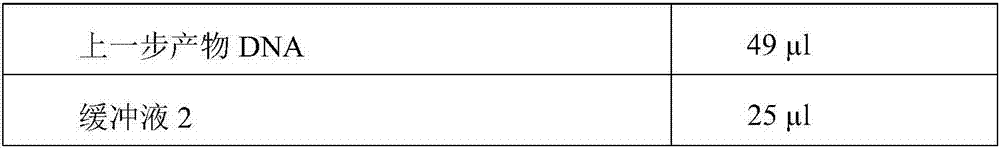
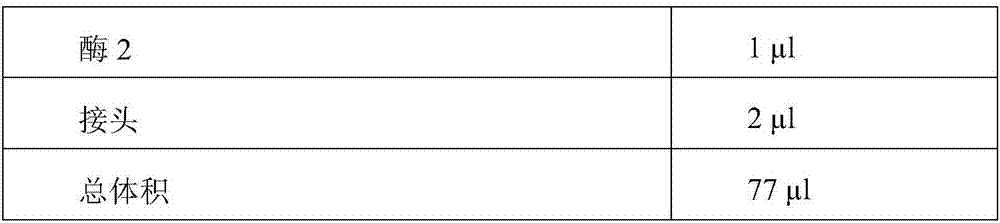
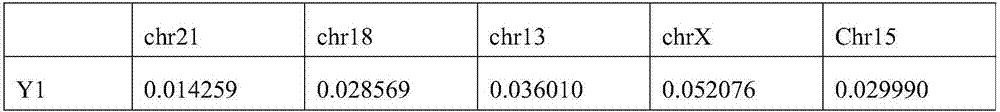
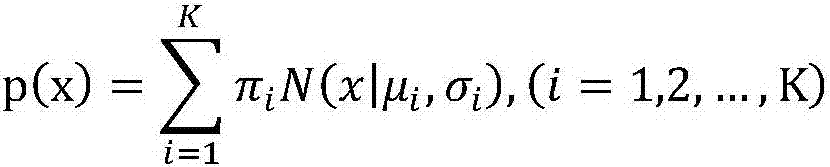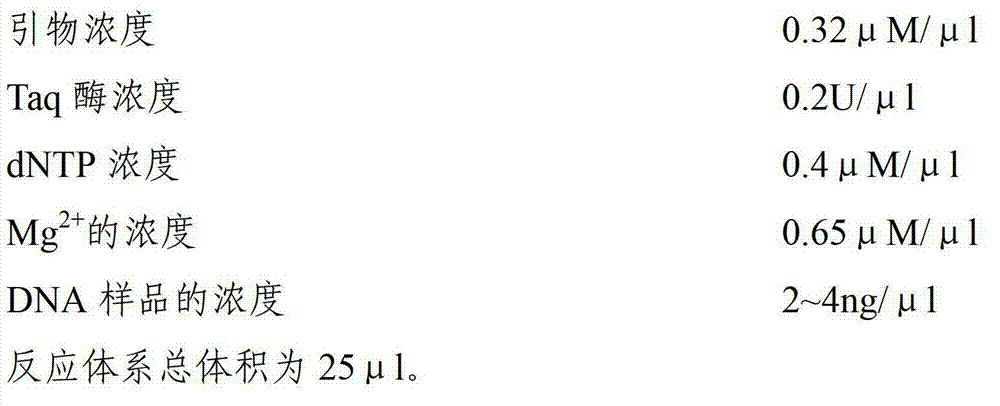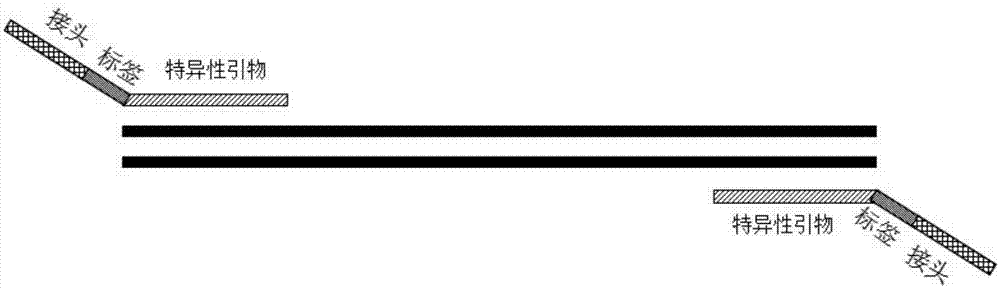Patents
Literature
264 results about "Dna concentration" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA concentration is estimated by measuring the absorbance at 260nm, adjusting the A 260 measurement for turbidity (measured by absorbance at 320nm), multiplying by the dilution factor, and using the relationship that an A 260 of 1.0 = 50µg/ml pure dsDNA. Concentration (µg/ml) = (A 260 reading – A 320 reading)...
Fetal genomic analysis from a maternal biological sample
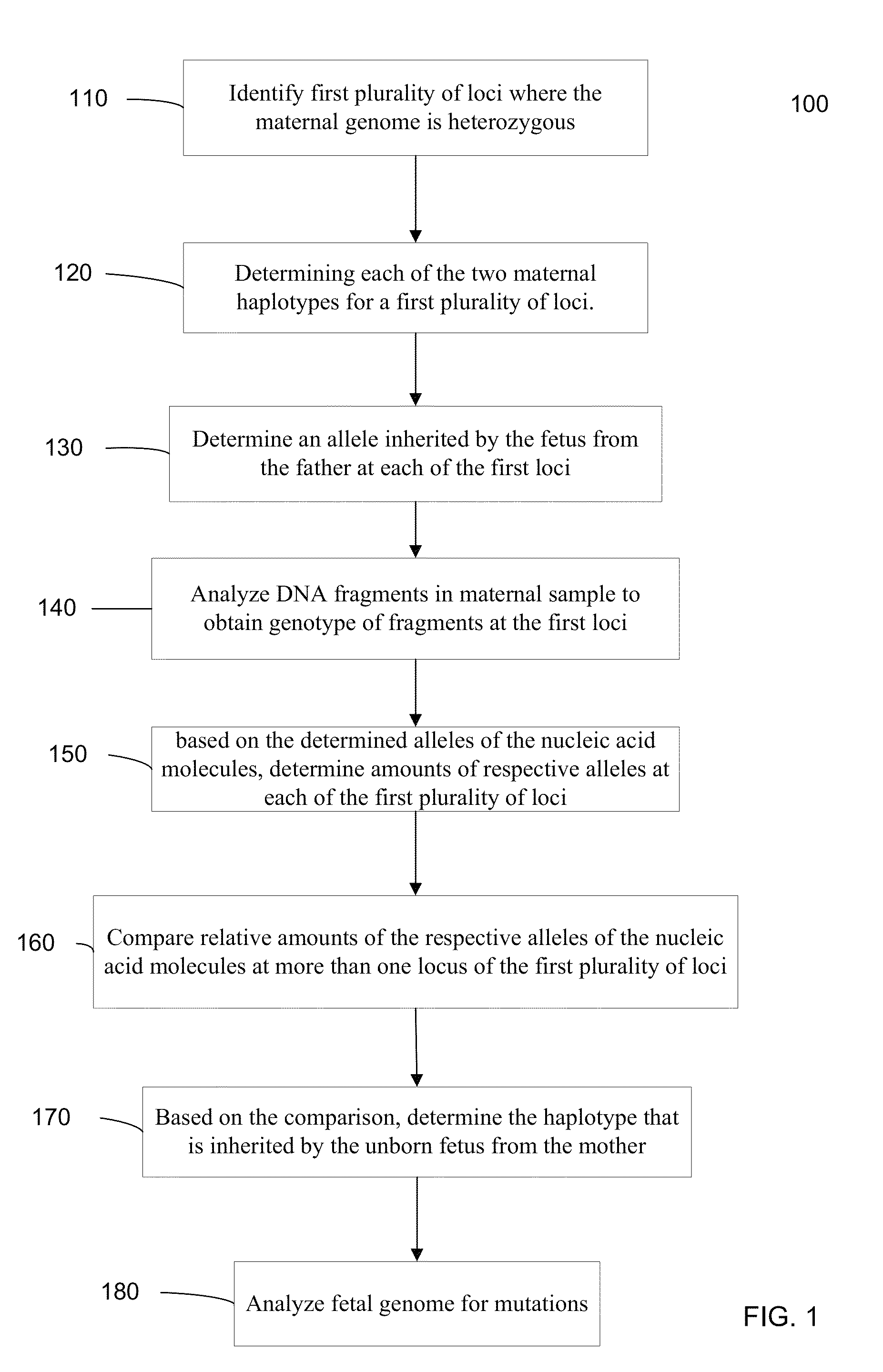
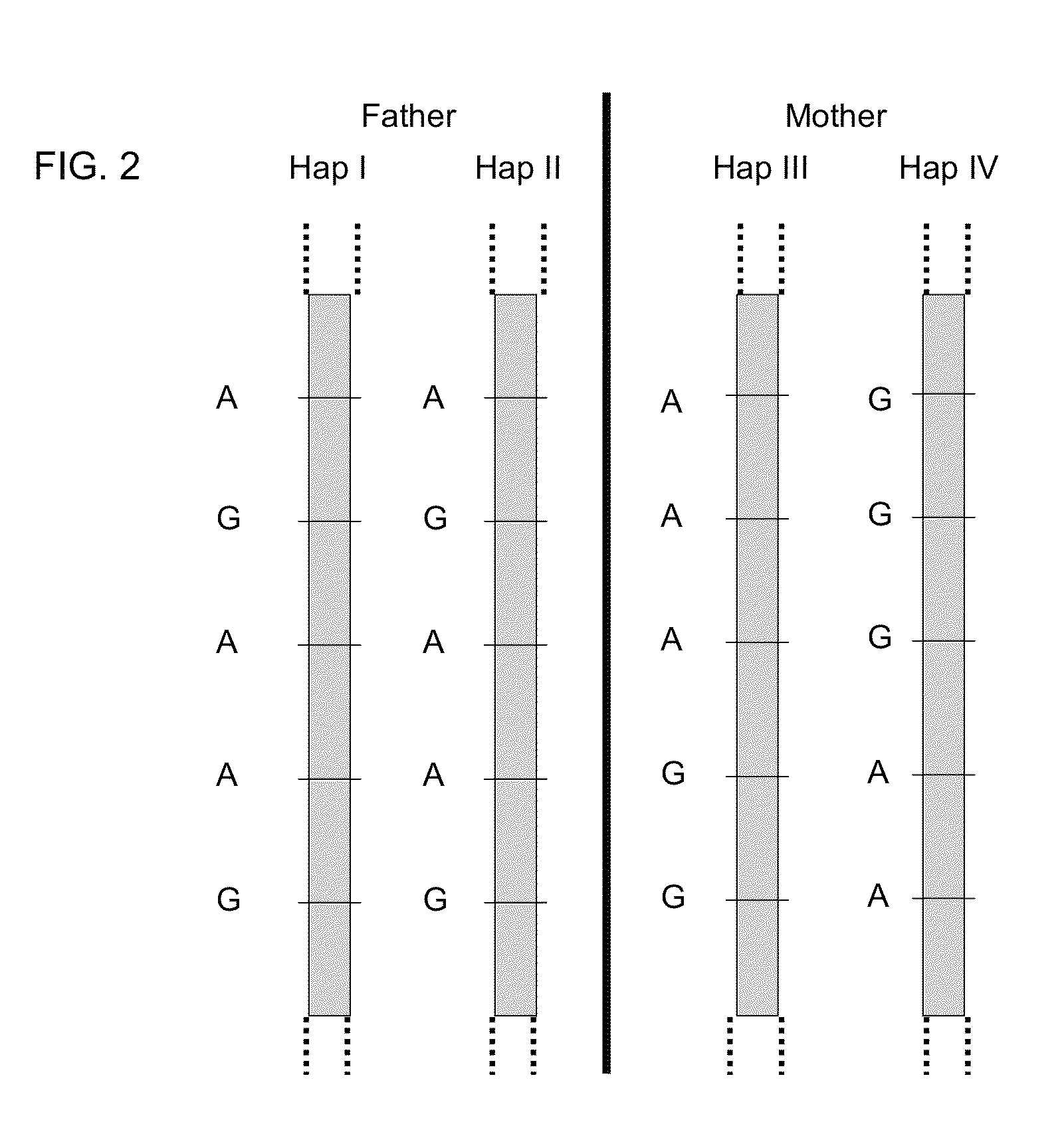
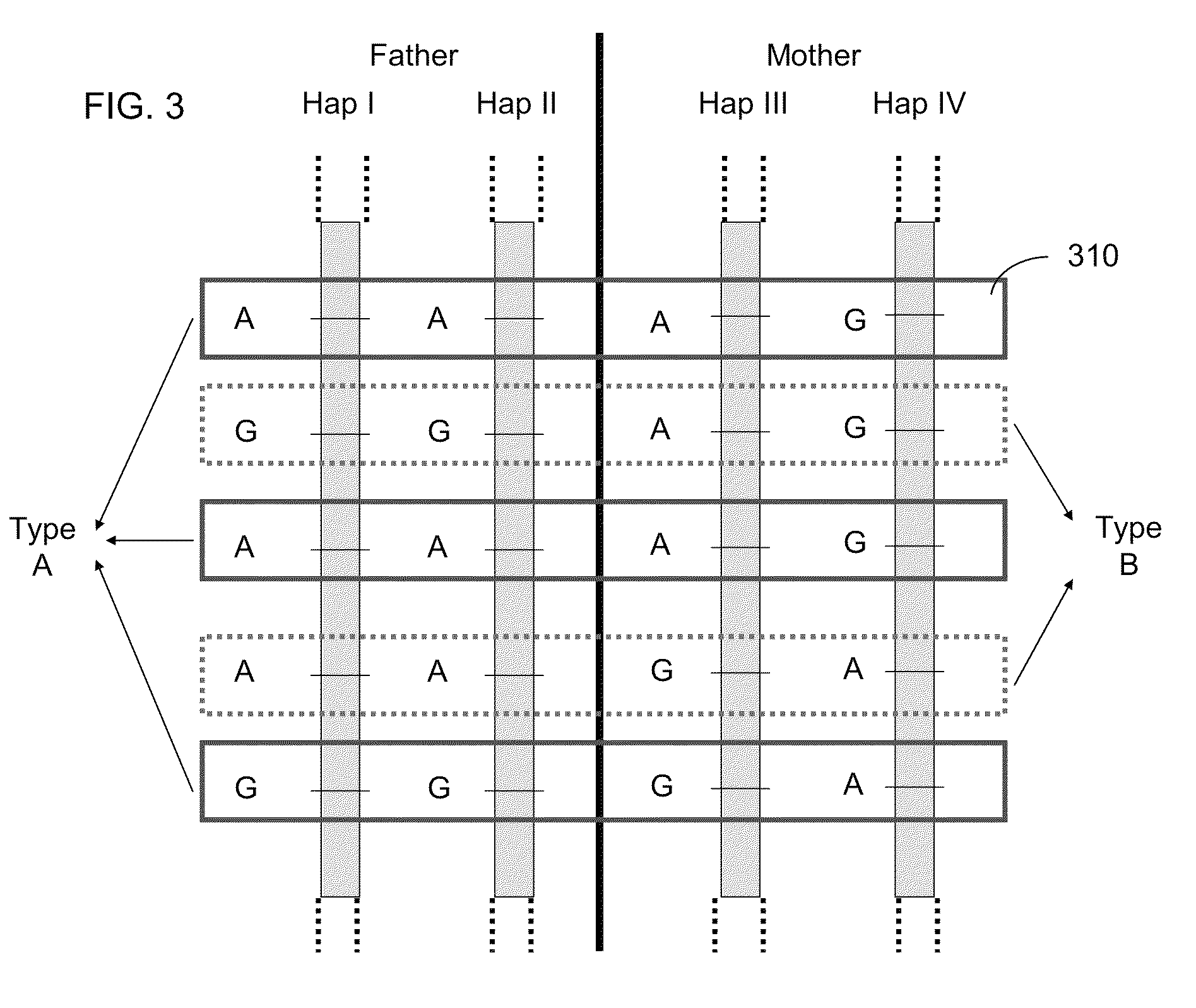
Systems, methods, and apparatus for determining at least a portion of fetal genome are provided. DNA fragments from a maternal sample (maternal and fetal DNA) can be analyzed to identify alleles at certain loci. The amounts of DNA fragments of the respective alleles at these loci can be analyzed together to determine relative amounts of the haplotypes for these loci and determine which haplotypes have been inherited from the parental genomes. Loci where the parents are a specific combination of homozygous and heterozygous can be analyzed to determine regions of the fetal genome. Reference haplotypes common in the population can be used along with the analysis of the DNA fragments of the maternal sample to determine the maternal and paternal genomes. Determination of mutations, a fractional fetal DNA concentration in a maternal sample, and a proportion of coverage of a sequencing of the maternal sample can also be provided.
Owner:SEQUENOM INC +1
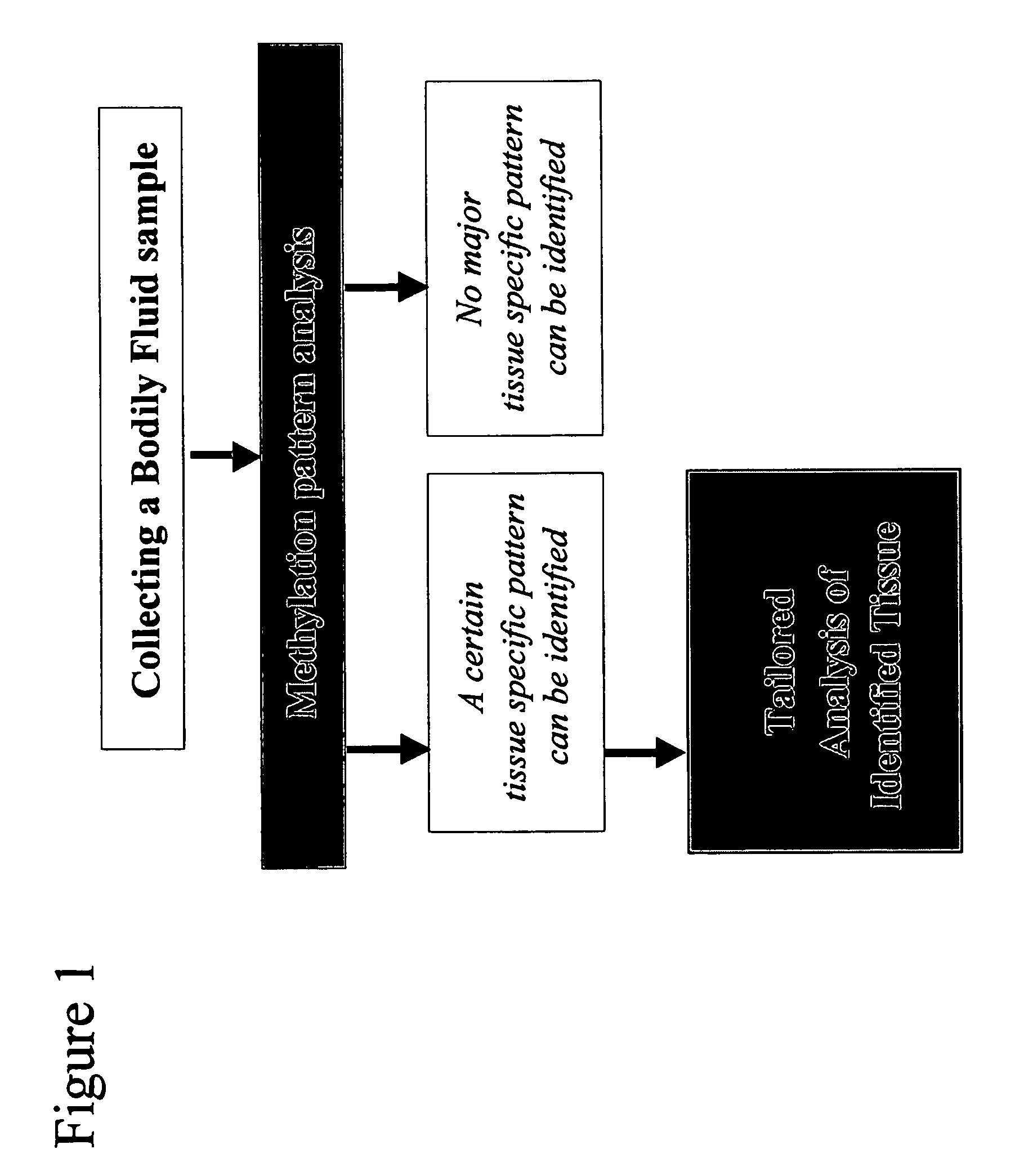
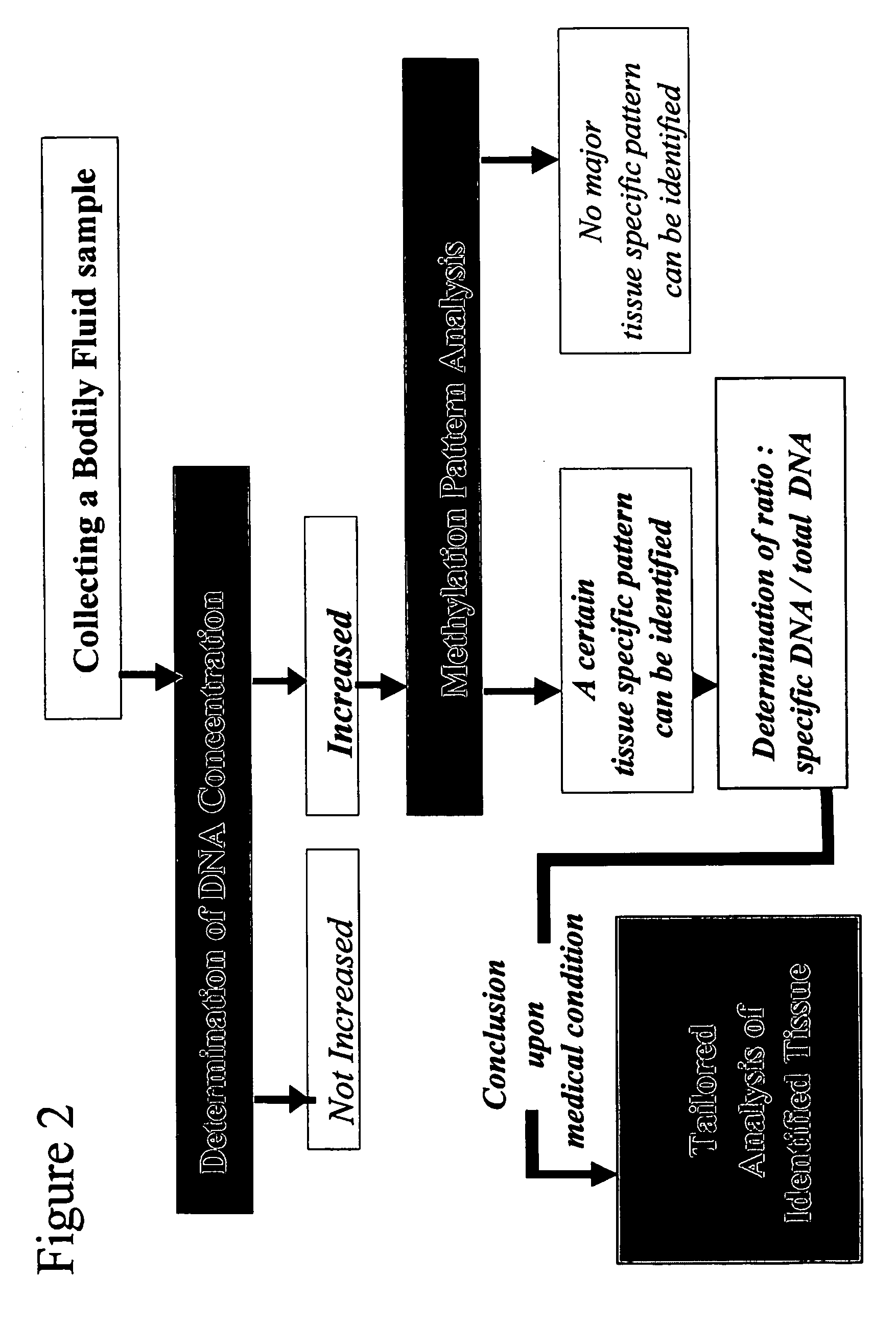
Method and device for determination of tissue specificity of free floating dna in bodily fluids
InactiveUS20050221314A1Diagnostic value of dramaticallyMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseBlood plasma
Owner:EPIGEONOMICS
HBV (hepatitis B virus) fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit
ActiveCN102174660ARapid determinationAccurate measurementMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesDna concentrationBlood serum
The invention discloses an HBV (hepatitis B virus) fluorescent quantitative PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection kit which comprises a probe for detecting the target polynucleotide, an upstream primer and a downstream primer for amplifying the target polynucleotide, a PCR buffer solution and DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) polymerase, wherein the probe for detecting the target polynucleotide hasa SEQ No.1 sequence. As the probe for detecting the target polynucleotide has the SEQ No.1 sequence, the kit disclosed by the invention has good specificity; by using the kit provided by the invention, the HBV-DNA concentration in the unknown sample such as serum, plasma or milk can be quickly and accurately measured; and the kit has good specificity and can detect eight gene types of HBV.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH
Fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit of hepatitis B virus and application thereof
ActiveCN101701267AStrong specificityHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesPositive controlFluorescence
The invention discloses a fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit of hepatitis B virus and an application thereof. The kit is composed of the following independent components: DNA extraction solution I, DNA extraction solution II, DNA extraction solution III, DNA extraction solution IV, positive control interior label, PCR reaction liquid, probe HBV-SP, enzyme mixed liquor containing heat resistant DNA polyase and uracil DNA glycosylase, quantitative hepatitis B virus reference material, hepatitis B virus positive control serum and hepatitis B virus negative control serum, wherein DNA extraction solution I contains 0.2-1.0% of lauryl sodium sulphate (mass / volume), 1.0-4.0% of Triton (volume / volume) and 0.2-1.0mol / L of guanidinium isothiocyanate; DNA extraction solution II contains 100-300mmol / L of 4-HEPES, 100-300mmol / L of sodium chloride with pH of 6.5+ / -0.2 and 100-400 mu g / ml of magnetic beads; DNA extraction solution III contains 0.1-1.0% of Triton (volume / volume) and 100-300mmol / L of sodium chloride; DNA extraction solution IV contains mineral oil. The fluorescence quantitative PCR detection kit of hepatitis B virus of the invention can be used for detecting the HBV-DNA concentration in samples of serum, blood plasma or latex and the like.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH
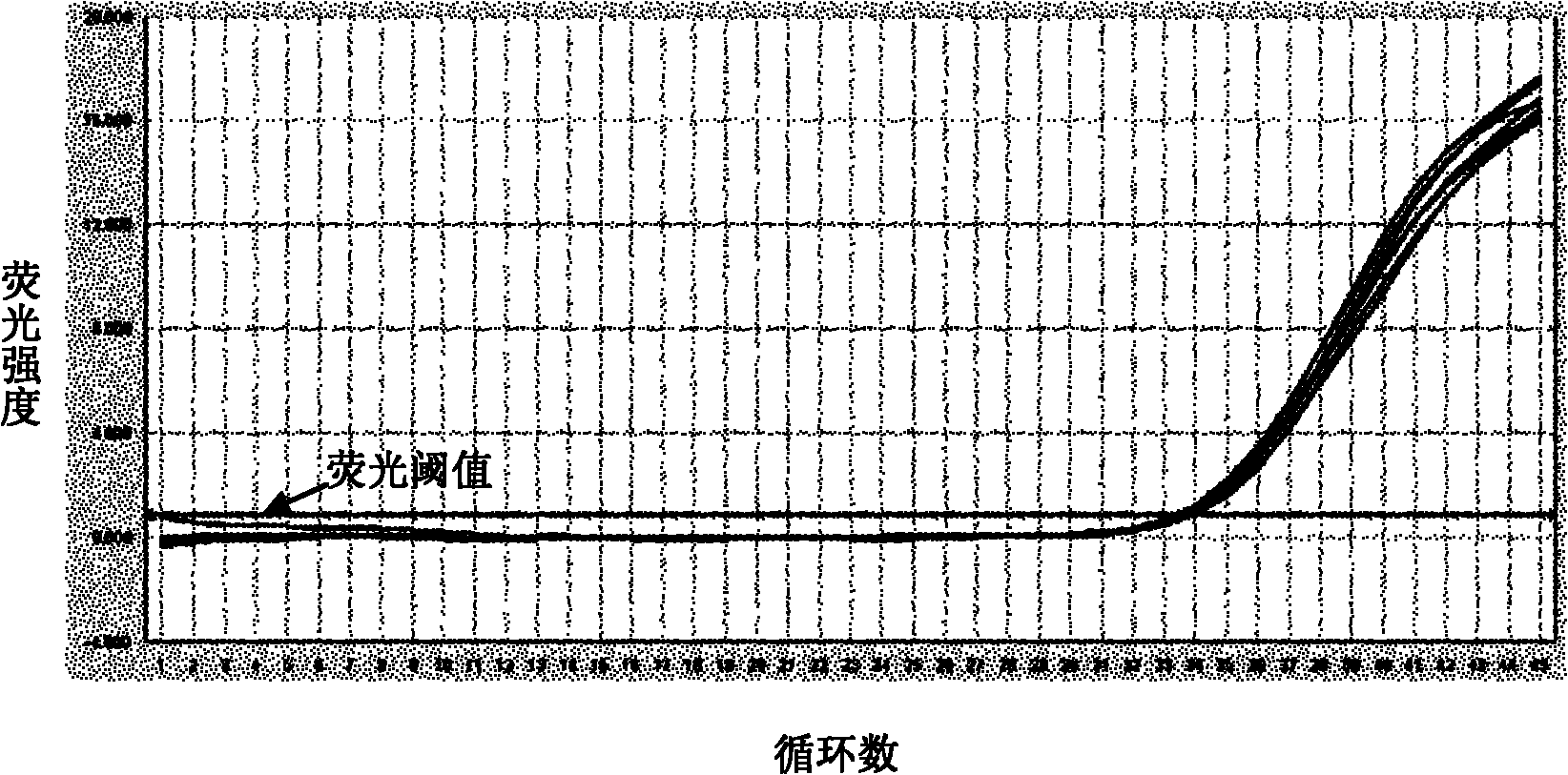
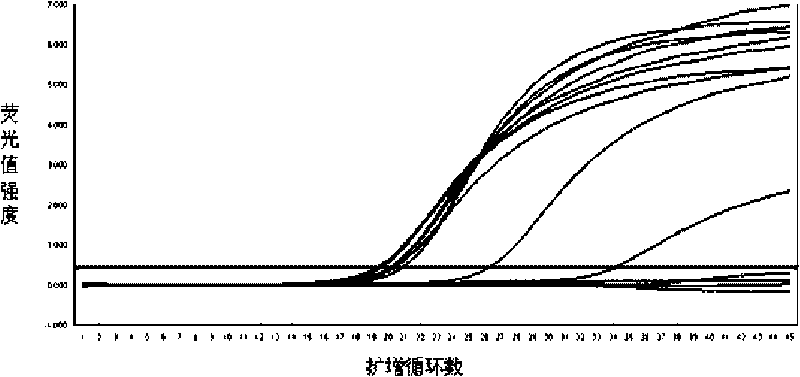
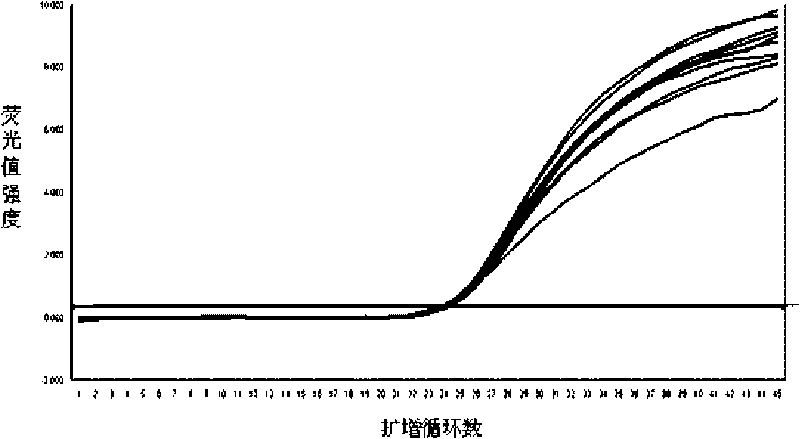
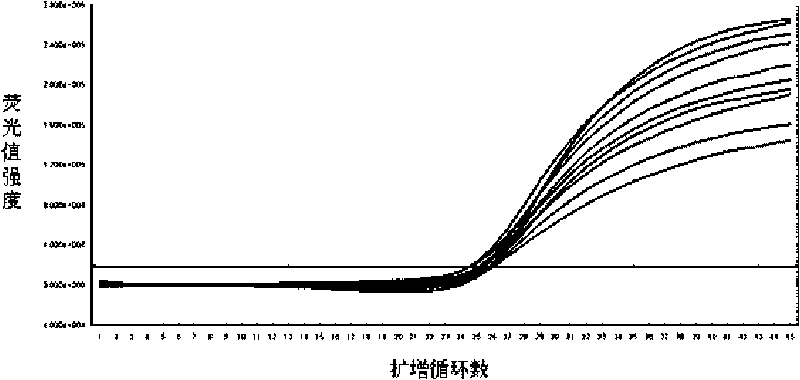
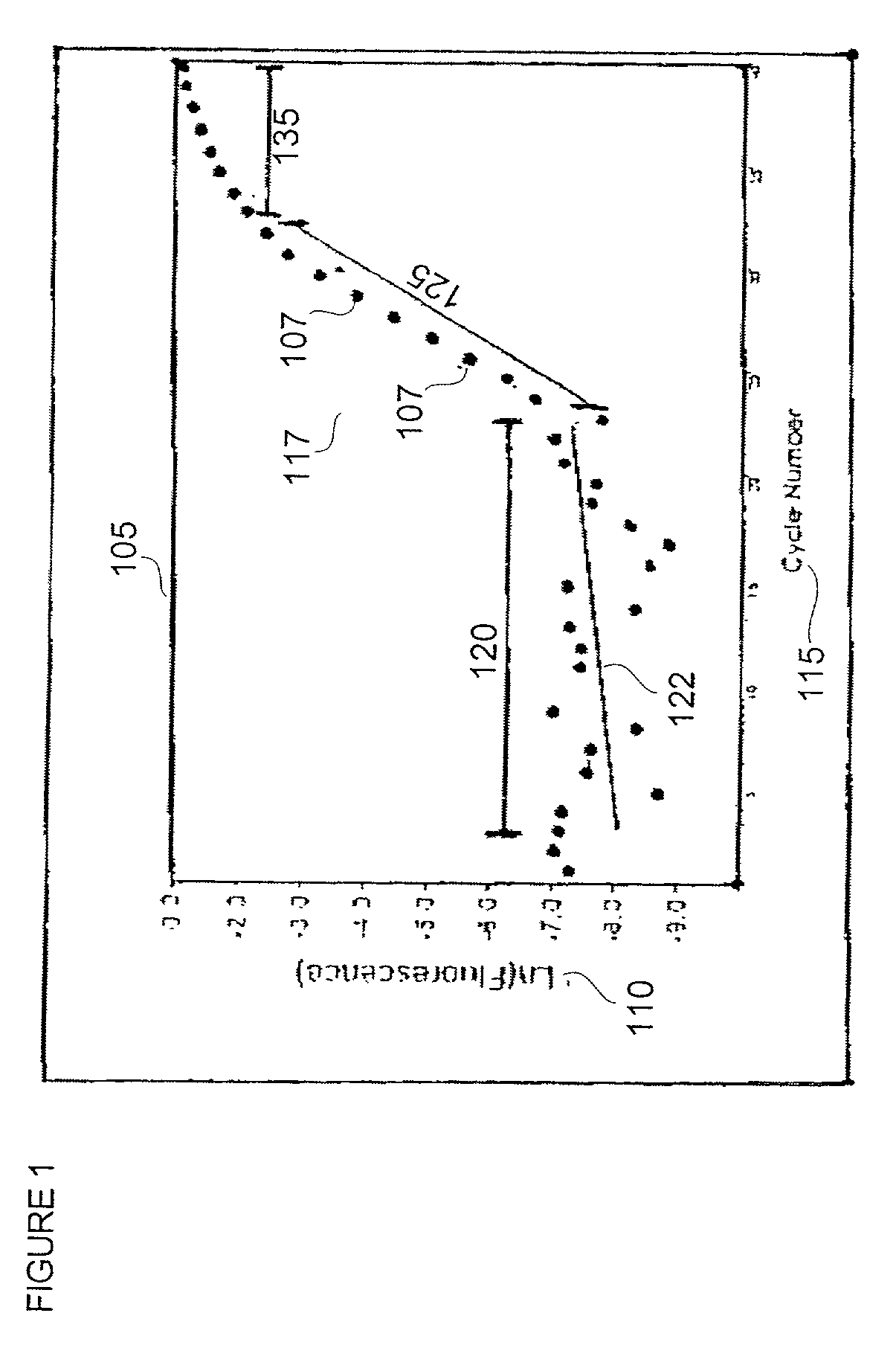
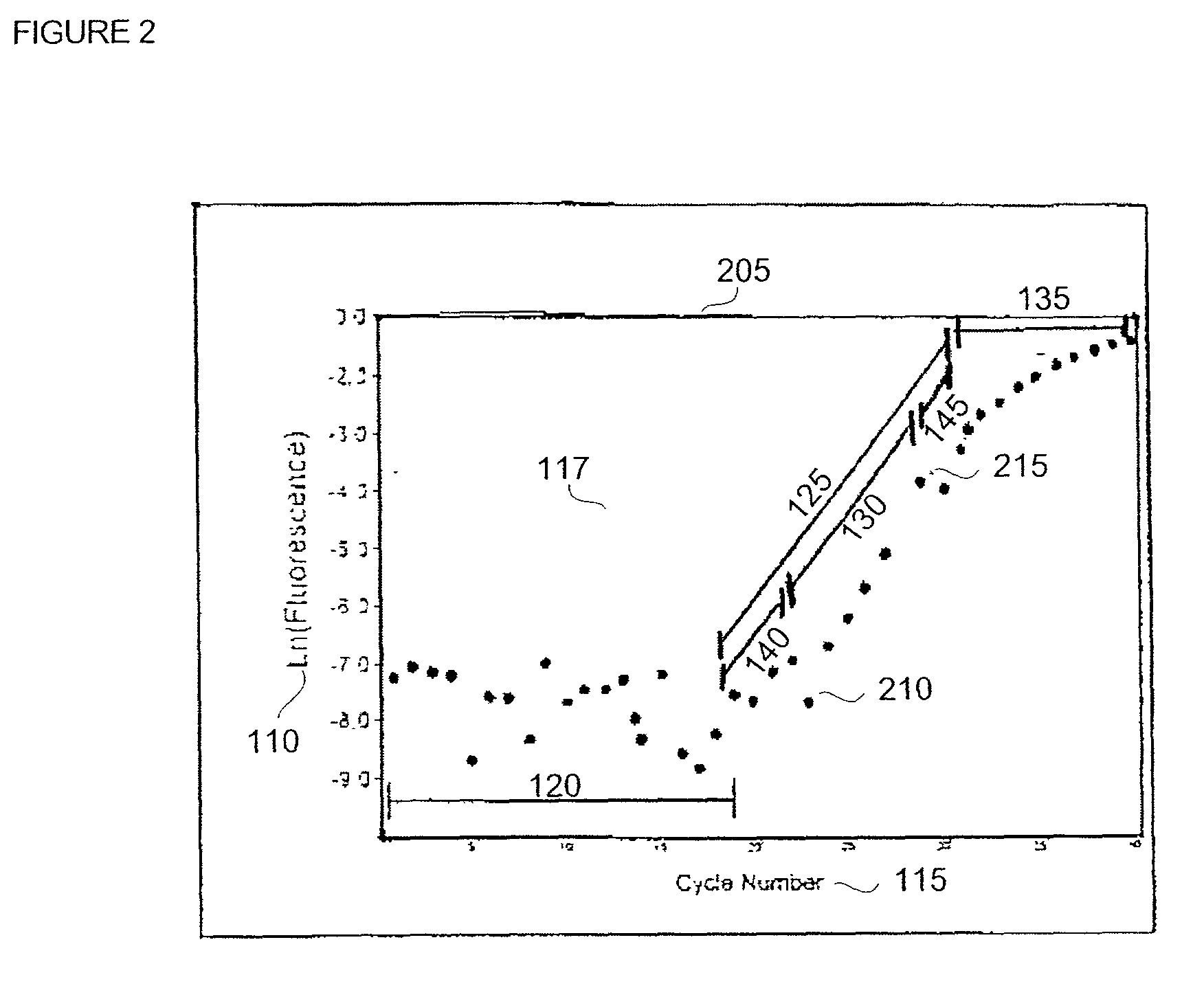
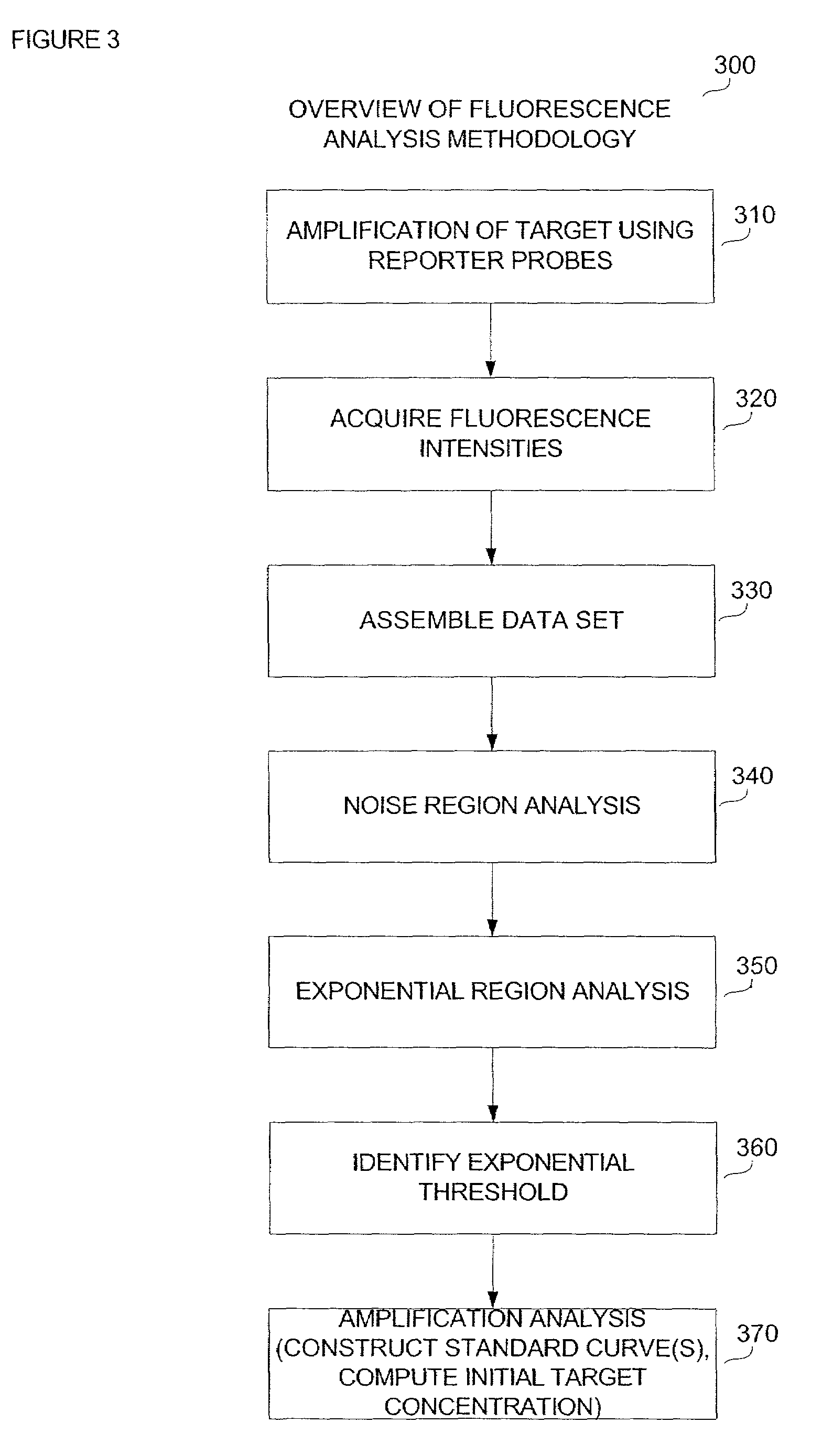
Automatic threshold setting for quantitative polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS20030044826A1Microbiological testing/measurementRecognisation of pattern in signalsFluorescenceBiology
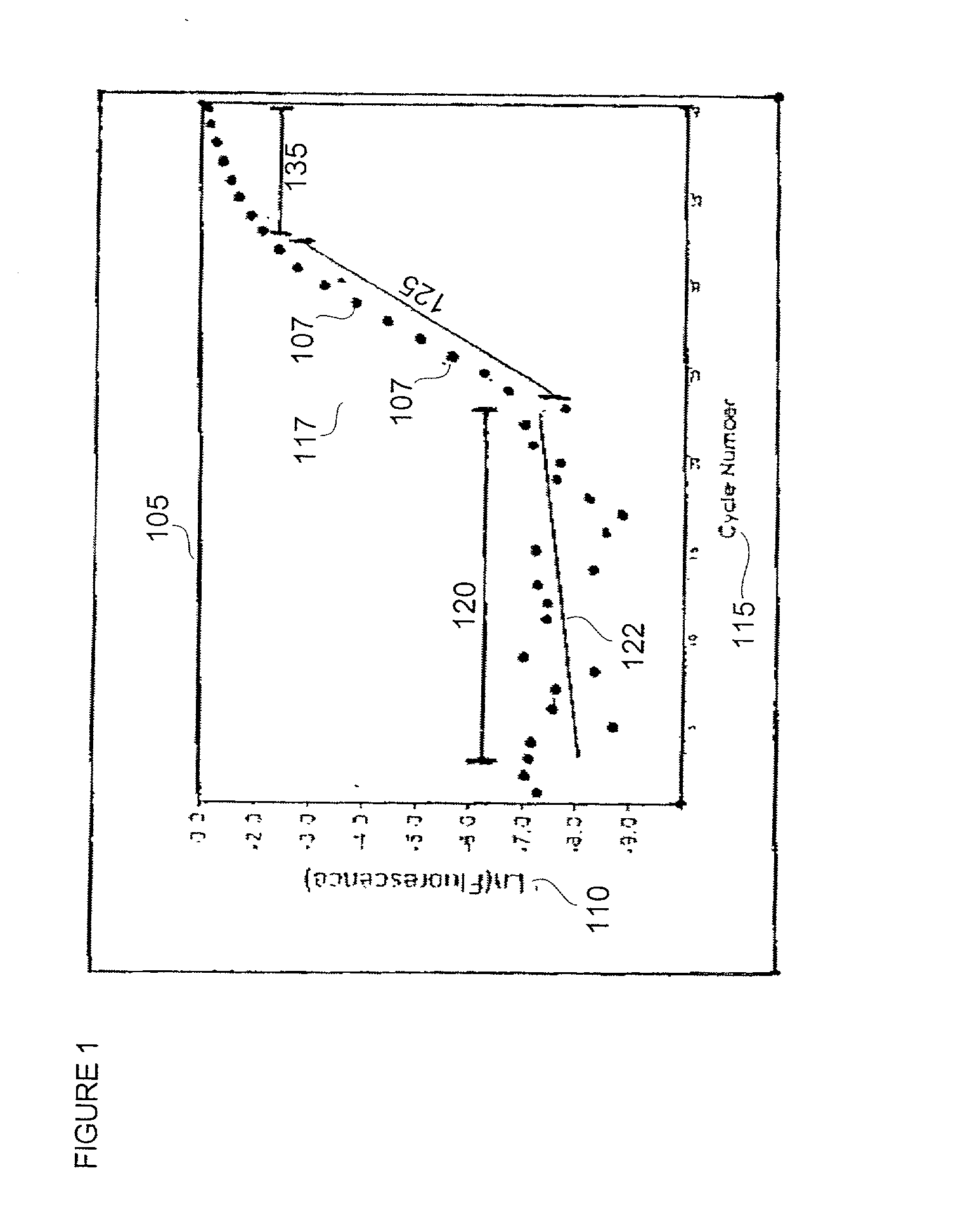
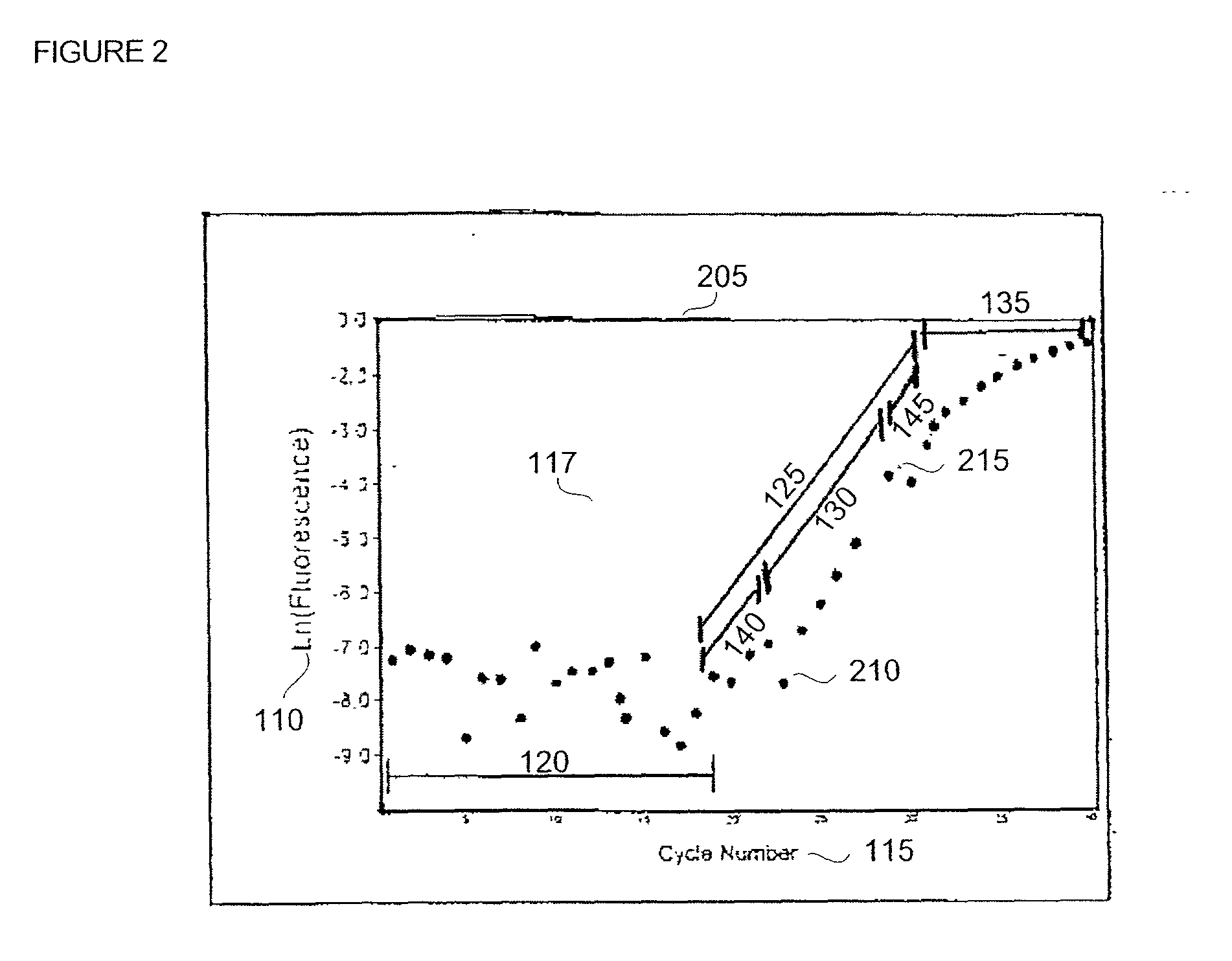
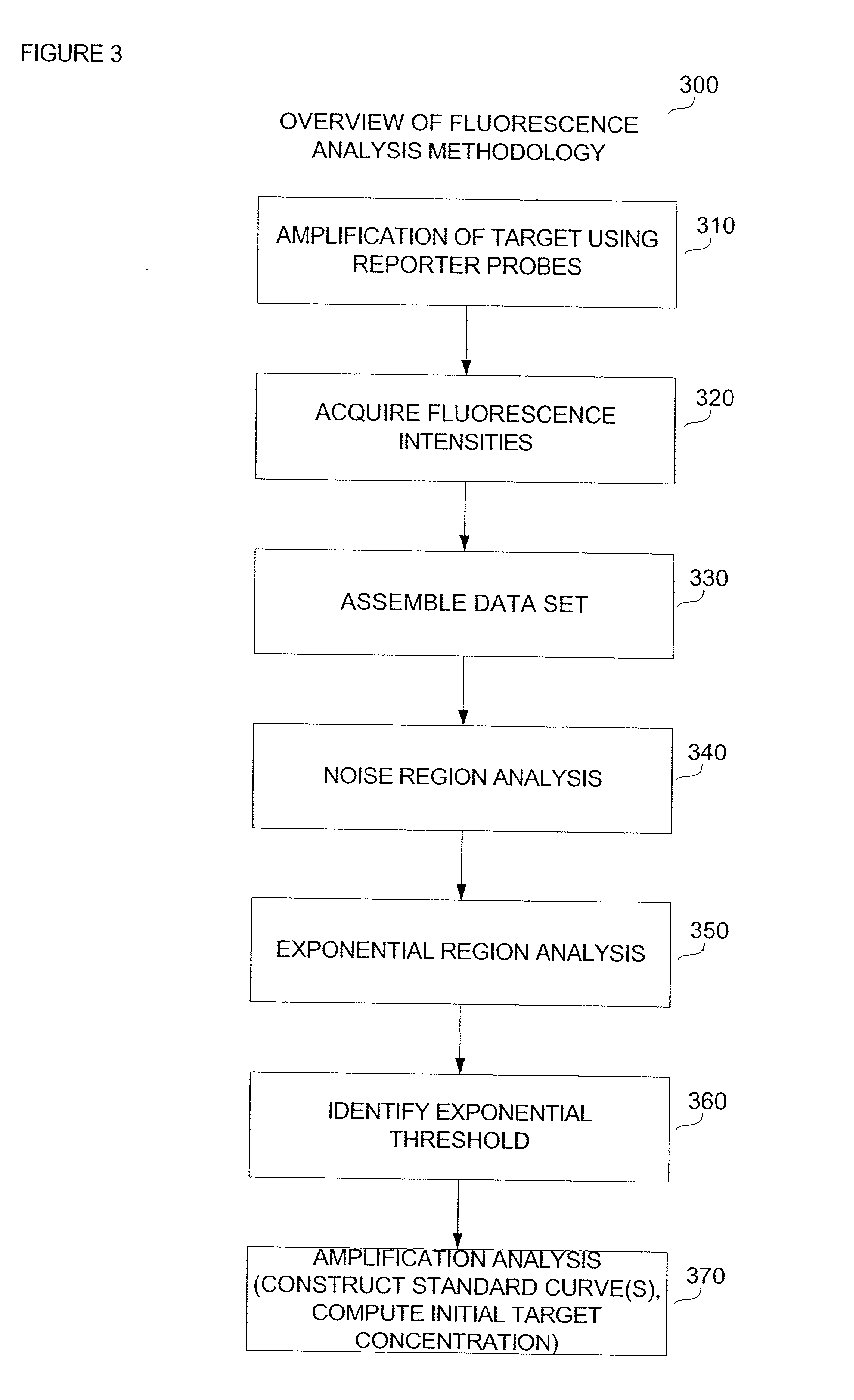
Disclosed are systems and methods for identifying and quantitating the presence of one or more DNA species in a sample population through PCR amplification. DNA species quantitation includes a determination of a threshold fluorescence value used in the assessment of the PCR amplification reaction. Various embodiments of the present invention incorporate an enhancement function useful in selecting appropriate threshold fluorescence values and facilitate the determination of DNA concentrations by quantitative PCR based methodologies.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Process for abstracting total DNA of swine waste sample
The invention relates to the microbiology and molecular biology technical field, in particular to a method for extracting pig manure sample total DNA. The method mainly comprises manure sample pretreatment and sample total DNA extraction. Moreover, the method comprises the following steps that: collected fresh manure sample or frozen manure sample is taken as a material; the pretreatment of the manure sample is carried out by means of a PBS buffer solution, a paraformaldehyde solution and anhydrous alcohol so as to obtain manure sample bacteria suspension; and a CTAB solution and beta-mercaptoethanol, etc. are used to carry out cell fragmentation, thereby releasing DNA. The method has the characteristics of simple operation, quickness, high efficiency and ideal repeatability and economical efficiency, etc.; moreover, the extracted DNA has high concentration, purity and yield, and can be directly used in subsequent molecular biology experimental researches such as PCR amplification without purification.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
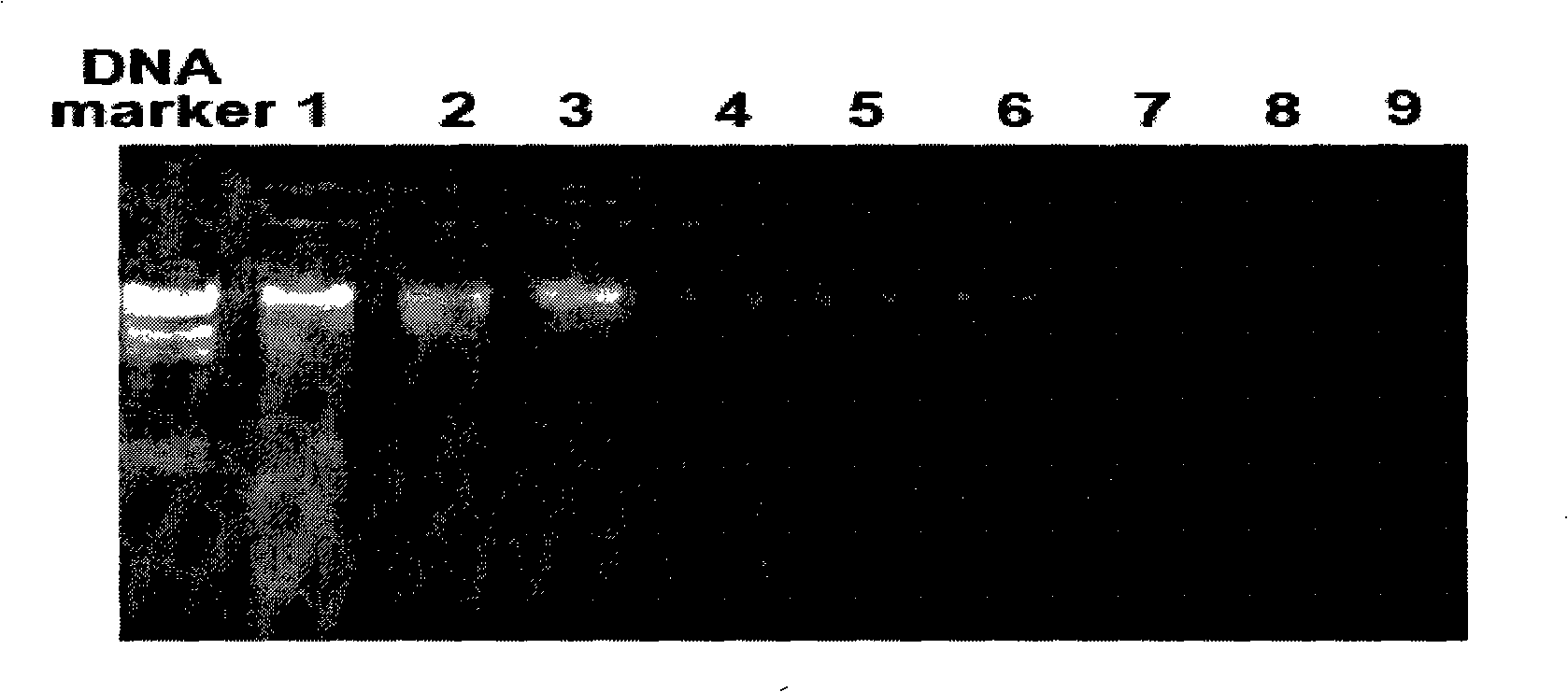
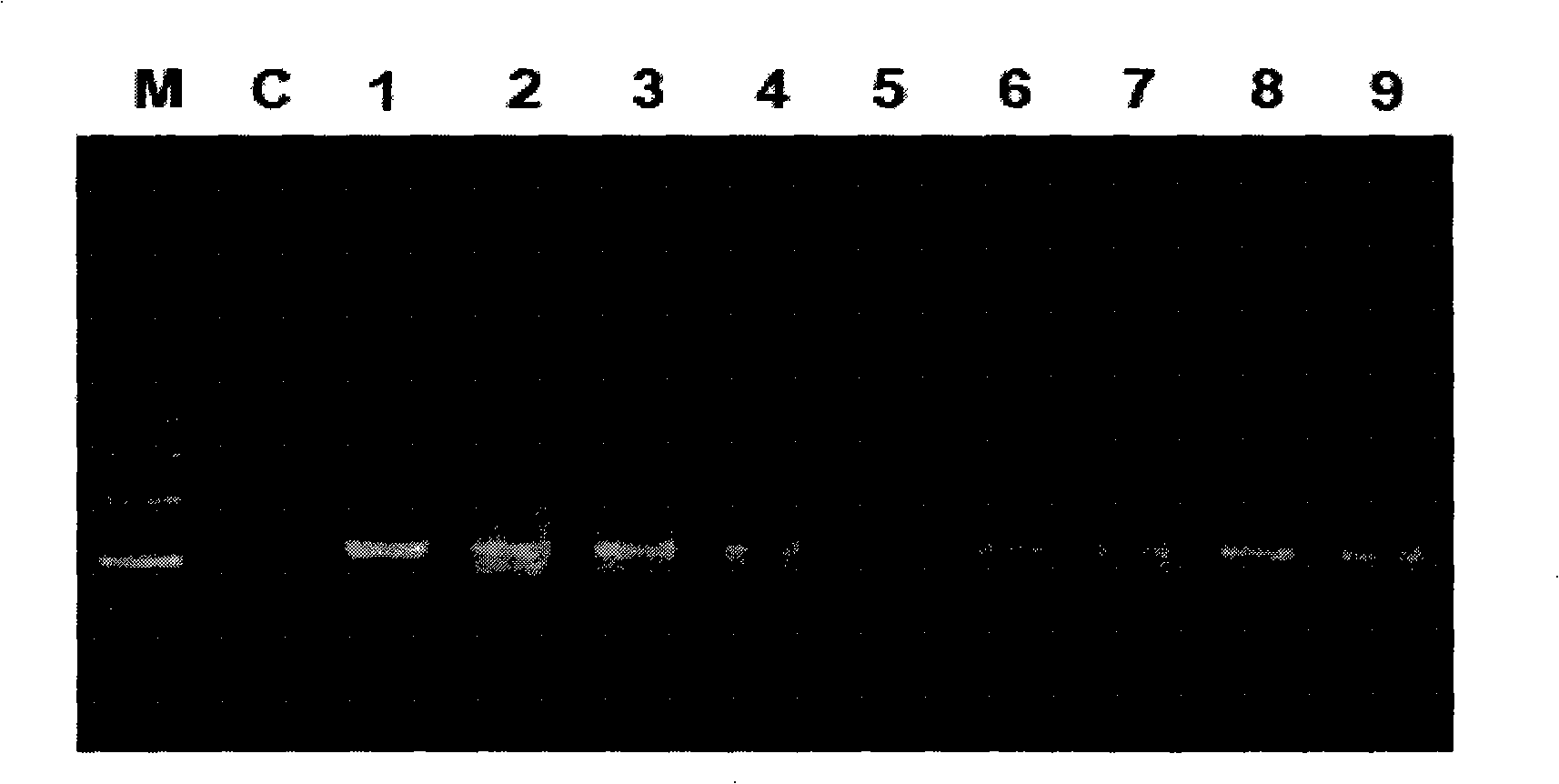
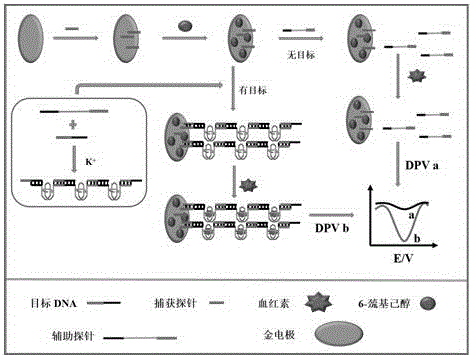
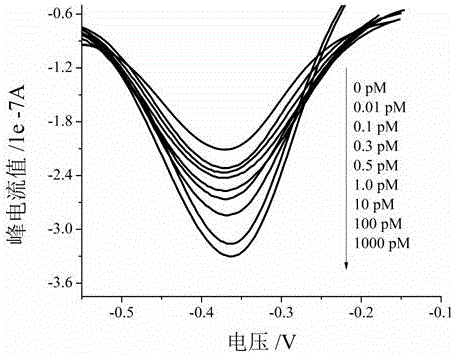
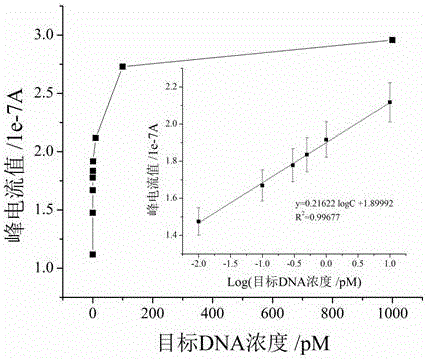
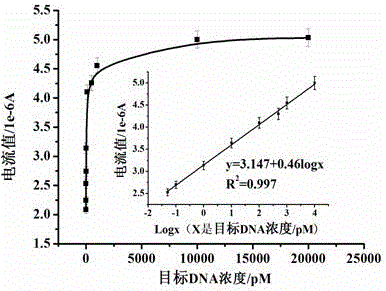
Electrochemical method of detecting single-chain target DNA concentration based on G-quadruplex-heme compound and polymeric chain type amplification reaction
ActiveCN106525940AHigh sensitivityRealize highly sensitive detectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemistryDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention relates to an electrochemical method of detecting single-chain target DNA concentration based on G-quadruplex-heme compound and polymeric chain type amplification reaction, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. A capture probe and an auxiliary probe are designed, the two ends of the auxiliary probe each contain a nucleotide sequence complemented with the target DNA, and the middle of the auxiliary probe contains a base sequence capable of forming G-quadruplex. The capture probe and the target DNA recognize each other and are subjected to continuous polymeric chain type reaction to form chain-shaped polymer, the chain-shaped polymer is fixed to an electrode through the capture probe on the surface of the gold electrode, and a great number of G-quadruplex structures are introduced onto the surface of the electrode. Then, G-quadruplex and heme are combined to form the compound with powerful electrochemical signals, and the target DNA is detected through the corresponding relation among the electrochemical signals obtained through differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) scanning, the G-quadruplex-heme compound on the surface of the electrode and the concentration of the target DNA added into the system. HIV DNA in the sample is detected through the method, and an ideal effect is obtained. The electrochemical method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:ANHUI HUATENG AGRI TECH CO LTD
Automatic threshold setting for quantitative polymerase chain reaction
InactiveUS7188030B2More complete automationQuantitative precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementRecognisation of pattern in signalsBioinformaticsPolymerase
Disclosed are systems and methods for identifying and quantitating the presence of one or more DNA species in a sample population through PCR amplification. DNA species quantitation includes a determination of a threshold fluorescence value used in the assessment of the PCR amplification reaction. Various embodiments of the present invention incorporate an enhancement function useful in selecting appropriate threshold fluorescence values and facilitate the determination of DNA concentrations by quantitative PCR based methodologies.
Owner:APPL BIOSYSTEMS INC
Fetal free DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) library quantitative standard and preparation method therefor
ActiveCN105239164ACoefficient of variation between differences is smallEasy to storeNucleotide librariesLibrary creationIon semiconductor sequencingQuality control
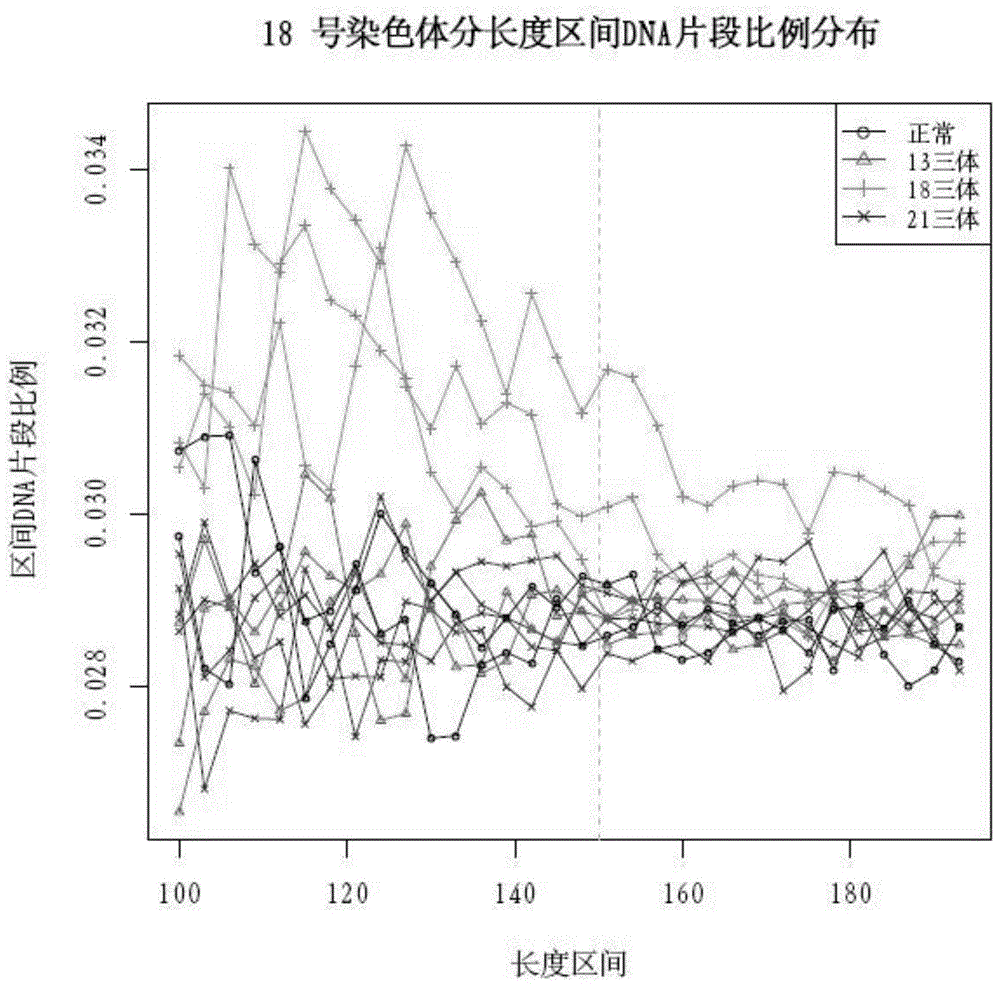
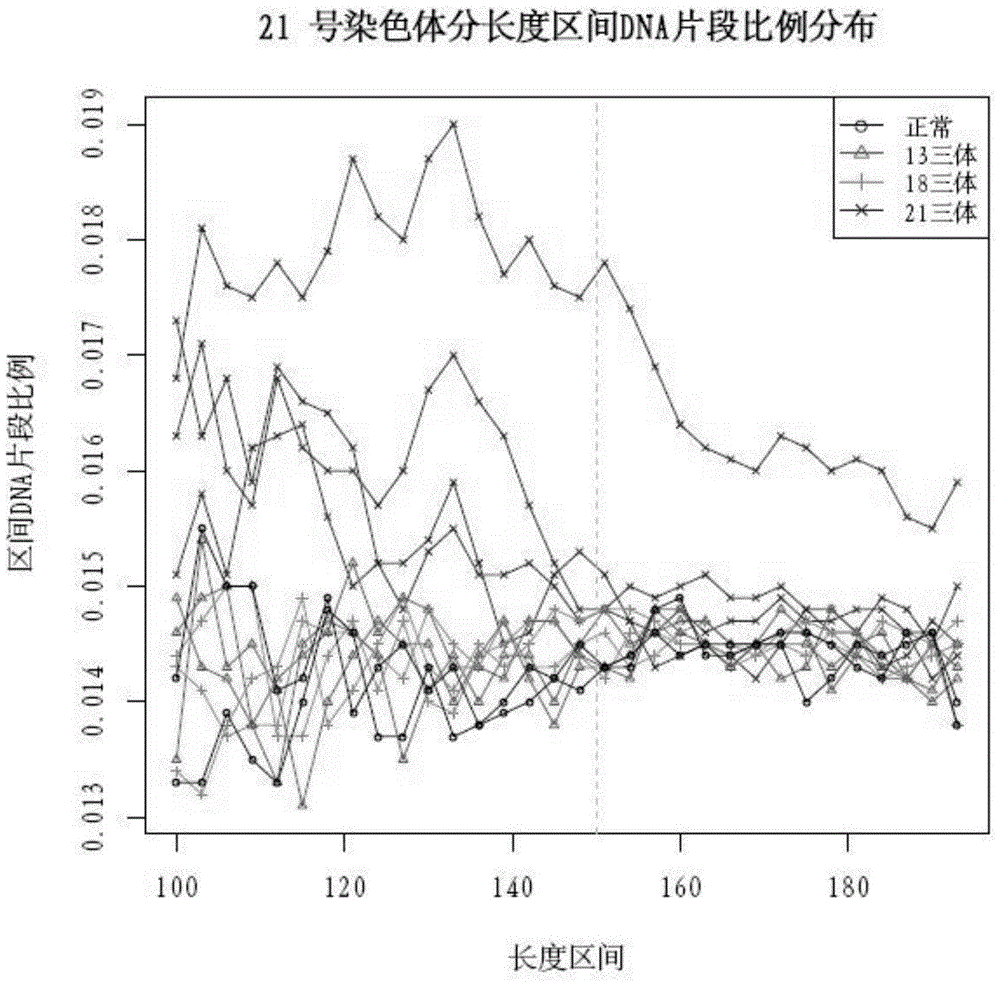
The invention discloses a qPCR (quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction) quantitative standard for detecting library DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) concentration of aneuploids, i.e., 21 trisome, 18 trisome and 13 trisome of fetal chromosomes based on a semiconductor sequencing method and a preparation method therefor and belongs to the field of noninvasive prenatal detection on fetal aneuploids. The standard is used for carrying out quality control on detection concentration of detected samples. The preparation method for the qPCR quantitative standard disclosed by the invention comprises five steps: (1) synthesizing joint sequences and primers; (2) preparing simulated fetal free DNA libraries; (3) amplifying and purifying the libraries; (4) producing a library standard curve; and (5) carrying out sample detection. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the DNA concentration of sample libraries can be rapidly determined, and a guarantee of accuracy and validity of noninvasive prenatal detection on the aneuploids, i.e., the 21 trisome, the 18 trisome and the 13 trisome of the fetal chromosomes is provided.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH +1
Quantitative method for free fetal DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) proportion in maternal peripheral blood
ActiveCN104846089AIncreased free DNA concentrationImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA extractionBlood plasma
The invention discloses a quantitative method for free fetal DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) proportion in maternal peripheral blood. DNA containing designed SNP (single nucleotide polymorphism) in plasma is extracted by the aid of a designed primer and loaded on a machine after a series of treatment, sequencing products are compared to a human genome sequence, and a basic group of each SNP site is determined. The concentration of the free fetal DNA is quantified by analyzing the proportion of the basic groups in the SNP. Induced errors can be corrected by the aid of a plurality of SNP sites, the SNP sites are simultaneously calculated by a statistics method, and calculated free fetal DNA concentration accuracy is improved.
Owner:厦门万基生物科技有限公司
Kit and method for quickly extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from colla corii asini
ActiveCN104046616AIncrease concentrationHigh purityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationChelex 100A-DNA
The invention discloses a kit and a method for quickly extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from colla corii asini. A combined technology of an SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate)-protease K and Chelex-100 combined process DNA extraction technology and a Glassmilk DNA purification technology is applied to DNA extraction of the colla corii asini. The dosage of needed colla corii asini paste is controlled to be 0.3ml to 0.5ml, the weight of colla corii asini blocks can be controlled to be 0.2mg to 0.6mg, and extracted DNA is high in concentration, excellent in purity, stable and difficult to degrade; due to extracted DNA, sequence fragments of 100bp-500bp can be amplified, and subsequent molecular biology experiments of gene cloning, sequencing and the like can be carried out. According to the method, the operation is simple, the dosage is low, and the consumed time is short; the method is especially suitable for DNA extraction of various types of colla corii asini products with low nucleic acid content and high degradation degree caused by deep processing; a foundation is provided for realizing colla corii asini source identification by adopting a DNA molecular biology identification technology.
Owner:VEGETABLE RES INST OF SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Phage display
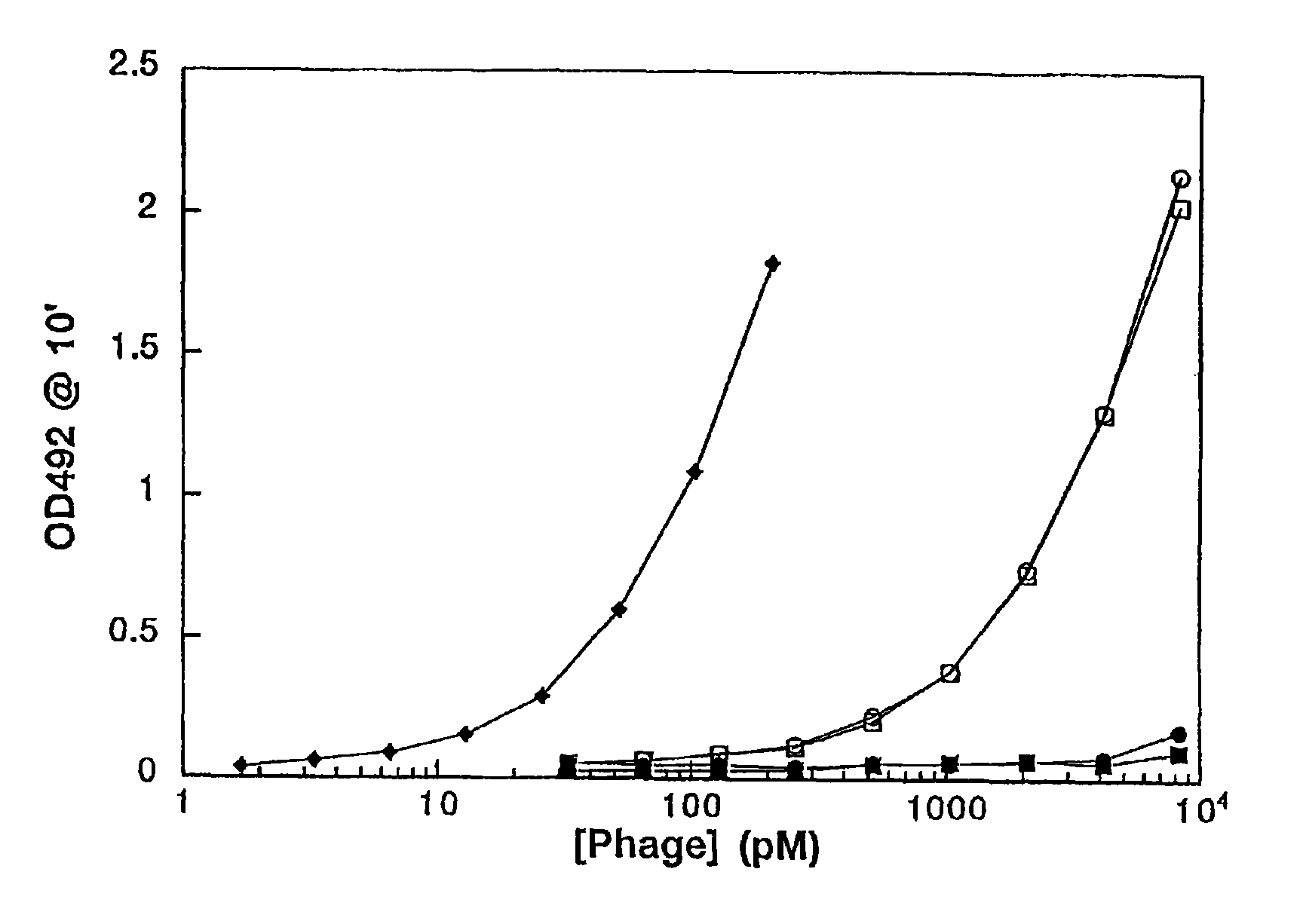
The transformation yield of electroporation is increased by using higher DNA concentrations and DNA affinity purification. Fusion proteins of a viral coat protein variant and a heterologous polypeptide are useful in phage display systems.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
Aneuploidy biological information analysis method and system
ActiveCN107133495AEliminate fluctuationsReduce error interferenceBiostatisticsSequence analysisReference databaseInformation analysis
The invention discloses an aneuploidy biological information analysis method and system, wherein the method comprises: 1) constructing a reference database; 2) calculating UR ratio; 3) constructing statistical parameters of the reference database; 4) calculating Z value; 5) decreasing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy false positives due to microdeletion or micro-duplication present in maternal chromosomes according to the above process of decreasing fetal chromosomal aneuploidy false positives due to microdeletion or micro-duplication present in maternal chromosomes; 6) constructing a fetal DNA concentration prediction model to predict fetal DNA concentration according to the above process of constructing a fetal DNA concentration prediction model; 7) calculating percentage of DNA of each fetal chromosome to total DNA; 8) judging autosomal aneuploidy; 9) judging allosomal anomalies. By using the method and system according to the technical scheme, analytical accuracy is improved greatly.
Owner:BEIJING HOSPITAL +1
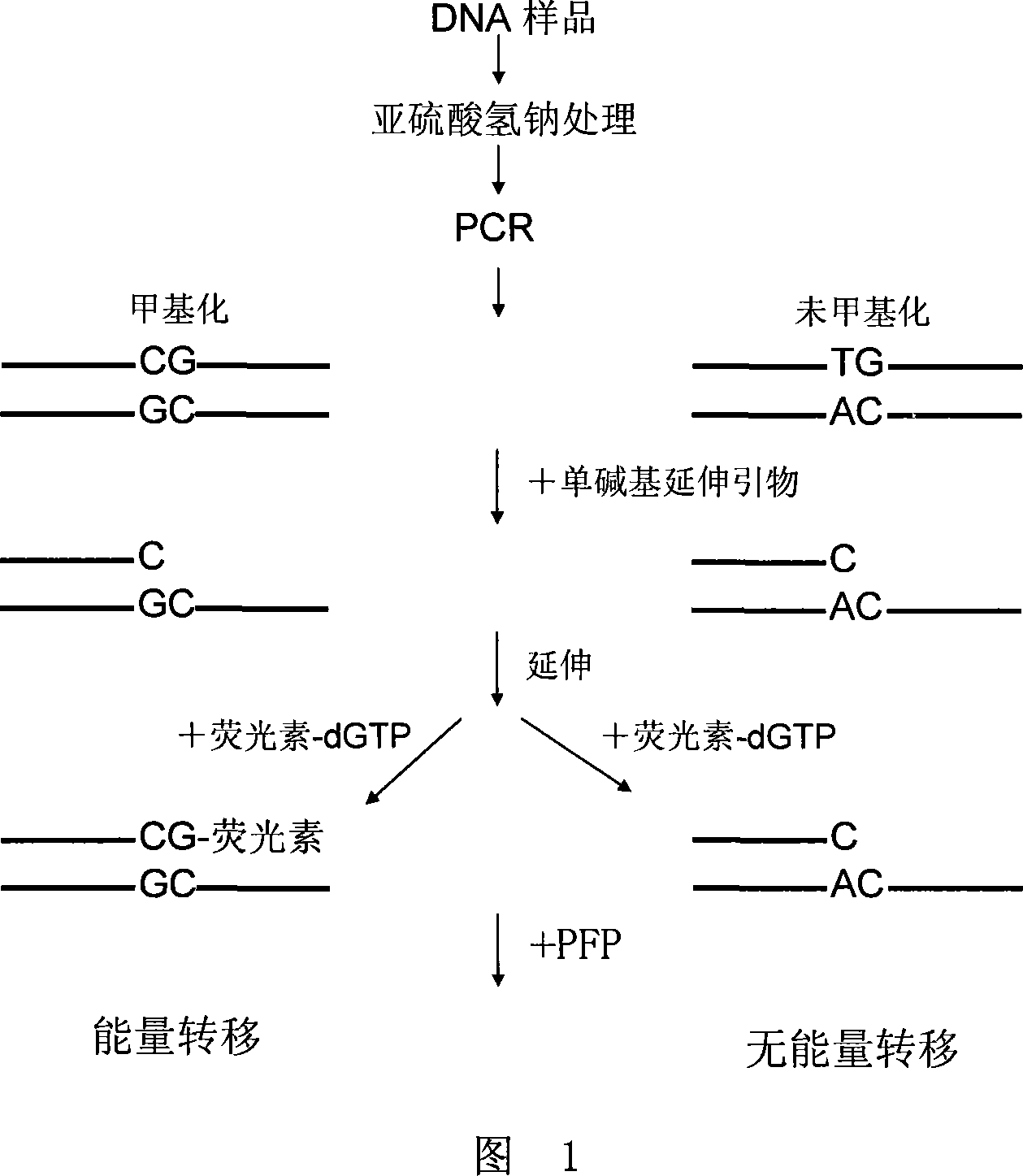
Method for detecting DNA methylation
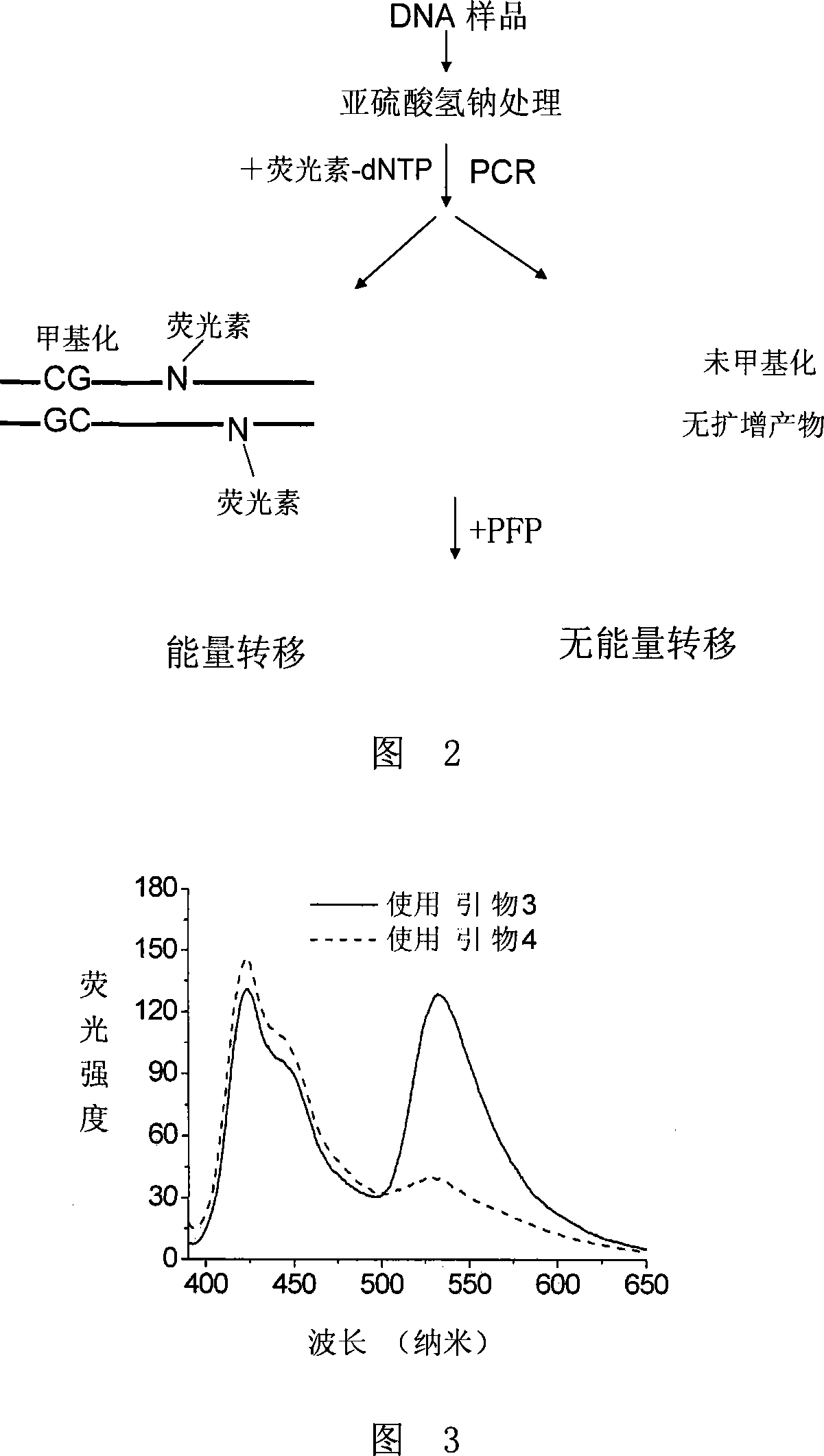
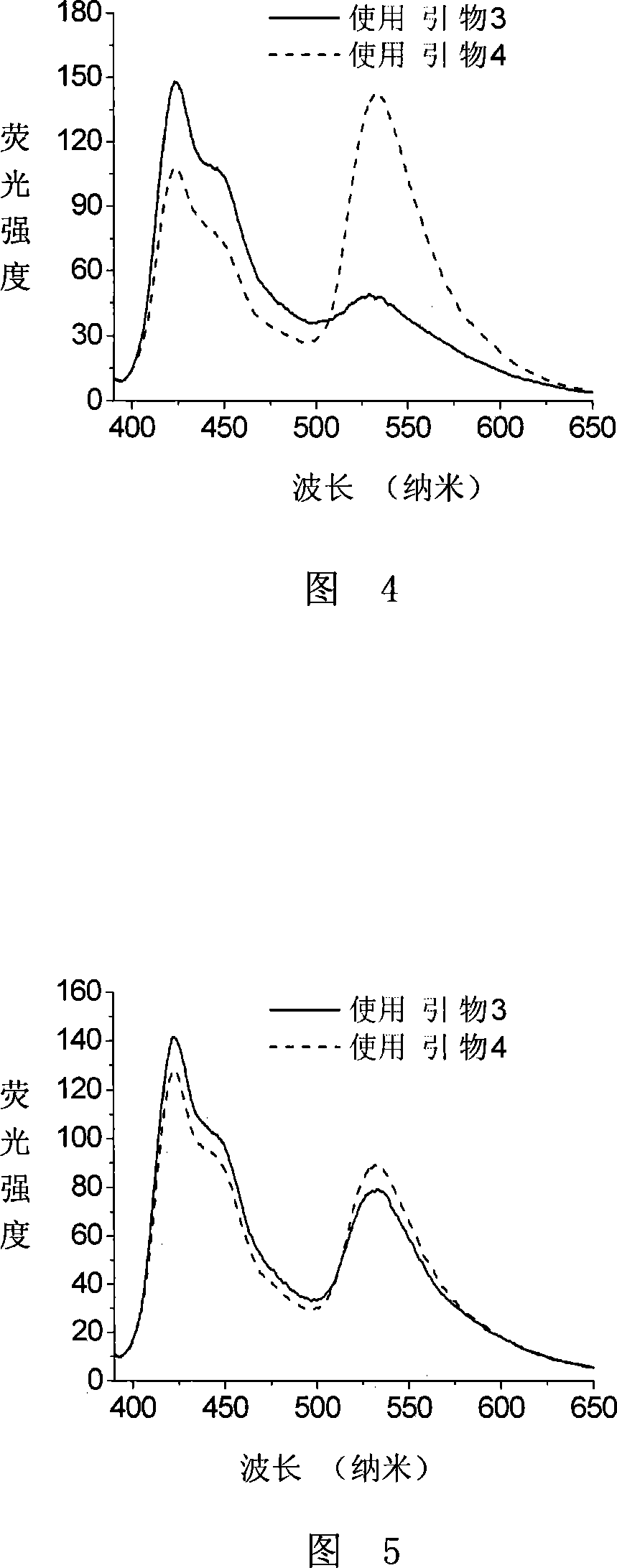
ActiveCN101230399AEasy to detectHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA methylationClinical diagnosis
The invention discloses a method of detecting the methylation of DNA. With high sensitivity and fast processing, the method provided by the invention can detect DAN with lower concentration and can conveniently detect low-level methylation of DNA without steps of separation and purification. Compared with the clinical histological method which has high demand onto samples, the invention only needs a little mount of DNA to sensitively detect the methylation level of tumor suppressor gene, thereby having significance in clinical diagnoses of early cancers.
Owner:INST OF CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Simple method for efficiently extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from soil samples
ActiveCN103993007APracticalHigh degree of reliabilityMicroorganism based processesDNA preparationFreeze thawingHigh concentration
The invention provides a simple method for efficiently extracting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) from soil samples. According to the simple method, the DNA in environmental samples is fully released and exposed by using combination of methods such as glass bead grinding, liquid nitrogen repetitive freeze-thawing, SDS (sodium-dodecyl sulphate), lysozyme and a protease-K method for the different soil samples, the DNA purification is carried out through multiple phenol imitation extraction processes, and the determination of the DNA extraction efficiency is carried out by adding an internal standard bacterial strain Xcc8004. The simple method has simple requirements on sample pretreatment; the quantity of the required environmental samples is small; the obtained DNA has relatively high concentration and purity; the extraction efficiency is relatively high; the analysis and detection of antibiotic resistance gene pollution in the complex environmental samples can be met; and the method is simple and reliable and has practical application value.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Analysis method for detecting diversity of soil microorganism
The invention relates to a biological analysis method, especially to an analysis method for detecting the diversity of soil microorganism. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) carrying out DNA extraction in soil; (2) detecting DNA concentration and purity in soil by using the DNA extract obtained from Step (1); (3) carrying out PCR specific amplification on the extracted DNA from soil; and (4) carrying out denaturing gradient gel electrophoresis analysis on the PCR reaction product. By the adoption of the method for detection and analysis of various soils, the result is consistent with the real state of microorganisms as there is no loss of the extracted DNA solution during the treatment process. Therefore, the invention provides a perfect solution for the research of the soil microorganism state.
Owner:SHANGHAI HAIDI GARDENING
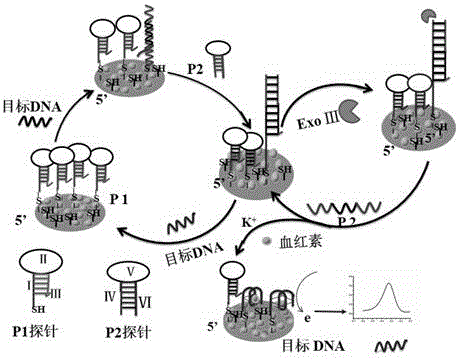
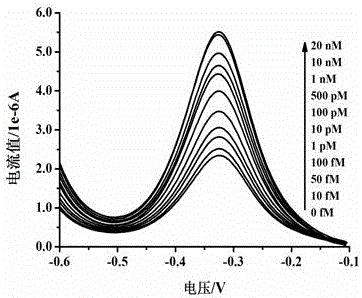
Method for electrochemically detecting concentration of specific single-stranded DNA based on exonuclease and nucleic acid probe
ActiveCN105821132AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementHaem-haem interactionNanoparticle
The invention relates to a method for electrochemically detecting concentration of specific single-stranded DNA based on exonuclease and a nucleic acid probe and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The invention designs and synthesizes two types of hairpin-type probes P1 and P2. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly modifying a gold electrode with gold nanoparticles by adopting 1,6-hexanedithiol (HDT), preparing an AuNPs-HDT-Au electrode, and then modifying the probe P1 onto the electrode; taking a specific single stranded target DNA as a to-be-detected object, so that the probes P1 and P2 can coexist when no target DNA exists, and the target DNA can trigger two independent reaction cycles when the target DNA, the probe P2 and the exonuclease ExoIII exist; and finally when heme exists, generating a strong signal under the interaction of a G-tetraplex sequence of the probe P1 on the surface of the electrode and heme, and detecting the target DNA by adopting a differential pulse voltammetry, wherein a peak current signal and the target DNA concentration are correlated in a certain concentration range, so that detection on the target DNA concentration is realized. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and strong specificity.
Owner:北京聚合美生物科技有限公司
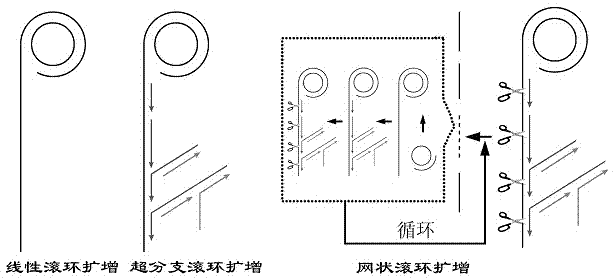
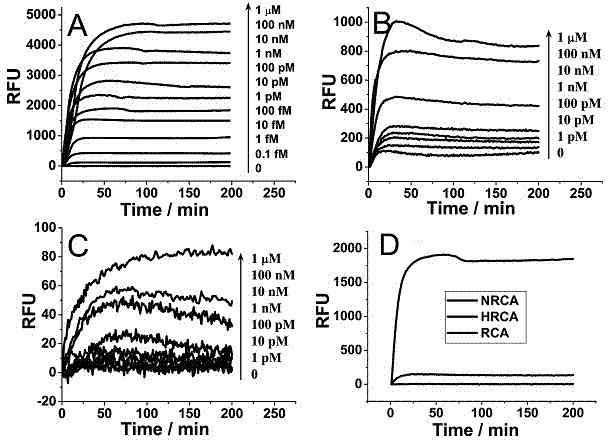
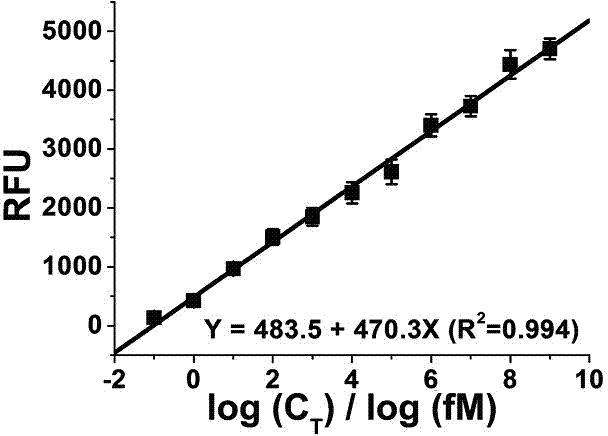
Nicking endonuclease-based netted rolling cycle amplification system and use thereof
InactiveCN104212792AIncrease fluorescence signal intensityImprove efficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationFluorescenceEndonuclease
The invention relates to a nicking endonuclease-based netted rolling cycle amplification system and a use thereof. Based on the existing second-generation hyperbranched rolling cycle amplification technology, the amplification system utilizes a special endonuclease which is nicking endonuclease Nb.BsrDI so that a third-generation rolling cycle amplification technology which is a netted rolling cycle amplification (NGCA) technology is produced. Intensity of fluorescence signals produced by the netted rolling cycle amplification is increased with increasing of a target DNA concentration, is obviously stronger than that of fluorescence signals produced by linear rolling cycle amplification and hyperbranched rolling cycle amplification and has a detection limit of 0.1fM. Compared with the first-generation linear rolling cycle amplification and the second-generation hyperbranched rolling cycle amplification, the nicking endonuclease-based netted rolling cycle amplification system retains the prior art advantages in operationality, use cost and amplification time, further realizes signal amplification based on the prior art thereby providing good technical conditions for ultralow-abundance nucleic acid sample analysis and detection, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Molecular detection method for Fusarium circinatum
InactiveCN1880476ASensitive detectionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementElectrophoresisDesign software
The invention discloses a molecular detecting method of pine grease ulcer germ, which is characterized by the following: utilizing primer designing software Prime 5.1 to design a couple of general prime G1 / G2 and astopic prime S1 / S2 on the fusarium IGS segment; adopting pine germ sample DNA extract as form; proceeding the first-turn PCR augmenting reaction of general prime; diluting the PCR augmented product by 100 times; fetching 1 mul as form to proceed the second-turn astopic prime PCR augmenting reaction; proceeding electrophoretic detection for augmented product; affirming the detected germ as pine grease ulcer germ if the DNA astopic band with 873bp exists. The invention needs only one working day to finish detect, whose density of reaches minimum quantity germ DNA is 5*10-3pg / mul and conidiospore is 10units / 100 mul.
Owner:中华人民共和国昆山出入境检验检疫局
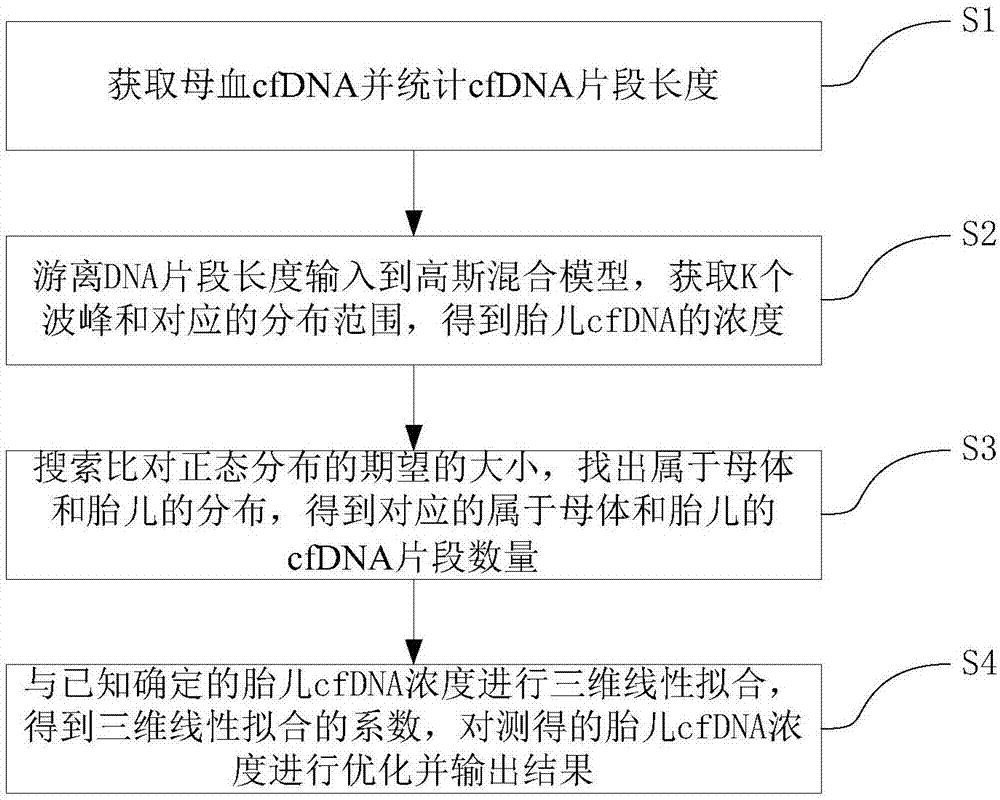
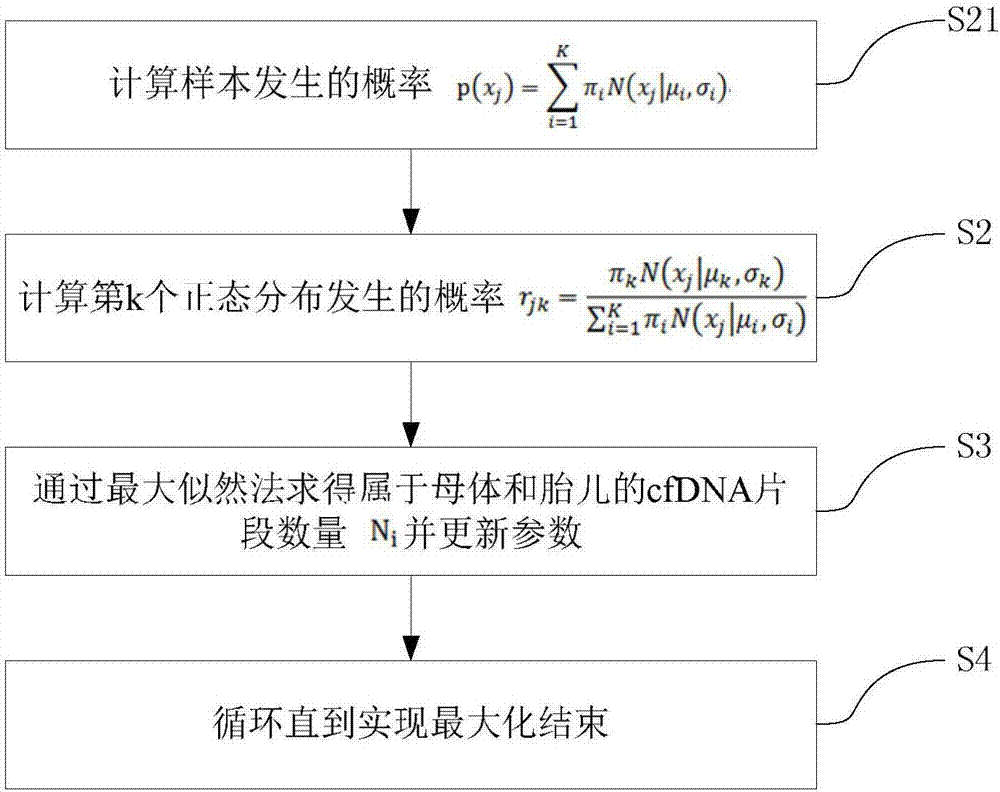
Method for acquiring concentration of fetal cell-free DNA
ActiveCN107133491AAppropriate concentration and reliableUniversalBioinformaticsSpecial data processing applicationsFemale fetusFetal cell
The invention discloses a method for acquiring the concentration of fetal cell-free DNA. For the length data of cfDNA fragments in maternal peripheral blood, a Gaussian mixture model with K normal distributions is adopted to quantize maternal and fetal cfDNA, five wave crests and corresponding distribution ranges are automatically and accurately acquired, and then the concentration of fetal cfDNA is obtained. The method provides more suitable and more reliable concentration of fetal cfDNA for non-invasive prenatal testing (NIPT) and has universality and accuracy. The method is effective to both male fetuses and female fetuses as the distribution areas of lengths of maternal and fetal cfDNA fragments are dynamically determined; besides, the distribution of maternal and fetal cfDNA can be automatically acquired and recognized for samples of different fetuses of different gestational ages, and thus the accuracy of the concentration of fetal cfDNA is guaranteed.
Owner:GUANGZHOU DARUI BIOTECH
Simple sequence repeat (SSR) marker polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction method applied to chrysanthemum and related species thereof universally
ActiveCN102876790AHigh sensitivityGood repeatabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementWild speciesCrossostephium
The invention discloses a simple sequence repeat (SSR) marker polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction method universally applied to chrysanthemum and related species thereof. In a PCR reaction system, the primer concentration is 0.32 MuM / Mul; the Taq enzyme concentration is 0.2 U / Mul; the dNTP concentration is 0.4 MuM / Mul; the Mg<2+> concentration is 0.65 MuM / Mul; and the DNA concentration is 2 to 4 ng / Mul. Stripes obtained by the method for performing SSR molecular marker PCR reaction are clear and have high polymorphism and high repeatability. The method is simple in operation and commonly used in wild species and varieties of chrysanthemum, Ajania, Opisthopappus Shih and Crossostephium Less, and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:BEIJING FORESTRY UNIVERSITY
Feces preservation solution, preparation method thereof and feces preservation method
PendingCN110004212AIncrease concentrationImprove integrityMicrobiological testing/measurementAnimal fecesGlycerol
The invention provides a feces preservation solution, a preparation method thereof and a feces preservation method. The feces preservation solution contains 0.10-0.20 M of Tris base, 0.25-0.75 M of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), 10 mM-room temperature saturated sodium chloride (NaCl), 5-15% of dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO), 2.5-10% of ethanol and 5-20% of glycerol, wherein the pH of the fecespreservation solution is 7.0-9.0. The feces preservation solution can stably preserve microbial diversity in feces samples at normal temperature and improve DNA concentration, can ensure the accuracyof sequencing analysis of intestinal flora, realizes normal-temperature preservation and transportation of the feces samples, has a good preservation effect compared with an existing preservation solution, does not contain toxic components such as guanidine thiocyanate, and is safer to operate.
Owner:康美华大基因技术有限公司
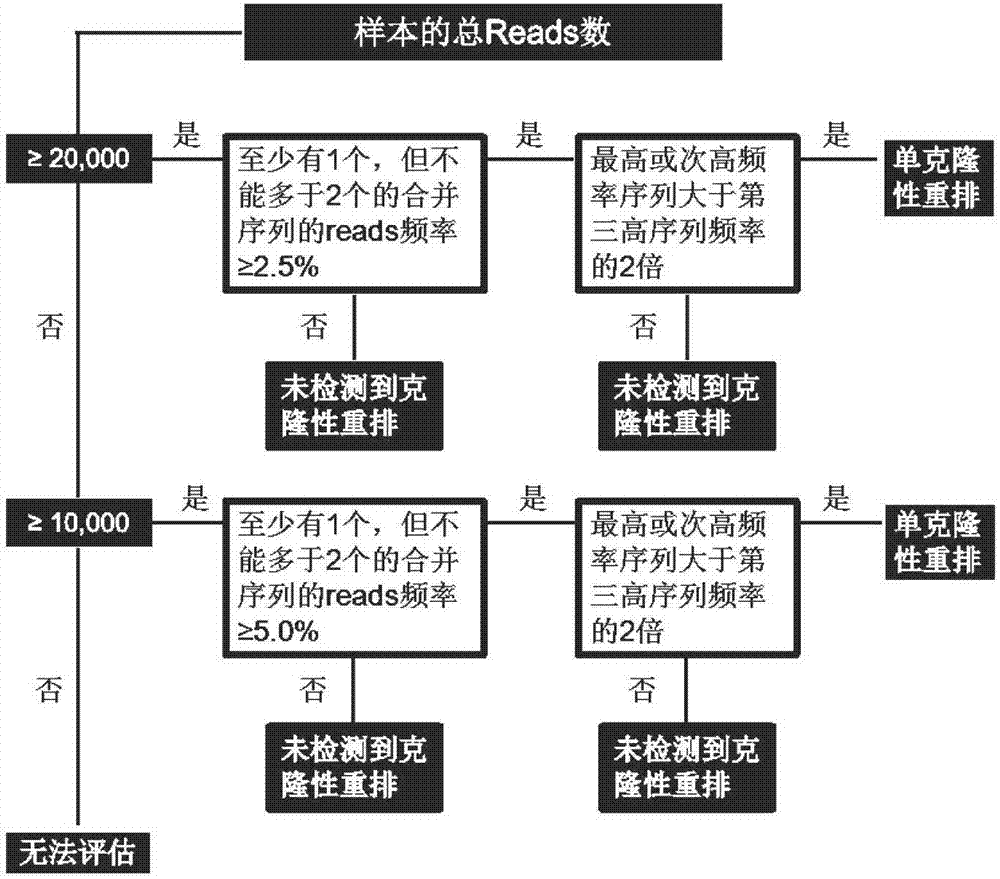
Method for detecting rearrangement clonality of correlative genes of lymphocyte
ActiveCN108004304AHigh detection throughputHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyDNA fragmentation
The invention discloses a method for detecting rearrangement clonality of correlative genes of lymphocyte and belongs to the technical field of biology. According to the method, a high-throughput next-generation sequencing method is adopted for detecting rearrangement clonality of the correlative genes of lymphocyte tissue, and specifically, a multifunctional primer and a PCR reagent are utilizedto conduct multiplication on samples to be detected at first to obtain a multi-sample gene locus multiplication sublibrary, wherein both ends of the multiplication sublibrary are connected with DNA segments of different connectors, one side of the multiplication sublibrary is a sequencing connector which can contain a sample tag for distinguishing sequencing results of the different samples, and the other side of the multiplication sublibrary is a fixed connector used for connecting caught particles; then, high-throughput sequencing is conducted on the multiplication sublibrary, sequencing results are subjected to classified sorting according to a tag sequence, the samples and target genetic loci, and whether or not there is clonality rearrangement of target genes is analyzed. The method has the advantages that the detection throughput, the sensitivity and the specificity are high, the sensitivity can reach 0.01%, and the DNA concentration of the samples can be lowered to 0.1-1ng / microliter.
Owner:北京旌准医疗科技有限公司
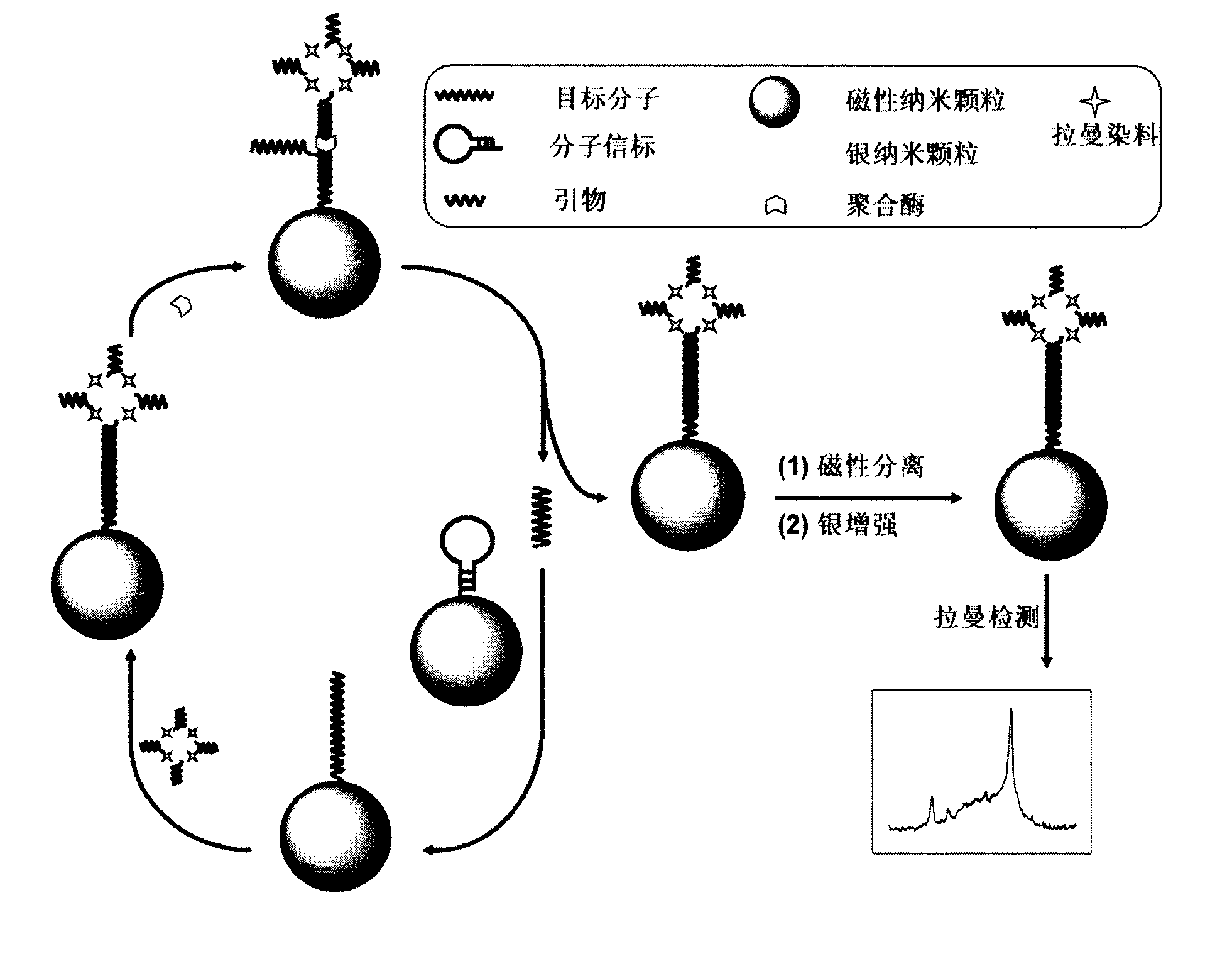
Method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) through high sensitivity Raman spectrum
The invention relates to a method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) through high sensitivity Raman spectrum. According to the method, chains on the surfaces of magnetic beads are used for substituting the potentiation of polymerization and silver so as to realize dual amplification of the signal. The magnetic beads are used for fixing molecular beacons and separating chain substituted products. After hybridization of the target DNA and the molecular beacons, beacon rings are opened, raman dye-silver nano-composite modified by a primer is connected with the magnetic beads through hybridization of the primer and the stem end of the beacon so as to induce the DNA chain to carry out polymerization reaction to release target molecules, and the released DNA molecules and the molecular beacon of the other magnetic bead are hybridized so as to generate the other polymerization circulation. After the circulation chain substitutes polymerization, a separation chain substitutes the product, a silver nanoparticle shell is deposited on the surface of the nano-composite, so as to enhance the raman signal of the dye. The correlation between the raman signal and the concentration and sequence of the target DNA are used for DNA analysis. The concentration range of DNA detected by the method is 10-13-10-8mol L-1, and the method can be used for distinguishing completely matched target DNA and single-base mismatch DNA, and has certain application value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Periplaneta Americana L. specific COI primer, kit containing same and application of Periplaneta Americana L. specific COI primer
ActiveCN107177680AImprove accuracyShorten the timeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationConserved sequenceGenetics
The invention belongs to the field of biotechnology and particularly provides a Periplaneta Americana L. specific COI primer, a kit containing the same and application of the Periplaneta Americana L. specific COI primer. According to a conserved sequence of Periplaneta Americana L. mtDNA, the invention designs a pair of the Periplaneta Americana L. specific COI primers JmF1 and JmR1 (such as SEQ ID No. 1 and SEQ ID No. 2), and detected that, the primer has the specific amplification ability to Periplaneta Americana L. only, the size of an amplified product is 452bp, and a sensitivity DNA concentration detection limit is 0.390625ng / uL. According to the Periplaneta Americana L. specific COI primer, the kit and the application, by utilizing a PCR detection technology, a specific single band is obtained through specific primer amplification, operation is simple, and the Periplaneta Americana L. specific COI primer has the characteristics of high efficiency, low cost and strong specificity and improves the accuracy of detection.
Owner:SICHUAN GOODDOCTOR PANXI PHARMA
Device for detecting aneuploidy of fetus chromosomes based on single-sample peripheral blood
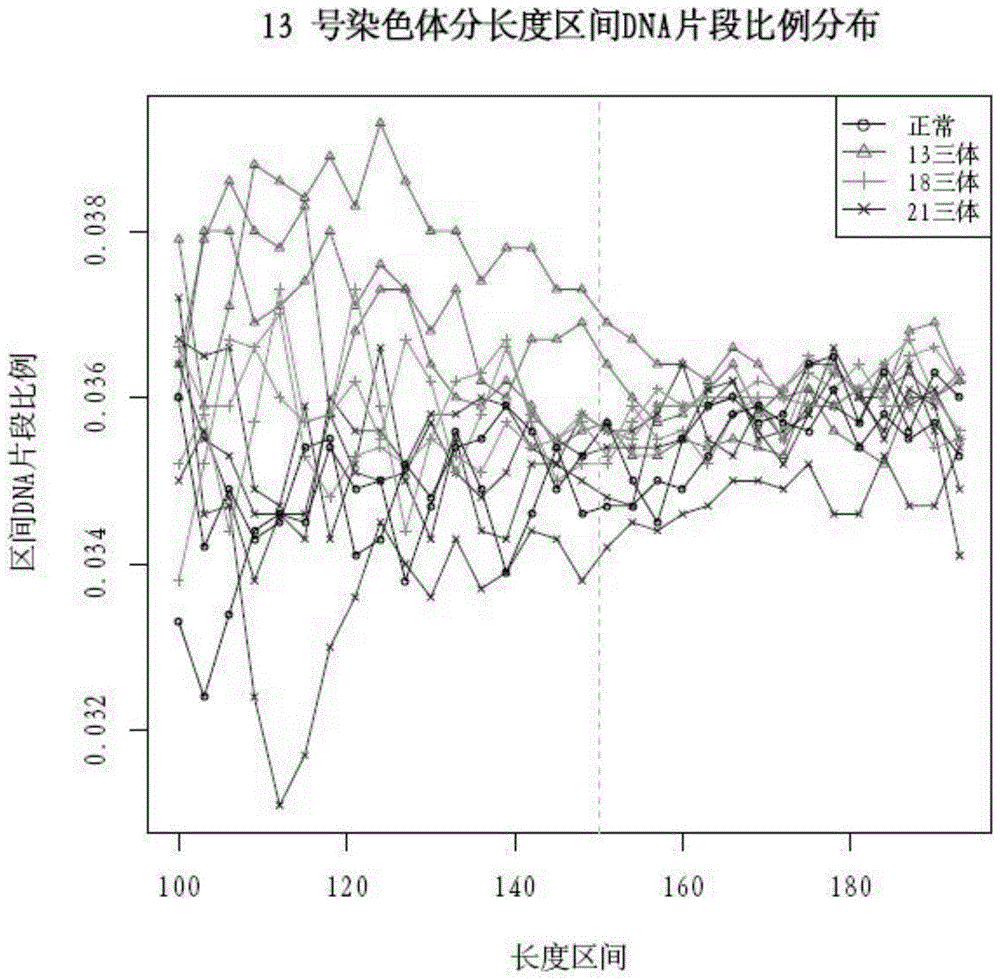
ActiveCN104951671AReduce dependenceEffective control of birth rateSpecial data processing applicationsConsequence analysisSingle sample
The invention discloses a device for detecting the aneuploidy of fetus chromosomes based on single-sample peripheral blood. The device comprises a sequencing data processing unit and a result analysis unit. Whether the chromosomes to be detected are aneuploid chromosomes or not are judged by comparing the quantity of short sequences of 101-150 bp with the quantity of long sequences of 151-200 bp on the same chromosome. According to the device, self control of samples is conducted, and accuracy is high; the dependency of fetus free DNA concentration is small, and the false-negative problem of the aneuploidy of the chromosomes under the condition of low fetus free DNA concentration is solved to a great extent; moreover, the requirement for the sequencing data size is low compared with an original method, and thus cost can be further lowered.
Owner:CAPITALBIO GENOMICS
Blood stabilizer and application thereof
ActiveCN104634628APrevent solidificationAvoid degradationPreparing sample for investigationMedicineIn vitro degradation
The invention relates to a blood stabilizer and application thereof. The blood stabilizer is used for stabilizing a blood sample. The blood stabilizer disclosed by the invention comprises the following components according to concentrations: 10-300micromol / L of beta-cyclodextrin, 15-350micromol / L of disodium cromoglycate, 0.01%-0.5% of potassium dichromate, 5-150micromol / L of triflusal, 0.05%-1.5% of lecithin and 2.5-5.0mumol / L of EDTA tripotassium salt, wherein the concentration of potassium dichromate and lecithin is mass percent concentration. The blood stabilizer is capable of stabilizing hemocyte, preventing karyocyte from cracking to avoid releasing DNA in cells, and avoiding increasing the concentration of DNA outside the hemocyte; and meanwhile, the blood stabilizer disclosed by the invention is capable of preventing in vitro degradation of the DNA and preventing blood coagulation.
Owner:GUANGDONG ASCENDAS GENOMICS TECH CO LTD
Body fluid suspension cell DNA extracting kit and extracting method
The invention belongs to the field of biology, and discloses a body fluid suspension cell DNA extracting kit. The extracting kit consists of a resuspension solution, a protease K solution, an RNA enzyme A solution, lysate, a precipitant, a washing solution A, a washing solution B and a DNA dissolved solution. A method for extracting body fluid suspension cell DNA by virtue of the kit comprises the following steps: conducting centrifuging, precipitating and re-suspending, adding the lysate, promoting lysis of the protease K solution, adding the precipitant and conducting centrifuging, adding the washing solution A, conducting centrifuging and washing with the washing solution B, and conducting drying at room temperature and adding the DNA dissolved solution. Different from an existing DNA extracting method or DNA extracting kit which is expensive, simple in object of using and relatively poor in integrity of extracted DNA and which are not applicable to extraction of the body fluid suspension cell DNA, the method and the kit provided by the invention are cheap, relatively high in concentration of the extracted DNA and good in integrity of the extracted DNA and are applicable to extraction of various body fluid suspension cell DNA.
Owner:GWP BIOTECHNOLOGIES INC
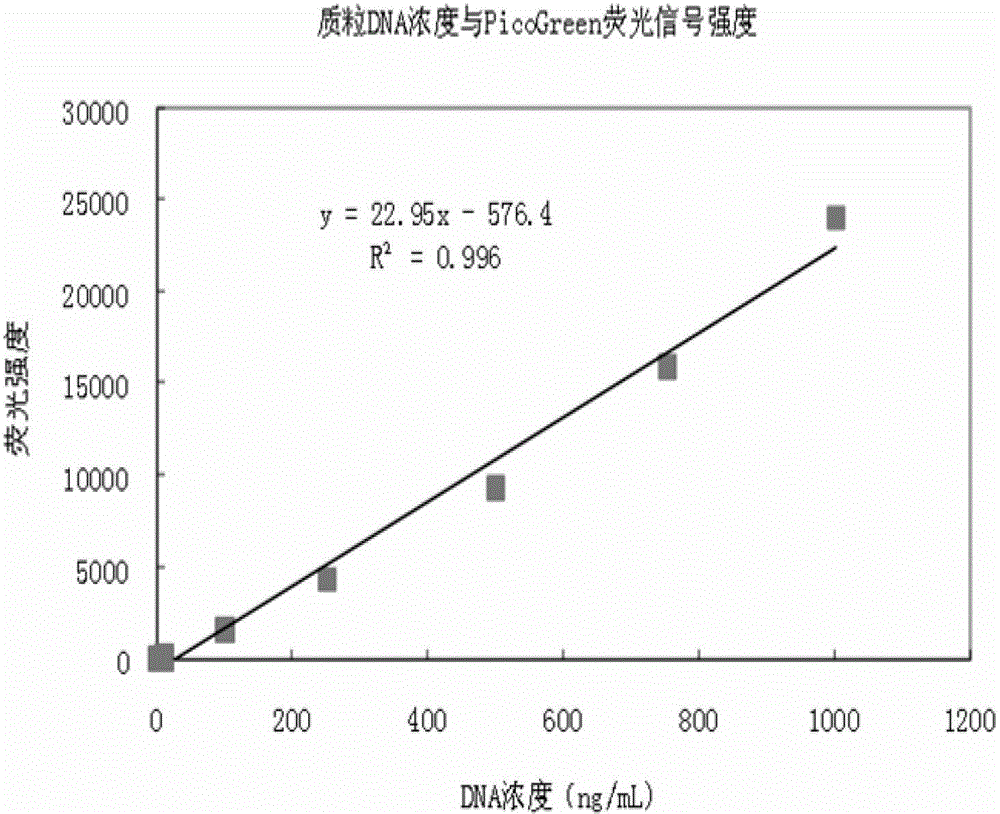
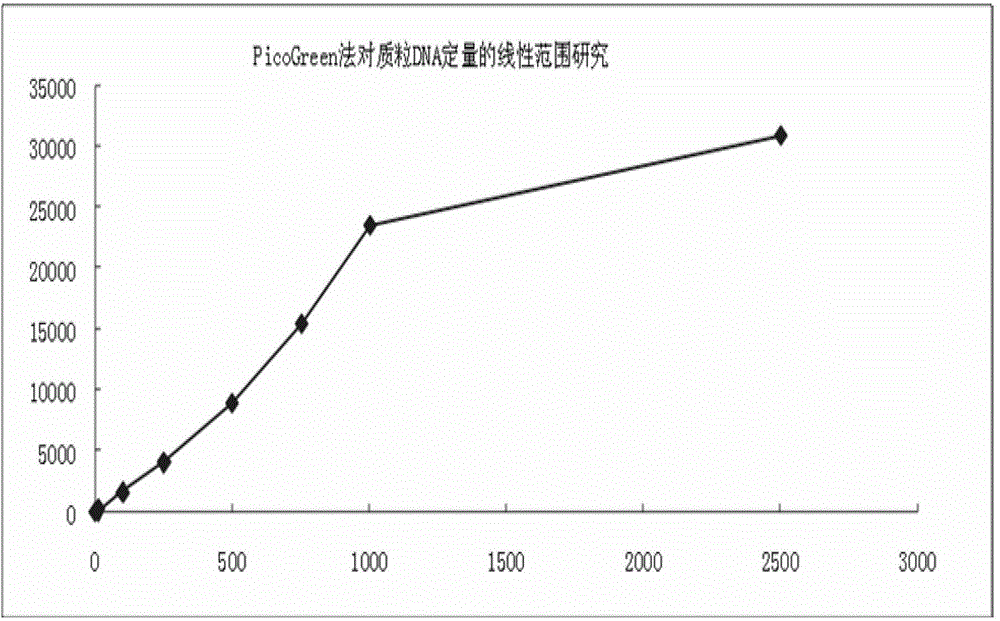
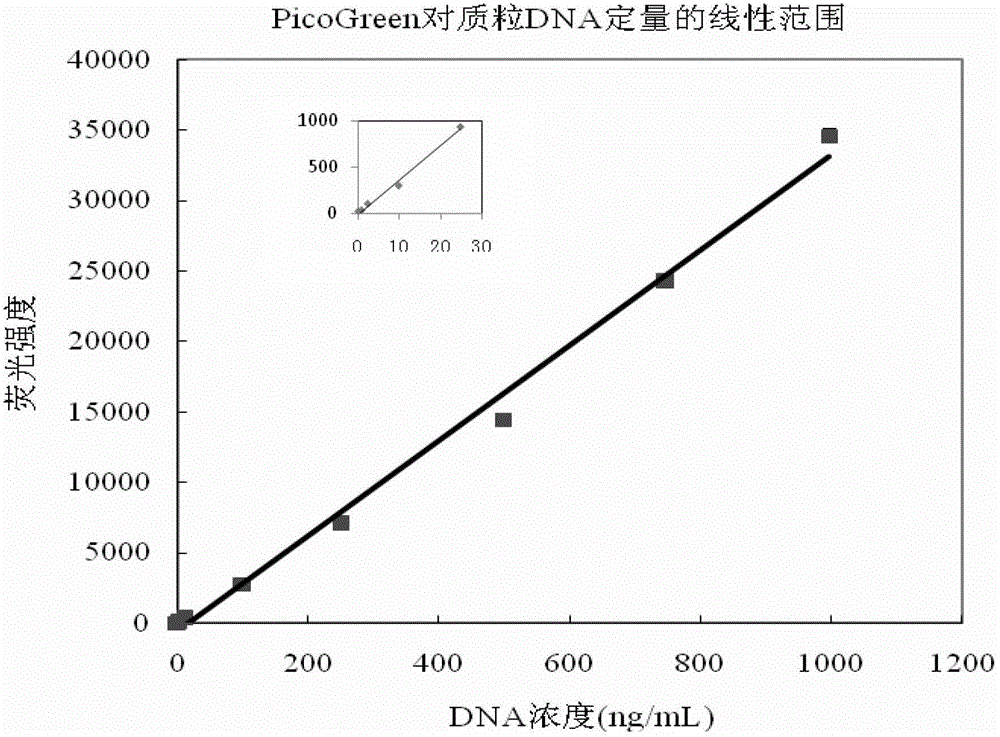
Quantitative plasmid DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) detection kit
InactiveCN102980878AMake up for the shortcomings of not being able to quantify quality DNAHigh sensitivityFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescencePlasmid dna
The invention provides a quantitative plasmid DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) detection kit which has the characteristics of adopting a plasmid DNA standard substance to accurately quantify by using an ultrasonic-isotope dilution mass-spectrography with high accuracy, and making up the defect that a conventional kit cannot quantify the plasmid DNA. The invention further provides a plasmid DNA quantitative detection method which comprises the following steps of: respectively measuring fluorescence signal strengths of the plasmid DNA standard substances of different concentrations; drawing a concentration-fluorescence signal strength standard curve; subsequently measuring the fluorescence signal strength of a plasmid DNA sample to be measured; and accurately calculating the DNA concentration of the sample to be measured according to the drawn standard curve. According to the method and the kit, standard plasmids are adopted to be used as the DNA standard to quantify in a fluorescent dye method for the first time with high sensitivity, and DNA as low as 1pg can be detected; the linear range is wide, and plasmid DNA of 0.25-1000ng / Ml can be detected; and the standard plasmids are quantified by using the ultrasonic-isotope dilution mass-spectrography, and the quantitative value obtained is low in uncertainty and high in accuracy.
Owner:NAT INST OF METROLOGY CHINA
Apple stem groove virus visual detection system based on CRISPR-Cas12a technology and detection method thereof
ActiveCN110567951ARealize visual detectionPrevent cross-linking reactionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence designConserved sequence
The invention belongs to the field of molecular biology and relates to an apple stem groove virus visual detection system based on the CRISPR-Cas12a technology and a detection method thereof. CrRNA isdesigned according to an ASGV conserved sequence, AuNP-DNA for colorimetric detection is manufactured, the influence of a Cas12a protein in-vitro cleavage reaction time and linker DNA concentration on a detection effect is explored, and the optimal ASGV visual detection system and the detection method thereof are established. The method is carried out under a constant-temperature reaction condition, a virus is recognized through a CRISPR-Cas12a-crRNA complex to improve the specificity, the linker DNA has universality, expensive double-labeled probes are not needed, a plurality of samples canbe detected within 40 minutes by means of low-speed centrifugation, the lower detection limit is 5.62*102 copies / reaction, and the sensitivity is 100 times higher than that of RT-PCR.
Owner:HENAN AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com