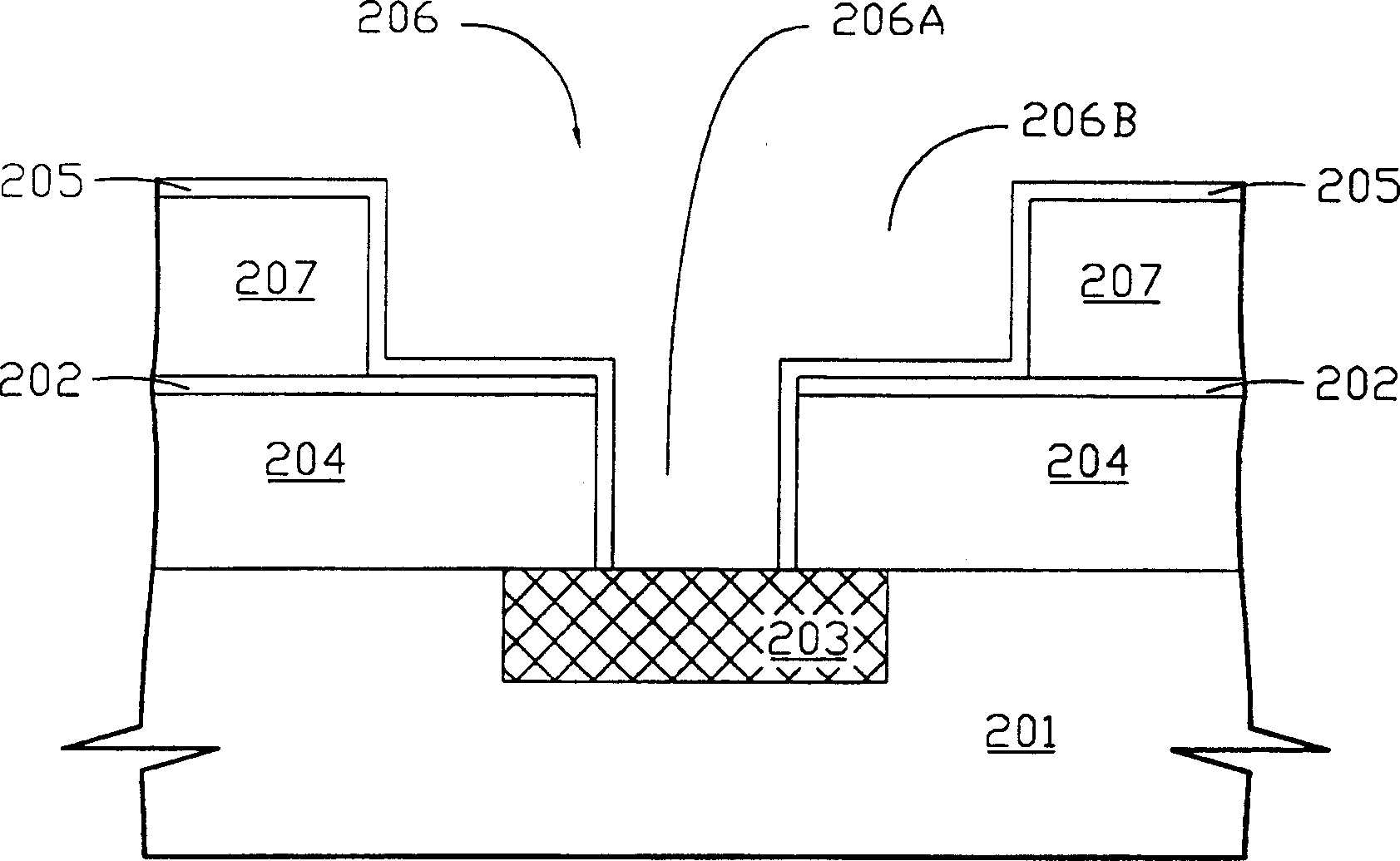
Method for reducing cracking and deformation of copper wire
InactiveCN1474439ACheap methodLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCopper wireInterconnection
A method for reducing copper wire cracking and deformation includes exerting a short term high-temp. heat treatment, during a long term low-temp. heat treatment to strengthen the internal stress of copper. The high-temp. means which is the highest temp. from the beginning of long term low-temp. heat treatment to the end of interconnection line metallization process, namely working temp. Under thesaid high-temp. rapid heating to strength copper film stress and maturate the copper grains. Therefore, in the followed process, temperature is below the highest temperature, the copper film structure becomes more stable and cracking can be reduced to a lowest degree.
Owner:UNITED MICROELECTRONICS CORP
Heat-resisting polyethylene plastic pipe with high heat conductivity
The invention discloses a heat-resisting polyethylene plastic pipe with high heat conductivity, which is characterized by being prepared from heat-resisting polyethylene resin with excellent corrosion resistance and heat resistance, a heat conducting material with high heat conductivity, and other auxiliaries through extrusion molding after the steps of melting and blending for modification. The heat-resisting polyethylene plastic pipe with high heat conductivity can be of single component and single layer, can also be of multiple components and multiple layers, and has the heat conduction coefficient more than two times higher than basic resin-heat resisting polyethylene; and when being used for conveying water as a medium, the heat-resisting polyethylene plastic pipe has the designed lifetime up to 50 years after continuously working at 70 DEG C, can work at the temperature up to 90 DEG C in a short period of six years and can work at the temperature up to 110 DEG C in a short period of one year. The heat-resisting polyethylene plastic pipe can be directly applied to a soil source heat pump, a seawater source heat pump system, a sewage source heat pump system and a radiation cooling and heating system to be used as a heat exchange pipe, is beneficial to improvement of system heat-transfer capability, can be welded and processed into heat exchangers with different forms and structures, and is used for chemical, food and medicine manufacturing processes with higher-temperature media.
Owner:TIANJIN JUNXING PIPE GRP CO LTD
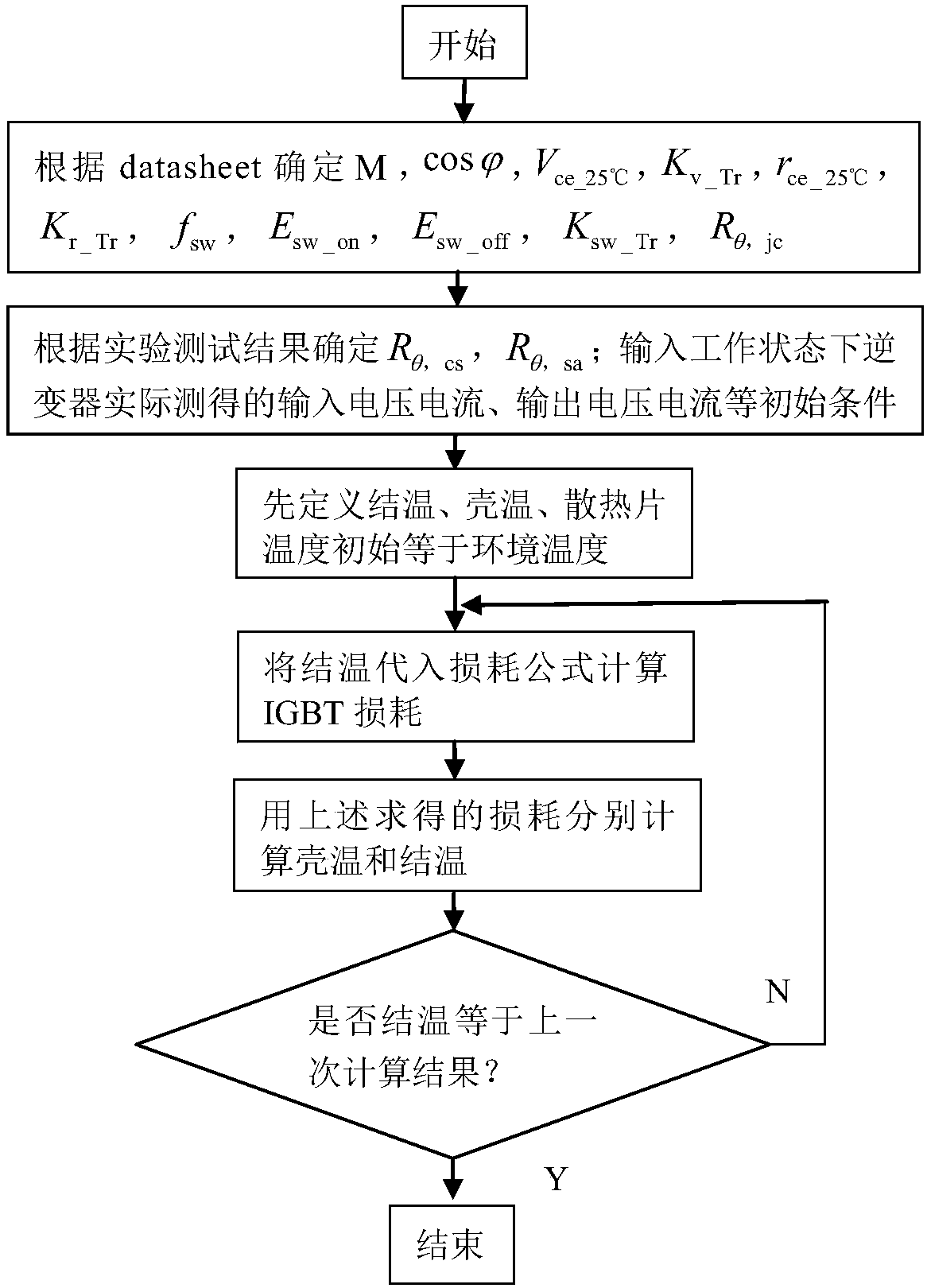
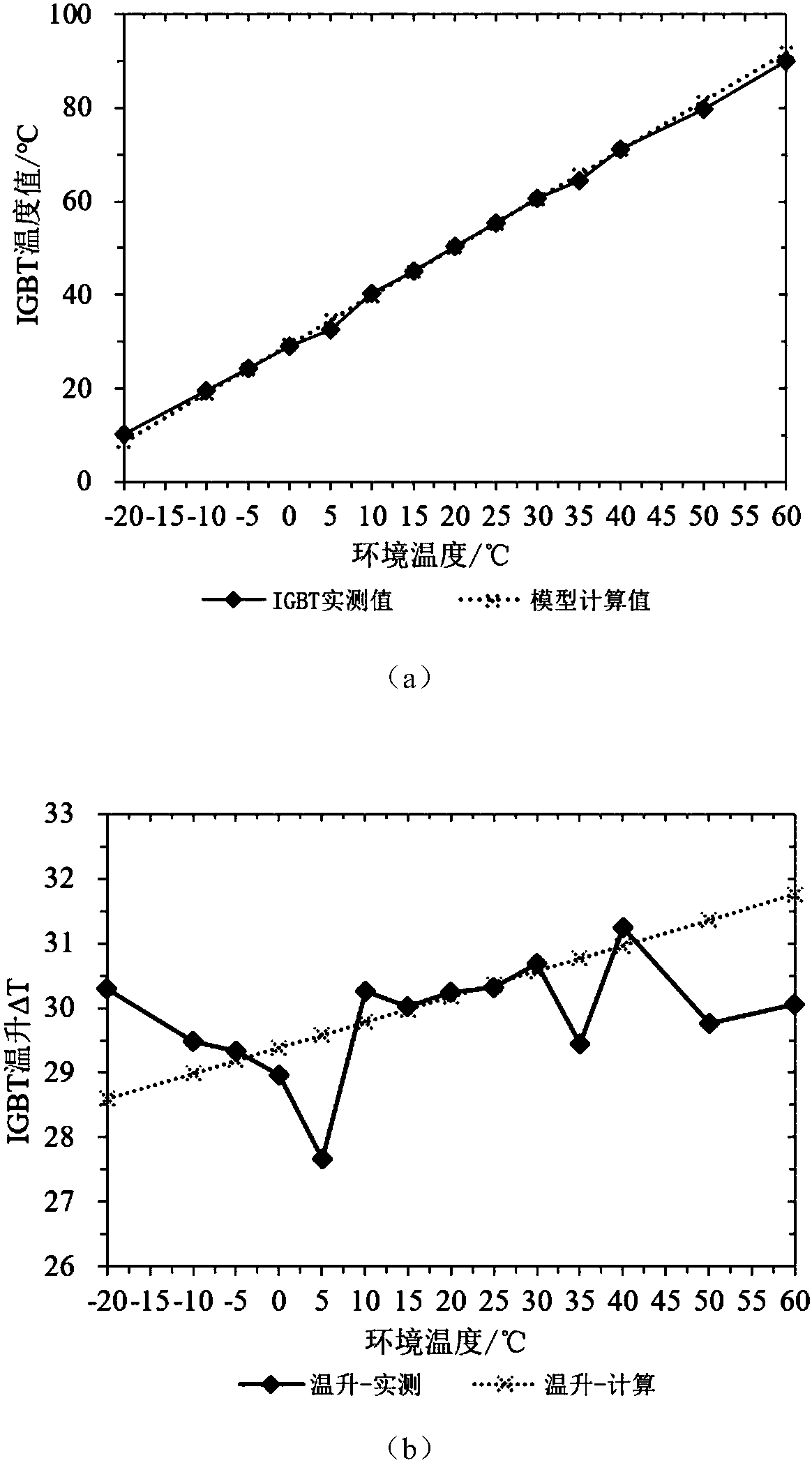
Method for calculating working temperature of component IGBT of photovoltaic inverter
The invention discloses a method for calculating a working temperature of a component IGBT of a photovoltaic inverter. Based on an energy conservation law, a mathematic relational formula of an external environment temperature, input power and IGBT loss and temperature rise is established through a loop iteration method by adopting a heat transfer principle and junction temperature and heat resistance principles; and calculation is performed by utilizing a loop iteration function in EXCEL to obtain shell temperatures and junction temperatures of the high-power component of the inverter under different environment temperatures and different input power. The errors between the predicted working temperatures of the IGBT under the different environment temperatures and the different input power, and the actually measured temperatures are within + / -8%; the method is used for predicting the working temperatures of the high-power component of the photovoltaic inverter under high and low-temperature environments and high and low-load ratios; and a theoretical basis is provided for assessing the reliability of the inverter.
Owner:HOHAI UNIV CHANGZHOU
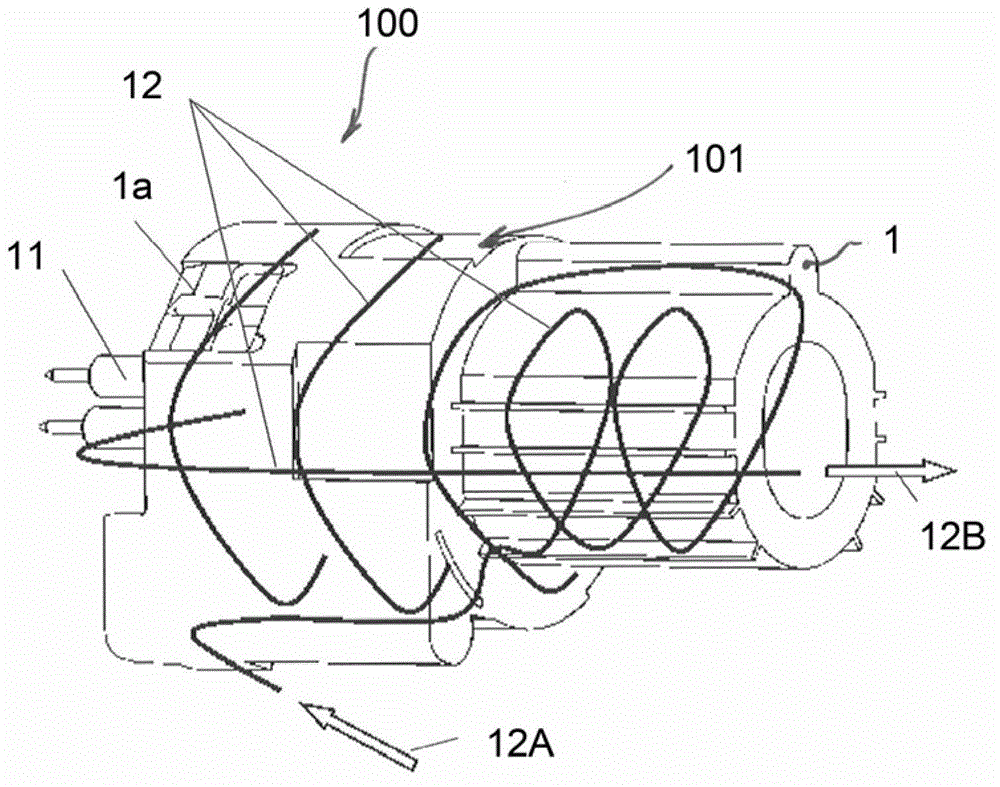
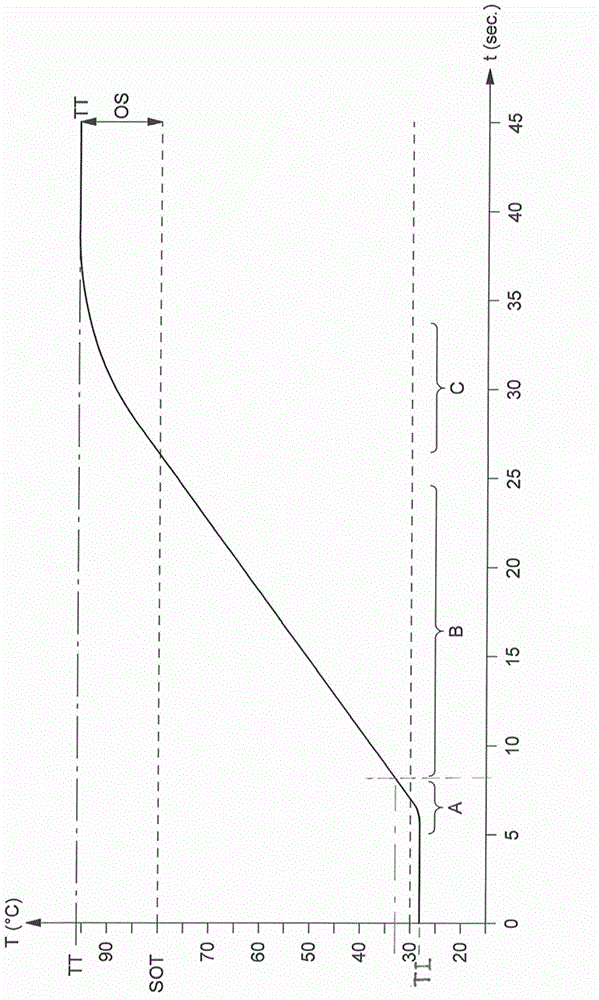
Fast heat-up of a thermal conditioning device e.g. for coffee machine
The invention concerns a unit (1000) for controlling transmission of power to a thermal conditioning device (100) e.g. for coffee machine, comprising a controller (2) with a start-up profile for starting-up said device (100) from a temperature of inactivity (TI) to an operative temperature for bringing to a target temperature (TT) a fluid circulating through said device (100) at start-up end, said controller (2) being arranged to allow circulation of fluid through said device (100) at start-up end and to compare the determined temperature (SOT) of fluid circulated at start-up end to the target temperature (TT) and derive a temperature difference therefrom. It is characterized in that the start-up profile has at least one parameter and in that said controller (2) has a self-learning mode for adjusting said parameter as a function of said temperature difference and to store the adjusted parameter for a subsequent starting-up of said device (100). The invention concerns in particular a method for optimized heating up of a coffee machine (104).
Owner:SOC DES PROD NESTLE SA
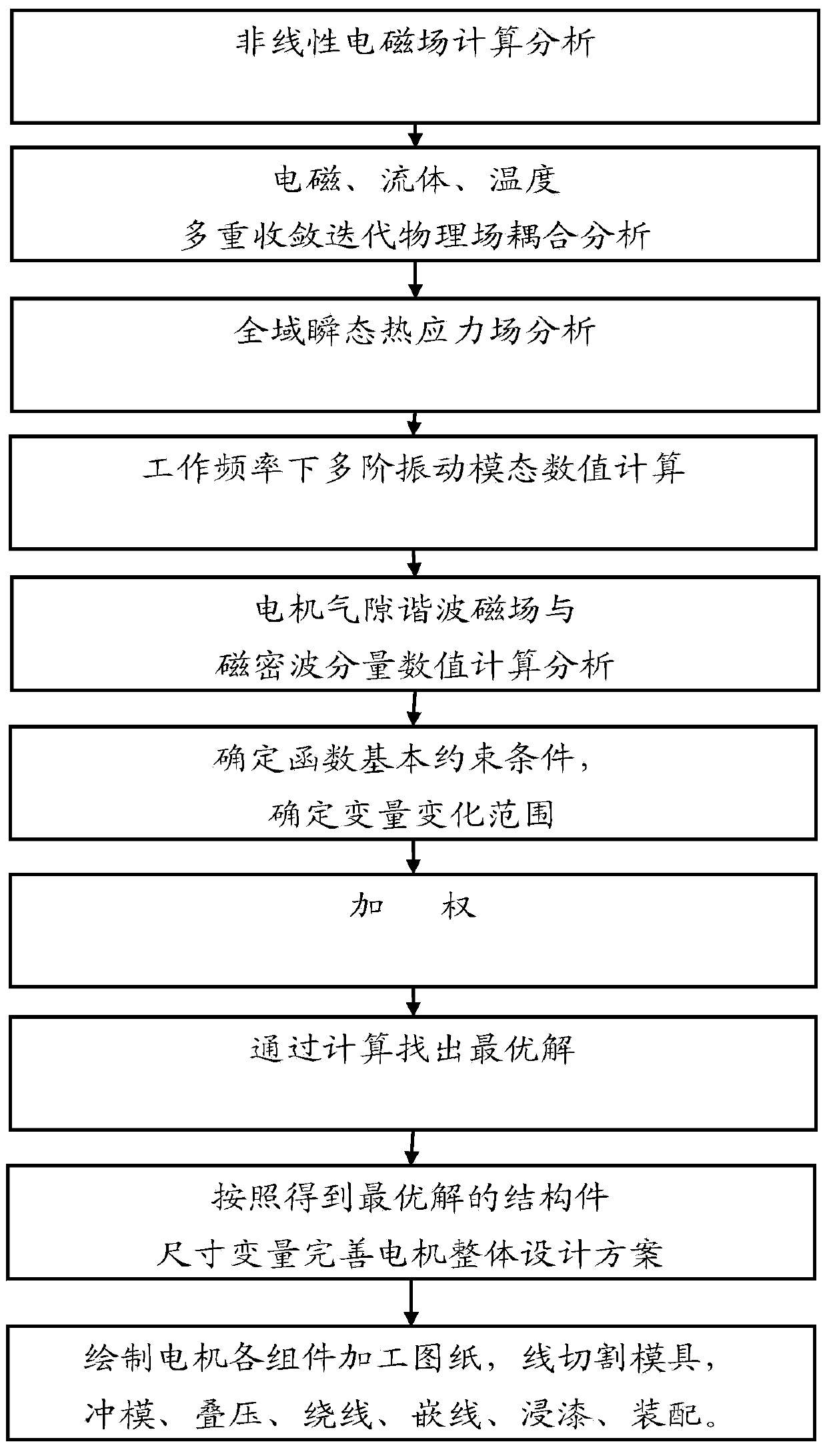
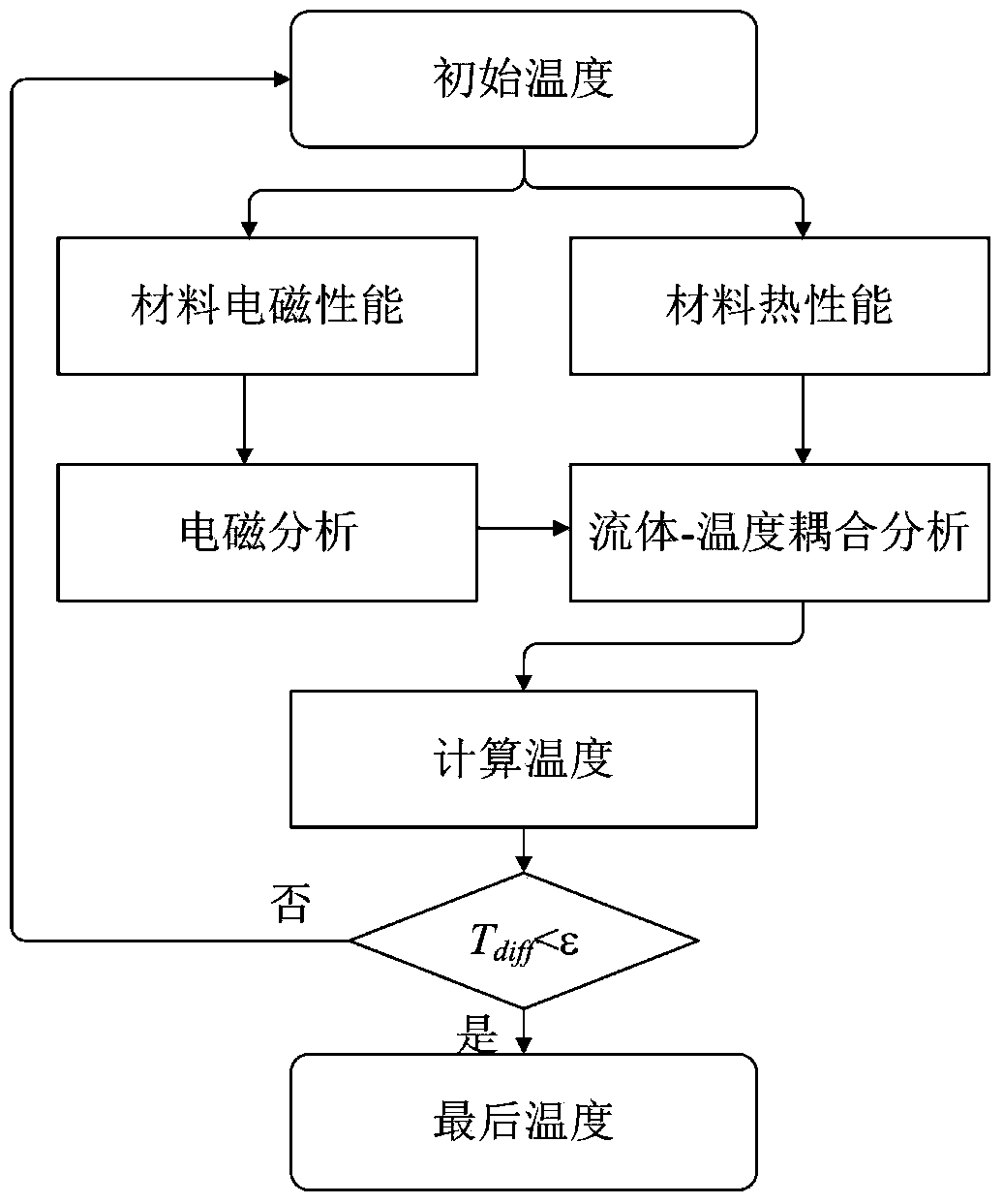
Method for designing motor through numerical calculation and analytical analysis combined parameter collaborative optimization
ActiveCN103793559AImprove calculation accuracyEliminate the effects ofSpecial data processing applicationsConstant frequencyPerformance index
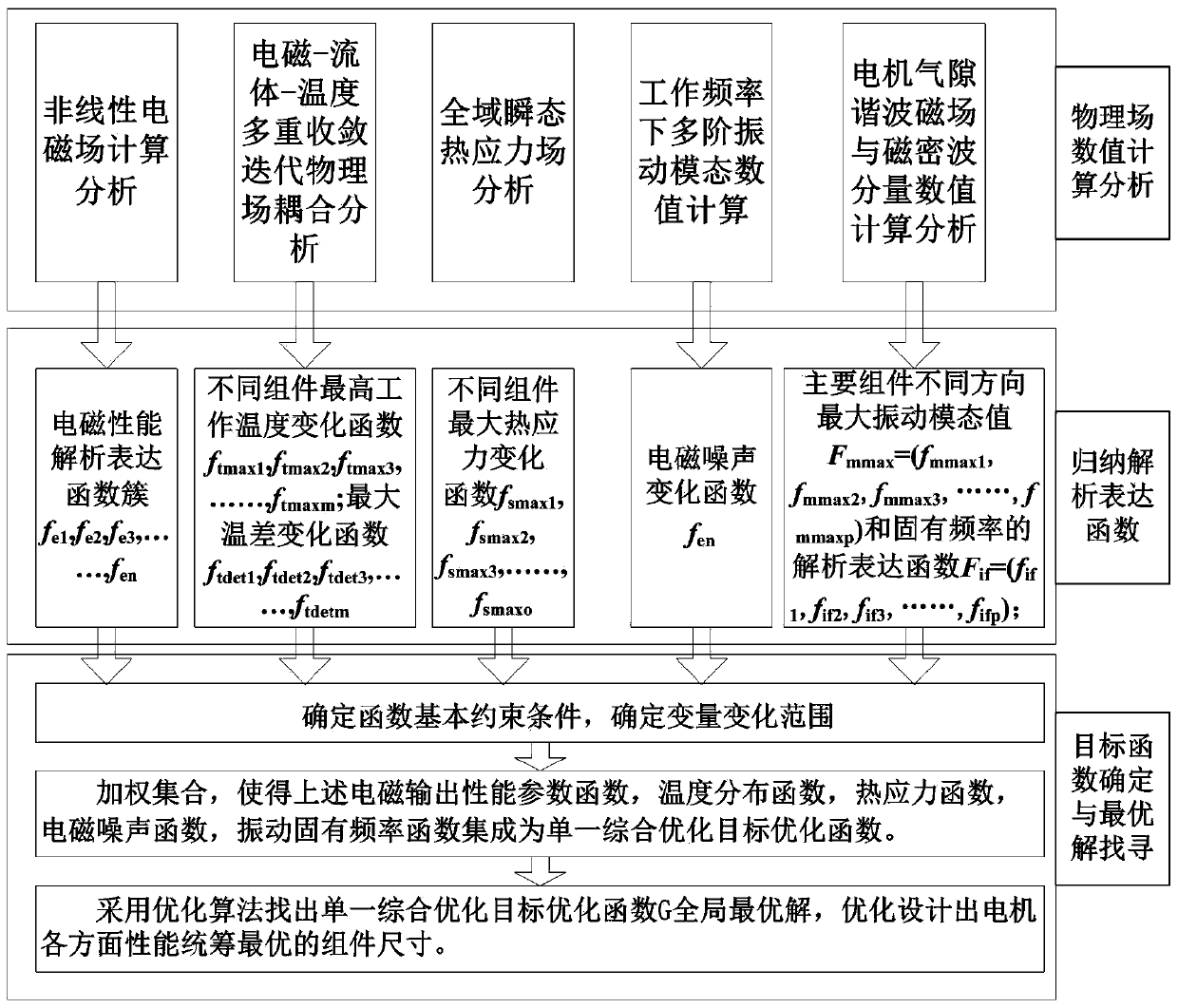
The invention belongs to the technical field of electrics, and particularly relates to a method for designing a motor through numerical calculation and analytical analysis combined parameter collaborative optimization. The changes of electromagnetism, temperature, fluid, thermal stress, vibration, noise and other physical parameters in the motor are studied through the numerical calculation, an electromagnetic performance analytical expression function cluster with the structural member size as the variant, a maximum working temperature analytical function of different assemblies, a maximum temperature difference analytical function of the different assemblies, a maximum thermal stress analytical expression function, a motor electromagnetic noise change function, a maximum vibration mode value of different directions of the assemblies and a constant frequency analytical expression function are concluded, then the refined designing of the structural member size is carried out by comprehensively taking performance of all aspects of the motor into consideration, and the calculating accuracy of all performance indexes is greatly improved. An objective function is improved through a non-equilibrium relative both-way weighting method, and the effect on a calculating result of the values of different performance indexes is removed. The quantum calculation is introduced into an intelligent optimization algorithm, and the algorithm has better population diversities, global optimization capabilities and higher convergence speed.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
Thermal infrared imager inhomogeneous correction coefficient generation and control method
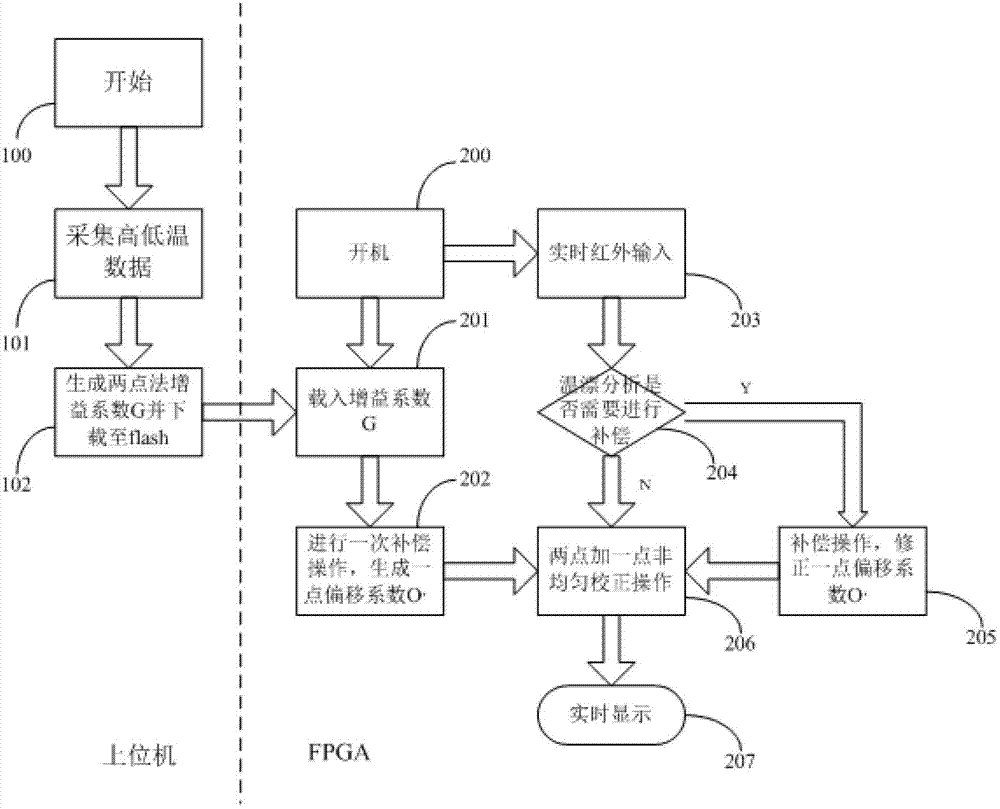
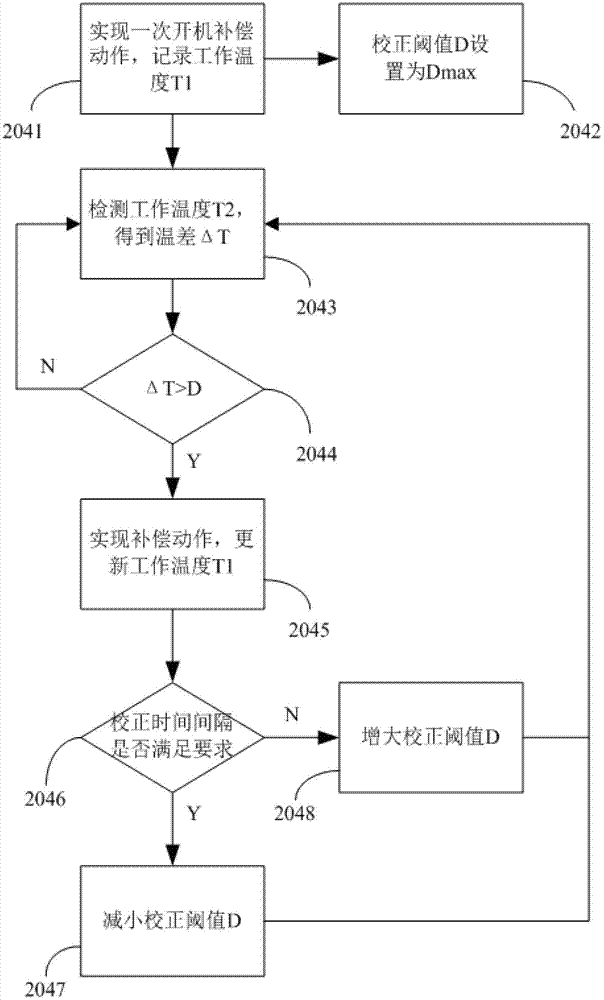
ActiveCN103033270AReduce storage capacityImprove operational efficiencyRadiation pyrometryInfraredStatic random-access memory
The invention discloses a thermal infrared imager inhomogeneous correction coefficient generation and control method. The thermal infrared imager inhomogeneous correction coefficient generation and control method comprises that 1.infrared focal plane response data when infrared focal plane is respectively in high temperature and in low temperature are collected. 2. A gain factor G of a two point correction method is calculated through an upper computer and the gain factor G is downloaded into a parallel flash. 3. A startup loads gain factor G into a static random access memory (SRAM) from the flash. 4. A deviation ratio O is received through one time one point correction coefficient motion. 5. An offset compensation correction coefficient generation is controlled by analyzing a detector work temperature. 6. Steps are that two points plus one point inhomogeneous correction is proceed and correction results are output and the like. The thermal infrared imager inhomogeneous correction coefficient generation and control method removes calculation and storage process of the two-point method coefficient and reduces a half of the flash memory capacity. The load process and the download process of the inhomogeneous coefficient are shortened. The thermal infrared imager inhomogeneous correction coefficient generation and control method quicken a read-write speed of the flash by utilizing the flash design. The efficiency of the circuit is improved greatly.
Owner:WUXI ALEADER INTELLIGENT TECH
Fluid cooling during hot-blow-forming of metal sheets and tubes
InactiveUS20110239721A1Type is limitedReduce strainShaping toolsMaintainance and safety accessoriesMetal alloyMetal sheet
Metal sheets and thin-wall metal tubes may be heated to a hot working temperature and transformed by a hot-blow-forming step to achieve shapes, difficult to attain, without excessive thinning or strain causing damage to the workpiece based on the inherent formability of the metal alloy. The stages of forming of the intended shape in the metal workpiece are analyzed and workpiece regions of potential damage during forming are identified. Then, during actual forming, these regions of the hot workpiece are selectively cooled with air (or other cooling fluid) to reduce thinning or strain in the critical region(s) and to redistribute this strain to adjacent lower strain areas of the workpiece. This hot-blow-forming practice is particularly useful in attaining complex shapes in workpieces of aluminum-based alloys and magnesium-based alloys.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
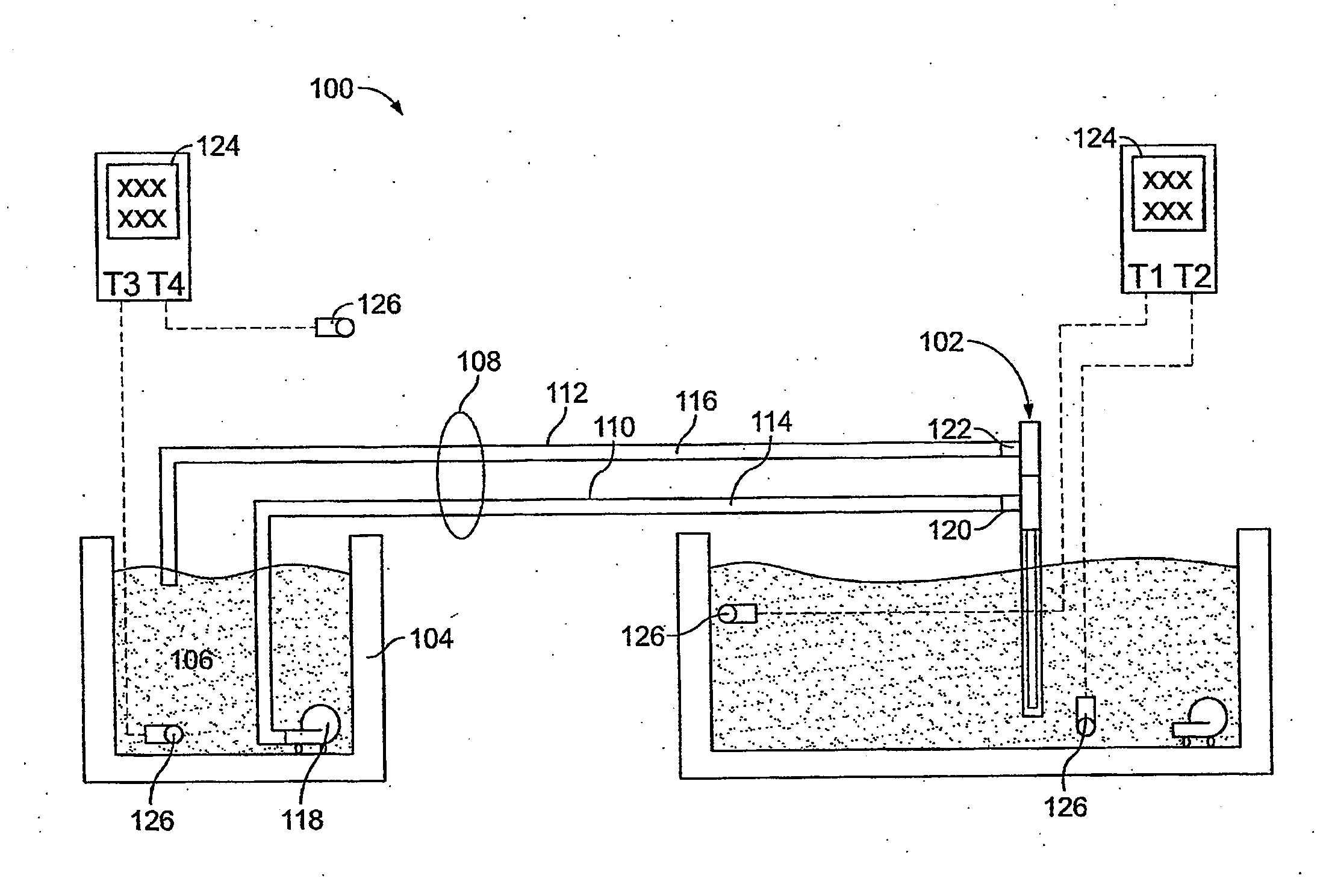
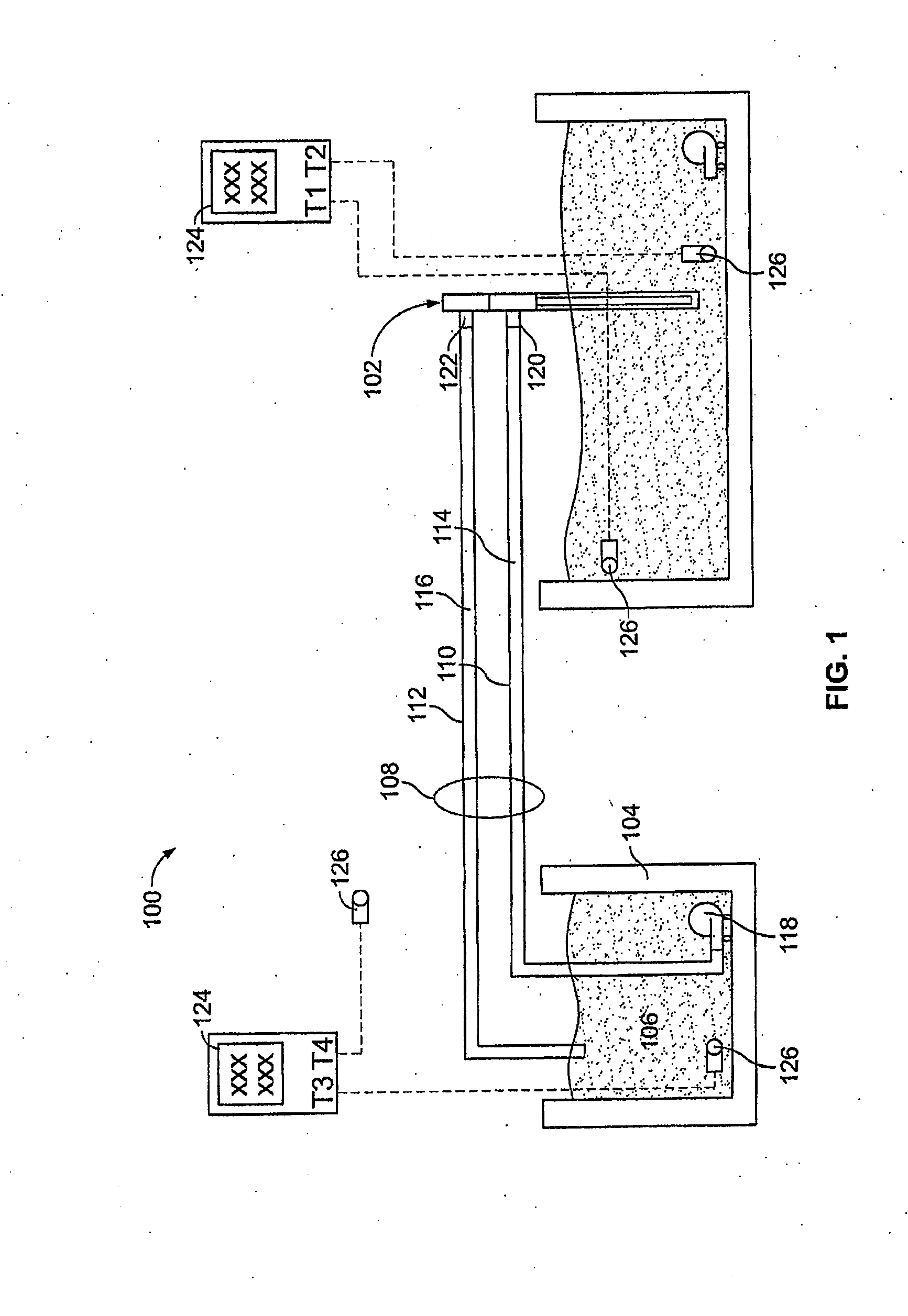
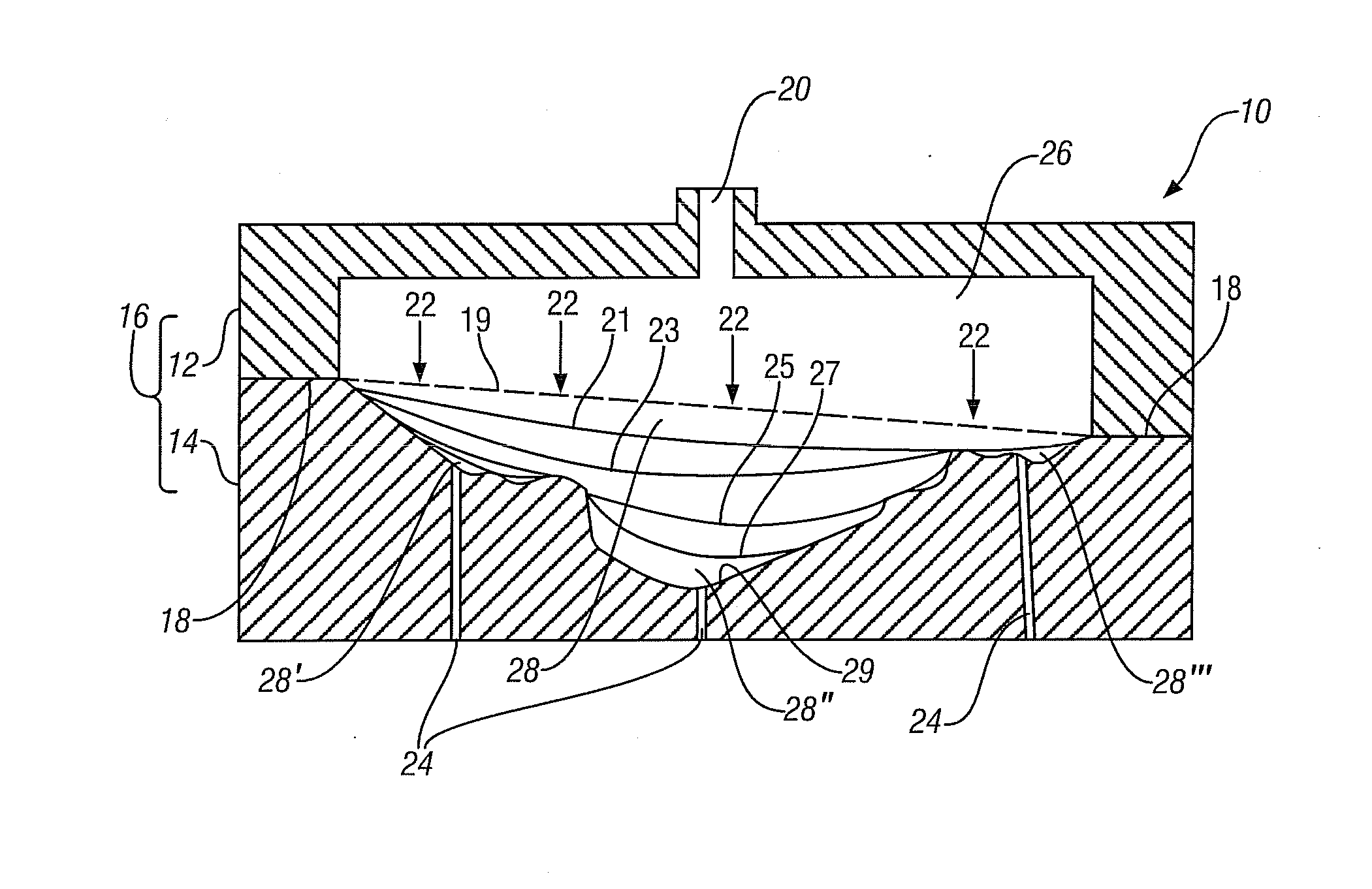
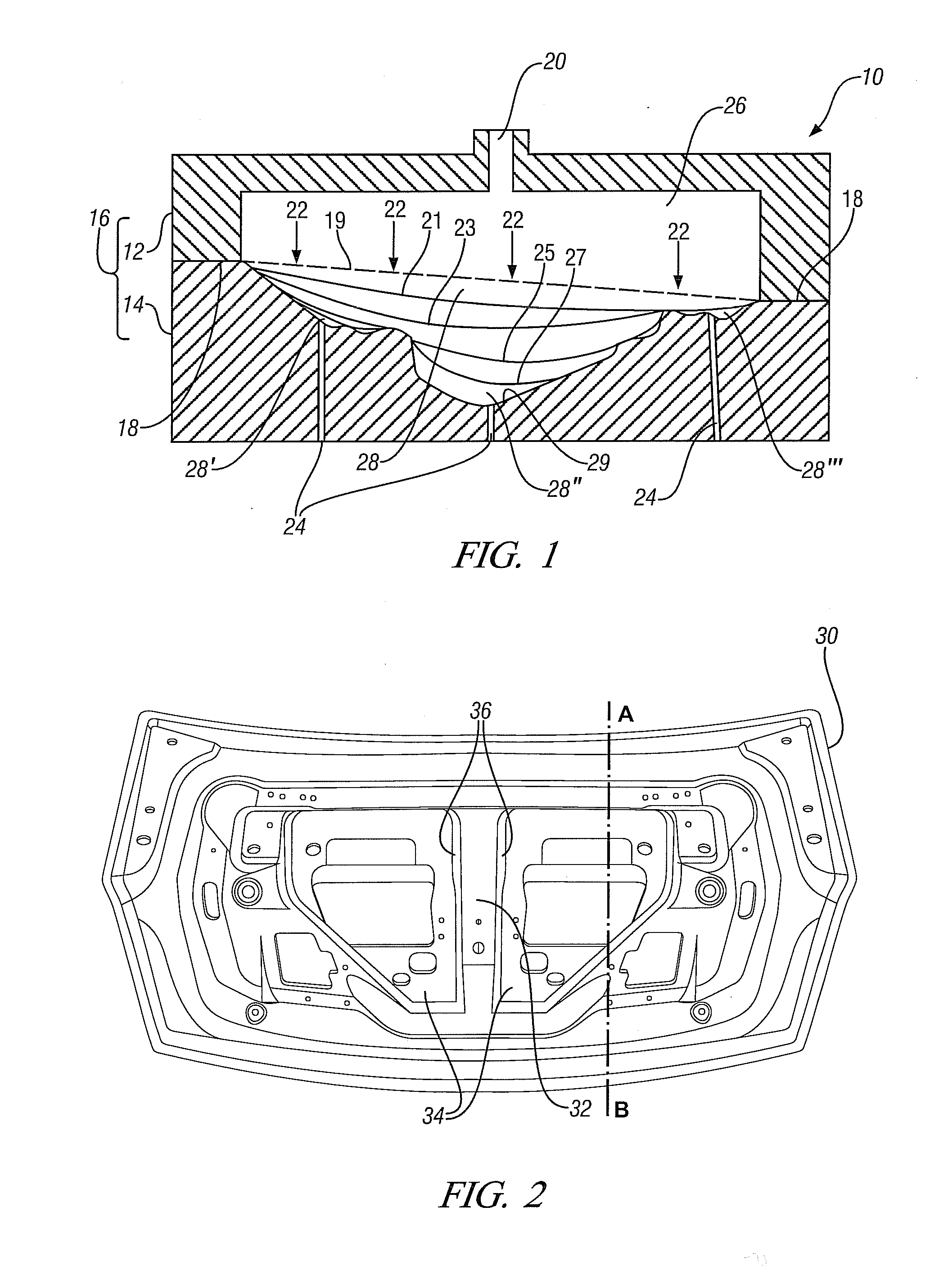
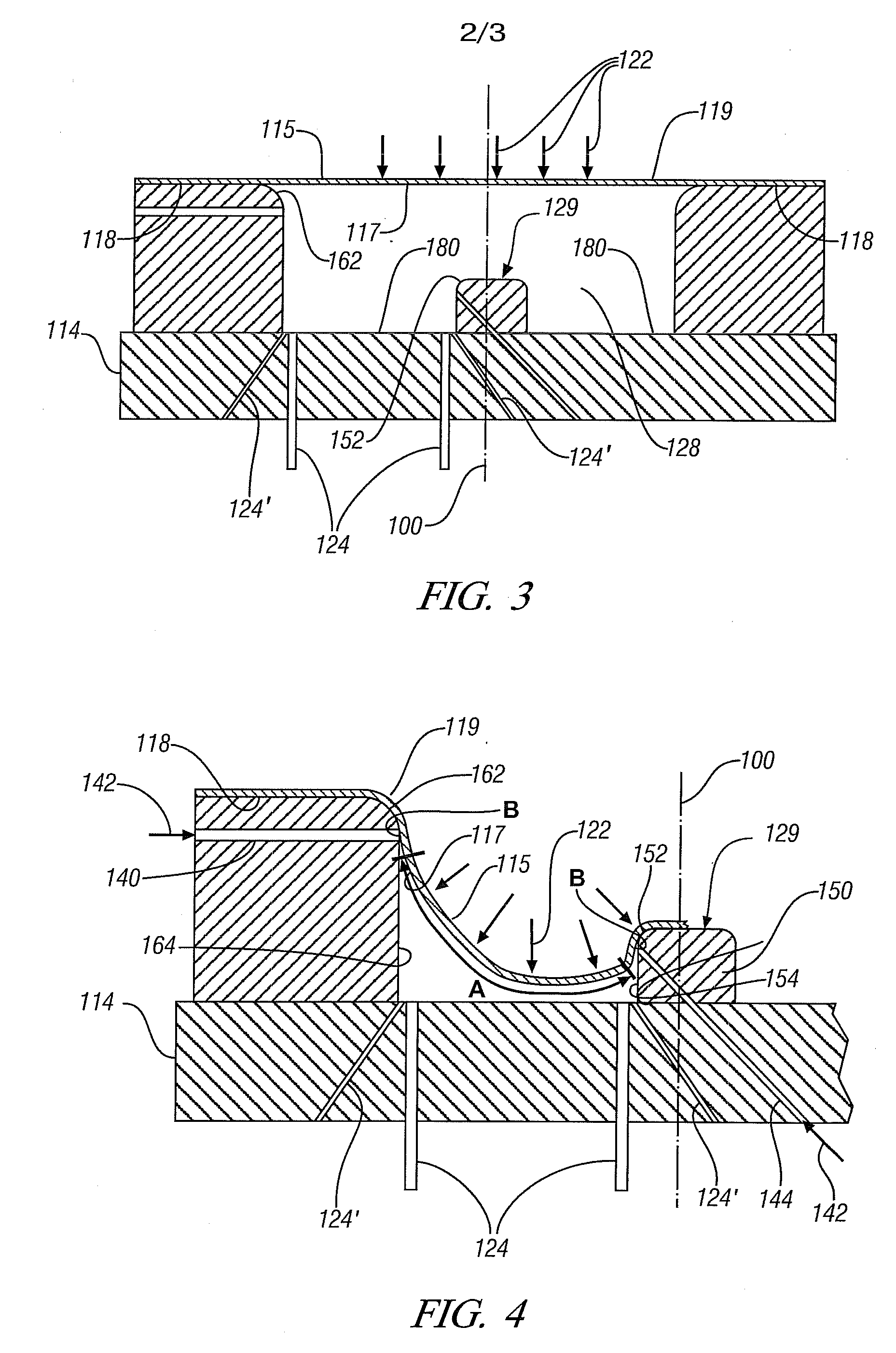
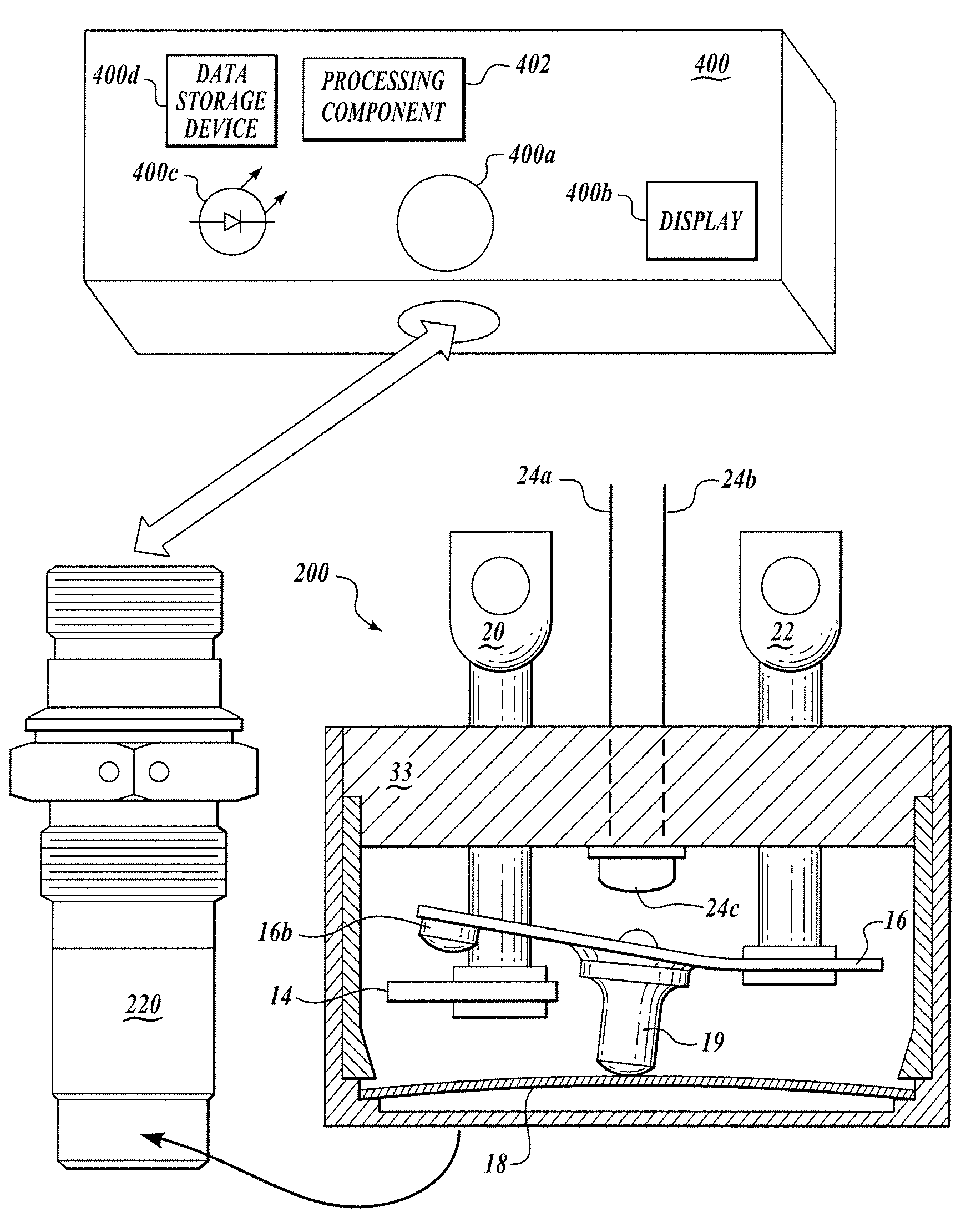
Thermal switch with self-test feature
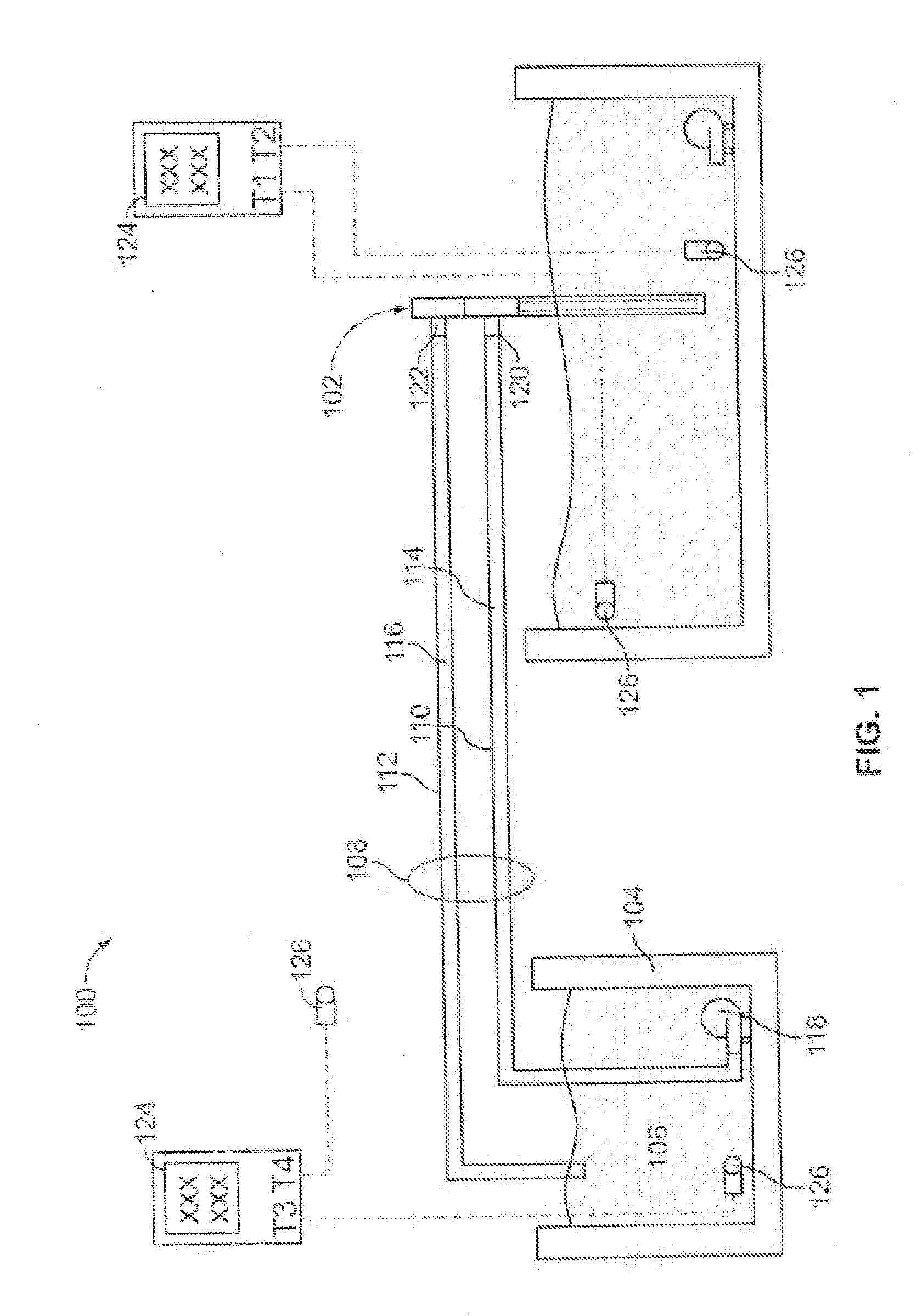
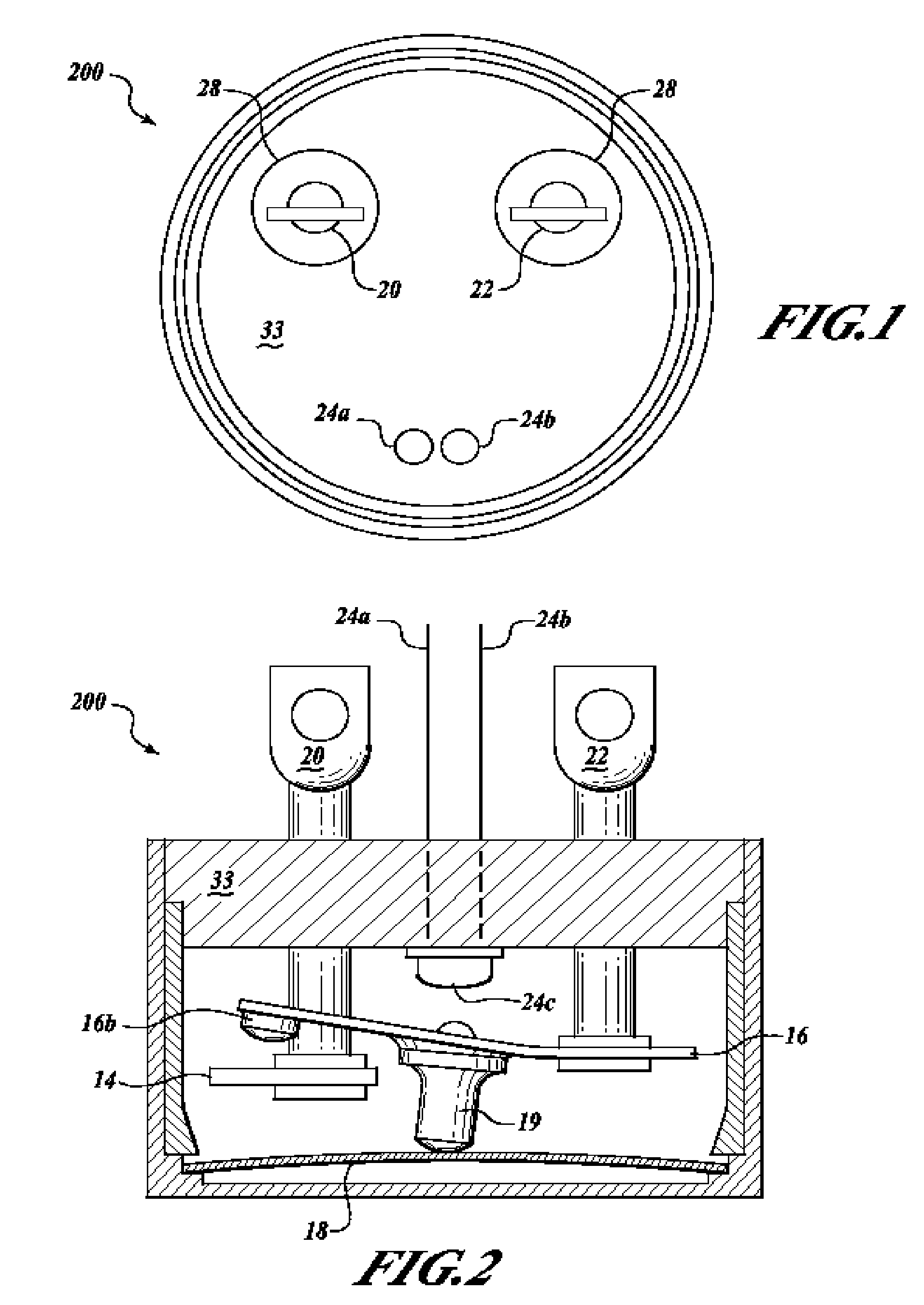
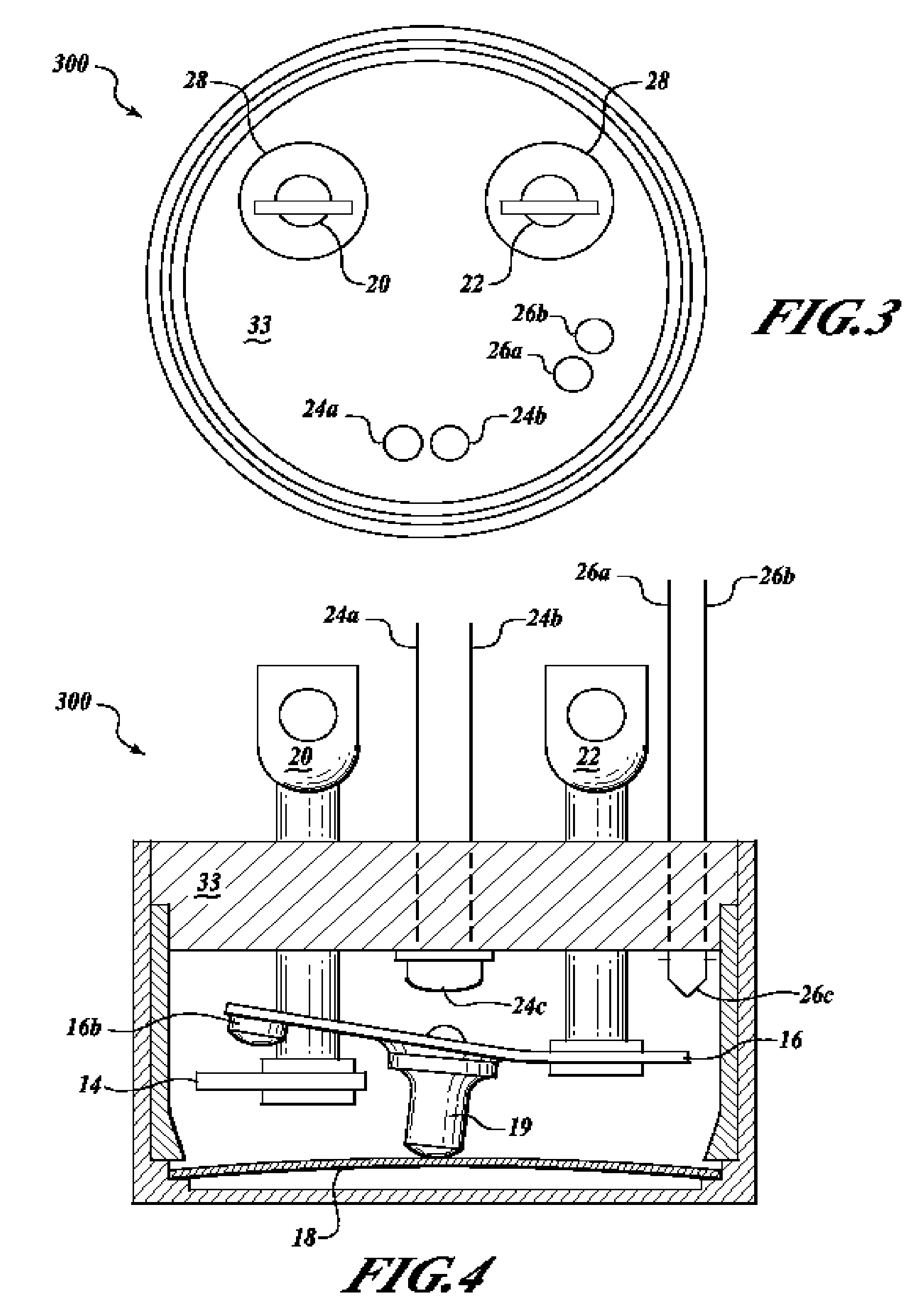
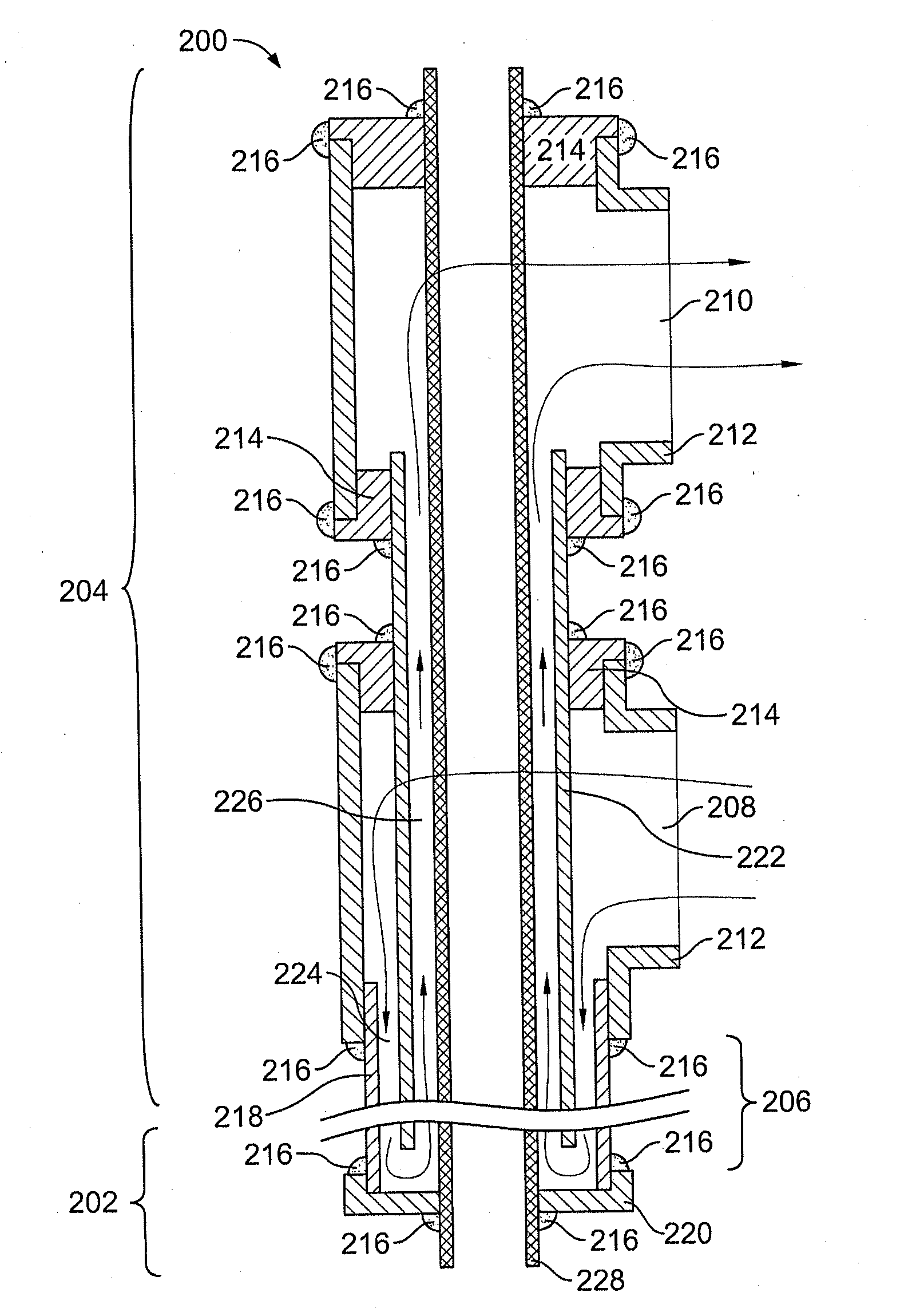
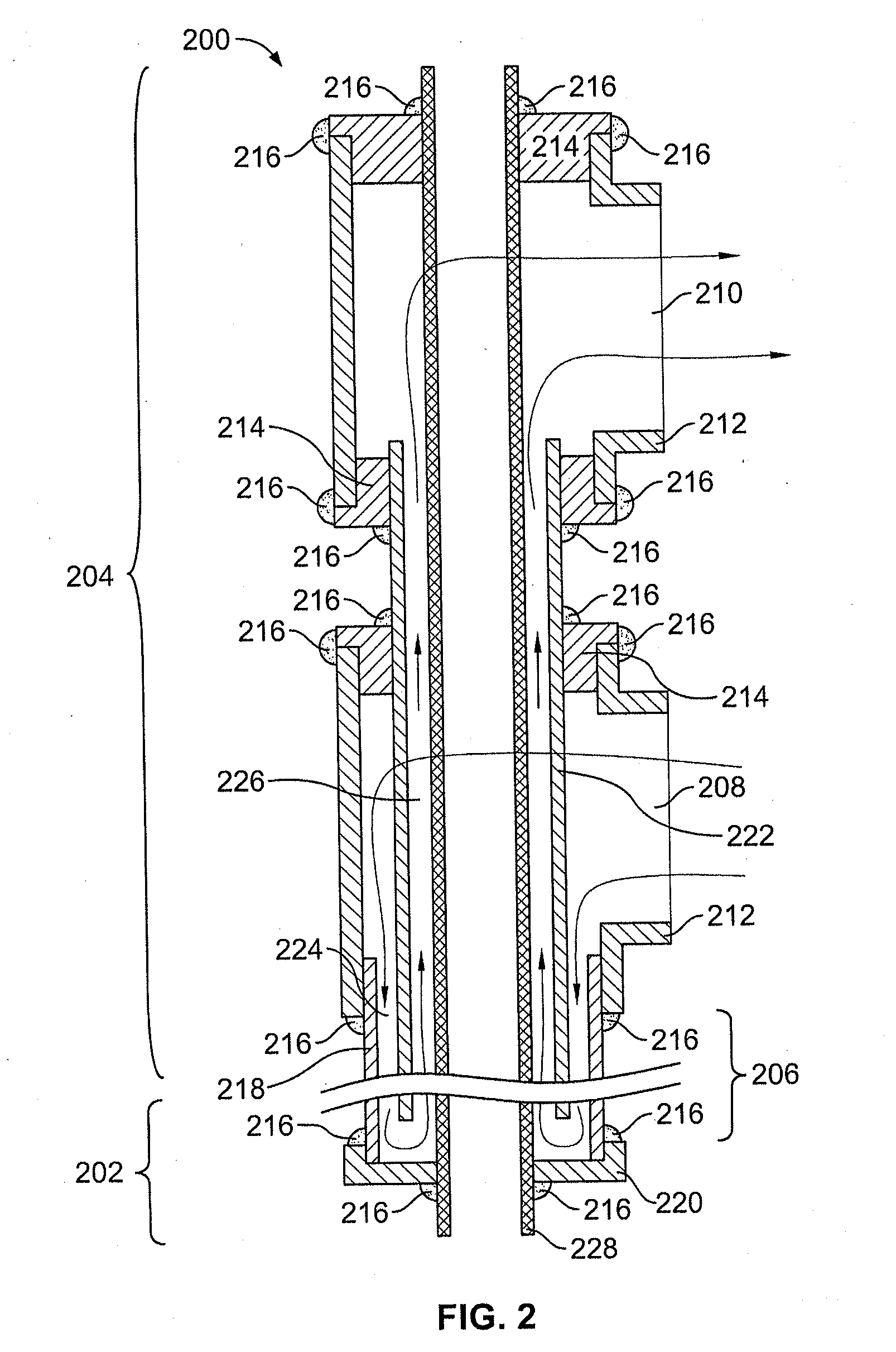
ActiveUS7358740B2Without incurring cost and inconvenienceProtective switch detailsElectrothermal relaysDisplay deviceOperative temperature
A normally open thermal switch (200) having a bimetallic disk (18) is configured for operational testing in its installed position when exposed to a changing temperature by a test box (400) having a power source (400a). The in-place testing advantageously confirms triggering action of the switch by an event indicator (400c) at the operational temperatures designed into the switch (200). The temperature of the triggering action is presented on a temperature display (400b) and recorded by a data recorder (400d) of the test box (400). The switch (200) incorporates a heating element (24c) to heat changing the bimetallic disk (18) to snap activate at the operative temperatures. The thermal switch (200) is coupled with the test box (400) to confirm its operation without having to remove the switch from its installed location.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
High-performance thermal barrier coating and ceramic layer thereof
ActiveCN107815633AImprove efficiencyIncrease working temperatureMolten spray coatingNano structuringThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a preparation method for a high-performance thermal barrier coating and specifically discloses a 4YSZ (4mol% Y2O3 stabilized ZrO2) thermal barrier coating and the preparation method of the 4YSZ thermal barrier coating. The 4YSZ powder which is of a fine nano-structure, uniform ingredients and a pure tetragonal phase structure is prepared utilizing a sol-spray pyrolysis synthetic process, and the 4YSZ powder is subjected to spray drying granulation, screening and atmospheric plasma spraying (APS) in sequence to prepare the coating. The high-performance thermal barrier coating prepared by the invention is of a pure tetragonal phase nano-structure with uniform ingredients, compared with a traditional YSZ casting, the high-performance thermal barrier coating has the advantages of being low in thermal diffusion coefficient, good in high temperature phase stability and thermal shock resistance, simple in preparation process and low in cost and the like; and the high-performance thermal barrier coating is more conducive to improving the efficiency and working temperature of a turbine engine, and the service life of the engine is prolonged.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
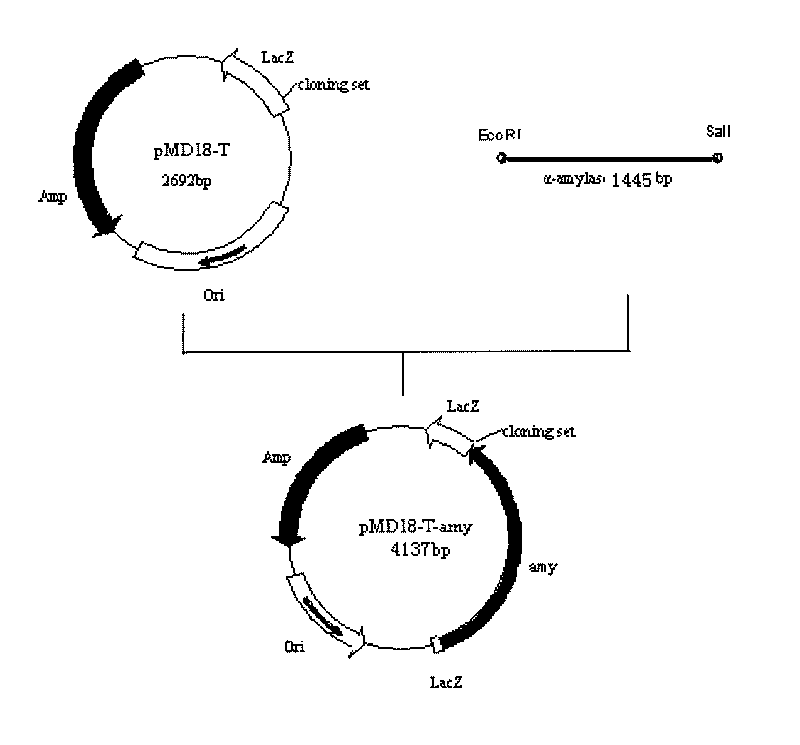
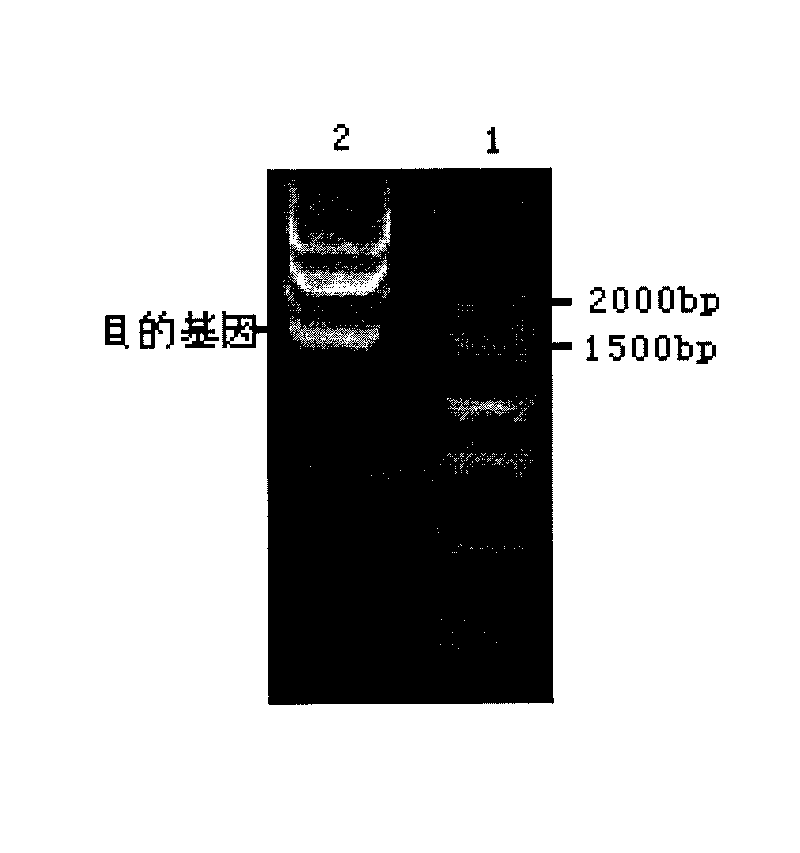
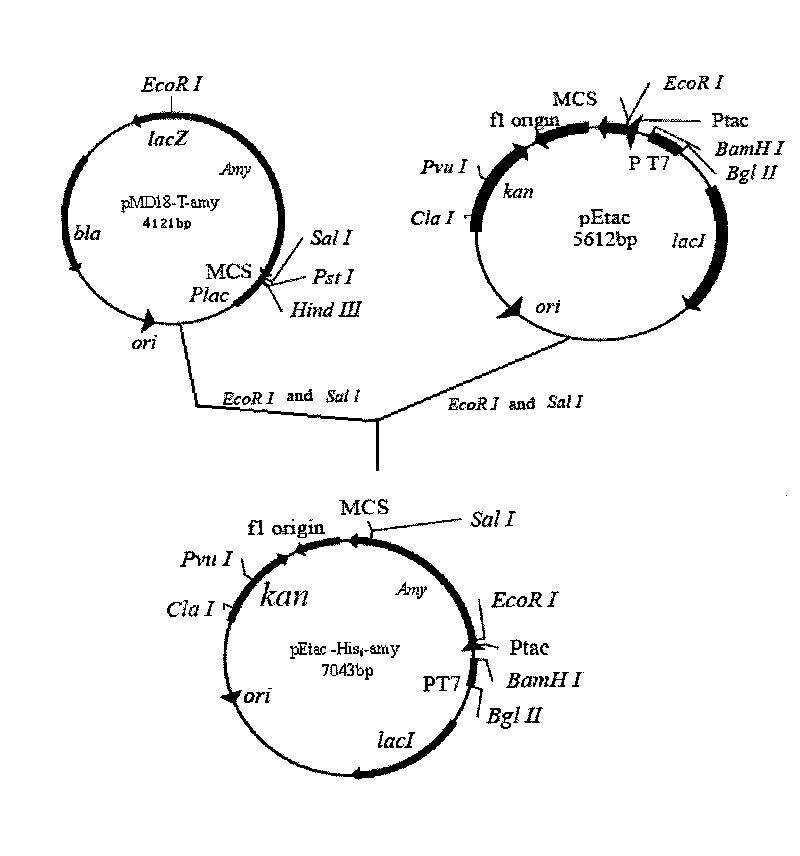
Marine low temperature alpha-amylase gene engineering bacteria, recombinant enzyme and application
InactiveCN101691579ASimple preparation processLow action temperatureBacteriaMicroorganism based processesIon exchangeAlpha-amylase
Owner:HUAIHAI INST OF TECH +1
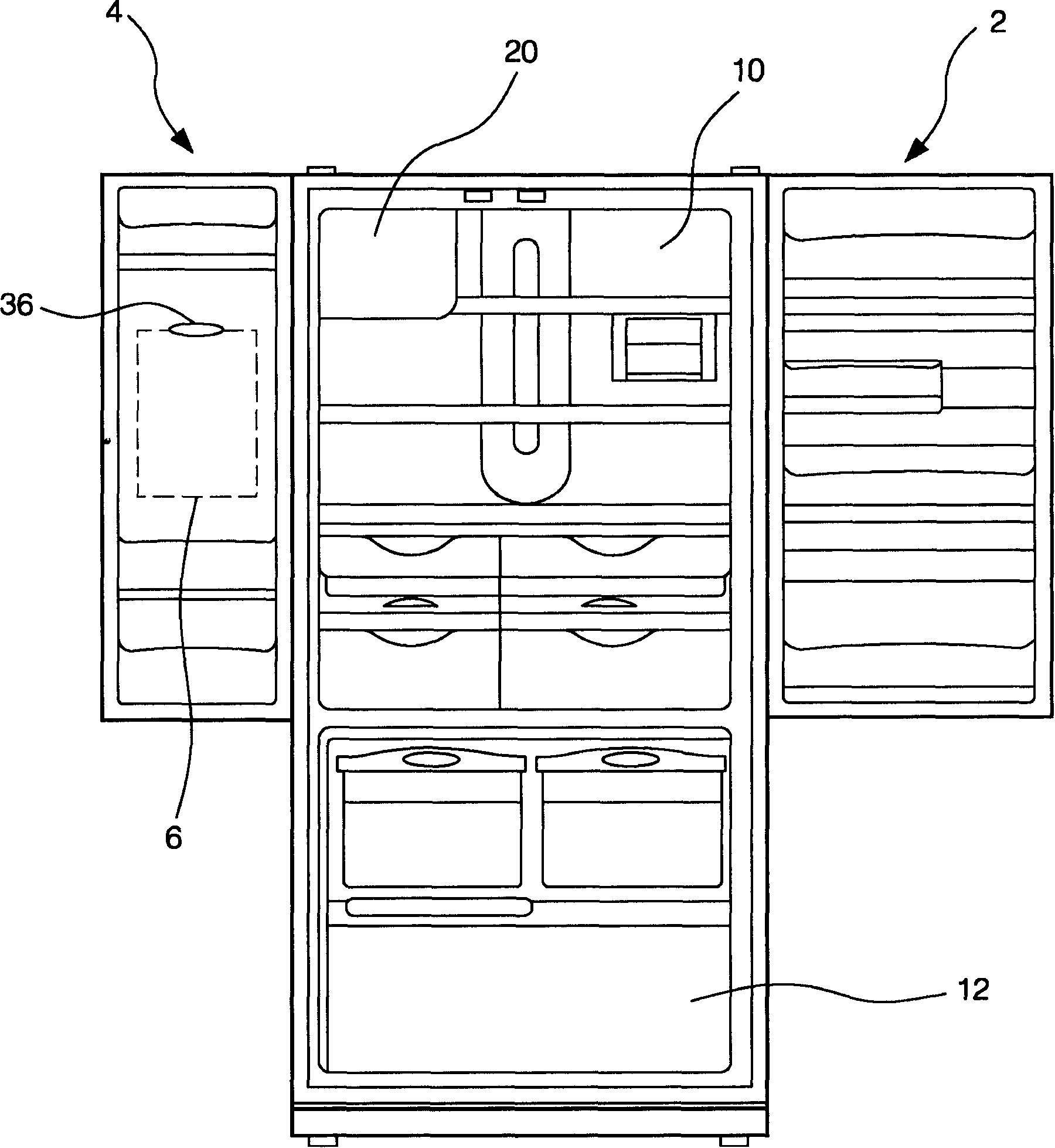
Refrigerator with ice maker in cold storage room
InactiveCN1683862ATemperature does not affectNormal working temperatureLighting and heating apparatusDomestic refrigeratorsCold airIce storage
The refrigerator with ice making machine in the cold storage chamber includes cold storage chamber in the upper part of the refrigerator; the freezing chamber in the upper part of the refrigerator; ice making chamber enclosed with heat isolating boards inside the cold storage chamber and with ice making machine and ice storage; the first evaporator inside the ice making chamber to lower the temperature inside the ice making chamber; and the second evaporator set inside the freezing chamber to provide cold air to both the freezing chamber and the cold storage chamber. The ice making chamber is inside the cold storage chamber, and has no influence on the normal temperature of the cold storage chamber. In addition, the separate control of evaporators in both the ice making chamber and the freezing chamber makes the refrigerator has high ice making capacity and low power consumption.
Owner:LG ELECTRONICS (TIANJIN) APPLIANCES CO LTD
Method for measuring heat productivity of heating substance for calorimeter
ActiveCN101063665AGuarantee stabilityGuaranteed accuracyMaterial heat developmentMaterial weighingCrucibleDistilled water
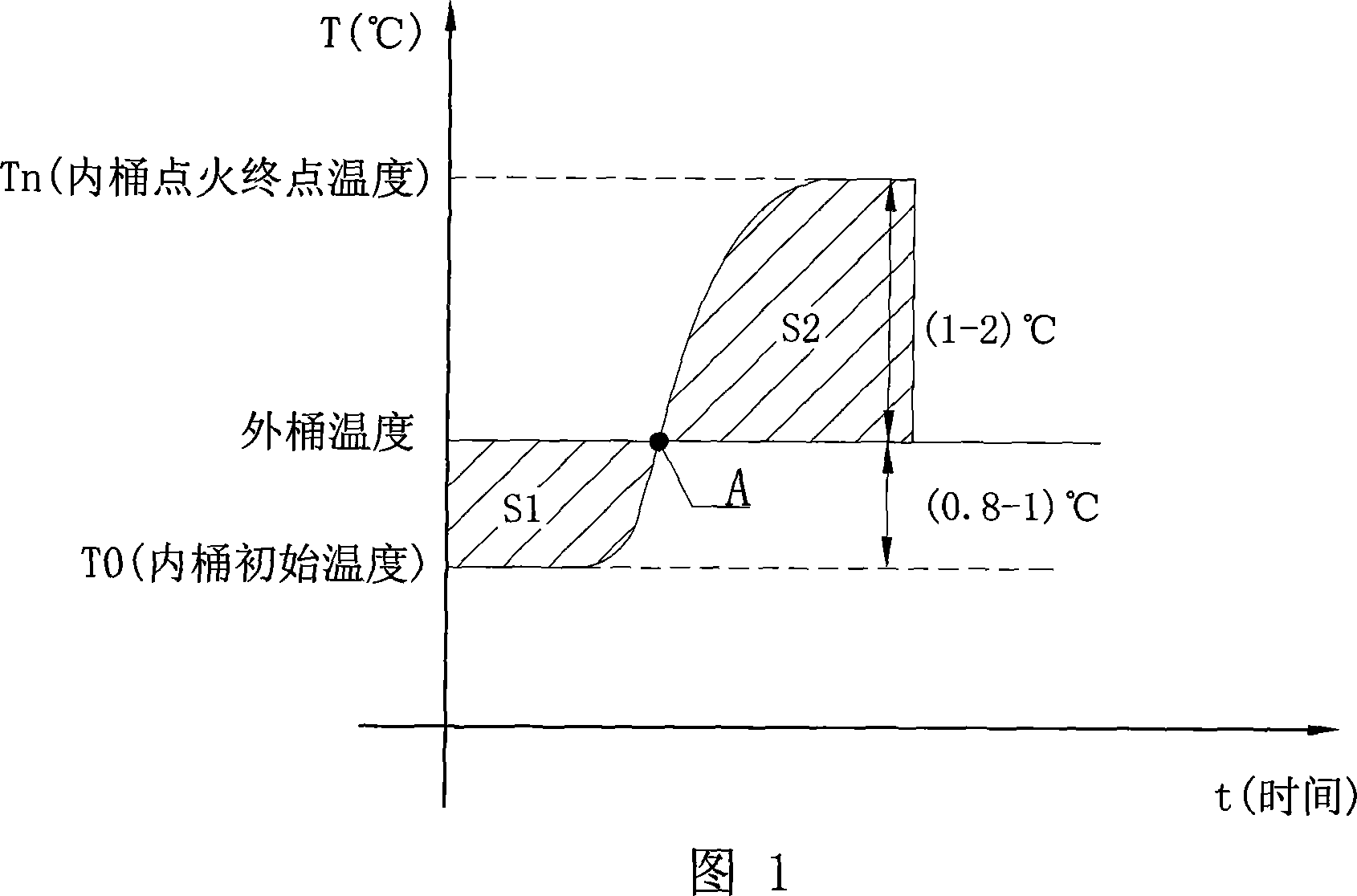
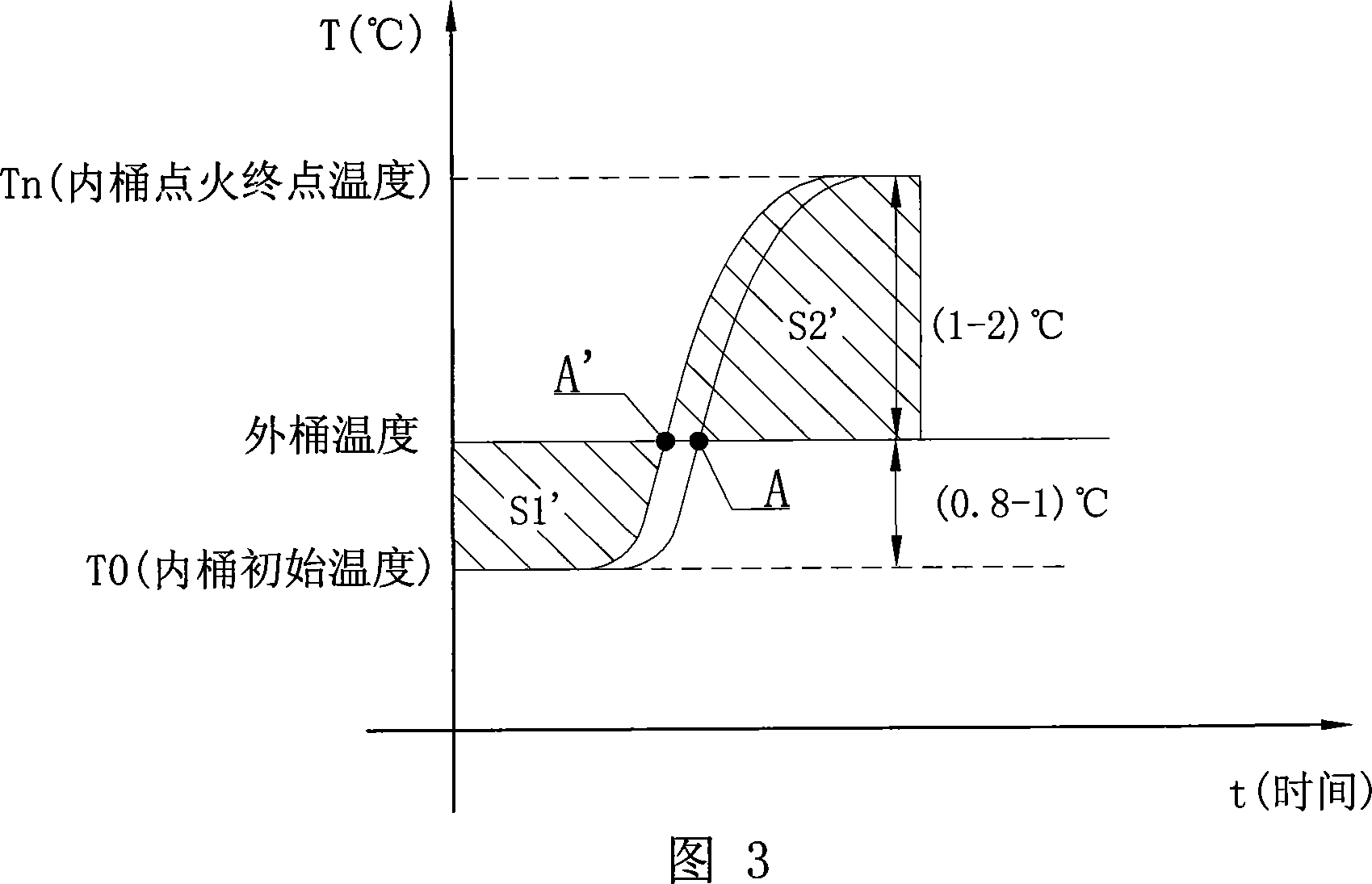
This invention discloses one measurement method for thermal device, which comprises the following steps: a, taking air drying device into pot and putting it on oxygen bomb rack and loading with light wire; adding stilled water into oxygen bomb injected with oxygen; b, adding proper water into inner barrel of thermal device and putting the bomb into inner barrel and covering; c, starting inner barrel mixing to keep inner temperature to balance T0 and controlling thermal device temperature to ensure work and whole curve between environment and control point sections; d, electrifying to read inner barrel temperature and experimenting main period when the temperature is lifted to zero; e, according to the computation results, computing the sample thermal volume.
Owner:HUNAN SUNDY SCI & TECH DEV
Devices and methods for controlling patient temperature
Relatively non-invasive devices and methods for heating or cooling a patient's body are disclosed. Devices and methods for treating ischemic conditions by inducing therapeutic hypothermia are disclosed. Devices and methods for inducing therapeutic hypothermia through esophageal cooling are disclosed. Devices and methods for operative temperature management are disclosed.
Owner:ADVANCED COOLING THERAPY INC
Temperature regulator for heat exchange loop
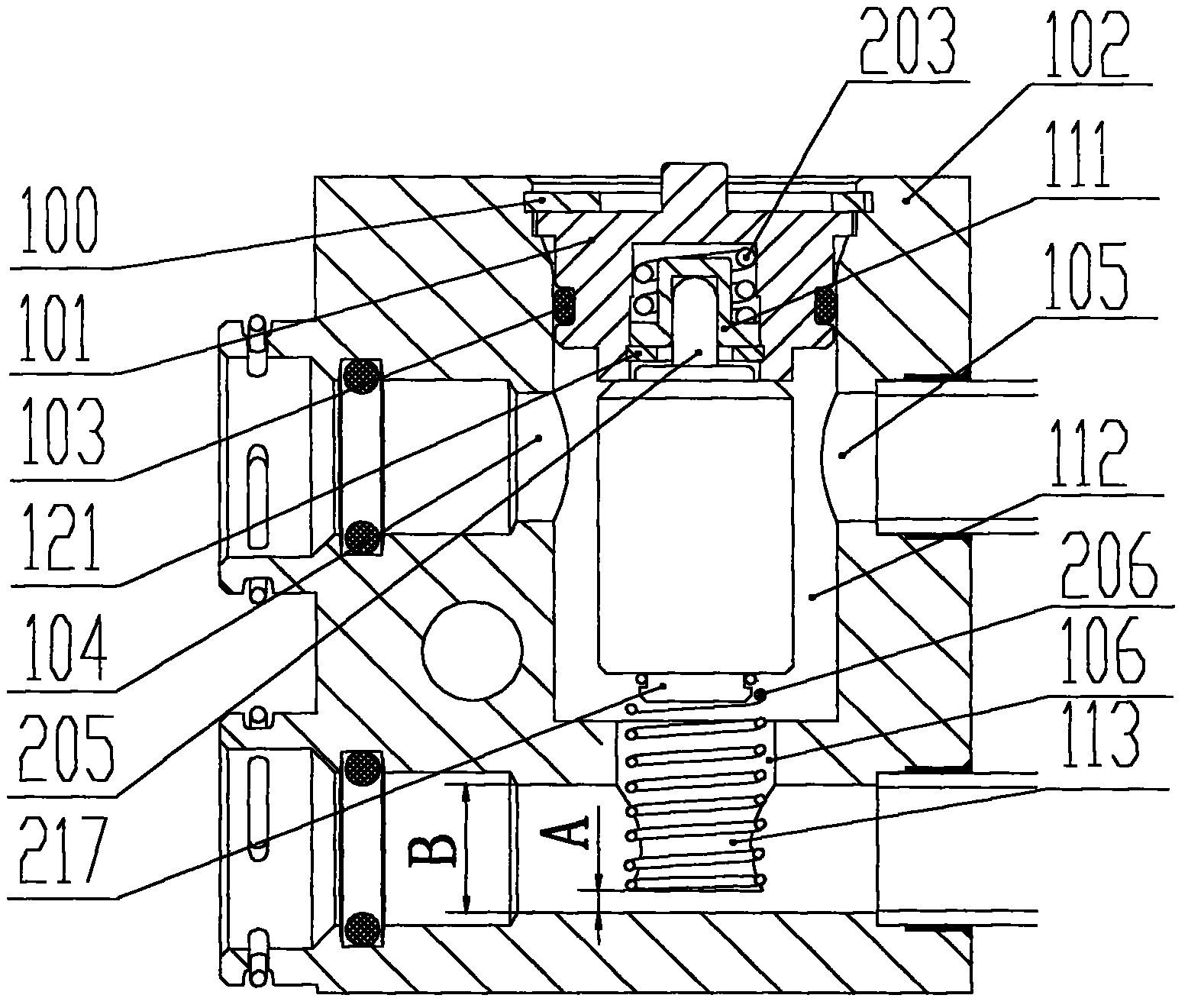
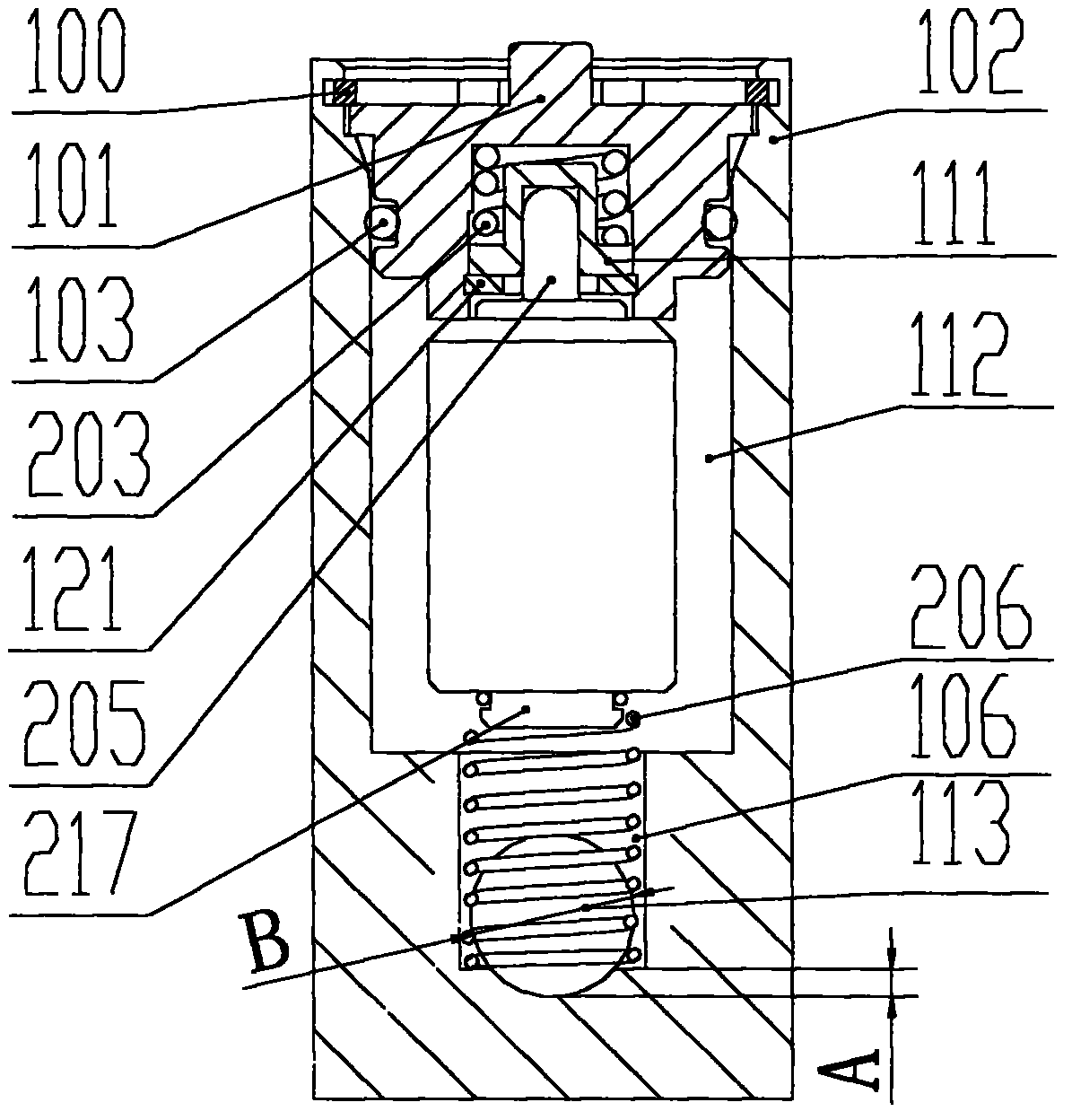
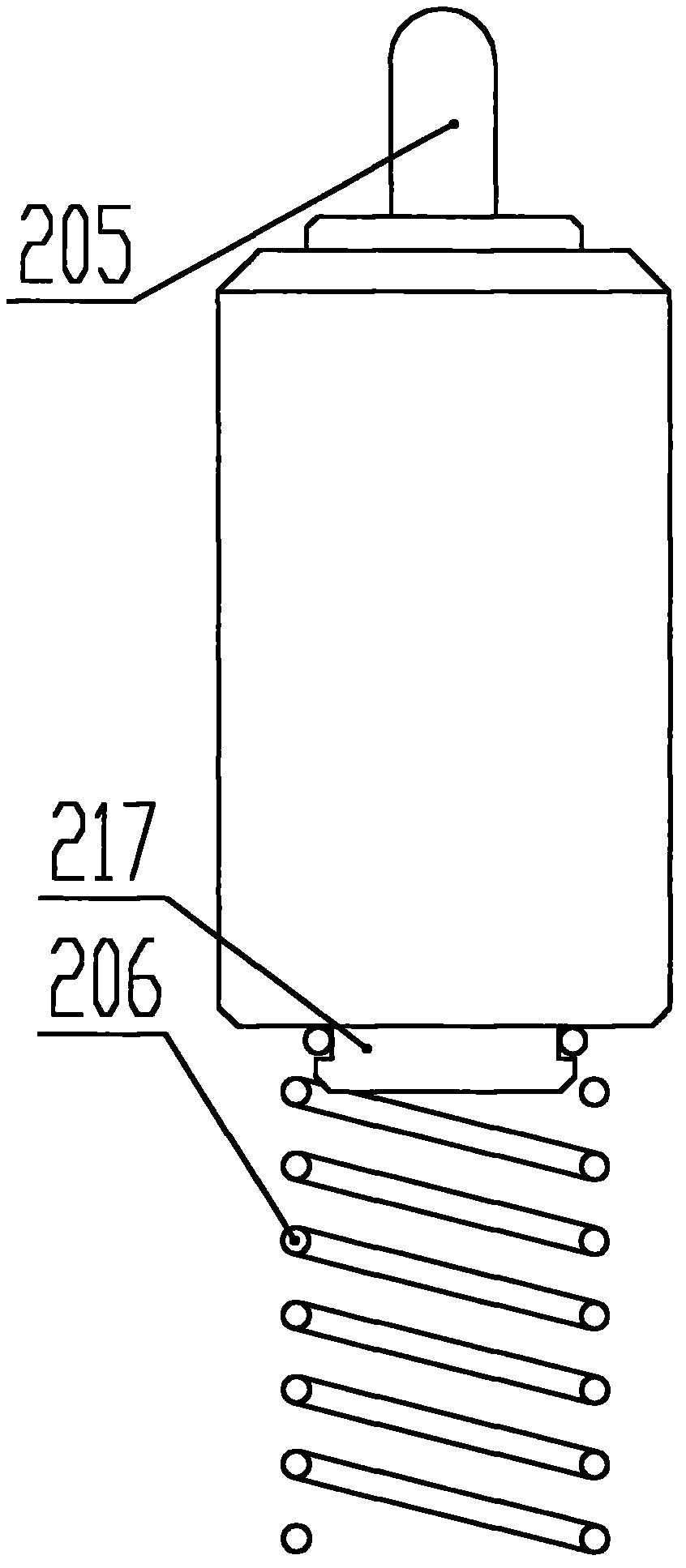
ActiveCN103574265AReduce fluid leak pointsReduce the number of partsOperating means/releasing devices for valvesValve housingsElastic componentEngineering
The invention relates to a temperature regulator for a heat exchange loop. The temperature regulator comprises a valve body and a thermal motive power element, wherein the cavity body is provided with a cavity, the thermal motive power element is arranged in the cavity in a matched way, the valve body also comprises two through holes which are respectively communicated with the cavity, the two through holes are respectively a first hole and a second hole, the first ends of the second hole and the first hole are respectively communicated with an inlet and an outlet of an external fluid cooling device, the second ends of the second hole and the first hole are respectively a fluid inlet and a fluid outlet, the inner diameter of the cavity is greater than the inner diameter of the second hole, in addition, the cavity is communicated with the second hole, one end, near the second hole, of the cavity is partially coincident with the second hole, the outer peripheral side of the thermal motive power element is sheathed with an elastic component, one end of the elastic component is tightly pressed, butted and connected onto the thermal motive power element, and the other end of the elastic component and the bottom of the cavity are tightly pressed, butted and connected with a shoulder part formed by the second hole. The temperature regulator for the heat exchange loop has the advantages that the work temperature of lubricating oil is controlled in an effective range, and the lubricating performance of the lubricating oil can be enabled to be maintained in the optimum state.
Owner:ZHEJIANG SANHUA AUTOMOTIVE COMPONENTS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com