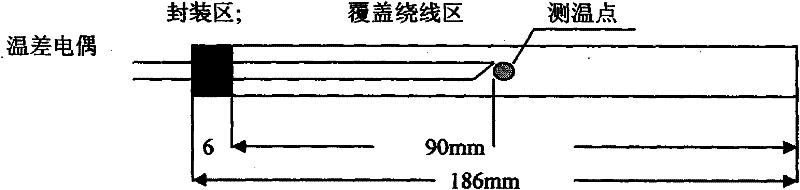
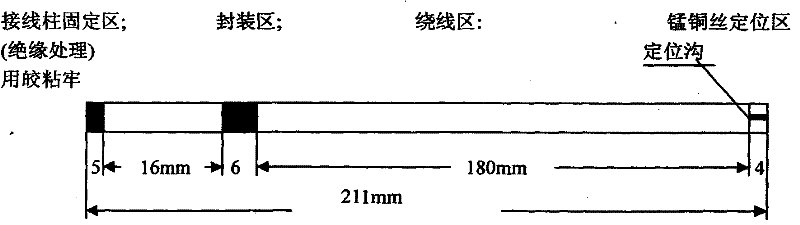
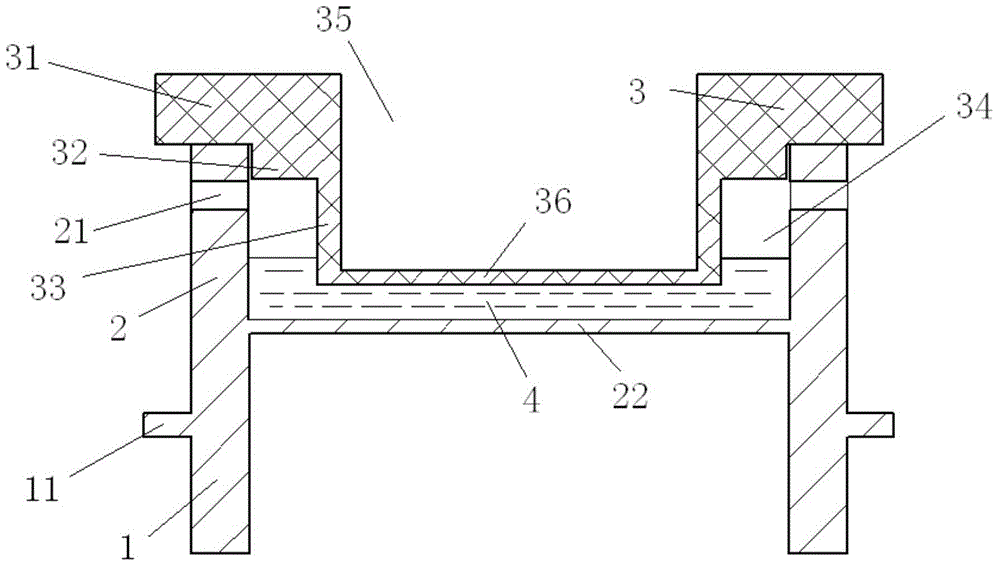
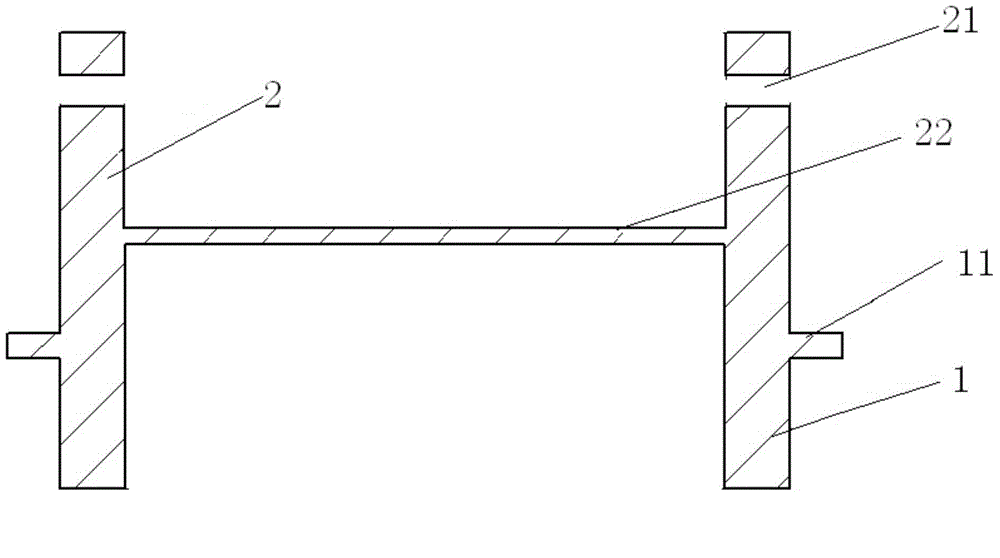
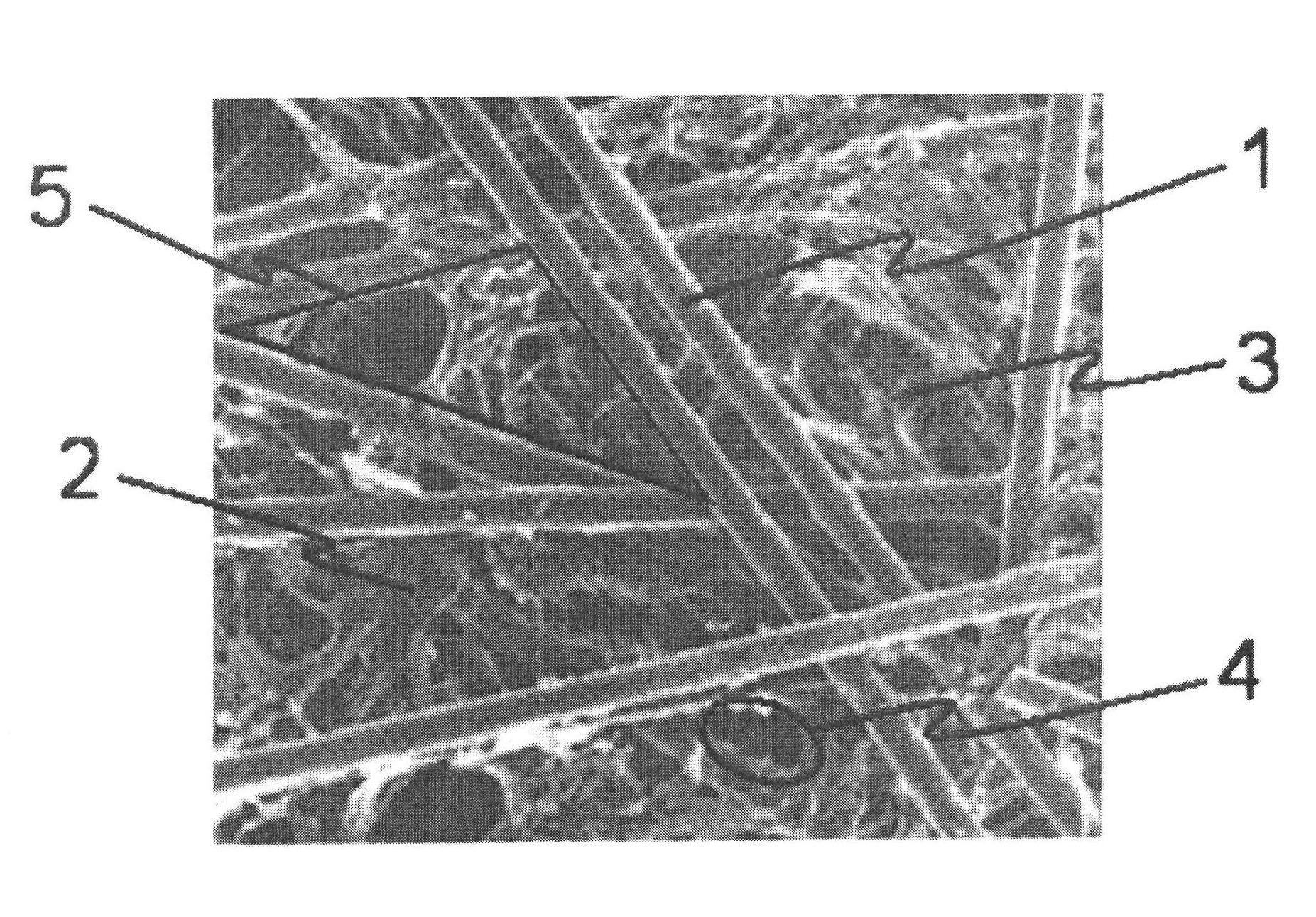
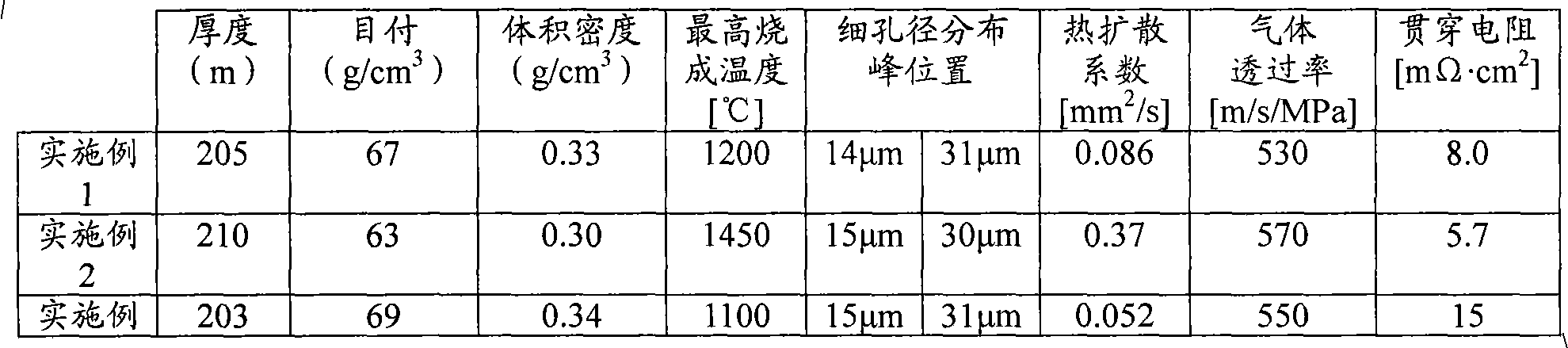
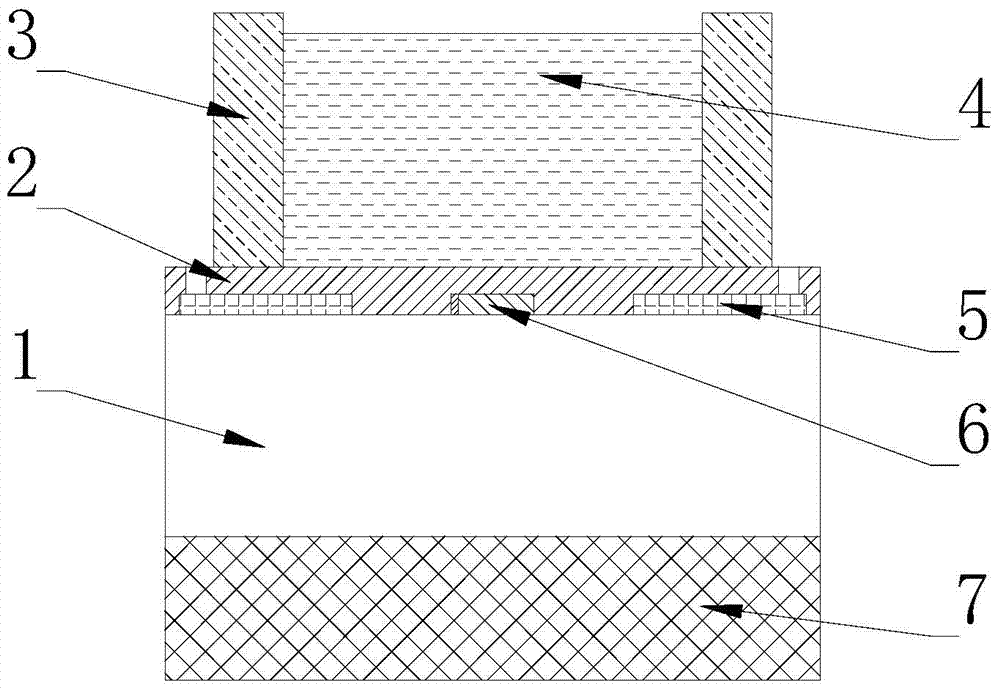
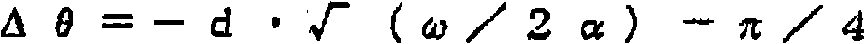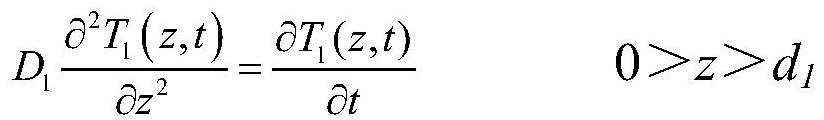Patents
Literature
187 results about "Thermal diffusion coefficient" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
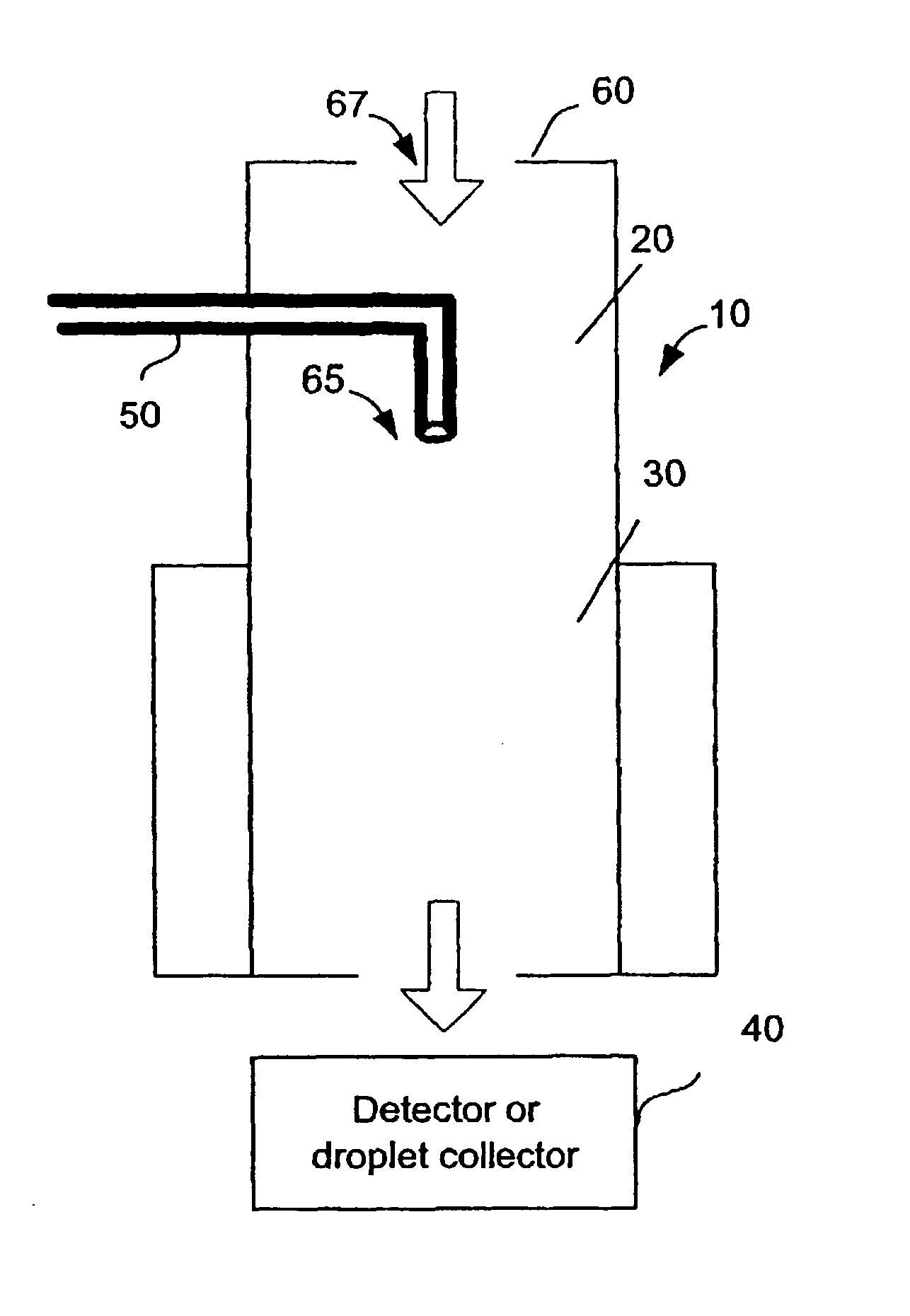
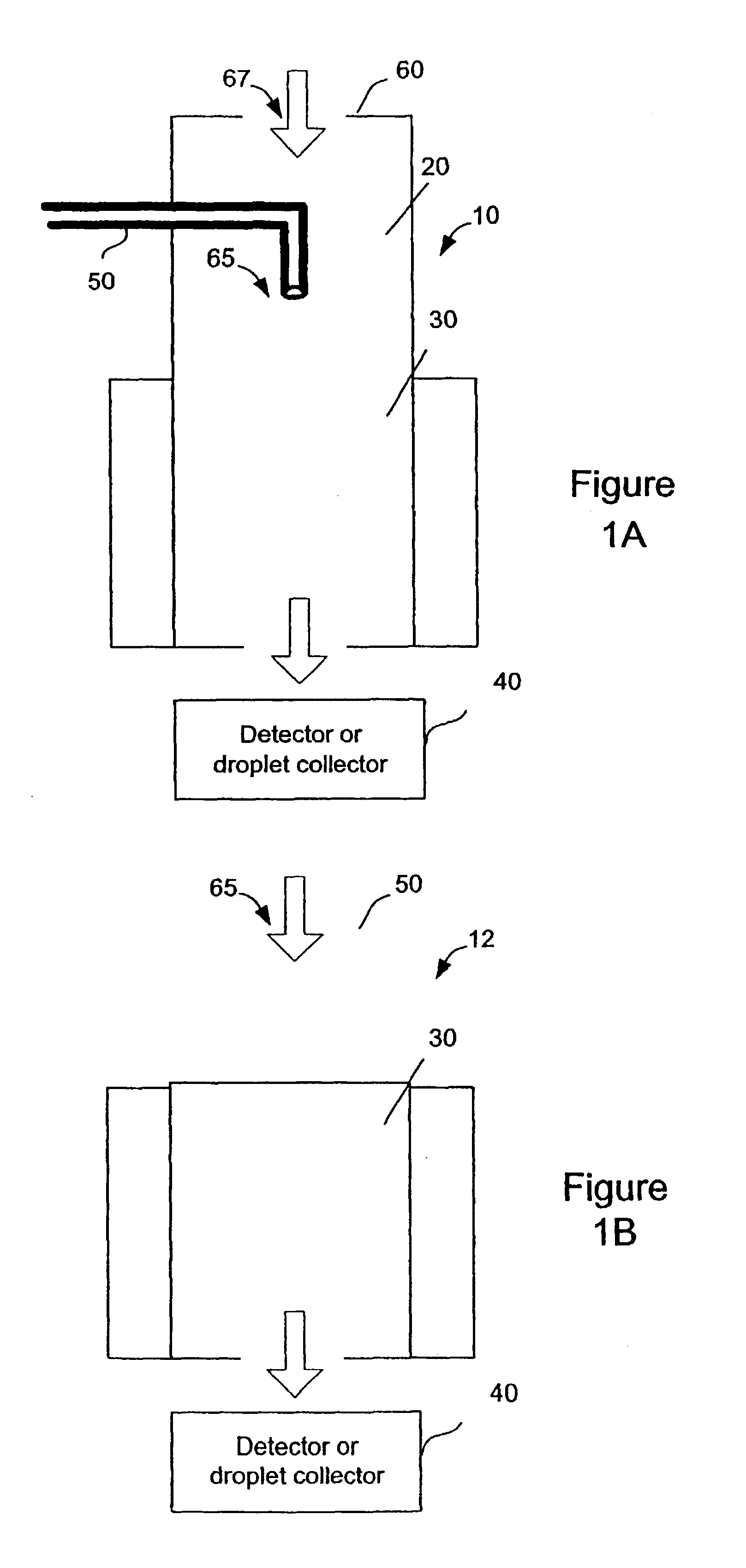
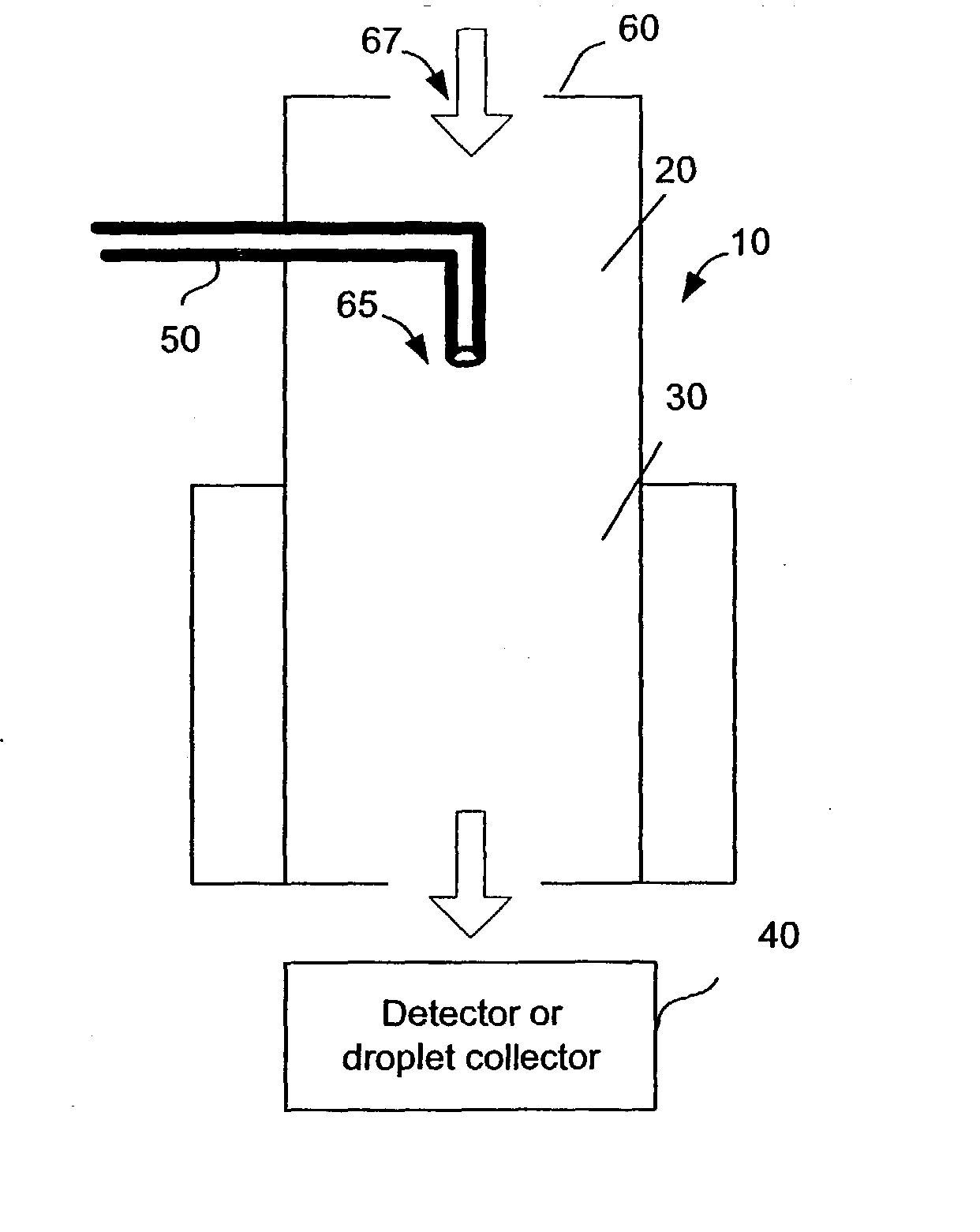
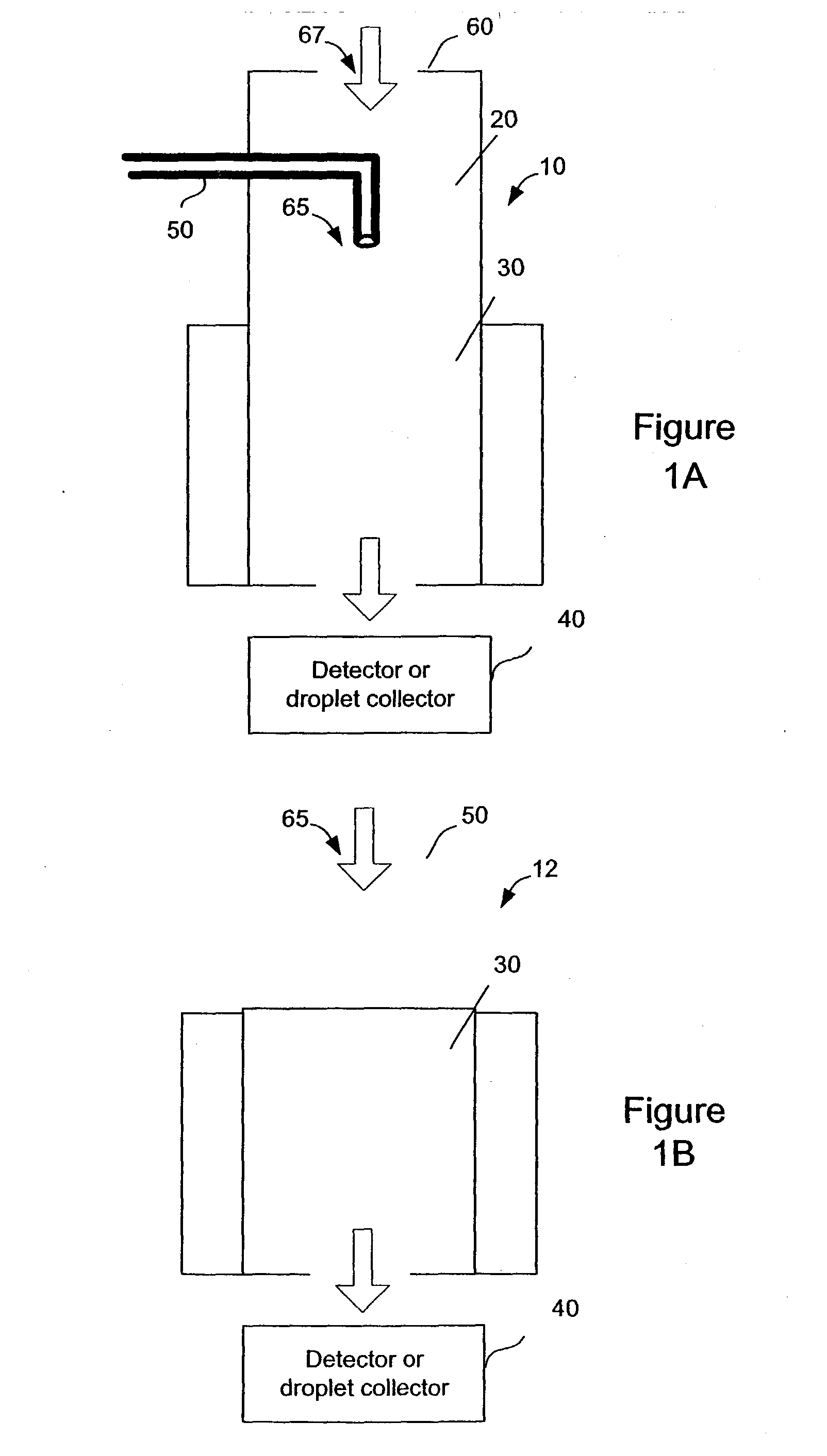
Continuous, laminar flow water-based particle condensation device and method
InactiveUS6712881B2Improve performanceLarge temperature differenceCombination devicesSolidificationWater basedThermal diffusion coefficient
An apparatus and method for producing a diffusive, continuous laminar flow for particle growth via condensation of vapors with a mass diffusivity near or higher than the thermal diffusivity of the surrounding gas. In an exemplary embodiment, the method uses the condensation of water vapor onto particles suspended in air.
Owner:AEROSOL DYNAMICS INC
High-thermal-diffusion-coefficient high molecular material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104559148AImprove thermal conductivityGood radiation cooling performancePolymer scienceAntioxidant
The invention discloses a high-thermal-diffusion-coefficient high molecular material and a preparation method thereof. The high-thermal-diffusion-coefficient high molecular material is prepared from the following steps: 20-65 parts of matrix resin, 35-65 parts of high-thermal diffusion heat-conducting filler, 0.1-5 parts of carbon fiber composite, 0.1-10 parts of a flexibilizer, 0.1-2 parts of coupling agent, 0.1-2 parts of antioxidant and 0.1-15 parts of other auxiliaries. According to the high-thermal-diffusion-coefficient high molecular material, the heat conduction capability of the high molecular material is remarkably enhanced by virtue of the positive synergetic hybrid effect of a three-dimensional heat-conducting network formed by the high-thermal-diffusion-coefficient heat-conducting fillers different in shape in the processing course, and therefore the problems of poor heat conduction and thermal diffusion properties of the high molecular material for the existing LED lamp cooling housing are solved; in the preparation process, the compatibility between the surface modified high-thermal-diffusion-coefficient high molecular material and a resin matrix is improved, the viscosity of the synthetic resin melt is reduced and the dispersity of the filler is improved to enhance the processability; as a result, the product has excellent surface quality and mechanical properties; the high molecular material further has the advantages of high thermal conductivity and high tenacity.
Owner:HUIZHOU KINGBALI TECH
Method for measuring thickness by pulse infrared thermal wave technology
ActiveCN102221339ASimple processing methodMaterial flaws investigationUsing optical meansThermal diffusion coefficientThermodynamics
The invention provides a method for measuring thickness or defect depth by a pulse infrared thermal wave technology, comprising the following steps of (1) heating an object to be measured by pulse heating equipment; obtaining a thermographic sequence on the surface of the object to be measured by an infrared thermal imaging device; memorizing the thermographic sequence in a general memory; (2) multiplying a temperature-time curve of each point in the thermaographic sequence with corresponding time, thus obtaining a new curve f; (3) working out first-order differential on the f; and obtaining a peak time tapst; (4) working out L by a formula, wherein Alpha is thermal diffusion coefficient and L is the thickness or the defect depth of the object to be measured. By adopting the technical scheme, the thickness or detect depth of a part to be measured can be measured, a reference curve is not needed, and only one-order differential treatment is needed for the measurement, so that the processing method is simpler.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
Thermally conductive polymer compostions to reduce molding cycle time
InactiveCN104364900ASemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesPolymer scienceThermal diffusion coefficient
A thermally conductive polymer composition comprising (1) a polymer material, and (2) a thermally conductive filler. The thermally conductive filler can be boron nitride. The thermally conductive polymer composition can be used in a molding operation to form a molded article and can reduce the molding cycle time of a molding process. In one embodiment, increasing the thermal conductivity of a polymer material (as compared to the thermal conductivity of the material in the absence of a thermally conductive filler) increases the thermal diffusivity and reduces the cooling time of the article. The present invention also provides methods of forming molded articles from such compositions.
Owner:MOMENTIVE PERFORMANCE MATERIALS INC
Device and method for dynamically measuring thermal physical parameters of film
The invention relates to a device for dynamically measuring thermal physical parameters of a film. The main body of the device provided by the invention comprises a heat source, a heat wave signal source, one-dimensional heat conductors, a data acquisition device, a data processing device, a heat insulating material and a heat radiating fin, wherein each one-dimensional heat conductor comprises two cylindrical sticks which are completely identical; a sample to be measured is sandwiched between the two one-dimensional heat conductors; the heat insulating material integrally wraps the one-dimensional heat conductors and the sample to be measured, thereby reducing heat exchange between the conductor sticks and the outside to the greatest extent; the two ends of the two one-dimensional heat conductors, which are not in contact with the sample to be measured, are respectively connected with two thermoelectric modules; and the other ends of the two thermoelectric modules are respectively connected with the heat radiating fin. By the adoption of the method for dynamically measuring the thermal physical parameters of the film provided by the invention, the thermal conductivity coefficients and thermal diffusion coefficients of different sample films can be calculated. The invention has the advantages that measuring equipment has small size, cost is low and measuring repeatability is high; the longitudinal thermal diffusion coefficients and thermal conductivity coefficients of a film material can be measured directly, errors cused by a contact surface can be overcome.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Unsteady-state measuring device and method of heat conduction performance of multi-phase porous material
InactiveCN101706463ASolve the problem of water evaporationOvercoming heat convectioMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentDiffusionThermal diffusion coefficient
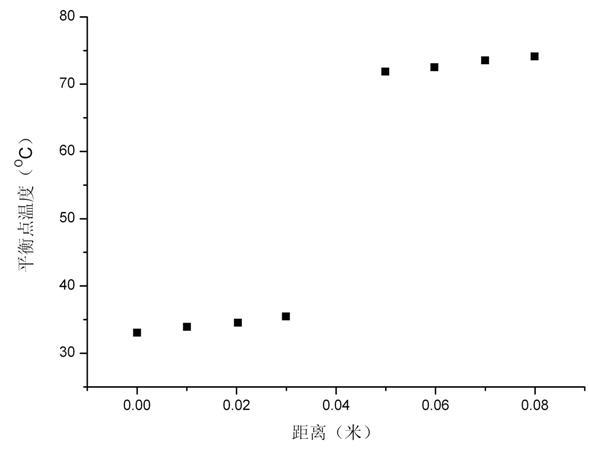
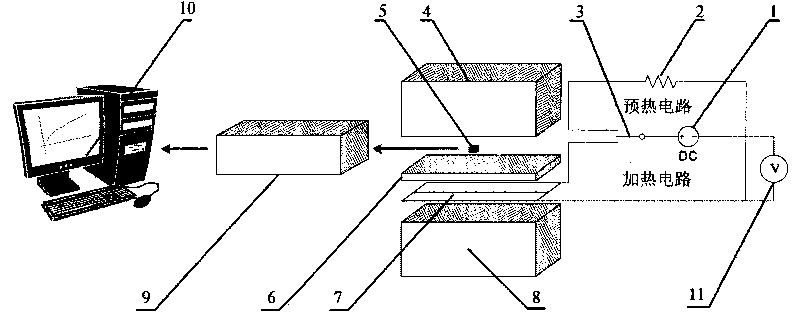
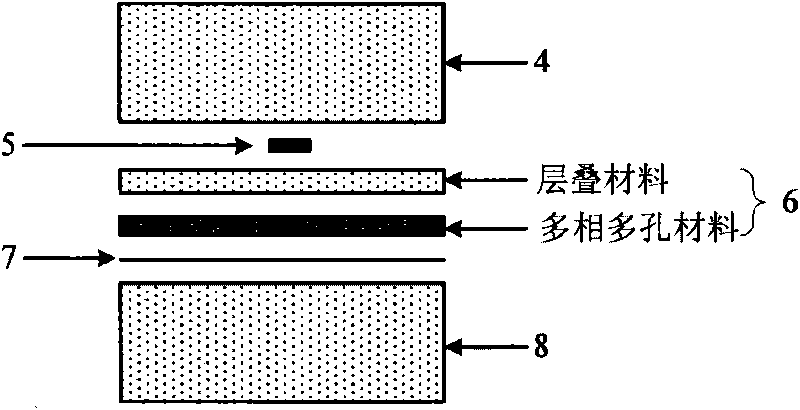
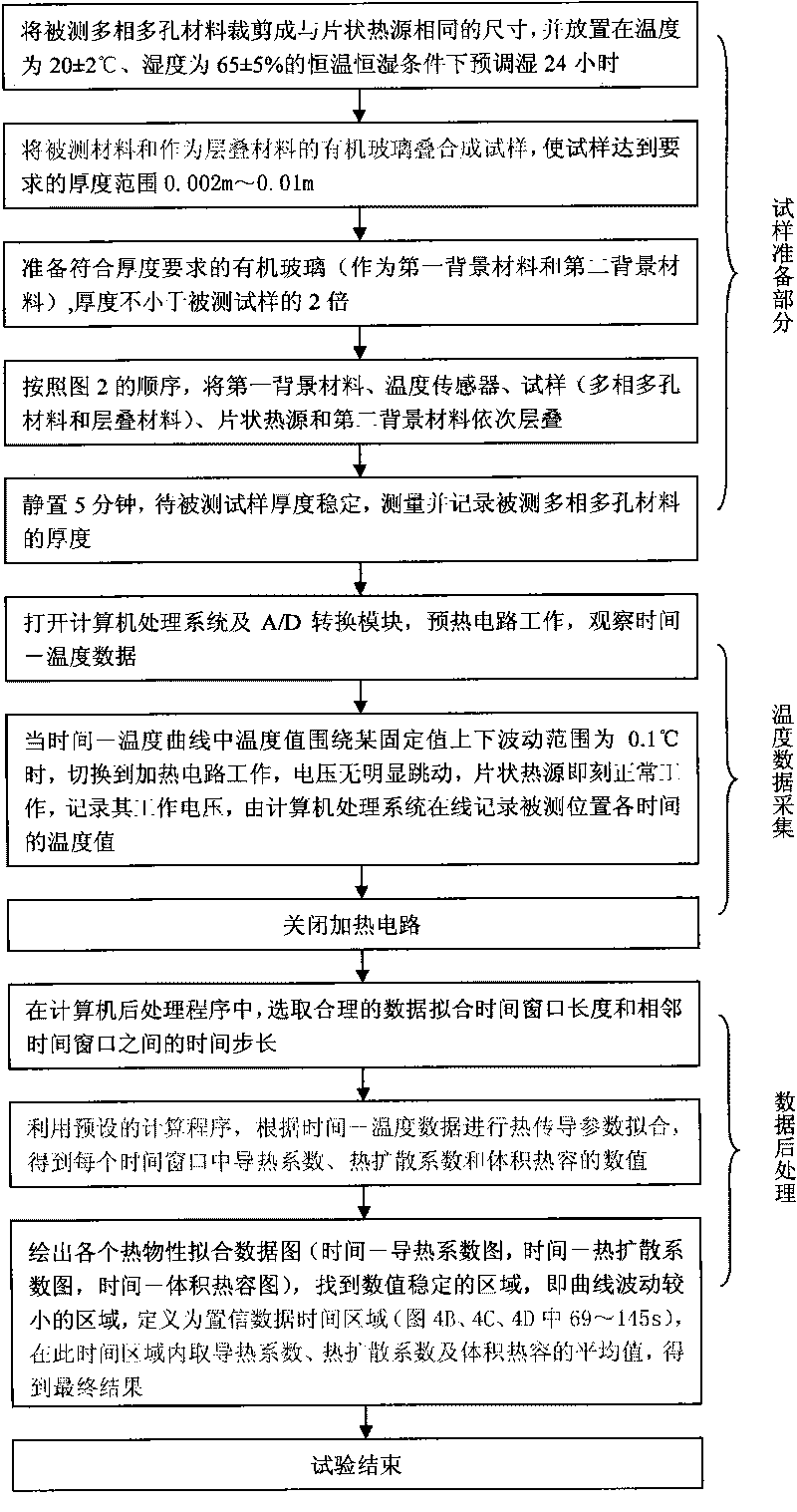
The invention relates to an unsteady-state measuring device and a method of heat conduction performance of a multi-phase porous material. The device comprises a sample heating device, a data acquisition system and a computer processing system. The invention is characterized in that the sample heating device consists of four parts, namely a heating circuit, a preheating circuit, a sample and a background material, wherein the sample consists of a measured multi-phase porous material and a laminated material (organic glass), and the organic glass is selected as a first background material and a second background material for measurement, thus forming the important advantage of the invention that various multi-phase porous materials from low volume density to high volume density can be measured. The testing method can be divided into three major parts, namely preparation of the sample and the background materials, temperature data acquisition and data post processing, and comprises six specific steps. The device can measure heat conduction coefficients, heat diffusion coefficients and volume heat capacity of the multi-phase porous sample, and is especially applicable to the multi-phase porous materials with low volume density. The device is simple and the testing speed is fast and can be finished only by minutes.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Continuous, lawinar flow water-based particle condensation device and method
InactiveUS20040020362A1Improve performanceLarge temperature differenceCombination devicesSolidificationWater basedThermal diffusion coefficient
An apparatus and method for producing a diffusive, continuous laminar flow for particle growth via condensation of vapors with a mass diffusivity near or higher than the thermal diffusivity of the surrounding gas. In an exemplary embodiment, the method uses the condensation of water vapor onto particles suspended in air.
Owner:AEROSOL DYNAMICS INC
Quantitative measurement method for pulse infrared thermal wave technology
ActiveCN102565124AEasy to measureImprove accuracyMaterial heat developmentMaterial flaws investigationThermodynamicsThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a quantitative measurement method for a pulse infrared thermal wave technology. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, heating the surface of a measured object by using a pulse heating device, continuously observing and recording the temperature field change of the surface of the measured object by using an infrared thermal image device, and acquiring a time sequence thermal wave signal through a computer control and acquisition system to obtain a thermograph sequence of the surface of the measured object; 2, according to the obtained thermograph sequence, extracting temperature reducing data of a defective area and a non-defective area, and comparing logarithmic temperature-logarithmic time curves; 3, setting a separation time point of defective and non-defective area curves in the logarithmic temperature-logarithmic time curves or a previous time point of the separation time point as t1, setting the maximum temperature difference time point of the two curves as t2, and extracting a temperature value or a radiation energy value delta T (0, t1) and delta T (0, t2) corresponding to the two time points; and 4, when two of an interface thermal reflection coefficient R of the defective area, a thermal diffusion coefficient alpha of the measured object and a defect depth L are given, solving the third coefficient by using a formula (4).
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY +2
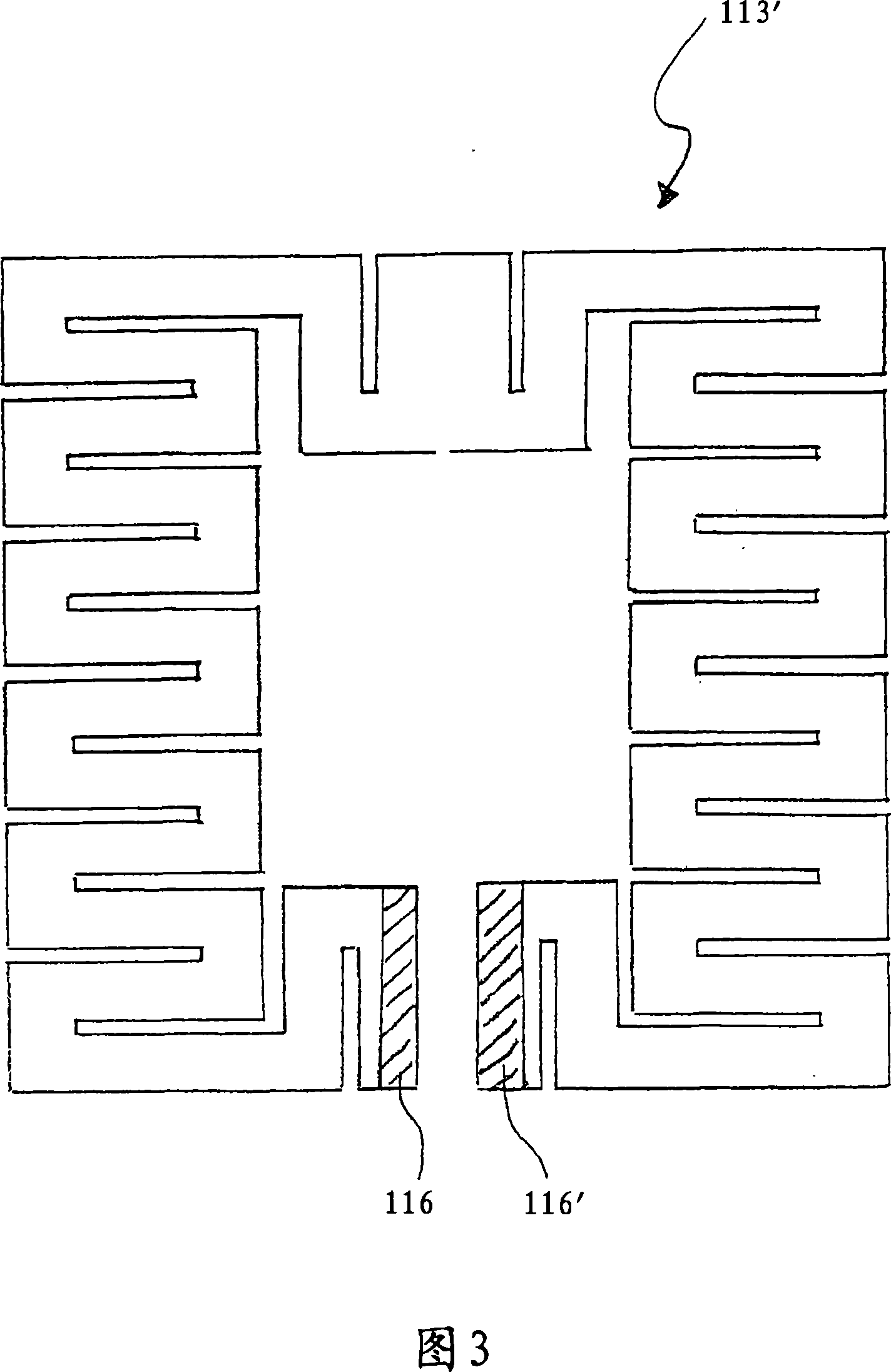
Radiant heater for heating the building material in a laser sintering device
InactiveCN101107882ALess lateral radiationLow thermal inertiaAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyRadiant heaterThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention relates to a radiant heater for heating the building material in a laser sintering device and to a laser sintering device comprising a radiant heater of this type. The radiant heater comprises a flat heat-emission element (113, 213, 313), which is characterised in that it consists of a material with low thermal inertia and a thermal diffusivity preferably in excess of 1.5 10-4 m2 / s and preferably a thickness less than or equal to 2 mm.
Owner:EOS ELECTRO OPTICAL SYST
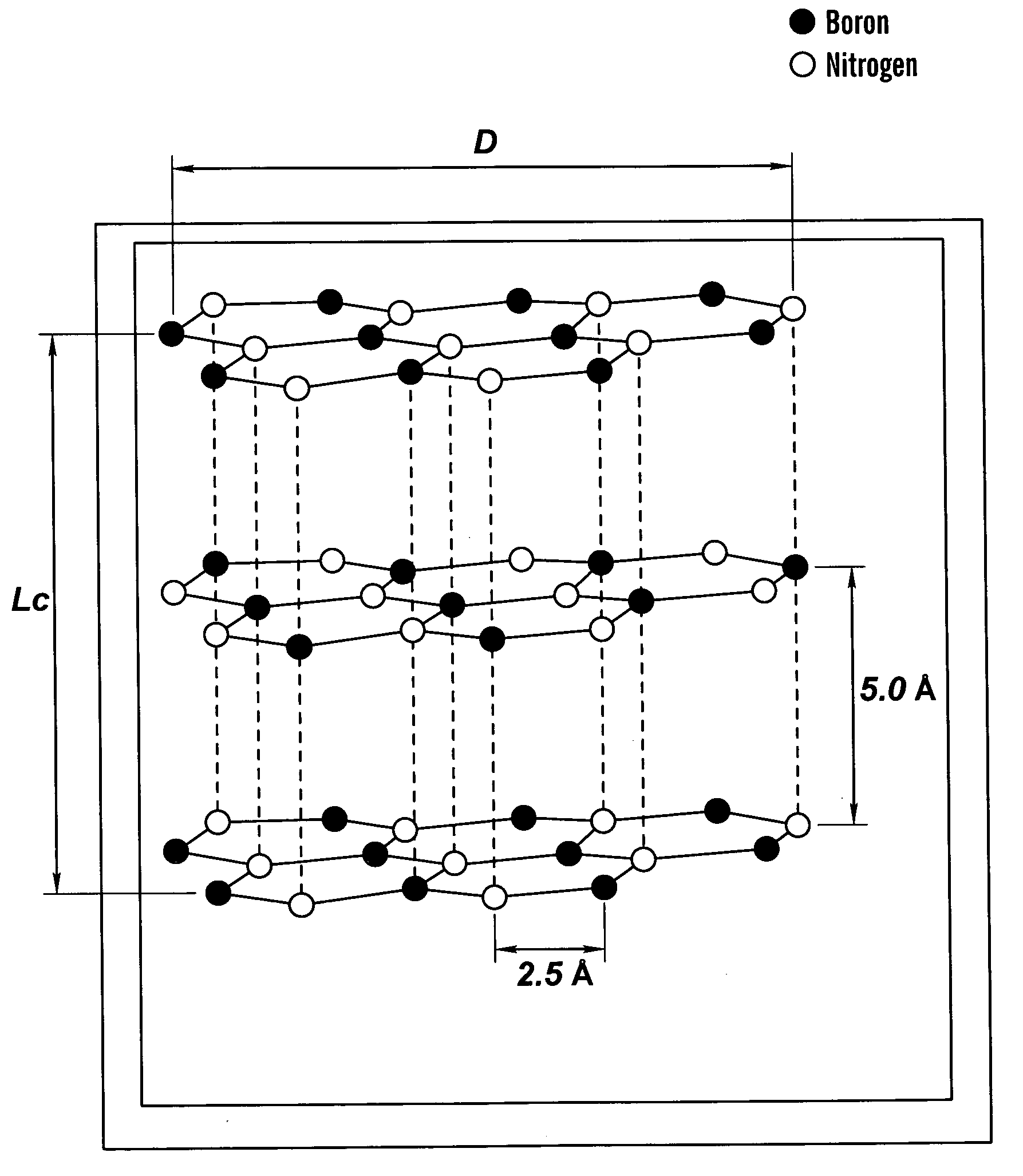
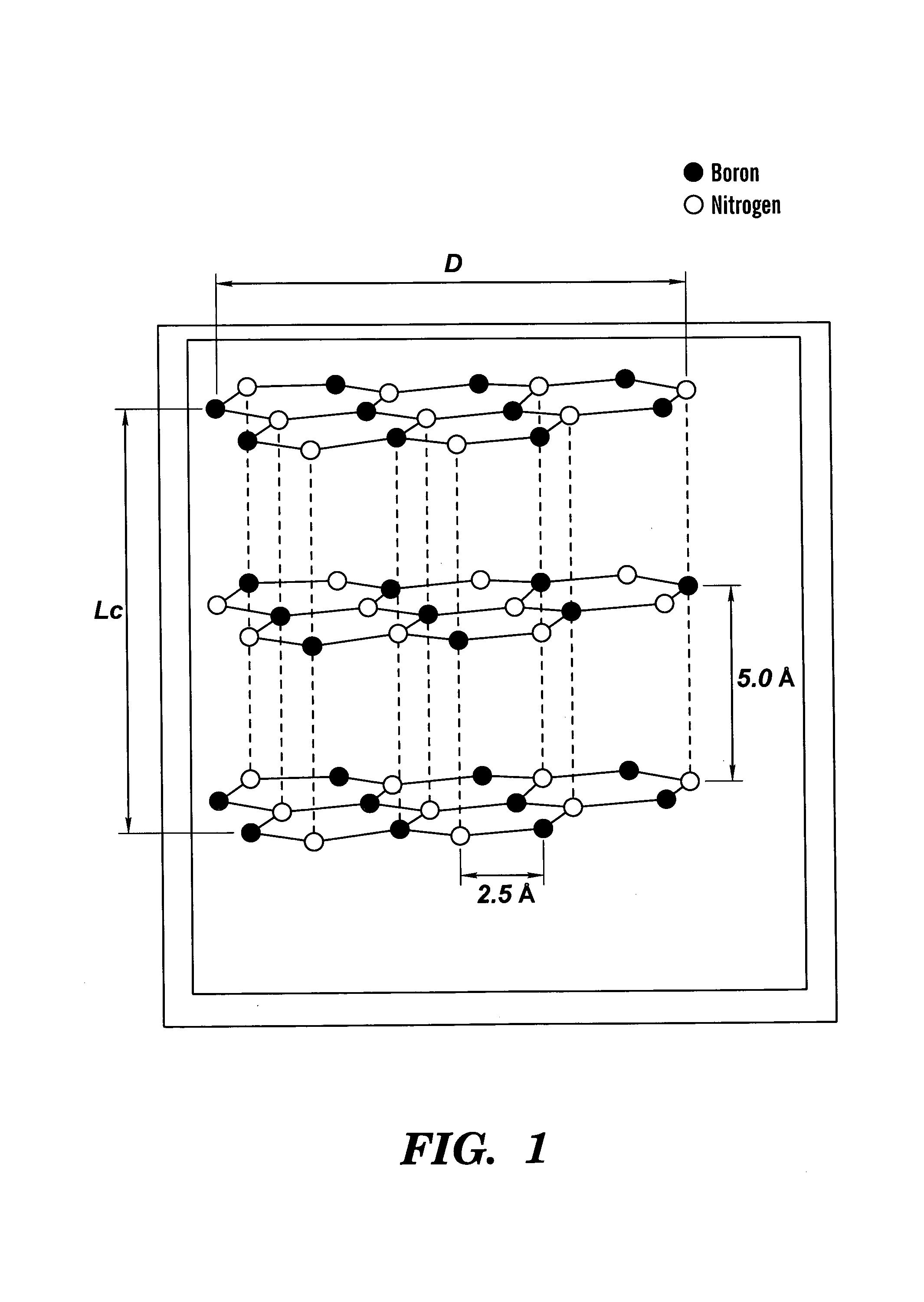
Method for making high thermal diffusivity boron nitride powders
InactiveUS7189774B2Excellent thermal diffusivityImprove thermal conductivityNitrogen compoundsBoron compoundsThermal diffusion coefficientMetallurgy
The present invention relates to a method for making boron nitride powder having a thermal diffusivity of from about 0.14 cm2 / s to about 0.20 cm2 / s. This method involves pressing high purity, hexagonal boron nitride having an average platelet size of at least 2 microns into a compacted form, sintering the compacted form of boron nitride to form a sintered body, and crushing the sintered body under conditions effective to produce boron nitride powder having a thermal diffusivity of from about 0.14 cm2 / s to about 0.20 cm2 / s. Another aspect of the present invention relates to boron nitride powder having a thermal diffusivity of from about 0.14 cm2 / s to about 0.20 cm2 / s.
Owner:SAINT GOBAIN CERAMICS & PLASTICS INC
High thermal conductivity carbon fiber resin-based composite material and preparation method thereof
The invention relates to a high thermal conductivity carbon fiber resin-based composite material and a preparation method thereof. According to the technical scheme, intermediate phase pitch based carbon fibers are taken as a heat conduction reinforcing material, a polymer resin is taken as a substrate material, and the volume packing rate of the intermediate phase pitch based carbon fibers is 10-60 percent. The preparation method comprises the following steps: uniformly coating the polymer resin on surfaces of intermediate phase pitch based carbon fiber filaments; unidirectionally paving or orthogonally paving in a cross shape in a mold; and performing casting moulding or hot press moulding to obtain the high thermal conductivity carbon fiber resin-based composite material. The preparation process is simple and high in repeatability; the internal carbon fibers of the prepared high thermal conductivity carbon fiber resin-based composite material have a high orientation arrangement structure, and the thermal diffusion coefficient and the thermal conductivity along the length direction of the fibers can be controlled in a range of 50-400mm<2> / s and a range of 80-500W / m.k according to the difference of carbon fiber filling amount. Therefore, the product has the characteristics of high orientation and high thermal conductivity, and the electrical and mechanical properties along the axial direction of the fibers can be obviously improved.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
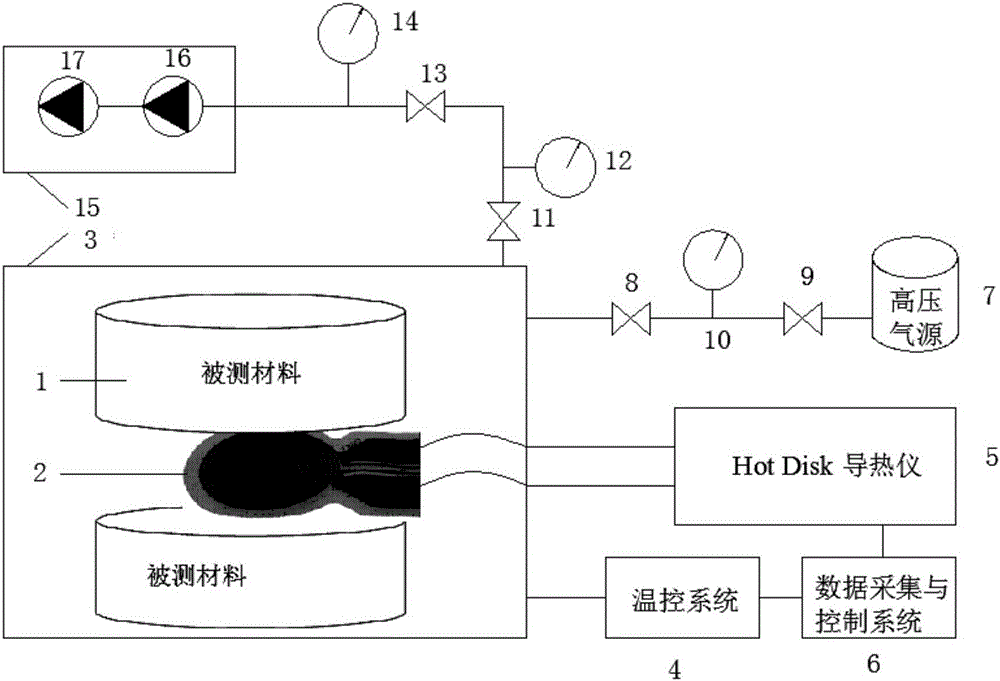
Variable-atmosphere pressure heat conductivity coefficient testing device based on transient plane source method
InactiveCN105928975AAccurate insulation performanceGood heat insulationMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentTest powerData acquisition
The invention relates to a variable-atmosphere pressure heat conductivity coefficient testing device based on a transient plane source method. A double-screw test probe is arranged between two same tested materials with smooth surfaces, the tested materials and the test probe are integrally arranged in a tube-type high temperature furnace, a controllable environment temperature is provided for the tube-type high temperature furnace and a temperature control system, a high pressure air source is matched with a molecular pump to control the type and pressure of the atmosphere inside the high temperature furnace, a data collection and control system is connected with a temperature control system and a Hot Disk conductometer respectively, the Hot Disk conductometer connected with the double-screw test probe is used for providing test power and heating time for the double-screw test probe, and the data collection and control system is used for obtaining the heat conductivity coefficients and heat diffusion coefficients of the tested materials according to theoretical calculation of the transient plane source method. The heat conductivity coefficient test for the transient plane source method under a variable-atmosphere pressure condition is realized for the first time internationally, and the atmosphere pressure range of porous material heat conductivity coefficient test is the maximum test range reported domestically at present.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method and apparatus for determining the thermal expansion of a material
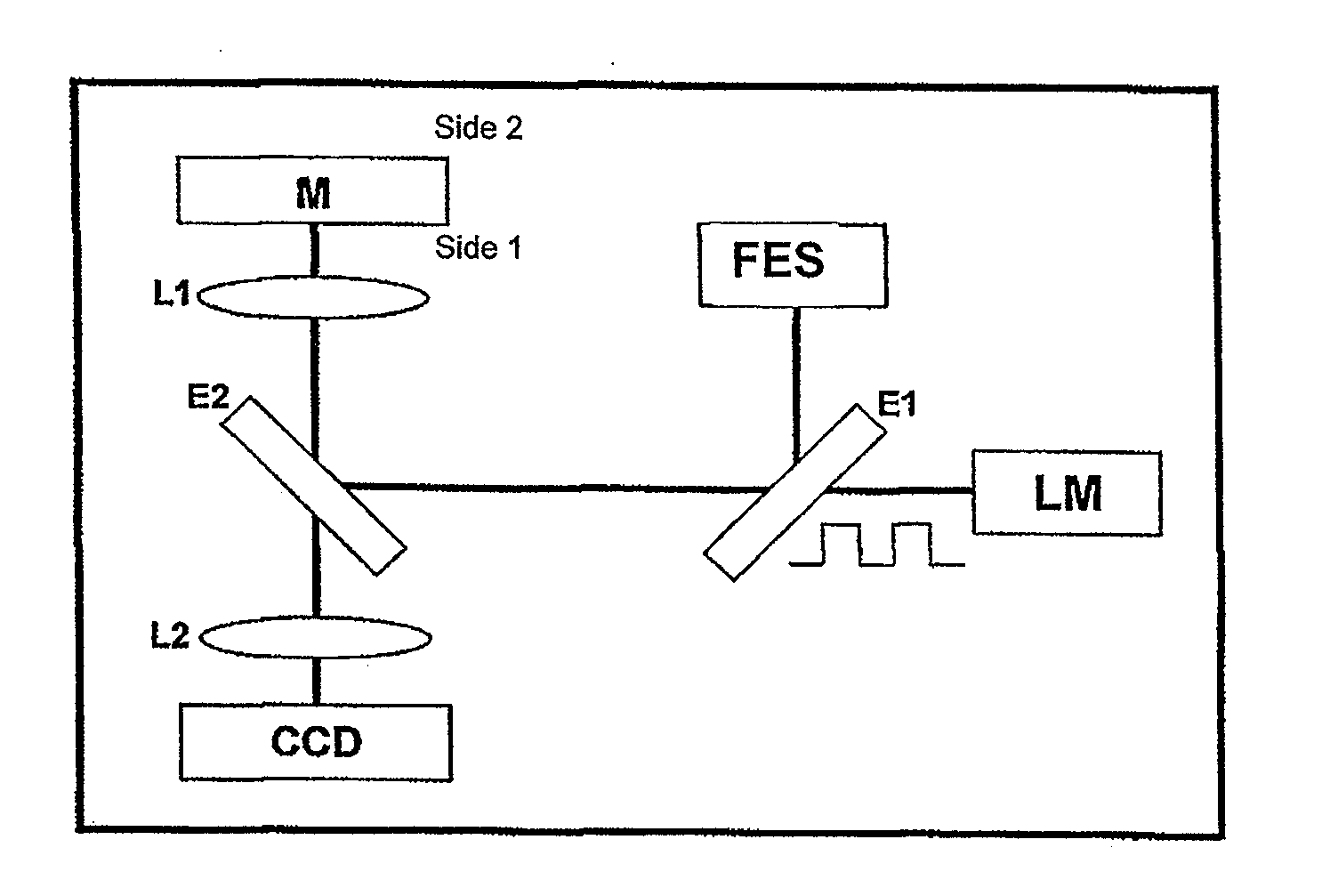
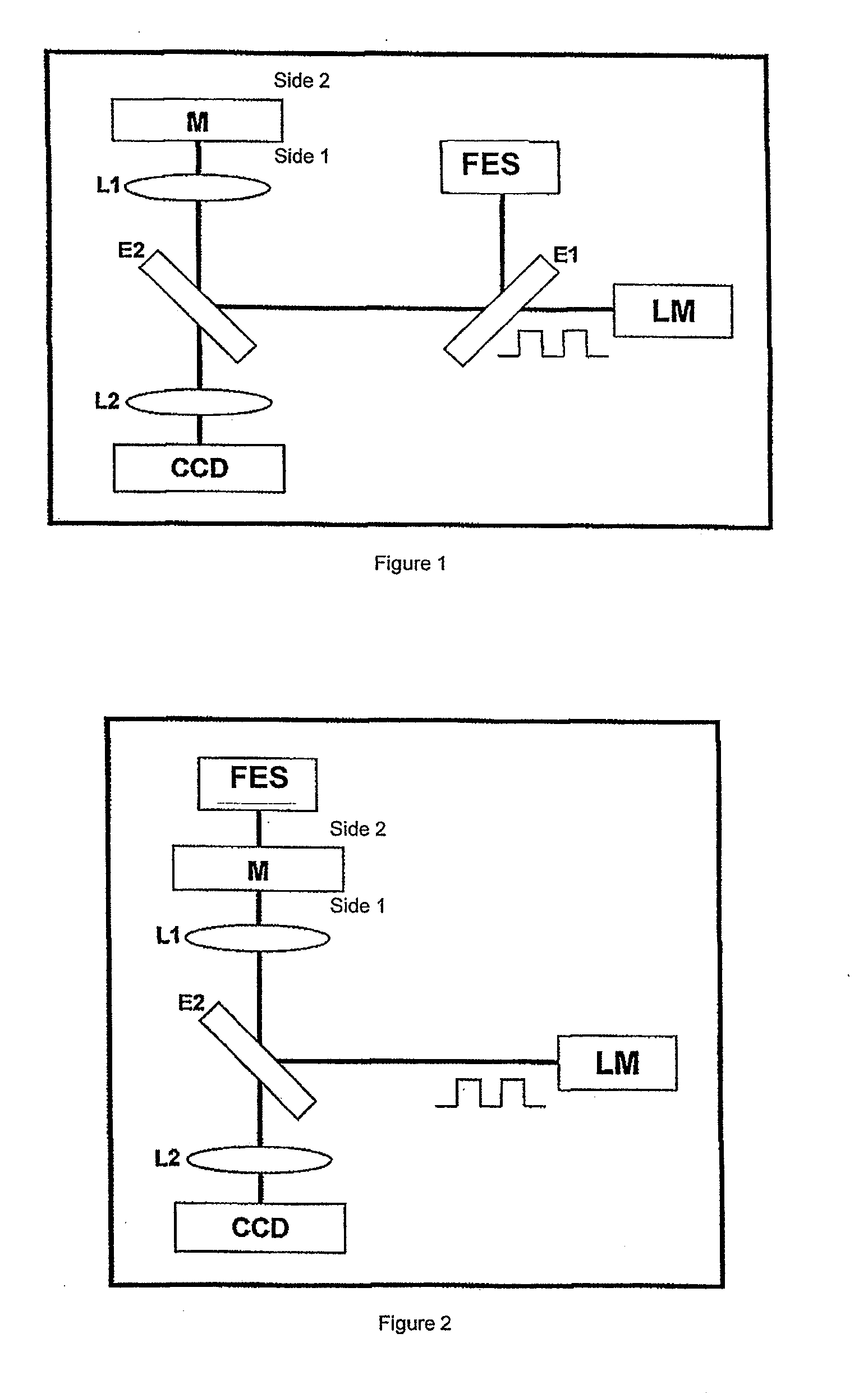
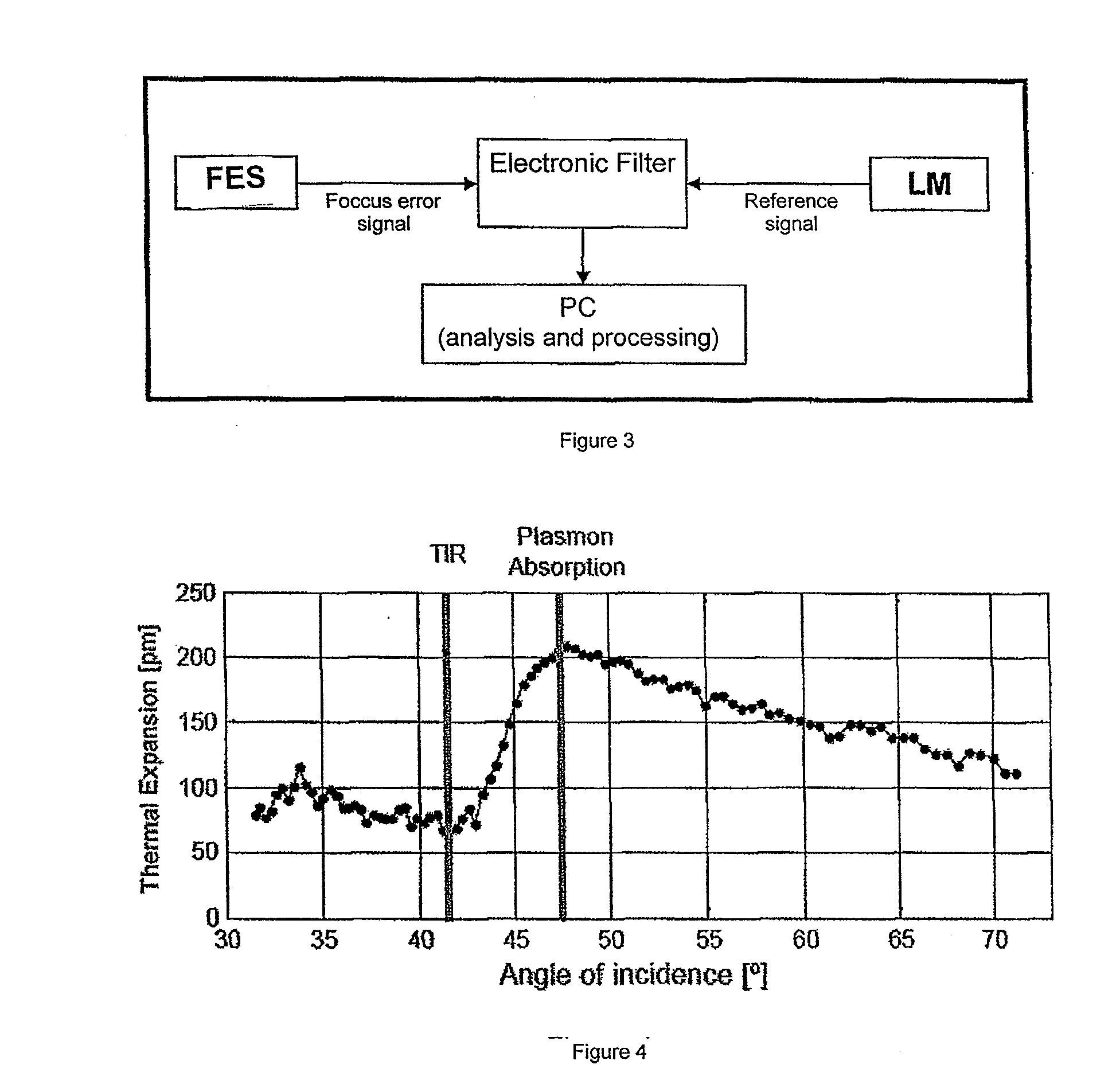
InactiveUS20100208242A1Accurate and sensitive measurementMaterial thermal coefficient of expansionColor/spectral properties measurementsAbsorbed energyThermal expansion
A focus error signal resulting from the photothermically-induced expansion is measured in a sample of material under analysis. A laser is disposed as a periodically modulated heating source which is directed to the sample and a device for focus error measuring which is directed to de surface being heated. A device measuring focus error generates a signal representative of the displacement of the surface of material in perpendicular direction due to the expansion produced by the periodic heating, which is filtered, either analogically or digitally, to discriminate the displacement component at the frequency in which it was modulated or at any other related frequency, such any harmonic or a sum with any other modulation. The focus error signal, appropriately calibrated, gives a precise and sensitive measure of the magnitude the expansion. Said magnitude and its dependence with the modulation frequency allows the determination of physical properties such as the thermal expansion or thermal diffusivity coefficient, the thickness of a coating film or the absorption coefficient of the light from the heating beam. By varying the wave length of the directed radiation it is possible to determine the absorption spectrum of the sample even for very small sized particles in which the fraction of absorbed energy is very little.
Owner:CONSEJO NAT DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS Y TECH CONICET
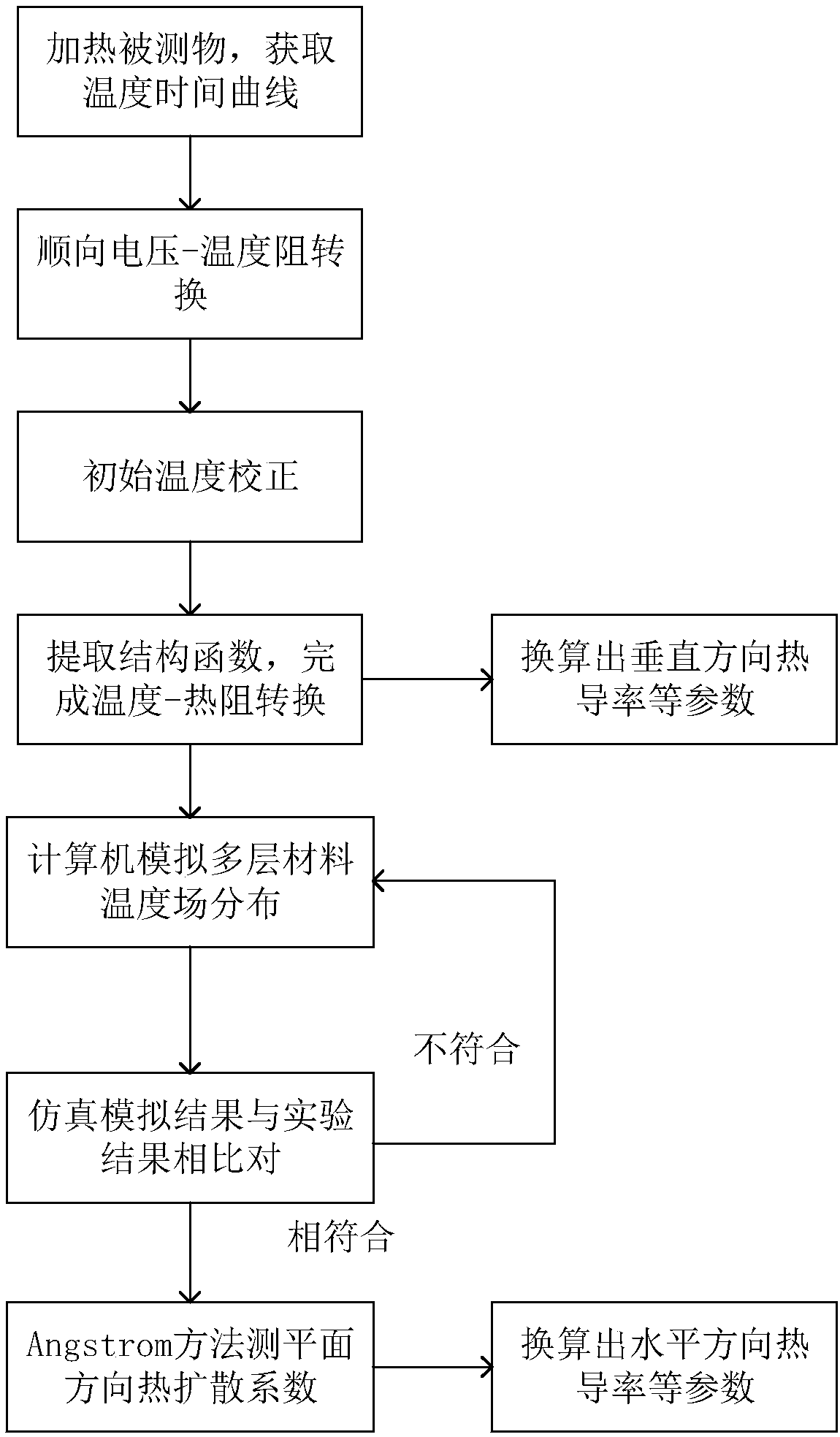
Test method and system for thermophysical parameters based on multilayer composite material
ActiveCN108614005AShort measurement timeImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentHeat flowThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a test method for thermophysical parameters based on a multilayer composite material, wherein the method comprises the following steps: heating a multilayer composite materialtested object by the system, and measuring the time-temperature curve T (t) of the tested object; calculating to obtain thermal resistance and interface thermal resistance of various layers of materials in the vertical direction of the multilayer composite material tested object by the system; carrying out analogue simulation by the system, to obtain heat transfer disturbance between the layers ofmaterials; and measuring planar thermophysical parameters via an Angstrom method by the system, and converting into related thermophysical parameters. A test system for the thermophysical parametersbased on the multilayer composite materials includes a time-temperature curve obtaining module, a thermal resistance conversion module, a system analogue simulation and a thermophysical parameter calculation module. The method can measure the vertical-direction thermal resistance and the horizontal-direction thermal diffusion coefficient of the multilayer composite material, and simulates the thermal crosstalk direction of heat flow among multiple layers of materials. The method can be widely applied in the field of material heat testing.
Owner:JIEYAO PRECISION HARDWARE SHENZHEN
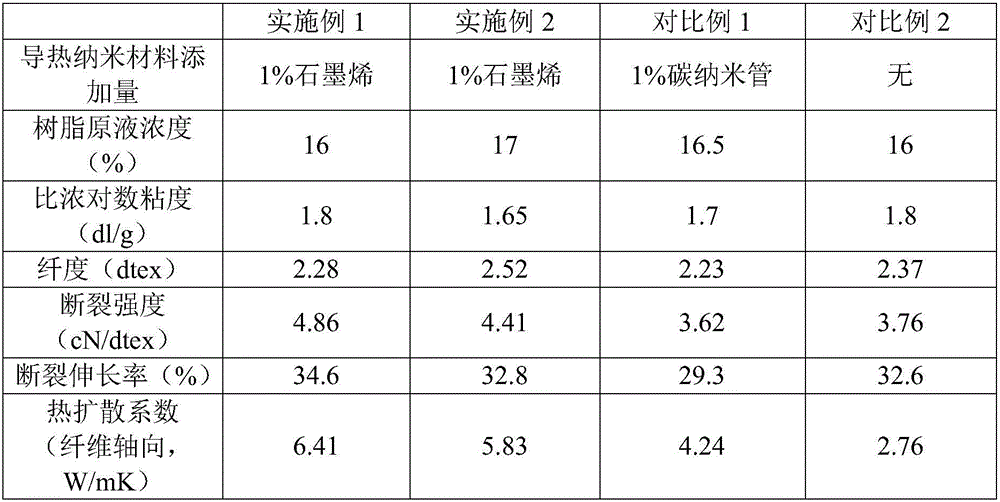
Preparation method and application of high-thermal-conductivity aromatic polyamide fibers
ActiveCN106498538AFast heat conductionReduced Diffusion Path ResistanceArtifical filament manufactureMonocomponent polyamides artificial filamentSolventAramid
A preparation method of high-thermal-conductivity aromatic polyamide fibers includes dispersing oxidized graphene in an organic solvent to obtain dispersion liquid; adding m-phenylenediamine monomers into the dispersion liquid under the protection of inert gas, and cooling a system to a temperature as required by the system; slowly adding part of isophthaloyl dichloride while stirring to allow a polycondensation reaction of the solvent, adding alkaline substances for neutralization, adding the rest isophthaloyl dichloride, and continuing to stir until complete reaction to obtain a meta-position aromatic polyamide resin solution; taking the meta-position aromatic polyamide resin solution as a spinning solution, adopting a dry-spraying and wet-spinning process to spin, and finally preparing the high-thermal-conductivity aromatic polyamide fibers. The high-thermal-conductivity aromatic polyamide fibers have high thermal diffusion coefficients; added carbon nano-materials, graphite nano-materials and the like have antifriction effect, and serve as structure reinforcing materials which obviously improve mechanical properties of aramid fibers.
Owner:ZHUZHOU TIMES NEW MATERIALS TECH
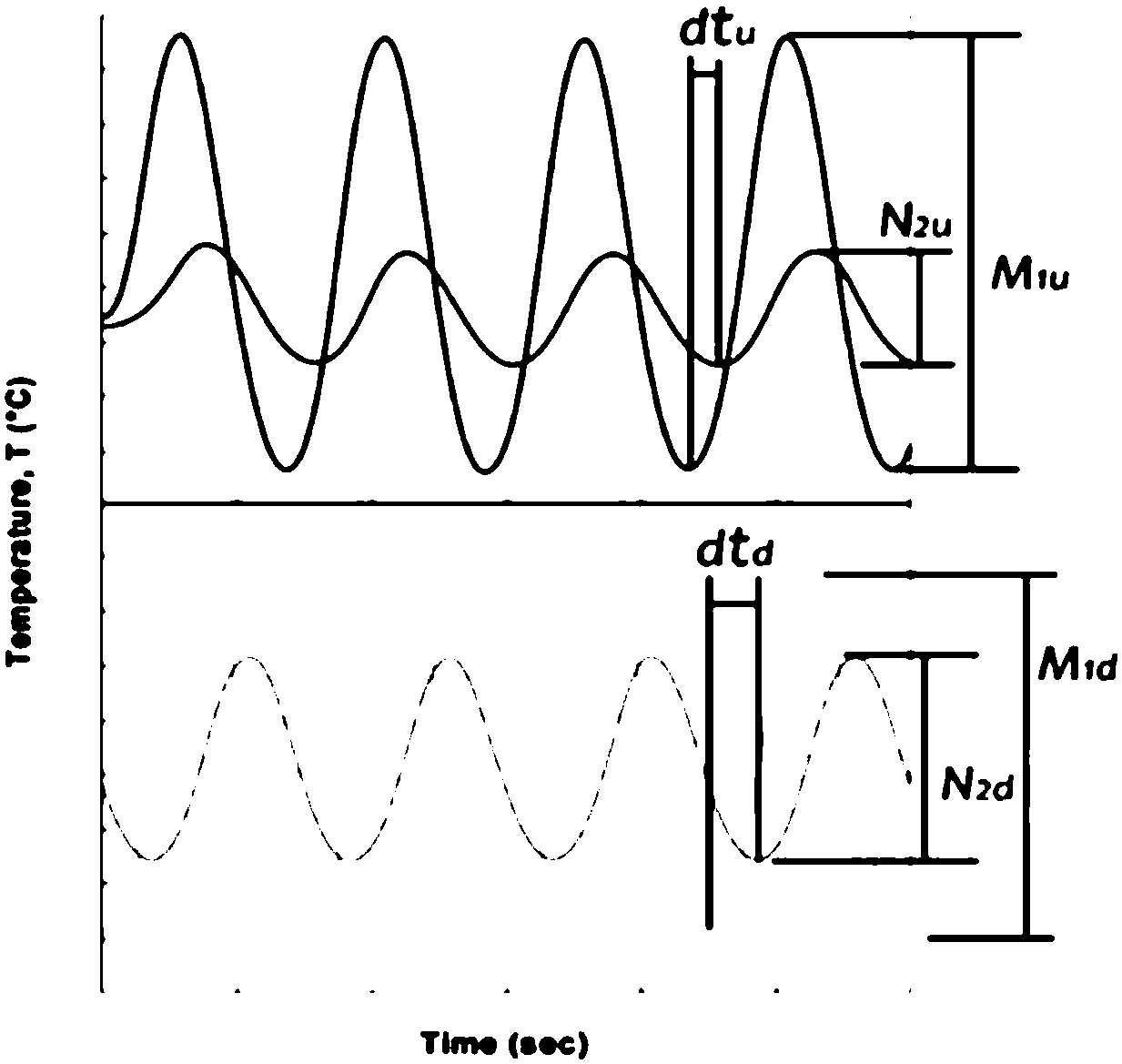
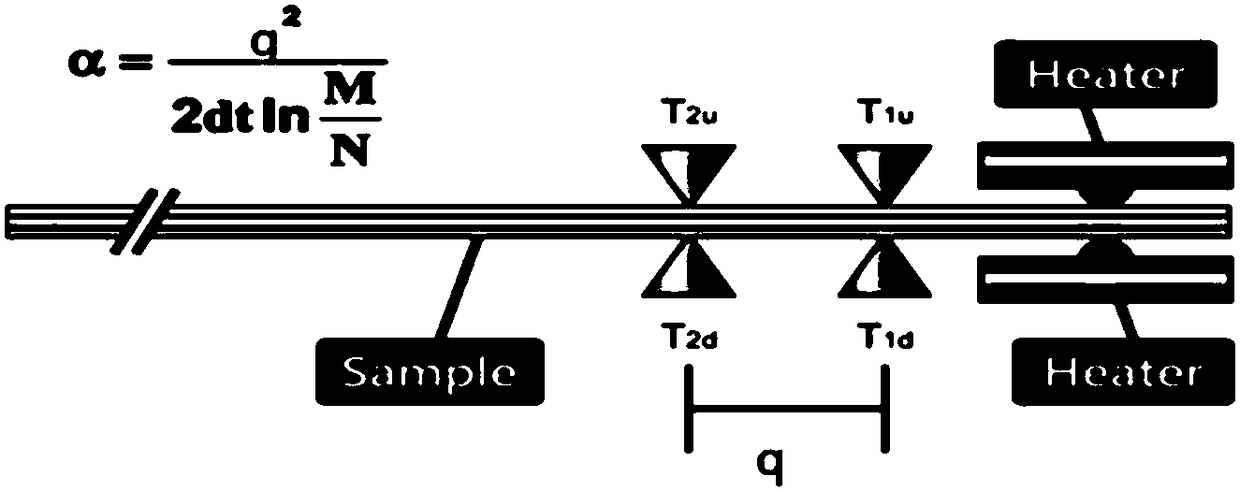
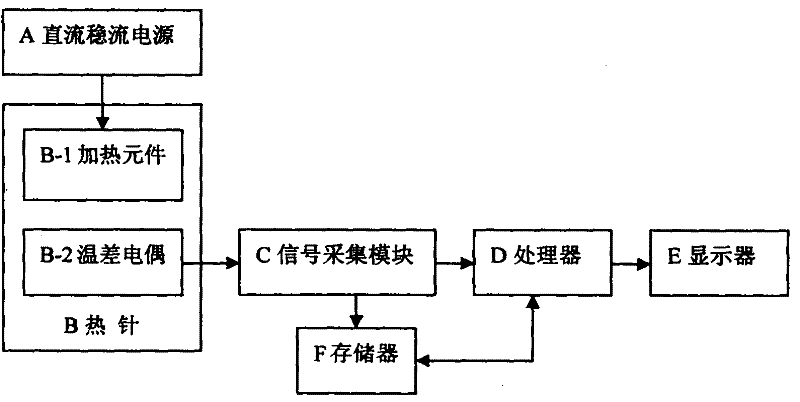
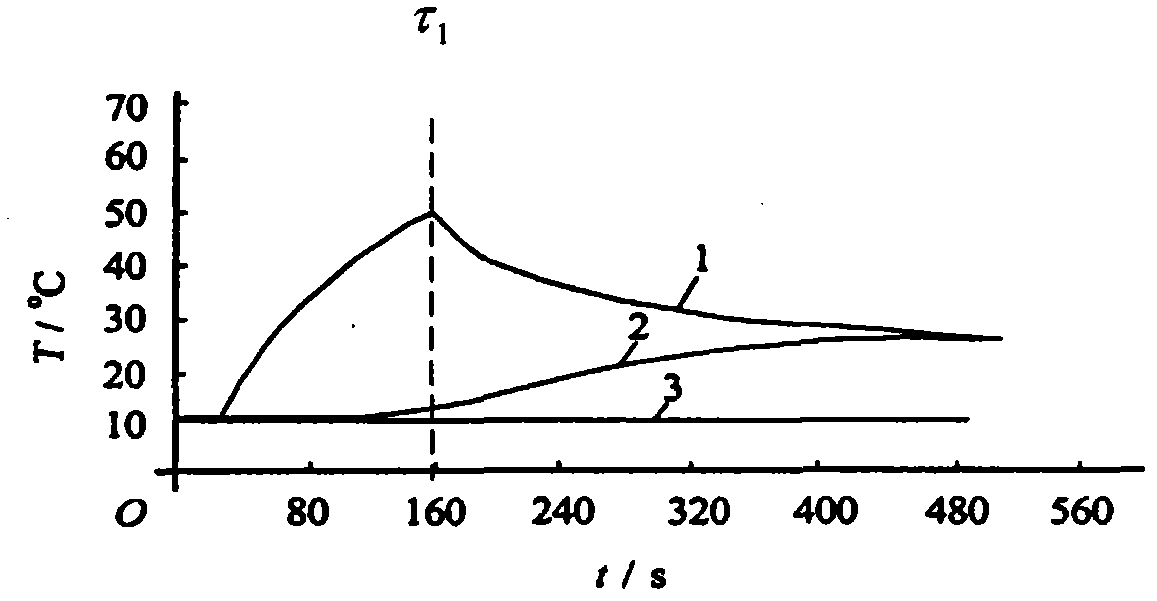
Thermal-property transient measurement method and device
InactiveCN102183544AShort time required for transient measurementsEasy to fixMaterial heat developmentSpecific gravity measurementCarbon fibersRegular pattern
The invention discloses a thermal-property transient measurement method and device, which are used for automatically measuring thermal conductivity, thermal diffusion coefficient, specific heat at constant pressure and density of a material and are also used for analysing the regular pattern of the thermal property of the material near the room temperature along the change of the temperature. The method comprises the following steps of: placing a cylindrical hot needle in a uniform and infinite medium; and continuously heating the medium by a constant thermal flow through the hot needle to form a one-dimensional cylindrical heat-transferring model in the radical direction. The measurement device comprises a direct-current stable-current power supply, the hot needle, a temperature signal collecting module, a signal processor, a memory and a display. A column body of the hot needle is made of carbon fibre and is composed of a core column and a sleeve pipe; the electric heating element is wounded on the core column through a double-head manganin lacquered wire and the double-head manganin lacquered wire is formed by doubling and winding one manganin lacquered wire along the central point; and an thermoelectric couple is formed by welding one copper wire and one konstantan wire in the thermoelectric couple grade.
Owner:陈昭栋
Laser flash method-based thermal diffusion coefficient test device and method
InactiveCN104407011AAvoid influenceReduce test errorMaterial heat developmentThermodynamicsThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention provides a laser flash-based thermal diffusion coefficient test device and method. The laser flash-based thermal diffusion coefficient test device comprises a laser conductometer, a base which is fixed on the laser conductometer, a sample vessel which is arranged at the top of the base and a cover covering the sample vessel, wherein a cut-through degassing hole is formed in the side wall of the sample vessel; the cover consists a first section, a second section and a third section, the diameters of which are gradually decreased; the bottom surface of the first section leans against the top surface of the sample vessel; an overflow space is formed between the outer surface of the third section and the inner surface of the sample vessel; the overflow space is communicated with the external environment through the degassing hole. According to the laser flash-based thermal diffusion coefficient test device, the overflow space formed between the outer surface of the third section and the inner surface of the sample vessel leaves a warming inflation space for samples, so that the samples are prevented from overflowing out of the sample vessel to influence the test result. In the test process, the gas in the samples is discharged from the overflow space to the external environment through the degassing hole, so that isotropic and uniform samples can be prepared.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF APPLIED PHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
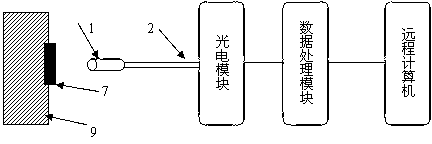
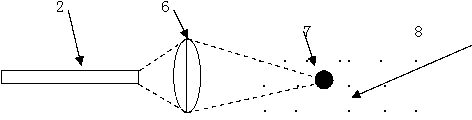
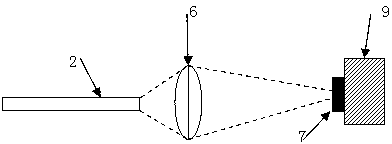
Material heat conduction analysis device based on fluorescence method
ActiveCN103134833AWill not be disturbedNo electromagnetic noiseMaterial heat developmentThermodynamicsThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention relates to a material heat conduction analysis device based on a fluorescence method, and belongs to the field of material thermal property analysis. The material heat conduction analysis device comprises a probe (1), a photoelectric module and a data processing module. The probe (1) is used for detecting fluorescence sensing materials (7) on an object to be tested and transmitting detected optical signals to the photoelectric module through optical fibers (2). The photoelectric module coverts the received optical signals into electric signals, and converts the electric signals into temperature signals and then transmits the temperature signals to the data processing module. The data processing module obtains a temperature change curve according to the temperature signals, obtains a thermal diffusion coefficient of the detected object through comparison with standard data, and transmits the thermal diffusion coefficient to an upper computer for heat conduction analysis. The material heat conduction analysis device can be applied to measurement of thermal diffusion coefficients of gas, liquid and solid, is simple in structure, high in flexibility, and has the advantages of being better in measurement accuracy and anti-electromagnetic interference capacity, and achieving functions of miniaturization, intellectualization and online monitoring.
Owner:南京五石金传感技术有限公司
Porous electrode substrate and manufacturing method thereof, film-electrode combination and solid high-polymer fuel cell
ActiveCN102104152ALow apparent thermal diffusivityHigh flood toleranceCell electrodesFinal product manufactureHigh current densityCarbon fibers
The present invention provides a porous electrode substrate and a manufacturing method thereof, a film-electrode combination with the substrate and a solid high-polymer fuel cell. The invention provides the porous electrode substrate with the advantages of low thermal diffusion coefficient in a thickness direction and high flooding resistance at high moisture state or high current density area, and the film-electrode combination with the substrate, and the solid high-polymer fuel cell. The porous electrode substrate is prepared through the method which comprises the following steps: a step of obtaining a piece of carbon fiber paper which is adhered with the resin and is obtained through causing carbon precursor resin to adhere with the carbon fiber paper that comprises the planar scattered short carbon fibers with an average fiber diameter of 3-9 mu m and original fiber-shaped object; a step of performing hot pressing and solidifying the carbon fiber paper which is adhered with resin for obtaining an intermediate substrate; and heating the intermediate substrate with a maximum temperature of 1000-1800 DEG C and carbonizing the carbon precursor resin.
Owner:MITSUBISHI CHEM CORP
Thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity sensor based on MEMS double heater
ActiveCN103698357AReduce temperature riseLower requirementMaterial heat developmentThermal diffusion coefficientInsulation layer
The invention relates to a thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity sensor based on a MEMS double heater. The thermal conductivity and thermal diffusivity sensor comprises a substrate, wherein a heater is arranged on the center of the upper surface of the substrate, welding disks are positioned on the both sides of the heater on the upper surface of the substrate and are connected with the heater, an insulation layer film covers on heater, the welding disks and the substrate, and is provided with chamber walls, the chamber walls and the insulation layer film form a cavity structure filled with a liquid requiring detection, the heater is concurrently adopted as a temperature sensor, is a multi-folding structure metal belt, is formed by connecting more than two parallel metal belts with the same width and the same distance in series, and is divided into the narrow heater and the wide heater, and a reference liquid with a known thermal conductivity and a known thermal diffusivity is adopted as the liquid requiring detection to reversely deduce the thermal conductivity and the thermal diffusivity of the substrate so as to improve measurement precision.
Owner:明石创新(烟台)微纳传感技术研究院有限公司
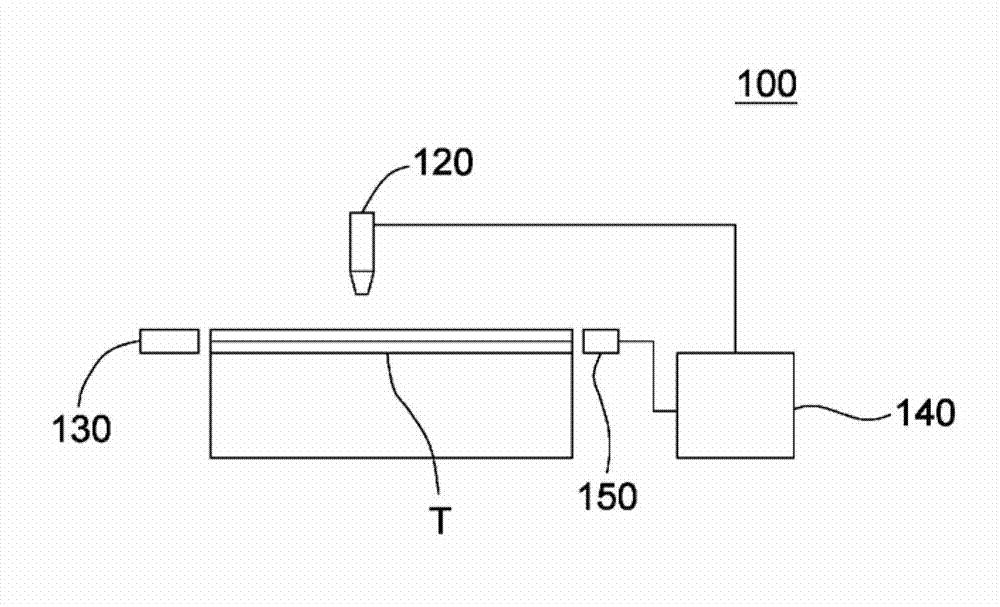
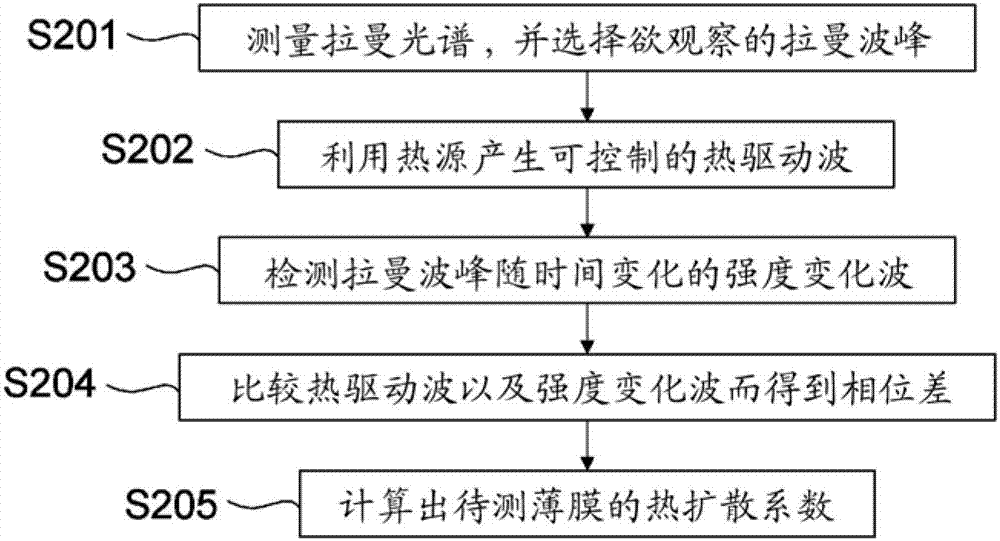
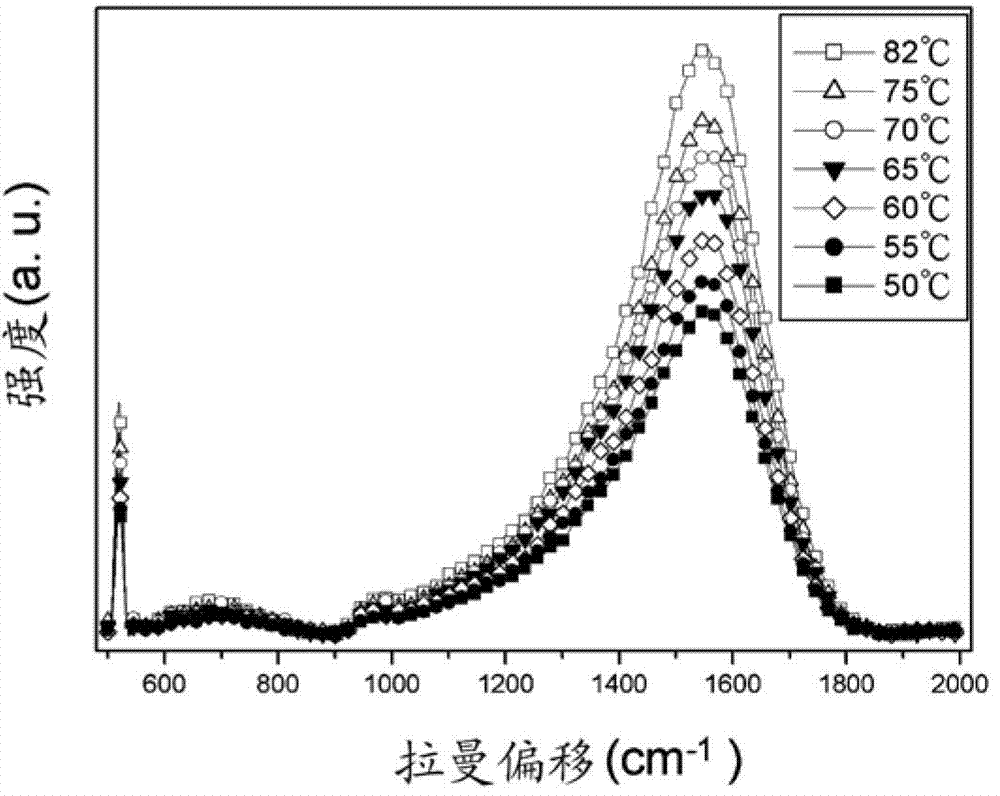
Apparatus and method for measuring thermal diffusivity
An apparatus for measuring thermal diffusivity includes a Raman spectroscope, a heating device, and a signal analyzing unit. The Raman spectroscope is utilized to measure a Raman scattering intensity of different sites of a film to be measured. The heating device is utilized to provide a controllable thermal driving wave. The signal analyzing unit is utilized to analyze the Raman scattering intensity from the Raman spectroscope and the thermal driving wave so as to evaluate the thermal diffusivity of the film to be measured.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Recording apparatus and method
InactiveUS6315403B1Short timeReduce processing timeMeasurement apparatus componentsPrintingSurface tension gradientThermal diffusion coefficient
An ink retained in an ink transfer block is heated by a heating device correspondingly to information to be printed, thereby developing a surface tension gradient and interfacial tension gradient on the ink surface, and a fluidity caused by the surface tension gradient and / or interfacial tension gradient of the ink surface is utilized to have the ink fly from the ink transfer block, thereby printing the information on a print receptor, the heating device having a heating velocity v (in K / s) which meets a requirement (Tb-Ti) / v>h2 / D where Tb is a boiling point of the ink in K; Ti is an initial temperature of the ink in K; h is the shortest distance between the surface of the heating means and ink surface in m; and D is a coefficient of thermal diffusion in m2 / s.
Owner:SONY CORP
Measuring method for thermal conductivity of metal at high temperature
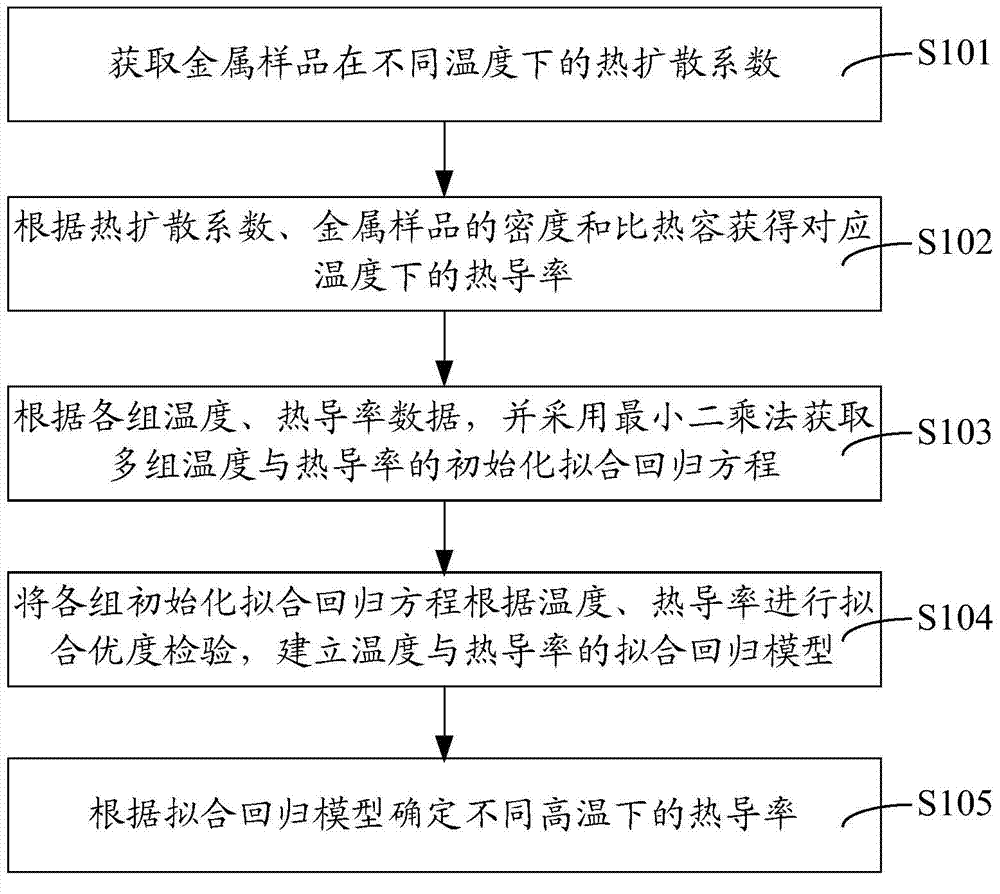
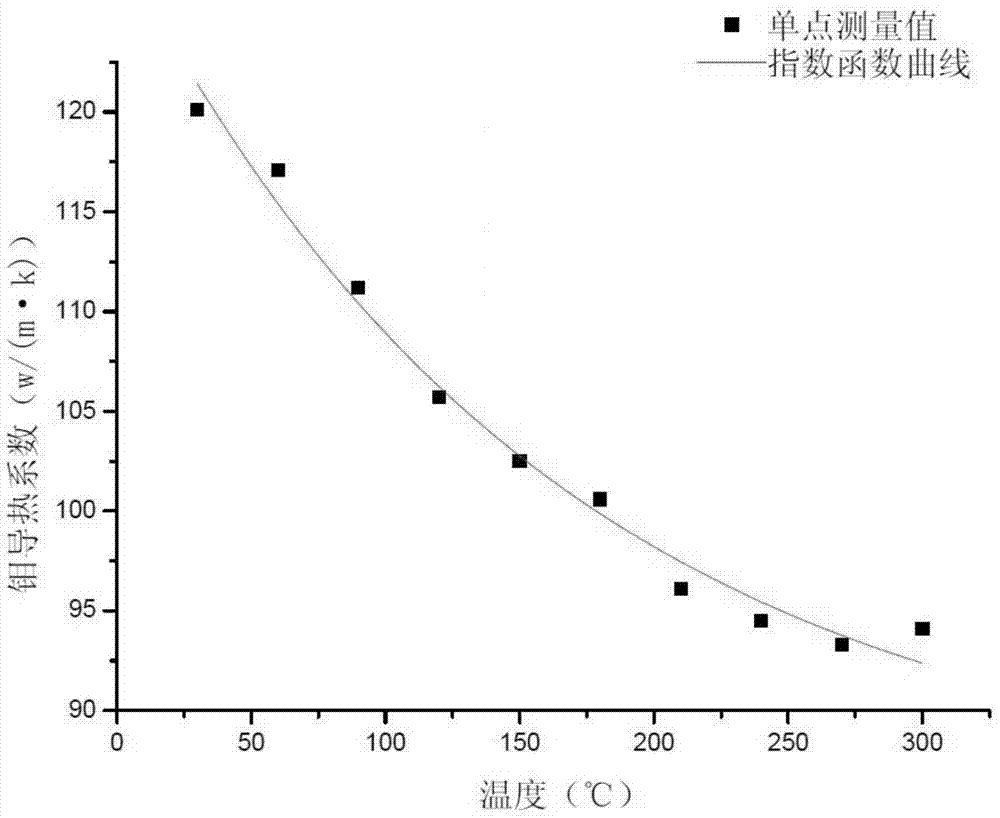
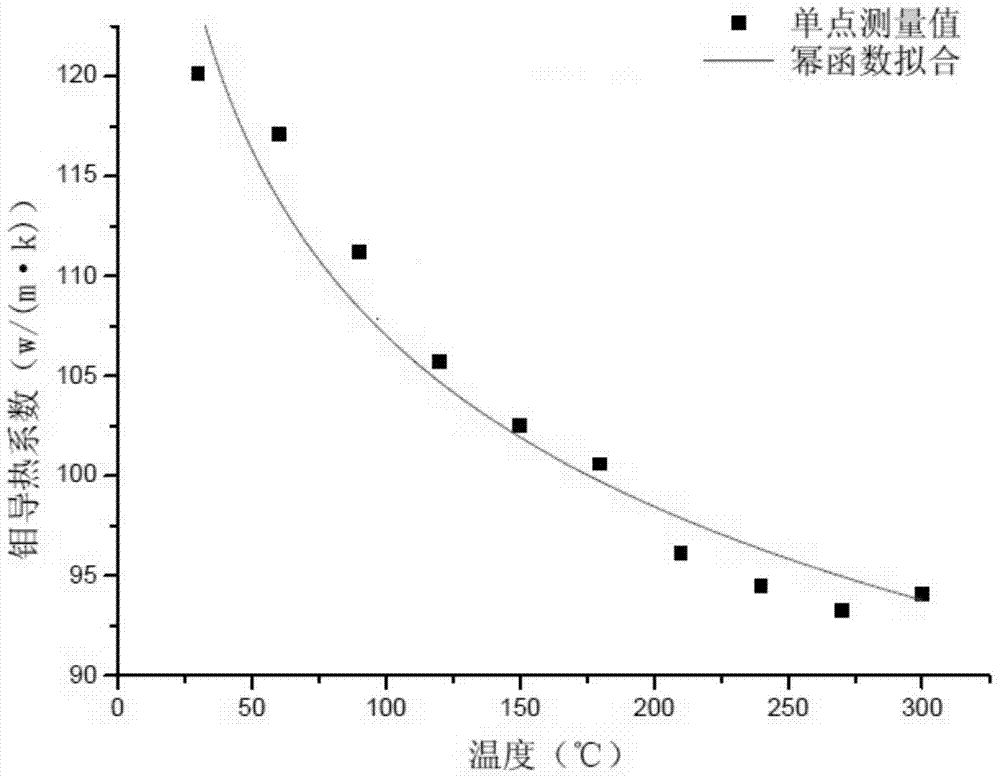
ActiveCN103940845AImprove accuracyImprove measurement accuracyMaterial heat developmentDiffusionThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention provides a measuring method for thermal conductivity of metal at high temperature. The measuring method comprises the following steps: acquiring thermal diffusion coefficients of a metal sample at different temperatures, wherein the temperatures refer to temperatures except the oxidizing temperature of the metal sample; acquiring thermal conductivity at a corresponding temperature according to the thermal diffusion coefficients and the density and specific heat capacity of the metal sample; acquiring a plurality of groups of initialization fitting regression equation of the temperatures and thermal conductivity according to each group of temperature and thermal conductivity data; subjecting each group of initialization fitting regression equation to test of goodness of fit according to the temperatures and thermal conductivity and establishing a fitting regression model of the temperatures and thermal conductivity; and determining thermal conductivity at different high temperatures according to the fitting regression model. With the method provided by the invention, thermal conductivity of metal at high temperature can be obtained, and accuracy of the obtained thermal conductivity is high.
Owner:FIFTH ELECTRONICS RES INST OF MINIST OF IND & INFORMATION TECH
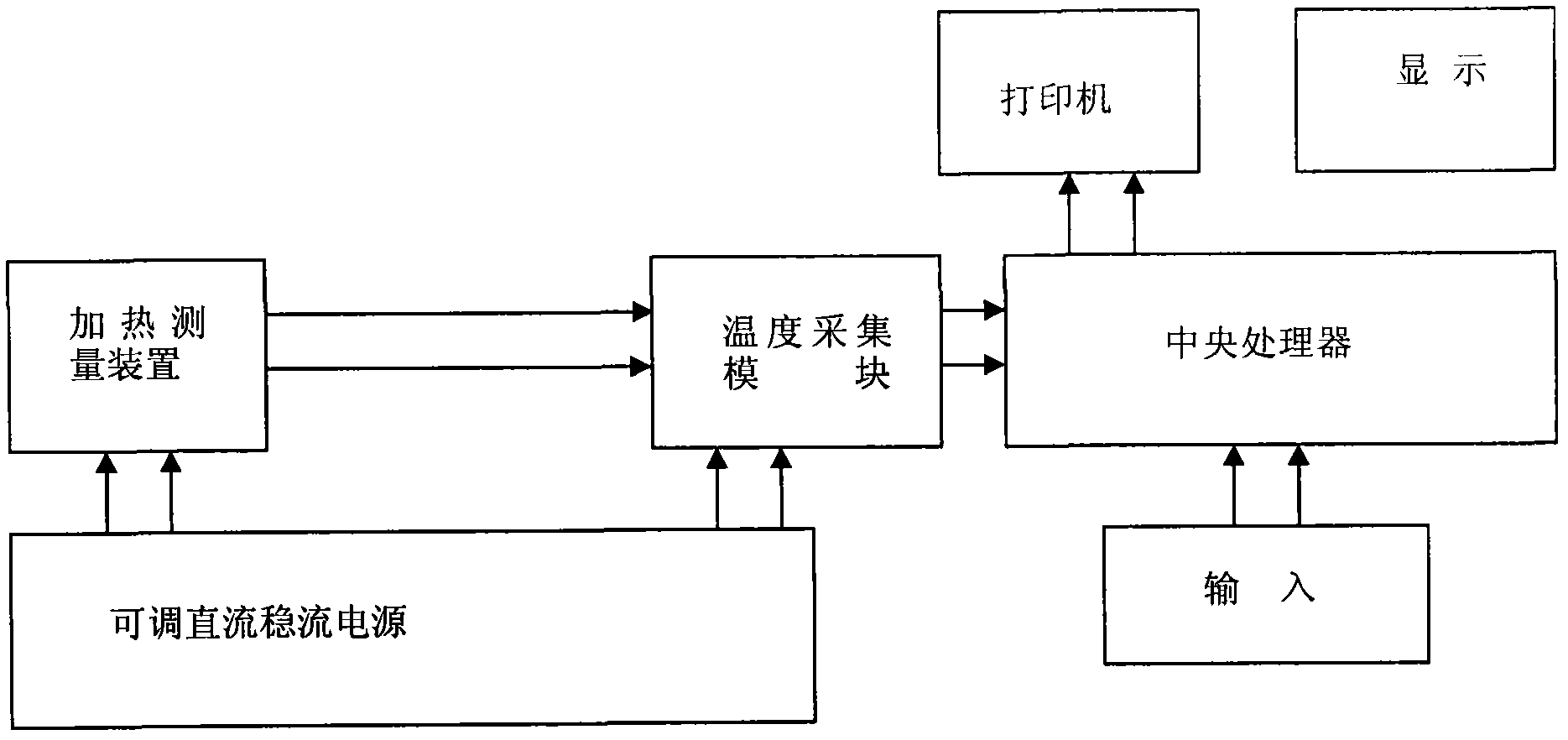
System for measuring thermal performance transiently by using pulsing method or constant current method
InactiveCN102608154AQuick measurementRealize measurementMaterial heat developmentFast measurementThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a system for measuring thermal performance transiently by using a pulsing method or a constant current method, which comprises an adjustable direct-current stabilized current supply, a heating measuring device, a temperature collecting module and a central processing unit, wherein the adjustable direct-current stabilized current supply is used for supplying power to the heating measuring device and the temperature collecting module, the heating measuring device internally comprises a main testing piece (3), an auxiliary testing piece (1) and an auxiliary testing piece (2), the auxiliary testing piece (1) is arranged at the bottom, and a plane heat source is arranged between the main testing piece (3) and the auxiliary testing piece (1). The system can realize fast measurement for the thermal performance of a material by calculating the thermal diffusion coefficient and the heat conductivity of the material to be measured through adopting an exact solution of a one-dimensional semi-infinite heat transfer model and collecting temperature changing data of a heat surface and a cold surface at the right moment. A novel automatic measuring instrument is researched and manufactured for detecting the thermal performances of various solid plates.
Owner:陈昭栋
High-performance thermal barrier coating and ceramic layer thereof
ActiveCN107815633AImprove efficiencyIncrease working temperatureMolten spray coatingNano structuringThermal diffusion coefficient
The invention discloses a preparation method for a high-performance thermal barrier coating and specifically discloses a 4YSZ (4mol% Y2O3 stabilized ZrO2) thermal barrier coating and the preparation method of the 4YSZ thermal barrier coating. The 4YSZ powder which is of a fine nano-structure, uniform ingredients and a pure tetragonal phase structure is prepared utilizing a sol-spray pyrolysis synthetic process, and the 4YSZ powder is subjected to spray drying granulation, screening and atmospheric plasma spraying (APS) in sequence to prepare the coating. The high-performance thermal barrier coating prepared by the invention is of a pure tetragonal phase nano-structure with uniform ingredients, compared with a traditional YSZ casting, the high-performance thermal barrier coating has the advantages of being low in thermal diffusion coefficient, good in high temperature phase stability and thermal shock resistance, simple in preparation process and low in cost and the like; and the high-performance thermal barrier coating is more conducive to improving the efficiency and working temperature of a turbine engine, and the service life of the engine is prolonged.
Owner:INST OF METAL RESEARCH - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
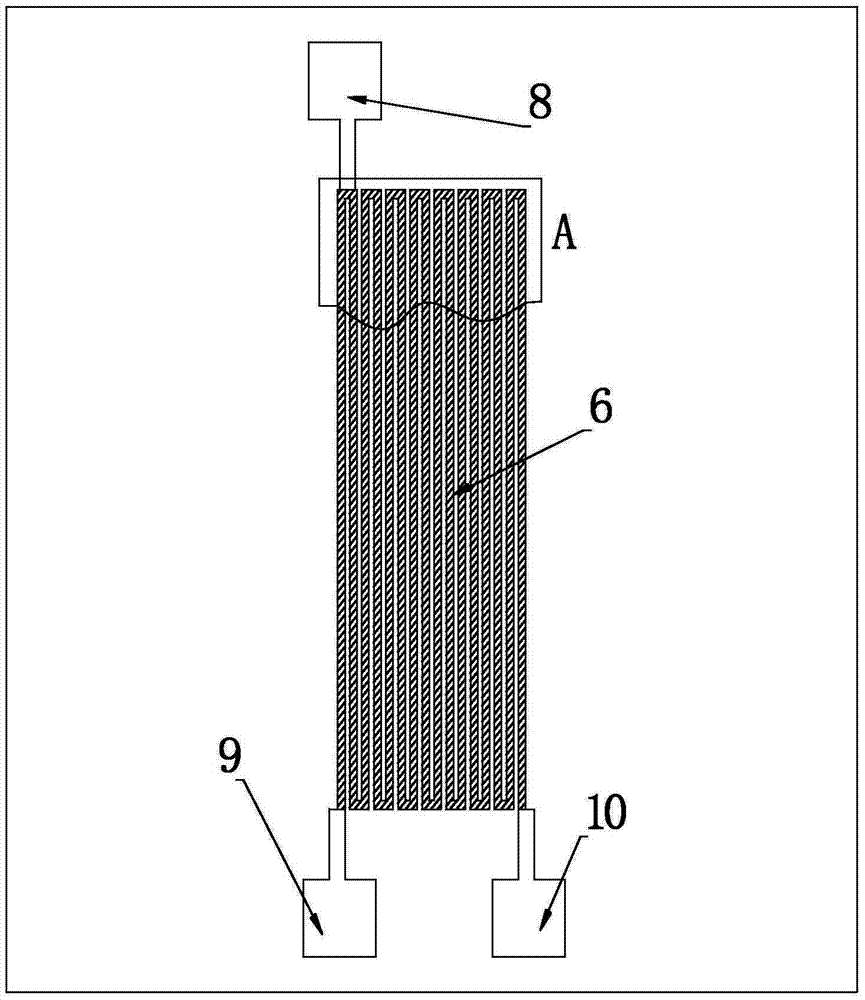
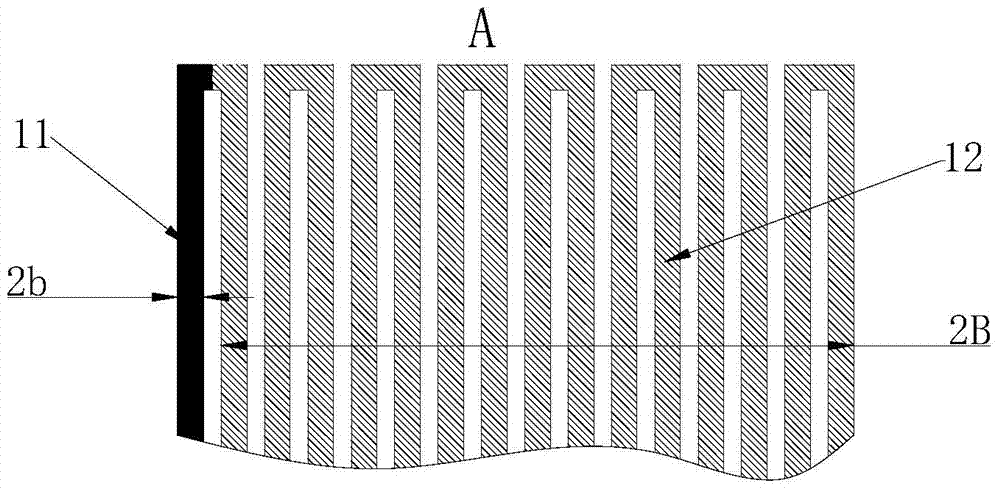
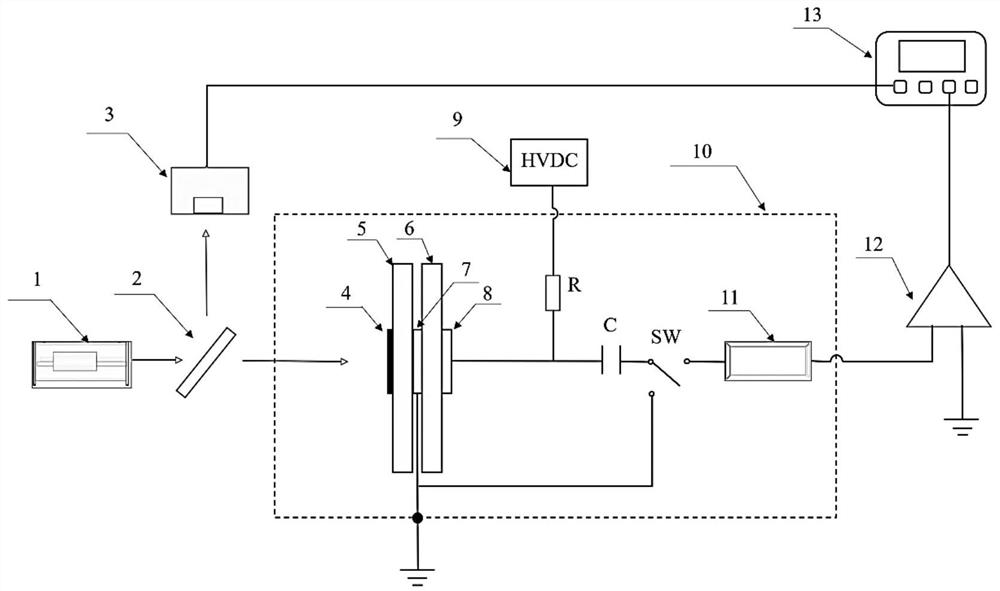
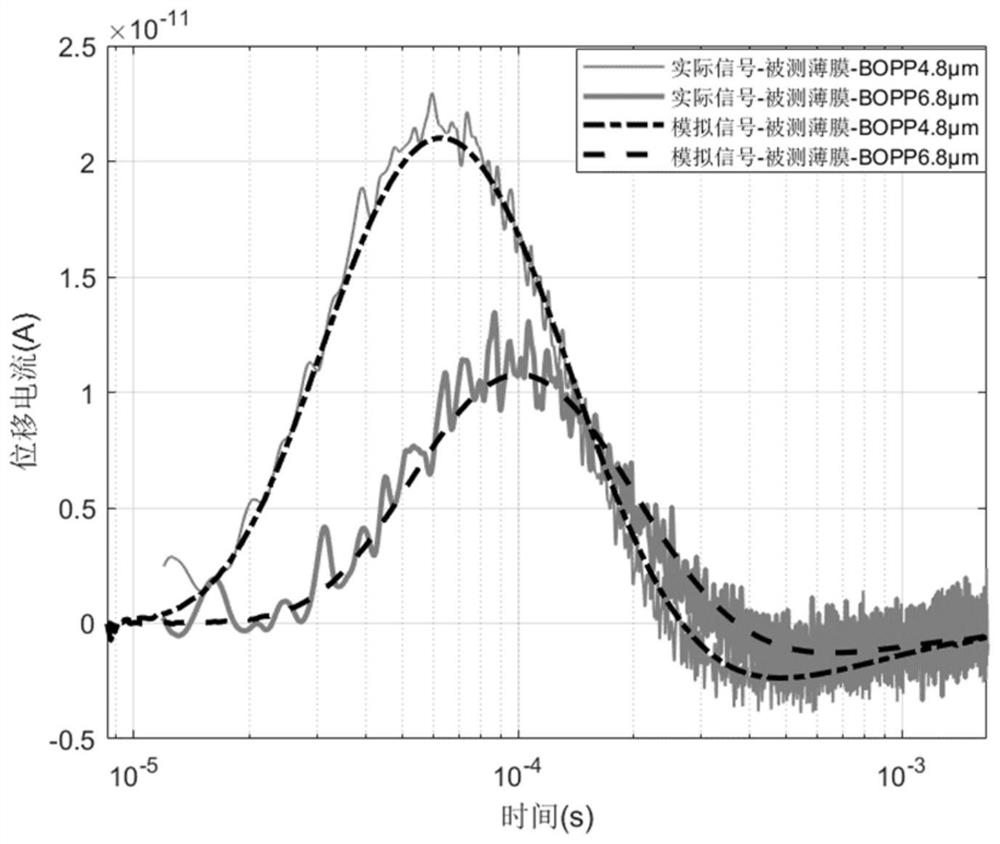
Film longitudinal thermal diffusion coefficient measuring system and method based on medium detector
ActiveCN112415046AInversion of thermal diffusivityThermal diffusivity derivationMaterial heat developmentDesign optimisation/simulationBeam splitterEngineering
The invention relates to a film longitudinal thermal diffusion coefficient measuring system and method based on a medium detector, which are used for measuring the longitudinal thermal diffusion coefficient of a film. The film longitudinal thermal diffusion coefficient measuring system comprises a pulse light source, a spectroscope, the medium detector, a preposed current amplifier, an oscilloscope and a photoelectric trigger device, wherein the dielectric detector comprises a grounding metal electrode, a dielectric film and a pressurizing metal electrode which are arranged in sequence, the grounding metal electrode is kept grounded, the pressurizing metal electrode is connected with a direct-current high-voltage power supply, the pressurizing metal electrode is further connected with an input end of a preposed current amplifier, a grounding end of the preposed current amplifier is grounded, one side of the measured film is provided with a laser light target, and the other side is usedfor connecting a grounding metal electrode end of the medium detector. Compared with the prior art, the film longitudinal thermal diffusion coefficient measuring system and the method are simple andeasy to operate, can quickly complete measurement, and can be used for measuring various dielectric films and other metal conductive thin layers which are widely applied to the fields of electrical insulation and microelectronic devices, such as BOPP, PI and PVDF.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Compact pure-phase lanthanum zirconate ceramic with low thermal conductivity and high strength, and preparation method thereof
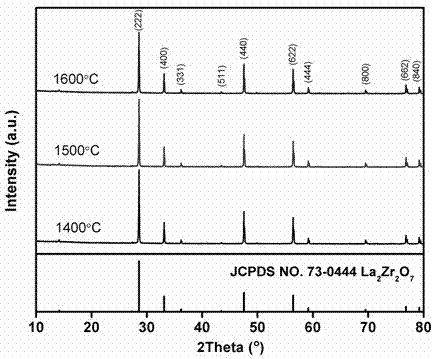
The invention discloses compact pure-phase lanthanum zirconate ceramic with low thermal conductivity and high strength, and a preparation method thereof. A chemical formula of the lanthanum zirconate ceramic is La2Zr2O7, the compactness is greater than 85%, the compression strength is 310-500MPa, the thermal conductivity and the thermal diffusion coefficient at normal temperature respectively are 1.55-1.79W / (m.K) and (0.90-0.76)*10<-6>m<2> / s; the thermal conductivity and the thermal diffusion coefficient at the temperature of 1200 DEG C respectively are 0.75-0.94W / (m.K) and (0.35-0.45)*10<-6>m<2> / s; the breaking tenacity is 1.45-1.70MPa. The lanthanum zirconate ceramic prepared according to the lanthanum zirconate ceramic preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of low thermal conductivity, high melting point, good inoxidizability, excellent mechanical property, good high temperature-phase stability and the like, and the requirements of hypersonic velocity aerospace vehicles on the performances of high-strength thermal insulation ceramic materials can be met.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Electrical heating wire containing carbon fiber
An electrical heating wire containing carbon fiber includes a heating unit and an insulation sleeve cladding on the heating unit. The heating unit is a carbon fiber bundle constituted by plural carbon fiber yarns or a structure formed by wrapping, weaving or twining the carbon fiber bundle with at least one element among a glass fiber bundle, a rock fiber bundle, a ceramic fiber bundle and a DuPont Kevlar® are fiber bundle (aromatic polyamide fiber bundle). The carbon fiber yarn can be a structure with metal particles on the surface, a dual-layered structure with a metal layer or a graphite layer on the surface, or a porous structure. Accordingly, by the present invention, the thermal conductivity can be increased, the resistance can be reduced, the thermal diffusion coefficient can be increased, the weight can be reduced and the hygroscopicity can be improved, thus providing a better efficiency of electrical heating.
Owner:TSAI I SHOU +1
Support-beam-type MEMS (micro electromechanical systems) fluid thermal conductivity and thermal diffusion coefficient sensor and preparation and testing methods thereof
ActiveCN107037079AThe testing process is simpleReduce lateral spreadMaterial thermal conductivityMaterial heat developmentThermal diffusion coefficientEngineering
The invention discloses a support-beam-type MEMS (micro electromechanical systems) fluid thermal conductivity and thermal diffusion coefficient sensor and preparation and testing methods thereof; a heater is arranged at the center of the upper surface of a substrate, a pad is arranged beside the heater on the upper surface of the substrate and is connected to the heater, film of an insulating layer covers the heater, the pad and the substrate, the film of the insulating layer is provided with cavities on two sides of the heater, the bottom of the substrate is provided with a back cavity, and a support beam structure is formed. The heater also acts as a temperature sensor; the heater is of elongated strip structure and is connected to the pad through four leads; by using the back cavity, a fluid under test is used as a substrate of the sensor, thermal conductivity and thermal diffusion coefficient of the fluid under test can be measured directly, and the test process is simplified. The sensor provided herein is suitable for measuring the thermal conductivity and thermal diffusion coefficient of conductive and nonconductive trace liquids.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method of non destructive measuring biological active tissue heat parameter
InactiveCN1555759AGet the thermal conductivityGet the thermal diffusivityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsNon destructiveThermal diffusion coefficient
A nondestructive method for measuring the thermal parameters of the tissue of living things by measuring the temp of three points on surface includes creating 2D heat-transfer. Pennes model of cylindrical living tissue in histogram coordinate system, using line-by-line method to find out the temp variation of living tissue under interference of step heat flow or square-wave heat flow, calculating its sensitivity, analyzing the correlation between the sensitivity coefficients of thermal parameters and the influence of thermal parameters to temp variation, optimizing the selection of three measured points, developing its measuring system, and using Gauss estimating method to obtain various thermal parameters.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH BEIJING
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com