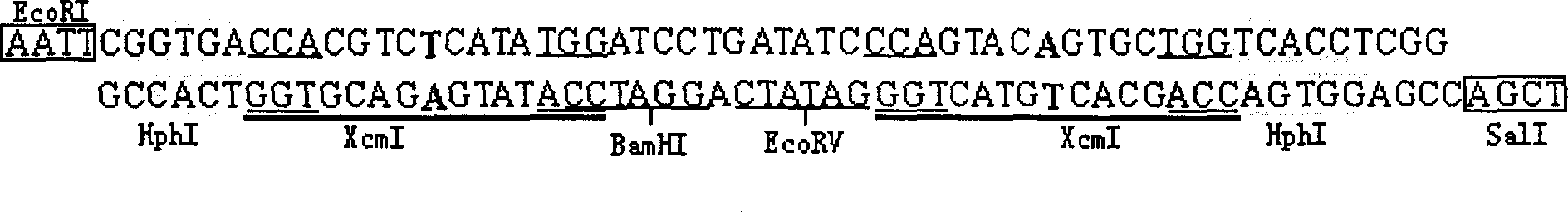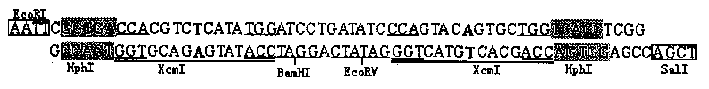Process for preparing T vector
A vector and endonuclease technology, applied in the direction of using vectors to introduce foreign genetic material, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the quality and instability of T vectors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0014] Embodiment 1. Construction of plasmid pUC-HX (pre-T vector)
[0015] According to the sequence shown in Figure 1, the HphI-XcmI linker sequence was synthesized by conventional methods. The two strands of the linker were synthesized separately, then dissolved in double-distilled water, mixed equimolarly, and annealed at 37°C for 15 minutes to obtain a double-stranded HphI-XcmI linker with a full length of 60bp (such as figure 1 shown). The linker contains two concatemers of HphI and XcmI recognition sequences arranged in an inverted repeat manner GGTG A (NNNNT / NNNN) (The first base upstream of the cut site 5' of the endonuclease XcmI in the sequence is set as T), and the endonuclease XcmI digests the vector containing the linker to obtain a mature T vector.
[0016] The DNA linker HphI-XcmI synthesized above was inserted into the EcoRI+SalI window of the plasmid pUC18, and after ligation and transformation, the recombinant plasmid pUC-HX was obtained, and its rest...
Embodiment 2
[0017] The synthesis of embodiment 2.ECS
[0018] Two exonuclease competitive substrates ECS1 and ECS2 were synthesized according to conventional methods, and their specific sequences were 5'p-CCAGCGCTGGT and 5'-CAAGAATTCATGGAATTTGGCAACCTA, respectively. ECS1 is an oligo DNA molecule with a palindromic structure of 11 nucleotides containing a 5' phosphate group, which can pair with each other in a 37°C overdigestion system to form a double-stranded structure with DNA ends similar to T vectors. ECS2 is a common PCR primer of 27 nucleotides (without 5' phosphate group), which can maintain a single-stranded structure in the overdigestion system at 37°C.
Embodiment 3
[0019] Example 3. Acquisition of carrier pUC-HX-T (T carrier)
[0020] In the three cases of adding ECS1 and ECS2 and not adding exonuclease competitive substrates, respectively, the vector pUC-HX was digested with restriction endonuclease XcmI to obtain the mature T vector pUC-HX-T.
[0021] The enzyme digestion reaction system is as follows:
[0022] pUC-HX 2 μg
[0023] Exonuclease competitive substrate (ECS1 / ECS2) 2μg / NULL
[0024] XcmI 15U
[0025] Buffer 2 (NEB) 10μl
[0026] wxya 2 O to a final volume of 100 μl
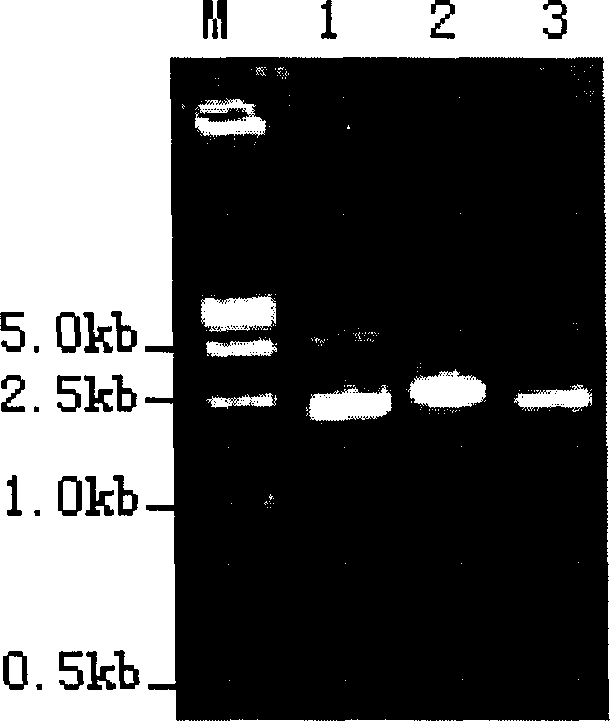
[0027] React at 37°C for 2 hours, phenol extraction will inactivate the enzyme. The digested product was run on 1.0% agarose gel electrophoresis, and a DNA fragment with a size of about 2.7 kb was recovered from the gel (refer to the QIAGEN gel recovery kit manual), which was the vector pUC-HX-T.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com