Electrochemical detection of capsaicinoid compounds in a sample
A technology for capsaicin and substances, which is applied in the field of detection of capsaicinoid substances in detection samples, and can solve problems such as cost, complexity, limiting electrode performance or measurement reliability, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
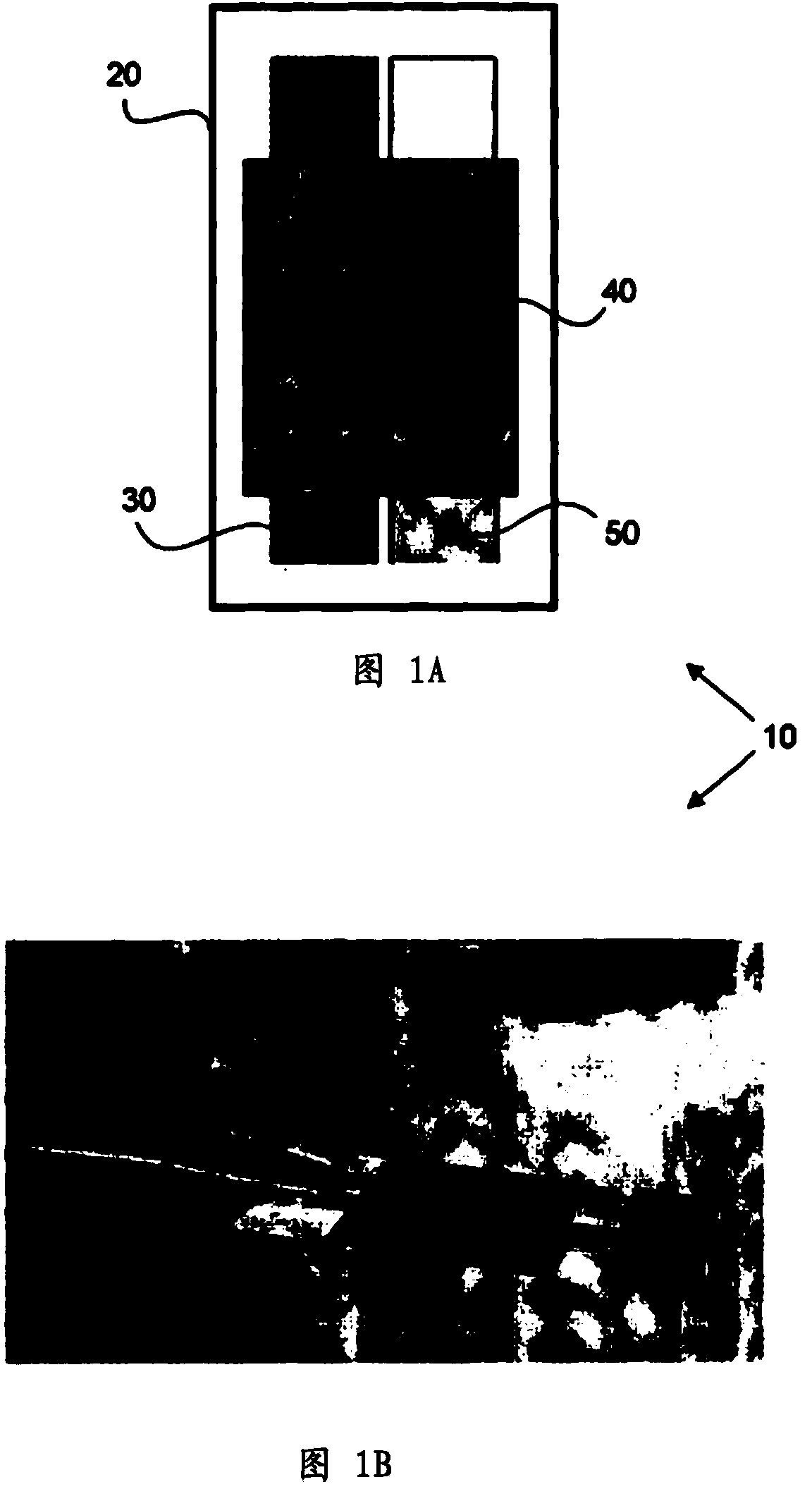
[0072] Preparation of screen-printed electrodes
[0073] By, for example, automatic or semi-automatic screen printing machine screen printing conductive carbon ink onto polyvinyl chloride (PVC), prepared as Figure 1Aand / or screen-printed carbon electrodes or electrode structures with working and reference electrodes as shown in IB. For the reference electrode, the rescreening process involved rescreening with a silver / silver chloride layer and then baking the screen printed carbon electrode at a temperature of approximately 55 degrees Celsius for 24 hours. The working and reference electrodes are again screen printed with insulating ink on the outermost, upper, or upper surface of the electrode structure.
[0074] sample preparation
[0075] An electrolyte solution is prepared by dissolving potassium chloride in a phosphate buffer in a molar range of about 0.1 to 0.2 moles. Specifically, an electrolyte solution for pepper samples was prepared by dissolving approximatel...
Embodiment 1
[0094] Example 1: Analysis of Capsaicin in Specific Capsicum Species by DPV
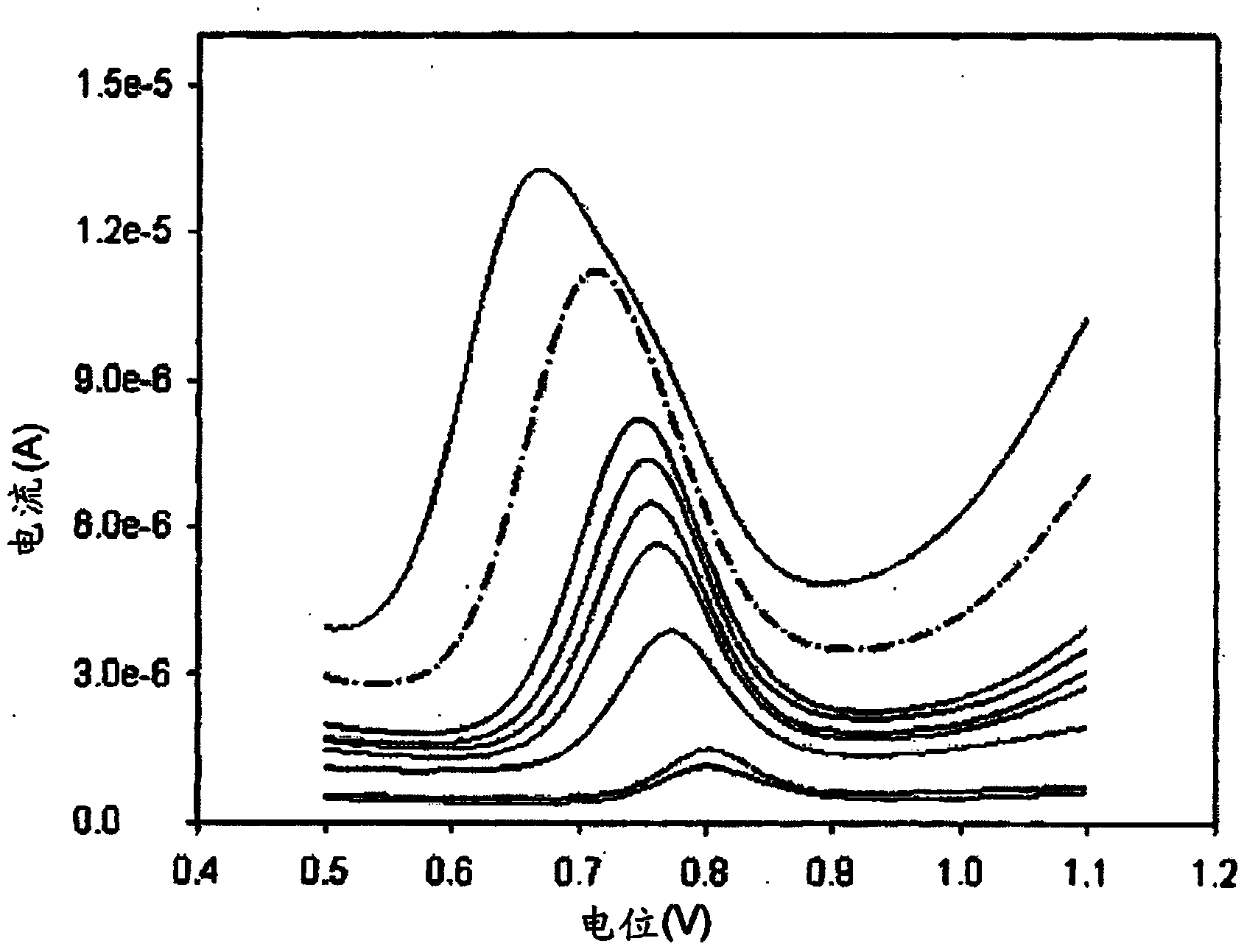
[0095] Electrolyte solutions were prepared by dissolving potassium chloride in 0.1 molar, pH 7 phosphate buffer. Specifically, an electrolyte solution for pepper samples was prepared by dissolving approximately 0.2 M potassium chloride with 0.1 M phosphate buffer. Preparation of fresh pepper samples was performed at room temperature. A mixture of about 2 g of fresh pepper sample and 1 ml of ethanol was sonicated for about 15 minutes. The mixture was centrifuged at approximately 35,000 rpm for approximately 5 minutes, with the rotation slowed down for a few minutes. The samples were also diluted 500 times with the electrolyte formulation.
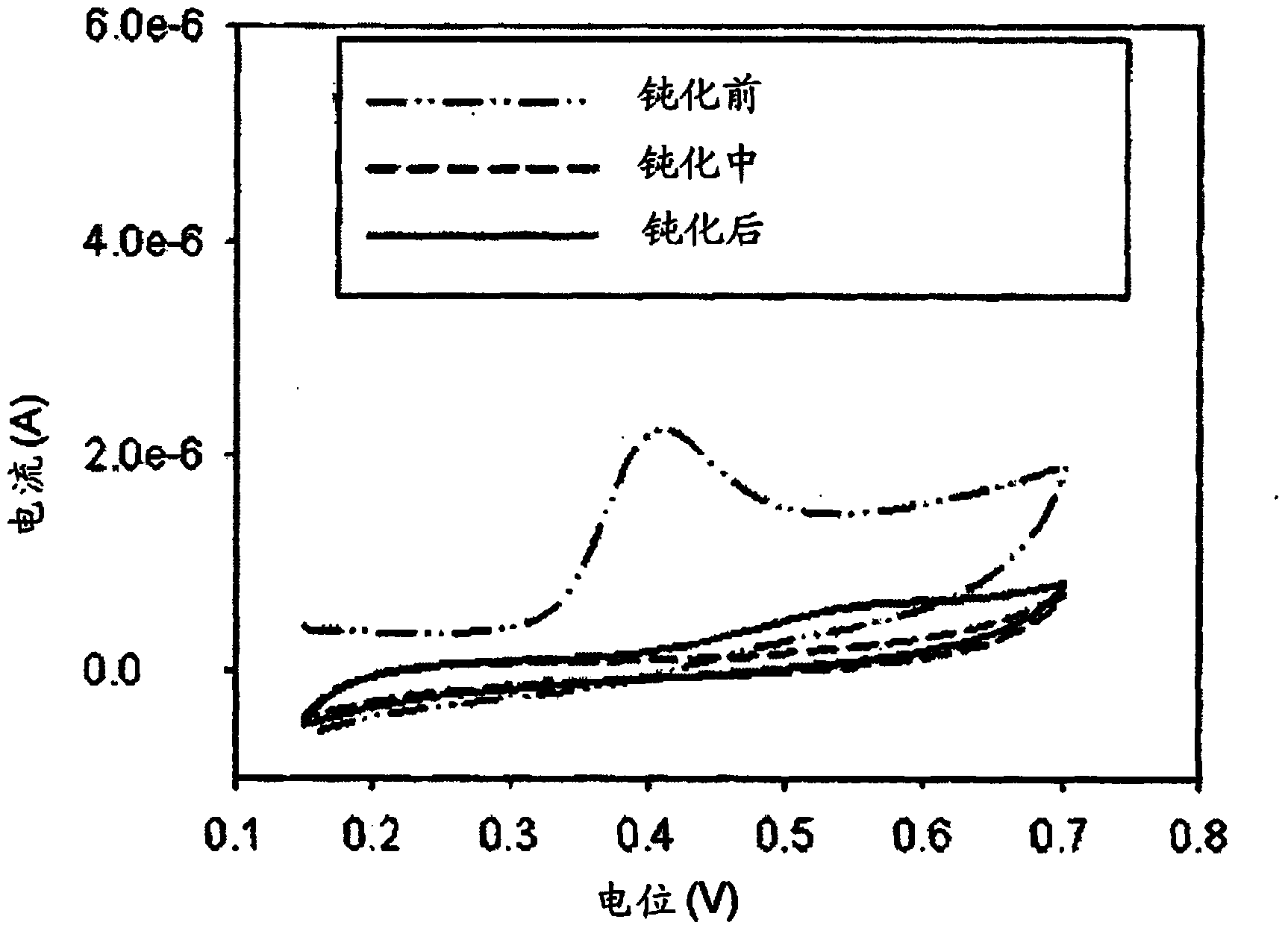
[0096] By contacting the sample solution with a screen-printed electrode (eg, dropping the sample solution onto the screen-printed electrode), and applying a potential of about 0.0 volts to about 1.0 volts by differential pulse voltammetry, wherein the different...
Embodiment 2
[0099] Example 2: Analysis of capsaicin in dry and wet food samples by DPV
[0100] Electrolyte solutions were prepared by dissolving potassium chloride in 0.1 molar, pH 7 phosphate buffer. Specifically, an electrolyte solution for pepper samples was prepared by dissolving approximately 0.2 molar potassium chloride with approximately 0.1 molar phosphate buffer.
[0101] Dry spicy food sample preparation was performed at room temperature. The preparation consisted of dissolving approximately 1 g of a dry spicy food mixture in 1 ml of ethanol, then sonicating the sample for approximately 15 minutes. The mixture was centrifuged at approximately 35,000 rpm for approximately 5 minutes, with the rotation slowed down for a few minutes. Samples were also diluted approximately 30 times with the electrolyte formulation. Wet food sample preparation was performed at room temperature. A mixture of about 2 g of fresh pepper and about 1 ml of ethanol was sonicated for about 15 minutes. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com