Patents
Literature
525results about "Recognisation of pattern in signals" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method and system for determining an individual's state of attention
Owner:FICO MIRRORS SA
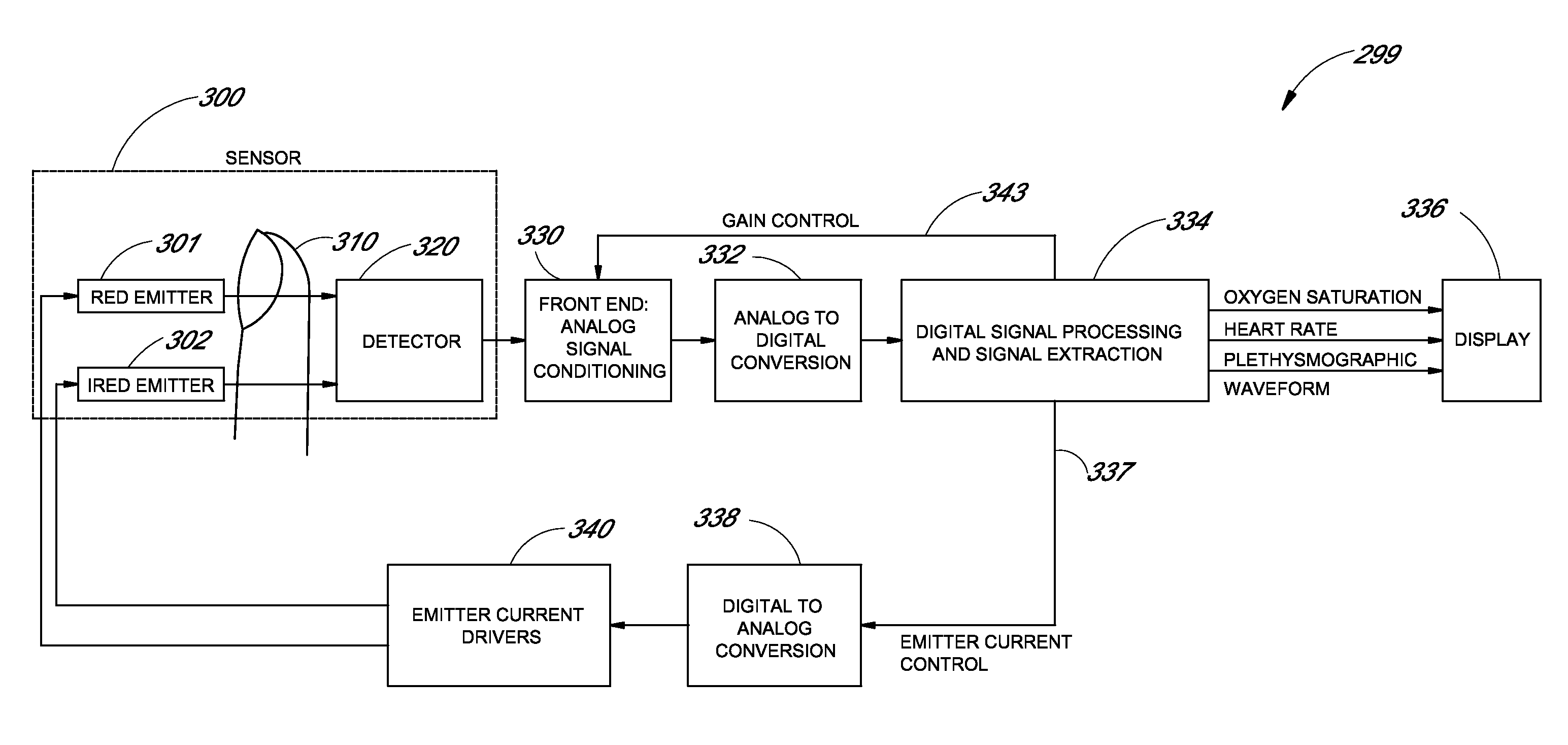
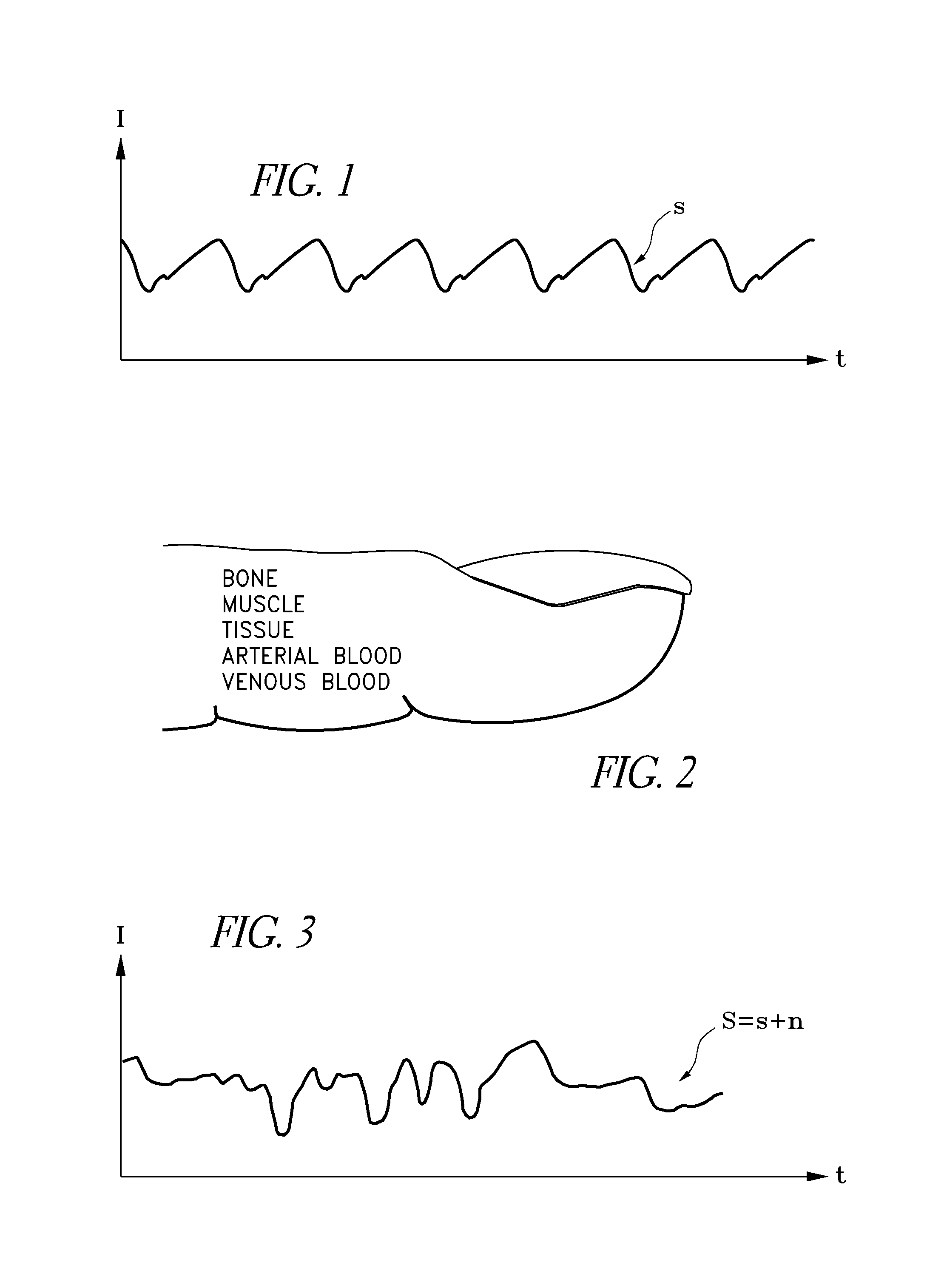
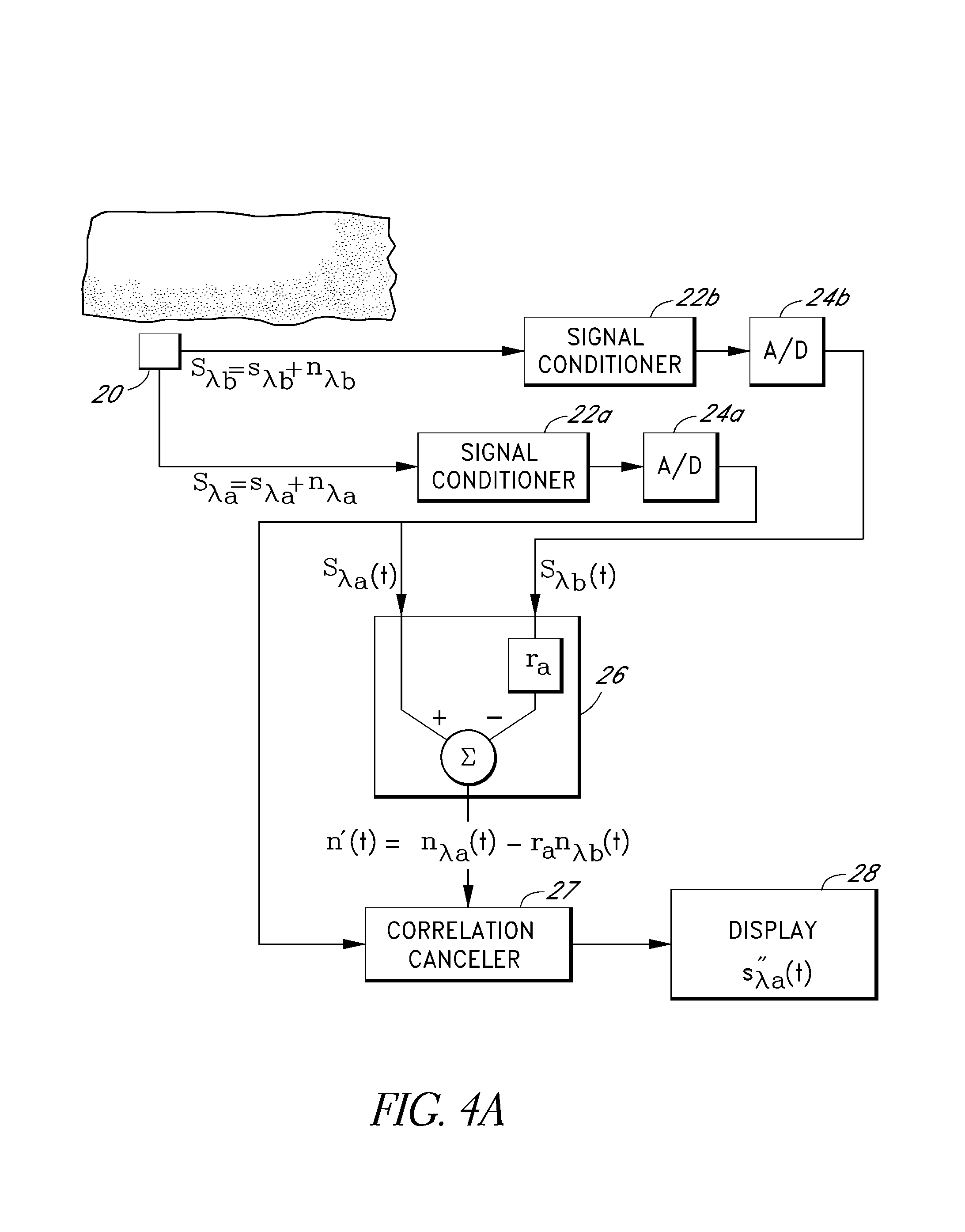
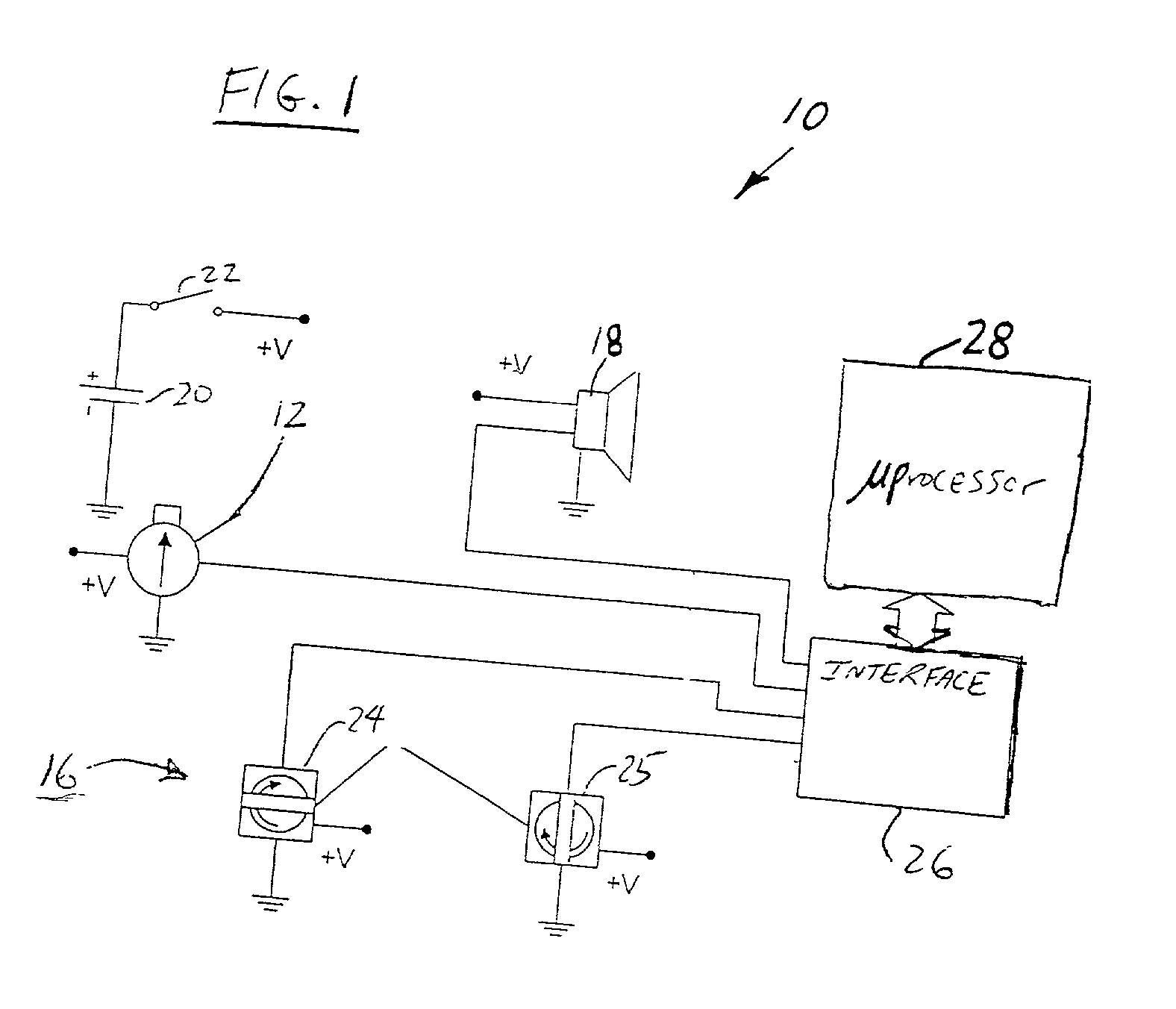
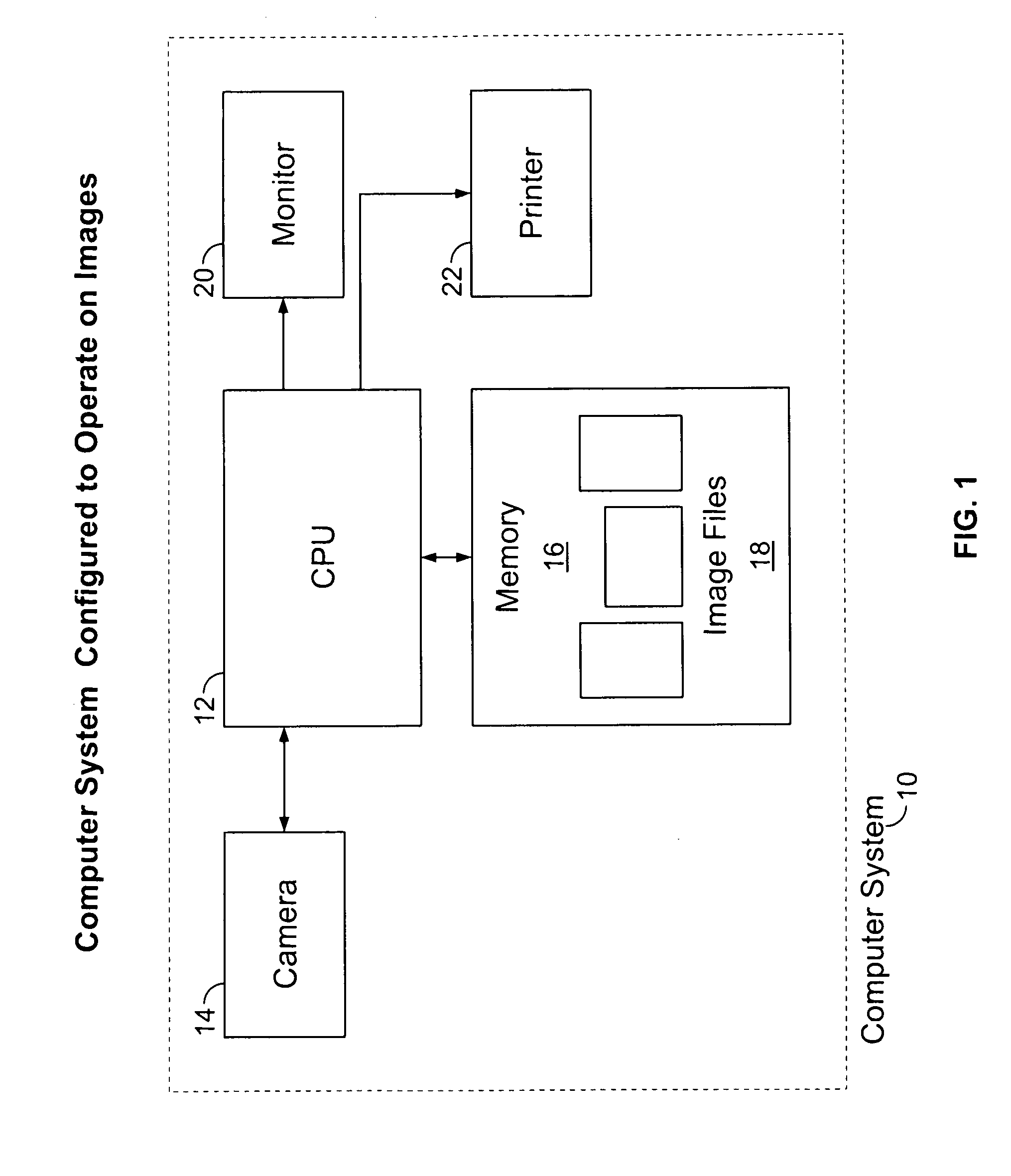
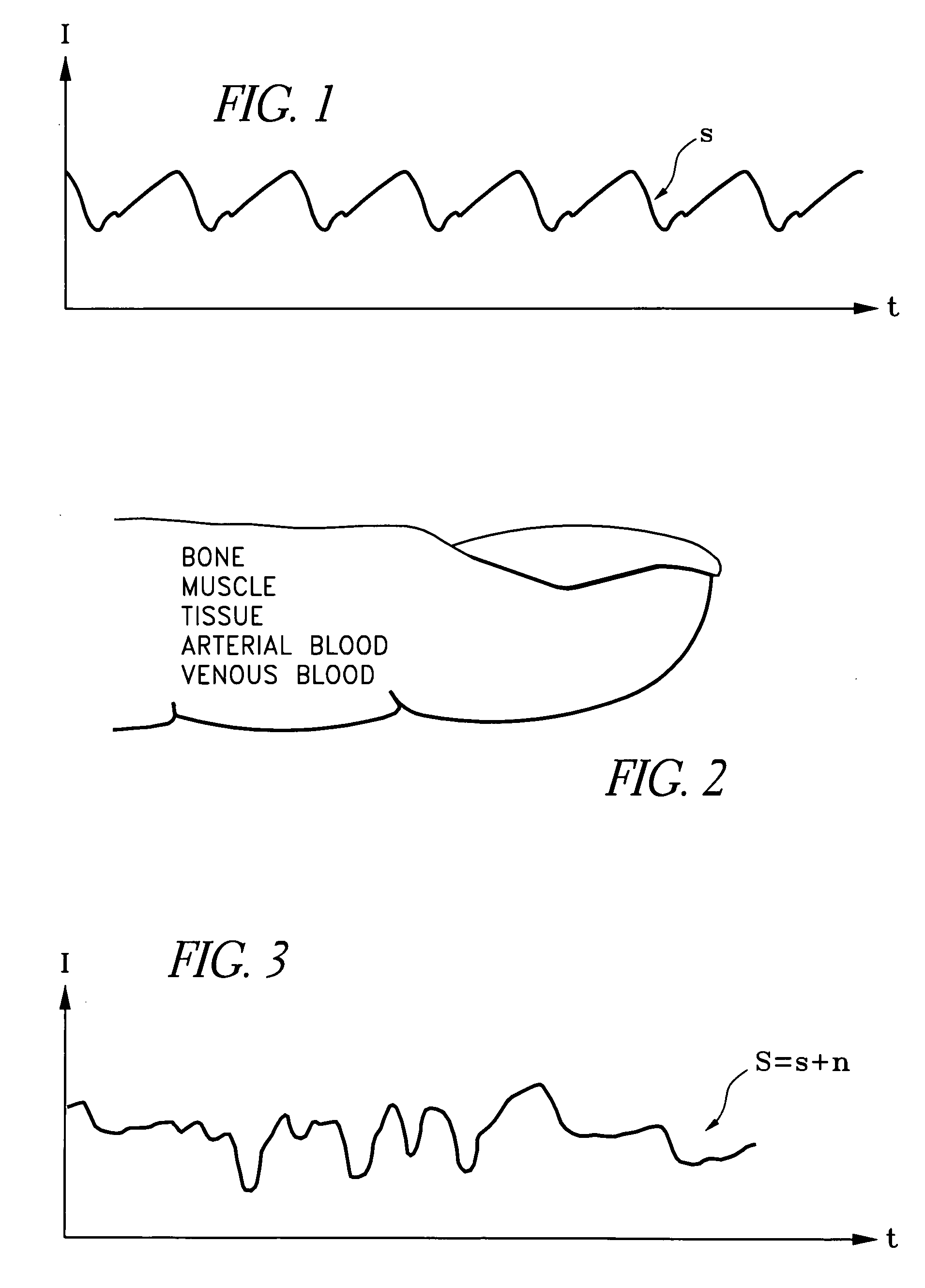
Signal processing apparatus
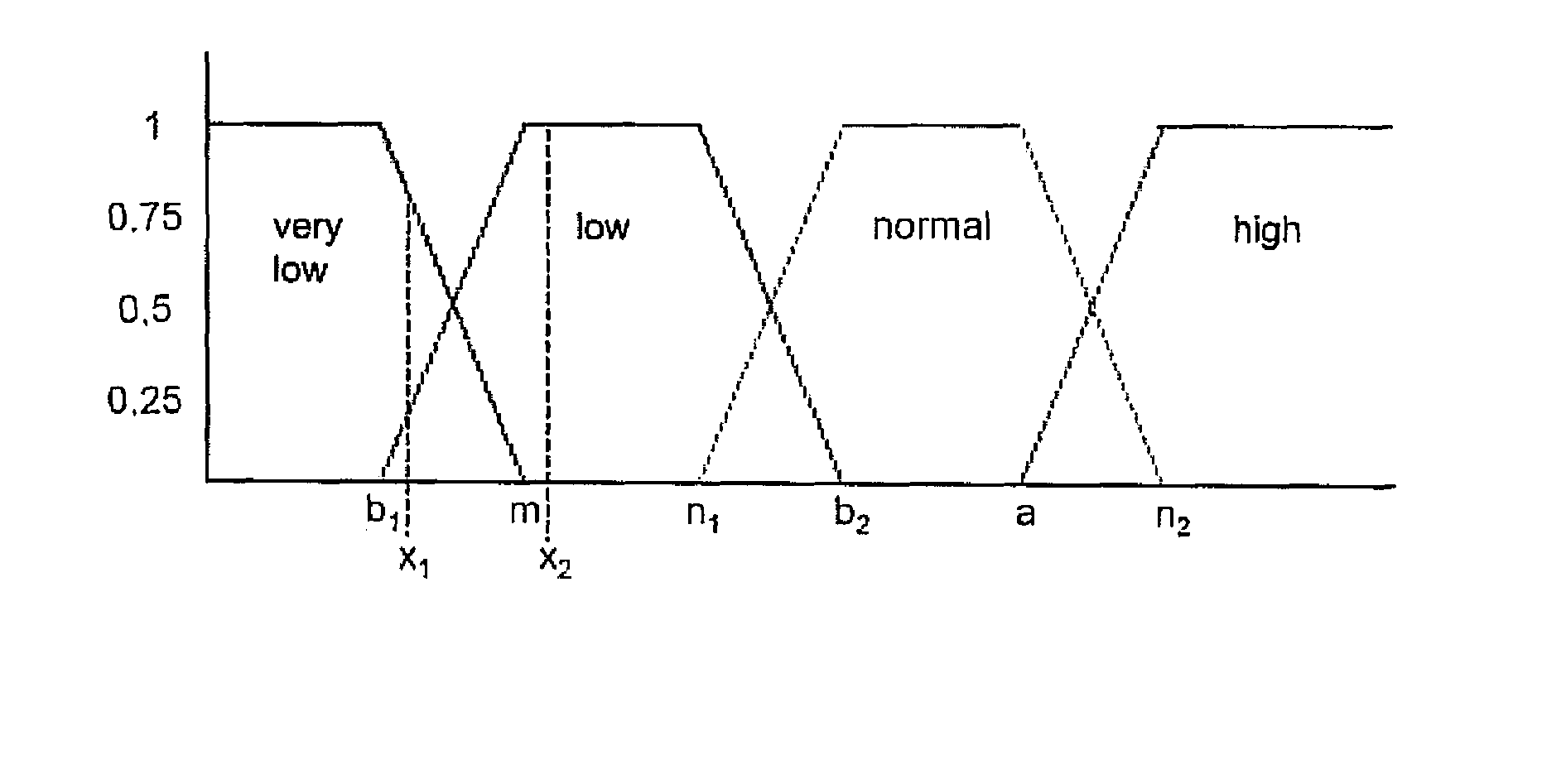
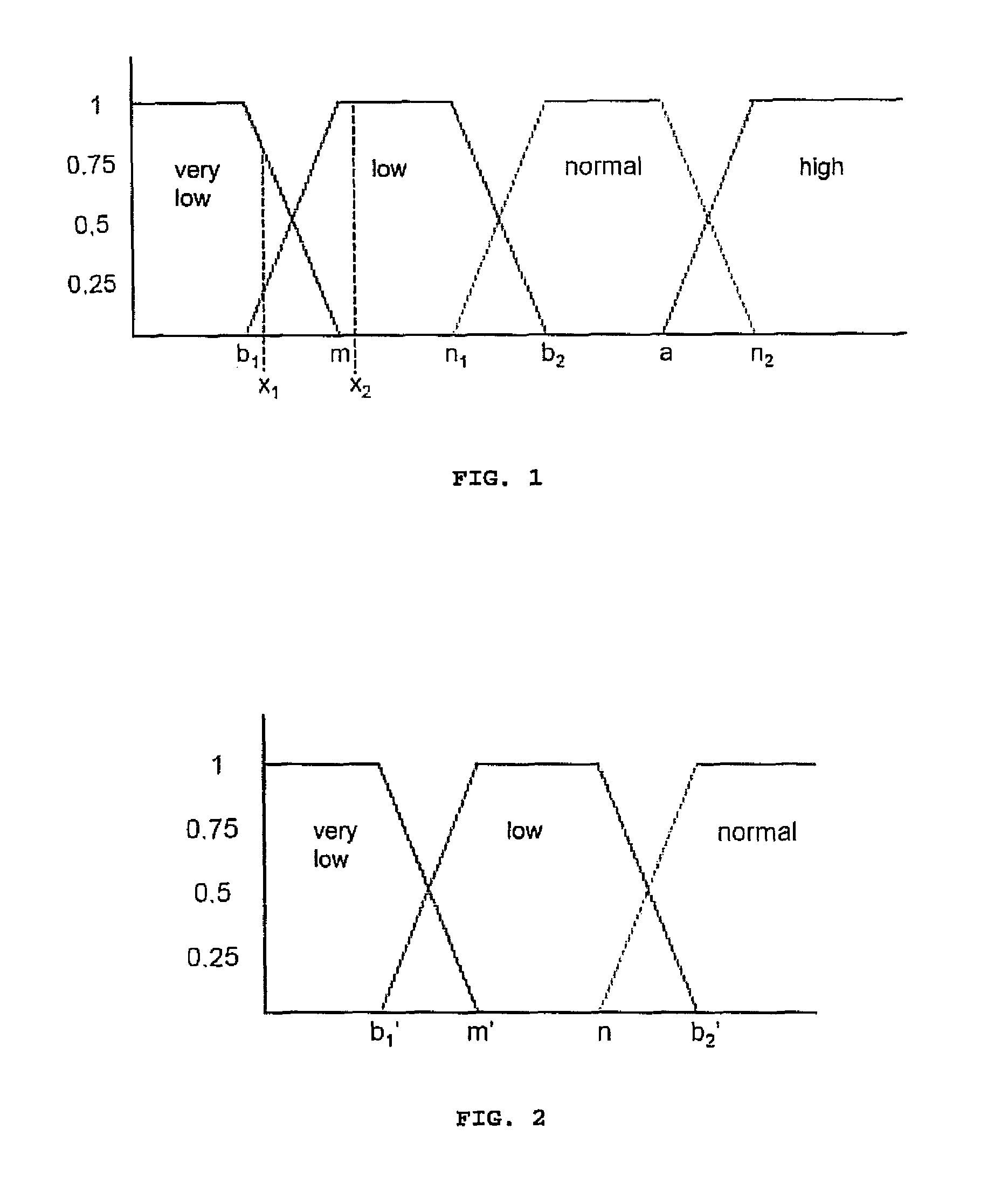
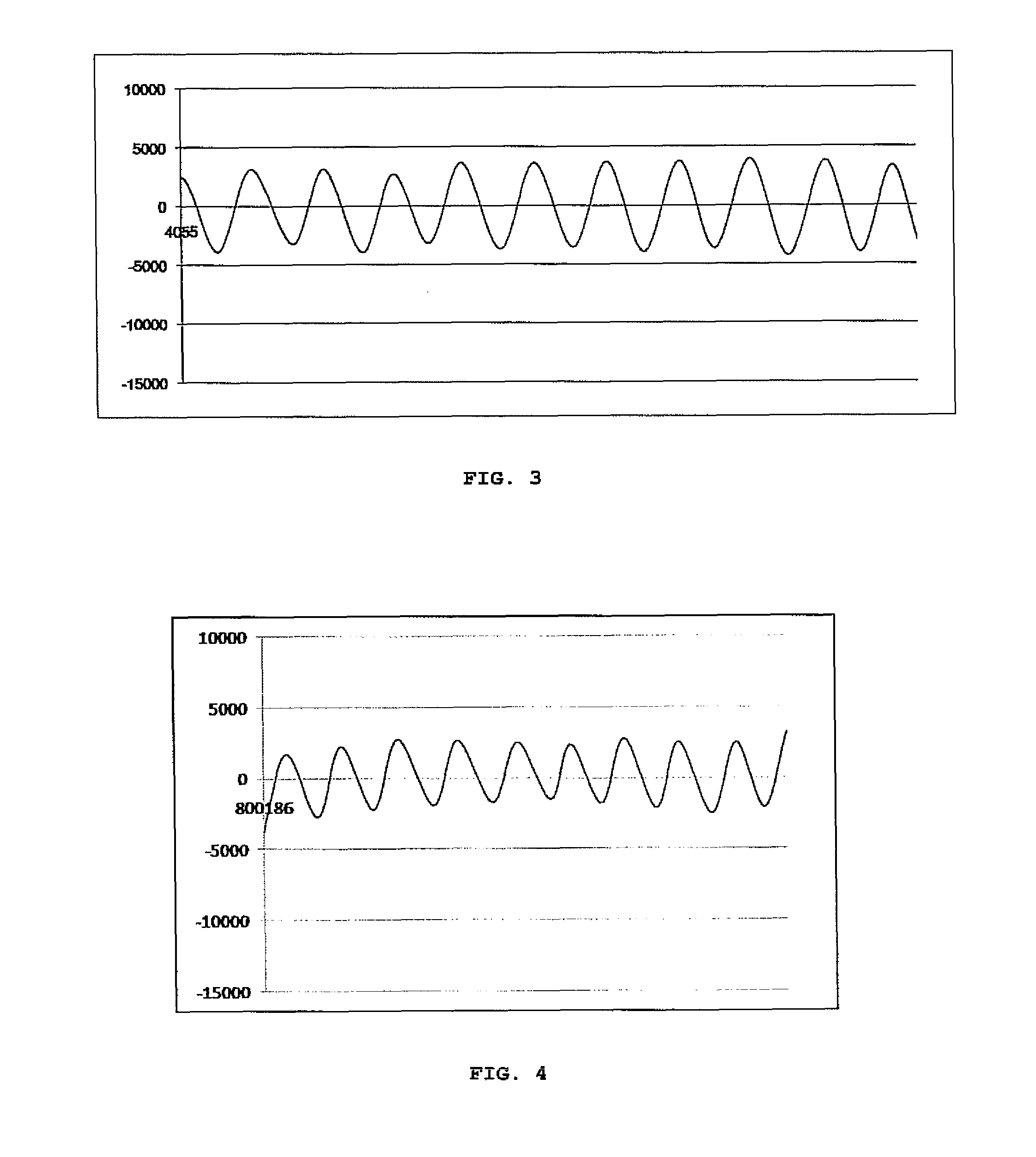
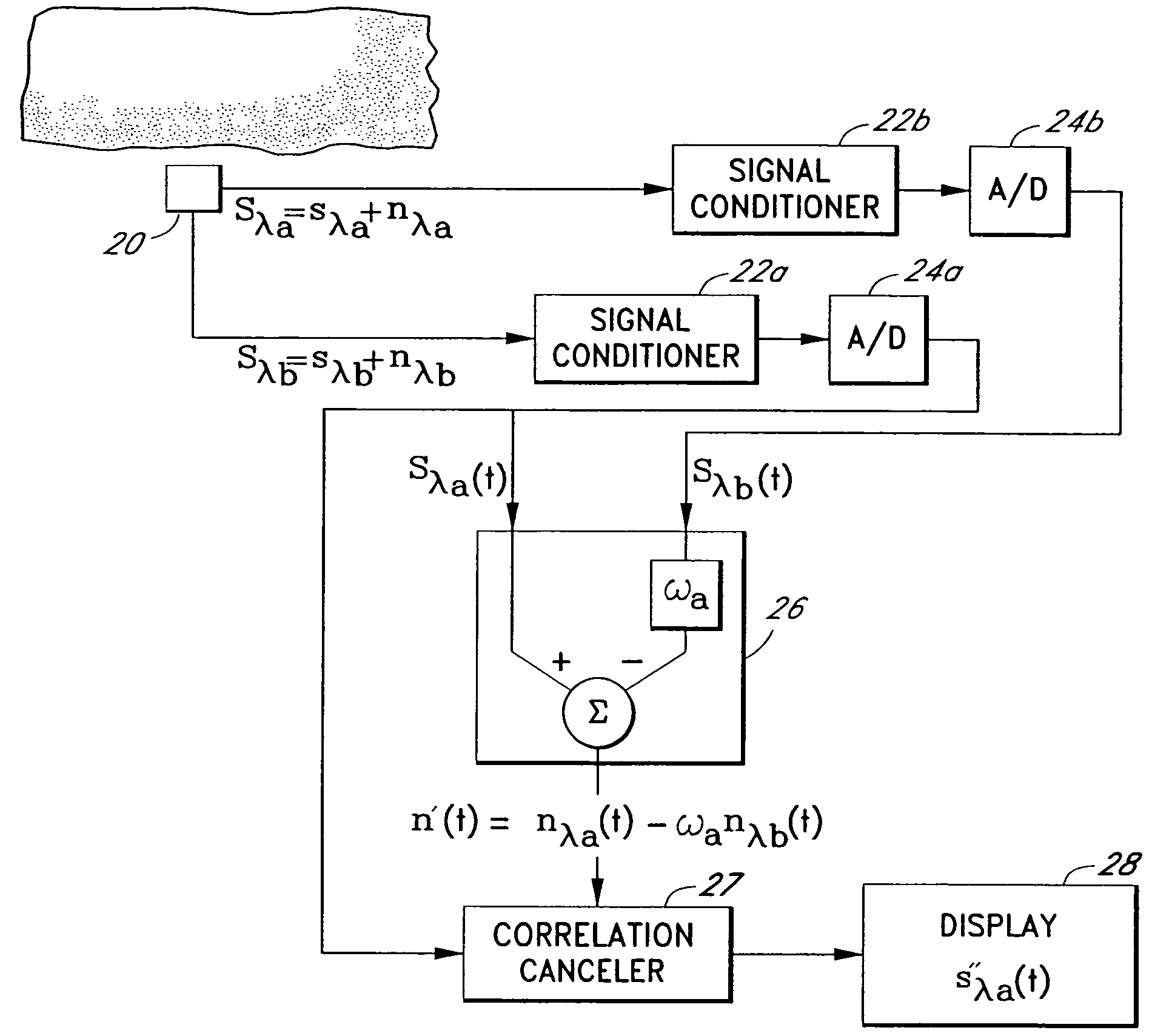
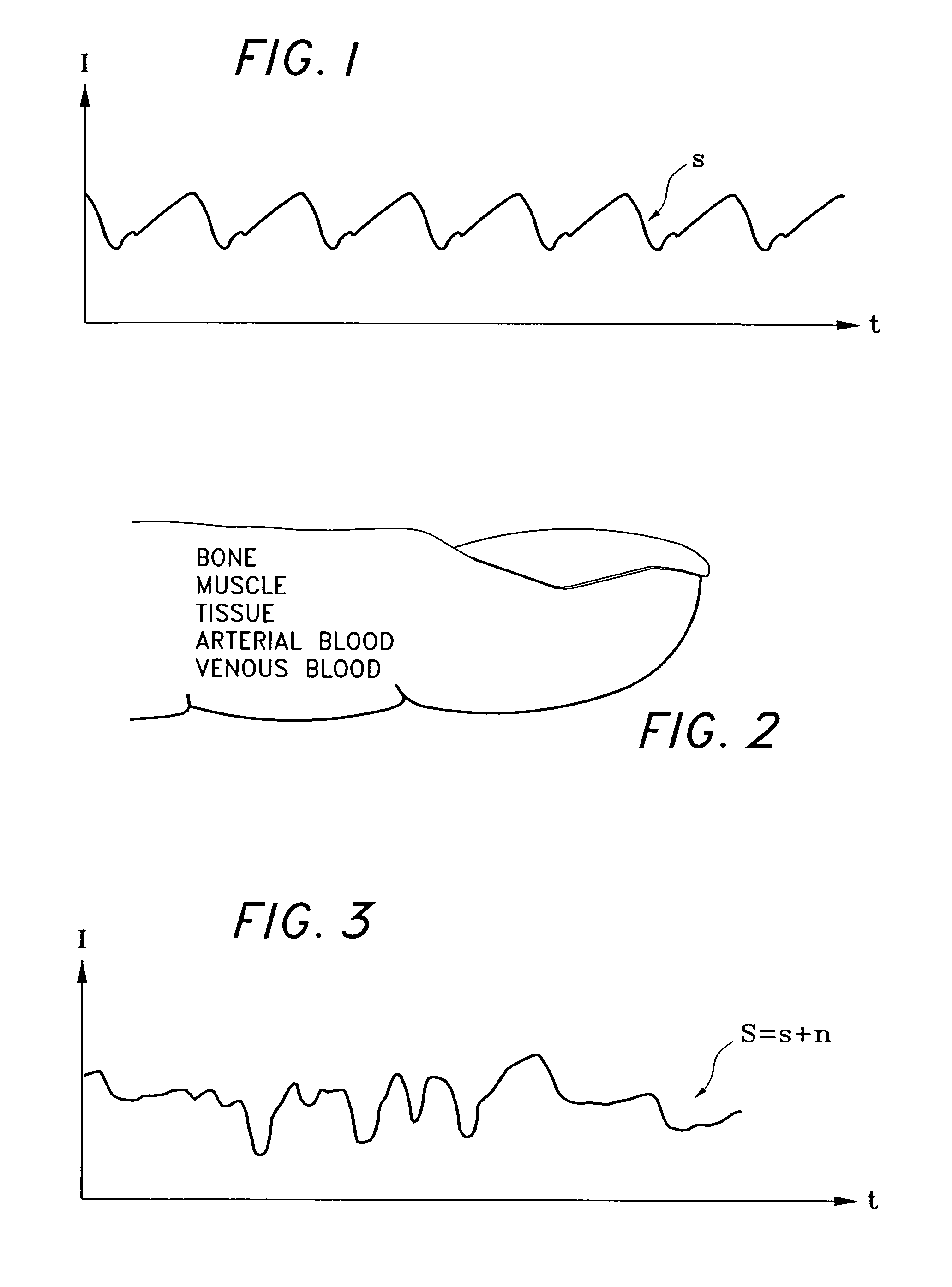
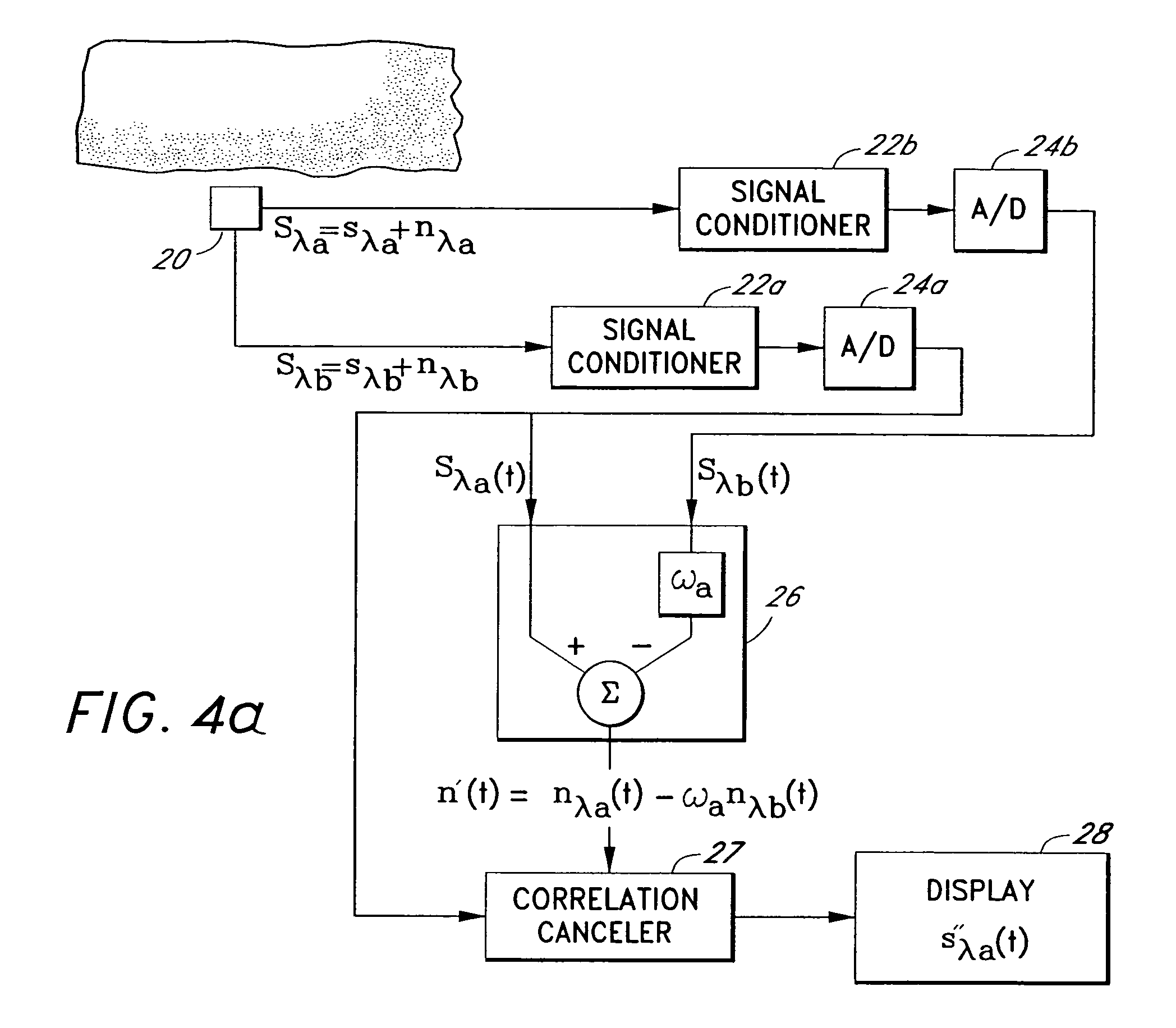
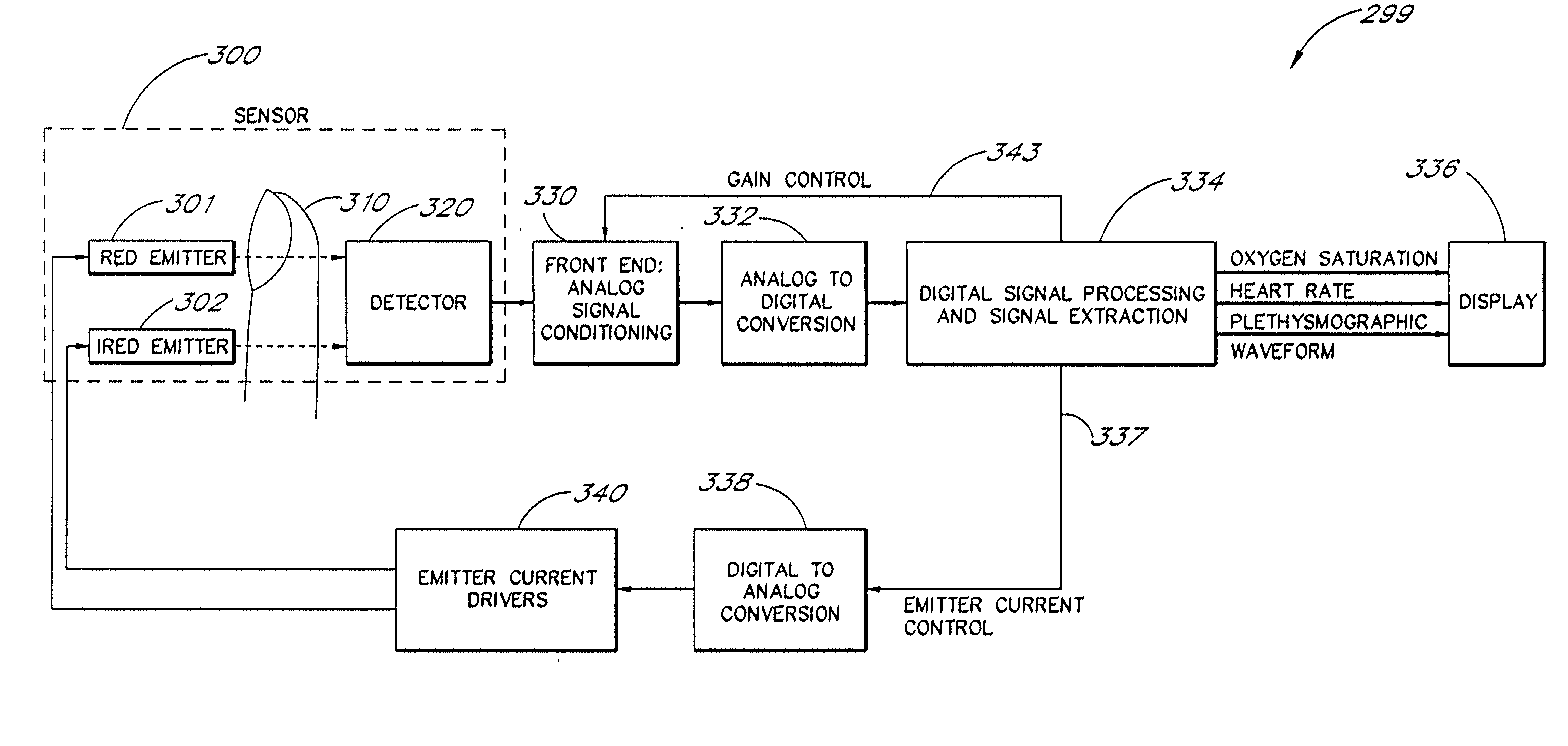
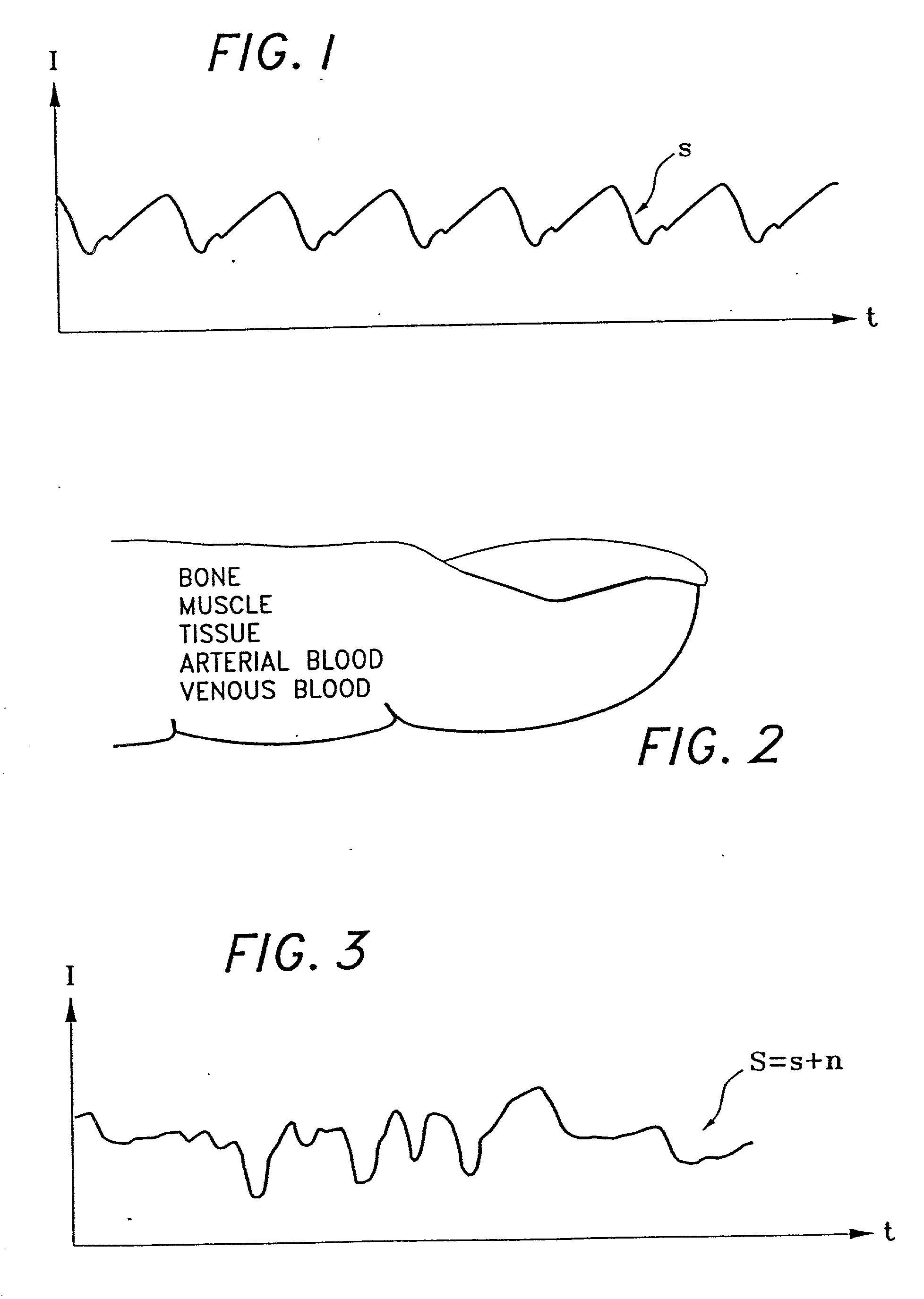
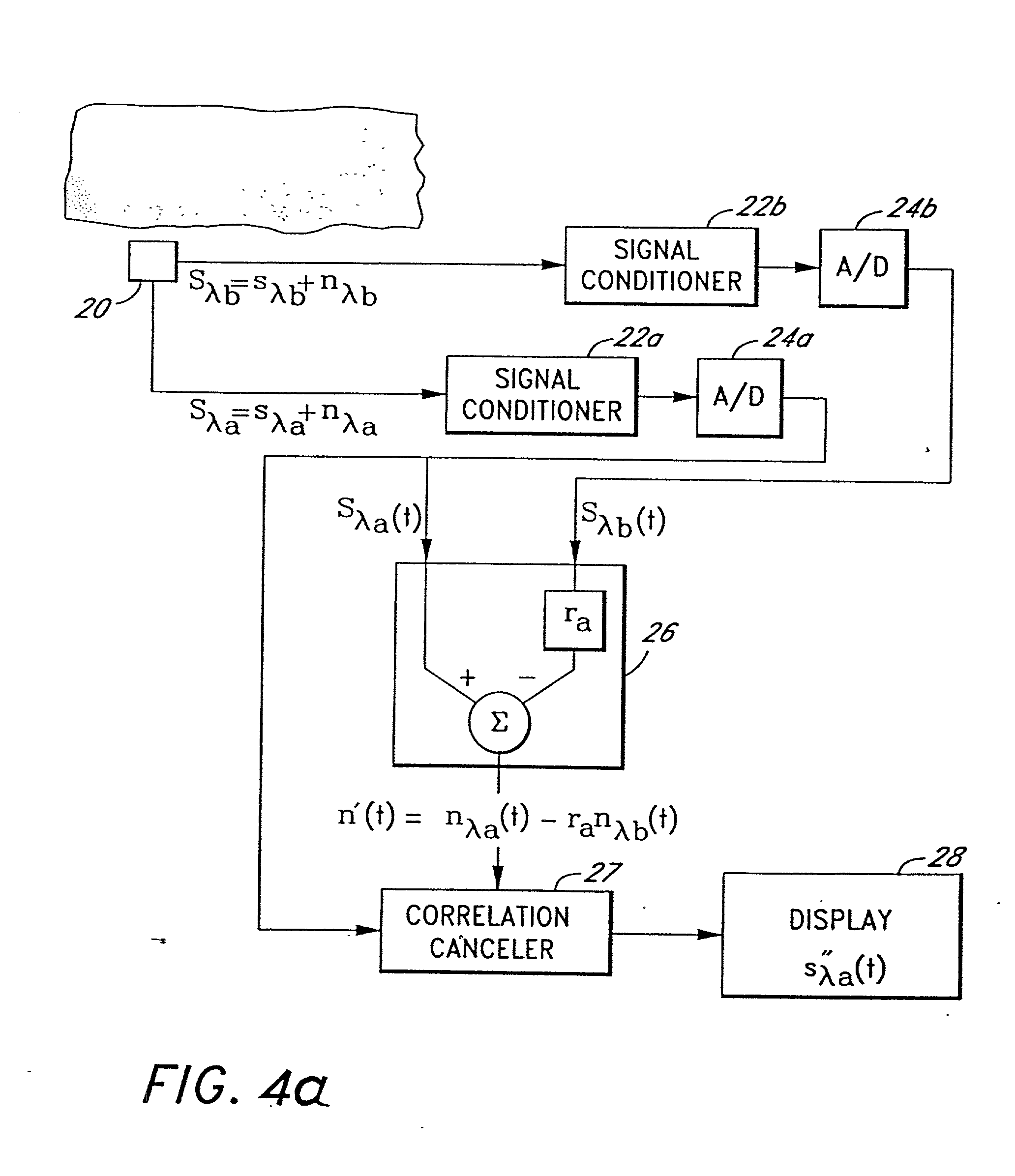
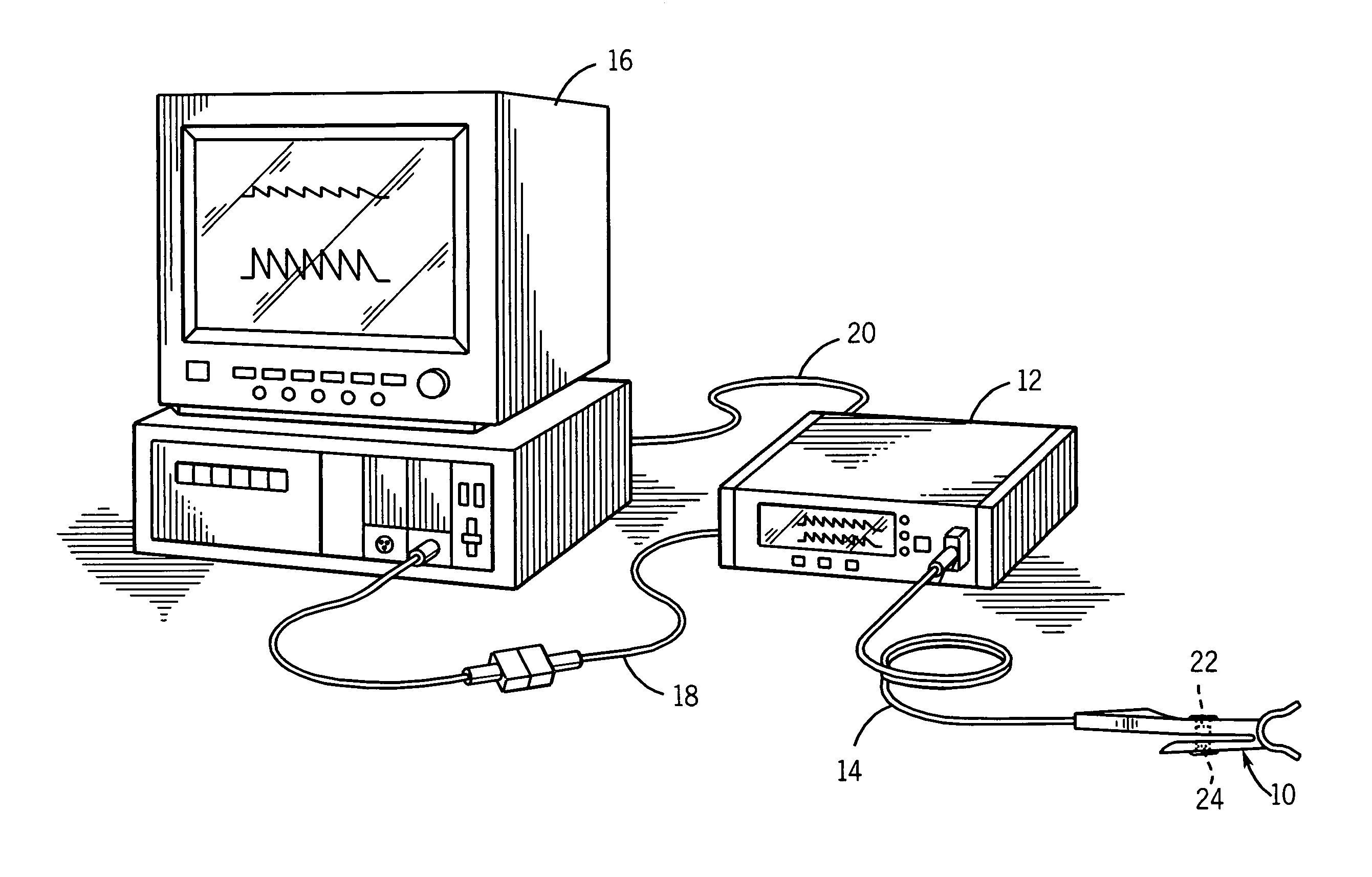
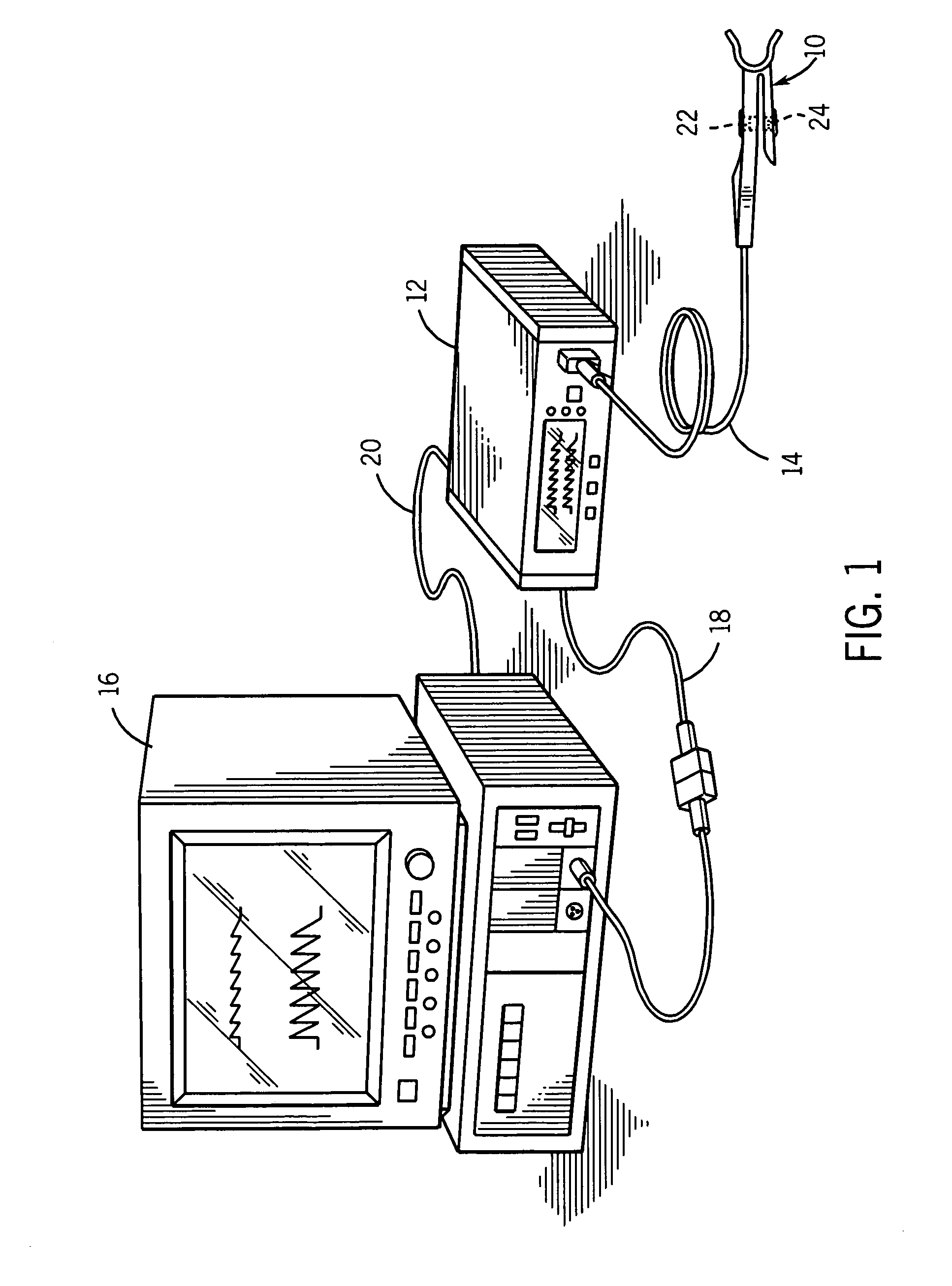
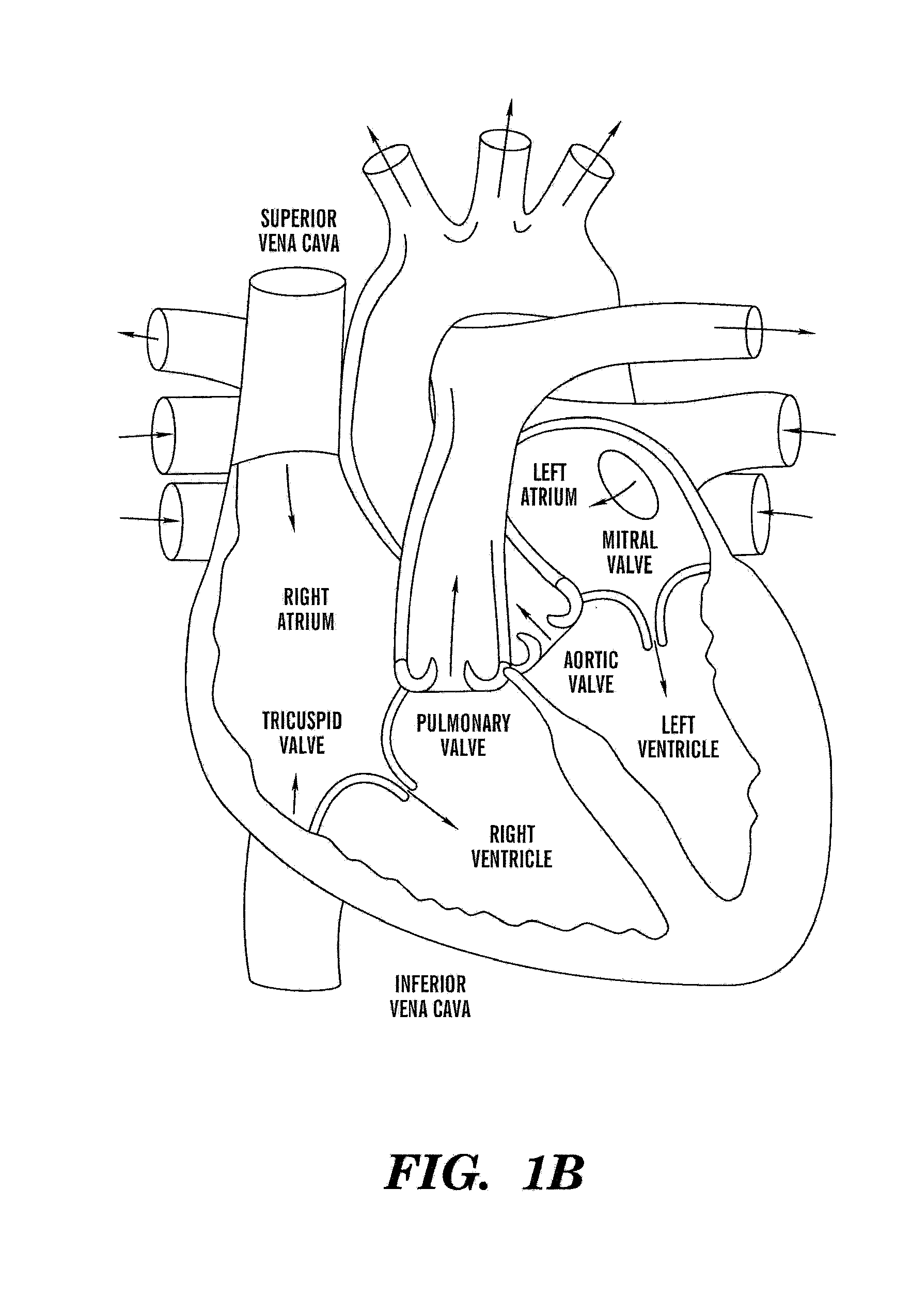
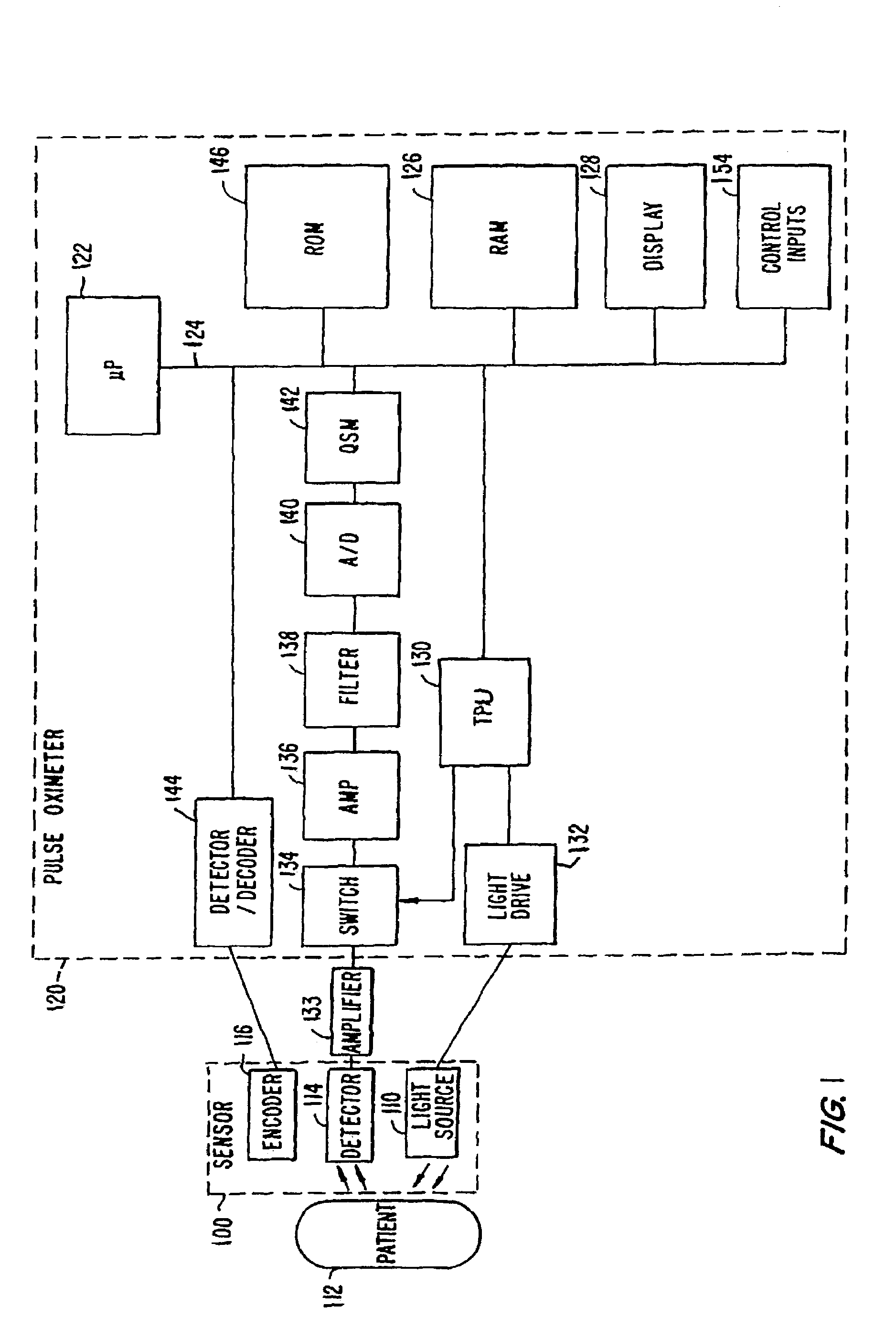
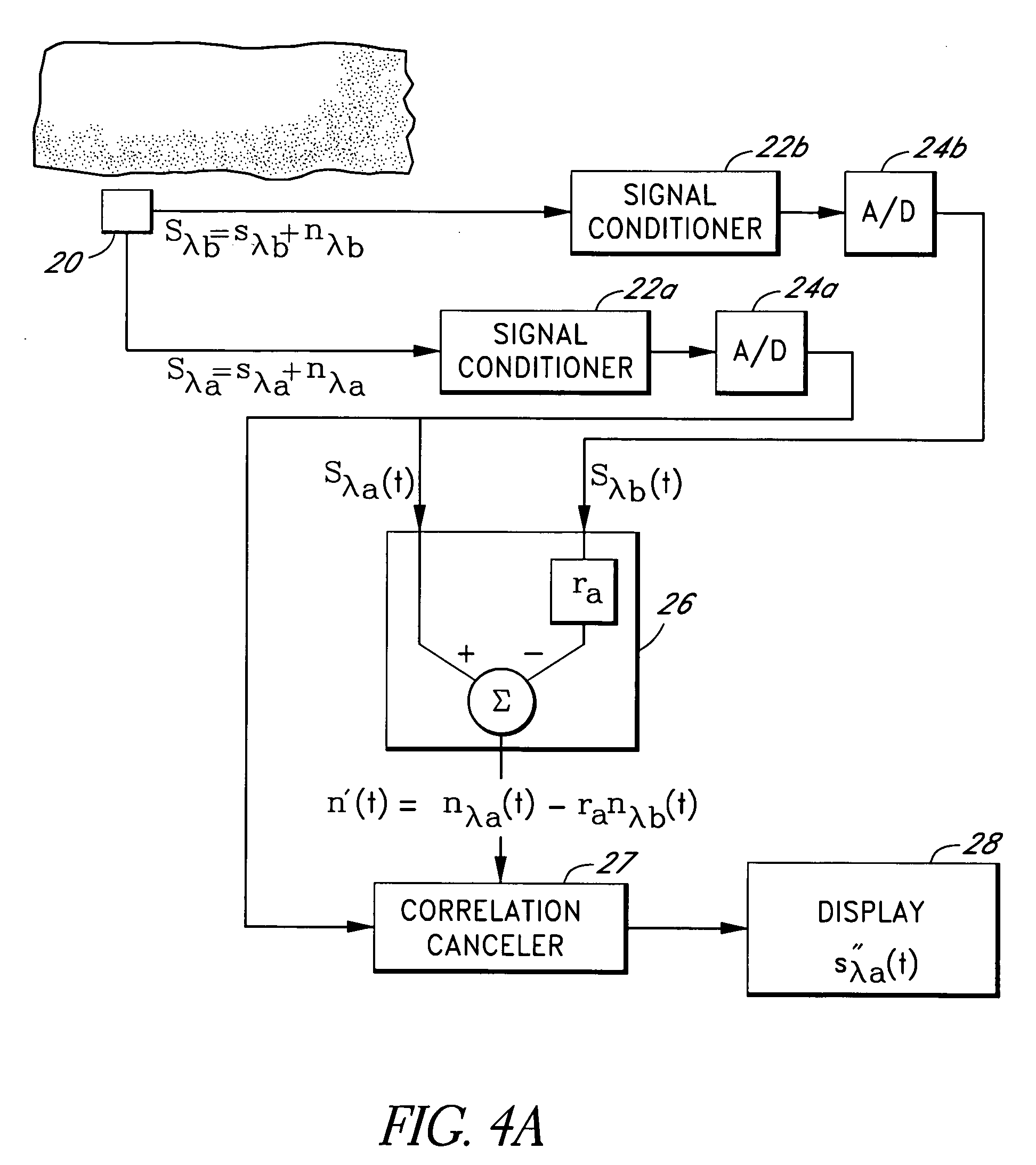
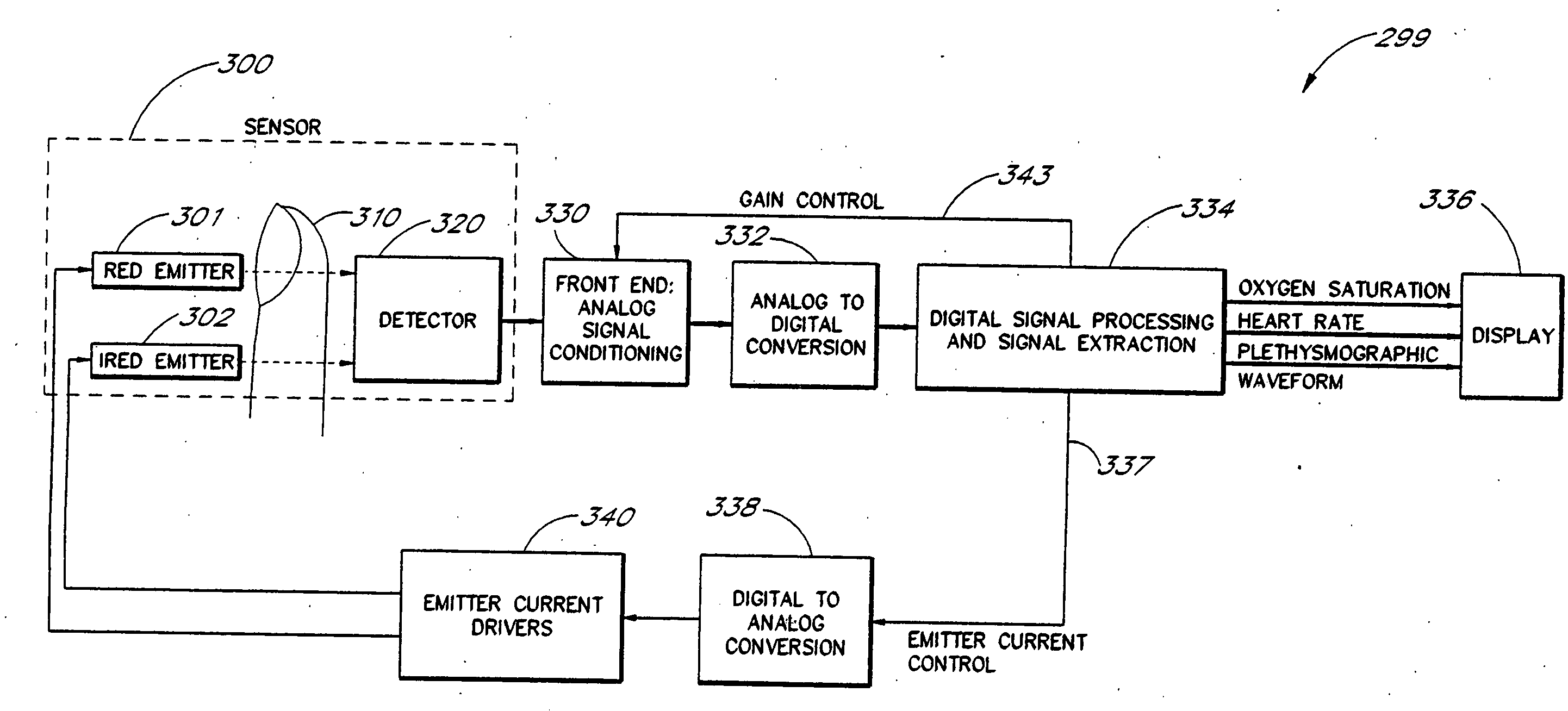
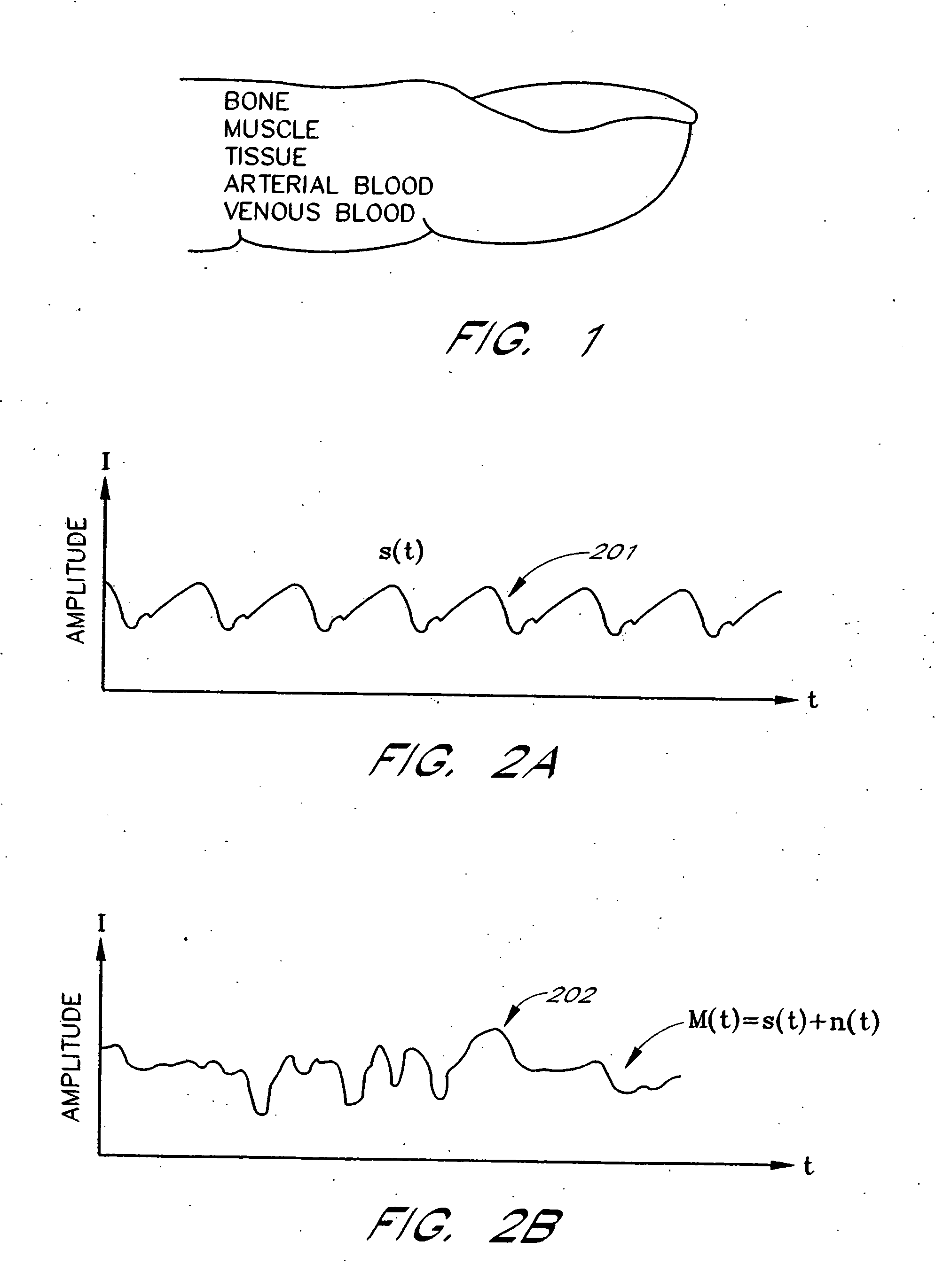
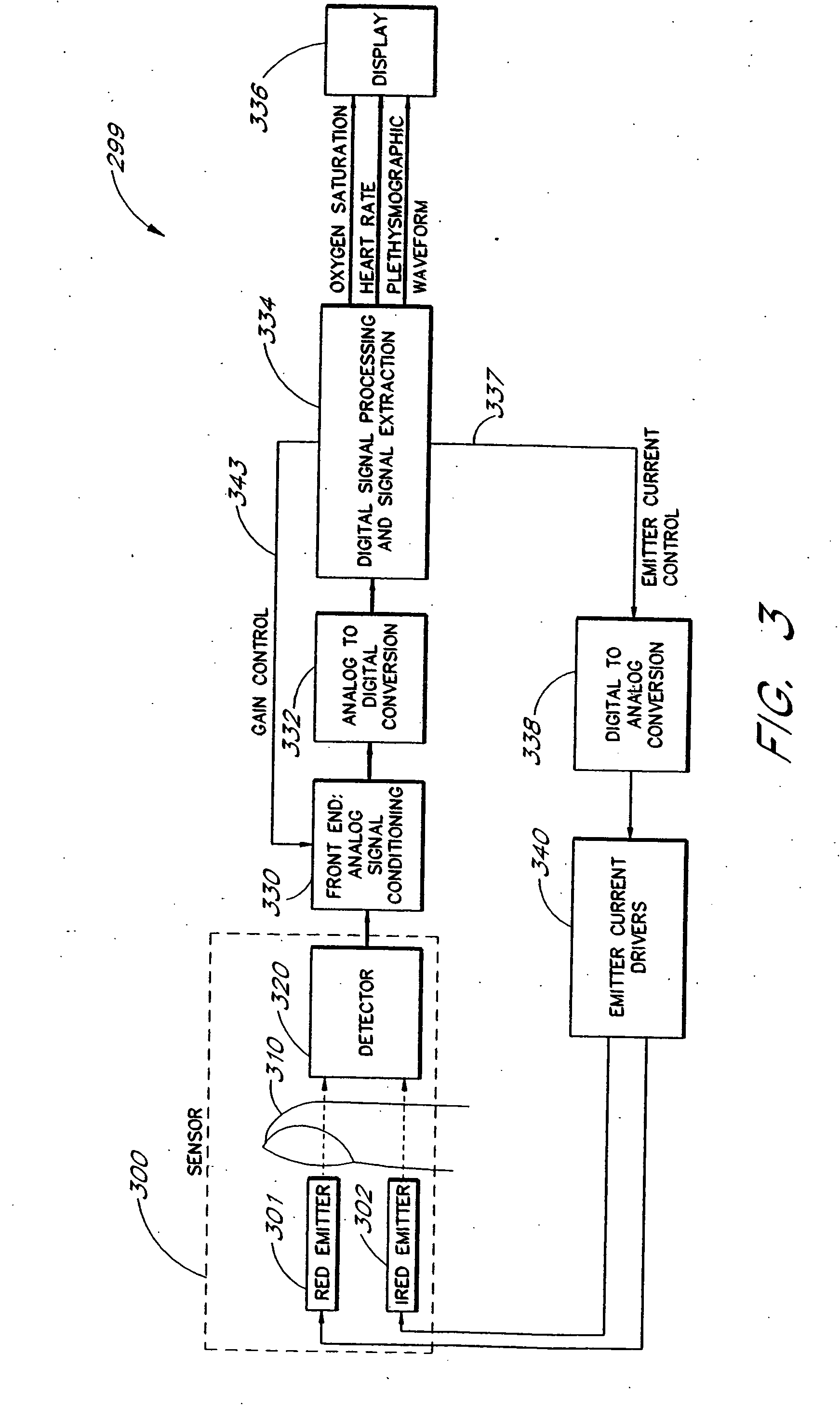
A signal processor which acquires a first signal, including a first primary signal portion and a first secondary signal portion, and a second signal, including a second primary signal portion and a second secondary signal portion, wherein the first and second primary signal portions are correlated. The signals may be acquired by propagating energy through a medium and measuring an attenuated signal after transmission or reflection. Alternatively, the signals may be acquired by measuring energy generated by the medium. A processor of the present invention generates a primary or secondary reference signal which is a combination, respectively, of only the primary or secondary signal portions. The secondary reference signal is then used to remove the secondary portion of each of the first and second measured signals via a correlation canceler, such as an adaptive noise canceler, preferably of the joint process estimator type. The primary reference signal is used to remove the primary portion of each of the first and second measured signals via a correlation canceler. The processor of the present invention may be employed in conjunction with a correlation canceler in physiological monitors wherein the known properties of energy attenuation through a medium are used to determine physiological characteristics of the medium. Many physiological conditions, such as the pulse, or blood pressure of a patient or the concentration of a constituent in a medium, can be determined from the primary or secondary portions of the signal after other signal portion is removed.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
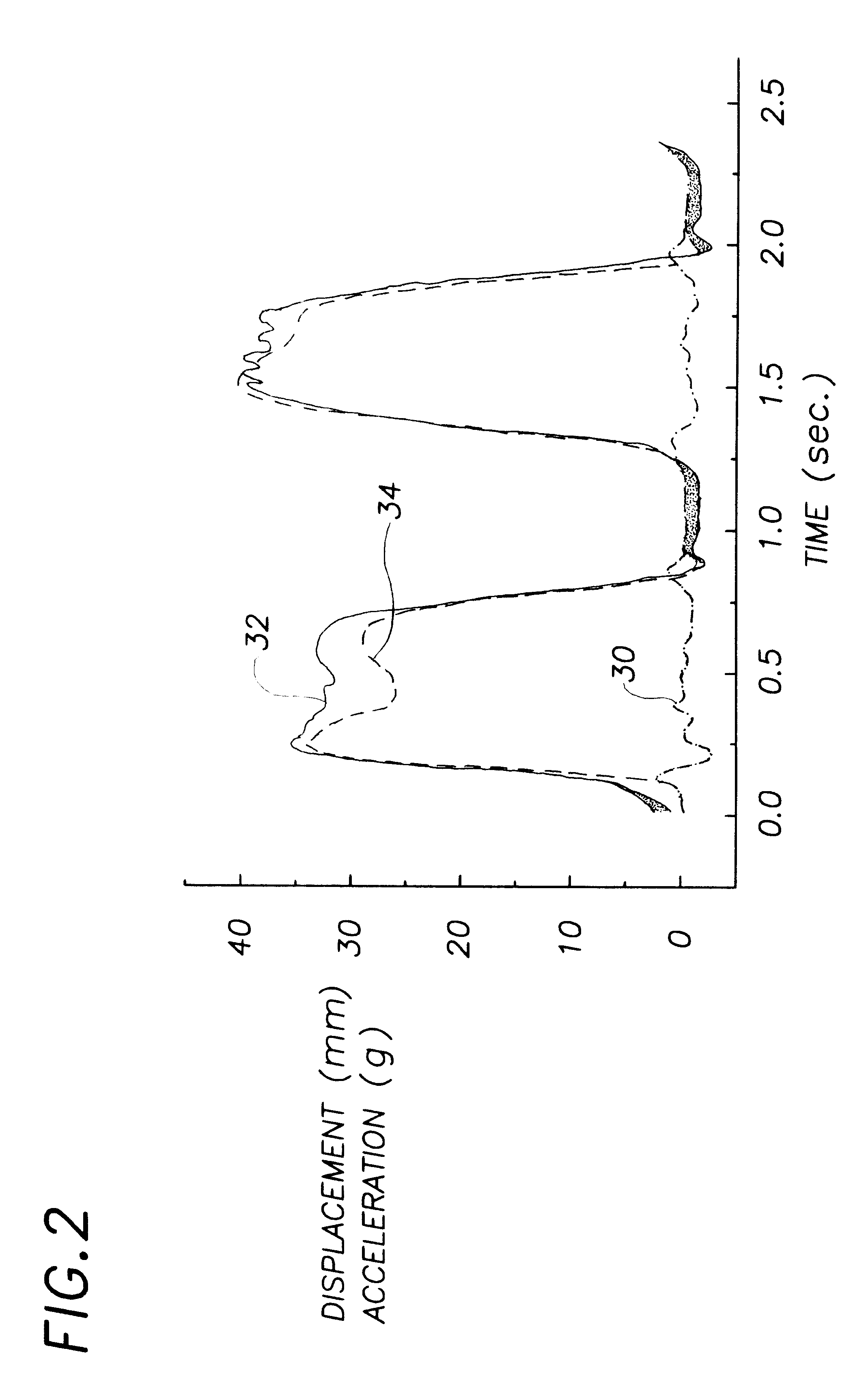
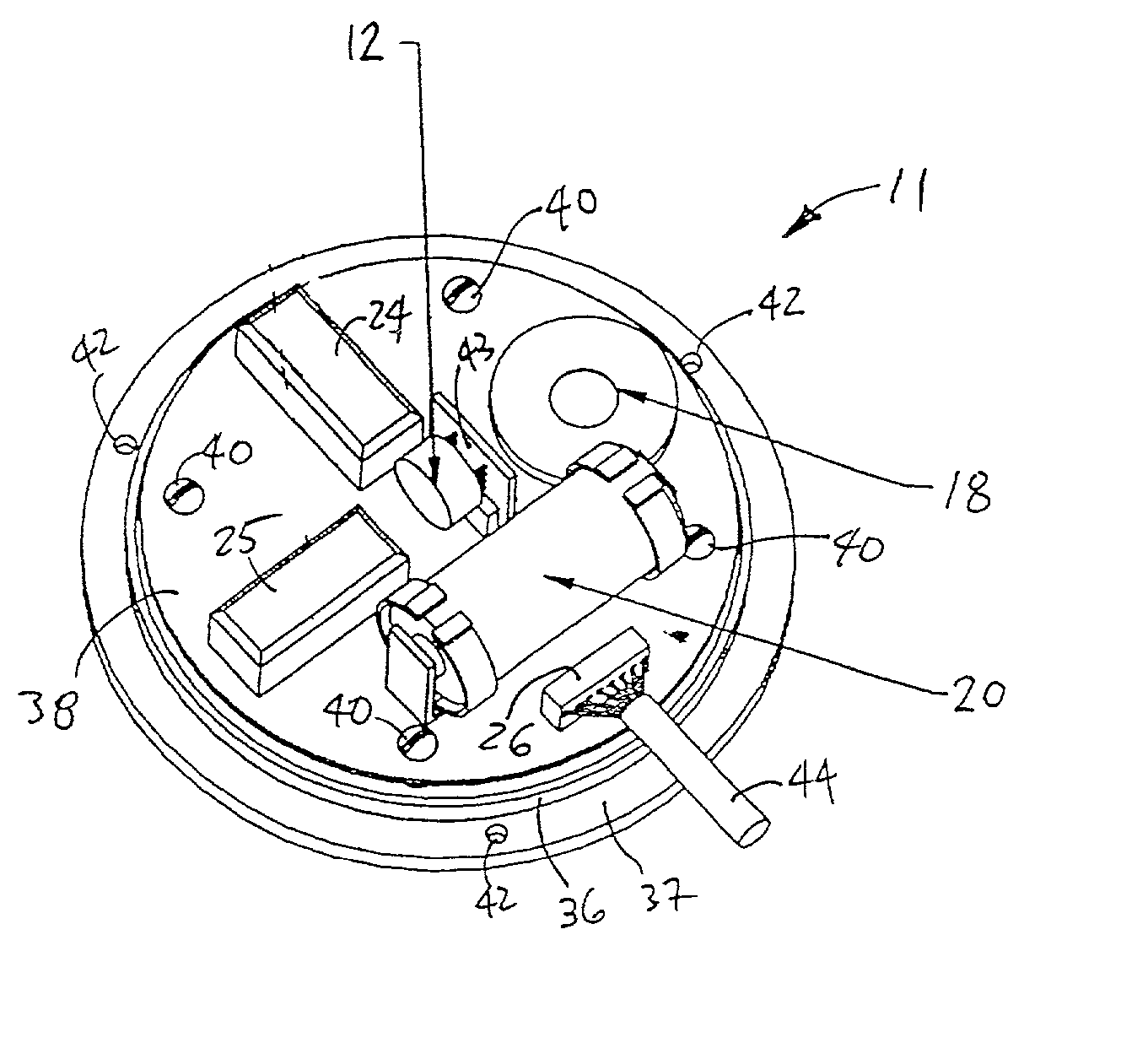
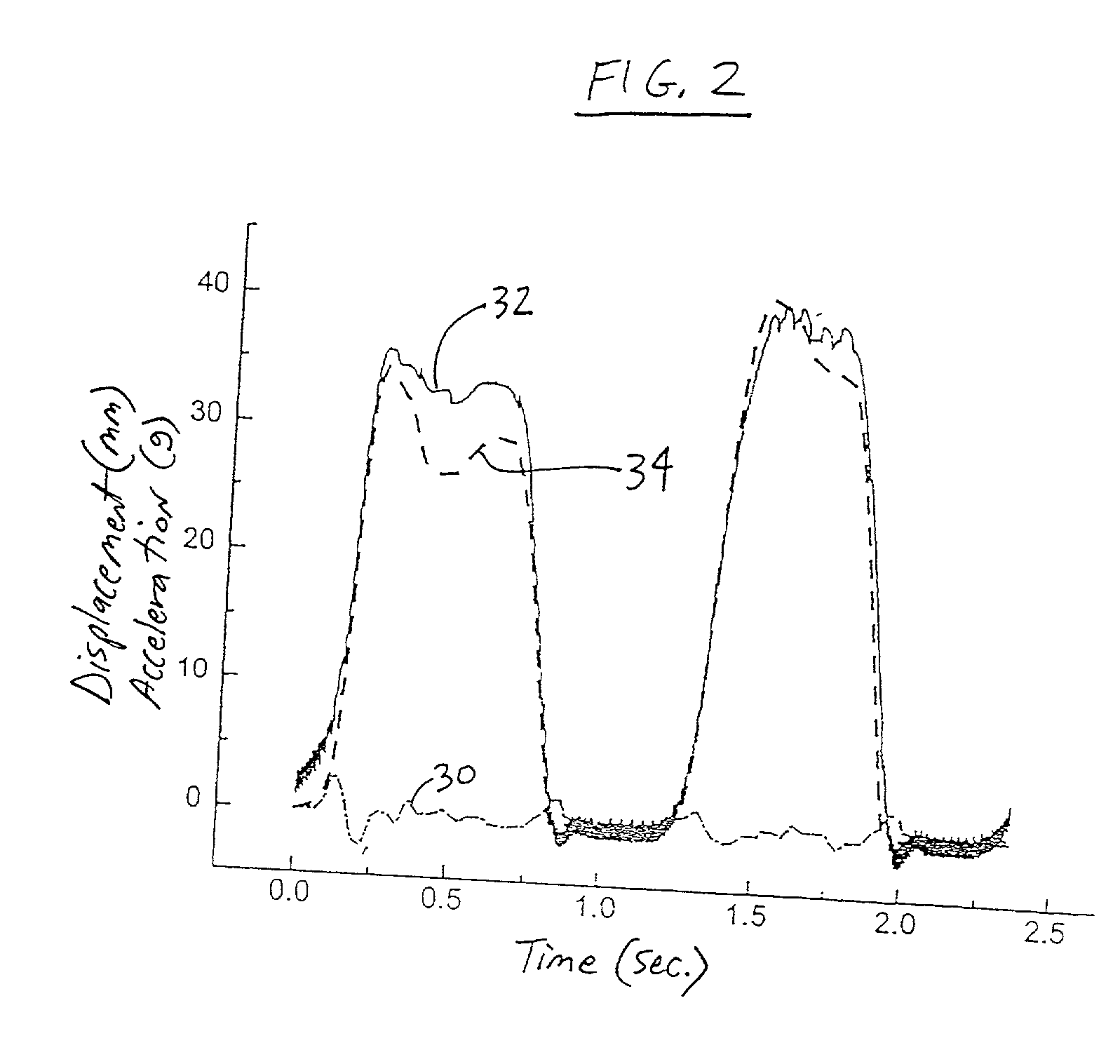
CPR chest compression monitor
InactiveUS6390996B1Accurate measurementSmall sizeHeart defibrillatorsInertial sensorsEcg signalEmergency medicine
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS8560034B1Improve approximationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsCatheterFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
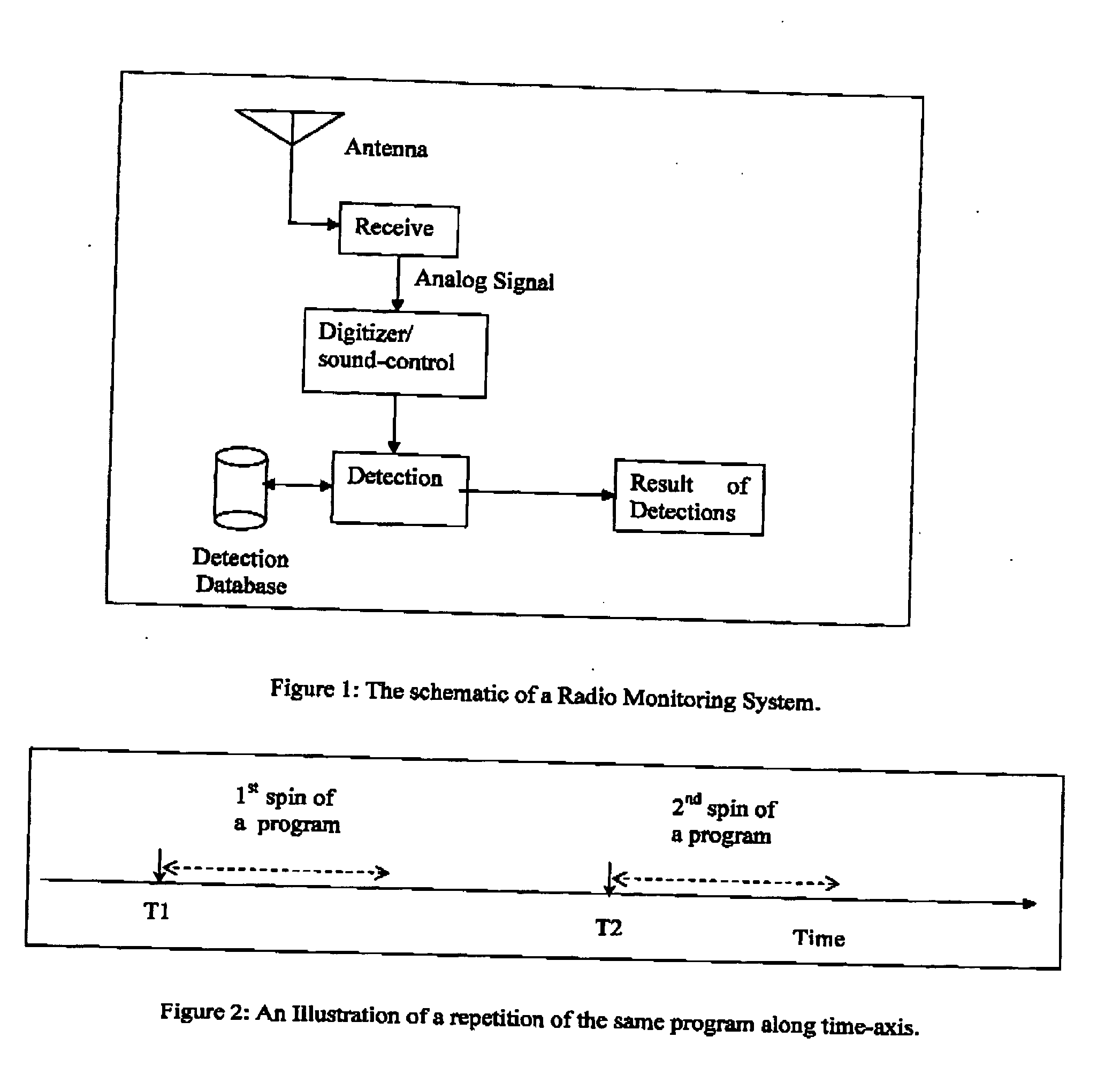
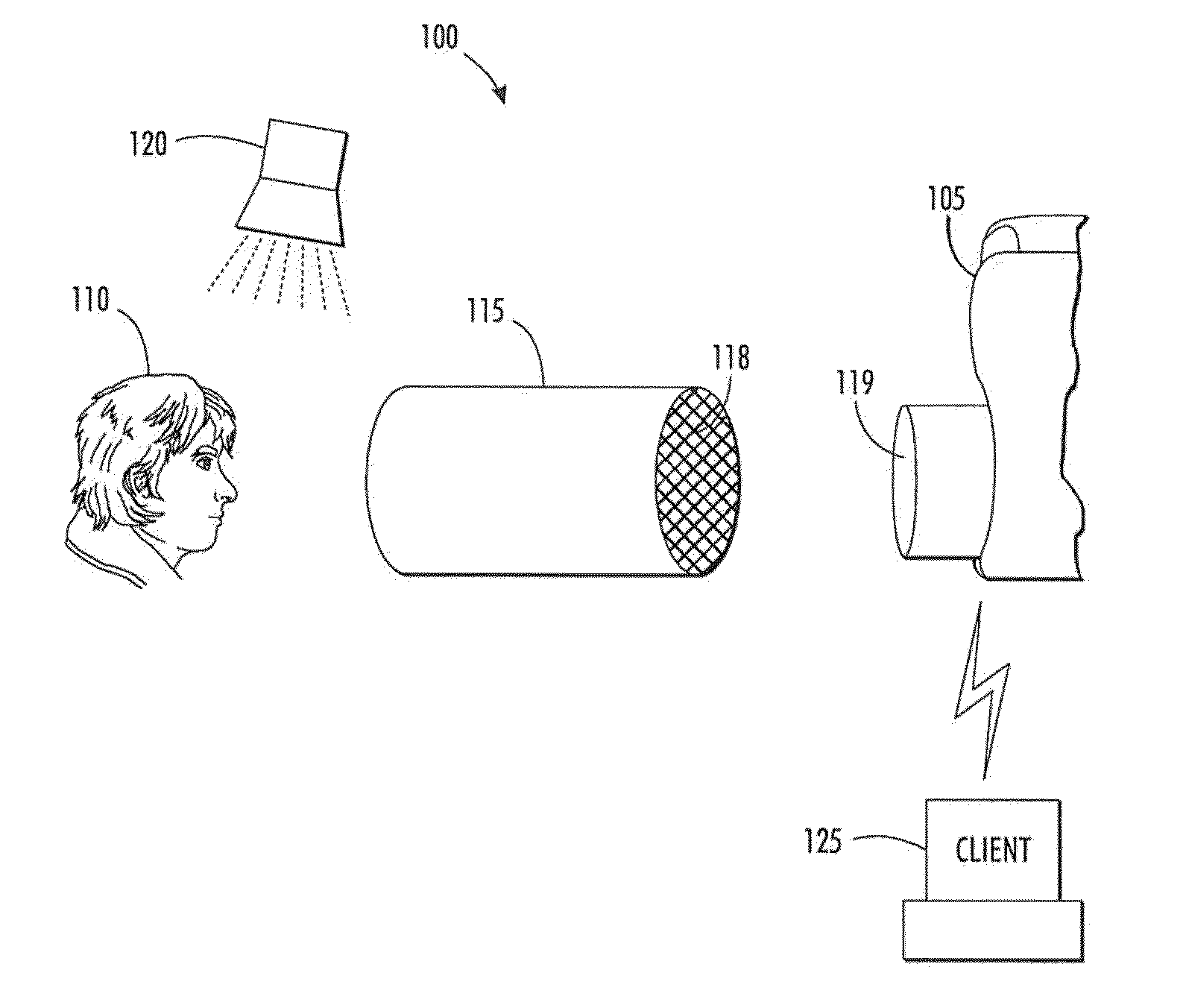
Method and apparatus for automatically recognizing input audio and/or video streams
InactiveUS7194752B1Improve accuracyMinimal timeSpeech analysisAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSingle sampleFeature set
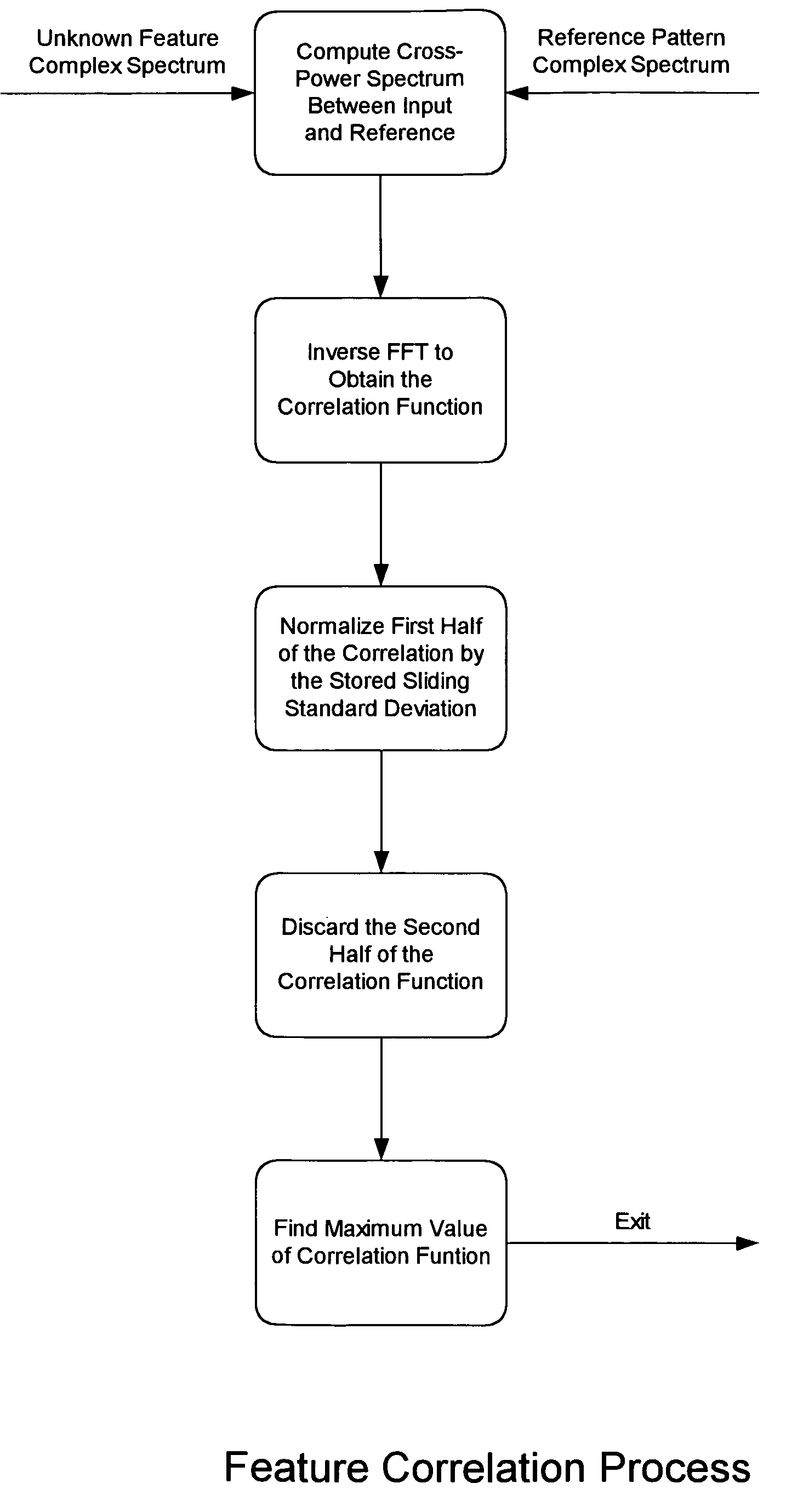
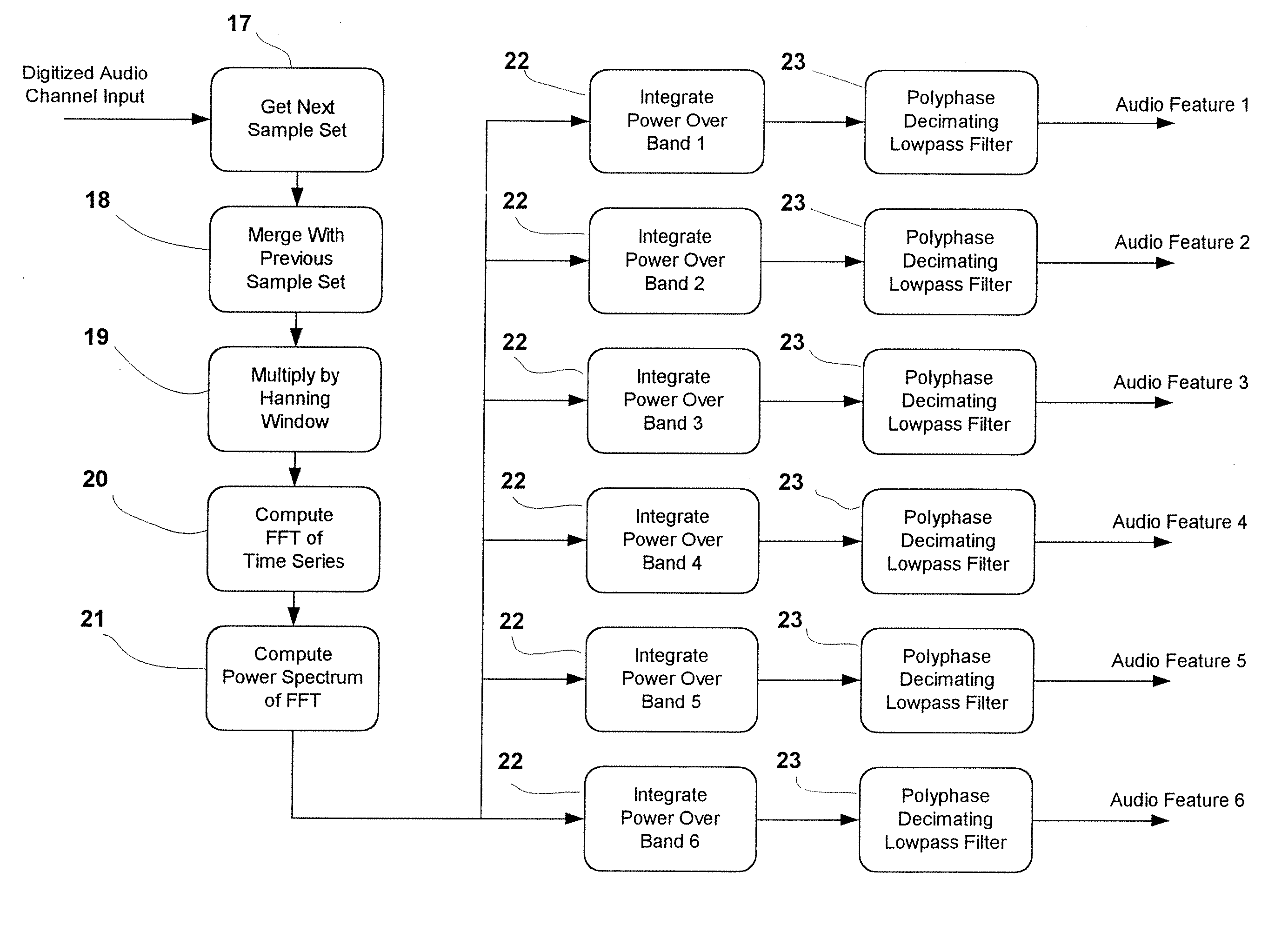
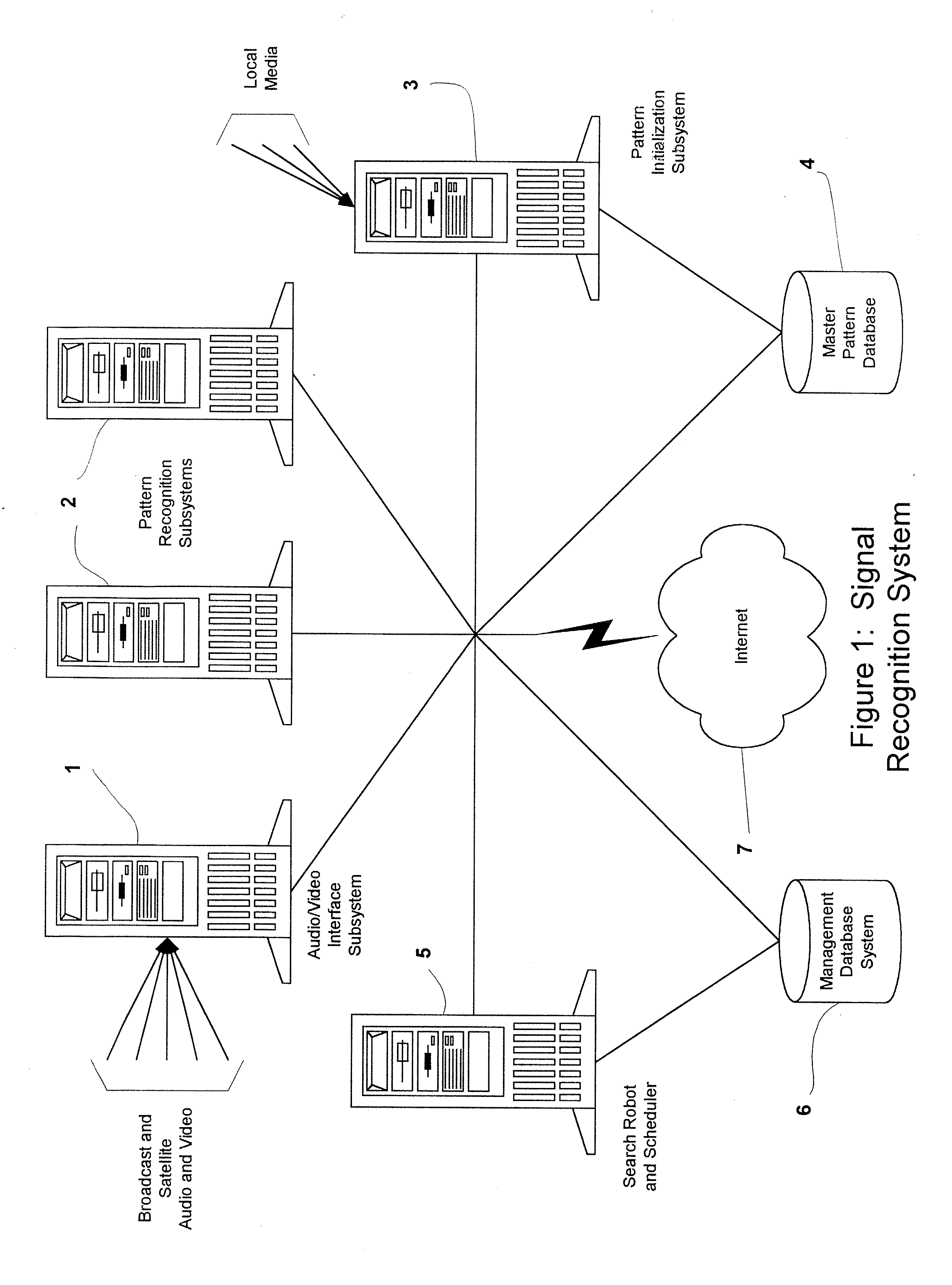
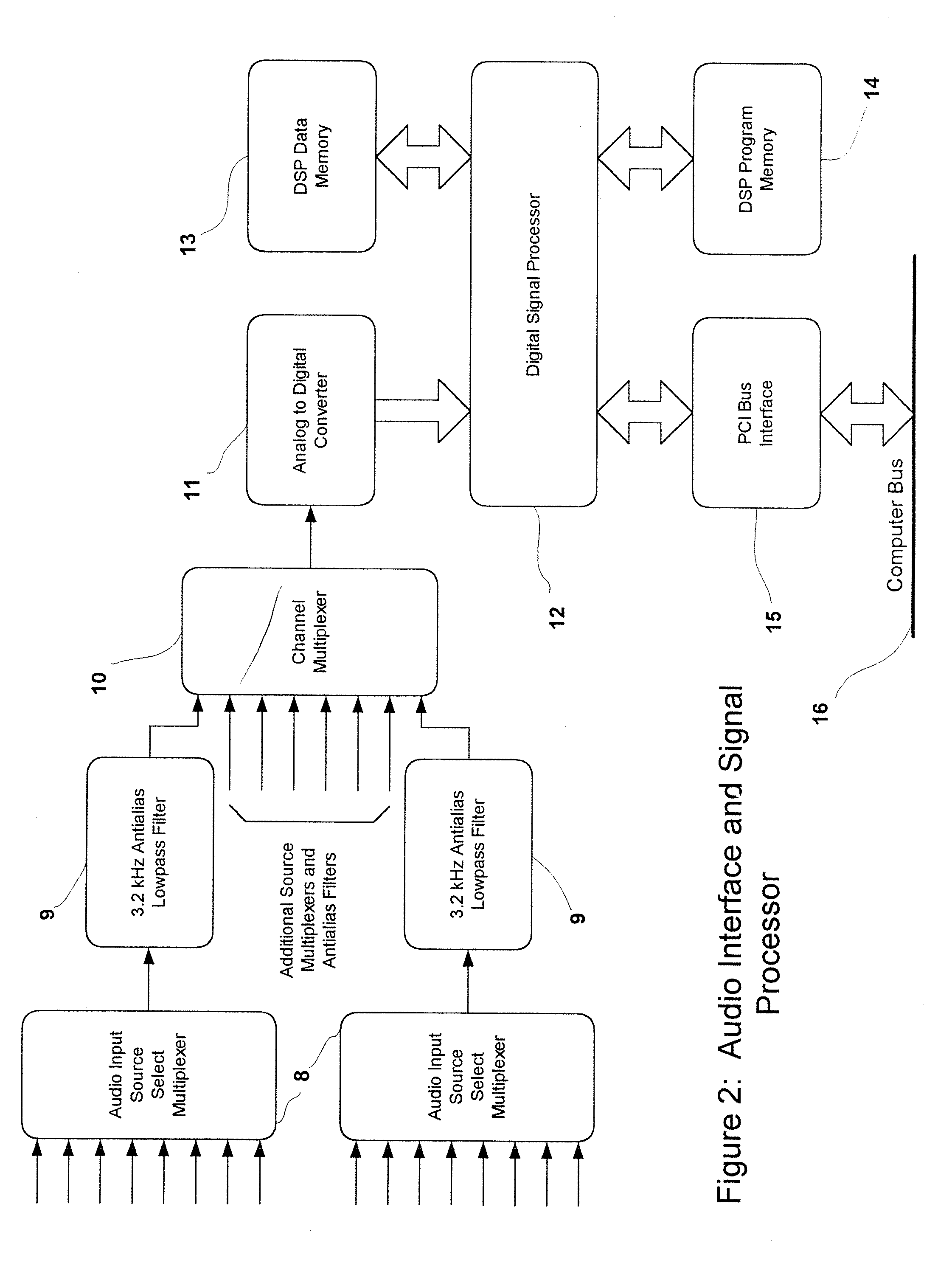
A method and system for the automatic identification of audio, video, multimedia, and / or data recordings based on immutable characteristics of these works. The invention does not require the insertion of identifying codes or signals into the recording. This allows the system to be used to identify existing recordings that have not been through a coding process at the time that they were generated. Instead, each work to be recognized is “played” into the system where it is subjected to an automatic signal analysis process that locates salient features and computes a statistical representation of these properties. These features are then stored as patterns for later recognition of live input signal streams. A different set of features is derived for each audio or video work to be identified and stored. During real-time monitoring of a signal stream, a similar automatic signal analysis process is carried out, and many features are computed for comparison with the patterns stored in a large feature database. For each particular pattern stored in the database, only the relevant characteristics are compared with the real-time feature set. Preferably, during analysis and generation of reference patterns, data are extracted from all time intervals of a recording. This allows a work to be recognized from a single sample taken from any part of the recording.
Owner:ICEBERG IND
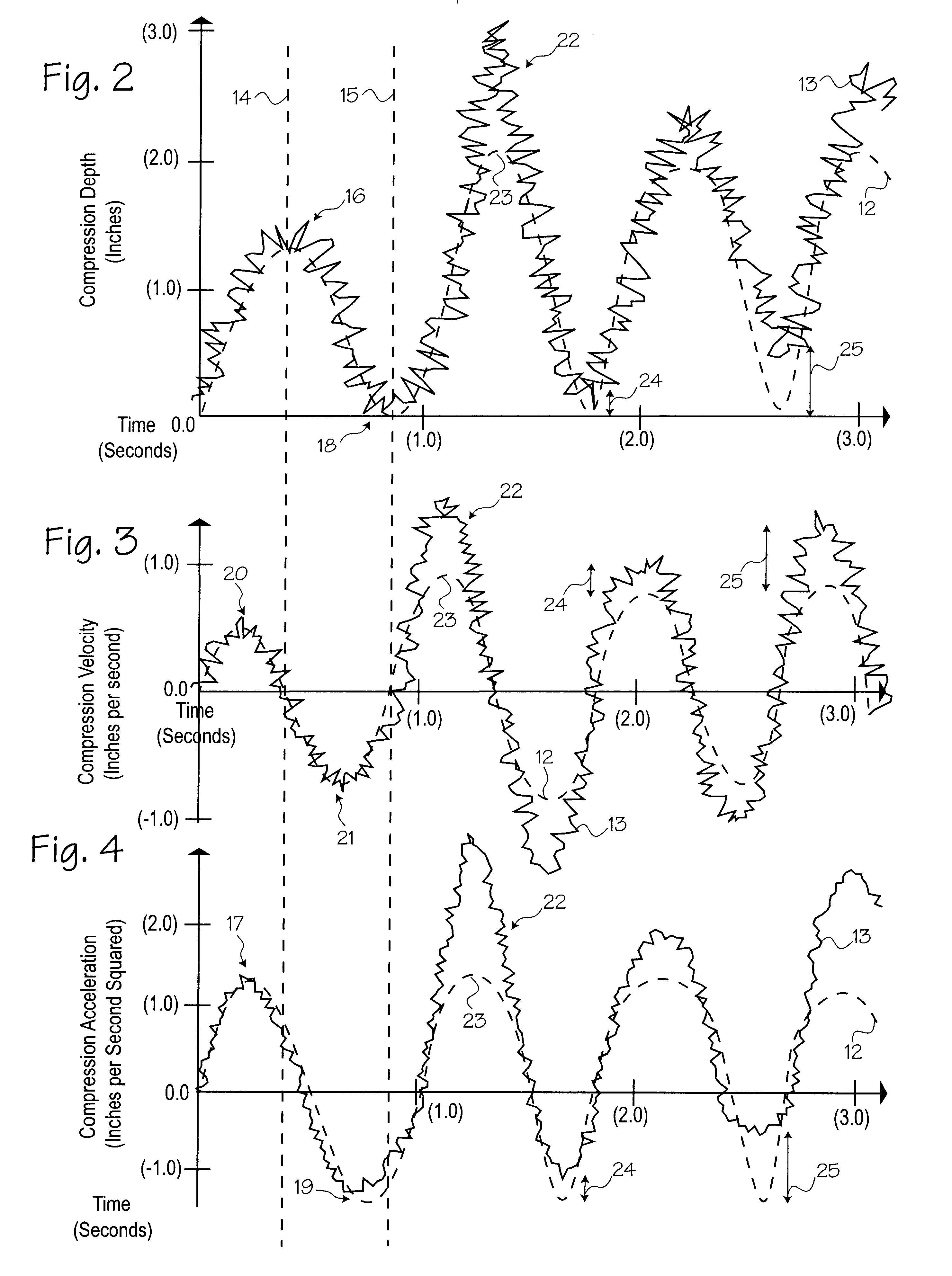
Method of determining depth of compressions during cardio-pulmonary resuscitation
Owner:ZOLL CIRCULATION
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20020128544A1Improve approximationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansFourier transform on finite groupsComputer science
The present invention involves method and apparatus for analyzing two measured signals that are modeled as containing primary and secondary portions. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, the present invention involves utilizing a transformation which evaluates a plurality of possible signal coefficients in order to find appropriate coefficients. Alternatively, the present invention involves using statistical functions or Fourier transform and windowing techniques to determine the coefficients relating to two measured signals. Use of this invention is described in particular detail with respect to blood oximetry measurements.
Owner:DIAB MOHAMED K +5
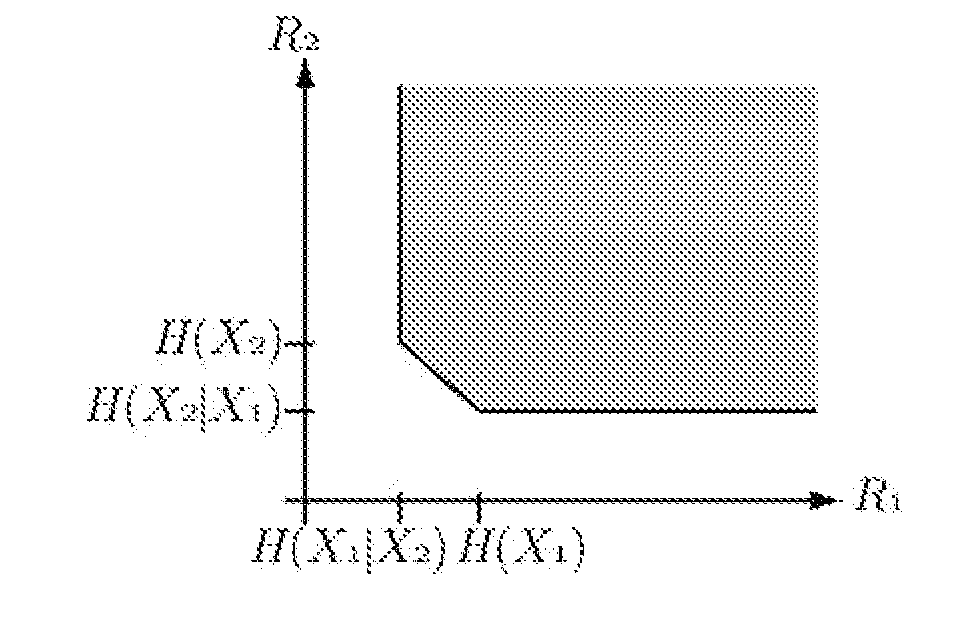
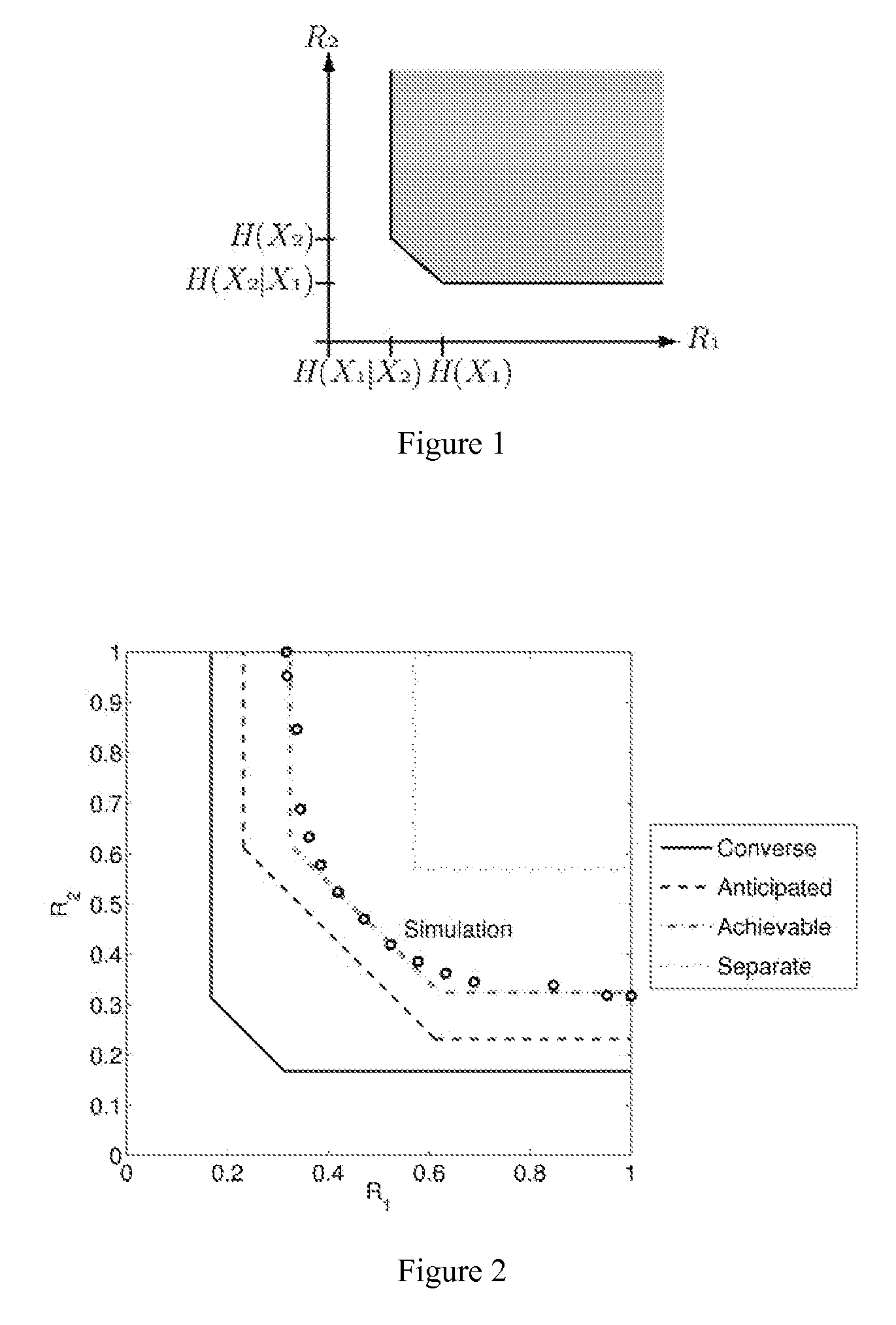
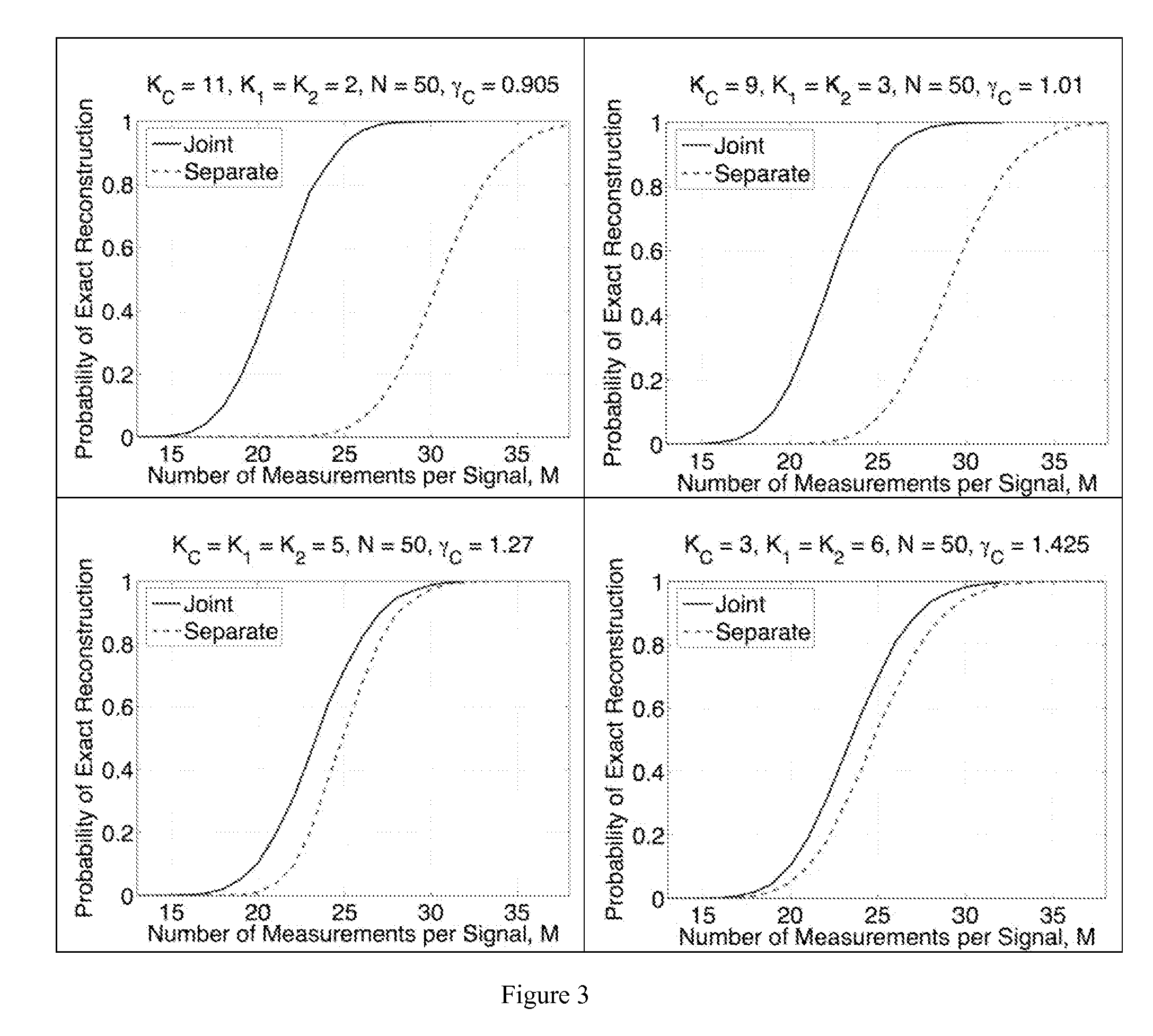
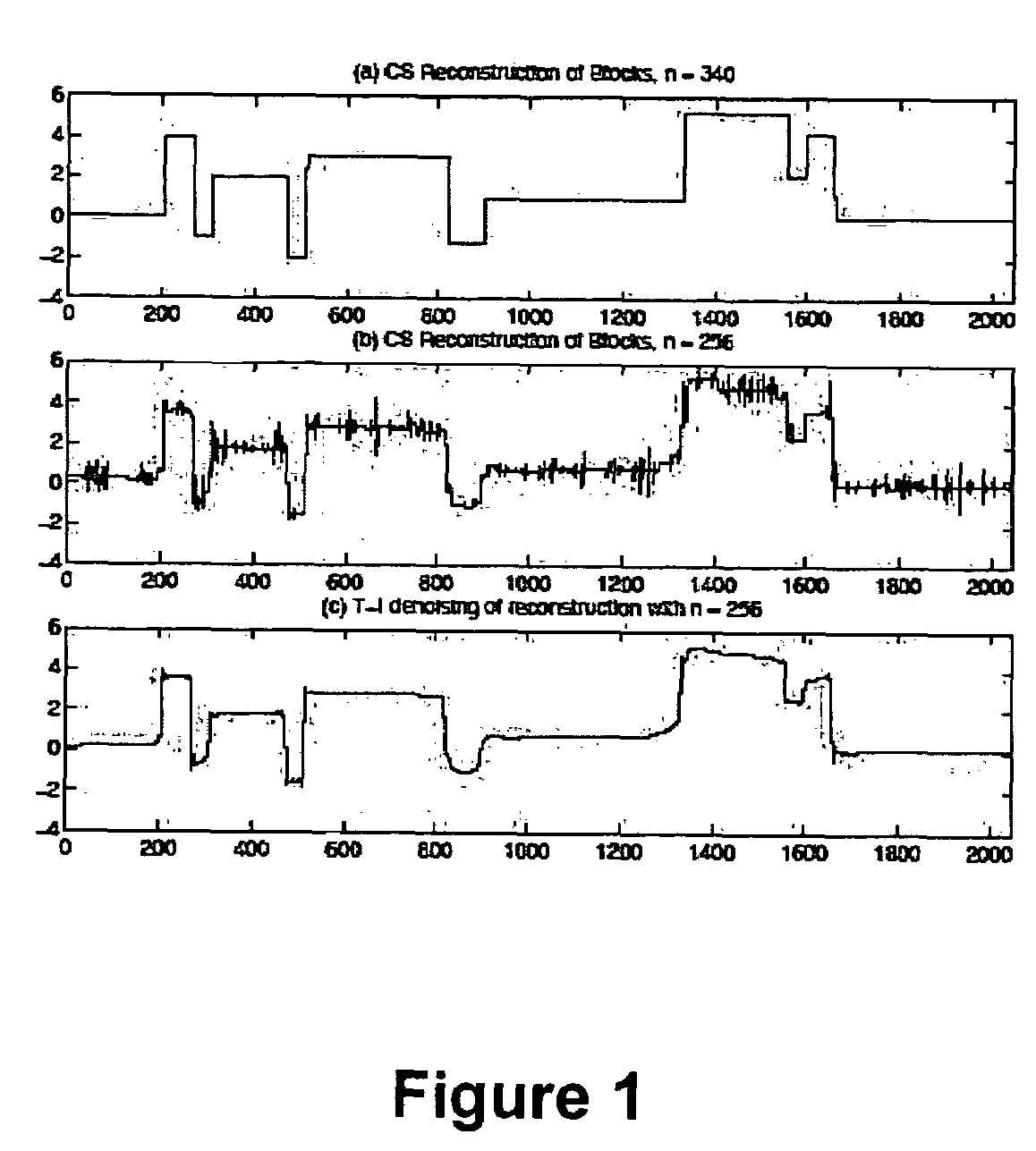
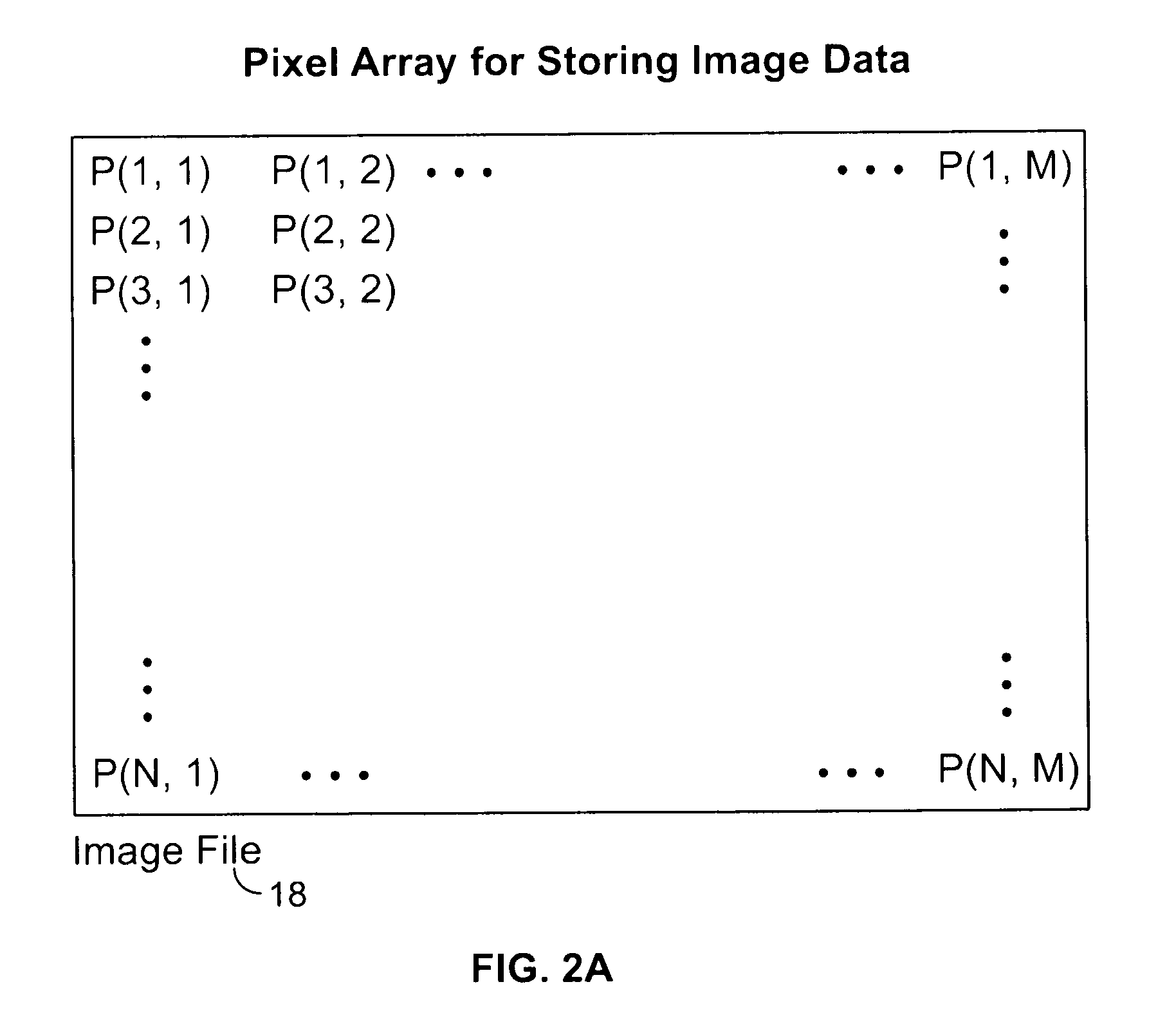
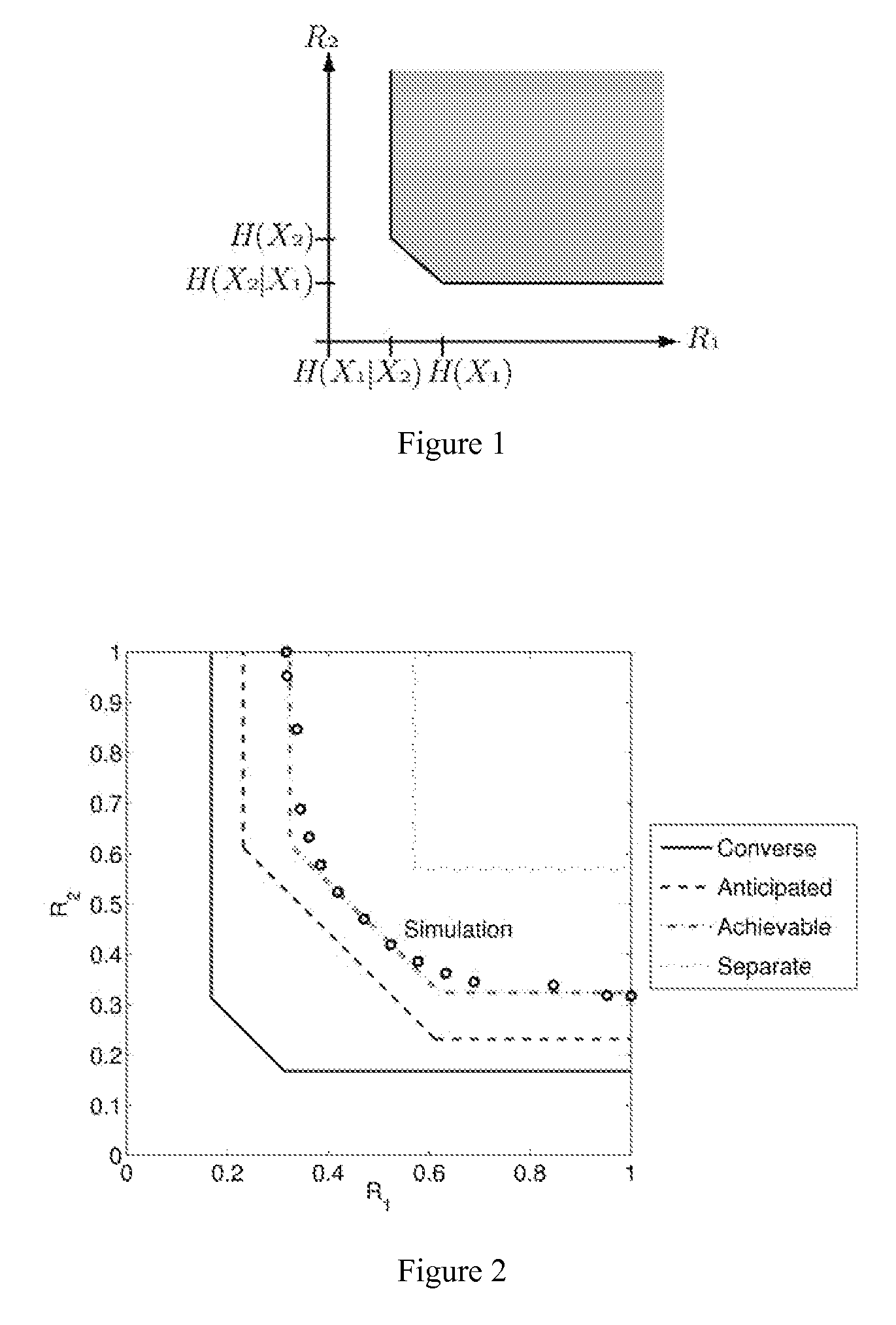
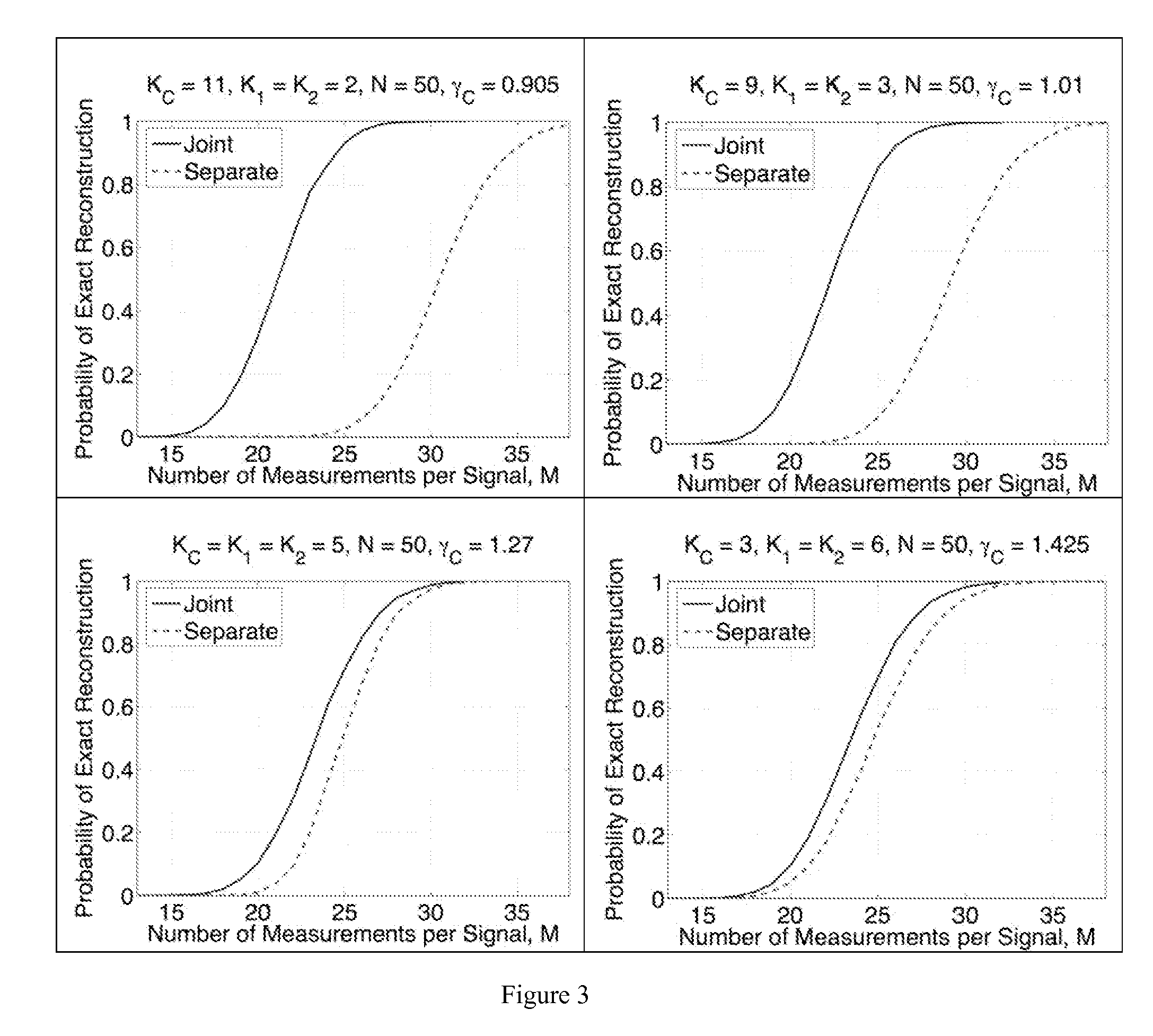
Method and apparatus for distributed compressed sensing
ActiveUS7271747B2Efficient captureAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceCode conversionCompressed sensingComputer science
A method for approximating a plurality of digital signals or images using compressed sensing. In a scheme where a common component xc of said plurality of digital signals or images an innovative component xi of each of said plurality of digital signals each are represented as a vector with m entries, the method comprises the steps of making a measurement yc, where yc comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, making a measurement yi for each of said correlated digital signals, where yi comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, and from each said innovation components yi, producing an approximate reconstruction of each m-vector xi using said common component yc and said innovative component yi.
Owner:RICE UNIV
System and method for pre-processing waveforms
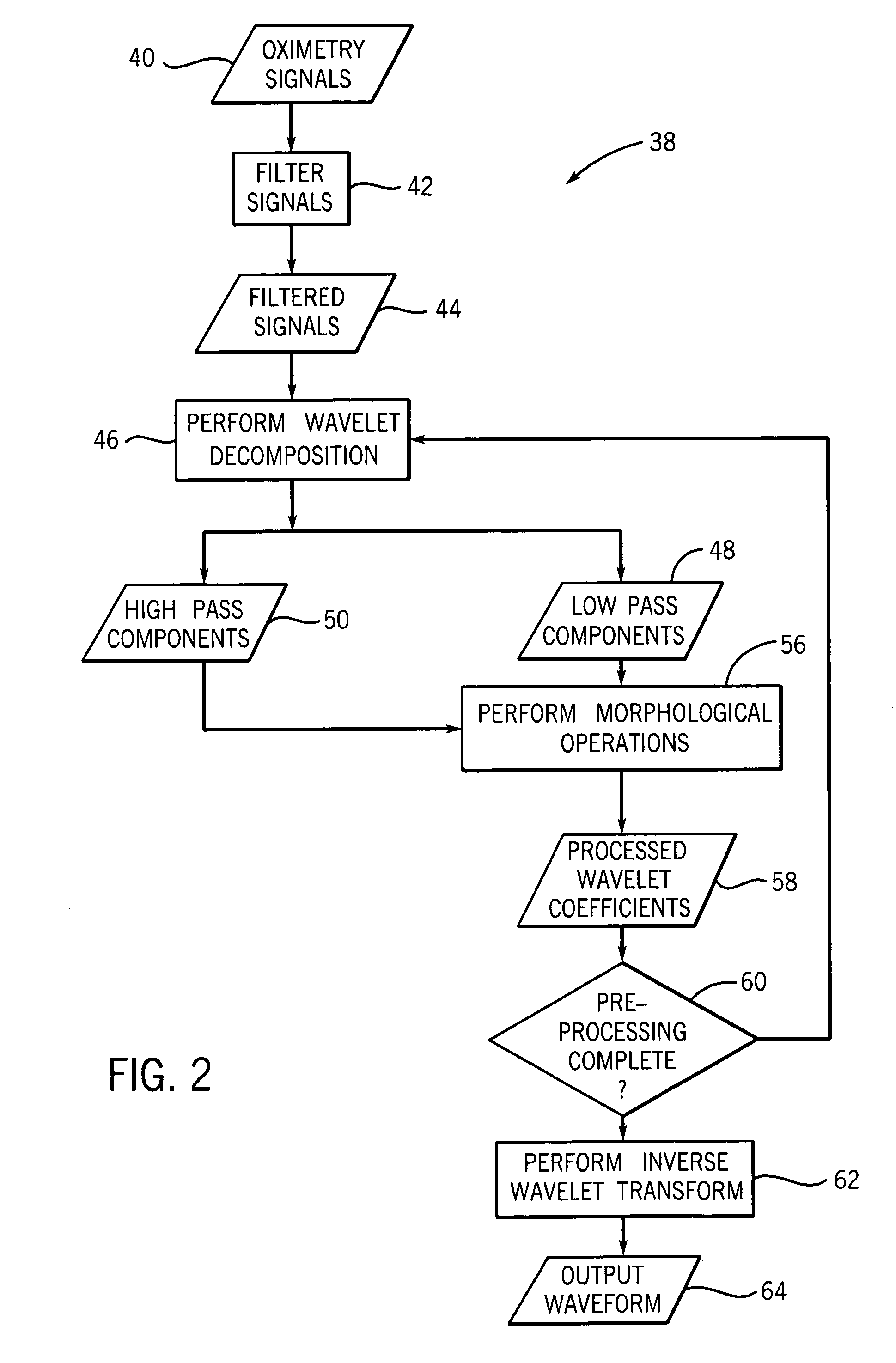
A technique is provided for processing a physiological signal. The technique includes performing one or more multi-resolution decompositions on a physiological signal and one or more morphological operations on some or all of the respective decomposition components. In one embodiment, the technique is implemented as iteratively wavelet transformations where morphological operations, such as erosions and dilations, are applied to modify some or all of the respective wavelet coefficients. The modified wavelet coefficients may then be reconstructed to generate a clean version of the physiological signal from which some or all of the noise and / or artifacts have been removed.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
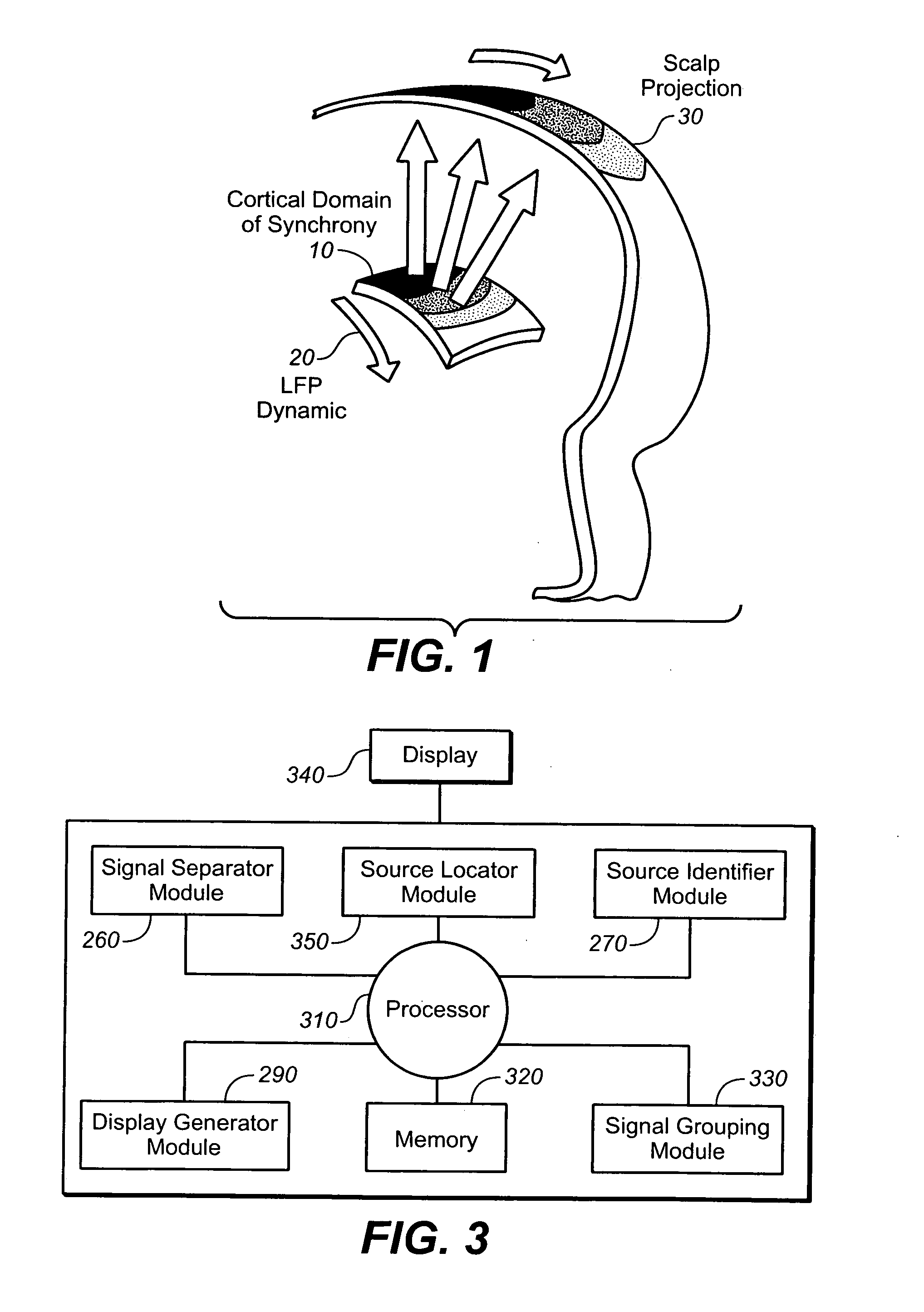
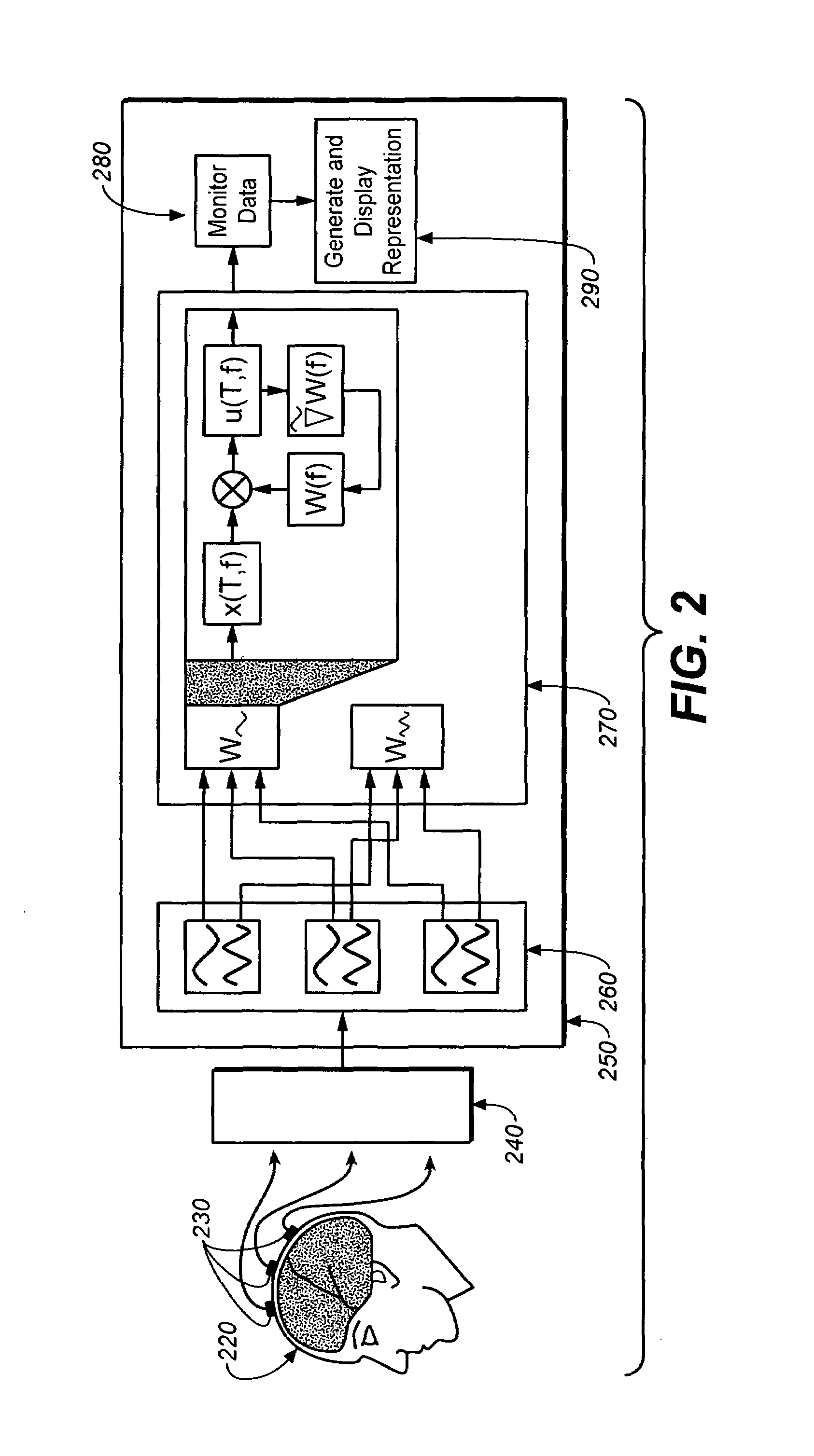
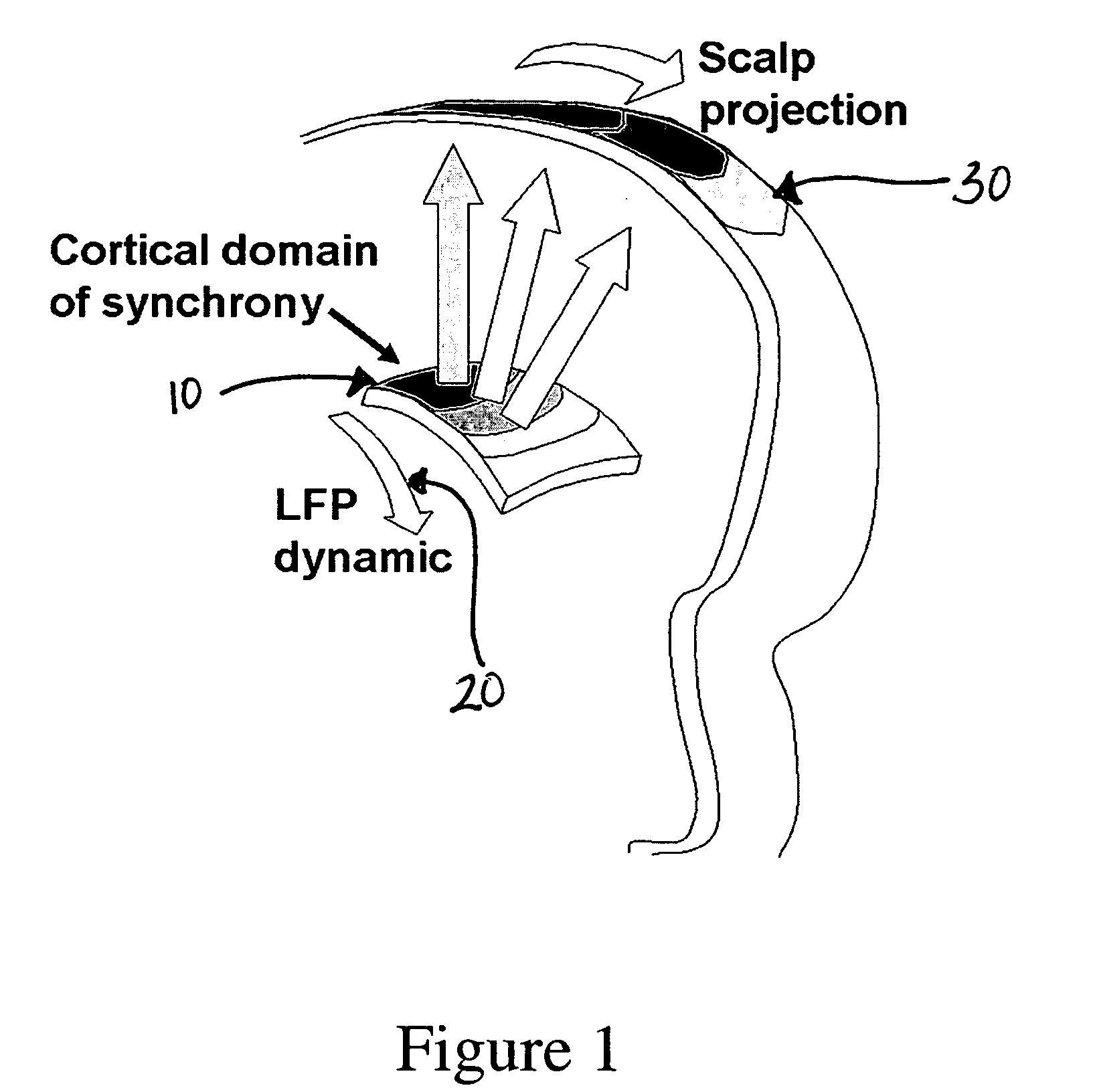
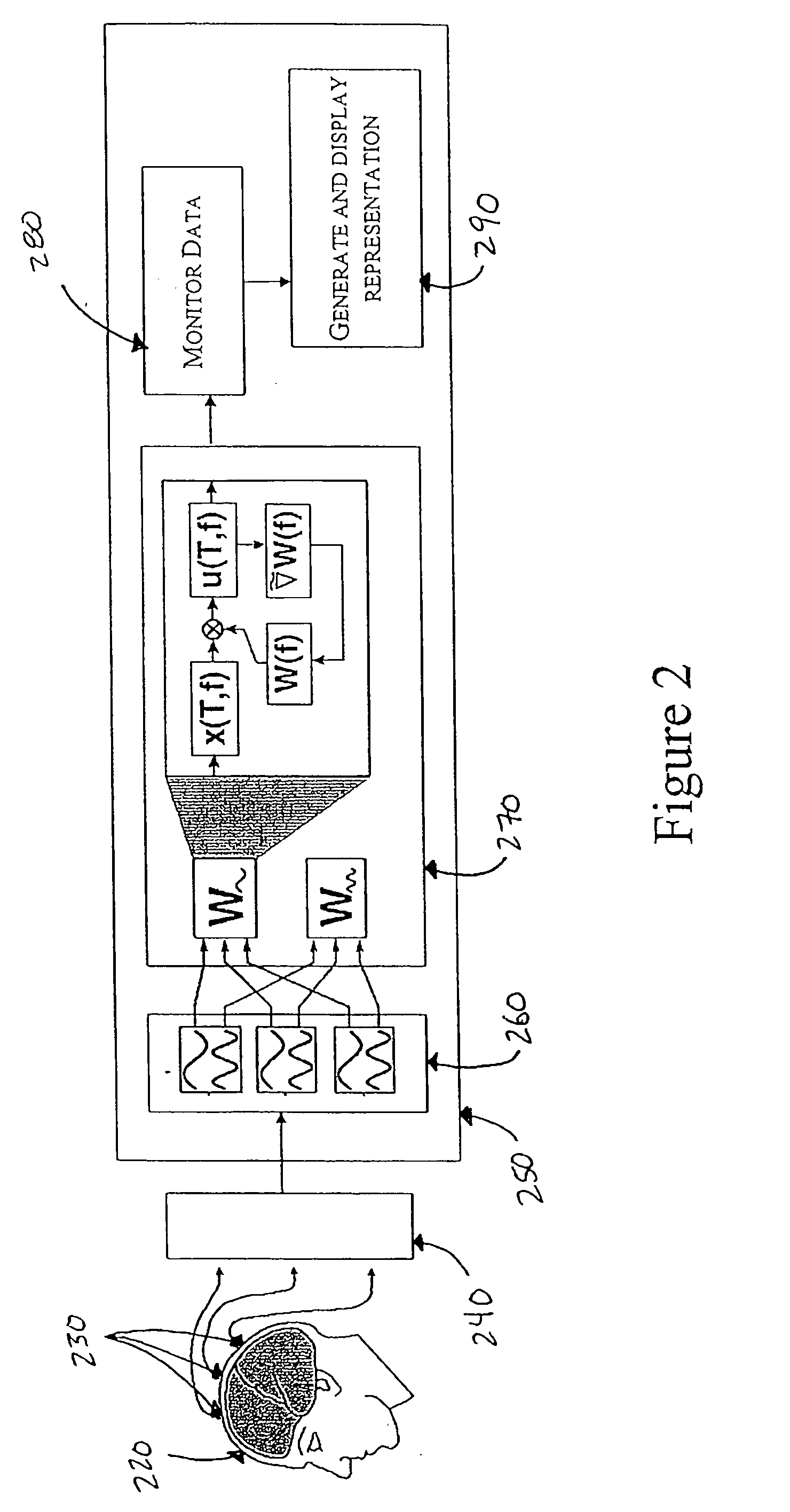
Monitoring and representing complex signals
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
System and method for inferring disease similarity by shape matching of ECG time series
A method for inferring disease similarity by similarity retrieval of electrocardiogram time-series, comprising: acquiring user ECG waveforms correspondingly depicting many cardiac cycles of the heart of many users stored in a database; pre-processing each of the user ECG waveforms through pre-processing steps to isolate sets of single cardiac cycles corresponding to different heart-rates detected for each of the user ECG waveforms, each single cardiac cycle within the many cardiac cycles of the heart of many users corresponds to one single heart-rate detected. acquiring patient ECG waveforms depicting multiple cardiac cycles of the heart of a query patient; pre-processing the patient ECG waveforms through pre-processing steps to isolate sets of single cardiac cycles corresponding to different heart-rates detected for each of the patient ECG waveforms of the query patient, each single cardiac cycle within the multiple cardiac cycles of the heart of the query patient corresponds to one single heart-rate detected.
Owner:LINKEDIN
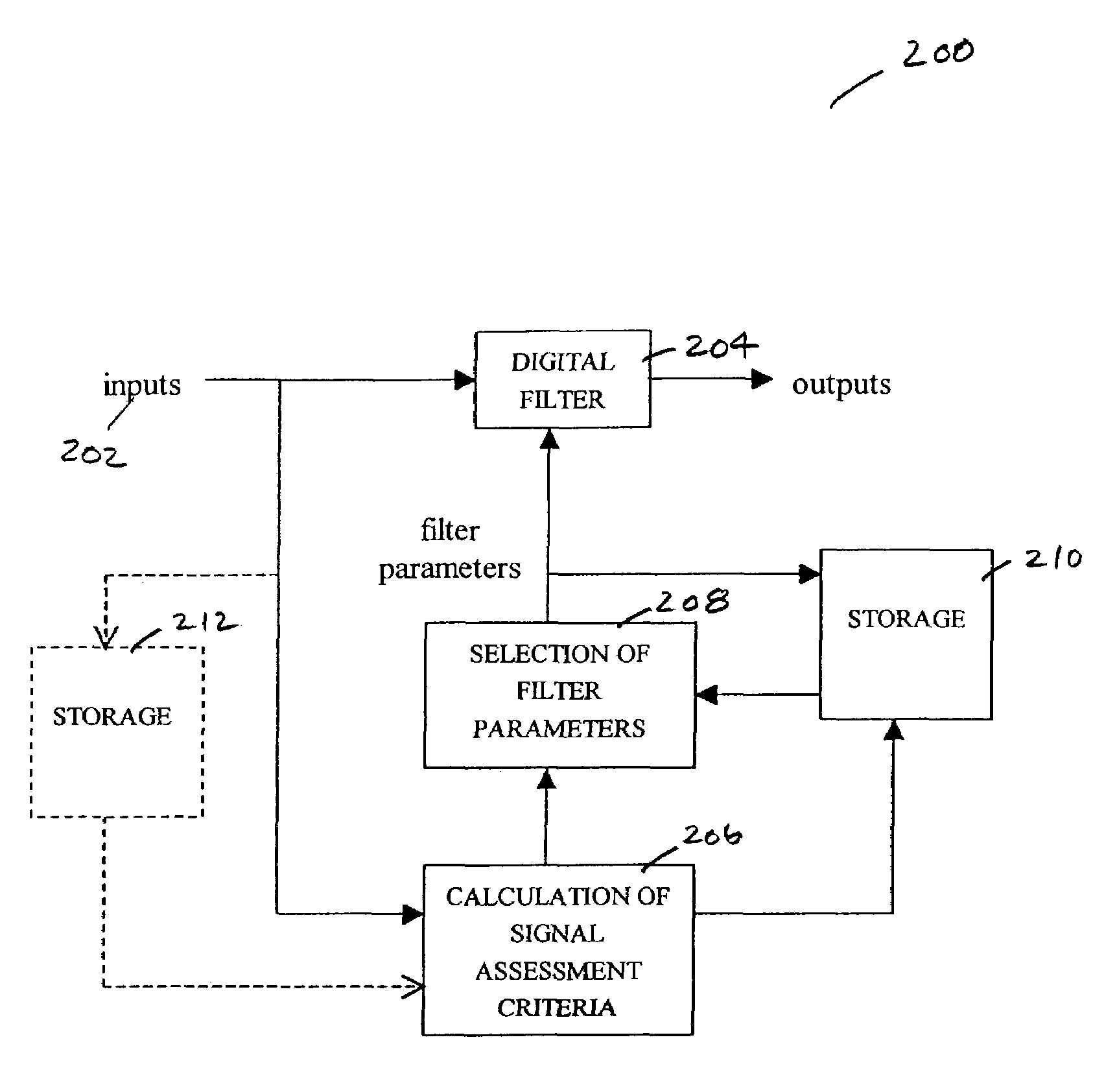
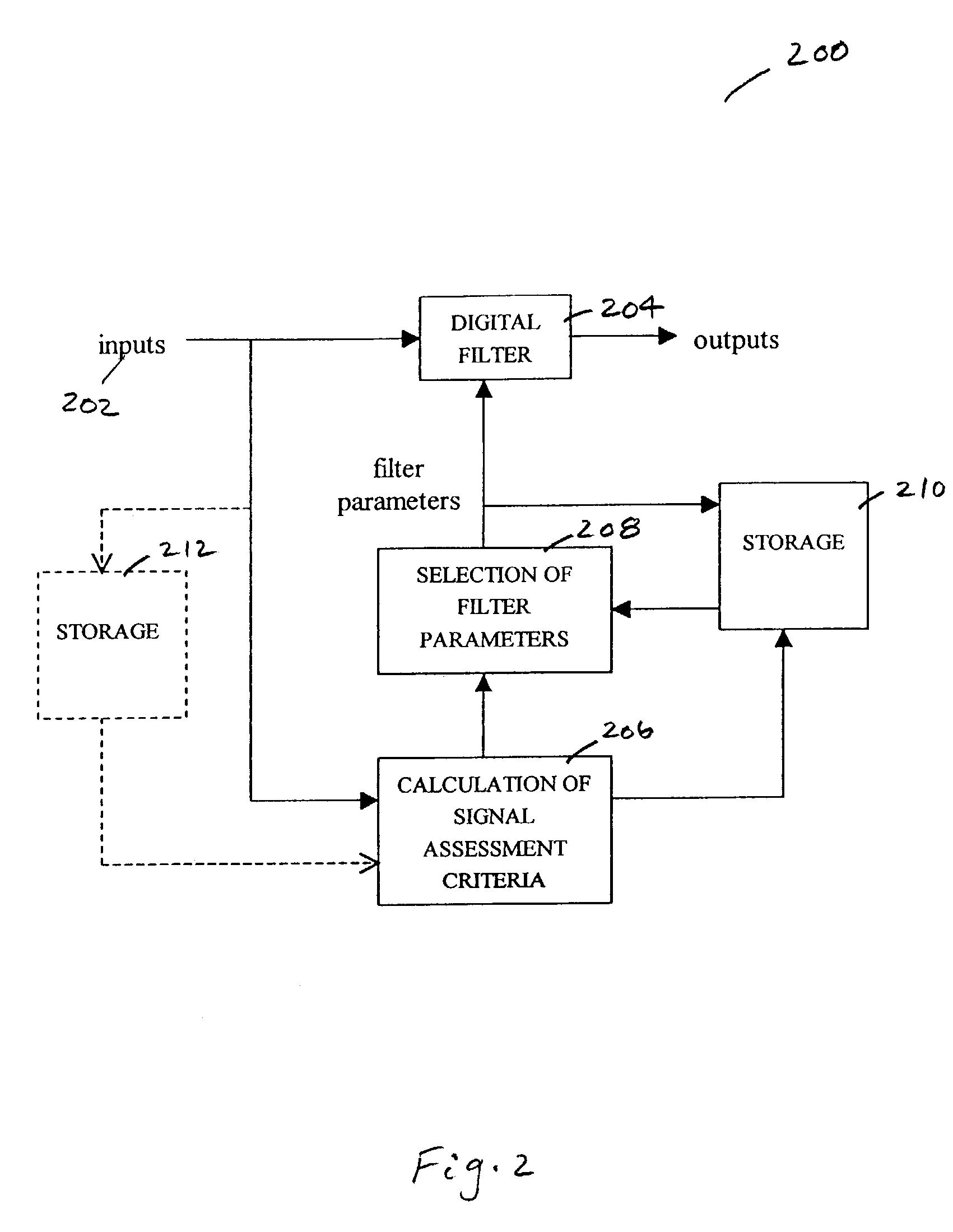
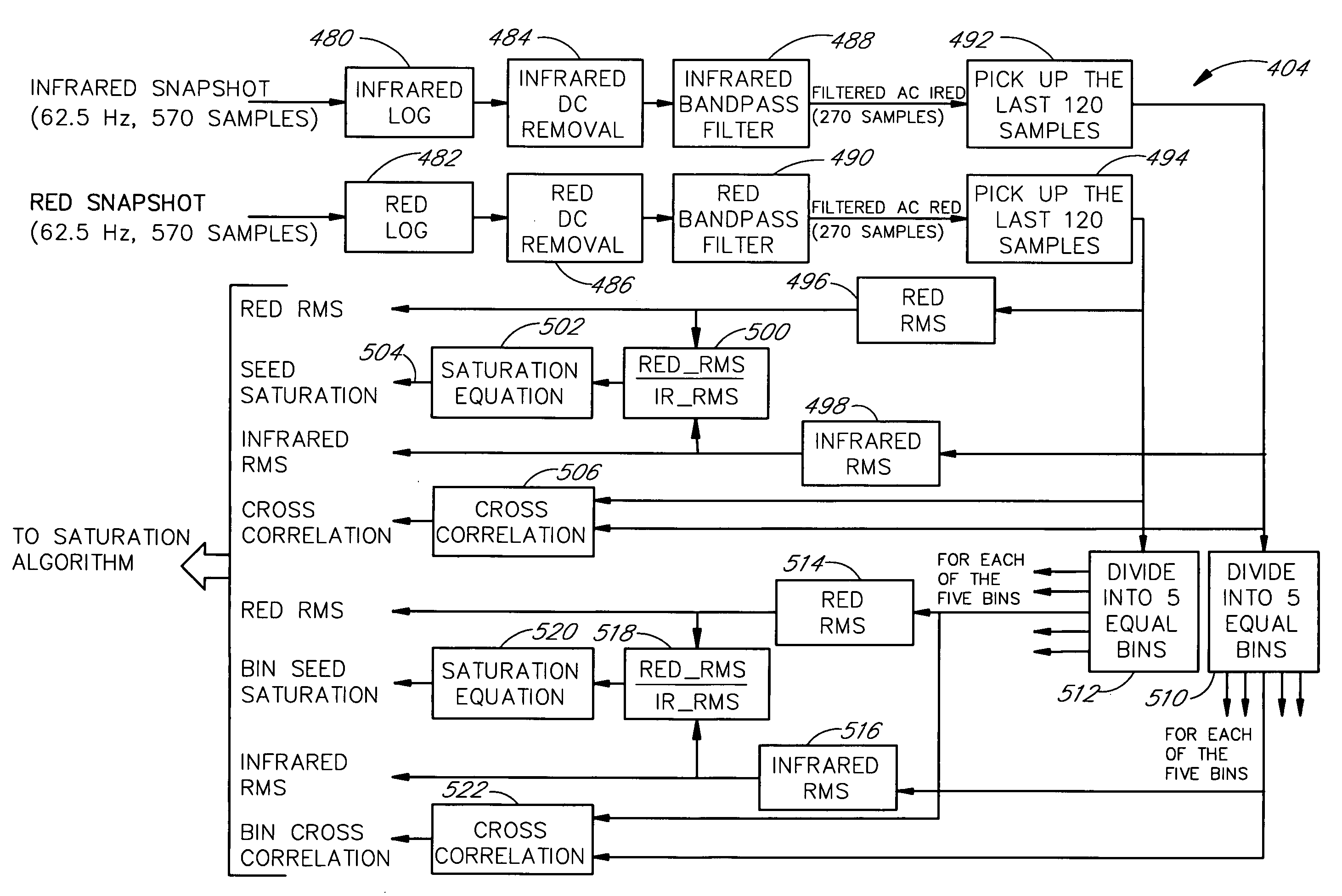
Selection of preset filter parameters based on signal quality
InactiveUS7016715B2Amplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsSignal qualityDigital filter
Methods and devices for reducing noise effects in a system for measuring a physiological parameter, including receiving an input signal; obtaining an assessment of the signal quality of the input signal; selecting coefficients for a digital filter using the assessment of signal quality; and filtering the input signal using the digital filter, without comparing the filter's output signal with the input signal.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
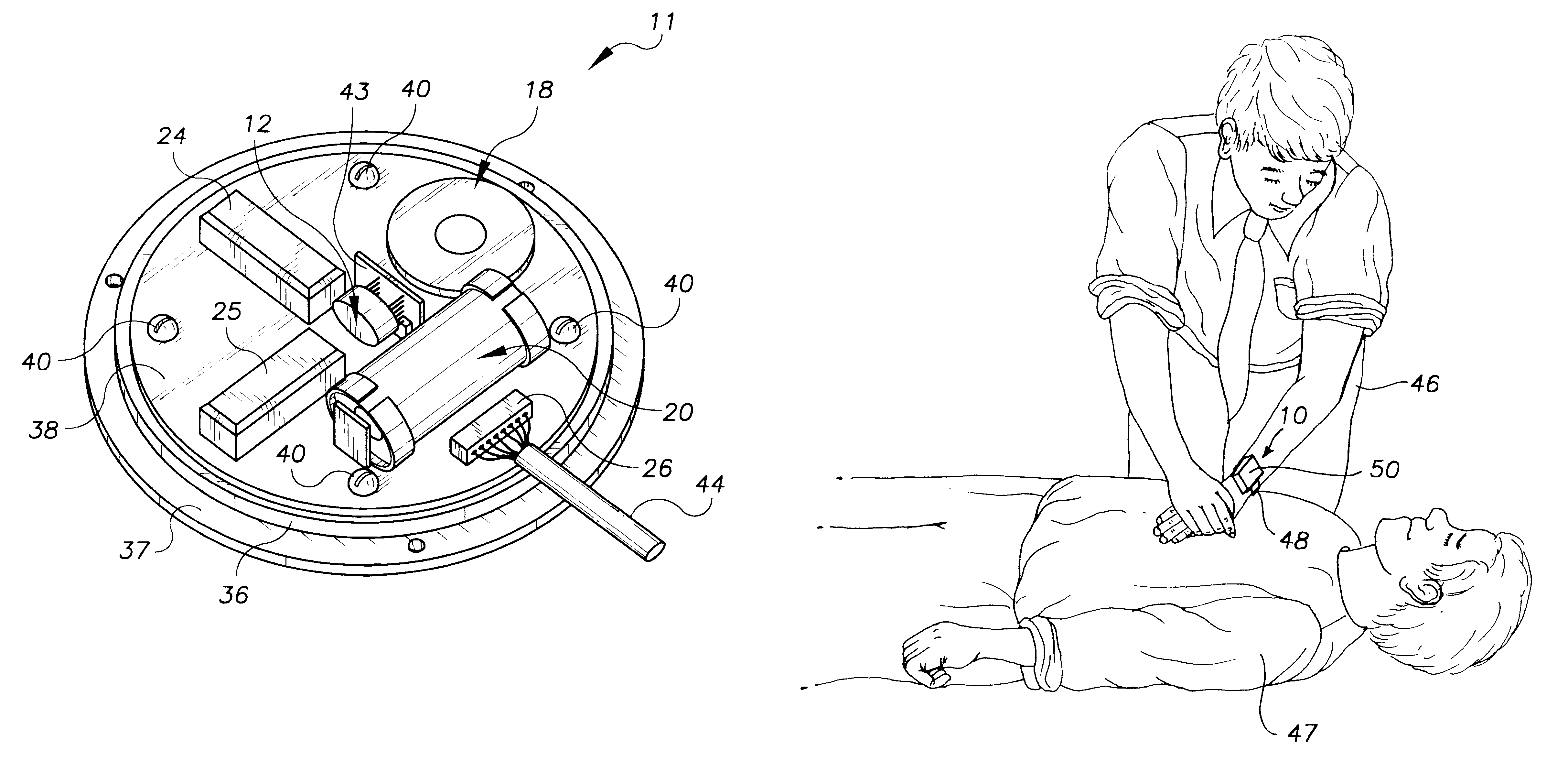
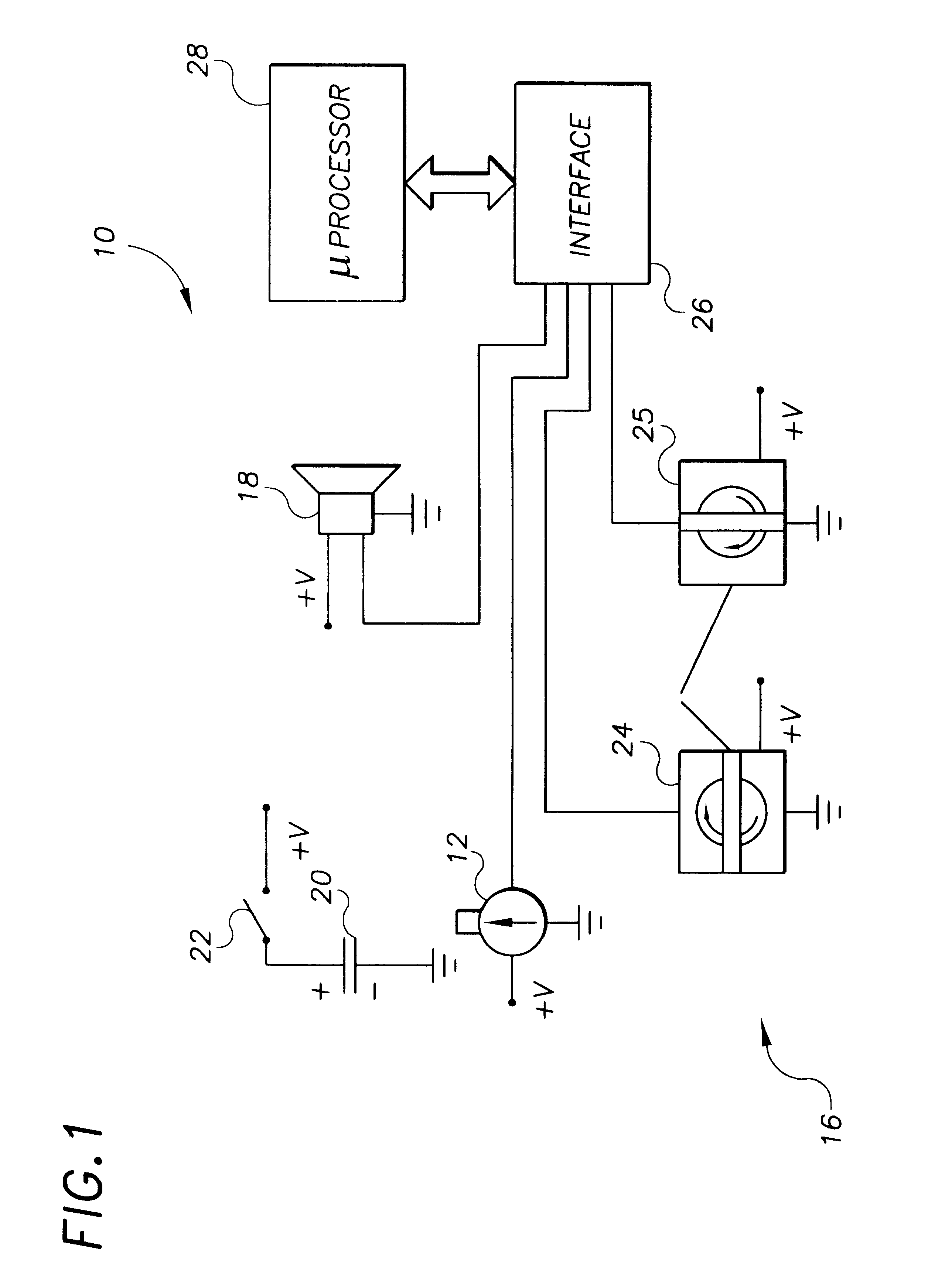
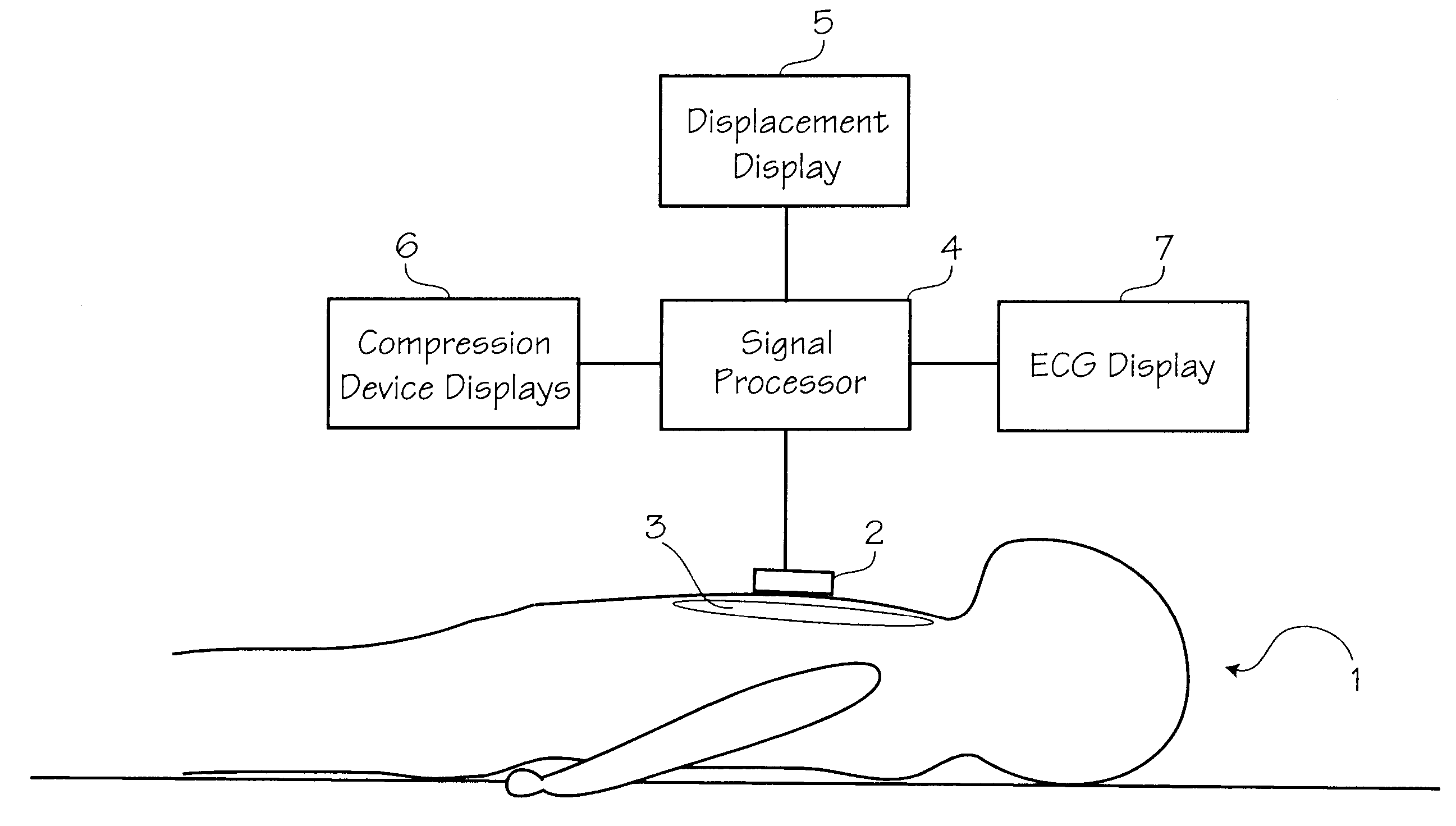
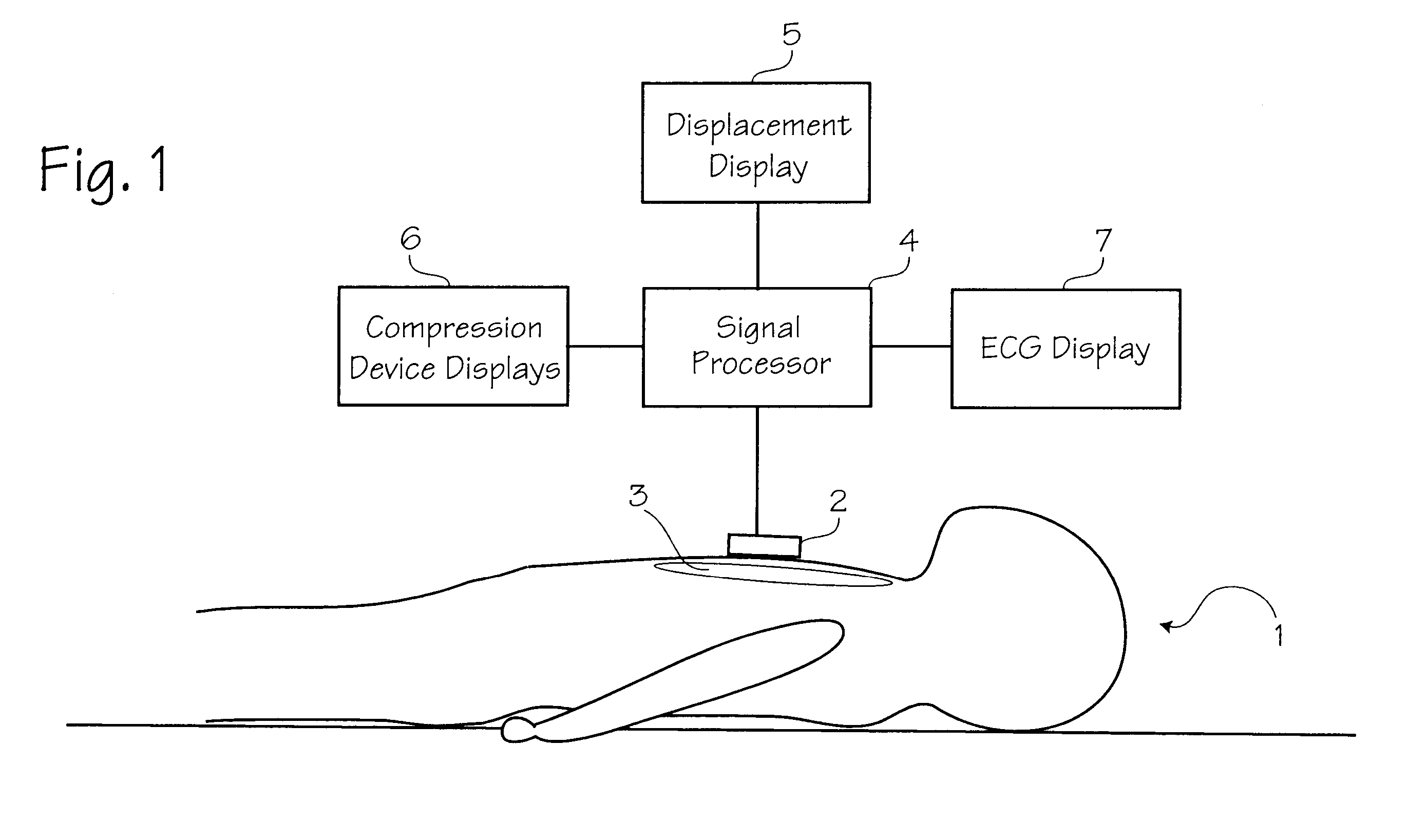
CPR chest compression monitor and method of use
InactiveUS20020055694A1Accurate measurementSmall sizeRespiratorsElectrocardiographyEcg signalEmergency medicine
Chest compressions are measured and prompted to facilitate the effective administration of CPR. A displacement detector produces a displacement indicative signal indicative of the displacement of the CPR recipient's chest toward the recipient's spine. A signaling mechanism provides chest compression indication signals directing a chest compression force being applied to the chest and a frequency of such compressions. An automated controller and an automated constricting device may be provided for applying CPR to the recipient in an automated fashion. The automated controller receives the chest compression indication signals from the signaling mechanism, and, in accordance with the chest compression indication signals, controls the force and frequency of constrictions. The system may be provided with a tilt compensator comprising a tilt sensor mechanism outputting a tilt compensation signal indicative of the extent of tilt of the device, and may be further provided with an adjuster for adjusting the distance value in accordance with the tilt compensation signal. An ECG signal processor may be provided which removes the CPR-induced artifact from a measured ECG signal obtained during the administration of CPR.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
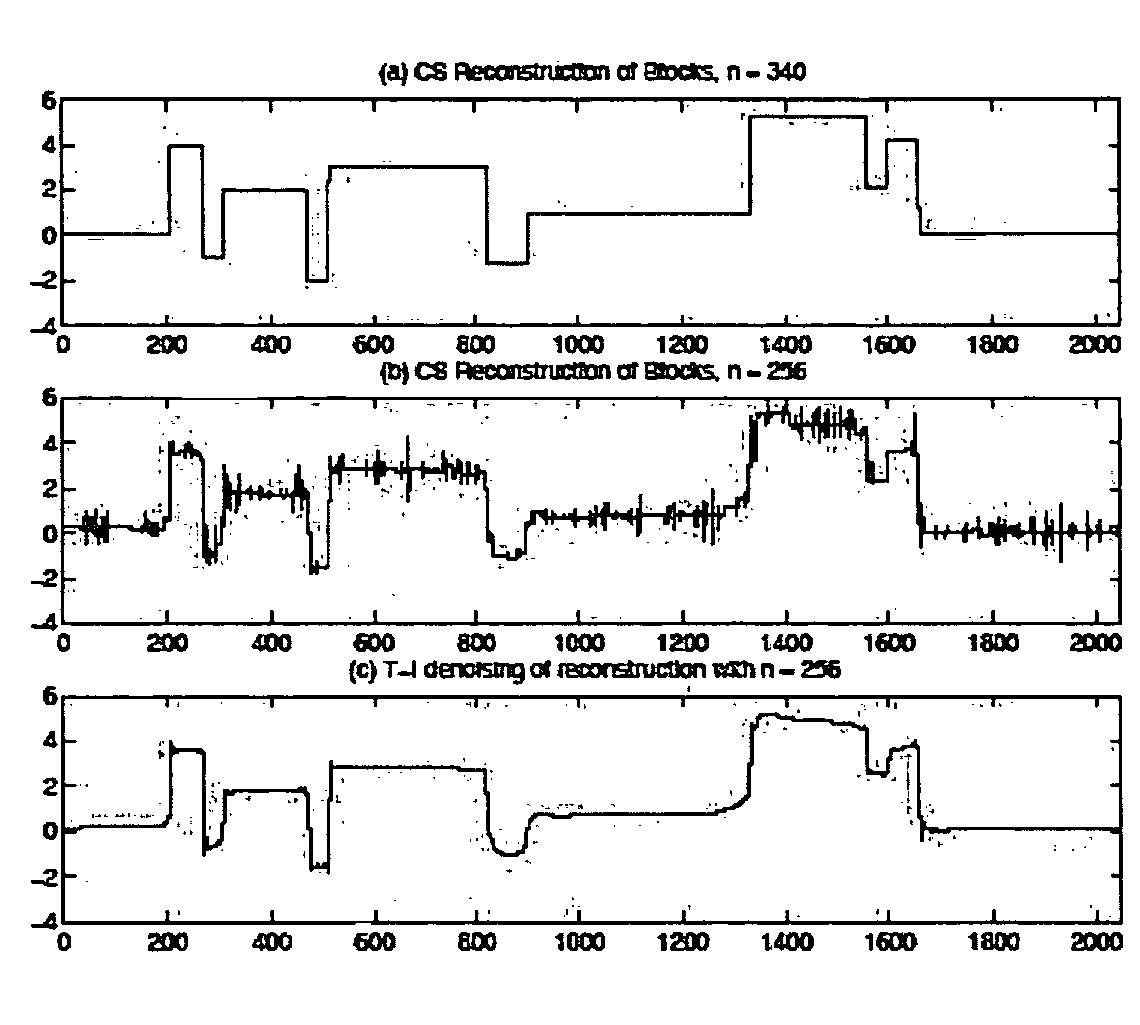
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing
ActiveUS7646924B2Image enhancementReconstruction from projectionArray data structureComputer science
Method and apparatus for compressed sensing yields acceptable quality reconstructions of an object from reduced numbers of measurements. A component x of a signal or image is represented as a vector having m entries. Measurements y, comprising a vector with n entries, where n is less than m, are made. An approximate reconstruction of the m-vector x is made from y. Special measurement matrices allow measurements y=Ax+z, where y is the measured m-vector, x the desired n-vector and z an m-vector representing noise. “A” is an n by m matrix, i.e. an array with fewer rows than columns. “A” enables delivery of an approximate reconstruction, x#, of x. An embodiment discloses approximate reconstruction of x from the reduced-dimensionality measurement y. Given y, and the matrix A, x# of x is possible. This embodiment is driven by the goal of promoting the approximate sparsity of x#.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
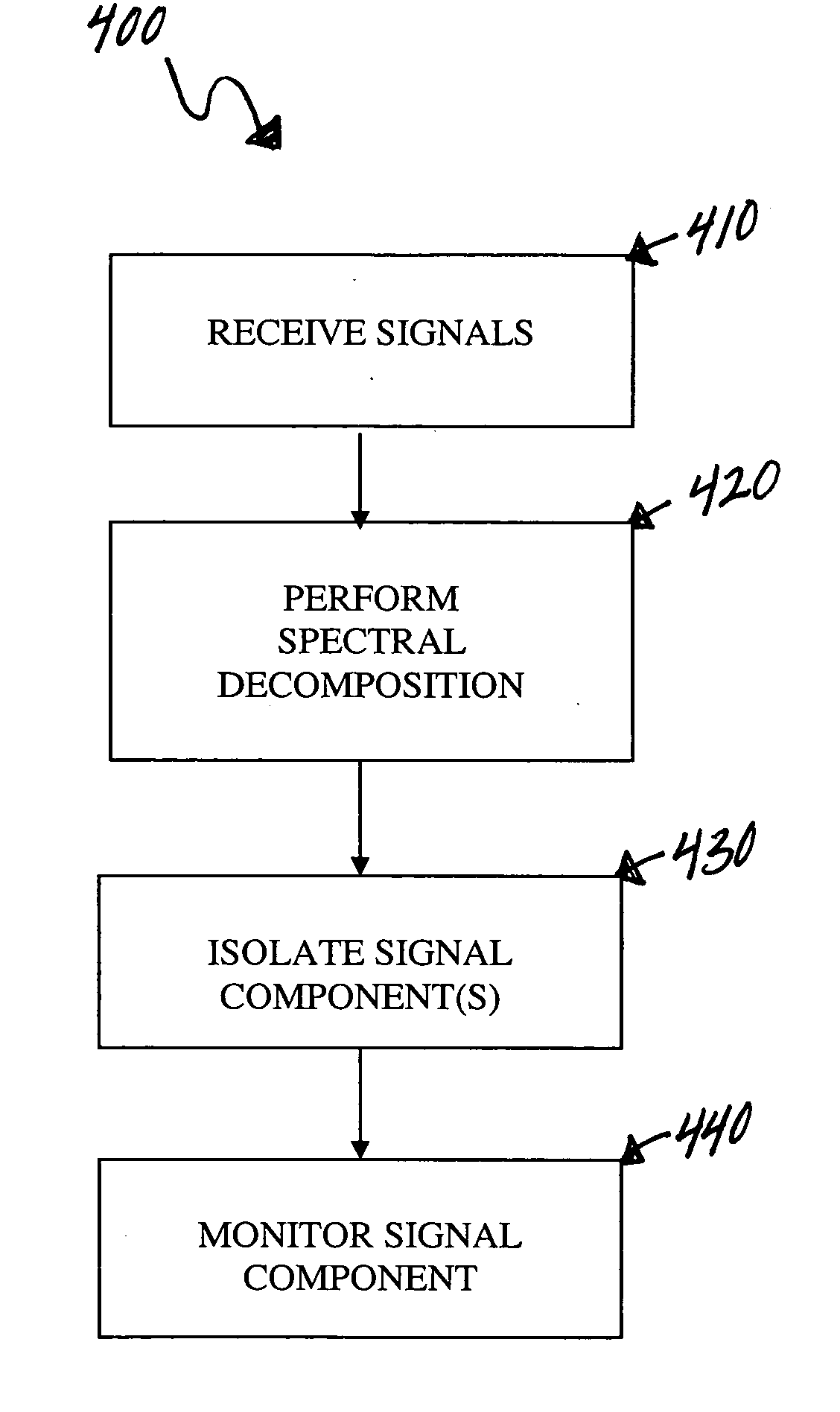
Monitoring and representing complex signals
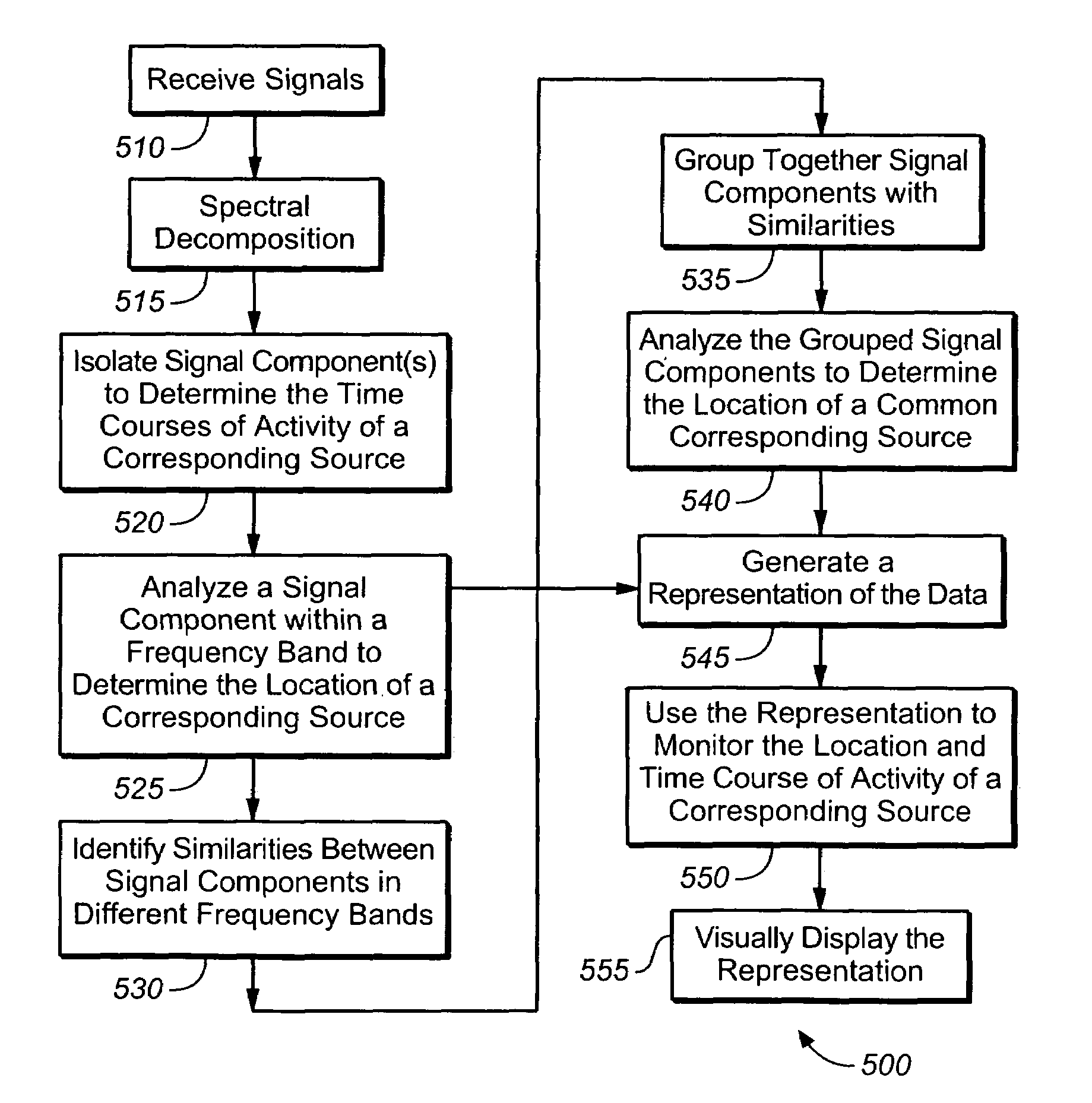
A method of displaying signals containing a spatial and a temporal aspect, where multiple signals are received by multiple sensors. The received signals are decomposed into separate signal components within one or more distinct frequency bands. Signal components are isolated within each frequency band based on differences between the signal components within the same frequency band, and the signal components are displayed. The signal components may be analyzed to determine a time course of activity and a location of the associated source. Representations of the source may also be generated and displayed to aid in monitoring the signals.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Parallel and adaptive signal processing
InactiveUS8055095B2Reduce energy consumptionReduce data volumeImage enhancementRecognisation of pattern in signalsStandard stateSelf adaptive
A method and apparatus for parallel and adaptive signal reconstruction from a multitude of signal measurements. Algorithms and hardware are disclosed to denoise the measured signals, to compress the measured signals, and to reconstruct the signal from fewer measurements than standard state-of-the-art methods require. A parallel hardware design is disclosed in which the methods that are described can be efficiently executed.
Owner:SPARSENSE
Method, apparatus, and system for removing motion artifacts from measurements of bodily parameters
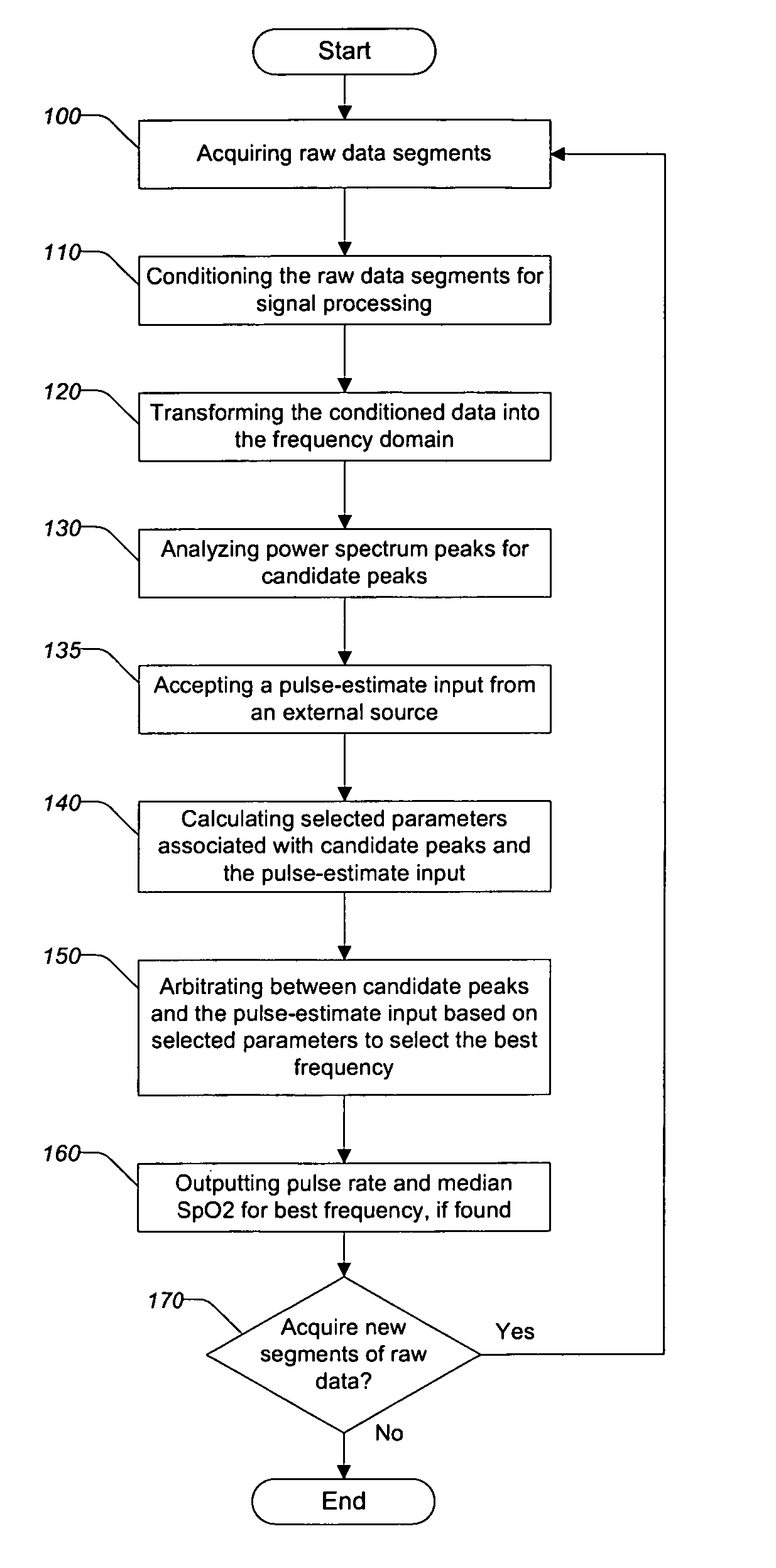
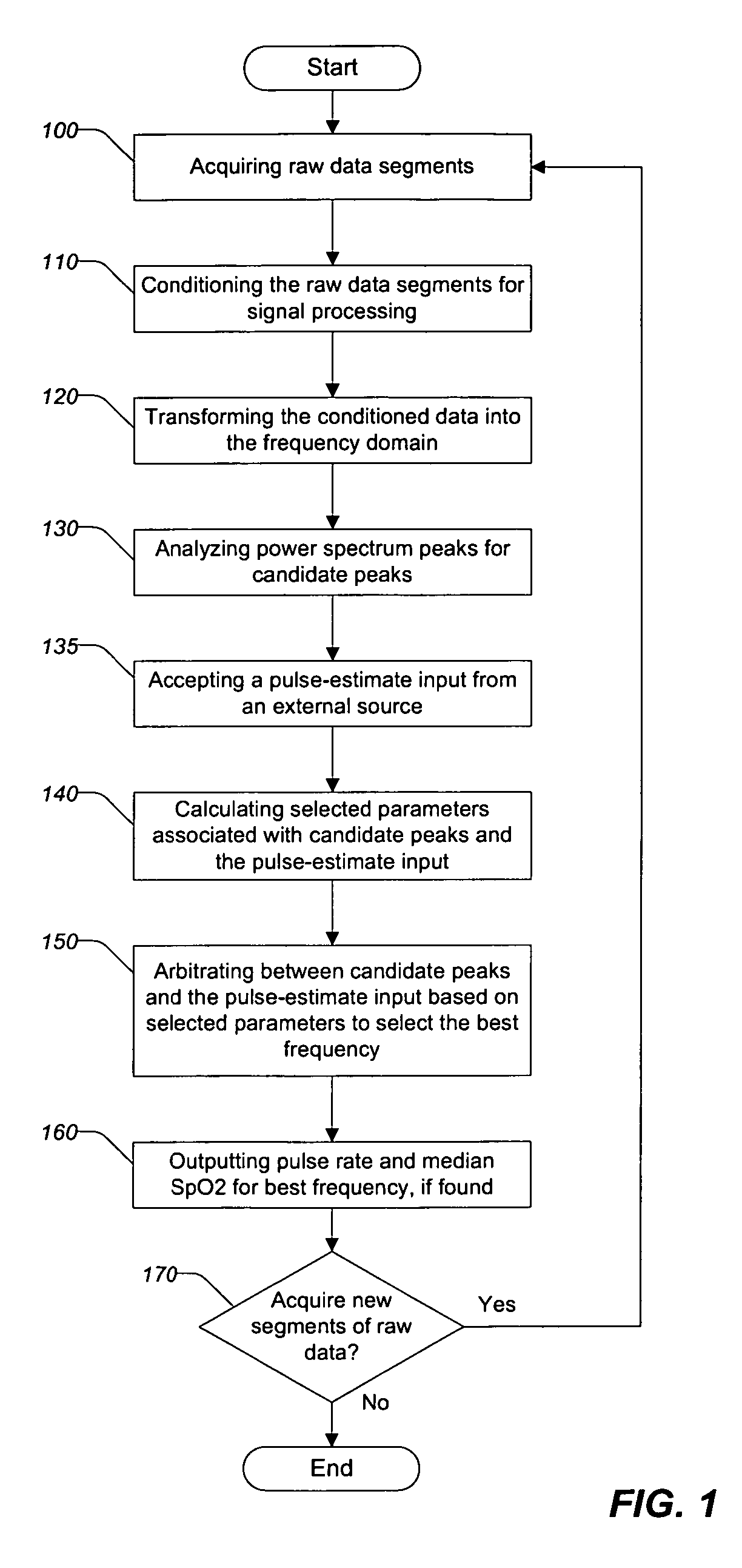
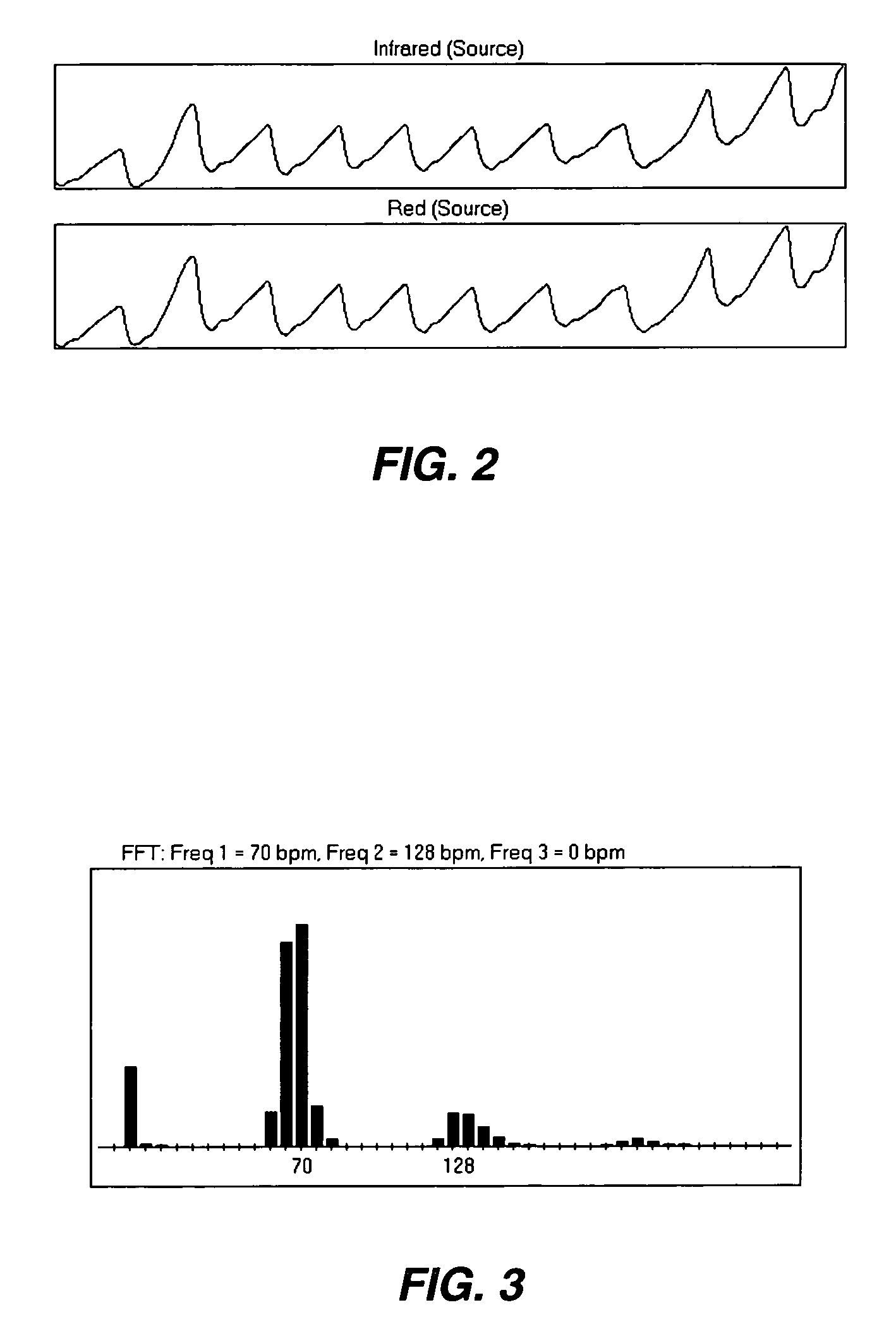
InactiveUS7991448B2Cancel noiseSimple calculationCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringData segmentPulse rate
A method for removing motion artifacts from devices for sensing bodily parameters and apparatus and system for effecting same that includes analyzing segments of measured data representing bodily parameters and possibly noise from motion artifacts. Each data segment is frequency analyzed to determine up to three candidate peaks for further analysis. Up to three candidate frequencies may be filtered and various parameters associated with each candidate frequency are calculated. A pulse-estimate input may also be accepted from an external source. The best frequency, if one exists, is determined by arbitrating the candidate frequencies and the pulse-estimate input using the calculated parameters according to predefined criteria. If a best frequency is found, a pulse rate and SpO2 may be output. If a best frequency is not found, other, conventional techniques for calculating pulse rate and SpO2 may be used.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NORTH AMERICA
Image segregation system architecture
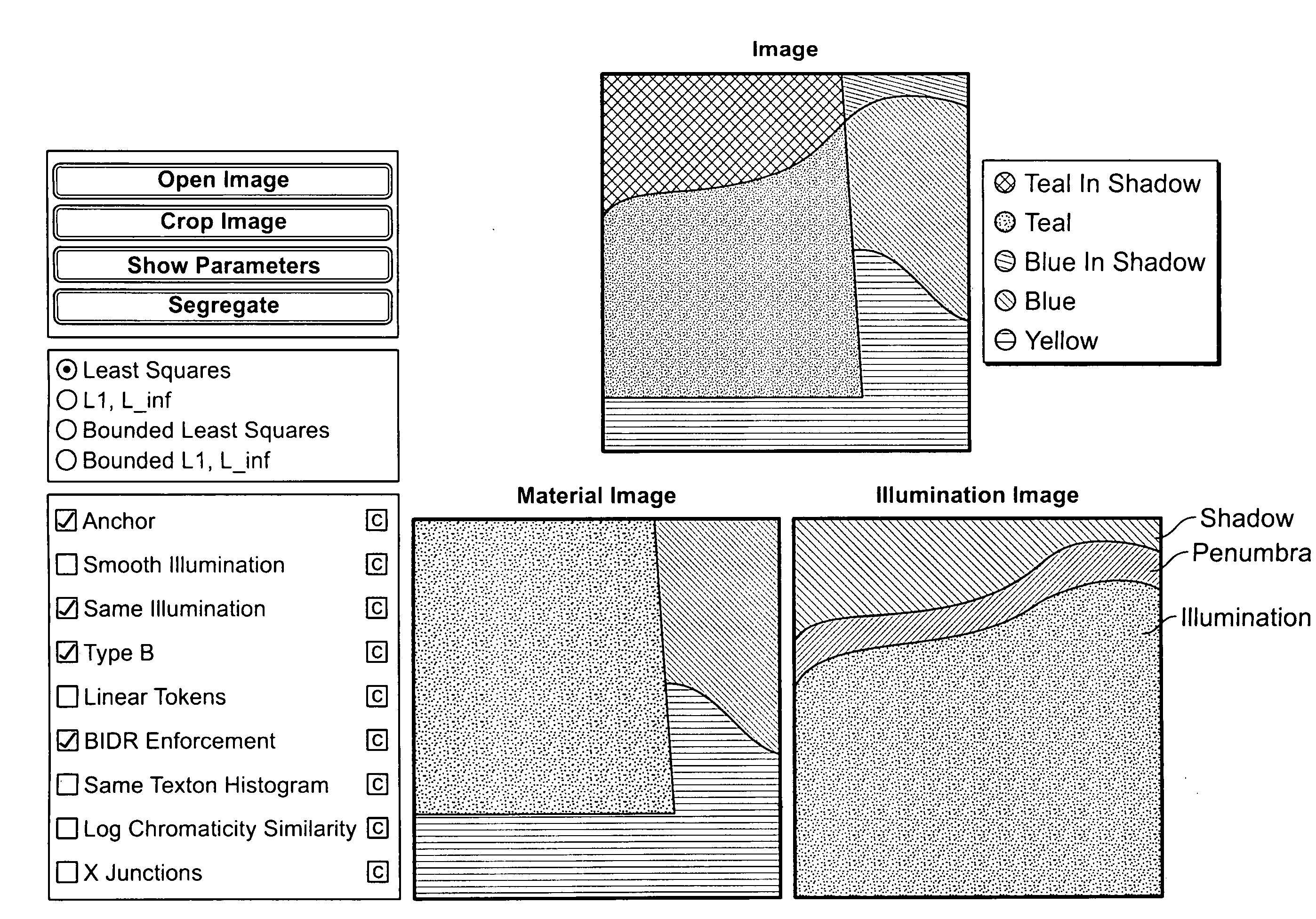
ActiveUS20100142825A1Accurately correctly identifyRecognisation of pattern in signalsSpatial spectrumImage generation
In an exemplary embodiment of the present invention, an automated, computerized method is provided for processing an image. According to a feature of the present invention, the method comprises the steps of generating spatio-spectral information for the image, defining a constraint as a function of the spatio-spectral information, and performing an optimization operation as a function of the constraint to generate an intrinsic image corresponding to the image.
Owner:INNOVATION ASSET COLLECTIVE
Signal processing apparatus
InactiveUS20050209517A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsMaterial analysis by optical meansMedicineSignal processing
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
Method and apparatus for automatically recognizing input audio and/or video streams
InactiveUS20070129952A1Improve accuracyMinimal timeAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsBroadcast information monitoringSingle sampleFeature set
A method and system for the automatic identification of audio, video, multimedia, and / or data recordings based on immutable characteristics of these works. The invention does not require the insertion of identifying codes or signals into the recording. This allows the system to be used to identify existing recordings that have not been through a coding process at the time that they were generated. Instead, each work to be recognized is “played” into the system where it is subjected to an automatic signal analysis process that locates salient features and computes a statistical representation of these properties. These features are then stored as patterns for later recognition of live input signal streams. A different set of features is derived for each audio or video work to be identified and stored. During real-time monitoring of a signal stream, a similar automatic signal analysis process is carried out, and many features are computed for comparison with the patterns stored in a large feature database. For each particular pattern stored in the database, only the relevant characteristics are compared with the real-time feature set. Preferably, during analysis and generation of reference patterns, data are extracted from all time intervals of a recording. This allows a work to be recognized from a single sample taken from any part of the recording.
Owner:ICEBERG IND
Methods for accurate component intensity extraction from separations-mass spectrometry data
InactiveUS20050255606A1Accurate representationBiological testingRecognisation of pattern in signalsMass Spectrometry-Mass SpectrometryUltimate tensile strength
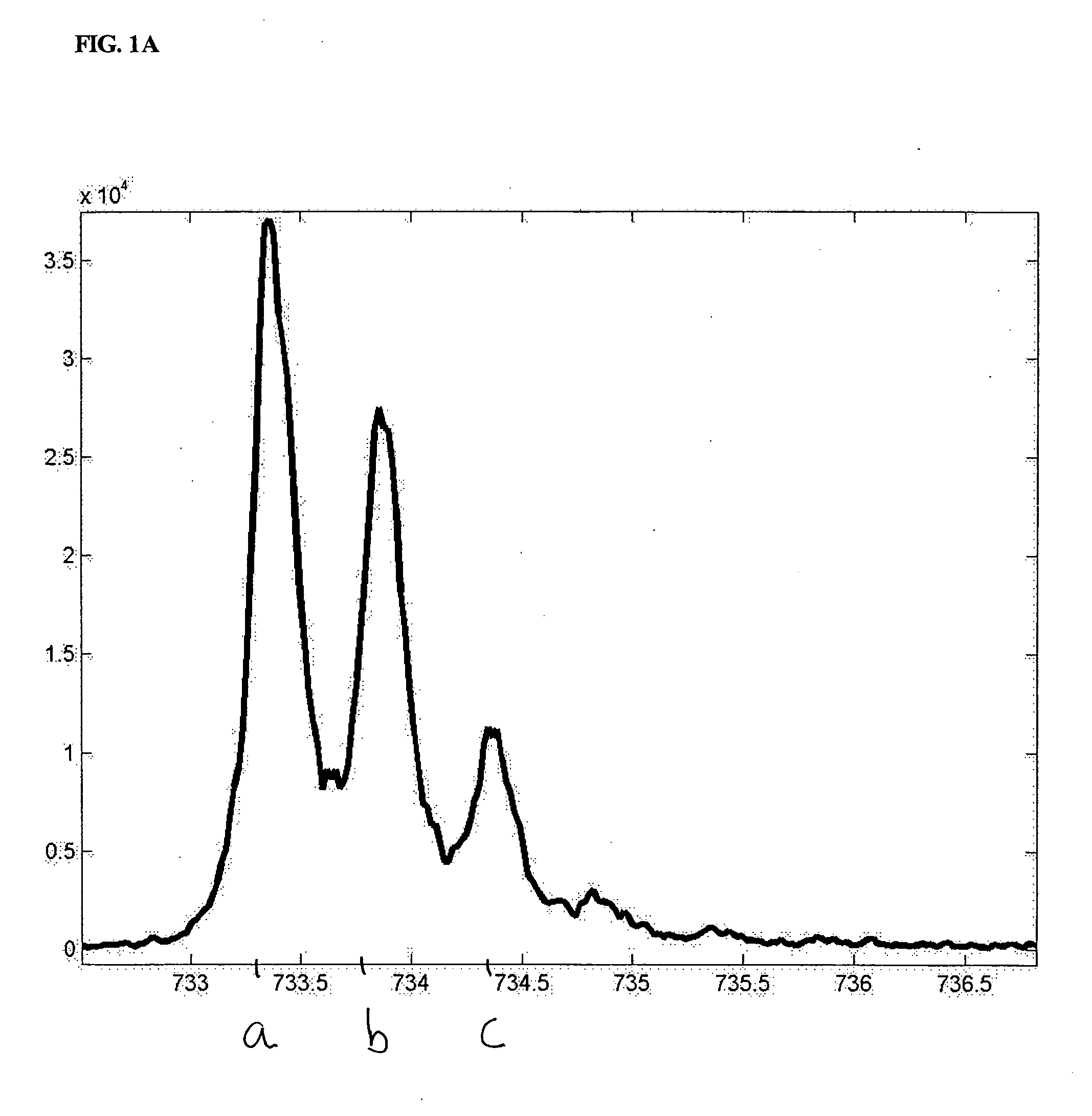
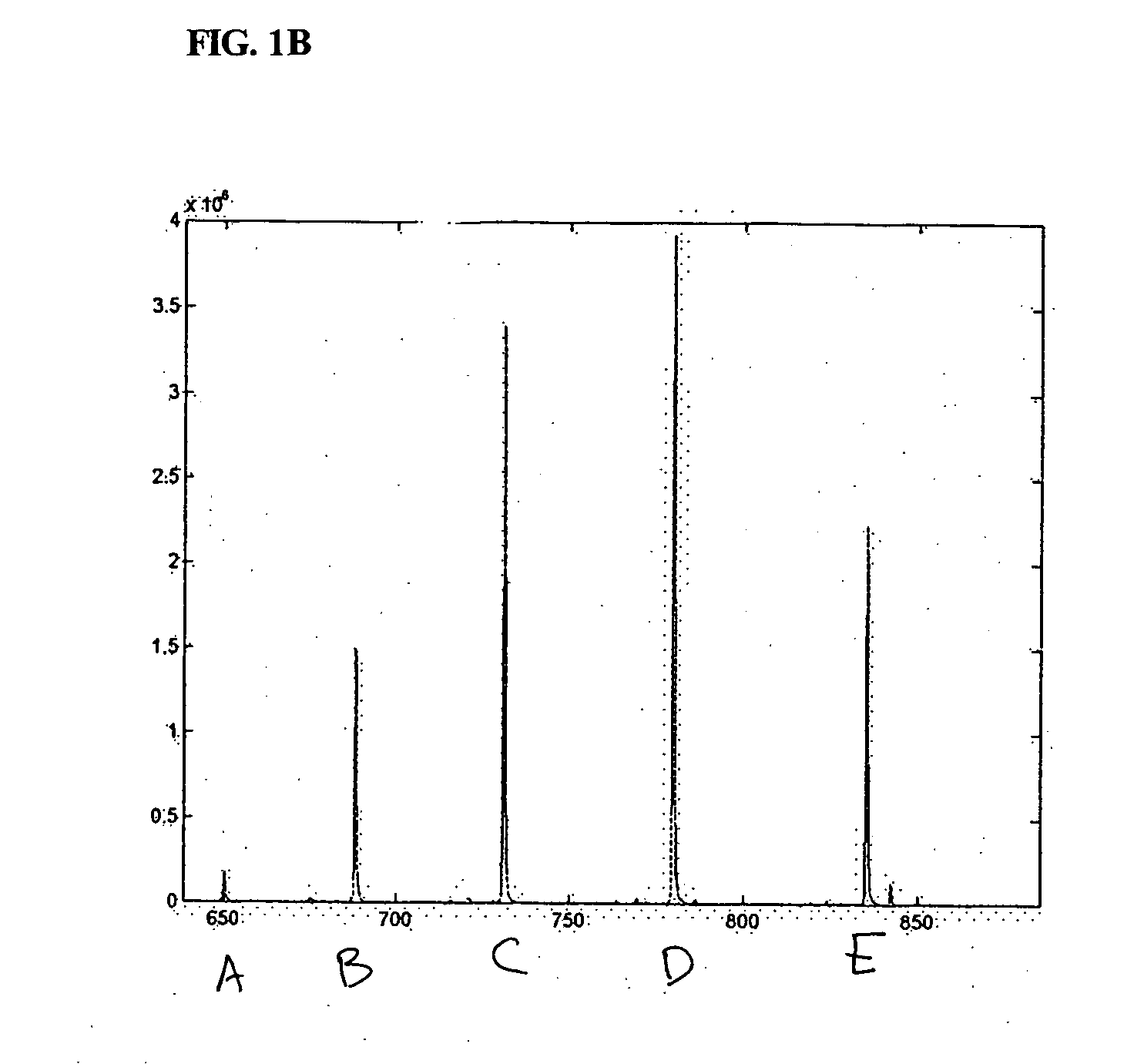
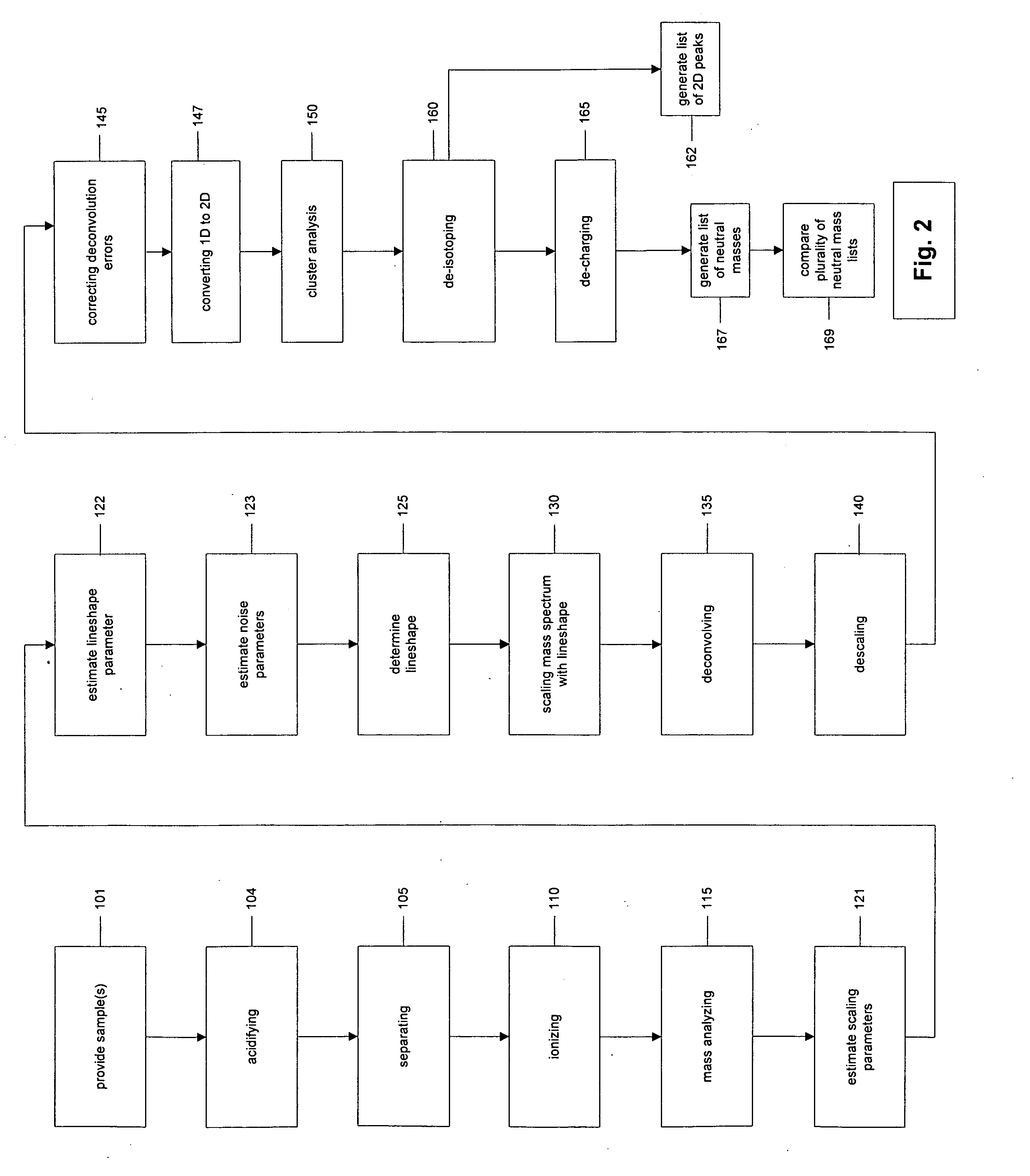
The present invention discloses methods for deconvolving and converting 1D mass spectra to 2D mass spectrum in order to obtain migration time centers and total intensities of the neutral mass envelopes of 2D spectra. The present invention also discloses devices that include a preparation / separation unit coupled to a mass spectrometer unit, and a computer unit capable of deconvolving mass spectra and calculating neutral mass envelopes.
Owner:V&M TCA LP +1
Signal processing apparatus and method
A method and an apparatus to analyze two measured signals that are modeled as containing desired and undesired portions such as noise, FM and AM modulation. Coefficients relate the two signals according to a model defined in accordance with the present invention. In one embodiment, a transformation is used to evaluate a ratio of the two measured signals in order to find appropriate coefficients. The measured signals are then fed into a signal scrubber which uses the coefficients to remove the unwanted portions. The signal scrubbing is performed in either the time domain or in the frequency domain. The method and apparatus are particularly advantageous to blood oximetry and pulserate measurements. In another embodiment, an estimate of the pulserate is obtained by applying a set of rules to a spectral transform of the scrubbed signal. In another embodiment, an estimate of the pulserate is obtained by transforming the scrubbed signal from a first spectral domain into a second spectral domain. The pulserate is found by identifying the largest spectral peak in the second spectral domain.
Owner:JPMORGAN CHASE BANK NA
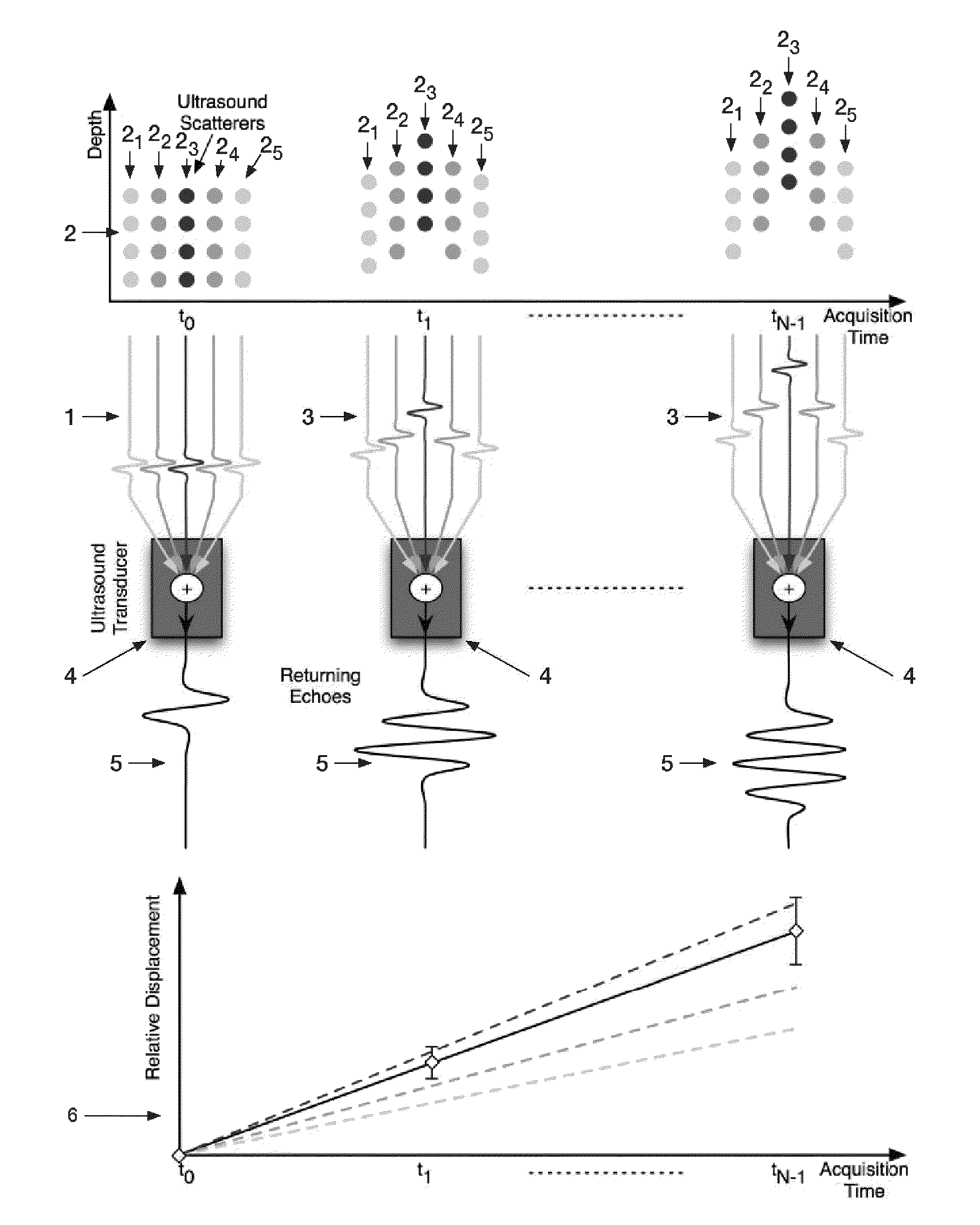
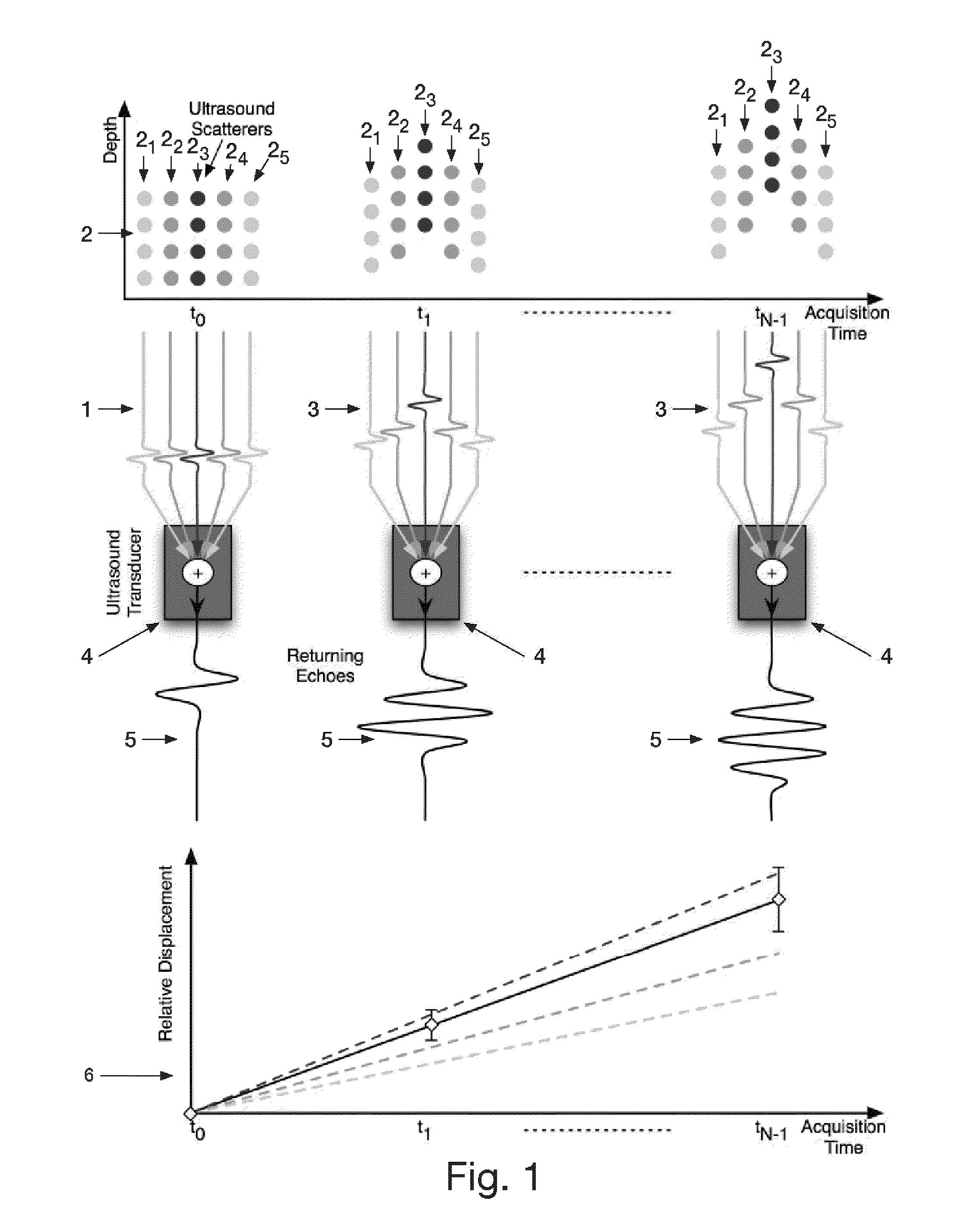
Reduction of echo decorrelation facilitating motion estimation
ActiveUS20090304246A1Recognisation of pattern in signalsRadio wave reradiation/reflectionComplex representationData mining
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
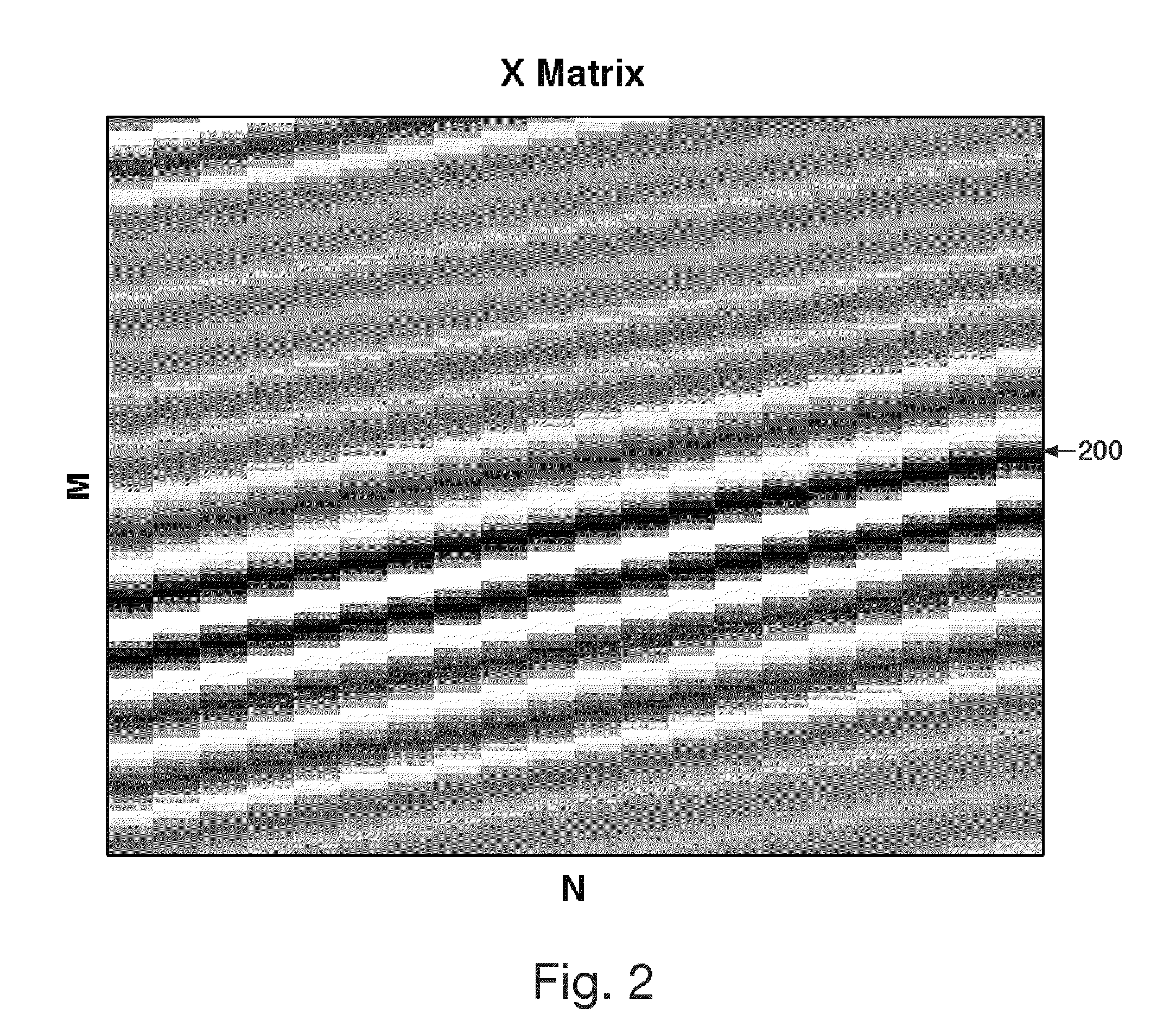
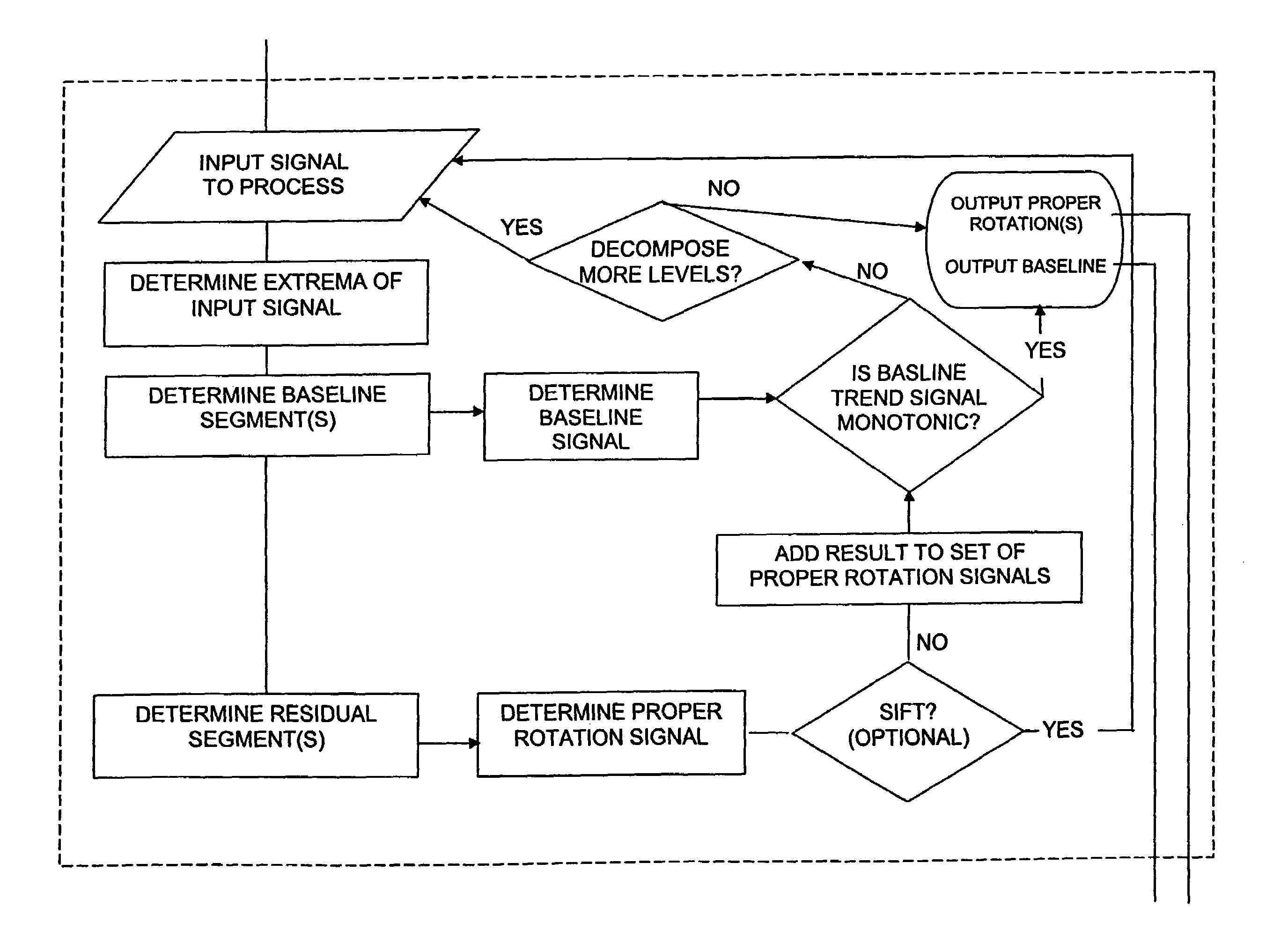
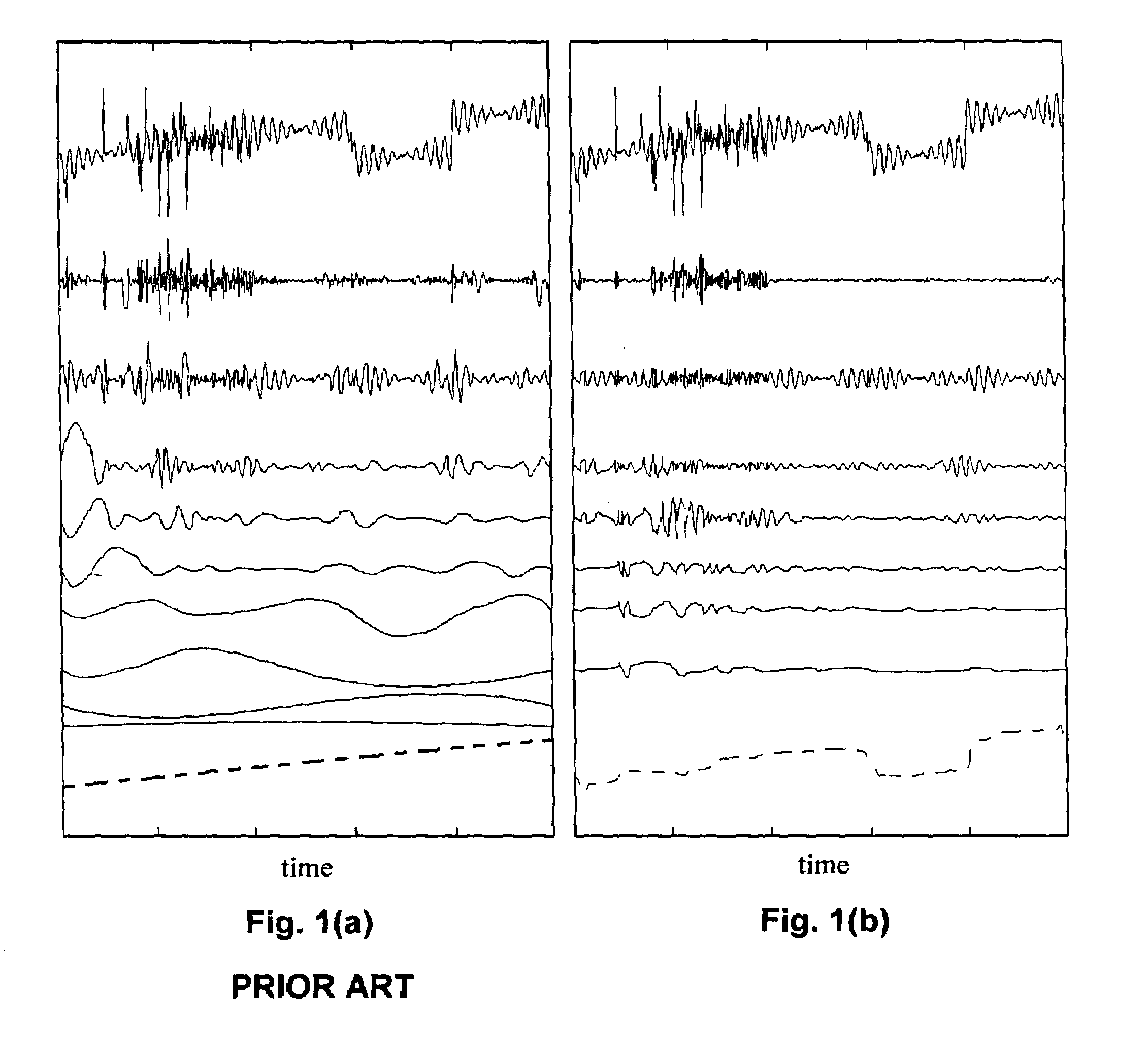
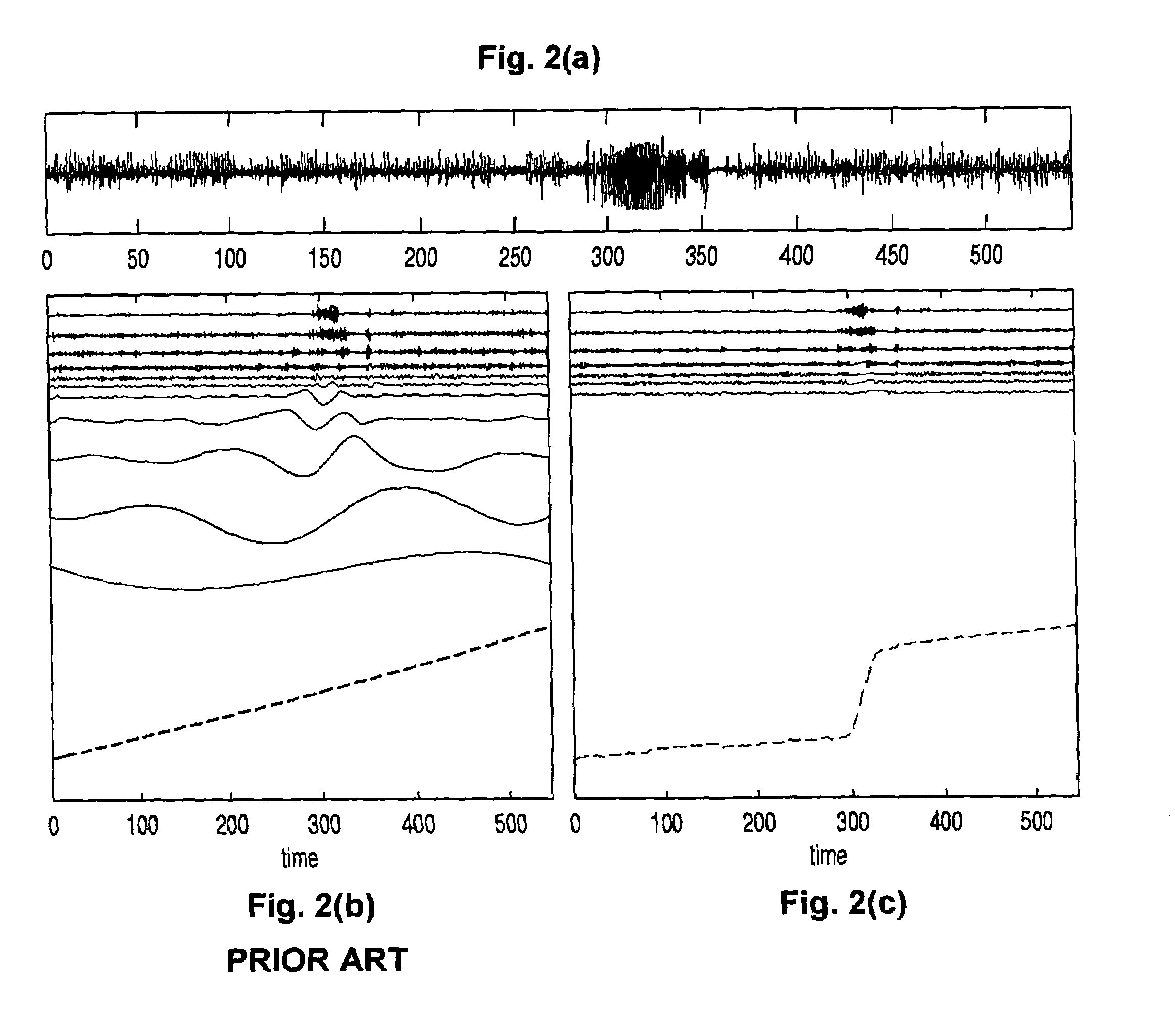
Method, computer program, and system for intrinsic timescale decomposition, filtering, and automated analysis of signals of arbitrary origin or timescale
ActiveUS7054792B2Easy to operateImprove performanceAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceTesting/monitoring control systemsTime markDecomposition
A method and system for intrinsic timescale decomposition, filtering, and automated analysis of signals of arbitrary origin or timescale including receiving an input signal, determining a baseline segment and a monotonic residual segment with strictly negative minimum and strictly positive maximum between two successive extrema of the input signal, and producing a baseline output signal and a residual output signal. The method and system also includes determining at least one instantaneous frequency estimate from a proper rotation signal, determining a zero-crossing and a local extremum of the proper rotation signal, and applying interpolation thereto to determine an instantaneous frequency estimate thereof. The method and system further includes determining at least one instantaneous frequency estimate from a proper rotation signal, extracting an amplitude-normalized half wave therefrom and applying an arc sine function to the amplitude-normalized half wave to determine an instantaneous frequency estimate of the proper rotation signal.
Owner:FLINT HILLS SCI L L C
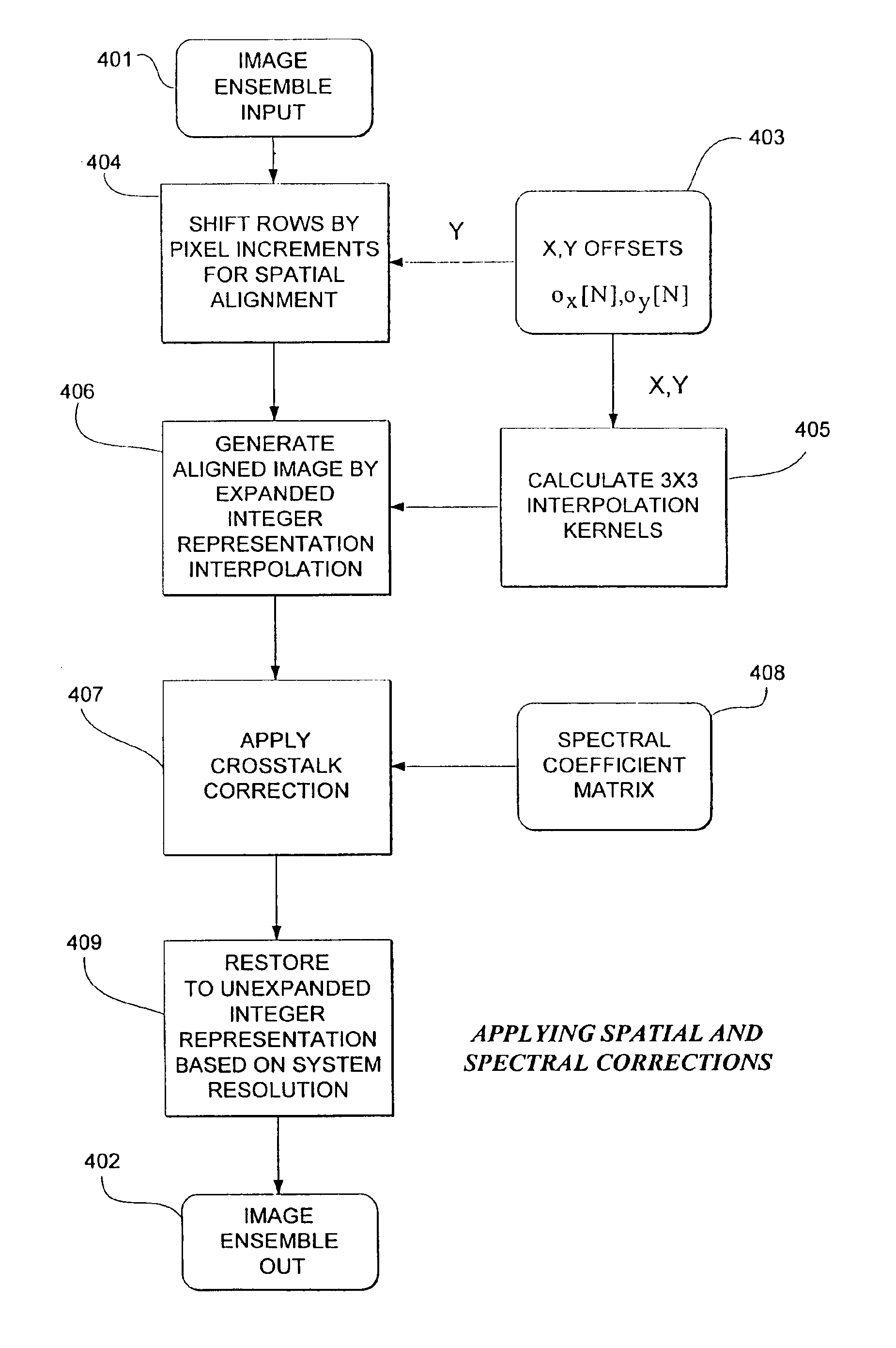
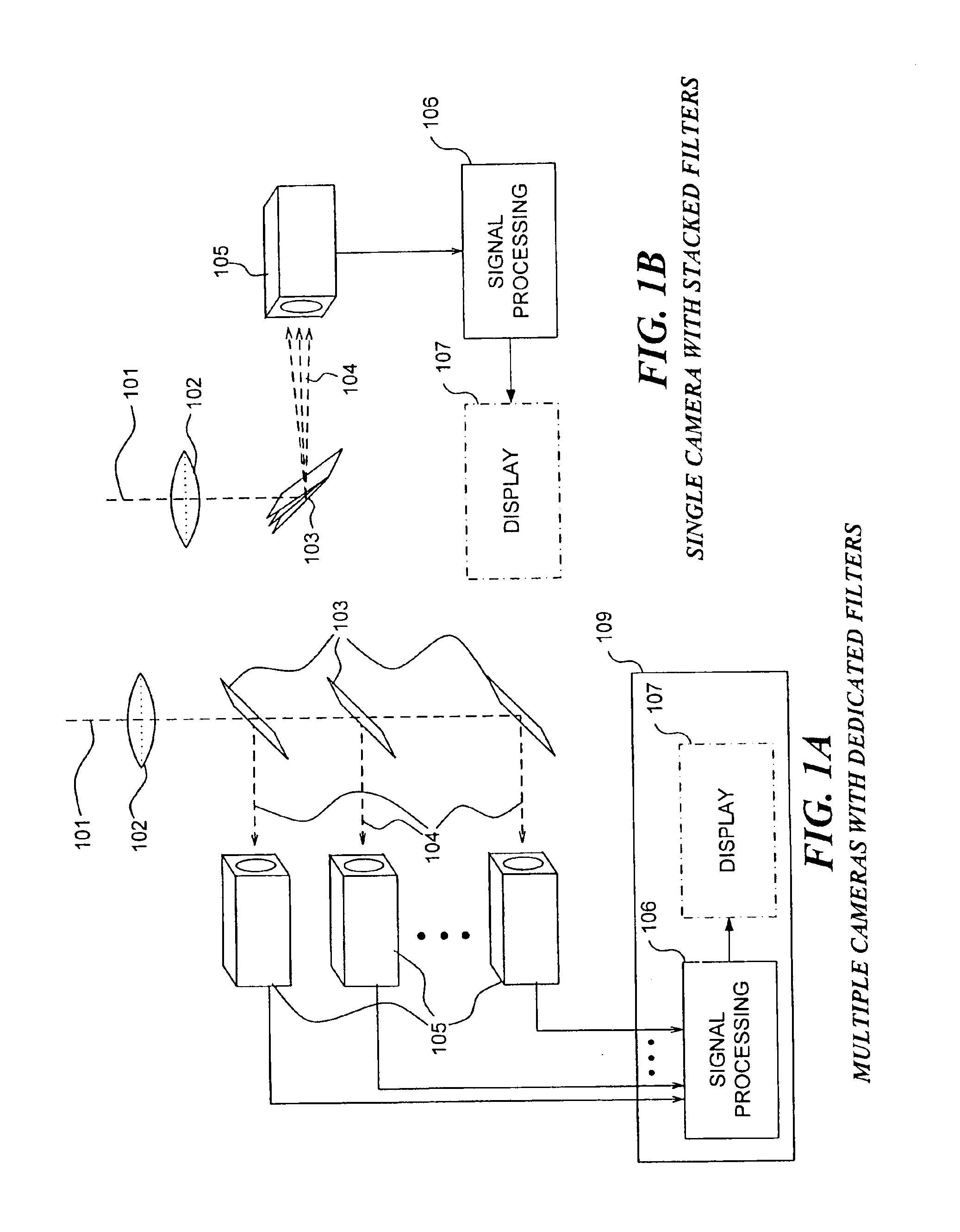
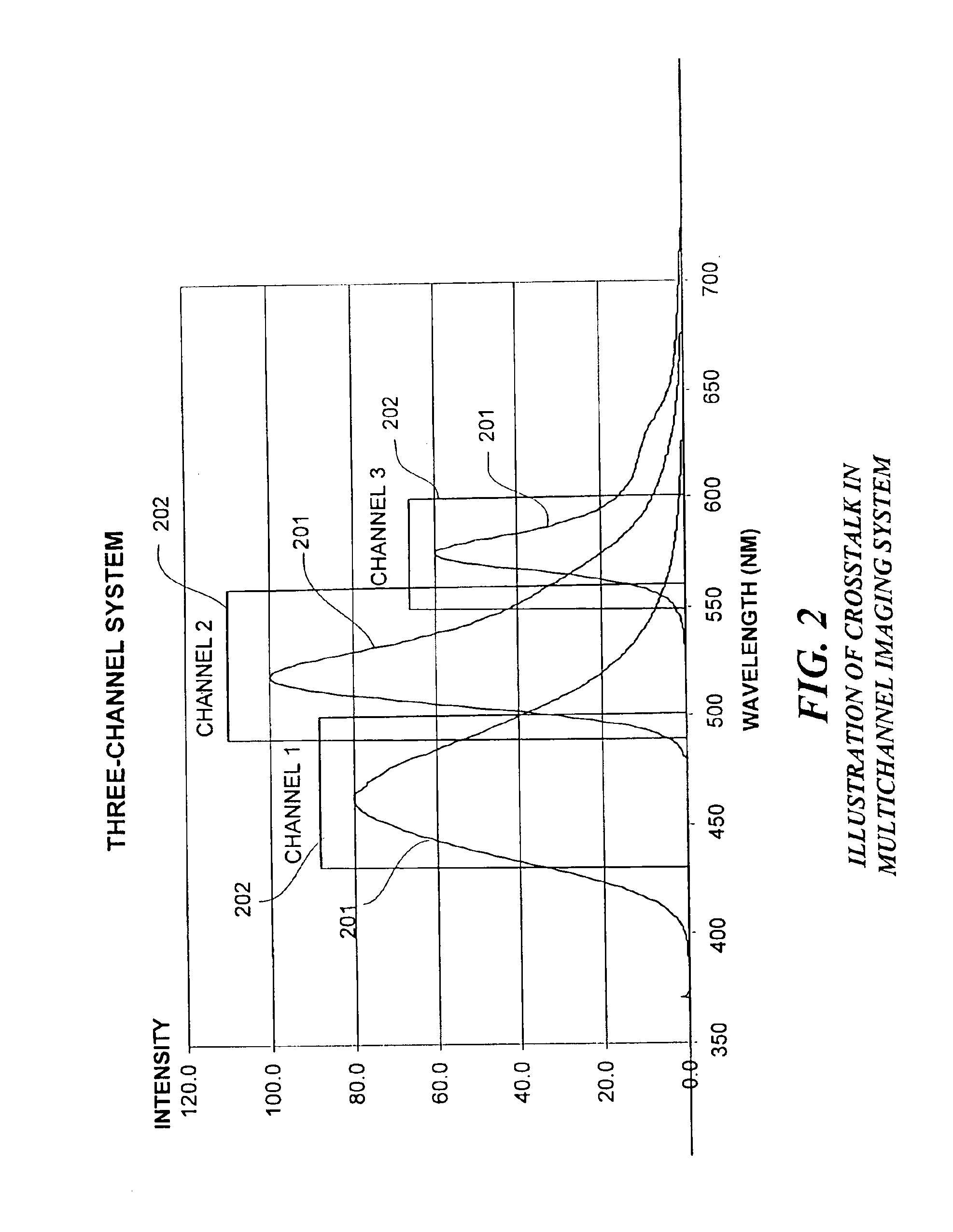
Method and apparatus for correcting crosstalk and spatial resolution for multichannel imaging
InactiveUS7006710B2Accurate dataReducing erroneous contributionImage enhancementImage analysisImage resolutionField of view
A multichannel imaging system generates an ensemble of images for each field of view of an object. Each image in the ensemble is intended to contain information from only one source among a plurality of sources for the object. However, due to crosstalk, at least a portion of the signal from a first source appears in a channel intended for a second source. Because the accuracy of the correction will be degraded if the images in an ensemble are spatially misaligned with respect to one another, the spatial offset between images is determined and a correction is applied to substantially eliminate the offset. Then, a correction to the signals is determined to substantially reduce the contributions to the signal in a channel from the signals in other channels. The signal processing can be employed to process the output signals for each of a plurality of different disclosed imaging systems.
Owner:CYTEK BIOSCI
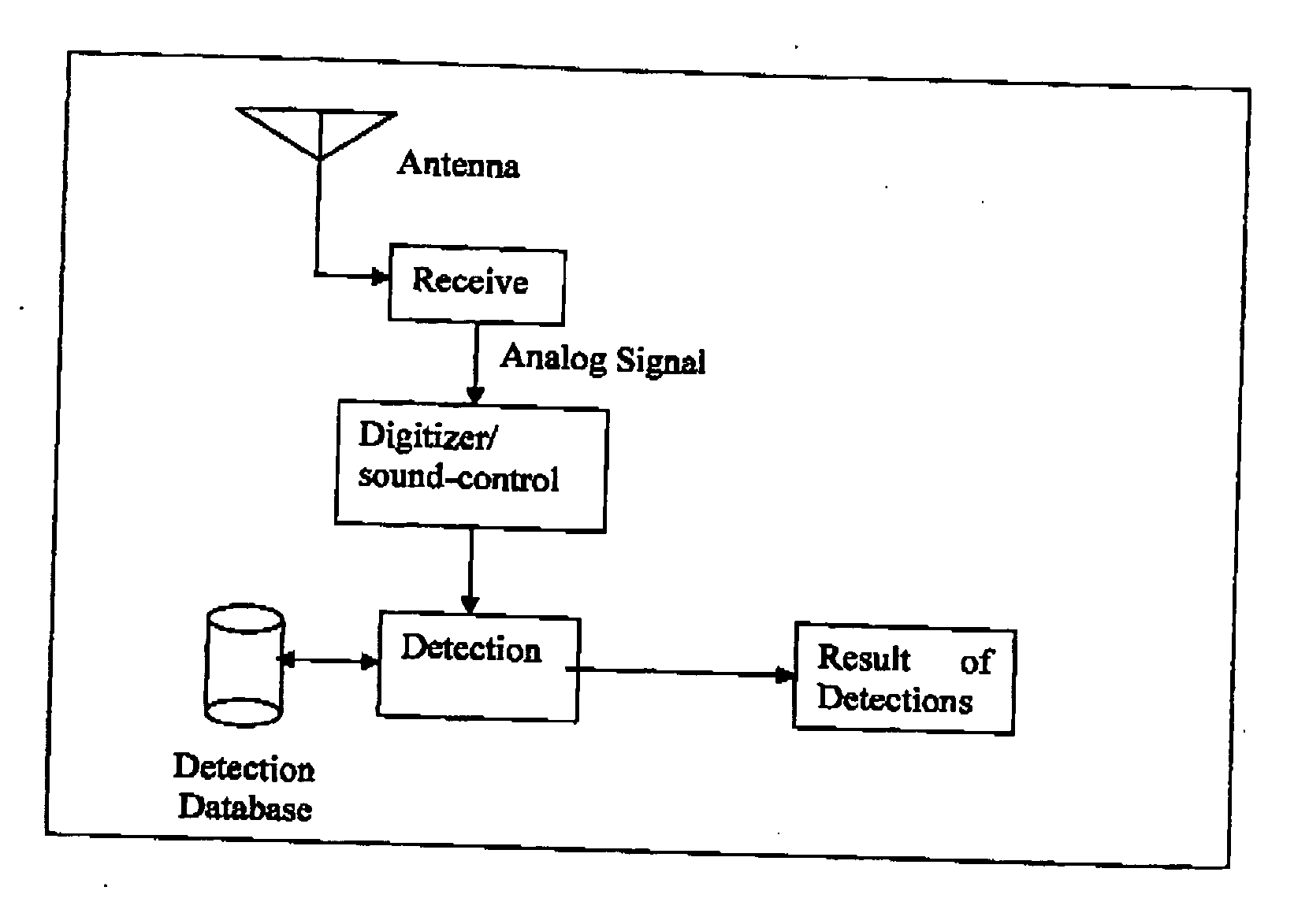
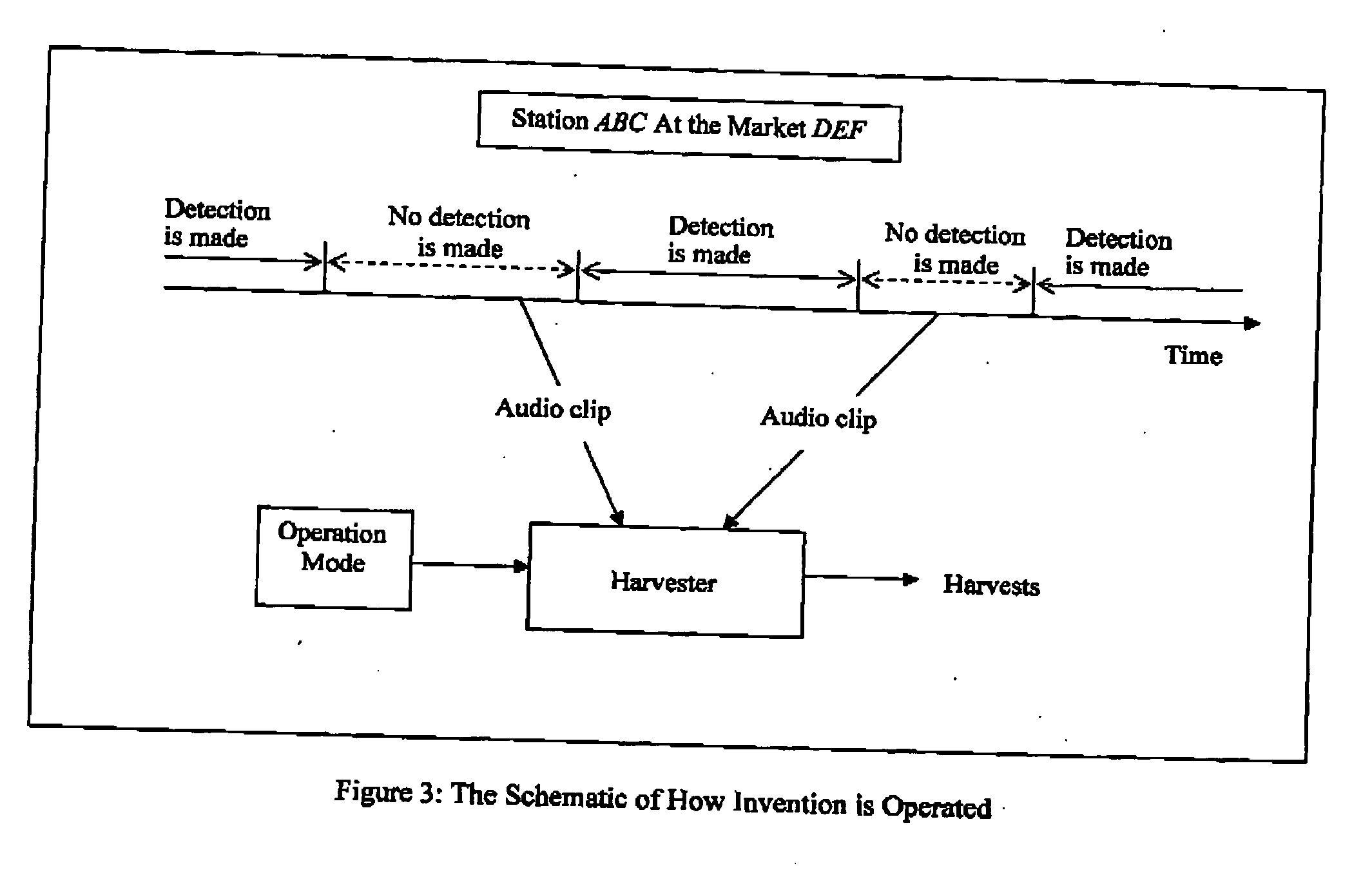
Method and apparatus for automatic detection and identification of unidentified broadcast audio or video signals
ActiveUS20070109449A1Digital data information retrievalColor signal processing circuitsBroadcast channelsCataloging
A system and method of detecting unidentified broadcast electronic media content using a self-similarity technique is presented. The process and system catalogues repeated instances of content that has not be positively identified, but are sufficiently similar as to infer repetitive broadcasts. These catalogued instances may be further processed on the basis of different broadcast channels, sources, geographic locations of broadcasts or format to further assist the identification thereof.
Owner:MOBILE RES LABS
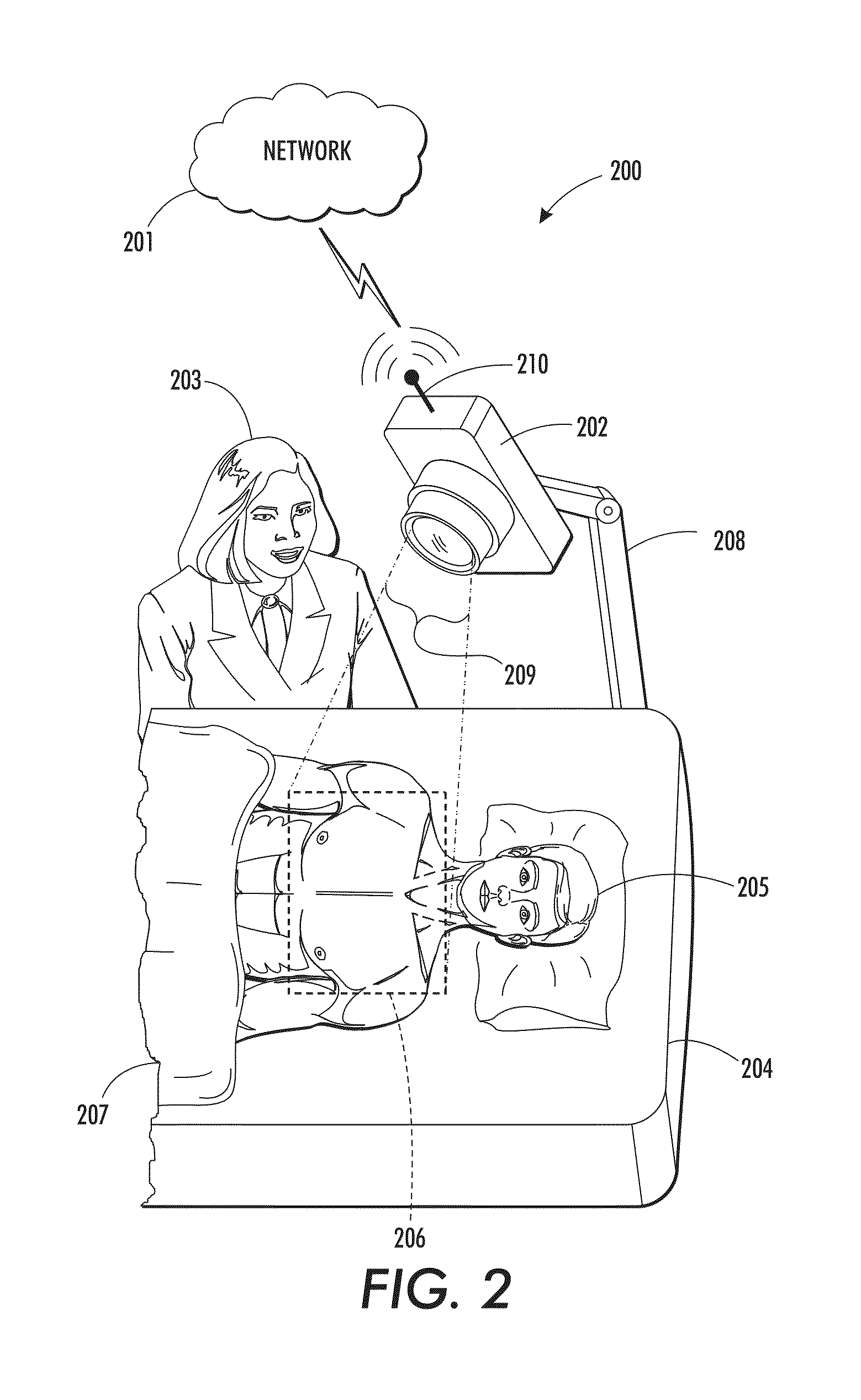
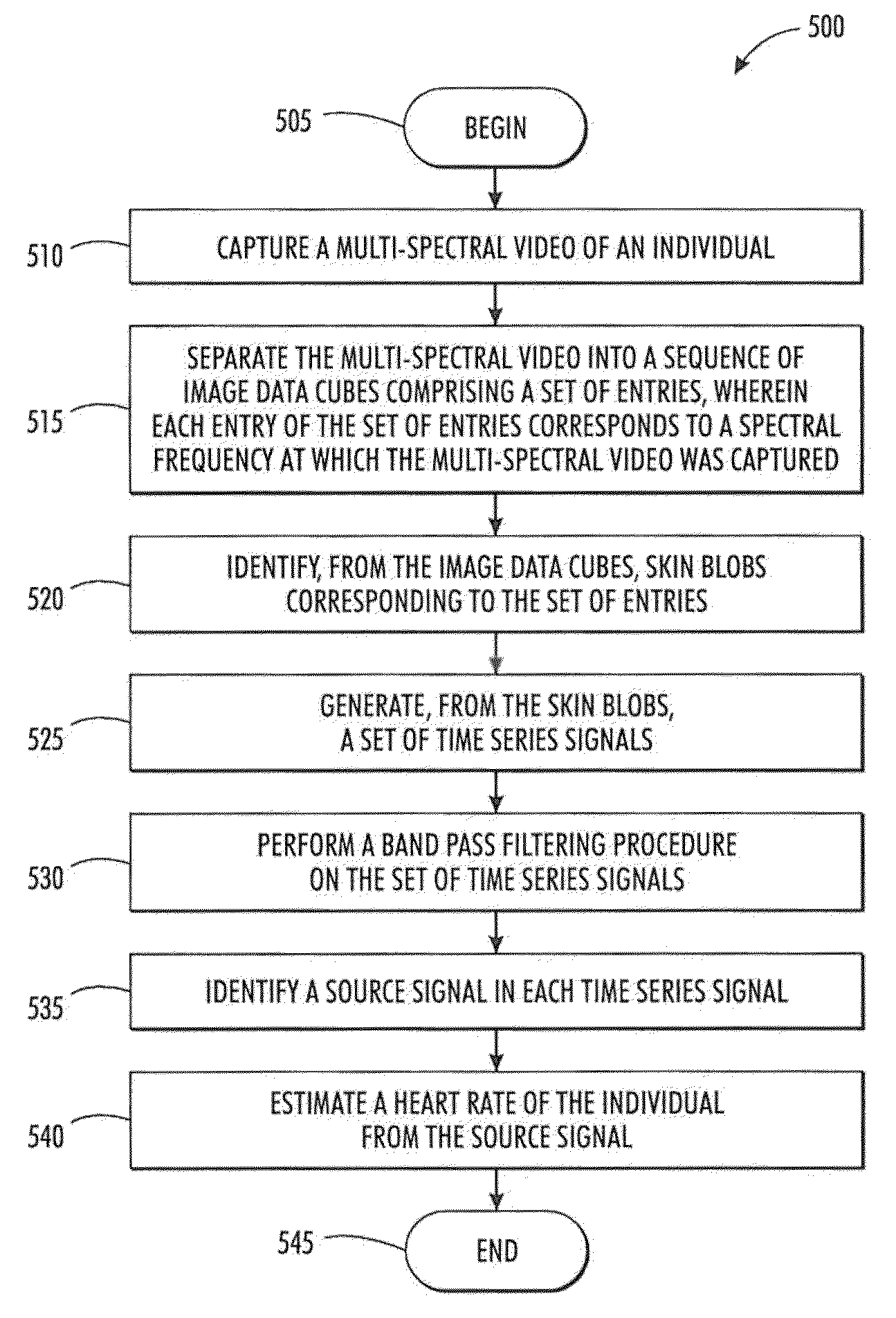
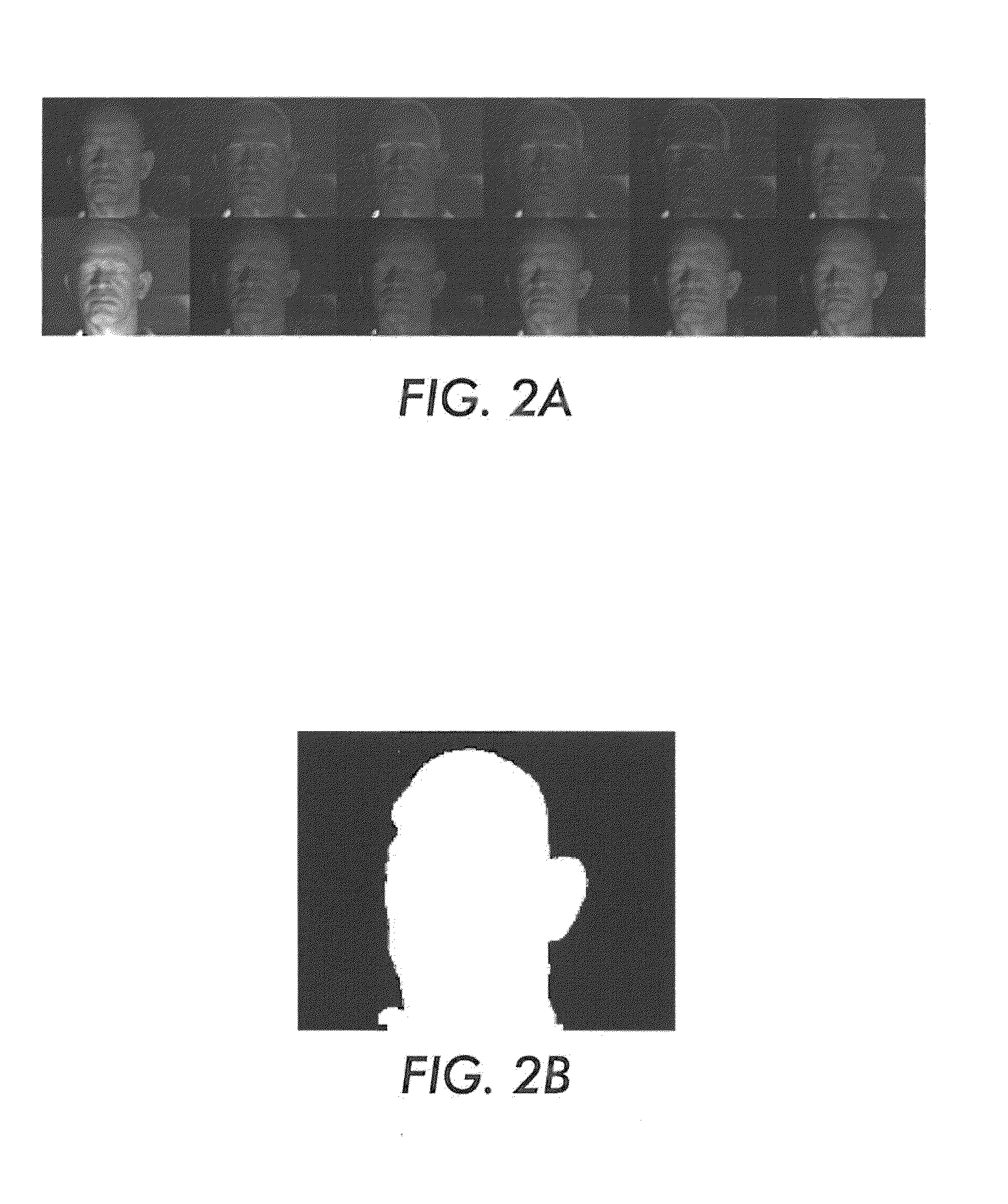
Systems and methods for non-contact heart rate sensing
An embodiment generally relates to systems and methods for estimating heart rates of individuals using non-contact imaging. A processing module can process multi-spectral video images of individuals and detect skin blobs within different images of the multi-spectral video images. The skin blobs, can be converted into time series signals and processed with a band pass filter. Further, the time series signals can be processed to separate pulse signals from unnecessary signals. The heart rate of the individual can be estimated according to the resulting time series signal processing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
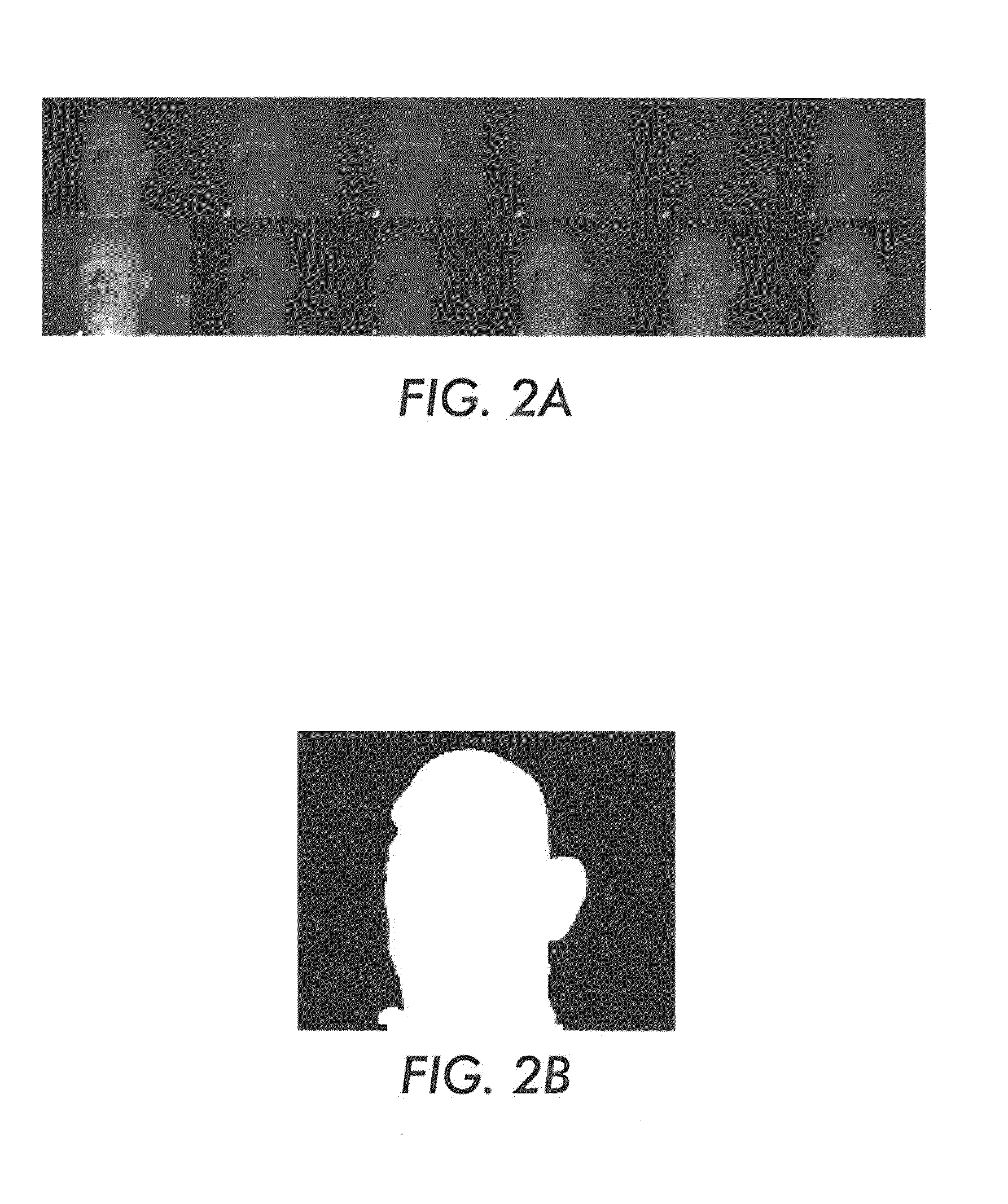
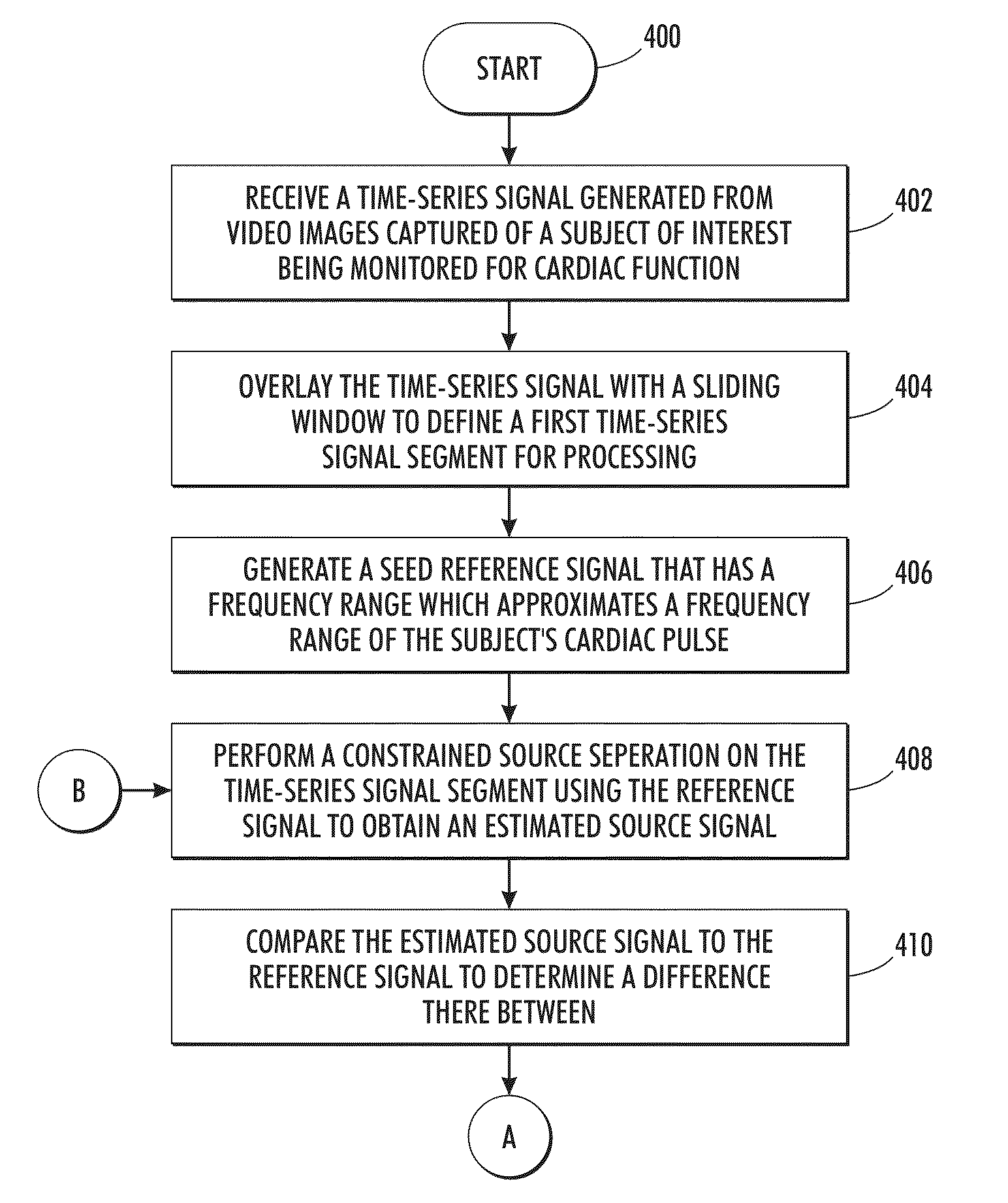
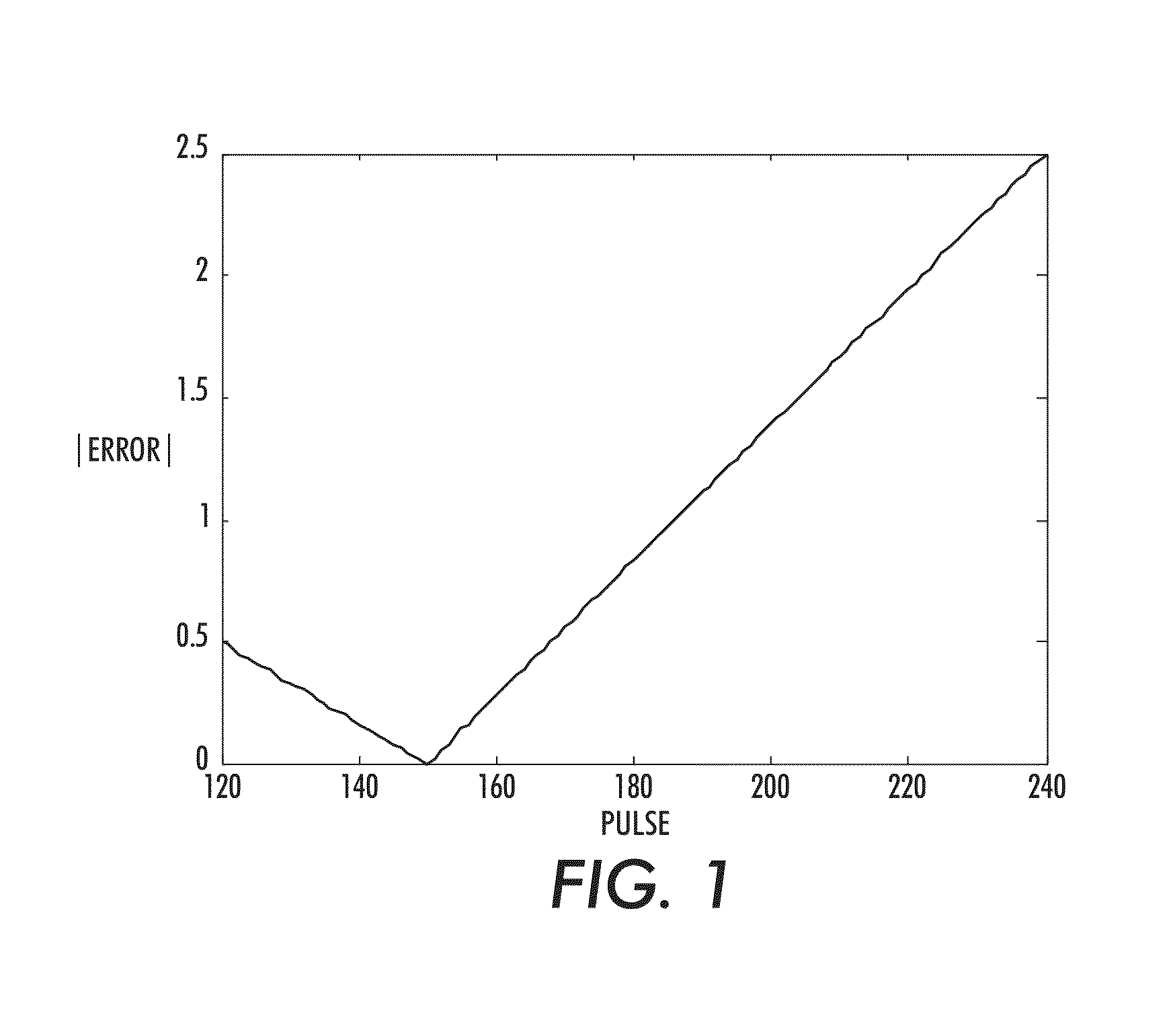
Continuous cardiac pulse rate estimation from multi-channel source video data
ActiveUS8855384B2Recognisation of pattern in signalsMeasuring/recording heart/pulse rateSlide windowPulse rate
What is disclosed is a computationally efficient system and method for estimating a subject's cardiac pulse rate from multi-channel source video data. In one embodiment, A time-series signal is received. A sliding window is used to define overlapping segments of the time-series signal. Signal segments are processed by performing constrained independent component analysis (cICA) until convergence to obtain an estimated source signal. A frequency of each estimated source signal obtained by the cICA at convergence is determined to be the subject's estimated cardiac pulse rate for each signal segment. A seed reference signal used by the cICA is repeatedly updated. A sliding window is shifted to define a next time-series signal segment for processing. The method repeats for each signal segment until a termination criteria is met. In such a manner, the subject's cardiac pulse rate is estimated from a video of the subject on a continuous basis.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Systems and methods for non-contact heart rate sensing
An embodiment generally relates to systems and methods for estimating heart rates of individuals using non-contact imaging. A processing module can process multi-spectral video images of individuals and detect skin blobs within different images of the multi-spectral video images. The skin blobs can be converted into time series signals and processed with a band pass filter. Further, the time series signals can be processed to separate pulse signals from unnecessary signals. The heart rate of the individual can be estimated according to the resulting time series signal processing.
Owner:XEROX CORP
Method and Apparatus for Distributed Compressed Sensing
ActiveUS20070027656A1Efficient captureAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsComputer scienceCompressed sensing
A method for approximating a plurality of digital signals or images using compressed sensing. In a scheme where a common component xc of said plurality of digital signals or images an innovative component xi of each of said plurality of digital signals each are represented as a vector with m entries, the method comprises the steps of making a measurement yc, where yc comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, making a measurement yi for each of said correlated digital signals, where yi comprises a vector with only ni entries, where ni is less than m, and from each said innovation components yi, producing an approximate reconstruction of each m-vector xi using said common component yc and said innovative component yi.
Owner:RICE UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com