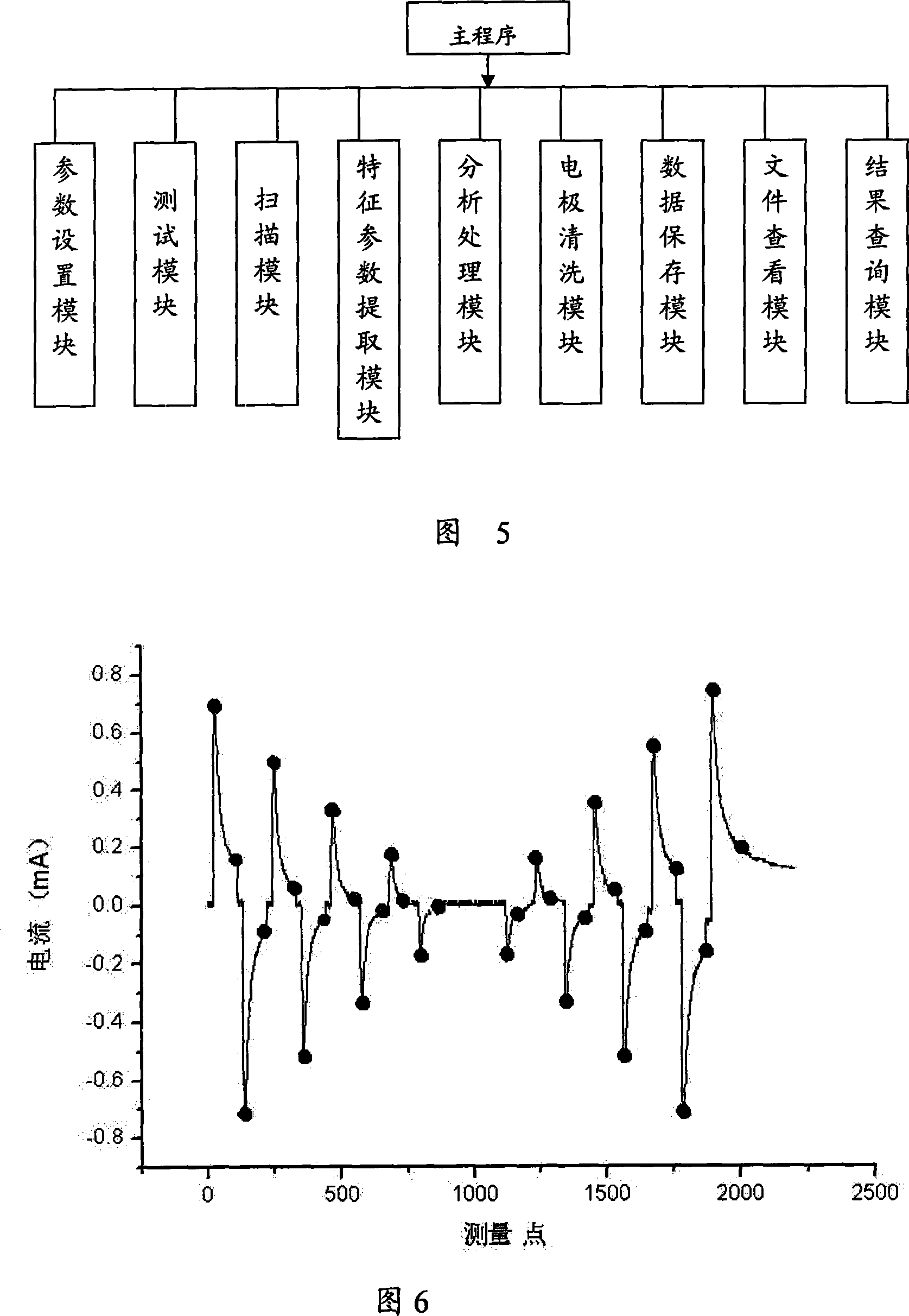
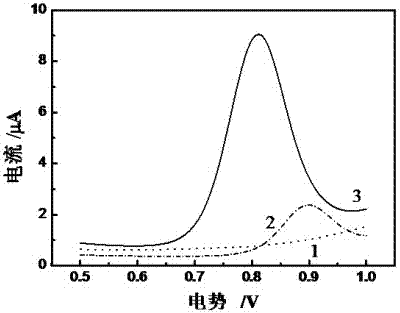
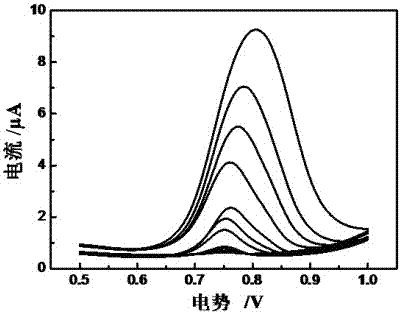
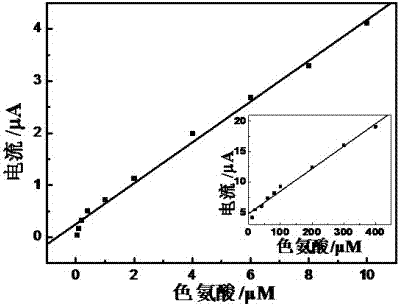
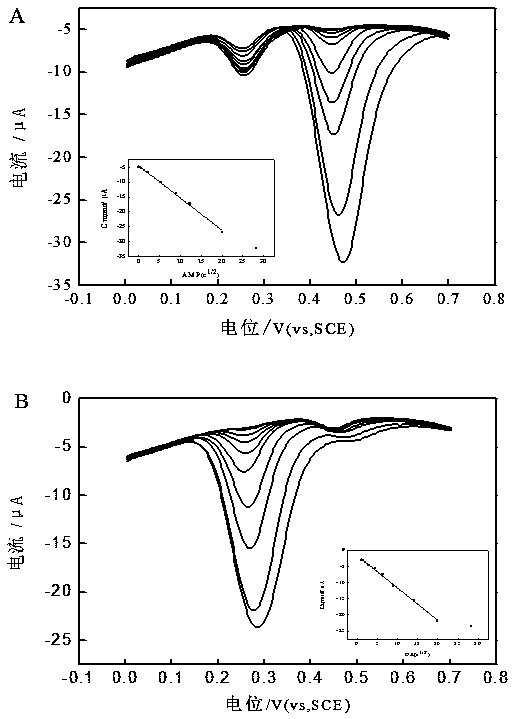
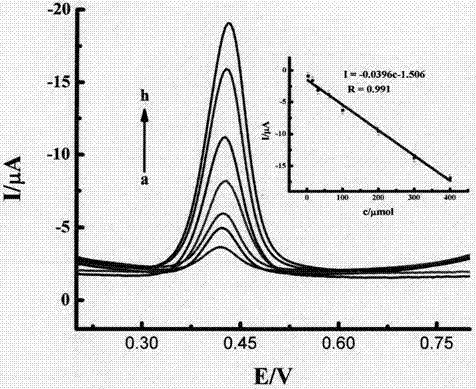
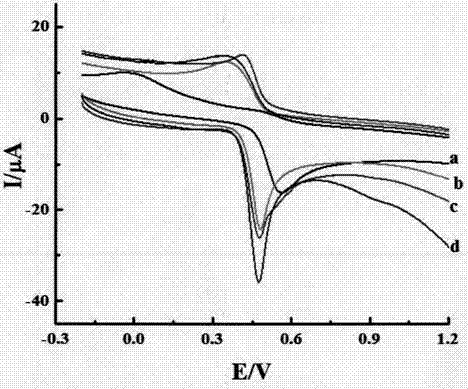
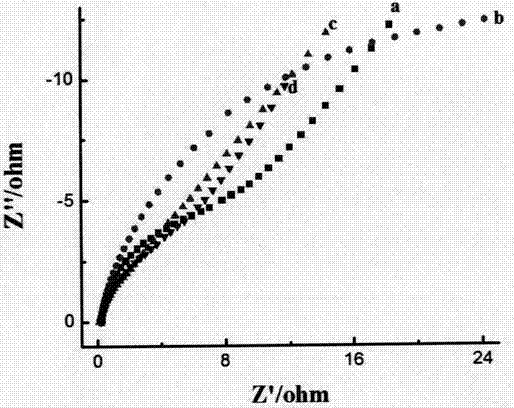
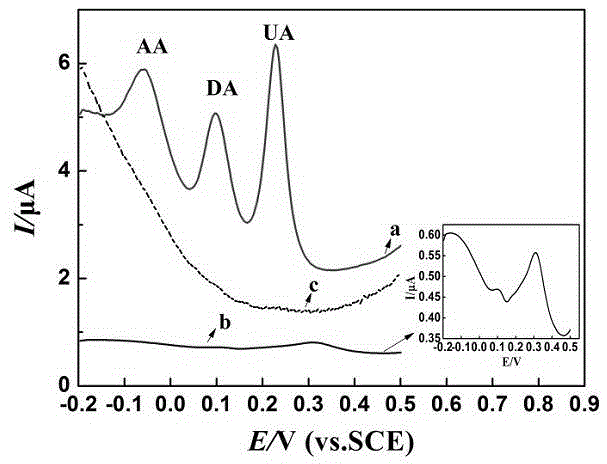
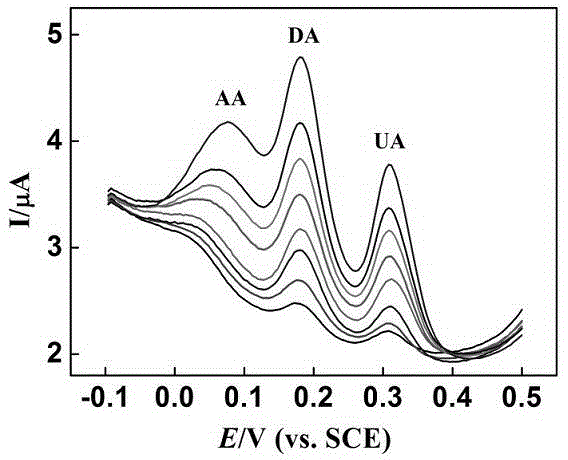
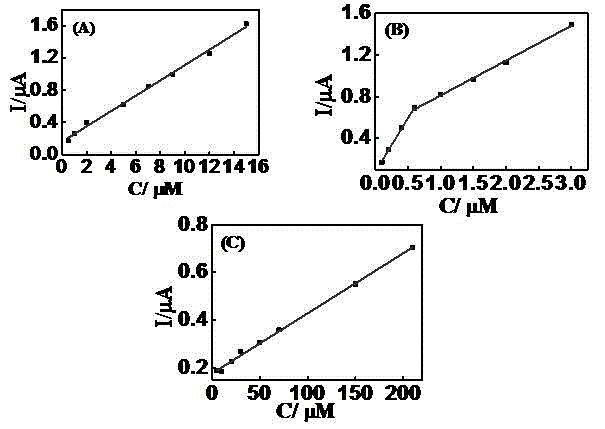
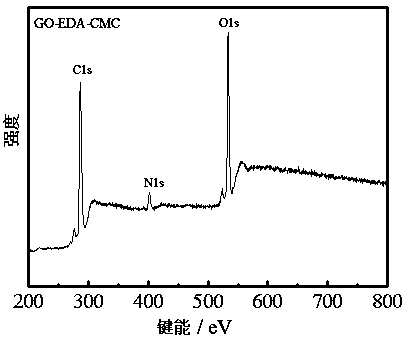
Patents
Literature
195 results about "Pulse voltammetry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Pulse voltammetry utilizes a regularly increasing pulse height that is applied at periodic intervals. In pulse and differential pulse polarography the pulses are applied just before the mercury drop falls from the electrode. Typically the pulse is applied for about 50–60 milliseconds; and the current….
Method for producing carbon magma bismuth membrane electrode
InactiveCN101074941AAchieve the purpose of regenerationPotential window widthMaterial electrochemical variablesOrganic solventSample water
A method for preparing chemical modified electrode of carbon paste Bi membrane includes mixing and grinding carbon powder and modifier as well as hydrophobic organic solvent to be carbon paste, packing prepared carbon paste in electrode tube with copper screw bar in proper size to form carbon paste electrode, placing formed carbon paste electrode into sample solution containing with Bi ion and carrying out constant-potential deposit to obtain chemical modified electrode of carbon paste Bi membrane.
Owner:CHANGZHOU INST OF ENERGY STORAGE MATERIALS &DEVICES
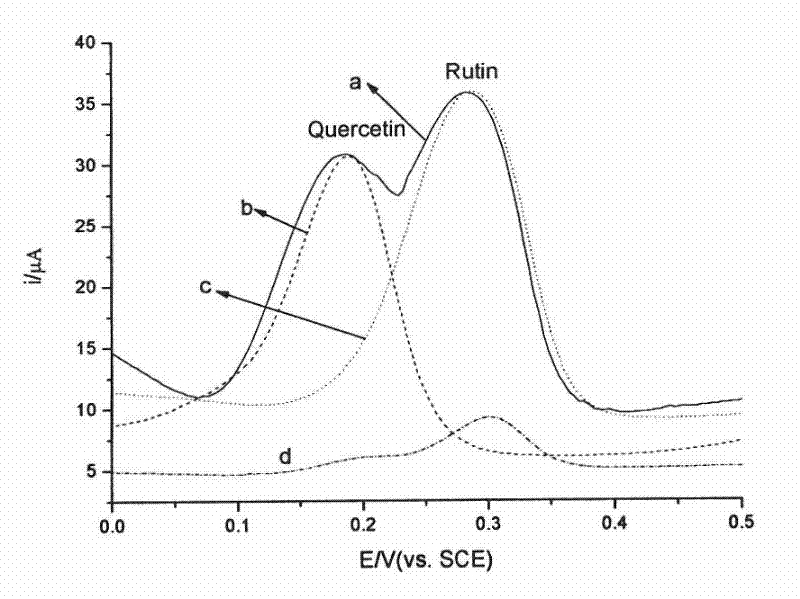
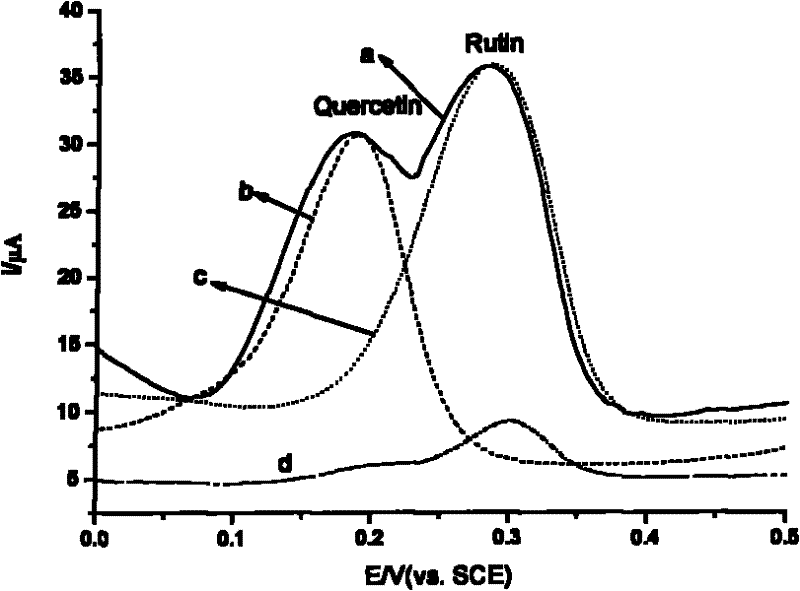
An electrochemical method for the simultaneous determination of rutin and quercetin based on a graphene-modified electrode
ActiveCN102288669AHigh catalytic activityHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesBudDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention discloses an electrochemical method based on a graphene-modified electrode for simultaneous determination of rutin and quercetin. The graphene-modified electrode is used as a working electrode, and cyclic voltammetry and differential pulse voltammetry are adopted for simultaneous determination of the rutin and the quercetin. Since grapheme is used as a modifying material for the electrode, electrochemical separation of two Chinese flavonoids, the rutin and the quercetin can be achieved on the modified electrode, and the contents of the rutin and the quercetin in sophora flower bud can be determined simultaneously through direct electrochemical determination.
Owner:QINGDAO UNIV
Method for detecting concentration of acrylamide in solution
ActiveCN104634853AIncrease surface areaStrong electrochemical signalMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetryGraphene
The invention provides a method for detecting the concentration of acrylamide in a solution. The method comprises the steps of detecting acrylamide in a sample solution by using a three-electrode system and a differential pulse voltammetry; and obtaining the concentration of acrylamide in the sample solution according to a differential pulse voltammetry curve of acrylamide, wherein a working electrode in the three-electrode system is an aminated graphene and single-chain DNA modified electrode. The invention also provides concrete steps for detecting the concentration of acrylamide in the solution and a preparation method of the working electrode. The content of acrylamide in the solution can be rapidly and quantitatively detected, and the detection limit of acrylamide can be up to 5.1*10<-8>mol / L.
Owner:浙江永金生物科技有限公司
Electrochemical electronic tongue based on wide-bard pulse voltammetry
InactiveCN101071117ADetermination of general characteristicsDetermination of concentration contentMaterial electrochemical variablesBroadband pulseAuxiliary electrode
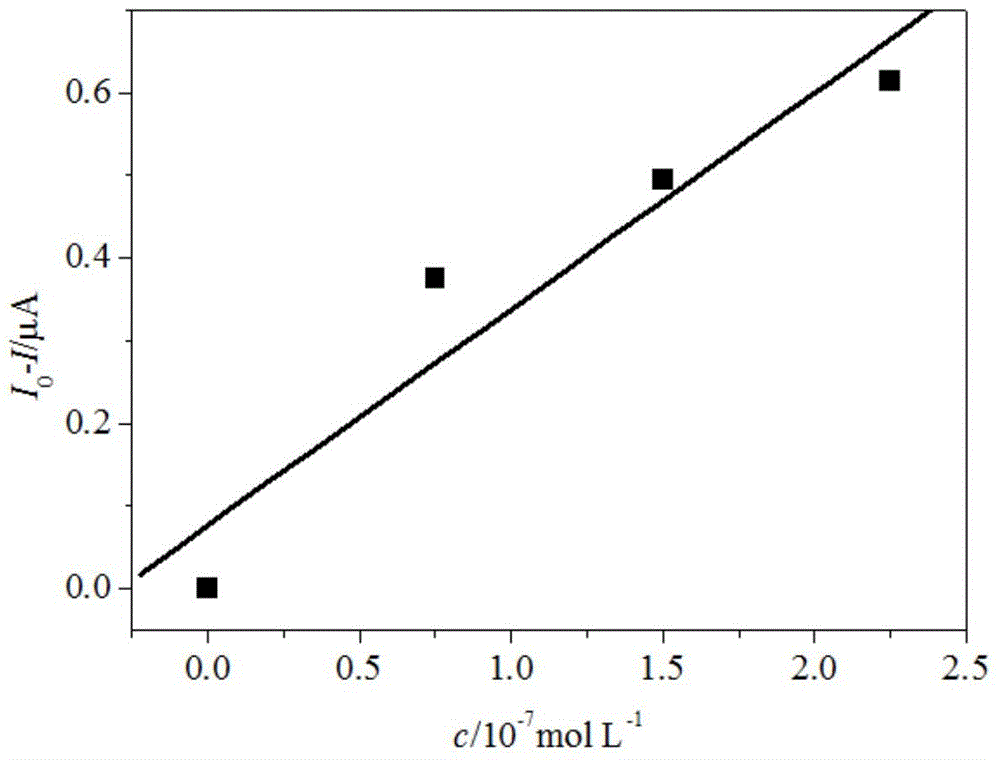
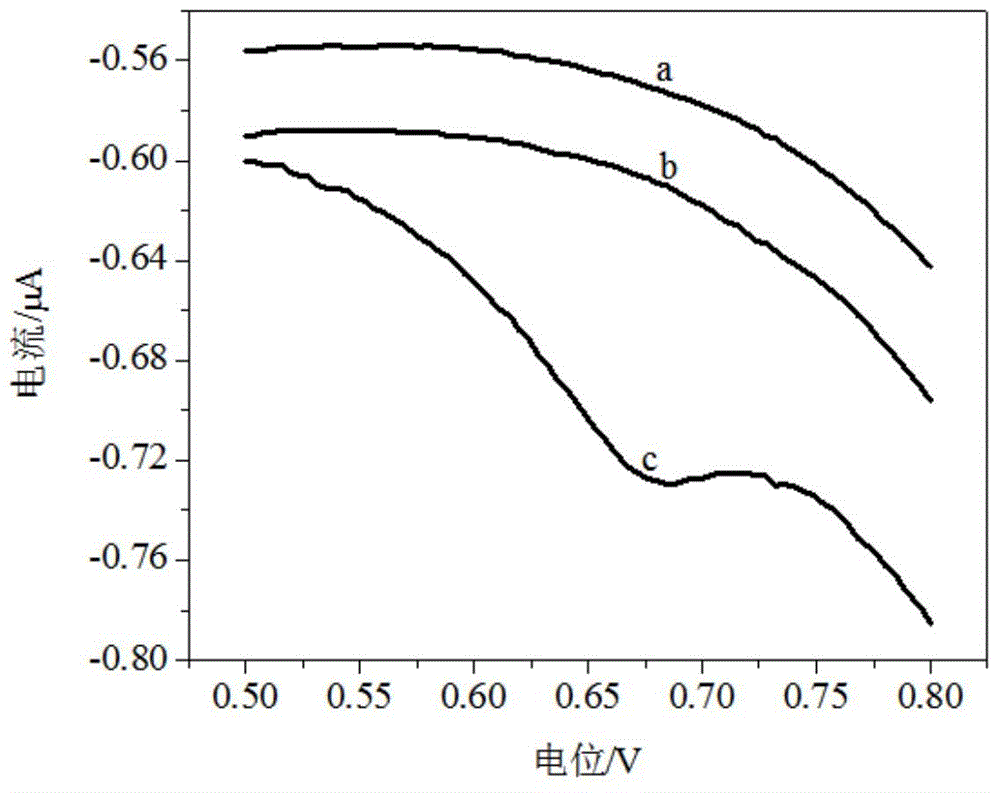
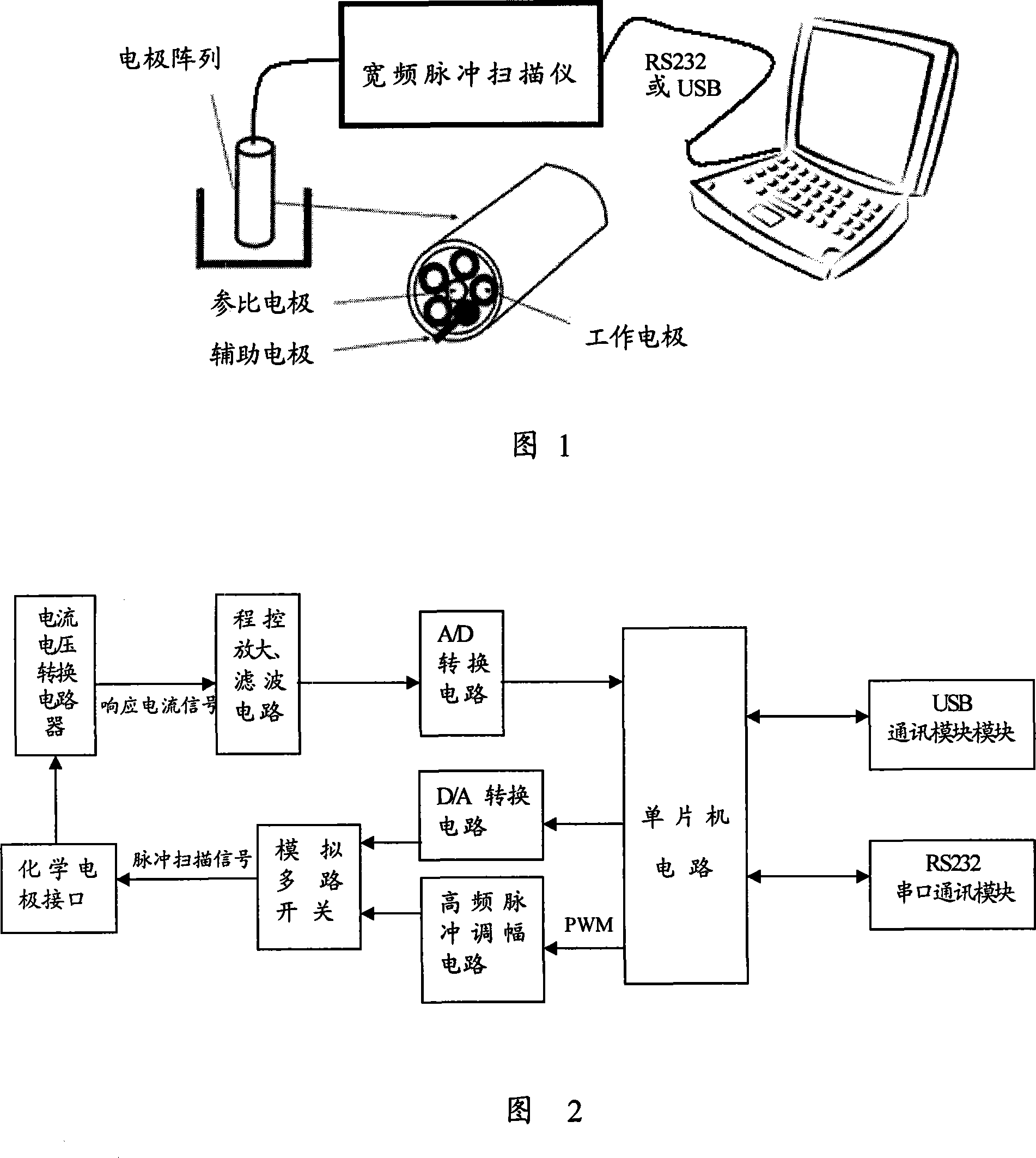
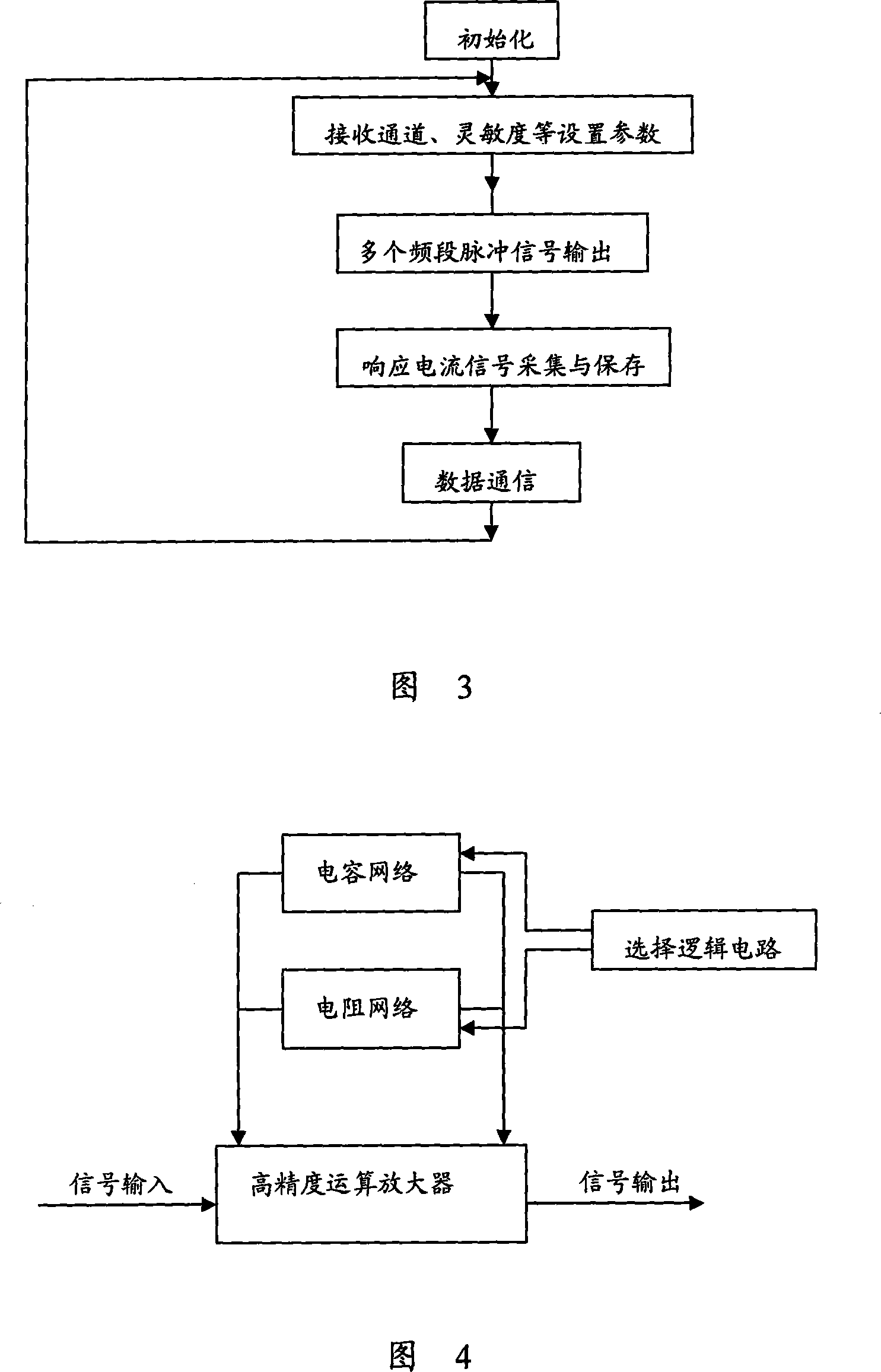
This invention discloses an electrochemical electronic tongue based on broadband pulse voltammetry, composed of the electrode array, broadband pulse scanners and data analysis software. The electrode array is electrochemical electrode group that is made up with the reference electrode, auxiliary electrodes and multi - the work - a multi-channel electrode. The data analysis software is installed on the computer; electrode array will be placed analyte solution system. The broadband pulse scanner output pulse of a number of different scanning frequency signal, and then the signal is imposed on the analyte solution through parameter electrode of electrode array and working electrode. The circuit response signals produced by the solution return to broadband pulse scanner through secondary electrode. The invention can detect overall features of material and the differences between the material characteristics effectively, and has analytical speed, wide frequency range, access informative features.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing electropolymerized sulfosalicylic acid modified glassy carbon electrode and application of glassy carbon electrode in measurement of tryptophan
InactiveCN102507686AIncreased current responseHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesPhosphateSalicylic acid
The invention relates to a method for preparing an electropolymerized sulfosalicylic acid modified glassy carbon electrode, and use of the glassy carbon electrode as a tryptophan electrochemical sensor in high-sensitivity measurement of tryptophan in compound amino acid injection, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical analysis and detection. The invention mainly aims to prepare the electropolymerized sulfosalicylic acid modified glassy carbon electrode to perform sensitive quantitative analysis and measurement on the tryptophan by a differential pulse voltammetry. Experimental results show that: the modified electrode has an obvious sensitization effect on the tryptophan in a phosphate buffer solution at the concentration of 0.1mol / L and the pH of 3.5, and under the optimal conditions, the differential pulse voltammetry is adopted for measurement, and the tryptophan at the concentration in a range of 5.0*10<-8>-4.0*10<-4> and peak current of the tryptophan have a good linear relation, and the detection limit is 4.0*10<-8>. When the method is used for measuring the tryptophan content in a medicine, results are satisfactory.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Electrochemical sensor for adapters and method for detecting chlorpyrifos
InactiveCN107367540AHigh sensitivityLow costMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansChlorpyrifosCarbon nanotube
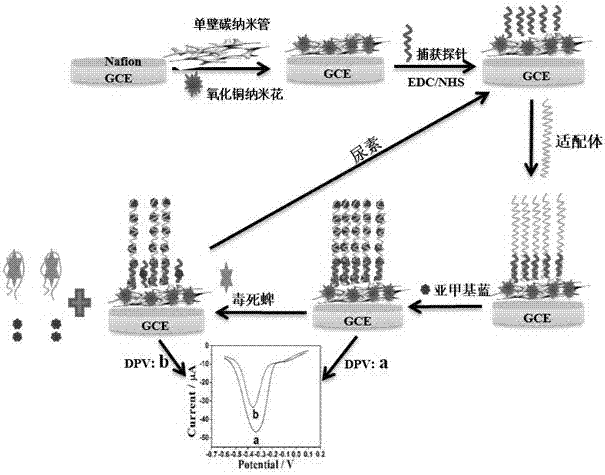
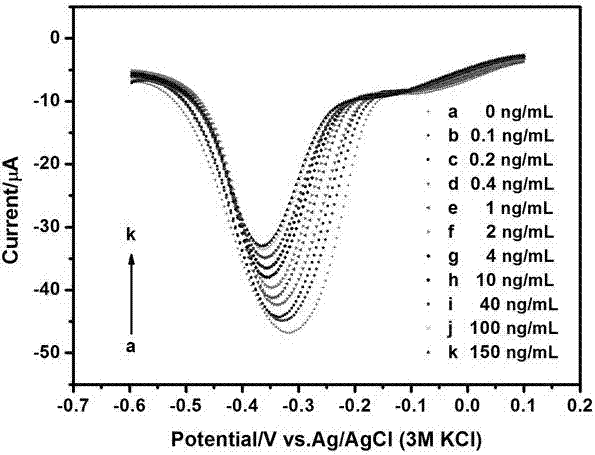
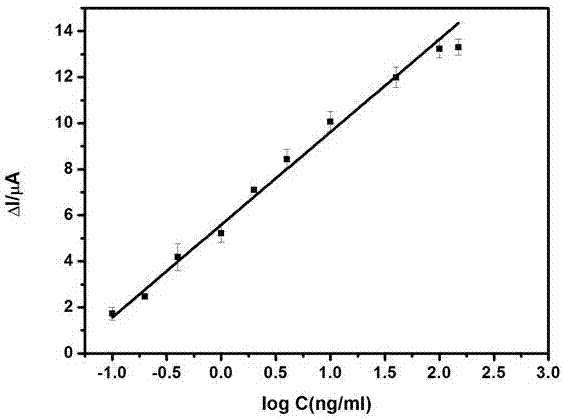
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensor for adapters and a method for detecting chlorpyrifos. The electrochemical sensor adopts a three-electrode system and comprises a first detection layer, a second detection layer and a fixed layer. A preparation method comprises the following steps of: preparing copper oxide nanoflower solution, preparing single-wall carbon nanotube solution, treating base electrodes, activating carboxyl groups, and fixing probes and the adapters; and then manufacturing a standard curve by utilizing a differential pulse voltammetry, and finally calculating out the concentration of the chlorpyrifos in samples according to the standard curve of the chlorpyrifos. The electrochemical sensor and the method disclosed by the invention have the advantages that the detection for the chlorpyrifos is specific, the sensitivity and the selectivity are high, the renewability is achieved, the materials are wide in source, the cost is low, and the preparation method is simple, so that the application prospect is good.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Method for electrochemically detecting concentration of specific single-stranded DNA based on exonuclease and nucleic acid probe
ActiveCN105821132AStrong specificityHigh sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementHaem-haem interactionNanoparticle
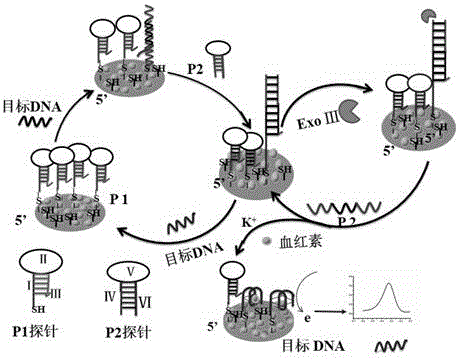
The invention relates to a method for electrochemically detecting concentration of specific single-stranded DNA based on exonuclease and a nucleic acid probe and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. The invention designs and synthesizes two types of hairpin-type probes P1 and P2. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly modifying a gold electrode with gold nanoparticles by adopting 1,6-hexanedithiol (HDT), preparing an AuNPs-HDT-Au electrode, and then modifying the probe P1 onto the electrode; taking a specific single stranded target DNA as a to-be-detected object, so that the probes P1 and P2 can coexist when no target DNA exists, and the target DNA can trigger two independent reaction cycles when the target DNA, the probe P2 and the exonuclease ExoIII exist; and finally when heme exists, generating a strong signal under the interaction of a G-tetraplex sequence of the probe P1 on the surface of the electrode and heme, and detecting the target DNA by adopting a differential pulse voltammetry, wherein a peak current signal and the target DNA concentration are correlated in a certain concentration range, so that detection on the target DNA concentration is realized. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity and strong specificity.
Owner:北京聚合美生物科技有限公司
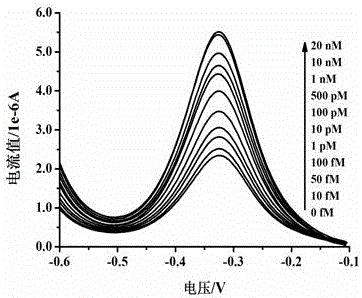
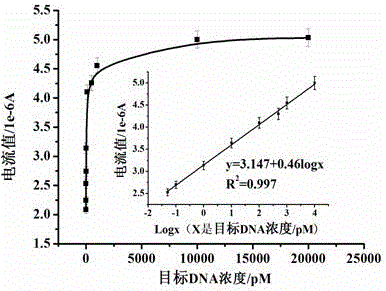
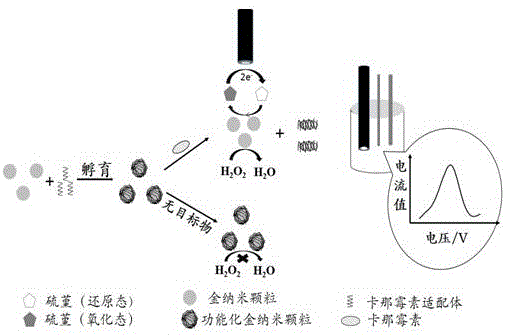
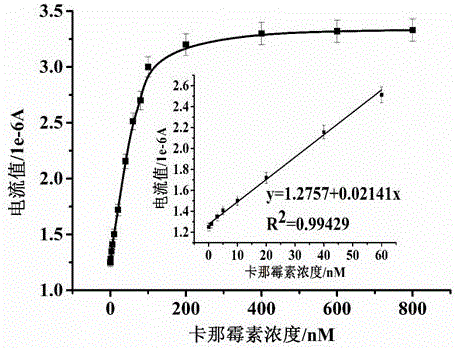
Electrochemical detection method for detecting kanamycin residues based on nucleic acid aptamer and nano analogue enzyme
ActiveCN105784799AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityMaterial electrochemical variablesPeroxidaseTyrosine
The invention provides an electrochemical detection method for detecting kanamycin residues based on a nucleic acid aptamer and a nano analogue enzyme and belongs to the technical field of analytical chemistry. Gold nano-particles are synthesized by reducing chloroauric acid through tyrosine, and hydrogen peroxide and reduced-state thionine are catalyzed to react to generate oxidized-state thionine; and the thionine can be detected through a difference pulse voltammetry. The gold nano-particles are modified through utilizing a kanamycin specific aptamer; and the aptamer is adsorbed on the surfaces of the gold nano-particles so that the peroxidase activity is inhibited. When a target object kanamycin exists, the aptamer can be competitively replaced from the surfaces of the gold nano-particles to form a compound, so that the peroxidase activity is recovered. The detection of the kanamycin can be realized through detecting a relation between a reduction peak current value of the oxidized-state thionine and an antibiotic concentration by utilizing the difference pulse voltammetry. The method provided by the invention has good repeatability, good stability and high sensitivity, and can be used for effectively detecting kanamycin residues in food samples.
Owner:上海谱尼医学检验实验室有限公司
Manufacturing method of L-glutamic-acid-modified carbon fiber microelectrode, and application thereof in detecting neurotransmitters
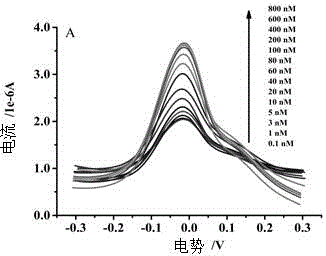
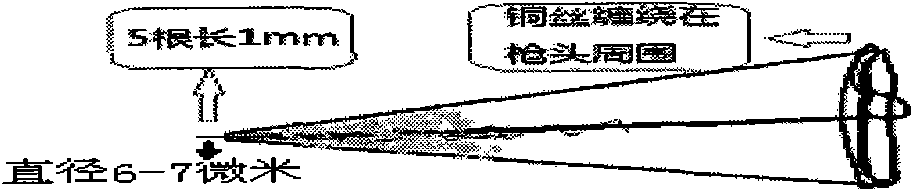
The invention relates to a project in which a research is carried out for simultaneously detecting dopamine and epinephrine by using carbon fiber modified microelectrode with a diameter of 7mum. As a result, L-glutamic-acid-modified carbon fiber microelectrode has a substantial catalytic effect upon electric oxidation-reduction of dopamine and epinephrine. In a phosphate buffer solution with a pH value of 6.0, a mixed solution of dopamine and epinephrine is detected by using a cathode differential pulse voltammetric method, and two relatively strong oxidation peaks are simultaneously detected. The peak with an electric potential located at 0.24V is dopamine, and the peak with an electric potential located at -0.14V is epinephrine. The peak currents thereof respectively have good linear relationships with the concentrations of dopamine and epinephrine. The linear range of dopamine is 5.0*10<-4>-1.0*10<7>mol / l, and a detection limit is 1.0*10<-8>mol / l. The linear range of epinephrine is 2.5*10<-4>-1.0*10<-5>mol / l, and a detection limit is 1.0*10<-7>mol / l.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
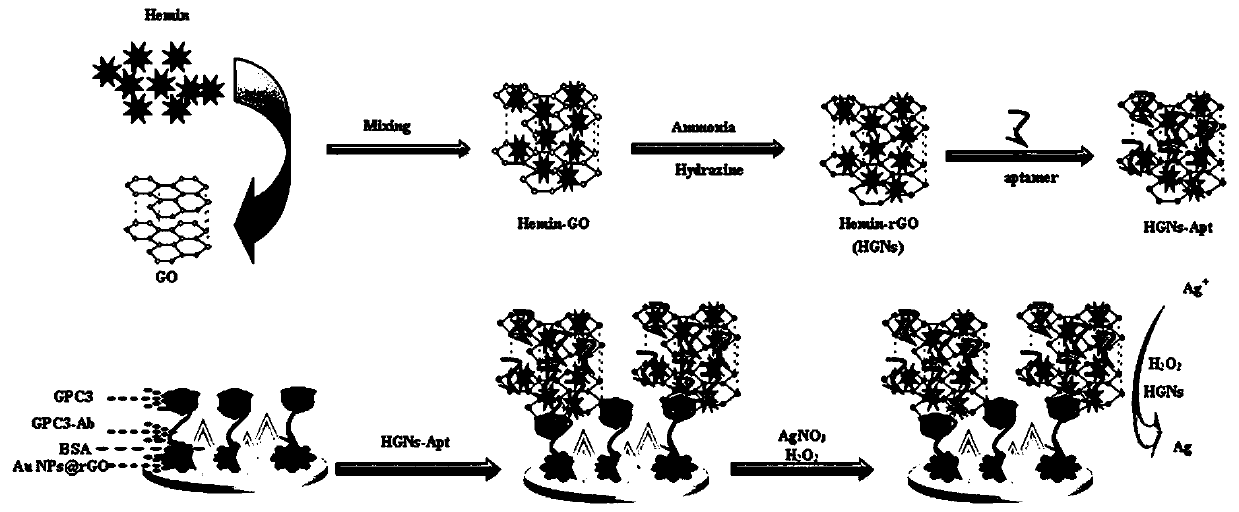
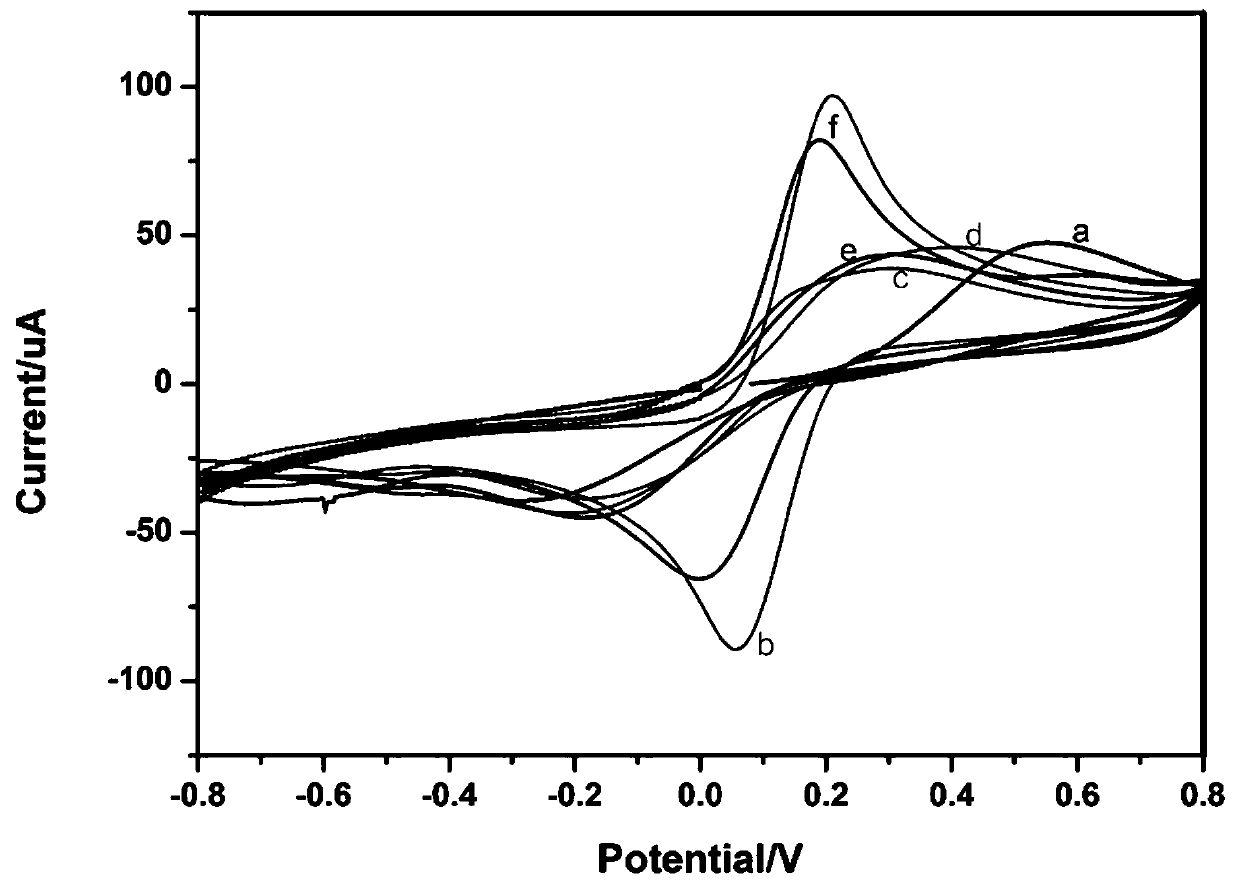
Peroxidase catalytic silver deposition-based method for detecting GPC3
ActiveCN110823980AAchieving Sensitive DetectionHigh sensitivityBiological testingMaterial electrochemical variablesPeroxidaseCatalytic effect
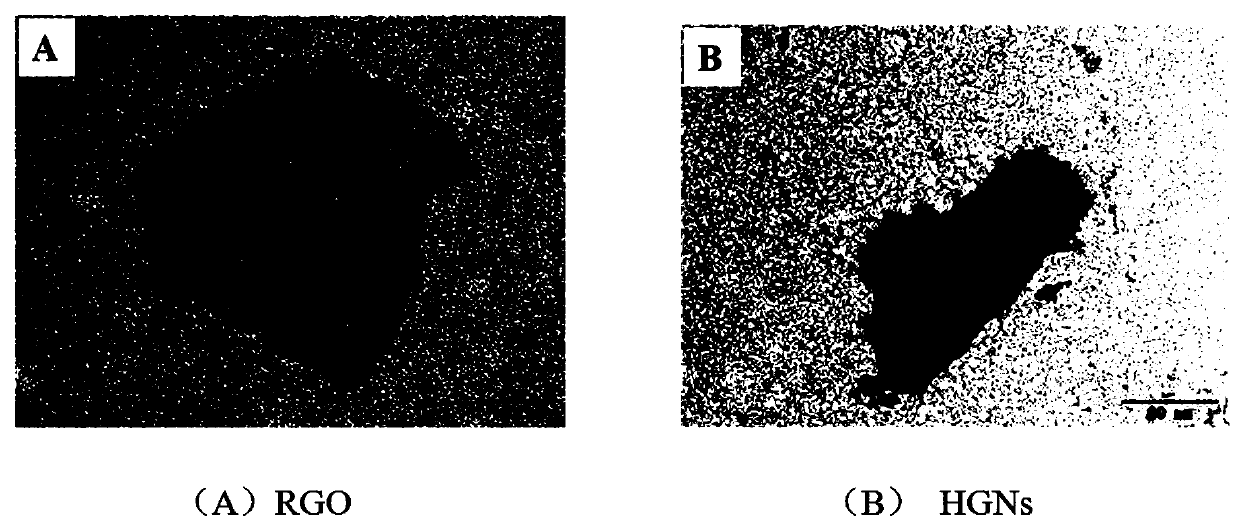
A peroxidase catalytic silver deposition-based method for detecting GPC3 comprises the steps of building an electrochemical nanometer sensor, activating and modifying a silk-screen printed electrode,building a biological sensing interface, drawing a working curve of the GPC3 and detecting a to-be-detected sample. An HGNs-Apt signal probe is fabricated by taking HGNs as a carrier, and an Apt-GPC3-HGNs-Apt sandwiched electrochemical nanometer aptamer sensor is built; silver ions in a solution are reduced to metal silver deposited on a surface of the electrode by H2O2 and by means of a catalyticeffect of peroxidase of HGNs, the deposition quantity of Ag is obtained according to quantity of GPC3 protein, and quantization is performed by differential pulse voltammetry (DPV); and current response of Ag and GPC3 concentration are in favorable positive correlation within a range being 10.0-100.0 micrograms per mL, and GPC3 detection is achieved.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
Preparation and application of HP-beta-CD (hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin) functionalized GO (graphene oxide) composite material
InactiveCN107474324ANot easy to fall offThe peak current value dropsMaterial electrochemical variablesEnantiomerTryptophan
The invention discloses preparation and application of HP-beta-CD (hydroxypropyl beta-cyclodextrin) functionalized GO (graphene oxide) chiral composite material, and belongs to the fields of material preparation and electrochemical application. The preparation comprises the following steps of firstly, enabling beta-CD and propylene oxide to react under the alkaline condition, so as to prepare the HP-beta-CD; then, performing in-situ reduction on the GO and the HP-beta-CD by hydrazine hydrate, so as to obtain the HP-beta-CD functionalized GO (rGO-HP-beta-CD) composite material; finally, dripping and spraying the rGO-HP-beta-CD composite material to the surface of a GCE (glassy carbon electrode), so as to obtain a rGO-HP-beta-CD / GCE chiral electrochemical sensor. The preparation has the advantage that the tryptophan enantiomer is chirally identified by a DPV (differential pulse voltammetry) method, so that the stronger identifying ability on the D-tryptophan by the chiral electrochemical sensor is found.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
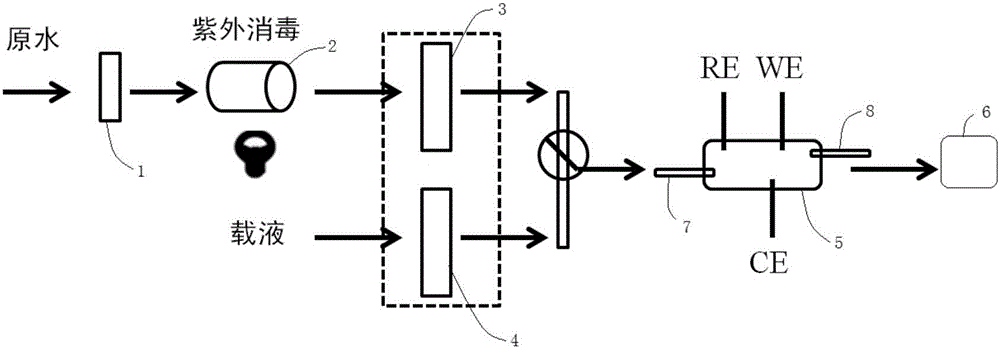
Detection system and method for real-time online monitoring of various heavy metal ions
ActiveCN106841334AHigh detection sensitivityImprove detection accuracyGeneral water supply conservationPreparing sample for investigationPhysical chemistryCarrier fluid
A detection system and method for real-time online monitoring of various heavy metal ions are provided. Heavy metal ion standard liquids with different concentrations are injected into the detection system by means of mobile sampling; standard curves of the different heavy metal ions are measured through differential pulse voltammetry; an actual water sample is subjected to online real-time detection; the actual water sample and a carrier liquid are mixed, the mixture is charged into the detection system, a detection curve of the actual water sample is acquired through differential pulse voltammetry, and the detection curve of the actual sample is compared with the standard curves to measure the types and concentrations of the heavy metals in the actual water sample. The heavy metal sensor technique based on differential pulse voltammetry according to the invention allows various heavy metal ions to be detected at the same time, has high detection sensitivity and accuracy, takes several minutes for detection, and may meet the common requirements for online and quick response.
Owner:BAOJI UNIV OF ARTS & SCI
Method used for detecting acrylamide concentration of solutions
ActiveCN105044194AIncreased sensitivityReduce testing costsMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetrySingle strand dna
The invention discloses a method used for detecting acrylamide concentration of solutions. The method comprises following steps: a three-electrode system, and differential pulse voltammetry are adopted to detect acrylamide in a solution to be detected, and the concentration of acrylamide is obtained based on an acrylamide linear equation, wherein a working electrode of the three-electrode system is a glassy carbon electrode modified with carboxylated grapheme and a characteristic single-stranded DNA, and the sequence of the characteristic single-stranded DNA is 5'-AAAAAAAAAGGAAAAAAAAA-(CH2)6-SH-3'. According to the method, differential pulse voltammetry is adopted for high sensitive detection on acrylamide; detection limit on acrylamide concentration can be as low as 1mol / L; operation is simple; detection is rapid; sensitivity and selectivity are high; and application prospect is promising.
Owner:NINGBO XIANAN CHEM
Electrochemical method for simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone based on graphene/chitosan-modified electrode
InactiveCN103063728AImprove stabilityImprove anti-interference abilityMaterial electrochemical variablesPeak currentDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention discloses an electrochemical method for simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone based on a graphene / chitosan-modified electrode. The electrochemical method utilizes a graphene / chitosan-modified glassy carbon electrode as a working electrode and realizes simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone by the cyclic voltammetry and the differential pulse voltammetry. The glassy carbon electrode is modified by graphene and chitosan so that two isomers of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone are subjected to electrochemical separation on the modified electrode and peak current intensity is large and thus simultaneous determination of tetrachlorocatechol and tetrachlorohydroquinone contents is realized by the direct electrochemical determination method.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method and application of nitrogen-doped carbon nano tube composite L-cysteine modified glassy carbon electrode
InactiveCN106290519AHigh catalytic activityIncreased current responseMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDifferential pulse voltammetrySodium sulfate
The invention discloses a preparation method and application of a nitrogen-doped carbon nano tube composite L-cysteine modified glassy carbon electrode. The preparation method mainly comprises the following steps: preparing an electrodeposit nitrogen-doped carbon nano tube and an electropolymerization L-cysteine modifed glassy carbon electrode; and performing sensitive quantitative analysis determination on theine and caffeine by use of a differential pulse voltammetry method. Experimental results indicate that in a 0.01mol / L sulfuric acid-sodium sulfate buffer solution with the pH value of 1.70, the modified electrode has obvious catalysis and sensitivity increasing effects on theine and caffeine; under optimum conditions, the differential pulse voltammetry method is adopted for measurement, the concentrations of theine and caffeine are respectively within a range of 0.1-70.0 microns and a range of 0.4-140.0 microns and have good linear relationship with a peak current, and the detection limits respectively reach 0.04 and 0.20 microns. The method is used for measuring contents of theine and caffeine in a theine slow-release tablets and a Coke sample, and the results are satisfactory.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Construction and application of electrochemical sensor based on copper porphyrin base covalence organic frame material
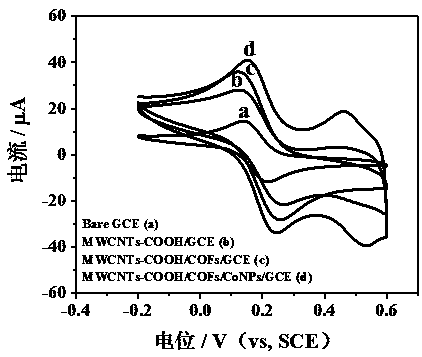
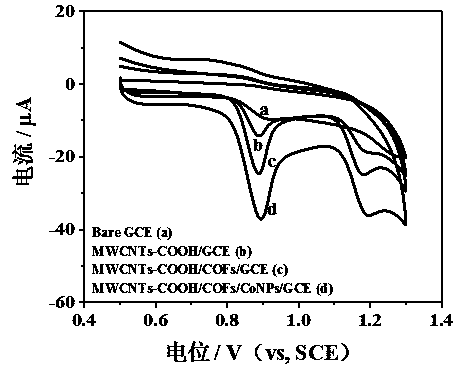
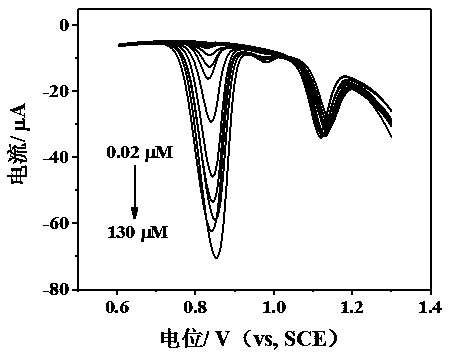
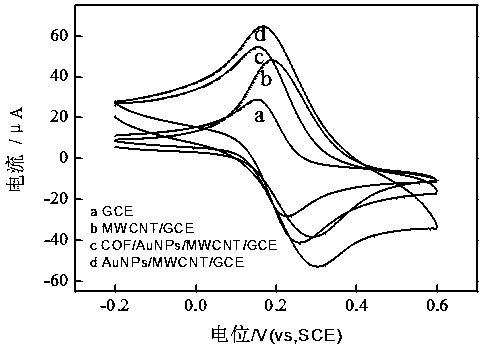
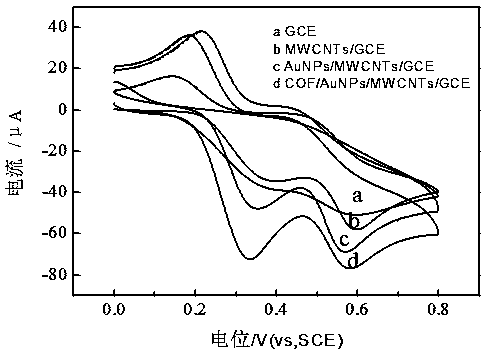
The invention provides preparation of an electrochemical sensor based on a copper porphyrin base covalence organic frame material. Dispensing parts are adopted for modifying a bare electrode through carboxylic carbon nano-tubes, the copper porphyrin base covalence organic frame material is modified through a circular voltmeter-ammeter method, then, a constant potential deposition method is used for depositing metal cobalt nano-particles CoNPs on the surface of the modified electrode, the obtained modified electrode is the electrochemical sensor MWCNTs-COOH / CuP-SQ COFs / CoNPs / GCE based on the copper porphyrin base covalence organic frame material. The electrochemical sensor is adopted as a working electrode, a platinum electrode is adopted as a counter electrode, a saturated calomel electrode is adopted as a reference electrode, and a differential pulse voltmeter-ammeter method is adopted for simultaneously detecting guanine and adenine. The constructed electrochemical sensor has the advantages of being high in sensitivity, low in detection limit, wide in linear range, good in stability, high in interference resistance and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Bisphenol A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN106018530AHigh sensitivityPracticalMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetryGraphene
The invention belongs to the electrochemical detection technical field, and discloses a molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for detecting bisphenol A and a preparation method and an application thereof. A glassy carbon electrode modified by a gold and reduced graphene oxide nano composite material is used as a working electrode, a poly-o-phenylenediamine and bisphenol A mixed film is prepared by cyclic voltammetry, and finally, the bisphenol A is eluted to obtain the molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor. The content of bisphenol A in a soil sample is detected by differential pulse voltammetry, and compared with a high performance liquid chromatography method, the methods have good correlation. The imprinted electrochemical sensor has the characteristics of fast response, high sensitivity, strong selectivity, wider linear range, high practicability, easy popularization and the like.
Owner:GUANGDONG UNIV OF TECH
Polydopamine-coated carbon nanotube enhancement ascorbic acid/glucose fuel cell
ActiveCN107768692AImprove bindingHigh catalytic activityCell electrodesFinal product manufactureCarbon nanotubeDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention belongs to the technical field of a fuel cell, and discloses a polydopamine-coated carbon nanotube enhancement ascorbic acid / glucose fuel cell. Dopamine is subjected to electrochemical polymerization on a carbon nanotube electrode by adopting a continuous differentiating pulse voltammetry, and an ordered polydopamine / carbon nanotube electrode is prepared and obtained; and next, by taking the polydopamine / carbon nanotubes as an electric catalyst of a negative electrode and a positive electrode, electrocatalytic oxidation of a low-cost non-enzymatic catalyst in a neutral environment on ascorbic acid and glucose is realized, and the high-performance ascorbic acid / glucose fuel cell is researched; and the established fuel cell has the advantages of low cost, environment protectionand safety, high biological compatibility, high power density and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
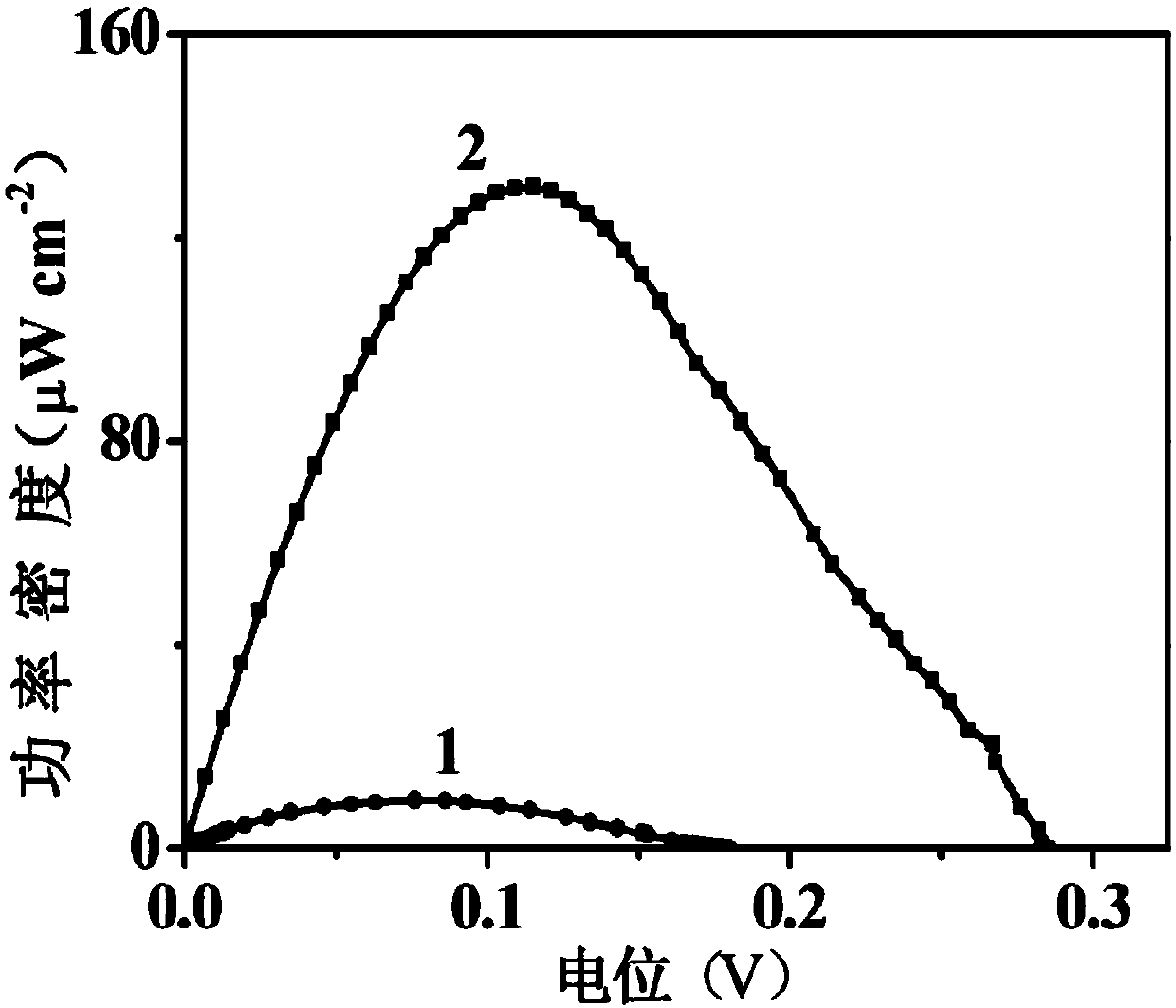
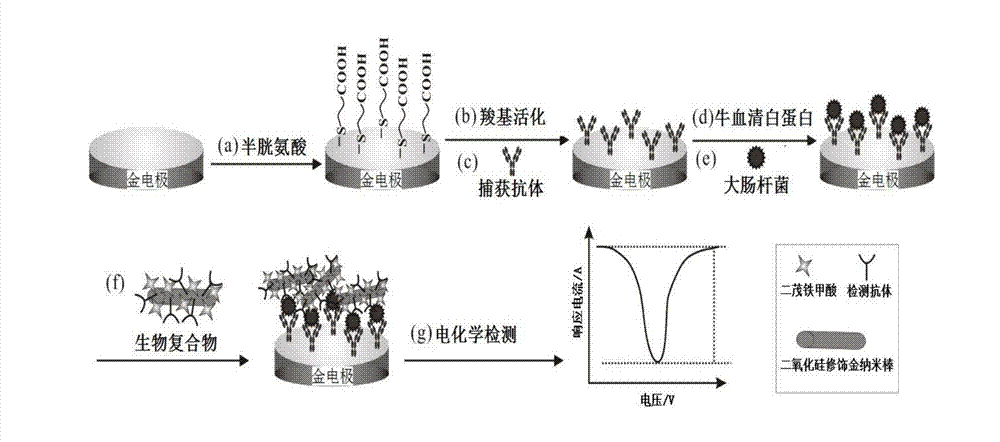
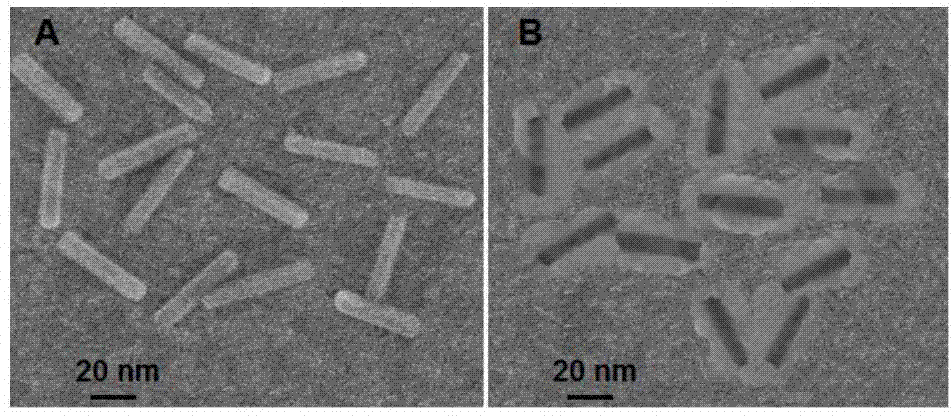
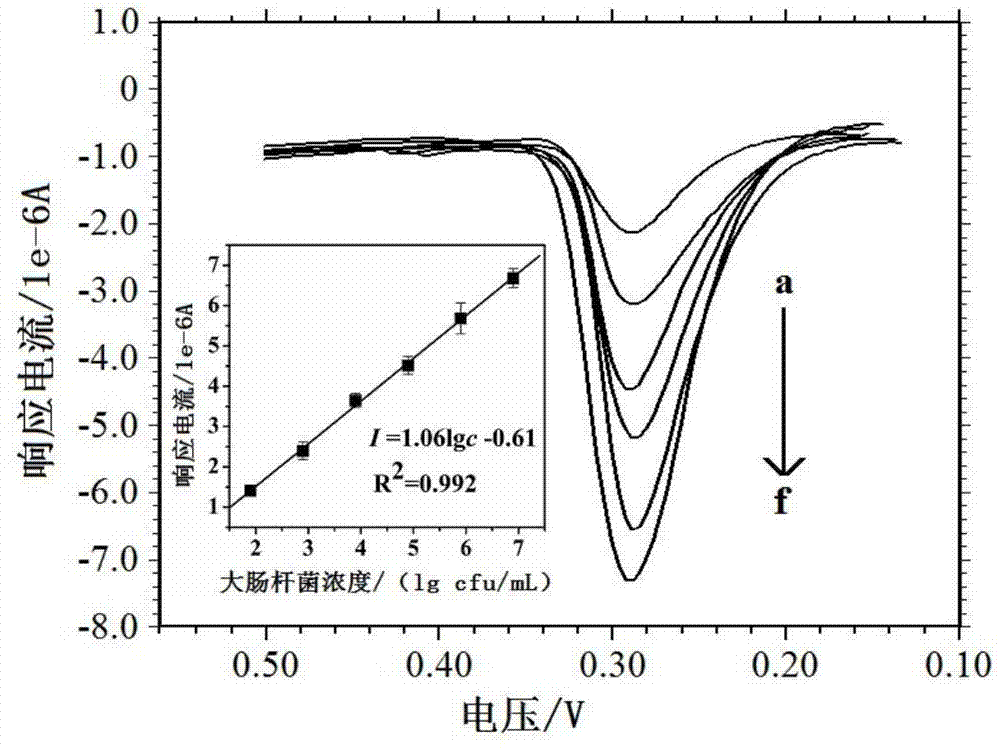
Gold nanorod biotic compound and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104493160AHigh sensitivityImprove accuracyMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial electrochemical variablesGold nanorodFerrocenecarboxylic acid
The invention discloses a gold nanorod biotic compound and a preparation method and applications thereof and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical analysis. A gold nanorod modified by silicon dioxide (AuNRs@SiO2) is used as a carrier and combined with a detection antibody (dAb) and ferrocenecarboxylic acid (Fc) to prepare dAb-AuNR-Fc which is used for amplifying escherichia coli in an electrochemical immunoassay dairy product. A 'sandwich' immunoassay model is established on basis of specificity interaction between the escherichia coli and escherichia coli antibody, and Fc combined with an electrode surface is measured by a differential pulse voltammetry to obtain a current signal. According to the gold nanorod biotic compound and the preparation method and the applications thereof, the electrochemical immunoassay method based on dAb-AuNR-Fc biotic compound is used for escherichia coli detection, the detection sensitivity, the specificity and the accuracy are high, and a novel method is provided for analysis and research of the escherichia coli in the dairy product.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
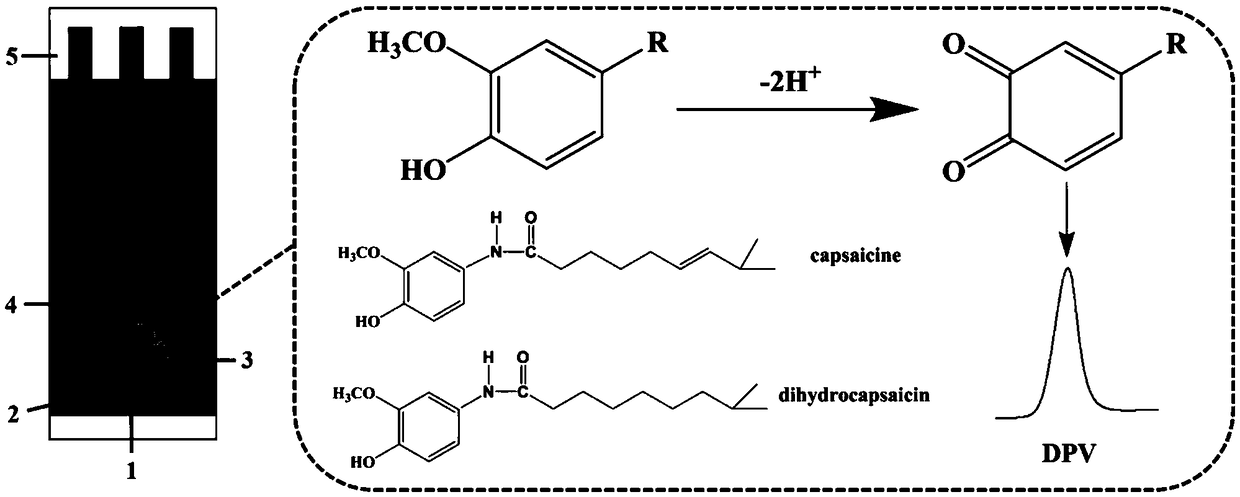
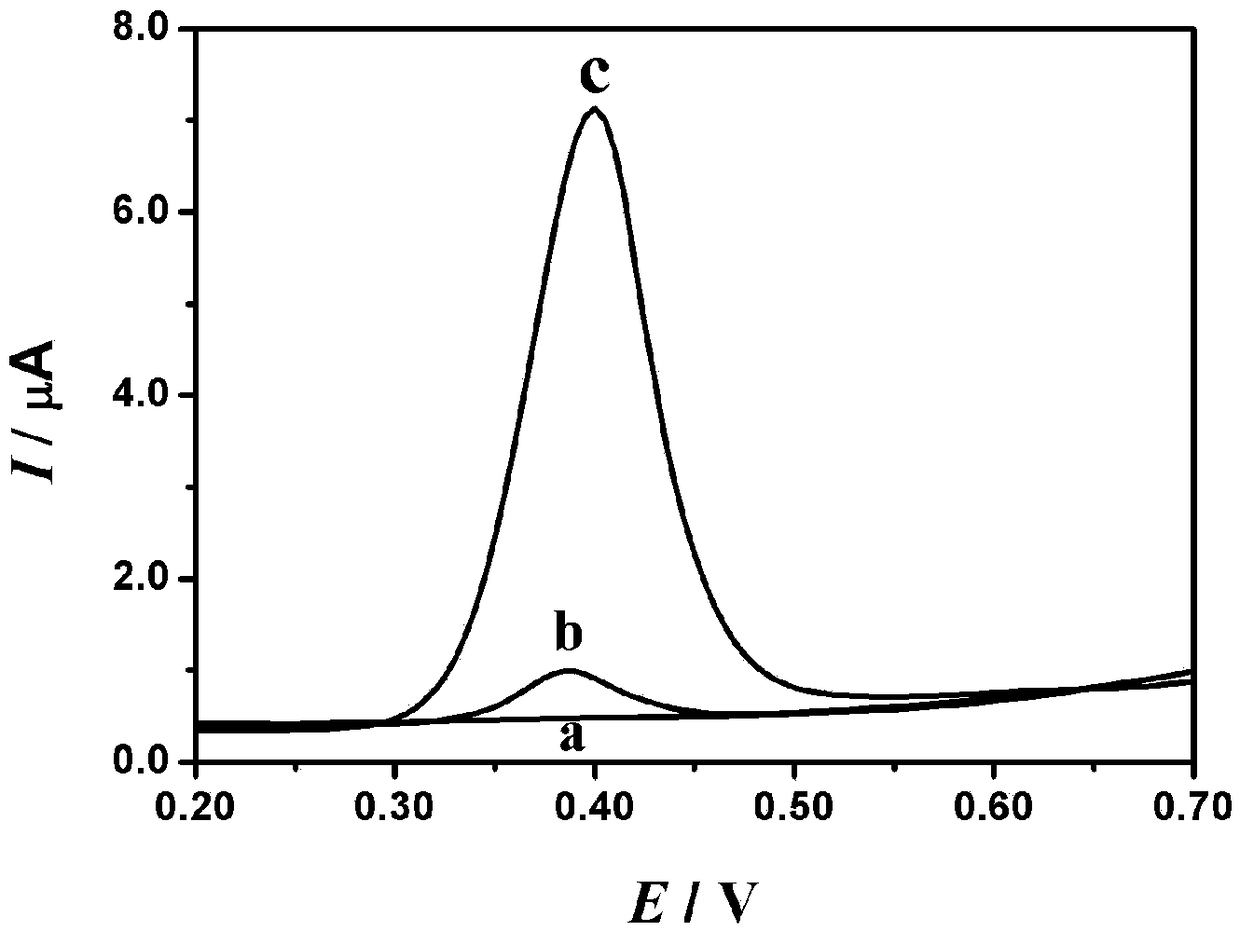
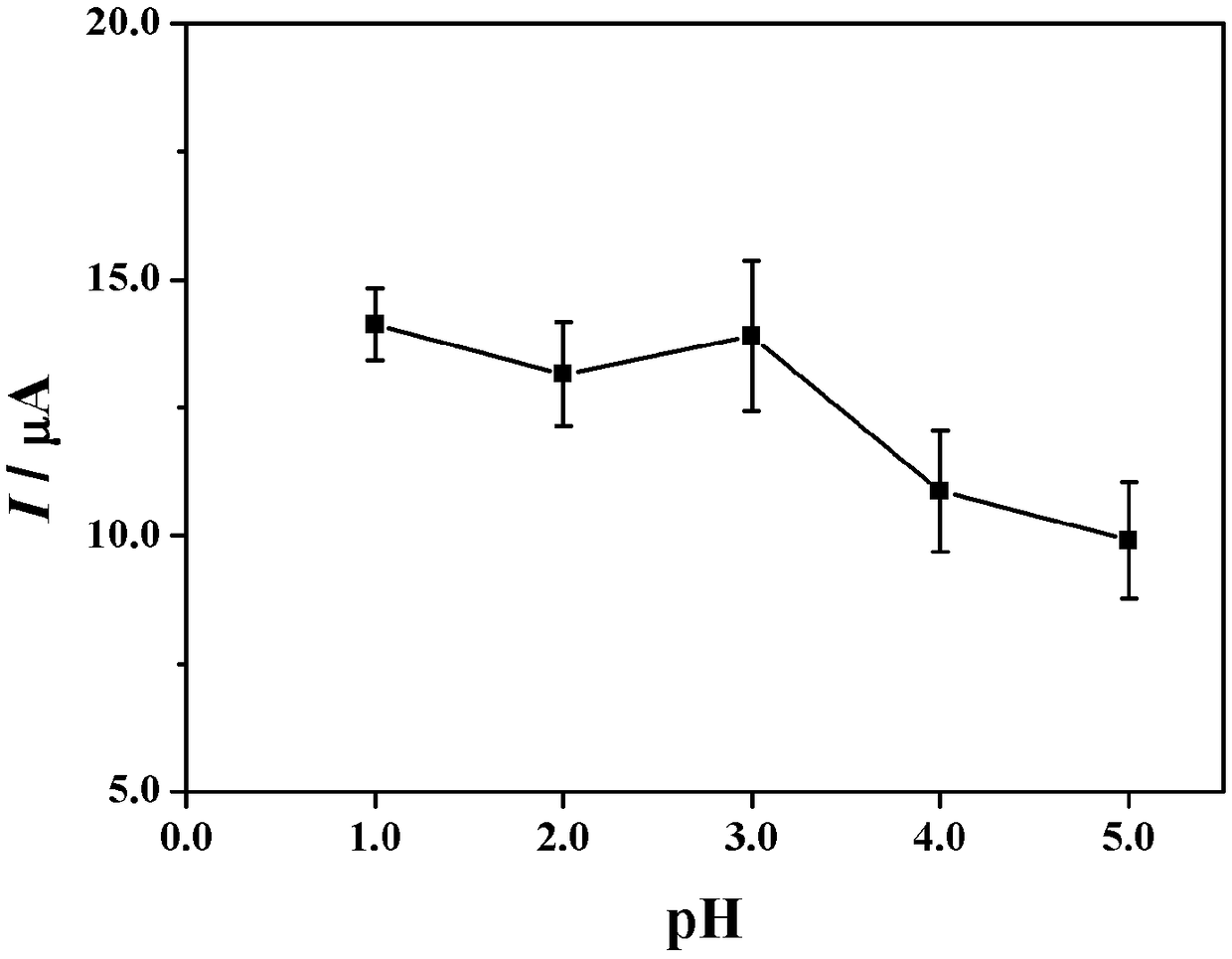
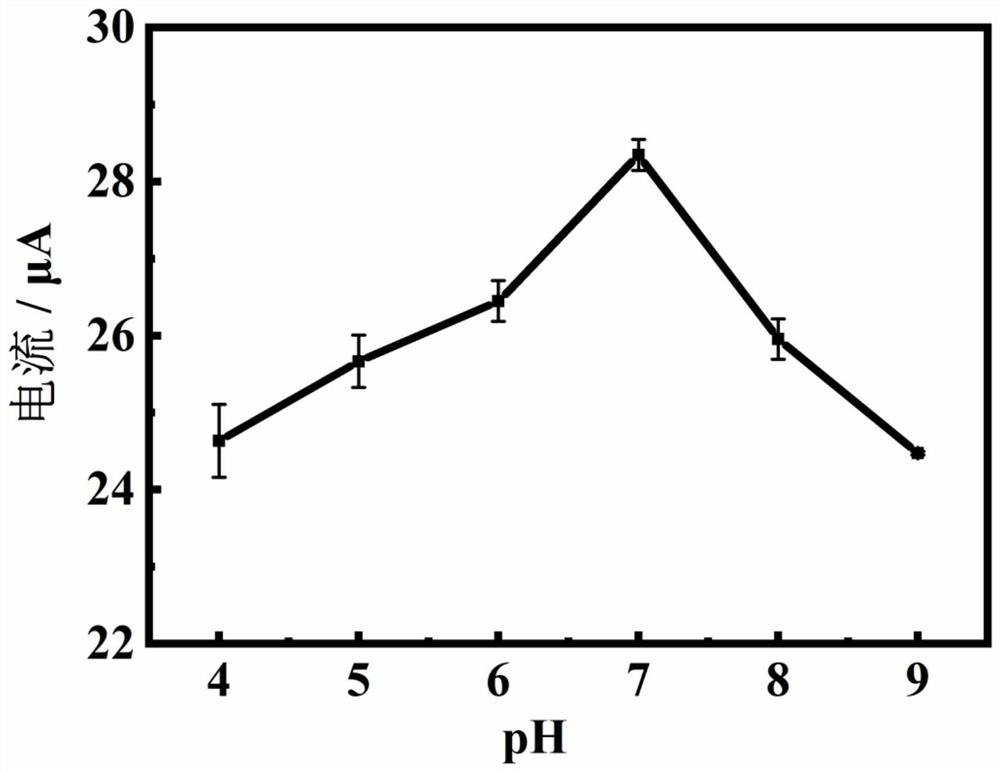
Electrochemical detection method for capsaicine in peppers
ActiveCN109254041AEasy to operateLow priceMaterial electrochemical variablesElectrochemical responseScreen printing
The invention discloses a simple and quick electrochemical capsaicine detection method. According to the method, simple, quick and correct quantitative detection for capsaicine is realized according to a linear relationship between electrochemical response signals and concentrations of to-be-detected objects by adoption of a differential pulse-adsorptive stripping voltammetry method through takinga non-modified silk-screen printing carbon electrode as an electrode material and combining the advantages that an adsorptive stripping voltammetry method is capable of greatly improving the detection sensitivity and a differential pulse voltammetry method is capable of effectively reducing the background current. The method is independent of large-scale instrument equipment; the used non-modified silk-screen printing carbon electrode is simple to prepare and low in cost; and the detection method is high in capsaicine detection sensitivity, simple and quick, can be used for detecting capsaicine in pepper samples, and is hopeful for being popularized and applied in the detection analysis and medicinal value research aspects of capsaicine.
Owner:重庆医科大学国际体外诊断研究院
Electrochemical sensor for detecting nitrite, preparation method and application
ActiveCN112034026ASimple manufacturing methodLess distracting factorsMaterial electrochemical variablesTitanium carbideDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention discloses an electrochemical sensor for detecting nitrite, a preparation method and application, and belongs to the field of electrochemical analysis. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: etching aluminum carbide to obtain titanium carbide with of accordion-like structure, calcining the titanium carbide serving as a titanium source to obtain titanium dioxide-titanium carbide, dispersing the compound into a solution containing hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide and chitosan, and performing ultrasonic treatment to obtain a composite solution. According to theelectrochemical sensor for detecting nitrite, the preparation method and the application, a three-electrode system is adopted, a glassy carbon electrode modified by a titanium dioxide titanium carbide / hexadecyl trimethyl ammonium bromide / chitosan compound is used as a working electrode, and the nitrite is determined by differential pulse voltammetry. The electrochemical sensor disclosed by the invention has the advantages of high sensitivity, good selectivity, low detection limit, quick response and the like in nitrite detection, and has a wide application prospect in the aspects of environment and food detection.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
Graphite phase nitrogen carbide-chitosan modified electrode, preparation method thereof, and method using same as work electrode to detect protocatechuic acid
InactiveCN106053564AImprove conductivityEasy to operateMaterial electrochemical variablesDifferential pulse voltammetryPhenolic acid
The invention discloses a graphite phase nitrogen carbide-chitosan modified electrode, a preparation method thereof, and a method using the same as a work electrode to detect protocatechuic acid. The preparation method comprises the following steps: directly heating melamine to synthesize g-C3N4, preparing g-C3N4 nano sheets through liquid phase peeling, and then utilizing a self-assembling method to fix g-C3N4 and chitosan onto the surface of a glass-carbon electrode in sequence so as to construct a graphite phase nitrogen carbide-chitosan modified electrode. The detection method of protocatechuic acid comprises the following steps: utilizing the graphite phase nitrogen carbide-chitosan modified electrode as the work electrode, through a differential pulse voltammetry, and drawing a curve representing linear relationship between the corresponding current and the protocatechuic acid concentration so as to analyze the protocatechuic acid in the environment quantitatively and qualitatively. The provided electrode has good chemical responding to protocatechuic acid, has a strong anti-interference performance, and can be used to detect an actual sample. The detection method has the advantages of simple operation, short time, little using amount, and low cost, and a novel thinking is provided for the detection of phenolic acids.
Owner:NANJING NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Electrode modification method for adopting nucleic acid aptamers for high sensitivity detection of tumor cells
InactiveCN103257167AHigh sensitivityLow background valueMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansAptamerDifferential pulse voltammetry
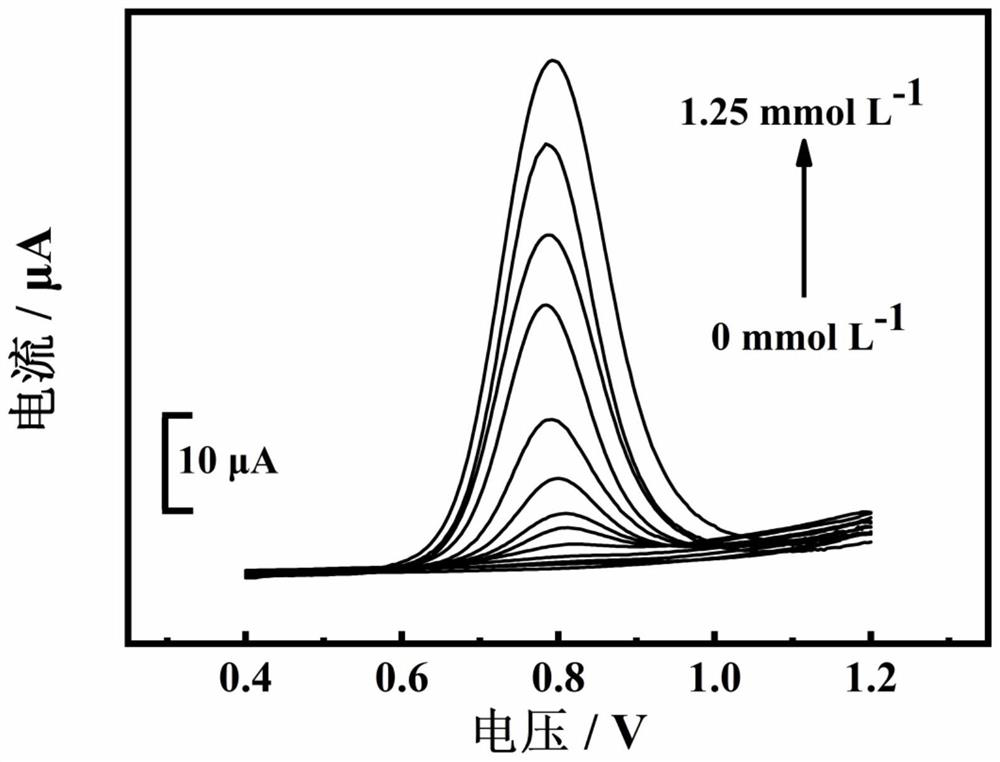
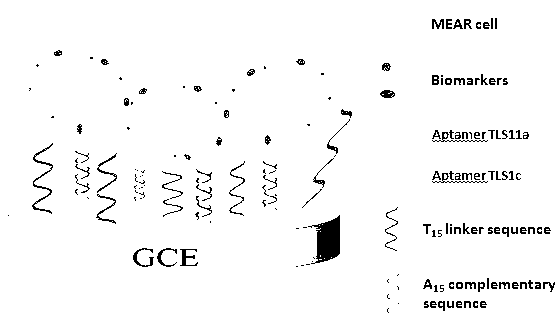
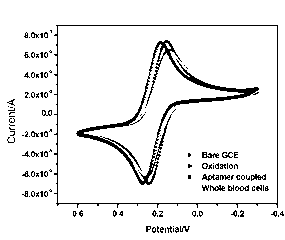
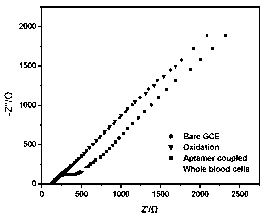
The invention discloses an electrode modification method for adopting nucleic acid aptamers for high sensitivity detection of tumor cells, wherein hepatic carcinoma cell BNL1MEA.7R.1(MEAR)-specific aptamers TLS1c and TLS11a are covalently modified on the surface of an electrode, and a cyclic voltammetry method, a differential pulse voltammetry method and an alternating current impedance method are adopted to detect MEAR cells, such that trace detection on the single MEAR cell can be achieved in 1 mL of 1*10<9> blood cells. With the technical scheme, a background value and a detection limitation can be significantly reduced, and sensitivity of electrochemical tumor cell detection can be improved.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
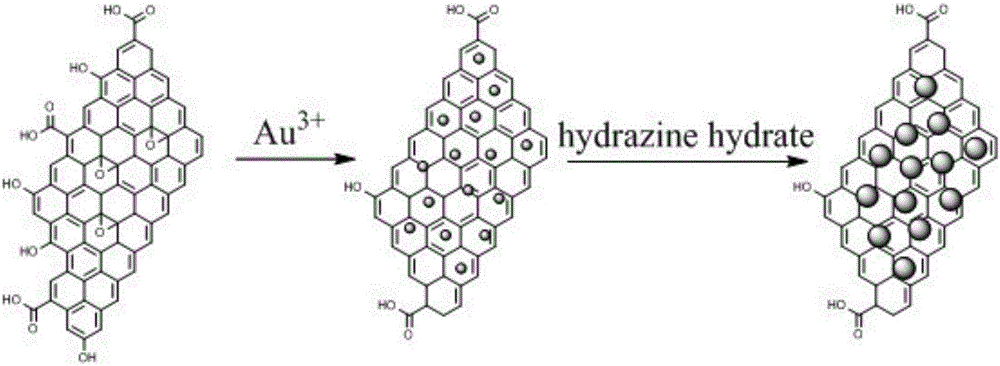
COFs material-based electrochemical sensor construction and application
The invention discloses a COFs material-based electrochemical sensor construction and application. The construction comprises the steps of preparation of a COOH-MWCNTs@NRs mixed solution, constructionof a COOH-MWCNTs@NRs / GCE electrode, construction of an AuNPs / COOH-MWCNTs@NRs / GCE electrode and construction of a COFs material-based electrochemical sensor. The COFs material-based electrochemical sensor serves as a working electrode, a platinum electrode is taken as a counter electrode, and a saturated calomel electrode is used as a reference electrode, and electrochemical detection on acetaminophen and dopamine is carried out at the same time through a differential pulse voltammetry method, and the maximum peak current is measured; and the concentration of acetaminophen and the concentration of dopamine are calculated according to the linear relation between the maximum peak current and the dopamine concentration. The construction process has the advantages of being high in sensitivity,wide in detection range, low in detection limit, high in stability, high in anti-interference capability and the like.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Preparation method of polymethyl blue/acetylene black composite modified glassy carbon electrode and application thereof in determination of paracetamol
InactiveCN106872544AImprove stabilityExtended service lifeMaterial electrochemical variablesCyclic voltametryRedox
The invention relates to a polymethyl blue / acetylene black composite modified glassy carbon electrode prepared by an electrodeposition method and a dispensing method. The electrochemical behavior of acetaminophen (PCT) on the modified electrode is studied by a cyclic voltammetry (CV). The experimental result shows that the modified electrode has a good electrocatalytic performance for the redox of PCT. Compared with a bare electrode and a polymethyl blue-acetylene black modified electrode, the oxidation peak current of PCT on the polymethyl blue / acetylene black modified glassy carbon electrode is obviously improved. Through the determination of a differential pulse voltammetry (DPV), the PCT has a good linear relationship with the oxidation peak current in the concentration range of 2.0 multiplied by 10<-6> to 0.4 multiplied by 10<-3>mol / L, and the correlation coefficient is 0.992, and the detection limit of PCT is 1.0 multiplied by 10<-6>mol / L when the signal to noise ratio is 3.
Owner:XINYANG NORMAL UNIVERSITY
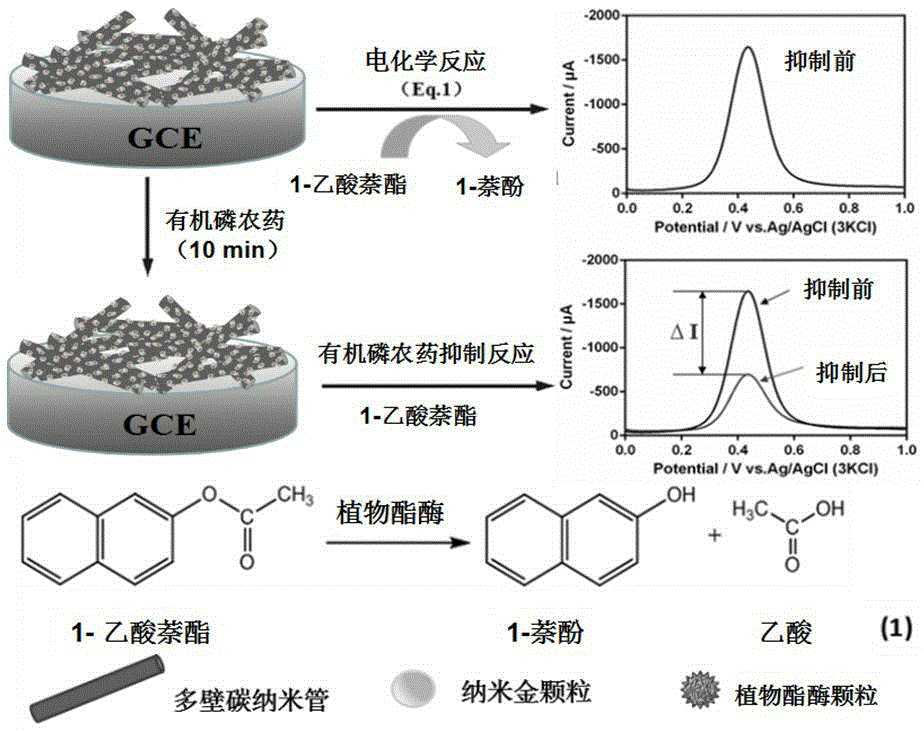
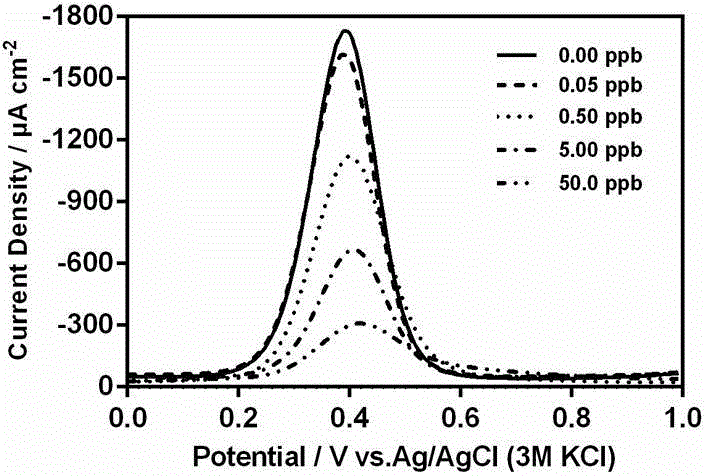
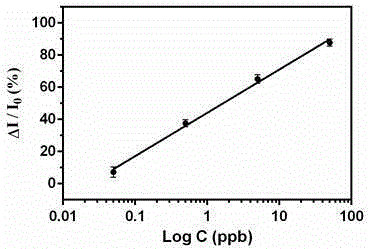
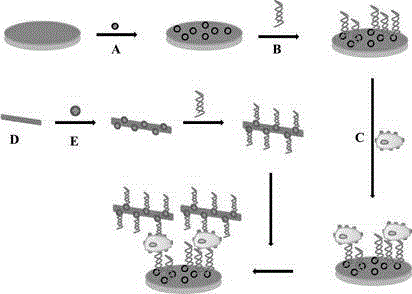
Method for rapidly detecting pesticide residue based on plant esterase
ActiveCN105403612AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionMaterial electrochemical variablesPesticide residueDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention provides a method for rapidly detecting pesticide residue based on plant esterase. The method comprises employing a three-electrode system, taking a biosensor as a working electrode, putting the three-electrode system in an organic phosphorus pesticide solution and performing inhibition for 6-15 min, then putting in a background solution and reacting for 3-8 min, selecting differential pulse voltammetry to establish a standard curve, and detecting the organic phosphorus pesticide content in a sample based on the standard curve. The biosensor is capable of realizing detection on a low-concentration organic phosphorus pesticide, the sensitivity is high, and the method possesses the following characteristics: the employed raw material is simple, cost is low, pretreatment is simple, the repeatability is high, and the application scope is extensive.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation and applications of electrochemical immunosensor used for detecting circulating tumor cells
InactiveCN105241943ASimple and fast operationAvoid the influence of subjective factorsMaterial nanotechnologyMaterial electrochemical variablesAptamerNanowire
The invention discloses a sensor used for detecting circulating tumor cells via differential pulse voltammetry. A preparation method of the sensor comprises following steps: vanadium pentoxide nanowires and gold-silver core-shell nanoparticles are prepared via a conventional method; the vanadium pentoxide nanowires and gold-silver core-shell nanoparticles are combined so as to modify aptamers; the surface of an electrode is modified with gold nanoparticles, and then the modified electrode is connected with the vanadium pentoxide nanowire gold-silver core-shell nanoparticle modified thiolation aptamers; the obtained electrochemical sensor is used for detecting circulating tumor cells via combination with an electrochemical workstation; and the electrochemical workstation is used for detecting. The sensor is high in specificity and sensitivity; operation is simple; and detection limit is low.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Polybromocresol green modified glassy carbon electrode and application thereof
InactiveCN104614426AIncreased current responseHigh sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesPhosphateDifferential pulse voltammetry
The invention relates to a polybromocresol green modified glassy carbon electrode and application thereof, and mainly relates to the preparation of electro-polymerized bromocresol green modified glassy carbon electrode, and the application of the electrode in the sensitive quantitative analysis determination of uric acid, dopamine and ascorbic acid through the differential pulse voltammetry. The experimental result shows that in a phosphate buffered solution with the concentration of 0.1 mol / L and the pH of 6, the modified electrode has obvious catalysis function and sensibilization on uric acid, dopamine and ascorbic acid, and under the optimum condition, and through the adoption of the differential pulse voltammetry, the concentrations of uric acid, dopamine and ascorbic acid have better linear relations with the peak current thereof within the ranges of 0.5-15 micrometers, 0.08-4.0 micrometers and 5-150 micrometers, and the detection limits reach 0.17, 0.017 and 0.17 micrometer respectively; the method shows satisfactory results when the electrode is applied to determination of contents of uric acid, dopamine and ascorbic acid in plasma.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
Preparation of graphene-based carboxymethylcellulose nanocrystalline composite material and application of graphene-based carboxymethylcellulose nanocrystalline composite material as chiral recognition material
The invention discloses preparation of a graphene-based carboxymethylcellulose nanocrystalline composite material. The preparation of the graphene-based carboxymethylcellulose nanocrystalline composite material comprises mixing graphene oxide dispersion liquid with sodium carboxymethylcellulose aqueous solution, and meanwhile adding in ethanediamine and a cross-linking agent of N-N-hydroxysuccinimide for continuous reaction at 48-55 DEG C for 50-53 h; then, adding in hydrazine hydrate to reduce superfluous oxygen-containing functional groups and carbon-oxygen double bonds on graphene oxide, and then performing suction filtration, washing and drying to obtain the graphene-based carboxymethylcellulose nanocrystalline composite material. Through a dripping method, the graphene-based carboxymethylcellulose nanocrystalline composite material is modified on a glassy carbon electrode to form an electrochemical chiral sensing interface, and the electrochemical chiral sensing interface is arranged inside L-tryptophan or D-tryptophan solution separately and scanned through differential pulse voltammetry. Due to the fact that the steric hindrances as well as the peak currents when L-tryptophan and D-tryptophan interact with the modified electrodes are different, the graphene-based carboxymethylcellulose nanocrystalline composite material can help rapidly and sensitively achieve recognition of tryptophan isomers.
Owner:NORTHWEST NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Graphite electrode modified by beta-cyclodextrin and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN110501398AEasy to handleShort detection cycleMaterial electrochemical variablesGraphite electrodeCopper wire
A graphite electrode modified by beta-cyclodextrin comprises a graphite rod with a copper wire wound at one end and a paraffin layer on the end surface of the other end, wherein the surface of the graphite rod is provided with a beta-cyclodextrin modification layer through electro-polymerization. A preparation method of the graphite electrode modified by beta-cyclodextrin is characterized by placing the graphite electrode in a buffer solution containing the beta-cyclodextrin and powering on the graphite electrode to obtain the graphite electrode modified by beta-cyclodextrin. A method for detecting o-methoxyaniline by using the graphite electrode modified by beta-cyclodextrin is characterized by connecting the graphite electrode modified by beta-cyclodextrin according to a three-electrodeworking system, and then, placing the graphite electrode in a solution to be detected to detect peak current; and calculating the o-methoxyaniline according to relationship between the peak current and concentration of the o-methoxyaniline. The graphite electrode is modified by the beta-CD through the electropolymerization method, and preparation conditions are optimized through differential pulsevoltammetry; and the prepared graphite electrode modified by beta-cyclodextrin is applied to detect the o-methoxyaniline with simple processing and short detection cycle.
Owner:XI'AN POLYTECHNIC UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com