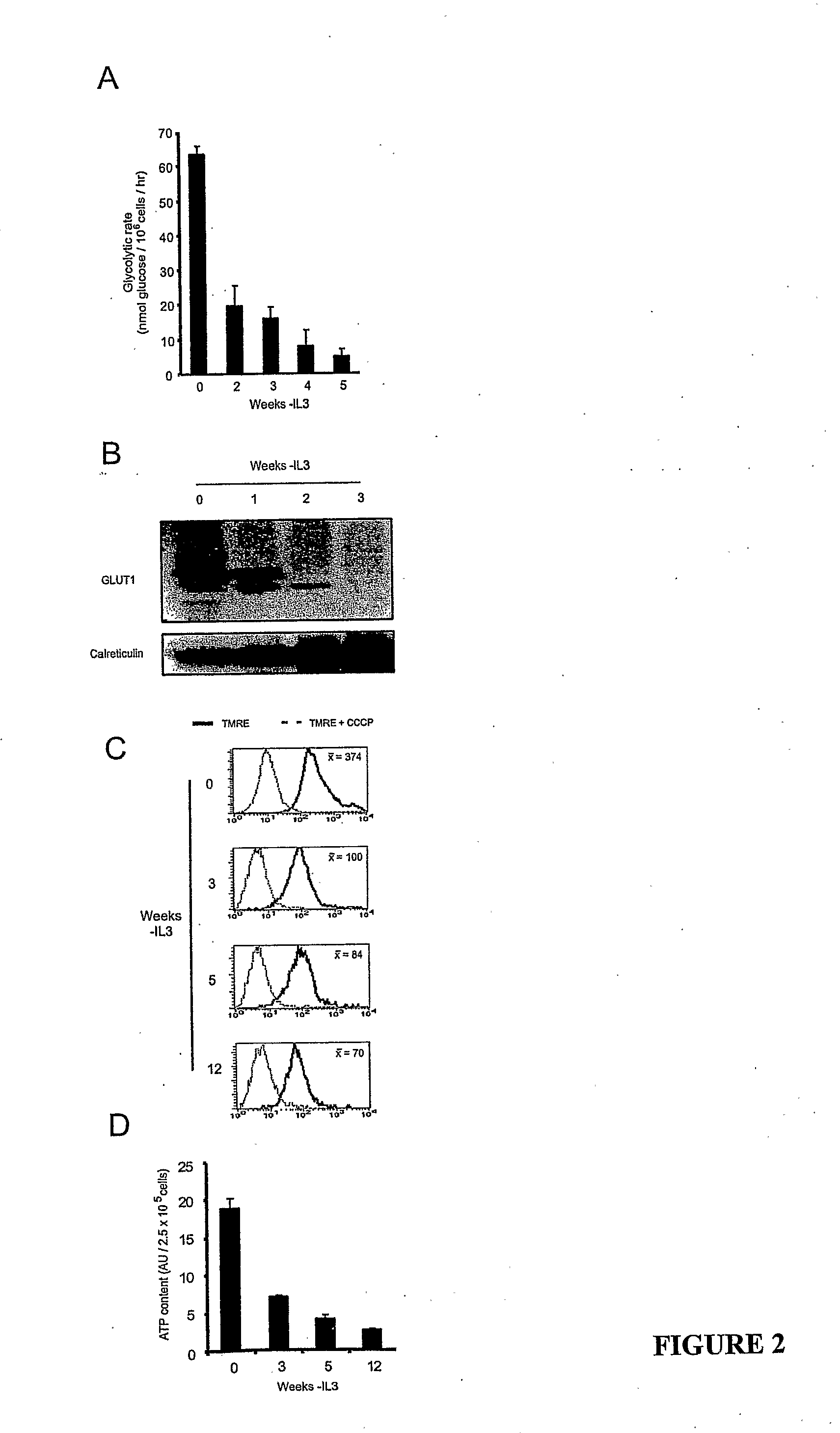
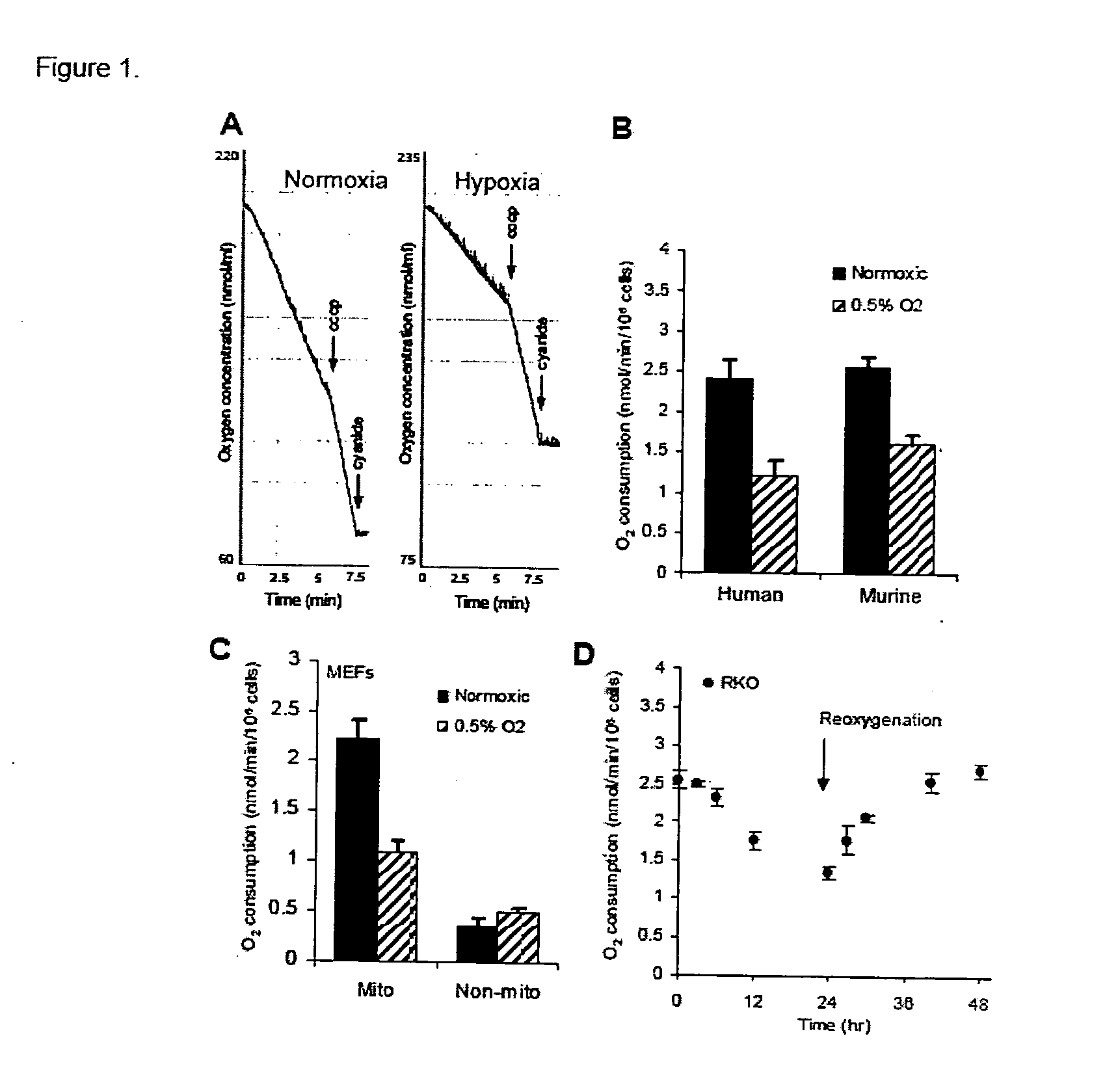
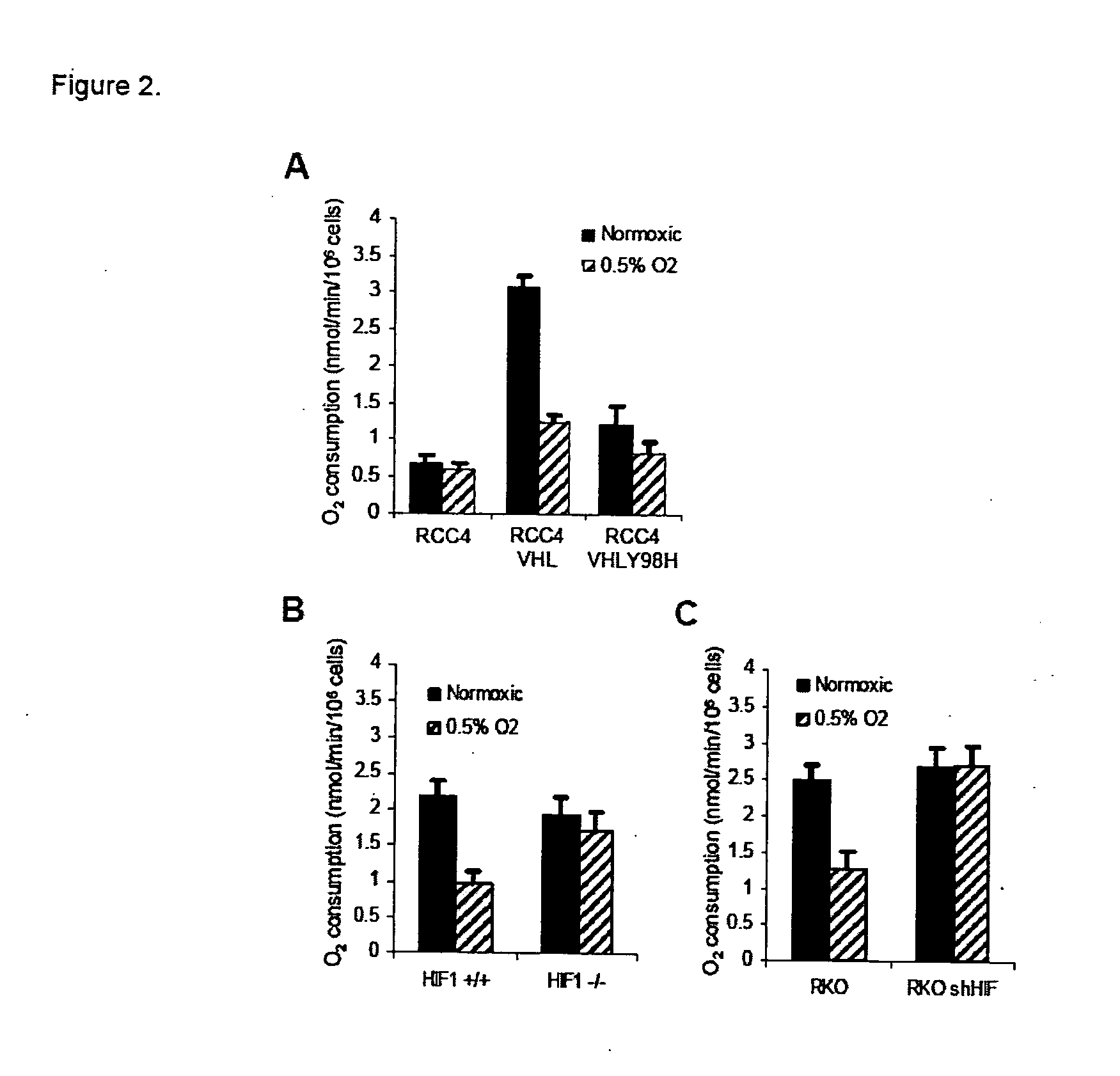
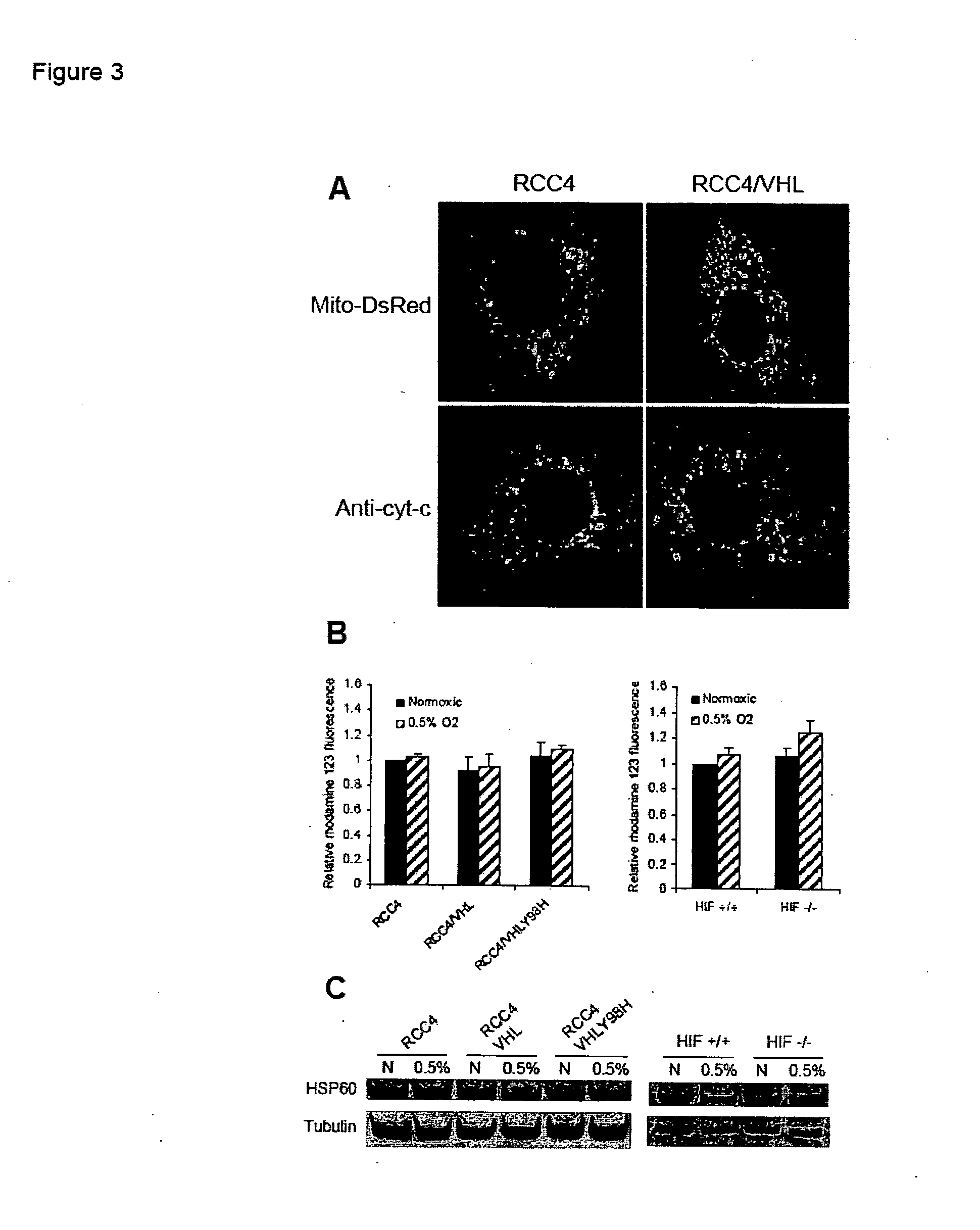
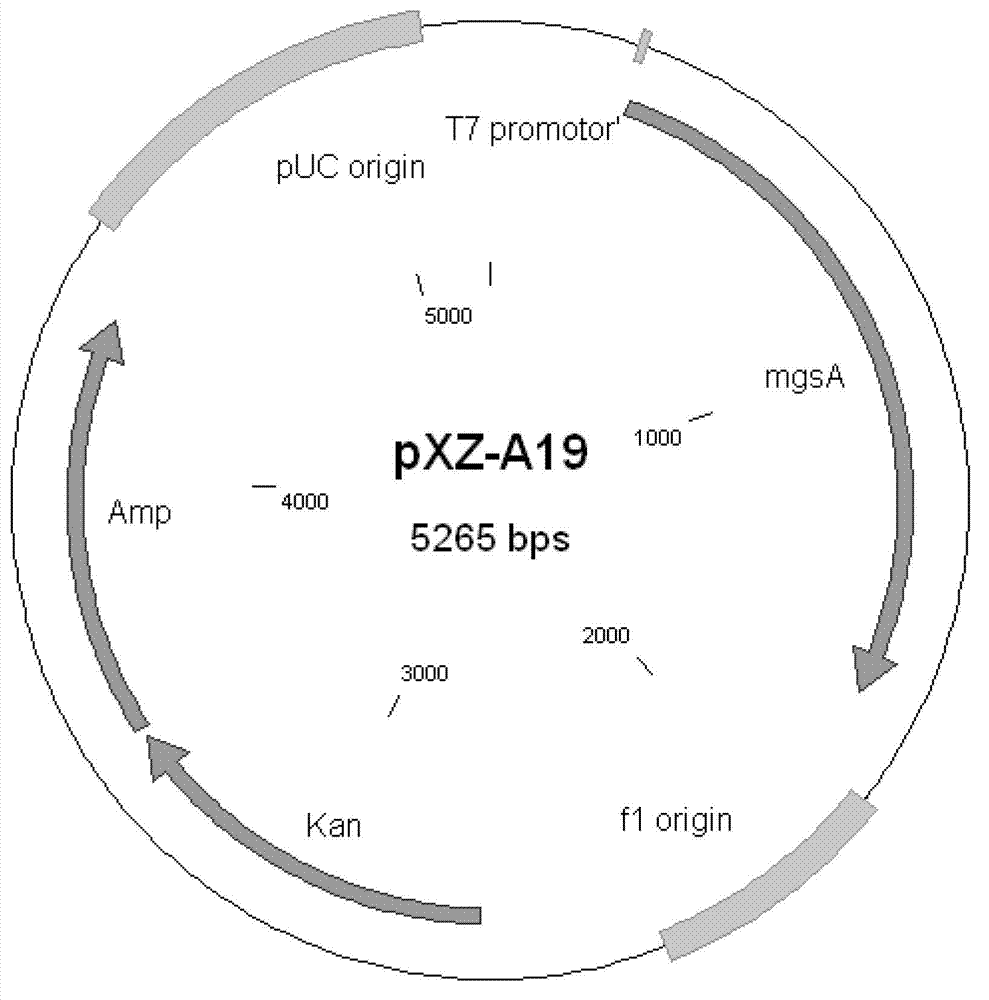
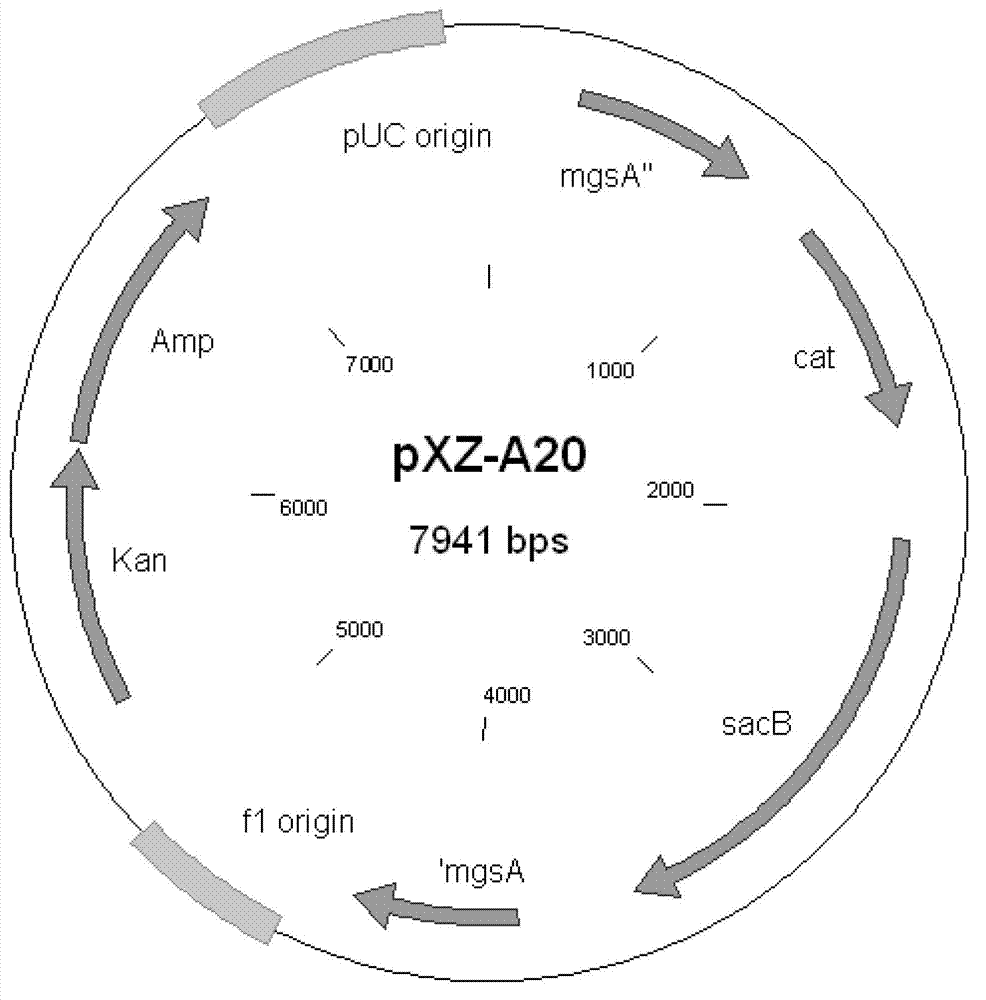
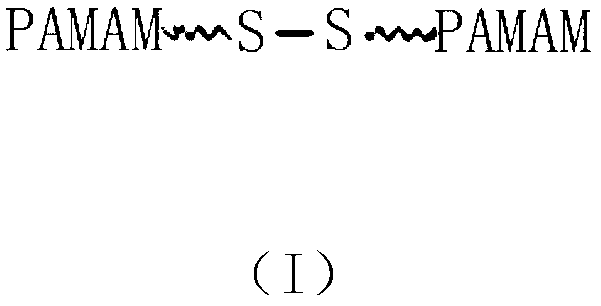Patents
Literature
412 results about "Glycolysis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
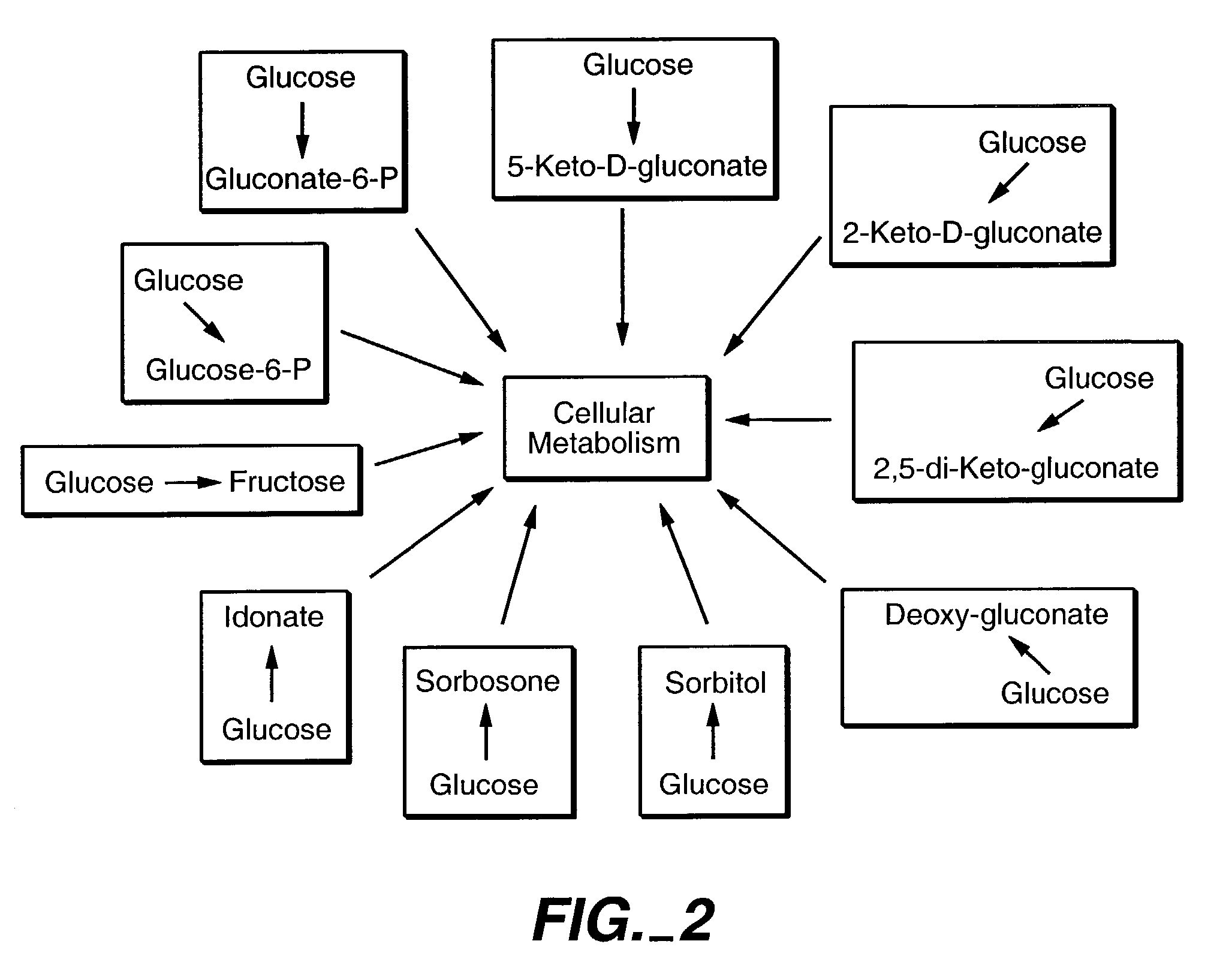
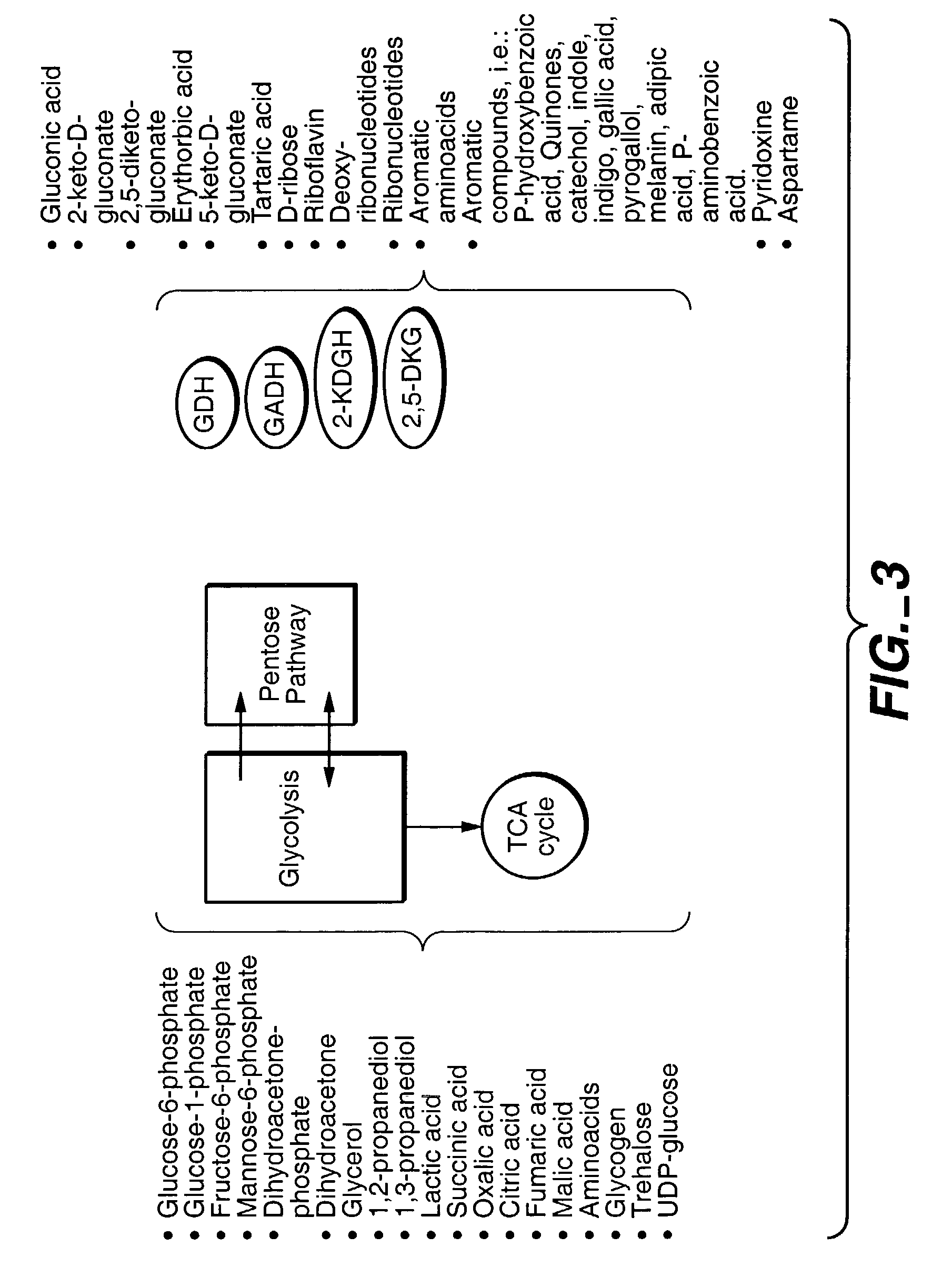
Glycolysis (from glycose, an older term for glucose + -lysis degradation) is the metabolic pathway that converts glucose C₆H₁₂O₆, into pyruvate, CH₃COCOO⁻ + H⁺. The free energy released in this process is used to form the high-energy molecules ATP (adenosine triphosphate) and NADH (reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide). Glycolysis is a sequence of ten enzyme-catalyzed reactions. Most monosaccharides, such as fructose and galactose, can be converted to one of these intermediates. The intermediates may also be directly useful rather than just utilized as steps in the overall reaction. For example, the intermediate dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) is a source of the glycerol that combines with fatty acids to form fat.
Method for preparing glycolysis Chinese herbal medicine preparations for feed
InactiveCN101116473AGood effectQuick balanceFood processingClimate change adaptationAdditive ingredientChinese traditional
A preparation method of a ferment Chinese Traditional Herbs for feeding belongs to the production field of the feed additives. The technical proposal provided by the present invention is that one or various intestinal probiotics is inoculated on a cultivation matrix containing extracts of Chinese Traditional Herbs, and undergoes ferment cultivation in a proper condition. The probiotics include Lactobacillus acidophilus, Bacillus subtilis, and candida utilis, etc, and the selected Chinese Traditional Herbs include astragalus, atractlylis lancea formalyrata, codonopsis pilosula, pericarpium citri reticulatae, and atractylis atractylis ovata, etc. The ferment Chinese Traditional Herbs for feeding provided by the present invention used to breed the livestock and the poultry is capable of preventing and treating epidemic diseases and improving the growth of the animal. The biological ferment of the water extract of Chinese Traditional Herbs by the probiotics is utilized to produce the elements with higher activities, thereby improving the absorption, transportation, metabolism, activation and medical efficacy of the Chinese Traditional Herbs in human body.
Owner:济南亿民动物药业有限公司
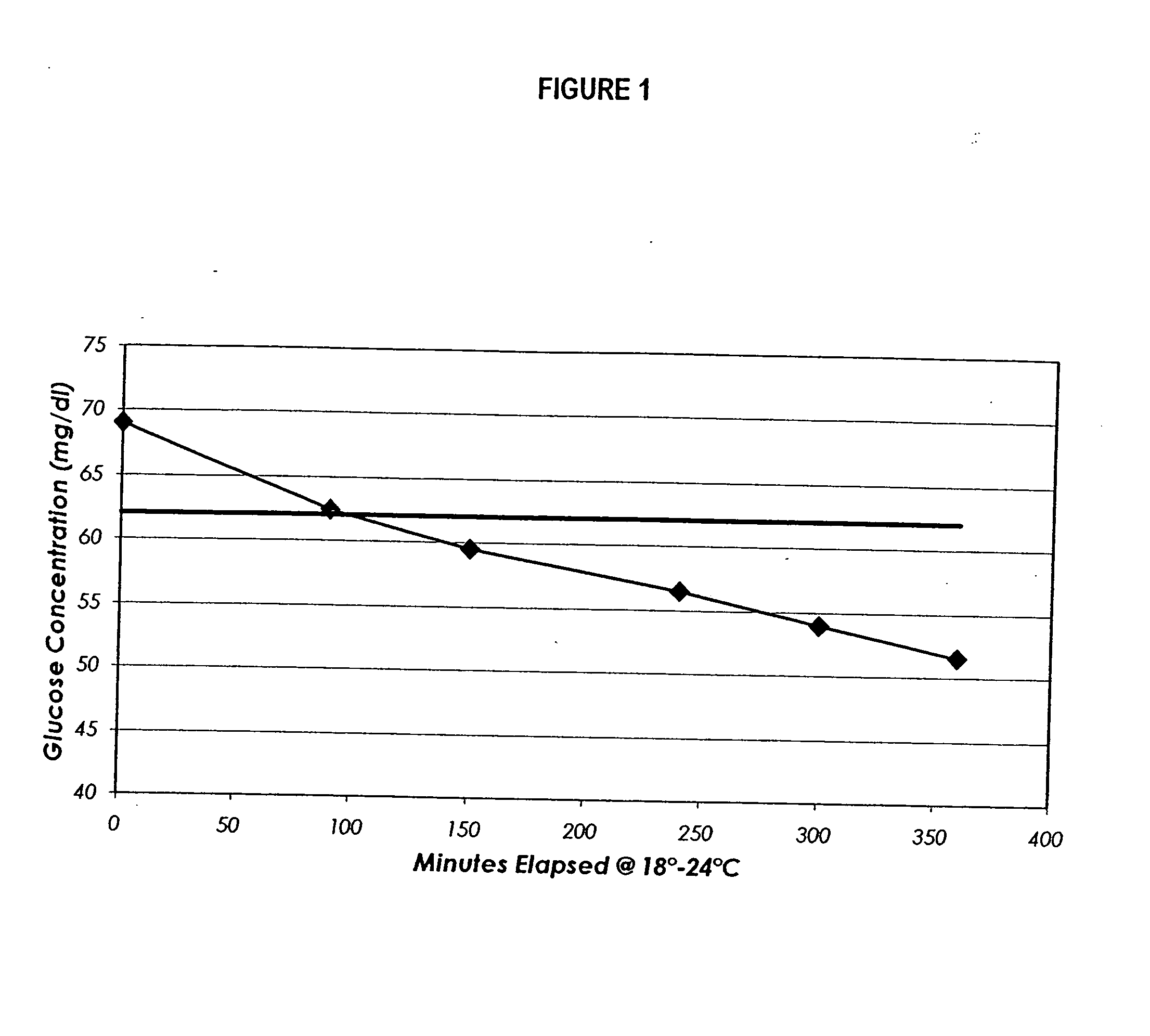
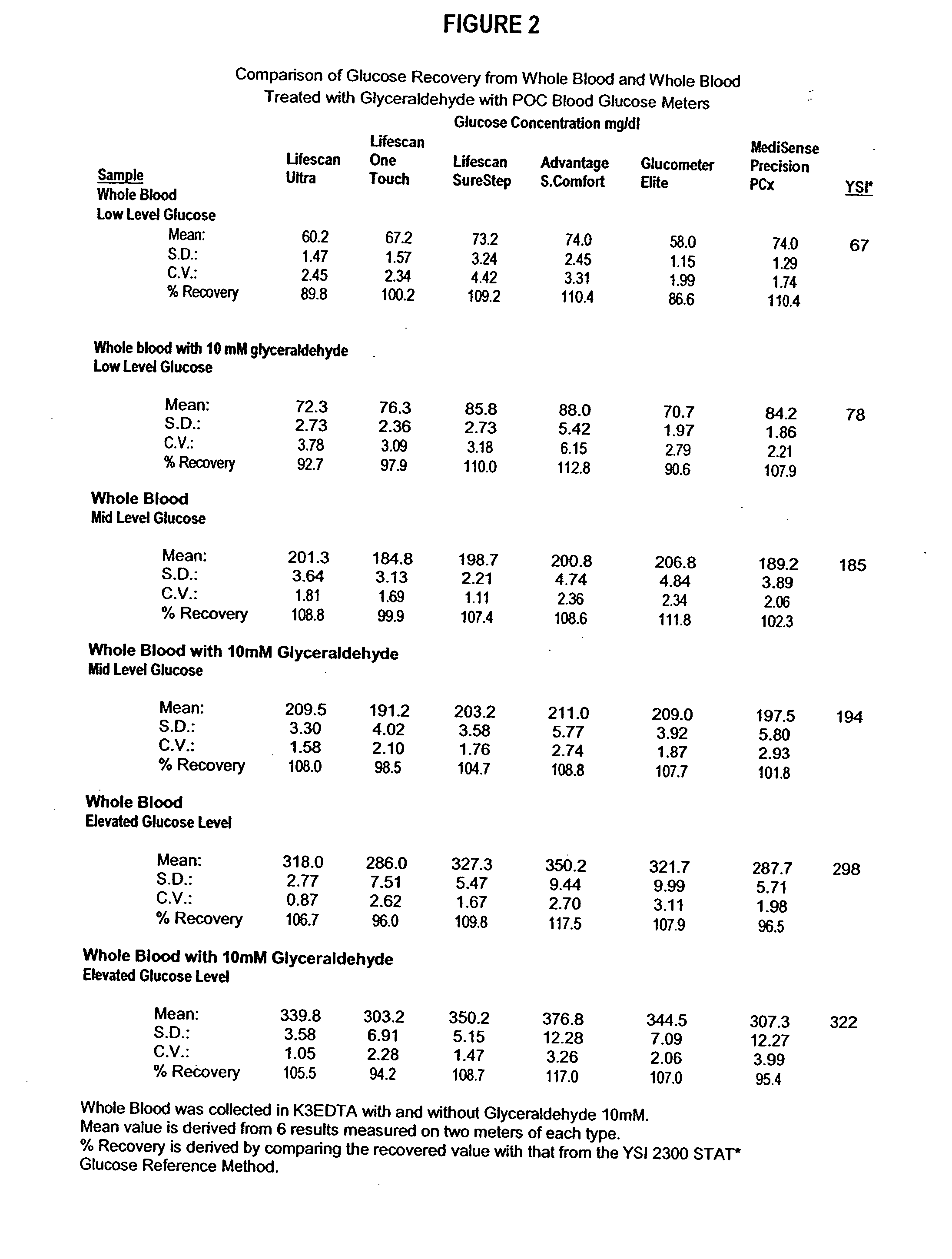
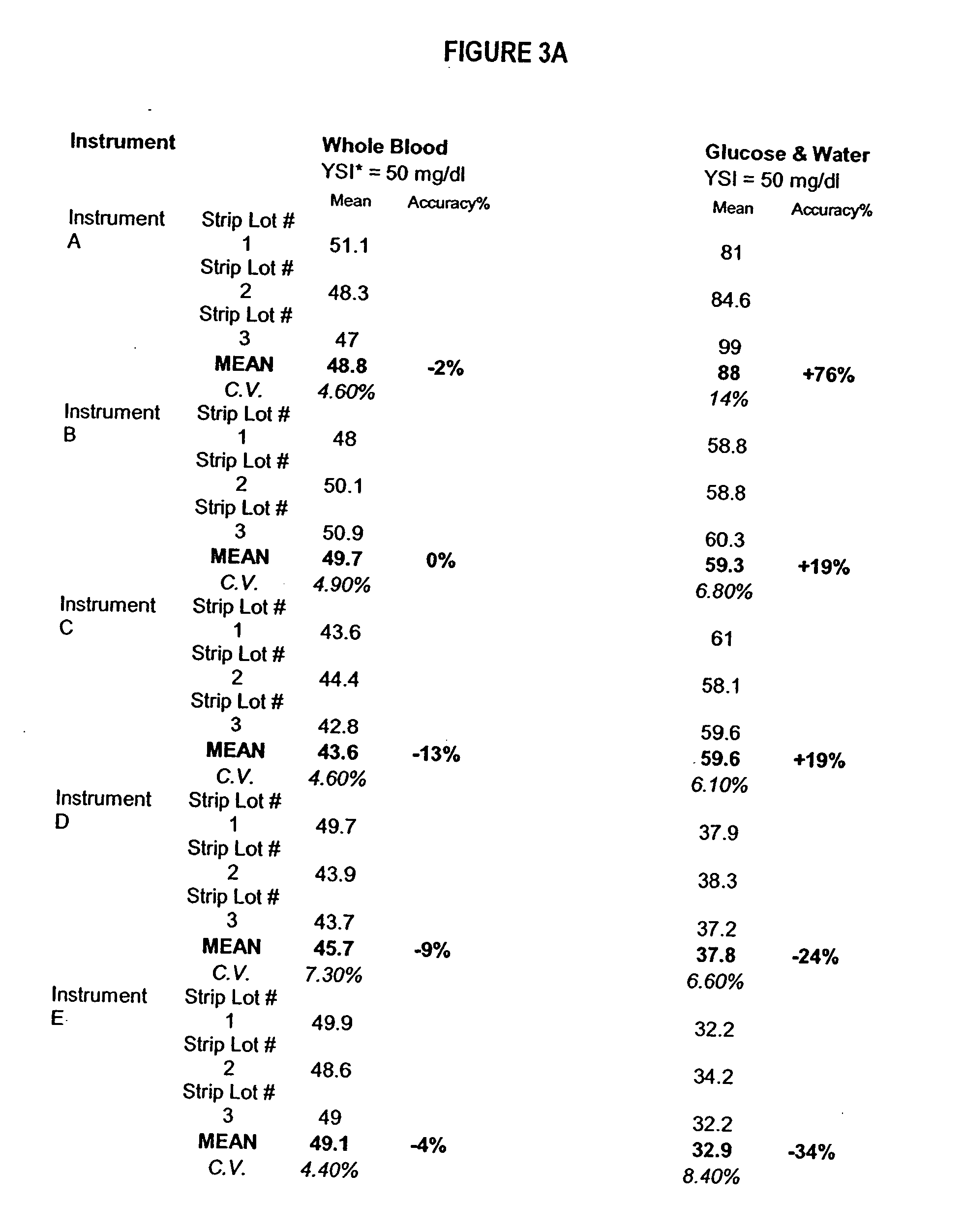
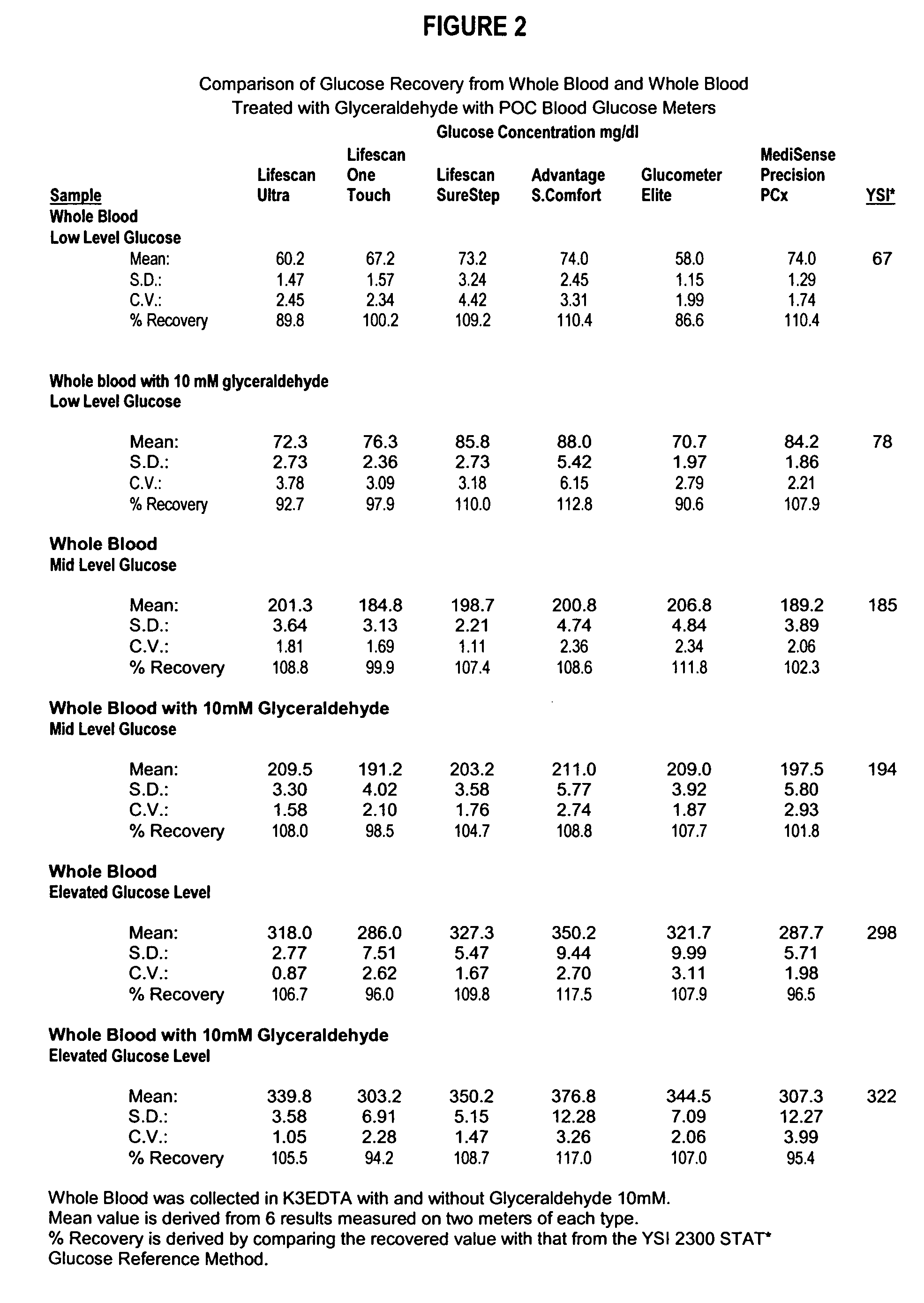
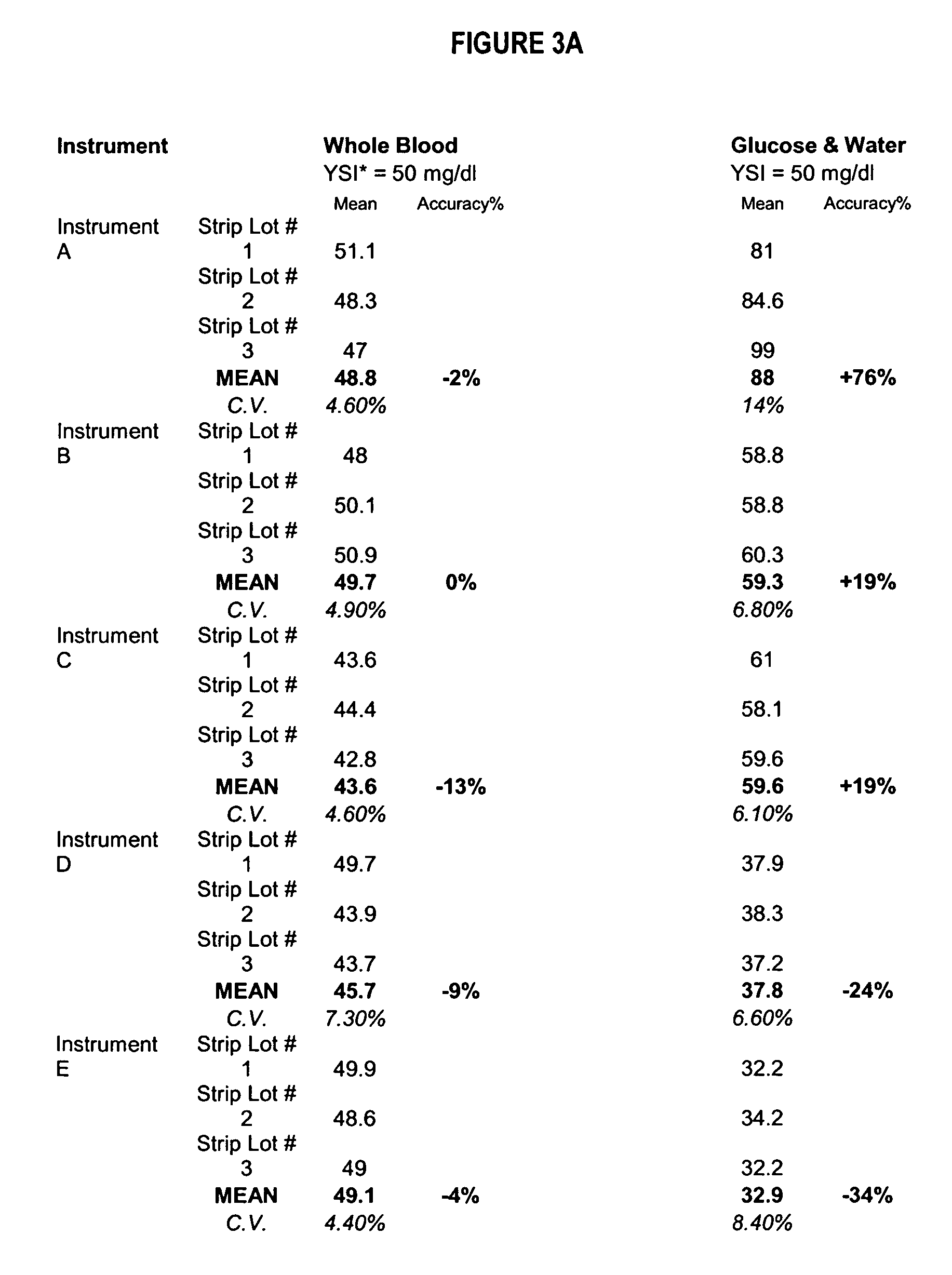
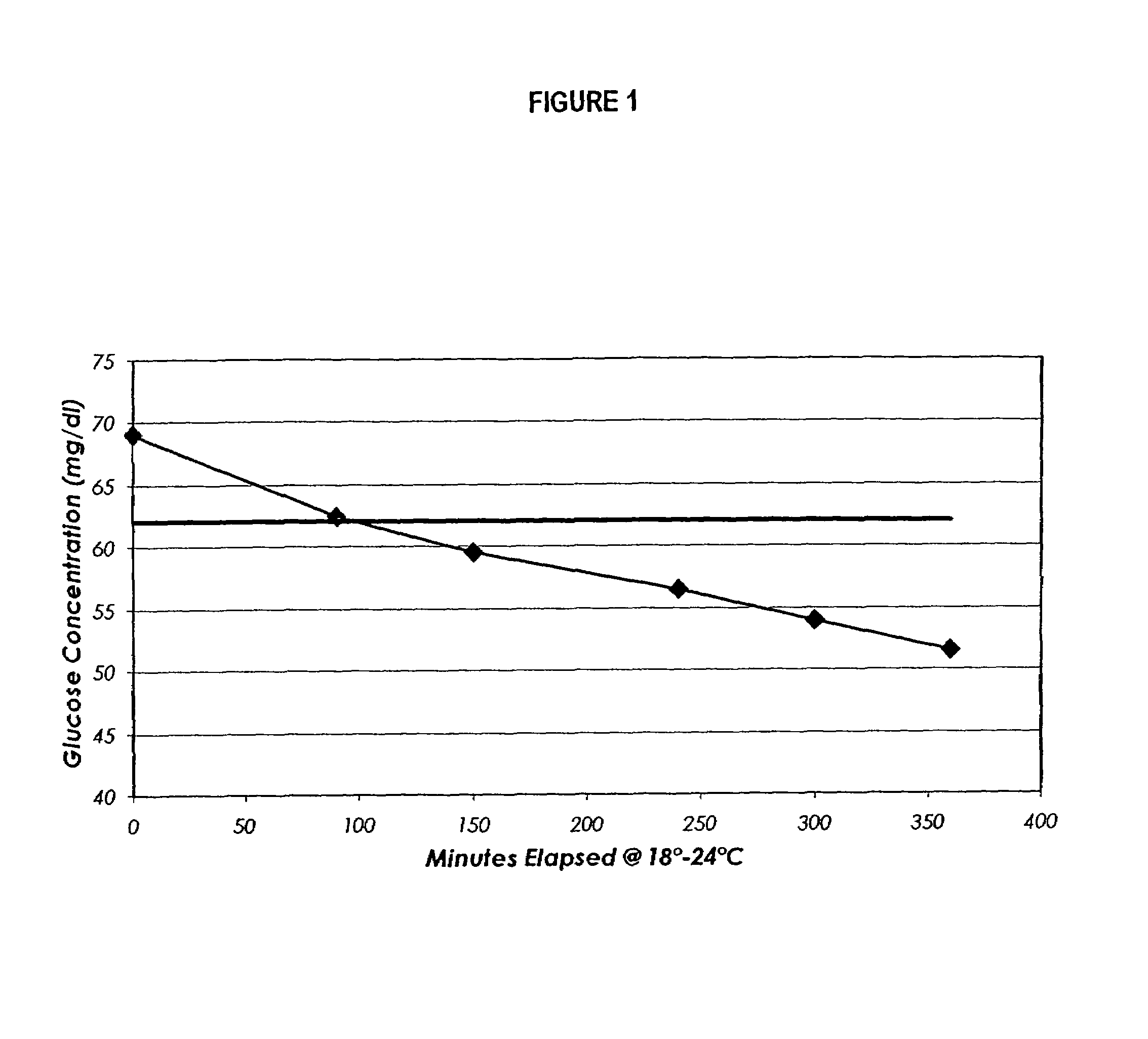
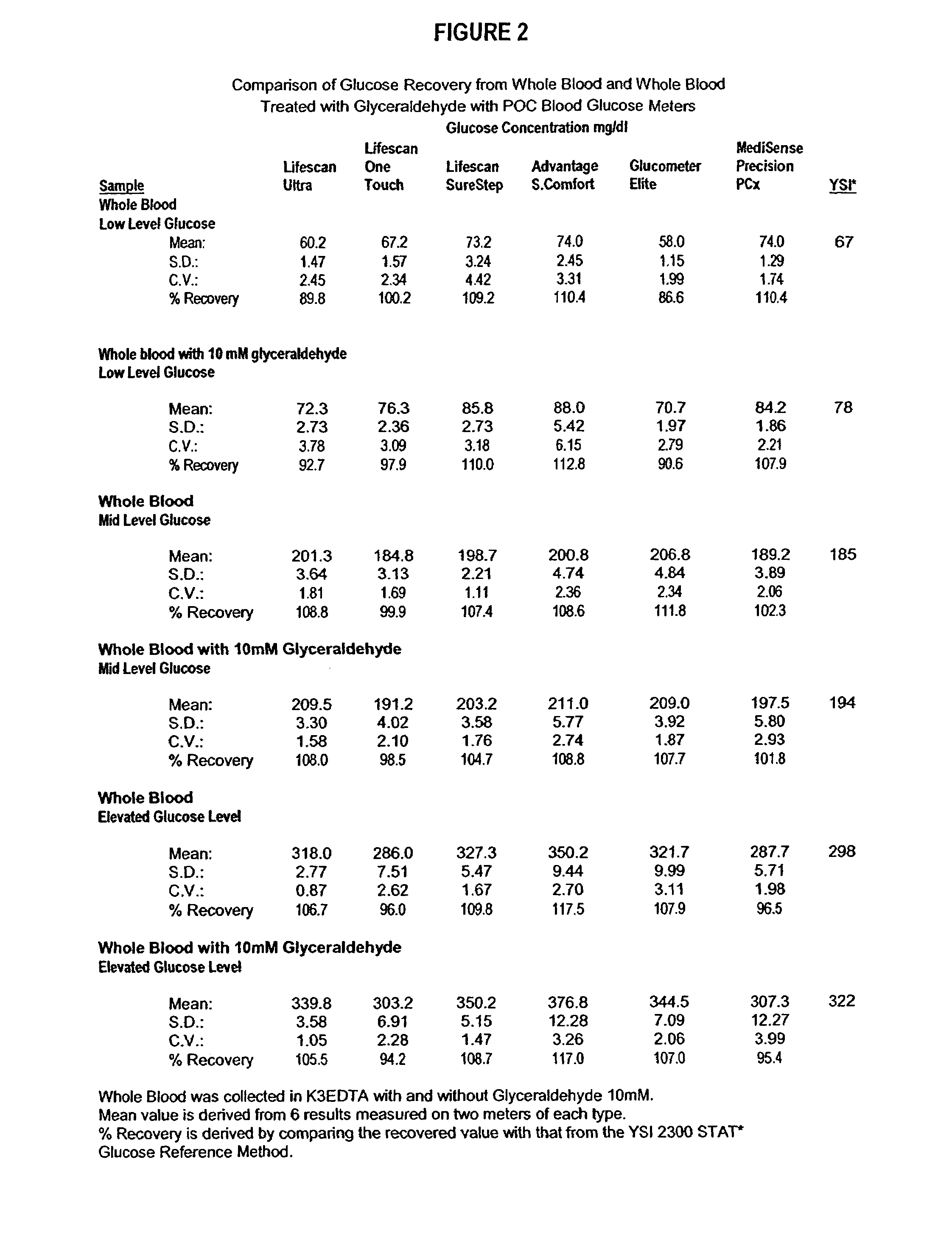
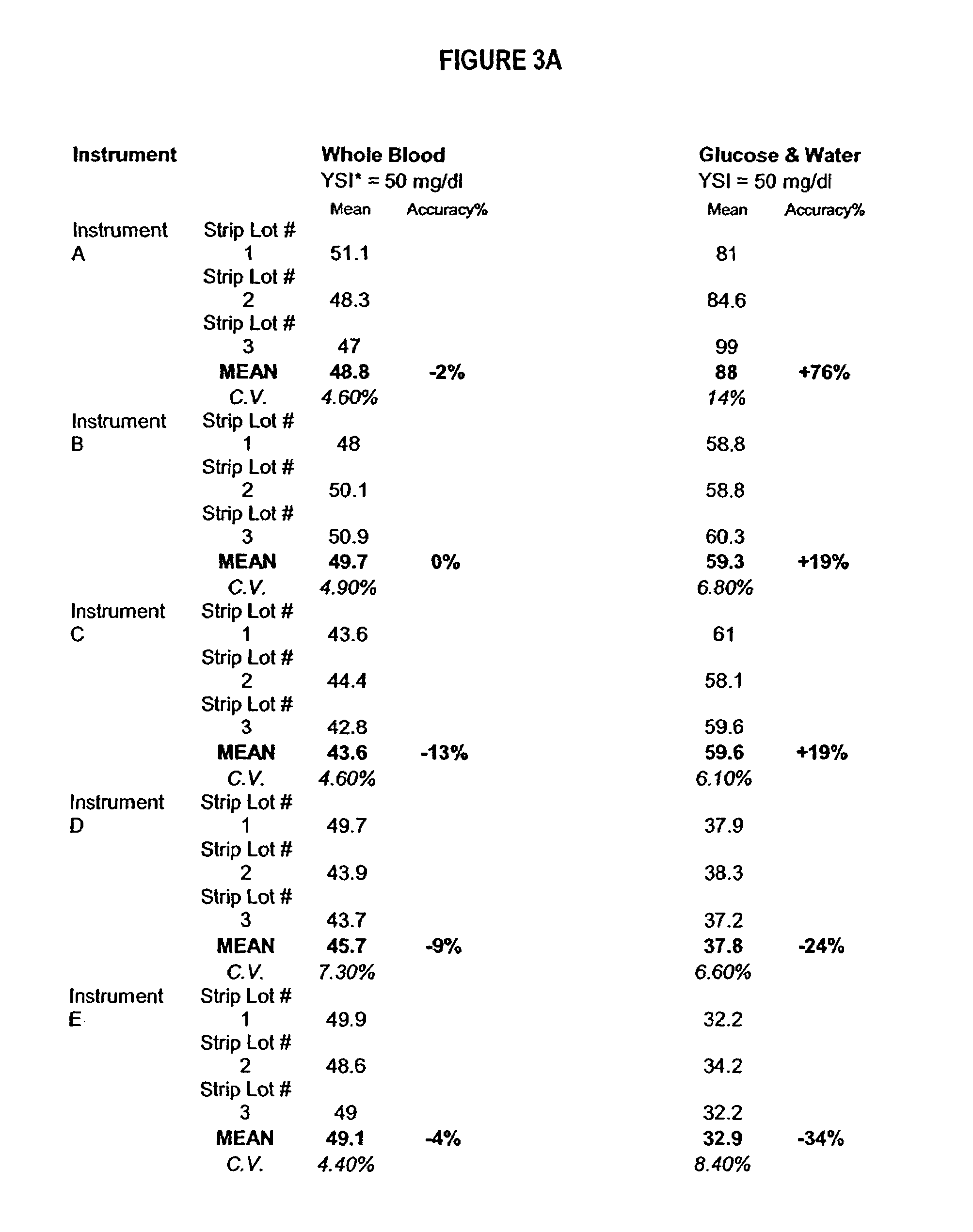
Process, composition and kit for providing a stable whole blood calibrator/control
InactiveUS20060211072A1Quality improvementSimple and elegantSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineConcentrations glucose
The present invention is directed toward a stable calibrator and / or control, kit and process for using in a glucose monitoring instrumentation. Principally, the instant invention teaches a glycolyzed red blood cell component which has been treated with a glycolysis stabilizing effective amount of at least one non-crosslinking aldehyde compound which may be added to fresh plasma along with an amount of glucose to form a simulated whole blood glucose control product, effective for maintaining a particular and essentially stable glucose concentration over a period of time sufficient for accurate measurement and calibration of a glucose measuring instrument.
Owner:STRECK INC
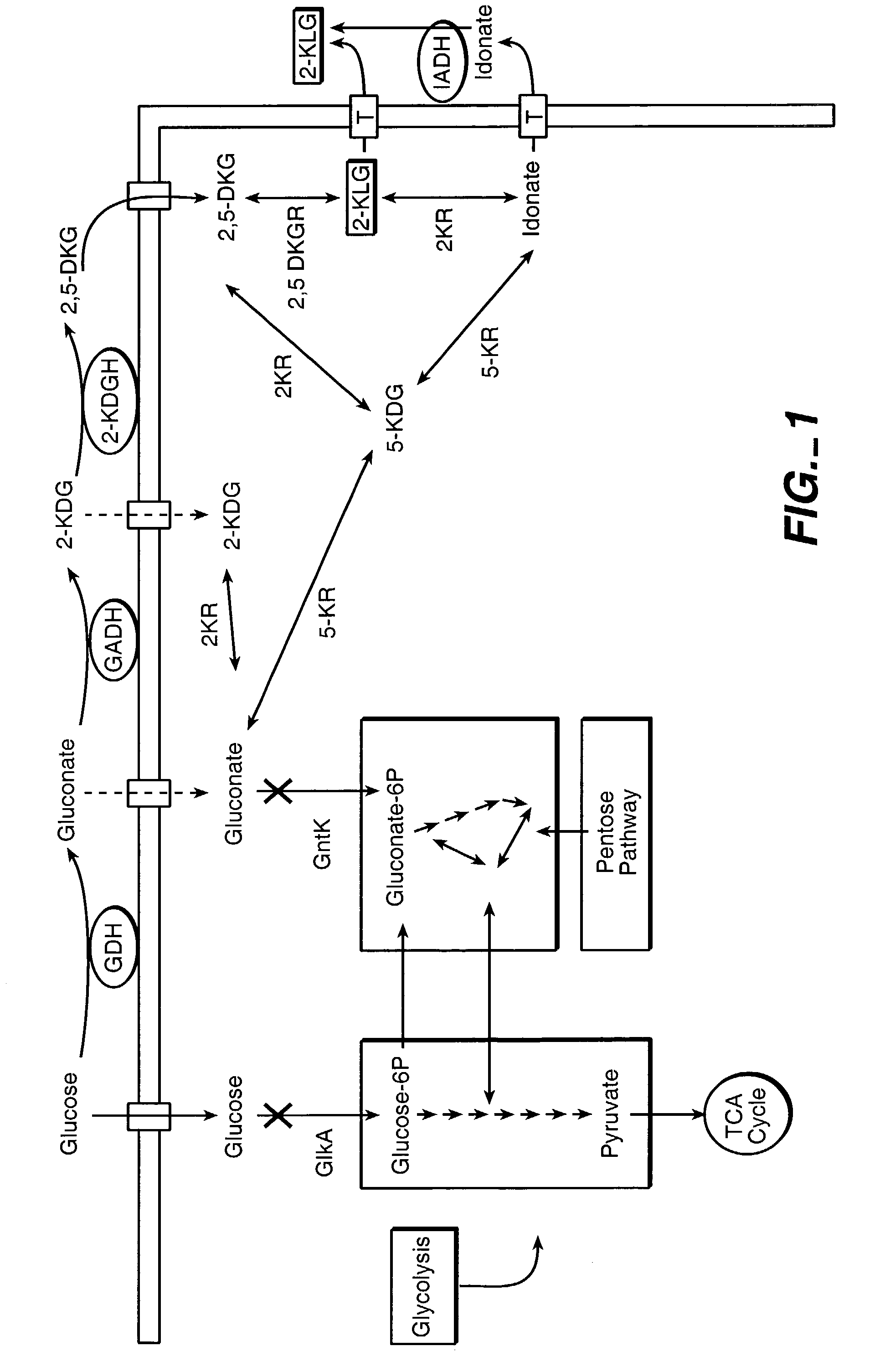
Method of uncoupling the catabolic pathway of glycolysis from the oxidative membrane bound pathway of glucose conversion
InactiveUS7241587B2Increase volumeMeet actual needsBacteriaSugar derivativesPhosphorylationGluconic acid
The invention provides methods for producing products comprising improved host cells genetically engineered to have uncoupled productive and catabolic pathways. In particular, the present invention provides host cells having a modification in nucleic acid encoding an endogenous enzymatic activity that phosphorylates D-glucose at its 6th carbon and / or a modification of nucleic acid encoding an enzymatic activity that phosphorylates D-gluconate at its 6th carbon. Such improved host cells are used for the production of products, such as, ascorbic acid intermediates. Methods for making and using the improved host cells are provided. Nucleic acid and amino acid sequences for glucokinase and gluconokinase are provided.
Owner:GENENCOR INT INC
Cryopreservation of human red blood cells
InactiveUS20060127375A1Lower Level RequirementsAvoid hemolysisBiocideDead animal preservationFreeze thawingPhosphorylation
A red blood cell storage composition includes a composition of red blood cells and biochemistry altering reagents, the biochemistry altering reagents being present at a concentration so as to reduce the percent hemolysis of the red blood cells during the freeze-thaw cycle below that of the percent hemolysis of the red blood cells in the absence the biochemistry altering reagents. The red blood cell storage composition preferably includes reagents selected from: modifiers of glycolytic / metabolic components, modifiers of antioxidant potential, effectors of intracellular ionic distribution, modifiers of membrane fluidity, modifiers of cytoskeletal structure, effectors of the cyclooxygenase second messenger pathway, effectors of the lipoxygenase second messenger pathway, effectors of the hexose monophosphate second messenger pathway, effectors of the phosphorylation second messenger pathway, modifiers of specific messenger molecules, and combinations thereof.
Owner:LIFECELL
Methods and materials for depolymerizing polyesters
Provided is a method of depolymerizing polyesters from post-consumer products, such as beverage bottles, to produce a high purity reaction product. For the depolymerization reaction, the polyesters are reacted with an alcohol having 2 to 5 carbons and an amine organocatalyst at a temperature of about 150° C. to about 250° C. In one application, the use an organocatalyst with a boiling point significantly lower than the boiling point of the reactant alcohol allows for the ready recycling of the amine organocatalyst. In another application, performing the depolymerization reaction under pressure at a temperature above that of the alcohol allows for accelerated depolymerization rates and the recovery of the organocatalyst with no further heat input. In a further application, glycolytic depolymerization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) (PET) from post-consumer beverage bottles produces a pure reaction product of bis(2-hydroxyethyl)terephthalate (BHET), which may in turn be used to produce high purity beverage bottle grade PET, in a closed loop process with minimal output and waste.
Owner:IBM CORP
Process, composition and kit for providing a stable whole blood calibrator/control
InactiveUS20060188995A1Quality improvementSimple and elegantMaterial analysis by optical meansBiological testingMedicineMeasuring instrument
The present invention is directed toward a stable calibrator and / or control, kit and process for using in a glucose monitoring instrumentation. Principally, the instant invention teaches a glycolyzed red blood cell component, which has been treated with a glycolysis stabilizing effective amount of at least one non-crosslinking aldehyde compound. The glycolyzed red blood cell component may be added to fresh plasma along with an amount of glucose to form a simulated whole blood glucose control product, effective for maintaining a particular and essentially stable glucose concentration over a period of time sufficient for accurate measurement and calibration of a glucose measuring instrument.
Owner:STRECK INC
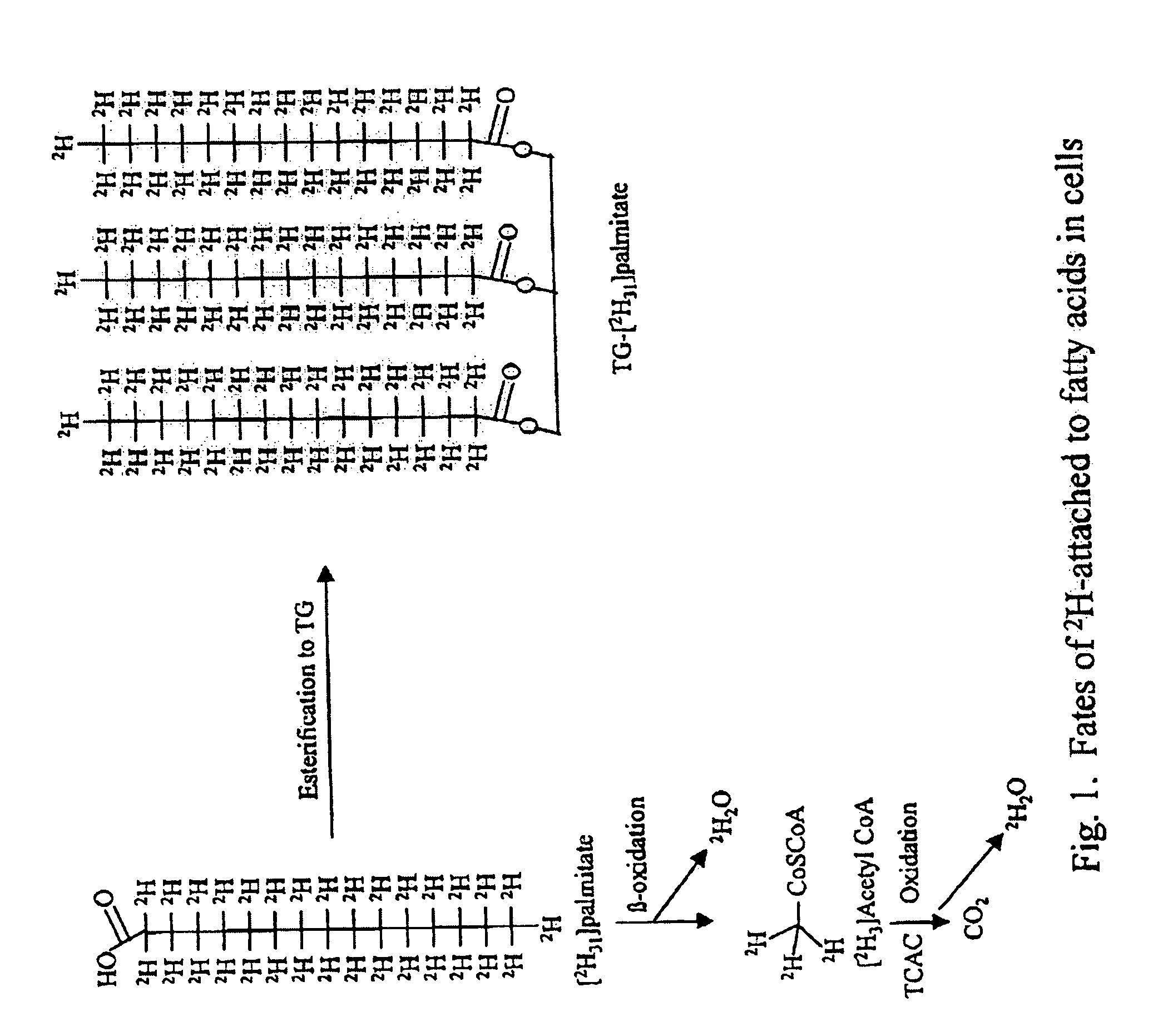
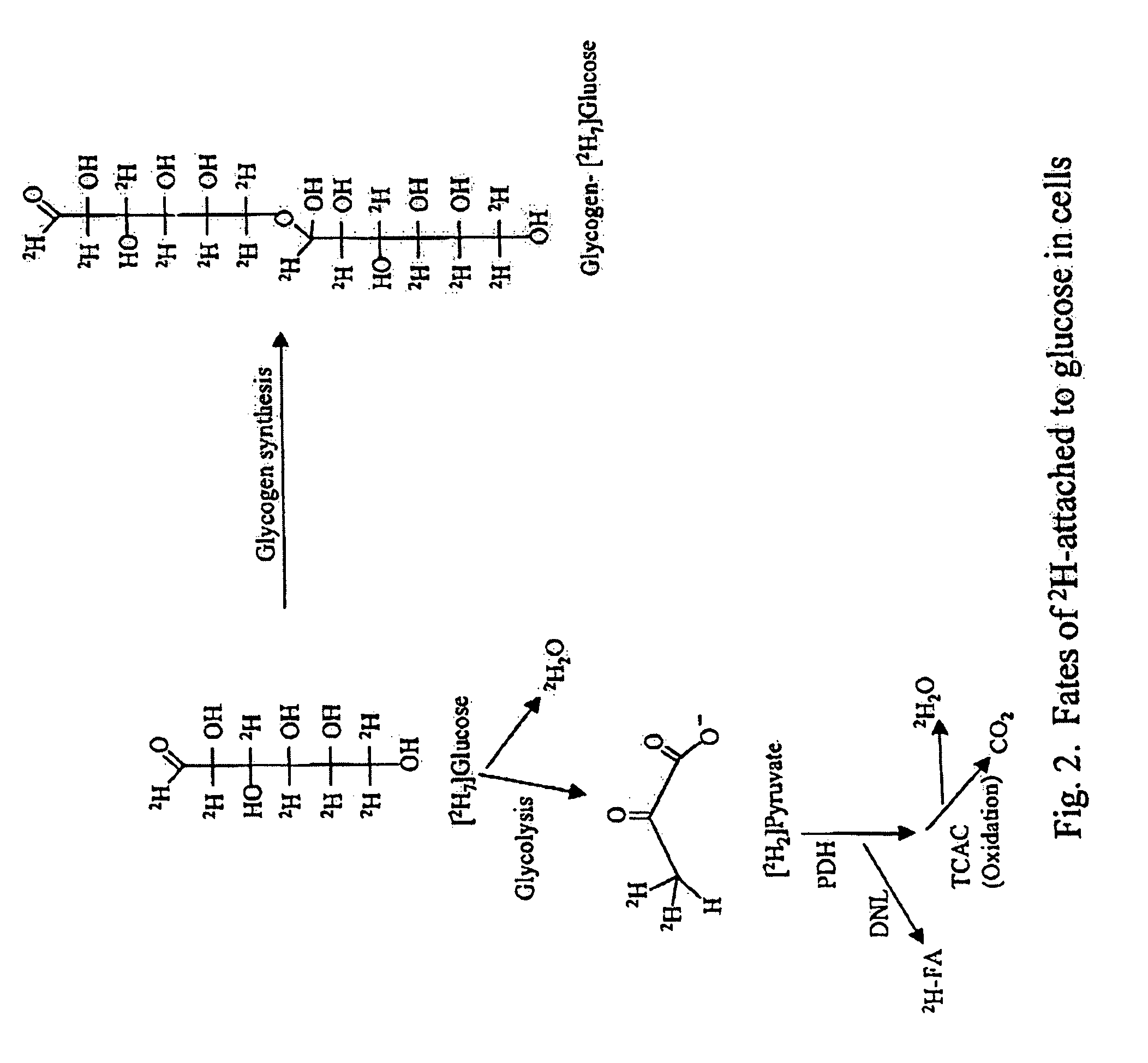
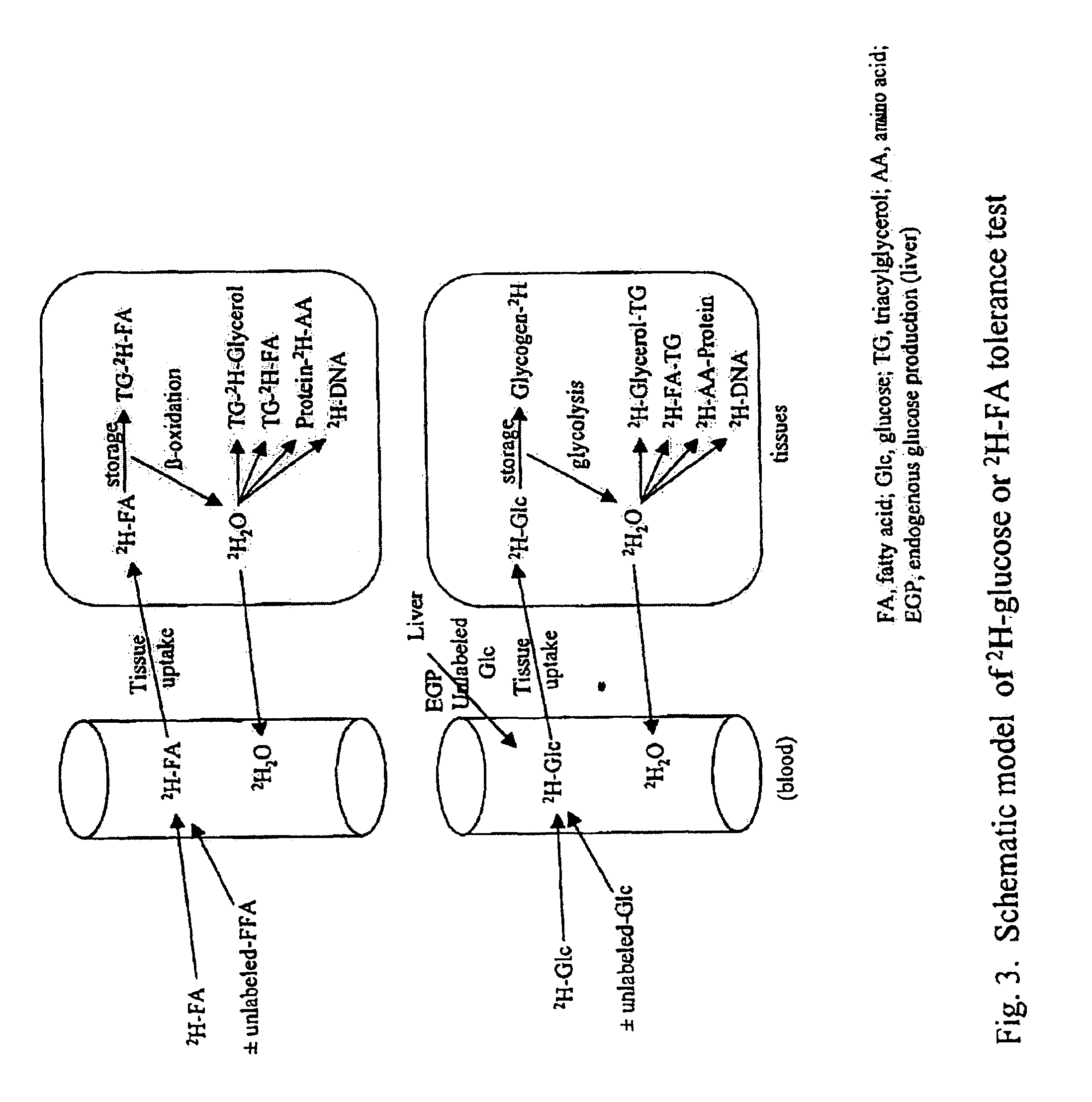
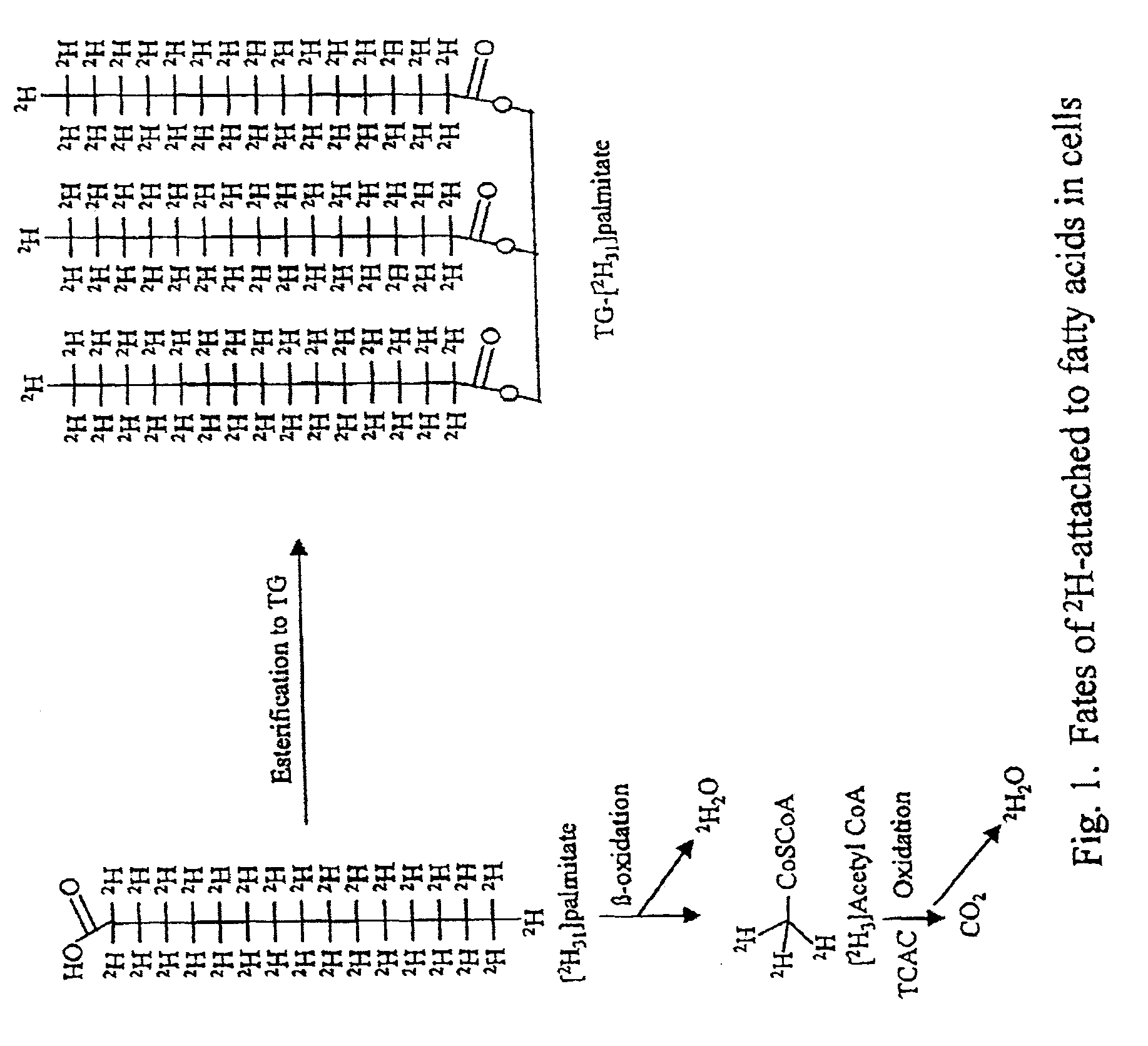
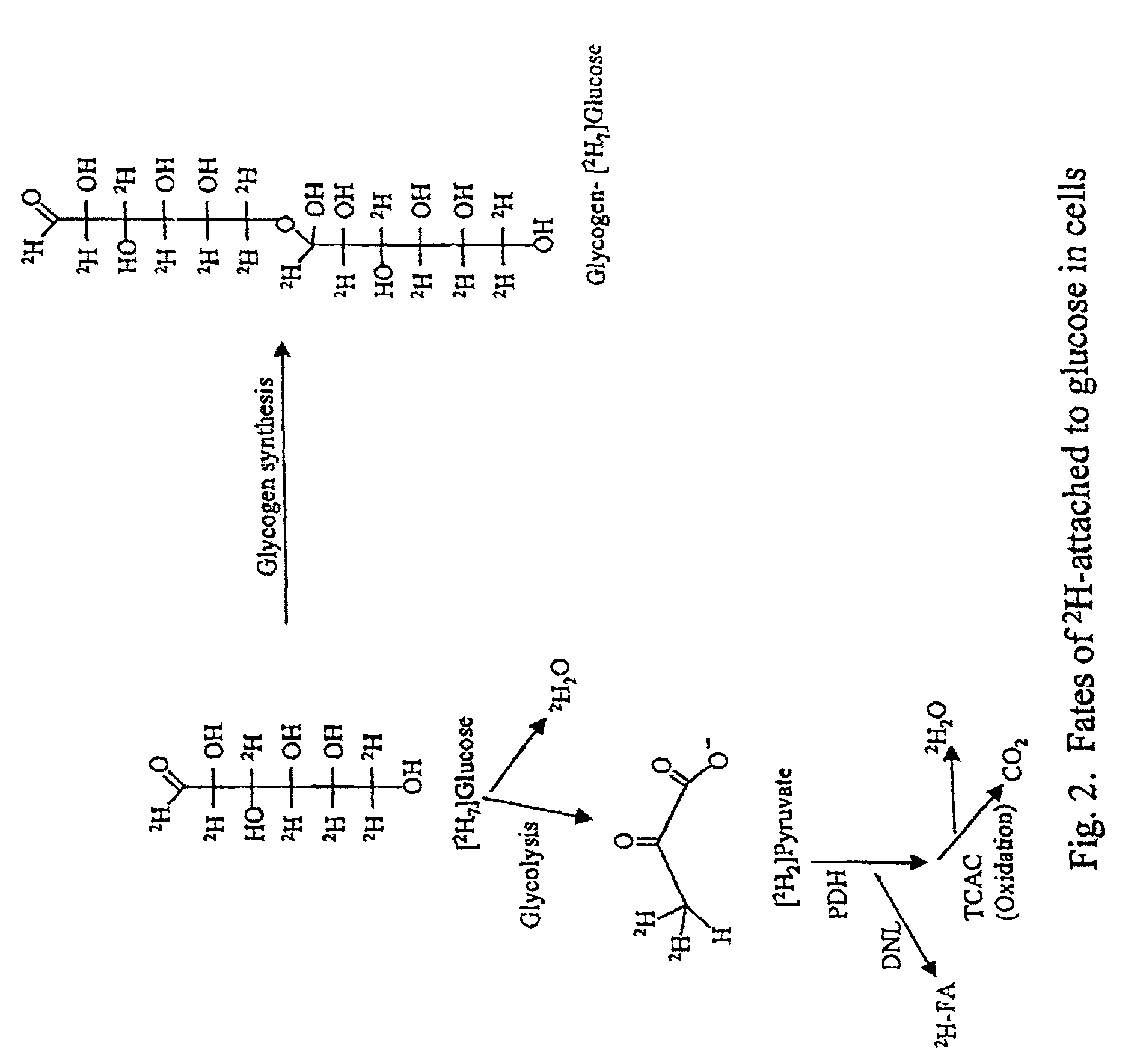
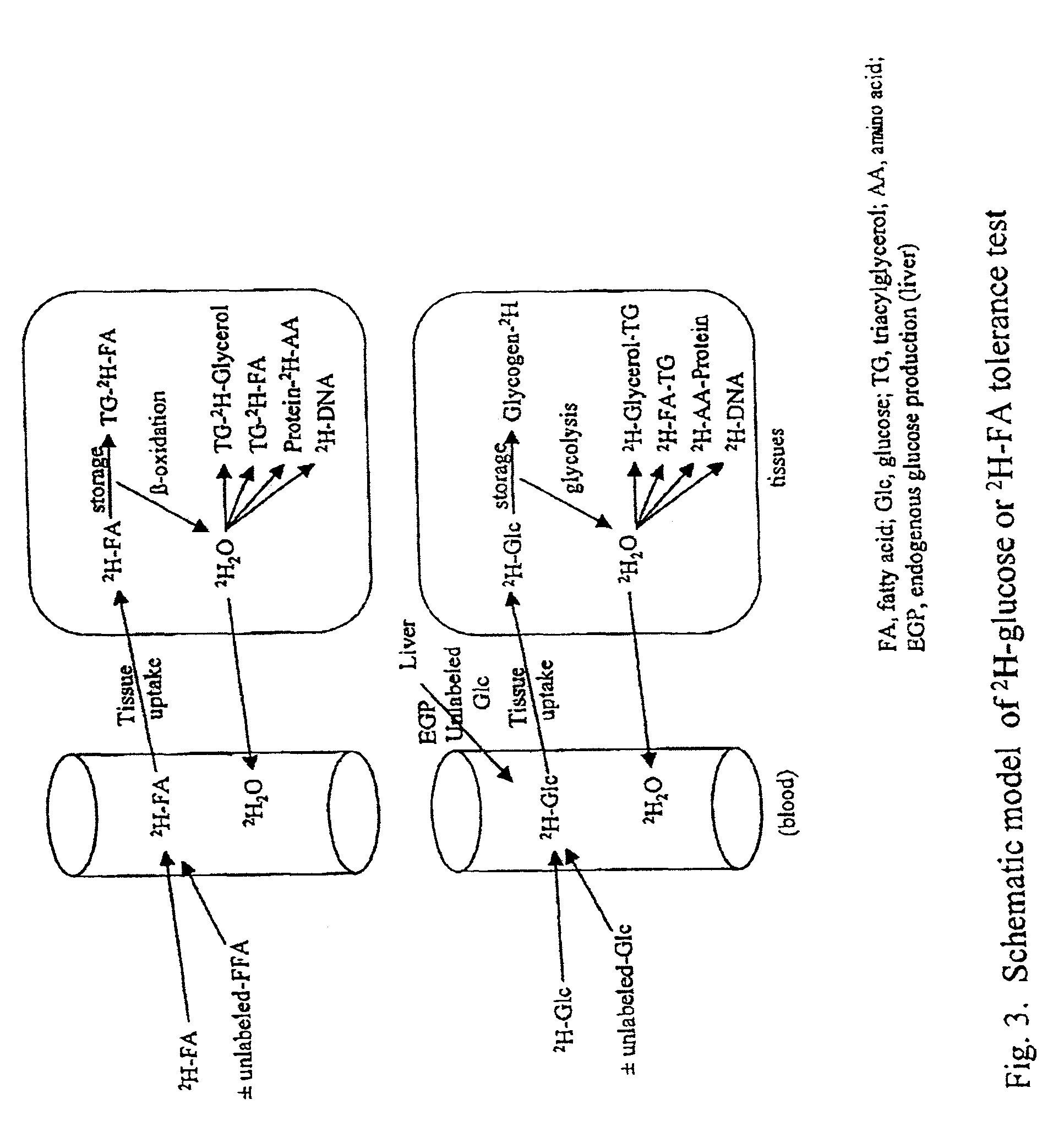
Methods for determining the metabolism of sugars and fats in an individual
ActiveUS7504233B2Compounds screening/testingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsTrial drugPreclinical testing
Provided herein are methods for determining the metabolism of one or more sugars and / or fatty acids, and applications thereof. Such applications include determining the rate of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis, which are believed to be early markers for predicting elevated risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Other applications include methods for screening drugs that effect sugar and / or fatty acid metabolism. The methods are useful for at least partially characterizing drugs for desirable or undesirable (toxic) characteristics. Drugs that are at least partially characterized using the methods of the invention can then be further developed in pre-clinical testing and clinical trials. Such drugs may be found to be useful in treating obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other disorders of metabolism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
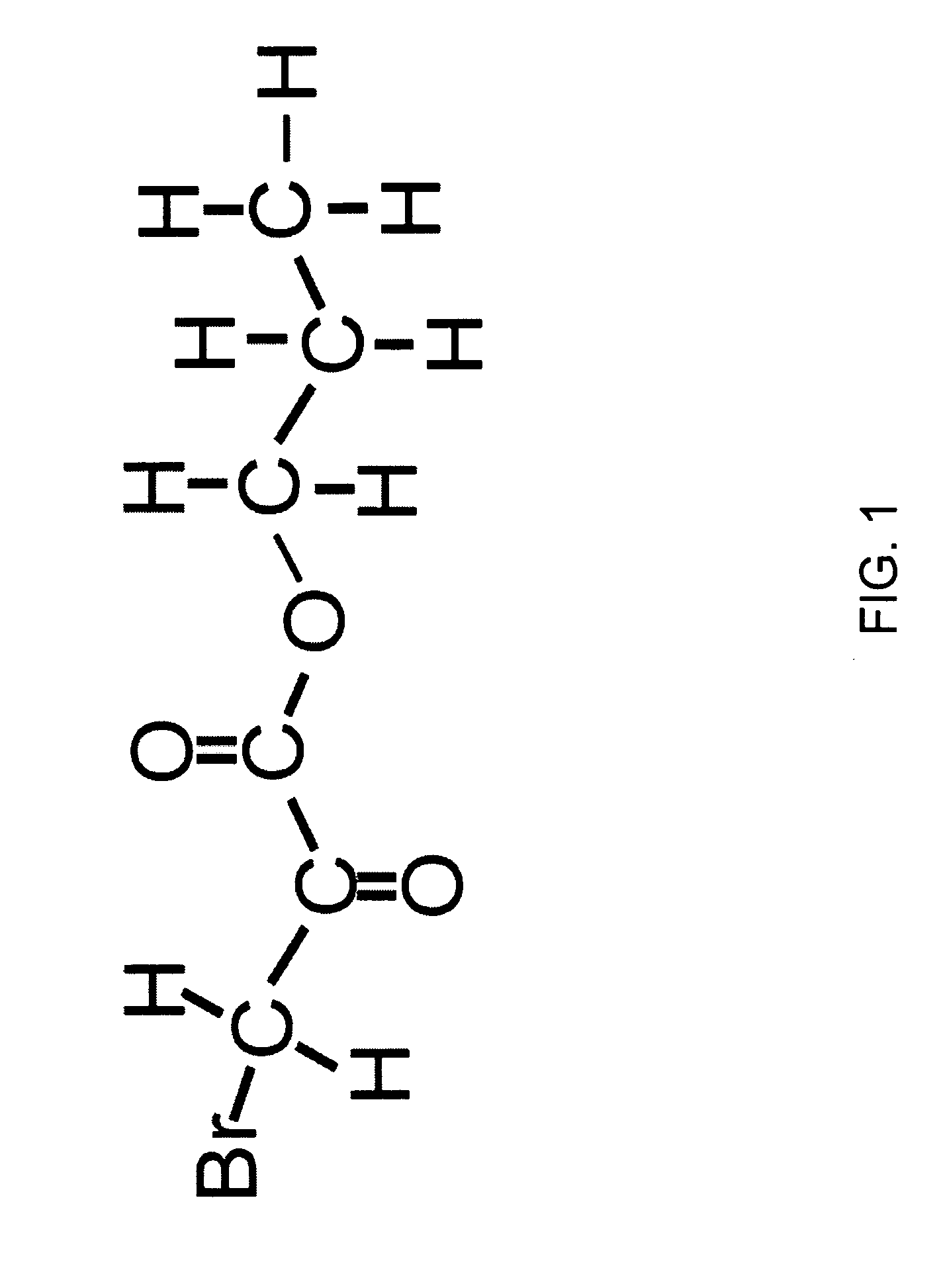
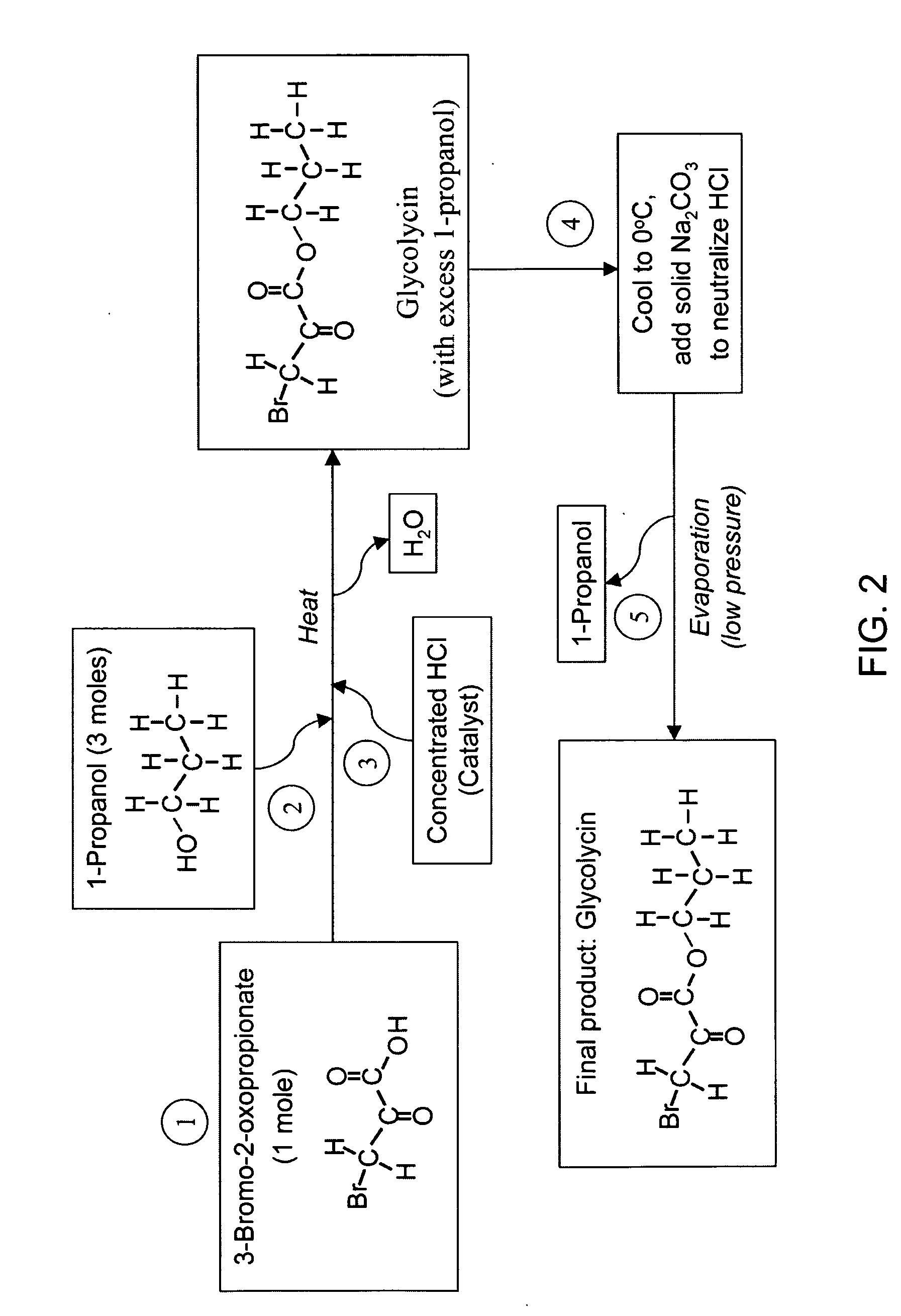
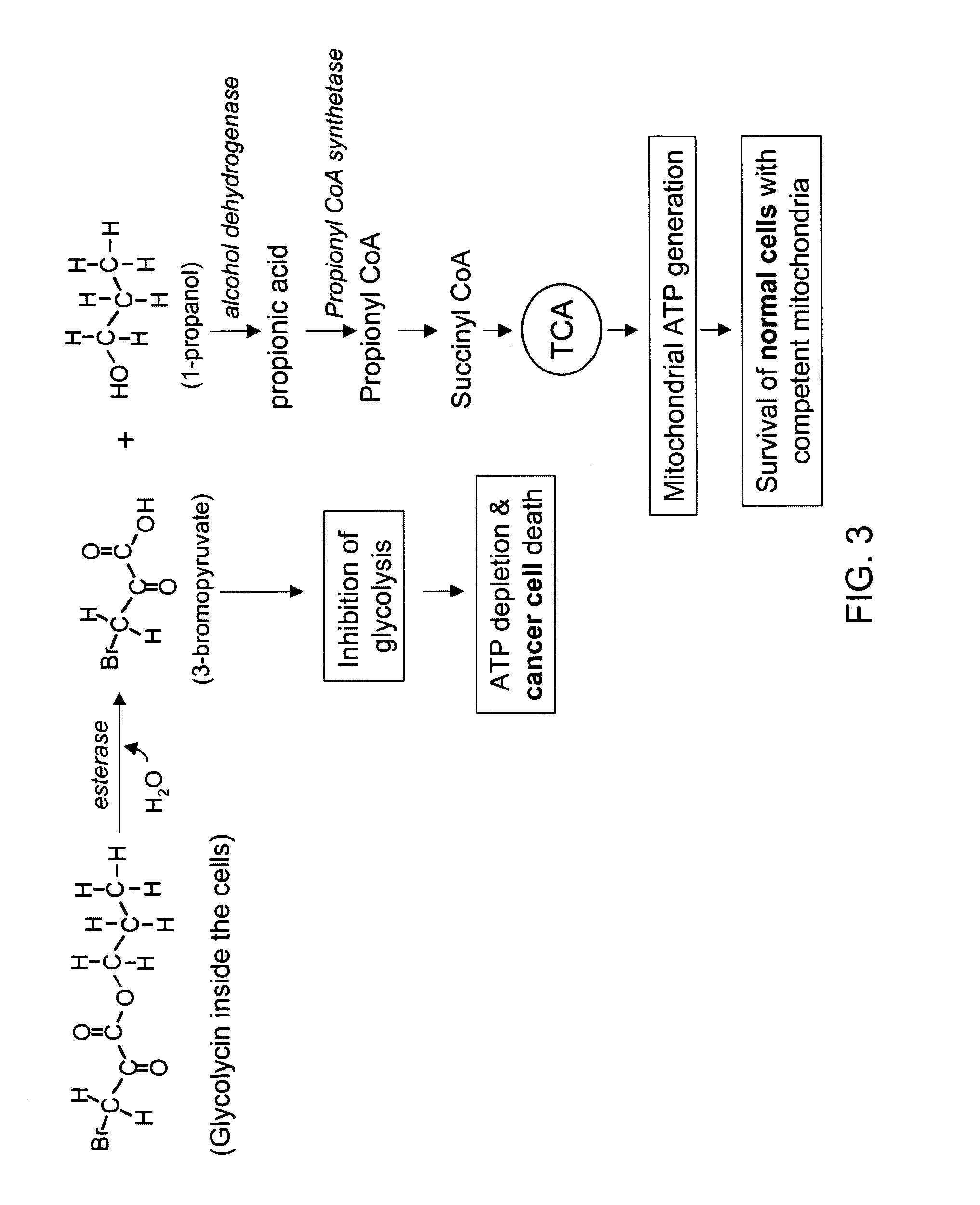
Propyl 3-bromo-2-oxopropionate and derivatives as novel anticancer agents
InactiveUS20060058383A1Overcome drug resistanceStrong therapeutic activityBiocideAnimal repellantsAnticarcinogenNormal cell
The present invention is directed to compositions that inhibit glycolysis, perferentially in cancer. Specifically, the anticancer compositions comprise 3-halo-2-oxopropionate and its derivatives, such as ester derivatives. However, in specific embodiments, the anticancer composition is sodium 3-halo-2-oxopropionate, such as sodium 3-bromo-2-oxopropionate and a stabilizing agent, such as carbonic acid. In particular embodiments, the compositions of the present invention further comprise a metabolic intermediate for normal cells to utilize in a pathway for an alternate energy source, thereby providing protection to normal cells. In other embodiments, the 3-halo-2-oxopropionate or its ester derivative is used in combination with an additional cancer therapy, such as radiation and / or a drug.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
Process, composition and kit for providing a stable whole blood calibrator/control
InactiveUS7390663B2Quality improvementSimple and elegantSamplingMicrobiological testing/measurementMedicineConcentrations glucose
The present invention is directed toward a stable calibrator and / or control, kit and process for using in a glucose monitoring instrumentation. Principally, the instant invention teaches a glycolyzed red blood cell component which has been treated with a glycolysis stabilizing effective amount of at least one non-crosslinking aldehyde compound which may be added to fresh plasma along with an amount of glucose to form a simulated whole blood glucose control product, effective for maintaining a particular and essentially stable glucose concentration over a period of time sufficient for accurate measurement and calibration of a glucose measuring instrument.
Owner:STRECK INC
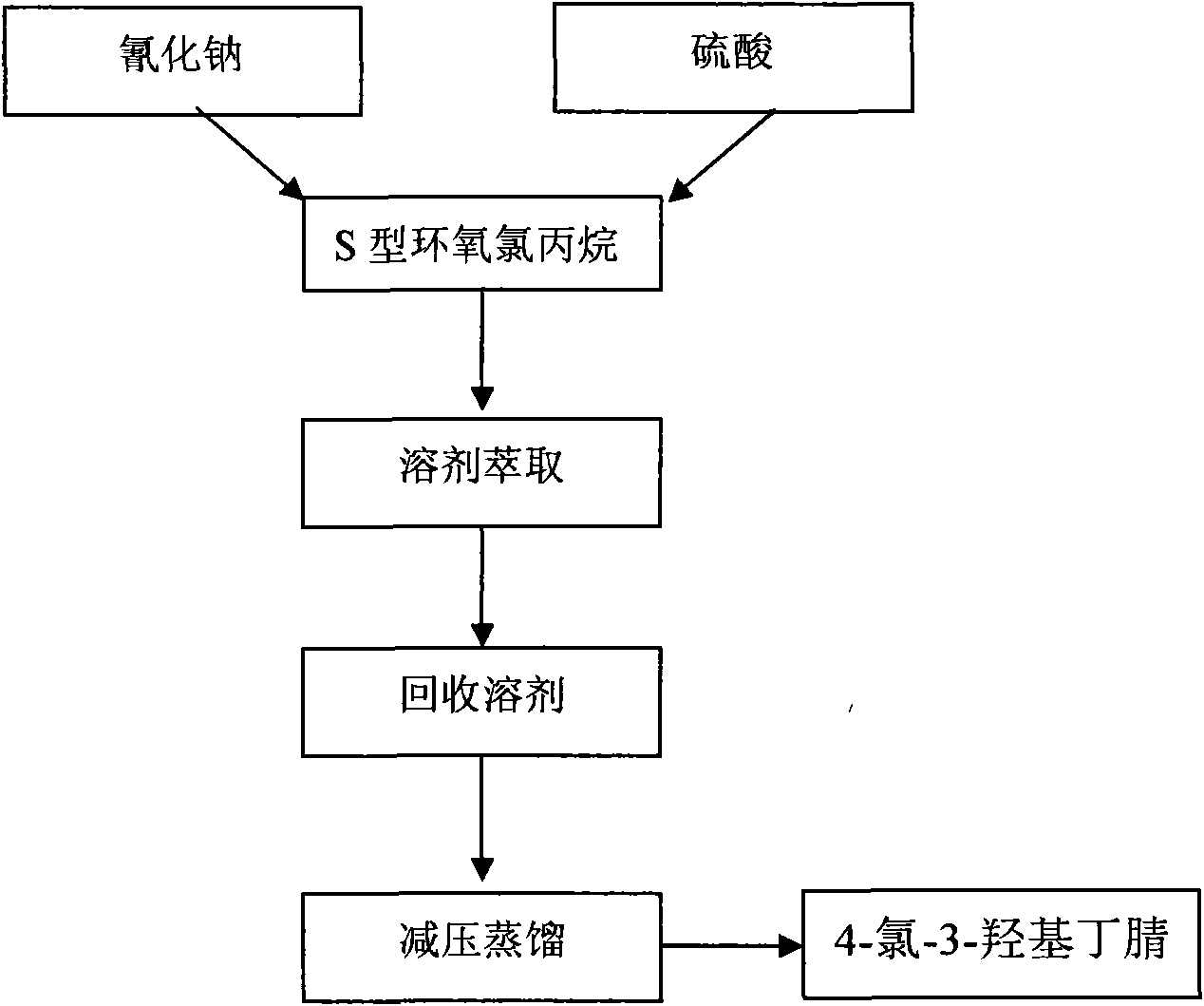
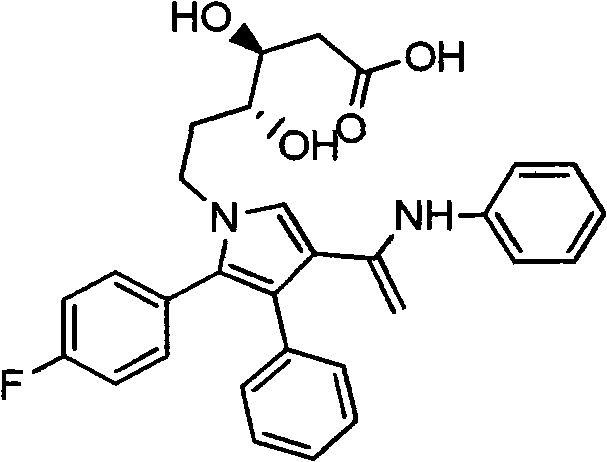
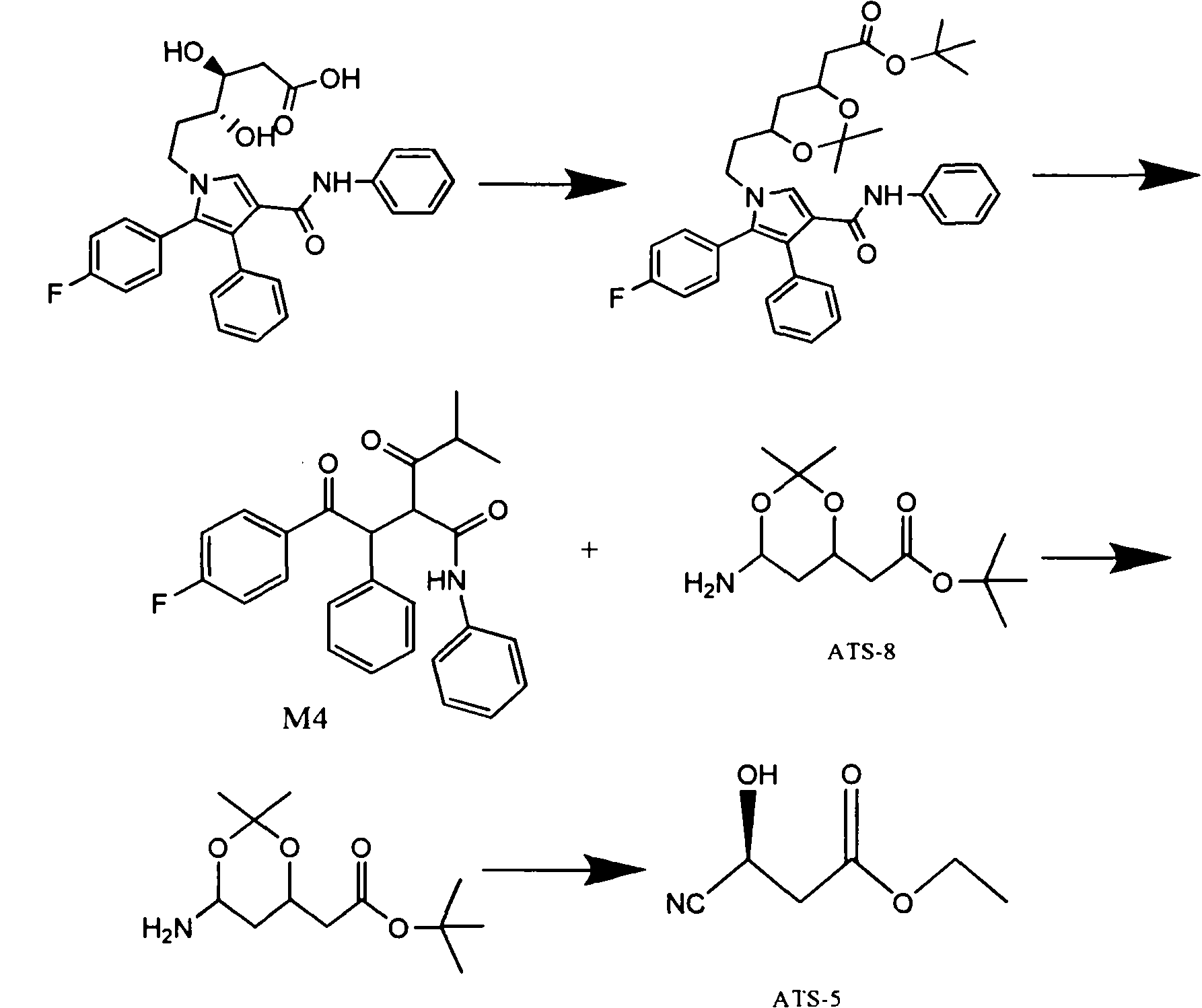
Manufacturing method of atorvastatin intermediate (R)-(-)-4-nitrile-3-hydroxybutyrate
InactiveCN101838221AIncrease profitEmission reductionPreparation by cyanide reactionState of artEnantiomer
The invention relates to a manufacturing method of atorvastatin intermediate (R)-(-)-4-nitrile-3-hydroxybutyrate (ATS-5), which solves the problems of high cost, expensive raw material price and the like of the prior art. The manufacturing method is characterized in that the atorvastatin intermediate is prepared from epichlorohydrin as a raw material through ring-opening addition, glycolysis esterification, cyaniding substitution synthesis and refining. The invention has simple synthesis route, abundant raw material resources, low equipment requirements and no high-temperature high-pressure reaction; the content of produced ATS-5 is more than 98 percent, the content of water is lower than 0.2 percent, and the content of enantiomer is less than 1.0 percent. The manufacturing method is a mature production process for manufacturing the intermediate of medicine atorvastatin and is applicable to medium-sized and small enterprises.
Owner:HUANGGANG HUAYANG PHARMA
Preparation method of raw tea enzyme
InactiveCN102613329AReduce pollutionHigh health valuePre-extraction tea treatmentFiberBULK ACTIVE INGREDIENT
The invention discloses a preparation method of a raw tea enzyme. The method comprises the following steps of: primary fermentation step: carrying out ozone sterilization treatment on raw tea, then, shredding and cutting out the raw tea under the clean conditions, adding dark brown sugar to uniformly mixing the raw tea, adding lucid ganoderma strains, bacillus subtilis strains and bifidobacterium strains, and carrying out fermentation for 30 to 50 days at room temperature; and secondary fermentation step: inoculating bacillus aceticus into semi finished products subjected to the primary fermentation, carrying out fermentation for 15 to 20 days at room temperature, and obtaining the raw tea enzyme raw liquid. The invention also discloses the corresponding raw tea raw tea enzyme. When the method provided by the invention is adopted for preparing the raw tea enzyme, the used time is short, the pollution is little, the raw tea can fast realize the glycolysis to obtain small molecular substances easily absorbed by the human body, the active ingredients of the tea can be remained to the maximum degree, in addition, a large number of physiological active products and various kinds of fiber enzymes, protein enzymes, hementerin enzymes, starch enzymes and the like can be accumulated, and the integrated health-care values of the raw tea enzyme are greatly improved.
Owner:桂林寻源文化有限责任公司
Molecules to perfect HbA1c levels
InactiveUS9254250B1Enhanced utilization and regulationFavorable cellular milieuCosmetic preparationsToilet preparationsCellular respirationAcute hyperglycaemia
This invention is of particular use to patients with Diabetes Mellitus. It uses alkyl analogs of the methyl pyruvate (MP) family to provide energy and improve insulin and glucose homeostasis via accelerated intracellular delivery of protons and ATP from each MP. The energy upregulates cellular cross talk and networking resulting in a surge of ATP enabling NADH (via glycolysis) that enables pancreatic islet cells to obtain increased ATP allowing excess insulin manufacture. This process improves cellular respiration and expedites protein, lipid and hormone manufacture. The increased energy also enables telomeres and delays Hayflick limit. Instead of cellular repair, silence, or apoptosis, energy is allocated for cell / organ function. This invention curbs inflammation and ROS by idealizing cellular respiration and diminishing hyperglycemia. In turn a reduction of advanced glycation end products (AGEs), lessened target RNA and nucleic acid toxins, i.e., diminished HbA1c occurs. By decreased drain of cellular energy, genomic function improves.
Owner:NEVILLE PHARMA
Regulation of Autophagy and Cell Survival
Methods of treating an individual who has been identified as having glycolysis dependent cancer are disclosed. The methods comprise the step of: administering to such an individual a combination of an anti-cancer composition that renders the cancer incapable of glycolysis and an autophagy inhibitor. Pharmaceutical compositions and kits comprising that renders the cancer incapable of glycolysis and an autophagy inhibit are also disclosed. Methods of treating an individual who has a disease characterized b cell degeneration and cell death due to autophagy are disclosed. The methods comprise administering to the individual a permeable form of a metabolic substrate that can be oxidized in the tricarboxylic acid cycle to produce NADH. Methods for identifying an autophagy inhibitor comprising performing a test assay using an apopto sis-resistant cell are disclosed.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Modulation of mitochondrial oxygen consumption for therapeutic purposes
InactiveUS20070212360A1Increased blood vessel formationReduced activityBiocideAntibody ingredientsPhysiologyTherapeutic intent
The HIF-1 transcription factor drives gene expression changes in hypoxia. While HIF-1 stimulates glycolysis, it also actively represses mitochondrial function and oxygen consumption by inducing pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 1 (PDK1). PDK1 phosphorylates and inhibits pyruvate dehydrogenase from converting pyruvate to acetyl-CoA to fuel the mitochondrial TCA cycle. This causes a drop in mitochondrial oxygen utilization and results in a relative increase in intracellular oxygen tension.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
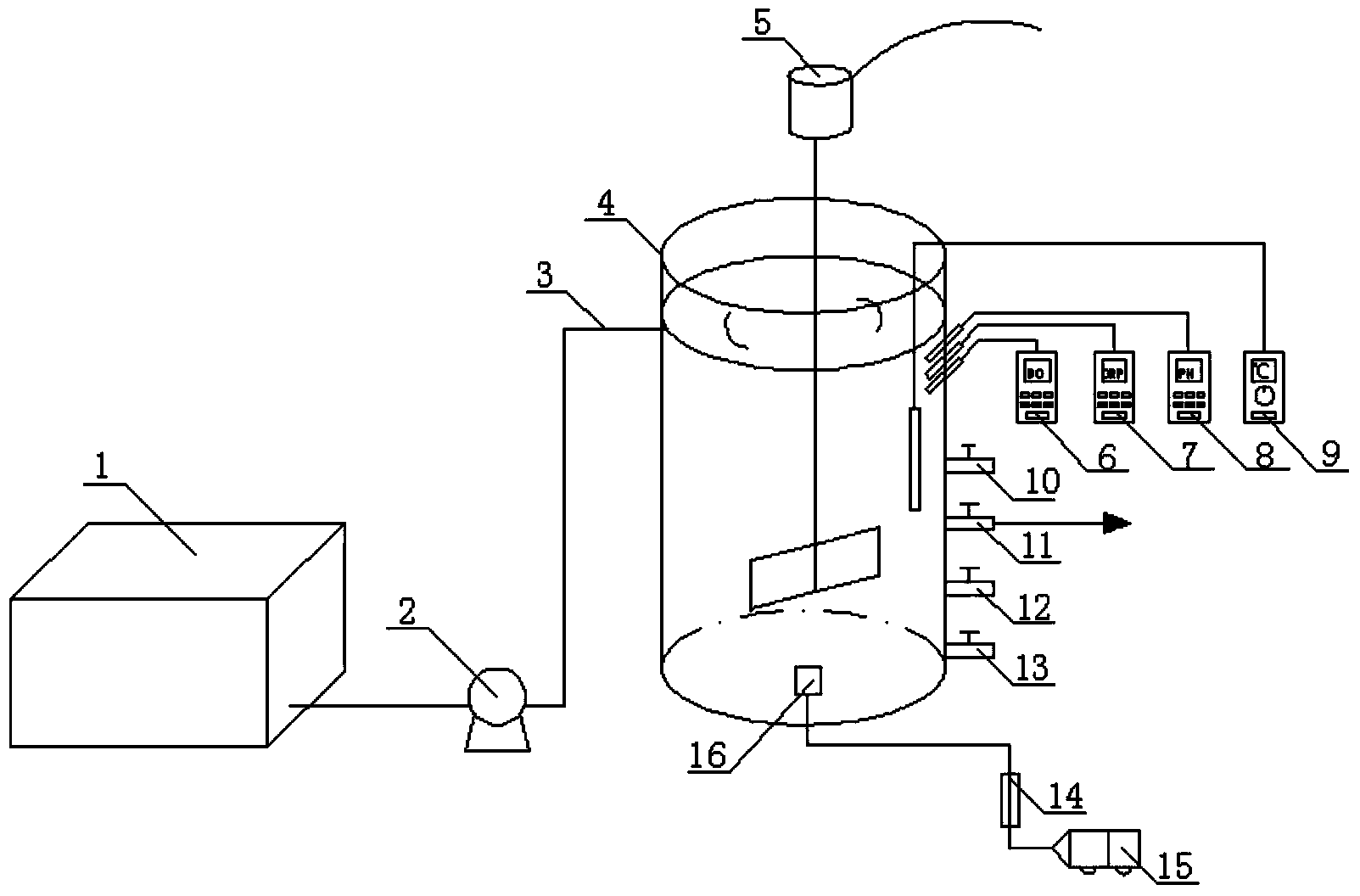
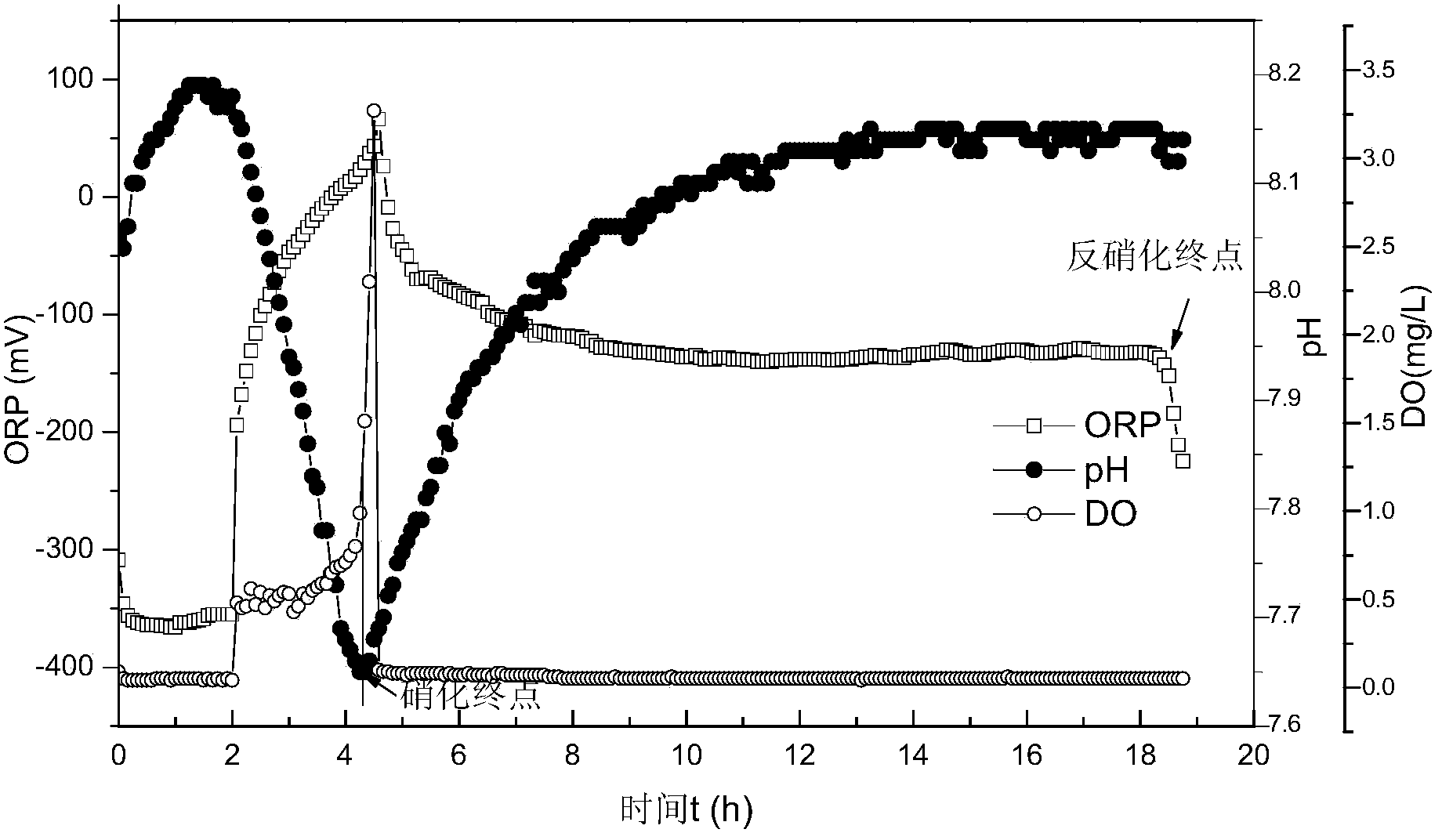
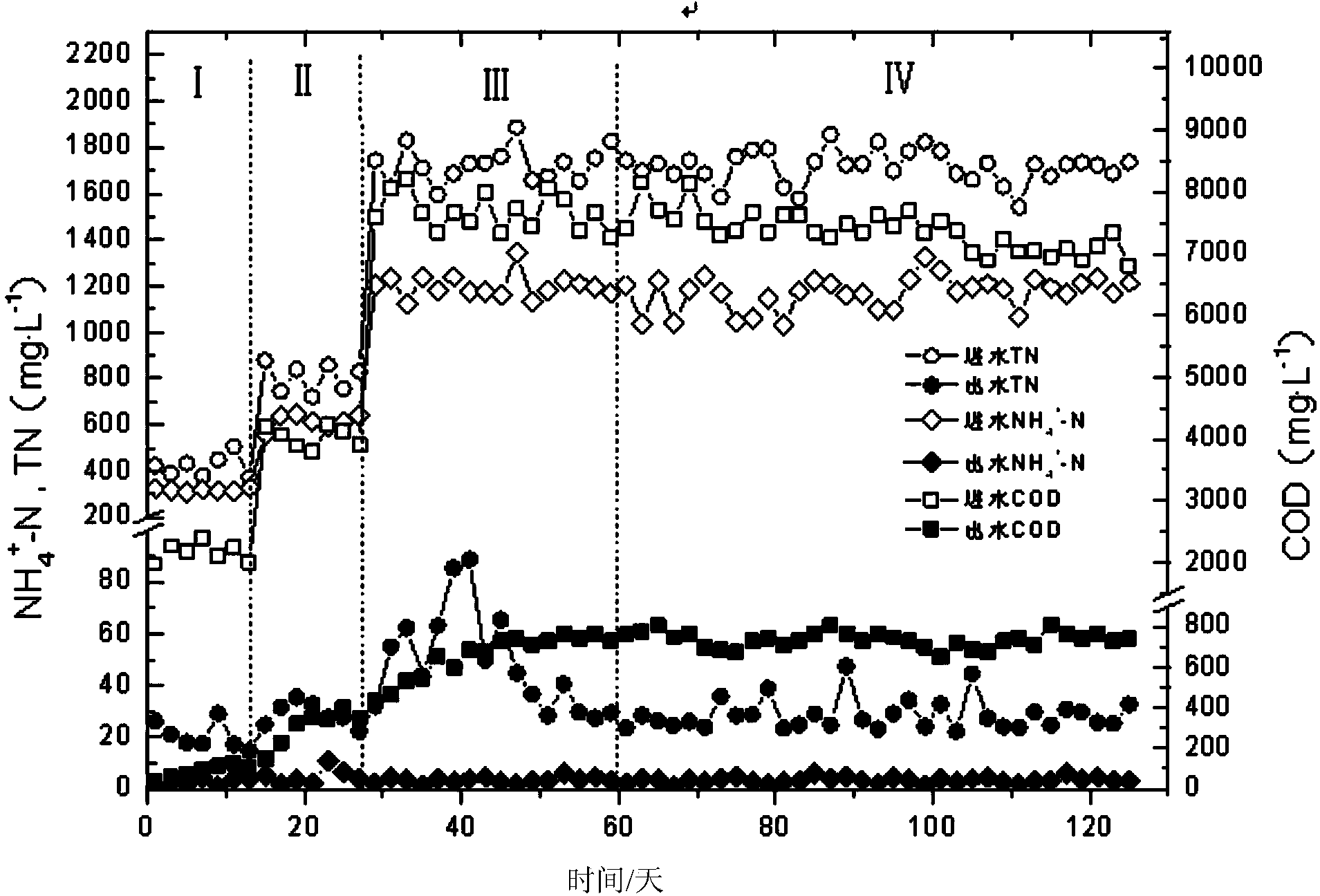
Method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment
ActiveCN103755028AStart fastThe reaction device is simpleTreatment with aerobic and anaerobic processesVolatile fatty acidsEmission standard
The invention discloses a method for deep denitrification of metaphase landfill leachate through single-stage SBR (Styrene Butadiene Rubber) post denitrification treatment, which belongs to the technical field of sewage treatment by using biochemical process. Aiming at the characteristics that the landfill leachate is high in organism concentration, high in ammonia concentration, high in C / P ratio (grater than 200), the invention discloses a real-time control method with the combination of 'anaerobic / aerobiotic / anoxic' operation modes, and SBR post denitrification is achieved. Under long-term domestication, glycan bacteria (GAO) can be enriched, volatile organic acids (VFA (Volatile Fatty Acid)) in water are converted into poly-beta-hydroxy-alkanoic acid ester (PHA) through glycogen glycolysis at an anaerobic stage by using GAO, in an aerobiotic stage (the dissolved oxygen is less than 0.8mg / L), when partial nitrification is carried out, most part of PHA is converted into glycogen, and in the anoxic stage, the residual PHA and the glycogen are utilized to perform carbon source denitrification, so that the effluent meets the latest national emission standard. The method has the advantages of simple devices, rapid starting, freedom of external carbon source, good denitrification effect, simplicity in operation, low cost and the like.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Methods for identifying the effect of a drug agent on the metabolism of sugars and fats in an individual
InactiveUS7910323B2Compounds screening/testingIn-vivo radioactive preparationsPharmacologyGlycolysis
Provided herein are methods for determining the metabolism of one or more sugars and / or fatty acids, and applications thereof. Such applications include determining the rate of glycogen synthesis and glycolysis, which are believed to be early markers for predicting elevated risk of diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Other applications include methods for screening drugs that effect sugar and / or fatty acid metabolism. The methods are useful for at least partially characterizing drugs for desirable or undesirable (toxic) characteristics. Drugs that are at least partially characterized using the methods of the invention can then be further developed in pre-clinical testing and clinical trials. Such drugs may be found to be useful in treating obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other disorders of metabolism.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
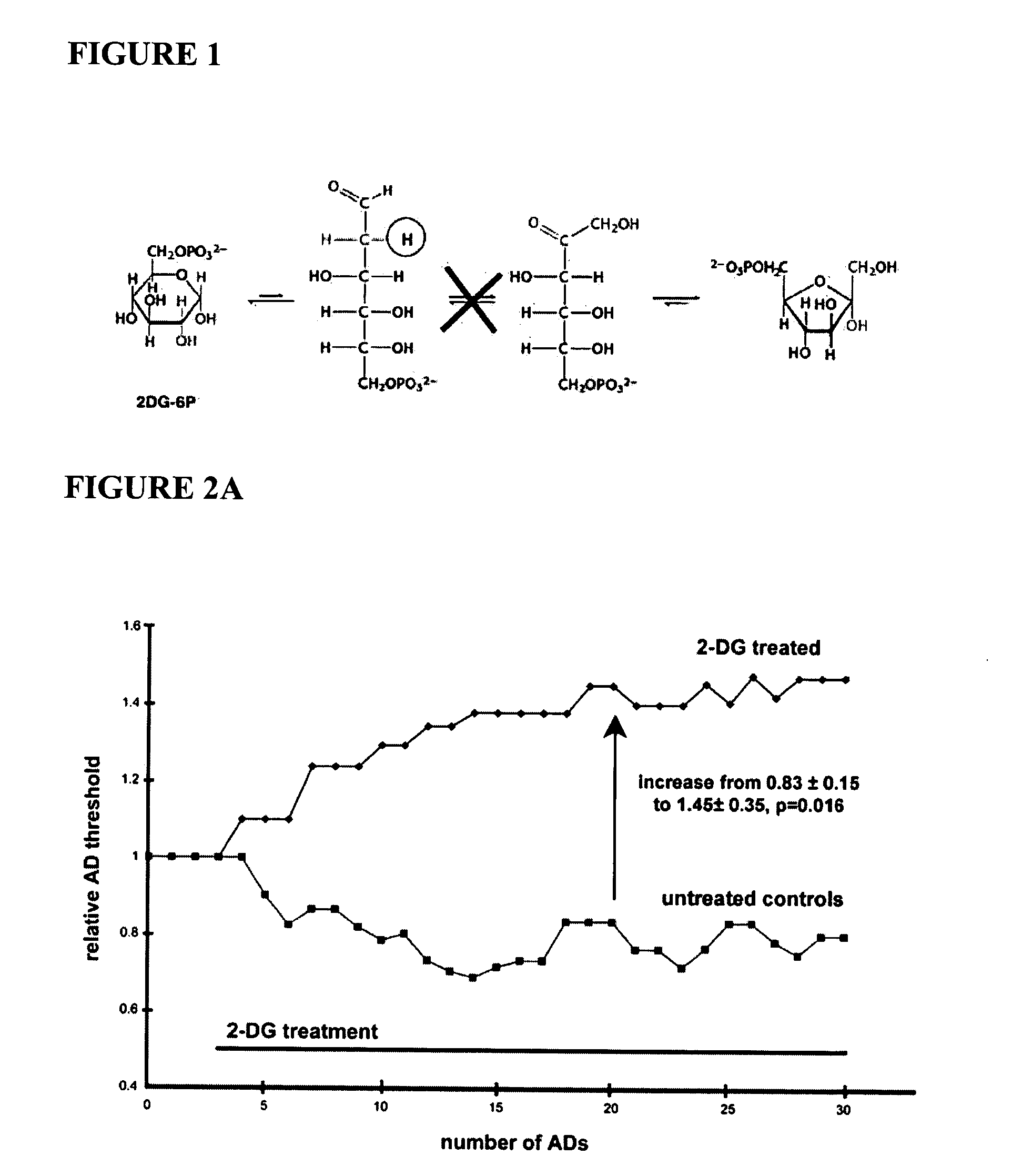
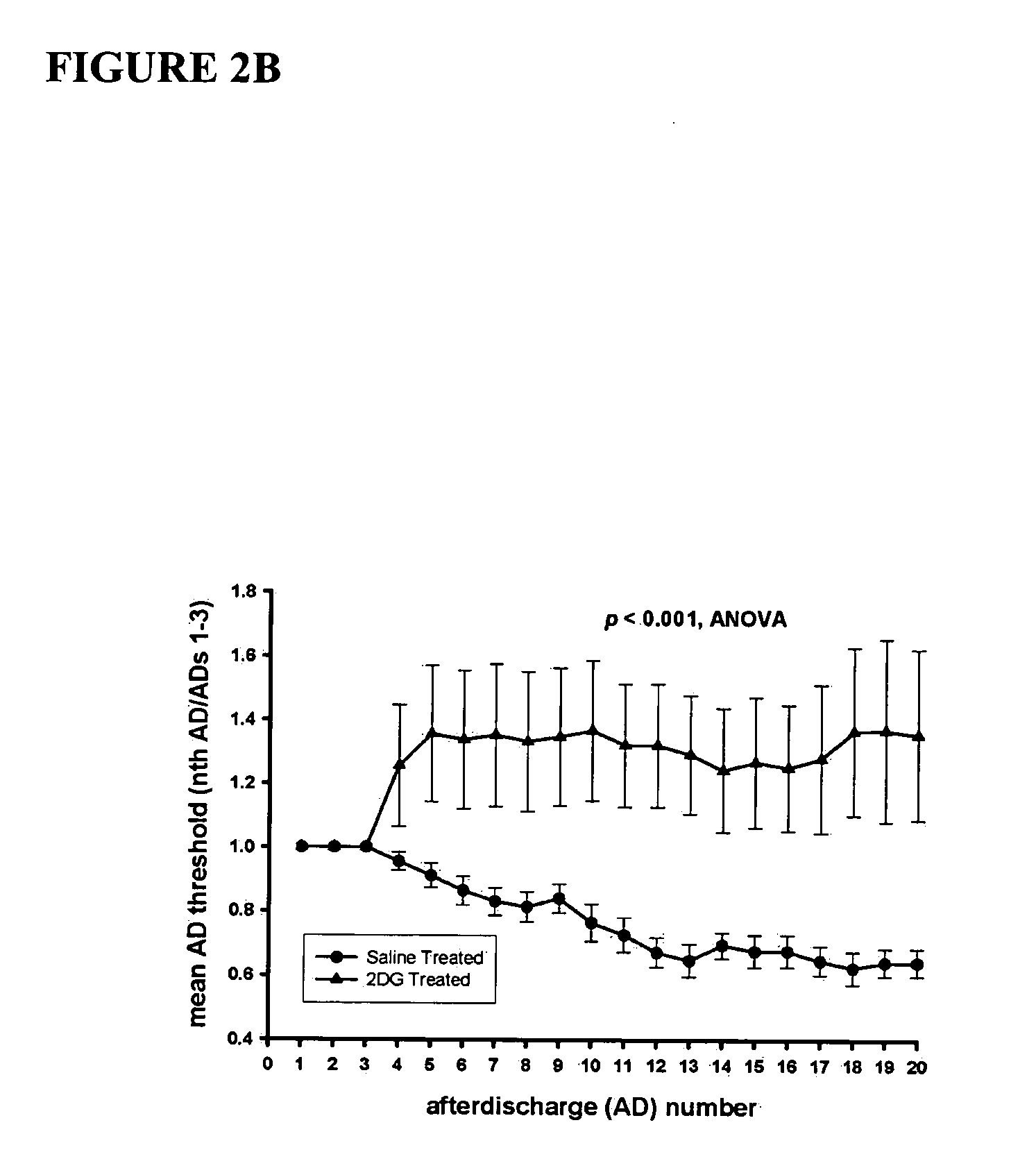
Compounds and methods for treating seizure disorders
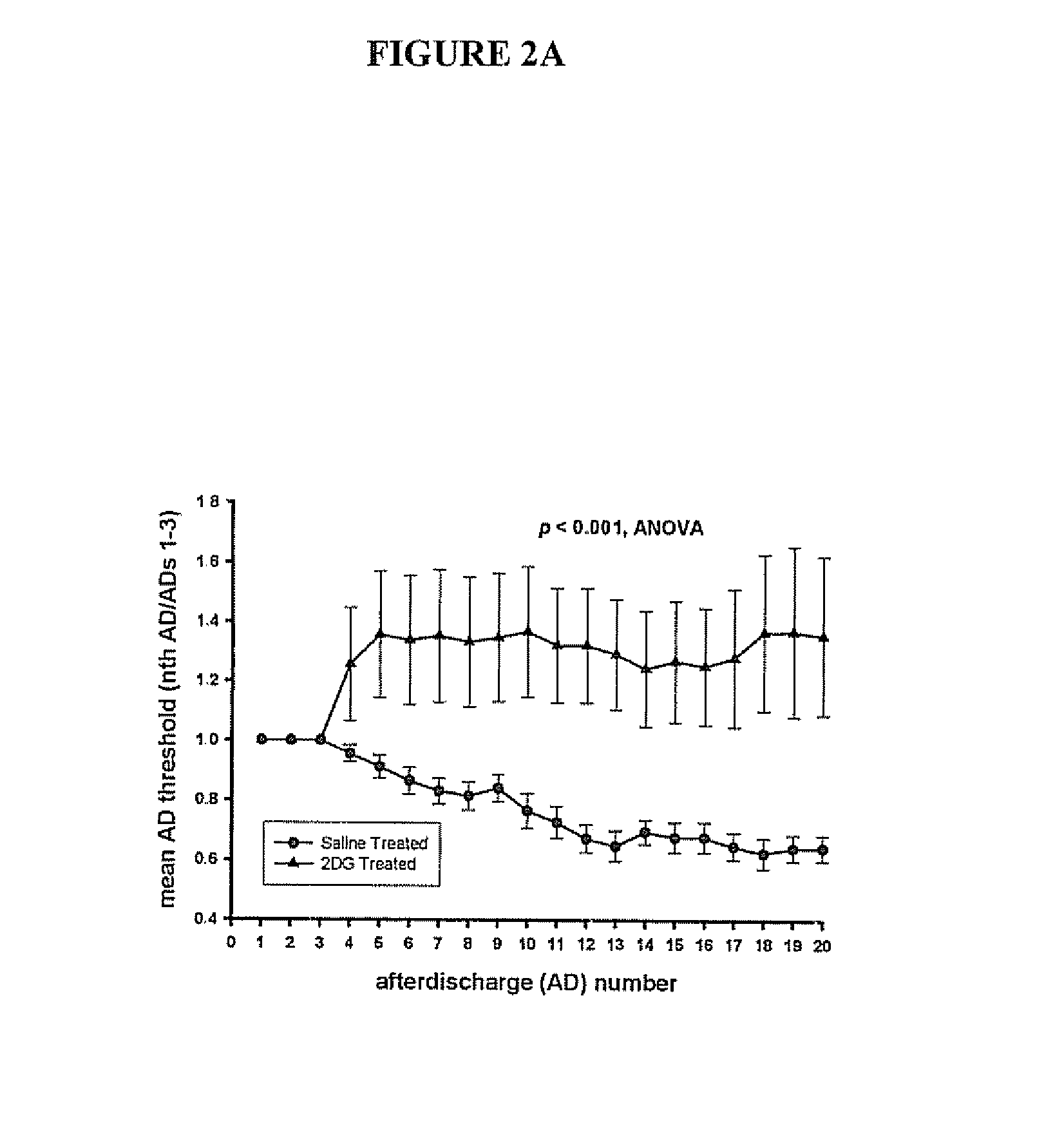
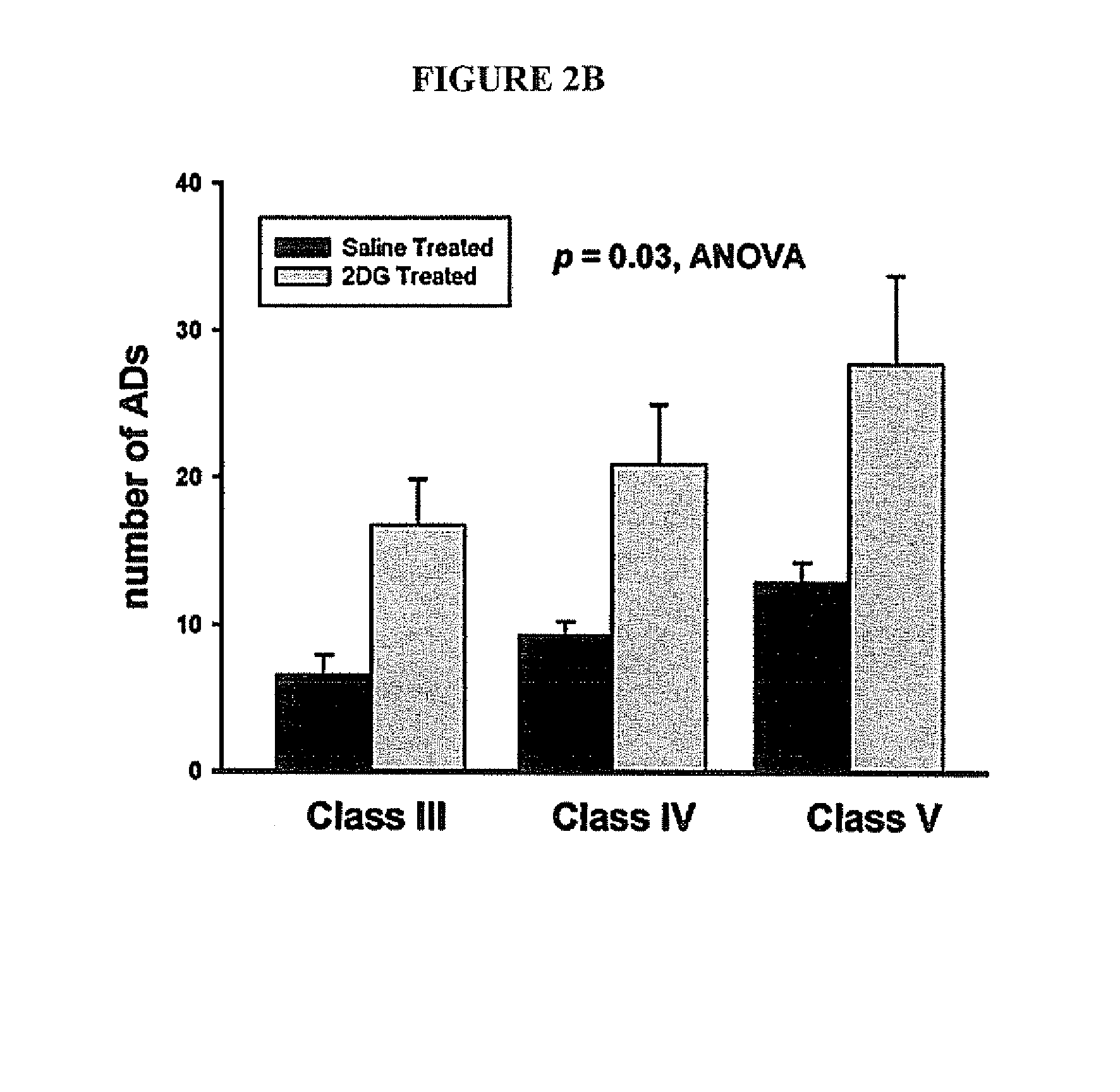
ActiveUS20060088517A1Restore responseIncreased Von Frye scoreBiocideNervous disorderParoxysmal AFMedicine
This invention provides methods for alleviating paroxysmal disorders in an animal, particularly epilepsy, by modulating glycolysis in brain cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Process for the Preparation of Polyesters with High Recycle Content
InactiveUS20130041053A1Reduce chain lengthReduce riskProductsReagentsDepolymerizationGlycol synthesis
Disclosed is a process for producing copolyesters with high levels of recycled content. Scrap or post-consumer poly(ethylene terephthalate) is depolymerized by methanolysis or glycolysis to produce a purified, recycled dimethyl terephthalate which can be repolymerized with 2 or more diols. The polyesters of this invention have physical properties and an appearance that is similar to polyesters prepared from virgin monomers. In addition to dimethyl terephthalate, the polyesters can be prepared from recycled ethylene glycol recovered from depolymerization of poly(ethylene terephthalate) and / or 1,4-cyclo-hexanedimethanol prepared by hydrogenation of recycled dimethyl terephthalate or recovered from depolymerized polyester mixtures.
Owner:EASTMAN CHEM CO
Tree-like polymer targeting nanometer drug delivery carrier and its preparation method
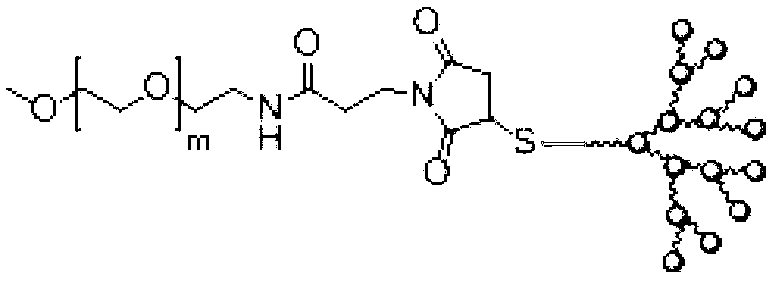
InactiveCN103127526AApplicable treatmentTargeted drug deliveryOrganic active ingredientsPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTreatment effectBiological activation
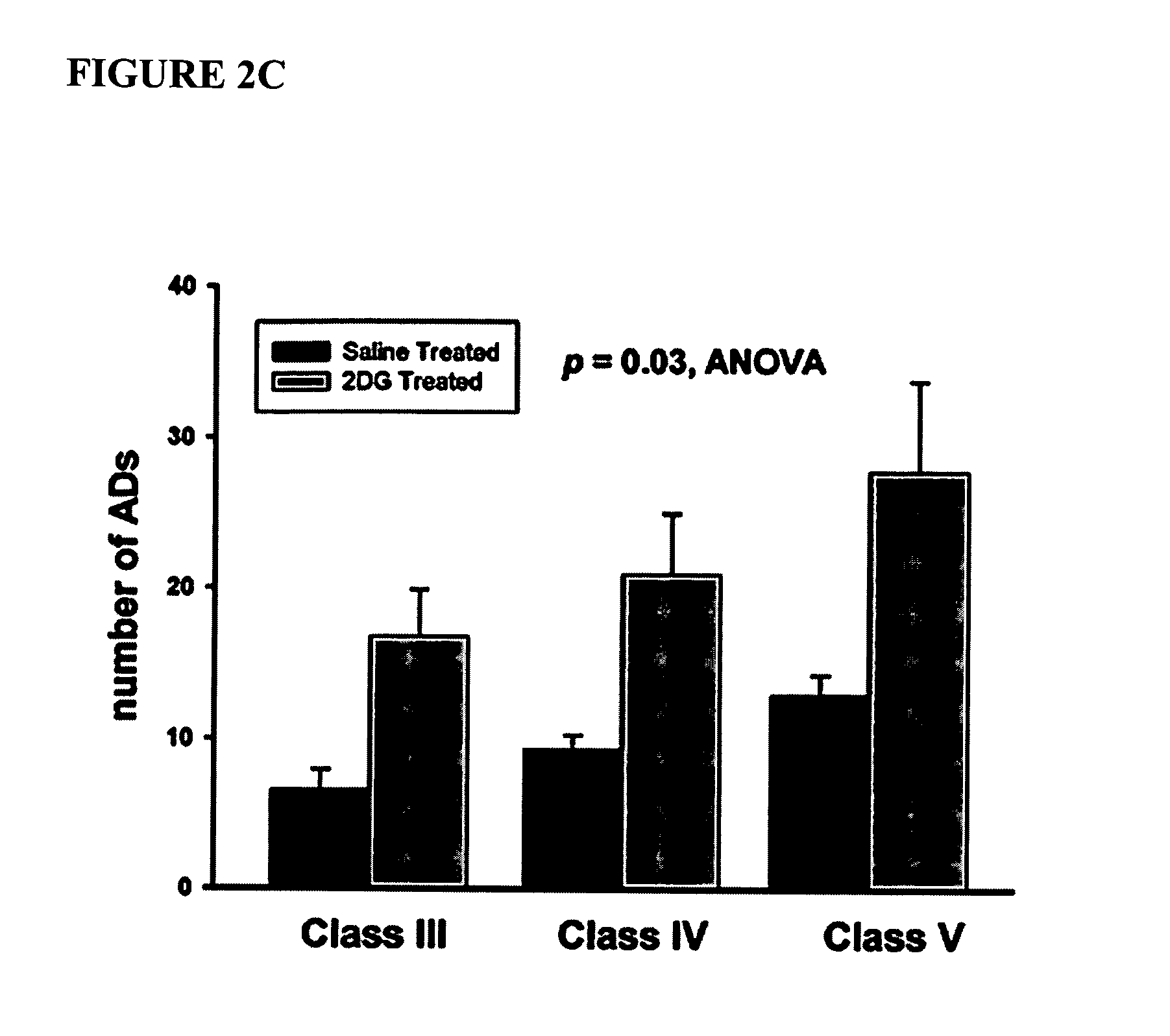
The invention relates to a tree-like polymer targeting nanometer drug delivery carrier. The structural general formula of the nanometer drug delivery carrier is PEG-b-PAMAM-(Cys)n. According to the invention, the carrier is sensitive to pH, and a hydrogen bond between the carrier and a drug will break when the pH of the environment is low, so the drug is released, and targeting drug delivery is realized. The carrier has an effective treatment effect on myeloma. A large amount of lactic acid generated in the myeloma cell propagation process because of glycolysis causes a case that the pH of focus positions is lower than the normal pH of a body fluid, and the osteoclast formation and activation and the enzyme catalysis bone break further reduce the pH, so complication syndromes, such as osteolytic damages and the like, are caused. The carrier has the characteristics of specificity, slow release and high drug load, and can substantially improve the treatment effects on liquid tumors, such as myeloma and the like.
Owner:万礼 +2
Method for the chemical depolymerization of waste polyethylene terephthalate
InactiveUS20100133088A1Increase chanceEasy to processOrganic compound preparationCarboxylic acid esters preparationPolyethylene terephthalate glycolDepolymerization
A method for the chemical depolymerization of waste polyethylene terephthalate by application of microwave radiation and solvolysis in the presence of a catalyst comprising the first stage where the waste polyethylene terephthalate is mixed up with an microwaves absorbing activator, the mixture is melted by its exposing to a microwave radiation on a frequency from 915 to 2450 MHz and with a power output from 0.1 to 0.5 kW per kg of a charge, at a temperature from 230 to 330° C., under atmospheric pressure and the second stage, where the molten mixture is subjected to solvolysis, including acidic or basic hydrolysis, alcoholysis or glycolysis in the presence of a catalyst under continuing microwave radiation and atmospheric pressure yielding terephthalic acid, salts or esters thereof, and ethylene glycol.
Owner:USTAV CHEMCH PROCESU AV CR V V I
Method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material
InactiveCN101701225AImprove enzymatic hydrolysis efficiencyOpportunity for facilitationMicroorganism based processesFermentationFiberCellulose compounds
The invention relates to a method for preparing bio-ethanol by taking seaweed processing waste as raw material, which is characterized by comprising the steps: selecting the seaweed processing waste, and pretreating the raw material by sulfuric acid or hydrogen peroxide; then, adding cellulase or cellobiase for cellulose compound enzymolysis, and filtering enzymolysis liquid to remove insoluble components; and finally, supplementing inorganic salt, inoculating saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and carrying out alcoholic fermentation under the anaerobic condition. The original structure of algae cellulose is changed by the pretreatment process, and the action probability between the cellulose and degrading enzyme can be promoted, so that the enzymolysis efficiency of the cellulose is improved; furthermore, after the cellulose is treated by the compound enzymolysis of the cellulase and the cellobiase, the feedback inhibition of the cellobiose for the cellulose can be effectively eliminated, the content of glycolysis sugar of yeast can be improved, and the yield of alcoholic fermentation is further improved.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
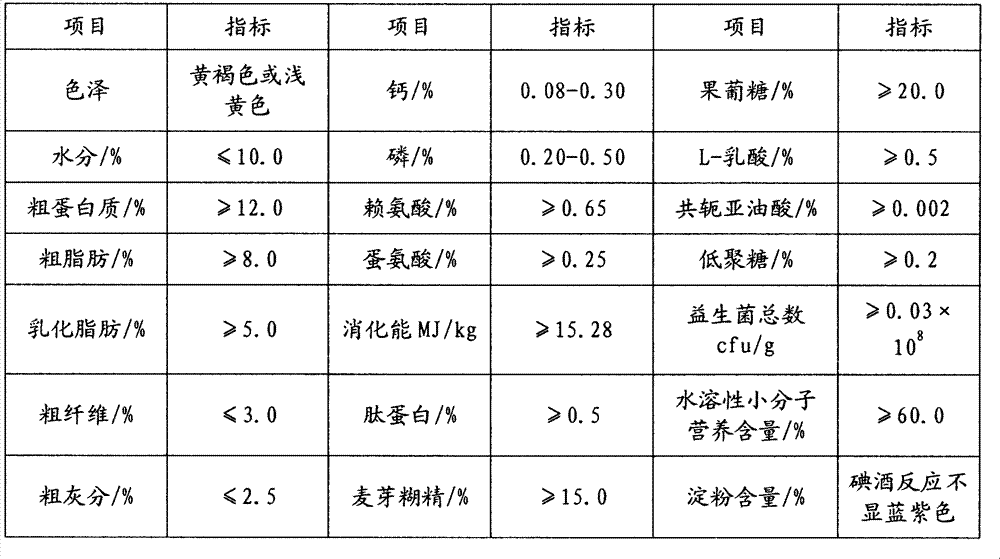
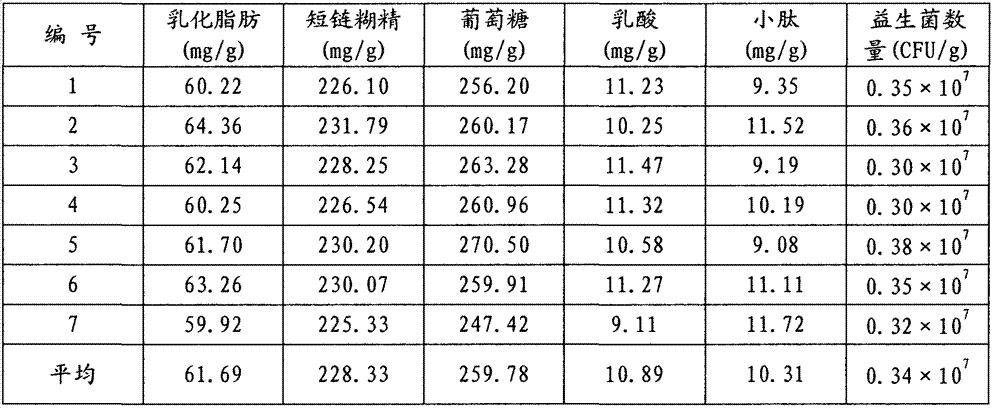
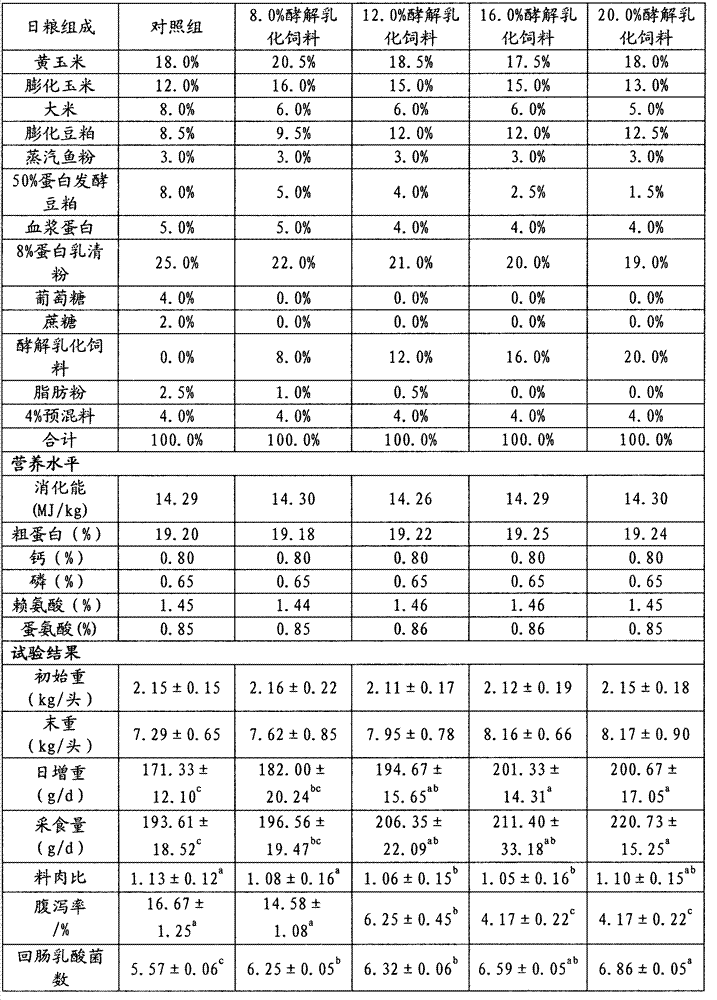
Preparation method of glycolysis and emulsification feed for young livestock and poultry
The invention belongs to the technical field of feed, enzyme preparations and microbes and particularly relates to a preparation method of glycolysis and emulsification feed for young livestock and poultry. The preparation method comprises the following steps: carrying out enzyme hydrolysis, liquefaction, saccharification and solid-liquid separation on grain starch to obtain grain solid content wet basis and grain polysaccharide liquid; mixing and fermenting the grain solid content wet basis, bean pulps and mixed culture liquid to obtain fermenting dreg pulp; mixing, grinding, emulsifying and homogenizing the grain polysaccharide liquid, compound feeding oil, the fermenting dreg pulp and an emulsifying agent to obtain chyle fat pulp; and mixing two or three of the grain polysaccharide liquid, the fermenting dreg pulp and the emulsified chyle fat pulp, and drying the mixture to obtain the glycolysis and emulsification feed for young livestock and poultry. The glycolysis and emulsification feed for young livestock and poultry, provided by the invention, is rich in chyle chat, short-chain dextrin, glucose, oligosaccharide, small peptides, lactic acid and probiotics and has the advantages of balanced amino acids, rich nutrition, easy digestion, good palatability, low content of anti-nutrient factors and the like.
Owner:FLSUGARPEPTIDE BIOLOGY ENG
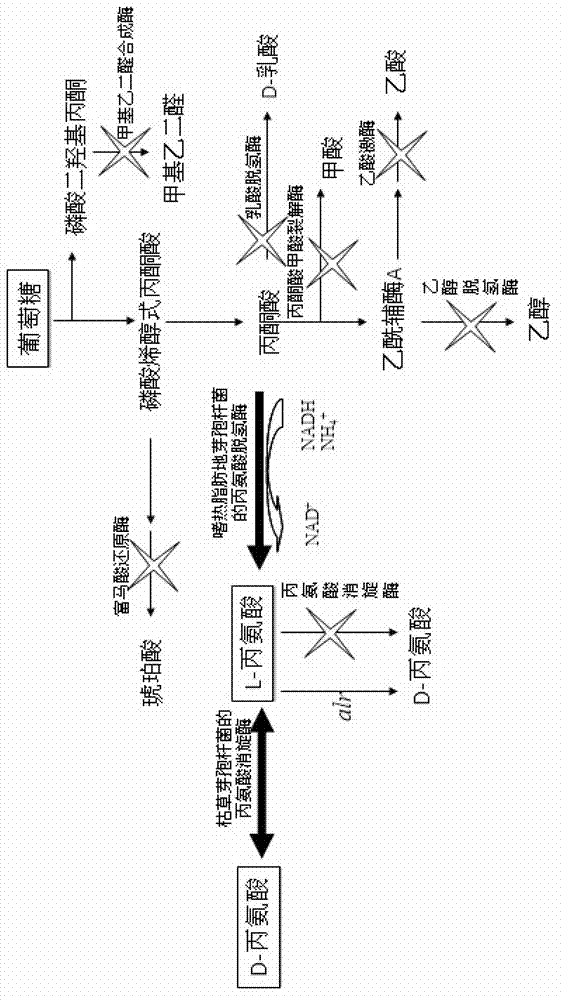
Engineering bacteria producing DL-alanine and method of producing DL-alanine by using engineering bacteria
ActiveCN103045528AIncrease productionHigh yieldBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEthanol dehydrogenaseAlanine racemase
The invention discloses a strain of engineering bacteria producing DL-alanine. Lactic dehydrogenase, pyruvate formate lyase, alcohol dehydrogenase, acetic acid kinase, fumaric acid reductase, alanine racemase and methyl glyoxal synthetase of the strain of engineering bacteria producing the DL-alanine are inactivated; and exogenous L-alanine dehydrogenase gene and alanine racemase gene are integrated on the chromosome of the engineering bacteria. According to the invention, pyroracemic acid, an intermediate product of the glycolysis is converted to L-alanine by integrating the exogenous L-alanine dehydrogenase gene into the chromosome of the engineering bacteria; and an exogenous alanine racemase gene is further integrated into the chromosome, and part of the L-alanine is converted into D-alanine. Then producing the DL-alanine from raw material sugar in one step is realized, the production period of the DL-alanine is decreased and the productivity of the DL-alanine is enhanced.
Owner:ANHUI HUAHENG BIOTECH
Recombinant materials for carotenoid production
The present invention provides recombinant DNA comprising a transcription promoter and a downstream sequence to be expressed, in operable linkage therewith, wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame of a highly expressed Phaffia gene, preferably a glycolytic pathway gene, more preferably the gene coding for Glyceraldehyde-3-Phosphate Dehydrogenase. Further preferred recombinant DNAs according to the invention contain promoters of ribosomal protein encoding genes, more preferably wherein the transcription promoter comprises a region found upstream of the open reading frame encoding a protein as represented by one of the amino acid sequences depicted in any one of SEQIDNOs: 24 to 50. According to a further aspect of the invention an isolated DNA sequence coding for an enzyme involved in the carotenoid biosynthetic pathway of Phaffia rhodozyma is provided, preferably wherein said enzyme has an activity selected from isopentenyl pyrophosphate isomerase activity, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate synthase activity, phytoene synthase activity, phytoene desaturase activity and lycopene cyclase activity, still more preferably those coding for an enzyme having an amino acid sequence selected from the one represented by SEQIDNO: 13, SEQIDNO: 15, SEQIDNO: 17, SEQIDNO: 19, SEQIDNO: 21 or SEQIDNO: 23. Further embodiments concern vectors, transformed host organisms, methods for making proteins and / or carotenoids, such as astaxanthin, and methods for isolating highly expressed promoters from Phaffa.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Substances and Pharmaceutical Compositions for the Inhibition of Glyoxalases and Their Use As Anti-Fungal Agents
InactiveUS20080300303A1To promote metabolismIncrease productionAntibacterial agentsBiocideMedicineCompound (substance)
The present invention pertains to substances of the formula (I) wherein X is O or S; and R1-R4 are defined in the claims as inhibitors of glyoxalase I and / or II, pharmaceutical compositions comprising one or more compounds according to formula (I) and the use of one or more compounds according to formula (I) for the treatment of diseases associated with increased glycolytic metabolism. In one embodiment, the disease is a fungal infection.
Owner:BIOMAC PRIVATINST FUR MEDIZINISCHE & ZAHNMEDIZINISCHE FORSCHUNG ENTWICKLUNG & DIAGNOSTIK
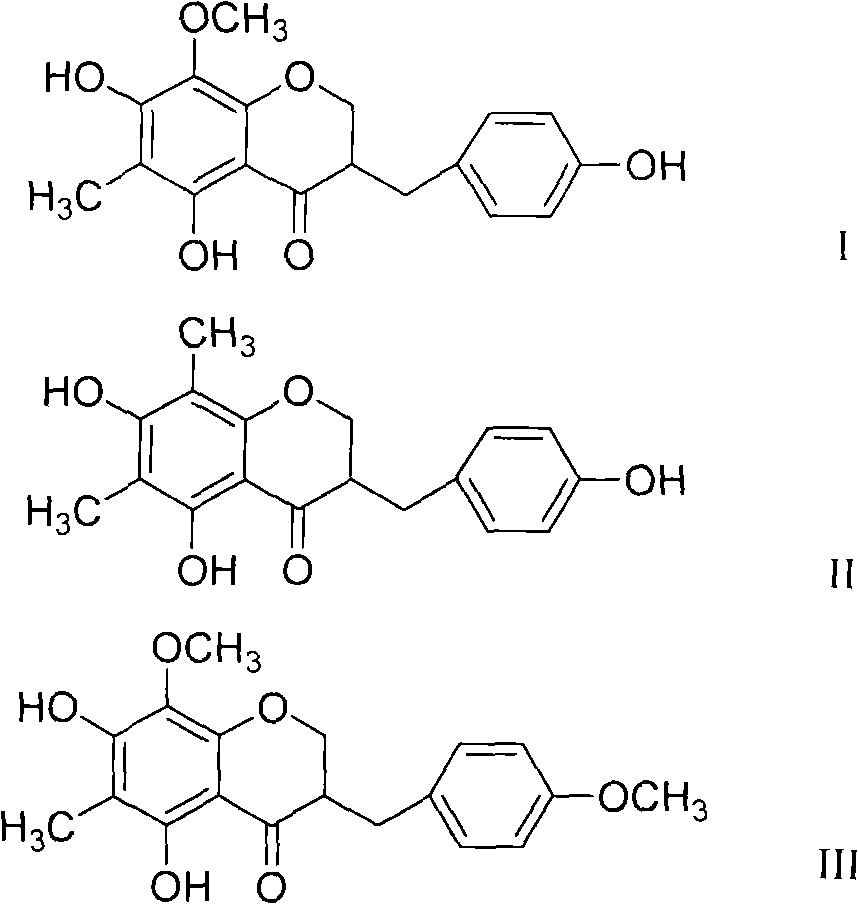
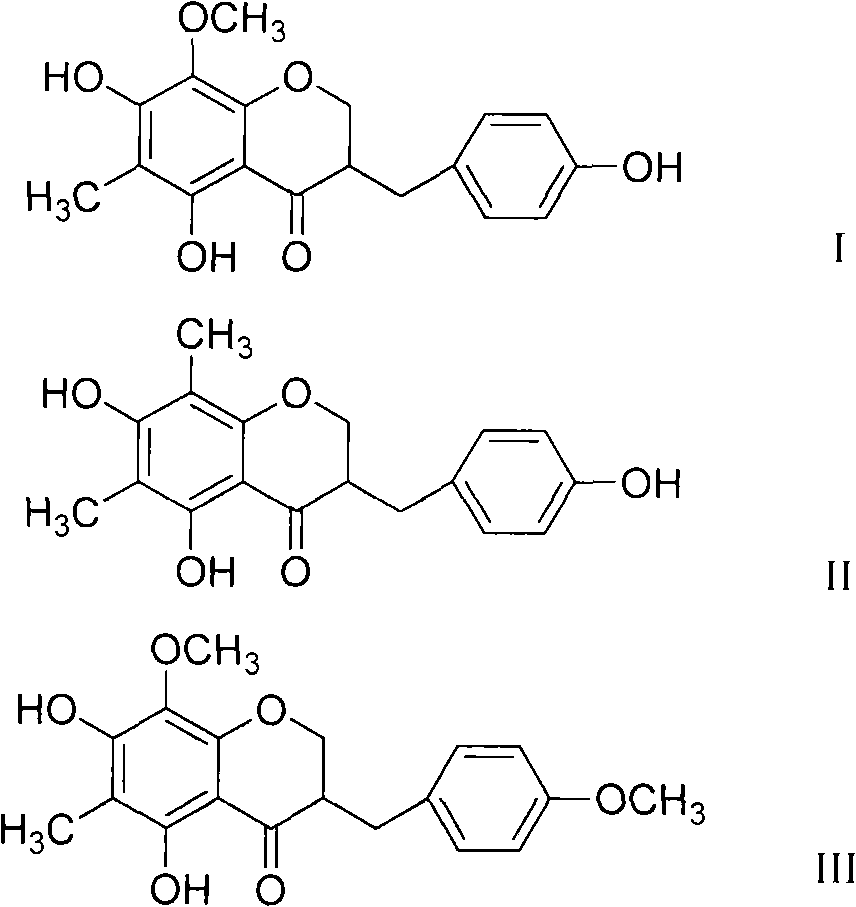
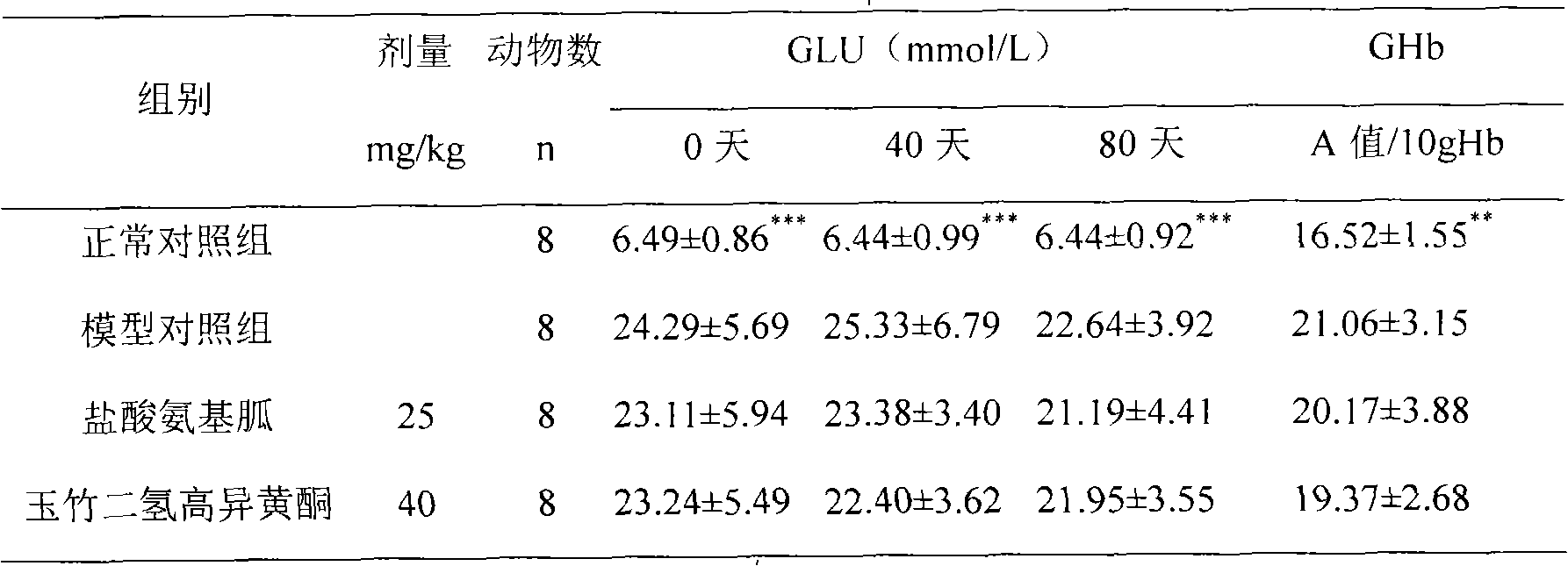
Fragrant solomonseal rhizome isoflavanone extract as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN101664404ASimple processEasy to operateOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderMedicineIsoflavonoid
The invention provides a fragrant solomonseal rhizome isoflavanone extract and a preparation method thereof. The fragrant solomonseal rhizome isoflavanone extract contains 3-(4'- hydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dyhydroxy-6-methyl-8-O-methylation-styrene acrylic dihydropyrane-4-ketone, 3-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dyhydroxy-6,8-dimethyl-styrene acrylic dihydropyrane-4-ketone and 3-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-5,7-dyhydroxy-6-methyl-8-O-methylation-styrene acrylic dihydropyrane-4-ketone, and the content sum of all components is larger than or equal to 15 percent. The invention also discloses an application of the fragrantsolomonseal rhizome isoflavanone extract in preparing a product for preventing and / or treating diabetic nephropathy and an application of a fragrant solomonseal rhizome isoflavanone compound containing the 3-(4'- hydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dyhydroxy-6-methyl-8-O-methylation-styrene acrylic dihydropyrane-4-ketone, the 3-(4'-hydroxyphenyl)-5,7-dyhydroxy-6,8-dimethyl-styrene acrylic dihydropyrane-4-ketone and the 3-(4'-methoxyphenyl)-5,7-dyhydroxy-6-methyl-8-O-methylation-styrene acrylic dihydropyrane-4-ketone in preparing an inhibitor product as a protein nonenzyme glycolysis end product.
Owner:吉林亚泰永安堂药业有限公司
Method for biosynthesis of glutathione by using yeast
InactiveCN101255454AHigh yieldImprove permeabilityMicroorganism based processesFermentationGlycalAdenosine triphosphate
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing glutathione using yeast cells. Gamma-GCS and GS in yeast cells are used, glucose is used as the energy, an intracellular glucolysis system is used to produce triphosadenine, glutamic acid, cysteine and glycin in reaction liquid are synthesized to form glutathione; saccharomyces cerevisiae, baker's yeast, candida and other yeast cells are permeabilized and then react in a reaction liquid composed of phosphate buffer, MgCl2.6H2O, CaCl2.2H2O, glucose, L-glutamic acid and L-cysteine, gamma-L-glutamoyl L- cysteine is produced, then glycin is added to produce glutathione; in the two-stage reaction, the inhabitation effect of glutathione to gamma-GCS catalytic reaction is greatly reduced; glutathione produced by the method has obviously improved product concentration and reaction yield.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Compounds and methods for treating seizure disorders
This invention provides methods for alleviating paroxysmal disorders in an animal, particularly epilepsy, by modulating glycolysis in brain cells.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
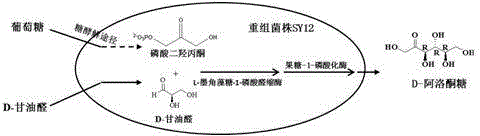
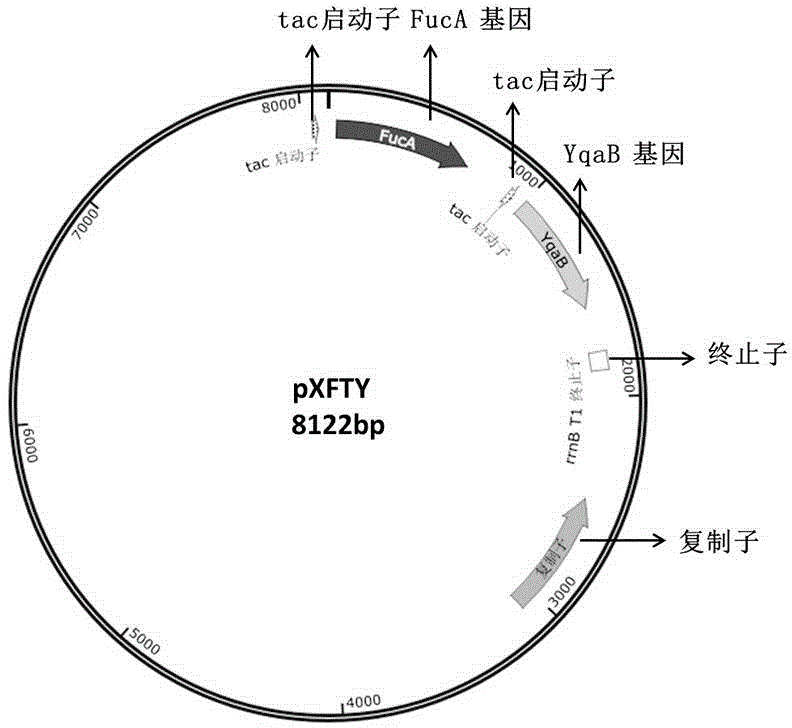
Method for synthesis of D-psicose by aldolase whole cell
The invention discloses a method for synthesis of D-psicose by microbiological fermentation, specifically a method for synthesis of D-psicose by aldolase whole cell. The method includes: firstly constructing recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum SY12 carrying L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase gene and fructose-1-phosphorylase gene (i.e. with aldehyde condensation approach), then adding glucose and D-glyceraldehyde into a basic salt medium, synthesizing dihydroxyacetone phosphate from glucose by means of intracellular glycolysis, synthesizing a single product D-psicose from D-glyceraldehyde and dihydroxyacetone phosphate (DHAP) under the action of the L-fucose-1-phosphate aldolase and fructose-1-phosphorylase carried by the corynebacterium glutamicum recombinant strain SY12, with the conversion rate of D-glyceraldehyde being 53%. Therefore, compared with the existing method for in vitro synthesis of D-psicose by ketose3-epimerase, the biosynthesis method of D-psicose provided by the invention has the advantages of high conversion rate, single product, easy separation and the like, and lays certain foundation for mass production of D-psicose.
Owner:天津怡和生物科技有限责任公司
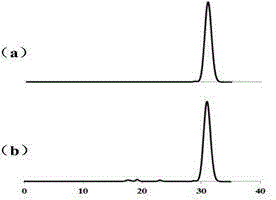
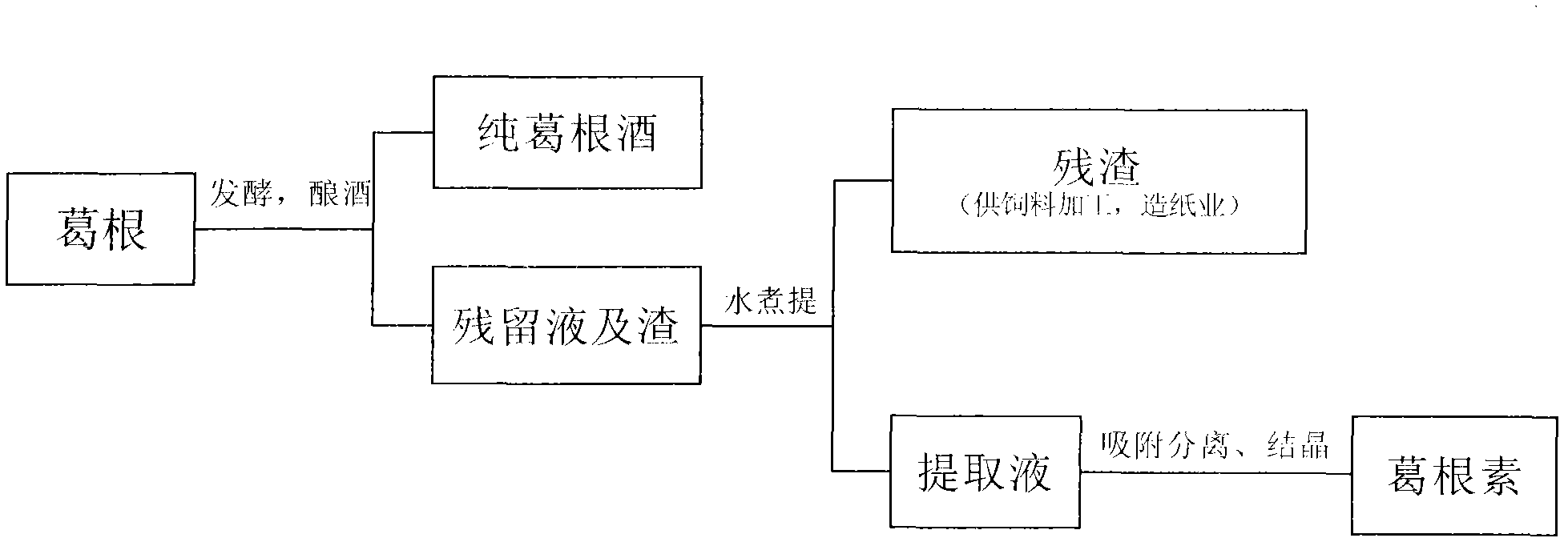
Kudzuvine root comprehensive processing and utilization scheme
The invention relates to the field of plant products application, in particular to a kudzuvine root comprehensive processing and utilization scheme. The scheme solves the problems in present kudzuvine root processing and utilization that products are concentrated on a single component such as starch or flavone, and the kudzuvine root resources can not be utilized well. The scheme breaks through a mindset in the present technical filed and comprises two steps that edible ethanol is prepared by adopting glycolysis starch, and then the kudzuvine root is extracted and prepared. Water serves as solvent in the process of extraction of the kudzuvine root, and a conventional method that 60% to 80% ethanol must be adopted so as to achieve the purpose of effective extraction caused by coexistence of starch is different from the kudzuvine root comprehensive processing and utilization scheme. Three products or raw materials are generated in the process of kudzuvine root extraction, the purpose of making full use of the kudzuvine root is achieved, and therefore the kudzuvine root comprehensive processing and utilization scheme is suitable for popularization and application.
Owner:ZHONGRUN YIYUAN BEIJING BIOTECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com