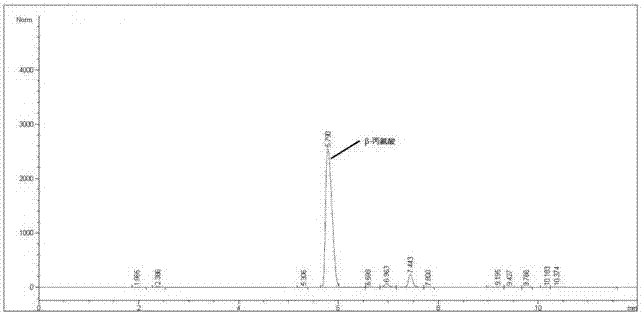
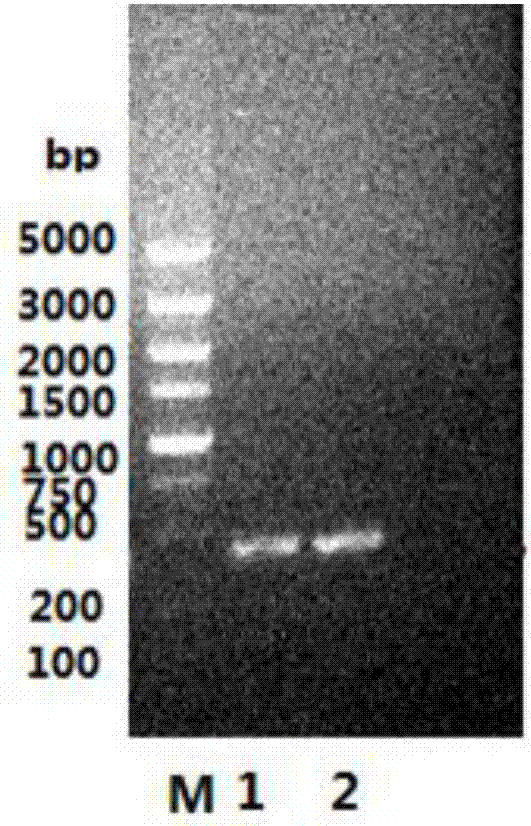
Immobilized L-aspartic acid-alpha-decarboxylase and preparation method and application thereof
A technology of aspartic acid and decarboxylase, applied in the field of bioengineering, can solve problems such as air pollution, environmental pollution, and high production costs, and achieve the effect of improving biological activity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0071] Example 1: Construction of expression plasmid vector containing L-aspartic acid-α-decarboxylase gene.
[0072] According to the sequence of Escherichia coli (Escherichia coli str.K-12substr.MG1655) gene reported on Genbank, the primers were designed using Vector NTI software. The primer sequences are shown in Table 1:
[0073] Table 1 Primer Sequence
[0074]
[0075]
[0076]According to the instructions provided by the manufacturer, the genomic DNA of Escherichia coli strain N (Escherichia coli str. / L) Agarose gel electrophoresis to detect the obtained genomic DNA, respectively using the extracted Escherichia coli genomic DNA as a template for PCR amplification.
[0077] The PCR (polymerase chain reaction) amplification system is: 2 μL of genomic DNA, 2 μL of primers panD-up and primer panD-down, 4 μL of dNTP, 5 μL of 10×Taq buffer, 1 μL of Taq enzyme, ddH 2 O 34 μL;
[0078] The PCR reaction program was: pre-denaturation at 94°C for 2 minutes; denaturation ...
Embodiment 2
[0089] Example 2: Induced expression of genetically engineered bacteria.
[0090] Two ways are used to induce expression of the genetically engineered bacteria obtained in Example 1:
[0091] (1) Prepare 1L of seed solution, the medium is LB liquid medium (peptone 10g / L, yeast powder 5g / L, NaCl 10g / L), after sterilizing at 121℃ for 30min, put it into several 500mL wide-mouth triangles in the bottle. Inject a loop of the genetically engineered bacteria in Example 1 into the seed solution with an inoculation needle, and place it on a shaker at 37° C. at a speed of 200 rpm for overnight cultivation. Prepare 1000 mL of LB medium containing 10 g / L of peptone, 5 g / L of yeast powder, and 10 g / L of NaCl, and distribute it in a wide-mouthed Erlenmeyer flask with a capacity of 500 mL. The volume of each bottle is 100 mL; ℃ autoclave for 30 minutes. After the culture medium is cooled, add 1mL of the overnight cultured seed solution, place the Erlenmeyer flask on a shaker at 37°C at a ...
Embodiment 3
[0093] Embodiment 3: Ni column pure enzyme and ultrafiltration concentrate
[0094] Take 500mL of genetically engineered bacterial fermentation broth, centrifuge at 8500rpm for 15min, wash with normal saline and centrifuge again, and ultrasonically crush to obtain the supernatant, connect to a peristaltic pump, pass through two 5mL Ni columns connected in series, and then filter the obtained eluate through a 3000Da ultrafiltration Tube, 5500rpm, 30min The upper layer is the concentrate. Detected by SDS-PAGE, the results are as follows Figure 4 As shown, there are characteristic proteins of corresponding size in whole cells and supernatants, but not in the permeate and washing liquid, and there are also characteristic proteins in the eluate, and the amount is very large, and it is more obvious in the concentrated solution, so the enzyme can be used Purification was carried out by any of the two methods of Ni column adsorption and ultrafiltration tube concentration.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com