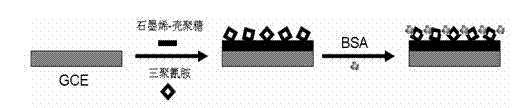
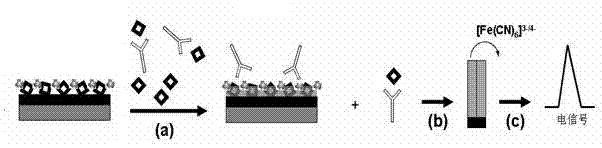
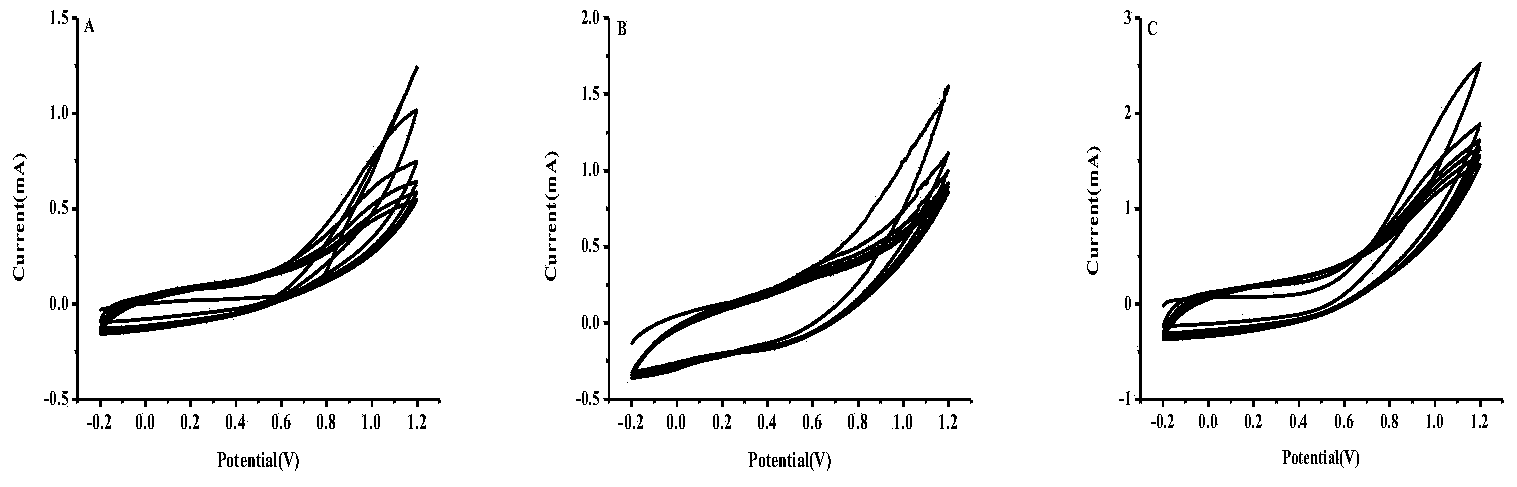
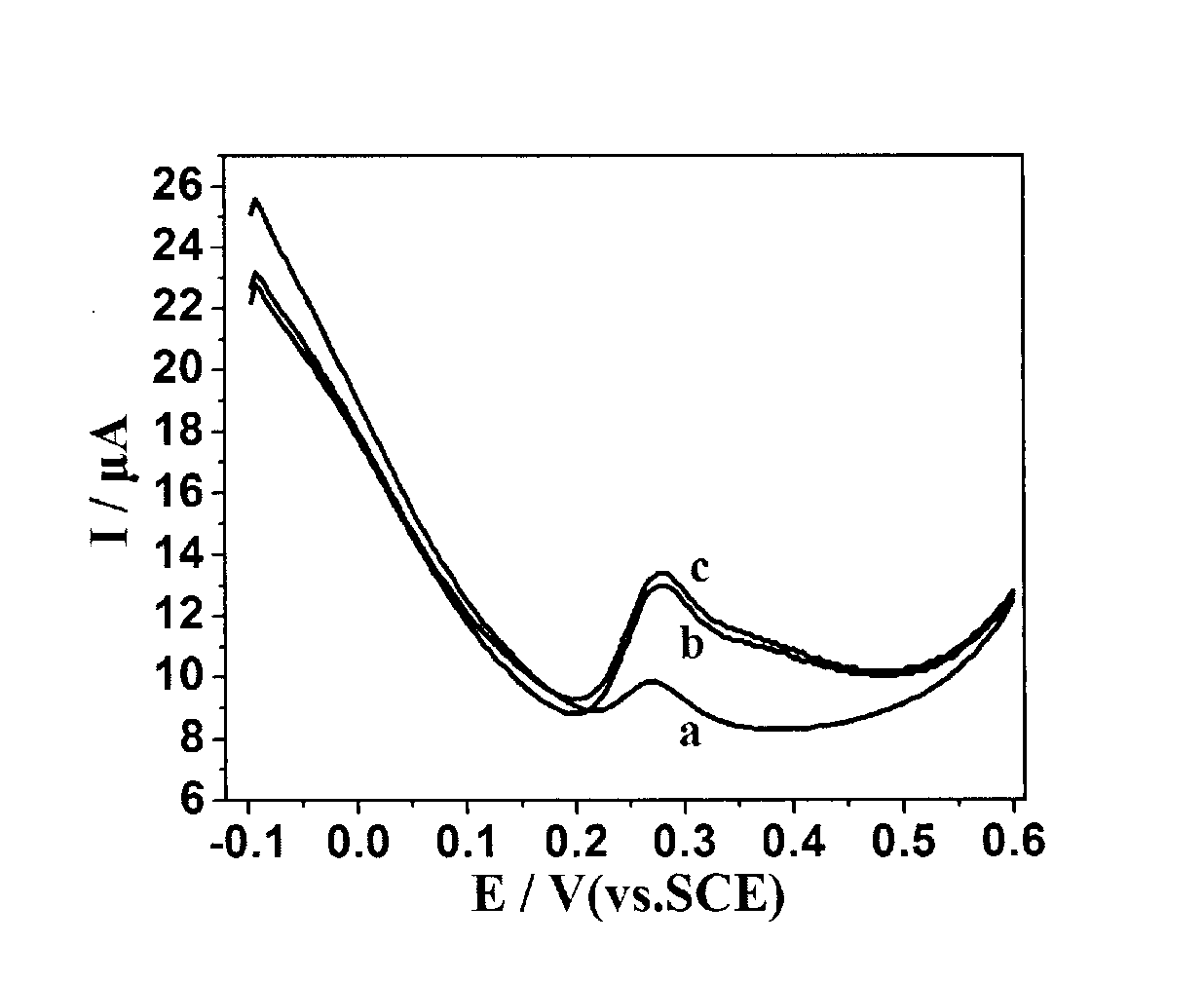
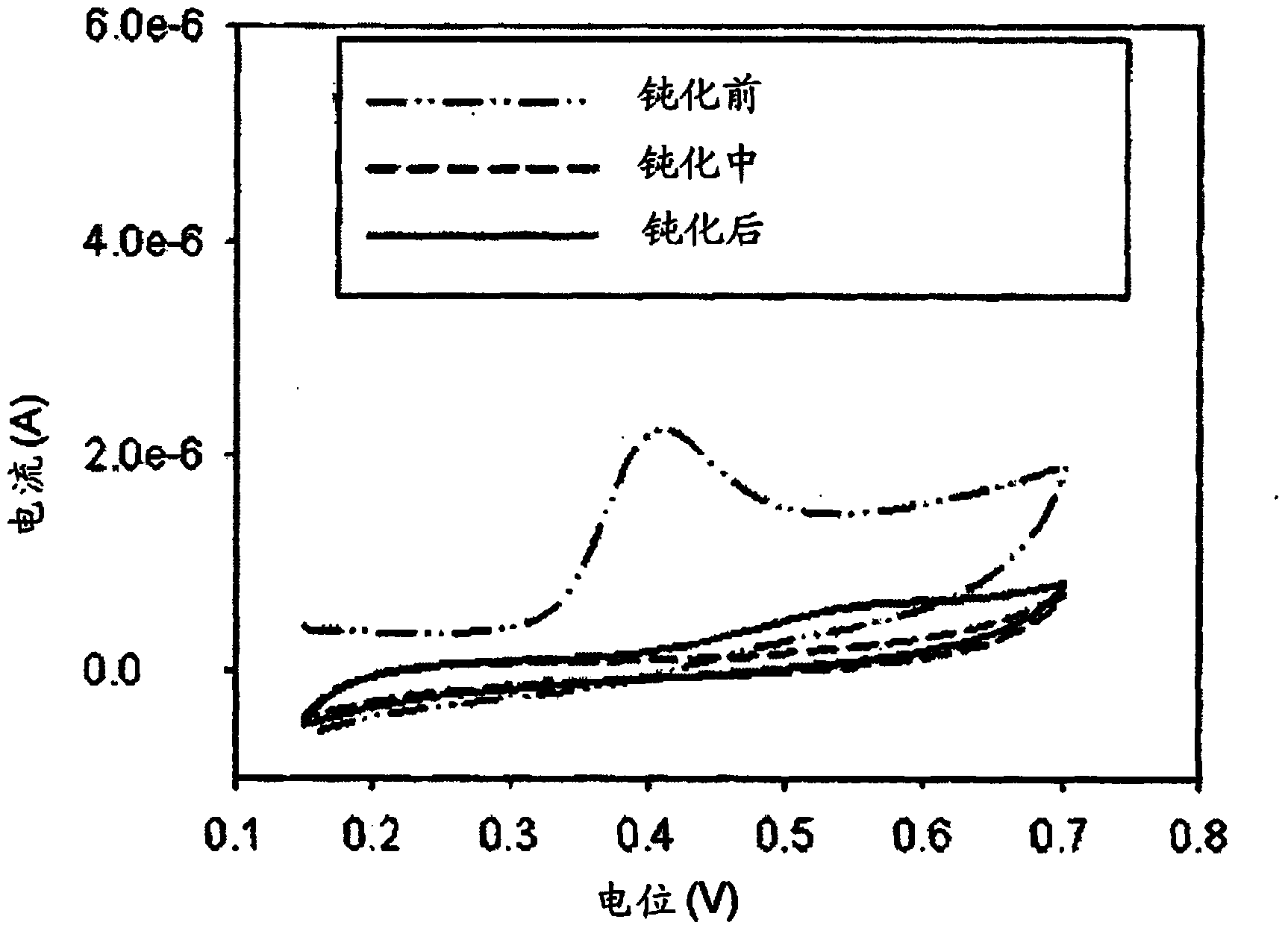
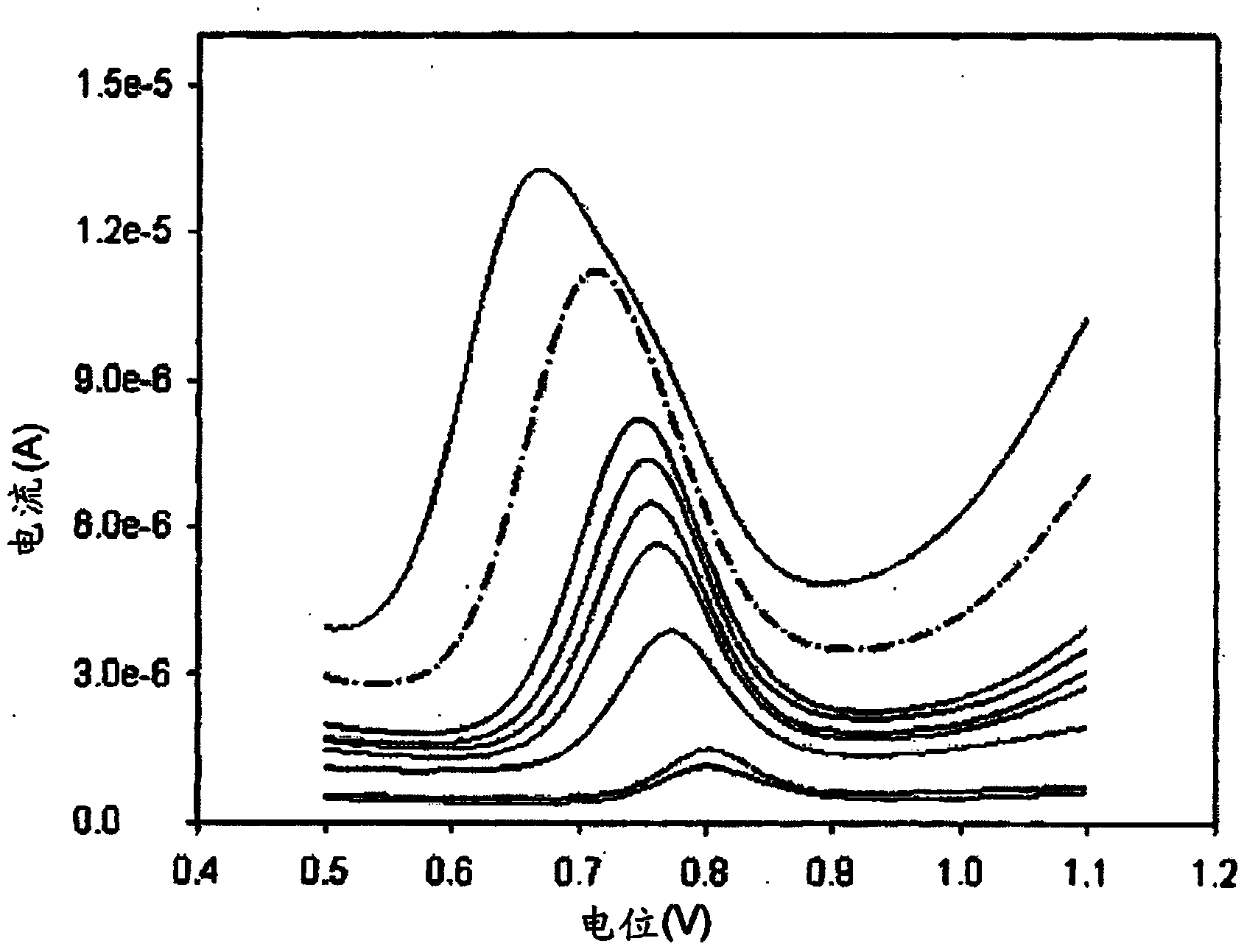
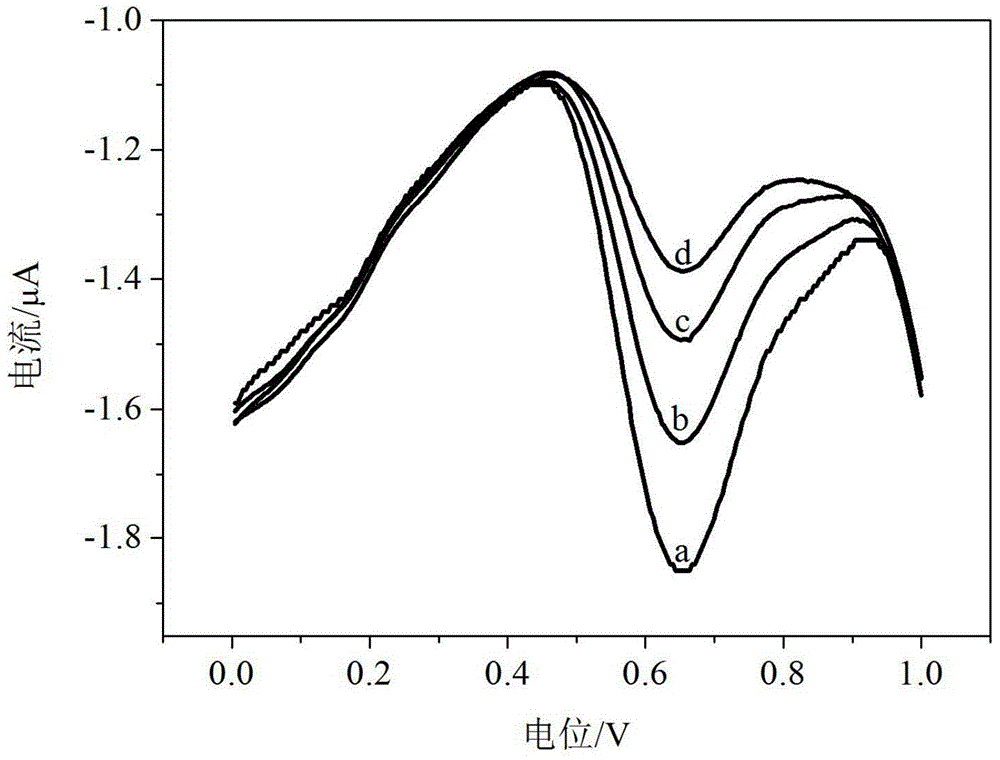
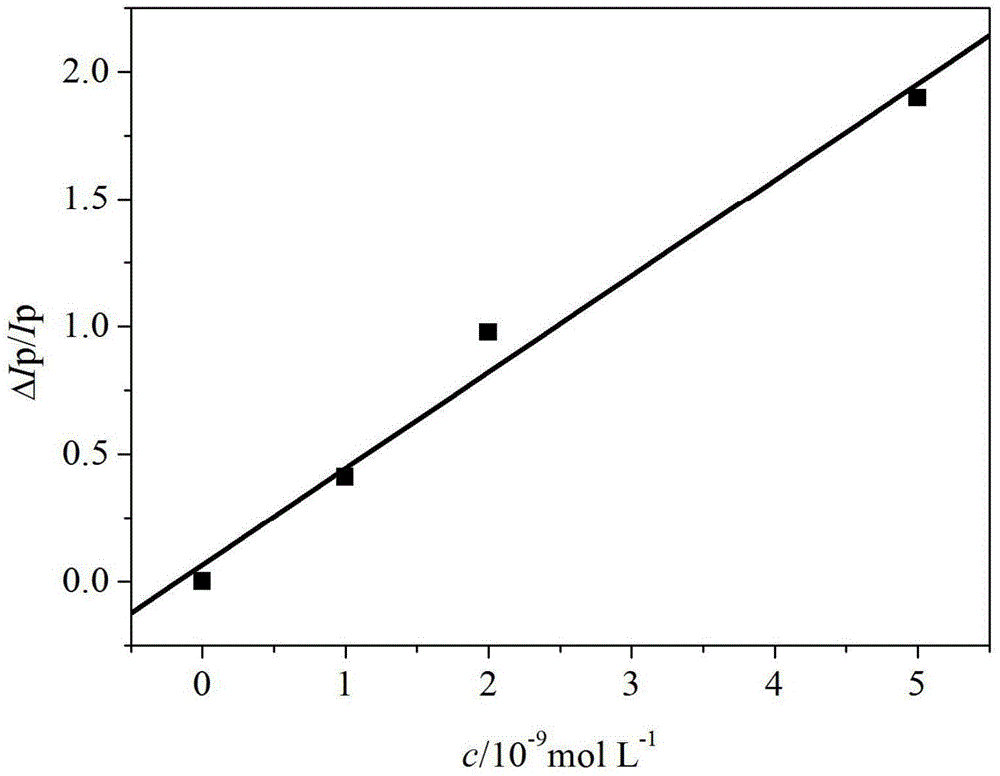
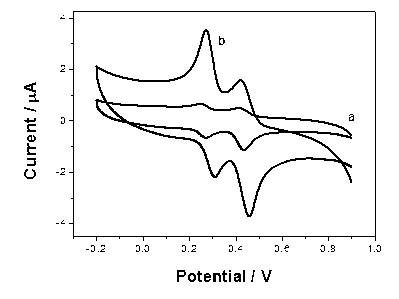
Patents
Literature
327 results about "Differential pulse voltammetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
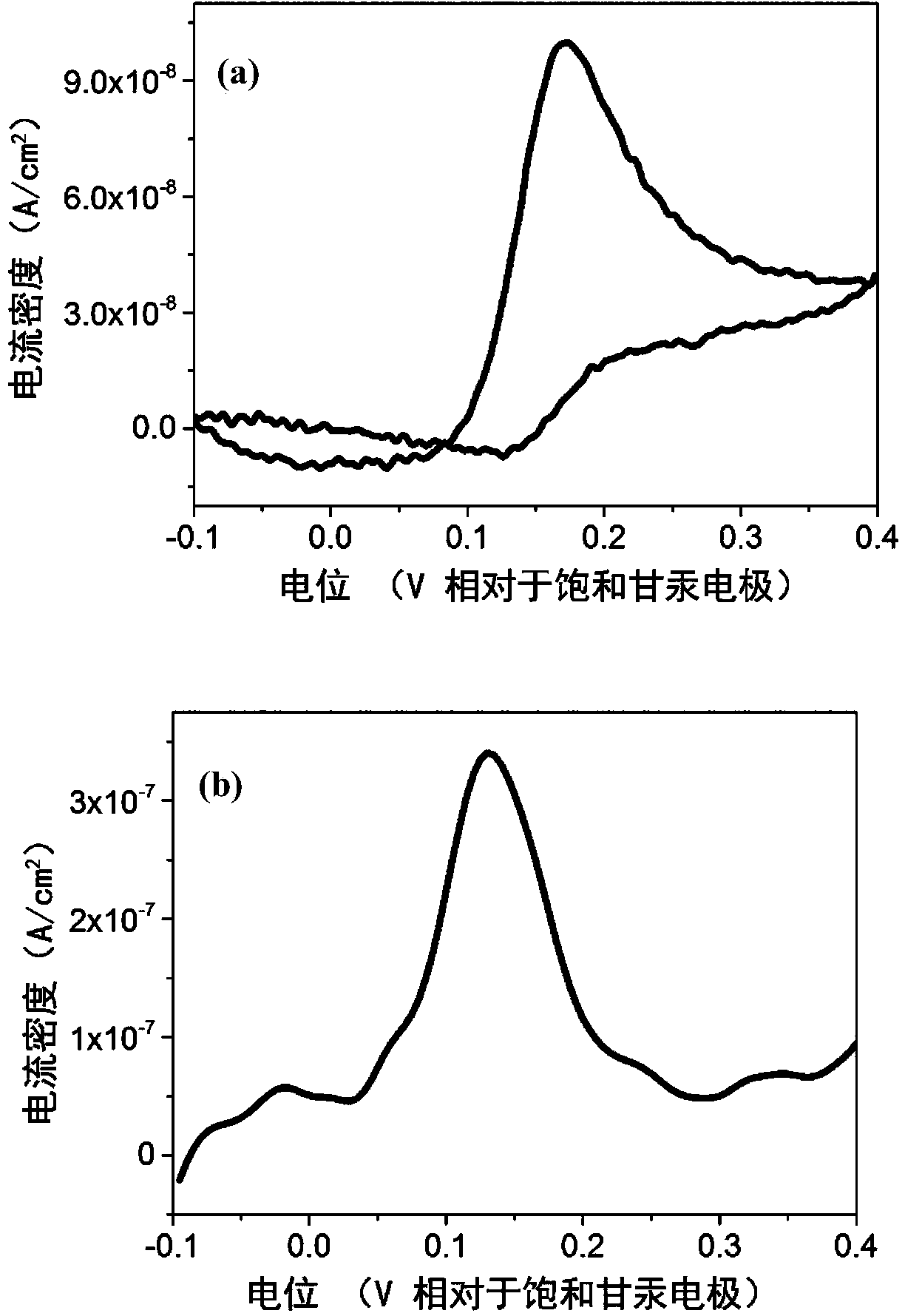
Differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) (also differential pulse polarography, DPP) is a voltammetry method used to make electrochemical measurements and a derivative of linear sweep voltammetry or staircase voltammetry, with a series of regular voltage pulses superimposed on the potential linear sweep or stairsteps. The current is measured immediately before each potential change, and the current difference is plotted as a function of potential. By sampling the current just before the potential is changed, the effect of the charging current can be decreased.
Electrochemical immunosensor for detecting diethylstilbestrol, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102262125AEasy to detectHigh sensitivityBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesDiethylstilbestrolGraphene
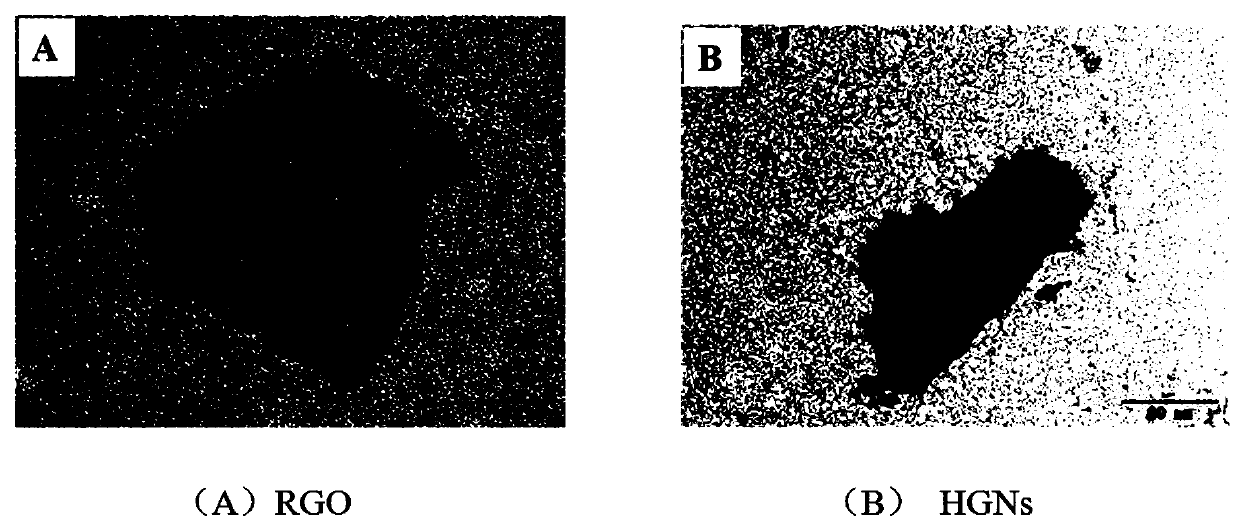
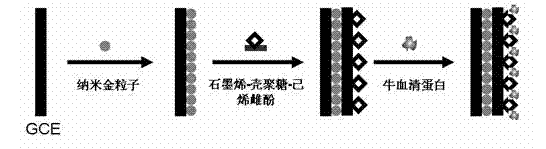
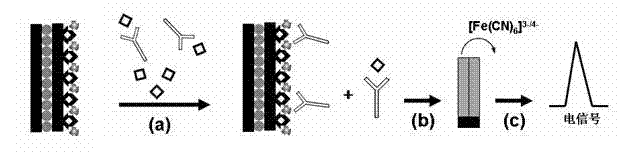
The invention relates to a non-labeled electrochemical immune sensor for detecting diethylstilbestrol and a preparation method and application of the sensor. The immune sensor comprises a substrate electrode; and after nanometer gold is deposited on the surface of the substrate electrode, a graphene-diethylstilbestrol-chitosan complex is modified, and non-specific active loci are sealed by bovineserum albumin. The preparation method comprises the following step of: after depositing the nanometer gold on the surface of the substrate electrode, enveloping graphene and the diethylstilbestrol byusing chitosan and fixing to the surface of the electrode. In the immune sensor, on the basis of a competitive mode of immune reaction, the immune reaction is monitored by taking K3Fe(CN)6 as a probeand by differential pulse voltammetry, so the immune sensor can be used for detecting the diethylstilbestrol. The non-labeled electrochemical immune sensor has the characteristics of high sensitivityand specificity, quick on-site detection, low cost and the like; and a detection method is simple and wide in application range, the detection limit can reach 0.1 ng / ml, and the linear range is between 0.5 and 1,500 ng / ml.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
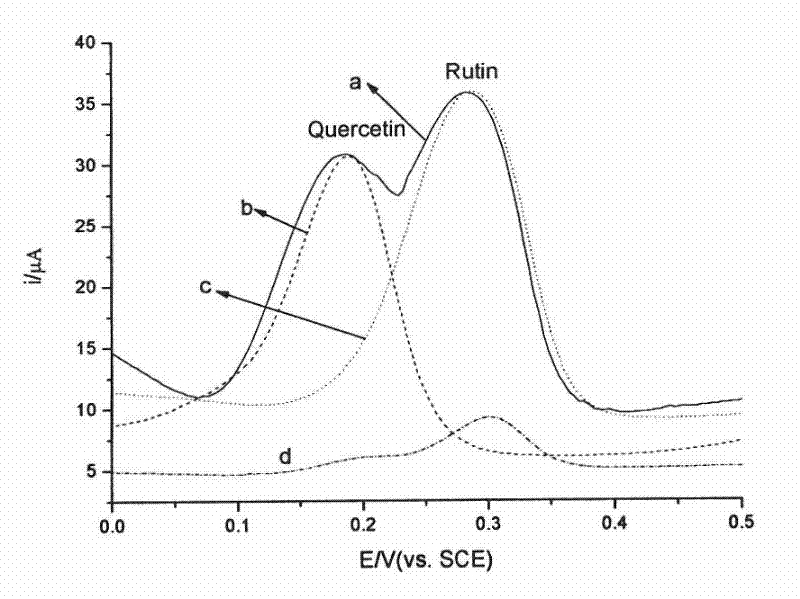
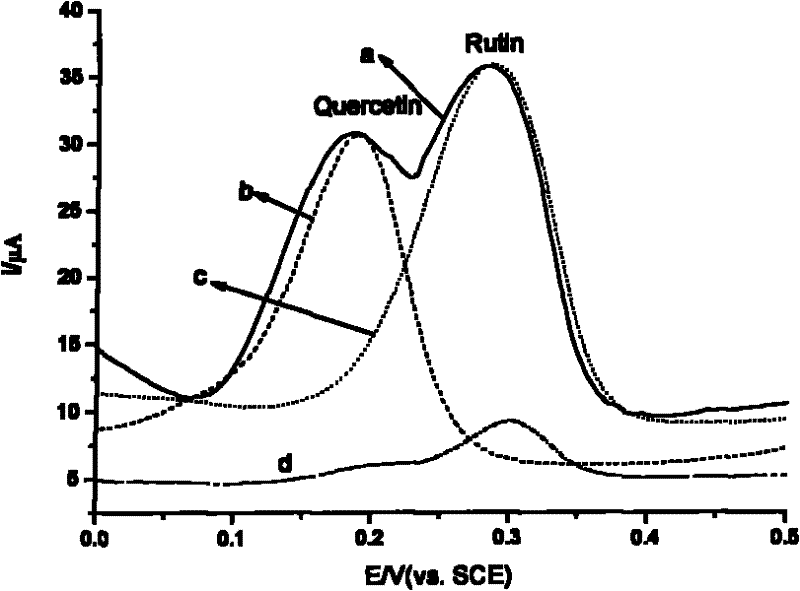
An electrochemical method for the simultaneous determination of rutin and quercetin based on a graphene-modified electrode
ActiveCN102288669AHigh catalytic activityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesBudDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention discloses an electrochemical method based on a graphene-modified electrode for simultaneous determination of rutin and quercetin. The graphene-modified electrode is used as a working electrode, and cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry are adopted for simultaneous determination of the rutin and the quercetin. Since grapheme is used as a modifying material for the electrode, electrochemical separation of two Chinese flavonoids, the rutin and the quercetin can be achieved on the modified electrode, and the contents of the rutin and the quercetin in sophora flower bud can be determined simultaneously through direct electrochemical determination.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
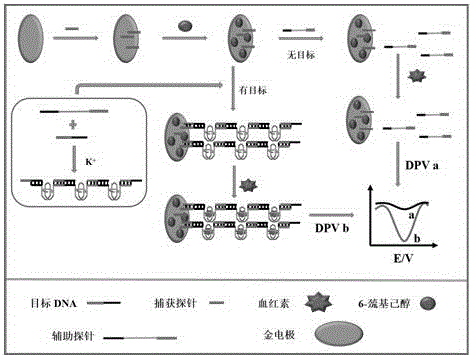
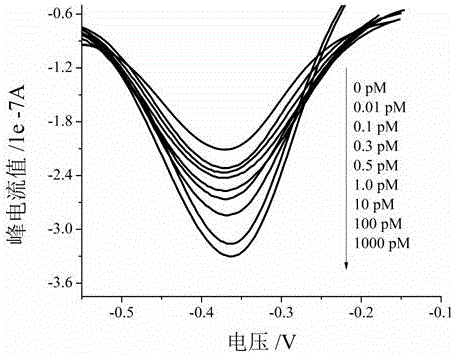
Electrochemical method of detecting single-chain target DNA concentration based on G-quadruplex-heme compound and polymeric chain type amplification reaction
ActiveCN106525940AHigh sensitivityRealize highly sensitive detectionMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectrochemistryDifferential pulse voltammetry
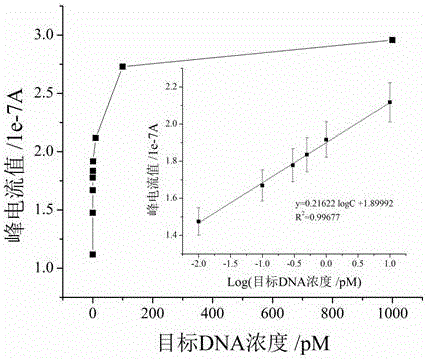
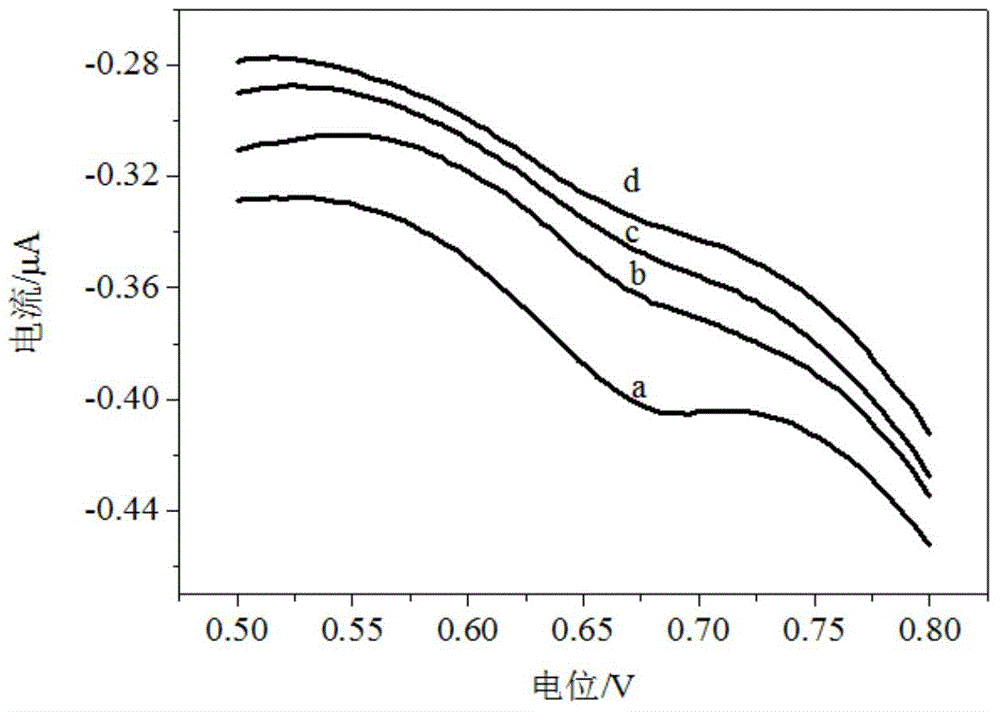
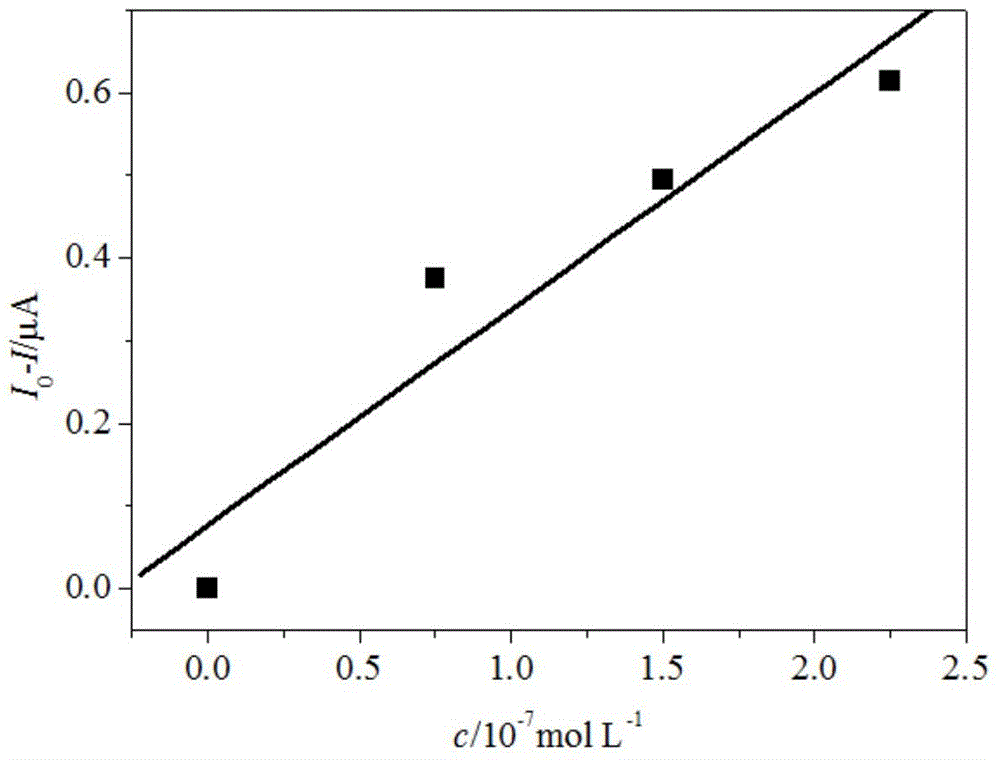
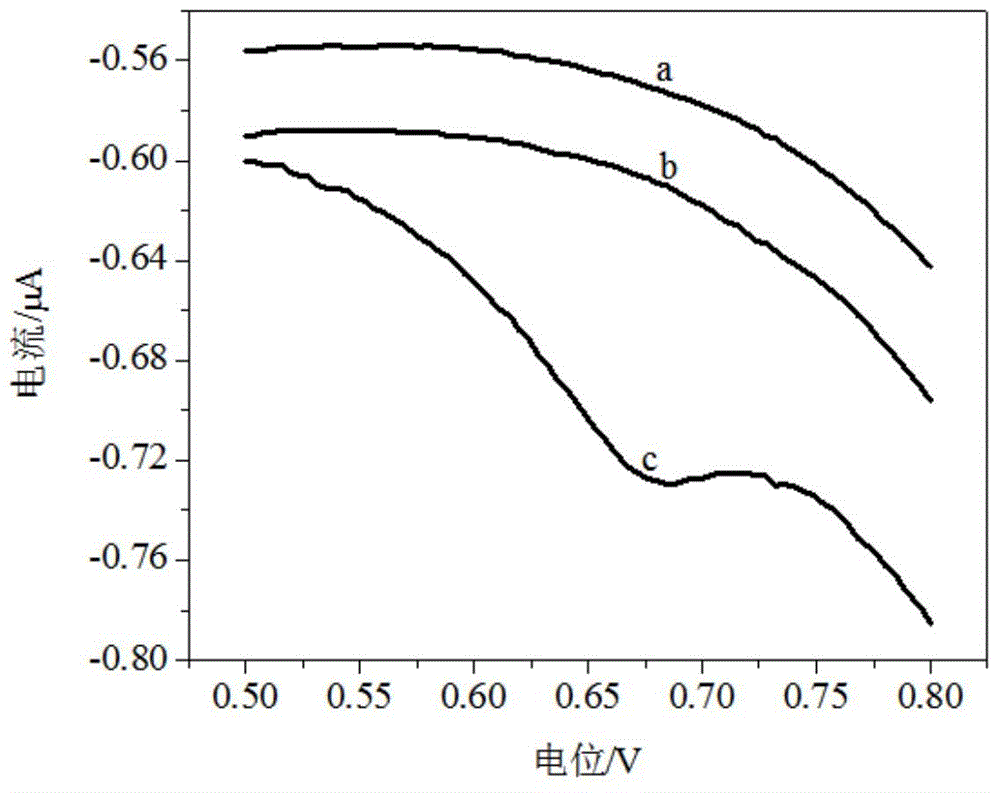
The invention relates to an electrochemical method of detecting single-chain target DNA concentration based on G-quadruplex-heme compound and polymeric chain type amplification reaction, and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. A capture probe and an auxiliary probe are designed, the two ends of the auxiliary probe each contain a nucleotide sequence complemented with the target DNA, and the middle of the auxiliary probe contains a base sequence capable of forming G-quadruplex. The capture probe and the target DNA recognize each other and are subjected to continuous polymeric chain type reaction to form chain-shaped polymer, the chain-shaped polymer is fixed to an electrode through the capture probe on the surface of the gold electrode, and a great number of G-quadruplex structures are introduced onto the surface of the electrode. Then, G-quadruplex and heme are combined to form the compound with powerful electrochemical signals, and the target DNA is detected through the corresponding relation among the electrochemical signals obtained through differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) scanning, the G-quadruplex-heme compound on the surface of the electrode and the concentration of the target DNA added into the system. HIV DNA in the sample is detected through the method, and an ideal effect is obtained. The electrochemical method has the advantages of being high in sensitivity and specificity.
Owner:ANHUI HUATENG AGRI TECH CO LTD
Method for detecting concentration of acrylamide in solution
ActiveCN104634853AIncrease surface areaStrong electrochemical signalMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetryGraphene
The invention provides a method for detecting the concentration of acrylamide in a solution. The method comprises the steps of detecting acrylamide in a sample solution by using a three-electrode system and a differential pulse voltammetry; and obtaining the concentration of acrylamide in the sample solution according to a differential pulse voltammetry curve of acrylamide, wherein a working electrode in the three-electrode system is an aminated graphene and single-chain DNA modified electrode. The invention also provides concrete steps for detecting the concentration of acrylamide in the solution and a preparation method of the working electrode. The content of acrylamide in the solution can be rapidly and quantitatively detected, and the detection limit of acrylamide can be up to 5.1*10<-8>mol / L.
Owner:浙江永金生物科技有限公司
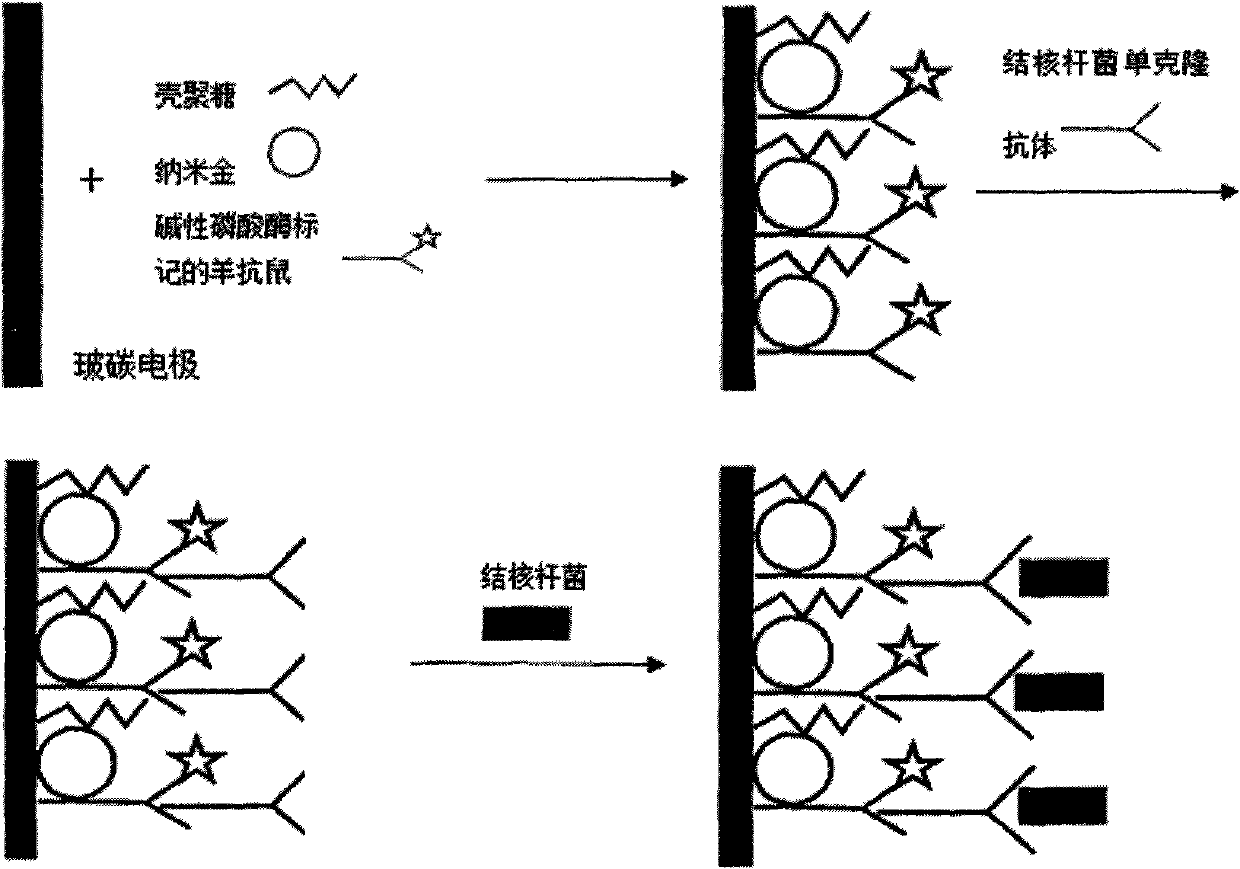
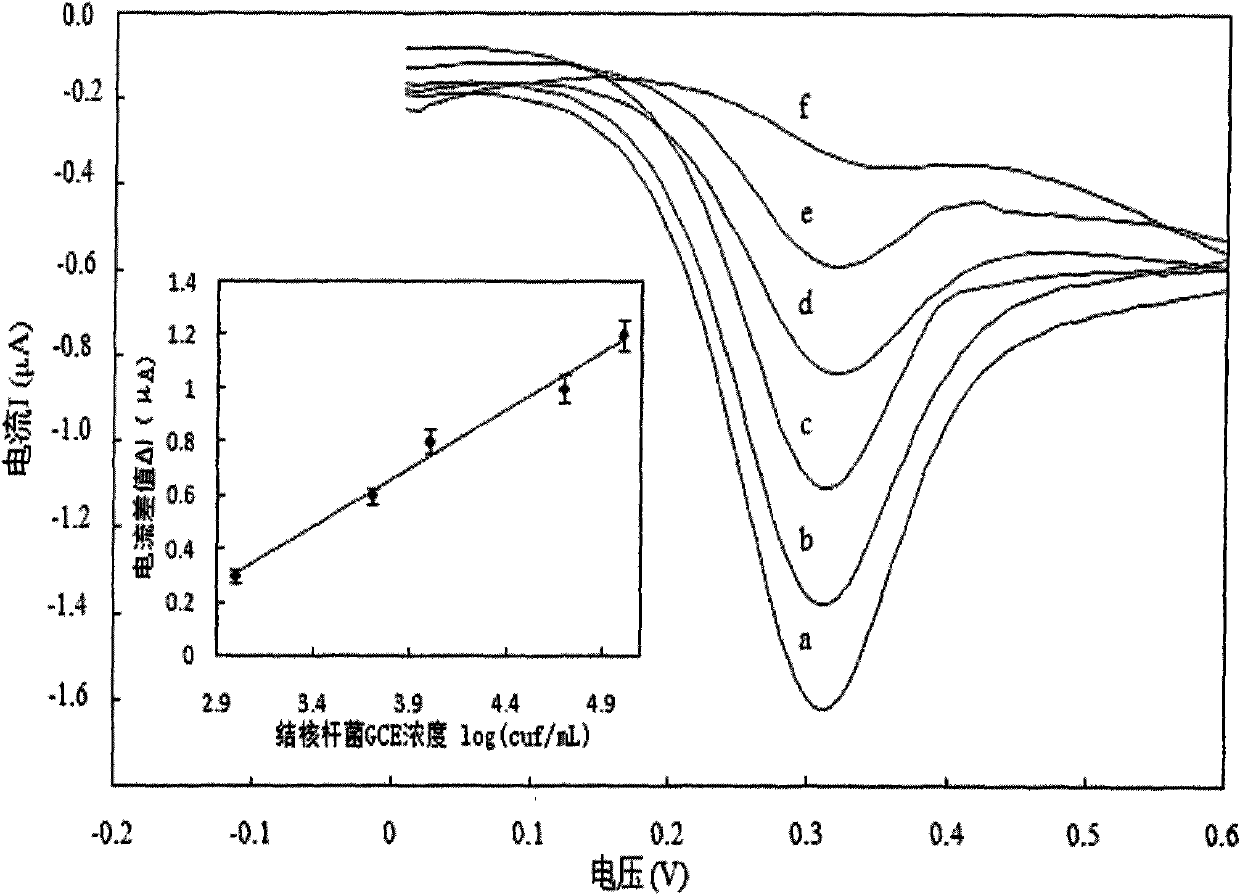
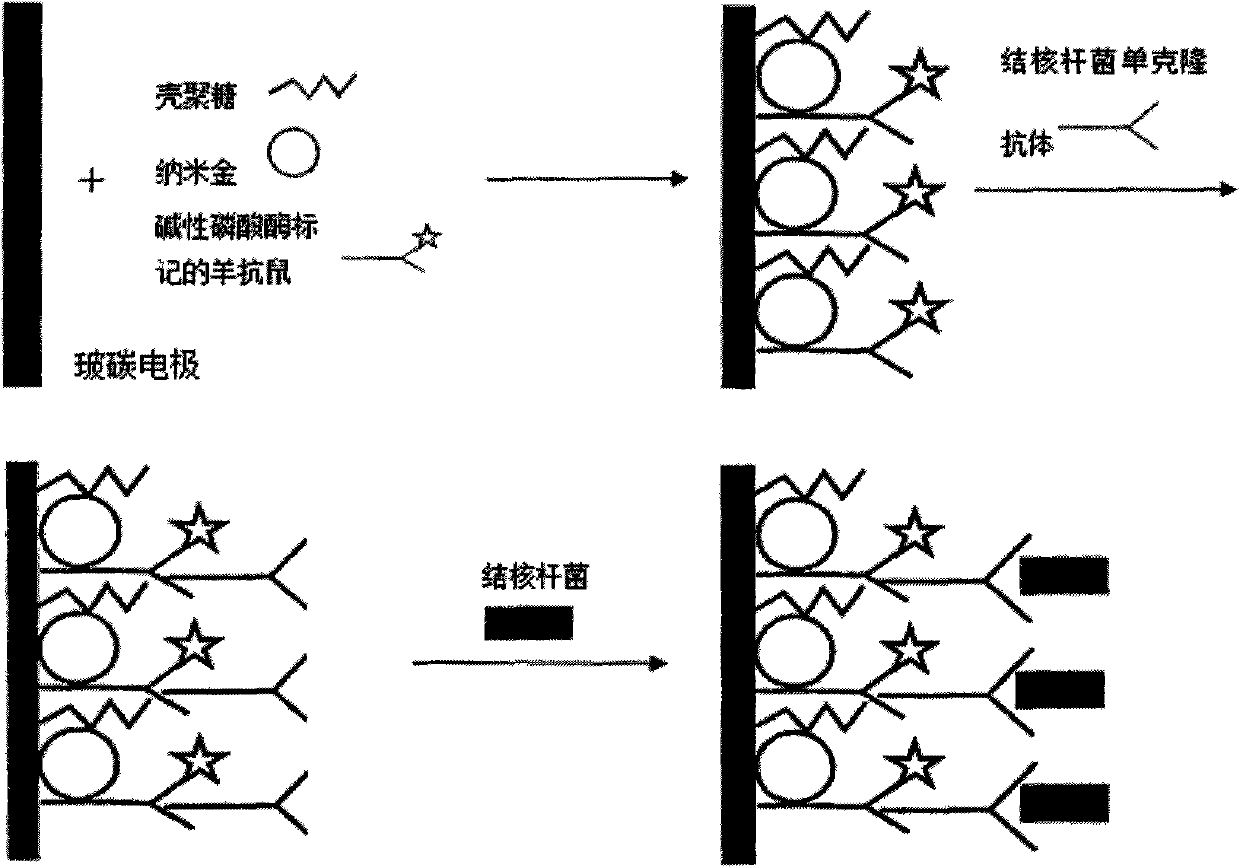
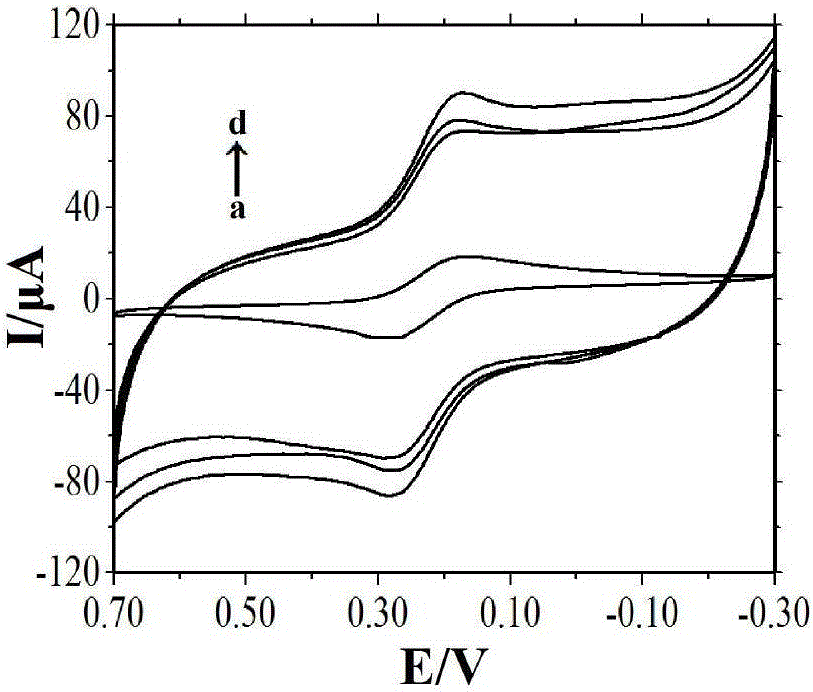
Chitosan-nano-gold enzyme immunosensor for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis and application thereof
InactiveCN102087283AEasy to prepareMaintain biological activityBacteriaMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDifferential pulse voltammetryCell wall
The invention relates to an enzyme immunosensor based on chitosan and nano-gold, and by using the specific combination of the monoclonal antibody of the cell wall of mycobacterium trberculosis with mycobacterium trberculosis, the enzyme immunosensor is applicable to the rapid detection of mycobacterium trberculosis in milk. The characteristic is that the enzyme immunosensor for detecting mycobacterium tuberculosis is prepared by the following steps: modifying the surface of a glassy carbon electrode through electrochemical deposition method by a mixed solution of chitosan gel, nano-gold solution, and goat anti-mouse antibody labeled by alkaline phosphatase; and fixing the mycobacterium trberculosis monoclonal mouse antibody on the surface of the glassy carbon electrode modified by the goat anti-mouse-chitosan-nano-gold film which is labeled by alkaline phosphatase through the specific antigen-antibody reaction. Quantitative analysis is performed by detecting the electric signal changegenerated before and after the incubation reaction of mycobacterium trberculosis and the modified electrode through differential pulse voltammetry. The preparation method of the sensor is simple, andthe sensor has the advantages of high sensitivity, short detection time, and simple operation, and is applicable to the method for the rapid detection of mycobacterium trberculosis.
Owner:HUAZHONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation and application method of electrochemical reduction graphene oxide and nanogold modified electrode based DNA sensor
InactiveCN105758918AEasy to makeLow priceMaterial electrochemical variablesNanoparticleCarbon paste electrode
The invention discloses a novel electrochemical DNA sensor constructed by a nanogold and partially-reduced graphene oxide (p-RGO) modified ionic liquid carbon paste electrode (CILE) as a platform prepared by an electrochemical method, and a method of applying the CILE to detect the Listeria feature gene sequence. 1-hexylpyridiniumhexafluorophosphate as a modifier is used for preparing the substrate electrode CILE, gold nanoparticles are deposited on the surface of the substrate electrode CILE and then the p-RGO is prepared by controlling electrochemical reduction conditions; an amino-modified probe ssDNA is fixed on the surface of the electrode by an amido bond covalent bonding method through carboxyl groups remained on the surface of p-RGO to constitute ssDNA / p-RGO / AuNPs / CILE; methylene blue (MB) as an indicator is used for detecting the hybridization reaction after a target sequence is hybridized, and a differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) is used for detecting the Listeria feature gene segment.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation and detection methods of screen-printed electrode immunosensor for rapidly detecting microcystin
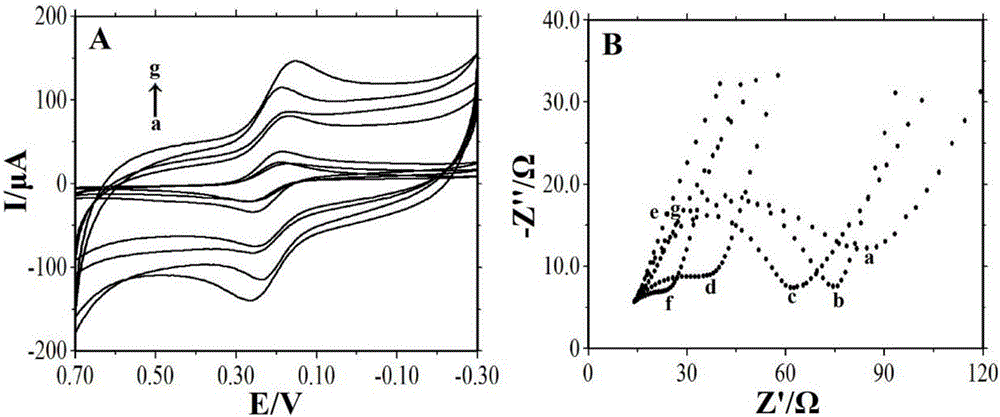
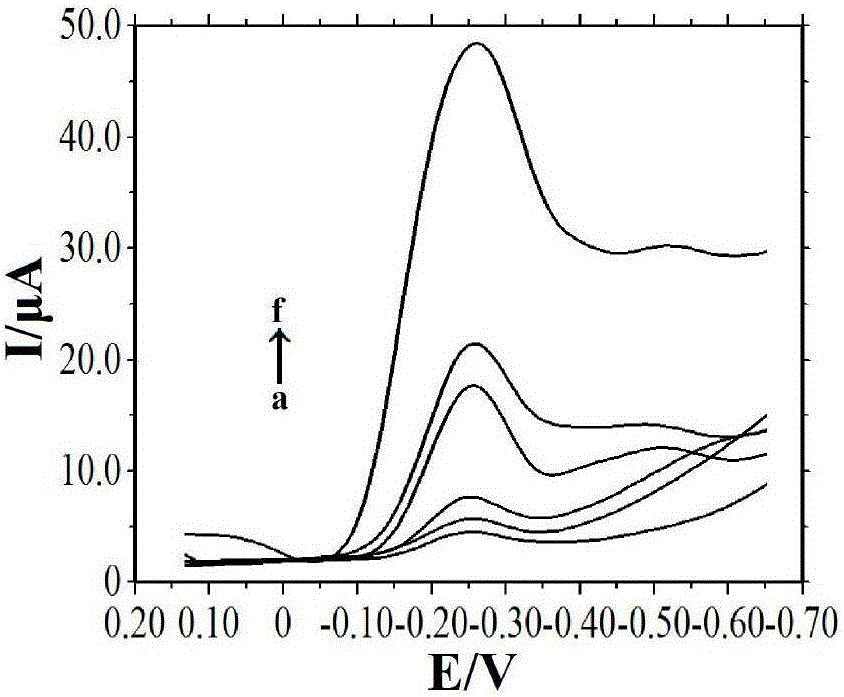
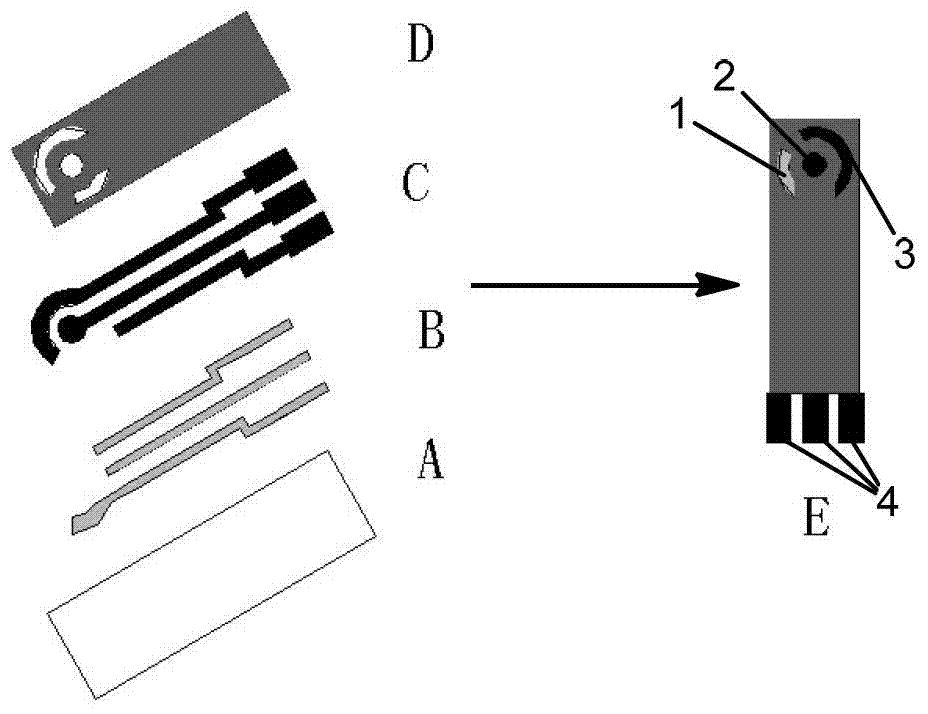
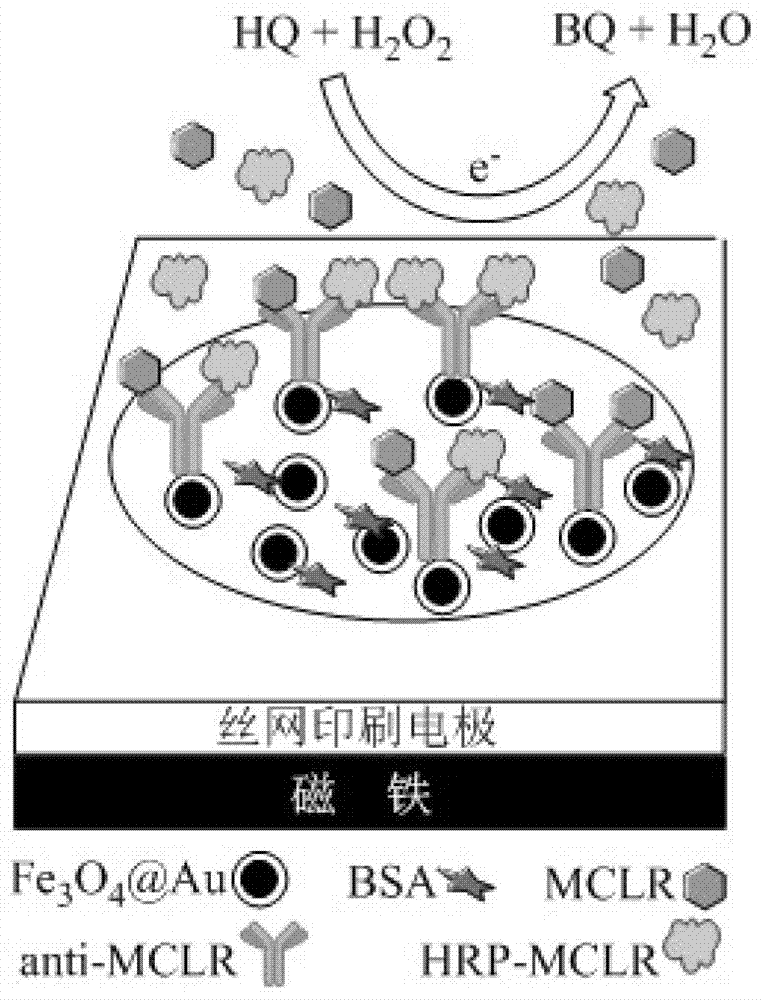
ActiveCN103308675AEasy to makeEasy to processMaterial electrochemical variablesMagnetite NanoparticlesHorse radish peroxidase
The invention discloses preparation and detection methods of a screen-printed electrode immunosensor for rapidly detecting microcystin, and belongs to the field of environment monitoring technologies. Through a magnetic field formed by a magnet below a screen-printed electrode, core-shell magnetic nanoparticles Fe3O4@Au are fixed on the surface of a working electrode; through the adsorption between nano-Au and a microcystin antibody, the microcystin antibody is fixed on the surface of the electrode to prepare an MCLR antibody electrode; a certain concentration of MCLR and MCLR which is marked by horse radish peroxidase are together modified on the surface of the working electrode; after immunoreaction is performed for a period of time, a peak current value is measured by using DPV (differential pulse voltammetry) to obtain standard curves of the MCLR and the oxidation peak current; the steps are repeatedly carried out on water samples to be detected, and the obtained oxidation peak currents are compared with standard curves to obtain the MCLR concentration. According to the preparation and detection methods of the screen-printed electrode immunosensor for rapidly detecting microcystin, benefit is brought to rapidly detect the MCLR, the water samples do not need purification treatment, simplicity and rapidness are achieved, and the detection cost is reduced.
Owner:网都河北科技服务有限公司
Electrochemical immunosensor for measuring melamine content, preparation method and application
InactiveCN102262115AAchieve qualitativeEasy to detectBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesAntigenDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention discloses a label-free electrochemical immunosensor for melamine content determination, and a preparation method and application thereof. The immunosensor comprises a substrate electrode, wherein the surface of the substrate electrode is modified by a graphene-melamine-chitosan composite, and nonspecific active sites are sealed by bovine serum proteins. The method for preparing the electrochemical immunosensor is implemented by fixing melamine antigens on the surface of a glass carbon electrode with graphene / chitosan composite materials. Based on an immunoreactive competition mode, the electrochemical immunosensor monitors immune reaction through cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry by taking K3Fe(CN)6 as a probe,, and can be used for melamine content detection. The immunosensor disclosed by the invention is high in sensitivity and specificity, simple in detection method and wide in application range; the limit of detection can reach 0.2 ng / ml, and the linear range is 5-1500 ng / ml; and the immunosensor has the characteristics of high speed, high efficiency, high sensitivity, good specificity, simple operation, low cost and the like.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation and application of CS/IL-GR modified bovine serum albumin molecular imprinting electrode
ActiveCN103926294AAchieving Sensitive DetectionGood linear relationshipMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansPower flowProtein molecules
The invention discloses a preparation of a CS / IL-GR modified bovine serum albumin molecular imprinting electrode. The preparation comprises the following steps of the preparation of a CS / IL-GR / GCE, and the preparation of MIPs / CS / IL-GR / GCE. The invention also discloses an application of the CS / IL-GR modified bovine serum albumin molecular imprinting electrode to the detection on BSA. The application is characterized in that a [Fe(CN)6]<3- / 4-> is adopted as an electrochemical probe, an electrochemical impedance (EIS) and a differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) are adopted to represent a property of the MIPs / CS / IL-GR / GCE, the imprinting electrode can express a good linear relation on the BSA within a 1.0*10<-10>-1.0*10<-4>g / L concentration range, the peak current change value deltaI can be calculated as follows: deltaI (muA)=27.42+2.21*log(CBSA)(g / L), R=0.996, and the detection limit can be up to 2.02*10<-11>g / L. The preparation method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that an imprinting sensor can express the good selectivity, sensitivity and reproducibility based on a synergistic effect of an IL-GR compound and the interaction of a chitosan molecule and a protein molecule, and the preparation method is used for clinical analysis detection on a trace sample.
Owner:青岛博亭科技有限公司
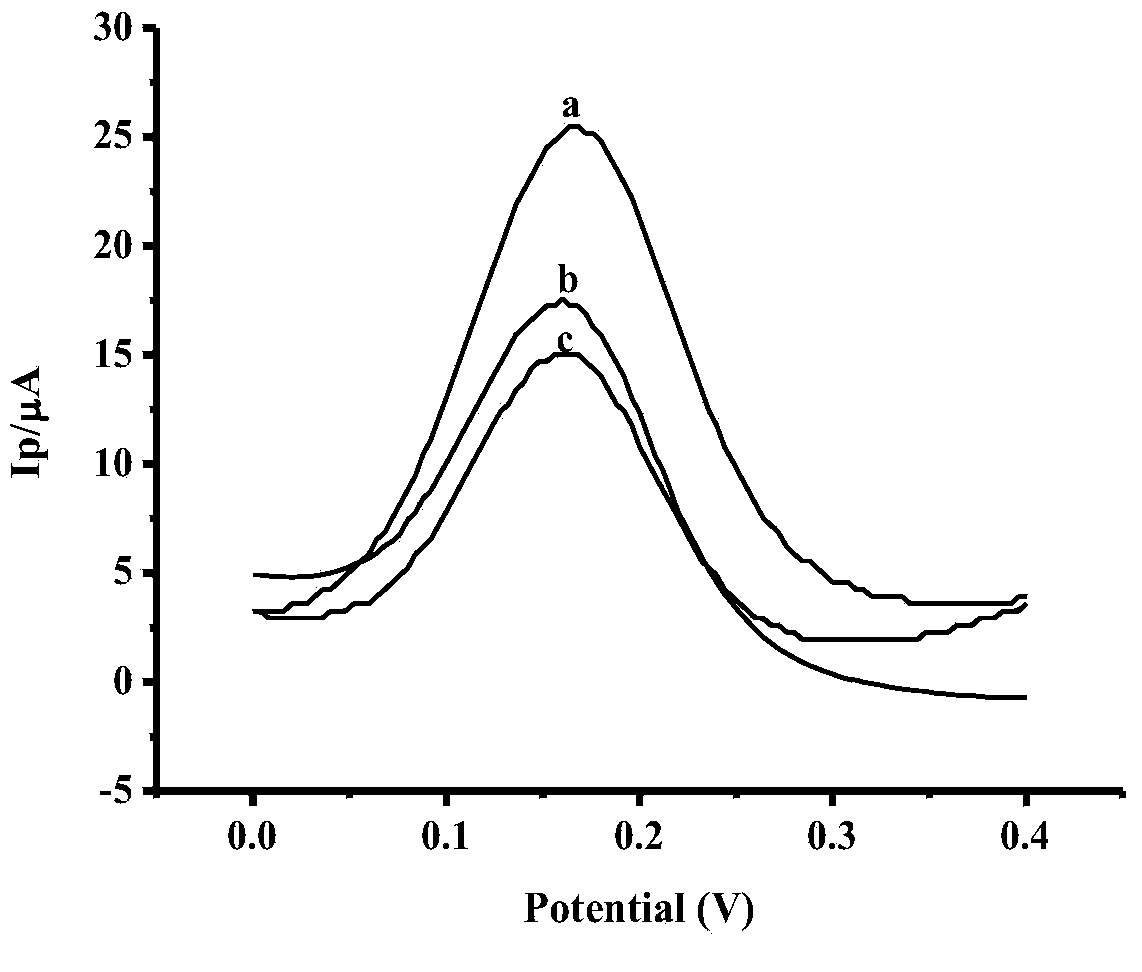
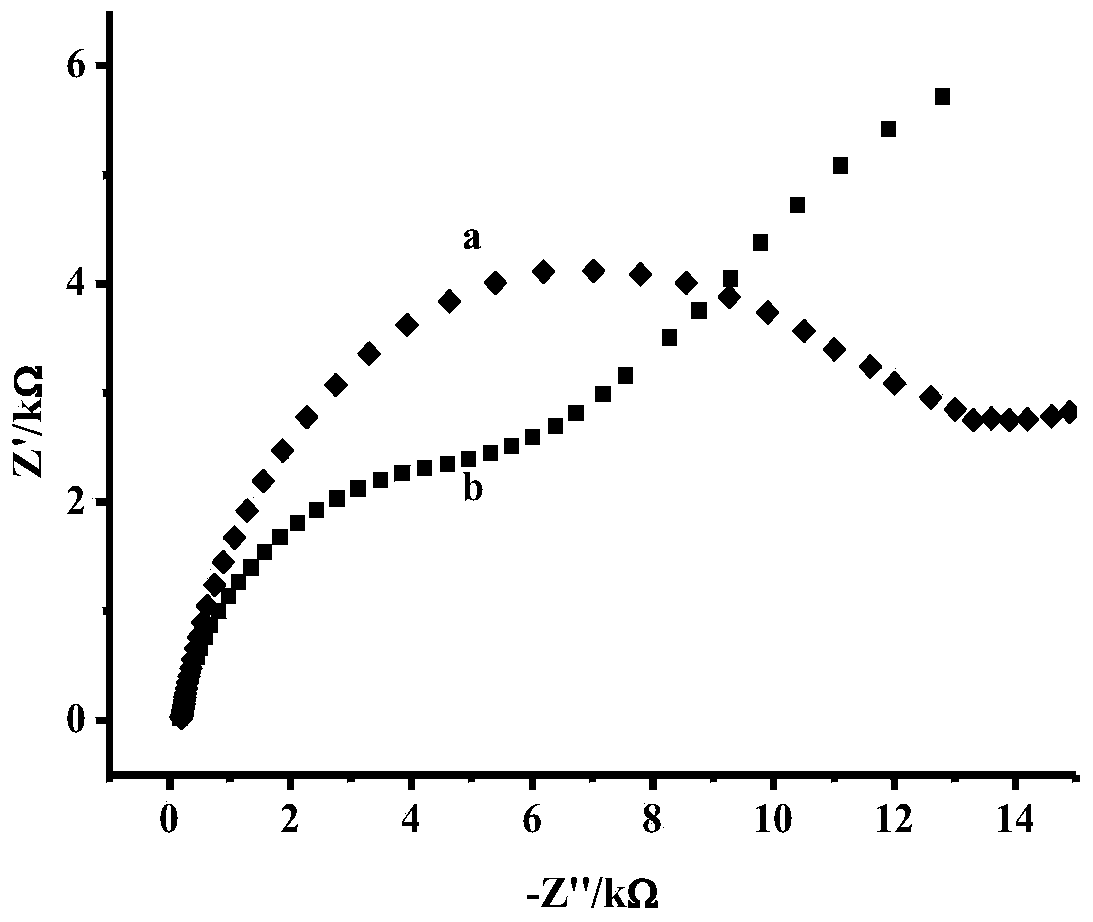
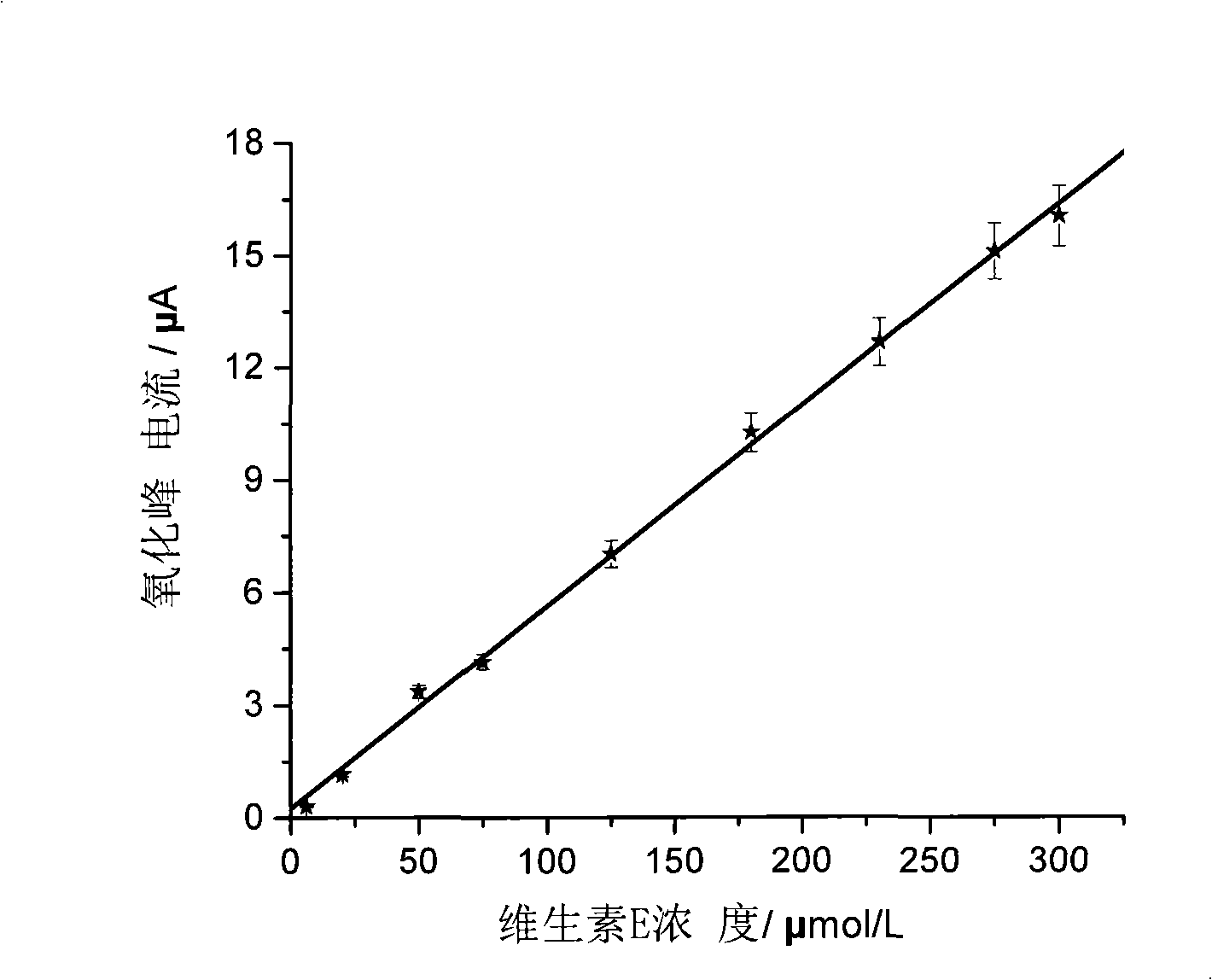
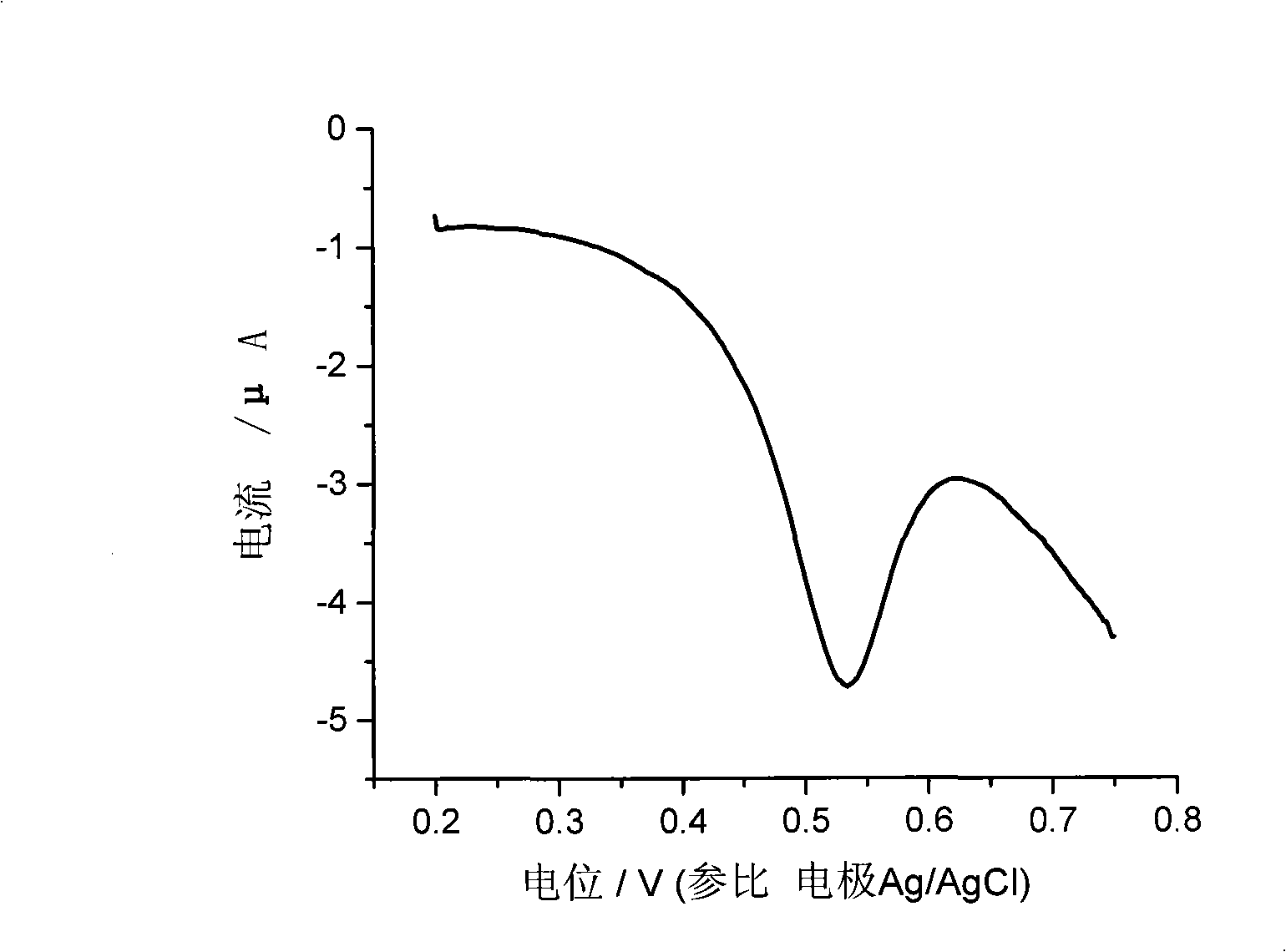
Method for fast detecting vitamin E content
InactiveCN101320015AImprove stabilityStrong anti-interferenceMaterial electrochemical variablesVegetable oilDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention relates to a poly-pyrrole modified electrode doped with p-toluene sulphonic acid and provides a method using the modified electrode for rapidly detecting the content of vitamin E. the method comprises: 1) using experimental conditions which are the same with the detecting conditions of a sampler for drawing a standard curve of the content of vitamin E and oxidation peak current; 2) dissolving the sample in the mixed solvent of ethanol-1 and 2 dichloroethane and regulating the pH value to be 2-5 to obtain the sample solution; 3) arranging the modified electrode in the sample solution, detecting the oxidation peak current through a differential pulse voltammetry and calculating the concentration of vitamin E in the sample. The method can be used for rapidly detecting the content of vitamin E in vegetable oil and has the advantages of simple sample preparation, convenience, fast speed, strong anti-interference ability and accurate detecting result which is identical with the detecting result of a liquid chromatography.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
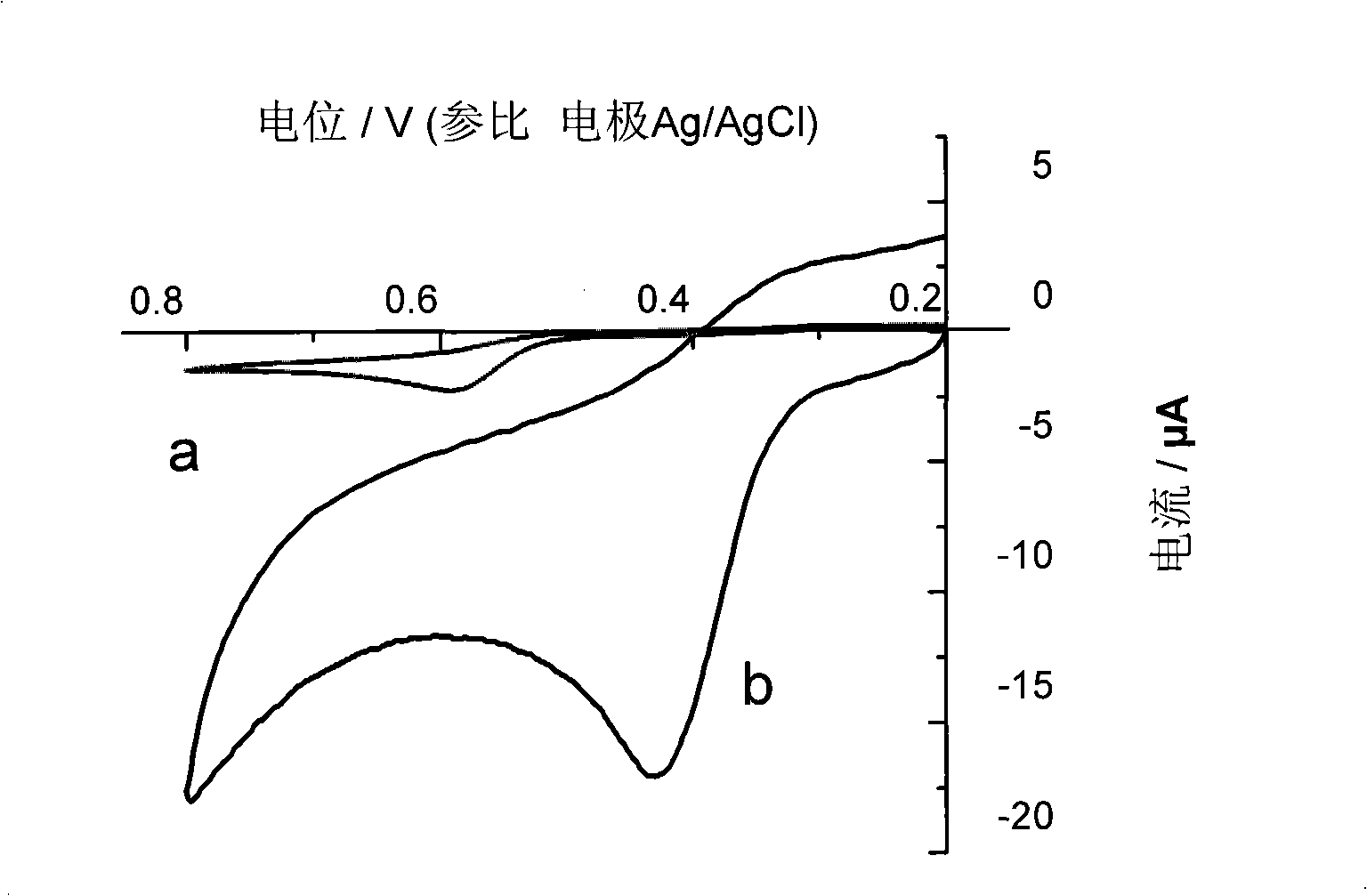
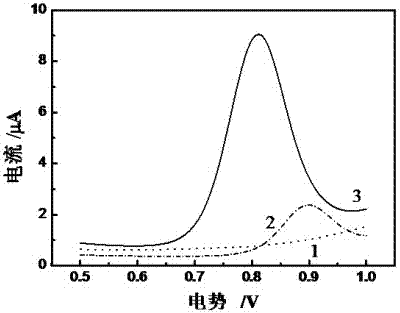
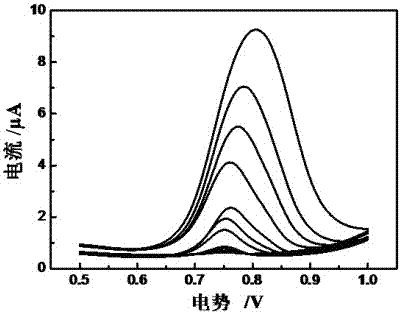
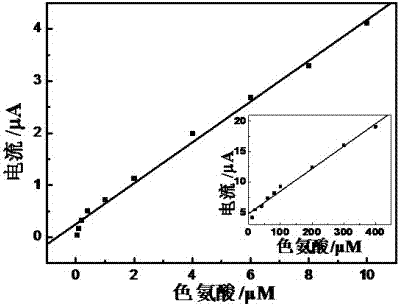
Method for preparing electropolymerized sulfosalicylic acid modified glassy carbon electrode and application of glassy carbon electrode in measurement of tryptophan
InactiveCN102507686AIncreased current responseHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesPhosphateSalicylic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing an electropolymerized sulfosalicylic acid modified glassy carbon electrode, and use of the glassy carbon electrode as a tryptophan electrochemical sensor in high-sensitivity measurement of tryptophan in compound amino acid injection, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical analysis and detection. The invention mainly aims to prepare the electropolymerized sulfosalicylic acid modified glassy carbon electrode to perform sensitive quantitative analysis and measurement on the tryptophan by a differential pulse voltammetry. Experimental results show that: the modified electrode has an obvious sensitization effect on the tryptophan in a phosphate buffer solution at the concentration of 0.1mol / L and the pH of 3.5, and under the optimal conditions, the differential pulse voltammetry is adopted for measurement, and the tryptophan at the concentration in a range of 5.0*10<-8>-4.0*10<-4> and peak current of the tryptophan have a good linear relation, and the detection limit is 4.0*10<-8>. When the method is used for measuring the tryptophan content in a medicine, results are satisfactory.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Method for electrochemical detection of acephate by aid of molecularly imprinted polymer film supported on surface of metal-organic framework material
InactiveCN106198701ALarge specific surface areaMass transfer speedMaterial electrochemical variablesMetal-organic frameworkDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention relates to a method for electrochemical detection of acephate by the aid of a molecularly imprinted polymer film supported on the surface of a metal-organic framework material. The metal-organic framework material formed by cupric nitrate and 4,4'-biphenyldicarboxylic acid is taken as a support body, acephate is taken as a template molecule, methacrylic acid is taken as a function monomer, ethylene glycol dimethacrylate is taken as a crosslinking agent, azodiisobutyronitrile is taken as an initiator, the molecularly imprinted polymer film supported on the surface of the metal-organic framework material is synthesized and ultrasonically dispersed in a nafion solution for spin-coating of the surface of an electrode, and acephate is detected with a differential pulse voltammetry method. A molecularly imprinted polymer with large specific surface area and high mass transfer speed is obtained and is used for detecting acephate. The method has good stability and high sensitivity.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
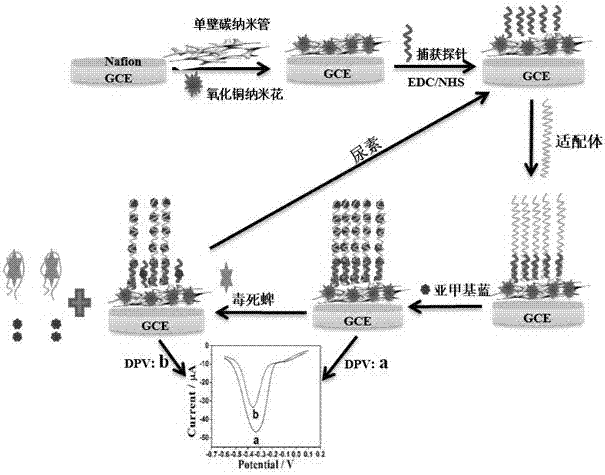
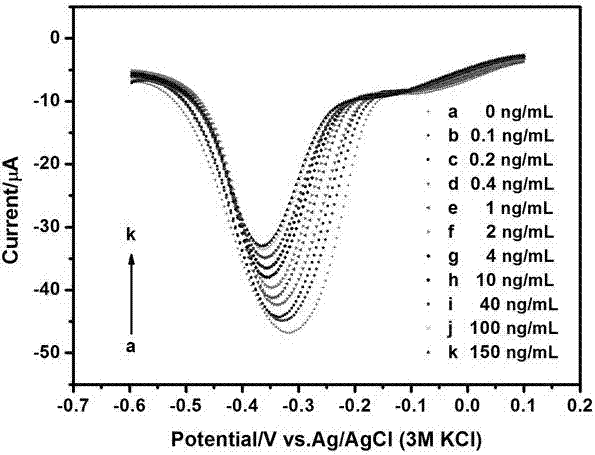
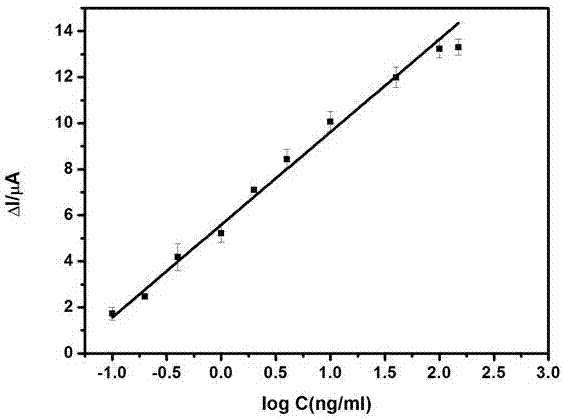
Electrochemical sensor for adapters and method for detecting chlorpyrifos
InactiveCN107367540AHigh sensitivityLow costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChlorpyrifosCarbon nanotube
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensor for adapters and a method for detecting chlorpyrifos. The electrochemical sensor adopts a three-electrode system and comprises a first detection layer, a second detection layer and a fixed layer. A preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing copper oxide nanoflower solution, preparing single-wall carbon nanotube solution, treating base electrodes, activating carboxyl groups, and fixing probes and the adapters; and then manufacturing a standard curve by utilizing a differential pulse voltammetry, and finally calculating out the concentration of the chlorpyrifos in samples according to the standard curve of the chlorpyrifos. The electrochemical sensor and the method disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the detection for the chlorpyrifos is specific, the sensitivity and the selectivity are high, the renewability is achieved, the materials are wide in source, the cost is low, and the preparation method is simple, so that the application prospect is good.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
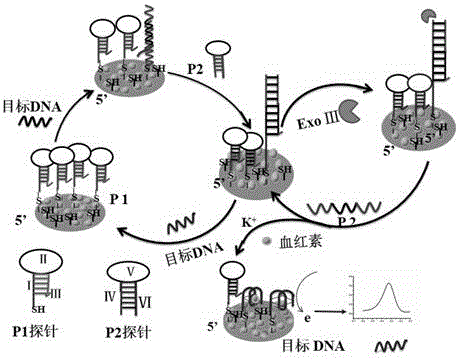
Method for electrochemically detecting concentration of specific single-stranded DNA based on exonuclease and nucleic acid probe
ActiveCN105821132AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementHaem-haem interactionNanoparticle
The invention relates to a method for electrochemically detecting concentration of specific single-stranded DNA based on exonuclease and a nucleic acid probe and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The invention designs and synthesizes two types of hairpin-type probes P1 and P2. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly modifying a gold electrode with gold nanoparticles by adopting 1,6-hexanedithiol (HDT), preparing an AuNPs-HDT-Au electrode, and then modifying the probe P1 onto the electrode; taking a specific single stranded target DNA as a to-be-detected object, so that the probes P1 and P2 can coexist when no target DNA exists, and the target DNA can trigger two independent reaction cycles when the target DNA, the probe P2 and the exonuclease ExoIII exist; and finally when heme exists, generating a strong signal under the interaction of a G-tetraplex sequence of the probe P1 on the surface of the electrode and heme, and detecting the target DNA by adopting a differential pulse voltammetry, wherein a peak current signal and the target DNA concentration are correlated in a certain concentration range, so that detection on the target DNA concentration is realized. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and strong specificity.
Owner:北京聚合美生物科技有限公司
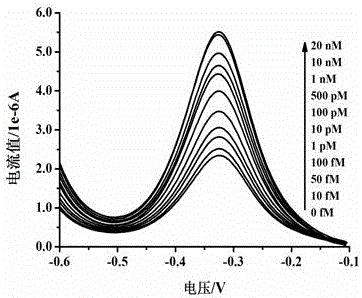
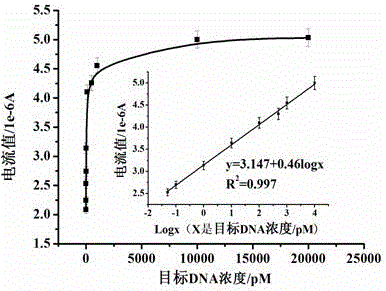
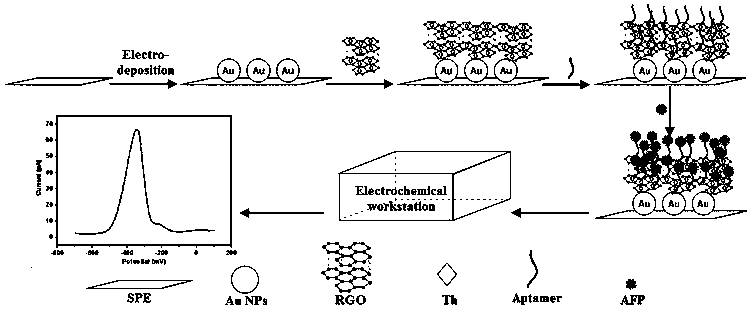
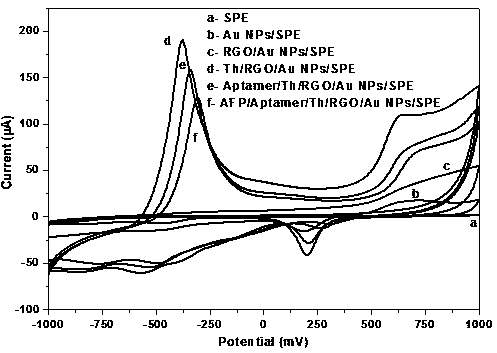
Method used for detecting alpha fetoprotein based on graphene, thionine, and nucleic acid aptamer
ActiveCN107677719ALow costImprove performanceMaterial electrochemical variablesPeak valueDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention discloses a method used for detecting alpha fetoprotein based on graphene, thionine, and a nucleic acid aptamer. According to the method, electrodeposition technology is adopted for deposition of nano-gold on the surface of a screen-printed electrode, electrostatic adsorption is adopted for absorption of graphene and thionine which drop on an electrode surface onto the surface of thescreen-printed electrode, thionine is taken as a bridge molecule for capturing of the nucleic acid aptamer onto the surface of a modified electrode. A nanometer aptamer biosensor can be constructed based on the extremely large specific surface area and signal amplification effect of graphene, the high loading capacity of thionine on the aptamer, and the specific recognition effect of the aptameron alpha fetoprotein. Peak value current is measured through differential pulse voltammetry, and the relation curve of the current to the alpha fetoprotein concentration is drawn, so that detection onalpha fetoprotein is short in time, low in cost, and high in the specificity.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
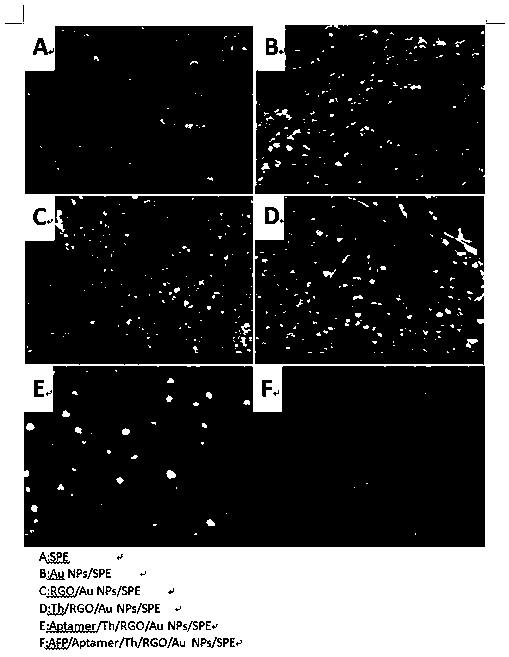
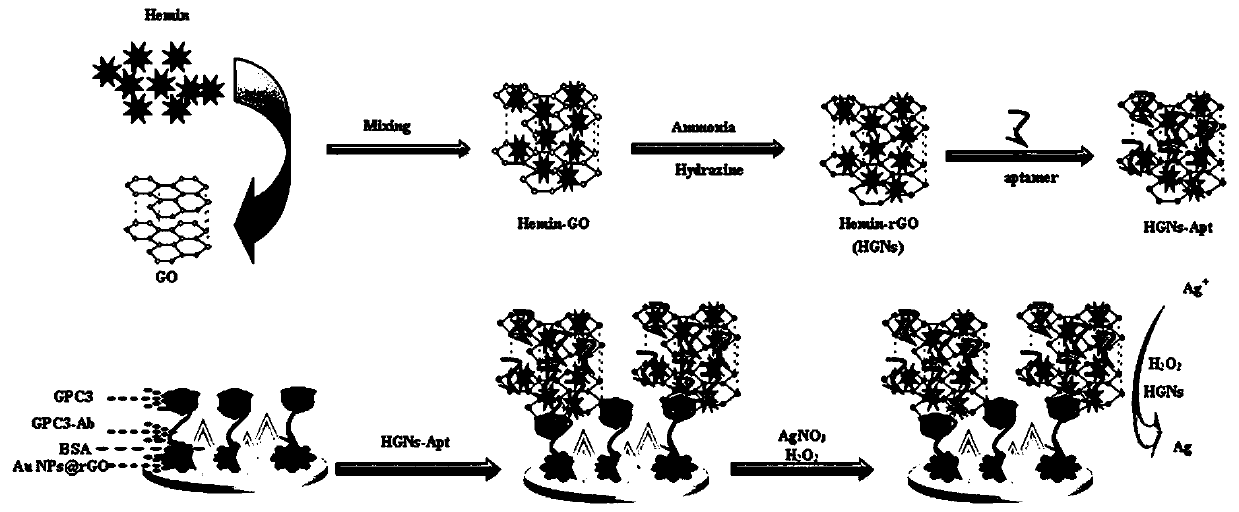
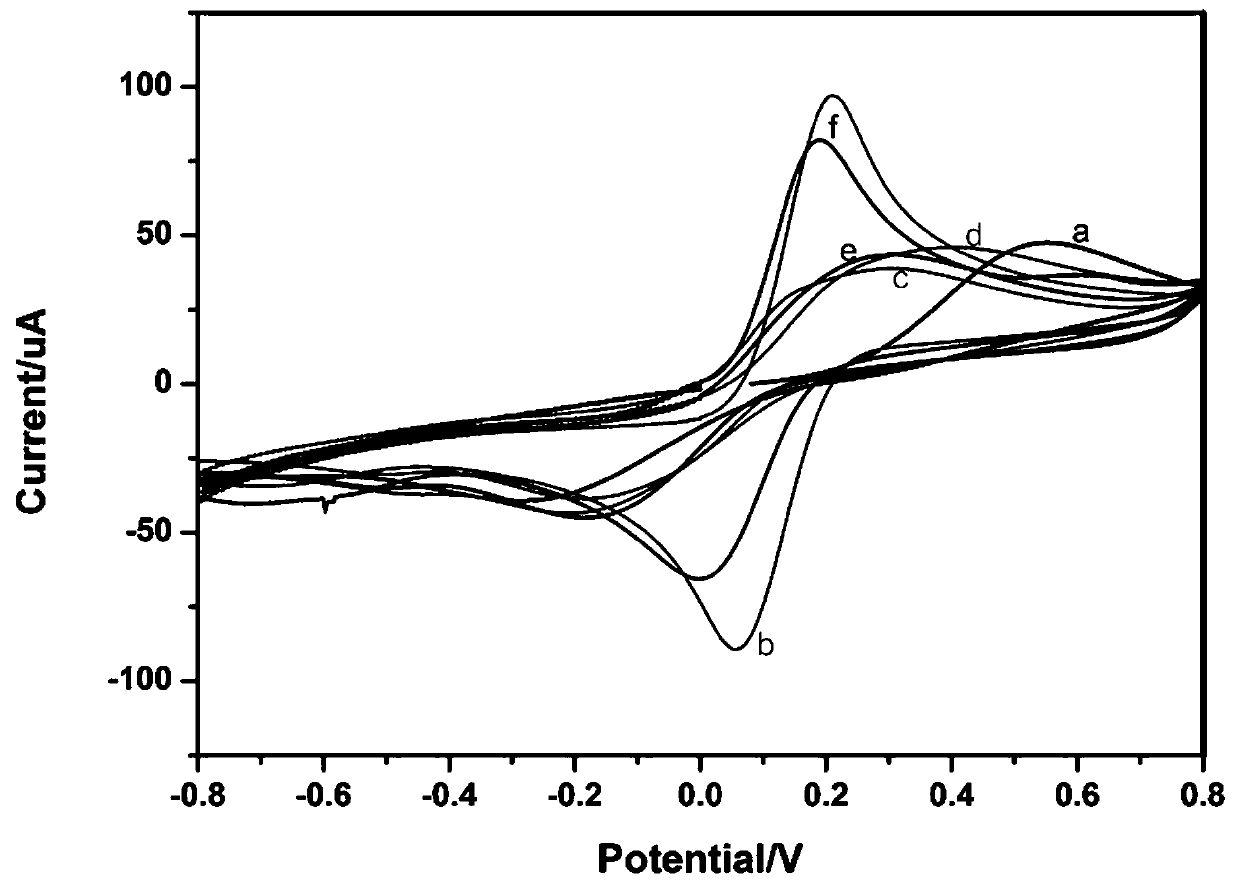
Peroxidase catalytic silver deposition-based method for detecting GPC3
ActiveCN110823980AAchieving Sensitive DetectionHigh sensitivityBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesPeroxidaseCatalytic effect
A peroxidase catalytic silver deposition-based method for detecting GPC3 comprises the steps of building an electrochemical nanometer sensor, activating and modifying a silk-screen printed electrode,building a biological sensing interface, drawing a working curve of the GPC3 and detecting a to-be-detected sample. An HGNs-Apt signal probe is fabricated by taking HGNs as a carrier, and an Apt-GPC3-HGNs-Apt sandwiched electrochemical nanometer aptamer sensor is built; silver ions in a solution are reduced to metal silver deposited on a surface of the electrode by H2O2 and by means of a catalyticeffect of peroxidase of HGNs, the deposition quantity of Ag is obtained according to quantity of GPC3 protein, and quantization is performed by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV); and current response of Ag and GPC3 concentration are in favorable positive correlation within a range being 10.0-100.0 micrograms per mL, and GPC3 detection is achieved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Novel method for detecting lead ions based on sensitivity of DNA-MOF material
InactiveCN106324068AImprove stabilityGood biocompatibilityMaterial electrochemical variablesPorphyrinChloride
The invention discloses a novel method for detecting lead ions based on the sensitivity of a DNA-MOF material. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a gold-paper chip working electrode Au-PWE; synthesizing Au-MOF from 5,10,15,20-tetra(4-methoxy phenyl)porphyrin, ferric chloride and nanogold; carrying out functionalization by virtue of GR DNA, so as to synthesize a GR-Au-MOF material; modifying the prepared Au-PWE with HP DNA, and dropwise adding a GR-Au-MOF solution mixed with 3,3',5,5'-tetramethyl benzidine, hydrogen peroxide and a sample solution to HP modified Au-PWE; and connecting the modified chip to an electrochemical working station by virtue of a three-electrode system, and detecting the concentration of lead ions by virtue of a differential pulse voltammetry. The novel method for detecting the lead ions is high in sensitivity and good in selectivity, and the real-time monitoring of samples can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Application of nickel aluminum layered double metal hydroxide modified electrode to measurement of uric acid
InactiveCN103063717AThe detection method is simpleHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetryReaction system
The invention discloses an application of a nickel aluminum layered double metal hydroxide modified electrode to the measurement of uric acid. The application comprises the following steps: (1) preparing the nickel aluminum layered double metal hydroxide modified electrode NiAl-LDH / G; (2) inspecting the electric catalytic performance of a NiAl-LDH / G compound; (3) inspecting the DPV (differential pulse voltammetry) behaviors of UA (uric acid) on different modified electrodes; (4) quantitatively detecting UA; and (5) inspecting the repeatability, the stability and the interference test of the electrode. Compared with the prior art, the application has the advantages as follows: compared with other conventional detection modes, the detection method is simple and quick, the sensitivity is high, the detection limit is low, and a reaction system is nonhazardous; the method is high in stability, low in requirement on instruments and easy to popularize and use; and the method also has the characteristics of being simple, convenient and quick to operate.
Owner:CHINA NAT TOBACCO QUALITY SUPERVISION & TEST CENT
Electrochemical sensor detection method for rapidly detecting trace carbendazim pesticide
InactiveCN103472122AFast analysisWide detection rangeMaterial electrochemical variablesDiacrylate esterMontmorillonite
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensor detection method for rapidly detecting a trace carbendazim pesticide. The method comprises the following steps: 1, adding 0.2-2g of montmorillonite to 100mL of water to heat to 80 DEG C for 2 hours; 2, adding 0.2g of phthalate glycol acrylate to 100mL of water, adding 1g of NaCl, regulating pH to 9-10 by 0.1 mol / L NaOH solution; 3, mixing and heating the solution in the step 2 with the solution in the step 1 to 60 DEG C from constant temperature, and forming powder; 4, polishing a glassy carbon electrode, and respectively cleaning by acetone, ethanol, 10% NaOH solution, HNO3 of 1:1 and water; 5, scanning the glassy carbon electrode in the step 4 at the speed of 50 mV.S<-1>; 6, taking 0.005g of phthalate glycol acrylate modified montmorillonite, so as to obtain a sensor; 7, putting the sensor into a carbendazim solution, adding a B-R buffer solution, and detecting by a differential pulse voltammetry. The method is simple and fast.
Owner:ZUNYI NORMAL COLLEGE
Electrochemical detection of capsaicinoid compounds in a sample
InactiveCN103492869ATesting foodMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetrySilver chloride
An electrochemical method for capsaicinoid and / or related compound detection in a sample by way of a screen printed electrode having a working electrode, a reference electrode, and a counter electrode. The working electrode can be screen-printed using conductive carbon ink; the reference electrode can be screen printed using conductive carbon ink; the counter electrode can be screen printed using silver / silver chloride. The method includes contacting the electrode with the sample in the presence of electrolyte solution, and determining whether a change in redox potential occurs by way of differential pulse voltammetry, wherein a modulation amplitude is between approximately 0.1 volt / min and approximately 2.0 volt / min, a step potential is between approximately 0.0005 volt and approximately 0.01 volt, a modulation time is 0.05 seconds, and a corresponding interval time is approximately 0.5 second.
Owner:AGRI RES DEV AGENCY PUBLIC ORG
Detection method of copper ion concentration in solution
ActiveCN106525931AIncrease surface areaExcellent electron transfer abilityMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityPhytic acid
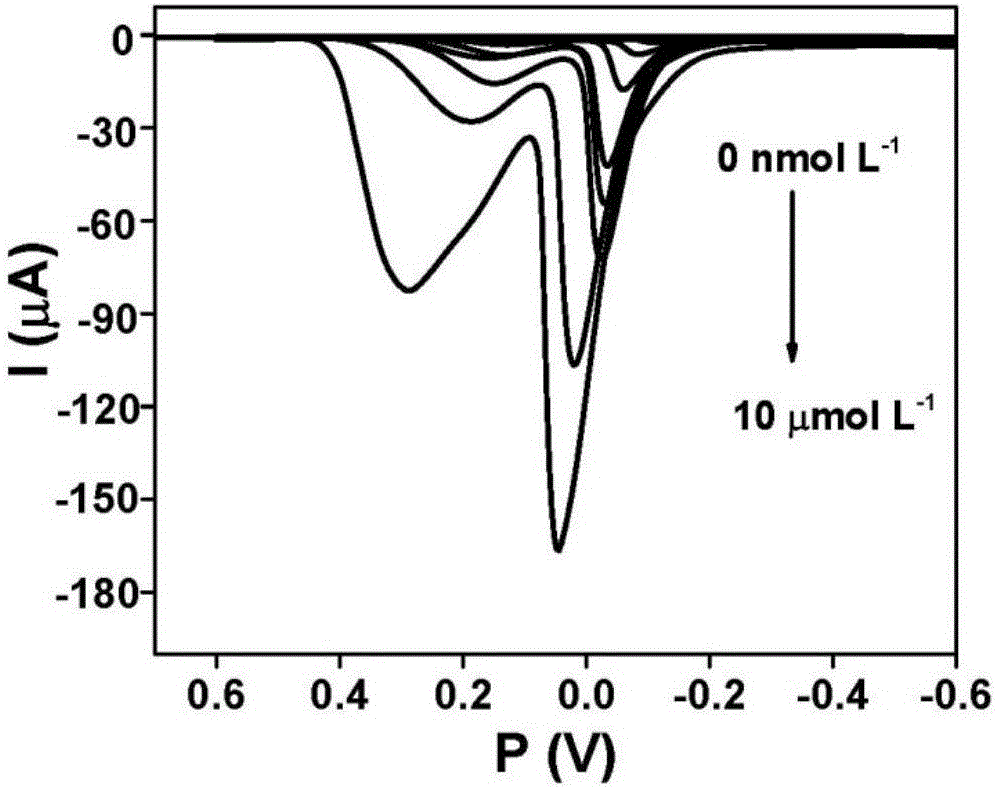
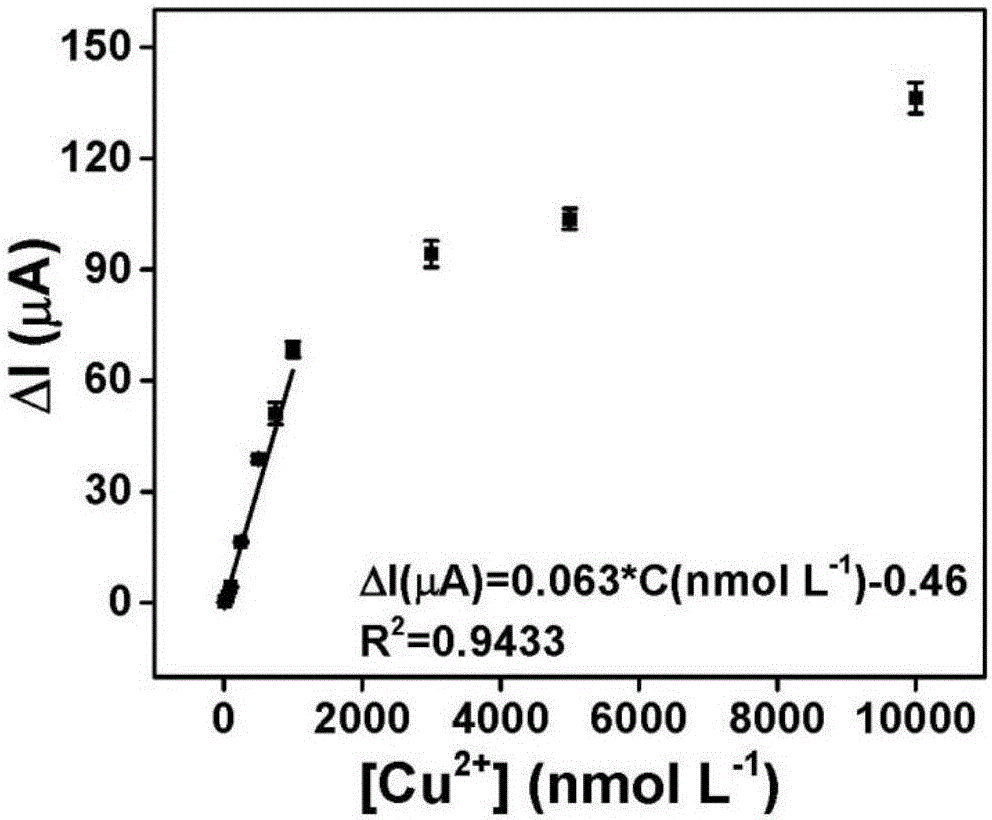
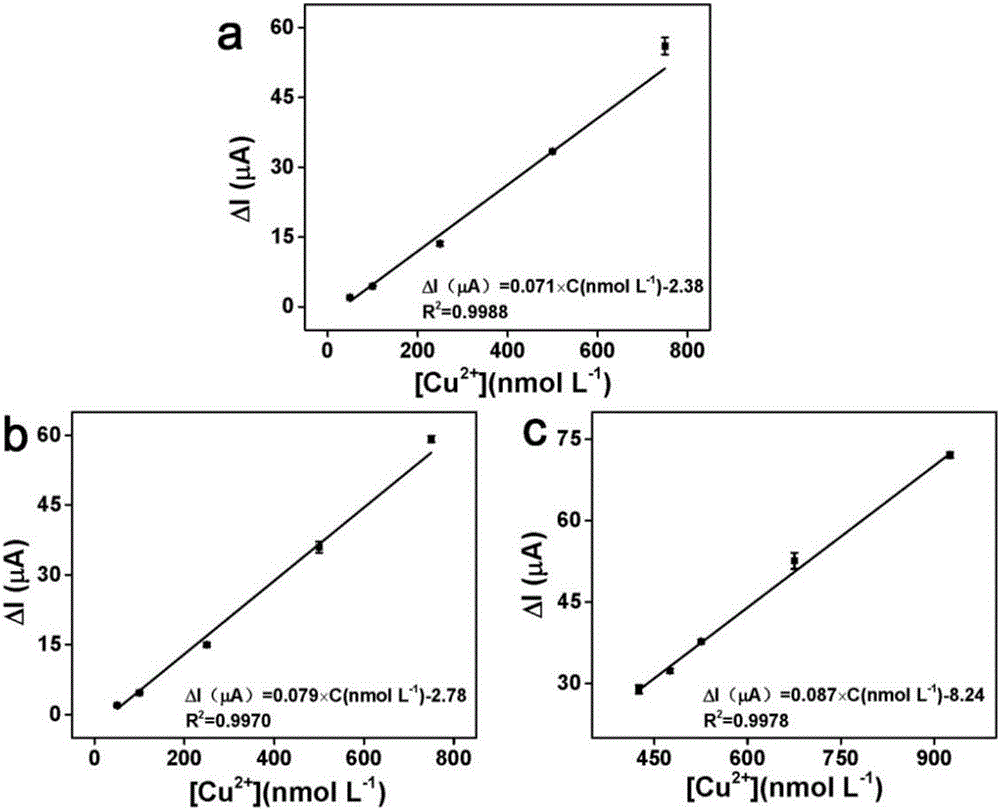
Belonging to the technical field of ion concentration detection method, the invention provides a detection method of copper ion concentration in a solution. The method includes: firstly preparing a work electrode three-dimensional polyacrylamide-phytic acid-polydopamine conductive hydrogel modified glassy carbon electrode or printed electrode, and preparing copper ion solutions of different concentrations; then employing the work electrode prepared by step 1 to react with the copper ion solutions of different concentrations respectively, and recording current response values corresponding to the copper ion solutions respectively by differential pulse voltammetry; then drawing a standard curve and calculating a linear equation; and employing the work electrode prepared by step 1 to react with a to-be-detected sample solution, scanning the detection solution to obtain a differential pulse voltammetry curve, and substituting a current response value into the linear equation obtained in step 3 so as to obtain the copper ion concentration of the to-be-detected sample solution. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of simple operation, rapid detection, high sensitivity and good selectivity.
Owner:CHANGCHUN INST OF APPLIED CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
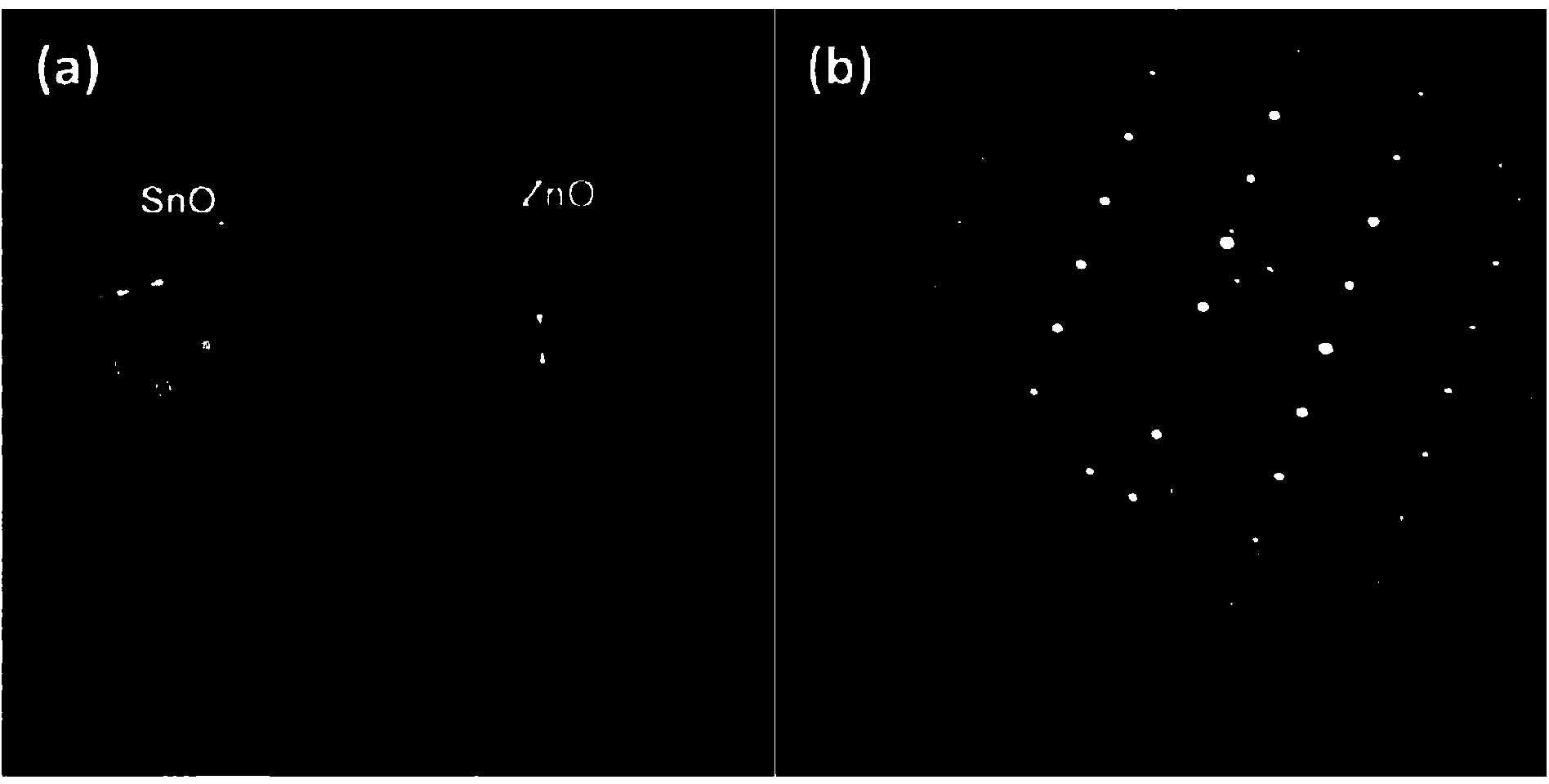
Perfluorinated sulfonic acid resin modified SnO2-coated ZnO nanotube array electrode used for detecting dopamine and application of nanotube array electrode
The invention belongs to the technical field of nano material application, and particularly relates to a perfluorinated sulfonic acid resin (Nafion) modified SnO2-coated ZnO nanotube array electrode used for detecting dopamine and the application of the nanotube array electrode. The nanotube array electrode comprises a conductive substrate and a Nafion modified polycrystal SiO2 nano-particle film-coated single-crystal ZnO nanotube array which vertically grows on the conductive substrate. The Nafion modified SnO2-coated ZnO nanotube array electrode used for detecting the dopamine can be used for detecting the dopamine in water solution; when the nanotube array electrode is taken as a working electrode, a platinum gauze electrode is used as a counter electrode, a saturated calomel electrode is used as a reference electrode, and a cyclic voltammetry (CV) or differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) is used for detecting the dopamine in water solution, the nanotube array electrode is capable of generating very strong electrochemical signals.
Owner:TECHNICAL INST OF PHYSICS & CHEMISTRY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation and application of HP-beta-CD (hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin) functionalized GO (graphene oxide) composite material
InactiveCN107474324ANot easy to fall offThe peak current value dropsMaterial electrochemical variablesEnantiomerTryptophan
The invention discloses preparation and application of HP-beta-CD (hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin) functionalized GO (graphene oxide) chiral composite material, and belongs to the fields of material preparation and electrochemical application. The preparation comprises the following steps of firstly, enabling beta-CD and propylene oxide to react under the alkaline condition, so as to prepare the HP-beta-CD; then, performing in-situ reduction on the GO and the HP-beta-CD by hydrazine hydrate, so as to obtain the HP-beta-CD functionalized GO (rGO-HP-beta-CD) composite material; finally, dripping and spraying the rGO-HP-beta-CD composite material to the surface of a GCE (glassy carbon electrode), so as to obtain a rGO-HP-beta-CD / GCE chiral electrochemical sensor. The preparation has the advantage that the tryptophan enantiomer is chirally identified by a DPV (differential pulse voltammetry) method, so that the stronger identifying ability on the D-tryptophan by the chiral electrochemical sensor is found.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Detection system and method for real-time online monitoring of various heavy metal ions
ActiveCN106841334AHigh detection sensitivityImprove detection accuracyGeneral water supply conservationPreparing sample for investigationPhysical chemistryCarrier fluid
A detection system and method for real-time online monitoring of various heavy metal ions are provided. Heavy metal ion standard liquids with different concentrations are injected into the detection system by means of mobile sampling; standard curves of the different heavy metal ions are measured through differential pulse voltammetry; an actual water sample is subjected to online real-time detection; the actual water sample and a carrier liquid are mixed, the mixture is charged into the detection system, a detection curve of the actual water sample is acquired through differential pulse voltammetry, and the detection curve of the actual sample is compared with the standard curves to measure the types and concentrations of the heavy metals in the actual water sample. The heavy metal sensor technique based on differential pulse voltammetry according to the invention allows various heavy metal ions to be detected at the same time, has high detection sensitivity and accuracy, takes several minutes for detection, and may meet the common requirements for online and quick response.
Owner:BAOJI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Method used for detecting acrylamide concentration of solutions
ActiveCN105044194AIncreased sensitivityReduce testing costsMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetrySingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method used for detecting acrylamide concentration of solutions. The method comprises following steps: a three-electrode system, and differential pulse voltammetry are adopted to detect acrylamide in a solution to be detected, and the concentration of acrylamide is obtained based on an acrylamide linear equation, wherein a working electrode of the three-electrode system is a glassy carbon electrode modified with carboxylated grapheme and a characteristic single-stranded DNA, and the sequence of the characteristic single-stranded DNA is 5'-AAAAAAAAAGGAAAAAAAAA-(CH2)6-SH-3'. According to the method, differential pulse voltammetry is adopted for high sensitive detection on acrylamide; detection limit on acrylamide concentration can be as low as 1mol / L; operation is simple; detection is rapid; sensitivity and selectivity are high; and application prospect is promising.
Owner:NINGBO XIANAN CHEM
Electrochemical method for simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone based on graphene/chitosan-modified electrode
InactiveCN103063728AImprove stabilityImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial electrochemical variablesPeak currentDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention discloses an electrochemical method for simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone based on a graphene / chitosan-modified electrode. The electrochemical method utilizes a graphene / chitosan-modified glassy carbon electrode as a working electrode and realizes simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone by the cyclic voltammetry and the differential pulse voltammetry. The glassy carbon electrode is modified by graphene and chitosan so that two isomers of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone are subjected to electrochemical separation on the modified electrode and peak current intensity is large and thus simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone contents is realized by the direct electrochemical determination method.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for measuring analyte concentration in a liquid sample
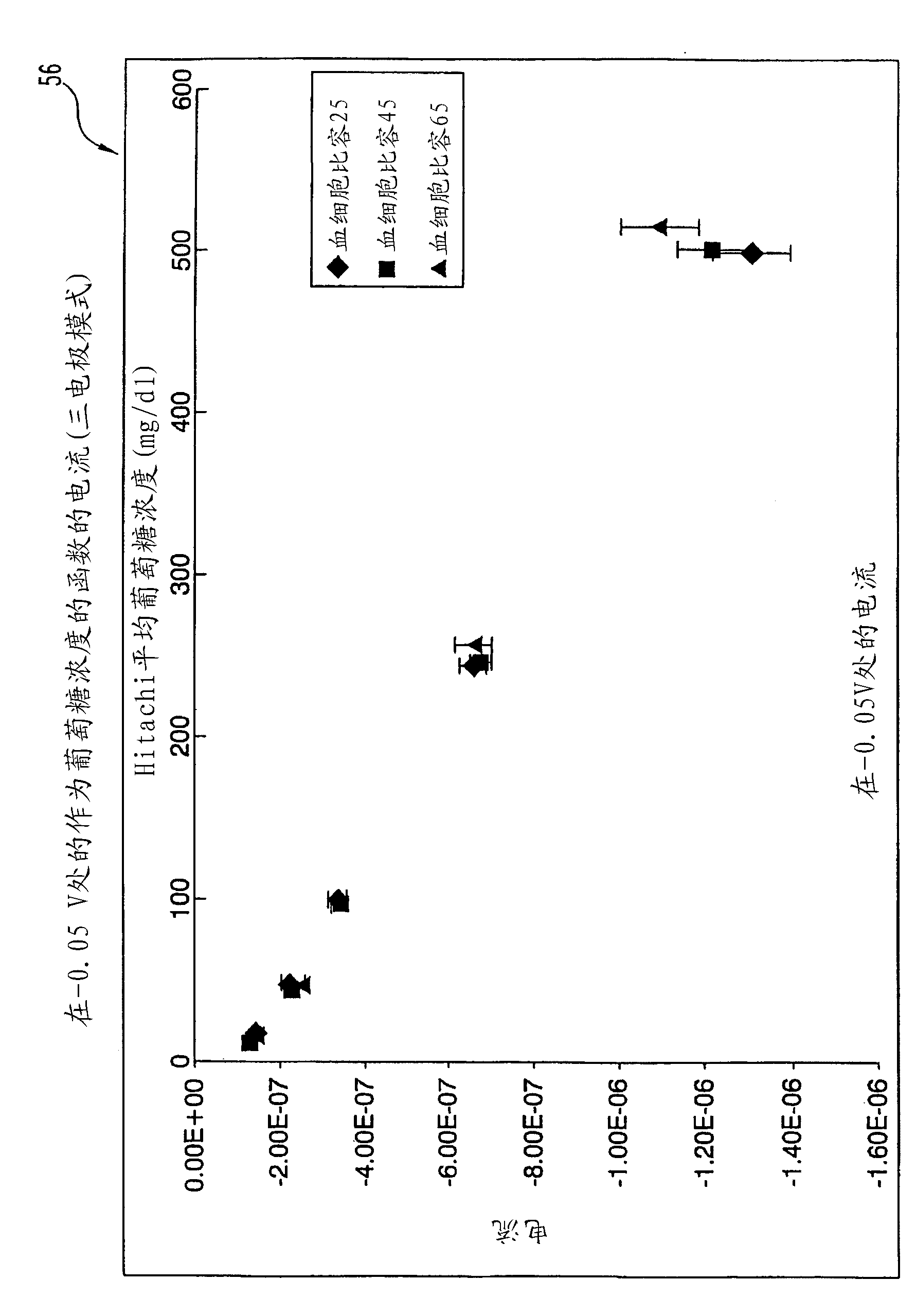
InactiveCN102667475ABiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesVoltage pulseConcentrations glucose
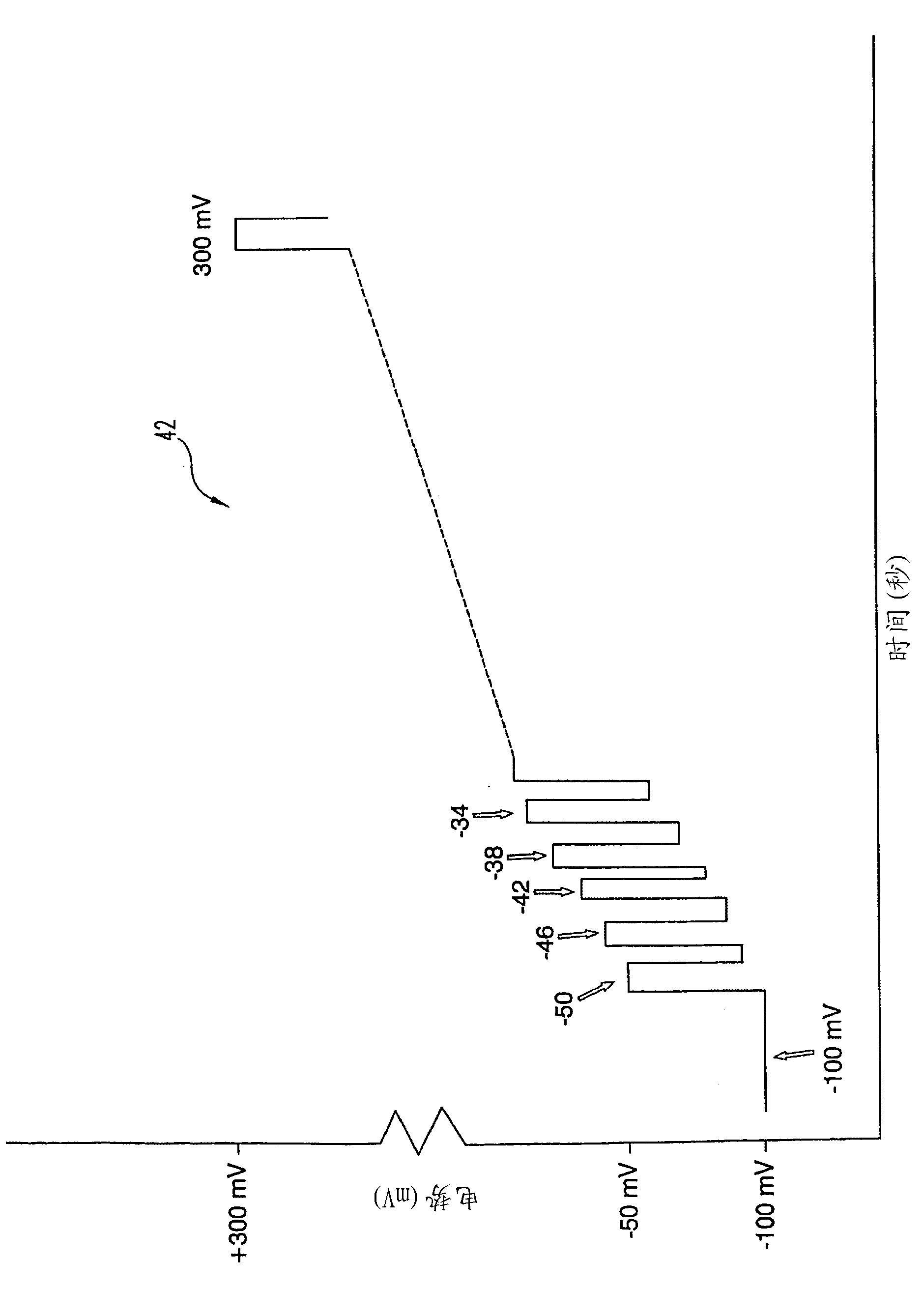
The blood glucose analysis technique and system described herein address the issue of hematocrit interference when rapidly detecting glucose concentrations. It addresses this issue by using a differential pulse voltammetry technique in which short high, frequency voltage pulses are applied to keep the diffusion layer within the reagent of the working electrode, and the pulses are applied in a limited voltage window (or range) that is below the peak, diffusion-limited current. The readings below the peak are then used to determine glucose concentrations. With this technique, glucose concentrations can be determined relatively fast (e.g., within 5 seconds) and independently of the hematocrit levels of the fluid being analyzed.
Owner:F HOFFMANN LA ROCHE & CO AG
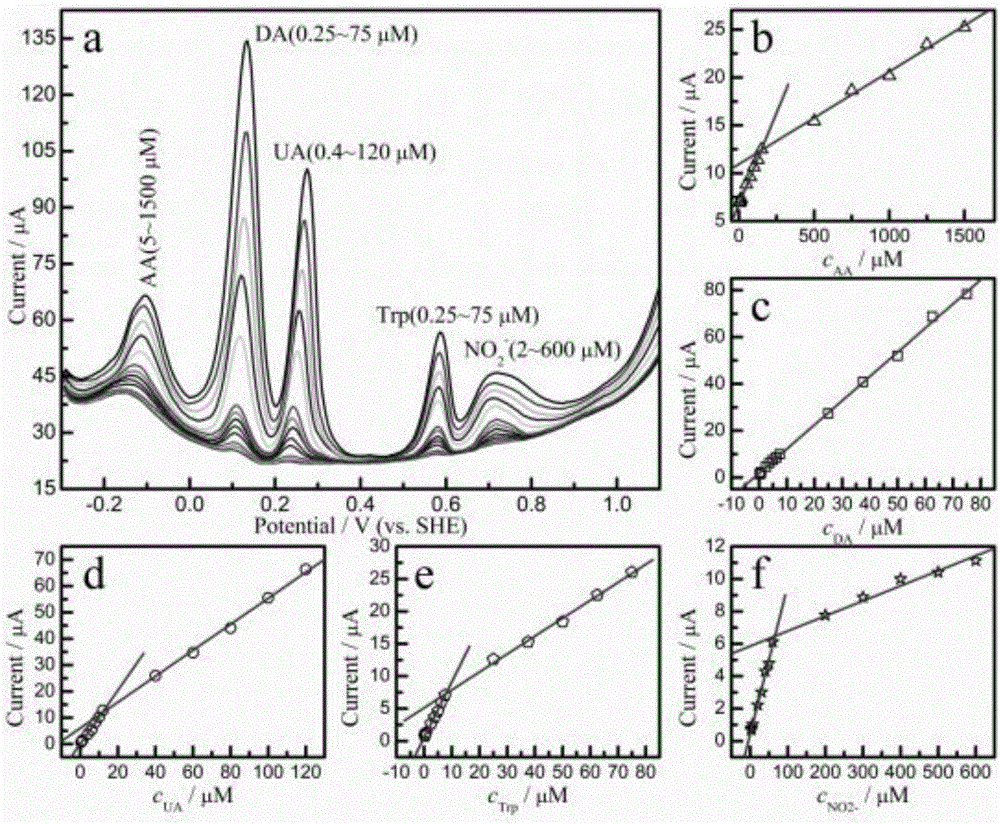
Method for simultaneously detecting ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, tryptophan and nitrite
ActiveCN105758905ARapid detection of concentrationWide detection linear rangeMaterial electrochemical variablesTryptophanPeak current
The invention discloses a method for simultaneously detecting ascorbic acid, dopamine, uric acid, tryptophan and nitrite.The method is implemented by a three-electrode system sensor with a working electrode, a reference electrode and a counter electrode.The working electrode is made of graphene / tantalum, graphene / boron-doped diamond films and graphene / titanium; the reference electrode can be a saturated calomel electrode or an Ag / AgCl electrode or a mercury / mercurous sulfate electrode; the counter electrode is a platinum sheet electrode.The method includes acquiring working curves by the aid of mixed solution of five to-be-detected materials with different concentrations and differential pulse voltammetry; diluting human serum; adjusting the concentrations until the concentrations are within the ranges of the working curves; comparing peak currents obtained by the aid of the differential pulse voltammetry to the working curves to obtain the concentrations of the five to-be-detected materials in the serum.The method has the advantages that characteristics of the concentrations of the five to-be-detected materials can be quickly simultaneously detected, and the method is high in sensitivity and low in detection limit.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
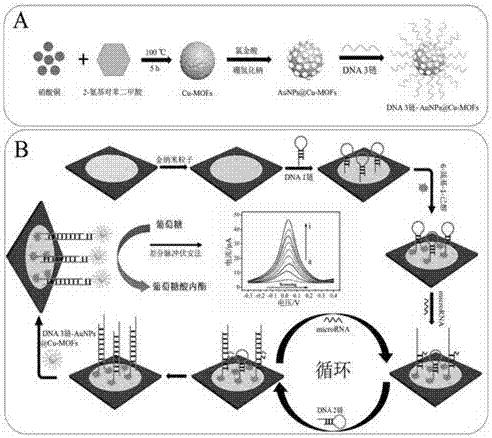
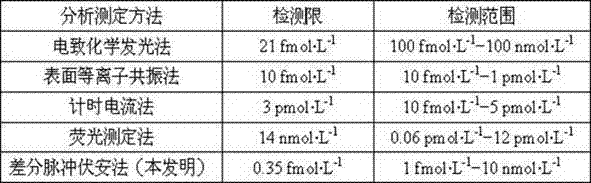
Metal organic frame material signal amplification electrochemical analysis paper chip sensor
InactiveCN107478701ARealize electrochemical signal amplificationSimple preparation stepsMaterial electrochemical variablesHybridization reactionD-Glucose
The invention discloses a metal organic frame material signal amplification electrochemical analysis paper chip sensor and a method thereof for measuring microRNA. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a paper chip three-electrode system of which the surface is modified by nanogold particles; starting a chain hybridization reaction by adding microRNA while modifying the electrode surface with a functionalized metal organic frame material; dropwise adding a glucose-containing buffer solution in the detection area; through a catalytic reaction between the functionalized metal organic frame material and the glucose, realizing signal amplification and high-sensitivity detection of microRNA by a differential pulse voltammetry.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Electrochemical detection method of cocaine based on rolling circle amplification and supramolecular aptamer
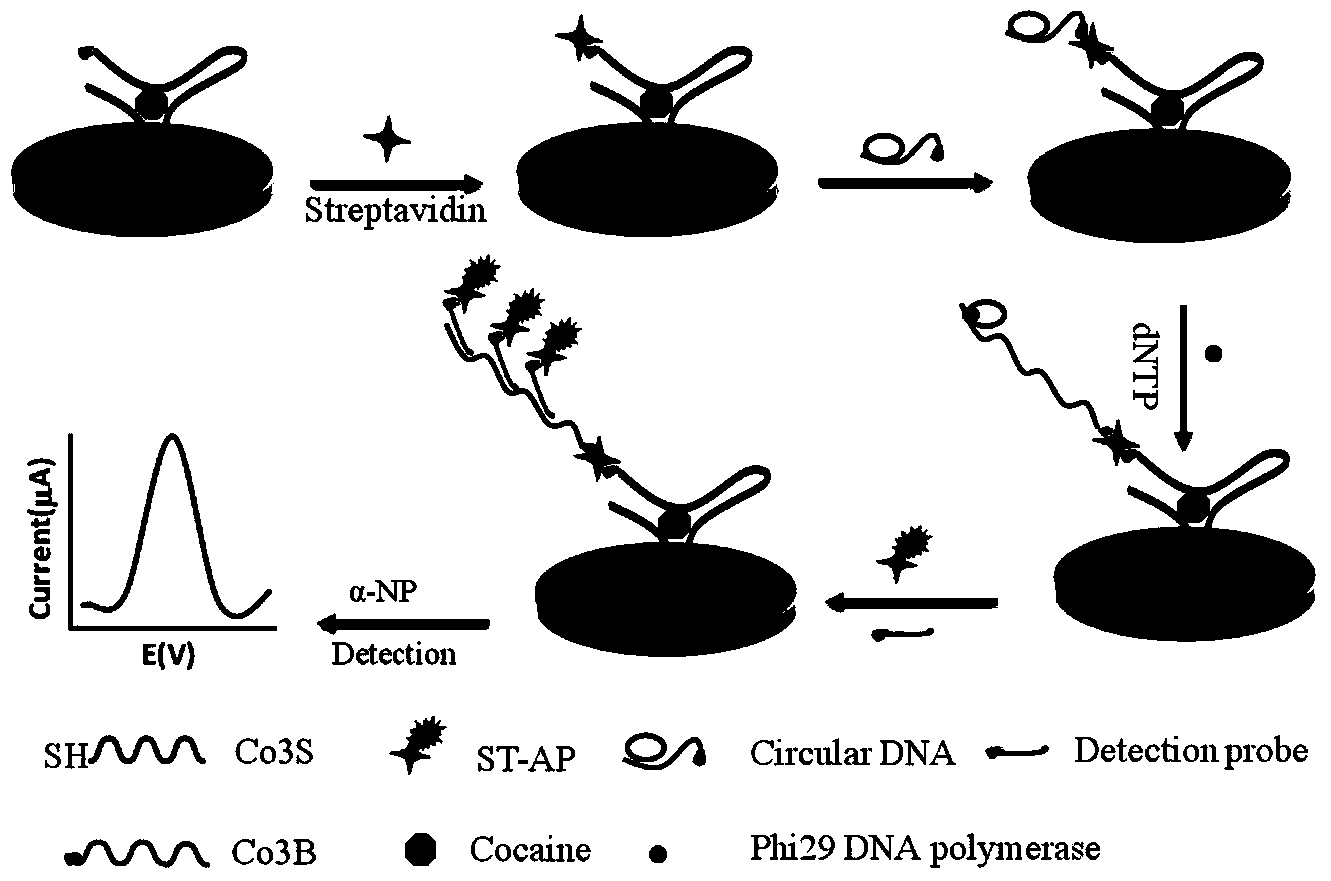
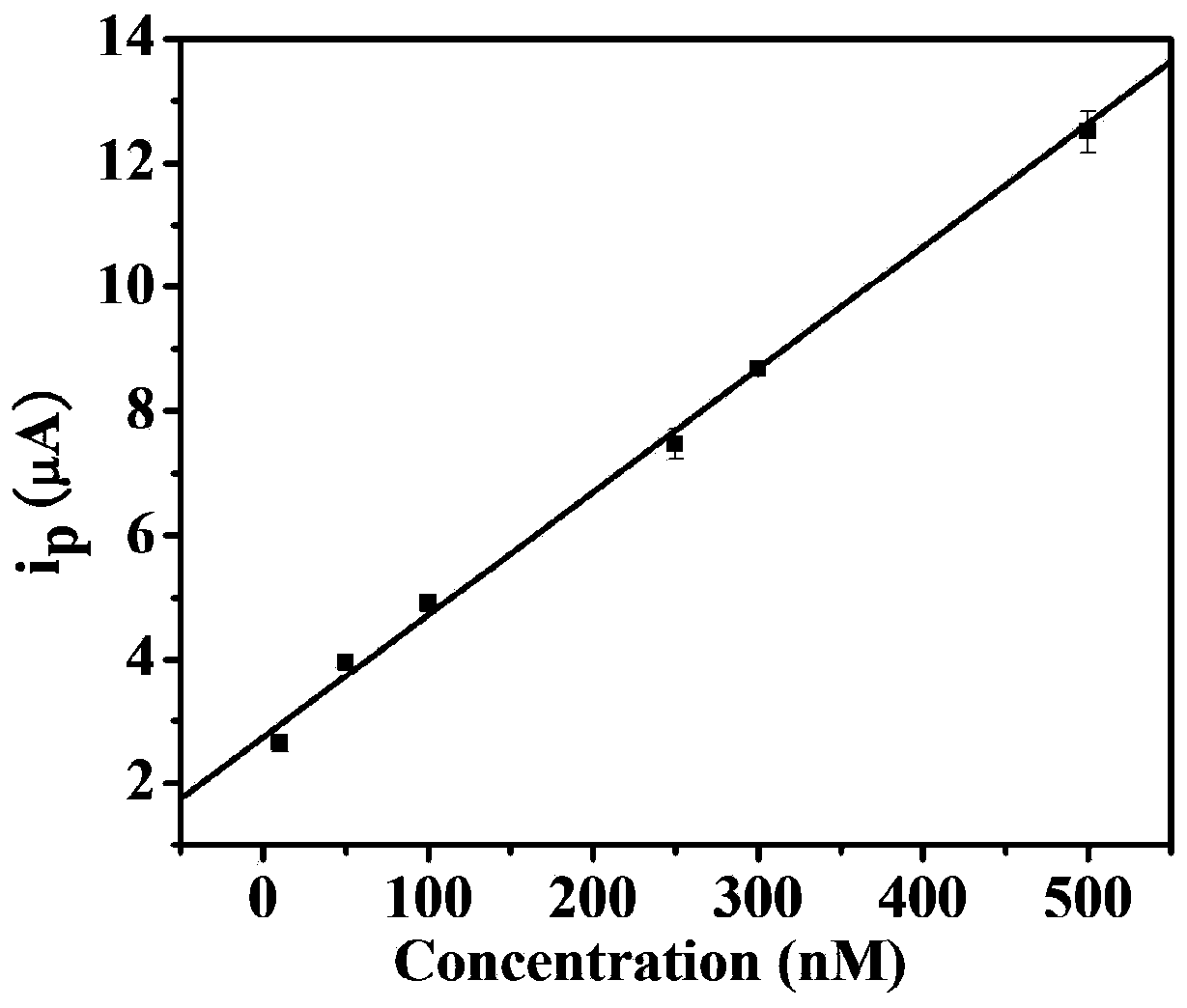
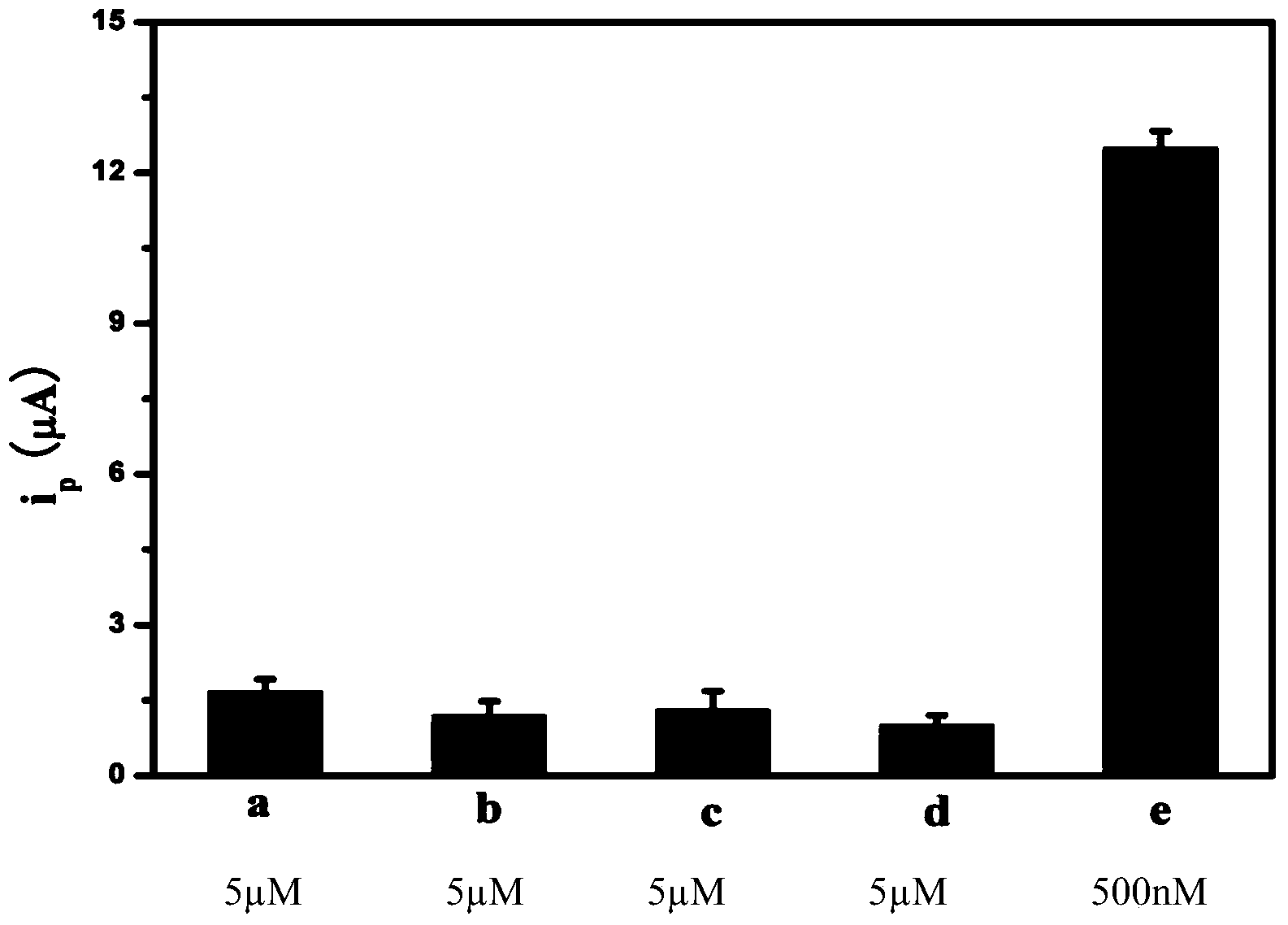
InactiveCN103630598AHigh sensitivityImprove featuresMaterial electrochemical variablesBiotin-streptavidin complexAptamer
The invention discloses an electrochemical detection method of cocaine based on rolling circle amplification and a supramolecular aptamer. The method comprises the steps of dropwise adding an aptamer segment Co3S onto a cleaned gold electrode, taking out for sealing after overnighting in a refrigerator, dropwise adding an aptamer segment Co3B and a sample to be detected on the gold electrode, after reaction at 37 DEG C, dropwise adding a streptavidin solution for incubation, then adding a cyclized DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) solution for incubation, performing rolling circle amplification, adding a detection probe for hybridization and performing DPV (differential pulse voltammetry) signal detection. The method utilizes the rolling circle amplification and the supramolecular aptamer for electrochemical detection of the cocaine for the first time, greatly improves sensitivity and specificity of cocaine detection, and allows a linear detection range to reach 10-500nM. The streptavidin solution and cyclized DNA in the same volume and at the same concentration are utilized, an identification element and an amplifier element are separated, a blank signal is decreased by a bridge connection effect of streptavidin is only utilized, and the sensitivity and the linear range of the detection are greatly improved and extended.
Owner:CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com