Method for detecting DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) through high sensitivity Raman spectrum
A sensitive Raman and spectral detection technology, applied in the field of high-sensitive Raman spectral detection of DNA, can solve the problems of light quenching, limit the application of fluorescence analysis technology, etc., and achieve the effects of simple operation, improved detection sensitivity, and low price.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
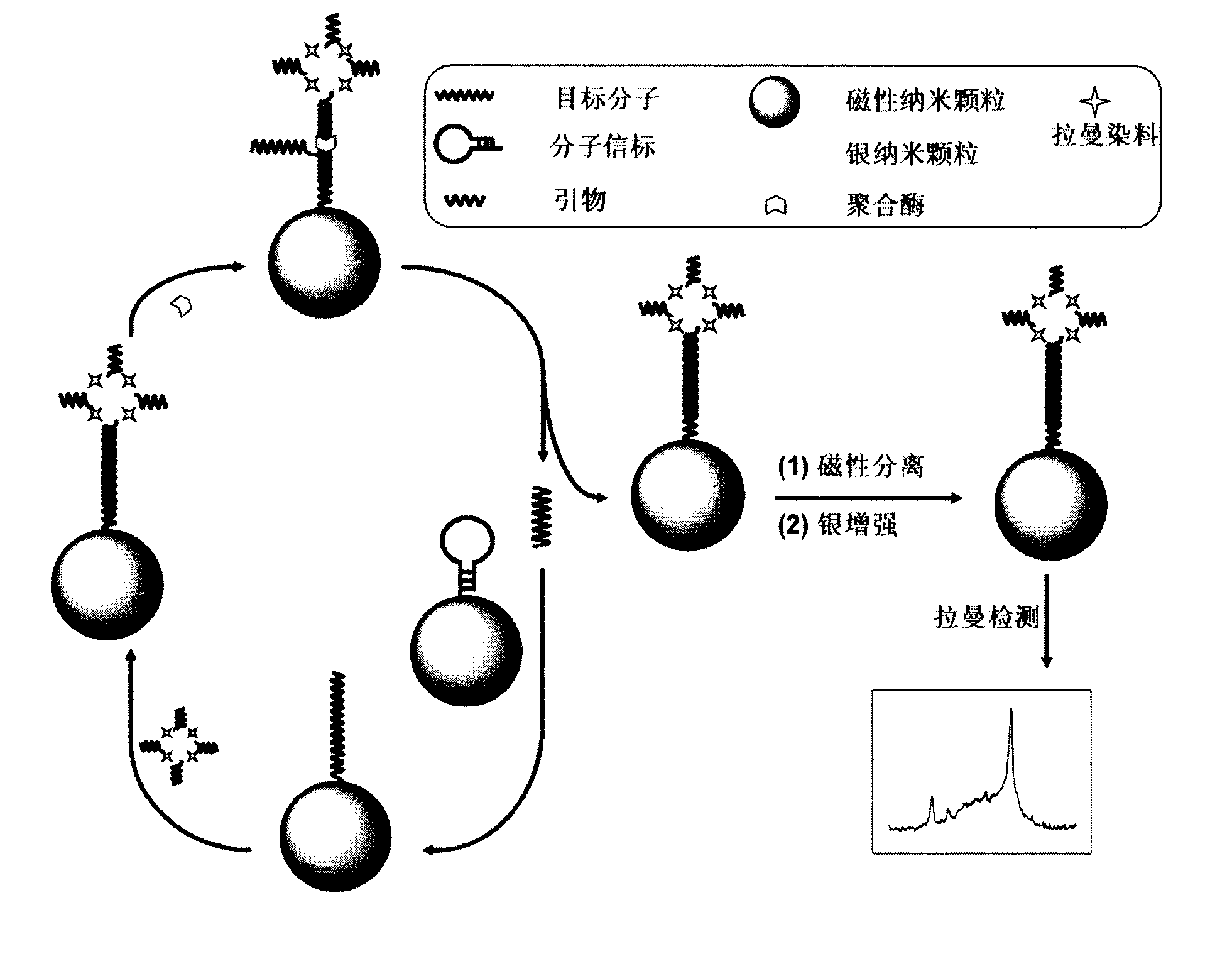
[0023] Embodiment 1: the preparation of the Raman dye-silver nanocomposite of primer modification
[0024] After boiling 200mL of 1.0mM silver nitrate solution, 5mL of 35mM sodium citrate solution was added under stirring, and the mixture was stirred and heated for 1 hour to obtain a colloidal solution of silver nanoparticles, which was stored in the dark at 4°C. Further, 100 μL of sulfhydryl-modified primers (10 μM) were added to 1 mL of colloidal solution of silver nanoparticles, stirred for 18 hours, and purified by centrifugation at 8000 rpm for 15 minutes for three times, and the obtained primer-modified silver nanoparticles were redispersed in 1 mL 10mM PBS solution. Then, 4 μL of 1 mM 4-mercaptobenzoic acid solution was added to this solution, stirred for 12 hours, and centrifuged and purified three times to obtain the primer-modified Raman dye-silver nanocomposite, which was re-introduced into 1 mL of 10 mM PBS solution for use.
Embodiment 2
[0025] Example 2: Immobilization of molecular beacons on the surface of magnetic beads
[0026] Disperse 50 μL of carboxylated magnetic nanoparticles into 1 mL of PBS (0.01M, pH 7.4), dropwise into 200 μL of 0.1M 1-ethyl-3-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-carbodiimide hydrochloride Saline solution, 400 μL 0.05M N-hydroxysuccinimide solution and 150 μL 5.4 μM molecular beacon, stirred at room temperature for 4 hours, separated magnetic nanoparticles using a magnetic field, and washed several times with water to obtain molecular beacon-modified magnetic nanoparticles , redispersed in 1 mL of PBS (0.01M, pH 7.4) and stored at 4°C until use.
Embodiment 3
[0027] Embodiment 3: Raman spectroscopy detects DNA
[0028] (1) In 10 μL molecular beacon-modified magnetic nanoparticle dispersion, 10 μL DNA solution of different concentrations, 5 μL primer-modified Raman dye-silver nanocomposite solution, 2 μL polymerase (4 U) and dNTPs (each Nucleotides are all 12 μM), incubated at 37°C for 100 minutes, and then separated by a magnetic field to replace the strands immobilized on the surface of the magnetic nanoparticles;
[0029] (2) The chain substitution product was mixed with 10 μL of the mixture containing 1:1 silver enhancement solutions A and B, and Raman detection was performed after 2 minutes of silver enhancement reaction.
[0030] (3) Record the Raman signals of different concentrations of DNA solutions and samples, obtain the working curve of DNA detection, and calculate the concentration of DNA in the sample.
[0031] (4) By comparing the Raman signals at the same DNA concentration, the single base mismatch or unpaired DNA s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com