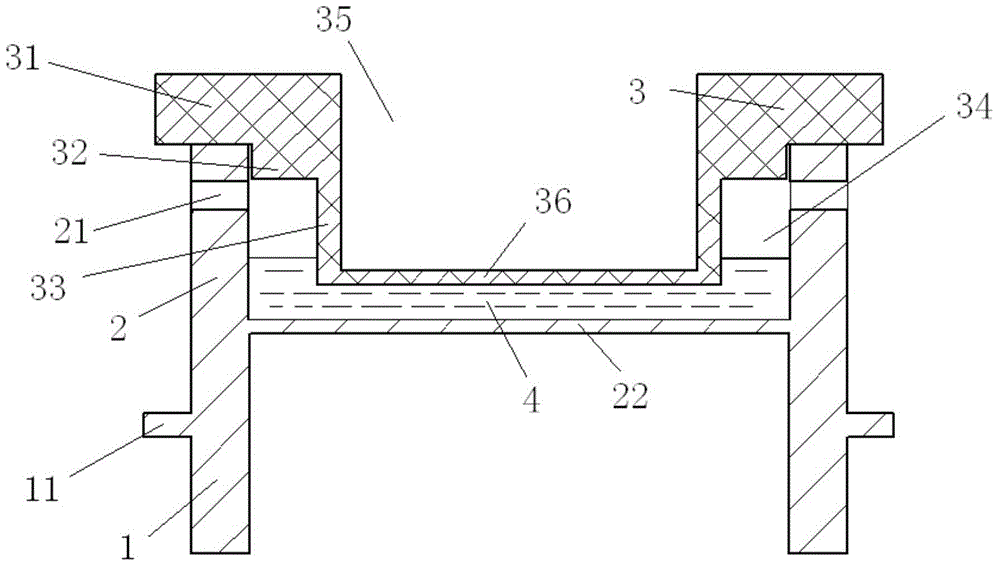
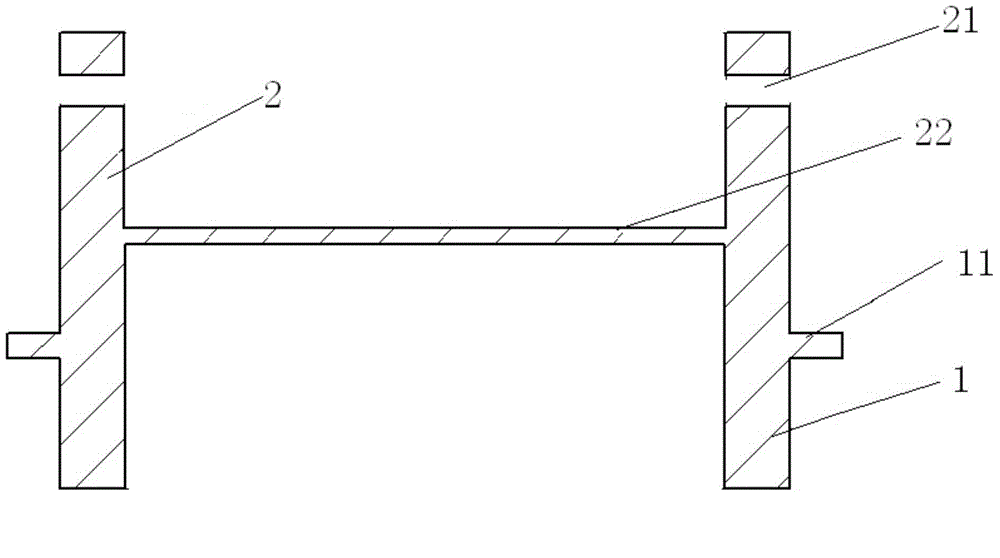
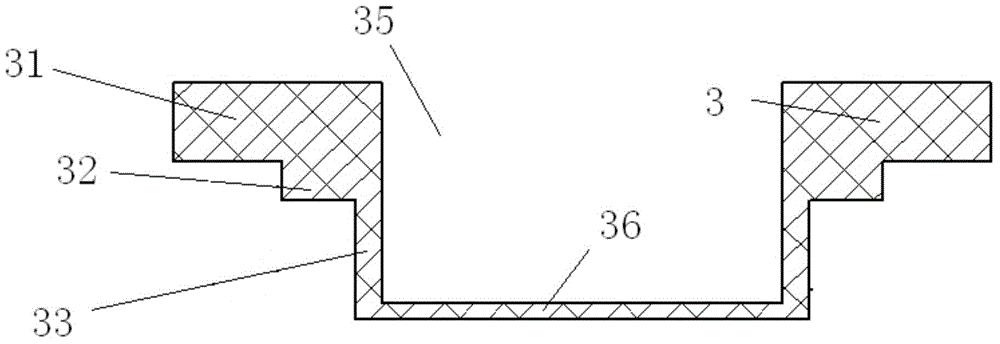
Laser flash method-based thermal diffusion coefficient test device and method
A technology of thermal diffusivity and testing equipment, applied in the direction of material thermal development, etc., can solve the problems of hydraulic and thermal inlet length evaluation errors, large errors, and inability to obtain isotropic molten salt
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0032] Example 1: KNO 3 Measurement of thermal diffusivity
[0033] Pure take 2~3g pure (purity is 99.9%) KNO 3 Molten salt powder is pressed into flakes and placed in a sample dish, and repeatedly melted and cooled for 3 times under the condition of less than 100Pa to ensure KNO 3 After there are no visible bubbles in the molten salt, the molten salt sample and the sample dish are transferred to the LFA1000 laser thermal conductivity meter, and the test is carried out under the protective atmosphere of He gas. Three tests were carried out at 350°C, 400°C, and 450°C respectively. The test results are as follows: Figure 4 shown, from Figure 4 KNO can be seen in 3 The thermal diffusivity increases with increasing temperature, and the relative standard deviation of three tests is less than 4%. Pure KNO tested by Ohta and other scholars 3 The value of thermal diffusivity of molten salt is 1.4×10 -3 cm 2 / s~1.6×10 -3 cm 2 Within the / range, it is consistent with the re...
example 2
[0034] Example 2: Li 2 CO 3 -Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 Measurement of thermal diffusivity of eutectic salt
[0035] Will Li 2 CO 3 -Na 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 The pure (99.9% purity) molten salt powder was dried at 300°C for 24 hours at high temperature. After removing the water, the three pure molten salts were fully mixed according to the ratio of 32.12:33.36:34.52wt.%. Under an inert atmosphere, Cool at 450°C for 48 hours to prepare Li 2 CO 3 -K 2 CO 3 -Na 2 CO 3 (abbreviated as (Li, Na, K) 2 CO 3 ) eutectic molten salt. Take 2~3g (Li, Na, K) 2 CO 3 The molten salt is mechanically ground into powder under the condition of isolating water and oxygen, and under the condition of isolating water and oxygen, the (Li, Na, K) 2 CO 3 The powder is compressed into a thin disc with a thickness of 1.5-3 mm and a diameter of 23 mm, placed in a sample dish and covered with a lid. will be filled with (Li,Na,K) 2 CO 3 The sample dish of molten salt is transferred to the furna...
example 3
[0036] Example 3: Measurement of thermal diffusivity of LiF-KF-NaF eutectic salt
[0037] Pure (99.9% pure) LiF, KF, and NaF powders were fully mixed and melted according to the eutectic molten salt composition, kept at 50°C above the eutectic temperature for 8 hours, cooled, and the molten salt was taken out. After chemical composition analysis, LiF, The ratios of KF and NaF are 11.5mol%, 46mol%, and 42.5mol%, indicating that the prepared molten salt is a eutectic molten salt (marked as FLiNaK). Prepare 2-3g of bulk FLiNaK molten salt into powder under the condition of isolating water and oxygen, and press it into thin slices, place it in a sample dish, and repeat heating, melting and cooling in a heating furnace with a vacuum degree lower than 100Pa for 3~ Take it out after 10 times, and observe that there are no visible bubbles in the FLiNaK molten salt, and it is in complete contact with the upper and lower surfaces of the sample dish. Put the prepared sample in the sampl...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com